User login
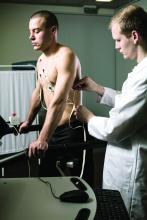
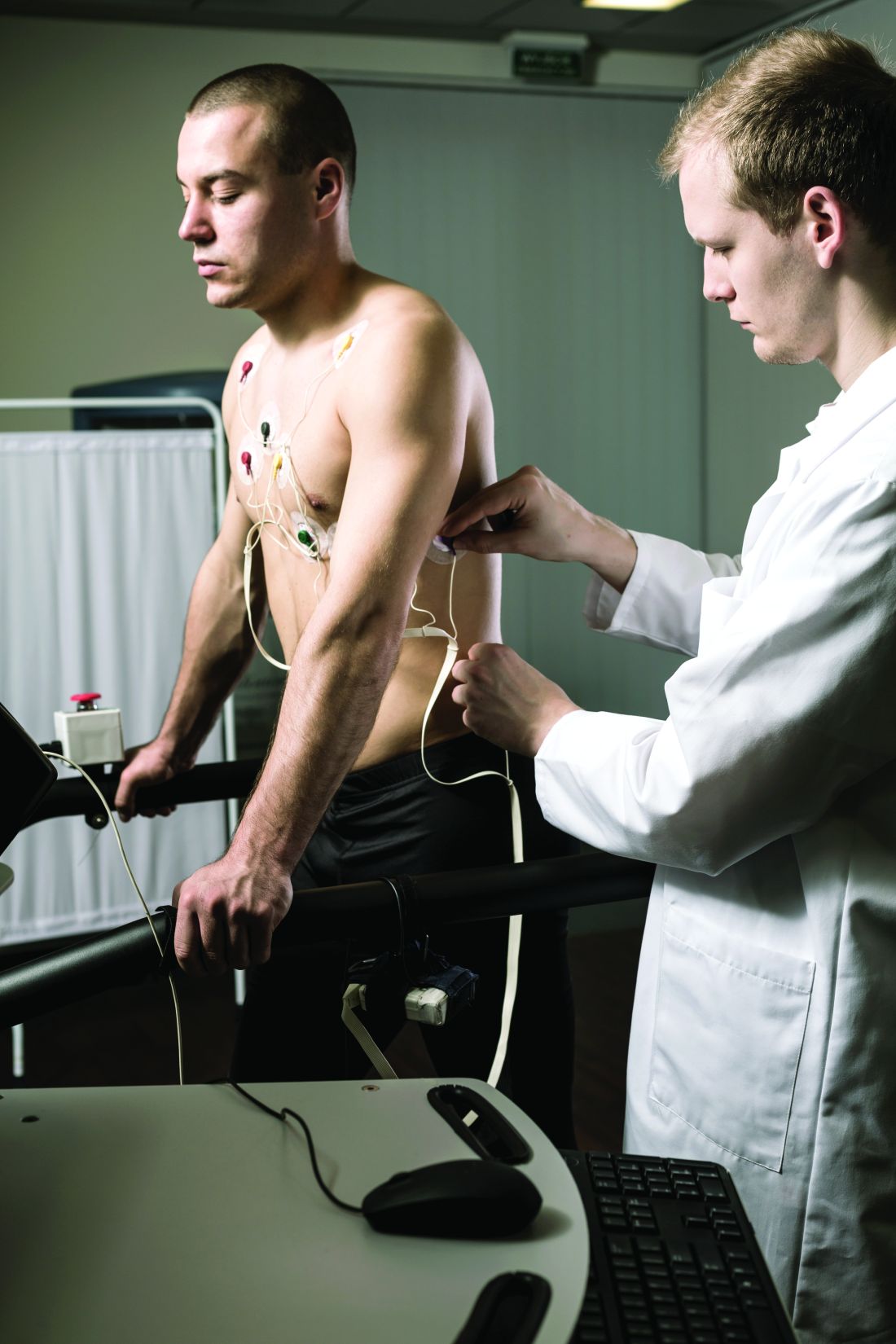
International group identifies actions to improve lung cancer survival
The International Cancer Benchmarking Partnership, a collaboration of physicians, clinicians, researchers, policy makers, and data experts, has reached a consensus on key actions designed to standardize and homogenize lung cancer care that includes early diagnosis and access to care for all patients.
This consensus, reported at the 2022 European Lung Cancer Congress, is an effort to address disparities in care recognized by the group’s in-house research team. The team identified significantly different survival rates in early stage lung cancer patients from a group of countries with similar health care metrics, such as health care expenditure and universal access to health care.
“This group of countries is very comparable, but we saw a 20% difference in survival in localized, stage I and II cancers. When you consider that lung cancer is a bigger killer than any other cancer –more than breast, prostate, and colon cancer combined – that’s thousands of people,” said the project’s lead clinician, Christian Finley, MD, a thoracic surgeon with St. Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton (Ont.).
Founded in 2009, the ICBP includes about 500 experts in its core countries of Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Australia, the United Kingdom, and Canada; New Zealand and Ireland have also participated. The goal of the partnership is to benchmark survival and other outcomes in cancer and to research why disparities between countries exist.
“That’s why we keep the membership fairly small, so that we can actually make more meaningful research projects to get into depth in factors beyond benchmarking survival and mortality,” said study author Charlotte Lynch, MSc, a senior researcher with Cancer Research UK in London.
To help narrow the disparity gap, Ms. Lynch, Dr. Finley and colleagues brought together nine key informants from ICBP countries to discuss local clinical insights and best practices, and ultimately came up a list of five recommendations considered most crucial: implementing cost-effective, equitable, and effective screening; ensuring diagnoses of lung cancer within 30 days of referral; developing thoracic centers of excellence; launching an international audit of lung cancer care; and prioritizing the recognition of improvements in lung cancer care and outcomes.
“For example, points supporting the screening call to action focus on timely access to cross-sectional imaging and availability and development of patient and health care practitioner lung cancer awareness materials,” Ms. Lynch said.
Another example would be the point that describes the need for a minimum data set to evaluate lung cancer patients’ diagnosis, treatment, and aftercare.
“I think we all work in a very disrupted system right now. Screening programs really took a hit during the pandemic, and I think people coming out of those disruptions are trying to imagine a more effective system using tools like information technologies, mobile clinics and having a better understanding of equity,” Dr. Finley said.
Ms. Lynch said the ICBP intends to use the consensus to generate concrete actions. “We’re thinking about how we can get everyone in the room to share lessons learned and best practices to push things forward rather than saying, ‘this is what should be done,’ making sure we do the next steps, collaborative thinking, and moving forward.”
In a press release, Antonio Passaro, MD, a lung cancer expert from the European Institute of Oncology in Milan, said there is a need to prioritize primary and secondary prevention of lung cancer.
“Although a much-debated topic in recent years, a strong body of research has now shown that lung cancer screening through annual computed tomography scans in individuals with a history of smoking can improve detection rates. Targeting the right populations with these interventions will be crucial to implementing screening approaches that are both efficacious and cost effective,” he stated.
The authors declared no conflicts of interest and this study was not funded.
The International Cancer Benchmarking Partnership, a collaboration of physicians, clinicians, researchers, policy makers, and data experts, has reached a consensus on key actions designed to standardize and homogenize lung cancer care that includes early diagnosis and access to care for all patients.
This consensus, reported at the 2022 European Lung Cancer Congress, is an effort to address disparities in care recognized by the group’s in-house research team. The team identified significantly different survival rates in early stage lung cancer patients from a group of countries with similar health care metrics, such as health care expenditure and universal access to health care.
“This group of countries is very comparable, but we saw a 20% difference in survival in localized, stage I and II cancers. When you consider that lung cancer is a bigger killer than any other cancer –more than breast, prostate, and colon cancer combined – that’s thousands of people,” said the project’s lead clinician, Christian Finley, MD, a thoracic surgeon with St. Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton (Ont.).
Founded in 2009, the ICBP includes about 500 experts in its core countries of Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Australia, the United Kingdom, and Canada; New Zealand and Ireland have also participated. The goal of the partnership is to benchmark survival and other outcomes in cancer and to research why disparities between countries exist.
“That’s why we keep the membership fairly small, so that we can actually make more meaningful research projects to get into depth in factors beyond benchmarking survival and mortality,” said study author Charlotte Lynch, MSc, a senior researcher with Cancer Research UK in London.
To help narrow the disparity gap, Ms. Lynch, Dr. Finley and colleagues brought together nine key informants from ICBP countries to discuss local clinical insights and best practices, and ultimately came up a list of five recommendations considered most crucial: implementing cost-effective, equitable, and effective screening; ensuring diagnoses of lung cancer within 30 days of referral; developing thoracic centers of excellence; launching an international audit of lung cancer care; and prioritizing the recognition of improvements in lung cancer care and outcomes.
“For example, points supporting the screening call to action focus on timely access to cross-sectional imaging and availability and development of patient and health care practitioner lung cancer awareness materials,” Ms. Lynch said.
Another example would be the point that describes the need for a minimum data set to evaluate lung cancer patients’ diagnosis, treatment, and aftercare.
“I think we all work in a very disrupted system right now. Screening programs really took a hit during the pandemic, and I think people coming out of those disruptions are trying to imagine a more effective system using tools like information technologies, mobile clinics and having a better understanding of equity,” Dr. Finley said.
Ms. Lynch said the ICBP intends to use the consensus to generate concrete actions. “We’re thinking about how we can get everyone in the room to share lessons learned and best practices to push things forward rather than saying, ‘this is what should be done,’ making sure we do the next steps, collaborative thinking, and moving forward.”
In a press release, Antonio Passaro, MD, a lung cancer expert from the European Institute of Oncology in Milan, said there is a need to prioritize primary and secondary prevention of lung cancer.
“Although a much-debated topic in recent years, a strong body of research has now shown that lung cancer screening through annual computed tomography scans in individuals with a history of smoking can improve detection rates. Targeting the right populations with these interventions will be crucial to implementing screening approaches that are both efficacious and cost effective,” he stated.
The authors declared no conflicts of interest and this study was not funded.
The International Cancer Benchmarking Partnership, a collaboration of physicians, clinicians, researchers, policy makers, and data experts, has reached a consensus on key actions designed to standardize and homogenize lung cancer care that includes early diagnosis and access to care for all patients.
This consensus, reported at the 2022 European Lung Cancer Congress, is an effort to address disparities in care recognized by the group’s in-house research team. The team identified significantly different survival rates in early stage lung cancer patients from a group of countries with similar health care metrics, such as health care expenditure and universal access to health care.
“This group of countries is very comparable, but we saw a 20% difference in survival in localized, stage I and II cancers. When you consider that lung cancer is a bigger killer than any other cancer –more than breast, prostate, and colon cancer combined – that’s thousands of people,” said the project’s lead clinician, Christian Finley, MD, a thoracic surgeon with St. Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton (Ont.).
Founded in 2009, the ICBP includes about 500 experts in its core countries of Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Australia, the United Kingdom, and Canada; New Zealand and Ireland have also participated. The goal of the partnership is to benchmark survival and other outcomes in cancer and to research why disparities between countries exist.
“That’s why we keep the membership fairly small, so that we can actually make more meaningful research projects to get into depth in factors beyond benchmarking survival and mortality,” said study author Charlotte Lynch, MSc, a senior researcher with Cancer Research UK in London.
To help narrow the disparity gap, Ms. Lynch, Dr. Finley and colleagues brought together nine key informants from ICBP countries to discuss local clinical insights and best practices, and ultimately came up a list of five recommendations considered most crucial: implementing cost-effective, equitable, and effective screening; ensuring diagnoses of lung cancer within 30 days of referral; developing thoracic centers of excellence; launching an international audit of lung cancer care; and prioritizing the recognition of improvements in lung cancer care and outcomes.
“For example, points supporting the screening call to action focus on timely access to cross-sectional imaging and availability and development of patient and health care practitioner lung cancer awareness materials,” Ms. Lynch said.
Another example would be the point that describes the need for a minimum data set to evaluate lung cancer patients’ diagnosis, treatment, and aftercare.
“I think we all work in a very disrupted system right now. Screening programs really took a hit during the pandemic, and I think people coming out of those disruptions are trying to imagine a more effective system using tools like information technologies, mobile clinics and having a better understanding of equity,” Dr. Finley said.
Ms. Lynch said the ICBP intends to use the consensus to generate concrete actions. “We’re thinking about how we can get everyone in the room to share lessons learned and best practices to push things forward rather than saying, ‘this is what should be done,’ making sure we do the next steps, collaborative thinking, and moving forward.”
In a press release, Antonio Passaro, MD, a lung cancer expert from the European Institute of Oncology in Milan, said there is a need to prioritize primary and secondary prevention of lung cancer.
“Although a much-debated topic in recent years, a strong body of research has now shown that lung cancer screening through annual computed tomography scans in individuals with a history of smoking can improve detection rates. Targeting the right populations with these interventions will be crucial to implementing screening approaches that are both efficacious and cost effective,” he stated.
The authors declared no conflicts of interest and this study was not funded.
FROM ELCC 2022
Are free lunches back? Docs start seeing drug reps again
In their heyday, drug reps had big expense budgets and would wine and dine physicians, golf with them, and give gifts to their potential physician clients.
