User login
The Official Newspaper of the American Association for Thoracic Surgery
DOJ charges 412 in massive health care fraud bust
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) has charged more than 400 health professionals with fraud for allegedly bilking $1.3 billion from the government through false billings to the Medicare, Medicaid, and TRICARE programs.
In all, 412 people, including 56 doctors, were charged across 41 federal districts for their participation in the alleged schemes, a large portion of which involved unnecessarily prescribing and distributing opioids to patients, according to a July 13 announcement by the DOJ. The agency called the enforcement the largest health care fraud action in DOJ history.
Defendants were charged in more than 20 states, including Florida, Michigan, Texas, California, Illinois, and Louisiana, where the federal government operates Medicare Fraud Strike Forces.
Southern Florida had the highest number of defendants, with 77 health professionals charged with a combined $141 million in false billings for alleged home health care, mental health services, and pharmacy fraud. In one case, an owner and operator of a Florida addiction treatment center is accused of actively recruiting addicted patients to move to South Florida so that coconspirators could bill for treatment and testing. In return, the coconspirators offered kickbacks to patients in the form of gift cards, free airline travel, trips to casinos and strip clubs, and drugs, according to the DOJ.
Health care fraud is not only a criminal act that costs billions of taxpayer dollars, it is an affront to all Americans who rely on national health care programs, Tom Price, MD, Secretary of Health and Human Services, said in a statement. “The United States is home to the world’s best medical professionals, but their ability to provide affordable, high-quality care to their patients is jeopardized every time a criminal commits health care fraud,” Dr. Price said.
[email protected]
On Twitter @legal_med
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) has charged more than 400 health professionals with fraud for allegedly bilking $1.3 billion from the government through false billings to the Medicare, Medicaid, and TRICARE programs.
In all, 412 people, including 56 doctors, were charged across 41 federal districts for their participation in the alleged schemes, a large portion of which involved unnecessarily prescribing and distributing opioids to patients, according to a July 13 announcement by the DOJ. The agency called the enforcement the largest health care fraud action in DOJ history.
Defendants were charged in more than 20 states, including Florida, Michigan, Texas, California, Illinois, and Louisiana, where the federal government operates Medicare Fraud Strike Forces.
Southern Florida had the highest number of defendants, with 77 health professionals charged with a combined $141 million in false billings for alleged home health care, mental health services, and pharmacy fraud. In one case, an owner and operator of a Florida addiction treatment center is accused of actively recruiting addicted patients to move to South Florida so that coconspirators could bill for treatment and testing. In return, the coconspirators offered kickbacks to patients in the form of gift cards, free airline travel, trips to casinos and strip clubs, and drugs, according to the DOJ.
Health care fraud is not only a criminal act that costs billions of taxpayer dollars, it is an affront to all Americans who rely on national health care programs, Tom Price, MD, Secretary of Health and Human Services, said in a statement. “The United States is home to the world’s best medical professionals, but their ability to provide affordable, high-quality care to their patients is jeopardized every time a criminal commits health care fraud,” Dr. Price said.
[email protected]
On Twitter @legal_med
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) has charged more than 400 health professionals with fraud for allegedly bilking $1.3 billion from the government through false billings to the Medicare, Medicaid, and TRICARE programs.
In all, 412 people, including 56 doctors, were charged across 41 federal districts for their participation in the alleged schemes, a large portion of which involved unnecessarily prescribing and distributing opioids to patients, according to a July 13 announcement by the DOJ. The agency called the enforcement the largest health care fraud action in DOJ history.
Defendants were charged in more than 20 states, including Florida, Michigan, Texas, California, Illinois, and Louisiana, where the federal government operates Medicare Fraud Strike Forces.
Southern Florida had the highest number of defendants, with 77 health professionals charged with a combined $141 million in false billings for alleged home health care, mental health services, and pharmacy fraud. In one case, an owner and operator of a Florida addiction treatment center is accused of actively recruiting addicted patients to move to South Florida so that coconspirators could bill for treatment and testing. In return, the coconspirators offered kickbacks to patients in the form of gift cards, free airline travel, trips to casinos and strip clubs, and drugs, according to the DOJ.
Health care fraud is not only a criminal act that costs billions of taxpayer dollars, it is an affront to all Americans who rely on national health care programs, Tom Price, MD, Secretary of Health and Human Services, said in a statement. “The United States is home to the world’s best medical professionals, but their ability to provide affordable, high-quality care to their patients is jeopardized every time a criminal commits health care fraud,” Dr. Price said.
[email protected]
On Twitter @legal_med
Evolute transcatheter valve, now FDA approved for intermediate-risk patients, impresses in real-world practice
PARIS – The Evolut R transcatheter aortic valve demonstrated excellent 30-day results in a real-world, mixed surgical risk population in the large Evolut R FORWARD study.
In this 1,038-patient observational study conducted at 53 sites in 20 countries, the Evolut R valve showed excellent forward hemodynamics and low 30-day rates of all-cause mortality and stroke that were unaffected by utilization of the device’s repositioning feature, Eberhard Grube, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
The importance of the FORWARD study, Dr. Grube observed, is that it illustrates the clinical outcomes obtained in a large population drawn from routine clinical practice. Unlike in a randomized trial such as SURTAVI, the participating sites in the Evolut R Forward study weren’t all high-volume enrollment centers, and operators had widely varying degrees of experience with the valve.
Also, SURTAVI utilized the first generation of the self-expanding CoreValve, which lacked the repositioning feature introduced in the second-generation Evolut R. The FORWARD study is the first rigorous evaluation of Evolut R with centrally adjudicated outcomes.
The mean Society of Thoracic Surgeons predicted risk of mortality score in participants was 5.5%, and 47% had a low-risk score of less than 4%. However, the patients had a mean age of 82 years, one-third were deemed frail, 30% had diabetes, and 26% had chronic lung disease.
The primary study endpoint was 30-day all-cause mortality. The rate was 1.9%, compared with a predicted 5.5% rate based on STS score, for an impressive observed-to-expected ratio of 0.35.
Hemodynamically, the effective orifice area improved from 0.8 cm2 at baseline to 1.9 cm2 at 30 days, while the mean aortic valve gradient plunged from 41.7 to 8.5 mm Hg.
At baseline only 1.5% of patients were New York Heart Association functional class I and 26.5% were class II. At 30 days, 44.7% were class I and 43.4% were class II. The prevalence of NYHA class III status decreased from 63.8% to 11.3%.
There was no or only trace paravalvular leak at discharge in 67.2% of patients as adjudicated in a core laboratory, mild leak in 30.9%, moderate in 1.9%, and severe leak in just 0.1%.
The 30-day total stroke rate was 2.8%, including a 1.8% rate of disabling stroke. Major vascular complications occurred in 6.5% of patients, valve embolization in 0.7%, and life-threatening or disabling bleeding in 3.3%. There were no cases of coronary obstruction or annular rupture.
New pacemaker implantation was required within 30 days in 17.5% of patients. Three-quarters of the pacemakers were placed because of third-degree atrioventricular block.
The new valve ended up in proper anatomic position in 98.9% of patients.
The repositioning feature was utilized in 26% of participants. It had no impact on the rate of pacemaker implantation, mortality, stroke, or other safety endpoints.
“I think the ability to reposition this valve, which is a safety feature, is an important feature, particularly for centers that don’t have so much experience. If the valve is considered to be too high or too low, or you see, for example, a higher degree of paravalvular leak, you have the chance to correct that by using this feature. So it’s an important feature for the operator. It helps to get an optimal result. And the most important thing is there was no price in terms of safety that we paid for repositioning,” said Dr. Grube, professor of cardiology and head of the Center for Innovative Intervention in Cardiology at the University of Bonn in Siegberg, Germany.
Session cochair Alain Cribier, MD, famed for having performed the world’s first TAVR procedure, pronounced the FORWARD results “very impressive.”
“Less than 2% mortality, around a 2% disabling stroke rate, and the data on paravalvular leak are excellent as well. It’s very nice to see that what was a limited data set earlier, with a smaller number of patients, has now been replicated in 1,000 patients. So I think now we can confidently talk about the clinical outcomes – and they are excellent,” declared Dr. Cribier, professor of medicine at the University of Rouen (France) and chief of cardiology at Charles Nicolle Hospital.
The FORWARD study was sponsored by Medtronic. Dr. Grube reported serving as a consultant to that company as well as to Boston Scientific, Abbott, and Millipede Medical.
PARIS – The Evolut R transcatheter aortic valve demonstrated excellent 30-day results in a real-world, mixed surgical risk population in the large Evolut R FORWARD study.
In this 1,038-patient observational study conducted at 53 sites in 20 countries, the Evolut R valve showed excellent forward hemodynamics and low 30-day rates of all-cause mortality and stroke that were unaffected by utilization of the device’s repositioning feature, Eberhard Grube, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
The importance of the FORWARD study, Dr. Grube observed, is that it illustrates the clinical outcomes obtained in a large population drawn from routine clinical practice. Unlike in a randomized trial such as SURTAVI, the participating sites in the Evolut R Forward study weren’t all high-volume enrollment centers, and operators had widely varying degrees of experience with the valve.
Also, SURTAVI utilized the first generation of the self-expanding CoreValve, which lacked the repositioning feature introduced in the second-generation Evolut R. The FORWARD study is the first rigorous evaluation of Evolut R with centrally adjudicated outcomes.
The mean Society of Thoracic Surgeons predicted risk of mortality score in participants was 5.5%, and 47% had a low-risk score of less than 4%. However, the patients had a mean age of 82 years, one-third were deemed frail, 30% had diabetes, and 26% had chronic lung disease.
The primary study endpoint was 30-day all-cause mortality. The rate was 1.9%, compared with a predicted 5.5% rate based on STS score, for an impressive observed-to-expected ratio of 0.35.
Hemodynamically, the effective orifice area improved from 0.8 cm2 at baseline to 1.9 cm2 at 30 days, while the mean aortic valve gradient plunged from 41.7 to 8.5 mm Hg.
At baseline only 1.5% of patients were New York Heart Association functional class I and 26.5% were class II. At 30 days, 44.7% were class I and 43.4% were class II. The prevalence of NYHA class III status decreased from 63.8% to 11.3%.
There was no or only trace paravalvular leak at discharge in 67.2% of patients as adjudicated in a core laboratory, mild leak in 30.9%, moderate in 1.9%, and severe leak in just 0.1%.
The 30-day total stroke rate was 2.8%, including a 1.8% rate of disabling stroke. Major vascular complications occurred in 6.5% of patients, valve embolization in 0.7%, and life-threatening or disabling bleeding in 3.3%. There were no cases of coronary obstruction or annular rupture.
New pacemaker implantation was required within 30 days in 17.5% of patients. Three-quarters of the pacemakers were placed because of third-degree atrioventricular block.
The new valve ended up in proper anatomic position in 98.9% of patients.
The repositioning feature was utilized in 26% of participants. It had no impact on the rate of pacemaker implantation, mortality, stroke, or other safety endpoints.
