User login
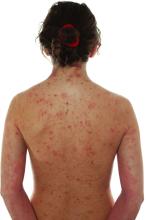
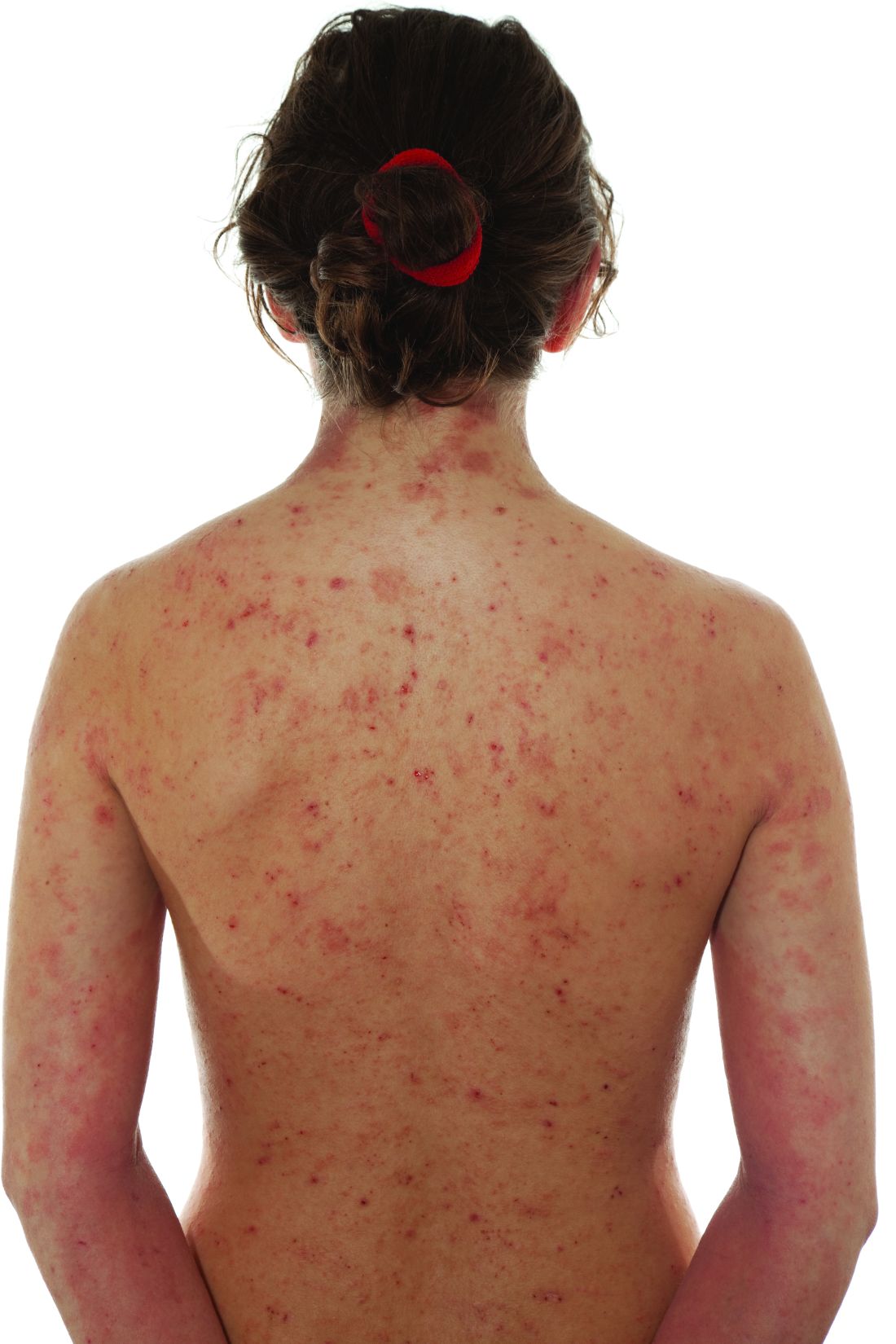
The earlier baricitinib for severe alopecia areata is started, the better
NEW ORLEANS – In the nearly 1 year .
“The journey to JAK inhibition in alopecia areata has been incredible,” Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “JAK inhibitors are here to stay, and I think baricitinib offers an amazing opportunity for the right patients.”
The efficacy and safety of baricitinib (Olumiant) for AA was studied in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) for more than 6 months. Patients in these trials received either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary measurement of efficacy for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, or at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36. The researchers found that 36%-39% of individuals in the 4-mg arm achieved a SALT score of less than 20, compared with 19%-23% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. Similar outcomes were observed for eyebrow and eyelash hair loss.
Most adverse events observed in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 were in the mild to moderate range, and the actual number of adverse events leading to permanent discontinuation was extremely low. The most common adverse events were upper respiratory tract infections, headache, nasopharyngitis, acne, urinary tract infections, and an increase in blood creatine kinase.
Baricitinib is not recommended for use in combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologic immunomodulators, or other potent immunosuppressants, Dr. Chovatiya said. Required lab evaluations include baseline testing for tuberculosis and viral hepatitis; CBC, hepatic function, and renal function at baseline and then as clinically indicated; and lipids after 12 weeks of therapy, then as clinically indicated. The recommended starting dose of baricitinib is 2 mg per day, which can be increased to 4 mg per day if the response is not adequate. “However, for patients with nearly complete or complete scalp hair loss, with or without substantial eyelash or eyebrow hair loss, 4 mg once daily is recommended,” he said. “Once an adequate response is achieved, it’s recommended to reduce from 4 to 2 mg daily.”
52-week, 76-week data
According to pooled data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 published online March 1, 2023, efficacy continues to increase out to 52 weeks. Specifically, by week 52, 39% of individuals in the 4 mg arm achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 22.6% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. “You see similar linear growth in the eyebrow and eyelash response loss as well,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
In other findings, patients in the 4 mg treatment arm who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized down titration, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of baricitinib from initial randomization. According to data from baricitinib manufacturer Eli Lilly, 77.5% of patients who stepped down to the 2 mg dose from the 4 mg dose at week 52 achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 76, Dr. Chovatiya said. “If I can keep someone on 4 mg that’s great, but it looks like you can go to a lower dose and do a pretty good job,” he said.
Patients in the baricitinib arms who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized withdrawal, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of the drug from initial randomization. According to Dr. Chovatiya, 89.4% of individuals who remained on the 4 mg dose to week 76 maintained a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 33.3% of those who switched from the 4 mg to placebo. “The takeaway here is that clinically, longitudinal treatment looks to be required in this time period” for continued efficacy, he said. “However, what this looks like in the real world remains to be seen.”
A recently published integrated analysis of safety data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 reported that no deaths occurred and of the few reported serious infections, nearly half were COVID-19. There was a single case of multidermatomal herpes zoster and no cases of tuberculosis. One patient with risk factors for MI had an MI during a placebo-controlled period, and one study participant with a history of COVID-19 infection developed a pulmonary embolism at day 638. There was one case each of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, breast cancer, and appendicitis.
Baseline severity and treatment response
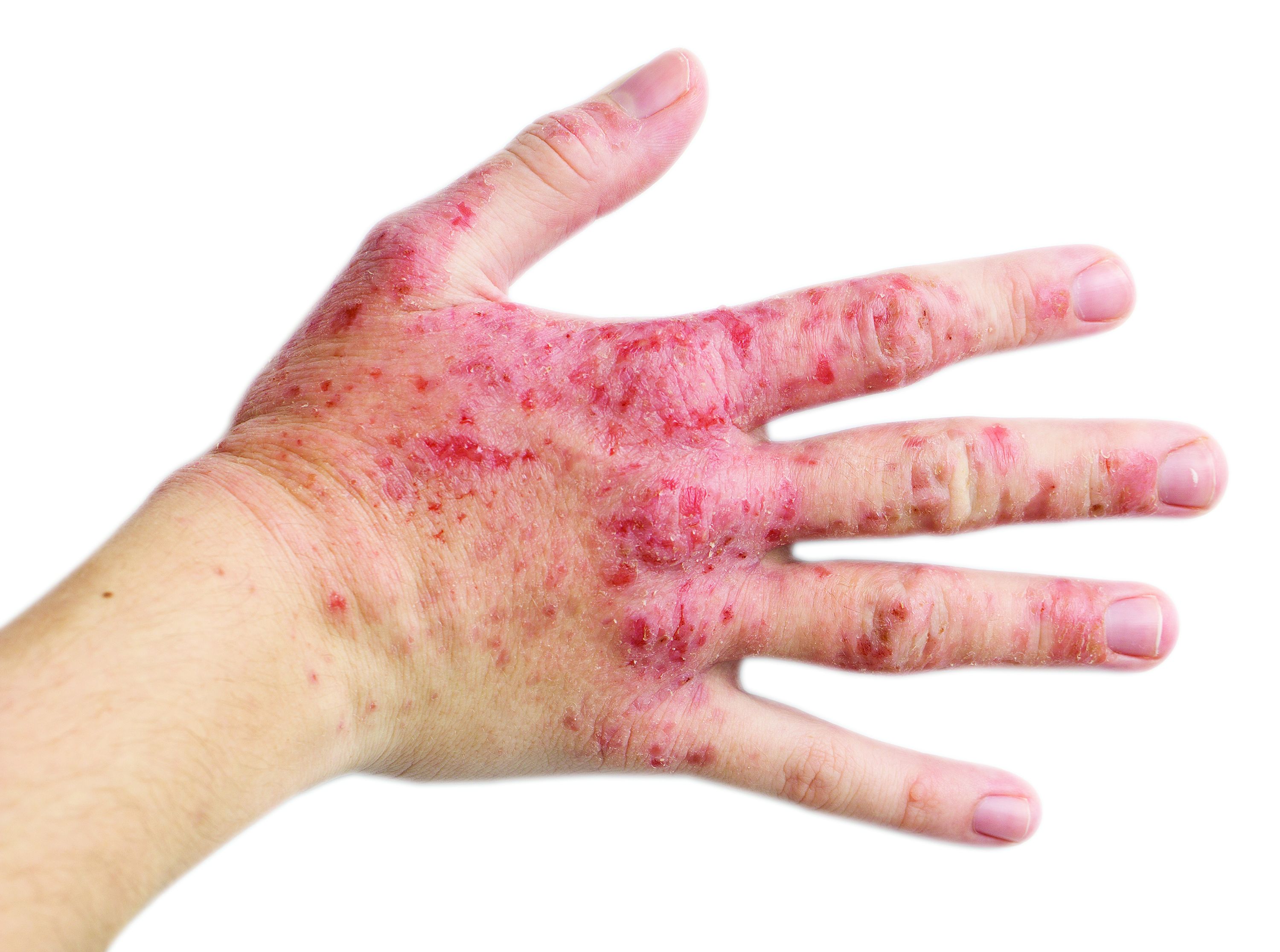
“Does treatment response vary with baseline disease status?” Dr. Chovatiya asked. “Yes. People with very severe hair loss [defined as a SALT score of 95 or higher] tended to do worse, while the rest of the study population did even better – an almost twofold difference. This means that you want to treat as early as you possibly can. It’s interesting to note that you don’t see this difference as much in the case of eyebrows and eyelashes. This makes sense, though. Eyebrows and eyelashes probably behave differently in terms of growth than the scalp does.”
Certain baseline characteristics of patients in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 portended better outcomes. Women tended to fare better than men, but individuals who had longer histories of AA did not respond well. “People who had a shorter duration of their current episode of AA also did better than people who had a longer current episode, so we want to think about treating as soon as we possibly can,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including Eli Lilly.
NEW ORLEANS – In the nearly 1 year .
“The journey to JAK inhibition in alopecia areata has been incredible,” Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “JAK inhibitors are here to stay, and I think baricitinib offers an amazing opportunity for the right patients.”
The efficacy and safety of baricitinib (Olumiant) for AA was studied in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) for more than 6 months. Patients in these trials received either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary measurement of efficacy for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, or at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36. The researchers found that 36%-39% of individuals in the 4-mg arm achieved a SALT score of less than 20, compared with 19%-23% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. Similar outcomes were observed for eyebrow and eyelash hair loss.
Most adverse events observed in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 were in the mild to moderate range, and the actual number of adverse events leading to permanent discontinuation was extremely low. The most common adverse events were upper respiratory tract infections, headache, nasopharyngitis, acne, urinary tract infections, and an increase in blood creatine kinase.
Baricitinib is not recommended for use in combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologic immunomodulators, or other potent immunosuppressants, Dr. Chovatiya said. Required lab evaluations include baseline testing for tuberculosis and viral hepatitis; CBC, hepatic function, and renal function at baseline and then as clinically indicated; and lipids after 12 weeks of therapy, then as clinically indicated. The recommended starting dose of baricitinib is 2 mg per day, which can be increased to 4 mg per day if the response is not adequate. “However, for patients with nearly complete or complete scalp hair loss, with or without substantial eyelash or eyebrow hair loss, 4 mg once daily is recommended,” he said. “Once an adequate response is achieved, it’s recommended to reduce from 4 to 2 mg daily.”
52-week, 76-week data
According to pooled data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 published online March 1, 2023, efficacy continues to increase out to 52 weeks. Specifically, by week 52, 39% of individuals in the 4 mg arm achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 22.6% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. “You see similar linear growth in the eyebrow and eyelash response loss as well,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
In other findings, patients in the 4 mg treatment arm who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized down titration, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of baricitinib from initial randomization. According to data from baricitinib manufacturer Eli Lilly, 77.5% of patients who stepped down to the 2 mg dose from the 4 mg dose at week 52 achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 76, Dr. Chovatiya said. “If I can keep someone on 4 mg that’s great, but it looks like you can go to a lower dose and do a pretty good job,” he said.
Patients in the baricitinib arms who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized withdrawal, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of the drug from initial randomization. According to Dr. Chovatiya, 89.4% of individuals who remained on the 4 mg dose to week 76 maintained a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 33.3% of those who switched from the 4 mg to placebo. “The takeaway here is that clinically, longitudinal treatment looks to be required in this time period” for continued efficacy, he said. “However, what this looks like in the real world remains to be seen.”
A recently published integrated analysis of safety data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 reported that no deaths occurred and of the few reported serious infections, nearly half were COVID-19. There was a single case of multidermatomal herpes zoster and no cases of tuberculosis. One patient with risk factors for MI had an MI during a placebo-controlled period, and one study participant with a history of COVID-19 infection developed a pulmonary embolism at day 638. There was one case each of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, breast cancer, and appendicitis.
Baseline severity and treatment response
“Does treatment response vary with baseline disease status?” Dr. Chovatiya asked. “Yes. People with very severe hair loss [defined as a SALT score of 95 or higher] tended to do worse, while the rest of the study population did even better – an almost twofold difference. This means that you want to treat as early as you possibly can. It’s interesting to note that you don’t see this difference as much in the case of eyebrows and eyelashes. This makes sense, though. Eyebrows and eyelashes probably behave differently in terms of growth than the scalp does.”
Certain baseline characteristics of patients in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 portended better outcomes. Women tended to fare better than men, but individuals who had longer histories of AA did not respond well. “People who had a shorter duration of their current episode of AA also did better than people who had a longer current episode, so we want to think about treating as soon as we possibly can,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including Eli Lilly.
NEW ORLEANS – In the nearly 1 year .
“The journey to JAK inhibition in alopecia areata has been incredible,” Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “JAK inhibitors are here to stay, and I think baricitinib offers an amazing opportunity for the right patients.”
The efficacy and safety of baricitinib (Olumiant) for AA was studied in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) for more than 6 months. Patients in these trials received either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary measurement of efficacy for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, or at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36. The researchers found that 36%-39% of individuals in the 4-mg arm achieved a SALT score of less than 20, compared with 19%-23% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. Similar outcomes were observed for eyebrow and eyelash hair loss.
Most adverse events observed in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 were in the mild to moderate range, and the actual number of adverse events leading to permanent discontinuation was extremely low. The most common adverse events were upper respiratory tract infections, headache, nasopharyngitis, acne, urinary tract infections, and an increase in blood creatine kinase.
Baricitinib is not recommended for use in combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologic immunomodulators, or other potent immunosuppressants, Dr. Chovatiya said. Required lab evaluations include baseline testing for tuberculosis and viral hepatitis; CBC, hepatic function, and renal function at baseline and then as clinically indicated; and lipids after 12 weeks of therapy, then as clinically indicated. The recommended starting dose of baricitinib is 2 mg per day, which can be increased to 4 mg per day if the response is not adequate. “However, for patients with nearly complete or complete scalp hair loss, with or without substantial eyelash or eyebrow hair loss, 4 mg once daily is recommended,” he said. “Once an adequate response is achieved, it’s recommended to reduce from 4 to 2 mg daily.”
52-week, 76-week data
According to pooled data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 published online March 1, 2023, efficacy continues to increase out to 52 weeks. Specifically, by week 52, 39% of individuals in the 4 mg arm achieved a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 22.6% of individuals in the 2 mg arm. “You see similar linear growth in the eyebrow and eyelash response loss as well,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
In other findings, patients in the 4 mg treatment arm who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized down titration, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of baricitinib from initial randomization. According to data from baricitinib manufacturer Eli Lilly, 77.5% of patients who stepped down to the 2 mg dose from the 4 mg dose at week 52 achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 76, Dr. Chovatiya said. “If I can keep someone on 4 mg that’s great, but it looks like you can go to a lower dose and do a pretty good job,” he said.
Patients in the baricitinib arms who achieved a SALT score of 20 or less at week 52 were eligible for randomized withdrawal, provided that they had stayed on the same dose of the drug from initial randomization. According to Dr. Chovatiya, 89.4% of individuals who remained on the 4 mg dose to week 76 maintained a SALT score of 20 or less, compared with 33.3% of those who switched from the 4 mg to placebo. “The takeaway here is that clinically, longitudinal treatment looks to be required in this time period” for continued efficacy, he said. “However, what this looks like in the real world remains to be seen.”
A recently published integrated analysis of safety data from BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 reported that no deaths occurred and of the few reported serious infections, nearly half were COVID-19. There was a single case of multidermatomal herpes zoster and no cases of tuberculosis. One patient with risk factors for MI had an MI during a placebo-controlled period, and one study participant with a history of COVID-19 infection developed a pulmonary embolism at day 638. There was one case each of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, breast cancer, and appendicitis.
Baseline severity and treatment response
“Does treatment response vary with baseline disease status?” Dr. Chovatiya asked. “Yes. People with very severe hair loss [defined as a SALT score of 95 or higher] tended to do worse, while the rest of the study population did even better – an almost twofold difference. This means that you want to treat as early as you possibly can. It’s interesting to note that you don’t see this difference as much in the case of eyebrows and eyelashes. This makes sense, though. Eyebrows and eyelashes probably behave differently in terms of growth than the scalp does.”
