User login
In Case You Missed It: COVID
A hot dog a day takes 36 minutes away
The death ‘dog’
Imagine you’re out in your backyard managing the grill for a big family barbecue. You’ve got a dazzling assortment of meat assorted on your fancy new propane grill, all charring nicely. Naturally, the hot dogs finish first, and as you pull them off, you figure you’ll help yourself to one now. After all, you are the chef, you deserve a reward. But, as you bite into your smoking hot sandwich, a cold, bony finger taps you on the shoulder. You turn and come face to face with the Grim Reaper. “YOU JUST LOST 36 MINUTES,” Death says. “ALSO, MAY I HAVE ONE OF THOSE? THEY LOOK DELICIOUS.”
Nonplussed and moving automatically, you scoop up another hot dog and place it in a bun. “WITH KETCHUP PLEASE,” Death says. “I NEVER CARED FOR MUSTARD.”
“I don’t understand,” you say. “Surely I won’t die at a family barbecue.”
“DO NOT CALL ME SHIRLEY,” Death says. “AND YOU WILL NOT. IT’S PART OF MY NEW CONTRACT.”
A new study, published in Nature Food, found that a person may lose up to 36 minutes for every hot dog consumed. Researchers from the University of Michigan analyzed nearly 6,000 different foods using a new nutritional index to quantify their health effects in minutes of healthy life lost or gained. Eating a serving of nuts adds an extra 26 minutes of life. The researchers determined that replacing just 10% of daily caloric intake from beef and processed foods with fruits, vegetables, and nuts can add 48 minutes per day. It would also reduce the daily carbon footprint by 33%.
“So you go around to everyone eating bad food and tell them how much life they’ve lost?” you ask when the Grim Reaper finishes his story. “Sounds like a drag.”
“IT IS. WE’VE HAD TO HIRE NEW BLOOD.” Death chuckles at its own bad pun. “NOW IF YOU’LL EXCUSE ME, I MUST CHASTISE A MAN IN FLORIDA FOR EATING A WELL-DONE STEAK.”
More stress, less sex
As the world becomes a more stressful place, the human population could face a 50% drop by the end of the century.
Think of stress as a one-two punch to the libido and human fertility. The more people are stressed out, the less likely they are to have quality interactions with others. Many of us would rather be alone with our wine and cheese to watch our favorite show.
Researchers have found that high stress levels have been known to drop sperm count, ovulation, and sexual activity. Guess what? There has been a 50% decrease in sperm counts over the last 50 years. That’s the second punch. But let’s not forget, the times are changing.
“Changes in reproductive behavior that contribute to the population drop include more young couples choosing to be ‘child-free,’ people having fewer children, and couples waiting longer to start families,” said Alexander Suvorov, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts, the paper’s author.
Let’s summarize: The more stress we’re dealing with, the less people want to deal with each other.
Who would have thought the future would be less fun?
‘You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.’
WARNING: The following descriptions of COVID-19–related insanity may be offensive to some readers.
Greetings, ladies and gentlemen! Welcome to the first round of Pandemic Pandemonium. Let’s get right to the action.
This week’s preshow match-off involves face mask woes. The first comes to us from Alabama, where a woman wore a space helmet to a school board meeting to protest mask mandates. The second comes from Australia, in the form of mischievous magpies. We will explain.
It is not uncommon for magpies to attack those who come too close to their nests in the spring, or “swooping season,” as it’s affectionately called. The magpies are smart enough to recognize the faces of people they see regularly and not attack; however, it’s feared that mask wearing will change this.
While you’re chewing on that exciting appetizer, let’s take a look at our main course, which has a distinct governmental flavor. Jeff Landry is the attorney general of Louisiana, and, like our space-helmet wearer, he’s not a fan of mask mandates. According to Business Insider, Mr. Landry “drafted and distributed sample letters intended to help parents evade mask-wearing ordinances and COVID-19 vaccination requirements for their children in schools.”
Up against him is the Food and Drug Administration’s Twitter account. In an unrelated matter, the agency tweeted, “You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.” This was in response to people using the nonhuman forms of ivermectin to treat very human COVID-19.
Well, there you have it. Who will win tonight’s exciting edition of Pandemic Pandemonium? The first reader to contact us gets to decide the fate of these worthy contestants.
From venomous poison to heart drug
It’s not likely that anyone who sees a giant, venomous spider is thinking, “Hey! That thing could save my life!” It’s usually quite the opposite. Honestly, we would run away from just about any spider. But what if one of the deadliest spiders in the world could also save you from dying of a heart attack?
You probably don’t believe us, right? That’s fair, but the deadly Fraser Island (K’gari) funnel web spider, might also be the most helpful. Investigators from the University of Queensland in Australia have found a way to extract a molecule from the spider’s venom that might help stop damage from heart attacks and may even preserve hearts being used for transplants. “The Hi1a protein from spider venom blocks acid-sensing ion channels in the heart, so the death message is blocked, cell death is reduced, and we see improved heart cell survival,” Nathan Palpant, PhD, of the university, noted in a written statement.
No one has ever developed a drug to stop the “death signal,” so maybe it’s time to befriend spiders instead of running away from them in horror. Just leave the venom extraction to the professionals.
The death ‘dog’
Imagine you’re out in your backyard managing the grill for a big family barbecue. You’ve got a dazzling assortment of meat assorted on your fancy new propane grill, all charring nicely. Naturally, the hot dogs finish first, and as you pull them off, you figure you’ll help yourself to one now. After all, you are the chef, you deserve a reward. But, as you bite into your smoking hot sandwich, a cold, bony finger taps you on the shoulder. You turn and come face to face with the Grim Reaper. “YOU JUST LOST 36 MINUTES,” Death says. “ALSO, MAY I HAVE ONE OF THOSE? THEY LOOK DELICIOUS.”
Nonplussed and moving automatically, you scoop up another hot dog and place it in a bun. “WITH KETCHUP PLEASE,” Death says. “I NEVER CARED FOR MUSTARD.”
“I don’t understand,” you say. “Surely I won’t die at a family barbecue.”
“DO NOT CALL ME SHIRLEY,” Death says. “AND YOU WILL NOT. IT’S PART OF MY NEW CONTRACT.”
A new study, published in Nature Food, found that a person may lose up to 36 minutes for every hot dog consumed. Researchers from the University of Michigan analyzed nearly 6,000 different foods using a new nutritional index to quantify their health effects in minutes of healthy life lost or gained. Eating a serving of nuts adds an extra 26 minutes of life. The researchers determined that replacing just 10% of daily caloric intake from beef and processed foods with fruits, vegetables, and nuts can add 48 minutes per day. It would also reduce the daily carbon footprint by 33%.
“So you go around to everyone eating bad food and tell them how much life they’ve lost?” you ask when the Grim Reaper finishes his story. “Sounds like a drag.”
“IT IS. WE’VE HAD TO HIRE NEW BLOOD.” Death chuckles at its own bad pun. “NOW IF YOU’LL EXCUSE ME, I MUST CHASTISE A MAN IN FLORIDA FOR EATING A WELL-DONE STEAK.”
More stress, less sex
As the world becomes a more stressful place, the human population could face a 50% drop by the end of the century.
Think of stress as a one-two punch to the libido and human fertility. The more people are stressed out, the less likely they are to have quality interactions with others. Many of us would rather be alone with our wine and cheese to watch our favorite show.
Researchers have found that high stress levels have been known to drop sperm count, ovulation, and sexual activity. Guess what? There has been a 50% decrease in sperm counts over the last 50 years. That’s the second punch. But let’s not forget, the times are changing.
“Changes in reproductive behavior that contribute to the population drop include more young couples choosing to be ‘child-free,’ people having fewer children, and couples waiting longer to start families,” said Alexander Suvorov, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts, the paper’s author.
Let’s summarize: The more stress we’re dealing with, the less people want to deal with each other.
Who would have thought the future would be less fun?
‘You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.’
WARNING: The following descriptions of COVID-19–related insanity may be offensive to some readers.
Greetings, ladies and gentlemen! Welcome to the first round of Pandemic Pandemonium. Let’s get right to the action.
This week’s preshow match-off involves face mask woes. The first comes to us from Alabama, where a woman wore a space helmet to a school board meeting to protest mask mandates. The second comes from Australia, in the form of mischievous magpies. We will explain.
It is not uncommon for magpies to attack those who come too close to their nests in the spring, or “swooping season,” as it’s affectionately called. The magpies are smart enough to recognize the faces of people they see regularly and not attack; however, it’s feared that mask wearing will change this.
While you’re chewing on that exciting appetizer, let’s take a look at our main course, which has a distinct governmental flavor. Jeff Landry is the attorney general of Louisiana, and, like our space-helmet wearer, he’s not a fan of mask mandates. According to Business Insider, Mr. Landry “drafted and distributed sample letters intended to help parents evade mask-wearing ordinances and COVID-19 vaccination requirements for their children in schools.”
Up against him is the Food and Drug Administration’s Twitter account. In an unrelated matter, the agency tweeted, “You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.” This was in response to people using the nonhuman forms of ivermectin to treat very human COVID-19.
Well, there you have it. Who will win tonight’s exciting edition of Pandemic Pandemonium? The first reader to contact us gets to decide the fate of these worthy contestants.
From venomous poison to heart drug
It’s not likely that anyone who sees a giant, venomous spider is thinking, “Hey! That thing could save my life!” It’s usually quite the opposite. Honestly, we would run away from just about any spider. But what if one of the deadliest spiders in the world could also save you from dying of a heart attack?
You probably don’t believe us, right? That’s fair, but the deadly Fraser Island (K’gari) funnel web spider, might also be the most helpful. Investigators from the University of Queensland in Australia have found a way to extract a molecule from the spider’s venom that might help stop damage from heart attacks and may even preserve hearts being used for transplants. “The Hi1a protein from spider venom blocks acid-sensing ion channels in the heart, so the death message is blocked, cell death is reduced, and we see improved heart cell survival,” Nathan Palpant, PhD, of the university, noted in a written statement.
No one has ever developed a drug to stop the “death signal,” so maybe it’s time to befriend spiders instead of running away from them in horror. Just leave the venom extraction to the professionals.
The death ‘dog’
Imagine you’re out in your backyard managing the grill for a big family barbecue. You’ve got a dazzling assortment of meat assorted on your fancy new propane grill, all charring nicely. Naturally, the hot dogs finish first, and as you pull them off, you figure you’ll help yourself to one now. After all, you are the chef, you deserve a reward. But, as you bite into your smoking hot sandwich, a cold, bony finger taps you on the shoulder. You turn and come face to face with the Grim Reaper. “YOU JUST LOST 36 MINUTES,” Death says. “ALSO, MAY I HAVE ONE OF THOSE? THEY LOOK DELICIOUS.”
Nonplussed and moving automatically, you scoop up another hot dog and place it in a bun. “WITH KETCHUP PLEASE,” Death says. “I NEVER CARED FOR MUSTARD.”
“I don’t understand,” you say. “Surely I won’t die at a family barbecue.”
“DO NOT CALL ME SHIRLEY,” Death says. “AND YOU WILL NOT. IT’S PART OF MY NEW CONTRACT.”
A new study, published in Nature Food, found that a person may lose up to 36 minutes for every hot dog consumed. Researchers from the University of Michigan analyzed nearly 6,000 different foods using a new nutritional index to quantify their health effects in minutes of healthy life lost or gained. Eating a serving of nuts adds an extra 26 minutes of life. The researchers determined that replacing just 10% of daily caloric intake from beef and processed foods with fruits, vegetables, and nuts can add 48 minutes per day. It would also reduce the daily carbon footprint by 33%.
“So you go around to everyone eating bad food and tell them how much life they’ve lost?” you ask when the Grim Reaper finishes his story. “Sounds like a drag.”
“IT IS. WE’VE HAD TO HIRE NEW BLOOD.” Death chuckles at its own bad pun. “NOW IF YOU’LL EXCUSE ME, I MUST CHASTISE A MAN IN FLORIDA FOR EATING A WELL-DONE STEAK.”
More stress, less sex
As the world becomes a more stressful place, the human population could face a 50% drop by the end of the century.
Think of stress as a one-two punch to the libido and human fertility. The more people are stressed out, the less likely they are to have quality interactions with others. Many of us would rather be alone with our wine and cheese to watch our favorite show.
Researchers have found that high stress levels have been known to drop sperm count, ovulation, and sexual activity. Guess what? There has been a 50% decrease in sperm counts over the last 50 years. That’s the second punch. But let’s not forget, the times are changing.
“Changes in reproductive behavior that contribute to the population drop include more young couples choosing to be ‘child-free,’ people having fewer children, and couples waiting longer to start families,” said Alexander Suvorov, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts, the paper’s author.
Let’s summarize: The more stress we’re dealing with, the less people want to deal with each other.
Who would have thought the future would be less fun?
‘You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.’
WARNING: The following descriptions of COVID-19–related insanity may be offensive to some readers.
Greetings, ladies and gentlemen! Welcome to the first round of Pandemic Pandemonium. Let’s get right to the action.
This week’s preshow match-off involves face mask woes. The first comes to us from Alabama, where a woman wore a space helmet to a school board meeting to protest mask mandates. The second comes from Australia, in the form of mischievous magpies. We will explain.
It is not uncommon for magpies to attack those who come too close to their nests in the spring, or “swooping season,” as it’s affectionately called. The magpies are smart enough to recognize the faces of people they see regularly and not attack; however, it’s feared that mask wearing will change this.
While you’re chewing on that exciting appetizer, let’s take a look at our main course, which has a distinct governmental flavor. Jeff Landry is the attorney general of Louisiana, and, like our space-helmet wearer, he’s not a fan of mask mandates. According to Business Insider, Mr. Landry “drafted and distributed sample letters intended to help parents evade mask-wearing ordinances and COVID-19 vaccination requirements for their children in schools.”
Up against him is the Food and Drug Administration’s Twitter account. In an unrelated matter, the agency tweeted, “You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.” This was in response to people using the nonhuman forms of ivermectin to treat very human COVID-19.
Well, there you have it. Who will win tonight’s exciting edition of Pandemic Pandemonium? The first reader to contact us gets to decide the fate of these worthy contestants.
From venomous poison to heart drug
It’s not likely that anyone who sees a giant, venomous spider is thinking, “Hey! That thing could save my life!” It’s usually quite the opposite. Honestly, we would run away from just about any spider. But what if one of the deadliest spiders in the world could also save you from dying of a heart attack?
You probably don’t believe us, right? That’s fair, but the deadly Fraser Island (K’gari) funnel web spider, might also be the most helpful. Investigators from the University of Queensland in Australia have found a way to extract a molecule from the spider’s venom that might help stop damage from heart attacks and may even preserve hearts being used for transplants. “The Hi1a protein from spider venom blocks acid-sensing ion channels in the heart, so the death message is blocked, cell death is reduced, and we see improved heart cell survival,” Nathan Palpant, PhD, of the university, noted in a written statement.
No one has ever developed a drug to stop the “death signal,” so maybe it’s time to befriend spiders instead of running away from them in horror. Just leave the venom extraction to the professionals.
Fauci corrects prediction on when pandemic will be under control
The United States could get the COVID-19 pandemic under control by the spring of 2022 if enough Americans become vaccinated, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said.
Speaking to Anderson Cooper on CNN, Dr. Fauci corrected the timeline he gave in an interview earlier with Mary Louise Kelly of NPR.
In the NPR interview, he had said that if “the overwhelming majority of the people vaccinated, I think as we get into the fall and the winter, we could start to really get some good control over this as we get into 2022.”
Dr. Fauci told Mr. Cooper that he listened to a recording of the NPR interview later and realized his mistake.
“I meant to say the spring of 2022,” Dr. Fauci told CNN. “I misspoke. My bad.”
Dr. Fauci, the head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and the chief White House medical adviser, said the pandemic will be under control when the large majority of Americans have gotten vaccinated or been infected with COVID-19 and recovered, which offers some protection against the virus.
People who have been infected and recovered should still get vaccinated, he said.
“The degree of protection you could induce in someone who’s been infected and then recovered and then vaccinated is an enormous increase in the degree of protection,” Dr. Fauci said.