“I think the ability to reposition this valve, which is a safety feature, is an important feature, particularly for centers that don’t have so much experience. If the valve is considered to be too high or too low, or you see, for example, a higher degree of paravalvular leak, you have the chance to correct that by using this feature. So it’s an important feature for the operator. It helps to get an optimal result. And the most important thing is there was no price in terms of safety that we paid for repositioning,” said Dr. Grube, professor of cardiology and head of the Center for Innovative Intervention in Cardiology at the University of Bonn in Siegberg, Germany.
Session cochair Alain Cribier, MD, famed for having performed the world’s first TAVR procedure, pronounced the FORWARD results “very impressive.”
“Less than 2% mortality, around a 2% disabling stroke rate, and the data on paravalvular leak are excellent as well. It’s very nice to see that what was a limited data set earlier, with a smaller number of patients, has now been replicated in 1,000 patients. So I think now we can confidently talk about the clinical outcomes – and they are excellent,” declared Dr. Cribier, professor of medicine at the University of Rouen (France) and chief of cardiology at Charles Nicolle Hospital.
The FORWARD study was sponsored by Medtronic. Dr. Grube reported serving as a consultant to that company as well as to Boston Scientific, Abbott, and Millipede Medical.
PARIS – The Evolut R transcatheter aortic valve demonstrated excellent 30-day results in a real-world, mixed surgical risk population in the large Evolut R FORWARD study.
In this 1,038-patient observational study conducted at 53 sites in 20 countries, the Evolut R valve showed excellent forward hemodynamics and low 30-day rates of all-cause mortality and stroke that were unaffected by utilization of the device’s repositioning feature, Eberhard Grube, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
The importance of the FORWARD study, Dr. Grube observed, is that it illustrates the clinical outcomes obtained in a large population drawn from routine clinical practice. Unlike in a randomized trial such as SURTAVI, the participating sites in the Evolut R Forward study weren’t all high-volume enrollment centers, and operators had widely varying degrees of experience with the valve.
Also, SURTAVI utilized the first generation of the self-expanding CoreValve, which lacked the repositioning feature introduced in the second-generation Evolut R. The FORWARD study is the first rigorous evaluation of Evolut R with centrally adjudicated outcomes.
The mean Society of Thoracic Surgeons predicted risk of mortality score in participants was 5.5%, and 47% had a low-risk score of less than 4%. However, the patients had a mean age of 82 years, one-third were deemed frail, 30% had diabetes, and 26% had chronic lung disease.
The primary study endpoint was 30-day all-cause mortality. The rate was 1.9%, compared with a predicted 5.5% rate based on STS score, for an impressive observed-to-expected ratio of 0.35.
Hemodynamically, the effective orifice area improved from 0.8 cm2 at baseline to 1.9 cm2 at 30 days, while the mean aortic valve gradient plunged from 41.7 to 8.5 mm Hg.
At baseline only 1.5% of patients were New York Heart Association functional class I and 26.5% were class II. At 30 days, 44.7% were class I and 43.4% were class II. The prevalence of NYHA class III status decreased from 63.8% to 11.3%.
There was no or only trace paravalvular leak at discharge in 67.2% of patients as adjudicated in a core laboratory, mild leak in 30.9%, moderate in 1.9%, and severe leak in just 0.1%.
The 30-day total stroke rate was 2.8%, including a 1.8% rate of disabling stroke. Major vascular complications occurred in 6.5% of patients, valve embolization in 0.7%, and life-threatening or disabling bleeding in 3.3%. There were no cases of coronary obstruction or annular rupture.
New pacemaker implantation was required within 30 days in 17.5% of patients. Three-quarters of the pacemakers were placed because of third-degree atrioventricular block.
The new valve ended up in proper anatomic position in 98.9% of patients.
The repositioning feature was utilized in 26% of participants. It had no impact on the rate of pacemaker implantation, mortality, stroke, or other safety endpoints.
“I think the ability to reposition this valve, which is a safety feature, is an important feature, particularly for centers that don’t have so much experience. If the valve is considered to be too high or too low, or you see, for example, a higher degree of paravalvular leak, you have the chance to correct that by using this feature. So it’s an important feature for the operator. It helps to get an optimal result. And the most important thing is there was no price in terms of safety that we paid for repositioning,” said Dr. Grube, professor of cardiology and head of the Center for Innovative Intervention in Cardiology at the University of Bonn in Siegberg, Germany.
Session cochair Alain Cribier, MD, famed for having performed the world’s first TAVR procedure, pronounced the FORWARD results “very impressive.”
“Less than 2% mortality, around a 2% disabling stroke rate, and the data on paravalvular leak are excellent as well. It’s very nice to see that what was a limited data set earlier, with a smaller number of patients, has now been replicated in 1,000 patients. So I think now we can confidently talk about the clinical outcomes – and they are excellent,” declared Dr. Cribier, professor of medicine at the University of Rouen (France) and chief of cardiology at Charles Nicolle Hospital.
The FORWARD study was sponsored by Medtronic. Dr. Grube reported serving as a consultant to that company as well as to Boston Scientific, Abbott, and Millipede Medical.
AT EUROPCR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Thirty-day all-cause mortality was 1.9% with a 2.8% stroke rate in a large, real-world study of TAVR with the repositionable self-expanding Evolut R transcatheter aortic valve.
Data source: The Evolut R FORWARD study of 1,038 recipients of the Evolut R transcatheter aortic valve at 53 sites in 20 countries.
Disclosures: The FORWARD study was sponsored by Medtronic. The presenter reported serving as a consultant to that company as well as to Boston Scientific, Abbott, and Millipede Medical.
Watchman device for AF patients ineligible for oral anticoagulation gains support from 1-year registry outcomes
PARIS – Patients with atrial fibrillation at high stroke risk and a contraindication for oral anticoagulation experienced an 83% reduction in their risk of ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack during their first year after receiving the Watchman left atrial appendage closure device backed by limited-duration dual-antiplatelet therapy, according to a report from the EWOLUTION registry.
Of 605 participants in the European registry who went on dual-antiplatelet treatment (DAPT) in conjunction with receiving the Watchman device, 39% discontinued DAPT within 3 months and 72% were off DAPT by 6 months. Yet the 1-year rate of ischemic stroke or TIA in the EWOLUTION group was just 1.8%, an 83% relative risk reduction compared with the expected 10.5% rate based on the participants’ mean CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4.6 in the absence of oral anticoagulation, Martin W. Bergmann, MD, said at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“Obviously this isn’t a randomized trial. This is just reassuring data that we are going in the right direction in terms of efficacy,” said Dr. Bergmann of Cardiologicum Hamburg, a large German group practice.
However, the ESC guidelines were largely based on randomized trials of the Watchman versus oral anticoagulation, including PREVAIL and PROTECT-AF, showing noninferiority. The safety and efficacy of the device in warfarin-ineligible patients was less well studied at the time the guidelines were formulated. And in fact, such patients are excluded from the Food and Drug Administration’s approved indication, which is specifically for patients judged “suitable for warfarin.”
“This gap is now filled by EWOLUTION. This is a registry that’s as good as it gets. We have all the things in place that you need these days to be able to rely on the outcome data,” according to the cardiologist.
EWOLUTION is a prospective, multicenter, all-comers registry. The EWOLUTION population of AF patients on DAPT was high risk: 89% had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 3 or more, 31% were at least 80 years old, the mean HAS-BLED score was 2.4, and oral anticoagulation was contraindicated in 84% of participants.
Eighty-seven percent of subjects underwent follow-up transesophageal echocardiography. The imaging study showed the Watchman effectively sealed the left atrial appendage in 99.2% of patients as defined by no leak greater than 5 mm. The echo exam also showed the presence of thrombus on the device at follow-up in 4% of patients, although only 1 of the 22 patients with device thrombus experienced a stroke.
“We can conclude two things from this which are in line with earlier studies. First, the rate of thrombus on the device is equal to the rate reported in the randomized controlled trials, which was also 4%, even if the patients were on warfarin for the first 45 days. And second, these thrombi are not related to stroke,” Dr. Bergmann said.
At the 1-year mark, 71% of patients had switched to a single antiplatelet agent, while 17% remained on DAPT, mainly because of comorbid coronary disease for which DAPT is indicated. Seven percent of patients were on no antithrombotic medications. The remaining 5% were transiently on warfarin or a novel oral anticoagulant.
The 1-year cumulative rate of ischemic stroke or TIA was 1.8%, with no instances of systemic embolism. Of note, there were no hemorrhagic strokes. And of the 11 cases of ischemic stroke, none were fatal and only one was disabling.
“This is a sign that comes also from the PREVAIL trial, that if you have a stroke while on left atrial appendage–closure therapy, most of the time it’s not disabling. It’s much less severe on the modified Rankin Scale than if you’re on oral anticoagulation,” said Dr. Bergmann.
The 1.4% rate of ischemic stroke at 1 year in Watchman recipients represents an 81% reduction in risk compared with the expected 7.5% rate in patients with similar CHA2DS2-VASc scores not on oral anticoagulation. This level of stroke risk reduction is similar to that seen in the pivotal ARISTOTLE trial of apixaban (Eliquis) in a high-risk AF population (Lancet. 2012 Nov 17;380[9855]:1749-58).
Major bleeding occurred in 2.5% of patients. The rate of fatal bleeding was 0.5%. To put that in perspective, the 2.5% major bleeding rate was 52% lower than would be expected based upon similar HAS-BLED scores in patients on warfarin. Still, 2.5% is unacceptably high.
“The major serious adverse event is not pericardial effusion or late device embolization, it’s major bleeding occurring during the time the patient is on DAPT, mostly within the first 3 months. So I think we have to do something about this,” he said.
One possibility worthy of formal study is 3 months of periprocedural NOAC monotherapy. “Maybe even low-dose therapy, like 75 mg of dabigatran [Pradaxa] twice daily. We have an antidote that works nicely [idarucizumab, Praxbind] so I think maybe this is the way to go,” Dr. Bergmann observed.
The ongoing EWOLUTION registry is sponsored by Boston Scientific. Dr. Bergmann is a consultant to that company as well as Bayer AG, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, and St. Jude Medical.
PARIS – Patients with atrial fibrillation at high stroke risk and a contraindication for oral anticoagulation experienced an 83% reduction in their risk of ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack during their first year after receiving the Watchman left atrial appendage closure device backed by limited-duration dual-antiplatelet therapy, according to a report from the EWOLUTION registry.
Of 605 participants in the European registry who went on dual-antiplatelet treatment (DAPT) in conjunction with receiving the Watchman device, 39% discontinued DAPT within 3 months and 72% were off DAPT by 6 months. Yet the 1-year rate of ischemic stroke or TIA in the EWOLUTION group was just 1.8%, an 83% relative risk reduction compared with the expected 10.5% rate based on the participants’ mean CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4.6 in the absence of oral anticoagulation, Martin W. Bergmann, MD, said at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“Obviously this isn’t a randomized trial. This is just reassuring data that we are going in the right direction in terms of efficacy,” said Dr. Bergmann of Cardiologicum Hamburg, a large German group practice.
However, the ESC guidelines were largely based on randomized trials of the Watchman versus oral anticoagulation, including PREVAIL and PROTECT-AF, showing noninferiority. The safety and efficacy of the device in warfarin-ineligible patients was less well studied at the time the guidelines were formulated. And in fact, such patients are excluded from the Food and Drug Administration’s approved indication, which is specifically for patients judged “suitable for warfarin.”