But in 2002, pressure from Congress and increased scrutiny from the American Medical Association prompted the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America to adopt a set of voluntary ethical codes to regulate the gifts given to physicians. Now, physicians must report even small gifts or meals to the National Practitioner Data Bank.
Before the restrictions, physician/pharmaceutical rep relationships relied on face-to-face meetings. These included lunches with a limited budget or sharing a cup of coffee during a morning visit to a practice. The parties got to know each other, which led to trust and long-term relationships.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, everything changed. “It was culture shock for us,” admitted Craig F, a career pharmaceutical rep. “We didn’t know what we were going to do.”
The pharmaceutical industry pivoted and quickly got up to speed with Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and the like. “We began by reaching out to doctors via email and cell phones to set up virtual meetings,” Craig said. “Most of the doctors were working from home, doing telehealth whenever possible. For new sales reps, this was particularly difficult, because they couldn’t visit offices and get to know doctors.”
Many physicians didn’t want to devote time to Zoom meetings with pharma reps. “We worked around their schedules, and sometimes this even looked like Sunday calls,” he said.
As vaccination levels increased and medical offices began to reopen, so too did some of the old-school, face-to-face pharma rep/doctor meetings. But most proceeded with caution. “Some pharmaceutical companies didn’t put reps back into the field until the fall of 2020,” said Craig. “If we weren’t welcome in an office, we didn’t push it.”
Once much of the population was vaccinated, the thaw began in earnest, although the drug reps continued to tread cautiously, mask up, and respect the wishes of physicians. Today, Craig estimated that about two-thirds of his appointments are in person.
Still, it’s unlikely that the drug rep–supplied “free staff lunch” will ever regain its former popularity. Medical office staff are still keeping distance, owing to COVID; office schedules may be more crowded and may not allow the time; and many physicians are still nervous about having to report “gifts” or “paid lunches” from pharma.
The post-COVID paradigm shift
The pandemic put a dent in the pharma rep/doctor relationship, said Suzy Jackson, managing director of life sciences at Accenture and an author of The “New” Rules of Healthcare Provider Engagement . “COVID started moving power away from reps because they lost the ability to simply wander into a building and have a conversation with a health care provider. We’re seeing the pandemic evolve the meeting model into a hybrid in-person and virtual.”
“Many doctors are operating in a slower fashion because they’re balancing a hybrid model with patients, as well,” said Craig. “Some of my visits now involve talking to nurses or front-office staff, not getting in to see the doctors.”
The push from some doctors to see reps virtually as opposed to in person is a challenge for the pharma companies. “We get more done in person, so virtual is not our favorite way to do business,” said Craig. “But we’re thankful for any time we can get with doctors, so when they ask to do virtual, we agree.”
Still, the Accenture survey offered good news for pharma reps: Only 4% of respondents didn’t want to continue with in-person meetings at all. “I think of this as a positive,” Ms. Jackson said. “It shows that physicians value these relationships, if they’re done in the right way.”
But a survey by Boston Consulting Group confirms that virtual visits are likely to continue. BCG’s Doctors’ Changing Expectations of Pharma Are Here to Stay revealed that three-quarters of respondent physicians prefer to maintain or increase the amount of virtual engagements with pharma reps after becoming accustomed to the practice during the pandemic.
Under these changing scenarios, said Ms. Jackson, pharma reps have to think about more meaningful ways to engage with doctors.
“I feel that doctors are more crunched for time now, managing hybrid environments,” Craig said. “They have less time and want more patient-specific information that leads to fewer calls back to their offices.”
More physicians now value webinars, virtual training, and speaker programs. Virtual channels, the survey found, “give physicians access to the information they need in an easy and convenient manner.”
Still, physicians have noted that the survey indicated that email communications from pharma reps had increased. Often, physicians found the useful information buried in irrelevant “clutter.”
Restrictions on drug reps became tighter
In the 20 years since the guidelines came into existence, PhRMA has continued to strengthen the codes. In 2009, PhRMA issued new recommendations surrounding noneducational gifts and placed a cap of $100 for meals, drug samples, and other items. In 2022, they added layers to the code that focus on speaker programs. For instance, while companies can provide “modest” meals to attendees as an incidental courtesy, pharma reps can no longer pay for or provide alcohol in conjunction with these programs.
The rules vary from state to state. In Minnesota, for instance, gifts from pharma companies cannot exceed $50 per year. Some institutions – such as the Cleveland Clinic – have even stricter rules. “When we have conventions, we put up signage reminding doctors from the strictest states that they can’t even accept a cup of coffee from a rep,” said Craig.
However, COVID hasn’t completely changed doctor/pharma relationships. In Ms. Jackson’s words, “In spite of the shift to a more hybrid model, this is a very human relationship yielding real human results.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In their heyday, drug reps had big expense budgets and would wine and dine physicians, golf with them, and give gifts to their potential physician clients.
But in 2002, pressure from Congress and increased scrutiny from the American Medical Association prompted the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America to adopt a set of voluntary ethical codes to regulate the gifts given to physicians. Now, physicians must report even small gifts or meals to the National Practitioner Data Bank.
Before the restrictions, physician/pharmaceutical rep relationships relied on face-to-face meetings. These included lunches with a limited budget or sharing a cup of coffee during a morning visit to a practice. The parties got to know each other, which led to trust and long-term relationships.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, everything changed. “It was culture shock for us,” admitted Craig F, a career pharmaceutical rep. “We didn’t know what we were going to do.”
The pharmaceutical industry pivoted and quickly got up to speed with Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and the like. “We began by reaching out to doctors via email and cell phones to set up virtual meetings,” Craig said. “Most of the doctors were working from home, doing telehealth whenever possible. For new sales reps, this was particularly difficult, because they couldn’t visit offices and get to know doctors.”
Many physicians didn’t want to devote time to Zoom meetings with pharma reps. “We worked around their schedules, and sometimes this even looked like Sunday calls,” he said.
As vaccination levels increased and medical offices began to reopen, so too did some of the old-school, face-to-face pharma rep/doctor meetings. But most proceeded with caution. “Some pharmaceutical companies didn’t put reps back into the field until the fall of 2020,” said Craig. “If we weren’t welcome in an office, we didn’t push it.”
Once much of the population was vaccinated, the thaw began in earnest, although the drug reps continued to tread cautiously, mask up, and respect the wishes of physicians. Today, Craig estimated that about two-thirds of his appointments are in person.
Still, it’s unlikely that the drug rep–supplied “free staff lunch” will ever regain its former popularity. Medical office staff are still keeping distance, owing to COVID; office schedules may be more crowded and may not allow the time; and many physicians are still nervous about having to report “gifts” or “paid lunches” from pharma.
The post-COVID paradigm shift
The pandemic put a dent in the pharma rep/doctor relationship, said Suzy Jackson, managing director of life sciences at Accenture and an author of The “New” Rules of Healthcare Provider Engagement . “COVID started moving power away from reps because they lost the ability to simply wander into a building and have a conversation with a health care provider. We’re seeing the pandemic evolve the meeting model into a hybrid in-person and virtual.”
“Many doctors are operating in a slower fashion because they’re balancing a hybrid model with patients, as well,” said Craig. “Some of my visits now involve talking to nurses or front-office staff, not getting in to see the doctors.”
The push from some doctors to see reps virtually as opposed to in person is a challenge for the pharma companies. “We get more done in person, so virtual is not our favorite way to do business,” said Craig. “But we’re thankful for any time we can get with doctors, so when they ask to do virtual, we agree.”
Still, the Accenture survey offered good news for pharma reps: Only 4% of respondents didn’t want to continue with in-person meetings at all. “I think of this as a positive,” Ms. Jackson said. “It shows that physicians value these relationships, if they’re done in the right way.”
But a survey by Boston Consulting Group confirms that virtual visits are likely to continue. BCG’s Doctors’ Changing Expectations of Pharma Are Here to Stay revealed that three-quarters of respondent physicians prefer to maintain or increase the amount of virtual engagements with pharma reps after becoming accustomed to the practice during the pandemic.
Under these changing scenarios, said Ms. Jackson, pharma reps have to think about more meaningful ways to engage with doctors.
“I feel that doctors are more crunched for time now, managing hybrid environments,” Craig said. “They have less time and want more patient-specific information that leads to fewer calls back to their offices.”
More physicians now value webinars, virtual training, and speaker programs. Virtual channels, the survey found, “give physicians access to the information they need in an easy and convenient manner.”
Still, physicians have noted that the survey indicated that email communications from pharma reps had increased. Often, physicians found the useful information buried in irrelevant “clutter.”
Restrictions on drug reps became tighter
In the 20 years since the guidelines came into existence, PhRMA has continued to strengthen the codes. In 2009, PhRMA issued new recommendations surrounding noneducational gifts and placed a cap of $100 for meals, drug samples, and other items. In 2022, they added layers to the code that focus on speaker programs. For instance, while companies can provide “modest” meals to attendees as an incidental courtesy, pharma reps can no longer pay for or provide alcohol in conjunction with these programs.
The rules vary from state to state. In Minnesota, for instance, gifts from pharma companies cannot exceed $50 per year. Some institutions – such as the Cleveland Clinic – have even stricter rules. “When we have conventions, we put up signage reminding doctors from the strictest states that they can’t even accept a cup of coffee from a rep,” said Craig.
However, COVID hasn’t completely changed doctor/pharma relationships. In Ms. Jackson’s words, “In spite of the shift to a more hybrid model, this is a very human relationship yielding real human results.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In their heyday, drug reps had big expense budgets and would wine and dine physicians, golf with them, and give gifts to their potential physician clients.
But in 2002, pressure from Congress and increased scrutiny from the American Medical Association prompted the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America to adopt a set of voluntary ethical codes to regulate the gifts given to physicians. Now, physicians must report even small gifts or meals to the National Practitioner Data Bank.
Before the restrictions, physician/pharmaceutical rep relationships relied on face-to-face meetings. These included lunches with a limited budget or sharing a cup of coffee during a morning visit to a practice. The parties got to know each other, which led to trust and long-term relationships.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, everything changed. “It was culture shock for us,” admitted Craig F, a career pharmaceutical rep. “We didn’t know what we were going to do.”
The pharmaceutical industry pivoted and quickly got up to speed with Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and the like. “We began by reaching out to doctors via email and cell phones to set up virtual meetings,” Craig said. “Most of the doctors were working from home, doing telehealth whenever possible. For new sales reps, this was particularly difficult, because they couldn’t visit offices and get to know doctors.”
Many physicians didn’t want to devote time to Zoom meetings with pharma reps. “We worked around their schedules, and sometimes this even looked like Sunday calls,” he said.
As vaccination levels increased and medical offices began to reopen, so too did some of the old-school, face-to-face pharma rep/doctor meetings. But most proceeded with caution. “Some pharmaceutical companies didn’t put reps back into the field until the fall of 2020,” said Craig. “If we weren’t welcome in an office, we didn’t push it.”
Once much of the population was vaccinated, the thaw began in earnest, although the drug reps continued to tread cautiously, mask up, and respect the wishes of physicians. Today, Craig estimated that about two-thirds of his appointments are in person.
Still, it’s unlikely that the drug rep–supplied “free staff lunch” will ever regain its former popularity. Medical office staff are still keeping distance, owing to COVID; office schedules may be more crowded and may not allow the time; and many physicians are still nervous about having to report “gifts” or “paid lunches” from pharma.
The post-COVID paradigm shift
The pandemic put a dent in the pharma rep/doctor relationship, said Suzy Jackson, managing director of life sciences at Accenture and an author of The “New” Rules of Healthcare Provider Engagement . “COVID started moving power away from reps because they lost the ability to simply wander into a building and have a conversation with a health care provider. We’re seeing the pandemic evolve the meeting model into a hybrid in-person and virtual.”
“Many doctors are operating in a slower fashion because they’re balancing a hybrid model with patients, as well,” said Craig. “Some of my visits now involve talking to nurses or front-office staff, not getting in to see the doctors.”
The push from some doctors to see reps virtually as opposed to in person is a challenge for the pharma companies. “We get more done in person, so virtual is not our favorite way to do business,” said Craig. “But we’re thankful for any time we can get with doctors, so when they ask to do virtual, we agree.”
Still, the Accenture survey offered good news for pharma reps: Only 4% of respondents didn’t want to continue with in-person meetings at all. “I think of this as a positive,” Ms. Jackson said. “It shows that physicians value these relationships, if they’re done in the right way.”
But a survey by Boston Consulting Group confirms that virtual visits are likely to continue. BCG’s Doctors’ Changing Expectations of Pharma Are Here to Stay revealed that three-quarters of respondent physicians prefer to maintain or increase the amount of virtual engagements with pharma reps after becoming accustomed to the practice during the pandemic.
Under these changing scenarios, said Ms. Jackson, pharma reps have to think about more meaningful ways to engage with doctors.
“I feel that doctors are more crunched for time now, managing hybrid environments,” Craig said. “They have less time and want more patient-specific information that leads to fewer calls back to their offices.”
More physicians now value webinars, virtual training, and speaker programs. Virtual channels, the survey found, “give physicians access to the information they need in an easy and convenient manner.”
Still, physicians have noted that the survey indicated that email communications from pharma reps had increased. Often, physicians found the useful information buried in irrelevant “clutter.”