“I think we can get a degree of overall blanket protection of the community that as we get into the early part of 2022 ... we could start getting back to a degree of normality.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States could get the COVID-19 pandemic under control by the spring of 2022 if enough Americans become vaccinated, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said.
Speaking to Anderson Cooper on CNN, Dr. Fauci corrected the timeline he gave in an interview earlier with Mary Louise Kelly of NPR.
In the NPR interview, he had said that if “the overwhelming majority of the people vaccinated, I think as we get into the fall and the winter, we could start to really get some good control over this as we get into 2022.”
Dr. Fauci told Mr. Cooper that he listened to a recording of the NPR interview later and realized his mistake.
“I meant to say the spring of 2022,” Dr. Fauci told CNN. “I misspoke. My bad.”
Dr. Fauci, the head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and the chief White House medical adviser, said the pandemic will be under control when the large majority of Americans have gotten vaccinated or been infected with COVID-19 and recovered, which offers some protection against the virus.
People who have been infected and recovered should still get vaccinated, he said.
“The degree of protection you could induce in someone who’s been infected and then recovered and then vaccinated is an enormous increase in the degree of protection,” Dr. Fauci said.
“I think we can get a degree of overall blanket protection of the community that as we get into the early part of 2022 ... we could start getting back to a degree of normality.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States could get the COVID-19 pandemic under control by the spring of 2022 if enough Americans become vaccinated, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said.
Speaking to Anderson Cooper on CNN, Dr. Fauci corrected the timeline he gave in an interview earlier with Mary Louise Kelly of NPR.
In the NPR interview, he had said that if “the overwhelming majority of the people vaccinated, I think as we get into the fall and the winter, we could start to really get some good control over this as we get into 2022.”
Dr. Fauci told Mr. Cooper that he listened to a recording of the NPR interview later and realized his mistake.
“I meant to say the spring of 2022,” Dr. Fauci told CNN. “I misspoke. My bad.”
Dr. Fauci, the head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and the chief White House medical adviser, said the pandemic will be under control when the large majority of Americans have gotten vaccinated or been infected with COVID-19 and recovered, which offers some protection against the virus.
People who have been infected and recovered should still get vaccinated, he said.
“The degree of protection you could induce in someone who’s been infected and then recovered and then vaccinated is an enormous increase in the degree of protection,” Dr. Fauci said.
“I think we can get a degree of overall blanket protection of the community that as we get into the early part of 2022 ... we could start getting back to a degree of normality.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
New recommendations address ME/CFS diagnosis and management
New consensus recommendations address diagnosis and management of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), with advice that may also be helpful for patients with lingering symptoms following acute COVID-19 infection.
The document was published online Aug. 25, 2021, in the Mayo Clinic Proceedings by the 23-member U.S. ME/CFS Clinician Coalition, headed by Lucinda Bateman, MD, of the Bateman Horne Center of Excellence, Salt Lake City. The document is the culmination of work that began with a summit held at the center in March 2018.
The target audience is both generalist and specialist health care providers. While ME/CFS is estimated to affect up to 2.5 million Americans, more than 90% are either undiagnosed or misdiagnosed with other conditions such as depression. And those who are diagnosed often receive inappropriate, outdated treatments such as psychotherapy and exercise prescriptions.
“Despite myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome affecting millions of people worldwide, many clinicians lack the knowledge to appropriately diagnose or manage ME/CFS. Unfortunately, clinical guidance has been scarce, obsolete, or potentially harmful,” Dr. Bateman and colleagues wrote.
The urgency of appropriate recognition and management of ME/CFS has increased as growing numbers of people are exhibiting signs and symptoms of ME/CFS following acute COVID-19 infection. This isn’t surprising because the illness has long been linked to other infections, including Epstein-Barr virus, the authors noted.
The document covers the epidemiology, impact, and prognosis of ME/CFS, as well as etiology and pathophysiology. “Scientific studies demonstrate multiple dysfunctional organ systems, including neuro, immune, and metabolic, in ME/CFS. These findings are not explained merely by deconditioning,” document coauthor Lily Chu, MD, an independent consultant in Burlingame, Calif., said in an interview.
The document reviews the 2015 U.S. Institute of Medicine (now Academy of Medicine) diagnostic criteria that are now also recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. They are based on four main symptoms: substantial reduction or impairment in the ability to engage in preillness levels of occupational, educational, social or personal activities for longer than 6 months; postexertional malaise, a worsening of all current symptoms, that patients often describe as a “crash”; unrefreshing sleep; and cognitive impairment and/or orthostatic intolerance.
“The new diagnostic criteria focusing on the key symptom of postexertional malaise rather than chronic fatigue, which is common in many conditions, may make the diagnostic process quicker and more accurate. Diagnosis now is both an inclusionary and not just exclusionary process, so it’s not necessary to eliminate all causes of fatigue. Diagnose patients who fit the criteria and be alert for it in people with persistent symptoms post COVID,” Dr. Chu said.
The document provides advice for taking a clinical history to obtain the information necessary for making the diagnosis, including use of laboratory testing to rule out other conditions. Physical exams, while they may not reveal specific abnormalities, may help in identifying comorbidities and ruling out alternative diagnoses.
A long list of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic treatment and management approaches is offered for each of the individual core and common ME/CFS symptoms, including postexertional malaise, orthostatic intolerance, sleep issues, cognitive dysfunction and fatigue, immune dysfunction, pain, and gastrointestinal issues.
The document recommends against using the “outdated standard of care” cognitive-behavioral therapy and graded exercise therapy as primary treatments for the illness. Instead, the authors recommend teaching patients “pacing,” an individualized approach to energy conservation aimed at minimizing the frequency, duration, and severity of postexertional malaise.
Clinicians are also advised to assess patients’ daily living needs and provide support, including acquiring handicap placards, work or school accommodations, and disability benefits.
“There are things clinicians can do now to help patients even without a disease-modifying treatment. These are actions they are already familiar with and carry out for people with other chronic diseases, which often have limited treatment options as well. Don’t underestimate the importance and value of supportive care for patients.” Dr. Chu said.
The recommendations are based primarily on clinical expertise because there are very few randomized trials, and much of the evidence from other types of trials has been flawed, document coauthor Anthony L. Komaroff, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said in an interview.
“The sad reality is there aren’t very many large randomized clinical trials with this illness and so what a group of very experienced clinicians did was to gather their collective experience and report it as that. It’s largely uncontrolled experience, but from people who have seen a lot of patients, for what it’s worth to the medical community.”
Dr. Komaroff also advised that clinicians watch out for ME/CFS in patients with long COVID. “If we find that those called long COVID meet ME/CFS criteria, the reason for knowing that is that there are already some treatments that according to experienced clinicians are helpful for ME/CFS, and it would be perfectly appropriate to try some of them in long COVID, particularly the ones that have minimal adverse reactions.”
The guidelines project was supported by the Open Medicine Foundation. Dr. Komaroff reported receiving personal fees from Serimmune outside the submitted work. Dr. Chu has no disclosures.
New consensus recommendations address diagnosis and management of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), with advice that may also be helpful for patients with lingering symptoms following acute COVID-19 infection.
The document was published online Aug. 25, 2021, in the Mayo Clinic Proceedings by the 23-member U.S. ME/CFS Clinician Coalition, headed by Lucinda Bateman, MD, of the Bateman Horne Center of Excellence, Salt Lake City. The document is the culmination of work that began with a summit held at the center in March 2018.
The target audience is both generalist and specialist health care providers. While ME/CFS is estimated to affect up to 2.5 million Americans, more than 90% are either undiagnosed or misdiagnosed with other conditions such as depression. And those who are diagnosed often receive inappropriate, outdated treatments such as psychotherapy and exercise prescriptions.
“Despite myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome affecting millions of people worldwide, many clinicians lack the knowledge to appropriately diagnose or manage ME/CFS. Unfortunately, clinical guidance has been scarce, obsolete, or potentially harmful,” Dr. Bateman and colleagues wrote.
The urgency of appropriate recognition and management of ME/CFS has increased as growing numbers of people are exhibiting signs and symptoms of ME/CFS following acute COVID-19 infection. This isn’t surprising because the illness has long been linked to other infections, including Epstein-Barr virus, the authors noted.
The document covers the epidemiology, impact, and prognosis of ME/CFS, as well as etiology and pathophysiology. “Scientific studies demonstrate multiple dysfunctional organ systems, including neuro, immune, and metabolic, in ME/CFS. These findings are not explained merely by deconditioning,” document coauthor Lily Chu, MD, an independent consultant in Burlingame, Calif., said in an interview.
The document reviews the 2015 U.S. Institute of Medicine (now Academy of Medicine) diagnostic criteria that are now also recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. They are based on four main symptoms: substantial reduction or impairment in the ability to engage in preillness levels of occupational, educational, social or personal activities for longer than 6 months; postexertional malaise, a worsening of all current symptoms, that patients often describe as a “crash”; unrefreshing sleep; and cognitive impairment and/or orthostatic intolerance.
“The new diagnostic criteria focusing on the key symptom of postexertional malaise rather than chronic fatigue, which is common in many conditions, may make the diagnostic process quicker and more accurate. Diagnosis now is both an inclusionary and not just exclusionary process, so it’s not necessary to eliminate all causes of fatigue. Diagnose patients who fit the criteria and be alert for it in people with persistent symptoms post COVID,” Dr. Chu said.
The document provides advice for taking a clinical history to obtain the information necessary for making the diagnosis, including use of laboratory testing to rule out other conditions. Physical exams, while they may not reveal specific abnormalities, may help in identifying comorbidities and ruling out alternative diagnoses.
A long list of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic treatment and management approaches is offered for each of the individual core and common ME/CFS symptoms, including postexertional malaise, orthostatic intolerance, sleep issues, cognitive dysfunction and fatigue, immune dysfunction, pain, and gastrointestinal issues.
The document recommends against using the “outdated standard of care” cognitive-behavioral therapy and graded exercise therapy as primary treatments for the illness. Instead, the authors recommend teaching patients “pacing,” an individualized approach to energy conservation aimed at minimizing the frequency, duration, and severity of postexertional malaise.
Clinicians are also advised to assess patients’ daily living needs and provide support, including acquiring handicap placards, work or school accommodations, and disability benefits.
“There are things clinicians can do now to help patients even without a disease-modifying treatment. These are actions they are already familiar with and carry out for people with other chronic diseases, which often have limited treatment options as well. Don’t underestimate the importance and value of supportive care for patients.” Dr. Chu said.
The recommendations are based primarily on clinical expertise because there are very few randomized trials, and much of the evidence from other types of trials has been flawed, document coauthor Anthony L. Komaroff, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said in an interview.
“The sad reality is there aren’t very many large randomized clinical trials with this illness and so what a group of very experienced clinicians did was to gather their collective experience and report it as that. It’s largely uncontrolled experience, but from people who have seen a lot of patients, for what it’s worth to the medical community.”
Dr. Komaroff also advised that clinicians watch out for ME/CFS in patients with long COVID. “If we find that those called long COVID meet ME/CFS criteria, the reason for knowing that is that there are already some treatments that according to experienced clinicians are helpful for ME/CFS, and it would be perfectly appropriate to try some of them in long COVID, particularly the ones that have minimal adverse reactions.”
The guidelines project was supported by the Open Medicine Foundation. Dr. Komaroff reported receiving personal fees from Serimmune outside the submitted work. Dr. Chu has no disclosures.
New consensus recommendations address diagnosis and management of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), with advice that may also be helpful for patients with lingering symptoms following acute COVID-19 infection.
The document was published online Aug. 25, 2021, in the Mayo Clinic Proceedings by the 23-member U.S. ME/CFS Clinician Coalition, headed by Lucinda Bateman, MD, of the Bateman Horne Center of Excellence, Salt Lake City. The document is the culmination of work that began with a summit held at the center in March 2018.
The target audience is both generalist and specialist health care providers. While ME/CFS is estimated to affect up to 2.5 million Americans, more than 90% are either undiagnosed or misdiagnosed with other conditions such as depression. And those who are diagnosed often receive inappropriate, outdated treatments such as psychotherapy and exercise prescriptions.
“Despite myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome affecting millions of people worldwide, many clinicians lack the knowledge to appropriately diagnose or manage ME/CFS. Unfortunately, clinical guidance has been scarce, obsolete, or potentially harmful,” Dr. Bateman and colleagues wrote.
The urgency of appropriate recognition and management of ME/CFS has increased as growing numbers of people are exhibiting signs and symptoms of ME/CFS following acute COVID-19 infection. This isn’t surprising because the illness has long been linked to other infections, including Epstein-Barr virus, the authors noted.
The document covers the epidemiology, impact, and prognosis of ME/CFS, as well as etiology and pathophysiology. “Scientific studies demonstrate multiple dysfunctional organ systems, including neuro, immune, and metabolic, in ME/CFS. These findings are not explained merely by deconditioning,” document coauthor Lily Chu, MD, an independent consultant in Burlingame, Calif., said in an interview.
The document reviews the 2015 U.S. Institute of Medicine (now Academy of Medicine) diagnostic criteria that are now also recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. They are based on four main symptoms: substantial reduction or impairment in the ability to engage in preillness levels of occupational, educational, social or personal activities for longer than 6 months; postexertional malaise, a worsening of all current symptoms, that patients often describe as a “crash”; unrefreshing sleep; and cognitive impairment and/or orthostatic intolerance.
“The new diagnostic criteria focusing on the key symptom of postexertional malaise rather than chronic fatigue, which is common in many conditions, may make the diagnostic process quicker and more accurate. Diagnosis now is both an inclusionary and not just exclusionary process, so it’s not necessary to eliminate all causes of fatigue. Diagnose patients who fit the criteria and be alert for it in people with persistent symptoms post COVID,” Dr. Chu said.
The document provides advice for taking a clinical history to obtain the information necessary for making the diagnosis, including use of laboratory testing to rule out other conditions. Physical exams, while they may not reveal specific abnormalities, may help in identifying comorbidities and ruling out alternative diagnoses.
A long list of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic treatment and management approaches is offered for each of the individual core and common ME/CFS symptoms, including postexertional malaise, orthostatic intolerance, sleep issues, cognitive dysfunction and fatigue, immune dysfunction, pain, and gastrointestinal issues.
The document recommends against using the “outdated standard of care” cognitive-behavioral therapy and graded exercise therapy as primary treatments for the illness. Instead, the authors recommend teaching patients “pacing,” an individualized approach to energy conservation aimed at minimizing the frequency, duration, and severity of postexertional malaise.
Clinicians are also advised to assess patients’ daily living needs and provide support, including acquiring handicap placards, work or school accommodations, and disability benefits.
“There are things clinicians can do now to help patients even without a disease-modifying treatment. These are actions they are already familiar with and carry out for people with other chronic diseases, which often have limited treatment options as well. Don’t underestimate the importance and value of supportive care for patients.” Dr. Chu said.
The recommendations are based primarily on clinical expertise because there are very few randomized trials, and much of the evidence from other types of trials has been flawed, document coauthor Anthony L. Komaroff, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said in an interview.
“The sad reality is there aren’t very many large randomized clinical trials with this illness and so what a group of very experienced clinicians did was to gather their collective experience and report it as that. It’s largely uncontrolled experience, but from people who have seen a lot of patients, for what it’s worth to the medical community.”
Dr. Komaroff also advised that clinicians watch out for ME/CFS in patients with long COVID. “If we find that those called long COVID meet ME/CFS criteria, the reason for knowing that is that there are already some treatments that according to experienced clinicians are helpful for ME/CFS, and it would be perfectly appropriate to try some of them in long COVID, particularly the ones that have minimal adverse reactions.”
The guidelines project was supported by the Open Medicine Foundation. Dr. Komaroff reported receiving personal fees from Serimmune outside the submitted work. Dr. Chu has no disclosures.
FROM THE MAYO CLINIC PROCEEDINGS
COVID booster may benefit active-treatment cancer patients
A COVID-19 booster shot may be beneficial for patients with cancer who are undergoing treatment, according to new findings from an Israeli case-control study.