Certain baseline characteristics of patients in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 portended better outcomes. Women tended to fare better than men, but individuals who had longer histories of AA did not respond well. “People who had a shorter duration of their current episode of AA also did better than people who had a longer current episode, so we want to think about treating as soon as we possibly can,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including Eli Lilly.
AT AAD 2023
What are the clinical implications of recent skin dysbiosis discoveries?
NEW ORLEANS – .
“There’s still a lot for us to learn,” Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Multiple factors contribute to the variability in the skin microbiota, including age, sex, environment, immune system, host genotype, lifestyle, and pathobiology. The question becomes, when do these factors or impacts on the microbiota become clinically significant?”
According to Dr. Friedman, there are 10 times more bacteria cells than human cells in the human body, “but it’s not a fight to the finish; it’s not us versus them,” he said. “Together, we are a super organism.” There are also more than 500 species of bacteria on human skin excluding viruses and fungi, and each person carries up to 5 pounds of bacteria, which is akin to finding a new organ in the body.
“What’s so unique is that we each have our own bacterial fingerprint,” he said. “Whoever is sitting next to you? Their microbiota makeup is different than yours.”
Beyond genetics and environment, activities that can contribute to alterations in skin flora or skin dysbiosis include topical application of steroids, antibiotics, retinoids, harsh soaps, chemical and physical exfoliants, and resurfacing techniques. “With anything we apply or do to the skin, we are literally changing the home of many microorganisms, for good or bad,” he said.
In the realm of atopic dermatitis (AD), Staphylococcus aureus has been implicated as an offender in the pathophysiology of the disease. “It’s not about one single species of Staphylococcus, though,” said Dr. Friedman, who also is director of translational research at George Washington University. “We’re finding out that, depending on the severity of disease, Staph. epidermis may be part of the problem as opposed to it just being about Staph. aureus. Furthermore, and more importantly, these changes in the microbiota, specifically a decrease in microbial diversity, has been shown to precede a disease flare, highlighting the central role of maintaining microbial diversity and by definition, supporting the living barrier in our management of AD.”
With this in mind, researchers in one study used high-throughput sequencing to evaluate the microbial communities associated with affected and unaffected skin of 49 patients with AD before and after emollient treatment. Following 84 days of emollient application, clinical symptoms of AD improved in 72% of the study population and Stenotrophomonas species were significantly more abundant among responders.
Prebiotics, probiotics
“Our treatments certainly can positively impact the microbiota, as we have seen even recently with some of our new targeted therapies, but we can also directly provide support,” he continued. Prebiotics, which he defined as supplements or foods that contain a nondigestible ingredient that selectively stimulates the growth and/or activity of indigenous bacteria, can be found in many over-the-counter moisturizers.
For example, colloidal oatmeal has been found to support the growth of S. epidermidis and enhance the production of lactic acid. “We really don’t know much about what these induced changes mean from a clinical perspective; that has yet to be elucidated,” Dr. Friedman said.
In light of the recent attention to the early application of moisturizers in infants at high risk of developing AD in an effort to prevent or limit AD, “maybe part of this has to do with applying something that’s nurturing an evolving microbiota,” Dr. Friedman noted. “It’s something to think about.”
Yet another area of study involves the use of probiotics, which Dr. Friedman defined as supplements or foods that contain viable microorganisms that alter the microflora of the host. In a first-of-its-kind trial, researchers evaluated the safety and efficacy of self-administered topical Roseomonas mucosa in 10 adults and 5 children with AD. No adverse events or treatment complications were observed, and the topical R. mucosa was associated with significant decreases in measures of disease severity, topical steroid requirement, and S. aureus burden
In a more recent randomized trial of 11 patients with AD, Richard L. Gallo, MD, PhD, chair of dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and colleagues found that application of a personalized topical cream formulated from coagulase-negative Staphylococcus with antimicrobial activity against S. aureus reduced colonization of S. aureus and improved disease severity.
And in another randomized, controlled trial, Italian researchers enrolled 80 adults with mild to severe AD to receive a placebo or a supplement that was a mixture of lactobacilli for 56 days. They found that adults in the treatment arm showed an improvement in skin smoothness, skin moisturization, self-perception, and a decrease in the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) index as well as in levels of inflammatory markers associated with AD.
Dr. Friedman also discussed postbiotics, nonviable bacterial products or metabolic byproducts from probiotic microorganisms that have biologic activity in the host. In one trial, French researchers enrolled 75 people with AD who ranged in age from 6 to 70 years to receive a cream containing a 5% lysate of the nonpathogenic bacteria Vitreoscilla filiformis, or a vehicle cream for 30 days. They found that compared with the vehicle, V. filiformis lysate significantly decreased SCORAD levels and pruritus; active cream was shown to significantly decrease loss of sleep from day 0 to day 29.
Dr. Friedman characterized these novel approaches to AD as “an exciting area, one we need to pay attention to. But what I really want to know is, aside from these purposefully made and marketed products that have pre- and postprobiotics, is there a difference with some of the products we use already? My assumption is that there is, but we need to see that data.”
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant and/or advisory board member for Medscape/SanovaWorks, Oakstone Institute, L’Oréal, La Roche Posay, Galderma, Aveeno, Ortho Dermatologic, Microcures, Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, Hoth Therapeutics, Zylo Therapeutics, BMS, Vial, Janssen, Novocure, Dermavant, Regeneron/Sanofi, and Incyte. He has also received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Lilly, Janssen, Incyte, and Galderma.
NEW ORLEANS – .
“There’s still a lot for us to learn,” Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Multiple factors contribute to the variability in the skin microbiota, including age, sex, environment, immune system, host genotype, lifestyle, and pathobiology. The question becomes, when do these factors or impacts on the microbiota become clinically significant?”
According to Dr. Friedman, there are 10 times more bacteria cells than human cells in the human body, “but it’s not a fight to the finish; it’s not us versus them,” he said. “Together, we are a super organism.” There are also more than 500 species of bacteria on human skin excluding viruses and fungi, and each person carries up to 5 pounds of bacteria, which is akin to finding a new organ in the body.
“What’s so unique is that we each have our own bacterial fingerprint,” he said. “Whoever is sitting next to you? Their microbiota makeup is different than yours.”
Beyond genetics and environment, activities that can contribute to alterations in skin flora or skin dysbiosis include topical application of steroids, antibiotics, retinoids, harsh soaps, chemical and physical exfoliants, and resurfacing techniques. “With anything we apply or do to the skin, we are literally changing the home of many microorganisms, for good or bad,” he said.
In the realm of atopic dermatitis (AD), Staphylococcus aureus has been implicated as an offender in the pathophysiology of the disease. “It’s not about one single species of Staphylococcus, though,” said Dr. Friedman, who also is director of translational research at George Washington University. “We’re finding out that, depending on the severity of disease, Staph. epidermis may be part of the problem as opposed to it just being about Staph. aureus. Furthermore, and more importantly, these changes in the microbiota, specifically a decrease in microbial diversity, has been shown to precede a disease flare, highlighting the central role of maintaining microbial diversity and by definition, supporting the living barrier in our management of AD.”
With this in mind, researchers in one study used high-throughput sequencing to evaluate the microbial communities associated with affected and unaffected skin of 49 patients with AD before and after emollient treatment. Following 84 days of emollient application, clinical symptoms of AD improved in 72% of the study population and Stenotrophomonas species were significantly more abundant among responders.
Prebiotics, probiotics
“Our treatments certainly can positively impact the microbiota, as we have seen even recently with some of our new targeted therapies, but we can also directly provide support,” he continued. Prebiotics, which he defined as supplements or foods that contain a nondigestible ingredient that selectively stimulates the growth and/or activity of indigenous bacteria, can be found in many over-the-counter moisturizers.
For example, colloidal oatmeal has been found to support the growth of S. epidermidis and enhance the production of lactic acid. “We really don’t know much about what these induced changes mean from a clinical perspective; that has yet to be elucidated,” Dr. Friedman said.
In light of the recent attention to the early application of moisturizers in infants at high risk of developing AD in an effort to prevent or limit AD, “maybe part of this has to do with applying something that’s nurturing an evolving microbiota,” Dr. Friedman noted. “It’s something to think about.”
Yet another area of study involves the use of probiotics, which Dr. Friedman defined as supplements or foods that contain viable microorganisms that alter the microflora of the host. In a first-of-its-kind trial, researchers evaluated the safety and efficacy of self-administered topical Roseomonas mucosa in 10 adults and 5 children with AD. No adverse events or treatment complications were observed, and the topical R. mucosa was associated with significant decreases in measures of disease severity, topical steroid requirement, and S. aureus burden
In a more recent randomized trial of 11 patients with AD, Richard L. Gallo, MD, PhD, chair of dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and colleagues found that application of a personalized topical cream formulated from coagulase-negative Staphylococcus with antimicrobial activity against S. aureus reduced colonization of S. aureus and improved disease severity.
And in another randomized, controlled trial, Italian researchers enrolled 80 adults with mild to severe AD to receive a placebo or a supplement that was a mixture of lactobacilli for 56 days. They found that adults in the treatment arm showed an improvement in skin smoothness, skin moisturization, self-perception, and a decrease in the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) index as well as in levels of inflammatory markers associated with AD.
Dr. Friedman also discussed postbiotics, nonviable bacterial products or metabolic byproducts from probiotic microorganisms that have biologic activity in the host. In one trial, French researchers enrolled 75 people with AD who ranged in age from 6 to 70 years to receive a cream containing a 5% lysate of the nonpathogenic bacteria Vitreoscilla filiformis, or a vehicle cream for 30 days. They found that compared with the vehicle, V. filiformis lysate significantly decreased SCORAD levels and pruritus; active cream was shown to significantly decrease loss of sleep from day 0 to day 29.
Dr. Friedman characterized these novel approaches to AD as “an exciting area, one we need to pay attention to. But what I really want to know is, aside from these purposefully made and marketed products that have pre- and postprobiotics, is there a difference with some of the products we use already? My assumption is that there is, but we need to see that data.”
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant and/or advisory board member for Medscape/SanovaWorks, Oakstone Institute, L’Oréal, La Roche Posay, Galderma, Aveeno, Ortho Dermatologic, Microcures, Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, Hoth Therapeutics, Zylo Therapeutics, BMS, Vial, Janssen, Novocure, Dermavant, Regeneron/Sanofi, and Incyte. He has also received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Lilly, Janssen, Incyte, and Galderma.
NEW ORLEANS – .
“There’s still a lot for us to learn,” Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Multiple factors contribute to the variability in the skin microbiota, including age, sex, environment, immune system, host genotype, lifestyle, and pathobiology. The question becomes, when do these factors or impacts on the microbiota become clinically significant?”
According to Dr. Friedman, there are 10 times more bacteria cells than human cells in the human body, “but it’s not a fight to the finish; it’s not us versus them,” he said. “Together, we are a super organism.” There are also more than 500 species of bacteria on human skin excluding viruses and fungi, and each person carries up to 5 pounds of bacteria, which is akin to finding a new organ in the body.
“What’s so unique is that we each have our own bacterial fingerprint,” he said. “Whoever is sitting next to you? Their microbiota makeup is different than yours.”
Beyond genetics and environment, activities that can contribute to alterations in skin flora or skin dysbiosis include topical application of steroids, antibiotics, retinoids, harsh soaps, chemical and physical exfoliants, and resurfacing techniques. “With anything we apply or do to the skin, we are literally changing the home of many microorganisms, for good or bad,” he said.
In the realm of atopic dermatitis (AD), Staphylococcus aureus has been implicated as an offender in the pathophysiology of the disease. “It’s not about one single species of Staphylococcus, though,” said Dr. Friedman, who also is director of translational research at George Washington University. “We’re finding out that, depending on the severity of disease, Staph. epidermis may be part of the problem as opposed to it just being about Staph. aureus. Furthermore, and more importantly, these changes in the microbiota, specifically a decrease in microbial diversity, has been shown to precede a disease flare, highlighting the central role of maintaining microbial diversity and by definition, supporting the living barrier in our management of AD.”
With this in mind, researchers in one study used high-throughput sequencing to evaluate the microbial communities associated with affected and unaffected skin of 49 patients with AD before and after emollient treatment. Following 84 days of emollient application, clinical symptoms of AD improved in 72% of the study population and Stenotrophomonas species were significantly more abundant among responders.
Prebiotics, probiotics
“Our treatments certainly can positively impact the microbiota, as we have seen even recently with some of our new targeted therapies, but we can also directly provide support,” he continued. Prebiotics, which he defined as supplements or foods that contain a nondigestible ingredient that selectively stimulates the growth and/or activity of indigenous bacteria, can be found in many over-the-counter moisturizers.
For example, colloidal oatmeal has been found to support the growth of S. epidermidis and enhance the production of lactic acid. “We really don’t know much about what these induced changes mean from a clinical perspective; that has yet to be elucidated,” Dr. Friedman said.
In light of the recent attention to the early application of moisturizers in infants at high risk of developing AD in an effort to prevent or limit AD, “maybe part of this has to do with applying something that’s nurturing an evolving microbiota,” Dr. Friedman noted. “It’s something to think about.”
Yet another area of study involves the use of probiotics, which Dr. Friedman defined as supplements or foods that contain viable microorganisms that alter the microflora of the host. In a first-of-its-kind trial, researchers evaluated the safety and efficacy of self-administered topical Roseomonas mucosa in 10 adults and 5 children with AD. No adverse events or treatment complications were observed, and the topical R. mucosa was associated with significant decreases in measures of disease severity, topical steroid requirement, and S. aureus burden
In a more recent randomized trial of 11 patients with AD, Richard L. Gallo, MD, PhD, chair of dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and colleagues found that application of a personalized topical cream formulated from coagulase-negative Staphylococcus with antimicrobial activity against S. aureus reduced colonization of S. aureus and improved disease severity.
And in another randomized, controlled trial, Italian researchers enrolled 80 adults with mild to severe AD to receive a placebo or a supplement that was a mixture of lactobacilli for 56 days. They found that adults in the treatment arm showed an improvement in skin smoothness, skin moisturization, self-perception, and a decrease in the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) index as well as in levels of inflammatory markers associated with AD.
Dr. Friedman also discussed postbiotics, nonviable bacterial products or metabolic byproducts from probiotic microorganisms that have biologic activity in the host. In one trial, French researchers enrolled 75 people with AD who ranged in age from 6 to 70 years to receive a cream containing a 5% lysate of the nonpathogenic bacteria Vitreoscilla filiformis, or a vehicle cream for 30 days. They found that compared with the vehicle, V. filiformis lysate significantly decreased SCORAD levels and pruritus; active cream was shown to significantly decrease loss of sleep from day 0 to day 29.
Dr. Friedman characterized these novel approaches to AD as “an exciting area, one we need to pay attention to. But what I really want to know is, aside from these purposefully made and marketed products that have pre- and postprobiotics, is there a difference with some of the products we use already? My assumption is that there is, but we need to see that data.”
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant and/or advisory board member for Medscape/SanovaWorks, Oakstone Institute, L’Oréal, La Roche Posay, Galderma, Aveeno, Ortho Dermatologic, Microcures, Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, Hoth Therapeutics, Zylo Therapeutics, BMS, Vial, Janssen, Novocure, Dermavant, Regeneron/Sanofi, and Incyte. He has also received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Lilly, Janssen, Incyte, and Galderma.
AT AAD 2023
Practicing ethical medicine ‘is a requirement,’ not a luxury, expert says
NEW ORLEANS – , but results from a national survey of dermatology residency program directors suggest that ethics training is not a priority.
Of the 139 dermatology residency program or associate program directors surveyed in 2022, only 43% responded. Of these, 55% said that their program had no ethics curriculum. Among programs with an ethics curriculum, 75% were implemented in the past 10 years, and the most common settings for teaching ethics were formal didactics (32%) and ad hoc during clinical encounters (28%). Reported barriers to implementing and/or maintaining an ethics curriculum included a lack of time (30%), lack of faculty with expertise (24%), and lack of useful resources (20%).
“Clearly, medical ethics is needed more to be part of our dermatology residency curriculum,” one of the study authors, Jane M. Grant-Kels, MD, professor of dermatology, pathology, and pediatrics, and founding chair of dermatology at the University of Connecticut, Farmington, said during a plenary lecture at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Why? Because even though we’re physicians, and some of us have big egos, we are just human beings. We have all the faults and frailties of other humans. What we do as doctors often has unintended consequences that impact patients and society at large.”
Dr. Grant-Kels, one of the editors of the textbook “Dermatoethics”, said that, while she does not believe that physicians are intentionally unethical, “we stumble into bad behavior because we fool ourselves. We think that we are ethical. We think our colleagues are ethical, and we don’t view them with a clear, transparent eye. This is referred to as ethical fading or bounded ethicality.”
Similar to religion and good behavior, one can’t really teach someone to be ethical, she continued. “But you can teach people to think about ethics and to recognize an ethical dilemma when they’re in one,” she said. “Most articles that are available [pertain to] whether ethics can be taught or not, but there are very few resources available on how to actually teach ethics.”
That, she added, has been her goal for the last 2 decades: “How do I teach ethics without sounding like I’m more ethical than anybody else, and how do I make it relevant and fun? It’s a difficult challenge.”
Pillars of medical ethics
Dr. Grant-Kels defined ethics as a way of determining how individuals ought to act based on concepts of right and wrong. An ethical dilemma is when an individual faces two competing possibilities: either both justifiable or both unjustifiable, and you have to make a decision. The four pillars of medical ethics, she noted, are beneficence (the notion that the patient’s best interests come first); nonmaleficence (do no intentional harm); autonomy (the patient’s right to refuse or choose a treatment); and justice (fairness in how health care is distributed).
“Medical ethics are the moral principles by which physicians should conduct themselves,” she said. “There is normative ethics, which involves decisions about which moral norms or ethical arguments should we accept and why; and applied ethics, or applications of these norms to specific problems or cases. No ethics is better than bad ethics, and we can see that even in today’s world. The lack of ethics, or poor ethics, or the wrong ethics has terrible consequences.”
Ethics instruction
Dr. Grant-Kels provided a “top 10 list” of tips for incorporating ethics instruction into dermatology residency programs and clinical practices:
- Make room for ethics in your curriculum. “It’s not science, and it needs to be discussed and developed with faculty and residents,” she said.
- Focus on real situations that residents will experience. Discuss what you should do, what you might have done, and why.
- Share stories and be truthful. Include other faculty members, “because you need different perspectives,” she said.
- Go beyond what is right and wrong, and the rationale. “You have to talk about the impact, because decisions you make have unintended consequences for individual patients and for patient care in general,” Dr. Grant-Kels said.
- Practice, practice, practice. Make time for discussions involving ethics, “because it takes a lot of education to be able to identify ethical issues and process them,” she said. “The truth is, we can rationalize almost anything and convince ourselves that we made the right choice. That’s why we need to continue to practice good ethics.”
- Challenge the residents. “Decisions are not always straightforward,” she said. “Pressures push us and we start to justify small decisions and then bigger decisions. This is a very gray zone. What’s ethical for one person may not be ethical to another.”