Restrictions on drug reps became tighter
In the 20 years since the guidelines came into existence, PhRMA has continued to strengthen the codes. In 2009, PhRMA issued new recommendations surrounding noneducational gifts and placed a cap of $100 for meals, drug samples, and other items. In 2022, they added layers to the code that focus on speaker programs. For instance, while companies can provide “modest” meals to attendees as an incidental courtesy, pharma reps can no longer pay for or provide alcohol in conjunction with these programs.
The rules vary from state to state. In Minnesota, for instance, gifts from pharma companies cannot exceed $50 per year. Some institutions – such as the Cleveland Clinic – have even stricter rules. “When we have conventions, we put up signage reminding doctors from the strictest states that they can’t even accept a cup of coffee from a rep,” said Craig.
However, COVID hasn’t completely changed doctor/pharma relationships. In Ms. Jackson’s words, “In spite of the shift to a more hybrid model, this is a very human relationship yielding real human results.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC panel lists reasons to get second COVID booster
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is considering what to tell the public about second booster shots with mRNA vaccinations for COVID-19.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration in March authorized a second booster dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccines for people aged 50 and older and certain immunocompromised adults, even though many top infectious disease experts questioned the need before the agency’s decision.
In a meeting April 20, the CDC asked its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices to discuss second booster shots, but did not ask the group of experts to vote on formal recommendations.
Instead,
ACIP member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said she’s concerned about the potential for “booster fatigue.”
“A vaccination program that’s going to require boosting large proportions of the population every 4-6 months is really not sustainable and probably not something that most people want to participate in,” she said.
The benefit of additional COVID-19 shots for now appears to be smaller than what people get from the initial doses, Dr. Bell said.
Earlier in the meeting, CDC staff presented estimates about how well the COVID-19 vaccines work to prevent one case of hospitalization from the disease over 4 months among people aged 50 and older.
The major gain in preventing hospitalizations occurs with the first vaccination series and then wanes, the CDC said.
It appears that one hospitalization is prevented for every 135 people who get the first round of COVID-19 vaccinations. But it takes 674 people getting a first booster dose to prevent one hospitalization. A second booster prevents one hospitalization for every 1,205 people vaccinated.
Dr. Bell said she’s concerned about considering additional doses for “smaller and smaller return and creating an impression that we don’t have a very effective vaccination program,” even though the CDC’s data show a clear benefit.
Reasons to get a second booster
Elisha Hall, PhD, RD, of the CDC presented slides with some factors to help determine the urgency for a person to get a second booster:
- Having certain underlying medical conditions that increase the risk of severe COVID-19 illness.
- Being moderately or severely immunocompromised.
- Living with someone who is immunocompromised, at increased risk for severe disease, or who cannot be vaccinated because of age or contraindication.
- Being at increased risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, such as through occupational, institutional, or other activities (e.g., travel or large gatherings).
- Living or working in an area where there is a medium or high level of COVID-19 in the community.
In contrast, people might want to wait if they had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 within the past 3 months, Dr. Hall said in her presentation. Another reason for delay might be a concern that a booster dose may be more important later in the year.
The experts also addressed public confusion over boosters. For the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines, a second booster is a fourth dose, but for those who received the one-shot J&J vaccine, the second booster is a third dose.
Going forward, it may be easier to refer to subsequent doses as “annual boosters,” the CDC’s Sara Oliver, MD, MSPH, told the panel. It will be important to keep language about subsequent vaccinations clear and easy for the public to follow, she said.
Dr. Oliver also said there’s already been a drop-off in the acceptance of second rounds of COVID-19 vaccinations. CDC data show that 77% of people in the United States have had at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine, but only 66% of the population is fully vaccinated, and only 45% have had a first booster dose.
In her presentation, Dr. Oliver said the top priority in COVID-19 vaccination efforts remains initial vaccinations for people who haven’t gotten them.
Kids younger than 5
During the public comment session of the CDC meeting, several people called on the FDA to move quickly to expand authorization of COVID-19 vaccines to children aged 5 years and younger.
“We know that many parents and caregivers and health care providers are anxious to have COVID vaccines available” for young children, said Doran Fink, MD, PhD, a deputy director of the FDA’s vaccines division.
He said the agency is working to be ready to authorize the shots for young children while it awaits research results from the manufacturers.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is considering what to tell the public about second booster shots with mRNA vaccinations for COVID-19.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration in March authorized a second booster dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccines for people aged 50 and older and certain immunocompromised adults, even though many top infectious disease experts questioned the need before the agency’s decision.
In a meeting April 20, the CDC asked its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices to discuss second booster shots, but did not ask the group of experts to vote on formal recommendations.
Instead,
ACIP member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said she’s concerned about the potential for “booster fatigue.”
“A vaccination program that’s going to require boosting large proportions of the population every 4-6 months is really not sustainable and probably not something that most people want to participate in,” she said.
The benefit of additional COVID-19 shots for now appears to be smaller than what people get from the initial doses, Dr. Bell said.
Earlier in the meeting, CDC staff presented estimates about how well the COVID-19 vaccines work to prevent one case of hospitalization from the disease over 4 months among people aged 50 and older.
The major gain in preventing hospitalizations occurs with the first vaccination series and then wanes, the CDC said.
It appears that one hospitalization is prevented for every 135 people who get the first round of COVID-19 vaccinations. But it takes 674 people getting a first booster dose to prevent one hospitalization. A second booster prevents one hospitalization for every 1,205 people vaccinated.
Dr. Bell said she’s concerned about considering additional doses for “smaller and smaller return and creating an impression that we don’t have a very effective vaccination program,” even though the CDC’s data show a clear benefit.
Reasons to get a second booster
Elisha Hall, PhD, RD, of the CDC presented slides with some factors to help determine the urgency for a person to get a second booster:
- Having certain underlying medical conditions that increase the risk of severe COVID-19 illness.
- Being moderately or severely immunocompromised.
- Living with someone who is immunocompromised, at increased risk for severe disease, or who cannot be vaccinated because of age or contraindication.
- Being at increased risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, such as through occupational, institutional, or other activities (e.g., travel or large gatherings).
- Living or working in an area where there is a medium or high level of COVID-19 in the community.
In contrast, people might want to wait if they had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 within the past 3 months, Dr. Hall said in her presentation. Another reason for delay might be a concern that a booster dose may be more important later in the year.
The experts also addressed public confusion over boosters. For the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines, a second booster is a fourth dose, but for those who received the one-shot J&J vaccine, the second booster is a third dose.
Going forward, it may be easier to refer to subsequent doses as “annual boosters,” the CDC’s Sara Oliver, MD, MSPH, told the panel. It will be important to keep language about subsequent vaccinations clear and easy for the public to follow, she said.
Dr. Oliver also said there’s already been a drop-off in the acceptance of second rounds of COVID-19 vaccinations. CDC data show that 77% of people in the United States have had at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine, but only 66% of the population is fully vaccinated, and only 45% have had a first booster dose.
In her presentation, Dr. Oliver said the top priority in COVID-19 vaccination efforts remains initial vaccinations for people who haven’t gotten them.
Kids younger than 5
During the public comment session of the CDC meeting, several people called on the FDA to move quickly to expand authorization of COVID-19 vaccines to children aged 5 years and younger.
“We know that many parents and caregivers and health care providers are anxious to have COVID vaccines available” for young children, said Doran Fink, MD, PhD, a deputy director of the FDA’s vaccines division.
He said the agency is working to be ready to authorize the shots for young children while it awaits research results from the manufacturers.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is considering what to tell the public about second booster shots with mRNA vaccinations for COVID-19.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration in March authorized a second booster dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccines for people aged 50 and older and certain immunocompromised adults, even though many top infectious disease experts questioned the need before the agency’s decision.
In a meeting April 20, the CDC asked its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices to discuss second booster shots, but did not ask the group of experts to vote on formal recommendations.
Instead,
ACIP member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said she’s concerned about the potential for “booster fatigue.”
“A vaccination program that’s going to require boosting large proportions of the population every 4-6 months is really not sustainable and probably not something that most people want to participate in,” she said.
The benefit of additional COVID-19 shots for now appears to be smaller than what people get from the initial doses, Dr. Bell said.
Earlier in the meeting, CDC staff presented estimates about how well the COVID-19 vaccines work to prevent one case of hospitalization from the disease over 4 months among people aged 50 and older.
The major gain in preventing hospitalizations occurs with the first vaccination series and then wanes, the CDC said.
It appears that one hospitalization is prevented for every 135 people who get the first round of COVID-19 vaccinations. But it takes 674 people getting a first booster dose to prevent one hospitalization. A second booster prevents one hospitalization for every 1,205 people vaccinated.
Dr. Bell said she’s concerned about considering additional doses for “smaller and smaller return and creating an impression that we don’t have a very effective vaccination program,” even though the CDC’s data show a clear benefit.
Reasons to get a second booster
Elisha Hall, PhD, RD, of the CDC presented slides with some factors to help determine the urgency for a person to get a second booster:
- Having certain underlying medical conditions that increase the risk of severe COVID-19 illness.
- Being moderately or severely immunocompromised.
- Living with someone who is immunocompromised, at increased risk for severe disease, or who cannot be vaccinated because of age or contraindication.
- Being at increased risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, such as through occupational, institutional, or other activities (e.g., travel or large gatherings).
- Living or working in an area where there is a medium or high level of COVID-19 in the community.
In contrast, people might want to wait if they had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 within the past 3 months, Dr. Hall said in her presentation. Another reason for delay might be a concern that a booster dose may be more important later in the year.
The experts also addressed public confusion over boosters. For the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines, a second booster is a fourth dose, but for those who received the one-shot J&J vaccine, the second booster is a third dose.
Going forward, it may be easier to refer to subsequent doses as “annual boosters,” the CDC’s Sara Oliver, MD, MSPH, told the panel. It will be important to keep language about subsequent vaccinations clear and easy for the public to follow, she said.
Dr. Oliver also said there’s already been a drop-off in the acceptance of second rounds of COVID-19 vaccinations. CDC data show that 77% of people in the United States have had at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine, but only 66% of the population is fully vaccinated, and only 45% have had a first booster dose.
In her presentation, Dr. Oliver said the top priority in COVID-19 vaccination efforts remains initial vaccinations for people who haven’t gotten them.
Kids younger than 5
During the public comment session of the CDC meeting, several people called on the FDA to move quickly to expand authorization of COVID-19 vaccines to children aged 5 years and younger.
“We know that many parents and caregivers and health care providers are anxious to have COVID vaccines available” for young children, said Doran Fink, MD, PhD, a deputy director of the FDA’s vaccines division.
He said the agency is working to be ready to authorize the shots for young children while it awaits research results from the manufacturers.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Retro-orbital headache and nausea
On the basis of his presentation, this patient is probably experiencing migraine with visual aura. Migraine is a condition in children and adolescents whose prevalence increases with age: 1%-3% between age 3 and 7 years, 4%-11% between age 7 and 11 years, and 8%-23% by age 15 years. Although migraine without aura is relatively uncommon in the pediatric population, visual aura is a hallmark sign of migraine headache and excludes the other headache types in the differential diagnosis. Basilar migraine is unlikely because the patient has not experienced symptoms that suggest occipital or brainstem area dysfunction post-aura.
The diagnosis of migraine is largely clinical, but the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) guidelines for the acute treatment of pediatric migraine recommend that when assessing children and adolescents with headache, clinicians should diagnose a specific headache type: primary, secondary, or other headache syndrome. Migraine in pediatric patients is often related to triggering factors such as infection, physical or psychological stress, or dietary choices, but on the basis of the patient's history, this headache appears to be primary in nature.
Most pediatric patients can achieve control of their migraines with acute treatments and benefit from nonprescription oral analgesics, including acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and naproxen. Clinicians should prescribe ibuprofen orally (10 mg/kg) as an initial treatment for children and adolescents with migraine. The US Food and Drug Administration has only approved certain triptans for pediatric patients: almotriptan, sumatriptan-naproxen, and zolmitriptan nasal spray for patients aged 12 years or older and rizatriptan for patients aged 6-17 years.
The AAN guidelines for the pharmacologic treatment of pediatric migraine prevention report that for those who experience migraine with aura, taking a triptan during the aura is safe, though it may be more effective when taken at the onset of head pain, as is the case with other acute treatments.
In pediatric patients, avoidance of known headache triggers is generally sufficient for migraine prevention. This includes managing anxiety, depression, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and other psychiatric comorbidities that can exacerbate headache. Lifestyle management also includes ensuring adequate sleep, exercise, hydration, and stress management.
The guidelines conclude that although the majority of randomized controlled trials exploring the efficacy of preventive medications in the pediatric population fail to demonstrate superiority to placebo, migraine prophylaxis should be considered when headaches occur with high frequency and severity and cause migraine-related disability based on the Pediatric Migraine Disability Assessment (PedMIDAS).