The seropositivity rate among the patients with cancer remained high (87%) about 4 months after the patients had received the second BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech) vaccination. However, the median IgG titer in the patients and the control persons who were without cancer decreased over time. Notably, in a previous analysis that the authors conducted and in the current one, the IgG titers were statistically significantly lower in the patients with cancer as compared to control persons.
The correlation between antibody levels following vaccination and clinical protection has yet to be proven, but the accumulating evidence supports antibody response as a possible correlate of disease protection.
“Our data can’t predict if a third booster dose is necessary,” said study author Salomon M. Stemmer, MD, professor at the Institute of Oncology of Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel. “It does seem quite logical that a booster dose will cause an increase in IgG levels.”
The findings were published Aug. 11, 2021, in a research letter in JAMA Oncology.
In their previous study, Dr. Stemmer and colleagues compared the rates of anti–spike antibody response to the initial shot of the BNT162b2 vaccine among 102 adults with solid-tumor cancers who were undergoing treatment with that of 78 healthy control persons. They found that a high percentage of patients undergoing treatment for cancer (90%) achieved a sufficient antibody response to the BNT162b2 vaccine.
Booster endorsed
Responses to COVID-19 vaccination have varied among patients with cancer. For patients with solid tumors, responses have been good even while the patients were receiving systemic therapy. However, among patients with blood cancers, particularly those receiving immunosuppressive therapies, responses have been poor. Studies have identified factors associated with a poor response, but it has been unclear whether to recommend booster shots.
In August the Food and Drug Administration authorized a third dose of either the Pfizer or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine for all individuals with compromised immune systems. Those eligible for a third dose include solid-organ transplant recipients, those undergoing cancer treatments, and people with autoimmune diseases that suppress their immune systems.
IgG titers lower in cancer patients
In the current analysis, the authors evaluated the anti-S response in the patients with cancer approximately 4 months after they had received the second vaccine dose. They compared the responses in those patients with the responses in a control group.
The cohort included 95 patients from the prior study and 66 control persons. The most common malignancies were gastrointestinal (26%), lung (25%), and breast (18%).
All patients were receiving systemic therapy. Chemotherapy was the most common (28%), followed by immunotherapy (21%) and combination chemotherapy/biological therapy (20%).
At a median of 123 days after the second vaccination, 83 patients with cancer (87%) and all of the control patients (100%) were seropositive for anti-S IgG antibodies. The median titer levels were significantly lower among case patients as compared with control patients (417 AU/mL [interquartile range, 136-895] vs. 1,220 AU/mL [IQR, 588-1,987]; P < .001)
There was a 3.6-fold range in median titer values across tumor types and an even wider range (8.8-fold) across the different types of treatment. The lowest titers were observed among patients who had received immunotherapy plus chemotherapy/biological therapy (median [IQR], 94.4 [49.4-191] AU/mL vs. 147 [62.8-339] AU/mL).
In an exploratory multivariable analysis, treatments with chemotherapy plus immunotherapy and immunotherapy plus biological therapy were significantly associated with lower IgG titers.
No downside for cancer patients
The Biden administration announced a plan to begin booster COVID-19 vaccinations for all American adults in September, with recommendations that the third vaccine be given at least 8 months after the second mRNA vaccine dose.
Jeremy M. Levin, DPhil, the chairman and CEO of Ovid Therapeutics, explained that, concerning boosters, “it is inconceivable that we will have all data at this stage.
“Knowledge about how boosters work and don’t work and when you should ideally have them is imperfect,” he told this news organization. “However, we can have a lot of confidence in the fact that hundreds of millions of people have received the vaccine, so we know a lot about the safety and efficacy.”
Immunocompromised adults represent less than 5% of the total population, and most of the available data on vaccination are from patients who have undergone solid-organ transplant, Dr. Levin explained. Studies have shown that their response is less robust to vaccination in comparison with adults in the general population.
“Although it is still preliminary, the strongest data come from Israel,” he said, “where they found that the booster was highly effective and doubled the number of transplant patients who developed antibodies.”
But data are not yet available in the setting of cancer. “But even though we don’t have the data yet, the answer is that no matter, the booster process is essential,” he said. “The evidence we have is that boosters raise the immune response, and it is the best data we have now.”
Martin J. Edelman, MD, chair, department of hematology/oncology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, noted that the current recommendation is that patients who are immunocompromised receive a booster immediately.
At his health system, this is interpreted to include patients who have undergone the following treatments: Transplant (solid-organ and bone marrow transplant), hemodialysis, hematologic malignancy treatment, active immunosuppressive (chemotherapy, chemoimmunotherapy, and nonhormonal or single-agent immunotherapy) treatment, rheumatology treatments, and high-dose steroids.
“As for cancer patients, we are making arrangements to vaccinate patients who meet the above criteria now,” he said. “There is no known downside to receiving booster immediately. While there may be less of a response than waiting for completion of treatment, we know that patients on active therapy are frequently able to mount a response, and any response is better than none.”
Dr. Edelman added that this area is changing very rapidly. “We will modify our approach as information and guidance from appropriate organizations, such as the FDA and CDC, become available.”
Dr. Stemmer has received institutional research grants from CAN-FITE, AstraZeneca, Bioline RX, BMS, Halozyme, Clovis Oncology, CTG Pharma, Exelixis, Geicam, Incyte, Lilly, Moderna, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Roche, and owns stocks and options in CTG Pharma, DocBoxMD, Tyrnovo, VYPE, Cytora, and CAN-FITE. Dr. Edelman has received personal fees and other compensation from Windmil, Biomarker Strategies, AstraZeneca, Takeda, GlaxoSmithKline, Apexigen, Nektar, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Armo, Bergen Bio, and Apexigen outside the submitted work. He has submitted a patent for epigenetic modifications to increase susceptibility to radiopharmaceuticals and is a paid adviser for Kanaph and Flame. Dr. Levin is chairman and CEO of Ovid Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A COVID-19 booster shot may be beneficial for patients with cancer who are undergoing treatment, according to new findings from an Israeli case-control study.
The seropositivity rate among the patients with cancer remained high (87%) about 4 months after the patients had received the second BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech) vaccination. However, the median IgG titer in the patients and the control persons who were without cancer decreased over time. Notably, in a previous analysis that the authors conducted and in the current one, the IgG titers were statistically significantly lower in the patients with cancer as compared to control persons.
The correlation between antibody levels following vaccination and clinical protection has yet to be proven, but the accumulating evidence supports antibody response as a possible correlate of disease protection.
“Our data can’t predict if a third booster dose is necessary,” said study author Salomon M. Stemmer, MD, professor at the Institute of Oncology of Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel. “It does seem quite logical that a booster dose will cause an increase in IgG levels.”
The findings were published Aug. 11, 2021, in a research letter in JAMA Oncology.
In their previous study, Dr. Stemmer and colleagues compared the rates of anti–spike antibody response to the initial shot of the BNT162b2 vaccine among 102 adults with solid-tumor cancers who were undergoing treatment with that of 78 healthy control persons. They found that a high percentage of patients undergoing treatment for cancer (90%) achieved a sufficient antibody response to the BNT162b2 vaccine.
Booster endorsed
Responses to COVID-19 vaccination have varied among patients with cancer. For patients with solid tumors, responses have been good even while the patients were receiving systemic therapy. However, among patients with blood cancers, particularly those receiving immunosuppressive therapies, responses have been poor. Studies have identified factors associated with a poor response, but it has been unclear whether to recommend booster shots.
In August the Food and Drug Administration authorized a third dose of either the Pfizer or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine for all individuals with compromised immune systems. Those eligible for a third dose include solid-organ transplant recipients, those undergoing cancer treatments, and people with autoimmune diseases that suppress their immune systems.
IgG titers lower in cancer patients
In the current analysis, the authors evaluated the anti-S response in the patients with cancer approximately 4 months after they had received the second vaccine dose. They compared the responses in those patients with the responses in a control group.
The cohort included 95 patients from the prior study and 66 control persons. The most common malignancies were gastrointestinal (26%), lung (25%), and breast (18%).
All patients were receiving systemic therapy. Chemotherapy was the most common (28%), followed by immunotherapy (21%) and combination chemotherapy/biological therapy (20%).
At a median of 123 days after the second vaccination, 83 patients with cancer (87%) and all of the control patients (100%) were seropositive for anti-S IgG antibodies. The median titer levels were significantly lower among case patients as compared with control patients (417 AU/mL [interquartile range, 136-895] vs. 1,220 AU/mL [IQR, 588-1,987]; P < .001)
There was a 3.6-fold range in median titer values across tumor types and an even wider range (8.8-fold) across the different types of treatment. The lowest titers were observed among patients who had received immunotherapy plus chemotherapy/biological therapy (median [IQR], 94.4 [49.4-191] AU/mL vs. 147 [62.8-339] AU/mL).
In an exploratory multivariable analysis, treatments with chemotherapy plus immunotherapy and immunotherapy plus biological therapy were significantly associated with lower IgG titers.
No downside for cancer patients
The Biden administration announced a plan to begin booster COVID-19 vaccinations for all American adults in September, with recommendations that the third vaccine be given at least 8 months after the second mRNA vaccine dose.
Jeremy M. Levin, DPhil, the chairman and CEO of Ovid Therapeutics, explained that, concerning boosters, “it is inconceivable that we will have all data at this stage.
“Knowledge about how boosters work and don’t work and when you should ideally have them is imperfect,” he told this news organization. “However, we can have a lot of confidence in the fact that hundreds of millions of people have received the vaccine, so we know a lot about the safety and efficacy.”
Immunocompromised adults represent less than 5% of the total population, and most of the available data on vaccination are from patients who have undergone solid-organ transplant, Dr. Levin explained. Studies have shown that their response is less robust to vaccination in comparison with adults in the general population.
“Although it is still preliminary, the strongest data come from Israel,” he said, “where they found that the booster was highly effective and doubled the number of transplant patients who developed antibodies.”
But data are not yet available in the setting of cancer. “But even though we don’t have the data yet, the answer is that no matter, the booster process is essential,” he said. “The evidence we have is that boosters raise the immune response, and it is the best data we have now.”
Martin J. Edelman, MD, chair, department of hematology/oncology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, noted that the current recommendation is that patients who are immunocompromised receive a booster immediately.
At his health system, this is interpreted to include patients who have undergone the following treatments: Transplant (solid-organ and bone marrow transplant), hemodialysis, hematologic malignancy treatment, active immunosuppressive (chemotherapy, chemoimmunotherapy, and nonhormonal or single-agent immunotherapy) treatment, rheumatology treatments, and high-dose steroids.
“As for cancer patients, we are making arrangements to vaccinate patients who meet the above criteria now,” he said. “There is no known downside to receiving booster immediately. While there may be less of a response than waiting for completion of treatment, we know that patients on active therapy are frequently able to mount a response, and any response is better than none.”
Dr. Edelman added that this area is changing very rapidly. “We will modify our approach as information and guidance from appropriate organizations, such as the FDA and CDC, become available.”
Dr. Stemmer has received institutional research grants from CAN-FITE, AstraZeneca, Bioline RX, BMS, Halozyme, Clovis Oncology, CTG Pharma, Exelixis, Geicam, Incyte, Lilly, Moderna, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Roche, and owns stocks and options in CTG Pharma, DocBoxMD, Tyrnovo, VYPE, Cytora, and CAN-FITE. Dr. Edelman has received personal fees and other compensation from Windmil, Biomarker Strategies, AstraZeneca, Takeda, GlaxoSmithKline, Apexigen, Nektar, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Armo, Bergen Bio, and Apexigen outside the submitted work. He has submitted a patent for epigenetic modifications to increase susceptibility to radiopharmaceuticals and is a paid adviser for Kanaph and Flame. Dr. Levin is chairman and CEO of Ovid Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A COVID-19 booster shot may be beneficial for patients with cancer who are undergoing treatment, according to new findings from an Israeli case-control study.
The seropositivity rate among the patients with cancer remained high (87%) about 4 months after the patients had received the second BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech) vaccination. However, the median IgG titer in the patients and the control persons who were without cancer decreased over time. Notably, in a previous analysis that the authors conducted and in the current one, the IgG titers were statistically significantly lower in the patients with cancer as compared to control persons.
The correlation between antibody levels following vaccination and clinical protection has yet to be proven, but the accumulating evidence supports antibody response as a possible correlate of disease protection.
“Our data can’t predict if a third booster dose is necessary,” said study author Salomon M. Stemmer, MD, professor at the Institute of Oncology of Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel. “It does seem quite logical that a booster dose will cause an increase in IgG levels.”
The findings were published Aug. 11, 2021, in a research letter in JAMA Oncology.
In their previous study, Dr. Stemmer and colleagues compared the rates of anti–spike antibody response to the initial shot of the BNT162b2 vaccine among 102 adults with solid-tumor cancers who were undergoing treatment with that of 78 healthy control persons. They found that a high percentage of patients undergoing treatment for cancer (90%) achieved a sufficient antibody response to the BNT162b2 vaccine.
Booster endorsed
Responses to COVID-19 vaccination have varied among patients with cancer. For patients with solid tumors, responses have been good even while the patients were receiving systemic therapy. However, among patients with blood cancers, particularly those receiving immunosuppressive therapies, responses have been poor. Studies have identified factors associated with a poor response, but it has been unclear whether to recommend booster shots.
In August the Food and Drug Administration authorized a third dose of either the Pfizer or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine for all individuals with compromised immune systems. Those eligible for a third dose include solid-organ transplant recipients, those undergoing cancer treatments, and people with autoimmune diseases that suppress their immune systems.
IgG titers lower in cancer patients
In the current analysis, the authors evaluated the anti-S response in the patients with cancer approximately 4 months after they had received the second vaccine dose. They compared the responses in those patients with the responses in a control group.
The cohort included 95 patients from the prior study and 66 control persons. The most common malignancies were gastrointestinal (26%), lung (25%), and breast (18%).
All patients were receiving systemic therapy. Chemotherapy was the most common (28%), followed by immunotherapy (21%) and combination chemotherapy/biological therapy (20%).
At a median of 123 days after the second vaccination, 83 patients with cancer (87%) and all of the control patients (100%) were seropositive for anti-S IgG antibodies. The median titer levels were significantly lower among case patients as compared with control patients (417 AU/mL [interquartile range, 136-895] vs. 1,220 AU/mL [IQR, 588-1,987]; P < .001)
There was a 3.6-fold range in median titer values across tumor types and an even wider range (8.8-fold) across the different types of treatment. The lowest titers were observed among patients who had received immunotherapy plus chemotherapy/biological therapy (median [IQR], 94.4 [49.4-191] AU/mL vs. 147 [62.8-339] AU/mL).
In an exploratory multivariable analysis, treatments with chemotherapy plus immunotherapy and immunotherapy plus biological therapy were significantly associated with lower IgG titers.
No downside for cancer patients
The Biden administration announced a plan to begin booster COVID-19 vaccinations for all American adults in September, with recommendations that the third vaccine be given at least 8 months after the second mRNA vaccine dose.
Jeremy M. Levin, DPhil, the chairman and CEO of Ovid Therapeutics, explained that, concerning boosters, “it is inconceivable that we will have all data at this stage.
“Knowledge about how boosters work and don’t work and when you should ideally have them is imperfect,” he told this news organization. “However, we can have a lot of confidence in the fact that hundreds of millions of people have received the vaccine, so we know a lot about the safety and efficacy.”
Immunocompromised adults represent less than 5% of the total population, and most of the available data on vaccination are from patients who have undergone solid-organ transplant, Dr. Levin explained. Studies have shown that their response is less robust to vaccination in comparison with adults in the general population.
“Although it is still preliminary, the strongest data come from Israel,” he said, “where they found that the booster was highly effective and doubled the number of transplant patients who developed antibodies.”
But data are not yet available in the setting of cancer. “But even though we don’t have the data yet, the answer is that no matter, the booster process is essential,” he said. “The evidence we have is that boosters raise the immune response, and it is the best data we have now.”
Martin J. Edelman, MD, chair, department of hematology/oncology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, noted that the current recommendation is that patients who are immunocompromised receive a booster immediately.