- Encourage residents and colleagues to ask the right questions and give them confidence to make the right decisions. “We have to work in an environment of ethics,” Dr. Grant-Kels said. “Many of us are role models, and we are not always behaving the way we should be. As role models, we need to be aware of that.”
- Expose residents to a variety of issues. Ethics vary depending on the situation, the people involved, and the information presented.
- Ethics cannot just come up in an ethics class. “We need to foster a culture of ethics,” she said. “If things go wrong and unethical behavior is noted, it needs to be brought to the floor and discussed.”
- Discuss the misguided pursuit of happiness and ethical decision-making. In the opinion of Dr. Grant-Kels, people can behave badly when they’re pursuing something like a career advancement, a new house, or an expensive object like a car or a boat. “They think that if they get that job or get that promotion or if they buy that big house or they buy that sports car, they’re going to be really happy,” she said.
“That’s called impact bias, which causes focalism, where you focus on that one thing, like ‘I’m going to make a lot of money’ or ‘I’m going to buy that big house on the mountain.’ The truth is, buying that car doesn’t make you happy. Buying that big house doesn’t make you happy. We need to combat focalism with professionalism, which means conducting oneself with responsibility, integrity, accountability, and excellence. Practicing ethical medicine is not a luxury; it’s a requirement. We should all try for aspirational ethics.”
Dr. Grant-Kels reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – , but results from a national survey of dermatology residency program directors suggest that ethics training is not a priority.
Of the 139 dermatology residency program or associate program directors surveyed in 2022, only 43% responded. Of these, 55% said that their program had no ethics curriculum. Among programs with an ethics curriculum, 75% were implemented in the past 10 years, and the most common settings for teaching ethics were formal didactics (32%) and ad hoc during clinical encounters (28%). Reported barriers to implementing and/or maintaining an ethics curriculum included a lack of time (30%), lack of faculty with expertise (24%), and lack of useful resources (20%).
“Clearly, medical ethics is needed more to be part of our dermatology residency curriculum,” one of the study authors, Jane M. Grant-Kels, MD, professor of dermatology, pathology, and pediatrics, and founding chair of dermatology at the University of Connecticut, Farmington, said during a plenary lecture at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Why? Because even though we’re physicians, and some of us have big egos, we are just human beings. We have all the faults and frailties of other humans. What we do as doctors often has unintended consequences that impact patients and society at large.”
Dr. Grant-Kels, one of the editors of the textbook “Dermatoethics”, said that, while she does not believe that physicians are intentionally unethical, “we stumble into bad behavior because we fool ourselves. We think that we are ethical. We think our colleagues are ethical, and we don’t view them with a clear, transparent eye. This is referred to as ethical fading or bounded ethicality.”
Similar to religion and good behavior, one can’t really teach someone to be ethical, she continued. “But you can teach people to think about ethics and to recognize an ethical dilemma when they’re in one,” she said. “Most articles that are available [pertain to] whether ethics can be taught or not, but there are very few resources available on how to actually teach ethics.”
That, she added, has been her goal for the last 2 decades: “How do I teach ethics without sounding like I’m more ethical than anybody else, and how do I make it relevant and fun? It’s a difficult challenge.”
Pillars of medical ethics
Dr. Grant-Kels defined ethics as a way of determining how individuals ought to act based on concepts of right and wrong. An ethical dilemma is when an individual faces two competing possibilities: either both justifiable or both unjustifiable, and you have to make a decision. The four pillars of medical ethics, she noted, are beneficence (the notion that the patient’s best interests come first); nonmaleficence (do no intentional harm); autonomy (the patient’s right to refuse or choose a treatment); and justice (fairness in how health care is distributed).
“Medical ethics are the moral principles by which physicians should conduct themselves,” she said. “There is normative ethics, which involves decisions about which moral norms or ethical arguments should we accept and why; and applied ethics, or applications of these norms to specific problems or cases. No ethics is better than bad ethics, and we can see that even in today’s world. The lack of ethics, or poor ethics, or the wrong ethics has terrible consequences.”
Ethics instruction
Dr. Grant-Kels provided a “top 10 list” of tips for incorporating ethics instruction into dermatology residency programs and clinical practices:
- Make room for ethics in your curriculum. “It’s not science, and it needs to be discussed and developed with faculty and residents,” she said.
- Focus on real situations that residents will experience. Discuss what you should do, what you might have done, and why.
- Share stories and be truthful. Include other faculty members, “because you need different perspectives,” she said.
- Go beyond what is right and wrong, and the rationale. “You have to talk about the impact, because decisions you make have unintended consequences for individual patients and for patient care in general,” Dr. Grant-Kels said.
- Practice, practice, practice. Make time for discussions involving ethics, “because it takes a lot of education to be able to identify ethical issues and process them,” she said. “The truth is, we can rationalize almost anything and convince ourselves that we made the right choice. That’s why we need to continue to practice good ethics.”
- Challenge the residents. “Decisions are not always straightforward,” she said. “Pressures push us and we start to justify small decisions and then bigger decisions. This is a very gray zone. What’s ethical for one person may not be ethical to another.”
- Encourage residents and colleagues to ask the right questions and give them confidence to make the right decisions. “We have to work in an environment of ethics,” Dr. Grant-Kels said. “Many of us are role models, and we are not always behaving the way we should be. As role models, we need to be aware of that.”
- Expose residents to a variety of issues. Ethics vary depending on the situation, the people involved, and the information presented.
- Ethics cannot just come up in an ethics class. “We need to foster a culture of ethics,” she said. “If things go wrong and unethical behavior is noted, it needs to be brought to the floor and discussed.”
- Discuss the misguided pursuit of happiness and ethical decision-making. In the opinion of Dr. Grant-Kels, people can behave badly when they’re pursuing something like a career advancement, a new house, or an expensive object like a car or a boat. “They think that if they get that job or get that promotion or if they buy that big house or they buy that sports car, they’re going to be really happy,” she said.
“That’s called impact bias, which causes focalism, where you focus on that one thing, like ‘I’m going to make a lot of money’ or ‘I’m going to buy that big house on the mountain.’ The truth is, buying that car doesn’t make you happy. Buying that big house doesn’t make you happy. We need to combat focalism with professionalism, which means conducting oneself with responsibility, integrity, accountability, and excellence. Practicing ethical medicine is not a luxury; it’s a requirement. We should all try for aspirational ethics.”
Dr. Grant-Kels reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – , but results from a national survey of dermatology residency program directors suggest that ethics training is not a priority.
Of the 139 dermatology residency program or associate program directors surveyed in 2022, only 43% responded. Of these, 55% said that their program had no ethics curriculum. Among programs with an ethics curriculum, 75% were implemented in the past 10 years, and the most common settings for teaching ethics were formal didactics (32%) and ad hoc during clinical encounters (28%). Reported barriers to implementing and/or maintaining an ethics curriculum included a lack of time (30%), lack of faculty with expertise (24%), and lack of useful resources (20%).
“Clearly, medical ethics is needed more to be part of our dermatology residency curriculum,” one of the study authors, Jane M. Grant-Kels, MD, professor of dermatology, pathology, and pediatrics, and founding chair of dermatology at the University of Connecticut, Farmington, said during a plenary lecture at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Why? Because even though we’re physicians, and some of us have big egos, we are just human beings. We have all the faults and frailties of other humans. What we do as doctors often has unintended consequences that impact patients and society at large.”
Dr. Grant-Kels, one of the editors of the textbook “Dermatoethics”, said that, while she does not believe that physicians are intentionally unethical, “we stumble into bad behavior because we fool ourselves. We think that we are ethical. We think our colleagues are ethical, and we don’t view them with a clear, transparent eye. This is referred to as ethical fading or bounded ethicality.”
Similar to religion and good behavior, one can’t really teach someone to be ethical, she continued. “But you can teach people to think about ethics and to recognize an ethical dilemma when they’re in one,” she said. “Most articles that are available [pertain to] whether ethics can be taught or not, but there are very few resources available on how to actually teach ethics.”
That, she added, has been her goal for the last 2 decades: “How do I teach ethics without sounding like I’m more ethical than anybody else, and how do I make it relevant and fun? It’s a difficult challenge.”
Pillars of medical ethics
Dr. Grant-Kels defined ethics as a way of determining how individuals ought to act based on concepts of right and wrong. An ethical dilemma is when an individual faces two competing possibilities: either both justifiable or both unjustifiable, and you have to make a decision. The four pillars of medical ethics, she noted, are beneficence (the notion that the patient’s best interests come first); nonmaleficence (do no intentional harm); autonomy (the patient’s right to refuse or choose a treatment); and justice (fairness in how health care is distributed).
“Medical ethics are the moral principles by which physicians should conduct themselves,” she said. “There is normative ethics, which involves decisions about which moral norms or ethical arguments should we accept and why; and applied ethics, or applications of these norms to specific problems or cases. No ethics is better than bad ethics, and we can see that even in today’s world. The lack of ethics, or poor ethics, or the wrong ethics has terrible consequences.”
Ethics instruction
Dr. Grant-Kels provided a “top 10 list” of tips for incorporating ethics instruction into dermatology residency programs and clinical practices:
- Make room for ethics in your curriculum. “It’s not science, and it needs to be discussed and developed with faculty and residents,” she said.
- Focus on real situations that residents will experience. Discuss what you should do, what you might have done, and why.
- Share stories and be truthful. Include other faculty members, “because you need different perspectives,” she said.
- Go beyond what is right and wrong, and the rationale. “You have to talk about the impact, because decisions you make have unintended consequences for individual patients and for patient care in general,” Dr. Grant-Kels said.
- Practice, practice, practice. Make time for discussions involving ethics, “because it takes a lot of education to be able to identify ethical issues and process them,” she said. “The truth is, we can rationalize almost anything and convince ourselves that we made the right choice. That’s why we need to continue to practice good ethics.”
- Challenge the residents. “Decisions are not always straightforward,” she said. “Pressures push us and we start to justify small decisions and then bigger decisions. This is a very gray zone. What’s ethical for one person may not be ethical to another.”
- Encourage residents and colleagues to ask the right questions and give them confidence to make the right decisions. “We have to work in an environment of ethics,” Dr. Grant-Kels said. “Many of us are role models, and we are not always behaving the way we should be. As role models, we need to be aware of that.”
- Expose residents to a variety of issues. Ethics vary depending on the situation, the people involved, and the information presented.
- Ethics cannot just come up in an ethics class. “We need to foster a culture of ethics,” she said. “If things go wrong and unethical behavior is noted, it needs to be brought to the floor and discussed.”
- Discuss the misguided pursuit of happiness and ethical decision-making. In the opinion of Dr. Grant-Kels, people can behave badly when they’re pursuing something like a career advancement, a new house, or an expensive object like a car or a boat. “They think that if they get that job or get that promotion or if they buy that big house or they buy that sports car, they’re going to be really happy,” she said.
“That’s called impact bias, which causes focalism, where you focus on that one thing, like ‘I’m going to make a lot of money’ or ‘I’m going to buy that big house on the mountain.’ The truth is, buying that car doesn’t make you happy. Buying that big house doesn’t make you happy. We need to combat focalism with professionalism, which means conducting oneself with responsibility, integrity, accountability, and excellence. Practicing ethical medicine is not a luxury; it’s a requirement. We should all try for aspirational ethics.”
Dr. Grant-Kels reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
AT AAD 2023
Expect increased demand for experienced dermatologic care of Asian skin
NEW ORLEANS – With the Asian population estimated to increase to 41 million by 2050 in the United States, expect the demand for experienced dermatologic care of patients with Asian skin to increase in the coming years, Hye Jin (Leah) Chung, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Asians account for about 60% of the global population,” said Dr. Chung, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, and director of the Asian Skin Clinic at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston. Along with the estimate that Asians are expected to make up 25% of Canada’s population by 2036, “we will most likely encounter more Asian skin type patients in North America,” Dr. Chung said, noting that the Asian population “is very diverse, ranging from skin type 3 in Far East Asia to skin type 5 in India.”
During her presentation, she provided tips for treating hypertrophic scars and keloids in this patient population when intralesional corticosteroids fail. Typically, her first option is to combine an intralesional corticosteroid with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a pyrimidine analogue with antimetabolite activity. 5-FU “can cause cell apoptosis of endothelial cells and fibroblasts (which steroids cannot), cell cycle arrest, and TGF-beta [transforming growth factor beta]-induced COL1A2 transcription,” Dr. Chung said. The recommended ratio between 5-FU and steroids in the literature is variable, from a 9:1 ratio to a 1:1 ratio. “In my practice I do not inject more than 100 mg at a time,” she said. Several studies of this approach led by Asian investigators used weekly injections, “but that’s not practical in the U.S. I usually do monthly injections.”
A large systematic review and meta-analysis confirmed that the combination of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide and 5-FU achieved a better efficacy and fewer complications than triamcinolone alone for treating hypertrophic scars and keloids. Potential side effects from 5-FU injections include pain/pruritus, transient hyperpigmentation (especially in skin types 4-6), ulceration, teratogenicity, and transient alopecia.
A more recent meta-analysis comparing the efficacy of multiple drug injections for hypertrophic scars and keloids confirmed that the combination of triamcinolone and 5-FU was superior to bleomycin, verapamil, 5-FU alone, and triamcinolone alone. “And, there was no difference between 5-FU/steroid combination and botulinum toxin A,” Dr. Chung added. “Some parts of the world are using botulinum toxin with mixed results. Based on the amount of toxin required for keloids, this would be cost prohibitive in the U.S.”
Another approach to treating hypertrophic scars and keloids in Asian skin is laser-assisted drug delivery. “First, you can use a fractional ablative laser to create a hole in the epidermis and dermis,” Dr. Chung said. “Then you can apply the suspension topically to the holes. You can also use a steroid ointment or cream after laser treatment for drug delivery.”
Combining pulsed dye laser with steroid injections is another option. Pulsed dye lasers coagulate microvasculature within keloid tissue, “which can cause tissue hypoxia and can decrease growth factors or cytokines for fibrosis within the tissue,” Dr. Chung said. At the cellular level, pulsed dye laser alone can decrease connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), TGF-beta 1, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and collagen III, and increases matrix metalloproteinase–13 (MMP-13), P53, ERK and p38 MAPK, apoptosis, blockade of AP-1 transcription, and cell cycle changes.
In 2004, plastic surgeons in Korea described a new approach for removing earlobe keloids, which they termed a “keloid fillet flap”. For the procedure, about 50% of the keloid margin is incised with a #15 scalpel blade. “Then you dissect the keloid from the surrounding tissue with a blade or curved scissors,” Dr. Chung said. “Next, you excise the keloid, so you have some dead space. After hemostasis you place the fillet flap to cover the wound. After you trim the redundant tissue, you can close it with epidermal sutures.”
In her clinical experience, she finds the fillet flap “very helpful for fast recovery” and it is associated with less pain. “Several studies have confirmed an excellent improvement of keloids, low recurrence rate, and rare side effects from a fillet flap and adjuvant intralesional corticosteroids. Occasionally, you may see flap necrosis but usually patients do well with topical antibiotics or petrolatum jelly.”
Dr. Chung also discussed her approach to treating papular scars in Asian patients. She described papular scars as underrecognized, anetoderma-like scars on the central face and trunk. “They comprise about 11% of all acne scars but up to 19% of patients with such scars may not recall a history of acne,” she said. Biopsies of papular scars reveal marked reduction or thinning of elastic fibers around hair follicles.
“Papular scars are difficult to treat,” she said. “If you have a conventional Er:YAG or CO2 laser, you can create tiny holes within the scars,” she said, referring to studies on these approaches. Another treatment option is needle-guided radiofrequency, she noted.
Dr. Chung reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – With the Asian population estimated to increase to 41 million by 2050 in the United States, expect the demand for experienced dermatologic care of patients with Asian skin to increase in the coming years, Hye Jin (Leah) Chung, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Asians account for about 60% of the global population,” said Dr. Chung, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, and director of the Asian Skin Clinic at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston. Along with the estimate that Asians are expected to make up 25% of Canada’s population by 2036, “we will most likely encounter more Asian skin type patients in North America,” Dr. Chung said, noting that the Asian population “is very diverse, ranging from skin type 3 in Far East Asia to skin type 5 in India.”
During her presentation, she provided tips for treating hypertrophic scars and keloids in this patient population when intralesional corticosteroids fail. Typically, her first option is to combine an intralesional corticosteroid with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a pyrimidine analogue with antimetabolite activity. 5-FU “can cause cell apoptosis of endothelial cells and fibroblasts (which steroids cannot), cell cycle arrest, and TGF-beta [transforming growth factor beta]-induced COL1A2 transcription,” Dr. Chung said. The recommended ratio between 5-FU and steroids in the literature is variable, from a 9:1 ratio to a 1:1 ratio. “In my practice I do not inject more than 100 mg at a time,” she said. Several studies of this approach led by Asian investigators used weekly injections, “but that’s not practical in the U.S. I usually do monthly injections.”
A large systematic review and meta-analysis confirmed that the combination of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide and 5-FU achieved a better efficacy and fewer complications than triamcinolone alone for treating hypertrophic scars and keloids. Potential side effects from 5-FU injections include pain/pruritus, transient hyperpigmentation (especially in skin types 4-6), ulceration, teratogenicity, and transient alopecia.
A more recent meta-analysis comparing the efficacy of multiple drug injections for hypertrophic scars and keloids confirmed that the combination of triamcinolone and 5-FU was superior to bleomycin, verapamil, 5-FU alone, and triamcinolone alone. “And, there was no difference between 5-FU/steroid combination and botulinum toxin A,” Dr. Chung added. “Some parts of the world are using botulinum toxin with mixed results. Based on the amount of toxin required for keloids, this would be cost prohibitive in the U.S.”
Another approach to treating hypertrophic scars and keloids in Asian skin is laser-assisted drug delivery. “First, you can use a fractional ablative laser to create a hole in the epidermis and dermis,” Dr. Chung said. “Then you can apply the suspension topically to the holes. You can also use a steroid ointment or cream after laser treatment for drug delivery.”
Combining pulsed dye laser with steroid injections is another option. Pulsed dye lasers coagulate microvasculature within keloid tissue, “which can cause tissue hypoxia and can decrease growth factors or cytokines for fibrosis within the tissue,” Dr. Chung said. At the cellular level, pulsed dye laser alone can decrease connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), TGF-beta 1, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and collagen III, and increases matrix metalloproteinase–13 (MMP-13), P53, ERK and p38 MAPK, apoptosis, blockade of AP-1 transcription, and cell cycle changes.
In 2004, plastic surgeons in Korea described a new approach for removing earlobe keloids, which they termed a “keloid fillet flap”. For the procedure, about 50% of the keloid margin is incised with a #15 scalpel blade. “Then you dissect the keloid from the surrounding tissue with a blade or curved scissors,” Dr. Chung said. “Next, you excise the keloid, so you have some dead space. After hemostasis you place the fillet flap to cover the wound. After you trim the redundant tissue, you can close it with epidermal sutures.”