“This gap is now filled by EWOLUTION. This is a registry that’s as good as it gets. We have all the things in place that you need these days to be able to rely on the outcome data,” according to the cardiologist.
EWOLUTION is a prospective, multicenter, all-comers registry. The EWOLUTION population of AF patients on DAPT was high risk: 89% had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 3 or more, 31% were at least 80 years old, the mean HAS-BLED score was 2.4, and oral anticoagulation was contraindicated in 84% of participants.
Eighty-seven percent of subjects underwent follow-up transesophageal echocardiography. The imaging study showed the Watchman effectively sealed the left atrial appendage in 99.2% of patients as defined by no leak greater than 5 mm. The echo exam also showed the presence of thrombus on the device at follow-up in 4% of patients, although only 1 of the 22 patients with device thrombus experienced a stroke.
“We can conclude two things from this which are in line with earlier studies. First, the rate of thrombus on the device is equal to the rate reported in the randomized controlled trials, which was also 4%, even if the patients were on warfarin for the first 45 days. And second, these thrombi are not related to stroke,” Dr. Bergmann said.
At the 1-year mark, 71% of patients had switched to a single antiplatelet agent, while 17% remained on DAPT, mainly because of comorbid coronary disease for which DAPT is indicated. Seven percent of patients were on no antithrombotic medications. The remaining 5% were transiently on warfarin or a novel oral anticoagulant.
The 1-year cumulative rate of ischemic stroke or TIA was 1.8%, with no instances of systemic embolism. Of note, there were no hemorrhagic strokes. And of the 11 cases of ischemic stroke, none were fatal and only one was disabling.
“This is a sign that comes also from the PREVAIL trial, that if you have a stroke while on left atrial appendage–closure therapy, most of the time it’s not disabling. It’s much less severe on the modified Rankin Scale than if you’re on oral anticoagulation,” said Dr. Bergmann.
The 1.4% rate of ischemic stroke at 1 year in Watchman recipients represents an 81% reduction in risk compared with the expected 7.5% rate in patients with similar CHA2DS2-VASc scores not on oral anticoagulation. This level of stroke risk reduction is similar to that seen in the pivotal ARISTOTLE trial of apixaban (Eliquis) in a high-risk AF population (Lancet. 2012 Nov 17;380[9855]:1749-58).
Major bleeding occurred in 2.5% of patients. The rate of fatal bleeding was 0.5%. To put that in perspective, the 2.5% major bleeding rate was 52% lower than would be expected based upon similar HAS-BLED scores in patients on warfarin. Still, 2.5% is unacceptably high.
“The major serious adverse event is not pericardial effusion or late device embolization, it’s major bleeding occurring during the time the patient is on DAPT, mostly within the first 3 months. So I think we have to do something about this,” he said.
One possibility worthy of formal study is 3 months of periprocedural NOAC monotherapy. “Maybe even low-dose therapy, like 75 mg of dabigatran [Pradaxa] twice daily. We have an antidote that works nicely [idarucizumab, Praxbind] so I think maybe this is the way to go,” Dr. Bergmann observed.
The ongoing EWOLUTION registry is sponsored by Boston Scientific. Dr. Bergmann is a consultant to that company as well as Bayer AG, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, and St. Jude Medical.
PARIS – Patients with atrial fibrillation at high stroke risk and a contraindication for oral anticoagulation experienced an 83% reduction in their risk of ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack during their first year after receiving the Watchman left atrial appendage closure device backed by limited-duration dual-antiplatelet therapy, according to a report from the EWOLUTION registry.
Of 605 participants in the European registry who went on dual-antiplatelet treatment (DAPT) in conjunction with receiving the Watchman device, 39% discontinued DAPT within 3 months and 72% were off DAPT by 6 months. Yet the 1-year rate of ischemic stroke or TIA in the EWOLUTION group was just 1.8%, an 83% relative risk reduction compared with the expected 10.5% rate based on the participants’ mean CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4.6 in the absence of oral anticoagulation, Martin W. Bergmann, MD, said at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“Obviously this isn’t a randomized trial. This is just reassuring data that we are going in the right direction in terms of efficacy,” said Dr. Bergmann of Cardiologicum Hamburg, a large German group practice.
However, the ESC guidelines were largely based on randomized trials of the Watchman versus oral anticoagulation, including PREVAIL and PROTECT-AF, showing noninferiority. The safety and efficacy of the device in warfarin-ineligible patients was less well studied at the time the guidelines were formulated. And in fact, such patients are excluded from the Food and Drug Administration’s approved indication, which is specifically for patients judged “suitable for warfarin.”
“This gap is now filled by EWOLUTION. This is a registry that’s as good as it gets. We have all the things in place that you need these days to be able to rely on the outcome data,” according to the cardiologist.
EWOLUTION is a prospective, multicenter, all-comers registry. The EWOLUTION population of AF patients on DAPT was high risk: 89% had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 3 or more, 31% were at least 80 years old, the mean HAS-BLED score was 2.4, and oral anticoagulation was contraindicated in 84% of participants.
Eighty-seven percent of subjects underwent follow-up transesophageal echocardiography. The imaging study showed the Watchman effectively sealed the left atrial appendage in 99.2% of patients as defined by no leak greater than 5 mm. The echo exam also showed the presence of thrombus on the device at follow-up in 4% of patients, although only 1 of the 22 patients with device thrombus experienced a stroke.
“We can conclude two things from this which are in line with earlier studies. First, the rate of thrombus on the device is equal to the rate reported in the randomized controlled trials, which was also 4%, even if the patients were on warfarin for the first 45 days. And second, these thrombi are not related to stroke,” Dr. Bergmann said.
At the 1-year mark, 71% of patients had switched to a single antiplatelet agent, while 17% remained on DAPT, mainly because of comorbid coronary disease for which DAPT is indicated. Seven percent of patients were on no antithrombotic medications. The remaining 5% were transiently on warfarin or a novel oral anticoagulant.
The 1-year cumulative rate of ischemic stroke or TIA was 1.8%, with no instances of systemic embolism. Of note, there were no hemorrhagic strokes. And of the 11 cases of ischemic stroke, none were fatal and only one was disabling.
“This is a sign that comes also from the PREVAIL trial, that if you have a stroke while on left atrial appendage–closure therapy, most of the time it’s not disabling. It’s much less severe on the modified Rankin Scale than if you’re on oral anticoagulation,” said Dr. Bergmann.
The 1.4% rate of ischemic stroke at 1 year in Watchman recipients represents an 81% reduction in risk compared with the expected 7.5% rate in patients with similar CHA2DS2-VASc scores not on oral anticoagulation. This level of stroke risk reduction is similar to that seen in the pivotal ARISTOTLE trial of apixaban (Eliquis) in a high-risk AF population (Lancet. 2012 Nov 17;380[9855]:1749-58).
Major bleeding occurred in 2.5% of patients. The rate of fatal bleeding was 0.5%. To put that in perspective, the 2.5% major bleeding rate was 52% lower than would be expected based upon similar HAS-BLED scores in patients on warfarin. Still, 2.5% is unacceptably high.
“The major serious adverse event is not pericardial effusion or late device embolization, it’s major bleeding occurring during the time the patient is on DAPT, mostly within the first 3 months. So I think we have to do something about this,” he said.
One possibility worthy of formal study is 3 months of periprocedural NOAC monotherapy. “Maybe even low-dose therapy, like 75 mg of dabigatran [Pradaxa] twice daily. We have an antidote that works nicely [idarucizumab, Praxbind] so I think maybe this is the way to go,” Dr. Bergmann observed.
The ongoing EWOLUTION registry is sponsored by Boston Scientific. Dr. Bergmann is a consultant to that company as well as Bayer AG, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, and St. Jude Medical.
AT EUROPCR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Patients with AF at high stroke risk and ineligible for oral anticoagulation experienced an 81% reduction in their expected risk of ischemic stroke during their first year of LAA closure with the Watchman device backed by limited-duration dual-antiplatelet therapy
Data source: A prospective, multicenter, single-arm registry that includes 605 patients with AF who underwent left atrial appendage closure with the WATCHMAN device supported by limited-duration dual-antiplatelet therapy.
Disclosures: The ongoing EWOLUTION registry is sponsored by Boston Scientific. The presenter is a consultant to that company and several others.
Federal exchanges attract fewer insurers for 2018
The number of health plans submitting applications to offer coverage on the federal insurance exchanges in 2018 was down 38% from last year, officials at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid announced July 10. At this year’s initial filing deadline for fiscal year 2018, 141 qualified health plans had submitted applications to offer coverage in the 39 states that use healthcare.gov, the federally facilitated exchange platform, compared with 227 last year and 281 the year before, CMS officials said in a statement.
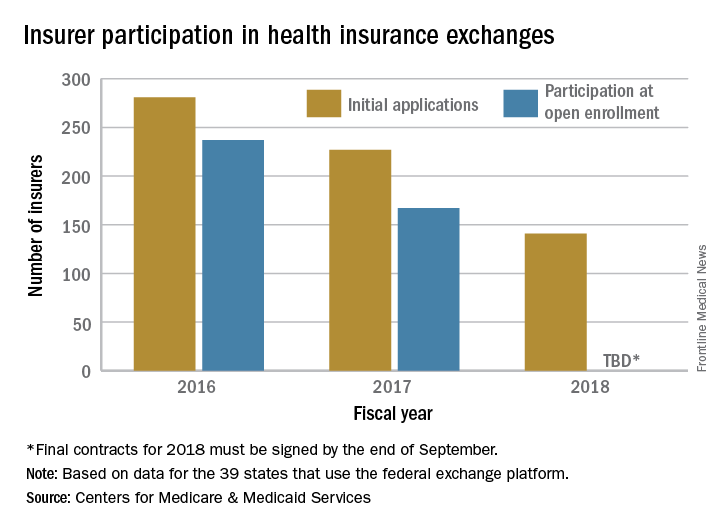
“This is further proof that the Affordable Care Act is failing,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in the statement. “Insurers continue to flee the Exchanges, causing Americans to lose their choice for health insurance or lose their coverage all together. These numbers are clear; the status quo is not working. The American people deserve health care choices and access to quality, affordable health care coverage.”
The number of health plans submitting applications to offer coverage on the federal insurance exchanges in 2018 was down 38% from last year, officials at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid announced July 10. At this year’s initial filing deadline for fiscal year 2018, 141 qualified health plans had submitted applications to offer coverage in the 39 states that use healthcare.gov, the federally facilitated exchange platform, compared with 227 last year and 281 the year before, CMS officials said in a statement.

“This is further proof that the Affordable Care Act is failing,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in the statement. “Insurers continue to flee the Exchanges, causing Americans to lose their choice for health insurance or lose their coverage all together. These numbers are clear; the status quo is not working. The American people deserve health care choices and access to quality, affordable health care coverage.”
The number of health plans submitting applications to offer coverage on the federal insurance exchanges in 2018 was down 38% from last year, officials at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid announced July 10. At this year’s initial filing deadline for fiscal year 2018, 141 qualified health plans had submitted applications to offer coverage in the 39 states that use healthcare.gov, the federally facilitated exchange platform, compared with 227 last year and 281 the year before, CMS officials said in a statement.

