User login
In Case You Missed It: COVID
COVID-detecting dogs pilot first airport program
If she identifies a specific scent, she’ll let her handler know simply by sitting down. When this good girl sits, that means Cobra has detected an olfactory signal of the coronavirus, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Cobra, a Belgian Malinois, is one of two canines – her partner is One Betta, a Dutch shepherd – working this checkpoint at Miami International. They are part of a pilot program with the Global Forensic and Justice Center at Florida International University, using the detection dogs as a quick screen for people who have COVID-19.
Their detection rate is high, at more than 98%, and the program has been such a success that it’s being extended for another month at the airport.
If these two dogs continue to accurately detect COVID-19, they and other canines with similar training could be deployed to other places with lots of people coming and going at once, including other airports or even schools. In fact, COVID-sniffing dogs are in use in some university classrooms already.
But building up a big brigade of live animals as disease detectors involves some thorny issues, including where the animals retire once their careers are complete.
“When COVID first arose, we said let’s see if we can train these two dogs on either the virus or the odor of COVID-19,” says Kenneth Furton, PhD, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry, provost, and executive vice president at Florida International University.
His team had completed a study with what he calls “medical detector dogs,” animals that might be able to detect the odor of someone having a seizure. That led them to see how well the animals could detect other kinds of disorders.
Training a dog to sniff out specific odors starts with getting them to understand the task in general. Dr. Furton says that the animals first are trained to grasp that their job is to detect one odor among many. Once the dogs grasp that, they can be trained on just about any specific odor.
In fact, in addition to detecting seizures, dogs reportedly have been able to identify diabetes and even some cancers, such as ovarian cancer.
Dr. Furton says he’s not aware of any previous use of dogs to screen for infectious disease. That may simply be because nothing recently has struck with the global ferocity of COVID, driving humans to turn to their best friends for help.
Cobra and One Betta got their start learning to identify the presence of laurel wilt, a fungus that attacks avocado trees and kills them, costing Florida growers millions. With that expertise under their collars, the two dogs need only a few weeks to get good at detecting other smells assigned to them.
Training the dogs, safely
To train Cobra and One Betta on COVID-19 odors, Dr. Furton’s team first acquired mask samples from people hospitalized with COVID and people who did not have the disease. In battling the viruses, people produce certain chemicals that they exhale every time they breathe. When Dr. Furton and his colleagues compared the exhaled components trapped in the masks, they found differences between masks from people with COVID and those without.
Having confirmed that exhalations can be COVID-specific, the research team trained four dogs – Cobra, One Betta, Hubble, and Max – to detect masks from people with COVID among an assortment of mask choices. Before this step, though, the researchers made sure that any trace of active virus was destroyed by ultraviolet light so that the dogs would not be infected.
Each time the dogs accurately selected a mask from a COVID patient, their reward was access to a favorite toy: A red ball to chew on. Although all four dogs performed very well, yes, they did, Cobra and One Betta showed the most accuracy, outperforming their training colleagues. From their training scores, Cobra ranked first, with 99.45% accuracy. Despite her name, says Dr. Furton, One Betta was “not one better,” coming in second at 98.1%, which is still quite high.
Both dogs are good at their airport screening duties. If one of them sits after sniffing a mask at the checkpoint, the next step is for the mask owner to be tested.
From Aug. 23 to Sept. 8, the two canines screened 1,093 people during 8 working days, alerting on only one case, according to Greg Chin, communications director for the Miami-Dade Aviation Department. That person had tested positive for COVID 2 weeks earlier and was returning to work after quarantine, and their rapid test after the dog alerted was negative.
Dr. Furton says that there are some reports of dogs also alerting before tests can show a positive result, suggesting the dogs’ odor detection can be more precise. They hope to expand their study to see how tight the window of dog-based detection is.
For now, the detector dogs are doing so well that the program has been extended for 30 more days, Mr. Chin says.
As promising as this seems, using dogs for screening carries some logistical and ethical tangles. Training a canine army to deploy for high-volume detection points means that once the work is done, a whole lot of dogs will need a safe place to retire. In addition, the initial training takes several months, says Dr. Furton, whereas if a device were developed for screening, manufacturing could likely be ramped up quickly to meet demand.
The dogs might not need to retire right away, though.
“We envision that they could be redeployed to another type of detection for another infectious disease” if the need arises, Dr. Furton says. But in the end, when working with dogs, he says, there is “a moral connection that you don’t have to deal with using instruments.”
Although the pilot screening at Miami International is the first airport test, the dogs have also done this work in other venues, including at a state emergency operations center in Florida and in some university classrooms, says Dr. Furton.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
If she identifies a specific scent, she’ll let her handler know simply by sitting down. When this good girl sits, that means Cobra has detected an olfactory signal of the coronavirus, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Cobra, a Belgian Malinois, is one of two canines – her partner is One Betta, a Dutch shepherd – working this checkpoint at Miami International. They are part of a pilot program with the Global Forensic and Justice Center at Florida International University, using the detection dogs as a quick screen for people who have COVID-19.
Their detection rate is high, at more than 98%, and the program has been such a success that it’s being extended for another month at the airport.
If these two dogs continue to accurately detect COVID-19, they and other canines with similar training could be deployed to other places with lots of people coming and going at once, including other airports or even schools. In fact, COVID-sniffing dogs are in use in some university classrooms already.
But building up a big brigade of live animals as disease detectors involves some thorny issues, including where the animals retire once their careers are complete.
“When COVID first arose, we said let’s see if we can train these two dogs on either the virus or the odor of COVID-19,” says Kenneth Furton, PhD, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry, provost, and executive vice president at Florida International University.
His team had completed a study with what he calls “medical detector dogs,” animals that might be able to detect the odor of someone having a seizure. That led them to see how well the animals could detect other kinds of disorders.
Training a dog to sniff out specific odors starts with getting them to understand the task in general. Dr. Furton says that the animals first are trained to grasp that their job is to detect one odor among many. Once the dogs grasp that, they can be trained on just about any specific odor.
In fact, in addition to detecting seizures, dogs reportedly have been able to identify diabetes and even some cancers, such as ovarian cancer.
Dr. Furton says he’s not aware of any previous use of dogs to screen for infectious disease. That may simply be because nothing recently has struck with the global ferocity of COVID, driving humans to turn to their best friends for help.
Cobra and One Betta got their start learning to identify the presence of laurel wilt, a fungus that attacks avocado trees and kills them, costing Florida growers millions. With that expertise under their collars, the two dogs need only a few weeks to get good at detecting other smells assigned to them.
Training the dogs, safely
To train Cobra and One Betta on COVID-19 odors, Dr. Furton’s team first acquired mask samples from people hospitalized with COVID and people who did not have the disease. In battling the viruses, people produce certain chemicals that they exhale every time they breathe. When Dr. Furton and his colleagues compared the exhaled components trapped in the masks, they found differences between masks from people with COVID and those without.
Having confirmed that exhalations can be COVID-specific, the research team trained four dogs – Cobra, One Betta, Hubble, and Max – to detect masks from people with COVID among an assortment of mask choices. Before this step, though, the researchers made sure that any trace of active virus was destroyed by ultraviolet light so that the dogs would not be infected.
Each time the dogs accurately selected a mask from a COVID patient, their reward was access to a favorite toy: A red ball to chew on. Although all four dogs performed very well, yes, they did, Cobra and One Betta showed the most accuracy, outperforming their training colleagues. From their training scores, Cobra ranked first, with 99.45% accuracy. Despite her name, says Dr. Furton, One Betta was “not one better,” coming in second at 98.1%, which is still quite high.
Both dogs are good at their airport screening duties. If one of them sits after sniffing a mask at the checkpoint, the next step is for the mask owner to be tested.
From Aug. 23 to Sept. 8, the two canines screened 1,093 people during 8 working days, alerting on only one case, according to Greg Chin, communications director for the Miami-Dade Aviation Department. That person had tested positive for COVID 2 weeks earlier and was returning to work after quarantine, and their rapid test after the dog alerted was negative.
Dr. Furton says that there are some reports of dogs also alerting before tests can show a positive result, suggesting the dogs’ odor detection can be more precise. They hope to expand their study to see how tight the window of dog-based detection is.
For now, the detector dogs are doing so well that the program has been extended for 30 more days, Mr. Chin says.
As promising as this seems, using dogs for screening carries some logistical and ethical tangles. Training a canine army to deploy for high-volume detection points means that once the work is done, a whole lot of dogs will need a safe place to retire. In addition, the initial training takes several months, says Dr. Furton, whereas if a device were developed for screening, manufacturing could likely be ramped up quickly to meet demand.
The dogs might not need to retire right away, though.
“We envision that they could be redeployed to another type of detection for another infectious disease” if the need arises, Dr. Furton says. But in the end, when working with dogs, he says, there is “a moral connection that you don’t have to deal with using instruments.”
Although the pilot screening at Miami International is the first airport test, the dogs have also done this work in other venues, including at a state emergency operations center in Florida and in some university classrooms, says Dr. Furton.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
If she identifies a specific scent, she’ll let her handler know simply by sitting down. When this good girl sits, that means Cobra has detected an olfactory signal of the coronavirus, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Cobra, a Belgian Malinois, is one of two canines – her partner is One Betta, a Dutch shepherd – working this checkpoint at Miami International. They are part of a pilot program with the Global Forensic and Justice Center at Florida International University, using the detection dogs as a quick screen for people who have COVID-19.
Their detection rate is high, at more than 98%, and the program has been such a success that it’s being extended for another month at the airport.
If these two dogs continue to accurately detect COVID-19, they and other canines with similar training could be deployed to other places with lots of people coming and going at once, including other airports or even schools. In fact, COVID-sniffing dogs are in use in some university classrooms already.
But building up a big brigade of live animals as disease detectors involves some thorny issues, including where the animals retire once their careers are complete.
“When COVID first arose, we said let’s see if we can train these two dogs on either the virus or the odor of COVID-19,” says Kenneth Furton, PhD, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry, provost, and executive vice president at Florida International University.
His team had completed a study with what he calls “medical detector dogs,” animals that might be able to detect the odor of someone having a seizure. That led them to see how well the animals could detect other kinds of disorders.
Training a dog to sniff out specific odors starts with getting them to understand the task in general. Dr. Furton says that the animals first are trained to grasp that their job is to detect one odor among many. Once the dogs grasp that, they can be trained on just about any specific odor.
In fact, in addition to detecting seizures, dogs reportedly have been able to identify diabetes and even some cancers, such as ovarian cancer.
Dr. Furton says he’s not aware of any previous use of dogs to screen for infectious disease. That may simply be because nothing recently has struck with the global ferocity of COVID, driving humans to turn to their best friends for help.
Cobra and One Betta got their start learning to identify the presence of laurel wilt, a fungus that attacks avocado trees and kills them, costing Florida growers millions. With that expertise under their collars, the two dogs need only a few weeks to get good at detecting other smells assigned to them.
Training the dogs, safely
To train Cobra and One Betta on COVID-19 odors, Dr. Furton’s team first acquired mask samples from people hospitalized with COVID and people who did not have the disease. In battling the viruses, people produce certain chemicals that they exhale every time they breathe. When Dr. Furton and his colleagues compared the exhaled components trapped in the masks, they found differences between masks from people with COVID and those without.
Having confirmed that exhalations can be COVID-specific, the research team trained four dogs – Cobra, One Betta, Hubble, and Max – to detect masks from people with COVID among an assortment of mask choices. Before this step, though, the researchers made sure that any trace of active virus was destroyed by ultraviolet light so that the dogs would not be infected.
Each time the dogs accurately selected a mask from a COVID patient, their reward was access to a favorite toy: A red ball to chew on. Although all four dogs performed very well, yes, they did, Cobra and One Betta showed the most accuracy, outperforming their training colleagues. From their training scores, Cobra ranked first, with 99.45% accuracy. Despite her name, says Dr. Furton, One Betta was “not one better,” coming in second at 98.1%, which is still quite high.
Both dogs are good at their airport screening duties. If one of them sits after sniffing a mask at the checkpoint, the next step is for the mask owner to be tested.
From Aug. 23 to Sept. 8, the two canines screened 1,093 people during 8 working days, alerting on only one case, according to Greg Chin, communications director for the Miami-Dade Aviation Department. That person had tested positive for COVID 2 weeks earlier and was returning to work after quarantine, and their rapid test after the dog alerted was negative.
Dr. Furton says that there are some reports of dogs also alerting before tests can show a positive result, suggesting the dogs’ odor detection can be more precise. They hope to expand their study to see how tight the window of dog-based detection is.
For now, the detector dogs are doing so well that the program has been extended for 30 more days, Mr. Chin says.
As promising as this seems, using dogs for screening carries some logistical and ethical tangles. Training a canine army to deploy for high-volume detection points means that once the work is done, a whole lot of dogs will need a safe place to retire. In addition, the initial training takes several months, says Dr. Furton, whereas if a device were developed for screening, manufacturing could likely be ramped up quickly to meet demand.
The dogs might not need to retire right away, though.
“We envision that they could be redeployed to another type of detection for another infectious disease” if the need arises, Dr. Furton says. But in the end, when working with dogs, he says, there is “a moral connection that you don’t have to deal with using instruments.”
Although the pilot screening at Miami International is the first airport test, the dogs have also done this work in other venues, including at a state emergency operations center in Florida and in some university classrooms, says Dr. Furton.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Surge in new-onset tics in adults tied to COVID-19 stress
, new research suggests.
Results from a large, single-center study show several cases of tic-like movements and vocalizations with abrupt onset among older adolescents and adults during the pandemic. None had a previous diagnosis of a tic disorder. Among 10 patients, two were diagnosed with a purely functional movement disorder, four with an organic tic disorder, and four with both.
“Within our movement disorders clinic specifically ... we’ve been seeing an increased number of patients with an almost explosive onset of these tic-like movements and vocalizations later in life than what is typically seen with organic tic disorders and Tourette syndrome, which is typically in school-aged children,” said study investigator Caroline Olvera, MD, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago.
“Abrupt onset of symptoms can be seen in patients with tic disorders, although this is typically quoted as less than 10%, or even 5% is more characteristic of functional neurological disorders in general and also with psychogenic tics,” she added.
The findings were presented at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders.
Anxiety, other psychiatric conditions
Tic disorders typically start in childhood. However, the researchers observed an increase in the number of patients with abrupt onset of tic-like movements and vocalizations later in life, which is more often characteristic of functional neurological disorders.
To examine the profile, associated conditions, and risk factors in this population, the investigators conducted a thorough chart review of patients attending movement disorder clinics between March 2020, when the COVID pandemic was officially declared, and March 2021.
Patients with acute onset of tics were identified using the International Classification of Diseases codes for behavioral tics, tic vocalizations, and Tourette syndrome.
The charts were then narrowed down to patients with no previous diagnosis of these conditions. Most patients were videotaped for assessment by the rest of the movement disorder neurologists in the practice. Since the end of the study inclusion period in March 2021, Dr. Olvera estimates that the clinic experienced a doubling or tripling of the number of similar patients.
In the study cohort of 10 patients, the median age at presentation was 19 years (range, 15-41 years), nine were female, the gender of the other one was unknown, and the duration of tics was 8 weeks (range, 1-24 weeks) by the time they were first seen in the clinic. Four patients reported having COVID infection before tic onset.
All exhibited motor tics and nine had vocal tics. Two were diagnosed with a purely functional neurologic disorder, four with only an organic tic disorder, and four with organic tics with a functional overlay.
“All patients, including those with organic tic disorders, had a history of anxiety and also reported worsening anxiety in the setting of the COVID pandemic,” Dr. Olvera said.
The majority of patients were on a psychotropic medication prior to coming to the clinic, and these were primarily for anxiety and depression. Three patients had a history of suicidality, often very severe and leading to hospitalization, she noted.
“In terms of our conclusions from the project, we feel that this phenotype of acute explosive onset of tic-like movements and vocalizations in this older population of adults, compared with typical organic tic disorders and Tourette syndrome, appears novel to the pandemic,” she said.
She cautioned that functional and organic tics share many characteristics and therefore may be difficult to differentiate.
COVID stress
Commenting on the findings, Michele Tagliati, MD, director of the movement disorders program at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said the research highlights how clinicians’ understanding of particular diseases can be challenged during extraordinary events such as COVID-19 and the heightened stress it causes.
“I’m not surprised that these [disorders] might have had a spike during a stressful time as COVID,” he said.
Patients are “really scared and really anxious, they’re afraid to die, and they’re afraid that their life will be over. So they might express their psychological difficulty, their discomfort, with these calls for help that look like tics. But they’re not what we consider physiological or organic things,” he added.
Dr. Tagliati added that he doesn’t believe rapid tic onset in adults is not a complication of the coronavirus infection, but rather a consequence of psychological pressure brought on by the pandemic.
Treating underlying anxiety may be a useful approach, possibly with the support of psychiatrists, which in many cases is enough to relieve the conditions and overcome the symptoms, he noted.
However, at other times, it’s not that simple, he added. Sometimes patients “fall through the cracks between neurology and psychiatry,” Dr. Tagliati said.
Dr. Olvera and Dr. Tagliati have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
Results from a large, single-center study show several cases of tic-like movements and vocalizations with abrupt onset among older adolescents and adults during the pandemic. None had a previous diagnosis of a tic disorder. Among 10 patients, two were diagnosed with a purely functional movement disorder, four with an organic tic disorder, and four with both.
“Within our movement disorders clinic specifically ... we’ve been seeing an increased number of patients with an almost explosive onset of these tic-like movements and vocalizations later in life than what is typically seen with organic tic disorders and Tourette syndrome, which is typically in school-aged children,” said study investigator Caroline Olvera, MD, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago.