In her clinical experience, she finds the fillet flap “very helpful for fast recovery” and it is associated with less pain. “Several studies have confirmed an excellent improvement of keloids, low recurrence rate, and rare side effects from a fillet flap and adjuvant intralesional corticosteroids. Occasionally, you may see flap necrosis but usually patients do well with topical antibiotics or petrolatum jelly.”
Dr. Chung also discussed her approach to treating papular scars in Asian patients. She described papular scars as underrecognized, anetoderma-like scars on the central face and trunk. “They comprise about 11% of all acne scars but up to 19% of patients with such scars may not recall a history of acne,” she said. Biopsies of papular scars reveal marked reduction or thinning of elastic fibers around hair follicles.
“Papular scars are difficult to treat,” she said. “If you have a conventional Er:YAG or CO2 laser, you can create tiny holes within the scars,” she said, referring to studies on these approaches. Another treatment option is needle-guided radiofrequency, she noted.
Dr. Chung reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – With the Asian population estimated to increase to 41 million by 2050 in the United States, expect the demand for experienced dermatologic care of patients with Asian skin to increase in the coming years, Hye Jin (Leah) Chung, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Asians account for about 60% of the global population,” said Dr. Chung, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, and director of the Asian Skin Clinic at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston. Along with the estimate that Asians are expected to make up 25% of Canada’s population by 2036, “we will most likely encounter more Asian skin type patients in North America,” Dr. Chung said, noting that the Asian population “is very diverse, ranging from skin type 3 in Far East Asia to skin type 5 in India.”
During her presentation, she provided tips for treating hypertrophic scars and keloids in this patient population when intralesional corticosteroids fail. Typically, her first option is to combine an intralesional corticosteroid with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a pyrimidine analogue with antimetabolite activity. 5-FU “can cause cell apoptosis of endothelial cells and fibroblasts (which steroids cannot), cell cycle arrest, and TGF-beta [transforming growth factor beta]-induced COL1A2 transcription,” Dr. Chung said. The recommended ratio between 5-FU and steroids in the literature is variable, from a 9:1 ratio to a 1:1 ratio. “In my practice I do not inject more than 100 mg at a time,” she said. Several studies of this approach led by Asian investigators used weekly injections, “but that’s not practical in the U.S. I usually do monthly injections.”
A large systematic review and meta-analysis confirmed that the combination of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide and 5-FU achieved a better efficacy and fewer complications than triamcinolone alone for treating hypertrophic scars and keloids. Potential side effects from 5-FU injections include pain/pruritus, transient hyperpigmentation (especially in skin types 4-6), ulceration, teratogenicity, and transient alopecia.
A more recent meta-analysis comparing the efficacy of multiple drug injections for hypertrophic scars and keloids confirmed that the combination of triamcinolone and 5-FU was superior to bleomycin, verapamil, 5-FU alone, and triamcinolone alone. “And, there was no difference between 5-FU/steroid combination and botulinum toxin A,” Dr. Chung added. “Some parts of the world are using botulinum toxin with mixed results. Based on the amount of toxin required for keloids, this would be cost prohibitive in the U.S.”
Another approach to treating hypertrophic scars and keloids in Asian skin is laser-assisted drug delivery. “First, you can use a fractional ablative laser to create a hole in the epidermis and dermis,” Dr. Chung said. “Then you can apply the suspension topically to the holes. You can also use a steroid ointment or cream after laser treatment for drug delivery.”
Combining pulsed dye laser with steroid injections is another option. Pulsed dye lasers coagulate microvasculature within keloid tissue, “which can cause tissue hypoxia and can decrease growth factors or cytokines for fibrosis within the tissue,” Dr. Chung said. At the cellular level, pulsed dye laser alone can decrease connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), TGF-beta 1, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and collagen III, and increases matrix metalloproteinase–13 (MMP-13), P53, ERK and p38 MAPK, apoptosis, blockade of AP-1 transcription, and cell cycle changes.
In 2004, plastic surgeons in Korea described a new approach for removing earlobe keloids, which they termed a “keloid fillet flap”. For the procedure, about 50% of the keloid margin is incised with a #15 scalpel blade. “Then you dissect the keloid from the surrounding tissue with a blade or curved scissors,” Dr. Chung said. “Next, you excise the keloid, so you have some dead space. After hemostasis you place the fillet flap to cover the wound. After you trim the redundant tissue, you can close it with epidermal sutures.”
In her clinical experience, she finds the fillet flap “very helpful for fast recovery” and it is associated with less pain. “Several studies have confirmed an excellent improvement of keloids, low recurrence rate, and rare side effects from a fillet flap and adjuvant intralesional corticosteroids. Occasionally, you may see flap necrosis but usually patients do well with topical antibiotics or petrolatum jelly.”
Dr. Chung also discussed her approach to treating papular scars in Asian patients. She described papular scars as underrecognized, anetoderma-like scars on the central face and trunk. “They comprise about 11% of all acne scars but up to 19% of patients with such scars may not recall a history of acne,” she said. Biopsies of papular scars reveal marked reduction or thinning of elastic fibers around hair follicles.
“Papular scars are difficult to treat,” she said. “If you have a conventional Er:YAG or CO2 laser, you can create tiny holes within the scars,” she said, referring to studies on these approaches. Another treatment option is needle-guided radiofrequency, she noted.
Dr. Chung reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
AT AAD 2023
Limited treatment options exist for brittle nail syndrome
NEW ORLEANS – .
“The mainstay of treatment is irritant avoidance and moisturization,” Shari R. Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical dermatology and director of the nail division at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “This works well if patients are religious about doing it.”
Brittle nail syndrome affects about 20% of adults, she said, and is more common in females, particularly those older than age 50. Most cases are idiopathic, but some are secondary to dermatologic diseases including nail psoriasis and nail lichen planus, and systemic diseases such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. They are more common in patients in certain occupations such as carpentry. “The pathogenesis is poorly understood but is thought to be due to weakened intercellular keratinocyte bridges, decreased cholesterol sulphate in the nail plate, and reduced water content in the nail plate,” Dr. Lipner said.
Key clinical findings include onychoschizia (peeling of the nail plate), onychorrhexis (an increase in the longitudinal ridges and furrows, sometimes leading to splitting), and superficial granulation of keratin. Treatment involves general measures. “You want to treat the underlying cause and recommend that the patient avoid water and irritant exposure,” she said. Her general instructions for affected patients are to wear latex gloves for wet work and cotton gloves for dry work, avoid triclosan-based hand sanitizers, avoid nail cosmetics, minimize nail trauma, and foster moisturization.“It’s important to give these instructions verbally and in written form,” she said. “In our practice, we designed a QR code that links to our patient handout.”
According to Dr. Lipner, the promotion of vitamins and supplements such as biotin, vitamin D, amino acids, and chromium for treating brittle nail syndrome is rampant on the Internet and on social media, but no rigorously designed clinical trials have shown efficacy for any of them. “Very few people are deficient in biotin, except for those with inherited enzyme deficiencies,” and most people “can get all the biotin they need from a regular diet,” she said.
The initial rationale for using biotin for nails comes from the veterinary literature, she continued. In the 1940s, chickens with biotin deficiency developed fissures in their feet and parrot-like beaks. In the 1970s, pigs with biotin deficiency developed friable hooves, which was corrected with biotin supplementation. “By the 1980s it was standard practice to supplement the feet of pigs with biotin,” she said.
In a human trial from 1989, German researchers enrolled 71 patients with brittle nail syndrome who took oral biotin, 2.5 mg daily. Of the 45 patients evaluated, 41 (91%) showed improvement in firmness and hardness of the fingernails over the course of 5.5 months, but there was no good control group, Dr. Lipner said. In a follow-up study, the same German researchers used scanning electron microscopy to evaluate 22 patients with brittle nails who took oral biotin 2.5 mg daily and compared them with 10 patients with normal nails who did not take biotin. They found a 25% increase in nail plate thickness in the biotin group and onychoschizia resolved in 50% of patients who received biotin. “But again, there was no good control group,” Dr. Lipner said.
In a third study on the topic, researchers surveyed 46 patients who presented with onychorrhexis and/or onychoschizia on clinical exam and took 2.5 mg of biotin daily. Of the 35 survey respondents, 63% subjectively reported improvement in their nails at a mean of 2 months. “This is where we are today: There have been studies of only 80 patients that were done 25 years ago,” Dr. Lipner said. “That’s all of our evidence for biotin for the treatment of brittle nail syndrome.”
FDA warning about biotin
Additional cause for concern, she continued, is the safety communication issued by the FDA in 2017, stating that the use of biotin may interfere with certain lab tests such as thyroid tests and cardiac enzymes, in some cases leading to death. The safety communication was updated in 2019.
In 2018, Dr. Lipner and colleagues administered an anonymous survey to 447 patients at their clinic asking about their use of biotin supplements. Of the 447 patients, 34% reported current use of biotin. Among biotin users, 7% were aware of the FDA warning, 29% of respondents reported that it was recommended by either a primary care physician or a dermatologist, and 56% underwent laboratory testing while taking biotin. “It’s our duty to warn our patients about the evidence for biotin for treating brittle nails, and about this interference on laboratory tests,” Dr. Lipner said.
Other treatment options for brittle nail syndrome include two lacquers that are available by prescription. One contains hydroxypropyl chitosan, Equisetum arvense, and methylsulphonylmethane; the other contains 16% poly-ureaurethane, but has not been well studied. “These products can be very expensive if not covered by insurance,” Dr. Lipner said.
As an alternative, she recommends Nail Tek CITRA 2 Nail Strengthener, which is available for less than $10 from Walmart and other retailers.
Cyclosporine emulsion also has been studied for brittle nail syndrome, but results to date have been underwhelming. Dr. Lipner and colleagues are exploring the effect of platelet rich plasma for treating brittle nails on the premise that it will improve nail growth and promote healing, in a 16-week trial that has enrolled 10 patients and includes both a Physician Global Improvement Assessment (PGIA) and a Physician Global Assessment (PGA) score. “Our data is being analyzed by three independent nail experts, and we hope to report the findings next year,” she said.
Dr. Lipner reported having no disclosures relevant to her presentation.
NEW ORLEANS – .
“The mainstay of treatment is irritant avoidance and moisturization,” Shari R. Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical dermatology and director of the nail division at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “This works well if patients are religious about doing it.”
Brittle nail syndrome affects about 20% of adults, she said, and is more common in females, particularly those older than age 50. Most cases are idiopathic, but some are secondary to dermatologic diseases including nail psoriasis and nail lichen planus, and systemic diseases such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. They are more common in patients in certain occupations such as carpentry. “The pathogenesis is poorly understood but is thought to be due to weakened intercellular keratinocyte bridges, decreased cholesterol sulphate in the nail plate, and reduced water content in the nail plate,” Dr. Lipner said.
Key clinical findings include onychoschizia (peeling of the nail plate), onychorrhexis (an increase in the longitudinal ridges and furrows, sometimes leading to splitting), and superficial granulation of keratin. Treatment involves general measures. “You want to treat the underlying cause and recommend that the patient avoid water and irritant exposure,” she said. Her general instructions for affected patients are to wear latex gloves for wet work and cotton gloves for dry work, avoid triclosan-based hand sanitizers, avoid nail cosmetics, minimize nail trauma, and foster moisturization.“It’s important to give these instructions verbally and in written form,” she said. “In our practice, we designed a QR code that links to our patient handout.”
According to Dr. Lipner, the promotion of vitamins and supplements such as biotin, vitamin D, amino acids, and chromium for treating brittle nail syndrome is rampant on the Internet and on social media, but no rigorously designed clinical trials have shown efficacy for any of them. “Very few people are deficient in biotin, except for those with inherited enzyme deficiencies,” and most people “can get all the biotin they need from a regular diet,” she said.
The initial rationale for using biotin for nails comes from the veterinary literature, she continued. In the 1940s, chickens with biotin deficiency developed fissures in their feet and parrot-like beaks. In the 1970s, pigs with biotin deficiency developed friable hooves, which was corrected with biotin supplementation. “By the 1980s it was standard practice to supplement the feet of pigs with biotin,” she said.
In a human trial from 1989, German researchers enrolled 71 patients with brittle nail syndrome who took oral biotin, 2.5 mg daily. Of the 45 patients evaluated, 41 (91%) showed improvement in firmness and hardness of the fingernails over the course of 5.5 months, but there was no good control group, Dr. Lipner said. In a follow-up study, the same German researchers used scanning electron microscopy to evaluate 22 patients with brittle nails who took oral biotin 2.5 mg daily and compared them with 10 patients with normal nails who did not take biotin. They found a 25% increase in nail plate thickness in the biotin group and onychoschizia resolved in 50% of patients who received biotin. “But again, there was no good control group,” Dr. Lipner said.
In a third study on the topic, researchers surveyed 46 patients who presented with onychorrhexis and/or onychoschizia on clinical exam and took 2.5 mg of biotin daily. Of the 35 survey respondents, 63% subjectively reported improvement in their nails at a mean of 2 months. “This is where we are today: There have been studies of only 80 patients that were done 25 years ago,” Dr. Lipner said. “That’s all of our evidence for biotin for the treatment of brittle nail syndrome.”
FDA warning about biotin
Additional cause for concern, she continued, is the safety communication issued by the FDA in 2017, stating that the use of biotin may interfere with certain lab tests such as thyroid tests and cardiac enzymes, in some cases leading to death. The safety communication was updated in 2019.
In 2018, Dr. Lipner and colleagues administered an anonymous survey to 447 patients at their clinic asking about their use of biotin supplements. Of the 447 patients, 34% reported current use of biotin. Among biotin users, 7% were aware of the FDA warning, 29% of respondents reported that it was recommended by either a primary care physician or a dermatologist, and 56% underwent laboratory testing while taking biotin. “It’s our duty to warn our patients about the evidence for biotin for treating brittle nails, and about this interference on laboratory tests,” Dr. Lipner said.
Other treatment options for brittle nail syndrome include two lacquers that are available by prescription. One contains hydroxypropyl chitosan, Equisetum arvense, and methylsulphonylmethane; the other contains 16% poly-ureaurethane, but has not been well studied. “These products can be very expensive if not covered by insurance,” Dr. Lipner said.
As an alternative, she recommends Nail Tek CITRA 2 Nail Strengthener, which is available for less than $10 from Walmart and other retailers.
Cyclosporine emulsion also has been studied for brittle nail syndrome, but results to date have been underwhelming. Dr. Lipner and colleagues are exploring the effect of platelet rich plasma for treating brittle nails on the premise that it will improve nail growth and promote healing, in a 16-week trial that has enrolled 10 patients and includes both a Physician Global Improvement Assessment (PGIA) and a Physician Global Assessment (PGA) score. “Our data is being analyzed by three independent nail experts, and we hope to report the findings next year,” she said.
Dr. Lipner reported having no disclosures relevant to her presentation.
NEW ORLEANS – .
“The mainstay of treatment is irritant avoidance and moisturization,” Shari R. Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical dermatology and director of the nail division at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “This works well if patients are religious about doing it.”
Brittle nail syndrome affects about 20% of adults, she said, and is more common in females, particularly those older than age 50. Most cases are idiopathic, but some are secondary to dermatologic diseases including nail psoriasis and nail lichen planus, and systemic diseases such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. They are more common in patients in certain occupations such as carpentry. “The pathogenesis is poorly understood but is thought to be due to weakened intercellular keratinocyte bridges, decreased cholesterol sulphate in the nail plate, and reduced water content in the nail plate,” Dr. Lipner said.
Key clinical findings include onychoschizia (peeling of the nail plate), onychorrhexis (an increase in the longitudinal ridges and furrows, sometimes leading to splitting), and superficial granulation of keratin. Treatment involves general measures. “You want to treat the underlying cause and recommend that the patient avoid water and irritant exposure,” she said. Her general instructions for affected patients are to wear latex gloves for wet work and cotton gloves for dry work, avoid triclosan-based hand sanitizers, avoid nail cosmetics, minimize nail trauma, and foster moisturization.“It’s important to give these instructions verbally and in written form,” she said. “In our practice, we designed a QR code that links to our patient handout.”
According to Dr. Lipner, the promotion of vitamins and supplements such as biotin, vitamin D, amino acids, and chromium for treating brittle nail syndrome is rampant on the Internet and on social media, but no rigorously designed clinical trials have shown efficacy for any of them. “Very few people are deficient in biotin, except for those with inherited enzyme deficiencies,” and most people “can get all the biotin they need from a regular diet,” she said.
The initial rationale for using biotin for nails comes from the veterinary literature, she continued. In the 1940s, chickens with biotin deficiency developed fissures in their feet and parrot-like beaks. In the 1970s, pigs with biotin deficiency developed friable hooves, which was corrected with biotin supplementation. “By the 1980s it was standard practice to supplement the feet of pigs with biotin,” she said.
In a human trial from 1989, German researchers enrolled 71 patients with brittle nail syndrome who took oral biotin, 2.5 mg daily. Of the 45 patients evaluated, 41 (91%) showed improvement in firmness and hardness of the fingernails over the course of 5.5 months, but there was no good control group, Dr. Lipner said. In a follow-up study, the same German researchers used scanning electron microscopy to evaluate 22 patients with brittle nails who took oral biotin 2.5 mg daily and compared them with 10 patients with normal nails who did not take biotin. They found a 25% increase in nail plate thickness in the biotin group and onychoschizia resolved in 50% of patients who received biotin. “But again, there was no good control group,” Dr. Lipner said.
In a third study on the topic, researchers surveyed 46 patients who presented with onychorrhexis and/or onychoschizia on clinical exam and took 2.5 mg of biotin daily. Of the 35 survey respondents, 63% subjectively reported improvement in their nails at a mean of 2 months. “This is where we are today: There have been studies of only 80 patients that were done 25 years ago,” Dr. Lipner said. “That’s all of our evidence for biotin for the treatment of brittle nail syndrome.”
FDA warning about biotin
Additional cause for concern, she continued, is the safety communication issued by the FDA in 2017, stating that the use of biotin may interfere with certain lab tests such as thyroid tests and cardiac enzymes, in some cases leading to death. The safety communication was updated in 2019.
In 2018, Dr. Lipner and colleagues administered an anonymous survey to 447 patients at their clinic asking about their use of biotin supplements. Of the 447 patients, 34% reported current use of biotin. Among biotin users, 7% were aware of the FDA warning, 29% of respondents reported that it was recommended by either a primary care physician or a dermatologist, and 56% underwent laboratory testing while taking biotin. “It’s our duty to warn our patients about the evidence for biotin for treating brittle nails, and about this interference on laboratory tests,” Dr. Lipner said.
Other treatment options for brittle nail syndrome include two lacquers that are available by prescription. One contains hydroxypropyl chitosan, Equisetum arvense, and methylsulphonylmethane; the other contains 16% poly-ureaurethane, but has not been well studied. “These products can be very expensive if not covered by insurance,” Dr. Lipner said.