At his health system, this is interpreted to include patients who have undergone the following treatments: Transplant (solid-organ and bone marrow transplant), hemodialysis, hematologic malignancy treatment, active immunosuppressive (chemotherapy, chemoimmunotherapy, and nonhormonal or single-agent immunotherapy) treatment, rheumatology treatments, and high-dose steroids.
“As for cancer patients, we are making arrangements to vaccinate patients who meet the above criteria now,” he said. “There is no known downside to receiving booster immediately. While there may be less of a response than waiting for completion of treatment, we know that patients on active therapy are frequently able to mount a response, and any response is better than none.”
Dr. Edelman added that this area is changing very rapidly. “We will modify our approach as information and guidance from appropriate organizations, such as the FDA and CDC, become available.”
Dr. Stemmer has received institutional research grants from CAN-FITE, AstraZeneca, Bioline RX, BMS, Halozyme, Clovis Oncology, CTG Pharma, Exelixis, Geicam, Incyte, Lilly, Moderna, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Roche, and owns stocks and options in CTG Pharma, DocBoxMD, Tyrnovo, VYPE, Cytora, and CAN-FITE. Dr. Edelman has received personal fees and other compensation from Windmil, Biomarker Strategies, AstraZeneca, Takeda, GlaxoSmithKline, Apexigen, Nektar, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Armo, Bergen Bio, and Apexigen outside the submitted work. He has submitted a patent for epigenetic modifications to increase susceptibility to radiopharmaceuticals and is a paid adviser for Kanaph and Flame. Dr. Levin is chairman and CEO of Ovid Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Military Medical Teams Deploy to Relieve COVID-Battered Hospitals
Last summer, a team of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care professionals deployed to Alabama’s Bill Nichols State Veterans Home to help during the COVID-19 crisis. They were there as part of the “Fourth Mission”—supporting national, state, and local emergency management, public health, safety and homeland security efforts. “It was a really humbling experience,” said Mary Holloway, an RN with the Birmingham VA Health Care System. “Seeing the dedication of the staff there, some coming back to work after recovering from COVID themselves, was inspiring.”
But that turned out to be only one battle in a sadly long and drawn-out war. Since March 2020, more than 5,000 military medical personnel have deployed to 14 states and the Navajo Nation, 51 cities, 71 hospitals, all struggling to keep their heads above a cresting tsunami of new COVID patients.
Last year, the crisis spots for deployments included major metropolitan areas in coastal states: New York, California, and New Jersey. The urgency now is in the Southern states. Those tend to be reporting the highest numbers of new cases and deaths. Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, and Mississippi, for example, have all ranked among the highest rates of cases and hospitalizations per 100,000 people across the country in the last seven days.
This year, military teams have also deployed to support vaccination centers in 25 states and 42 cities. Nearly all—97%—of the new COVID patients in recent months are unvaccinated. And, again, they predominate in Southern states. In Alabama, for instance, only 37% of the population are fully vaccinated. In Louisiana, that number is 40%.
The at-risk states also tend to be the ones that are rapidly running out of space to put the patients in, ICU or otherwise. Where patients who might have been in the intensive care unit (ICU) are housed in the emergency department and in hallways, and where patients without COVID-19 who might have been hospitalized are being turned away. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
These states are at a breaking point. Take Alabama. On August 18, it was “negative 11.” It had 1,568 patients with COVID-19 who needed ICU beds. Only 1,557 beds were available. Patients “may even stay on the regular floor where you’re already stretched for capacity to take care of these people because so many of our staff are out with COVID,” Jeanne Marrazzo, director, Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told a CNN reporter. “It’s really just a domino effect that then clogs up our ERs, clogs up everything else. … It’s a very very tenuous situation.”
The state reported more than 4,000 new cases of COVID-19—“a new high for us,” Marrazzo said. “If you project these numbers out, you can expect that we will at some point, probably around Sept. 1, have at least 5,000 people in our hospitals. If the ratio of people who have to go to the ICU remains stable. That means that probably a third of those people are going to require ICU beds,” she continued. “That is frankly untenable, given the infrastructure, the resources, and really importantly, the staff that we have. I think it is basically apocalyptic. I do not use that word lightly.”
Thus, the US Defense Department (DoD) must once again rise to a sad and desperate occasion. At the request of Federal Emergency Management Agency and the state of Louisiana, the first of five teams of Navy doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists were sent last week to Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center in Lafayette, Louisiana.
The teams, consisting of approximately 20 members each, are coming from throughout the DoD’s universe, including the National Guard. US Army North, under US Northern Command’s oversight, is providing operational command of the active-duty military COVID-19 response. Lt. Gen. Laura J. Richardson, ARNORTH commander, noting that “[t]his is the second time Department of Defense medical assets have deployed to support Louisiana during the pandemic,” calls it a “whole-of-government fight against COVID-19.”
Why Louisiana and Mississippi, with so many states in dire need? “Our joint forces go where FEMA needs us,” Richardson says. “[R]ight now FEMA has determined the military’s unique surge capabilities are most needed in these two states.”
In a press briefing at the time, Pentagon Press Secretary Rear Adm. John Kirby said, “We expect that there could be additional requests from other states for other teams, so that’s why we’re being prepared to stand up five teams.” He was right: An Air Force team has now headed to Our Lady of the Lake Regional Medical Center in Baton Rouge. Mississippi also asked for assistance; an Air Force team will be supporting at University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson, and an Army team at North Mississippi Medical Center-Tupelo.
The support will likely include bolstering and extending the infrastructure. From July to December 2020, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Emergency Management Coordination Cell delivered Fold-Out Rigid Temporary Shelters (FORTS), C-FORTS (clinics), mobile ICUs and isolation units to locations across the US, such as North Chicago, El Paso, and Oklahoma City. In 2021, they’ll be needed in more hospitals unprepared to house the spiking numbers of patients. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
The first go-round with COVID taught hard lessons that can help hone the Fourth Mission responses. One lesson, according to the VHA COVID-19 Response Report- Annex A, published this May, was the need to conduct due diligence, to be both efficient and effective. VHA, it says, now works to determine actual need before deploying resources. “For example, VHA might receive a request from a [State Veterans Home] for 50 RNs. But once VHA delved into the request and worked with the associated VISNs, it would find that 20 RNs or 10 LPNs could meet the needs of the request.”
Meeting the requests is, for the beleaguered hospitals, like answering letters to Santa. When the team of doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists arrived at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center (OLGMC) last week the hospital staff greeted them with cheers and applause.
OLGMC CEO Al Patin said, "We're already in a nursing shortage, coupled with high numbers of this pandemic [which] creates a situation where we need additional support. We have patients boarding in our emergency rooms, patients in our ICU setting that can't transition out. That creates a bottleneck and does not allow us to continue to take in patients from our community."
That day, OLG posted on Twitter:
“Today, we received some much-needed assistance in the fight against COVID-19. Our team at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center is being expanded by four doctors, 14 nurses and two respiratory therapists – all highly trained personnel on loan from the U.S. Navy.
“These healthcare professionals are being onboarded in our facility today and are specially trained for the emergency department, ICU and Med Surg. Because of them, we’ll be able to staff an additional 16-18 beds – beds sorely needed as cases continue to rise in our area.
“We requested support from the Federal Emergency Management Agency and we were one of five U.S. cities to receive it.. We are most grateful and humbled.”
Last summer, a team of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care professionals deployed to Alabama’s Bill Nichols State Veterans Home to help during the COVID-19 crisis. They were there as part of the “Fourth Mission”—supporting national, state, and local emergency management, public health, safety and homeland security efforts. “It was a really humbling experience,” said Mary Holloway, an RN with the Birmingham VA Health Care System. “Seeing the dedication of the staff there, some coming back to work after recovering from COVID themselves, was inspiring.”
But that turned out to be only one battle in a sadly long and drawn-out war. Since March 2020, more than 5,000 military medical personnel have deployed to 14 states and the Navajo Nation, 51 cities, 71 hospitals, all struggling to keep their heads above a cresting tsunami of new COVID patients.
Last year, the crisis spots for deployments included major metropolitan areas in coastal states: New York, California, and New Jersey. The urgency now is in the Southern states. Those tend to be reporting the highest numbers of new cases and deaths. Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, and Mississippi, for example, have all ranked among the highest rates of cases and hospitalizations per 100,000 people across the country in the last seven days.
This year, military teams have also deployed to support vaccination centers in 25 states and 42 cities. Nearly all—97%—of the new COVID patients in recent months are unvaccinated. And, again, they predominate in Southern states. In Alabama, for instance, only 37% of the population are fully vaccinated. In Louisiana, that number is 40%.
The at-risk states also tend to be the ones that are rapidly running out of space to put the patients in, ICU or otherwise. Where patients who might have been in the intensive care unit (ICU) are housed in the emergency department and in hallways, and where patients without COVID-19 who might have been hospitalized are being turned away. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
These states are at a breaking point. Take Alabama. On August 18, it was “negative 11.” It had 1,568 patients with COVID-19 who needed ICU beds. Only 1,557 beds were available. Patients “may even stay on the regular floor where you’re already stretched for capacity to take care of these people because so many of our staff are out with COVID,” Jeanne Marrazzo, director, Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told a CNN reporter. “It’s really just a domino effect that then clogs up our ERs, clogs up everything else. … It’s a very very tenuous situation.”
The state reported more than 4,000 new cases of COVID-19—“a new high for us,” Marrazzo said. “If you project these numbers out, you can expect that we will at some point, probably around Sept. 1, have at least 5,000 people in our hospitals. If the ratio of people who have to go to the ICU remains stable. That means that probably a third of those people are going to require ICU beds,” she continued. “That is frankly untenable, given the infrastructure, the resources, and really importantly, the staff that we have. I think it is basically apocalyptic. I do not use that word lightly.”
Thus, the US Defense Department (DoD) must once again rise to a sad and desperate occasion. At the request of Federal Emergency Management Agency and the state of Louisiana, the first of five teams of Navy doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists were sent last week to Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center in Lafayette, Louisiana.
The teams, consisting of approximately 20 members each, are coming from throughout the DoD’s universe, including the National Guard. US Army North, under US Northern Command’s oversight, is providing operational command of the active-duty military COVID-19 response. Lt. Gen. Laura J. Richardson, ARNORTH commander, noting that “[t]his is the second time Department of Defense medical assets have deployed to support Louisiana during the pandemic,” calls it a “whole-of-government fight against COVID-19.”
Why Louisiana and Mississippi, with so many states in dire need? “Our joint forces go where FEMA needs us,” Richardson says. “[R]ight now FEMA has determined the military’s unique surge capabilities are most needed in these two states.”
In a press briefing at the time, Pentagon Press Secretary Rear Adm. John Kirby said, “We expect that there could be additional requests from other states for other teams, so that’s why we’re being prepared to stand up five teams.” He was right: An Air Force team has now headed to Our Lady of the Lake Regional Medical Center in Baton Rouge. Mississippi also asked for assistance; an Air Force team will be supporting at University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson, and an Army team at North Mississippi Medical Center-Tupelo.
The support will likely include bolstering and extending the infrastructure. From July to December 2020, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Emergency Management Coordination Cell delivered Fold-Out Rigid Temporary Shelters (FORTS), C-FORTS (clinics), mobile ICUs and isolation units to locations across the US, such as North Chicago, El Paso, and Oklahoma City. In 2021, they’ll be needed in more hospitals unprepared to house the spiking numbers of patients. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
The first go-round with COVID taught hard lessons that can help hone the Fourth Mission responses. One lesson, according to the VHA COVID-19 Response Report- Annex A, published this May, was the need to conduct due diligence, to be both efficient and effective. VHA, it says, now works to determine actual need before deploying resources. “For example, VHA might receive a request from a [State Veterans Home] for 50 RNs. But once VHA delved into the request and worked with the associated VISNs, it would find that 20 RNs or 10 LPNs could meet the needs of the request.”
Meeting the requests is, for the beleaguered hospitals, like answering letters to Santa. When the team of doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists arrived at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center (OLGMC) last week the hospital staff greeted them with cheers and applause.
OLGMC CEO Al Patin said, "We're already in a nursing shortage, coupled with high numbers of this pandemic [which] creates a situation where we need additional support. We have patients boarding in our emergency rooms, patients in our ICU setting that can't transition out. That creates a bottleneck and does not allow us to continue to take in patients from our community."
That day, OLG posted on Twitter:
“Today, we received some much-needed assistance in the fight against COVID-19. Our team at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center is being expanded by four doctors, 14 nurses and two respiratory therapists – all highly trained personnel on loan from the U.S. Navy.
“These healthcare professionals are being onboarded in our facility today and are specially trained for the emergency department, ICU and Med Surg. Because of them, we’ll be able to staff an additional 16-18 beds – beds sorely needed as cases continue to rise in our area.
“We requested support from the Federal Emergency Management Agency and we were one of five U.S. cities to receive it.. We are most grateful and humbled.”
Last summer, a team of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care professionals deployed to Alabama’s Bill Nichols State Veterans Home to help during the COVID-19 crisis. They were there as part of the “Fourth Mission”—supporting national, state, and local emergency management, public health, safety and homeland security efforts. “It was a really humbling experience,” said Mary Holloway, an RN with the Birmingham VA Health Care System. “Seeing the dedication of the staff there, some coming back to work after recovering from COVID themselves, was inspiring.”
But that turned out to be only one battle in a sadly long and drawn-out war. Since March 2020, more than 5,000 military medical personnel have deployed to 14 states and the Navajo Nation, 51 cities, 71 hospitals, all struggling to keep their heads above a cresting tsunami of new COVID patients.
Last year, the crisis spots for deployments included major metropolitan areas in coastal states: New York, California, and New Jersey. The urgency now is in the Southern states. Those tend to be reporting the highest numbers of new cases and deaths. Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, and Mississippi, for example, have all ranked among the highest rates of cases and hospitalizations per 100,000 people across the country in the last seven days.
This year, military teams have also deployed to support vaccination centers in 25 states and 42 cities. Nearly all—97%—of the new COVID patients in recent months are unvaccinated. And, again, they predominate in Southern states. In Alabama, for instance, only 37% of the population are fully vaccinated. In Louisiana, that number is 40%.
The at-risk states also tend to be the ones that are rapidly running out of space to put the patients in, ICU or otherwise. Where patients who might have been in the intensive care unit (ICU) are housed in the emergency department and in hallways, and where patients without COVID-19 who might have been hospitalized are being turned away. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
These states are at a breaking point. Take Alabama. On August 18, it was “negative 11.” It had 1,568 patients with COVID-19 who needed ICU beds. Only 1,557 beds were available. Patients “may even stay on the regular floor where you’re already stretched for capacity to take care of these people because so many of our staff are out with COVID,” Jeanne Marrazzo, director, Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told a CNN reporter. “It’s really just a domino effect that then clogs up our ERs, clogs up everything else. … It’s a very very tenuous situation.”
The state reported more than 4,000 new cases of COVID-19—“a new high for us,” Marrazzo said. “If you project these numbers out, you can expect that we will at some point, probably around Sept. 1, have at least 5,000 people in our hospitals. If the ratio of people who have to go to the ICU remains stable. That means that probably a third of those people are going to require ICU beds,” she continued. “That is frankly untenable, given the infrastructure, the resources, and really importantly, the staff that we have. I think it is basically apocalyptic. I do not use that word lightly.”
Thus, the US Defense Department (DoD) must once again rise to a sad and desperate occasion. At the request of Federal Emergency Management Agency and the state of Louisiana, the first of five teams of Navy doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists were sent last week to Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center in Lafayette, Louisiana.
The teams, consisting of approximately 20 members each, are coming from throughout the DoD’s universe, including the National Guard. US Army North, under US Northern Command’s oversight, is providing operational command of the active-duty military COVID-19 response. Lt. Gen. Laura J. Richardson, ARNORTH commander, noting that “[t]his is the second time Department of Defense medical assets have deployed to support Louisiana during the pandemic,” calls it a “whole-of-government fight against COVID-19.”
Why Louisiana and Mississippi, with so many states in dire need? “Our joint forces go where FEMA needs us,” Richardson says. “[R]ight now FEMA has determined the military’s unique surge capabilities are most needed in these two states.”