“Abrupt onset of symptoms can be seen in patients with tic disorders, although this is typically quoted as less than 10%, or even 5% is more characteristic of functional neurological disorders in general and also with psychogenic tics,” she added.
The findings were presented at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders.
Anxiety, other psychiatric conditions
Tic disorders typically start in childhood. However, the researchers observed an increase in the number of patients with abrupt onset of tic-like movements and vocalizations later in life, which is more often characteristic of functional neurological disorders.
To examine the profile, associated conditions, and risk factors in this population, the investigators conducted a thorough chart review of patients attending movement disorder clinics between March 2020, when the COVID pandemic was officially declared, and March 2021.
Patients with acute onset of tics were identified using the International Classification of Diseases codes for behavioral tics, tic vocalizations, and Tourette syndrome.
The charts were then narrowed down to patients with no previous diagnosis of these conditions. Most patients were videotaped for assessment by the rest of the movement disorder neurologists in the practice. Since the end of the study inclusion period in March 2021, Dr. Olvera estimates that the clinic experienced a doubling or tripling of the number of similar patients.
In the study cohort of 10 patients, the median age at presentation was 19 years (range, 15-41 years), nine were female, the gender of the other one was unknown, and the duration of tics was 8 weeks (range, 1-24 weeks) by the time they were first seen in the clinic. Four patients reported having COVID infection before tic onset.
All exhibited motor tics and nine had vocal tics. Two were diagnosed with a purely functional neurologic disorder, four with only an organic tic disorder, and four with organic tics with a functional overlay.
“All patients, including those with organic tic disorders, had a history of anxiety and also reported worsening anxiety in the setting of the COVID pandemic,” Dr. Olvera said.
The majority of patients were on a psychotropic medication prior to coming to the clinic, and these were primarily for anxiety and depression. Three patients had a history of suicidality, often very severe and leading to hospitalization, she noted.
“In terms of our conclusions from the project, we feel that this phenotype of acute explosive onset of tic-like movements and vocalizations in this older population of adults, compared with typical organic tic disorders and Tourette syndrome, appears novel to the pandemic,” she said.
She cautioned that functional and organic tics share many characteristics and therefore may be difficult to differentiate.
COVID stress
Commenting on the findings, Michele Tagliati, MD, director of the movement disorders program at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said the research highlights how clinicians’ understanding of particular diseases can be challenged during extraordinary events such as COVID-19 and the heightened stress it causes.
“I’m not surprised that these [disorders] might have had a spike during a stressful time as COVID,” he said.
Patients are “really scared and really anxious, they’re afraid to die, and they’re afraid that their life will be over. So they might express their psychological difficulty, their discomfort, with these calls for help that look like tics. But they’re not what we consider physiological or organic things,” he added.
Dr. Tagliati added that he doesn’t believe rapid tic onset in adults is not a complication of the coronavirus infection, but rather a consequence of psychological pressure brought on by the pandemic.
Treating underlying anxiety may be a useful approach, possibly with the support of psychiatrists, which in many cases is enough to relieve the conditions and overcome the symptoms, he noted.
However, at other times, it’s not that simple, he added. Sometimes patients “fall through the cracks between neurology and psychiatry,” Dr. Tagliati said.
Dr. Olvera and Dr. Tagliati have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
Results from a large, single-center study show several cases of tic-like movements and vocalizations with abrupt onset among older adolescents and adults during the pandemic. None had a previous diagnosis of a tic disorder. Among 10 patients, two were diagnosed with a purely functional movement disorder, four with an organic tic disorder, and four with both.
“Within our movement disorders clinic specifically ... we’ve been seeing an increased number of patients with an almost explosive onset of these tic-like movements and vocalizations later in life than what is typically seen with organic tic disorders and Tourette syndrome, which is typically in school-aged children,” said study investigator Caroline Olvera, MD, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago.
“Abrupt onset of symptoms can be seen in patients with tic disorders, although this is typically quoted as less than 10%, or even 5% is more characteristic of functional neurological disorders in general and also with psychogenic tics,” she added.
The findings were presented at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders.
Anxiety, other psychiatric conditions
Tic disorders typically start in childhood. However, the researchers observed an increase in the number of patients with abrupt onset of tic-like movements and vocalizations later in life, which is more often characteristic of functional neurological disorders.
To examine the profile, associated conditions, and risk factors in this population, the investigators conducted a thorough chart review of patients attending movement disorder clinics between March 2020, when the COVID pandemic was officially declared, and March 2021.
Patients with acute onset of tics were identified using the International Classification of Diseases codes for behavioral tics, tic vocalizations, and Tourette syndrome.
The charts were then narrowed down to patients with no previous diagnosis of these conditions. Most patients were videotaped for assessment by the rest of the movement disorder neurologists in the practice. Since the end of the study inclusion period in March 2021, Dr. Olvera estimates that the clinic experienced a doubling or tripling of the number of similar patients.
In the study cohort of 10 patients, the median age at presentation was 19 years (range, 15-41 years), nine were female, the gender of the other one was unknown, and the duration of tics was 8 weeks (range, 1-24 weeks) by the time they were first seen in the clinic. Four patients reported having COVID infection before tic onset.
All exhibited motor tics and nine had vocal tics. Two were diagnosed with a purely functional neurologic disorder, four with only an organic tic disorder, and four with organic tics with a functional overlay.
“All patients, including those with organic tic disorders, had a history of anxiety and also reported worsening anxiety in the setting of the COVID pandemic,” Dr. Olvera said.
The majority of patients were on a psychotropic medication prior to coming to the clinic, and these were primarily for anxiety and depression. Three patients had a history of suicidality, often very severe and leading to hospitalization, she noted.
“In terms of our conclusions from the project, we feel that this phenotype of acute explosive onset of tic-like movements and vocalizations in this older population of adults, compared with typical organic tic disorders and Tourette syndrome, appears novel to the pandemic,” she said.
She cautioned that functional and organic tics share many characteristics and therefore may be difficult to differentiate.
COVID stress
Commenting on the findings, Michele Tagliati, MD, director of the movement disorders program at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said the research highlights how clinicians’ understanding of particular diseases can be challenged during extraordinary events such as COVID-19 and the heightened stress it causes.
“I’m not surprised that these [disorders] might have had a spike during a stressful time as COVID,” he said.
Patients are “really scared and really anxious, they’re afraid to die, and they’re afraid that their life will be over. So they might express their psychological difficulty, their discomfort, with these calls for help that look like tics. But they’re not what we consider physiological or organic things,” he added.
Dr. Tagliati added that he doesn’t believe rapid tic onset in adults is not a complication of the coronavirus infection, but rather a consequence of psychological pressure brought on by the pandemic.
Treating underlying anxiety may be a useful approach, possibly with the support of psychiatrists, which in many cases is enough to relieve the conditions and overcome the symptoms, he noted.
However, at other times, it’s not that simple, he added. Sometimes patients “fall through the cracks between neurology and psychiatry,” Dr. Tagliati said.
Dr. Olvera and Dr. Tagliati have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MDS VIRTUAL CONGRESS 2021
Will ‘Dr. Disinformation’ ever face the music?
On Sept. 5, Rashid Buttar, DO, posted on Twitter that COVID-19 “was a planned operation” and shared an article alleging that most people who got the COVID vaccine would be dead by 2025.
Others include testimony in June by Sherri Jane Tenpenny, DO, before Ohio state legislators that the vaccine could cause people to become magnetized. Clips from the hearing went viral on the Internet. On April 9, 2020, Joseph Mercola, DO, posted a video titled “Could hydrogen peroxide treat coronavirus?” which was shared more than 4,600 times. In the video, Dr. Mercola said inhaling hydrogen peroxide through a nebulizer could prevent or cure COVID.
These physicians are identified as members of the “Disinformation Dozen,” a group of top superspreaders of COVID vaccine misinformation on social media, according to a 2021 report by the nonprofit Center for Countering Digital Hate. The report, based on an analysis of antivaccine content on social media platforms, found that 12 people were responsible for 65% of it. The group is composed of physicians, antivaccine activists, and people known for promoting alternative medicine.
The physician voices are of particular concern because their medical credentials lend credence to their unproven, often dangerous pronouncements. All three continue to hold medical licenses and have not faced consequences for their COVID-related statements.
But leaders of professional medical organizations increasingly are calling for that to change and urging medical oversight boards to take more aggressive action.
In July, the Federation of State Medical Boards, the national umbrella organization for the state-based boards, issued a statement making clear that doctors who generate and spread COVID misinformation could be subject to disciplinary action, including the suspension or revocation of their licenses. The American Board of Family Medicine, American Board of Internal Medicine, and American Board of Pediatrics issued a joint statement Sept. 9 in support of the state boards’ position, warning that “such unethical or unprofessional conduct may prompt their respective board to take action that could put their certification at risk.”
And the superspreaders identified by the center’s report are not alone. KHN identified 20 other doctors who have made false or misleading claims about COVID by combing through published fact checks and other news coverage.
For example, at an Indiana school board meeting in August, Dan Stock, MD, claimed the surge in covid cases this summer was due to “antibody mediated viral enhancement” from people receiving covid vaccines. PolitiFact rated his claim “Pants on Fire” false.
Stella Immanuel, MD, a member of a group America’s Frontline Doctors, which has consistently made false statements about COVID, said in a video that went viral in July 2020 that masks weren’t needed because covid could be cured by hydroxychloroquine. Dr. Immanuel’s website currently promotes a set of vitamins, as well as hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin, as COVID treatments.
Two of the doctors mentioned by name in this article responded to requests for comment. Dr. Mercola offered documents to rebut criticisms of his hydrogen peroxide COVID treatment and took issue with the center’s “Disinformation Dozen” report methodology. Dr. Buttar defended his positions, saying via email that “the science is clear and anyone who contests it, has a suspect agenda at best and/or lacks a moral compass.” He also pointed to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Adverse Event Recording System, considered inconclusive by many experts.
Since the onset of the COVID pandemic, misinformation has been widespread on social media platforms. And many experts blame it for undermining efforts to curb the coronavirus’s spread. A recent poll showed that more than 50% of Americans who won’t get vaccinated cited conspiracy theories as their reasons – for example, saying the vaccines cause infertility or alter DNA.
Some physicians have gained notoriety by embracing COVID-related fringe ideas, quack treatments and falsehoods via social media, conservative talk shows, and even in person with patients. Whether promoting the use of ivermectin, an antiparasitic drug for animals, or a mix of vitamins to treat COVID, doctors’ words can be especially powerful. Public opinion polls consistently show that Americans have high trust in doctors.
“There is a sense of credibility that comes with being a doctor,” said Rachel Moran, PhD, a researcher who studies COVID misinformation at the University of Washington. “There is also a sense they have access to insider info that we don’t. This is a very confusing time, and it can seem that if anyone knows what I should be doing in this situation, it’s a doctor.”
While COVID is a novel and complicated infectious disease, physicians spreading misinformation generally have no particular expertise in infectious diseases. Scott Atlas, MD, who endorsed former President Donald Trump’s unproven statements about the course of the pandemic, is a radiation oncologist.
Traditionally, the responsibility of policing physicians has fallen to state medical boards. Beyond overseeing the licensing process, these panels investigate complaints about doctors and discipline those who engage in unethical, unprofessional or, in extreme cases, criminal activity. Any member of the public can submit a complaint about a physician.
“The boards are relatively slow and weak and it’s a long, slow process to pull somebody’s license,” said Arthur Caplan, PhD, founding head of the department of medical ethics at New York University. “In many states, they have their hands full with doctors who have committed felonies, doctors who are molesting their patients. Keeping an eye on misinformation is somewhat down on the priority list.”
To date, only two doctors have reportedly faced such sanctions. In Oregon, Steven LaTulippe, MD, had his license suspended in December 2020 for refusing to wear a face mask at his clinic and telling patients that masks were ineffective in curbing the spread of COVID, and even dangerous. Thomas Cowan, MD, a San Francisco physician who posted a YouTube video that went viral in March 2020 stating that 5G networks cause COVID, voluntarily surrendered his medical license to California’s medical board in February 2021.
Humayun Chaudhry, DO, president of the Federation of State Medical Boards, however, said it’s possible some doctors could already be the subject of inquiries and investigations, since these actions are not made public until sanctions are handed down.
KHN reached out to the medical and osteopathic boards of all 50 states and the District of Columbia to see if they had received COVID misinformation complaints. Of the 43 that responded, only a handful shared specifics.
During a 1-week period in August, Kansas’ medical board received six such complaints. In all, the state has received 35 complaints against 20 licensees about spreading covid misinformation on social media and in person. Indiana has received about 30 in the past year. South Carolina said it had about 10 since January. Rhode Island didn’t share the number of complaints but said it has taken disciplinary action against one doctor for spreading misinformation, though it hasn’t moved to suspend his license. (The disciplinary measures include a fine, a reprimand on the doctor’s record and a mandate to complete an ethics course.) Five states said they had received only a couple, and 11 states reported receiving no complaints regarding COVID misinformation.
Confidentiality laws in 13 states prevented those boards from sharing information about complaints.
Social media companies have also been slow to take action. Some doctors’ accounts – specifically those among the Disinformation Dozen – have been suspended, but others are still active and posting misinformation.
Imran Ahmed, CEO of the Center for Countering Digital Hate, said social media platforms often don’t consistently apply their rules against spreading misinformation.
“Even when it’s the same companies, Facebook will sometimes take posts down, but Instagram will not,” Mr. Ahmed said, referring to Facebook’s ownership of Instagram. “It goes to show their piecemeal, ineffective approach to enforcing their own rules.”
A Facebook spokesperson said the company has removed over 3,000 accounts, pages and groups for repeatedly violating COVID and vaccine misinformation policies since the beginning of the pandemic. Dr. Buttar’s Facebook and Instagram pages and Tenpenny’s Facebook page have been removed, while Dr. Mercola’s Facebook posts have been demoted, which means fewer people will see them. Dr. Tenpenny and Dr. Mercola still have Instagram accounts.
Part of the challenge may be that these doctors sometimes present scientific opinions that aren’t mainstream but are viewed as potentially valid by some of their colleagues.
“It can be difficult to prove that what is being said is outside the range of scientific and medical consensus,” said Dr. Caplan. “The doctors who were advising Trump – like Scott Atlas – recommended herd immunity. That was far from the consensus of epidemiologists, but you couldn’t get a board to take his license away because it was a fringe opinion.”
Even if these physicians don’t face consequences, it is likely, experts said, that the public health will.
“Medical misinformation doesn’t just result in people making bad personal and community health choices, but it also divides communities and families, leaving an emotional toll,” said Dr. Moran. “Misinformation narratives have real sticking power and impact people’s ability to make safe health choices.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
On Sept. 5, Rashid Buttar, DO, posted on Twitter that COVID-19 “was a planned operation” and shared an article alleging that most people who got the COVID vaccine would be dead by 2025.
Others include testimony in June by Sherri Jane Tenpenny, DO, before Ohio state legislators that the vaccine could cause people to become magnetized. Clips from the hearing went viral on the Internet. On April 9, 2020, Joseph Mercola, DO, posted a video titled “Could hydrogen peroxide treat coronavirus?” which was shared more than 4,600 times. In the video, Dr. Mercola said inhaling hydrogen peroxide through a nebulizer could prevent or cure COVID.
These physicians are identified as members of the “Disinformation Dozen,” a group of top superspreaders of COVID vaccine misinformation on social media, according to a 2021 report by the nonprofit Center for Countering Digital Hate. The report, based on an analysis of antivaccine content on social media platforms, found that 12 people were responsible for 65% of it. The group is composed of physicians, antivaccine activists, and people known for promoting alternative medicine.
The physician voices are of particular concern because their medical credentials lend credence to their unproven, often dangerous pronouncements. All three continue to hold medical licenses and have not faced consequences for their COVID-related statements.
But leaders of professional medical organizations increasingly are calling for that to change and urging medical oversight boards to take more aggressive action.
In July, the Federation of State Medical Boards, the national umbrella organization for the state-based boards, issued a statement making clear that doctors who generate and spread COVID misinformation could be subject to disciplinary action, including the suspension or revocation of their licenses. The American Board of Family Medicine, American Board of Internal Medicine, and American Board of Pediatrics issued a joint statement Sept. 9 in support of the state boards’ position, warning that “such unethical or unprofessional conduct may prompt their respective board to take action that could put their certification at risk.”
And the superspreaders identified by the center’s report are not alone. KHN identified 20 other doctors who have made false or misleading claims about COVID by combing through published fact checks and other news coverage.
For example, at an Indiana school board meeting in August, Dan Stock, MD, claimed the surge in covid cases this summer was due to “antibody mediated viral enhancement” from people receiving covid vaccines. PolitiFact rated his claim “Pants on Fire” false.
Stella Immanuel, MD, a member of a group America’s Frontline Doctors, which has consistently made false statements about COVID, said in a video that went viral in July 2020 that masks weren’t needed because covid could be cured by hydroxychloroquine. Dr. Immanuel’s website currently promotes a set of vitamins, as well as hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin, as COVID treatments.
Two of the doctors mentioned by name in this article responded to requests for comment. Dr. Mercola offered documents to rebut criticisms of his hydrogen peroxide COVID treatment and took issue with the center’s “Disinformation Dozen” report methodology. Dr. Buttar defended his positions, saying via email that “the science is clear and anyone who contests it, has a suspect agenda at best and/or lacks a moral compass.” He also pointed to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Adverse Event Recording System, considered inconclusive by many experts.
Since the onset of the COVID pandemic, misinformation has been widespread on social media platforms. And many experts blame it for undermining efforts to curb the coronavirus’s spread. A recent poll showed that more than 50% of Americans who won’t get vaccinated cited conspiracy theories as their reasons – for example, saying the vaccines cause infertility or alter DNA.