As an alternative, she recommends Nail Tek CITRA 2 Nail Strengthener, which is available for less than $10 from Walmart and other retailers.
Cyclosporine emulsion also has been studied for brittle nail syndrome, but results to date have been underwhelming. Dr. Lipner and colleagues are exploring the effect of platelet rich plasma for treating brittle nails on the premise that it will improve nail growth and promote healing, in a 16-week trial that has enrolled 10 patients and includes both a Physician Global Improvement Assessment (PGIA) and a Physician Global Assessment (PGA) score. “Our data is being analyzed by three independent nail experts, and we hope to report the findings next year,” she said.
Dr. Lipner reported having no disclosures relevant to her presentation.
AT AAD 2023
JAK inhibitor ivarmacitinib shows efficacy for atopic dermatitis in a pivotal trial
NEW ORLEANS – The presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Two doses were studied in the placebo-controlled trial and both demonstrated “a favorable benefit-to-risk profile in patients with moderate to severe AD,” reported Yan Zhao, MD, a clinician and researcher in the department of dermatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing.
In the study, called QUARTZ3, 336 patients aged 12 and older at 51 sites in China and Canada were randomized to 4 mg once-daily ivarmacitinib, 8 mg once-daily QD ivarmacitinib, or placebo. The mean age of the population was 32 years and approximately one-third were female.
The mean duration of AD for participants was 10 years. The mean baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was near 30. On the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) tool, approximately 40% had a score of 4, which is the highest score on the scale and indicates severe disease. The remaining patients had an IGA score of 3.
The co-primary endpoints were change in IGA and EASI scores at 16 weeks, and both improved rapidly, showing statistical significance relative to placebo by 4 weeks with no plateauing effect at the end of the 16-week trial. By week 16, the proportion of patients with an EASI score of 75, signifying a 75% improvement, was 66%, 54%, and 22% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups (P < .001 versus placebo for both doses of active therapy), respectively.
The pattern of the IGA response was similar. By week 16, the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) was 42%, 36%, and 9% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups, respectively. The advantage of either dose over placebo was highly significant (P < .001) at 8, 12, and 16 weeks.
For the WI-NRS (Worst Itch – Numeric Rating Scale), the advantage of the 8-mg dose relative to placebo was significant (P < .001) at the 1-week evaluation. By 2 weeks, the 4-mg dose had gained the same degree of statistical significance relative to placebo. After week 4, when the maximum proportion of patients with a WI-NRS score ≤ 4 was reached (50%, 35%, and 10% in the 8-mg, 4-mg, and placebo groups), and the relative advantage of active treatment persisted until the end of the 16-week study.
Two scales were used to evaluate change in quality of life. On the DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) and POEM (Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure), improvements were again rapid and sustained. By week 4, improvement with the 8-mg dose was about fourfold greater (P < .001) than improvement with placebo for DLQI and about sixfold greater (P < .001) for POEM. For the 4-mg dose, the relative differences were approximately threefold and fourfold greater, and both were significant (P <.001).
There was no further gain in these quality-of-life scales from week 4 to week 16, but the advantages relative to placebo were generally sustained, Dr. Zhao reported.
Ivarmacitinib was safe and well-tolerated, according to Dr. Zhao. The proportion of patients with a treatment-emergent adverse event that led to drug discontinuation was numerically higher (5.4%) in the placebo group than in the 8-mg (3.6%) or 4-mg group (2.7%). Rates of infection in the three groups were similar, and there were no major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) or thromboembolism observed in any group.
Ivarmacitinib, which has about a 10-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK2 and a more than 70-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK3, is being tested for rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and alopecia areata in addition to AD, Dr. Zhao said. She also reported that an application for new drug approval has been submitted in China. Efforts to pursue regulatory approval elsewhere are anticipated.
Currently, there are three JAK inhibitors licensed for the treatment of AD in the United States. Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) and abrocitinib (Cibinqo) are also once-daily oral JAK1-selective inhibitors. Regulatory approval for AD by the Food and Drug Administration was granted to both in early 2022 and both now have an indication for moderate to severe disease in patients ages 12 years and older.
In September 2021, the first U.S. approval of a drug in this class for AD was granted for a topical formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), which has selectivity for both JAK1 and JAK2. The indication is for mild to moderate AD in patients aged 12 years and older.
In the phase 3 clinical trial that led to approval of abrocitinib for AD, the comparator groups included placebo and active treatment with 300 mg dupilumab administered subcutaneously every other week. The higher of two doses of abrocitinib (100 mg) was numerically superior to dupilumab in terms of EASI 75 response at week 12 and was statistically superior for relief of itch at week 2.
Relative to the first-generation JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz), both of the approved oral JAK inhibitors for AD, abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have greater JAK1-selectivity. However, selectivity for all JAK inhibitors is relative rather than absolute, according to a recent review article on oral JAK inhibitors for AD. Efficacy and safety are likely determined by relative inhibition of each of the four JAK enzymes (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2). Although JAK1 appears to be an important target for AD treatment, the clinical significance of the degree of selectivity among oral JAK inhibitors is not yet clear.
In an interview, the senior author of that review article, Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, emphasized this point. She said there is no evidence and no basis on which to speculate that any one drug in this class is better than another for AD. Dr. Guttman-Yassky is a professor and system chair of dermatology and immunology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The efficacy [of ivarmacitinib] seems, in general, to be in line with other JAK inhibitors,” said Dr. Guttman-Yassky, who attended the late-breaker session during which these data were presented. Although she acknowledged that rapid control of pruritus is important clinically, she said the speed of itch relief as reported in the phase 3 ivarmacitinib trial does not distinguish it from other oral drugs in the class.
Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, agreed.
“The rapid effects on itch of ivarmacitinib are consistent with those observed by the already approved JAK1-selective inhibitors abrocitinib and upadacitinib,” he said in an interview.
This suggests that head-to-head trials will be needed to draw any conclusions about the relative efficacy and safety of existing and emerging oral JAK inhibitors for AD.
Dr. Zhao has reported a financial relationship with Reistone Biopharma, which is developing ivarmacitinib and provided funding for the trial. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Kwatra has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Aslan, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – The presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Two doses were studied in the placebo-controlled trial and both demonstrated “a favorable benefit-to-risk profile in patients with moderate to severe AD,” reported Yan Zhao, MD, a clinician and researcher in the department of dermatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing.
In the study, called QUARTZ3, 336 patients aged 12 and older at 51 sites in China and Canada were randomized to 4 mg once-daily ivarmacitinib, 8 mg once-daily QD ivarmacitinib, or placebo. The mean age of the population was 32 years and approximately one-third were female.
The mean duration of AD for participants was 10 years. The mean baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was near 30. On the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) tool, approximately 40% had a score of 4, which is the highest score on the scale and indicates severe disease. The remaining patients had an IGA score of 3.
The co-primary endpoints were change in IGA and EASI scores at 16 weeks, and both improved rapidly, showing statistical significance relative to placebo by 4 weeks with no plateauing effect at the end of the 16-week trial. By week 16, the proportion of patients with an EASI score of 75, signifying a 75% improvement, was 66%, 54%, and 22% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups (P < .001 versus placebo for both doses of active therapy), respectively.
The pattern of the IGA response was similar. By week 16, the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) was 42%, 36%, and 9% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups, respectively. The advantage of either dose over placebo was highly significant (P < .001) at 8, 12, and 16 weeks.
For the WI-NRS (Worst Itch – Numeric Rating Scale), the advantage of the 8-mg dose relative to placebo was significant (P < .001) at the 1-week evaluation. By 2 weeks, the 4-mg dose had gained the same degree of statistical significance relative to placebo. After week 4, when the maximum proportion of patients with a WI-NRS score ≤ 4 was reached (50%, 35%, and 10% in the 8-mg, 4-mg, and placebo groups), and the relative advantage of active treatment persisted until the end of the 16-week study.
Two scales were used to evaluate change in quality of life. On the DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) and POEM (Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure), improvements were again rapid and sustained. By week 4, improvement with the 8-mg dose was about fourfold greater (P < .001) than improvement with placebo for DLQI and about sixfold greater (P < .001) for POEM. For the 4-mg dose, the relative differences were approximately threefold and fourfold greater, and both were significant (P <.001).
There was no further gain in these quality-of-life scales from week 4 to week 16, but the advantages relative to placebo were generally sustained, Dr. Zhao reported.
Ivarmacitinib was safe and well-tolerated, according to Dr. Zhao. The proportion of patients with a treatment-emergent adverse event that led to drug discontinuation was numerically higher (5.4%) in the placebo group than in the 8-mg (3.6%) or 4-mg group (2.7%). Rates of infection in the three groups were similar, and there were no major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) or thromboembolism observed in any group.
Ivarmacitinib, which has about a 10-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK2 and a more than 70-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK3, is being tested for rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and alopecia areata in addition to AD, Dr. Zhao said. She also reported that an application for new drug approval has been submitted in China. Efforts to pursue regulatory approval elsewhere are anticipated.
Currently, there are three JAK inhibitors licensed for the treatment of AD in the United States. Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) and abrocitinib (Cibinqo) are also once-daily oral JAK1-selective inhibitors. Regulatory approval for AD by the Food and Drug Administration was granted to both in early 2022 and both now have an indication for moderate to severe disease in patients ages 12 years and older.
In September 2021, the first U.S. approval of a drug in this class for AD was granted for a topical formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), which has selectivity for both JAK1 and JAK2. The indication is for mild to moderate AD in patients aged 12 years and older.
In the phase 3 clinical trial that led to approval of abrocitinib for AD, the comparator groups included placebo and active treatment with 300 mg dupilumab administered subcutaneously every other week. The higher of two doses of abrocitinib (100 mg) was numerically superior to dupilumab in terms of EASI 75 response at week 12 and was statistically superior for relief of itch at week 2.
Relative to the first-generation JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz), both of the approved oral JAK inhibitors for AD, abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have greater JAK1-selectivity. However, selectivity for all JAK inhibitors is relative rather than absolute, according to a recent review article on oral JAK inhibitors for AD. Efficacy and safety are likely determined by relative inhibition of each of the four JAK enzymes (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2). Although JAK1 appears to be an important target for AD treatment, the clinical significance of the degree of selectivity among oral JAK inhibitors is not yet clear.
In an interview, the senior author of that review article, Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, emphasized this point. She said there is no evidence and no basis on which to speculate that any one drug in this class is better than another for AD. Dr. Guttman-Yassky is a professor and system chair of dermatology and immunology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The efficacy [of ivarmacitinib] seems, in general, to be in line with other JAK inhibitors,” said Dr. Guttman-Yassky, who attended the late-breaker session during which these data were presented. Although she acknowledged that rapid control of pruritus is important clinically, she said the speed of itch relief as reported in the phase 3 ivarmacitinib trial does not distinguish it from other oral drugs in the class.
Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, agreed.
“The rapid effects on itch of ivarmacitinib are consistent with those observed by the already approved JAK1-selective inhibitors abrocitinib and upadacitinib,” he said in an interview.
This suggests that head-to-head trials will be needed to draw any conclusions about the relative efficacy and safety of existing and emerging oral JAK inhibitors for AD.
Dr. Zhao has reported a financial relationship with Reistone Biopharma, which is developing ivarmacitinib and provided funding for the trial. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Kwatra has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Aslan, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – The presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Two doses were studied in the placebo-controlled trial and both demonstrated “a favorable benefit-to-risk profile in patients with moderate to severe AD,” reported Yan Zhao, MD, a clinician and researcher in the department of dermatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing.
In the study, called QUARTZ3, 336 patients aged 12 and older at 51 sites in China and Canada were randomized to 4 mg once-daily ivarmacitinib, 8 mg once-daily QD ivarmacitinib, or placebo. The mean age of the population was 32 years and approximately one-third were female.
The mean duration of AD for participants was 10 years. The mean baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was near 30. On the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) tool, approximately 40% had a score of 4, which is the highest score on the scale and indicates severe disease. The remaining patients had an IGA score of 3.
The co-primary endpoints were change in IGA and EASI scores at 16 weeks, and both improved rapidly, showing statistical significance relative to placebo by 4 weeks with no plateauing effect at the end of the 16-week trial. By week 16, the proportion of patients with an EASI score of 75, signifying a 75% improvement, was 66%, 54%, and 22% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups (P < .001 versus placebo for both doses of active therapy), respectively.
The pattern of the IGA response was similar. By week 16, the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) was 42%, 36%, and 9% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups, respectively. The advantage of either dose over placebo was highly significant (P < .001) at 8, 12, and 16 weeks.
For the WI-NRS (Worst Itch – Numeric Rating Scale), the advantage of the 8-mg dose relative to placebo was significant (P < .001) at the 1-week evaluation. By 2 weeks, the 4-mg dose had gained the same degree of statistical significance relative to placebo. After week 4, when the maximum proportion of patients with a WI-NRS score ≤ 4 was reached (50%, 35%, and 10% in the 8-mg, 4-mg, and placebo groups), and the relative advantage of active treatment persisted until the end of the 16-week study.
Two scales were used to evaluate change in quality of life. On the DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) and POEM (Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure), improvements were again rapid and sustained. By week 4, improvement with the 8-mg dose was about fourfold greater (P < .001) than improvement with placebo for DLQI and about sixfold greater (P < .001) for POEM. For the 4-mg dose, the relative differences were approximately threefold and fourfold greater, and both were significant (P <.001).
There was no further gain in these quality-of-life scales from week 4 to week 16, but the advantages relative to placebo were generally sustained, Dr. Zhao reported.
Ivarmacitinib was safe and well-tolerated, according to Dr. Zhao. The proportion of patients with a treatment-emergent adverse event that led to drug discontinuation was numerically higher (5.4%) in the placebo group than in the 8-mg (3.6%) or 4-mg group (2.7%). Rates of infection in the three groups were similar, and there were no major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) or thromboembolism observed in any group.
Ivarmacitinib, which has about a 10-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK2 and a more than 70-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK3, is being tested for rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and alopecia areata in addition to AD, Dr. Zhao said. She also reported that an application for new drug approval has been submitted in China. Efforts to pursue regulatory approval elsewhere are anticipated.
Currently, there are three JAK inhibitors licensed for the treatment of AD in the United States. Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) and abrocitinib (Cibinqo) are also once-daily oral JAK1-selective inhibitors. Regulatory approval for AD by the Food and Drug Administration was granted to both in early 2022 and both now have an indication for moderate to severe disease in patients ages 12 years and older.
In September 2021, the first U.S. approval of a drug in this class for AD was granted for a topical formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), which has selectivity for both JAK1 and JAK2. The indication is for mild to moderate AD in patients aged 12 years and older.
In the phase 3 clinical trial that led to approval of abrocitinib for AD, the comparator groups included placebo and active treatment with 300 mg dupilumab administered subcutaneously every other week. The higher of two doses of abrocitinib (100 mg) was numerically superior to dupilumab in terms of EASI 75 response at week 12 and was statistically superior for relief of itch at week 2.
Relative to the first-generation JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz), both of the approved oral JAK inhibitors for AD, abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have greater JAK1-selectivity. However, selectivity for all JAK inhibitors is relative rather than absolute, according to a recent review article on oral JAK inhibitors for AD. Efficacy and safety are likely determined by relative inhibition of each of the four JAK enzymes (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2). Although JAK1 appears to be an important target for AD treatment, the clinical significance of the degree of selectivity among oral JAK inhibitors is not yet clear.
In an interview, the senior author of that review article, Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, emphasized this point. She said there is no evidence and no basis on which to speculate that any one drug in this class is better than another for AD. Dr. Guttman-Yassky is a professor and system chair of dermatology and immunology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The efficacy [of ivarmacitinib] seems, in general, to be in line with other JAK inhibitors,” said Dr. Guttman-Yassky, who attended the late-breaker session during which these data were presented. Although she acknowledged that rapid control of pruritus is important clinically, she said the speed of itch relief as reported in the phase 3 ivarmacitinib trial does not distinguish it from other oral drugs in the class.
Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, agreed.
“The rapid effects on itch of ivarmacitinib are consistent with those observed by the already approved JAK1-selective inhibitors abrocitinib and upadacitinib,” he said in an interview.
This suggests that head-to-head trials will be needed to draw any conclusions about the relative efficacy and safety of existing and emerging oral JAK inhibitors for AD.
Dr. Zhao has reported a financial relationship with Reistone Biopharma, which is developing ivarmacitinib and provided funding for the trial. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Kwatra has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Aslan, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
Topical delgocitinib shows promise for chronic hand eczema, pivotal trial shows
NEW ORLEANS – , compared with those who received vehicle cream, results from a pivotal phase 3 trial showed.
“Chronic hand eczema is the most frequent chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the hands,” Robert Bissonnette, MD, a dermatologist who is founder and CEO of Innovaderm Research, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during a late-breaking research session. “It’s associated with pain, pruritus, and has a huge impact on quality of life,” and results with current topical treatments are often unsatisfactory, he noted.
Delgocitinib is an investigational topical pan-JAK inhibitor that inhibits activation of the JAK-STAT pathway and targets key mediators of chronic hand eczema. In a phase 2b dose-ranging trial, twice-daily treatment with delgocitinib cream demonstrated significantly greater efficacy, compared with the cream vehicle, and was well tolerated in adults with mild to severe chronic hand eczema.
For the phase 3 study, known as DELTA 1, researchers randomized 487 adults with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema to receive twice-daily applications of delgocitinib cream 20 mg/g or cream vehicle for 16 weeks. After week 16, patients had the option to enter a long-term extension trial, which is currently ongoing. DELTA 1 was limited to adults with a diagnosis of chronic hand eczema defined as hand eczema that had persisted for more than 3 months or had returned more than twice within the past 12 months; an Investigator’s Global Assessment for chronic hand eczema (IGA-CHE) score of 3 (moderate) or 4 (severe); a weekly average Hand Eczema Symptom Diary (HESD) itch score of 4 or more points, and a medical history of inadequate response to topical corticosteroids within the past 12 months or for whom treatment with topical corticosteroids was not medically advisable.
The IGA-CHE scale used in the trial was new, “where, in order to be almost clear, the only sign that could be present on the skin was barely perceptible erythema,” Dr. Bissonnette said. He noted that he has used many IGA scales over the more than 25 years he has been involved with clinical trials, and “this was the first that used a scale with a bar so high.” Key secondary endpoints include a 75% and 90% improvement in Hand Eczema Severity Index (HECSI) from baseline at week 16 and a 4-point or greater improvement in the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) from baseline at week 16.
The median age of patients was 44 years, 88% were White, 4% were Asian, 1% were Black, and the remainder were from other racial groups. One-third of patients (33%) had severe hand eczema based on their IGA-CHE score, the median HECSI was 65 (in line with severe disease), and the median DLQI was 12. As for previous chronic hand eczema treatments, 19% had undergone phototherapy, 14% had tried oral retinoids, and 12% had tried oral corticosteroids.