In a press briefing at the time, Pentagon Press Secretary Rear Adm. John Kirby said, “We expect that there could be additional requests from other states for other teams, so that’s why we’re being prepared to stand up five teams.” He was right: An Air Force team has now headed to Our Lady of the Lake Regional Medical Center in Baton Rouge. Mississippi also asked for assistance; an Air Force team will be supporting at University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson, and an Army team at North Mississippi Medical Center-Tupelo.
The support will likely include bolstering and extending the infrastructure. From July to December 2020, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Emergency Management Coordination Cell delivered Fold-Out Rigid Temporary Shelters (FORTS), C-FORTS (clinics), mobile ICUs and isolation units to locations across the US, such as North Chicago, El Paso, and Oklahoma City. In 2021, they’ll be needed in more hospitals unprepared to house the spiking numbers of patients. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
The first go-round with COVID taught hard lessons that can help hone the Fourth Mission responses. One lesson, according to the VHA COVID-19 Response Report- Annex A, published this May, was the need to conduct due diligence, to be both efficient and effective. VHA, it says, now works to determine actual need before deploying resources. “For example, VHA might receive a request from a [State Veterans Home] for 50 RNs. But once VHA delved into the request and worked with the associated VISNs, it would find that 20 RNs or 10 LPNs could meet the needs of the request.”
Meeting the requests is, for the beleaguered hospitals, like answering letters to Santa. When the team of doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists arrived at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center (OLGMC) last week the hospital staff greeted them with cheers and applause.
OLGMC CEO Al Patin said, "We're already in a nursing shortage, coupled with high numbers of this pandemic [which] creates a situation where we need additional support. We have patients boarding in our emergency rooms, patients in our ICU setting that can't transition out. That creates a bottleneck and does not allow us to continue to take in patients from our community."
That day, OLG posted on Twitter:
“Today, we received some much-needed assistance in the fight against COVID-19. Our team at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center is being expanded by four doctors, 14 nurses and two respiratory therapists – all highly trained personnel on loan from the U.S. Navy.
“These healthcare professionals are being onboarded in our facility today and are specially trained for the emergency department, ICU and Med Surg. Because of them, we’ll be able to staff an additional 16-18 beds – beds sorely needed as cases continue to rise in our area.
“We requested support from the Federal Emergency Management Agency and we were one of five U.S. cities to receive it.. We are most grateful and humbled.”
Military Medical Teams Deploy to Relieve COVID-Battered Hospitals
Last summer, a team of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care professionals deployed to Alabama’s Bill Nichols State Veterans Home to help during the COVID-19 crisis. They were there as part of the “Fourth Mission”—supporting national, state, and local emergency management, public health, safety and homeland security efforts. “It was a really humbling experience,” said Mary Holloway, an RN with the Birmingham VA Health Care System. “Seeing the dedication of the staff there, some coming back to work after recovering from COVID themselves, was inspiring.”
But that turned out to be only one battle in a sadly long and drawn-out war. Since March 2020, more than 5,000 military medical personnel have deployed to 14 states and the Navajo Nation, 51 cities, 71 hospitals, all struggling to keep their heads above a cresting tsunami of new COVID patients.
Last year, the crisis spots for deployments included major metropolitan areas in coastal states: New York, California, and New Jersey. The urgency now is in the Southern states. Those tend to be reporting the highest numbers of new cases and deaths. Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, and Mississippi, for example, have all ranked among the highest rates of cases and hospitalizations per 100,000 people across the country in the last seven days.
This year, military teams have also deployed to support vaccination centers in 25 states and 42 cities. Nearly all—97%—of the new COVID patients in recent months are unvaccinated. And, again, they predominate in Southern states. In Alabama, for instance, only 37% of the population are fully vaccinated. In Louisiana, that number is 40%.
The at-risk states also tend to be the ones that are rapidly running out of space to put the patients in, ICU or otherwise. Where patients who might have been in the intensive care unit (ICU) are housed in the emergency department and in hallways, and where patients without COVID-19 who might have been hospitalized are being turned away. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
These states are at a breaking point. Take Alabama. On August 18, it was “negative 11.” It had 1,568 patients with COVID-19 who needed ICU beds. Only 1,557 beds were available. Patients “may even stay on the regular floor where you’re already stretched for capacity to take care of these people because so many of our staff are out with COVID,” Jeanne Marrazzo, director, Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told a CNN reporter. “It’s really just a domino effect that then clogs up our ERs, clogs up everything else. … It’s a very very tenuous situation.”
The state reported more than 4,000 new cases of COVID-19—“a new high for us,” Marrazzo said. “If you project these numbers out, you can expect that we will at some point, probably around Sept. 1, have at least 5,000 people in our hospitals. If the ratio of people who have to go to the ICU remains stable. That means that probably a third of those people are going to require ICU beds,” she continued. “That is frankly untenable, given the infrastructure, the resources, and really importantly, the staff that we have. I think it is basically apocalyptic. I do not use that word lightly.”
Thus, the US Defense Department (DoD) must once again rise to a sad and desperate occasion. At the request of Federal Emergency Management Agency and the state of Louisiana, the first of five teams of Navy doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists were sent last week to Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center in Lafayette, Louisiana.
The teams, consisting of approximately 20 members each, are coming from throughout the DoD’s universe, including the National Guard. US Army North, under US Northern Command’s oversight, is providing operational command of the active-duty military COVID-19 response. Lt. Gen. Laura J. Richardson, ARNORTH commander, noting that “[t]his is the second time Department of Defense medical assets have deployed to support Louisiana during the pandemic,” calls it a “whole-of-government fight against COVID-19.”
Why Louisiana and Mississippi, with so many states in dire need? “Our joint forces go where FEMA needs us,” Richardson says. “[R]ight now FEMA has determined the military’s unique surge capabilities are most needed in these two states.”
In a press briefing at the time, Pentagon Press Secretary Rear Adm. John Kirby said, “We expect that there could be additional requests from other states for other teams, so that’s why we’re being prepared to stand up five teams.” He was right: An Air Force team has now headed to Our Lady of the Lake Regional Medical Center in Baton Rouge. Mississippi also asked for assistance; an Air Force team will be supporting at University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson, and an Army team at North Mississippi Medical Center-Tupelo.
The support will likely include bolstering and extending the infrastructure. From July to December 2020, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Emergency Management Coordination Cell delivered Fold-Out Rigid Temporary Shelters (FORTS), C-FORTS (clinics), mobile ICUs and isolation units to locations across the US, such as North Chicago, El Paso, and Oklahoma City. In 2021, they’ll be needed in more hospitals unprepared to house the spiking numbers of patients. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
The first go-round with COVID taught hard lessons that can help hone the Fourth Mission responses. One lesson, according to the VHA COVID-19 Response Report- Annex A, published this May, was the need to conduct due diligence, to be both efficient and effective. VHA, it says, now works to determine actual need before deploying resources. “For example, VHA might receive a request from a [State Veterans Home] for 50 RNs. But once VHA delved into the request and worked with the associated VISNs, it would find that 20 RNs or 10 LPNs could meet the needs of the request.”
Meeting the requests is, for the beleaguered hospitals, like answering letters to Santa. When the team of doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists arrived at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center (OLGMC) last week the hospital staff greeted them with cheers and applause.
OLGMC CEO Al Patin said, "We're already in a nursing shortage, coupled with high numbers of this pandemic [which] creates a situation where we need additional support. We have patients boarding in our emergency rooms, patients in our ICU setting that can't transition out. That creates a bottleneck and does not allow us to continue to take in patients from our community."
That day, OLG posted on Twitter:
“Today, we received some much-needed assistance in the fight against COVID-19. Our team at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center is being expanded by four doctors, 14 nurses and two respiratory therapists – all highly trained personnel on loan from the U.S. Navy.
“These healthcare professionals are being onboarded in our facility today and are specially trained for the emergency department, ICU and Med Surg. Because of them, we’ll be able to staff an additional 16-18 beds – beds sorely needed as cases continue to rise in our area.
“We requested support from the Federal Emergency Management Agency and we were one of five U.S. cities to receive it.. We are most grateful and humbled.”
Last summer, a team of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care professionals deployed to Alabama’s Bill Nichols State Veterans Home to help during the COVID-19 crisis. They were there as part of the “Fourth Mission”—supporting national, state, and local emergency management, public health, safety and homeland security efforts. “It was a really humbling experience,” said Mary Holloway, an RN with the Birmingham VA Health Care System. “Seeing the dedication of the staff there, some coming back to work after recovering from COVID themselves, was inspiring.”
But that turned out to be only one battle in a sadly long and drawn-out war. Since March 2020, more than 5,000 military medical personnel have deployed to 14 states and the Navajo Nation, 51 cities, 71 hospitals, all struggling to keep their heads above a cresting tsunami of new COVID patients.
Last year, the crisis spots for deployments included major metropolitan areas in coastal states: New York, California, and New Jersey. The urgency now is in the Southern states. Those tend to be reporting the highest numbers of new cases and deaths. Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, and Mississippi, for example, have all ranked among the highest rates of cases and hospitalizations per 100,000 people across the country in the last seven days.
This year, military teams have also deployed to support vaccination centers in 25 states and 42 cities. Nearly all—97%—of the new COVID patients in recent months are unvaccinated. And, again, they predominate in Southern states. In Alabama, for instance, only 37% of the population are fully vaccinated. In Louisiana, that number is 40%.
The at-risk states also tend to be the ones that are rapidly running out of space to put the patients in, ICU or otherwise. Where patients who might have been in the intensive care unit (ICU) are housed in the emergency department and in hallways, and where patients without COVID-19 who might have been hospitalized are being turned away. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
These states are at a breaking point. Take Alabama. On August 18, it was “negative 11.” It had 1,568 patients with COVID-19 who needed ICU beds. Only 1,557 beds were available. Patients “may even stay on the regular floor where you’re already stretched for capacity to take care of these people because so many of our staff are out with COVID,” Jeanne Marrazzo, director, Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told a CNN reporter. “It’s really just a domino effect that then clogs up our ERs, clogs up everything else. … It’s a very very tenuous situation.”
The state reported more than 4,000 new cases of COVID-19—“a new high for us,” Marrazzo said. “If you project these numbers out, you can expect that we will at some point, probably around Sept. 1, have at least 5,000 people in our hospitals. If the ratio of people who have to go to the ICU remains stable. That means that probably a third of those people are going to require ICU beds,” she continued. “That is frankly untenable, given the infrastructure, the resources, and really importantly, the staff that we have. I think it is basically apocalyptic. I do not use that word lightly.”
Thus, the US Defense Department (DoD) must once again rise to a sad and desperate occasion. At the request of Federal Emergency Management Agency and the state of Louisiana, the first of five teams of Navy doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists were sent last week to Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center in Lafayette, Louisiana.
The teams, consisting of approximately 20 members each, are coming from throughout the DoD’s universe, including the National Guard. US Army North, under US Northern Command’s oversight, is providing operational command of the active-duty military COVID-19 response. Lt. Gen. Laura J. Richardson, ARNORTH commander, noting that “[t]his is the second time Department of Defense medical assets have deployed to support Louisiana during the pandemic,” calls it a “whole-of-government fight against COVID-19.”
Why Louisiana and Mississippi, with so many states in dire need? “Our joint forces go where FEMA needs us,” Richardson says. “[R]ight now FEMA has determined the military’s unique surge capabilities are most needed in these two states.”
In a press briefing at the time, Pentagon Press Secretary Rear Adm. John Kirby said, “We expect that there could be additional requests from other states for other teams, so that’s why we’re being prepared to stand up five teams.” He was right: An Air Force team has now headed to Our Lady of the Lake Regional Medical Center in Baton Rouge. Mississippi also asked for assistance; an Air Force team will be supporting at University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson, and an Army team at North Mississippi Medical Center-Tupelo.
The support will likely include bolstering and extending the infrastructure. From July to December 2020, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Emergency Management Coordination Cell delivered Fold-Out Rigid Temporary Shelters (FORTS), C-FORTS (clinics), mobile ICUs and isolation units to locations across the US, such as North Chicago, El Paso, and Oklahoma City. In 2021, they’ll be needed in more hospitals unprepared to house the spiking numbers of patients. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
The first go-round with COVID taught hard lessons that can help hone the Fourth Mission responses. One lesson, according to the VHA COVID-19 Response Report- Annex A, published this May, was the need to conduct due diligence, to be both efficient and effective. VHA, it says, now works to determine actual need before deploying resources. “For example, VHA might receive a request from a [State Veterans Home] for 50 RNs. But once VHA delved into the request and worked with the associated VISNs, it would find that 20 RNs or 10 LPNs could meet the needs of the request.”
Meeting the requests is, for the beleaguered hospitals, like answering letters to Santa. When the team of doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists arrived at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center (OLGMC) last week the hospital staff greeted them with cheers and applause.
OLGMC CEO Al Patin said, "We're already in a nursing shortage, coupled with high numbers of this pandemic [which] creates a situation where we need additional support. We have patients boarding in our emergency rooms, patients in our ICU setting that can't transition out. That creates a bottleneck and does not allow us to continue to take in patients from our community."
That day, OLG posted on Twitter:
“Today, we received some much-needed assistance in the fight against COVID-19. Our team at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center is being expanded by four doctors, 14 nurses and two respiratory therapists – all highly trained personnel on loan from the U.S. Navy.
“These healthcare professionals are being onboarded in our facility today and are specially trained for the emergency department, ICU and Med Surg. Because of them, we’ll be able to staff an additional 16-18 beds – beds sorely needed as cases continue to rise in our area.
“We requested support from the Federal Emergency Management Agency and we were one of five U.S. cities to receive it.. We are most grateful and humbled.”
Last summer, a team of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care professionals deployed to Alabama’s Bill Nichols State Veterans Home to help during the COVID-19 crisis. They were there as part of the “Fourth Mission”—supporting national, state, and local emergency management, public health, safety and homeland security efforts. “It was a really humbling experience,” said Mary Holloway, an RN with the Birmingham VA Health Care System. “Seeing the dedication of the staff there, some coming back to work after recovering from COVID themselves, was inspiring.”
But that turned out to be only one battle in a sadly long and drawn-out war. Since March 2020, more than 5,000 military medical personnel have deployed to 14 states and the Navajo Nation, 51 cities, 71 hospitals, all struggling to keep their heads above a cresting tsunami of new COVID patients.
Last year, the crisis spots for deployments included major metropolitan areas in coastal states: New York, California, and New Jersey. The urgency now is in the Southern states. Those tend to be reporting the highest numbers of new cases and deaths. Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, and Mississippi, for example, have all ranked among the highest rates of cases and hospitalizations per 100,000 people across the country in the last seven days.
This year, military teams have also deployed to support vaccination centers in 25 states and 42 cities. Nearly all—97%—of the new COVID patients in recent months are unvaccinated. And, again, they predominate in Southern states. In Alabama, for instance, only 37% of the population are fully vaccinated. In Louisiana, that number is 40%.
The at-risk states also tend to be the ones that are rapidly running out of space to put the patients in, ICU or otherwise. Where patients who might have been in the intensive care unit (ICU) are housed in the emergency department and in hallways, and where patients without COVID-19 who might have been hospitalized are being turned away. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
These states are at a breaking point. Take Alabama. On August 18, it was “negative 11.” It had 1,568 patients with COVID-19 who needed ICU beds. Only 1,557 beds were available. Patients “may even stay on the regular floor where you’re already stretched for capacity to take care of these people because so many of our staff are out with COVID,” Jeanne Marrazzo, director, Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told a CNN reporter. “It’s really just a domino effect that then clogs up our ERs, clogs up everything else. … It’s a very very tenuous situation.”
The state reported more than 4,000 new cases of COVID-19—“a new high for us,” Marrazzo said. “If you project these numbers out, you can expect that we will at some point, probably around Sept. 1, have at least 5,000 people in our hospitals. If the ratio of people who have to go to the ICU remains stable. That means that probably a third of those people are going to require ICU beds,” she continued. “That is frankly untenable, given the infrastructure, the resources, and really importantly, the staff that we have. I think it is basically apocalyptic. I do not use that word lightly.”