Some physicians have gained notoriety by embracing COVID-related fringe ideas, quack treatments and falsehoods via social media, conservative talk shows, and even in person with patients. Whether promoting the use of ivermectin, an antiparasitic drug for animals, or a mix of vitamins to treat COVID, doctors’ words can be especially powerful. Public opinion polls consistently show that Americans have high trust in doctors.
“There is a sense of credibility that comes with being a doctor,” said Rachel Moran, PhD, a researcher who studies COVID misinformation at the University of Washington. “There is also a sense they have access to insider info that we don’t. This is a very confusing time, and it can seem that if anyone knows what I should be doing in this situation, it’s a doctor.”
While COVID is a novel and complicated infectious disease, physicians spreading misinformation generally have no particular expertise in infectious diseases. Scott Atlas, MD, who endorsed former President Donald Trump’s unproven statements about the course of the pandemic, is a radiation oncologist.
Traditionally, the responsibility of policing physicians has fallen to state medical boards. Beyond overseeing the licensing process, these panels investigate complaints about doctors and discipline those who engage in unethical, unprofessional or, in extreme cases, criminal activity. Any member of the public can submit a complaint about a physician.
“The boards are relatively slow and weak and it’s a long, slow process to pull somebody’s license,” said Arthur Caplan, PhD, founding head of the department of medical ethics at New York University. “In many states, they have their hands full with doctors who have committed felonies, doctors who are molesting their patients. Keeping an eye on misinformation is somewhat down on the priority list.”
To date, only two doctors have reportedly faced such sanctions. In Oregon, Steven LaTulippe, MD, had his license suspended in December 2020 for refusing to wear a face mask at his clinic and telling patients that masks were ineffective in curbing the spread of COVID, and even dangerous. Thomas Cowan, MD, a San Francisco physician who posted a YouTube video that went viral in March 2020 stating that 5G networks cause COVID, voluntarily surrendered his medical license to California’s medical board in February 2021.
Humayun Chaudhry, DO, president of the Federation of State Medical Boards, however, said it’s possible some doctors could already be the subject of inquiries and investigations, since these actions are not made public until sanctions are handed down.
KHN reached out to the medical and osteopathic boards of all 50 states and the District of Columbia to see if they had received COVID misinformation complaints. Of the 43 that responded, only a handful shared specifics.
During a 1-week period in August, Kansas’ medical board received six such complaints. In all, the state has received 35 complaints against 20 licensees about spreading covid misinformation on social media and in person. Indiana has received about 30 in the past year. South Carolina said it had about 10 since January. Rhode Island didn’t share the number of complaints but said it has taken disciplinary action against one doctor for spreading misinformation, though it hasn’t moved to suspend his license. (The disciplinary measures include a fine, a reprimand on the doctor’s record and a mandate to complete an ethics course.) Five states said they had received only a couple, and 11 states reported receiving no complaints regarding COVID misinformation.
Confidentiality laws in 13 states prevented those boards from sharing information about complaints.
Social media companies have also been slow to take action. Some doctors’ accounts – specifically those among the Disinformation Dozen – have been suspended, but others are still active and posting misinformation.
Imran Ahmed, CEO of the Center for Countering Digital Hate, said social media platforms often don’t consistently apply their rules against spreading misinformation.
“Even when it’s the same companies, Facebook will sometimes take posts down, but Instagram will not,” Mr. Ahmed said, referring to Facebook’s ownership of Instagram. “It goes to show their piecemeal, ineffective approach to enforcing their own rules.”
A Facebook spokesperson said the company has removed over 3,000 accounts, pages and groups for repeatedly violating COVID and vaccine misinformation policies since the beginning of the pandemic. Dr. Buttar’s Facebook and Instagram pages and Tenpenny’s Facebook page have been removed, while Dr. Mercola’s Facebook posts have been demoted, which means fewer people will see them. Dr. Tenpenny and Dr. Mercola still have Instagram accounts.
Part of the challenge may be that these doctors sometimes present scientific opinions that aren’t mainstream but are viewed as potentially valid by some of their colleagues.
“It can be difficult to prove that what is being said is outside the range of scientific and medical consensus,” said Dr. Caplan. “The doctors who were advising Trump – like Scott Atlas – recommended herd immunity. That was far from the consensus of epidemiologists, but you couldn’t get a board to take his license away because it was a fringe opinion.”
Even if these physicians don’t face consequences, it is likely, experts said, that the public health will.
“Medical misinformation doesn’t just result in people making bad personal and community health choices, but it also divides communities and families, leaving an emotional toll,” said Dr. Moran. “Misinformation narratives have real sticking power and impact people’s ability to make safe health choices.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
On Sept. 5, Rashid Buttar, DO, posted on Twitter that COVID-19 “was a planned operation” and shared an article alleging that most people who got the COVID vaccine would be dead by 2025.
Others include testimony in June by Sherri Jane Tenpenny, DO, before Ohio state legislators that the vaccine could cause people to become magnetized. Clips from the hearing went viral on the Internet. On April 9, 2020, Joseph Mercola, DO, posted a video titled “Could hydrogen peroxide treat coronavirus?” which was shared more than 4,600 times. In the video, Dr. Mercola said inhaling hydrogen peroxide through a nebulizer could prevent or cure COVID.
These physicians are identified as members of the “Disinformation Dozen,” a group of top superspreaders of COVID vaccine misinformation on social media, according to a 2021 report by the nonprofit Center for Countering Digital Hate. The report, based on an analysis of antivaccine content on social media platforms, found that 12 people were responsible for 65% of it. The group is composed of physicians, antivaccine activists, and people known for promoting alternative medicine.
The physician voices are of particular concern because their medical credentials lend credence to their unproven, often dangerous pronouncements. All three continue to hold medical licenses and have not faced consequences for their COVID-related statements.
But leaders of professional medical organizations increasingly are calling for that to change and urging medical oversight boards to take more aggressive action.
In July, the Federation of State Medical Boards, the national umbrella organization for the state-based boards, issued a statement making clear that doctors who generate and spread COVID misinformation could be subject to disciplinary action, including the suspension or revocation of their licenses. The American Board of Family Medicine, American Board of Internal Medicine, and American Board of Pediatrics issued a joint statement Sept. 9 in support of the state boards’ position, warning that “such unethical or unprofessional conduct may prompt their respective board to take action that could put their certification at risk.”
And the superspreaders identified by the center’s report are not alone. KHN identified 20 other doctors who have made false or misleading claims about COVID by combing through published fact checks and other news coverage.
For example, at an Indiana school board meeting in August, Dan Stock, MD, claimed the surge in covid cases this summer was due to “antibody mediated viral enhancement” from people receiving covid vaccines. PolitiFact rated his claim “Pants on Fire” false.
Stella Immanuel, MD, a member of a group America’s Frontline Doctors, which has consistently made false statements about COVID, said in a video that went viral in July 2020 that masks weren’t needed because covid could be cured by hydroxychloroquine. Dr. Immanuel’s website currently promotes a set of vitamins, as well as hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin, as COVID treatments.
Two of the doctors mentioned by name in this article responded to requests for comment. Dr. Mercola offered documents to rebut criticisms of his hydrogen peroxide COVID treatment and took issue with the center’s “Disinformation Dozen” report methodology. Dr. Buttar defended his positions, saying via email that “the science is clear and anyone who contests it, has a suspect agenda at best and/or lacks a moral compass.” He also pointed to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Adverse Event Recording System, considered inconclusive by many experts.
Since the onset of the COVID pandemic, misinformation has been widespread on social media platforms. And many experts blame it for undermining efforts to curb the coronavirus’s spread. A recent poll showed that more than 50% of Americans who won’t get vaccinated cited conspiracy theories as their reasons – for example, saying the vaccines cause infertility or alter DNA.
Some physicians have gained notoriety by embracing COVID-related fringe ideas, quack treatments and falsehoods via social media, conservative talk shows, and even in person with patients. Whether promoting the use of ivermectin, an antiparasitic drug for animals, or a mix of vitamins to treat COVID, doctors’ words can be especially powerful. Public opinion polls consistently show that Americans have high trust in doctors.
“There is a sense of credibility that comes with being a doctor,” said Rachel Moran, PhD, a researcher who studies COVID misinformation at the University of Washington. “There is also a sense they have access to insider info that we don’t. This is a very confusing time, and it can seem that if anyone knows what I should be doing in this situation, it’s a doctor.”
While COVID is a novel and complicated infectious disease, physicians spreading misinformation generally have no particular expertise in infectious diseases. Scott Atlas, MD, who endorsed former President Donald Trump’s unproven statements about the course of the pandemic, is a radiation oncologist.
Traditionally, the responsibility of policing physicians has fallen to state medical boards. Beyond overseeing the licensing process, these panels investigate complaints about doctors and discipline those who engage in unethical, unprofessional or, in extreme cases, criminal activity. Any member of the public can submit a complaint about a physician.
“The boards are relatively slow and weak and it’s a long, slow process to pull somebody’s license,” said Arthur Caplan, PhD, founding head of the department of medical ethics at New York University. “In many states, they have their hands full with doctors who have committed felonies, doctors who are molesting their patients. Keeping an eye on misinformation is somewhat down on the priority list.”
To date, only two doctors have reportedly faced such sanctions. In Oregon, Steven LaTulippe, MD, had his license suspended in December 2020 for refusing to wear a face mask at his clinic and telling patients that masks were ineffective in curbing the spread of COVID, and even dangerous. Thomas Cowan, MD, a San Francisco physician who posted a YouTube video that went viral in March 2020 stating that 5G networks cause COVID, voluntarily surrendered his medical license to California’s medical board in February 2021.
Humayun Chaudhry, DO, president of the Federation of State Medical Boards, however, said it’s possible some doctors could already be the subject of inquiries and investigations, since these actions are not made public until sanctions are handed down.
KHN reached out to the medical and osteopathic boards of all 50 states and the District of Columbia to see if they had received COVID misinformation complaints. Of the 43 that responded, only a handful shared specifics.
During a 1-week period in August, Kansas’ medical board received six such complaints. In all, the state has received 35 complaints against 20 licensees about spreading covid misinformation on social media and in person. Indiana has received about 30 in the past year. South Carolina said it had about 10 since January. Rhode Island didn’t share the number of complaints but said it has taken disciplinary action against one doctor for spreading misinformation, though it hasn’t moved to suspend his license. (The disciplinary measures include a fine, a reprimand on the doctor’s record and a mandate to complete an ethics course.) Five states said they had received only a couple, and 11 states reported receiving no complaints regarding COVID misinformation.
Confidentiality laws in 13 states prevented those boards from sharing information about complaints.
Social media companies have also been slow to take action. Some doctors’ accounts – specifically those among the Disinformation Dozen – have been suspended, but others are still active and posting misinformation.
Imran Ahmed, CEO of the Center for Countering Digital Hate, said social media platforms often don’t consistently apply their rules against spreading misinformation.
“Even when it’s the same companies, Facebook will sometimes take posts down, but Instagram will not,” Mr. Ahmed said, referring to Facebook’s ownership of Instagram. “It goes to show their piecemeal, ineffective approach to enforcing their own rules.”
A Facebook spokesperson said the company has removed over 3,000 accounts, pages and groups for repeatedly violating COVID and vaccine misinformation policies since the beginning of the pandemic. Dr. Buttar’s Facebook and Instagram pages and Tenpenny’s Facebook page have been removed, while Dr. Mercola’s Facebook posts have been demoted, which means fewer people will see them. Dr. Tenpenny and Dr. Mercola still have Instagram accounts.
Part of the challenge may be that these doctors sometimes present scientific opinions that aren’t mainstream but are viewed as potentially valid by some of their colleagues.
“It can be difficult to prove that what is being said is outside the range of scientific and medical consensus,” said Dr. Caplan. “The doctors who were advising Trump – like Scott Atlas – recommended herd immunity. That was far from the consensus of epidemiologists, but you couldn’t get a board to take his license away because it was a fringe opinion.”
Even if these physicians don’t face consequences, it is likely, experts said, that the public health will.
“Medical misinformation doesn’t just result in people making bad personal and community health choices, but it also divides communities and families, leaving an emotional toll,” said Dr. Moran. “Misinformation narratives have real sticking power and impact people’s ability to make safe health choices.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Ten lessons learned from the pandemic, and a way forward: Report
The federal government is taking “steps in the right direction” to help control this pandemic, but there have been many hard lessons learned, according to a new report from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC).
This is among 10 recommendations that address what AAMC views as systemic inadequacies in the nation’s COVID-19 response that can help advise policy makers on how to better prepare for the next pandemic.
The recommendations are:
- The White House must lead the charge and ensure coordination among departments and agencies.
- The federal government must engage industry and research universities at the outset, commit to purchasing needed supplies and therapeutics in advance.
- The federal government must ensure an effective supply chain for critical goods and materials.
- Congress must appropriate needed funding to meet public health needs.
- Federal and state governments must relax regulatory restrictions on clinical care during a national emergency.
- Both government and the private sector must invest in needed data infrastructure.
- Federal and state policies must increase supply and well-being of physicians and other health professionals.
- Congress must continue to commit to basic and clinical research.
- Federal government should expand and improve health insurance coverage.
- Stakeholders must commit to improving equity and patient-centered care through community engagement.
Current crisis ‘avoidable’
Although the Biden administration’s COVID-19 strategy is moving in the right direction, says Atul Grover, MD, PhD, executive director of the AAMC Research and Action Institute, the branch of the association that prepared the report, “the severity of this phase of the COVID-19 pandemic was avoidable.”
According to the report, only the federal government can provide the level of coordination that is needed across states and international borders to fight the virus successfully. “The response should not rely on a piecemeal approach that varies by locality and region.”
In the absence of clear federal leadership during the pandemic’s earlier phase, the report states, “key policies were either absent or conflicting across states, counties, and municipalities. Without federal direction and coordination, states were forced to compete against each other (and, sometimes, against the federal government) for supplies.”
As a recent Kaiser Health News report shows, the states are still falling short on the COVID-19 front: For example, at least 26 states have restricted the ability of their public health authorities to take action against COVID in various ways.
In an interview, William Schaffner, MD, a professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., agrees on the need for the federal government to lead the COVID fight.
Noting that the cooperation of states with each other and with the national government is voluntary, Dr. Schaffner asserted that “subcontracting [the COVID response] to the states doesn’t work. That results in chaos and a crazy quilt of responses that persists to this day.”
Inadequate control of COVID effort
Within the federal government, the AAMC report maintains, the White House must be directly in charge of coordinating the fight against the pandemic. The AAMC calls for the establishment of a top-level office or a coordinating team to lead the COVID effort, similar to what was done during the 2014-2015 Ebola outbreak.
Earlier this year, President Biden appointed Jeffrey Zients as White House Coronavirus Response Coordinator, succeeding Deborah Birx, MD, in that role. Dr. Grover was asked in an interview why that doesn’t meet AAMC’s requirements.
“Jeff and his team are doing a good job,” Dr. Grover said. “But the reason I think we could be doing a better job is that the messaging has not been consistent across agencies and across the federal government.”
“Jeff may not have the authority to overrule individual decisions and to ensure that all decisions are integrated across organizations. Maybe that is happening, but it’s not clear to those of us who are not in the meetings every day. At a minimum, we’ve got to get the messaging right, and it needs to be more transparent.”
Dr. Grover cites a recent press conference by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention about the national strategy for vaccine booster shots. “No one from the FDA was there,” he said. “Theoretically, [the] FDA has signed off on boosters, but their scientists were caught off guard. The administration’s messaging needs to be consistent, and that would be more likely if someone were in charge of these agencies overall,” Dr. Grover said.
Dr. Schaffner said he prefers not to comment on this point, “but I won’t argue with the observation.”
Supplies still not adequate
In light of the medical supply shortages that have plagued the COVID-19 response, the AAMC report recommends that the federal government ensure an effective supply chain for all critical goods and materials, starting with the Strategic National Stockpile (SNS), which was created in 1999 to supplement state and local medical supplies during public health emergencies.
“The SNS should enable the nation to support care for a minimum number of critically ill patients until the federal government can assure an adequate functional supply chain for a short period of time,” the AAMC report states.
The SNS was not replenished after the 2009 H1N1 pandemic and wasn’t prepared for the COVID-19 emergency, according to the report. “Despite having built up the supply over the last year, the nation is just one major outbreak or incident away from another monumental shortage of very basic needs such as gloves, masks, and gowns.”
Dr. Grover said the national stockpile now has more gowns and gloves than it did at the pandemic’s start. But he’s concerned about what might happen if a new type of pathogen emerged. “If we were to face the same kind of COVID surge we’re now facing in the unvaccinated communities more broadly across the U.S. – for example, if we got another variant that was even more infectious or deadly – I’m not sure we’d be prepared.”
Just-in-time purchasing
Hospitals were caught short when COVID struck because of their just-in-time supply chain approach, which relied on punctual deliveries of new supplies and equipment, the report states. Of course, when demand soared and every provider was competing for scarce supplies, that didn’t happen.
Now, Dr. Grover pointed out, there is still no central system to keep track of where PPE, ventilators, oxygen tanks, and other critical items are in the supply chains of hospitals and physician practices.
So, even if policymakers determined that the nation should use both the SNS and private locations to stockpile enough supplies to care for a certain number of patients for a period of time, there wouldn’t be any way to determine what was on hand or where it was stored.
Moreover, while hospitals have built up their stockpiles to prepare for new COVID surges, he expects them to go back to just-in-time purchasing when the pandemic wanes. Although health care organizations want to take good care of patients, they have financial and physical constraints on how many supplies they can store, Dr. Grover said.