In the study, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients achieved the primary endpoint of IGA-CHE 0/1, compared with the cream vehicle group at week 4 (15.4% vs. 4.9%; P < .001); week 8 (22.8% vs. 10.5%; P = .001), and week 16 (19.7% vs. 9.9%; P = .006). “As early as week 2, there is a separation between cream and vehicle,” Dr. Bissonnette said. When reviewing the results and the patients in the trial, he said that, in his personal opinion, “I don’t think this is uniquely representative of the efficacy of the drug,” because of the IGA scale that was used, which set such a high bar for efficacy.
As for secondary endpoints, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients than those in the vehicle group achieved a HESCI-75 (49.2% vs. 23.5%), a HECSI-90 (29.5% vs. 12.3%), and a 4-point or greater improvement on the DLQI (74.4% vs 50%; P < .001 for all endpoints).
Delgocitinib had a similar safety profile as the vehicle over 16 weeks, with no difference between the delgocitinib and vehicle arms in the proportion of patients who had adverse events (45.2% vs. 50.6%, respectively) and serious adverse events (1.8% vs. 1.9%). The most common adverse events (defined as 5% or greater in any treatment group) during the study were COVID-19 infections and nasopharyngitis; rates were comparable in the two arms.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, a dermatologist who directs the Center for Eczema and Itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study, said that chronic hand eczema can be functionally limiting for many patients. “Given its focal symptoms but multifaceted immunopathogenesis, topical JAK inhibition represents a rational strategy for targeted treatment,” Dr. Chovatiya told this news organization. He was not an investigator in the trial.
“In the phase 3 DELTA 1 study, topical delgocitinib cream was superior to vehicle control with nearly one out of five patients achieving clear or almost clear skin, with no difference in total adverse events between groups. While both comparative and long-term data would be helpful to better assess how delgocitinib cream stacks up against common topical anti-inflammatories and how it may be used for a chronic condition that typically requires ongoing treatment, these findings move us closer to a potential first-in-class approved therapy for chronic hand eczema.”
Dr. Bissonnette disclosed that he served as a consultant and investigator for the developer of delgocitinib, LEO Pharma, on this study. He has also received grants and research funding from many other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including LEO Pharma.
NEW ORLEANS – , compared with those who received vehicle cream, results from a pivotal phase 3 trial showed.
“Chronic hand eczema is the most frequent chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the hands,” Robert Bissonnette, MD, a dermatologist who is founder and CEO of Innovaderm Research, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during a late-breaking research session. “It’s associated with pain, pruritus, and has a huge impact on quality of life,” and results with current topical treatments are often unsatisfactory, he noted.
Delgocitinib is an investigational topical pan-JAK inhibitor that inhibits activation of the JAK-STAT pathway and targets key mediators of chronic hand eczema. In a phase 2b dose-ranging trial, twice-daily treatment with delgocitinib cream demonstrated significantly greater efficacy, compared with the cream vehicle, and was well tolerated in adults with mild to severe chronic hand eczema.
For the phase 3 study, known as DELTA 1, researchers randomized 487 adults with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema to receive twice-daily applications of delgocitinib cream 20 mg/g or cream vehicle for 16 weeks. After week 16, patients had the option to enter a long-term extension trial, which is currently ongoing. DELTA 1 was limited to adults with a diagnosis of chronic hand eczema defined as hand eczema that had persisted for more than 3 months or had returned more than twice within the past 12 months; an Investigator’s Global Assessment for chronic hand eczema (IGA-CHE) score of 3 (moderate) or 4 (severe); a weekly average Hand Eczema Symptom Diary (HESD) itch score of 4 or more points, and a medical history of inadequate response to topical corticosteroids within the past 12 months or for whom treatment with topical corticosteroids was not medically advisable.
The IGA-CHE scale used in the trial was new, “where, in order to be almost clear, the only sign that could be present on the skin was barely perceptible erythema,” Dr. Bissonnette said. He noted that he has used many IGA scales over the more than 25 years he has been involved with clinical trials, and “this was the first that used a scale with a bar so high.” Key secondary endpoints include a 75% and 90% improvement in Hand Eczema Severity Index (HECSI) from baseline at week 16 and a 4-point or greater improvement in the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) from baseline at week 16.
The median age of patients was 44 years, 88% were White, 4% were Asian, 1% were Black, and the remainder were from other racial groups. One-third of patients (33%) had severe hand eczema based on their IGA-CHE score, the median HECSI was 65 (in line with severe disease), and the median DLQI was 12. As for previous chronic hand eczema treatments, 19% had undergone phototherapy, 14% had tried oral retinoids, and 12% had tried oral corticosteroids.
In the study, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients achieved the primary endpoint of IGA-CHE 0/1, compared with the cream vehicle group at week 4 (15.4% vs. 4.9%; P < .001); week 8 (22.8% vs. 10.5%; P = .001), and week 16 (19.7% vs. 9.9%; P = .006). “As early as week 2, there is a separation between cream and vehicle,” Dr. Bissonnette said. When reviewing the results and the patients in the trial, he said that, in his personal opinion, “I don’t think this is uniquely representative of the efficacy of the drug,” because of the IGA scale that was used, which set such a high bar for efficacy.
As for secondary endpoints, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients than those in the vehicle group achieved a HESCI-75 (49.2% vs. 23.5%), a HECSI-90 (29.5% vs. 12.3%), and a 4-point or greater improvement on the DLQI (74.4% vs 50%; P < .001 for all endpoints).
Delgocitinib had a similar safety profile as the vehicle over 16 weeks, with no difference between the delgocitinib and vehicle arms in the proportion of patients who had adverse events (45.2% vs. 50.6%, respectively) and serious adverse events (1.8% vs. 1.9%). The most common adverse events (defined as 5% or greater in any treatment group) during the study were COVID-19 infections and nasopharyngitis; rates were comparable in the two arms.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, a dermatologist who directs the Center for Eczema and Itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study, said that chronic hand eczema can be functionally limiting for many patients. “Given its focal symptoms but multifaceted immunopathogenesis, topical JAK inhibition represents a rational strategy for targeted treatment,” Dr. Chovatiya told this news organization. He was not an investigator in the trial.
“In the phase 3 DELTA 1 study, topical delgocitinib cream was superior to vehicle control with nearly one out of five patients achieving clear or almost clear skin, with no difference in total adverse events between groups. While both comparative and long-term data would be helpful to better assess how delgocitinib cream stacks up against common topical anti-inflammatories and how it may be used for a chronic condition that typically requires ongoing treatment, these findings move us closer to a potential first-in-class approved therapy for chronic hand eczema.”
Dr. Bissonnette disclosed that he served as a consultant and investigator for the developer of delgocitinib, LEO Pharma, on this study. He has also received grants and research funding from many other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including LEO Pharma.
NEW ORLEANS – , compared with those who received vehicle cream, results from a pivotal phase 3 trial showed.
“Chronic hand eczema is the most frequent chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the hands,” Robert Bissonnette, MD, a dermatologist who is founder and CEO of Innovaderm Research, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during a late-breaking research session. “It’s associated with pain, pruritus, and has a huge impact on quality of life,” and results with current topical treatments are often unsatisfactory, he noted.
Delgocitinib is an investigational topical pan-JAK inhibitor that inhibits activation of the JAK-STAT pathway and targets key mediators of chronic hand eczema. In a phase 2b dose-ranging trial, twice-daily treatment with delgocitinib cream demonstrated significantly greater efficacy, compared with the cream vehicle, and was well tolerated in adults with mild to severe chronic hand eczema.
For the phase 3 study, known as DELTA 1, researchers randomized 487 adults with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema to receive twice-daily applications of delgocitinib cream 20 mg/g or cream vehicle for 16 weeks. After week 16, patients had the option to enter a long-term extension trial, which is currently ongoing. DELTA 1 was limited to adults with a diagnosis of chronic hand eczema defined as hand eczema that had persisted for more than 3 months or had returned more than twice within the past 12 months; an Investigator’s Global Assessment for chronic hand eczema (IGA-CHE) score of 3 (moderate) or 4 (severe); a weekly average Hand Eczema Symptom Diary (HESD) itch score of 4 or more points, and a medical history of inadequate response to topical corticosteroids within the past 12 months or for whom treatment with topical corticosteroids was not medically advisable.
The IGA-CHE scale used in the trial was new, “where, in order to be almost clear, the only sign that could be present on the skin was barely perceptible erythema,” Dr. Bissonnette said. He noted that he has used many IGA scales over the more than 25 years he has been involved with clinical trials, and “this was the first that used a scale with a bar so high.” Key secondary endpoints include a 75% and 90% improvement in Hand Eczema Severity Index (HECSI) from baseline at week 16 and a 4-point or greater improvement in the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) from baseline at week 16.
The median age of patients was 44 years, 88% were White, 4% were Asian, 1% were Black, and the remainder were from other racial groups. One-third of patients (33%) had severe hand eczema based on their IGA-CHE score, the median HECSI was 65 (in line with severe disease), and the median DLQI was 12. As for previous chronic hand eczema treatments, 19% had undergone phototherapy, 14% had tried oral retinoids, and 12% had tried oral corticosteroids.
In the study, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients achieved the primary endpoint of IGA-CHE 0/1, compared with the cream vehicle group at week 4 (15.4% vs. 4.9%; P < .001); week 8 (22.8% vs. 10.5%; P = .001), and week 16 (19.7% vs. 9.9%; P = .006). “As early as week 2, there is a separation between cream and vehicle,” Dr. Bissonnette said. When reviewing the results and the patients in the trial, he said that, in his personal opinion, “I don’t think this is uniquely representative of the efficacy of the drug,” because of the IGA scale that was used, which set such a high bar for efficacy.
As for secondary endpoints, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients than those in the vehicle group achieved a HESCI-75 (49.2% vs. 23.5%), a HECSI-90 (29.5% vs. 12.3%), and a 4-point or greater improvement on the DLQI (74.4% vs 50%; P < .001 for all endpoints).
Delgocitinib had a similar safety profile as the vehicle over 16 weeks, with no difference between the delgocitinib and vehicle arms in the proportion of patients who had adverse events (45.2% vs. 50.6%, respectively) and serious adverse events (1.8% vs. 1.9%). The most common adverse events (defined as 5% or greater in any treatment group) during the study were COVID-19 infections and nasopharyngitis; rates were comparable in the two arms.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, a dermatologist who directs the Center for Eczema and Itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study, said that chronic hand eczema can be functionally limiting for many patients. “Given its focal symptoms but multifaceted immunopathogenesis, topical JAK inhibition represents a rational strategy for targeted treatment,” Dr. Chovatiya told this news organization. He was not an investigator in the trial.
“In the phase 3 DELTA 1 study, topical delgocitinib cream was superior to vehicle control with nearly one out of five patients achieving clear or almost clear skin, with no difference in total adverse events between groups. While both comparative and long-term data would be helpful to better assess how delgocitinib cream stacks up against common topical anti-inflammatories and how it may be used for a chronic condition that typically requires ongoing treatment, these findings move us closer to a potential first-in-class approved therapy for chronic hand eczema.”
Dr. Bissonnette disclosed that he served as a consultant and investigator for the developer of delgocitinib, LEO Pharma, on this study. He has also received grants and research funding from many other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including LEO Pharma.
AT AAD 2023
New data forecast more oral PDE4 inhibitors for psoriasis
NEW ORLEANS – according to results of a phase 2 clinical trial presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The phase 2b data, which are prompting a phase 3 trial, suggest that the drug, called orismilast, “is a potential new addition to the psoriasis armamentarium,” reported Lars E. French, MD, professor and chair, department of dermatology, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany).
At the same session, findings from another study supported off-label use of oral roflumilast (Daliresp and generic), a PDE4 inhibitor approved for severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The only PDE4 inhibitors with an indication for psoriasis are roflumilast, approved as a cream (Zoryve), and apremilast (Otezla), approved as an oral therapy.
Phase 2 study of orismilast
In the orismilast trial, Dr. French attributed the efficacy observed to the potency of orismilast on the B and D subtypes of PDE4 associated with inflammation. One clue is that these specific subtypes are overly expressed in the skin of patients with either psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
“When compared to apremilast, orismilast is at least two to fivefold more potent on all PDE4 isoforms and up to 39 times more potent on some of the PDE4 B and D isoforms,” said Dr. French, referring to preclinical findings in human whole blood and blood cells and in a mouse model of chronic inflammation.
The efficacy of orismilast in an immediate-release oral formulation was previously demonstrated in a recently published phase 2a trial, but the newest study tested a modified-release formulation of orismilast to test its potential to improve tolerability.
In the study, 202 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis (Psoriasis Area Severity Index [PASI] score ≥ 12) were randomly assigned to one of three doses of orismilast or to placebo. Each of the three doses – 20 mg, 30 mg, or 40 mg – were administered twice daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI score at 16 weeks. Secondary endpoints included PASI 75 responses (signifying 75% clearance) and safety.
Relative to placebo, which was associated with a PASI improvement of 17%, all three of the tested orismilast doses were superior in a dose-dependent manner. The rates of response were 53%, 61%, and 64% for the 20-mg, 30-mg, and 40-mg twice-daily doses, respectively.
The PASI improvements were rapid, Dr. French said. At 4 weeks, PASI scores climbed from baseline by nearly 40% for those on all orismilast doses, which was more than double the improvement in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis with missing data counted as nonresponders, the proportion of patients reaching PASI-75 scores at 16 weeks were 39%, 49%, 45%, and 17%, in the 20-mg, 30-mg, 40-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. The proportion of patients experiencing complete or near-complete skin clearance defined by a PASI 90 were 24%, 22%, 28%, and 8%, respectively.
The side-effect profile was consistent with other PDE4 inhibitors. The most common adverse events included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea and nausea, as well as headache and dizziness. But the majority of these events were of low grade, and they were largely confined to the first 4 weeks of treatment, which is a pattern reported with other PDE4 inhibitors in psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory diseases, such as COPD, according to Dr. French.
“There were no discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event in the arms receiving either the 20-mg or the 30-mg doses,” Dr. French reported. There were only two serious adverse events, and neither were considered by trial investigators to be related to orismilast.
Based on the limited therapeutic gain but greater risk for adverse events on the 40-mg twice-daily dose, “the question is now whether to move forward with the 20-mg or the 30-mg dose,” said Dr. French, who said planning of a phase 3 trial is underway.
Phase 2 study of roflumilast
However, this was not the only set of data on an oral PDE4 inhibitor presented as a late-breaker at the AAD meeting. For clinicians looking for a more immediate and less expensive alternative to apremilast, another study indicated that off-label use of oral roflumilast is an option.
In an investigator-initiated, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in Denmark, the rate of response to oral roflumilast at 24 weeks, including the clear or almost clear response, was on the same general order of magnitude as that seen in the orismilast study, reported Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Copenhagen.
“At 24 weeks, 21.7% had achieved a PASI 90, and 8.7% achieved a PASI 100,” Dr. Egeberg said.
Oral roflumilast has been available for the treatment of COPD for more than 10 years and is now available in a generic formulation. This study was conducted independent of any pharmaceutical company involvement, and the high rate of response and low risk of adverse events suggests that patients can benefit from a PDE4 inhibitor in a very low-cost form.
“Generic oral roflumilast is cheaper than a Starbucks coffee,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In this trial, 46 patients were randomly assigned to placebo or to the COPD-approved roflumilast dose of 500 mcg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI scores from baseline to week 12, which Dr. Egeberg pointed out is a shorter time frame than the 16 weeks more typical of psoriasis treatment studies.
At week 12, the median improvement in PASI was 34.8% in the roflumilast group versus 0% in the placebo group. Patients were then followed for an additional 12 weeks, but those randomized to placebo were switched to the active treatment. By week 24, the switch patients had largely caught up to those initiated on roflumilast for median PASI improvement (39.1% vs. 43.5%).
Similar to orismilast, roflumilast “was generally well tolerated,” Dr. Egeberg said. The adverse events were consistent with those associated with PDE4 inhibitors in previous trials, whether in psoriasis or COPD. There was only one serious adverse event, and it was not considered treatment related. Discontinuations for adverse events “were very low.”
In a population with a relatively high rate of smoking, Dr. Egeberg further reported, lung function was improved, a remark initially interpreted as a joke by some attending the presentation. However, Dr. Egeberg confirmed that lung function was monitored, and objective improvements were recorded.
By Danish law, the investigators were required to inform the manufacturers of roflumilast. Despite the results of this study, he is not aware of any plans to seek an indication for roflumilast in psoriasis, but he noted that the drug is readily available at a low price.
For those willing to offer this therapy off label, “you can start using it tomorrow if you’d like,” he said.
Dr. French reports financial relationships with Almirall, Amgen, Biotest, Galderma, Janssen Cilag, Leo Pharma, Pincell, Regeneron, UCB, and UNION Therapeutics, which provided funding for this trial. Dr. Egeberg reports financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – according to results of a phase 2 clinical trial presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The phase 2b data, which are prompting a phase 3 trial, suggest that the drug, called orismilast, “is a potential new addition to the psoriasis armamentarium,” reported Lars E. French, MD, professor and chair, department of dermatology, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany).
At the same session, findings from another study supported off-label use of oral roflumilast (Daliresp and generic), a PDE4 inhibitor approved for severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The only PDE4 inhibitors with an indication for psoriasis are roflumilast, approved as a cream (Zoryve), and apremilast (Otezla), approved as an oral therapy.
Phase 2 study of orismilast
In the orismilast trial, Dr. French attributed the efficacy observed to the potency of orismilast on the B and D subtypes of PDE4 associated with inflammation. One clue is that these specific subtypes are overly expressed in the skin of patients with either psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
“When compared to apremilast, orismilast is at least two to fivefold more potent on all PDE4 isoforms and up to 39 times more potent on some of the PDE4 B and D isoforms,” said Dr. French, referring to preclinical findings in human whole blood and blood cells and in a mouse model of chronic inflammation.
The efficacy of orismilast in an immediate-release oral formulation was previously demonstrated in a recently published phase 2a trial, but the newest study tested a modified-release formulation of orismilast to test its potential to improve tolerability.
In the study, 202 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis (Psoriasis Area Severity Index [PASI] score ≥ 12) were randomly assigned to one of three doses of orismilast or to placebo. Each of the three doses – 20 mg, 30 mg, or 40 mg – were administered twice daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI score at 16 weeks. Secondary endpoints included PASI 75 responses (signifying 75% clearance) and safety.
Relative to placebo, which was associated with a PASI improvement of 17%, all three of the tested orismilast doses were superior in a dose-dependent manner. The rates of response were 53%, 61%, and 64% for the 20-mg, 30-mg, and 40-mg twice-daily doses, respectively.
The PASI improvements were rapid, Dr. French said. At 4 weeks, PASI scores climbed from baseline by nearly 40% for those on all orismilast doses, which was more than double the improvement in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis with missing data counted as nonresponders, the proportion of patients reaching PASI-75 scores at 16 weeks were 39%, 49%, 45%, and 17%, in the 20-mg, 30-mg, 40-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. The proportion of patients experiencing complete or near-complete skin clearance defined by a PASI 90 were 24%, 22%, 28%, and 8%, respectively.