“This is further proof that the Affordable Care Act is failing,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in the statement. “Insurers continue to flee the Exchanges, causing Americans to lose their choice for health insurance or lose their coverage all together. These numbers are clear; the status quo is not working. The American people deserve health care choices and access to quality, affordable health care coverage.”
New federal health IT leadership, same goals
WASHINGTON – Although the leadership at the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology is new, the focus of the federal office – reducing physician burden and improving interoperability of electronic heath records – remains the same.
“One priority is on the whole question of burden of [EHR] usability,” said Don Rucker, MD, the new national coordinator, at a July 11 press briefing. “The other is interoperability. We’ve obviously spent a lot of money collectively in the country on these systems, and there’s a widespread dissatisfaction with the level of interoperability.”
“We are looking at documentation and the whole quality framework around value-based purchasing,” he said. “For a lot of practices now, this has become a challenge that we just have to think about what’s the win. At some point, the expense of complying with the quality measures is a much greater expense than the innate value of the quality measures. ”
EHRs “have become symbolic of physician administrative burden, but by no means are they the whole cause,” John Flemming, MD, ONC deputy assistant secretary for health technology reform, said at the briefing. “The physician, particularly in an independent practice, must manage the practice. So he or she is the CEO. They are also on the assembly line, seeing patients. Now with EHRs, they have to be the data input person as well. It’s time consuming.”
Dr. Fleming is a family physician from Louisiana and a former Republican member of congress.
Dr. Rucker acknowledged that reducing the burden of EHRs has been discussed for quite a long time now. He recalled beginning working with them in his private practice back in 1988 and figured, based on the quick rate of technological innovation demonstrated in Silicon Valley, the issues would be solved by 1992 or 1993 at the latest.
“Right now, [EHRs] are really about documentation, about billing, but that is a funny kind of beast,” he said. “Every other industry uses their enterprise computer software to do automation, to become more efficient. We are the only business that I am aware of to have used computers to become less efficient. ... I think part of what we are trying to do ... is let some of these newer technologies that will actually reduce costs, reduce variance, have those technologies have an entrée into some of these data collections that are out there.”
WASHINGTON – Although the leadership at the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology is new, the focus of the federal office – reducing physician burden and improving interoperability of electronic heath records – remains the same.
“One priority is on the whole question of burden of [EHR] usability,” said Don Rucker, MD, the new national coordinator, at a July 11 press briefing. “The other is interoperability. We’ve obviously spent a lot of money collectively in the country on these systems, and there’s a widespread dissatisfaction with the level of interoperability.”
“We are looking at documentation and the whole quality framework around value-based purchasing,” he said. “For a lot of practices now, this has become a challenge that we just have to think about what’s the win. At some point, the expense of complying with the quality measures is a much greater expense than the innate value of the quality measures. ”
EHRs “have become symbolic of physician administrative burden, but by no means are they the whole cause,” John Flemming, MD, ONC deputy assistant secretary for health technology reform, said at the briefing. “The physician, particularly in an independent practice, must manage the practice. So he or she is the CEO. They are also on the assembly line, seeing patients. Now with EHRs, they have to be the data input person as well. It’s time consuming.”
Dr. Fleming is a family physician from Louisiana and a former Republican member of congress.
Dr. Rucker acknowledged that reducing the burden of EHRs has been discussed for quite a long time now. He recalled beginning working with them in his private practice back in 1988 and figured, based on the quick rate of technological innovation demonstrated in Silicon Valley, the issues would be solved by 1992 or 1993 at the latest.
“Right now, [EHRs] are really about documentation, about billing, but that is a funny kind of beast,” he said. “Every other industry uses their enterprise computer software to do automation, to become more efficient. We are the only business that I am aware of to have used computers to become less efficient. ... I think part of what we are trying to do ... is let some of these newer technologies that will actually reduce costs, reduce variance, have those technologies have an entrée into some of these data collections that are out there.”
WASHINGTON – Although the leadership at the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology is new, the focus of the federal office – reducing physician burden and improving interoperability of electronic heath records – remains the same.
“One priority is on the whole question of burden of [EHR] usability,” said Don Rucker, MD, the new national coordinator, at a July 11 press briefing. “The other is interoperability. We’ve obviously spent a lot of money collectively in the country on these systems, and there’s a widespread dissatisfaction with the level of interoperability.”
“We are looking at documentation and the whole quality framework around value-based purchasing,” he said. “For a lot of practices now, this has become a challenge that we just have to think about what’s the win. At some point, the expense of complying with the quality measures is a much greater expense than the innate value of the quality measures. ”
EHRs “have become symbolic of physician administrative burden, but by no means are they the whole cause,” John Flemming, MD, ONC deputy assistant secretary for health technology reform, said at the briefing. “The physician, particularly in an independent practice, must manage the practice. So he or she is the CEO. They are also on the assembly line, seeing patients. Now with EHRs, they have to be the data input person as well. It’s time consuming.”
Dr. Fleming is a family physician from Louisiana and a former Republican member of congress.
Dr. Rucker acknowledged that reducing the burden of EHRs has been discussed for quite a long time now. He recalled beginning working with them in his private practice back in 1988 and figured, based on the quick rate of technological innovation demonstrated in Silicon Valley, the issues would be solved by 1992 or 1993 at the latest.
“Right now, [EHRs] are really about documentation, about billing, but that is a funny kind of beast,” he said. “Every other industry uses their enterprise computer software to do automation, to become more efficient. We are the only business that I am aware of to have used computers to become less efficient. ... I think part of what we are trying to do ... is let some of these newer technologies that will actually reduce costs, reduce variance, have those technologies have an entrée into some of these data collections that are out there.”
How to pump up the donor heart pool
COLORADO SPRINGS – Diminished left ventricular systolic function alone should not be used as a basis for declining a donor heart for transplantation, Agustin Sibona, MD, asserted at the annual meeting of the Western Thoracic Surgical Association.
“Expansion of the donor pool to include more of these organs is appropriate,” said Dr. Sibona of Loma Linda (Calif.) University.
He presented an analysis of the United Network for Organ Sharing database that encompassed all adult isolated first-time heart transplants in the United States from 2000 through March 2016.
“Carefully selected potential donor hearts with LVEF of 30% or higher should not be excluded from consideration of transplantation on the basis of depressed LVEF alone,” he concluded. “We’re not saying we should use every heart that has an EF of 35% or 45%. We say you should thoroughly evaluate those patients and those hearts and consider them.”
Roughly 500,000 people develop new end-stage heart failure each year. Heart transplantation has long been considered the definitive therapy for this condition. However, heart transplantation rates have remained static at 2,000-2,500 per year in the United States for the past 15 years because of the shortage of donor organs.
Previous work by Dr. Sibona’s senior coinvestigators has documented that 19% of potential donor hearts are not utilized for transplant solely based upon the presence of left ventricular dysfunction. That’s about 1,300 hearts per year.
“About 60% of those hearts had an LVEF greater than 40%. That’s 785 hearts. If only half of those are used, that still represents an increase in the domestic transplant rate of almost 20%,” he observed.
Twenty-one patients in the study received a heart with an LVEF of 20%-29.9%. They had an unacceptably high perioperative mortality.
There was no significant difference between the LVEF groups in terms of race, cause of death, or ischemic time.
Mean transplantation hospital length of stay varied inversely with donor heart LVEF, from 20.3 days in patients with a normal LVEF, to 23.9 days with an LVEF of 40%-49.9%, and 31.1 days with an LVEF of 30%-39.9%.
Dr. Sibona replied that unfortunately the UNOS database is not informative on that score.
Dr. Kwon offered a practical reservation about embracing the use of compromised donor hearts: “Ninety-one percent of programs in the U.S. do less than 30 heart transplants per year, and 76% do less than 20. Smaller programs won’t necessarily have the luxury of 6,000 days to see if their survival statistics bear out. If they have two or three deaths per year, that’s enough to get a notice from UNOS and CMS and private payers. So I would note some caution in that regard.”
He also posed a question: In this new era of highly effective left ventricular assist devices serving as a long-term bridge to transplant, does it make sense to turn to dysfunctional donor hearts?
“Ventricular assist devices are an evolving technology,” Dr. Sibona responded. “Short-term outcomes are equivalent to transplant, but the devices often have complications: GI bleed, stroke, thrombosis, and infections. So we still believe that heart transplantation is the gold standard for treatment. Remember, these patients have end-stage heart failure. Many can’t get out of bed without shortness of breath. So, yes, I would take those hearts.”
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study, which was supported by Loma Linda and Stanford universities.
COLORADO SPRINGS – Diminished left ventricular systolic function alone should not be used as a basis for declining a donor heart for transplantation, Agustin Sibona, MD, asserted at the annual meeting of the Western Thoracic Surgical Association.
“Expansion of the donor pool to include more of these organs is appropriate,” said Dr. Sibona of Loma Linda (Calif.) University.
He presented an analysis of the United Network for Organ Sharing database that encompassed all adult isolated first-time heart transplants in the United States from 2000 through March 2016.
“Carefully selected potential donor hearts with LVEF of 30% or higher should not be excluded from consideration of transplantation on the basis of depressed LVEF alone,” he concluded. “We’re not saying we should use every heart that has an EF of 35% or 45%. We say you should thoroughly evaluate those patients and those hearts and consider them.”
Roughly 500,000 people develop new end-stage heart failure each year. Heart transplantation has long been considered the definitive therapy for this condition. However, heart transplantation rates have remained static at 2,000-2,500 per year in the United States for the past 15 years because of the shortage of donor organs.
Previous work by Dr. Sibona’s senior coinvestigators has documented that 19% of potential donor hearts are not utilized for transplant solely based upon the presence of left ventricular dysfunction. That’s about 1,300 hearts per year.
“About 60% of those hearts had an LVEF greater than 40%. That’s 785 hearts. If only half of those are used, that still represents an increase in the domestic transplant rate of almost 20%,” he observed.
Twenty-one patients in the study received a heart with an LVEF of 20%-29.9%. They had an unacceptably high perioperative mortality.
There was no significant difference between the LVEF groups in terms of race, cause of death, or ischemic time.
Mean transplantation hospital length of stay varied inversely with donor heart LVEF, from 20.3 days in patients with a normal LVEF, to 23.9 days with an LVEF of 40%-49.9%, and 31.1 days with an LVEF of 30%-39.9%.
Dr. Sibona replied that unfortunately the UNOS database is not informative on that score.
Dr. Kwon offered a practical reservation about embracing the use of compromised donor hearts: “Ninety-one percent of programs in the U.S. do less than 30 heart transplants per year, and 76% do less than 20. Smaller programs won’t necessarily have the luxury of 6,000 days to see if their survival statistics bear out. If they have two or three deaths per year, that’s enough to get a notice from UNOS and CMS and private payers. So I would note some caution in that regard.”
He also posed a question: In this new era of highly effective left ventricular assist devices serving as a long-term bridge to transplant, does it make sense to turn to dysfunctional donor hearts?
“Ventricular assist devices are an evolving technology,” Dr. Sibona responded. “Short-term outcomes are equivalent to transplant, but the devices often have complications: GI bleed, stroke, thrombosis, and infections. So we still believe that heart transplantation is the gold standard for treatment. Remember, these patients have end-stage heart failure. Many can’t get out of bed without shortness of breath. So, yes, I would take those hearts.”