Testing conundrum
An analogous challenge exists for companies that make COVID-19 tests, Dr. Grover said. “The testing companies don’t want to produce more than they’re going to be able to sell. They’re a for-profit industry.” Partly as a result, the nation has never had as many tests as it needs, according to the report.
To solve this problem, the report authors suggest that the federal government take an approach similar to that of the Trump administration’s Operation Warp Speed (OWS), which used advance funding and vaccine prepurchases to spur development.
“The CDC is unlikely to meet testing demands in future outbreaks and pandemics using existing public health lab partnerships, even under the best conditions. Industry was reluctant to mass produce testing kits for fear demand would fail to materialize; an OWS-like advance purchasing strategy and investment in private production could have reduced the spread of COVID-19 and will be critical in mitigating a future outbreak or pandemic.”
Public health infrastructure
The report also calls for Congress to appropriate “robust and continuous funding for public health infrastructure … Chronic underfunding of public health has hurt the nation’s emergency preparedness framework and contributes to health inequity.”
This applies not only to federal funding but also to state and local funding, which has primarily been allocated on a crisis-response basis, the report states.
Dr. Grover is glad that the fiscal 2022 budget legislation includes $15 billion to finance this infrastructure, but that’s only a start, he said.
Dr. Schaffner stresses the importance of improving the IT infrastructure of public health agencies. “We need a better, higher-quality mechanism for quickly gathering critical data from doctors’ offices and hospitals and sending that information through a public health stream so it can be gathered.”
“Today, data come in at the national level, sometimes slowly, sometimes in fragmented fashion, from different jurisdictions around the country, and it’s very difficult to make secure statements and plan effectively.”
Dr. Schaffner agrees with the report’s emphasis on the need for long-term planning to prepare for the next pandemic but is pessimistic about the odds of it occurring.
“This challenges us as Americans. We have notoriously short attention spans. And we like to put difficult things behind us and look to the future,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The federal government is taking “steps in the right direction” to help control this pandemic, but there have been many hard lessons learned, according to a new report from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC).
This is among 10 recommendations that address what AAMC views as systemic inadequacies in the nation’s COVID-19 response that can help advise policy makers on how to better prepare for the next pandemic.
The recommendations are:
- The White House must lead the charge and ensure coordination among departments and agencies.
- The federal government must engage industry and research universities at the outset, commit to purchasing needed supplies and therapeutics in advance.
- The federal government must ensure an effective supply chain for critical goods and materials.
- Congress must appropriate needed funding to meet public health needs.
- Federal and state governments must relax regulatory restrictions on clinical care during a national emergency.
- Both government and the private sector must invest in needed data infrastructure.
- Federal and state policies must increase supply and well-being of physicians and other health professionals.
- Congress must continue to commit to basic and clinical research.
- Federal government should expand and improve health insurance coverage.
- Stakeholders must commit to improving equity and patient-centered care through community engagement.
Current crisis ‘avoidable’
Although the Biden administration’s COVID-19 strategy is moving in the right direction, says Atul Grover, MD, PhD, executive director of the AAMC Research and Action Institute, the branch of the association that prepared the report, “the severity of this phase of the COVID-19 pandemic was avoidable.”
According to the report, only the federal government can provide the level of coordination that is needed across states and international borders to fight the virus successfully. “The response should not rely on a piecemeal approach that varies by locality and region.”
In the absence of clear federal leadership during the pandemic’s earlier phase, the report states, “key policies were either absent or conflicting across states, counties, and municipalities. Without federal direction and coordination, states were forced to compete against each other (and, sometimes, against the federal government) for supplies.”
As a recent Kaiser Health News report shows, the states are still falling short on the COVID-19 front: For example, at least 26 states have restricted the ability of their public health authorities to take action against COVID in various ways.
In an interview, William Schaffner, MD, a professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., agrees on the need for the federal government to lead the COVID fight.
Noting that the cooperation of states with each other and with the national government is voluntary, Dr. Schaffner asserted that “subcontracting [the COVID response] to the states doesn’t work. That results in chaos and a crazy quilt of responses that persists to this day.”
Inadequate control of COVID effort
Within the federal government, the AAMC report maintains, the White House must be directly in charge of coordinating the fight against the pandemic. The AAMC calls for the establishment of a top-level office or a coordinating team to lead the COVID effort, similar to what was done during the 2014-2015 Ebola outbreak.
Earlier this year, President Biden appointed Jeffrey Zients as White House Coronavirus Response Coordinator, succeeding Deborah Birx, MD, in that role. Dr. Grover was asked in an interview why that doesn’t meet AAMC’s requirements.
“Jeff and his team are doing a good job,” Dr. Grover said. “But the reason I think we could be doing a better job is that the messaging has not been consistent across agencies and across the federal government.”
“Jeff may not have the authority to overrule individual decisions and to ensure that all decisions are integrated across organizations. Maybe that is happening, but it’s not clear to those of us who are not in the meetings every day. At a minimum, we’ve got to get the messaging right, and it needs to be more transparent.”
Dr. Grover cites a recent press conference by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention about the national strategy for vaccine booster shots. “No one from the FDA was there,” he said. “Theoretically, [the] FDA has signed off on boosters, but their scientists were caught off guard. The administration’s messaging needs to be consistent, and that would be more likely if someone were in charge of these agencies overall,” Dr. Grover said.
Dr. Schaffner said he prefers not to comment on this point, “but I won’t argue with the observation.”
Supplies still not adequate
In light of the medical supply shortages that have plagued the COVID-19 response, the AAMC report recommends that the federal government ensure an effective supply chain for all critical goods and materials, starting with the Strategic National Stockpile (SNS), which was created in 1999 to supplement state and local medical supplies during public health emergencies.
“The SNS should enable the nation to support care for a minimum number of critically ill patients until the federal government can assure an adequate functional supply chain for a short period of time,” the AAMC report states.
The SNS was not replenished after the 2009 H1N1 pandemic and wasn’t prepared for the COVID-19 emergency, according to the report. “Despite having built up the supply over the last year, the nation is just one major outbreak or incident away from another monumental shortage of very basic needs such as gloves, masks, and gowns.”
Dr. Grover said the national stockpile now has more gowns and gloves than it did at the pandemic’s start. But he’s concerned about what might happen if a new type of pathogen emerged. “If we were to face the same kind of COVID surge we’re now facing in the unvaccinated communities more broadly across the U.S. – for example, if we got another variant that was even more infectious or deadly – I’m not sure we’d be prepared.”
Just-in-time purchasing
Hospitals were caught short when COVID struck because of their just-in-time supply chain approach, which relied on punctual deliveries of new supplies and equipment, the report states. Of course, when demand soared and every provider was competing for scarce supplies, that didn’t happen.
Now, Dr. Grover pointed out, there is still no central system to keep track of where PPE, ventilators, oxygen tanks, and other critical items are in the supply chains of hospitals and physician practices.
So, even if policymakers determined that the nation should use both the SNS and private locations to stockpile enough supplies to care for a certain number of patients for a period of time, there wouldn’t be any way to determine what was on hand or where it was stored.
Moreover, while hospitals have built up their stockpiles to prepare for new COVID surges, he expects them to go back to just-in-time purchasing when the pandemic wanes. Although health care organizations want to take good care of patients, they have financial and physical constraints on how many supplies they can store, Dr. Grover said.
Testing conundrum
An analogous challenge exists for companies that make COVID-19 tests, Dr. Grover said. “The testing companies don’t want to produce more than they’re going to be able to sell. They’re a for-profit industry.” Partly as a result, the nation has never had as many tests as it needs, according to the report.
To solve this problem, the report authors suggest that the federal government take an approach similar to that of the Trump administration’s Operation Warp Speed (OWS), which used advance funding and vaccine prepurchases to spur development.
“The CDC is unlikely to meet testing demands in future outbreaks and pandemics using existing public health lab partnerships, even under the best conditions. Industry was reluctant to mass produce testing kits for fear demand would fail to materialize; an OWS-like advance purchasing strategy and investment in private production could have reduced the spread of COVID-19 and will be critical in mitigating a future outbreak or pandemic.”
Public health infrastructure
The report also calls for Congress to appropriate “robust and continuous funding for public health infrastructure … Chronic underfunding of public health has hurt the nation’s emergency preparedness framework and contributes to health inequity.”
This applies not only to federal funding but also to state and local funding, which has primarily been allocated on a crisis-response basis, the report states.
Dr. Grover is glad that the fiscal 2022 budget legislation includes $15 billion to finance this infrastructure, but that’s only a start, he said.
Dr. Schaffner stresses the importance of improving the IT infrastructure of public health agencies. “We need a better, higher-quality mechanism for quickly gathering critical data from doctors’ offices and hospitals and sending that information through a public health stream so it can be gathered.”
“Today, data come in at the national level, sometimes slowly, sometimes in fragmented fashion, from different jurisdictions around the country, and it’s very difficult to make secure statements and plan effectively.”
Dr. Schaffner agrees with the report’s emphasis on the need for long-term planning to prepare for the next pandemic but is pessimistic about the odds of it occurring.
“This challenges us as Americans. We have notoriously short attention spans. And we like to put difficult things behind us and look to the future,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The federal government is taking “steps in the right direction” to help control this pandemic, but there have been many hard lessons learned, according to a new report from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC).
This is among 10 recommendations that address what AAMC views as systemic inadequacies in the nation’s COVID-19 response that can help advise policy makers on how to better prepare for the next pandemic.
The recommendations are:
- The White House must lead the charge and ensure coordination among departments and agencies.
- The federal government must engage industry and research universities at the outset, commit to purchasing needed supplies and therapeutics in advance.
- The federal government must ensure an effective supply chain for critical goods and materials.
- Congress must appropriate needed funding to meet public health needs.
- Federal and state governments must relax regulatory restrictions on clinical care during a national emergency.
- Both government and the private sector must invest in needed data infrastructure.
- Federal and state policies must increase supply and well-being of physicians and other health professionals.
- Congress must continue to commit to basic and clinical research.
- Federal government should expand and improve health insurance coverage.
- Stakeholders must commit to improving equity and patient-centered care through community engagement.
Current crisis ‘avoidable’
Although the Biden administration’s COVID-19 strategy is moving in the right direction, says Atul Grover, MD, PhD, executive director of the AAMC Research and Action Institute, the branch of the association that prepared the report, “the severity of this phase of the COVID-19 pandemic was avoidable.”
According to the report, only the federal government can provide the level of coordination that is needed across states and international borders to fight the virus successfully. “The response should not rely on a piecemeal approach that varies by locality and region.”
In the absence of clear federal leadership during the pandemic’s earlier phase, the report states, “key policies were either absent or conflicting across states, counties, and municipalities. Without federal direction and coordination, states were forced to compete against each other (and, sometimes, against the federal government) for supplies.”
As a recent Kaiser Health News report shows, the states are still falling short on the COVID-19 front: For example, at least 26 states have restricted the ability of their public health authorities to take action against COVID in various ways.
In an interview, William Schaffner, MD, a professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., agrees on the need for the federal government to lead the COVID fight.
Noting that the cooperation of states with each other and with the national government is voluntary, Dr. Schaffner asserted that “subcontracting [the COVID response] to the states doesn’t work. That results in chaos and a crazy quilt of responses that persists to this day.”
Inadequate control of COVID effort
Within the federal government, the AAMC report maintains, the White House must be directly in charge of coordinating the fight against the pandemic. The AAMC calls for the establishment of a top-level office or a coordinating team to lead the COVID effort, similar to what was done during the 2014-2015 Ebola outbreak.
Earlier this year, President Biden appointed Jeffrey Zients as White House Coronavirus Response Coordinator, succeeding Deborah Birx, MD, in that role. Dr. Grover was asked in an interview why that doesn’t meet AAMC’s requirements.
“Jeff and his team are doing a good job,” Dr. Grover said. “But the reason I think we could be doing a better job is that the messaging has not been consistent across agencies and across the federal government.”
“Jeff may not have the authority to overrule individual decisions and to ensure that all decisions are integrated across organizations. Maybe that is happening, but it’s not clear to those of us who are not in the meetings every day. At a minimum, we’ve got to get the messaging right, and it needs to be more transparent.”
Dr. Grover cites a recent press conference by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention about the national strategy for vaccine booster shots. “No one from the FDA was there,” he said. “Theoretically, [the] FDA has signed off on boosters, but their scientists were caught off guard. The administration’s messaging needs to be consistent, and that would be more likely if someone were in charge of these agencies overall,” Dr. Grover said.
Dr. Schaffner said he prefers not to comment on this point, “but I won’t argue with the observation.”
Supplies still not adequate
In light of the medical supply shortages that have plagued the COVID-19 response, the AAMC report recommends that the federal government ensure an effective supply chain for all critical goods and materials, starting with the Strategic National Stockpile (SNS), which was created in 1999 to supplement state and local medical supplies during public health emergencies.
“The SNS should enable the nation to support care for a minimum number of critically ill patients until the federal government can assure an adequate functional supply chain for a short period of time,” the AAMC report states.
The SNS was not replenished after the 2009 H1N1 pandemic and wasn’t prepared for the COVID-19 emergency, according to the report. “Despite having built up the supply over the last year, the nation is just one major outbreak or incident away from another monumental shortage of very basic needs such as gloves, masks, and gowns.”
Dr. Grover said the national stockpile now has more gowns and gloves than it did at the pandemic’s start. But he’s concerned about what might happen if a new type of pathogen emerged. “If we were to face the same kind of COVID surge we’re now facing in the unvaccinated communities more broadly across the U.S. – for example, if we got another variant that was even more infectious or deadly – I’m not sure we’d be prepared.”
Just-in-time purchasing
Hospitals were caught short when COVID struck because of their just-in-time supply chain approach, which relied on punctual deliveries of new supplies and equipment, the report states. Of course, when demand soared and every provider was competing for scarce supplies, that didn’t happen.
Now, Dr. Grover pointed out, there is still no central system to keep track of where PPE, ventilators, oxygen tanks, and other critical items are in the supply chains of hospitals and physician practices.
So, even if policymakers determined that the nation should use both the SNS and private locations to stockpile enough supplies to care for a certain number of patients for a period of time, there wouldn’t be any way to determine what was on hand or where it was stored.
Moreover, while hospitals have built up their stockpiles to prepare for new COVID surges, he expects them to go back to just-in-time purchasing when the pandemic wanes. Although health care organizations want to take good care of patients, they have financial and physical constraints on how many supplies they can store, Dr. Grover said.
Testing conundrum
An analogous challenge exists for companies that make COVID-19 tests, Dr. Grover said. “The testing companies don’t want to produce more than they’re going to be able to sell. They’re a for-profit industry.” Partly as a result, the nation has never had as many tests as it needs, according to the report.
To solve this problem, the report authors suggest that the federal government take an approach similar to that of the Trump administration’s Operation Warp Speed (OWS), which used advance funding and vaccine prepurchases to spur development.
“The CDC is unlikely to meet testing demands in future outbreaks and pandemics using existing public health lab partnerships, even under the best conditions. Industry was reluctant to mass produce testing kits for fear demand would fail to materialize; an OWS-like advance purchasing strategy and investment in private production could have reduced the spread of COVID-19 and will be critical in mitigating a future outbreak or pandemic.”
Public health infrastructure
The report also calls for Congress to appropriate “robust and continuous funding for public health infrastructure … Chronic underfunding of public health has hurt the nation’s emergency preparedness framework and contributes to health inequity.”
This applies not only to federal funding but also to state and local funding, which has primarily been allocated on a crisis-response basis, the report states.
Dr. Grover is glad that the fiscal 2022 budget legislation includes $15 billion to finance this infrastructure, but that’s only a start, he said.
Dr. Schaffner stresses the importance of improving the IT infrastructure of public health agencies. “We need a better, higher-quality mechanism for quickly gathering critical data from doctors’ offices and hospitals and sending that information through a public health stream so it can be gathered.”
“Today, data come in at the national level, sometimes slowly, sometimes in fragmented fashion, from different jurisdictions around the country, and it’s very difficult to make secure statements and plan effectively.”
Dr. Schaffner agrees with the report’s emphasis on the need for long-term planning to prepare for the next pandemic but is pessimistic about the odds of it occurring.
“This challenges us as Americans. We have notoriously short attention spans. And we like to put difficult things behind us and look to the future,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should I get a COVID-19 booster shot?
When I was in Florida a few weeks ago, I met a friend outside who approached me wearing an N-95 mask. He said he was wearing it because the Delta variant was running wild in Florida, and several of his younger unvaccinated employees had contracted it, and he encouraged me to get a COVID booster shot. In the late summer, although the federal government recommended booster shots for anyone 8 months after their original vaccination series, national confusion still reigns, with an Food and Drug Administration advisory panel more recently recommending against a Pfizer booster for all adults, but supporting a booster for those ages 65 and older or at a high risk for severe COVID-19.
At the end of December, I was excited when the local hospital whose staff I am on made the Moderna vaccine available. I had to wait several hours but it was worth it, and I did not care about the low-grade fever and malaise I experienced after the second dose. Astoundingly, I still have patients who have not been vaccinated, although many of them are elderly, frail, or immunocompromised. I think people who publicly argue against vaccination need to visit their local intensive care unit.
While less so than some other physicians, – and you must lean in to see anything. We take all reasonable precautions, wearing masks, wiping down exam rooms and door handles, keeping the waiting room as empty as possible, using HEPA filters, and keeping exhaust fans going in the rooms continuously. My staff have all been vaccinated (I’m lucky there).