Jasmin Harpe, MD, MPH, Headache Fellow, Department of Neurology, Harvard University, John R. Graham Headache Center, Mass General Brigham, Boston, MA
Jasmin Harpe, MD, MPH, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships
On the basis of his presentation, this patient is probably experiencing migraine with visual aura. Migraine is a condition in children and adolescents whose prevalence increases with age: 1%-3% between age 3 and 7 years, 4%-11% between age 7 and 11 years, and 8%-23% by age 15 years. Although migraine without aura is relatively uncommon in the pediatric population, visual aura is a hallmark sign of migraine headache and excludes the other headache types in the differential diagnosis. Basilar migraine is unlikely because the patient has not experienced symptoms that suggest occipital or brainstem area dysfunction post-aura.
The diagnosis of migraine is largely clinical, but the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) guidelines for the acute treatment of pediatric migraine recommend that when assessing children and adolescents with headache, clinicians should diagnose a specific headache type: primary, secondary, or other headache syndrome. Migraine in pediatric patients is often related to triggering factors such as infection, physical or psychological stress, or dietary choices, but on the basis of the patient's history, this headache appears to be primary in nature.
Most pediatric patients can achieve control of their migraines with acute treatments and benefit from nonprescription oral analgesics, including acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and naproxen. Clinicians should prescribe ibuprofen orally (10 mg/kg) as an initial treatment for children and adolescents with migraine. The US Food and Drug Administration has only approved certain triptans for pediatric patients: almotriptan, sumatriptan-naproxen, and zolmitriptan nasal spray for patients aged 12 years or older and rizatriptan for patients aged 6-17 years.
The AAN guidelines for the pharmacologic treatment of pediatric migraine prevention report that for those who experience migraine with aura, taking a triptan during the aura is safe, though it may be more effective when taken at the onset of head pain, as is the case with other acute treatments.
In pediatric patients, avoidance of known headache triggers is generally sufficient for migraine prevention. This includes managing anxiety, depression, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and other psychiatric comorbidities that can exacerbate headache. Lifestyle management also includes ensuring adequate sleep, exercise, hydration, and stress management.
The guidelines conclude that although the majority of randomized controlled trials exploring the efficacy of preventive medications in the pediatric population fail to demonstrate superiority to placebo, migraine prophylaxis should be considered when headaches occur with high frequency and severity and cause migraine-related disability based on the Pediatric Migraine Disability Assessment (PedMIDAS).
Jasmin Harpe, MD, MPH, Headache Fellow, Department of Neurology, Harvard University, John R. Graham Headache Center, Mass General Brigham, Boston, MA
Jasmin Harpe, MD, MPH, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships
On the basis of his presentation, this patient is probably experiencing migraine with visual aura. Migraine is a condition in children and adolescents whose prevalence increases with age: 1%-3% between age 3 and 7 years, 4%-11% between age 7 and 11 years, and 8%-23% by age 15 years. Although migraine without aura is relatively uncommon in the pediatric population, visual aura is a hallmark sign of migraine headache and excludes the other headache types in the differential diagnosis. Basilar migraine is unlikely because the patient has not experienced symptoms that suggest occipital or brainstem area dysfunction post-aura.
The diagnosis of migraine is largely clinical, but the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) guidelines for the acute treatment of pediatric migraine recommend that when assessing children and adolescents with headache, clinicians should diagnose a specific headache type: primary, secondary, or other headache syndrome. Migraine in pediatric patients is often related to triggering factors such as infection, physical or psychological stress, or dietary choices, but on the basis of the patient's history, this headache appears to be primary in nature.
Most pediatric patients can achieve control of their migraines with acute treatments and benefit from nonprescription oral analgesics, including acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and naproxen. Clinicians should prescribe ibuprofen orally (10 mg/kg) as an initial treatment for children and adolescents with migraine. The US Food and Drug Administration has only approved certain triptans for pediatric patients: almotriptan, sumatriptan-naproxen, and zolmitriptan nasal spray for patients aged 12 years or older and rizatriptan for patients aged 6-17 years.
The AAN guidelines for the pharmacologic treatment of pediatric migraine prevention report that for those who experience migraine with aura, taking a triptan during the aura is safe, though it may be more effective when taken at the onset of head pain, as is the case with other acute treatments.
In pediatric patients, avoidance of known headache triggers is generally sufficient for migraine prevention. This includes managing anxiety, depression, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and other psychiatric comorbidities that can exacerbate headache. Lifestyle management also includes ensuring adequate sleep, exercise, hydration, and stress management.
The guidelines conclude that although the majority of randomized controlled trials exploring the efficacy of preventive medications in the pediatric population fail to demonstrate superiority to placebo, migraine prophylaxis should be considered when headaches occur with high frequency and severity and cause migraine-related disability based on the Pediatric Migraine Disability Assessment (PedMIDAS).
Jasmin Harpe, MD, MPH, Headache Fellow, Department of Neurology, Harvard University, John R. Graham Headache Center, Mass General Brigham, Boston, MA
Jasmin Harpe, MD, MPH, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships
A 7-year-old boy presents with a retro-orbital headache, nausea, and photophobia. Height is 4 ft 2 in and weight is 70 lb (BMI 19.7). The patient's mother reports that he described seeing "rainbow shapes" in his line of vision about 20 minutes before the onset of head pain and notes that she herself has a history of headache. The patient is nonfebrile but sweating and drowsy. Physical examination is unrevealing. The patient has no known allergies and is not currently on medication.
RaDonda Vaught: Victim, felon, or both?
For 4 and a half years, I have followed the RaDonda Vaught medication error that led to the unfortunate death of a human being. I am not alone. Nurses across the country have followed the case with anxiety and fear, knowing a guilty verdict might have the potential to challenge basic tenets of care.
According to Kaiser Health News, nurses are “raging and quitting” following the announcement of a guilty verdict for two felonies: criminally negligent homicide and gross neglect of an impaired adult.
Thousands of nurses have claimed they could arrive in Nashville, Tenn., on May 13, the day Ms. Vaught is to be sentenced, to protest the conviction. Others have stated they believe justice is being conducted, as their sympathies lie with the victim, Charlene Murphey, who died 12 hours after being unable to draw breath, paralyzed from the inadvertent dose of vecuronium given intravenously by her nurse.
How should we feel as clinicians? according to sentencing guidelines?
My belief is that it is understandable to feel passionately about this case, including what it could mean to an era of “just culture” that nursing organizations have promoted. The concept of just culture looks at medication/nursing errors as opportunities for growth to avoid future errors, not as scenarios for punitive action. With the guilty verdict in Ms. Vaught’s case, nurses (and facilities) fear that nurses will avoid coming forward after mistakes, leading to cover-ups and a culture perspective.
Will nurses be hesitant to report errors (especially significant errors) that lead to patient harm? Will we fear retribution and reprisal for being truthful?
I believe that Ms. Vaught’s criminal case has changed little in the political landscape of caregiving. Before you let loose with a loud expletive (or two), hear me out.
When a patient dies from unintentional harm, someone must be held accountable. Society needs a scapegoat, and unfortunately, excrement slides downhill to the lowest common denominator, which may be the nurse. Initially, Ms. Vaught was contacted by her state licensing board (Tennessee) and informed there would be no professional repercussions for her mistake. That decision did not hold. She was later indicted criminally for the death of her patient. She also had her nursing license revoked.
Why? The hospital where she worked was threatened with Medicare reprisal if systemic issues were not addressed following the incident; for example, a bar-coding device was not available for Ms. Vaught to use prior to administering the vecuronium, and paralytic agents were stored unsafely in a Pyxis MedStation, readily available for any nurse to obtain via override.
In fact, the number of overrides performed by all nurses caring for Ms. Murphey in the days leading to her death was alarming, leading reviewers to assume that time to acquire medication for inpatients was a problem.
Ms. Vaught herself, stating the obvious on talk shows, said she should not have performed an override, that the situation was “not an emergency” and she should have taken time to check that Versed (midazolam) was available by the generic name and not the “VE” she entered as a search mechanism into the machine. She also stated she was “distracted” by a trainee assigned to her at the time.
We have all been there, feeling rushed to perform a task under stressful situations, skipping safety guidelines to sedate a patient while radiology is waiting. Someone is always on our a**, waiting to get to the next task, the next patient, the next admission, the next pseudo-emergency called nursing workload.
It never ends.
Which is why I wish to emphasize what the Ms. Vaught guilty verdict really means for nurses.
It means we must never forget that our actions have the potential to harm, even kill, our patients.
We must never forget that repercussions and reprisal may occur, whether personal guilt that may prove more damaging than the prison sentence Ms. Vaught might receive, or problems that could result if nurses attempt to hide or subvert medication issues.
In Ms. Vaught’s case, she did not document the medication that had been given to Ms. Murphey, facts the prosecution seized on to proclaim her guilt. Why? We can only guess at this point. But her claims of truthfulness need to be balanced by what occurred, and the facts are that she did not document the error after administering vecuronium that night.
When reflecting on this verdict, we need to remember a patient died, and she did so horribly, being unable to draw breath. This should never happen during our watch, ever, and as clinicians, we need to be vigilant.
In summary, protest if you believe justice has been too harsh or unfair, and that nurses may be fearful as a result. But please spare a moment to realize that someone should protest for Ms. Murphey as well. We cannot bring her back, nor can we right the system issues that may have led to her death.
But we should protest for safer systems, for improved staffing, for a need to catch our collective breaths, and a day to work and nurture patients when someone is not constantly on our a**. Only then will nurses be protected from unjust reprisal, from needing to be the lowest common denominator of guilt.
Ms. Goodman is a researcher and consultant in Libertyville, Ill. She disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For 4 and a half years, I have followed the RaDonda Vaught medication error that led to the unfortunate death of a human being. I am not alone. Nurses across the country have followed the case with anxiety and fear, knowing a guilty verdict might have the potential to challenge basic tenets of care.
According to Kaiser Health News, nurses are “raging and quitting” following the announcement of a guilty verdict for two felonies: criminally negligent homicide and gross neglect of an impaired adult.
Thousands of nurses have claimed they could arrive in Nashville, Tenn., on May 13, the day Ms. Vaught is to be sentenced, to protest the conviction. Others have stated they believe justice is being conducted, as their sympathies lie with the victim, Charlene Murphey, who died 12 hours after being unable to draw breath, paralyzed from the inadvertent dose of vecuronium given intravenously by her nurse.
How should we feel as clinicians? according to sentencing guidelines?
My belief is that it is understandable to feel passionately about this case, including what it could mean to an era of “just culture” that nursing organizations have promoted. The concept of just culture looks at medication/nursing errors as opportunities for growth to avoid future errors, not as scenarios for punitive action. With the guilty verdict in Ms. Vaught’s case, nurses (and facilities) fear that nurses will avoid coming forward after mistakes, leading to cover-ups and a culture perspective.
Will nurses be hesitant to report errors (especially significant errors) that lead to patient harm? Will we fear retribution and reprisal for being truthful?
I believe that Ms. Vaught’s criminal case has changed little in the political landscape of caregiving. Before you let loose with a loud expletive (or two), hear me out.
When a patient dies from unintentional harm, someone must be held accountable. Society needs a scapegoat, and unfortunately, excrement slides downhill to the lowest common denominator, which may be the nurse. Initially, Ms. Vaught was contacted by her state licensing board (Tennessee) and informed there would be no professional repercussions for her mistake. That decision did not hold. She was later indicted criminally for the death of her patient. She also had her nursing license revoked.
Why? The hospital where she worked was threatened with Medicare reprisal if systemic issues were not addressed following the incident; for example, a bar-coding device was not available for Ms. Vaught to use prior to administering the vecuronium, and paralytic agents were stored unsafely in a Pyxis MedStation, readily available for any nurse to obtain via override.
In fact, the number of overrides performed by all nurses caring for Ms. Murphey in the days leading to her death was alarming, leading reviewers to assume that time to acquire medication for inpatients was a problem.
Ms. Vaught herself, stating the obvious on talk shows, said she should not have performed an override, that the situation was “not an emergency” and she should have taken time to check that Versed (midazolam) was available by the generic name and not the “VE” she entered as a search mechanism into the machine. She also stated she was “distracted” by a trainee assigned to her at the time.
We have all been there, feeling rushed to perform a task under stressful situations, skipping safety guidelines to sedate a patient while radiology is waiting. Someone is always on our a**, waiting to get to the next task, the next patient, the next admission, the next pseudo-emergency called nursing workload.
It never ends.
Which is why I wish to emphasize what the Ms. Vaught guilty verdict really means for nurses.
It means we must never forget that our actions have the potential to harm, even kill, our patients.
We must never forget that repercussions and reprisal may occur, whether personal guilt that may prove more damaging than the prison sentence Ms. Vaught might receive, or problems that could result if nurses attempt to hide or subvert medication issues.
In Ms. Vaught’s case, she did not document the medication that had been given to Ms. Murphey, facts the prosecution seized on to proclaim her guilt. Why? We can only guess at this point. But her claims of truthfulness need to be balanced by what occurred, and the facts are that she did not document the error after administering vecuronium that night.
When reflecting on this verdict, we need to remember a patient died, and she did so horribly, being unable to draw breath. This should never happen during our watch, ever, and as clinicians, we need to be vigilant.
In summary, protest if you believe justice has been too harsh or unfair, and that nurses may be fearful as a result. But please spare a moment to realize that someone should protest for Ms. Murphey as well. We cannot bring her back, nor can we right the system issues that may have led to her death.