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study, which was supported by Loma Linda and Stanford universities.
COLORADO SPRINGS – Diminished left ventricular systolic function alone should not be used as a basis for declining a donor heart for transplantation, Agustin Sibona, MD, asserted at the annual meeting of the Western Thoracic Surgical Association.
“Expansion of the donor pool to include more of these organs is appropriate,” said Dr. Sibona of Loma Linda (Calif.) University.
He presented an analysis of the United Network for Organ Sharing database that encompassed all adult isolated first-time heart transplants in the United States from 2000 through March 2016.
“Carefully selected potential donor hearts with LVEF of 30% or higher should not be excluded from consideration of transplantation on the basis of depressed LVEF alone,” he concluded. “We’re not saying we should use every heart that has an EF of 35% or 45%. We say you should thoroughly evaluate those patients and those hearts and consider them.”
Roughly 500,000 people develop new end-stage heart failure each year. Heart transplantation has long been considered the definitive therapy for this condition. However, heart transplantation rates have remained static at 2,000-2,500 per year in the United States for the past 15 years because of the shortage of donor organs.
Previous work by Dr. Sibona’s senior coinvestigators has documented that 19% of potential donor hearts are not utilized for transplant solely based upon the presence of left ventricular dysfunction. That’s about 1,300 hearts per year.
“About 60% of those hearts had an LVEF greater than 40%. That’s 785 hearts. If only half of those are used, that still represents an increase in the domestic transplant rate of almost 20%,” he observed.
Twenty-one patients in the study received a heart with an LVEF of 20%-29.9%. They had an unacceptably high perioperative mortality.
There was no significant difference between the LVEF groups in terms of race, cause of death, or ischemic time.
Mean transplantation hospital length of stay varied inversely with donor heart LVEF, from 20.3 days in patients with a normal LVEF, to 23.9 days with an LVEF of 40%-49.9%, and 31.1 days with an LVEF of 30%-39.9%.
Dr. Sibona replied that unfortunately the UNOS database is not informative on that score.
Dr. Kwon offered a practical reservation about embracing the use of compromised donor hearts: “Ninety-one percent of programs in the U.S. do less than 30 heart transplants per year, and 76% do less than 20. Smaller programs won’t necessarily have the luxury of 6,000 days to see if their survival statistics bear out. If they have two or three deaths per year, that’s enough to get a notice from UNOS and CMS and private payers. So I would note some caution in that regard.”
He also posed a question: In this new era of highly effective left ventricular assist devices serving as a long-term bridge to transplant, does it make sense to turn to dysfunctional donor hearts?
“Ventricular assist devices are an evolving technology,” Dr. Sibona responded. “Short-term outcomes are equivalent to transplant, but the devices often have complications: GI bleed, stroke, thrombosis, and infections. So we still believe that heart transplantation is the gold standard for treatment. Remember, these patients have end-stage heart failure. Many can’t get out of bed without shortness of breath. So, yes, I would take those hearts.”
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study, which was supported by Loma Linda and Stanford universities.
AT THE WTSA ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Survival of heart transplant recipients whose donor organ had left ventricular systolic dysfunction with an LVEF as low as 30%-39% was not significantly less than for those with a normal donor heart.
Data source: A retrospective study of all of the nearly 31,000 isolated first-time adult heart transplants performed in the U.S. during 2000-March 2016.
Disclosures: Loma Linda and Stanford universities supported the study. The presenter reported having no financial conflicts.
ABS offers a new path to board certification
The American Board of Surgery announced a revised and reformulated path for surgeons to board certification that will replace the current Maintenance of Certification process now in place.
The new program will offer surgeons greater flexibility and more practice-relevant options to achieve lifelong learning in their field and continuous board certification. The ABS based the program on feedback from diplomates (ABS-certified surgeons) including the findings from a 2016 survey sent to 5,000 diplomates.
Effective immediately, diplomates will be asked to report their professional standing, CME activities, and practice assessment participation every 5 years, rather than every 3 years. All diplomates will have their current reporting cycle extended by 2 years. The self-assessment CME requirement has been has been reduced by half. For 2018, more options for recertification will be offered with a greater focus on ongoing, high-value, and practice-relevant learning. The current 10-year interval recertification examination will continue to be offered for those who choose it. Input from diplomates will be sought in the coming months to provide input on the new program.
Find the full statement at http://www.absurgery.org/default.jsp?news_mocchange0717.
The American Board of Surgery announced a revised and reformulated path for surgeons to board certification that will replace the current Maintenance of Certification process now in place.
The new program will offer surgeons greater flexibility and more practice-relevant options to achieve lifelong learning in their field and continuous board certification. The ABS based the program on feedback from diplomates (ABS-certified surgeons) including the findings from a 2016 survey sent to 5,000 diplomates.
Effective immediately, diplomates will be asked to report their professional standing, CME activities, and practice assessment participation every 5 years, rather than every 3 years. All diplomates will have their current reporting cycle extended by 2 years. The self-assessment CME requirement has been has been reduced by half. For 2018, more options for recertification will be offered with a greater focus on ongoing, high-value, and practice-relevant learning. The current 10-year interval recertification examination will continue to be offered for those who choose it. Input from diplomates will be sought in the coming months to provide input on the new program.
Find the full statement at http://www.absurgery.org/default.jsp?news_mocchange0717.
The American Board of Surgery announced a revised and reformulated path for surgeons to board certification that will replace the current Maintenance of Certification process now in place.
The new program will offer surgeons greater flexibility and more practice-relevant options to achieve lifelong learning in their field and continuous board certification. The ABS based the program on feedback from diplomates (ABS-certified surgeons) including the findings from a 2016 survey sent to 5,000 diplomates.
Effective immediately, diplomates will be asked to report their professional standing, CME activities, and practice assessment participation every 5 years, rather than every 3 years. All diplomates will have their current reporting cycle extended by 2 years. The self-assessment CME requirement has been has been reduced by half. For 2018, more options for recertification will be offered with a greater focus on ongoing, high-value, and practice-relevant learning. The current 10-year interval recertification examination will continue to be offered for those who choose it. Input from diplomates will be sought in the coming months to provide input on the new program.
Find the full statement at http://www.absurgery.org/default.jsp?news_mocchange0717.
Algorithm for identifying IPF has low PPV
ICD-9 codes were poor at picking out idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients from administrative databases for epidemiologic studies, but a new tool could improve diagnostic accuracy, according to Kaiser Permanente and University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), investigators.
“In the age of large administrative databases and electronic medical records, there is rich opportunity to conduct population-based studies” of disease behavior, outcomes, health care use, and other matters, but researchers first need to be able to accurately identify patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) in large data sets, said investigators led by Brett Ley, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at UCSF.
The research community has traditionally relied on claims for specific IPF diagnostic codes – ICD-9 code 516.3 or ICD-9-CM code 516.31 – to identify patients, but the approach had never been validated. To see how well it works, the investigators applied it to the nearly 5.4 million adults in the Kaiser Permanente Northern California system during 2000-2014. After patients with interstitial lung disease-associated codes entered on or after the day of the last IPF code were excluded, the algorithm identified 2,608 patients as having IPF (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Jun;14[6]:880-7).
Next, the investigators randomly selected 150 of those patients and examined their medical records, procedure codes, CTs, and other patient-level data to see how many of them really had IPF. The results weren’t good. The positive predictive value of the IPF code-based algorithm was only 42.2%, with a sensitivity 55.6%.
The widely used code-based IPF algorithm does “not generate accurate estimates of IPF incidence and prevalence. ... Over half of the patients identified as having IPF ... did not have IPF on case review. Alarmingly, whereas half of the misclassified cases had an alternative [interstitial lung disease] diagnosis, the other half had no clinical or radiologic evidence of ILD [interstitial lung disease] at all.” The algorithm also “likely misses a substantial proportion of patients who do have IPF,” Dr. Ley and his colleagues said.
“We can only speculate about the reasons. ... It seems likely to be due to a combination of misdiagnosis at the clinical level and miscoding at the administrative level,” they said.
To try to improve the situation, the team tweaked the algorithm to include only patients 50 years or older who had at least two 516.3 or 516.31 claims 1 month or more apart and a chest CT procedure code beforehand. They again excluded ILD-associated claims on or after the day of the last IPF code.
Although the sensitivity of the modified algorithm was lower than the original, it had a more robust positive predictive value of 70.4% in the derivation cohort and 61.8% in the validation cohort, both derived from the 150 patients used to validate the original algorithm.
“By making a few simple, empirically derived changes to the IPF algorithm,” it’s possible to “more reliably identif[y] patients” with IPF. “We believe the modified IPF algorithm will be useful for population-based studies of IPF ... that require high diagnostic certainty,” the investigators concluded.
The traditional algorithm found an incidence of 6.8 cases per 100,000 person-years, which was on the low end of previous reports, perhaps because of the relative health and youth of the 5.4 million patient pool. As in past studies, IPF incidence increased with older age and was highest in white patients and men.
“Whether the more specific codes provided by the ICD-10 system will allow for improved case classification of IPF requires further study,” the investigators noted.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ley reported speaker’s fees from Genentech, and one of the authors was an employee of the company. The senior author Harold Collard, MD, an associate professor in UCSF’s Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, reported personal fees from Takeda, ImmuneWorks, Parexel, Pharma Capital Partners, and others.
This study glaringly displays potential problems with using ICD codes for research purposes and calls into question results from a handful of studies that yielded epidemiological estimates for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. We are reminded that practitioner-generated diagnostic codes of IPF recorded in the medical record are subject to inaccuracies, which can be illuminated by the “gold standard” – multidisciplinary adjudication.
Moving forward, particularly as longitudinal, nationwide IPF registries come online, patient-level case validation should be employed. As we move into the era of ICD-10, the study should serve as a call to improve IPF case ascertainment accuracy for any investigators choosing to use large data analytic strategies. Doing so will mute the background noise and allow us to better hear the signals of this complex disease.
Evans R. Fernandez Perez, MD, is a pulmonologist at National Jewish Health, Denver. He made his comments in an editorial, and reported speaker’s fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Genentech (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Jun;14[6]:829-30).
This study glaringly displays potential problems with using ICD codes for research purposes and calls into question results from a handful of studies that yielded epidemiological estimates for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. We are reminded that practitioner-generated diagnostic codes of IPF recorded in the medical record are subject to inaccuracies, which can be illuminated by the “gold standard” – multidisciplinary adjudication.
Moving forward, particularly as longitudinal, nationwide IPF registries come online, patient-level case validation should be employed. As we move into the era of ICD-10, the study should serve as a call to improve IPF case ascertainment accuracy for any investigators choosing to use large data analytic strategies. Doing so will mute the background noise and allow us to better hear the signals of this complex disease.
Evans R. Fernandez Perez, MD, is a pulmonologist at National Jewish Health, Denver. He made his comments in an editorial, and reported speaker’s fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Genentech (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Jun;14[6]:829-30).
This study glaringly displays potential problems with using ICD codes for research purposes and calls into question results from a handful of studies that yielded epidemiological estimates for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. We are reminded that practitioner-generated diagnostic codes of IPF recorded in the medical record are subject to inaccuracies, which can be illuminated by the “gold standard” – multidisciplinary adjudication.