Thus, the US Defense Department (DoD) must once again rise to a sad and desperate occasion. At the request of Federal Emergency Management Agency and the state of Louisiana, the first of five teams of Navy doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists were sent last week to Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center in Lafayette, Louisiana.
The teams, consisting of approximately 20 members each, are coming from throughout the DoD’s universe, including the National Guard. US Army North, under US Northern Command’s oversight, is providing operational command of the active-duty military COVID-19 response. Lt. Gen. Laura J. Richardson, ARNORTH commander, noting that “[t]his is the second time Department of Defense medical assets have deployed to support Louisiana during the pandemic,” calls it a “whole-of-government fight against COVID-19.”
Why Louisiana and Mississippi, with so many states in dire need? “Our joint forces go where FEMA needs us,” Richardson says. “[R]ight now FEMA has determined the military’s unique surge capabilities are most needed in these two states.”
In a press briefing at the time, Pentagon Press Secretary Rear Adm. John Kirby said, “We expect that there could be additional requests from other states for other teams, so that’s why we’re being prepared to stand up five teams.” He was right: An Air Force team has now headed to Our Lady of the Lake Regional Medical Center in Baton Rouge. Mississippi also asked for assistance; an Air Force team will be supporting at University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson, and an Army team at North Mississippi Medical Center-Tupelo.
The support will likely include bolstering and extending the infrastructure. From July to December 2020, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Emergency Management Coordination Cell delivered Fold-Out Rigid Temporary Shelters (FORTS), C-FORTS (clinics), mobile ICUs and isolation units to locations across the US, such as North Chicago, El Paso, and Oklahoma City. In 2021, they’ll be needed in more hospitals unprepared to house the spiking numbers of patients. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
The first go-round with COVID taught hard lessons that can help hone the Fourth Mission responses. One lesson, according to the VHA COVID-19 Response Report- Annex A, published this May, was the need to conduct due diligence, to be both efficient and effective. VHA, it says, now works to determine actual need before deploying resources. “For example, VHA might receive a request from a [State Veterans Home] for 50 RNs. But once VHA delved into the request and worked with the associated VISNs, it would find that 20 RNs or 10 LPNs could meet the needs of the request.”
Meeting the requests is, for the beleaguered hospitals, like answering letters to Santa. When the team of doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists arrived at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center (OLGMC) last week the hospital staff greeted them with cheers and applause.
OLGMC CEO Al Patin said, "We're already in a nursing shortage, coupled with high numbers of this pandemic [which] creates a situation where we need additional support. We have patients boarding in our emergency rooms, patients in our ICU setting that can't transition out. That creates a bottleneck and does not allow us to continue to take in patients from our community."
That day, OLG posted on Twitter:
“Today, we received some much-needed assistance in the fight against COVID-19. Our team at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center is being expanded by four doctors, 14 nurses and two respiratory therapists – all highly trained personnel on loan from the U.S. Navy.
“These healthcare professionals are being onboarded in our facility today and are specially trained for the emergency department, ICU and Med Surg. Because of them, we’ll be able to staff an additional 16-18 beds – beds sorely needed as cases continue to rise in our area.
“We requested support from the Federal Emergency Management Agency and we were one of five U.S. cities to receive it.. We are most grateful and humbled.”
Military Medical Teams Deploy to Relieve COVID-Battered Hospitals
Last summer, a team of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care professionals deployed to Alabama’s Bill Nichols State Veterans Home to help during the COVID-19 crisis. They were there as part of the “Fourth Mission”—supporting national, state, and local emergency management, public health, safety and homeland security efforts. “It was a really humbling experience,” said Mary Holloway, an RN with the Birmingham VA Health Care System. “Seeing the dedication of the staff there, some coming back to work after recovering from COVID themselves, was inspiring.”
But that turned out to be only one battle in a sadly long and drawn-out war. Since March 2020, more than 5,000 military medical personnel have deployed to 14 states and the Navajo Nation, 51 cities, 71 hospitals, all struggling to keep their heads above a cresting tsunami of new COVID patients.
Last year, the crisis spots for deployments included major metropolitan areas in coastal states: New York, California, and New Jersey. The urgency now is in the Southern states. Those tend to be reporting the highest numbers of new cases and deaths. Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, and Mississippi, for example, have all ranked among the highest rates of cases and hospitalizations per 100,000 people across the country in the last seven days.
This year, military teams have also deployed to support vaccination centers in 25 states and 42 cities. Nearly all—97%—of the new COVID patients in recent months are unvaccinated. And, again, they predominate in Southern states. In Alabama, for instance, only 37% of the population are fully vaccinated. In Louisiana, that number is 40%.
The at-risk states also tend to be the ones that are rapidly running out of space to put the patients in, ICU or otherwise. Where patients who might have been in the intensive care unit (ICU) are housed in the emergency department and in hallways, and where patients without COVID-19 who might have been hospitalized are being turned away. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
These states are at a breaking point. Take Alabama. On August 18, it was “negative 11.” It had 1,568 patients with COVID-19 who needed ICU beds. Only 1,557 beds were available. Patients “may even stay on the regular floor where you’re already stretched for capacity to take care of these people because so many of our staff are out with COVID,” Jeanne Marrazzo, director, Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told a CNN reporter. “It’s really just a domino effect that then clogs up our ERs, clogs up everything else. … It’s a very very tenuous situation.”
The state reported more than 4,000 new cases of COVID-19—“a new high for us,” Marrazzo said. “If you project these numbers out, you can expect that we will at some point, probably around Sept. 1, have at least 5,000 people in our hospitals. If the ratio of people who have to go to the ICU remains stable. That means that probably a third of those people are going to require ICU beds,” she continued. “That is frankly untenable, given the infrastructure, the resources, and really importantly, the staff that we have. I think it is basically apocalyptic. I do not use that word lightly.”
Thus, the US Defense Department (DoD) must once again rise to a sad and desperate occasion. At the request of Federal Emergency Management Agency and the state of Louisiana, the first of five teams of Navy doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists were sent last week to Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center in Lafayette, Louisiana.
The teams, consisting of approximately 20 members each, are coming from throughout the DoD’s universe, including the National Guard. US Army North, under US Northern Command’s oversight, is providing operational command of the active-duty military COVID-19 response. Lt. Gen. Laura J. Richardson, ARNORTH commander, noting that “[t]his is the second time Department of Defense medical assets have deployed to support Louisiana during the pandemic,” calls it a “whole-of-government fight against COVID-19.”
Why Louisiana and Mississippi, with so many states in dire need? “Our joint forces go where FEMA needs us,” Richardson says. “[R]ight now FEMA has determined the military’s unique surge capabilities are most needed in these two states.”
In a press briefing at the time, Pentagon Press Secretary Rear Adm. John Kirby said, “We expect that there could be additional requests from other states for other teams, so that’s why we’re being prepared to stand up five teams.” He was right: An Air Force team has now headed to Our Lady of the Lake Regional Medical Center in Baton Rouge. Mississippi also asked for assistance; an Air Force team will be supporting at University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson, and an Army team at North Mississippi Medical Center-Tupelo.
The support will likely include bolstering and extending the infrastructure. From July to December 2020, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Emergency Management Coordination Cell delivered Fold-Out Rigid Temporary Shelters (FORTS), C-FORTS (clinics), mobile ICUs and isolation units to locations across the US, such as North Chicago, El Paso, and Oklahoma City. In 2021, they’ll be needed in more hospitals unprepared to house the spiking numbers of patients. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
The first go-round with COVID taught hard lessons that can help hone the Fourth Mission responses. One lesson, according to the VHA COVID-19 Response Report- Annex A, published this May, was the need to conduct due diligence, to be both efficient and effective. VHA, it says, now works to determine actual need before deploying resources. “For example, VHA might receive a request from a [State Veterans Home] for 50 RNs. But once VHA delved into the request and worked with the associated VISNs, it would find that 20 RNs or 10 LPNs could meet the needs of the request.”
Meeting the requests is, for the beleaguered hospitals, like answering letters to Santa. When the team of doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists arrived at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center (OLGMC) last week the hospital staff greeted them with cheers and applause.
OLGMC CEO Al Patin said, "We're already in a nursing shortage, coupled with high numbers of this pandemic [which] creates a situation where we need additional support. We have patients boarding in our emergency rooms, patients in our ICU setting that can't transition out. That creates a bottleneck and does not allow us to continue to take in patients from our community."
That day, OLG posted on Twitter:
“Today, we received some much-needed assistance in the fight against COVID-19. Our team at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center is being expanded by four doctors, 14 nurses and two respiratory therapists – all highly trained personnel on loan from the U.S. Navy.
“These healthcare professionals are being onboarded in our facility today and are specially trained for the emergency department, ICU and Med Surg. Because of them, we’ll be able to staff an additional 16-18 beds – beds sorely needed as cases continue to rise in our area.
“We requested support from the Federal Emergency Management Agency and we were one of five U.S. cities to receive it.. We are most grateful and humbled.”
Last summer, a team of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care professionals deployed to Alabama’s Bill Nichols State Veterans Home to help during the COVID-19 crisis. They were there as part of the “Fourth Mission”—supporting national, state, and local emergency management, public health, safety and homeland security efforts. “It was a really humbling experience,” said Mary Holloway, an RN with the Birmingham VA Health Care System. “Seeing the dedication of the staff there, some coming back to work after recovering from COVID themselves, was inspiring.”
But that turned out to be only one battle in a sadly long and drawn-out war. Since March 2020, more than 5,000 military medical personnel have deployed to 14 states and the Navajo Nation, 51 cities, 71 hospitals, all struggling to keep their heads above a cresting tsunami of new COVID patients.
Last year, the crisis spots for deployments included major metropolitan areas in coastal states: New York, California, and New Jersey. The urgency now is in the Southern states. Those tend to be reporting the highest numbers of new cases and deaths. Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, and Mississippi, for example, have all ranked among the highest rates of cases and hospitalizations per 100,000 people across the country in the last seven days.
This year, military teams have also deployed to support vaccination centers in 25 states and 42 cities. Nearly all—97%—of the new COVID patients in recent months are unvaccinated. And, again, they predominate in Southern states. In Alabama, for instance, only 37% of the population are fully vaccinated. In Louisiana, that number is 40%.
The at-risk states also tend to be the ones that are rapidly running out of space to put the patients in, ICU or otherwise. Where patients who might have been in the intensive care unit (ICU) are housed in the emergency department and in hallways, and where patients without COVID-19 who might have been hospitalized are being turned away. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
These states are at a breaking point. Take Alabama. On August 18, it was “negative 11.” It had 1,568 patients with COVID-19 who needed ICU beds. Only 1,557 beds were available. Patients “may even stay on the regular floor where you’re already stretched for capacity to take care of these people because so many of our staff are out with COVID,” Jeanne Marrazzo, director, Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told a CNN reporter. “It’s really just a domino effect that then clogs up our ERs, clogs up everything else. … It’s a very very tenuous situation.”
The state reported more than 4,000 new cases of COVID-19—“a new high for us,” Marrazzo said. “If you project these numbers out, you can expect that we will at some point, probably around Sept. 1, have at least 5,000 people in our hospitals. If the ratio of people who have to go to the ICU remains stable. That means that probably a third of those people are going to require ICU beds,” she continued. “That is frankly untenable, given the infrastructure, the resources, and really importantly, the staff that we have. I think it is basically apocalyptic. I do not use that word lightly.”
Thus, the US Defense Department (DoD) must once again rise to a sad and desperate occasion. At the request of Federal Emergency Management Agency and the state of Louisiana, the first of five teams of Navy doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists were sent last week to Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center in Lafayette, Louisiana.
The teams, consisting of approximately 20 members each, are coming from throughout the DoD’s universe, including the National Guard. US Army North, under US Northern Command’s oversight, is providing operational command of the active-duty military COVID-19 response. Lt. Gen. Laura J. Richardson, ARNORTH commander, noting that “[t]his is the second time Department of Defense medical assets have deployed to support Louisiana during the pandemic,” calls it a “whole-of-government fight against COVID-19.”
Why Louisiana and Mississippi, with so many states in dire need? “Our joint forces go where FEMA needs us,” Richardson says. “[R]ight now FEMA has determined the military’s unique surge capabilities are most needed in these two states.”
In a press briefing at the time, Pentagon Press Secretary Rear Adm. John Kirby said, “We expect that there could be additional requests from other states for other teams, so that’s why we’re being prepared to stand up five teams.” He was right: An Air Force team has now headed to Our Lady of the Lake Regional Medical Center in Baton Rouge. Mississippi also asked for assistance; an Air Force team will be supporting at University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson, and an Army team at North Mississippi Medical Center-Tupelo.
The support will likely include bolstering and extending the infrastructure. From July to December 2020, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Emergency Management Coordination Cell delivered Fold-Out Rigid Temporary Shelters (FORTS), C-FORTS (clinics), mobile ICUs and isolation units to locations across the US, such as North Chicago, El Paso, and Oklahoma City. In 2021, they’ll be needed in more hospitals unprepared to house the spiking numbers of patients. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
The first go-round with COVID taught hard lessons that can help hone the Fourth Mission responses. One lesson, according to the VHA COVID-19 Response Report- Annex A, published this May, was the need to conduct due diligence, to be both efficient and effective. VHA, it says, now works to determine actual need before deploying resources. “For example, VHA might receive a request from a [State Veterans Home] for 50 RNs. But once VHA delved into the request and worked with the associated VISNs, it would find that 20 RNs or 10 LPNs could meet the needs of the request.”
Meeting the requests is, for the beleaguered hospitals, like answering letters to Santa. When the team of doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists arrived at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center (OLGMC) last week the hospital staff greeted them with cheers and applause.
OLGMC CEO Al Patin said, "We're already in a nursing shortage, coupled with high numbers of this pandemic [which] creates a situation where we need additional support. We have patients boarding in our emergency rooms, patients in our ICU setting that can't transition out. That creates a bottleneck and does not allow us to continue to take in patients from our community."
That day, OLG posted on Twitter:
“Today, we received some much-needed assistance in the fight against COVID-19. Our team at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center is being expanded by four doctors, 14 nurses and two respiratory therapists – all highly trained personnel on loan from the U.S. Navy.
“These healthcare professionals are being onboarded in our facility today and are specially trained for the emergency department, ICU and Med Surg. Because of them, we’ll be able to staff an additional 16-18 beds – beds sorely needed as cases continue to rise in our area.
“We requested support from the Federal Emergency Management Agency and we were one of five U.S. cities to receive it.. We are most grateful and humbled.”
Last summer, a team of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care professionals deployed to Alabama’s Bill Nichols State Veterans Home to help during the COVID-19 crisis. They were there as part of the “Fourth Mission”—supporting national, state, and local emergency management, public health, safety and homeland security efforts. “It was a really humbling experience,” said Mary Holloway, an RN with the Birmingham VA Health Care System. “Seeing the dedication of the staff there, some coming back to work after recovering from COVID themselves, was inspiring.”
But that turned out to be only one battle in a sadly long and drawn-out war. Since March 2020, more than 5,000 military medical personnel have deployed to 14 states and the Navajo Nation, 51 cities, 71 hospitals, all struggling to keep their heads above a cresting tsunami of new COVID patients.
Last year, the crisis spots for deployments included major metropolitan areas in coastal states: New York, California, and New Jersey. The urgency now is in the Southern states. Those tend to be reporting the highest numbers of new cases and deaths. Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, and Mississippi, for example, have all ranked among the highest rates of cases and hospitalizations per 100,000 people across the country in the last seven days.
This year, military teams have also deployed to support vaccination centers in 25 states and 42 cities. Nearly all—97%—of the new COVID patients in recent months are unvaccinated. And, again, they predominate in Southern states. In Alabama, for instance, only 37% of the population are fully vaccinated. In Louisiana, that number is 40%.
The at-risk states also tend to be the ones that are rapidly running out of space to put the patients in, ICU or otherwise. Where patients who might have been in the intensive care unit (ICU) are housed in the emergency department and in hallways, and where patients without COVID-19 who might have been hospitalized are being turned away. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
These states are at a breaking point. Take Alabama. On August 18, it was “negative 11.” It had 1,568 patients with COVID-19 who needed ICU beds. Only 1,557 beds were available. Patients “may even stay on the regular floor where you’re already stretched for capacity to take care of these people because so many of our staff are out with COVID,” Jeanne Marrazzo, director, Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told a CNN reporter. “It’s really just a domino effect that then clogs up our ERs, clogs up everything else. … It’s a very very tenuous situation.”