Still, if you are seeing 30 or 40 patients a day of all age groups and working in small unventilated rooms, you could be exposed to the Delta variant. While breakthrough infections among fully vaccinated immunocompetent individuals may be rare, if you do develop a breakthrough case, even if mild or asymptomatic, CDC recommendations include quarantining for at least 10 days. Obviously, this can be disastrous to your practice as a COVID infection works through your office.
This brings us to back to booster shots. Personally, I think all health care workers should be eager to get a booster shot. I also think individuals who have wide public exposure, particularly indoors, such as teachers and retail sales workers, should be eager to get one too. Here are some of the pros, as well as some cons for boosters.
Arguments for booster shots
- Booster shots should elevate your antibody levels and make you more resistant to breakthrough infections, but this is still theoretical. Antibody levels decline over time – more rapidly in those over 56 years of age.
- Vaccine doses go to waste every month in the United States, although specific numbers are lacking.
- Vaccinated individuals almost never get hospitalized and die from COVID, presumably even fewer do so after receiving a booster.
- You could unwittingly become a vector. Many of the breakthrough infections are mild and without symptoms. If you do test positive, it could be devastating to your patients, and your medical practice.
Arguments against booster shots
- These vaccine doses should be going to other countries that have low vaccination levels where many of the nasty variants are developing.
- You may have side effects from the vaccine, though thrombosis has only been seen with the Astra-Zeneca and Johnson and Johnson vaccines. Myocarditis is usually seen in younger patients and is almost always self limited.
- Breakthrough infections are rare.
This COVID pandemic is moving and changing so fast, it is bewildering. But with a little luck, COVID could eventually become an annual nuisance like the flu, and the COVID vaccine will become an annual shot based on the newest mutations. For now, my opinion is, get your booster shot.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected].
When I was in Florida a few weeks ago, I met a friend outside who approached me wearing an N-95 mask. He said he was wearing it because the Delta variant was running wild in Florida, and several of his younger unvaccinated employees had contracted it, and he encouraged me to get a COVID booster shot. In the late summer, although the federal government recommended booster shots for anyone 8 months after their original vaccination series, national confusion still reigns, with an Food and Drug Administration advisory panel more recently recommending against a Pfizer booster for all adults, but supporting a booster for those ages 65 and older or at a high risk for severe COVID-19.
At the end of December, I was excited when the local hospital whose staff I am on made the Moderna vaccine available. I had to wait several hours but it was worth it, and I did not care about the low-grade fever and malaise I experienced after the second dose. Astoundingly, I still have patients who have not been vaccinated, although many of them are elderly, frail, or immunocompromised. I think people who publicly argue against vaccination need to visit their local intensive care unit.
While less so than some other physicians, – and you must lean in to see anything. We take all reasonable precautions, wearing masks, wiping down exam rooms and door handles, keeping the waiting room as empty as possible, using HEPA filters, and keeping exhaust fans going in the rooms continuously. My staff have all been vaccinated (I’m lucky there).
Still, if you are seeing 30 or 40 patients a day of all age groups and working in small unventilated rooms, you could be exposed to the Delta variant. While breakthrough infections among fully vaccinated immunocompetent individuals may be rare, if you do develop a breakthrough case, even if mild or asymptomatic, CDC recommendations include quarantining for at least 10 days. Obviously, this can be disastrous to your practice as a COVID infection works through your office.
This brings us to back to booster shots. Personally, I think all health care workers should be eager to get a booster shot. I also think individuals who have wide public exposure, particularly indoors, such as teachers and retail sales workers, should be eager to get one too. Here are some of the pros, as well as some cons for boosters.
Arguments for booster shots
- Booster shots should elevate your antibody levels and make you more resistant to breakthrough infections, but this is still theoretical. Antibody levels decline over time – more rapidly in those over 56 years of age.
- Vaccine doses go to waste every month in the United States, although specific numbers are lacking.
- Vaccinated individuals almost never get hospitalized and die from COVID, presumably even fewer do so after receiving a booster.
- You could unwittingly become a vector. Many of the breakthrough infections are mild and without symptoms. If you do test positive, it could be devastating to your patients, and your medical practice.
Arguments against booster shots
- These vaccine doses should be going to other countries that have low vaccination levels where many of the nasty variants are developing.
- You may have side effects from the vaccine, though thrombosis has only been seen with the Astra-Zeneca and Johnson and Johnson vaccines. Myocarditis is usually seen in younger patients and is almost always self limited.
- Breakthrough infections are rare.
This COVID pandemic is moving and changing so fast, it is bewildering. But with a little luck, COVID could eventually become an annual nuisance like the flu, and the COVID vaccine will become an annual shot based on the newest mutations. For now, my opinion is, get your booster shot.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected].
When I was in Florida a few weeks ago, I met a friend outside who approached me wearing an N-95 mask. He said he was wearing it because the Delta variant was running wild in Florida, and several of his younger unvaccinated employees had contracted it, and he encouraged me to get a COVID booster shot. In the late summer, although the federal government recommended booster shots for anyone 8 months after their original vaccination series, national confusion still reigns, with an Food and Drug Administration advisory panel more recently recommending against a Pfizer booster for all adults, but supporting a booster for those ages 65 and older or at a high risk for severe COVID-19.
At the end of December, I was excited when the local hospital whose staff I am on made the Moderna vaccine available. I had to wait several hours but it was worth it, and I did not care about the low-grade fever and malaise I experienced after the second dose. Astoundingly, I still have patients who have not been vaccinated, although many of them are elderly, frail, or immunocompromised. I think people who publicly argue against vaccination need to visit their local intensive care unit.
While less so than some other physicians, – and you must lean in to see anything. We take all reasonable precautions, wearing masks, wiping down exam rooms and door handles, keeping the waiting room as empty as possible, using HEPA filters, and keeping exhaust fans going in the rooms continuously. My staff have all been vaccinated (I’m lucky there).
Still, if you are seeing 30 or 40 patients a day of all age groups and working in small unventilated rooms, you could be exposed to the Delta variant. While breakthrough infections among fully vaccinated immunocompetent individuals may be rare, if you do develop a breakthrough case, even if mild or asymptomatic, CDC recommendations include quarantining for at least 10 days. Obviously, this can be disastrous to your practice as a COVID infection works through your office.
This brings us to back to booster shots. Personally, I think all health care workers should be eager to get a booster shot. I also think individuals who have wide public exposure, particularly indoors, such as teachers and retail sales workers, should be eager to get one too. Here are some of the pros, as well as some cons for boosters.
Arguments for booster shots
- Booster shots should elevate your antibody levels and make you more resistant to breakthrough infections, but this is still theoretical. Antibody levels decline over time – more rapidly in those over 56 years of age.
- Vaccine doses go to waste every month in the United States, although specific numbers are lacking.
- Vaccinated individuals almost never get hospitalized and die from COVID, presumably even fewer do so after receiving a booster.
- You could unwittingly become a vector. Many of the breakthrough infections are mild and without symptoms. If you do test positive, it could be devastating to your patients, and your medical practice.
Arguments against booster shots
- These vaccine doses should be going to other countries that have low vaccination levels where many of the nasty variants are developing.
- You may have side effects from the vaccine, though thrombosis has only been seen with the Astra-Zeneca and Johnson and Johnson vaccines. Myocarditis is usually seen in younger patients and is almost always self limited.
- Breakthrough infections are rare.
This COVID pandemic is moving and changing so fast, it is bewildering. But with a little luck, COVID could eventually become an annual nuisance like the flu, and the COVID vaccine will become an annual shot based on the newest mutations. For now, my opinion is, get your booster shot.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected].
When children and teens with cancer get COVID-19
Although most children and adolescents with cancer have mild illness from COVID-19 infection, some do experience severe disease and a small percentage even die, according to a recent analysis.
The findings, published online in Lancet Oncology, represent the first global registry data spanning different income groups to report COVID-19 outcomes in pediatric oncology patients.
“We wanted to create a global pool of evidence to answer the question: Do we see severe [COVID-19] infection [in children with cancer]?” corresponding author Sheena Mukkada, MD, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, said in an interview.
In a cohort of 1,319 pediatric patients followed for 30 days, Dr. Mukkada and colleagues reported that 80% of these patients had asymptomatic to moderate disease from COVID-19, while 1 in 5 experienced severe or critical illness and almost 4% died – four times the mortality rate observed in published cohorts of general pediatric patients.
The results highlight that “children and adolescents with cancer generally recover without incident from COVID-19, but can have a severe course of infection,” the authors concluded.
And knowing that some children can get very sick, investigators wanted “to identify who these patients are so that we can prioritize and protect that group,” she added.
Echoing that sentiment, Kathy Pritchard-Jones, MD, president of the International Society of Paediatric Oncology and coauthor on the study, noted in a press release that, “by working together to create this global registry, we have enabled hospitals around the world to rapidly share and learn how COVID-19 is affecting children with cancer.”
Dr. Pritchard-Jones commented that overall these results provide reassurance that “many children can continue their cancer treatment safely, but they also highlight important clinical features that may predict a more severe clinical course and the need for greater vigilance for some patients.”
Inside the Global Registry data
The Global Registry of COVID-19 in Childhood Cancer, created jointly by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital and SIOP, included data from 131 institutions in 45 countries. Children recruited into the registry between April 2020 and February 2021 ranged in age from infancy to 18 years old.
Most patients remained asymptomatic (35%) or experienced mild to moderate illness (45%), though 20% did develop severe or critical illness.
The investigators highlighted several factors associated with a greater risk of developing more severe illness from COVID-19, which included cancer type, intensity of therapy, age, absolute lymphocyte count, and presence of comorbidities or COVID-19 symptoms.
Notably, more than 80% of either severe or critical infections occurred in patients with hematologic malignancies – with 56% of cases in patients with acute lymphoblastic lymphoma or acute lymphoblastic leukemia – followed by extracranial solid tumors (15.8%), and central nervous system tumors (2.7%).
In patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or acute lymphoblastic lymphoma, severe or critical disease was most common in those receiving induction therapy (30%), relapse or refractory therapy (30%), and those in the maintenance or continuation phase of therapy (19%).
Older age was associated with a higher likelihood of having severe disease – with the lowest risk in infants (9.7%) and the highest in the 15- to 18-year-old cohort (27.3%).
Patients with lymphopenia who had an absolute lymphocyte count of 300 cells per mm3 or less and an absolute neutrophil count of 500 cells per mm3 or more also had an elevated risk of severe illness from COVID-19.
Regarding whether the presence of lymphopenia or neutropenia should change the treatment approach, Dr. Mukkada noted that, when possible, these patients should receive antiviral treatment, such as remdesivir, if the center has antivirals, or be prioritized for hospital admission.
Modifying cancer treatment might be recommended if patients are highly lymphopenic or have very low neutrophil counts, but a more effective strategy is simply to ensure that age-eligible children and adolescents with cancer or who have had a hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. For children who are not yet age-eligible, everyone around them should be vaccinated.
Pediatric patients in low- and middle-income countries were also more likely to have severe or critical outcomes from COVID-19 (41.7%), compared with patients in other income groups (23.9%).
The impact of COVID-19 “has been felt in every corner of the world, but particularly in low- and middle-income countries, compared to high-income countries,” senior author Carlos Rodriguez-Galindo, MD, global director at St. Jude, said in a statement.
In terms of the intersection of cancer treatment and COVID diagnosis, almost 83% of pediatric patients were receiving treatment for their cancer. Chemotherapy was withheld in about 45% of these patients and some modification to the treatment regimen occurred in almost 56% of participants on active therapy.
“Treatment modifications were least common in patients from upper-middle–income countries, compared with other income groups,” the authors wrote.
Although an interesting observation, Dr. Mukkada noted that the registry data could not explain why treatment modifications occurred less frequently in upper-middle income countries as opposed to high-income and lower-income countries.
U.K. Monitoring Project
Not all studies, however, have found that COVID-19 infection is significantly more severe in children with cancer. In a 2020 report from the U.K. Paediatric Coronavirus Cancer Monitoring Project, researchers evaluated all children in the United Kingdom under the age of 16 diagnosed with COVID and cancer.
“[Given that] we had complete coverage of every center in the U.K. that cares for children with cancer, we are confident that we picked up at least all the severe or critical cases,” lead author Gerard Millen, MD, honorary clinical research fellow, University of Birmingham (England), said in an interview.
Between March 2020 and July 2020, Dr. Millen and colleagues identified 54 positive cases of COVID-19, 15 (28%) of which were asymptomatic, 34 (63%) mild, and 4 (7.4%) severe or critical – more in line with the incidence of severe illness reported in the general pediatric population.
“Thankfully, we had no children with cancer in the U.K. who died from COVID-19,” Dr. Millen noted. “Overall, in the U.K., we have taken the approach that the majority of children with cancer in this country are at very low risk from COVID-19 and that we do not have good evidence to modify their treatment.”
Dr. Millen pointed out that the data in the U.K. study were “remarkably similar” to those from the high-income countries in the global St. Jude/SIOP cohort, where 7.4% of patients in that cohort had severe or critical disease, compared with 7.4% of patients from their own U.K. cohort.
“I think many of the key differences between the two cohorts reflect the fact that access to treatment in many low- to middle-income countries is more challenging with many factors contributing to overall poorer outcomes for both cancer and noncancer metrics,” Dr. Millen said.
Both the U.K. and registry studies were performed prior to vaccinations becoming available to older children, and before the emergence of certain variants, including the Delta variant, which is responsible for the most recent surge of COVID-19 infections around the world.
Data on COVID-19 vaccination in children with cancer are limited but promising so far.
As for whether the Delta variant might affect outcomes for children with cancer and COVID-19, Dr. Mukkada could only speculate, but she noted that “what we are hearing anecdotally about the [Delta] disease being more severe, even in patients who don’t have cancer, is leading us to say that we can’t close the registry yet. We are still actively enrolling children.”
The study was funded by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities and the National Cancer Institute. The study authors and Dr. Millen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although most children and adolescents with cancer have mild illness from COVID-19 infection, some do experience severe disease and a small percentage even die, according to a recent analysis.
The findings, published online in Lancet Oncology, represent the first global registry data spanning different income groups to report COVID-19 outcomes in pediatric oncology patients.
“We wanted to create a global pool of evidence to answer the question: Do we see severe [COVID-19] infection [in children with cancer]?” corresponding author Sheena Mukkada, MD, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, said in an interview.
In a cohort of 1,319 pediatric patients followed for 30 days, Dr. Mukkada and colleagues reported that 80% of these patients had asymptomatic to moderate disease from COVID-19, while 1 in 5 experienced severe or critical illness and almost 4% died – four times the mortality rate observed in published cohorts of general pediatric patients.
The results highlight that “children and adolescents with cancer generally recover without incident from COVID-19, but can have a severe course of infection,” the authors concluded.
And knowing that some children can get very sick, investigators wanted “to identify who these patients are so that we can prioritize and protect that group,” she added.
Echoing that sentiment, Kathy Pritchard-Jones, MD, president of the International Society of Paediatric Oncology and coauthor on the study, noted in a press release that, “by working together to create this global registry, we have enabled hospitals around the world to rapidly share and learn how COVID-19 is affecting children with cancer.”
Dr. Pritchard-Jones commented that overall these results provide reassurance that “many children can continue their cancer treatment safely, but they also highlight important clinical features that may predict a more severe clinical course and the need for greater vigilance for some patients.”
Inside the Global Registry data
The Global Registry of COVID-19 in Childhood Cancer, created jointly by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital and SIOP, included data from 131 institutions in 45 countries. Children recruited into the registry between April 2020 and February 2021 ranged in age from infancy to 18 years old.
Most patients remained asymptomatic (35%) or experienced mild to moderate illness (45%), though 20% did develop severe or critical illness.
The investigators highlighted several factors associated with a greater risk of developing more severe illness from COVID-19, which included cancer type, intensity of therapy, age, absolute lymphocyte count, and presence of comorbidities or COVID-19 symptoms.
Notably, more than 80% of either severe or critical infections occurred in patients with hematologic malignancies – with 56% of cases in patients with acute lymphoblastic lymphoma or acute lymphoblastic leukemia – followed by extracranial solid tumors (15.8%), and central nervous system tumors (2.7%).
In patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or acute lymphoblastic lymphoma, severe or critical disease was most common in those receiving induction therapy (30%), relapse or refractory therapy (30%), and those in the maintenance or continuation phase of therapy (19%).
Older age was associated with a higher likelihood of having severe disease – with the lowest risk in infants (9.7%) and the highest in the 15- to 18-year-old cohort (27.3%).
Patients with lymphopenia who had an absolute lymphocyte count of 300 cells per mm3 or less and an absolute neutrophil count of 500 cells per mm3 or more also had an elevated risk of severe illness from COVID-19.
Regarding whether the presence of lymphopenia or neutropenia should change the treatment approach, Dr. Mukkada noted that, when possible, these patients should receive antiviral treatment, such as remdesivir, if the center has antivirals, or be prioritized for hospital admission.
Modifying cancer treatment might be recommended if patients are highly lymphopenic or have very low neutrophil counts, but a more effective strategy is simply to ensure that age-eligible children and adolescents with cancer or who have had a hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. For children who are not yet age-eligible, everyone around them should be vaccinated.
Pediatric patients in low- and middle-income countries were also more likely to have severe or critical outcomes from COVID-19 (41.7%), compared with patients in other income groups (23.9%).
The impact of COVID-19 “has been felt in every corner of the world, but particularly in low- and middle-income countries, compared to high-income countries,” senior author Carlos Rodriguez-Galindo, MD, global director at St. Jude, said in a statement.
In terms of the intersection of cancer treatment and COVID diagnosis, almost 83% of pediatric patients were receiving treatment for their cancer. Chemotherapy was withheld in about 45% of these patients and some modification to the treatment regimen occurred in almost 56% of participants on active therapy.