Moving forward, particularly as longitudinal, nationwide IPF registries come online, patient-level case validation should be employed. As we move into the era of ICD-10, the study should serve as a call to improve IPF case ascertainment accuracy for any investigators choosing to use large data analytic strategies. Doing so will mute the background noise and allow us to better hear the signals of this complex disease.
Evans R. Fernandez Perez, MD, is a pulmonologist at National Jewish Health, Denver. He made his comments in an editorial, and reported speaker’s fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Genentech (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Jun;14[6]:829-30).
ICD-9 codes were poor at picking out idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients from administrative databases for epidemiologic studies, but a new tool could improve diagnostic accuracy, according to Kaiser Permanente and University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), investigators.
“In the age of large administrative databases and electronic medical records, there is rich opportunity to conduct population-based studies” of disease behavior, outcomes, health care use, and other matters, but researchers first need to be able to accurately identify patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) in large data sets, said investigators led by Brett Ley, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at UCSF.
The research community has traditionally relied on claims for specific IPF diagnostic codes – ICD-9 code 516.3 or ICD-9-CM code 516.31 – to identify patients, but the approach had never been validated. To see how well it works, the investigators applied it to the nearly 5.4 million adults in the Kaiser Permanente Northern California system during 2000-2014. After patients with interstitial lung disease-associated codes entered on or after the day of the last IPF code were excluded, the algorithm identified 2,608 patients as having IPF (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Jun;14[6]:880-7).
Next, the investigators randomly selected 150 of those patients and examined their medical records, procedure codes, CTs, and other patient-level data to see how many of them really had IPF. The results weren’t good. The positive predictive value of the IPF code-based algorithm was only 42.2%, with a sensitivity 55.6%.
The widely used code-based IPF algorithm does “not generate accurate estimates of IPF incidence and prevalence. ... Over half of the patients identified as having IPF ... did not have IPF on case review. Alarmingly, whereas half of the misclassified cases had an alternative [interstitial lung disease] diagnosis, the other half had no clinical or radiologic evidence of ILD [interstitial lung disease] at all.” The algorithm also “likely misses a substantial proportion of patients who do have IPF,” Dr. Ley and his colleagues said.
“We can only speculate about the reasons. ... It seems likely to be due to a combination of misdiagnosis at the clinical level and miscoding at the administrative level,” they said.
To try to improve the situation, the team tweaked the algorithm to include only patients 50 years or older who had at least two 516.3 or 516.31 claims 1 month or more apart and a chest CT procedure code beforehand. They again excluded ILD-associated claims on or after the day of the last IPF code.
Although the sensitivity of the modified algorithm was lower than the original, it had a more robust positive predictive value of 70.4% in the derivation cohort and 61.8% in the validation cohort, both derived from the 150 patients used to validate the original algorithm.
“By making a few simple, empirically derived changes to the IPF algorithm,” it’s possible to “more reliably identif[y] patients” with IPF. “We believe the modified IPF algorithm will be useful for population-based studies of IPF ... that require high diagnostic certainty,” the investigators concluded.
The traditional algorithm found an incidence of 6.8 cases per 100,000 person-years, which was on the low end of previous reports, perhaps because of the relative health and youth of the 5.4 million patient pool. As in past studies, IPF incidence increased with older age and was highest in white patients and men.
“Whether the more specific codes provided by the ICD-10 system will allow for improved case classification of IPF requires further study,” the investigators noted.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ley reported speaker’s fees from Genentech, and one of the authors was an employee of the company. The senior author Harold Collard, MD, an associate professor in UCSF’s Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, reported personal fees from Takeda, ImmuneWorks, Parexel, Pharma Capital Partners, and others.
ICD-9 codes were poor at picking out idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients from administrative databases for epidemiologic studies, but a new tool could improve diagnostic accuracy, according to Kaiser Permanente and University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), investigators.
“In the age of large administrative databases and electronic medical records, there is rich opportunity to conduct population-based studies” of disease behavior, outcomes, health care use, and other matters, but researchers first need to be able to accurately identify patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) in large data sets, said investigators led by Brett Ley, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at UCSF.
The research community has traditionally relied on claims for specific IPF diagnostic codes – ICD-9 code 516.3 or ICD-9-CM code 516.31 – to identify patients, but the approach had never been validated. To see how well it works, the investigators applied it to the nearly 5.4 million adults in the Kaiser Permanente Northern California system during 2000-2014. After patients with interstitial lung disease-associated codes entered on or after the day of the last IPF code were excluded, the algorithm identified 2,608 patients as having IPF (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Jun;14[6]:880-7).
Next, the investigators randomly selected 150 of those patients and examined their medical records, procedure codes, CTs, and other patient-level data to see how many of them really had IPF. The results weren’t good. The positive predictive value of the IPF code-based algorithm was only 42.2%, with a sensitivity 55.6%.
The widely used code-based IPF algorithm does “not generate accurate estimates of IPF incidence and prevalence. ... Over half of the patients identified as having IPF ... did not have IPF on case review. Alarmingly, whereas half of the misclassified cases had an alternative [interstitial lung disease] diagnosis, the other half had no clinical or radiologic evidence of ILD [interstitial lung disease] at all.” The algorithm also “likely misses a substantial proportion of patients who do have IPF,” Dr. Ley and his colleagues said.
“We can only speculate about the reasons. ... It seems likely to be due to a combination of misdiagnosis at the clinical level and miscoding at the administrative level,” they said.
To try to improve the situation, the team tweaked the algorithm to include only patients 50 years or older who had at least two 516.3 or 516.31 claims 1 month or more apart and a chest CT procedure code beforehand. They again excluded ILD-associated claims on or after the day of the last IPF code.
Although the sensitivity of the modified algorithm was lower than the original, it had a more robust positive predictive value of 70.4% in the derivation cohort and 61.8% in the validation cohort, both derived from the 150 patients used to validate the original algorithm.
“By making a few simple, empirically derived changes to the IPF algorithm,” it’s possible to “more reliably identif[y] patients” with IPF. “We believe the modified IPF algorithm will be useful for population-based studies of IPF ... that require high diagnostic certainty,” the investigators concluded.
The traditional algorithm found an incidence of 6.8 cases per 100,000 person-years, which was on the low end of previous reports, perhaps because of the relative health and youth of the 5.4 million patient pool. As in past studies, IPF incidence increased with older age and was highest in white patients and men.
“Whether the more specific codes provided by the ICD-10 system will allow for improved case classification of IPF requires further study,” the investigators noted.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ley reported speaker’s fees from Genentech, and one of the authors was an employee of the company. The senior author Harold Collard, MD, an associate professor in UCSF’s Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, reported personal fees from Takeda, ImmuneWorks, Parexel, Pharma Capital Partners, and others.
FROM THE ANNALS OF THE AMERICAN THORACIC SOCIETY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The positive predictive value of the traditional IPF code-based algorithm was only 42.2%, with a sensitivity of 55.6%.
Data source: A study including almost 5.4 million patients at Kaiser Permanente Northern California.
Disclosures: The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. One of the investigators was a Genentech employee. Others reported speaker’s and personal fees from Genentech and other companies.
VIDEO: Cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis have decreased over decades
MADRID – Recent improvements in the management of rheumatoid arthritis may have had a positive impact on common cardiovascular comorbidities, according to the results of a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Risk ratios (RR) for several CV events in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients were found to be lower for data published after 2000 and up to March 2016 when compared with data published up until 2000. Indeed, comparing these two time periods, French researchers found that the RR for myocardial infarction (MI) were a respective 1.32 and 1.18, for heart failure a respective 1.25 and 1.17, and for CV mortality a respective 1.21 and 1.07.
“Systemic inflammation is the cornerstone of both rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis,” Cécile Gaujoux-Viala, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at Montpellier University, Nîmes, France, and chief of the rheumatology service at Nîmes University Hospital, said during a press briefing at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
“Over the past 15 years, new treatment strategies such as ‘tight control,’ ‘treat-to-target,’ methotrexate optimization, and use of biologic DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] have led to better control of this inflammation,” Dr. Gaujoux-Viala added.
The aim of the meta-analysis was to look at the overall risk for CV events in RA patients versus the general population, she said, as well as to see if there had been any temporal shift by analyzing data obtained within two time periods – before 2000 and after 2000.
A systematic literature review was performed using the PubMed and Cochrane Library databases to search for observational studies that provided data about the occurrence of CV events in RA patients and controls. Of 5,714 papers that included reports of stroke, MI, heart failure, or CV death, 28 had the necessary data that could be used for the meta-analysis. Overall, the 28 studies included 227,871 RA patients, with a mean age of 55 years.
Results showed that RA patients had a 17% increased risk for stroke versus controls overall (P = .002), with a RR of 1.17. The RRs were 1.12 before 2000 and 1.23 after 2000, making stroke the only CV event that did not appear to show a downward trend.
Compared with the general population, RA patients had a 24% excess risk of MI, a 22% excess risk of heart failure, and a 18% excess risk of dying from a CV event (all P less than .00001).
These data provide “confirmation of an increased CV risk in RA patients compared to the general population,” said Dr. Gaujoux-Viala, who also discussed the study and its implications in a video interview.
Commenting on the study, Philip J. Mease, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, wondered where the studies used in the meta-analysis had been performed because of the potential impact that reduced access to CV medications or prevention strategies in certain countries could have on the results. However, the investigators did not determine where each of the studies used in the review took place.
Dr. Gaujoux-Viala had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
MADRID – Recent improvements in the management of rheumatoid arthritis may have had a positive impact on common cardiovascular comorbidities, according to the results of a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Risk ratios (RR) for several CV events in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients were found to be lower for data published after 2000 and up to March 2016 when compared with data published up until 2000. Indeed, comparing these two time periods, French researchers found that the RR for myocardial infarction (MI) were a respective 1.32 and 1.18, for heart failure a respective 1.25 and 1.17, and for CV mortality a respective 1.21 and 1.07.
“Systemic inflammation is the cornerstone of both rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis,” Cécile Gaujoux-Viala, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at Montpellier University, Nîmes, France, and chief of the rheumatology service at Nîmes University Hospital, said during a press briefing at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
“Over the past 15 years, new treatment strategies such as ‘tight control,’ ‘treat-to-target,’ methotrexate optimization, and use of biologic DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] have led to better control of this inflammation,” Dr. Gaujoux-Viala added.
The aim of the meta-analysis was to look at the overall risk for CV events in RA patients versus the general population, she said, as well as to see if there had been any temporal shift by analyzing data obtained within two time periods – before 2000 and after 2000.
A systematic literature review was performed using the PubMed and Cochrane Library databases to search for observational studies that provided data about the occurrence of CV events in RA patients and controls. Of 5,714 papers that included reports of stroke, MI, heart failure, or CV death, 28 had the necessary data that could be used for the meta-analysis. Overall, the 28 studies included 227,871 RA patients, with a mean age of 55 years.
Results showed that RA patients had a 17% increased risk for stroke versus controls overall (P = .002), with a RR of 1.17. The RRs were 1.12 before 2000 and 1.23 after 2000, making stroke the only CV event that did not appear to show a downward trend.