The side-effect profile was consistent with other PDE4 inhibitors. The most common adverse events included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea and nausea, as well as headache and dizziness. But the majority of these events were of low grade, and they were largely confined to the first 4 weeks of treatment, which is a pattern reported with other PDE4 inhibitors in psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory diseases, such as COPD, according to Dr. French.
“There were no discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event in the arms receiving either the 20-mg or the 30-mg doses,” Dr. French reported. There were only two serious adverse events, and neither were considered by trial investigators to be related to orismilast.
Based on the limited therapeutic gain but greater risk for adverse events on the 40-mg twice-daily dose, “the question is now whether to move forward with the 20-mg or the 30-mg dose,” said Dr. French, who said planning of a phase 3 trial is underway.
Phase 2 study of roflumilast
However, this was not the only set of data on an oral PDE4 inhibitor presented as a late-breaker at the AAD meeting. For clinicians looking for a more immediate and less expensive alternative to apremilast, another study indicated that off-label use of oral roflumilast is an option.
In an investigator-initiated, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in Denmark, the rate of response to oral roflumilast at 24 weeks, including the clear or almost clear response, was on the same general order of magnitude as that seen in the orismilast study, reported Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Copenhagen.
“At 24 weeks, 21.7% had achieved a PASI 90, and 8.7% achieved a PASI 100,” Dr. Egeberg said.
Oral roflumilast has been available for the treatment of COPD for more than 10 years and is now available in a generic formulation. This study was conducted independent of any pharmaceutical company involvement, and the high rate of response and low risk of adverse events suggests that patients can benefit from a PDE4 inhibitor in a very low-cost form.
“Generic oral roflumilast is cheaper than a Starbucks coffee,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In this trial, 46 patients were randomly assigned to placebo or to the COPD-approved roflumilast dose of 500 mcg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI scores from baseline to week 12, which Dr. Egeberg pointed out is a shorter time frame than the 16 weeks more typical of psoriasis treatment studies.
At week 12, the median improvement in PASI was 34.8% in the roflumilast group versus 0% in the placebo group. Patients were then followed for an additional 12 weeks, but those randomized to placebo were switched to the active treatment. By week 24, the switch patients had largely caught up to those initiated on roflumilast for median PASI improvement (39.1% vs. 43.5%).
Similar to orismilast, roflumilast “was generally well tolerated,” Dr. Egeberg said. The adverse events were consistent with those associated with PDE4 inhibitors in previous trials, whether in psoriasis or COPD. There was only one serious adverse event, and it was not considered treatment related. Discontinuations for adverse events “were very low.”
In a population with a relatively high rate of smoking, Dr. Egeberg further reported, lung function was improved, a remark initially interpreted as a joke by some attending the presentation. However, Dr. Egeberg confirmed that lung function was monitored, and objective improvements were recorded.
By Danish law, the investigators were required to inform the manufacturers of roflumilast. Despite the results of this study, he is not aware of any plans to seek an indication for roflumilast in psoriasis, but he noted that the drug is readily available at a low price.
For those willing to offer this therapy off label, “you can start using it tomorrow if you’d like,” he said.
Dr. French reports financial relationships with Almirall, Amgen, Biotest, Galderma, Janssen Cilag, Leo Pharma, Pincell, Regeneron, UCB, and UNION Therapeutics, which provided funding for this trial. Dr. Egeberg reports financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – according to results of a phase 2 clinical trial presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The phase 2b data, which are prompting a phase 3 trial, suggest that the drug, called orismilast, “is a potential new addition to the psoriasis armamentarium,” reported Lars E. French, MD, professor and chair, department of dermatology, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany).
At the same session, findings from another study supported off-label use of oral roflumilast (Daliresp and generic), a PDE4 inhibitor approved for severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The only PDE4 inhibitors with an indication for psoriasis are roflumilast, approved as a cream (Zoryve), and apremilast (Otezla), approved as an oral therapy.
Phase 2 study of orismilast
In the orismilast trial, Dr. French attributed the efficacy observed to the potency of orismilast on the B and D subtypes of PDE4 associated with inflammation. One clue is that these specific subtypes are overly expressed in the skin of patients with either psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
“When compared to apremilast, orismilast is at least two to fivefold more potent on all PDE4 isoforms and up to 39 times more potent on some of the PDE4 B and D isoforms,” said Dr. French, referring to preclinical findings in human whole blood and blood cells and in a mouse model of chronic inflammation.
The efficacy of orismilast in an immediate-release oral formulation was previously demonstrated in a recently published phase 2a trial, but the newest study tested a modified-release formulation of orismilast to test its potential to improve tolerability.
In the study, 202 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis (Psoriasis Area Severity Index [PASI] score ≥ 12) were randomly assigned to one of three doses of orismilast or to placebo. Each of the three doses – 20 mg, 30 mg, or 40 mg – were administered twice daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI score at 16 weeks. Secondary endpoints included PASI 75 responses (signifying 75% clearance) and safety.
Relative to placebo, which was associated with a PASI improvement of 17%, all three of the tested orismilast doses were superior in a dose-dependent manner. The rates of response were 53%, 61%, and 64% for the 20-mg, 30-mg, and 40-mg twice-daily doses, respectively.
The PASI improvements were rapid, Dr. French said. At 4 weeks, PASI scores climbed from baseline by nearly 40% for those on all orismilast doses, which was more than double the improvement in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis with missing data counted as nonresponders, the proportion of patients reaching PASI-75 scores at 16 weeks were 39%, 49%, 45%, and 17%, in the 20-mg, 30-mg, 40-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. The proportion of patients experiencing complete or near-complete skin clearance defined by a PASI 90 were 24%, 22%, 28%, and 8%, respectively.
The side-effect profile was consistent with other PDE4 inhibitors. The most common adverse events included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea and nausea, as well as headache and dizziness. But the majority of these events were of low grade, and they were largely confined to the first 4 weeks of treatment, which is a pattern reported with other PDE4 inhibitors in psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory diseases, such as COPD, according to Dr. French.
“There were no discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event in the arms receiving either the 20-mg or the 30-mg doses,” Dr. French reported. There were only two serious adverse events, and neither were considered by trial investigators to be related to orismilast.
Based on the limited therapeutic gain but greater risk for adverse events on the 40-mg twice-daily dose, “the question is now whether to move forward with the 20-mg or the 30-mg dose,” said Dr. French, who said planning of a phase 3 trial is underway.
Phase 2 study of roflumilast
However, this was not the only set of data on an oral PDE4 inhibitor presented as a late-breaker at the AAD meeting. For clinicians looking for a more immediate and less expensive alternative to apremilast, another study indicated that off-label use of oral roflumilast is an option.
In an investigator-initiated, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in Denmark, the rate of response to oral roflumilast at 24 weeks, including the clear or almost clear response, was on the same general order of magnitude as that seen in the orismilast study, reported Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Copenhagen.
“At 24 weeks, 21.7% had achieved a PASI 90, and 8.7% achieved a PASI 100,” Dr. Egeberg said.
Oral roflumilast has been available for the treatment of COPD for more than 10 years and is now available in a generic formulation. This study was conducted independent of any pharmaceutical company involvement, and the high rate of response and low risk of adverse events suggests that patients can benefit from a PDE4 inhibitor in a very low-cost form.
“Generic oral roflumilast is cheaper than a Starbucks coffee,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In this trial, 46 patients were randomly assigned to placebo or to the COPD-approved roflumilast dose of 500 mcg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI scores from baseline to week 12, which Dr. Egeberg pointed out is a shorter time frame than the 16 weeks more typical of psoriasis treatment studies.
At week 12, the median improvement in PASI was 34.8% in the roflumilast group versus 0% in the placebo group. Patients were then followed for an additional 12 weeks, but those randomized to placebo were switched to the active treatment. By week 24, the switch patients had largely caught up to those initiated on roflumilast for median PASI improvement (39.1% vs. 43.5%).
Similar to orismilast, roflumilast “was generally well tolerated,” Dr. Egeberg said. The adverse events were consistent with those associated with PDE4 inhibitors in previous trials, whether in psoriasis or COPD. There was only one serious adverse event, and it was not considered treatment related. Discontinuations for adverse events “were very low.”
In a population with a relatively high rate of smoking, Dr. Egeberg further reported, lung function was improved, a remark initially interpreted as a joke by some attending the presentation. However, Dr. Egeberg confirmed that lung function was monitored, and objective improvements were recorded.
By Danish law, the investigators were required to inform the manufacturers of roflumilast. Despite the results of this study, he is not aware of any plans to seek an indication for roflumilast in psoriasis, but he noted that the drug is readily available at a low price.
For those willing to offer this therapy off label, “you can start using it tomorrow if you’d like,” he said.
Dr. French reports financial relationships with Almirall, Amgen, Biotest, Galderma, Janssen Cilag, Leo Pharma, Pincell, Regeneron, UCB, and UNION Therapeutics, which provided funding for this trial. Dr. Egeberg reports financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
New JAK inhibitor study data confirm benefit in alopecia areata
from clinical trials of two drugs presented at a late-breaker research session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Based on phase 3 studies that document robust hair growth in about one third of patients, deuruxolitinib (CTP-543), an inhibitor of the JAK1 and JAK2 enzymes, has the potential to become the second JAK inhibitor available for the treatment of alopecia areata. If approved, it will join baricitinib (Olumiant), which received U.S. approval almost 1 year ago.
In his talk on THRIVE-AA2, a phase 3 trial of the investigational medicine deuruxolitinib, the principal investigator, Brett A. King, MD, PhD, displayed several before-and-after photos and said, “The photos tell the whole story. This is why there is so much excitement about these drugs.”
THRIVE-AA2 was the second of two phase 3 studies of deuruxolitinib. King was a principal investigator for both pivotal trials, called THRIVE-AA1 and THRIVE AA-2. He characterized the results of the two THRIVE trials as “comparable.”
Dr. King also was a principal investigator for the trials with baricitinib, called BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE AA-2, which were published last year in the New England Journal of Medicine. The trials for both drugs had similar designs and endpoints.
Deuruxolitinib and the THRIVE studies
In the THRIVE-AA2 trial, 517 adult patients were enrolled with moderate to severe alopecia areata, defined as a SALT (Severity of Alopecia Tool) score of ≥ 50%, which signifies a hair loss of at least 50%. Like THRIVE-AA1, patients participated at treatment centers in North America and Europe. About two-thirds were female. The mean age was 39 years. The majority of patients had complete or near complete hair loss at baseline.
“Many of these patients are the ones we have historically characterized as having alopecia totalis or universalis,” Dr. King said.
Participating patients were randomly assigned to 8 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, 12 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, or placebo. The primary endpoint was a SALT score of ≤ 20% at week 24.
At 24 weeks, almost no patients in the placebo group (1%) vs. 33% and 38% in the 8 mg and 12 mg twice-daily groups, respectively, met the primary endpoint. Each active treatment group was highly significant vs. placebo.
Of the responders, the majority achieved complete or near complete hair growth as defined by a SALT score of ≤ 10%, Dr. King reported.
Based on a graph that showed a relatively steep climb over the entire 24-week study period, deuruxolitinib “had a really fast onset of action,” Dr. King said. By week 8, which was the time of the first assessment, both doses of deuruxolitinib were superior to placebo.
The majority of patients had complete or significant loss of eyebrows and eye lashes at baseline, but more than two-thirds of these patients had regrowth by week 24, Dr. King said. Again, no significant regrowth was observed in the placebo arm.
On the Satisfaction of Hair Patient Reported Outcomes (SPRO), more than half of patients on both doses reported being satisfied or very satisfied with the improvement when evaluated at 24 weeks.
“The patient satisfaction overshot what one would expect by looking at the SALT scores, but a lot of subjects were at the precipice of the primary endpoint, sitting on SALT scores of 21, 25, or 30,” Dr. King said.
High participation in extension trial
More than 90% of the patients assigned to deuruxolitinib completed the trial and have entered an open-label extension (OLE). Dr. King credited the substantial rates of hair growth and the low rate of significant adverse events for the high rate of transition to OLE. Those who experienced the response were motivated to maintain it.
“This is a devastating disease. Patients want to get better,” Dr. King said.
There were no serious treatment-emergent adverse events associated with deuruxolitinib, including no thromboembolic events or other off-target events that have been reported previously with other JAK inhibitors in other disease states, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Although some adverse events, such as nasopharyngitis, were observed more often in those taking deuruxolitinib than placebo, there were “very few” discontinuations because of an adverse event, he said.
The data of THRIVE-AA2 are wholly compatible with the previously reported 706-patient THRIVE-AA1, according to Dr. King. In THRIVE-AA1, the primary endpoint of SALT ≤ 20% was reached by 29.6%, 41.5%, and 0.8% of the 8 mg, 12 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. Patient satisfaction scores, safety, and tolerability were also similar, according to Dr. King.
The experience with deuruxolitinib in the THRIVE-AA phase 3 program is similar to the experience with baricitinib in the BRAVE-AA trials. Although they cannot be compared directly because of potential differences between study populations, the 4-mg dose of baricitinib also achieved SALT score ≤ 20 in about 35% of patients, he said. The proportion was lower in the 2-mg group but was also superior to the placebo group.
“JAK inhibitors are changing the paradigm of alopecia areata,” Dr. King said. Responding to a question about payers reluctant to reimburse therapies for a “cosmetic” condition, Dr. King added that the effective treatments are “changing the landscape of how we think about this disease.” Dr. King believes these kinds of data show that “we are literally transforming lives forever.”
Baricitinib and the BRAVE studies
When baricitinib received regulatory approval for alopecia areata last year, it was not just the first JAK inhibitor approved for this disease, but the first systemic therapy of any kind, according to Maryanne Senna, MD, an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and the director of the Lahey Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Mass. Dr. Senna was a clinical investigator of BRAVE-AA1, as well as of THRIVE-AA2.
Providing an update on the BRAVE-AA program, Dr. Senna reported 104-week data that appear to support the idea of a life-changing benefit from JAK inhibitor therapy. This is because the effects appear durable.
In the data she presented at the AAD, responders and mixed responders at 52 weeks were followed to 104 weeks. Mixed responders were defined as those without a SALT response of ≤ 20 at week 52 but who had achieved this degree of hair regrowth at some earlier point.
Of the responders, 90% maintained their response at 104 weeks. In addition, many of the mixed responders and patients with a partial response but who never achieved a SALT score ≤ 20% gained additional hair growth, including complete or near complete hair growth, when maintained on treatment over the 2 years of follow-up.
“The follow-up suggests that, if you keep patients on treatment, you can get many of them to a meaningful response,” she said.
Meanwhile, “there have been no new safety signals,” Dr. Senna said. She based this statement not only of the 104-week data but on follow-up of up to 3.6 years among patients who have remained on treatment after participating in previous studies.
According to Dr. Senna, the off-target events that have been reported previously in other diseases with other JAK inhibitors, such as major adverse cardiovascular events and thromboembolic events, have not so far been observed in the BRAVE-AA phase 3 program.
Baricitinib, much like all but one of the JAK inhibitors with dermatologic indications, carries a black box warning that lists multiple risks for drugs in this class, based on a rheumatoid arthritis study.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted deuruxolitinib Breakthrough Therapy designation for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe alopecia areata and Fast Track designation for the treatment of alopecia areata, according to its manufacturer Concert Pharmaceuticals.
Dr. King reports financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Concert Pharmaceuticals, which provided the funding for the THRIVE-AA trial program, and for Eli Lilly, which provided funding for the BRAVE-AA trial program. Dr. Senna reports financial relationships with Arena pharmaceuticals, Follica, and both Concert Pharmaceuticals and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
from clinical trials of two drugs presented at a late-breaker research session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Based on phase 3 studies that document robust hair growth in about one third of patients, deuruxolitinib (CTP-543), an inhibitor of the JAK1 and JAK2 enzymes, has the potential to become the second JAK inhibitor available for the treatment of alopecia areata. If approved, it will join baricitinib (Olumiant), which received U.S. approval almost 1 year ago.
In his talk on THRIVE-AA2, a phase 3 trial of the investigational medicine deuruxolitinib, the principal investigator, Brett A. King, MD, PhD, displayed several before-and-after photos and said, “The photos tell the whole story. This is why there is so much excitement about these drugs.”
THRIVE-AA2 was the second of two phase 3 studies of deuruxolitinib. King was a principal investigator for both pivotal trials, called THRIVE-AA1 and THRIVE AA-2. He characterized the results of the two THRIVE trials as “comparable.”
Dr. King also was a principal investigator for the trials with baricitinib, called BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE AA-2, which were published last year in the New England Journal of Medicine. The trials for both drugs had similar designs and endpoints.
Deuruxolitinib and the THRIVE studies
In the THRIVE-AA2 trial, 517 adult patients were enrolled with moderate to severe alopecia areata, defined as a SALT (Severity of Alopecia Tool) score of ≥ 50%, which signifies a hair loss of at least 50%. Like THRIVE-AA1, patients participated at treatment centers in North America and Europe. About two-thirds were female. The mean age was 39 years. The majority of patients had complete or near complete hair loss at baseline.
“Many of these patients are the ones we have historically characterized as having alopecia totalis or universalis,” Dr. King said.
Participating patients were randomly assigned to 8 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, 12 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, or placebo. The primary endpoint was a SALT score of ≤ 20% at week 24.
At 24 weeks, almost no patients in the placebo group (1%) vs. 33% and 38% in the 8 mg and 12 mg twice-daily groups, respectively, met the primary endpoint. Each active treatment group was highly significant vs. placebo.
Of the responders, the majority achieved complete or near complete hair growth as defined by a SALT score of ≤ 10%, Dr. King reported.
Based on a graph that showed a relatively steep climb over the entire 24-week study period, deuruxolitinib “had a really fast onset of action,” Dr. King said. By week 8, which was the time of the first assessment, both doses of deuruxolitinib were superior to placebo.
The majority of patients had complete or significant loss of eyebrows and eye lashes at baseline, but more than two-thirds of these patients had regrowth by week 24, Dr. King said. Again, no significant regrowth was observed in the placebo arm.
On the Satisfaction of Hair Patient Reported Outcomes (SPRO), more than half of patients on both doses reported being satisfied or very satisfied with the improvement when evaluated at 24 weeks.
“The patient satisfaction overshot what one would expect by looking at the SALT scores, but a lot of subjects were at the precipice of the primary endpoint, sitting on SALT scores of 21, 25, or 30,” Dr. King said.
High participation in extension trial
More than 90% of the patients assigned to deuruxolitinib completed the trial and have entered an open-label extension (OLE). Dr. King credited the substantial rates of hair growth and the low rate of significant adverse events for the high rate of transition to OLE. Those who experienced the response were motivated to maintain it.