The state reported more than 4,000 new cases of COVID-19—“a new high for us,” Marrazzo said. “If you project these numbers out, you can expect that we will at some point, probably around Sept. 1, have at least 5,000 people in our hospitals. If the ratio of people who have to go to the ICU remains stable. That means that probably a third of those people are going to require ICU beds,” she continued. “That is frankly untenable, given the infrastructure, the resources, and really importantly, the staff that we have. I think it is basically apocalyptic. I do not use that word lightly.”
Thus, the US Defense Department (DoD) must once again rise to a sad and desperate occasion. At the request of Federal Emergency Management Agency and the state of Louisiana, the first of five teams of Navy doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists were sent last week to Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center in Lafayette, Louisiana.
The teams, consisting of approximately 20 members each, are coming from throughout the DoD’s universe, including the National Guard. US Army North, under US Northern Command’s oversight, is providing operational command of the active-duty military COVID-19 response. Lt. Gen. Laura J. Richardson, ARNORTH commander, noting that “[t]his is the second time Department of Defense medical assets have deployed to support Louisiana during the pandemic,” calls it a “whole-of-government fight against COVID-19.”
Why Louisiana and Mississippi, with so many states in dire need? “Our joint forces go where FEMA needs us,” Richardson says. “[R]ight now FEMA has determined the military’s unique surge capabilities are most needed in these two states.”
In a press briefing at the time, Pentagon Press Secretary Rear Adm. John Kirby said, “We expect that there could be additional requests from other states for other teams, so that’s why we’re being prepared to stand up five teams.” He was right: An Air Force team has now headed to Our Lady of the Lake Regional Medical Center in Baton Rouge. Mississippi also asked for assistance; an Air Force team will be supporting at University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson, and an Army team at North Mississippi Medical Center-Tupelo.
The support will likely include bolstering and extending the infrastructure. From July to December 2020, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Emergency Management Coordination Cell delivered Fold-Out Rigid Temporary Shelters (FORTS), C-FORTS (clinics), mobile ICUs and isolation units to locations across the US, such as North Chicago, El Paso, and Oklahoma City. In 2021, they’ll be needed in more hospitals unprepared to house the spiking numbers of patients. Some Louisiana hospitals, for instance, have been sending patients in ambulances to Texas for care.
The first go-round with COVID taught hard lessons that can help hone the Fourth Mission responses. One lesson, according to the VHA COVID-19 Response Report- Annex A, published this May, was the need to conduct due diligence, to be both efficient and effective. VHA, it says, now works to determine actual need before deploying resources. “For example, VHA might receive a request from a [State Veterans Home] for 50 RNs. But once VHA delved into the request and worked with the associated VISNs, it would find that 20 RNs or 10 LPNs could meet the needs of the request.”
Meeting the requests is, for the beleaguered hospitals, like answering letters to Santa. When the team of doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists arrived at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center (OLGMC) last week the hospital staff greeted them with cheers and applause.
OLGMC CEO Al Patin said, "We're already in a nursing shortage, coupled with high numbers of this pandemic [which] creates a situation where we need additional support. We have patients boarding in our emergency rooms, patients in our ICU setting that can't transition out. That creates a bottleneck and does not allow us to continue to take in patients from our community."
That day, OLG posted on Twitter:
“Today, we received some much-needed assistance in the fight against COVID-19. Our team at Ochsner Lafayette General Medical Center is being expanded by four doctors, 14 nurses and two respiratory therapists – all highly trained personnel on loan from the U.S. Navy.
“These healthcare professionals are being onboarded in our facility today and are specially trained for the emergency department, ICU and Med Surg. Because of them, we’ll be able to staff an additional 16-18 beds – beds sorely needed as cases continue to rise in our area.
“We requested support from the Federal Emergency Management Agency and we were one of five U.S. cities to receive it.. We are most grateful and humbled.”
Children and COVID: New cases soar to near-record level
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children jumped by nearly 50% in the United States, posting the highest count since hitting a pandemic high back in mid-January, a new report shows.
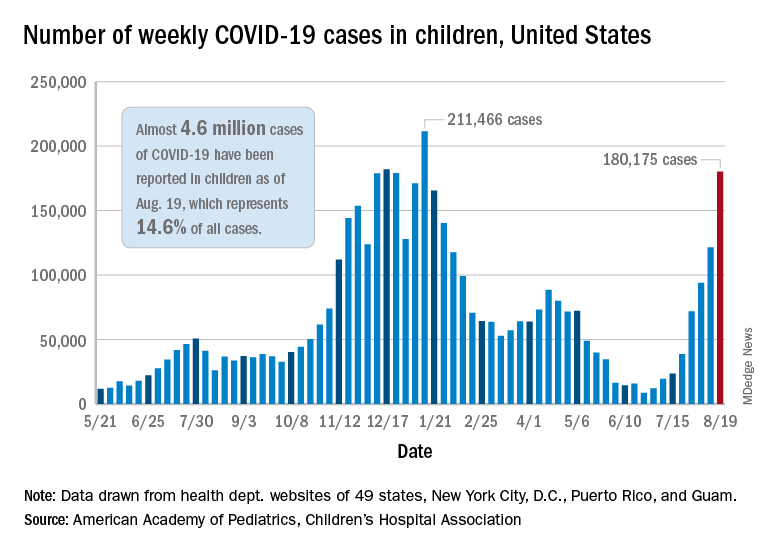
The latest weekly figure represents a 48% increase over the previous week and an increase of over 2,000% in the 8 weeks since the national count dropped to a low of 8,500 cases for the week of June 18-24, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
Vaccinations, in the meantime, appear to be headed in the opposite direction. Vaccine initiations were down for the second consecutive week, falling by 18% among 12- to 15-year-olds and by 15% in those aged 16-17 years, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, about 47% of children aged 12-15 and 56% of those aged 16-17 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Aug. 23, with 34% and 44%, respectively, reaching full vaccination. The total number of children with at least one dose is 11.6 million, including a relatively small number (about 200,000) of children under age 12 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
At the state level, vaccination is a source of considerable disparity. In Vermont, 73% of children aged 12-17 had received at least one dose by Aug. 18, and 63% were fully vaccinated. In Wyoming, however, just 25% of children had received at least one dose (17% are fully vaccinated), while Alabama has a lowest-in-the-nation full vaccination rate of 14%, based on a separate AAP analysis of CDC data.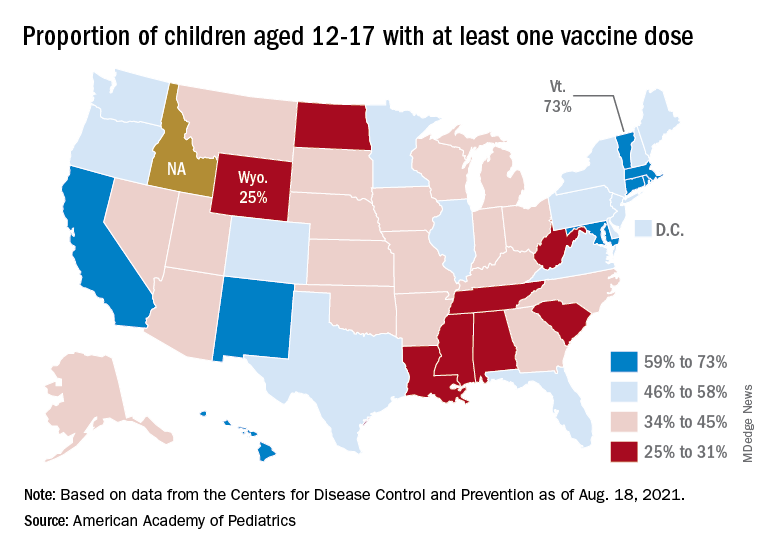
There are seven states in which over 60% of 12- to 17-year-olds have at least started the vaccine regimen and five states where less than 30% have received at least one dose, the AAP noted.
Back on the incidence side of the pandemic, Mississippi and Hawaii had the largest increases in new cases over the past 2 weeks, followed by Florida and West Virginia. Cumulative figures show that California has had the most cases overall in children (550,337), Vermont has the highest proportion of all cases in children (22.9%), and Rhode Island has the highest rate of cases per 100,000 (10,636), the AAP and CHA said in the joint report based on data from 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Add up all those jurisdictions, and it works out to 4.6 million children infected with SARS-CoV-2 as of Aug. 19, with children representing 14.6% of all cases since the start of the pandemic. There have been over 18,000 hospitalizations so far, which is just 2.3% of the total for all ages in the 23 states (and New York City) that are reporting such data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of COVID-related deaths in children is now 402 after the largest 1-week increase (24) since late May of 2020, when the AAP/CHA coverage began. Mortality data by age are available from 44 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children jumped by nearly 50% in the United States, posting the highest count since hitting a pandemic high back in mid-January, a new report shows.

The latest weekly figure represents a 48% increase over the previous week and an increase of over 2,000% in the 8 weeks since the national count dropped to a low of 8,500 cases for the week of June 18-24, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
Vaccinations, in the meantime, appear to be headed in the opposite direction. Vaccine initiations were down for the second consecutive week, falling by 18% among 12- to 15-year-olds and by 15% in those aged 16-17 years, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, about 47% of children aged 12-15 and 56% of those aged 16-17 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Aug. 23, with 34% and 44%, respectively, reaching full vaccination. The total number of children with at least one dose is 11.6 million, including a relatively small number (about 200,000) of children under age 12 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
At the state level, vaccination is a source of considerable disparity. In Vermont, 73% of children aged 12-17 had received at least one dose by Aug. 18, and 63% were fully vaccinated. In Wyoming, however, just 25% of children had received at least one dose (17% are fully vaccinated), while Alabama has a lowest-in-the-nation full vaccination rate of 14%, based on a separate AAP analysis of CDC data.
There are seven states in which over 60% of 12- to 17-year-olds have at least started the vaccine regimen and five states where less than 30% have received at least one dose, the AAP noted.
Back on the incidence side of the pandemic, Mississippi and Hawaii had the largest increases in new cases over the past 2 weeks, followed by Florida and West Virginia. Cumulative figures show that California has had the most cases overall in children (550,337), Vermont has the highest proportion of all cases in children (22.9%), and Rhode Island has the highest rate of cases per 100,000 (10,636), the AAP and CHA said in the joint report based on data from 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Add up all those jurisdictions, and it works out to 4.6 million children infected with SARS-CoV-2 as of Aug. 19, with children representing 14.6% of all cases since the start of the pandemic. There have been over 18,000 hospitalizations so far, which is just 2.3% of the total for all ages in the 23 states (and New York City) that are reporting such data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of COVID-related deaths in children is now 402 after the largest 1-week increase (24) since late May of 2020, when the AAP/CHA coverage began. Mortality data by age are available from 44 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children jumped by nearly 50% in the United States, posting the highest count since hitting a pandemic high back in mid-January, a new report shows.

The latest weekly figure represents a 48% increase over the previous week and an increase of over 2,000% in the 8 weeks since the national count dropped to a low of 8,500 cases for the week of June 18-24, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
Vaccinations, in the meantime, appear to be headed in the opposite direction. Vaccine initiations were down for the second consecutive week, falling by 18% among 12- to 15-year-olds and by 15% in those aged 16-17 years, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, about 47% of children aged 12-15 and 56% of those aged 16-17 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Aug. 23, with 34% and 44%, respectively, reaching full vaccination. The total number of children with at least one dose is 11.6 million, including a relatively small number (about 200,000) of children under age 12 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
At the state level, vaccination is a source of considerable disparity. In Vermont, 73% of children aged 12-17 had received at least one dose by Aug. 18, and 63% were fully vaccinated. In Wyoming, however, just 25% of children had received at least one dose (17% are fully vaccinated), while Alabama has a lowest-in-the-nation full vaccination rate of 14%, based on a separate AAP analysis of CDC data.
There are seven states in which over 60% of 12- to 17-year-olds have at least started the vaccine regimen and five states where less than 30% have received at least one dose, the AAP noted.
Back on the incidence side of the pandemic, Mississippi and Hawaii had the largest increases in new cases over the past 2 weeks, followed by Florida and West Virginia. Cumulative figures show that California has had the most cases overall in children (550,337), Vermont has the highest proportion of all cases in children (22.9%), and Rhode Island has the highest rate of cases per 100,000 (10,636), the AAP and CHA said in the joint report based on data from 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Add up all those jurisdictions, and it works out to 4.6 million children infected with SARS-CoV-2 as of Aug. 19, with children representing 14.6% of all cases since the start of the pandemic. There have been over 18,000 hospitalizations so far, which is just 2.3% of the total for all ages in the 23 states (and New York City) that are reporting such data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of COVID-related deaths in children is now 402 after the largest 1-week increase (24) since late May of 2020, when the AAP/CHA coverage began. Mortality data by age are available from 44 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Nearly 1 in 5 parents put off care for their kids in pandemic
Many families delayed much-needed health care for their children out of fears that they may be exposed to SARS-CoV-2, according to data from the Urban Institute April 2021 Health Reform Monitoring Survey.
Data from 9,067 adults aged 18 to 64 years indicate that nearly 1 in 5 parents delayed or did not get care for their children in the past 12 months because of fear of exposure to the virus.
“It’s not surprising given the timing of the survey – April 2021 – when many people couldn’t get a vaccine yet and were reporting delayed care because of concerns about exposure during the past 30 days,” study author Dulce Gonzalez, BA, a research associate in the Health Policy Center at the Urban Institute, said in an interview.
In a previous survey that the Urban Institute conducted in September 2020, 28.8% of parents reported delaying or forgoing one or more types of health care for their children because of virus concerns or health care practitioner service limits.
These concerns still affect parents’ decision making when it comes to their child’s health. Nearly 1 in 10 parents reported that they had skipped doctor’s appointments for their children in the past 30 days. More than 1 in 10 adults forwent their own health care in the past month for the same reason.
“I think it’s important for parents to understand that health care workers and health care facilities are equipped to prevent infections from spreading,” Mundeep Kainth, DO, MPH, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization. “COVID-19 is not the first infection that we’ve seen in the medical setting, and we definitely are well aware of how it can spread and have been taking many precautions.”
The most common type of delayed or forgone care was dental care (5.3%), followed by well-child visits (4.0%) and general or specialist visits (3.2%). About 3% of parents said their child had missed out on immunizations. Nearly 6% of parents said their child had missed out on multiple types of care.
One reason dental care is the most commonly skipped type of care is because people might not consider dental care to be as urgent as other types of care, Ms. Gonzalez said. However, oral health can affect a person’s overall wellness.
Dr. Kainth, an infection disease specialist at Cohen Children’s Medical Center, New Hyde Park, New York, said the lack of immunization because of COVID-19 can have adverse health effects on children and could possibly lead to outbreaks in schools and day care settings. In the Urban Institute’s 2020 survey, 18.5% of parents said putting off their child’s health care worsened their child’s health, and 15.6% said it limited their children’s ability to go to school or day care.
“We are already concerned that we will have pockets of [vaccine-preventable] infections that we normally did not see before in communities where they are not vaccinating their children at high enough numbers,” Dr. Kainth said. “It is a little concerning that there’s probably a lot of catch up to be done for particular vaccines that are specifically for those entering day care and school.”
The current survey also found that parents with incomes below 250% of the federal poverty level were more likely than those with higher incomes to have put off care for their children in the past 30 days. More than 12% of families living in poverty put off care for their children, compared with 6.5% of those with higher incomes. They were also more likely to delay or forgo multiple types of care, at 8.1% versus 3.3%. Parents with lower family incomes were also more likely to report that their children had unmet needs for dental care, checkups, or other preventive care.
“We know that lower-income parents could be more exposed to costs they might not be able to afford if they were to get sick,” Ms. Gonzalez said. “Low-income adults have been disproportionately affected by job loss during the pandemic. They are also more likely to live in communities that have faced the largest health impacts of COVID-19.”