Compared with the general population, RA patients had a 24% excess risk of MI, a 22% excess risk of heart failure, and a 18% excess risk of dying from a CV event (all P less than .00001).
These data provide “confirmation of an increased CV risk in RA patients compared to the general population,” said Dr. Gaujoux-Viala, who also discussed the study and its implications in a video interview.
Commenting on the study, Philip J. Mease, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, wondered where the studies used in the meta-analysis had been performed because of the potential impact that reduced access to CV medications or prevention strategies in certain countries could have on the results. However, the investigators did not determine where each of the studies used in the review took place.
Dr. Gaujoux-Viala had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
MADRID – Recent improvements in the management of rheumatoid arthritis may have had a positive impact on common cardiovascular comorbidities, according to the results of a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Risk ratios (RR) for several CV events in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients were found to be lower for data published after 2000 and up to March 2016 when compared with data published up until 2000. Indeed, comparing these two time periods, French researchers found that the RR for myocardial infarction (MI) were a respective 1.32 and 1.18, for heart failure a respective 1.25 and 1.17, and for CV mortality a respective 1.21 and 1.07.
“Systemic inflammation is the cornerstone of both rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis,” Cécile Gaujoux-Viala, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at Montpellier University, Nîmes, France, and chief of the rheumatology service at Nîmes University Hospital, said during a press briefing at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
“Over the past 15 years, new treatment strategies such as ‘tight control,’ ‘treat-to-target,’ methotrexate optimization, and use of biologic DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] have led to better control of this inflammation,” Dr. Gaujoux-Viala added.
The aim of the meta-analysis was to look at the overall risk for CV events in RA patients versus the general population, she said, as well as to see if there had been any temporal shift by analyzing data obtained within two time periods – before 2000 and after 2000.
A systematic literature review was performed using the PubMed and Cochrane Library databases to search for observational studies that provided data about the occurrence of CV events in RA patients and controls. Of 5,714 papers that included reports of stroke, MI, heart failure, or CV death, 28 had the necessary data that could be used for the meta-analysis. Overall, the 28 studies included 227,871 RA patients, with a mean age of 55 years.
Results showed that RA patients had a 17% increased risk for stroke versus controls overall (P = .002), with a RR of 1.17. The RRs were 1.12 before 2000 and 1.23 after 2000, making stroke the only CV event that did not appear to show a downward trend.
Compared with the general population, RA patients had a 24% excess risk of MI, a 22% excess risk of heart failure, and a 18% excess risk of dying from a CV event (all P less than .00001).
These data provide “confirmation of an increased CV risk in RA patients compared to the general population,” said Dr. Gaujoux-Viala, who also discussed the study and its implications in a video interview.
Commenting on the study, Philip J. Mease, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, wondered where the studies used in the meta-analysis had been performed because of the potential impact that reduced access to CV medications or prevention strategies in certain countries could have on the results. However, the investigators did not determine where each of the studies used in the review took place.
Dr. Gaujoux-Viala had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
AT THE EULAR 2017 CONGRESS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Risk ratios for myocardial infarction, heart failure, and CV mortality were lower between the period of 2000-2016 than for the period up to 2000.
Data source: Meta-analysis of 28 studies published up to March 2016 that provided data on CV event rates in RA patients and the general population.
Disclosures: Dr. Gaujoux-Viala had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Lithoplasty tames heavily calcified coronary lesions
PARIS – A novel therapeutic ultrasound-based technology known as lithoplasty is turning heads in interventional cardiology and vascular medicine because it addresses the bane of interventionalists’ existence: complex, heavily calcified coronary and peripheral artery lesions.
“Calcification is something we deal with every day in interventional cardiology. It makes the procedures more expensive, longer, and in fact several recent studies have shown that the complication rate for calcified lesions is higher than for any other lesion subtype. Calcification is the next big thing that we’re trying to take on in interventional cardiology,” Todd J. Brinton, MD, observed at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
At EuroPCR, he presented the results of DISRUPT CAD, a seven-center study in which 60 patients with heavily calcified coronary lesions underwent lithoplasty in order to facilitate stent placement. The study met all of its safety and performance endpoints. As a result, the week prior to EuroPCR the European regulatory agency granted marketing approval for Shockwave Medical’s coronary lithoplasty system; the indication is for coronary vessel preparation prior to stenting. A large phase III U.S. trial aimed at gaining FDA approval is planned.
Moreover, on the basis of the earlier favorable DISRUPT PAD trial, lithoplasty has already been approved for treatment of peripheral artery disease (PAD) in Europe since late 2015 and by the FDA since September 2016. Now underway is DISRUPT PAD III, a large postmarketing randomized trial comparing lithoplasty with conventional balloon angioplasty in patients with heavily calcified PAD, added Dr. Brinton, an interventional cardiologist at Stanford (Calif.) University and cofounder of Shockwave Medical.
Lithoplasty is a potentially transformative technology which he described as “lithotripsy inside a balloon.” Lithotripsy has an established 30-year track record for the safe treatment of kidney stones. However, lithotripsy utilizes focused ultrasound, while lithoplasty relies upon circumferential unfocused therapeutic ultrasound delivered by miniaturized emitters placed inside a 12-mm intravascular balloon. The balloon is crossed to the target lesion, inflated to a modest pressure of 4 atmospheres, then the operator delivers lithoplasty pulses lasting over 1 microsec in duration at a rate of 1/sec for 10 seconds in order to fracture the thick intramedial calcium plaque, allowing the lesion to open up and thereby normalize vessel compliance.
“Once you’ve cracked the calcium you can easily dilate the lesion. It’s the calcium that’s restricting the ability to dilate. The real fundamental need here is to maximize acute gain to get really good stent apposition. We’re trying to get expansion,” the cardiologist explained.
That was readily achieved in the DISRUPT CAD study. The 60 participants had reference vessel diameters of 2.5-4.0 mm, with an average target lesion length of 20 mm. The calcification was heavy, covering on average 270 degrees of the vessel circumference as measured by optical coherence tomography, with an average calcium thickness of 0.97 mm and a calcified segment length of 22.3 mm.
The mean stent expansion was 112%. The minimum luminal diameter improved from 0.9 mm pretreatment to 2.6 mm post treatment, for an acute gain of 1.7 mm. The amount of acute gain was similar across the full range of vessel diameters.
The mean diameter stenosis went from 68% pretreatment to 13% post-treatment.
The primary safety endpoint was the 30-day rate of MACE, defined as cardiac death, MI, or target vessel revascularization. The rate was 5%, consisting of 3 patients with mild non–Q-wave MI defined by creatine kinase–MB elevations more than three times the upper limit of normal. The 6-month MACE rate was 8.5%, which included the three non–Q-wave MIs plus two cardiac deaths not related to the procedure or technology.
Final angiographic results adjudicated in a central core laboratory showed no perforations, abrupt closures, slow or no reflow events, or residual dissections. These are complications commonly seen with debulking devices such as rotational or orbital atherectomy, Dr. Brinton noted.
The primary performance endpoint in DISRUPT CAD was clinical success, defined as a residual stenosis of less than 50% post PCI with no in-hospital MACE. This was achieved in 57 of 60 patients, or 95%. The device was successfully delivered to the target lesion with subsequent performance of lithoplasty in 59 of 60 patients. An even more flexible and deliverable device will be released in the coming year, according to the cardiologist.
“I’d say the take-home is that the disease has changed,” Dr. Brinton commented. “It’s not the same disease that we had when Gruentzig did his first balloon angioplasty. These lesions are more calcified, more complex, yet for the most part we use the same balloon we’ve been using for the last 40 years. So lithoplasty is really an attempt to modernize the therapy in a new patient subset we now take care of who are much more complicated than the patients we originally took care of.”
“The reality is, we’re having difficulty taking care of these patients. For myself as an interventionalist, it’s not uncommon to look around the table and see a massive amount of tools when we’re doing these complex cases. Lithoplasty is intended to bring the simplicity. I would say it’s not necessarily to make the best operators better, it’s to bring all operators up to the ability to take on these complex lesions that are now usually reserved for high-volume centers that can do debulking,” he added.
Session cochair David R. Holmes Jr., MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., pronounced lithoplasty “tremendously exciting.” He and the other panelists focused on questions of safety and potential collateral damage: Where does the calcified debris go? What are the effects of the unfocused sonic pressure waves on noncalcified plaque? How hot does the vessel get?
Dr. Brinton replied that thick calcium plaque is located mostly in the medial vessel wall and stays there after fracturing. That’s why distal embolization wasn’t an issue in DISRUPT CAD. In animal studies, even at 20 times the energy dose used in clinical practice, lithoplasty had no effect on softer, noncalcified plaque or normal tissue. Vessel temperature increases by about 1.2 degrees C during lithoplasty, which isn’t sufficient to cause injury or drive restenosis.
Elsewhere at EuroPCR, Alberto Cremonesi, MD, who chaired a press conference where Dr. Brinton presented highlights of DISRUPT CAD, declared lithoplasty is “in my mind a real breakthrough, not only for coronary disease but also for PAD.”
Is it possible that stand-alone lithoplasty could reduce the need for multiple stents in longer coronary lesions, instead making possible more focal stenting? asked Dr. Cremonesi of Maria Cecilia Hospital in Cotignola, Italy.
That’s one of several possibilities worthy of future investigation, Dr. Brinton replied. Lithoplasty might also facilitate the results obtainable with bioresorbable coronary scaffolds or drug-coated balloons, he added.
He noted that as cofounder of and a consultant to Shockwave Medical, he has a sizable financial involvement with the company.
PARIS – A novel therapeutic ultrasound-based technology known as lithoplasty is turning heads in interventional cardiology and vascular medicine because it addresses the bane of interventionalists’ existence: complex, heavily calcified coronary and peripheral artery lesions.
“Calcification is something we deal with every day in interventional cardiology. It makes the procedures more expensive, longer, and in fact several recent studies have shown that the complication rate for calcified lesions is higher than for any other lesion subtype. Calcification is the next big thing that we’re trying to take on in interventional cardiology,” Todd J. Brinton, MD, observed at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
At EuroPCR, he presented the results of DISRUPT CAD, a seven-center study in which 60 patients with heavily calcified coronary lesions underwent lithoplasty in order to facilitate stent placement. The study met all of its safety and performance endpoints. As a result, the week prior to EuroPCR the European regulatory agency granted marketing approval for Shockwave Medical’s coronary lithoplasty system; the indication is for coronary vessel preparation prior to stenting. A large phase III U.S. trial aimed at gaining FDA approval is planned.
Moreover, on the basis of the earlier favorable DISRUPT PAD trial, lithoplasty has already been approved for treatment of peripheral artery disease (PAD) in Europe since late 2015 and by the FDA since September 2016. Now underway is DISRUPT PAD III, a large postmarketing randomized trial comparing lithoplasty with conventional balloon angioplasty in patients with heavily calcified PAD, added Dr. Brinton, an interventional cardiologist at Stanford (Calif.) University and cofounder of Shockwave Medical.