“Treatment modifications were least common in patients from upper-middle–income countries, compared with other income groups,” the authors wrote.
Although an interesting observation, Dr. Mukkada noted that the registry data could not explain why treatment modifications occurred less frequently in upper-middle income countries as opposed to high-income and lower-income countries.
U.K. Monitoring Project
Not all studies, however, have found that COVID-19 infection is significantly more severe in children with cancer. In a 2020 report from the U.K. Paediatric Coronavirus Cancer Monitoring Project, researchers evaluated all children in the United Kingdom under the age of 16 diagnosed with COVID and cancer.
“[Given that] we had complete coverage of every center in the U.K. that cares for children with cancer, we are confident that we picked up at least all the severe or critical cases,” lead author Gerard Millen, MD, honorary clinical research fellow, University of Birmingham (England), said in an interview.
Between March 2020 and July 2020, Dr. Millen and colleagues identified 54 positive cases of COVID-19, 15 (28%) of which were asymptomatic, 34 (63%) mild, and 4 (7.4%) severe or critical – more in line with the incidence of severe illness reported in the general pediatric population.
“Thankfully, we had no children with cancer in the U.K. who died from COVID-19,” Dr. Millen noted. “Overall, in the U.K., we have taken the approach that the majority of children with cancer in this country are at very low risk from COVID-19 and that we do not have good evidence to modify their treatment.”
Dr. Millen pointed out that the data in the U.K. study were “remarkably similar” to those from the high-income countries in the global St. Jude/SIOP cohort, where 7.4% of patients in that cohort had severe or critical disease, compared with 7.4% of patients from their own U.K. cohort.
“I think many of the key differences between the two cohorts reflect the fact that access to treatment in many low- to middle-income countries is more challenging with many factors contributing to overall poorer outcomes for both cancer and noncancer metrics,” Dr. Millen said.
Both the U.K. and registry studies were performed prior to vaccinations becoming available to older children, and before the emergence of certain variants, including the Delta variant, which is responsible for the most recent surge of COVID-19 infections around the world.
Data on COVID-19 vaccination in children with cancer are limited but promising so far.
As for whether the Delta variant might affect outcomes for children with cancer and COVID-19, Dr. Mukkada could only speculate, but she noted that “what we are hearing anecdotally about the [Delta] disease being more severe, even in patients who don’t have cancer, is leading us to say that we can’t close the registry yet. We are still actively enrolling children.”
The study was funded by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities and the National Cancer Institute. The study authors and Dr. Millen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although most children and adolescents with cancer have mild illness from COVID-19 infection, some do experience severe disease and a small percentage even die, according to a recent analysis.
The findings, published online in Lancet Oncology, represent the first global registry data spanning different income groups to report COVID-19 outcomes in pediatric oncology patients.
“We wanted to create a global pool of evidence to answer the question: Do we see severe [COVID-19] infection [in children with cancer]?” corresponding author Sheena Mukkada, MD, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, said in an interview.
In a cohort of 1,319 pediatric patients followed for 30 days, Dr. Mukkada and colleagues reported that 80% of these patients had asymptomatic to moderate disease from COVID-19, while 1 in 5 experienced severe or critical illness and almost 4% died – four times the mortality rate observed in published cohorts of general pediatric patients.
The results highlight that “children and adolescents with cancer generally recover without incident from COVID-19, but can have a severe course of infection,” the authors concluded.
And knowing that some children can get very sick, investigators wanted “to identify who these patients are so that we can prioritize and protect that group,” she added.
Echoing that sentiment, Kathy Pritchard-Jones, MD, president of the International Society of Paediatric Oncology and coauthor on the study, noted in a press release that, “by working together to create this global registry, we have enabled hospitals around the world to rapidly share and learn how COVID-19 is affecting children with cancer.”
Dr. Pritchard-Jones commented that overall these results provide reassurance that “many children can continue their cancer treatment safely, but they also highlight important clinical features that may predict a more severe clinical course and the need for greater vigilance for some patients.”
Inside the Global Registry data
The Global Registry of COVID-19 in Childhood Cancer, created jointly by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital and SIOP, included data from 131 institutions in 45 countries. Children recruited into the registry between April 2020 and February 2021 ranged in age from infancy to 18 years old.
Most patients remained asymptomatic (35%) or experienced mild to moderate illness (45%), though 20% did develop severe or critical illness.
The investigators highlighted several factors associated with a greater risk of developing more severe illness from COVID-19, which included cancer type, intensity of therapy, age, absolute lymphocyte count, and presence of comorbidities or COVID-19 symptoms.
Notably, more than 80% of either severe or critical infections occurred in patients with hematologic malignancies – with 56% of cases in patients with acute lymphoblastic lymphoma or acute lymphoblastic leukemia – followed by extracranial solid tumors (15.8%), and central nervous system tumors (2.7%).
In patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or acute lymphoblastic lymphoma, severe or critical disease was most common in those receiving induction therapy (30%), relapse or refractory therapy (30%), and those in the maintenance or continuation phase of therapy (19%).
Older age was associated with a higher likelihood of having severe disease – with the lowest risk in infants (9.7%) and the highest in the 15- to 18-year-old cohort (27.3%).
Patients with lymphopenia who had an absolute lymphocyte count of 300 cells per mm3 or less and an absolute neutrophil count of 500 cells per mm3 or more also had an elevated risk of severe illness from COVID-19.
Regarding whether the presence of lymphopenia or neutropenia should change the treatment approach, Dr. Mukkada noted that, when possible, these patients should receive antiviral treatment, such as remdesivir, if the center has antivirals, or be prioritized for hospital admission.
Modifying cancer treatment might be recommended if patients are highly lymphopenic or have very low neutrophil counts, but a more effective strategy is simply to ensure that age-eligible children and adolescents with cancer or who have had a hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. For children who are not yet age-eligible, everyone around them should be vaccinated.
Pediatric patients in low- and middle-income countries were also more likely to have severe or critical outcomes from COVID-19 (41.7%), compared with patients in other income groups (23.9%).
The impact of COVID-19 “has been felt in every corner of the world, but particularly in low- and middle-income countries, compared to high-income countries,” senior author Carlos Rodriguez-Galindo, MD, global director at St. Jude, said in a statement.
In terms of the intersection of cancer treatment and COVID diagnosis, almost 83% of pediatric patients were receiving treatment for their cancer. Chemotherapy was withheld in about 45% of these patients and some modification to the treatment regimen occurred in almost 56% of participants on active therapy.
“Treatment modifications were least common in patients from upper-middle–income countries, compared with other income groups,” the authors wrote.
Although an interesting observation, Dr. Mukkada noted that the registry data could not explain why treatment modifications occurred less frequently in upper-middle income countries as opposed to high-income and lower-income countries.
U.K. Monitoring Project
Not all studies, however, have found that COVID-19 infection is significantly more severe in children with cancer. In a 2020 report from the U.K. Paediatric Coronavirus Cancer Monitoring Project, researchers evaluated all children in the United Kingdom under the age of 16 diagnosed with COVID and cancer.
“[Given that] we had complete coverage of every center in the U.K. that cares for children with cancer, we are confident that we picked up at least all the severe or critical cases,” lead author Gerard Millen, MD, honorary clinical research fellow, University of Birmingham (England), said in an interview.
Between March 2020 and July 2020, Dr. Millen and colleagues identified 54 positive cases of COVID-19, 15 (28%) of which were asymptomatic, 34 (63%) mild, and 4 (7.4%) severe or critical – more in line with the incidence of severe illness reported in the general pediatric population.
“Thankfully, we had no children with cancer in the U.K. who died from COVID-19,” Dr. Millen noted. “Overall, in the U.K., we have taken the approach that the majority of children with cancer in this country are at very low risk from COVID-19 and that we do not have good evidence to modify their treatment.”
Dr. Millen pointed out that the data in the U.K. study were “remarkably similar” to those from the high-income countries in the global St. Jude/SIOP cohort, where 7.4% of patients in that cohort had severe or critical disease, compared with 7.4% of patients from their own U.K. cohort.
“I think many of the key differences between the two cohorts reflect the fact that access to treatment in many low- to middle-income countries is more challenging with many factors contributing to overall poorer outcomes for both cancer and noncancer metrics,” Dr. Millen said.
Both the U.K. and registry studies were performed prior to vaccinations becoming available to older children, and before the emergence of certain variants, including the Delta variant, which is responsible for the most recent surge of COVID-19 infections around the world.
Data on COVID-19 vaccination in children with cancer are limited but promising so far.
As for whether the Delta variant might affect outcomes for children with cancer and COVID-19, Dr. Mukkada could only speculate, but she noted that “what we are hearing anecdotally about the [Delta] disease being more severe, even in patients who don’t have cancer, is leading us to say that we can’t close the registry yet. We are still actively enrolling children.”
The study was funded by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities and the National Cancer Institute. The study authors and Dr. Millen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 causes major interruption in global HIV progress
“We’ve been set back by COVID but we’ve seen remarkable resilience, a lot of innovation and creativity,” Siobhan Crowley MD, head of HIV at the Global Fund, said in an interview.
“If you consider that 21.9 million people are getting antiretrovirals at this point through the Global Fund, I think that needs to be appreciated. Ten years ago, that wouldn’t have been the case; all of those people would have disappeared into the ethers,” she said.
Through close partnerships with the U.S. Agency for International Development, the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief, and other Western countries and organizations, the Global Fund has invested $22.7 billion in programs to prevent and treat HIV and AIDS, and $3.8 billion in tuberculosis (TB)/HIV programs, according to the organization’s 2021 Results Report.
But the report also underscores the significant effect that the COVID-19 pandemic has had on funded countries’ progress toward achieving renewed 90-90-90 targets for HIV testing/diagnosis, treatment, and viral suppression by 2030.
The setbacks have been challenging and have touched nearly every service from prevention to treatment. According to the report, between 2019 and 2020:
- Voluntary male circumcision declined by 27%.
- Numbers reached by HIV prevention programs fell by 11%.
- 4.5% fewer mothers received medications to prevent HIV transmission to their babies.
- HIV testing services, including initiation, decreased by 22%.
The numbers tell only a part of the story, according to Dr. Crowley.
“We put in place an emergency mechanism to make funds available for countries to do everything except vaccines in support of COVID,” Dr. Crowley explained. (As of August 2021, these funds had been allocated to 107 countries and 16 multicountry programs.)
Countries were advised that they could use the emergency funds three different ways: 1) for COVID-specific purposes (e.g., diagnostics, oxygen, personal protective equipment; 2) to support mitigation strategies geared toward protecting existing HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria programs and getting them back on track; and 3) for so-called “health system fixes,” such as investing in data systems to track COVID, HIV, and other core diseases, as well as the community workforce.
With regard to HIV, each country supported by the Global Fund was asked to ensure that multimonth (3-6 months) dispensing was implemented and/or accelerated so that patients could avoid congested facilities, and, wherever possible, that drugs were delivered or accessed outside the facility. One example of the success of this effort was found in South Africa, where the number of people on antiretrovirals increased almost threefold, from 1.2 million to 4.2 million people.
Countries also were asked to adapt HIV testing procedures by, for example, moving organized testing out of the facilities and into neighborhoods to meet people where they are. Rapid diagnostic testing and triage care linkage using technologies such as WhatsApp were the result, as were opportunities for home testing which, Dr. Crowley noted, remains a critical component of the overall strategy.
“The self-test is important for two reasons, not just because you are trying to find people with HIV, but also, when people know that they’re negative, they know what they can or should do to stay negative,” she said. “It’s quite a powerful motivator.”
Self-testing might also help countries motivate the 6 million people who know that they have HIV but are not on treatment. But there are still 4.1 million residing in these countries who aren’t aware that they are infected, according to the report. This figure is especially troubling, considering that some may also be harboring TB coinfections, including multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).
The imperfect storm globally and in the U.S.
“One of the things that was striking in the report was the decline in the number of people reached with testing and prevention services,” Chris Beyrer, MD, MPH, the Desmond M. Tutu Professor of Public Health and Human Rights at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, said in an interview. Dr. Beyrer was not involved in the report’s development.
“You know, a 10% decline in 1 year to reach people in need is substantial,” he said. “Let’s say it continues; many people are predicting that we won’t have reasonable coverage for low-income countries with COVID until 2023. That adds up to a substantial decline in people reached with these services.”
Dr. Beyrer also expressed concern about the convergence of HIV and TB in already overburdened, fragile health care systems. “Globally, the No. 1 cause of death for people living with HIV is TB, and of course, it’s highly transmissible. So, in many high-burden countries, children are exposed, typically from household members early on, and so the number of people with latent TB infection is just enormous.
“If you look at the report, the worst outcomes are MDR-TB. Those multidrug-resistant and extensively-drug-resistant strains are really a threat to everybody,” Dr. Beyrer said.
But it’s not time for U.S. providers to rest on their laurels either. Dr. Beyrer noted that the 22% decline in HIV testing reported by the Global Fund is similar to what has been happening in the United States with elective procedures such as HIV testing and even preventive procedures like medical male circumcision.
“It’s very clear here in the Global Fund data that the majority of new infections worldwide are in key populations [that] include gay and bisexual men, men who have sex with men, transgender women who have sex with men, people who inject drugs, and sex workers of all genders. Those are people who already faced barriers to health care access and were made worse by COVID.”
Dr. Beyrer noted that, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in 2019 in the United States, 68% of new HIV infections occurred in gay and bisexual men, and the effect that COVID-19 will have is still unknown. He also noted the similarity between the most marginalized populations in the Global Fund report and African American men, who have not realized the same increase in the use of preexposure prophylaxis or the same decline in new infections as have their White counterparts.
“It’s also where we are seeing the worst of COVID, low immunization coverage, and high rates of hospitalization and death. ... It’s a dark, dark time for many,” Dr. Crowley said. “And there has also been some amazing resilience and adaptation. The weird thing is, the HIV platform is a natural platform; I mean, if we can keep 21.9 million people on treatment, we can probably deliver them a COVID test and a vaccine.”
Dr. Crowley and Dr. Beyrer report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“We’ve been set back by COVID but we’ve seen remarkable resilience, a lot of innovation and creativity,” Siobhan Crowley MD, head of HIV at the Global Fund, said in an interview.
“If you consider that 21.9 million people are getting antiretrovirals at this point through the Global Fund, I think that needs to be appreciated. Ten years ago, that wouldn’t have been the case; all of those people would have disappeared into the ethers,” she said.
Through close partnerships with the U.S. Agency for International Development, the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief, and other Western countries and organizations, the Global Fund has invested $22.7 billion in programs to prevent and treat HIV and AIDS, and $3.8 billion in tuberculosis (TB)/HIV programs, according to the organization’s 2021 Results Report.
But the report also underscores the significant effect that the COVID-19 pandemic has had on funded countries’ progress toward achieving renewed 90-90-90 targets for HIV testing/diagnosis, treatment, and viral suppression by 2030.
The setbacks have been challenging and have touched nearly every service from prevention to treatment. According to the report, between 2019 and 2020:
- Voluntary male circumcision declined by 27%.
- Numbers reached by HIV prevention programs fell by 11%.
- 4.5% fewer mothers received medications to prevent HIV transmission to their babies.
- HIV testing services, including initiation, decreased by 22%.
The numbers tell only a part of the story, according to Dr. Crowley.
“We put in place an emergency mechanism to make funds available for countries to do everything except vaccines in support of COVID,” Dr. Crowley explained. (As of August 2021, these funds had been allocated to 107 countries and 16 multicountry programs.)
Countries were advised that they could use the emergency funds three different ways: 1) for COVID-specific purposes (e.g., diagnostics, oxygen, personal protective equipment; 2) to support mitigation strategies geared toward protecting existing HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria programs and getting them back on track; and 3) for so-called “health system fixes,” such as investing in data systems to track COVID, HIV, and other core diseases, as well as the community workforce.
With regard to HIV, each country supported by the Global Fund was asked to ensure that multimonth (3-6 months) dispensing was implemented and/or accelerated so that patients could avoid congested facilities, and, wherever possible, that drugs were delivered or accessed outside the facility. One example of the success of this effort was found in South Africa, where the number of people on antiretrovirals increased almost threefold, from 1.2 million to 4.2 million people.
Countries also were asked to adapt HIV testing procedures by, for example, moving organized testing out of the facilities and into neighborhoods to meet people where they are. Rapid diagnostic testing and triage care linkage using technologies such as WhatsApp were the result, as were opportunities for home testing which, Dr. Crowley noted, remains a critical component of the overall strategy.
“The self-test is important for two reasons, not just because you are trying to find people with HIV, but also, when people know that they’re negative, they know what they can or should do to stay negative,” she said. “It’s quite a powerful motivator.”
Self-testing might also help countries motivate the 6 million people who know that they have HIV but are not on treatment. But there are still 4.1 million residing in these countries who aren’t aware that they are infected, according to the report. This figure is especially troubling, considering that some may also be harboring TB coinfections, including multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).
The imperfect storm globally and in the U.S.
“One of the things that was striking in the report was the decline in the number of people reached with testing and prevention services,” Chris Beyrer, MD, MPH, the Desmond M. Tutu Professor of Public Health and Human Rights at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, said in an interview. Dr. Beyrer was not involved in the report’s development.
“You know, a 10% decline in 1 year to reach people in need is substantial,” he said. “Let’s say it continues; many people are predicting that we won’t have reasonable coverage for low-income countries with COVID until 2023. That adds up to a substantial decline in people reached with these services.”