“This is a devastating disease. Patients want to get better,” Dr. King said.
There were no serious treatment-emergent adverse events associated with deuruxolitinib, including no thromboembolic events or other off-target events that have been reported previously with other JAK inhibitors in other disease states, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Although some adverse events, such as nasopharyngitis, were observed more often in those taking deuruxolitinib than placebo, there were “very few” discontinuations because of an adverse event, he said.
The data of THRIVE-AA2 are wholly compatible with the previously reported 706-patient THRIVE-AA1, according to Dr. King. In THRIVE-AA1, the primary endpoint of SALT ≤ 20% was reached by 29.6%, 41.5%, and 0.8% of the 8 mg, 12 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. Patient satisfaction scores, safety, and tolerability were also similar, according to Dr. King.
The experience with deuruxolitinib in the THRIVE-AA phase 3 program is similar to the experience with baricitinib in the BRAVE-AA trials. Although they cannot be compared directly because of potential differences between study populations, the 4-mg dose of baricitinib also achieved SALT score ≤ 20 in about 35% of patients, he said. The proportion was lower in the 2-mg group but was also superior to the placebo group.
“JAK inhibitors are changing the paradigm of alopecia areata,” Dr. King said. Responding to a question about payers reluctant to reimburse therapies for a “cosmetic” condition, Dr. King added that the effective treatments are “changing the landscape of how we think about this disease.” Dr. King believes these kinds of data show that “we are literally transforming lives forever.”
Baricitinib and the BRAVE studies
When baricitinib received regulatory approval for alopecia areata last year, it was not just the first JAK inhibitor approved for this disease, but the first systemic therapy of any kind, according to Maryanne Senna, MD, an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and the director of the Lahey Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Mass. Dr. Senna was a clinical investigator of BRAVE-AA1, as well as of THRIVE-AA2.
Providing an update on the BRAVE-AA program, Dr. Senna reported 104-week data that appear to support the idea of a life-changing benefit from JAK inhibitor therapy. This is because the effects appear durable.
In the data she presented at the AAD, responders and mixed responders at 52 weeks were followed to 104 weeks. Mixed responders were defined as those without a SALT response of ≤ 20 at week 52 but who had achieved this degree of hair regrowth at some earlier point.
Of the responders, 90% maintained their response at 104 weeks. In addition, many of the mixed responders and patients with a partial response but who never achieved a SALT score ≤ 20% gained additional hair growth, including complete or near complete hair growth, when maintained on treatment over the 2 years of follow-up.
“The follow-up suggests that, if you keep patients on treatment, you can get many of them to a meaningful response,” she said.
Meanwhile, “there have been no new safety signals,” Dr. Senna said. She based this statement not only of the 104-week data but on follow-up of up to 3.6 years among patients who have remained on treatment after participating in previous studies.
According to Dr. Senna, the off-target events that have been reported previously in other diseases with other JAK inhibitors, such as major adverse cardiovascular events and thromboembolic events, have not so far been observed in the BRAVE-AA phase 3 program.
Baricitinib, much like all but one of the JAK inhibitors with dermatologic indications, carries a black box warning that lists multiple risks for drugs in this class, based on a rheumatoid arthritis study.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted deuruxolitinib Breakthrough Therapy designation for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe alopecia areata and Fast Track designation for the treatment of alopecia areata, according to its manufacturer Concert Pharmaceuticals.
Dr. King reports financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Concert Pharmaceuticals, which provided the funding for the THRIVE-AA trial program, and for Eli Lilly, which provided funding for the BRAVE-AA trial program. Dr. Senna reports financial relationships with Arena pharmaceuticals, Follica, and both Concert Pharmaceuticals and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
from clinical trials of two drugs presented at a late-breaker research session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Based on phase 3 studies that document robust hair growth in about one third of patients, deuruxolitinib (CTP-543), an inhibitor of the JAK1 and JAK2 enzymes, has the potential to become the second JAK inhibitor available for the treatment of alopecia areata. If approved, it will join baricitinib (Olumiant), which received U.S. approval almost 1 year ago.
In his talk on THRIVE-AA2, a phase 3 trial of the investigational medicine deuruxolitinib, the principal investigator, Brett A. King, MD, PhD, displayed several before-and-after photos and said, “The photos tell the whole story. This is why there is so much excitement about these drugs.”
THRIVE-AA2 was the second of two phase 3 studies of deuruxolitinib. King was a principal investigator for both pivotal trials, called THRIVE-AA1 and THRIVE AA-2. He characterized the results of the two THRIVE trials as “comparable.”
Dr. King also was a principal investigator for the trials with baricitinib, called BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE AA-2, which were published last year in the New England Journal of Medicine. The trials for both drugs had similar designs and endpoints.
Deuruxolitinib and the THRIVE studies
In the THRIVE-AA2 trial, 517 adult patients were enrolled with moderate to severe alopecia areata, defined as a SALT (Severity of Alopecia Tool) score of ≥ 50%, which signifies a hair loss of at least 50%. Like THRIVE-AA1, patients participated at treatment centers in North America and Europe. About two-thirds were female. The mean age was 39 years. The majority of patients had complete or near complete hair loss at baseline.
“Many of these patients are the ones we have historically characterized as having alopecia totalis or universalis,” Dr. King said.
Participating patients were randomly assigned to 8 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, 12 mg deuruxolitinib twice daily, or placebo. The primary endpoint was a SALT score of ≤ 20% at week 24.
At 24 weeks, almost no patients in the placebo group (1%) vs. 33% and 38% in the 8 mg and 12 mg twice-daily groups, respectively, met the primary endpoint. Each active treatment group was highly significant vs. placebo.
Of the responders, the majority achieved complete or near complete hair growth as defined by a SALT score of ≤ 10%, Dr. King reported.
Based on a graph that showed a relatively steep climb over the entire 24-week study period, deuruxolitinib “had a really fast onset of action,” Dr. King said. By week 8, which was the time of the first assessment, both doses of deuruxolitinib were superior to placebo.
The majority of patients had complete or significant loss of eyebrows and eye lashes at baseline, but more than two-thirds of these patients had regrowth by week 24, Dr. King said. Again, no significant regrowth was observed in the placebo arm.
On the Satisfaction of Hair Patient Reported Outcomes (SPRO), more than half of patients on both doses reported being satisfied or very satisfied with the improvement when evaluated at 24 weeks.
“The patient satisfaction overshot what one would expect by looking at the SALT scores, but a lot of subjects were at the precipice of the primary endpoint, sitting on SALT scores of 21, 25, or 30,” Dr. King said.
High participation in extension trial
More than 90% of the patients assigned to deuruxolitinib completed the trial and have entered an open-label extension (OLE). Dr. King credited the substantial rates of hair growth and the low rate of significant adverse events for the high rate of transition to OLE. Those who experienced the response were motivated to maintain it.
“This is a devastating disease. Patients want to get better,” Dr. King said.
There were no serious treatment-emergent adverse events associated with deuruxolitinib, including no thromboembolic events or other off-target events that have been reported previously with other JAK inhibitors in other disease states, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Although some adverse events, such as nasopharyngitis, were observed more often in those taking deuruxolitinib than placebo, there were “very few” discontinuations because of an adverse event, he said.
The data of THRIVE-AA2 are wholly compatible with the previously reported 706-patient THRIVE-AA1, according to Dr. King. In THRIVE-AA1, the primary endpoint of SALT ≤ 20% was reached by 29.6%, 41.5%, and 0.8% of the 8 mg, 12 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. Patient satisfaction scores, safety, and tolerability were also similar, according to Dr. King.
The experience with deuruxolitinib in the THRIVE-AA phase 3 program is similar to the experience with baricitinib in the BRAVE-AA trials. Although they cannot be compared directly because of potential differences between study populations, the 4-mg dose of baricitinib also achieved SALT score ≤ 20 in about 35% of patients, he said. The proportion was lower in the 2-mg group but was also superior to the placebo group.
“JAK inhibitors are changing the paradigm of alopecia areata,” Dr. King said. Responding to a question about payers reluctant to reimburse therapies for a “cosmetic” condition, Dr. King added that the effective treatments are “changing the landscape of how we think about this disease.” Dr. King believes these kinds of data show that “we are literally transforming lives forever.”
Baricitinib and the BRAVE studies
When baricitinib received regulatory approval for alopecia areata last year, it was not just the first JAK inhibitor approved for this disease, but the first systemic therapy of any kind, according to Maryanne Senna, MD, an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and the director of the Lahey Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Mass. Dr. Senna was a clinical investigator of BRAVE-AA1, as well as of THRIVE-AA2.
Providing an update on the BRAVE-AA program, Dr. Senna reported 104-week data that appear to support the idea of a life-changing benefit from JAK inhibitor therapy. This is because the effects appear durable.
In the data she presented at the AAD, responders and mixed responders at 52 weeks were followed to 104 weeks. Mixed responders were defined as those without a SALT response of ≤ 20 at week 52 but who had achieved this degree of hair regrowth at some earlier point.
Of the responders, 90% maintained their response at 104 weeks. In addition, many of the mixed responders and patients with a partial response but who never achieved a SALT score ≤ 20% gained additional hair growth, including complete or near complete hair growth, when maintained on treatment over the 2 years of follow-up.
“The follow-up suggests that, if you keep patients on treatment, you can get many of them to a meaningful response,” she said.
Meanwhile, “there have been no new safety signals,” Dr. Senna said. She based this statement not only of the 104-week data but on follow-up of up to 3.6 years among patients who have remained on treatment after participating in previous studies.
According to Dr. Senna, the off-target events that have been reported previously in other diseases with other JAK inhibitors, such as major adverse cardiovascular events and thromboembolic events, have not so far been observed in the BRAVE-AA phase 3 program.
Baricitinib, much like all but one of the JAK inhibitors with dermatologic indications, carries a black box warning that lists multiple risks for drugs in this class, based on a rheumatoid arthritis study.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted deuruxolitinib Breakthrough Therapy designation for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe alopecia areata and Fast Track designation for the treatment of alopecia areata, according to its manufacturer Concert Pharmaceuticals.
Dr. King reports financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Concert Pharmaceuticals, which provided the funding for the THRIVE-AA trial program, and for Eli Lilly, which provided funding for the BRAVE-AA trial program. Dr. Senna reports financial relationships with Arena pharmaceuticals, Follica, and both Concert Pharmaceuticals and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
Pilot study evaluates sensitive skin burden in persons of color
NEW ORLEANS – .
Respondents also reported high rates of reactions to skin care products marketed for sensitive skin, and most said they had visited a dermatologist about their condition.
Those are among the key findings of a pilot study designed to assess the prevalence, symptom burden, and behaviors of self-identified persons of color with sensitive skin, which senior author Adam Friedman, MD, and colleagues defined as a subjective syndrome of cutaneous hyperreactivity to otherwise innocuous stimuli. “Improved understanding of sensitive skin is essential, and we encourage additional research into pathophysiology and creating a consensus definition for sensitive skin,” Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during an e-poster session. The findings were also reported online in JAAD International.
In May of 2022, Dr. Friedman, first author Erika McCormick, a 4th-year medical student at George Washington University, and colleagues invited individuals attending a community health fair in an undeserved area of Washington, to complete the Sensitive Scale-10 (SS-10) and to answer other questions after receiving a brief education about sensitive skin. Of the 58 respondents, 78% were female, and 86% self-identified as a person of color.
“Our study population predominantly self-identified as Black, which only represents one piece of those who would be characterized as persons of color,” Dr. Friedman said. “That said, improved representation of both our study population, and furthermore persons of color, in all aspects of dermatology research is crucial to at a minimum ensure generalizability of findings to the U.S. population, and research on sensitive skin is but one component of this.”
Nearly two-thirds of all respondents (63.8%) reported having an underlying skin condition, most commonly acne (21%), eczema (17%), and rosacea (6%). More than half (57%) reported sensitive skin, 27% of whom reported no other skin disease. Individuals with sensitive skin had higher mean SS-10 scores, compared with those with nonsensitive skin (14.61 vs. 4.32; P = .002) and burning was the main symptom among those with sensitive skin (56%), followed by itch (50%), redness (39%), dryness (39%) and pain (17%).
Compared with those who did not meet criteria for sensitive skin, those who did were more likely to report a personal history of allergy (56.25% vs. 8.33%; P = .0002) and were nearly seven times more likely to have seen a dermatologist about their concerns (odds ratio, 6.857; P = .0012).
In other findings limited to respondents with sensitive skin, 72% who reported reactions to general consumer skin care products also reported reacting to products marketed for sensitive skin, and 94% reported reactivity to at least one trigger, most commonly extreme temperatures (34%), stress (34%), sweat (33%), sun exposure (29%), and diet (28%). “We were particularly surprised by the high rates of reactivity to skin care products designed for and marketed to those suffering with sensitive skin,” Ms. McCormick told this news organization. “Importantly, there is currently no federal or legal standard regulating ingredients in products marketed for sensitive skin, and many products lack testing in sensitive skin specifically. Our data suggest an opportunity for improvement of sensitive skin care.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size. “Reconducting this survey in a larger population will help validate our findings,” she said.
The research was supported by two independent research grants from Galderma: one supporting Ms. McCormick with a Sensitive Skin Research Fellowship and the other a Sensitive Skin Research Acceleration Fund. Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – .
Respondents also reported high rates of reactions to skin care products marketed for sensitive skin, and most said they had visited a dermatologist about their condition.
Those are among the key findings of a pilot study designed to assess the prevalence, symptom burden, and behaviors of self-identified persons of color with sensitive skin, which senior author Adam Friedman, MD, and colleagues defined as a subjective syndrome of cutaneous hyperreactivity to otherwise innocuous stimuli. “Improved understanding of sensitive skin is essential, and we encourage additional research into pathophysiology and creating a consensus definition for sensitive skin,” Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during an e-poster session. The findings were also reported online in JAAD International.
In May of 2022, Dr. Friedman, first author Erika McCormick, a 4th-year medical student at George Washington University, and colleagues invited individuals attending a community health fair in an undeserved area of Washington, to complete the Sensitive Scale-10 (SS-10) and to answer other questions after receiving a brief education about sensitive skin. Of the 58 respondents, 78% were female, and 86% self-identified as a person of color.
“Our study population predominantly self-identified as Black, which only represents one piece of those who would be characterized as persons of color,” Dr. Friedman said. “That said, improved representation of both our study population, and furthermore persons of color, in all aspects of dermatology research is crucial to at a minimum ensure generalizability of findings to the U.S. population, and research on sensitive skin is but one component of this.”
Nearly two-thirds of all respondents (63.8%) reported having an underlying skin condition, most commonly acne (21%), eczema (17%), and rosacea (6%). More than half (57%) reported sensitive skin, 27% of whom reported no other skin disease. Individuals with sensitive skin had higher mean SS-10 scores, compared with those with nonsensitive skin (14.61 vs. 4.32; P = .002) and burning was the main symptom among those with sensitive skin (56%), followed by itch (50%), redness (39%), dryness (39%) and pain (17%).
Compared with those who did not meet criteria for sensitive skin, those who did were more likely to report a personal history of allergy (56.25% vs. 8.33%; P = .0002) and were nearly seven times more likely to have seen a dermatologist about their concerns (odds ratio, 6.857; P = .0012).
In other findings limited to respondents with sensitive skin, 72% who reported reactions to general consumer skin care products also reported reacting to products marketed for sensitive skin, and 94% reported reactivity to at least one trigger, most commonly extreme temperatures (34%), stress (34%), sweat (33%), sun exposure (29%), and diet (28%). “We were particularly surprised by the high rates of reactivity to skin care products designed for and marketed to those suffering with sensitive skin,” Ms. McCormick told this news organization. “Importantly, there is currently no federal or legal standard regulating ingredients in products marketed for sensitive skin, and many products lack testing in sensitive skin specifically. Our data suggest an opportunity for improvement of sensitive skin care.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size. “Reconducting this survey in a larger population will help validate our findings,” she said.
The research was supported by two independent research grants from Galderma: one supporting Ms. McCormick with a Sensitive Skin Research Fellowship and the other a Sensitive Skin Research Acceleration Fund. Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – .
Respondents also reported high rates of reactions to skin care products marketed for sensitive skin, and most said they had visited a dermatologist about their condition.
Those are among the key findings of a pilot study designed to assess the prevalence, symptom burden, and behaviors of self-identified persons of color with sensitive skin, which senior author Adam Friedman, MD, and colleagues defined as a subjective syndrome of cutaneous hyperreactivity to otherwise innocuous stimuli. “Improved understanding of sensitive skin is essential, and we encourage additional research into pathophysiology and creating a consensus definition for sensitive skin,” Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during an e-poster session. The findings were also reported online in JAAD International.
In May of 2022, Dr. Friedman, first author Erika McCormick, a 4th-year medical student at George Washington University, and colleagues invited individuals attending a community health fair in an undeserved area of Washington, to complete the Sensitive Scale-10 (SS-10) and to answer other questions after receiving a brief education about sensitive skin. Of the 58 respondents, 78% were female, and 86% self-identified as a person of color.
“Our study population predominantly self-identified as Black, which only represents one piece of those who would be characterized as persons of color,” Dr. Friedman said. “That said, improved representation of both our study population, and furthermore persons of color, in all aspects of dermatology research is crucial to at a minimum ensure generalizability of findings to the U.S. population, and research on sensitive skin is but one component of this.”
Nearly two-thirds of all respondents (63.8%) reported having an underlying skin condition, most commonly acne (21%), eczema (17%), and rosacea (6%). More than half (57%) reported sensitive skin, 27% of whom reported no other skin disease. Individuals with sensitive skin had higher mean SS-10 scores, compared with those with nonsensitive skin (14.61 vs. 4.32; P = .002) and burning was the main symptom among those with sensitive skin (56%), followed by itch (50%), redness (39%), dryness (39%) and pain (17%).
Compared with those who did not meet criteria for sensitive skin, those who did were more likely to report a personal history of allergy (56.25% vs. 8.33%; P = .0002) and were nearly seven times more likely to have seen a dermatologist about their concerns (odds ratio, 6.857; P = .0012).
In other findings limited to respondents with sensitive skin, 72% who reported reactions to general consumer skin care products also reported reacting to products marketed for sensitive skin, and 94% reported reactivity to at least one trigger, most commonly extreme temperatures (34%), stress (34%), sweat (33%), sun exposure (29%), and diet (28%). “We were particularly surprised by the high rates of reactivity to skin care products designed for and marketed to those suffering with sensitive skin,” Ms. McCormick told this news organization. “Importantly, there is currently no federal or legal standard regulating ingredients in products marketed for sensitive skin, and many products lack testing in sensitive skin specifically. Our data suggest an opportunity for improvement of sensitive skin care.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size. “Reconducting this survey in a larger population will help validate our findings,” she said.
The research was supported by two independent research grants from Galderma: one supporting Ms. McCormick with a Sensitive Skin Research Fellowship and the other a Sensitive Skin Research Acceleration Fund. Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant disclosures.
AT AAD 2023