But we should protest for safer systems, for improved staffing, for a need to catch our collective breaths, and a day to work and nurture patients when someone is not constantly on our a**. Only then will nurses be protected from unjust reprisal, from needing to be the lowest common denominator of guilt.
Ms. Goodman is a researcher and consultant in Libertyville, Ill. She disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For 4 and a half years, I have followed the RaDonda Vaught medication error that led to the unfortunate death of a human being. I am not alone. Nurses across the country have followed the case with anxiety and fear, knowing a guilty verdict might have the potential to challenge basic tenets of care.
According to Kaiser Health News, nurses are “raging and quitting” following the announcement of a guilty verdict for two felonies: criminally negligent homicide and gross neglect of an impaired adult.
Thousands of nurses have claimed they could arrive in Nashville, Tenn., on May 13, the day Ms. Vaught is to be sentenced, to protest the conviction. Others have stated they believe justice is being conducted, as their sympathies lie with the victim, Charlene Murphey, who died 12 hours after being unable to draw breath, paralyzed from the inadvertent dose of vecuronium given intravenously by her nurse.
How should we feel as clinicians? according to sentencing guidelines?
My belief is that it is understandable to feel passionately about this case, including what it could mean to an era of “just culture” that nursing organizations have promoted. The concept of just culture looks at medication/nursing errors as opportunities for growth to avoid future errors, not as scenarios for punitive action. With the guilty verdict in Ms. Vaught’s case, nurses (and facilities) fear that nurses will avoid coming forward after mistakes, leading to cover-ups and a culture perspective.
Will nurses be hesitant to report errors (especially significant errors) that lead to patient harm? Will we fear retribution and reprisal for being truthful?
I believe that Ms. Vaught’s criminal case has changed little in the political landscape of caregiving. Before you let loose with a loud expletive (or two), hear me out.
When a patient dies from unintentional harm, someone must be held accountable. Society needs a scapegoat, and unfortunately, excrement slides downhill to the lowest common denominator, which may be the nurse. Initially, Ms. Vaught was contacted by her state licensing board (Tennessee) and informed there would be no professional repercussions for her mistake. That decision did not hold. She was later indicted criminally for the death of her patient. She also had her nursing license revoked.
Why? The hospital where she worked was threatened with Medicare reprisal if systemic issues were not addressed following the incident; for example, a bar-coding device was not available for Ms. Vaught to use prior to administering the vecuronium, and paralytic agents were stored unsafely in a Pyxis MedStation, readily available for any nurse to obtain via override.
In fact, the number of overrides performed by all nurses caring for Ms. Murphey in the days leading to her death was alarming, leading reviewers to assume that time to acquire medication for inpatients was a problem.
Ms. Vaught herself, stating the obvious on talk shows, said she should not have performed an override, that the situation was “not an emergency” and she should have taken time to check that Versed (midazolam) was available by the generic name and not the “VE” she entered as a search mechanism into the machine. She also stated she was “distracted” by a trainee assigned to her at the time.
We have all been there, feeling rushed to perform a task under stressful situations, skipping safety guidelines to sedate a patient while radiology is waiting. Someone is always on our a**, waiting to get to the next task, the next patient, the next admission, the next pseudo-emergency called nursing workload.
It never ends.
Which is why I wish to emphasize what the Ms. Vaught guilty verdict really means for nurses.
It means we must never forget that our actions have the potential to harm, even kill, our patients.
We must never forget that repercussions and reprisal may occur, whether personal guilt that may prove more damaging than the prison sentence Ms. Vaught might receive, or problems that could result if nurses attempt to hide or subvert medication issues.
In Ms. Vaught’s case, she did not document the medication that had been given to Ms. Murphey, facts the prosecution seized on to proclaim her guilt. Why? We can only guess at this point. But her claims of truthfulness need to be balanced by what occurred, and the facts are that she did not document the error after administering vecuronium that night.
When reflecting on this verdict, we need to remember a patient died, and she did so horribly, being unable to draw breath. This should never happen during our watch, ever, and as clinicians, we need to be vigilant.
In summary, protest if you believe justice has been too harsh or unfair, and that nurses may be fearful as a result. But please spare a moment to realize that someone should protest for Ms. Murphey as well. We cannot bring her back, nor can we right the system issues that may have led to her death.
But we should protest for safer systems, for improved staffing, for a need to catch our collective breaths, and a day to work and nurture patients when someone is not constantly on our a**. Only then will nurses be protected from unjust reprisal, from needing to be the lowest common denominator of guilt.
Ms. Goodman is a researcher and consultant in Libertyville, Ill. She disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Biomarker testing gains momentum in NSCLC
Despite Spain’s lack of a national project or standard protocol for biomarker testing, , according to a Spanish national registry study reported at the 2022 European Lung Cancer Congress.
“In recent years we’ve developed drugs that target biomarkers, so it’s important to identify those biomarkers to guide treatment and have an impact on the survival of our patients,” said lead author Virginia Calvo, MD, a medical oncologist with the Puerta de Hierro Majadahonda University Hospital, Madrid.
“If we don’t know our patients’ biomarkers, we can’t treat them with targeted therapies,” she added, noting that the overall survival of lung cancer patients has increased by 15% in the last 10 years, largely because of better therapies such as targeted drugs for advanced stage disease and immunotherapies.
To assess the status of biomarker testing in Spain, Dr. Calvo and colleagues analyzed data from the country’s Thoracic Tumor Registry on 9,239 patients diagnosed with metastatic NSCLC from 2016 to the present, 7,467 (81%) with nonsquamous tumors and 1,772 (19%) with squamous tumors.
They found that 85% of patients with nonsquamous NSCLC and about 53% of those with squamous cancers had undergone biomarker testing. They discovered that 4,115 (44%) of patients tested positive for EGFR, ALK, KRAS, BRAF, ROS1, or PD-L1.
Dr. Calvo attributes the widespread use of biomarker testing and its significant increase in the last 5 years to the growing knowledge and understanding of the disease.
“We are learning more about NSCLC, and I think in the next few years the number of biomarkers are going to grow,” she said.
The study’s findings also highlight the importance of establishing and maintaining cancer registries, Dr. Calvo said, noting that 182 hospitals across Spain and more than 550 experts participate in the Thoracic Tumors Registry, which includes data on patients from every Spanish territory.
“It’s important to collect information on real-life cancer care so that we know what our real situation is and take steps to improve it,” she said.
She anticipates that treatment for NSCLC patients will become increasingly complex in the future with the growing number of different biomarkers and the proportion of patients who test positive for them. “We may need to establish national strategies to implement next generation sequencing so that we can identify different biomarkers and improve the survival of our patients.”
In a press release, Rolf Stahel, MD, president of the European Thoracic Oncology Platform, said that it would be helpful to look at how frequently molecular testing led to patients receiving appropriate targeted treatment.
In the United States, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends biomarker testing for eligible patients with newly diagnosed stage 4 NSCLC, and it can be considered for patients with squamous histology because 5%-10% of these tumors have targetable mutations. “This is because numerous lines of evidence show that patients with stage 4 NSCLC and a targetable mutation, typically have improved overall survival when treated with a targeted therapy,” wrote the authors of the NCCN recommendations.
“For newly diagnosed stage 4 NSCLC, there is always a tension between the need to start therapy versus waiting for molecular results. This is because if a recommended targeted option is identified, it is the optimal first-line therapy. Targeted therapy cannot be given to everyone. Different biomarkers predict response to different agents. This has been well illustrated and it makes testing critically important for patients with NSCLC,” Dara Aisner, MD, PhD, associate professor of pathology with the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, wrote in the NCCN guideline.
The study presented at ELCC was funded by a grant from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program. Dr. Calvo has received fees from Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD and AstraZeneca.
Despite Spain’s lack of a national project or standard protocol for biomarker testing, , according to a Spanish national registry study reported at the 2022 European Lung Cancer Congress.
“In recent years we’ve developed drugs that target biomarkers, so it’s important to identify those biomarkers to guide treatment and have an impact on the survival of our patients,” said lead author Virginia Calvo, MD, a medical oncologist with the Puerta de Hierro Majadahonda University Hospital, Madrid.
“If we don’t know our patients’ biomarkers, we can’t treat them with targeted therapies,” she added, noting that the overall survival of lung cancer patients has increased by 15% in the last 10 years, largely because of better therapies such as targeted drugs for advanced stage disease and immunotherapies.
To assess the status of biomarker testing in Spain, Dr. Calvo and colleagues analyzed data from the country’s Thoracic Tumor Registry on 9,239 patients diagnosed with metastatic NSCLC from 2016 to the present, 7,467 (81%) with nonsquamous tumors and 1,772 (19%) with squamous tumors.
They found that 85% of patients with nonsquamous NSCLC and about 53% of those with squamous cancers had undergone biomarker testing. They discovered that 4,115 (44%) of patients tested positive for EGFR, ALK, KRAS, BRAF, ROS1, or PD-L1.
Dr. Calvo attributes the widespread use of biomarker testing and its significant increase in the last 5 years to the growing knowledge and understanding of the disease.
“We are learning more about NSCLC, and I think in the next few years the number of biomarkers are going to grow,” she said.
The study’s findings also highlight the importance of establishing and maintaining cancer registries, Dr. Calvo said, noting that 182 hospitals across Spain and more than 550 experts participate in the Thoracic Tumors Registry, which includes data on patients from every Spanish territory.
“It’s important to collect information on real-life cancer care so that we know what our real situation is and take steps to improve it,” she said.
She anticipates that treatment for NSCLC patients will become increasingly complex in the future with the growing number of different biomarkers and the proportion of patients who test positive for them. “We may need to establish national strategies to implement next generation sequencing so that we can identify different biomarkers and improve the survival of our patients.”
In a press release, Rolf Stahel, MD, president of the European Thoracic Oncology Platform, said that it would be helpful to look at how frequently molecular testing led to patients receiving appropriate targeted treatment.
In the United States, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends biomarker testing for eligible patients with newly diagnosed stage 4 NSCLC, and it can be considered for patients with squamous histology because 5%-10% of these tumors have targetable mutations. “This is because numerous lines of evidence show that patients with stage 4 NSCLC and a targetable mutation, typically have improved overall survival when treated with a targeted therapy,” wrote the authors of the NCCN recommendations.
“For newly diagnosed stage 4 NSCLC, there is always a tension between the need to start therapy versus waiting for molecular results. This is because if a recommended targeted option is identified, it is the optimal first-line therapy. Targeted therapy cannot be given to everyone. Different biomarkers predict response to different agents. This has been well illustrated and it makes testing critically important for patients with NSCLC,” Dara Aisner, MD, PhD, associate professor of pathology with the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, wrote in the NCCN guideline.
The study presented at ELCC was funded by a grant from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program. Dr. Calvo has received fees from Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD and AstraZeneca.
Despite Spain’s lack of a national project or standard protocol for biomarker testing, , according to a Spanish national registry study reported at the 2022 European Lung Cancer Congress.
“In recent years we’ve developed drugs that target biomarkers, so it’s important to identify those biomarkers to guide treatment and have an impact on the survival of our patients,” said lead author Virginia Calvo, MD, a medical oncologist with the Puerta de Hierro Majadahonda University Hospital, Madrid.
“If we don’t know our patients’ biomarkers, we can’t treat them with targeted therapies,” she added, noting that the overall survival of lung cancer patients has increased by 15% in the last 10 years, largely because of better therapies such as targeted drugs for advanced stage disease and immunotherapies.
To assess the status of biomarker testing in Spain, Dr. Calvo and colleagues analyzed data from the country’s Thoracic Tumor Registry on 9,239 patients diagnosed with metastatic NSCLC from 2016 to the present, 7,467 (81%) with nonsquamous tumors and 1,772 (19%) with squamous tumors.
They found that 85% of patients with nonsquamous NSCLC and about 53% of those with squamous cancers had undergone biomarker testing. They discovered that 4,115 (44%) of patients tested positive for EGFR, ALK, KRAS, BRAF, ROS1, or PD-L1.
Dr. Calvo attributes the widespread use of biomarker testing and its significant increase in the last 5 years to the growing knowledge and understanding of the disease.
“We are learning more about NSCLC, and I think in the next few years the number of biomarkers are going to grow,” she said.
The study’s findings also highlight the importance of establishing and maintaining cancer registries, Dr. Calvo said, noting that 182 hospitals across Spain and more than 550 experts participate in the Thoracic Tumors Registry, which includes data on patients from every Spanish territory.
“It’s important to collect information on real-life cancer care so that we know what our real situation is and take steps to improve it,” she said.
She anticipates that treatment for NSCLC patients will become increasingly complex in the future with the growing number of different biomarkers and the proportion of patients who test positive for them. “We may need to establish national strategies to implement next generation sequencing so that we can identify different biomarkers and improve the survival of our patients.”
In a press release, Rolf Stahel, MD, president of the European Thoracic Oncology Platform, said that it would be helpful to look at how frequently molecular testing led to patients receiving appropriate targeted treatment.