Dr. Beyrer also expressed concern about the convergence of HIV and TB in already overburdened, fragile health care systems. “Globally, the No. 1 cause of death for people living with HIV is TB, and of course, it’s highly transmissible. So, in many high-burden countries, children are exposed, typically from household members early on, and so the number of people with latent TB infection is just enormous.
“If you look at the report, the worst outcomes are MDR-TB. Those multidrug-resistant and extensively-drug-resistant strains are really a threat to everybody,” Dr. Beyrer said.
But it’s not time for U.S. providers to rest on their laurels either. Dr. Beyrer noted that the 22% decline in HIV testing reported by the Global Fund is similar to what has been happening in the United States with elective procedures such as HIV testing and even preventive procedures like medical male circumcision.
“It’s very clear here in the Global Fund data that the majority of new infections worldwide are in key populations [that] include gay and bisexual men, men who have sex with men, transgender women who have sex with men, people who inject drugs, and sex workers of all genders. Those are people who already faced barriers to health care access and were made worse by COVID.”
Dr. Beyrer noted that, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in 2019 in the United States, 68% of new HIV infections occurred in gay and bisexual men, and the effect that COVID-19 will have is still unknown. He also noted the similarity between the most marginalized populations in the Global Fund report and African American men, who have not realized the same increase in the use of preexposure prophylaxis or the same decline in new infections as have their White counterparts.
“It’s also where we are seeing the worst of COVID, low immunization coverage, and high rates of hospitalization and death. ... It’s a dark, dark time for many,” Dr. Crowley said. “And there has also been some amazing resilience and adaptation. The weird thing is, the HIV platform is a natural platform; I mean, if we can keep 21.9 million people on treatment, we can probably deliver them a COVID test and a vaccine.”
Dr. Crowley and Dr. Beyrer report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“We’ve been set back by COVID but we’ve seen remarkable resilience, a lot of innovation and creativity,” Siobhan Crowley MD, head of HIV at the Global Fund, said in an interview.
“If you consider that 21.9 million people are getting antiretrovirals at this point through the Global Fund, I think that needs to be appreciated. Ten years ago, that wouldn’t have been the case; all of those people would have disappeared into the ethers,” she said.
Through close partnerships with the U.S. Agency for International Development, the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief, and other Western countries and organizations, the Global Fund has invested $22.7 billion in programs to prevent and treat HIV and AIDS, and $3.8 billion in tuberculosis (TB)/HIV programs, according to the organization’s 2021 Results Report.
But the report also underscores the significant effect that the COVID-19 pandemic has had on funded countries’ progress toward achieving renewed 90-90-90 targets for HIV testing/diagnosis, treatment, and viral suppression by 2030.
The setbacks have been challenging and have touched nearly every service from prevention to treatment. According to the report, between 2019 and 2020:
- Voluntary male circumcision declined by 27%.
- Numbers reached by HIV prevention programs fell by 11%.
- 4.5% fewer mothers received medications to prevent HIV transmission to their babies.
- HIV testing services, including initiation, decreased by 22%.
The numbers tell only a part of the story, according to Dr. Crowley.
“We put in place an emergency mechanism to make funds available for countries to do everything except vaccines in support of COVID,” Dr. Crowley explained. (As of August 2021, these funds had been allocated to 107 countries and 16 multicountry programs.)
Countries were advised that they could use the emergency funds three different ways: 1) for COVID-specific purposes (e.g., diagnostics, oxygen, personal protective equipment; 2) to support mitigation strategies geared toward protecting existing HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria programs and getting them back on track; and 3) for so-called “health system fixes,” such as investing in data systems to track COVID, HIV, and other core diseases, as well as the community workforce.
With regard to HIV, each country supported by the Global Fund was asked to ensure that multimonth (3-6 months) dispensing was implemented and/or accelerated so that patients could avoid congested facilities, and, wherever possible, that drugs were delivered or accessed outside the facility. One example of the success of this effort was found in South Africa, where the number of people on antiretrovirals increased almost threefold, from 1.2 million to 4.2 million people.
Countries also were asked to adapt HIV testing procedures by, for example, moving organized testing out of the facilities and into neighborhoods to meet people where they are. Rapid diagnostic testing and triage care linkage using technologies such as WhatsApp were the result, as were opportunities for home testing which, Dr. Crowley noted, remains a critical component of the overall strategy.
“The self-test is important for two reasons, not just because you are trying to find people with HIV, but also, when people know that they’re negative, they know what they can or should do to stay negative,” she said. “It’s quite a powerful motivator.”
Self-testing might also help countries motivate the 6 million people who know that they have HIV but are not on treatment. But there are still 4.1 million residing in these countries who aren’t aware that they are infected, according to the report. This figure is especially troubling, considering that some may also be harboring TB coinfections, including multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).
The imperfect storm globally and in the U.S.
“One of the things that was striking in the report was the decline in the number of people reached with testing and prevention services,” Chris Beyrer, MD, MPH, the Desmond M. Tutu Professor of Public Health and Human Rights at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, said in an interview. Dr. Beyrer was not involved in the report’s development.
“You know, a 10% decline in 1 year to reach people in need is substantial,” he said. “Let’s say it continues; many people are predicting that we won’t have reasonable coverage for low-income countries with COVID until 2023. That adds up to a substantial decline in people reached with these services.”
Dr. Beyrer also expressed concern about the convergence of HIV and TB in already overburdened, fragile health care systems. “Globally, the No. 1 cause of death for people living with HIV is TB, and of course, it’s highly transmissible. So, in many high-burden countries, children are exposed, typically from household members early on, and so the number of people with latent TB infection is just enormous.
“If you look at the report, the worst outcomes are MDR-TB. Those multidrug-resistant and extensively-drug-resistant strains are really a threat to everybody,” Dr. Beyrer said.
But it’s not time for U.S. providers to rest on their laurels either. Dr. Beyrer noted that the 22% decline in HIV testing reported by the Global Fund is similar to what has been happening in the United States with elective procedures such as HIV testing and even preventive procedures like medical male circumcision.
“It’s very clear here in the Global Fund data that the majority of new infections worldwide are in key populations [that] include gay and bisexual men, men who have sex with men, transgender women who have sex with men, people who inject drugs, and sex workers of all genders. Those are people who already faced barriers to health care access and were made worse by COVID.”
Dr. Beyrer noted that, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in 2019 in the United States, 68% of new HIV infections occurred in gay and bisexual men, and the effect that COVID-19 will have is still unknown. He also noted the similarity between the most marginalized populations in the Global Fund report and African American men, who have not realized the same increase in the use of preexposure prophylaxis or the same decline in new infections as have their White counterparts.
“It’s also where we are seeing the worst of COVID, low immunization coverage, and high rates of hospitalization and death. ... It’s a dark, dark time for many,” Dr. Crowley said. “And there has also been some amazing resilience and adaptation. The weird thing is, the HIV platform is a natural platform; I mean, if we can keep 21.9 million people on treatment, we can probably deliver them a COVID test and a vaccine.”
Dr. Crowley and Dr. Beyrer report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nurses ‘at the breaking point,’ consider quitting due to COVID issues: Survey
In the best of times, critical care nurses have one of the most difficult and stressful jobs in health care. The COVID-19 pandemic has made that immeasurably worse. As hospitals have been flooded with critically ill patients, nurses have been overwhelmed.
“What we’re hearing from our nurses is really shocking,” Amanda Bettencourt, PhD, APRN, CCRN-K, president-elect of the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACN), told this news organization. “They’re saying they’re at the breaking point.”
Between August 26 and August 30, the AACN surveyed more than 6,000 critical care nurses, zeroing in on four key questions regarding the pandemic and its impact on nursing. The results were alarming – not only with regard to individual nurses but also for the nursing profession and the future of health care. A full 66% of those surveyed said their experiences during the pandemic have caused them to consider leaving nursing. The respondents’ take on their colleagues was even more concerning. Ninety-two percent agreed with the following two statements: “I believe the pandemic has depleted nurses at my hospital. Their careers will be shorter than they intended.”
“This puts the entire health care system at risk,” says Dr. Bettencourt, who is assistant professor in the department of family and community health at the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing, Philadelphia. Intensive care unit (ICU) nurses are highly trained and are skilled in caring for critically ill patients with complex medical needs. “It’s not easy to replace a critical care nurse when one leaves,” she says.
And when nurses leave, patients suffer, says Beth Wathen, MSN, RN, CCRN-K, president of the ACCN and frontline nurse at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. “Hospitals can have all the beds and all the rooms and all the equipment they want, but without nurses and others at the front lines to provide that essential care, none of it really matters, whether we’re talking about caring for COVID patients or caring for patients with other health ailments.”
Heartbreak of the unvaccinated
The problem is not just overwork because of the flood of COVID-19 patients. The emotional strain is enormous as well. “What’s demoralizing for us is not that patients are sick and that it’s physically exhausting to take care of sick patients. We’re used to that,” says Dr. Bettencourt.
But few nurses have experienced the sheer magnitude of patients caused by this pandemic. “The past 18 months have been grueling,” says Ms. Wathen. “The burden on frontline caregivers and our nurses at the front line has been immense.”
The situation is made worse by how unnecessary much of the suffering is at this point. Seventy-six percent of the survey’s respondents agreed with the following statement: “People who hold out on getting vaccinated undermine nurses’ physical and mental well-being.” That comment doesn’t convey the nature or extent of the effect on caregivers’ well-being. “That 9 out of 10 of the people we’re seeing in ICU right now are unvaccinated just adds to the sense of heartbreak and frustration,” says Ms. Wathen. “These deaths don’t have to be happening right now. And that’s hard to bear witness to.”
The politicization of public health has also taken a toll. “That’s been the hard part of this entire pandemic,” says Ms. Wathen. “This really isn’t at all about politics. This is about your health; this is about my health. This is about our collective health as a community and as a country.”
Like the rest of the world, nurses are also concerned about their own loved ones. The survey statement, “I fear taking care of patients with COVID puts my family’s health at risk,” garnered 67% agreement. Ms. Wathen points out that nurses take the appropriate precautions but still worry about taking infection home to their families. “This disease is a tricky one,” she says. She points out that until this pandemic is over, in addition to being vaccinated, nurses and the public still need to be vigilant about wearing masks, social distancing, and taking other precautions to ensure the safety of us all. “Our individual decisions don’t just affect ourselves. They affect our family, the people in our circle, and the people in our community,” she says.
Avoiding a professional exodus
It’s too early yet to have reliable national data on how many nurses have already left their jobs because of COVID-19, but it is clear that there are too few nurses of all kinds. Earlier this month, the American Nurses Association sent a letter to the U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services urging the agency to declare the nursing shortage a crisis and to take immediate steps to find solutions.
The nursing shortage predates the pandemic, and COVID-19 has brought a simmering problem to a boil. Nurses are calling on the public and the health care system for help. From inside the industry, the needs are pretty much what they were before the pandemic. Dr. Bettencourt and Ms. Wathen point to the need for supportive leadership, healthy work environments, sufficient staffing to meet patients’ needs, and a voice in decisions, such as decisions about staffing, that affect nurses and their patients. Nurses want to be heard and appreciated. “It’s not that these are new things,” says Dr. Bettencourt. “We just need them even more now because we’re stressed even more than we were before.”
Critical care nurses have a different request of the public. They’re asking – pleading, actually – with the public to get vaccinated, wear masks in public, practice social distancing, and bring this pandemic to an end.
“COVID kills, and it’s a really difficult, tragic, and lonely death,” says Ms. Wathen. “We’ve witnessed hundreds of thousands of those deaths. But now we have a way to stop it. If many more people get vaccinated, we can stop this pandemic. And hopefully that will stop this current trend of nurses leaving.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the best of times, critical care nurses have one of the most difficult and stressful jobs in health care. The COVID-19 pandemic has made that immeasurably worse. As hospitals have been flooded with critically ill patients, nurses have been overwhelmed.
“What we’re hearing from our nurses is really shocking,” Amanda Bettencourt, PhD, APRN, CCRN-K, president-elect of the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACN), told this news organization. “They’re saying they’re at the breaking point.”
Between August 26 and August 30, the AACN surveyed more than 6,000 critical care nurses, zeroing in on four key questions regarding the pandemic and its impact on nursing. The results were alarming – not only with regard to individual nurses but also for the nursing profession and the future of health care. A full 66% of those surveyed said their experiences during the pandemic have caused them to consider leaving nursing. The respondents’ take on their colleagues was even more concerning. Ninety-two percent agreed with the following two statements: “I believe the pandemic has depleted nurses at my hospital. Their careers will be shorter than they intended.”
“This puts the entire health care system at risk,” says Dr. Bettencourt, who is assistant professor in the department of family and community health at the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing, Philadelphia. Intensive care unit (ICU) nurses are highly trained and are skilled in caring for critically ill patients with complex medical needs. “It’s not easy to replace a critical care nurse when one leaves,” she says.
And when nurses leave, patients suffer, says Beth Wathen, MSN, RN, CCRN-K, president of the ACCN and frontline nurse at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. “Hospitals can have all the beds and all the rooms and all the equipment they want, but without nurses and others at the front lines to provide that essential care, none of it really matters, whether we’re talking about caring for COVID patients or caring for patients with other health ailments.”
Heartbreak of the unvaccinated
The problem is not just overwork because of the flood of COVID-19 patients. The emotional strain is enormous as well. “What’s demoralizing for us is not that patients are sick and that it’s physically exhausting to take care of sick patients. We’re used to that,” says Dr. Bettencourt.
But few nurses have experienced the sheer magnitude of patients caused by this pandemic. “The past 18 months have been grueling,” says Ms. Wathen. “The burden on frontline caregivers and our nurses at the front line has been immense.”
The situation is made worse by how unnecessary much of the suffering is at this point. Seventy-six percent of the survey’s respondents agreed with the following statement: “People who hold out on getting vaccinated undermine nurses’ physical and mental well-being.” That comment doesn’t convey the nature or extent of the effect on caregivers’ well-being. “That 9 out of 10 of the people we’re seeing in ICU right now are unvaccinated just adds to the sense of heartbreak and frustration,” says Ms. Wathen. “These deaths don’t have to be happening right now. And that’s hard to bear witness to.”
The politicization of public health has also taken a toll. “That’s been the hard part of this entire pandemic,” says Ms. Wathen. “This really isn’t at all about politics. This is about your health; this is about my health. This is about our collective health as a community and as a country.”
Like the rest of the world, nurses are also concerned about their own loved ones. The survey statement, “I fear taking care of patients with COVID puts my family’s health at risk,” garnered 67% agreement. Ms. Wathen points out that nurses take the appropriate precautions but still worry about taking infection home to their families. “This disease is a tricky one,” she says. She points out that until this pandemic is over, in addition to being vaccinated, nurses and the public still need to be vigilant about wearing masks, social distancing, and taking other precautions to ensure the safety of us all. “Our individual decisions don’t just affect ourselves. They affect our family, the people in our circle, and the people in our community,” she says.
Avoiding a professional exodus
It’s too early yet to have reliable national data on how many nurses have already left their jobs because of COVID-19, but it is clear that there are too few nurses of all kinds. Earlier this month, the American Nurses Association sent a letter to the U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services urging the agency to declare the nursing shortage a crisis and to take immediate steps to find solutions.
The nursing shortage predates the pandemic, and COVID-19 has brought a simmering problem to a boil. Nurses are calling on the public and the health care system for help. From inside the industry, the needs are pretty much what they were before the pandemic. Dr. Bettencourt and Ms. Wathen point to the need for supportive leadership, healthy work environments, sufficient staffing to meet patients’ needs, and a voice in decisions, such as decisions about staffing, that affect nurses and their patients. Nurses want to be heard and appreciated. “It’s not that these are new things,” says Dr. Bettencourt. “We just need them even more now because we’re stressed even more than we were before.”
Critical care nurses have a different request of the public. They’re asking – pleading, actually – with the public to get vaccinated, wear masks in public, practice social distancing, and bring this pandemic to an end.
“COVID kills, and it’s a really difficult, tragic, and lonely death,” says Ms. Wathen. “We’ve witnessed hundreds of thousands of those deaths. But now we have a way to stop it. If many more people get vaccinated, we can stop this pandemic. And hopefully that will stop this current trend of nurses leaving.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the best of times, critical care nurses have one of the most difficult and stressful jobs in health care. The COVID-19 pandemic has made that immeasurably worse. As hospitals have been flooded with critically ill patients, nurses have been overwhelmed.
“What we’re hearing from our nurses is really shocking,” Amanda Bettencourt, PhD, APRN, CCRN-K, president-elect of the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACN), told this news organization. “They’re saying they’re at the breaking point.”
Between August 26 and August 30, the AACN surveyed more than 6,000 critical care nurses, zeroing in on four key questions regarding the pandemic and its impact on nursing. The results were alarming – not only with regard to individual nurses but also for the nursing profession and the future of health care. A full 66% of those surveyed said their experiences during the pandemic have caused them to consider leaving nursing. The respondents’ take on their colleagues was even more concerning. Ninety-two percent agreed with the following two statements: “I believe the pandemic has depleted nurses at my hospital. Their careers will be shorter than they intended.”
“This puts the entire health care system at risk,” says Dr. Bettencourt, who is assistant professor in the department of family and community health at the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing, Philadelphia. Intensive care unit (ICU) nurses are highly trained and are skilled in caring for critically ill patients with complex medical needs. “It’s not easy to replace a critical care nurse when one leaves,” she says.
And when nurses leave, patients suffer, says Beth Wathen, MSN, RN, CCRN-K, president of the ACCN and frontline nurse at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. “Hospitals can have all the beds and all the rooms and all the equipment they want, but without nurses and others at the front lines to provide that essential care, none of it really matters, whether we’re talking about caring for COVID patients or caring for patients with other health ailments.”