Lithoplasty is a potentially transformative technology which he described as “lithotripsy inside a balloon.” Lithotripsy has an established 30-year track record for the safe treatment of kidney stones. However, lithotripsy utilizes focused ultrasound, while lithoplasty relies upon circumferential unfocused therapeutic ultrasound delivered by miniaturized emitters placed inside a 12-mm intravascular balloon. The balloon is crossed to the target lesion, inflated to a modest pressure of 4 atmospheres, then the operator delivers lithoplasty pulses lasting over 1 microsec in duration at a rate of 1/sec for 10 seconds in order to fracture the thick intramedial calcium plaque, allowing the lesion to open up and thereby normalize vessel compliance.
“Once you’ve cracked the calcium you can easily dilate the lesion. It’s the calcium that’s restricting the ability to dilate. The real fundamental need here is to maximize acute gain to get really good stent apposition. We’re trying to get expansion,” the cardiologist explained.
That was readily achieved in the DISRUPT CAD study. The 60 participants had reference vessel diameters of 2.5-4.0 mm, with an average target lesion length of 20 mm. The calcification was heavy, covering on average 270 degrees of the vessel circumference as measured by optical coherence tomography, with an average calcium thickness of 0.97 mm and a calcified segment length of 22.3 mm.
The mean stent expansion was 112%. The minimum luminal diameter improved from 0.9 mm pretreatment to 2.6 mm post treatment, for an acute gain of 1.7 mm. The amount of acute gain was similar across the full range of vessel diameters.
The mean diameter stenosis went from 68% pretreatment to 13% post-treatment.
The primary safety endpoint was the 30-day rate of MACE, defined as cardiac death, MI, or target vessel revascularization. The rate was 5%, consisting of 3 patients with mild non–Q-wave MI defined by creatine kinase–MB elevations more than three times the upper limit of normal. The 6-month MACE rate was 8.5%, which included the three non–Q-wave MIs plus two cardiac deaths not related to the procedure or technology.
Final angiographic results adjudicated in a central core laboratory showed no perforations, abrupt closures, slow or no reflow events, or residual dissections. These are complications commonly seen with debulking devices such as rotational or orbital atherectomy, Dr. Brinton noted.
The primary performance endpoint in DISRUPT CAD was clinical success, defined as a residual stenosis of less than 50% post PCI with no in-hospital MACE. This was achieved in 57 of 60 patients, or 95%. The device was successfully delivered to the target lesion with subsequent performance of lithoplasty in 59 of 60 patients. An even more flexible and deliverable device will be released in the coming year, according to the cardiologist.
“I’d say the take-home is that the disease has changed,” Dr. Brinton commented. “It’s not the same disease that we had when Gruentzig did his first balloon angioplasty. These lesions are more calcified, more complex, yet for the most part we use the same balloon we’ve been using for the last 40 years. So lithoplasty is really an attempt to modernize the therapy in a new patient subset we now take care of who are much more complicated than the patients we originally took care of.”
“The reality is, we’re having difficulty taking care of these patients. For myself as an interventionalist, it’s not uncommon to look around the table and see a massive amount of tools when we’re doing these complex cases. Lithoplasty is intended to bring the simplicity. I would say it’s not necessarily to make the best operators better, it’s to bring all operators up to the ability to take on these complex lesions that are now usually reserved for high-volume centers that can do debulking,” he added.
Session cochair David R. Holmes Jr., MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., pronounced lithoplasty “tremendously exciting.” He and the other panelists focused on questions of safety and potential collateral damage: Where does the calcified debris go? What are the effects of the unfocused sonic pressure waves on noncalcified plaque? How hot does the vessel get?
Dr. Brinton replied that thick calcium plaque is located mostly in the medial vessel wall and stays there after fracturing. That’s why distal embolization wasn’t an issue in DISRUPT CAD. In animal studies, even at 20 times the energy dose used in clinical practice, lithoplasty had no effect on softer, noncalcified plaque or normal tissue. Vessel temperature increases by about 1.2 degrees C during lithoplasty, which isn’t sufficient to cause injury or drive restenosis.
Elsewhere at EuroPCR, Alberto Cremonesi, MD, who chaired a press conference where Dr. Brinton presented highlights of DISRUPT CAD, declared lithoplasty is “in my mind a real breakthrough, not only for coronary disease but also for PAD.”
Is it possible that stand-alone lithoplasty could reduce the need for multiple stents in longer coronary lesions, instead making possible more focal stenting? asked Dr. Cremonesi of Maria Cecilia Hospital in Cotignola, Italy.
That’s one of several possibilities worthy of future investigation, Dr. Brinton replied. Lithoplasty might also facilitate the results obtainable with bioresorbable coronary scaffolds or drug-coated balloons, he added.
He noted that as cofounder of and a consultant to Shockwave Medical, he has a sizable financial involvement with the company.
PARIS – A novel therapeutic ultrasound-based technology known as lithoplasty is turning heads in interventional cardiology and vascular medicine because it addresses the bane of interventionalists’ existence: complex, heavily calcified coronary and peripheral artery lesions.
“Calcification is something we deal with every day in interventional cardiology. It makes the procedures more expensive, longer, and in fact several recent studies have shown that the complication rate for calcified lesions is higher than for any other lesion subtype. Calcification is the next big thing that we’re trying to take on in interventional cardiology,” Todd J. Brinton, MD, observed at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
At EuroPCR, he presented the results of DISRUPT CAD, a seven-center study in which 60 patients with heavily calcified coronary lesions underwent lithoplasty in order to facilitate stent placement. The study met all of its safety and performance endpoints. As a result, the week prior to EuroPCR the European regulatory agency granted marketing approval for Shockwave Medical’s coronary lithoplasty system; the indication is for coronary vessel preparation prior to stenting. A large phase III U.S. trial aimed at gaining FDA approval is planned.
Moreover, on the basis of the earlier favorable DISRUPT PAD trial, lithoplasty has already been approved for treatment of peripheral artery disease (PAD) in Europe since late 2015 and by the FDA since September 2016. Now underway is DISRUPT PAD III, a large postmarketing randomized trial comparing lithoplasty with conventional balloon angioplasty in patients with heavily calcified PAD, added Dr. Brinton, an interventional cardiologist at Stanford (Calif.) University and cofounder of Shockwave Medical.
Lithoplasty is a potentially transformative technology which he described as “lithotripsy inside a balloon.” Lithotripsy has an established 30-year track record for the safe treatment of kidney stones. However, lithotripsy utilizes focused ultrasound, while lithoplasty relies upon circumferential unfocused therapeutic ultrasound delivered by miniaturized emitters placed inside a 12-mm intravascular balloon. The balloon is crossed to the target lesion, inflated to a modest pressure of 4 atmospheres, then the operator delivers lithoplasty pulses lasting over 1 microsec in duration at a rate of 1/sec for 10 seconds in order to fracture the thick intramedial calcium plaque, allowing the lesion to open up and thereby normalize vessel compliance.
“Once you’ve cracked the calcium you can easily dilate the lesion. It’s the calcium that’s restricting the ability to dilate. The real fundamental need here is to maximize acute gain to get really good stent apposition. We’re trying to get expansion,” the cardiologist explained.
That was readily achieved in the DISRUPT CAD study. The 60 participants had reference vessel diameters of 2.5-4.0 mm, with an average target lesion length of 20 mm. The calcification was heavy, covering on average 270 degrees of the vessel circumference as measured by optical coherence tomography, with an average calcium thickness of 0.97 mm and a calcified segment length of 22.3 mm.
The mean stent expansion was 112%. The minimum luminal diameter improved from 0.9 mm pretreatment to 2.6 mm post treatment, for an acute gain of 1.7 mm. The amount of acute gain was similar across the full range of vessel diameters.
The mean diameter stenosis went from 68% pretreatment to 13% post-treatment.
The primary safety endpoint was the 30-day rate of MACE, defined as cardiac death, MI, or target vessel revascularization. The rate was 5%, consisting of 3 patients with mild non–Q-wave MI defined by creatine kinase–MB elevations more than three times the upper limit of normal. The 6-month MACE rate was 8.5%, which included the three non–Q-wave MIs plus two cardiac deaths not related to the procedure or technology.
Final angiographic results adjudicated in a central core laboratory showed no perforations, abrupt closures, slow or no reflow events, or residual dissections. These are complications commonly seen with debulking devices such as rotational or orbital atherectomy, Dr. Brinton noted.
The primary performance endpoint in DISRUPT CAD was clinical success, defined as a residual stenosis of less than 50% post PCI with no in-hospital MACE. This was achieved in 57 of 60 patients, or 95%. The device was successfully delivered to the target lesion with subsequent performance of lithoplasty in 59 of 60 patients. An even more flexible and deliverable device will be released in the coming year, according to the cardiologist.
“I’d say the take-home is that the disease has changed,” Dr. Brinton commented. “It’s not the same disease that we had when Gruentzig did his first balloon angioplasty. These lesions are more calcified, more complex, yet for the most part we use the same balloon we’ve been using for the last 40 years. So lithoplasty is really an attempt to modernize the therapy in a new patient subset we now take care of who are much more complicated than the patients we originally took care of.”
“The reality is, we’re having difficulty taking care of these patients. For myself as an interventionalist, it’s not uncommon to look around the table and see a massive amount of tools when we’re doing these complex cases. Lithoplasty is intended to bring the simplicity. I would say it’s not necessarily to make the best operators better, it’s to bring all operators up to the ability to take on these complex lesions that are now usually reserved for high-volume centers that can do debulking,” he added.
Session cochair David R. Holmes Jr., MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., pronounced lithoplasty “tremendously exciting.” He and the other panelists focused on questions of safety and potential collateral damage: Where does the calcified debris go? What are the effects of the unfocused sonic pressure waves on noncalcified plaque? How hot does the vessel get?
Dr. Brinton replied that thick calcium plaque is located mostly in the medial vessel wall and stays there after fracturing. That’s why distal embolization wasn’t an issue in DISRUPT CAD. In animal studies, even at 20 times the energy dose used in clinical practice, lithoplasty had no effect on softer, noncalcified plaque or normal tissue. Vessel temperature increases by about 1.2 degrees C during lithoplasty, which isn’t sufficient to cause injury or drive restenosis.
Elsewhere at EuroPCR, Alberto Cremonesi, MD, who chaired a press conference where Dr. Brinton presented highlights of DISRUPT CAD, declared lithoplasty is “in my mind a real breakthrough, not only for coronary disease but also for PAD.”
Is it possible that stand-alone lithoplasty could reduce the need for multiple stents in longer coronary lesions, instead making possible more focal stenting? asked Dr. Cremonesi of Maria Cecilia Hospital in Cotignola, Italy.
That’s one of several possibilities worthy of future investigation, Dr. Brinton replied. Lithoplasty might also facilitate the results obtainable with bioresorbable coronary scaffolds or drug-coated balloons, he added.
He noted that as cofounder of and a consultant to Shockwave Medical, he has a sizable financial involvement with the company.
AT EUROPCR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Lithoplasty of heavily calcified coronary lesions improved the minimum luminal diameter from 0.9 mm pretreatment to 2.6 mm post-treatment, for an immediate gain of 1.7 mm prior to stent placement.
Data source: This study featured 6-month follow-up of 60 patients with heavily calcified coronary lesions who underwent lithoplasty followed by stenting.
Disclosures: The DISRUPT CAD study was sponsored by Shockwave Medical, which is developing lithoplasty. The presenter cofounded the company.