“There’s also advantages to the pediatrician visit that are not just about providing care but also providing guidance and advice to families and parents who are maybe struggling with certain issues that are above and beyond just the medical advice,” Dr. Kainth explained.
“That is probably the most tragic part of hearing that parents and kids are not going to the well visits, because that’s where families get a lot of support. And I think at this time, we probably need that more than ever,” she continued.
The authors said the findings highlight the importance of increasing rates of COVID-19 vaccinations among eligible adolescents and encouraging vaccinations for children younger than 12 when they become eligible, not only to protect them from COVID-19 but also to help families feel comfortable obtaining care.
The study was funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The authors and Dr. Kainth have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many families delayed much-needed health care for their children out of fears that they may be exposed to SARS-CoV-2, according to data from the Urban Institute April 2021 Health Reform Monitoring Survey.
Data from 9,067 adults aged 18 to 64 years indicate that nearly 1 in 5 parents delayed or did not get care for their children in the past 12 months because of fear of exposure to the virus.
“It’s not surprising given the timing of the survey – April 2021 – when many people couldn’t get a vaccine yet and were reporting delayed care because of concerns about exposure during the past 30 days,” study author Dulce Gonzalez, BA, a research associate in the Health Policy Center at the Urban Institute, said in an interview.
In a previous survey that the Urban Institute conducted in September 2020, 28.8% of parents reported delaying or forgoing one or more types of health care for their children because of virus concerns or health care practitioner service limits.
These concerns still affect parents’ decision making when it comes to their child’s health. Nearly 1 in 10 parents reported that they had skipped doctor’s appointments for their children in the past 30 days. More than 1 in 10 adults forwent their own health care in the past month for the same reason.
“I think it’s important for parents to understand that health care workers and health care facilities are equipped to prevent infections from spreading,” Mundeep Kainth, DO, MPH, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization. “COVID-19 is not the first infection that we’ve seen in the medical setting, and we definitely are well aware of how it can spread and have been taking many precautions.”
The most common type of delayed or forgone care was dental care (5.3%), followed by well-child visits (4.0%) and general or specialist visits (3.2%). About 3% of parents said their child had missed out on immunizations. Nearly 6% of parents said their child had missed out on multiple types of care.
One reason dental care is the most commonly skipped type of care is because people might not consider dental care to be as urgent as other types of care, Ms. Gonzalez said. However, oral health can affect a person’s overall wellness.
Dr. Kainth, an infection disease specialist at Cohen Children’s Medical Center, New Hyde Park, New York, said the lack of immunization because of COVID-19 can have adverse health effects on children and could possibly lead to outbreaks in schools and day care settings. In the Urban Institute’s 2020 survey, 18.5% of parents said putting off their child’s health care worsened their child’s health, and 15.6% said it limited their children’s ability to go to school or day care.
“We are already concerned that we will have pockets of [vaccine-preventable] infections that we normally did not see before in communities where they are not vaccinating their children at high enough numbers,” Dr. Kainth said. “It is a little concerning that there’s probably a lot of catch up to be done for particular vaccines that are specifically for those entering day care and school.”
The current survey also found that parents with incomes below 250% of the federal poverty level were more likely than those with higher incomes to have put off care for their children in the past 30 days. More than 12% of families living in poverty put off care for their children, compared with 6.5% of those with higher incomes. They were also more likely to delay or forgo multiple types of care, at 8.1% versus 3.3%. Parents with lower family incomes were also more likely to report that their children had unmet needs for dental care, checkups, or other preventive care.
“We know that lower-income parents could be more exposed to costs they might not be able to afford if they were to get sick,” Ms. Gonzalez said. “Low-income adults have been disproportionately affected by job loss during the pandemic. They are also more likely to live in communities that have faced the largest health impacts of COVID-19.”
“There’s also advantages to the pediatrician visit that are not just about providing care but also providing guidance and advice to families and parents who are maybe struggling with certain issues that are above and beyond just the medical advice,” Dr. Kainth explained.
“That is probably the most tragic part of hearing that parents and kids are not going to the well visits, because that’s where families get a lot of support. And I think at this time, we probably need that more than ever,” she continued.
The authors said the findings highlight the importance of increasing rates of COVID-19 vaccinations among eligible adolescents and encouraging vaccinations for children younger than 12 when they become eligible, not only to protect them from COVID-19 but also to help families feel comfortable obtaining care.
The study was funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The authors and Dr. Kainth have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many families delayed much-needed health care for their children out of fears that they may be exposed to SARS-CoV-2, according to data from the Urban Institute April 2021 Health Reform Monitoring Survey.
Data from 9,067 adults aged 18 to 64 years indicate that nearly 1 in 5 parents delayed or did not get care for their children in the past 12 months because of fear of exposure to the virus.
“It’s not surprising given the timing of the survey – April 2021 – when many people couldn’t get a vaccine yet and were reporting delayed care because of concerns about exposure during the past 30 days,” study author Dulce Gonzalez, BA, a research associate in the Health Policy Center at the Urban Institute, said in an interview.
In a previous survey that the Urban Institute conducted in September 2020, 28.8% of parents reported delaying or forgoing one or more types of health care for their children because of virus concerns or health care practitioner service limits.
These concerns still affect parents’ decision making when it comes to their child’s health. Nearly 1 in 10 parents reported that they had skipped doctor’s appointments for their children in the past 30 days. More than 1 in 10 adults forwent their own health care in the past month for the same reason.
“I think it’s important for parents to understand that health care workers and health care facilities are equipped to prevent infections from spreading,” Mundeep Kainth, DO, MPH, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization. “COVID-19 is not the first infection that we’ve seen in the medical setting, and we definitely are well aware of how it can spread and have been taking many precautions.”
The most common type of delayed or forgone care was dental care (5.3%), followed by well-child visits (4.0%) and general or specialist visits (3.2%). About 3% of parents said their child had missed out on immunizations. Nearly 6% of parents said their child had missed out on multiple types of care.
One reason dental care is the most commonly skipped type of care is because people might not consider dental care to be as urgent as other types of care, Ms. Gonzalez said. However, oral health can affect a person’s overall wellness.
Dr. Kainth, an infection disease specialist at Cohen Children’s Medical Center, New Hyde Park, New York, said the lack of immunization because of COVID-19 can have adverse health effects on children and could possibly lead to outbreaks in schools and day care settings. In the Urban Institute’s 2020 survey, 18.5% of parents said putting off their child’s health care worsened their child’s health, and 15.6% said it limited their children’s ability to go to school or day care.
“We are already concerned that we will have pockets of [vaccine-preventable] infections that we normally did not see before in communities where they are not vaccinating their children at high enough numbers,” Dr. Kainth said. “It is a little concerning that there’s probably a lot of catch up to be done for particular vaccines that are specifically for those entering day care and school.”
The current survey also found that parents with incomes below 250% of the federal poverty level were more likely than those with higher incomes to have put off care for their children in the past 30 days. More than 12% of families living in poverty put off care for their children, compared with 6.5% of those with higher incomes. They were also more likely to delay or forgo multiple types of care, at 8.1% versus 3.3%. Parents with lower family incomes were also more likely to report that their children had unmet needs for dental care, checkups, or other preventive care.
“We know that lower-income parents could be more exposed to costs they might not be able to afford if they were to get sick,” Ms. Gonzalez said. “Low-income adults have been disproportionately affected by job loss during the pandemic. They are also more likely to live in communities that have faced the largest health impacts of COVID-19.”
“There’s also advantages to the pediatrician visit that are not just about providing care but also providing guidance and advice to families and parents who are maybe struggling with certain issues that are above and beyond just the medical advice,” Dr. Kainth explained.
“That is probably the most tragic part of hearing that parents and kids are not going to the well visits, because that’s where families get a lot of support. And I think at this time, we probably need that more than ever,” she continued.
The authors said the findings highlight the importance of increasing rates of COVID-19 vaccinations among eligible adolescents and encouraging vaccinations for children younger than 12 when they become eligible, not only to protect them from COVID-19 but also to help families feel comfortable obtaining care.
The study was funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The authors and Dr. Kainth have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Health care workers eager for COVID booster shots
As COVID vaccine boosters move closer to reality, most physicians and nurses are ready and willing to get another shot in the arm, according to a new Medscape survey.
Altogether, 93% of physicians and 87% of nurses/advanced practice nurses (APNs) said they wanted to get a booster, although the timing of when they wanted the shots differed somewhat between the two groups surveyed Aug. 4-15.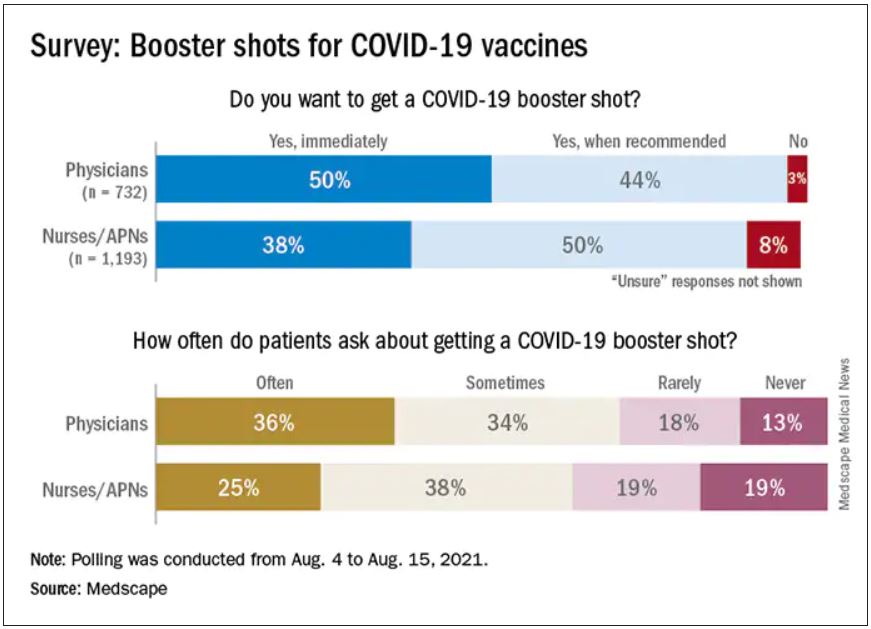
Among the 732 physicians polled, 50% wanted to get their shot immediately, compared with 38% of the 1,193 nurses/APNs who responded, while 44% of physicians and 50% of nurses/APNs said that they would wait until the vaccine booster was authorized and recommended.
At this point in time, almost all of the health care workers surveyed – 98% of physicians and 94% of nurses/APNs – have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. A small proportion of each group, however, received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine (1% of physicians and 3% of nurses) and are not included in the current plan for booster shots.
The Medscape survey sample did include one group that is already eligible for a third dose: About 20% of physicians and 26% of nurses/ANPs said they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system.
Respondents’ experiences with patient requests for boosters suggest a somewhat lower level of interest. About two-thirds of the health care workers (69% of physicians and 63% of nurses) said that patients frequently or sometimes asked about COVID boosters, compared with 13% (physicians) and 19% (nurses) who said their patients had never asked.
Interest lower among general population
In a separate survey conducted by WebMD, 82% of those who have been at least partially vaccinated said they want to get a COVID vaccine booster (14% immediately and 68% after authorization and recommendation). Of the remaining vaccinees, 7% said they do not want to get a booster and 11% were unsure.
The full sample of 592 respondents surveyed Aug. 5-10, however, included 19% who do not plan to get vaccinated and 6% who are planning to be vaccinated but have not yet done so.
The proportion of immunocompromised individuals in the two survey groups was similar, with about 25% of those in the WebMD survey reporting they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system. Those respondents were more than twice as likely to want to get a booster immediately, compared to those with an uncompromised immune system (24% vs. 11%).
The distribution of vaccines received by brand was also comparable between the two groups surveyed. Of health care workers and readers, over half of each group received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine (59% vs. 54%), followed by Moderna (38% vs. 40%) and Johnson & Johnson (3% vs. 5%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID vaccine boosters move closer to reality, most physicians and nurses are ready and willing to get another shot in the arm, according to a new Medscape survey.
Altogether, 93% of physicians and 87% of nurses/advanced practice nurses (APNs) said they wanted to get a booster, although the timing of when they wanted the shots differed somewhat between the two groups surveyed Aug. 4-15.
Among the 732 physicians polled, 50% wanted to get their shot immediately, compared with 38% of the 1,193 nurses/APNs who responded, while 44% of physicians and 50% of nurses/APNs said that they would wait until the vaccine booster was authorized and recommended.
At this point in time, almost all of the health care workers surveyed – 98% of physicians and 94% of nurses/APNs – have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. A small proportion of each group, however, received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine (1% of physicians and 3% of nurses) and are not included in the current plan for booster shots.
The Medscape survey sample did include one group that is already eligible for a third dose: About 20% of physicians and 26% of nurses/ANPs said they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system.
Respondents’ experiences with patient requests for boosters suggest a somewhat lower level of interest. About two-thirds of the health care workers (69% of physicians and 63% of nurses) said that patients frequently or sometimes asked about COVID boosters, compared with 13% (physicians) and 19% (nurses) who said their patients had never asked.
Interest lower among general population
In a separate survey conducted by WebMD, 82% of those who have been at least partially vaccinated said they want to get a COVID vaccine booster (14% immediately and 68% after authorization and recommendation). Of the remaining vaccinees, 7% said they do not want to get a booster and 11% were unsure.
The full sample of 592 respondents surveyed Aug. 5-10, however, included 19% who do not plan to get vaccinated and 6% who are planning to be vaccinated but have not yet done so.
The proportion of immunocompromised individuals in the two survey groups was similar, with about 25% of those in the WebMD survey reporting they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system. Those respondents were more than twice as likely to want to get a booster immediately, compared to those with an uncompromised immune system (24% vs. 11%).
The distribution of vaccines received by brand was also comparable between the two groups surveyed. Of health care workers and readers, over half of each group received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine (59% vs. 54%), followed by Moderna (38% vs. 40%) and Johnson & Johnson (3% vs. 5%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID vaccine boosters move closer to reality, most physicians and nurses are ready and willing to get another shot in the arm, according to a new Medscape survey.
Altogether, 93% of physicians and 87% of nurses/advanced practice nurses (APNs) said they wanted to get a booster, although the timing of when they wanted the shots differed somewhat between the two groups surveyed Aug. 4-15.
Among the 732 physicians polled, 50% wanted to get their shot immediately, compared with 38% of the 1,193 nurses/APNs who responded, while 44% of physicians and 50% of nurses/APNs said that they would wait until the vaccine booster was authorized and recommended.
At this point in time, almost all of the health care workers surveyed – 98% of physicians and 94% of nurses/APNs – have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. A small proportion of each group, however, received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine (1% of physicians and 3% of nurses) and are not included in the current plan for booster shots.
The Medscape survey sample did include one group that is already eligible for a third dose: About 20% of physicians and 26% of nurses/ANPs said they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system.
Respondents’ experiences with patient requests for boosters suggest a somewhat lower level of interest. About two-thirds of the health care workers (69% of physicians and 63% of nurses) said that patients frequently or sometimes asked about COVID boosters, compared with 13% (physicians) and 19% (nurses) who said their patients had never asked.
Interest lower among general population
In a separate survey conducted by WebMD, 82% of those who have been at least partially vaccinated said they want to get a COVID vaccine booster (14% immediately and 68% after authorization and recommendation). Of the remaining vaccinees, 7% said they do not want to get a booster and 11% were unsure.
The full sample of 592 respondents surveyed Aug. 5-10, however, included 19% who do not plan to get vaccinated and 6% who are planning to be vaccinated but have not yet done so.
The proportion of immunocompromised individuals in the two survey groups was similar, with about 25% of those in the WebMD survey reporting they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system. Those respondents were more than twice as likely to want to get a booster immediately, compared to those with an uncompromised immune system (24% vs. 11%).
The distribution of vaccines received by brand was also comparable between the two groups surveyed. Of health care workers and readers, over half of each group received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine (59% vs. 54%), followed by Moderna (38% vs. 40%) and Johnson & Johnson (3% vs. 5%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.