In the United States, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends biomarker testing for eligible patients with newly diagnosed stage 4 NSCLC, and it can be considered for patients with squamous histology because 5%-10% of these tumors have targetable mutations. “This is because numerous lines of evidence show that patients with stage 4 NSCLC and a targetable mutation, typically have improved overall survival when treated with a targeted therapy,” wrote the authors of the NCCN recommendations.
“For newly diagnosed stage 4 NSCLC, there is always a tension between the need to start therapy versus waiting for molecular results. This is because if a recommended targeted option is identified, it is the optimal first-line therapy. Targeted therapy cannot be given to everyone. Different biomarkers predict response to different agents. This has been well illustrated and it makes testing critically important for patients with NSCLC,” Dara Aisner, MD, PhD, associate professor of pathology with the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, wrote in the NCCN guideline.
The study presented at ELCC was funded by a grant from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program. Dr. Calvo has received fees from Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD and AstraZeneca.
FROM ELCC 2022
Young and older athletes show similar arrhythmia patterns with fQRS
The prevalence of exercise-induced arrhythmias in young athletes with fragmented QRS (fQRS) patterns in lead V1 was 27%, similar to that seen in adult athletes, based on data from nearly 700 individuals.
Recent data suggest that fQRS complex in lead V1 (fQRSV1) in healthy athletes may promote arrhythmias in the context of training-induced right ventricular remodeling, but the prevalence and significance in young athletes has not been well studied, Guilia Quinto, MD, of the University of Padova (Italy) said in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
Dr. Quinto and colleagues assessed data from of young athletes on ventricular arrhythmias during exercise tests.
The study population included 684 young athletes with a mean age of 15 years; 64% were male. Baseline data collection included medical history, physical exam, resting ECG, standardized maximum exercise tolerance, and echocardiography evaluation.
The overall prevalence of fQRSV1 was 27%. Individuals with fQRSV1 were significantly less likely than those without fQRSV1 to be female (22% vs. 43%), and to present with a lower resting heart rate (66.98 beats per minute vs. 70.08 beats per minute).
Echocardiographic data showed that individuals with fQRSV1 had significantly different morphological and functional right ventricular characteristics.
Notably, right ventricular end-diastolic diameter was 20.42 mm/m2 among individuals with fQRSV1 and 19.81 mm/m2 in those without, a significant difference (P = .019), Dr. Quinto said. Tricuspid annulus plain systolic excursion also differed significantly; 24.33 mm and 23.75 mm for individuals with and without fQRSV1, respectively (P = .013).
However, the individuals with fQRSV1 showed no increased occurrence of any type of exercise-induced arrhythmias regardless of morphology or complexity, said Dr. Quinto.
The prevalence of common and uncommon arrhythmias among individuals with and without fQRSV1 was 31% versus 34% and 13% versus 11%, respectively; these differences were not significant.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small size, but were strengthened by the review of echocardiographic data by two independent physicians, she said.
The results show that the overall prevalence of fQRSV1 in young athletes is comparable with patterns seen in studies of adult athletes, and no differences in exercise-induced arrhythmias occurred despite differences in right ventricular characteristics, she concluded.
Expanded insight into evaluation
The ECG pattern identified in the current study is often encountered in the evaluation of athletes, but its importance was unknown, Matthew Martinez, MD, a sports cardiologist at the Atlantic Health System in Morristown, N.J., said in an interview.
“Studies of ECG findings in athletes continues to inform us about which findings are important to evaluate. This study furthers our understanding of how to proceed,” and will serve as a guide for additional testing to reduce athlete risk, he said.
Looking ahead, “this study should guide clinicians about additional testing and evaluation when fQRS is present in adolescent athletes compared to adults,” Dr. Martinez noted. However, additional research is needed to determine which is the next best test, and whether the patient requires ongoing surveillance, or whether a single evaluation is sufficient, he said. “Further study should focus on best practices after fQRS is identified and whether outcomes can be linked to this finding.”
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Quinto and Dr. Martinez had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The prevalence of exercise-induced arrhythmias in young athletes with fragmented QRS (fQRS) patterns in lead V1 was 27%, similar to that seen in adult athletes, based on data from nearly 700 individuals.
Recent data suggest that fQRS complex in lead V1 (fQRSV1) in healthy athletes may promote arrhythmias in the context of training-induced right ventricular remodeling, but the prevalence and significance in young athletes has not been well studied, Guilia Quinto, MD, of the University of Padova (Italy) said in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
Dr. Quinto and colleagues assessed data from of young athletes on ventricular arrhythmias during exercise tests.
The study population included 684 young athletes with a mean age of 15 years; 64% were male. Baseline data collection included medical history, physical exam, resting ECG, standardized maximum exercise tolerance, and echocardiography evaluation.
The overall prevalence of fQRSV1 was 27%. Individuals with fQRSV1 were significantly less likely than those without fQRSV1 to be female (22% vs. 43%), and to present with a lower resting heart rate (66.98 beats per minute vs. 70.08 beats per minute).
Echocardiographic data showed that individuals with fQRSV1 had significantly different morphological and functional right ventricular characteristics.
Notably, right ventricular end-diastolic diameter was 20.42 mm/m2 among individuals with fQRSV1 and 19.81 mm/m2 in those without, a significant difference (P = .019), Dr. Quinto said. Tricuspid annulus plain systolic excursion also differed significantly; 24.33 mm and 23.75 mm for individuals with and without fQRSV1, respectively (P = .013).
However, the individuals with fQRSV1 showed no increased occurrence of any type of exercise-induced arrhythmias regardless of morphology or complexity, said Dr. Quinto.
The prevalence of common and uncommon arrhythmias among individuals with and without fQRSV1 was 31% versus 34% and 13% versus 11%, respectively; these differences were not significant.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small size, but were strengthened by the review of echocardiographic data by two independent physicians, she said.
The results show that the overall prevalence of fQRSV1 in young athletes is comparable with patterns seen in studies of adult athletes, and no differences in exercise-induced arrhythmias occurred despite differences in right ventricular characteristics, she concluded.
Expanded insight into evaluation
The ECG pattern identified in the current study is often encountered in the evaluation of athletes, but its importance was unknown, Matthew Martinez, MD, a sports cardiologist at the Atlantic Health System in Morristown, N.J., said in an interview.
“Studies of ECG findings in athletes continues to inform us about which findings are important to evaluate. This study furthers our understanding of how to proceed,” and will serve as a guide for additional testing to reduce athlete risk, he said.
Looking ahead, “this study should guide clinicians about additional testing and evaluation when fQRS is present in adolescent athletes compared to adults,” Dr. Martinez noted. However, additional research is needed to determine which is the next best test, and whether the patient requires ongoing surveillance, or whether a single evaluation is sufficient, he said. “Further study should focus on best practices after fQRS is identified and whether outcomes can be linked to this finding.”
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Quinto and Dr. Martinez had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The prevalence of exercise-induced arrhythmias in young athletes with fragmented QRS (fQRS) patterns in lead V1 was 27%, similar to that seen in adult athletes, based on data from nearly 700 individuals.
Recent data suggest that fQRS complex in lead V1 (fQRSV1) in healthy athletes may promote arrhythmias in the context of training-induced right ventricular remodeling, but the prevalence and significance in young athletes has not been well studied, Guilia Quinto, MD, of the University of Padova (Italy) said in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
Dr. Quinto and colleagues assessed data from of young athletes on ventricular arrhythmias during exercise tests.
The study population included 684 young athletes with a mean age of 15 years; 64% were male. Baseline data collection included medical history, physical exam, resting ECG, standardized maximum exercise tolerance, and echocardiography evaluation.
The overall prevalence of fQRSV1 was 27%. Individuals with fQRSV1 were significantly less likely than those without fQRSV1 to be female (22% vs. 43%), and to present with a lower resting heart rate (66.98 beats per minute vs. 70.08 beats per minute).
Echocardiographic data showed that individuals with fQRSV1 had significantly different morphological and functional right ventricular characteristics.
Notably, right ventricular end-diastolic diameter was 20.42 mm/m2 among individuals with fQRSV1 and 19.81 mm/m2 in those without, a significant difference (P = .019), Dr. Quinto said. Tricuspid annulus plain systolic excursion also differed significantly; 24.33 mm and 23.75 mm for individuals with and without fQRSV1, respectively (P = .013).
However, the individuals with fQRSV1 showed no increased occurrence of any type of exercise-induced arrhythmias regardless of morphology or complexity, said Dr. Quinto.
The prevalence of common and uncommon arrhythmias among individuals with and without fQRSV1 was 31% versus 34% and 13% versus 11%, respectively; these differences were not significant.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small size, but were strengthened by the review of echocardiographic data by two independent physicians, she said.
The results show that the overall prevalence of fQRSV1 in young athletes is comparable with patterns seen in studies of adult athletes, and no differences in exercise-induced arrhythmias occurred despite differences in right ventricular characteristics, she concluded.
Expanded insight into evaluation
The ECG pattern identified in the current study is often encountered in the evaluation of athletes, but its importance was unknown, Matthew Martinez, MD, a sports cardiologist at the Atlantic Health System in Morristown, N.J., said in an interview.
“Studies of ECG findings in athletes continues to inform us about which findings are important to evaluate. This study furthers our understanding of how to proceed,” and will serve as a guide for additional testing to reduce athlete risk, he said.
Looking ahead, “this study should guide clinicians about additional testing and evaluation when fQRS is present in adolescent athletes compared to adults,” Dr. Martinez noted. However, additional research is needed to determine which is the next best test, and whether the patient requires ongoing surveillance, or whether a single evaluation is sufficient, he said. “Further study should focus on best practices after fQRS is identified and whether outcomes can be linked to this finding.”
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Quinto and Dr. Martinez had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ESC PREVENTIVE CARDIOLOGY 2022
Excess weight over lifetime hikes risk for colorectal cancer
Excess weight over a lifetime may play a greater role in a person’s risk for colorectal cancer (CRC) than previously thought, according to new research.
In their paper published online March 17 in JAMA Oncology, the authors liken the cumulative effects of a lifetime with overweight or obesity to the increased risk of cancer the more people smoke over time.
This population-based, case-control study was led by Xiangwei Li, MSc, of the division of clinical epidemiology and aging research at the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg.
It looked at height and self-reported weight documented in 10-year increments starting at age 20 years up to the current age for 5,635 people with CRC compared with 4,515 people in a control group.
Odds for colorectal cancer increased substantially over the decades when people carried the excess weight long term compared with participants who remained within the normal weight range during the period.
Coauthor Hermann Brenner, MD, MPH, a colleague in Li’s division at the German Cancer Research Center, said in an interview that a key message in the research is that “overweight and obesity are likely to increase the risk of colorectal cancer more strongly than suggested by previous studies that typically had considered body weight only at a single point of time.”
The researchers used a measure of weighted number of years lived with overweight or obesity (WYOs) determined by multiplying excess body mass index by number of years the person carried the excess weight.
They found a link between WYOs and CRC risk, with adjusted odds ratios (ORs) increasing from 1.25 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.09-1.44) to 2.54 (95% CI, 2.24-2.89) from the first to the fourth quartile of WYOs, compared with people who stayed within normal weight parameters.
The odds went up substantially the longer the time carrying the excess weight.
“Each SD increment in WYOs was associated with an increase of CRC risk by 55% (adjusted OR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.46-1.64),” the authors wrote. “This OR was higher than the OR per SD increase of excess body mass index at any single point of time, which ranged from 1.04 (95% CI, 0.93-1.16) to 1.27 (95% CI 1.16-1.39).”
Dr. Brenner said that although this study focused on colorectal cancer, “the same is likely to apply for other cancers and other chronic diseases.”
Prevention of overweight and obesity to reduce burden of cancer and other chronic diseases “should become a public health priority,” he said.
Preventing overweight in childhood is important
Overweight and obesity increasingly are starting in childhood, he noted, and may be a lifelong burden.
Therefore, “efforts to prevent their development in childhood, adolescence, and young adulthood are particularly important,” Dr. Brenner said.
The average age of the patients was 68 years in both the CRC and control groups. There were more men than women in both groups: 59.7% were men in the CRC group and 61.1% were men in the control group.
“Our proposed concept of WYOs is comparable to the concept of pack-years in that WYOs can be considered a weighted measure of years lived with the exposure, with weights reflecting the intensity of exposure,” the authors wrote.
Study helps confirm what is becoming more clear to researchers
Kimmie Ng, MD, MPH, a professor at Harvard Medical School and oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, both in Boston, said in an interview that the study helps confirm what is becoming more clear to researchers.
“We do think that exposures over the life course are the ones that will be most strongly contributing to a risk of colorectal cancer as an adult,” she said. “With obesity, what we think is happening is that it’s setting up this milieu of chronic inflammation and insulin resistance and we know those two factors can lead to higher rates of colorectal cancer development and increased tumor growth.”
She said the ideal, but impractical, way to do the study would be to follow healthy people from childhood and document their weight over a lifetime. In this case-control study, people were asked to recall their weight at different time periods, which is a limitation and could lead to recall bias.
But the study is important, Dr. Ng said, and it adds convincing evidence that addressing the link between excess weight and CRC and chronic diseases should be a public health priority. “With the recent rise in young-onset colorectal cancer since the 1990s there has been a lot of interest in looking at whether obesity is a major contributor to that rising trend,” Dr. Ng noted. “If obesity is truly linked to colorectal cancer, these rising rates of obesity are very worrisome for potentially leading to more colorectal cancers in young adulthood and beyond.“
The study authors and Dr. Ng report no relevant financial relationships.