Heartbreak of the unvaccinated
The problem is not just overwork because of the flood of COVID-19 patients. The emotional strain is enormous as well. “What’s demoralizing for us is not that patients are sick and that it’s physically exhausting to take care of sick patients. We’re used to that,” says Dr. Bettencourt.
But few nurses have experienced the sheer magnitude of patients caused by this pandemic. “The past 18 months have been grueling,” says Ms. Wathen. “The burden on frontline caregivers and our nurses at the front line has been immense.”
The situation is made worse by how unnecessary much of the suffering is at this point. Seventy-six percent of the survey’s respondents agreed with the following statement: “People who hold out on getting vaccinated undermine nurses’ physical and mental well-being.” That comment doesn’t convey the nature or extent of the effect on caregivers’ well-being. “That 9 out of 10 of the people we’re seeing in ICU right now are unvaccinated just adds to the sense of heartbreak and frustration,” says Ms. Wathen. “These deaths don’t have to be happening right now. And that’s hard to bear witness to.”
The politicization of public health has also taken a toll. “That’s been the hard part of this entire pandemic,” says Ms. Wathen. “This really isn’t at all about politics. This is about your health; this is about my health. This is about our collective health as a community and as a country.”
Like the rest of the world, nurses are also concerned about their own loved ones. The survey statement, “I fear taking care of patients with COVID puts my family’s health at risk,” garnered 67% agreement. Ms. Wathen points out that nurses take the appropriate precautions but still worry about taking infection home to their families. “This disease is a tricky one,” she says. She points out that until this pandemic is over, in addition to being vaccinated, nurses and the public still need to be vigilant about wearing masks, social distancing, and taking other precautions to ensure the safety of us all. “Our individual decisions don’t just affect ourselves. They affect our family, the people in our circle, and the people in our community,” she says.
Avoiding a professional exodus
It’s too early yet to have reliable national data on how many nurses have already left their jobs because of COVID-19, but it is clear that there are too few nurses of all kinds. Earlier this month, the American Nurses Association sent a letter to the U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services urging the agency to declare the nursing shortage a crisis and to take immediate steps to find solutions.
The nursing shortage predates the pandemic, and COVID-19 has brought a simmering problem to a boil. Nurses are calling on the public and the health care system for help. From inside the industry, the needs are pretty much what they were before the pandemic. Dr. Bettencourt and Ms. Wathen point to the need for supportive leadership, healthy work environments, sufficient staffing to meet patients’ needs, and a voice in decisions, such as decisions about staffing, that affect nurses and their patients. Nurses want to be heard and appreciated. “It’s not that these are new things,” says Dr. Bettencourt. “We just need them even more now because we’re stressed even more than we were before.”
Critical care nurses have a different request of the public. They’re asking – pleading, actually – with the public to get vaccinated, wear masks in public, practice social distancing, and bring this pandemic to an end.
“COVID kills, and it’s a really difficult, tragic, and lonely death,” says Ms. Wathen. “We’ve witnessed hundreds of thousands of those deaths. But now we have a way to stop it. If many more people get vaccinated, we can stop this pandemic. And hopefully that will stop this current trend of nurses leaving.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Decline in child COVID may signal end of latest surge
A second consecutive week of falling COVID-19 cases in children, along with continued declines in new admissions, may indicate that the latest surge has peaked.
Children made up over 25% of all new cases each week over that 3-week period covering the end of August and the first half of September, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.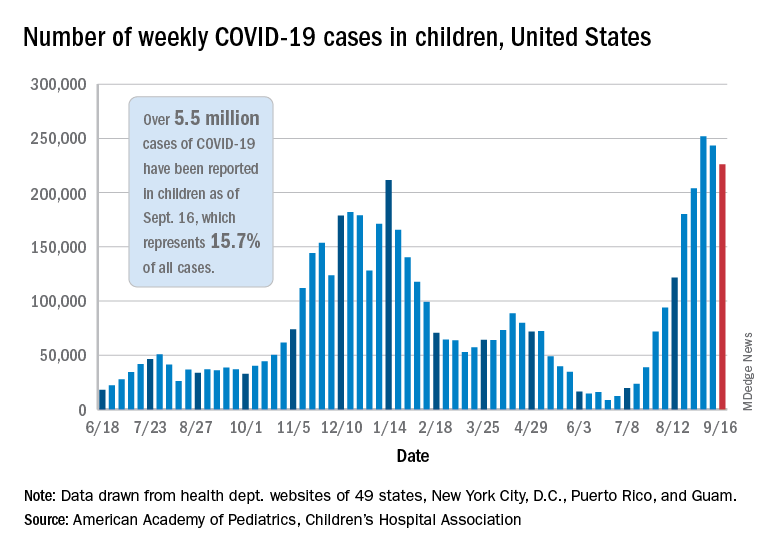
New hospitalizations in children aged 0-17 years peaked on Sept. 4 – when the rate reached 0.51 per 100,000 population – and were down to 0.47 as of Sept. 11, the latest date for which data should be considered reliable, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
The CDC’s data largely agree with the AAP/CHA report, showing that cases peaked during the week of Aug. 22-28. Cases per 100,000 for children that week looked like this: 154.7 (age 0-4 years), 276.6 (5-11 years), 320.0 (12-15), and 334.1 (16-17). The highest rates that week among adults were 288.6 per 100,000 in 30- to 39-year-olds and 286.5 for those aged 18-29, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
By the week of Sept. 5-11 – reporting delays can affect more recent data – the rates in children were down more than 20% in each of the four age groups, according to the CDC.
Vaccinations among children, unfortunately, continue to decline. Vaccine initiations for 12- to 15-year-olds slipped from 199,000 (Sept. 7-13) to 179,000 during the week of Sept. 14-20, while the 16- to 17-year-olds went from almost 83,000 down to 75,000. Initiations have dropped for 6 straight weeks in both age groups, based on the CDC data.
Despite those declines, however, the 16- and 17-year-olds just passed a couple of vaccination milestones. More than 60% – 60.9%, to be exact – have now received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, and 50.3% can be considered fully vaccinated. For those aged 12-15, the corresponding figures are 53.1% and 42.0%, the CDC reported.
When children under age 12 years are included – through clinical trial involvement or incorrect birth dates – the CDC data put the total count of Americans under age 18 who have received at least one dose of vaccine at almost 12.8 million, with vaccination complete in 10.3 million.
Total cases, as calculated by the APA and CHA, are now over 5.5 million, although that figure includes cases in individuals as old as 20 years, since many states differ from the CDC on the age range for a child. The CDC’s COVID Data Tracker put the total for children aged 0-17 at nearly 4.6 million.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 480 as of Sept. 16, the AAP and CHA said, based on data from 45 states, New York, City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, but the CDC provides a higher number, 548, since the pandemic began. Children aged 0-4 years represent the largest share (32.3%) of those 548 deaths, followed by the 12- to 15-year-olds (26.5%), based on the CDC data.
A second consecutive week of falling COVID-19 cases in children, along with continued declines in new admissions, may indicate that the latest surge has peaked.
Children made up over 25% of all new cases each week over that 3-week period covering the end of August and the first half of September, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New hospitalizations in children aged 0-17 years peaked on Sept. 4 – when the rate reached 0.51 per 100,000 population – and were down to 0.47 as of Sept. 11, the latest date for which data should be considered reliable, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
The CDC’s data largely agree with the AAP/CHA report, showing that cases peaked during the week of Aug. 22-28. Cases per 100,000 for children that week looked like this: 154.7 (age 0-4 years), 276.6 (5-11 years), 320.0 (12-15), and 334.1 (16-17). The highest rates that week among adults were 288.6 per 100,000 in 30- to 39-year-olds and 286.5 for those aged 18-29, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
By the week of Sept. 5-11 – reporting delays can affect more recent data – the rates in children were down more than 20% in each of the four age groups, according to the CDC.
Vaccinations among children, unfortunately, continue to decline. Vaccine initiations for 12- to 15-year-olds slipped from 199,000 (Sept. 7-13) to 179,000 during the week of Sept. 14-20, while the 16- to 17-year-olds went from almost 83,000 down to 75,000. Initiations have dropped for 6 straight weeks in both age groups, based on the CDC data.
Despite those declines, however, the 16- and 17-year-olds just passed a couple of vaccination milestones. More than 60% – 60.9%, to be exact – have now received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, and 50.3% can be considered fully vaccinated. For those aged 12-15, the corresponding figures are 53.1% and 42.0%, the CDC reported.
When children under age 12 years are included – through clinical trial involvement or incorrect birth dates – the CDC data put the total count of Americans under age 18 who have received at least one dose of vaccine at almost 12.8 million, with vaccination complete in 10.3 million.
Total cases, as calculated by the APA and CHA, are now over 5.5 million, although that figure includes cases in individuals as old as 20 years, since many states differ from the CDC on the age range for a child. The CDC’s COVID Data Tracker put the total for children aged 0-17 at nearly 4.6 million.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 480 as of Sept. 16, the AAP and CHA said, based on data from 45 states, New York, City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, but the CDC provides a higher number, 548, since the pandemic began. Children aged 0-4 years represent the largest share (32.3%) of those 548 deaths, followed by the 12- to 15-year-olds (26.5%), based on the CDC data.
A second consecutive week of falling COVID-19 cases in children, along with continued declines in new admissions, may indicate that the latest surge has peaked.
Children made up over 25% of all new cases each week over that 3-week period covering the end of August and the first half of September, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New hospitalizations in children aged 0-17 years peaked on Sept. 4 – when the rate reached 0.51 per 100,000 population – and were down to 0.47 as of Sept. 11, the latest date for which data should be considered reliable, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
The CDC’s data largely agree with the AAP/CHA report, showing that cases peaked during the week of Aug. 22-28. Cases per 100,000 for children that week looked like this: 154.7 (age 0-4 years), 276.6 (5-11 years), 320.0 (12-15), and 334.1 (16-17). The highest rates that week among adults were 288.6 per 100,000 in 30- to 39-year-olds and 286.5 for those aged 18-29, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
By the week of Sept. 5-11 – reporting delays can affect more recent data – the rates in children were down more than 20% in each of the four age groups, according to the CDC.
Vaccinations among children, unfortunately, continue to decline. Vaccine initiations for 12- to 15-year-olds slipped from 199,000 (Sept. 7-13) to 179,000 during the week of Sept. 14-20, while the 16- to 17-year-olds went from almost 83,000 down to 75,000. Initiations have dropped for 6 straight weeks in both age groups, based on the CDC data.
Despite those declines, however, the 16- and 17-year-olds just passed a couple of vaccination milestones. More than 60% – 60.9%, to be exact – have now received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, and 50.3% can be considered fully vaccinated. For those aged 12-15, the corresponding figures are 53.1% and 42.0%, the CDC reported.
When children under age 12 years are included – through clinical trial involvement or incorrect birth dates – the CDC data put the total count of Americans under age 18 who have received at least one dose of vaccine at almost 12.8 million, with vaccination complete in 10.3 million.
Total cases, as calculated by the APA and CHA, are now over 5.5 million, although that figure includes cases in individuals as old as 20 years, since many states differ from the CDC on the age range for a child. The CDC’s COVID Data Tracker put the total for children aged 0-17 at nearly 4.6 million.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 480 as of Sept. 16, the AAP and CHA said, based on data from 45 states, New York, City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, but the CDC provides a higher number, 548, since the pandemic began. Children aged 0-4 years represent the largest share (32.3%) of those 548 deaths, followed by the 12- to 15-year-olds (26.5%), based on the CDC data.
COVID-19 claims more than 675,000 U.S. lives, surpassing the 1918 flu
, according to data collected by Johns Hopkins University.
Although the raw numbers match, epidemiologists point out that 675,000 deaths in 1918 was a much greater proportion of the population. In 1918, the U.S. population was 105 million, less than one third of what it is today.
The AIDS pandemic of the 1980s remains the deadliest of the 20th Century, claiming the lives of 700,000 Americans. But at our current pace of 2,000 COVID deaths a day, we could quickly eclipse that death toll, too.
Even though the 1918 epidemic is often called the “Spanish Flu,” there is no universal consensus regarding where the virus originated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Still, the almost incomprehensible loss harkens back to a time when medicine and technology were far less advanced than they are today.
In 1918, the United States didn’t have access to a vaccine, or near real-time tools to trace the spread and communicate the threat.
In some ways, the United States has failed to learn from the mistakes of the past.
There are many similarities between the two pandemics. In the spring of 1918, when the first wave of influenza hit, the United States and its allies were nearing victory in Europe in World War I. Just this summer the United States has ended its longest war, the conflict in Afghanistan, as COVID cases surge.
In both pandemics, hospitals and funeral homes were overrun and makeshift clinics were opened where space was available. Mask mandates were installed; schools, churches, and theaters closed; and social distancing was encouraged.
As is the case today, different jurisdictions took different steps to fight the pandemic and some were more successful than others.
According to History.com, in 1918, Philadelphia’s mayor said a popular annual parade could be held, and an estimated 200,000 people attended. In less than 2 weeks, more than 1,000 local residents were dead. But in St. Louis, public gatherings were banned, schools and theaters closed, and the death toll there was one eighth of Philadelphia’s.
Just as in 1918, America has at times continued to fan the flames of the epidemic by relaxing restrictions too quickly and relying on unproven treatments. Poor communication allowed younger people to feel that they wouldn’t necessarily face the worst consequences of the virus, contributing to a false sense of security in the age group that was fueling the spread.
“A lot of the mistakes that we definitely fell into in 1918, we hoped we wouldn’t fall into in 2020,” epidemiologist Stephen Kissler, PhD, of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, told CNN. “We did.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to data collected by Johns Hopkins University.
Although the raw numbers match, epidemiologists point out that 675,000 deaths in 1918 was a much greater proportion of the population. In 1918, the U.S. population was 105 million, less than one third of what it is today.
The AIDS pandemic of the 1980s remains the deadliest of the 20th Century, claiming the lives of 700,000 Americans. But at our current pace of 2,000 COVID deaths a day, we could quickly eclipse that death toll, too.
Even though the 1918 epidemic is often called the “Spanish Flu,” there is no universal consensus regarding where the virus originated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Still, the almost incomprehensible loss harkens back to a time when medicine and technology were far less advanced than they are today.
In 1918, the United States didn’t have access to a vaccine, or near real-time tools to trace the spread and communicate the threat.
In some ways, the United States has failed to learn from the mistakes of the past.
There are many similarities between the two pandemics. In the spring of 1918, when the first wave of influenza hit, the United States and its allies were nearing victory in Europe in World War I. Just this summer the United States has ended its longest war, the conflict in Afghanistan, as COVID cases surge.
In both pandemics, hospitals and funeral homes were overrun and makeshift clinics were opened where space was available. Mask mandates were installed; schools, churches, and theaters closed; and social distancing was encouraged.
As is the case today, different jurisdictions took different steps to fight the pandemic and some were more successful than others.
According to History.com, in 1918, Philadelphia’s mayor said a popular annual parade could be held, and an estimated 200,000 people attended. In less than 2 weeks, more than 1,000 local residents were dead. But in St. Louis, public gatherings were banned, schools and theaters closed, and the death toll there was one eighth of Philadelphia’s.
Just as in 1918, America has at times continued to fan the flames of the epidemic by relaxing restrictions too quickly and relying on unproven treatments. Poor communication allowed younger people to feel that they wouldn’t necessarily face the worst consequences of the virus, contributing to a false sense of security in the age group that was fueling the spread.
“A lot of the mistakes that we definitely fell into in 1918, we hoped we wouldn’t fall into in 2020,” epidemiologist Stephen Kissler, PhD, of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, told CNN. “We did.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to data collected by Johns Hopkins University.
Although the raw numbers match, epidemiologists point out that 675,000 deaths in 1918 was a much greater proportion of the population. In 1918, the U.S. population was 105 million, less than one third of what it is today.
The AIDS pandemic of the 1980s remains the deadliest of the 20th Century, claiming the lives of 700,000 Americans. But at our current pace of 2,000 COVID deaths a day, we could quickly eclipse that death toll, too.
Even though the 1918 epidemic is often called the “Spanish Flu,” there is no universal consensus regarding where the virus originated, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Still, the almost incomprehensible loss harkens back to a time when medicine and technology were far less advanced than they are today.
In 1918, the United States didn’t have access to a vaccine, or near real-time tools to trace the spread and communicate the threat.
In some ways, the United States has failed to learn from the mistakes of the past.
There are many similarities between the two pandemics. In the spring of 1918, when the first wave of influenza hit, the United States and its allies were nearing victory in Europe in World War I. Just this summer the United States has ended its longest war, the conflict in Afghanistan, as COVID cases surge.
In both pandemics, hospitals and funeral homes were overrun and makeshift clinics were opened where space was available. Mask mandates were installed; schools, churches, and theaters closed; and social distancing was encouraged.
As is the case today, different jurisdictions took different steps to fight the pandemic and some were more successful than others.
According to History.com, in 1918, Philadelphia’s mayor said a popular annual parade could be held, and an estimated 200,000 people attended. In less than 2 weeks, more than 1,000 local residents were dead. But in St. Louis, public gatherings were banned, schools and theaters closed, and the death toll there was one eighth of Philadelphia’s.
Just as in 1918, America has at times continued to fan the flames of the epidemic by relaxing restrictions too quickly and relying on unproven treatments. Poor communication allowed younger people to feel that they wouldn’t necessarily face the worst consequences of the virus, contributing to a false sense of security in the age group that was fueling the spread.
“A lot of the mistakes that we definitely fell into in 1918, we hoped we wouldn’t fall into in 2020,” epidemiologist Stephen Kissler, PhD, of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, told CNN. “We did.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