The new research was funded by the German Research Council, the Interdisciplinary Research Program of the National Center for Tumor Diseases, Germany, and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
Help your patients understand colorectal cancer prevention and screening options by sharing AGA's patient education from the GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/CRC
Excess weight over a lifetime may play a greater role in a person’s risk for colorectal cancer (CRC) than previously thought, according to new research.
In their paper published online March 17 in JAMA Oncology, the authors liken the cumulative effects of a lifetime with overweight or obesity to the increased risk of cancer the more people smoke over time.
This population-based, case-control study was led by Xiangwei Li, MSc, of the division of clinical epidemiology and aging research at the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg.
It looked at height and self-reported weight documented in 10-year increments starting at age 20 years up to the current age for 5,635 people with CRC compared with 4,515 people in a control group.
Odds for colorectal cancer increased substantially over the decades when people carried the excess weight long term compared with participants who remained within the normal weight range during the period.
Coauthor Hermann Brenner, MD, MPH, a colleague in Li’s division at the German Cancer Research Center, said in an interview that a key message in the research is that “overweight and obesity are likely to increase the risk of colorectal cancer more strongly than suggested by previous studies that typically had considered body weight only at a single point of time.”
The researchers used a measure of weighted number of years lived with overweight or obesity (WYOs) determined by multiplying excess body mass index by number of years the person carried the excess weight.
They found a link between WYOs and CRC risk, with adjusted odds ratios (ORs) increasing from 1.25 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.09-1.44) to 2.54 (95% CI, 2.24-2.89) from the first to the fourth quartile of WYOs, compared with people who stayed within normal weight parameters.
The odds went up substantially the longer the time carrying the excess weight.
“Each SD increment in WYOs was associated with an increase of CRC risk by 55% (adjusted OR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.46-1.64),” the authors wrote. “This OR was higher than the OR per SD increase of excess body mass index at any single point of time, which ranged from 1.04 (95% CI, 0.93-1.16) to 1.27 (95% CI 1.16-1.39).”
Dr. Brenner said that although this study focused on colorectal cancer, “the same is likely to apply for other cancers and other chronic diseases.”
Prevention of overweight and obesity to reduce burden of cancer and other chronic diseases “should become a public health priority,” he said.
Preventing overweight in childhood is important
Overweight and obesity increasingly are starting in childhood, he noted, and may be a lifelong burden.
Therefore, “efforts to prevent their development in childhood, adolescence, and young adulthood are particularly important,” Dr. Brenner said.
The average age of the patients was 68 years in both the CRC and control groups. There were more men than women in both groups: 59.7% were men in the CRC group and 61.1% were men in the control group.
“Our proposed concept of WYOs is comparable to the concept of pack-years in that WYOs can be considered a weighted measure of years lived with the exposure, with weights reflecting the intensity of exposure,” the authors wrote.
Study helps confirm what is becoming more clear to researchers
Kimmie Ng, MD, MPH, a professor at Harvard Medical School and oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, both in Boston, said in an interview that the study helps confirm what is becoming more clear to researchers.
“We do think that exposures over the life course are the ones that will be most strongly contributing to a risk of colorectal cancer as an adult,” she said. “With obesity, what we think is happening is that it’s setting up this milieu of chronic inflammation and insulin resistance and we know those two factors can lead to higher rates of colorectal cancer development and increased tumor growth.”
She said the ideal, but impractical, way to do the study would be to follow healthy people from childhood and document their weight over a lifetime. In this case-control study, people were asked to recall their weight at different time periods, which is a limitation and could lead to recall bias.
But the study is important, Dr. Ng said, and it adds convincing evidence that addressing the link between excess weight and CRC and chronic diseases should be a public health priority. “With the recent rise in young-onset colorectal cancer since the 1990s there has been a lot of interest in looking at whether obesity is a major contributor to that rising trend,” Dr. Ng noted. “If obesity is truly linked to colorectal cancer, these rising rates of obesity are very worrisome for potentially leading to more colorectal cancers in young adulthood and beyond.“
The study authors and Dr. Ng report no relevant financial relationships.
The new research was funded by the German Research Council, the Interdisciplinary Research Program of the National Center for Tumor Diseases, Germany, and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
Help your patients understand colorectal cancer prevention and screening options by sharing AGA's patient education from the GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/CRC
Excess weight over a lifetime may play a greater role in a person’s risk for colorectal cancer (CRC) than previously thought, according to new research.
In their paper published online March 17 in JAMA Oncology, the authors liken the cumulative effects of a lifetime with overweight or obesity to the increased risk of cancer the more people smoke over time.
This population-based, case-control study was led by Xiangwei Li, MSc, of the division of clinical epidemiology and aging research at the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg.
It looked at height and self-reported weight documented in 10-year increments starting at age 20 years up to the current age for 5,635 people with CRC compared with 4,515 people in a control group.
Odds for colorectal cancer increased substantially over the decades when people carried the excess weight long term compared with participants who remained within the normal weight range during the period.
Coauthor Hermann Brenner, MD, MPH, a colleague in Li’s division at the German Cancer Research Center, said in an interview that a key message in the research is that “overweight and obesity are likely to increase the risk of colorectal cancer more strongly than suggested by previous studies that typically had considered body weight only at a single point of time.”
The researchers used a measure of weighted number of years lived with overweight or obesity (WYOs) determined by multiplying excess body mass index by number of years the person carried the excess weight.
They found a link between WYOs and CRC risk, with adjusted odds ratios (ORs) increasing from 1.25 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.09-1.44) to 2.54 (95% CI, 2.24-2.89) from the first to the fourth quartile of WYOs, compared with people who stayed within normal weight parameters.
The odds went up substantially the longer the time carrying the excess weight.
“Each SD increment in WYOs was associated with an increase of CRC risk by 55% (adjusted OR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.46-1.64),” the authors wrote. “This OR was higher than the OR per SD increase of excess body mass index at any single point of time, which ranged from 1.04 (95% CI, 0.93-1.16) to 1.27 (95% CI 1.16-1.39).”
Dr. Brenner said that although this study focused on colorectal cancer, “the same is likely to apply for other cancers and other chronic diseases.”
Prevention of overweight and obesity to reduce burden of cancer and other chronic diseases “should become a public health priority,” he said.
Preventing overweight in childhood is important
Overweight and obesity increasingly are starting in childhood, he noted, and may be a lifelong burden.
Therefore, “efforts to prevent their development in childhood, adolescence, and young adulthood are particularly important,” Dr. Brenner said.
The average age of the patients was 68 years in both the CRC and control groups. There were more men than women in both groups: 59.7% were men in the CRC group and 61.1% were men in the control group.
“Our proposed concept of WYOs is comparable to the concept of pack-years in that WYOs can be considered a weighted measure of years lived with the exposure, with weights reflecting the intensity of exposure,” the authors wrote.
Study helps confirm what is becoming more clear to researchers
Kimmie Ng, MD, MPH, a professor at Harvard Medical School and oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, both in Boston, said in an interview that the study helps confirm what is becoming more clear to researchers.
“We do think that exposures over the life course are the ones that will be most strongly contributing to a risk of colorectal cancer as an adult,” she said. “With obesity, what we think is happening is that it’s setting up this milieu of chronic inflammation and insulin resistance and we know those two factors can lead to higher rates of colorectal cancer development and increased tumor growth.”
She said the ideal, but impractical, way to do the study would be to follow healthy people from childhood and document their weight over a lifetime. In this case-control study, people were asked to recall their weight at different time periods, which is a limitation and could lead to recall bias.
But the study is important, Dr. Ng said, and it adds convincing evidence that addressing the link between excess weight and CRC and chronic diseases should be a public health priority. “With the recent rise in young-onset colorectal cancer since the 1990s there has been a lot of interest in looking at whether obesity is a major contributor to that rising trend,” Dr. Ng noted. “If obesity is truly linked to colorectal cancer, these rising rates of obesity are very worrisome for potentially leading to more colorectal cancers in young adulthood and beyond.“
The study authors and Dr. Ng report no relevant financial relationships.
The new research was funded by the German Research Council, the Interdisciplinary Research Program of the National Center for Tumor Diseases, Germany, and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
Help your patients understand colorectal cancer prevention and screening options by sharing AGA's patient education from the GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/CRC
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Diet’s impact on the microbiome: It’s real, and broad
WASHINGTON – – including amino acid metabolites – that may modify health, said Gary D. Wu, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
During the 2022 Gut Microbiota for Health World Summit, organized by the American Gastroenterological Association and the European Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, Dr. Wu led a plenary session in which the impact of diet on the microbiome was characterized as important, rapid, personalized, likely modest relative to other contributing ecological factors, influenced by the process of cooking, and exceedingly difficult to tease apart and characterize in human studies.
In a human study published in 2021, Dr. Wu and coinvestigators performed a controlled feeding experiment with 30 healthy volunteers, randomizing them to several weeks of a vegan diet, an omnivore diet (a typical American diet), and an exclusive enteral nutrition diet (EEN) devoid of dietary fiber.
They compared the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiome during three phases: an initial dietary phase (days 1-5), a purge phase in which antibiotics and polyethylene glycol were administered to transiently reduce bacterial load in the gut (days 6-8), and a recovery phase (days 9-15).
Diversity of the gut microbiota recovered from the purge phase in both vegans and omnivores, but not in those receiving EEN. “The EEN diet was having a profound effect on the [short-term] recovery of microbiota,” said Dr. Wu, the Ferdinand G. Weisbrod Professor in Gastroenterology, in describing the Food And Resulting Microbial Metabolites study.
Using genetic sequencing, microbial culturing, and bioinformatics processing, the researchers also determined that EEN subsequently led to metabolites that were distinct from omnivores and vegans. Unexpectedly, bacterial metabolites of amino acid origin – not only carbohydrate origin – were altered in the EEN group, suggesting a broad impact of dietary fiber on the bacterial metabolome. EEN-induced alterations in the microbiome and metabolome resolved after the study period, he noted.
In other words, “depriving or supplying the gut microbiome with one dietary component (i.e., fiber) can directly impact metabolites of an unrelated portion of the diet (i.e., amino acids) via the induction of specific gut bacterial taxa,” Dr. Wu and colleagues wrote.
Clinically, the results as a whole suggest that the combination of antibiotics with EEN may be less effective in patients with Crohn’s disease than EEN alone, and can be potentially harmful, they said.
At the meeting, sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association and the European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility, Dr. Wu said that, for patients in the ICU on EEN treatment and antibiotics, “we do need to think carefully about microbiota reconstitution because it could have a very significant effect not only on short-chain fatty acid metabolites but on amino acid metabolites that may be good or bad in the setting of disease.”
The scientific rationale for the effectiveness of EEN for IBD is still not well understood, he noted. “All I can say is that EEN works in IBD, but there are aspects about the microbiota and diet and IBD that we don’t understand.”
Dietary impact through the immigration lens
In another presentation, Dan Knights, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, described his lab’s findings on the association of U.S. immigration with loss of gut microbiome diversity, and the role of diet.
As part of the Immigration Microbiome Project reported several years ago, his team collected stool, dietary recalls, and anthropometrics from 550 Hmong and Karen individuals living in Thailand and the United States, including first- and second-generation immigrants, as well as some U.S.-born European American individuals. They found that the gut microbiome of immigrants changed within months of arriving in the United States, and that immigration status had a stronger effect on the microbiome than obesity status.
“By the time people were in their second generation, their microbiomes were roughly on the same order of diversity as U.S. controls,” said Dr. Knights, associate professor in the Biotechnology Institute and the department of computer science and engineering.
Dietary changes only partly explained microbiome variation, however. “By the second generation, the microbiome tended to be fully Westernized, but the diet was only partly Westernized,” he said. “Diet is only part of the story.”
Other research from his lab, including one study that performed daily fecal shotgun sequencing on 34 people, has found that effects of diet on the microbiome are likely to be observable within days, and that microbial responses to food are highly personalized. Diet appears to explain about 6% of the daily microbiome variation within an individual, and “an average diet explains about 4% of microbiome variation between people,” Dr. Knights said.
The impact of cooking
“The gut microbiota responds to food and to its form,” said Rachel N. Carmody, PhD, of the department of human evolutionary biology at Harvard University, Cambridge, during the plenary session. Her research has shown that, in mice, a plant diet served raw versus cooked quickly reshaped the gut microbiome and disrupted gut microbial physiology. Notably, shifts in gut microbiota modulated host energy status – one of the many areas that begs further research.
The effects of cooking have also been detectable in human pilot studies. “We saw different changes in the microbiome when [study participants] were eating the same plant items either raw or cooked,” she said. “Some microbes were affected only on the raw diet, other were affected only on the cooked diet.”
Other research in animal models and humans has demonstrated a significant amount of plasticity in the microbiome in response to diet. “In mice you get the microbiome signatures to shift within 24 hours by feeding them a new diet,” Dr. Carmody said.
In an interview about the plenary session, Eugene B. Chang, MD, the Martin Boyer Distinguished Professor of Medicine at the University of Chicago, said that he was struck both by the resiliency of individual gut microbiomes overall and by findings that, “in animal models where conditions and diets can be carefully controlled, diet and environment are major drivers of gut microbial membership and function.”
Dr. Chang coled a separate workshop on “defining a healthy gut microbiome” – a task that he said remains “a challenge [and is not yet] resolved, at least with general consensus.”
Dr. Chang, Dr. Wu, and Dr. Carmody reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Knights disclosed that he is a paid adviser to Diversigen, a company involved with the commercialization of microbiome analysis.
The 2022 Gut Microbiota for Health World Summit was supported by sponsorships from Danone, Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Aimmune Therapeutics and Seres Therapeutics, Sanofi, and Intrinsic Medicine Inc. with additional support from educational grants provided by Ferring Pharmaceuticals and Salix Pharmaceuticals.
Through the AGA Center for Gut Microbiome Research and Education, AGA is committed to keeping you up-to-speed on the latest news, research and policy updates related to the gut microbiome: www.gastro.org/
WASHINGTON – – including amino acid metabolites – that may modify health, said Gary D. Wu, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
During the 2022 Gut Microbiota for Health World Summit, organized by the American Gastroenterological Association and the European Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, Dr. Wu led a plenary session in which the impact of diet on the microbiome was characterized as important, rapid, personalized, likely modest relative to other contributing ecological factors, influenced by the process of cooking, and exceedingly difficult to tease apart and characterize in human studies.
In a human study published in 2021, Dr. Wu and coinvestigators performed a controlled feeding experiment with 30 healthy volunteers, randomizing them to several weeks of a vegan diet, an omnivore diet (a typical American diet), and an exclusive enteral nutrition diet (EEN) devoid of dietary fiber.
They compared the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiome during three phases: an initial dietary phase (days 1-5), a purge phase in which antibiotics and polyethylene glycol were administered to transiently reduce bacterial load in the gut (days 6-8), and a recovery phase (days 9-15).
Diversity of the gut microbiota recovered from the purge phase in both vegans and omnivores, but not in those receiving EEN. “The EEN diet was having a profound effect on the [short-term] recovery of microbiota,” said Dr. Wu, the Ferdinand G. Weisbrod Professor in Gastroenterology, in describing the Food And Resulting Microbial Metabolites study.
Using genetic sequencing, microbial culturing, and bioinformatics processing, the researchers also determined that EEN subsequently led to metabolites that were distinct from omnivores and vegans. Unexpectedly, bacterial metabolites of amino acid origin – not only carbohydrate origin – were altered in the EEN group, suggesting a broad impact of dietary fiber on the bacterial metabolome. EEN-induced alterations in the microbiome and metabolome resolved after the study period, he noted.
In other words, “depriving or supplying the gut microbiome with one dietary component (i.e., fiber) can directly impact metabolites of an unrelated portion of the diet (i.e., amino acids) via the induction of specific gut bacterial taxa,” Dr. Wu and colleagues wrote.
Clinically, the results as a whole suggest that the combination of antibiotics with EEN may be less effective in patients with Crohn’s disease than EEN alone, and can be potentially harmful, they said.
At the meeting, sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association and the European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility, Dr. Wu said that, for patients in the ICU on EEN treatment and antibiotics, “we do need to think carefully about microbiota reconstitution because it could have a very significant effect not only on short-chain fatty acid metabolites but on amino acid metabolites that may be good or bad in the setting of disease.”
The scientific rationale for the effectiveness of EEN for IBD is still not well understood, he noted. “All I can say is that EEN works in IBD, but there are aspects about the microbiota and diet and IBD that we don’t understand.”
Dietary impact through the immigration lens
In another presentation, Dan Knights, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, described his lab’s findings on the association of U.S. immigration with loss of gut microbiome diversity, and the role of diet.
As part of the Immigration Microbiome Project reported several years ago, his team collected stool, dietary recalls, and anthropometrics from 550 Hmong and Karen individuals living in Thailand and the United States, including first- and second-generation immigrants, as well as some U.S.-born European American individuals. They found that the gut microbiome of immigrants changed within months of arriving in the United States, and that immigration status had a stronger effect on the microbiome than obesity status.
“By the time people were in their second generation, their microbiomes were roughly on the same order of diversity as U.S. controls,” said Dr. Knights, associate professor in the Biotechnology Institute and the department of computer science and engineering.
Dietary changes only partly explained microbiome variation, however. “By the second generation, the microbiome tended to be fully Westernized, but the diet was only partly Westernized,” he said. “Diet is only part of the story.”
Other research from his lab, including one study that performed daily fecal shotgun sequencing on 34 people, has found that effects of diet on the microbiome are likely to be observable within days, and that microbial responses to food are highly personalized. Diet appears to explain about 6% of the daily microbiome variation within an individual, and “an average diet explains about 4% of microbiome variation between people,” Dr. Knights said.
The impact of cooking
“The gut microbiota responds to food and to its form,” said Rachel N. Carmody, PhD, of the department of human evolutionary biology at Harvard University, Cambridge, during the plenary session. Her research has shown that, in mice, a plant diet served raw versus cooked quickly reshaped the gut microbiome and disrupted gut microbial physiology. Notably, shifts in gut microbiota modulated host energy status – one of the many areas that begs further research.
The effects of cooking have also been detectable in human pilot studies. “We saw different changes in the microbiome when [study participants] were eating the same plant items either raw or cooked,” she said. “Some microbes were affected only on the raw diet, other were affected only on the cooked diet.”
Other research in animal models and humans has demonstrated a significant amount of plasticity in the microbiome in response to diet. “In mice you get the microbiome signatures to shift within 24 hours by feeding them a new diet,” Dr. Carmody said.
In an interview about the plenary session, Eugene B. Chang, MD, the Martin Boyer Distinguished Professor of Medicine at the University of Chicago, said that he was struck both by the resiliency of individual gut microbiomes overall and by findings that, “in animal models where conditions and diets can be carefully controlled, diet and environment are major drivers of gut microbial membership and function.”
Dr. Chang coled a separate workshop on “defining a healthy gut microbiome” – a task that he said remains “a challenge [and is not yet] resolved, at least with general consensus.”
Dr. Chang, Dr. Wu, and Dr. Carmody reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Knights disclosed that he is a paid adviser to Diversigen, a company involved with the commercialization of microbiome analysis.
The 2022 Gut Microbiota for Health World Summit was supported by sponsorships from Danone, Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Aimmune Therapeutics and Seres Therapeutics, Sanofi, and Intrinsic Medicine Inc. with additional support from educational grants provided by Ferring Pharmaceuticals and Salix Pharmaceuticals.
Through the AGA Center for Gut Microbiome Research and Education, AGA is committed to keeping you up-to-speed on the latest news, research and policy updates related to the gut microbiome: www.gastro.org/
WASHINGTON – – including amino acid metabolites – that may modify health, said Gary D. Wu, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
During the 2022 Gut Microbiota for Health World Summit, organized by the American Gastroenterological Association and the European Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, Dr. Wu led a plenary session in which the impact of diet on the microbiome was characterized as important, rapid, personalized, likely modest relative to other contributing ecological factors, influenced by the process of cooking, and exceedingly difficult to tease apart and characterize in human studies.
In a human study published in 2021, Dr. Wu and coinvestigators performed a controlled feeding experiment with 30 healthy volunteers, randomizing them to several weeks of a vegan diet, an omnivore diet (a typical American diet), and an exclusive enteral nutrition diet (EEN) devoid of dietary fiber.
They compared the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiome during three phases: an initial dietary phase (days 1-5), a purge phase in which antibiotics and polyethylene glycol were administered to transiently reduce bacterial load in the gut (days 6-8), and a recovery phase (days 9-15).
Diversity of the gut microbiota recovered from the purge phase in both vegans and omnivores, but not in those receiving EEN. “The EEN diet was having a profound effect on the [short-term] recovery of microbiota,” said Dr. Wu, the Ferdinand G. Weisbrod Professor in Gastroenterology, in describing the Food And Resulting Microbial Metabolites study.
Using genetic sequencing, microbial culturing, and bioinformatics processing, the researchers also determined that EEN subsequently led to metabolites that were distinct from omnivores and vegans. Unexpectedly, bacterial metabolites of amino acid origin – not only carbohydrate origin – were altered in the EEN group, suggesting a broad impact of dietary fiber on the bacterial metabolome. EEN-induced alterations in the microbiome and metabolome resolved after the study period, he noted.
In other words, “depriving or supplying the gut microbiome with one dietary component (i.e., fiber) can directly impact metabolites of an unrelated portion of the diet (i.e., amino acids) via the induction of specific gut bacterial taxa,” Dr. Wu and colleagues wrote.
Clinically, the results as a whole suggest that the combination of antibiotics with EEN may be less effective in patients with Crohn’s disease than EEN alone, and can be potentially harmful, they said.
At the meeting, sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association and the European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility, Dr. Wu said that, for patients in the ICU on EEN treatment and antibiotics, “we do need to think carefully about microbiota reconstitution because it could have a very significant effect not only on short-chain fatty acid metabolites but on amino acid metabolites that may be good or bad in the setting of disease.”
The scientific rationale for the effectiveness of EEN for IBD is still not well understood, he noted. “All I can say is that EEN works in IBD, but there are aspects about the microbiota and diet and IBD that we don’t understand.”
Dietary impact through the immigration lens
In another presentation, Dan Knights, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, described his lab’s findings on the association of U.S. immigration with loss of gut microbiome diversity, and the role of diet.
As part of the Immigration Microbiome Project reported several years ago, his team collected stool, dietary recalls, and anthropometrics from 550 Hmong and Karen individuals living in Thailand and the United States, including first- and second-generation immigrants, as well as some U.S.-born European American individuals. They found that the gut microbiome of immigrants changed within months of arriving in the United States, and that immigration status had a stronger effect on the microbiome than obesity status.
“By the time people were in their second generation, their microbiomes were roughly on the same order of diversity as U.S. controls,” said Dr. Knights, associate professor in the Biotechnology Institute and the department of computer science and engineering.
Dietary changes only partly explained microbiome variation, however. “By the second generation, the microbiome tended to be fully Westernized, but the diet was only partly Westernized,” he said. “Diet is only part of the story.”
Other research from his lab, including one study that performed daily fecal shotgun sequencing on 34 people, has found that effects of diet on the microbiome are likely to be observable within days, and that microbial responses to food are highly personalized. Diet appears to explain about 6% of the daily microbiome variation within an individual, and “an average diet explains about 4% of microbiome variation between people,” Dr. Knights said.
The impact of cooking
“The gut microbiota responds to food and to its form,” said Rachel N. Carmody, PhD, of the department of human evolutionary biology at Harvard University, Cambridge, during the plenary session. Her research has shown that, in mice, a plant diet served raw versus cooked quickly reshaped the gut microbiome and disrupted gut microbial physiology. Notably, shifts in gut microbiota modulated host energy status – one of the many areas that begs further research.
The effects of cooking have also been detectable in human pilot studies. “We saw different changes in the microbiome when [study participants] were eating the same plant items either raw or cooked,” she said. “Some microbes were affected only on the raw diet, other were affected only on the cooked diet.”
Other research in animal models and humans has demonstrated a significant amount of plasticity in the microbiome in response to diet. “In mice you get the microbiome signatures to shift within 24 hours by feeding them a new diet,” Dr. Carmody said.
In an interview about the plenary session, Eugene B. Chang, MD, the Martin Boyer Distinguished Professor of Medicine at the University of Chicago, said that he was struck both by the resiliency of individual gut microbiomes overall and by findings that, “in animal models where conditions and diets can be carefully controlled, diet and environment are major drivers of gut microbial membership and function.”
Dr. Chang coled a separate workshop on “defining a healthy gut microbiome” – a task that he said remains “a challenge [and is not yet] resolved, at least with general consensus.”
Dr. Chang, Dr. Wu, and Dr. Carmody reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Knights disclosed that he is a paid adviser to Diversigen, a company involved with the commercialization of microbiome analysis.
The 2022 Gut Microbiota for Health World Summit was supported by sponsorships from Danone, Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Aimmune Therapeutics and Seres Therapeutics, Sanofi, and Intrinsic Medicine Inc. with additional support from educational grants provided by Ferring Pharmaceuticals and Salix Pharmaceuticals.
Through the AGA Center for Gut Microbiome Research and Education, AGA is committed to keeping you up-to-speed on the latest news, research and policy updates related to the gut microbiome: www.gastro.org/
AT GMFH 2022
30% of COVID patients in study developed long COVID
University of California, Los Angeles, researchers said in a study published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
The UCLA researchers studied 1,038 people enrolled in the UCLA COVID Ambulatory Program between April 2020 and February 2021 and found that 309 developed long COVID.
A long-COVID diagnosis came if a patient answering a questionnaire reported persistent symptoms 60-90 days after they were infected or hospitalized. The most persistent symptoms were fatigue (31%) and shortness of breath (15%) in hospitalized participants. Among outpatients, 16% reported losing sense of smell.
The study’s findings differ from earlier research. The University of California, Davis, for example, estimated that 10% of COVID-19 patients develop long-haul symptoms. A 2021 study from Penn State University found that more than half of worldwide COVID-19 patients would develop long COVID.
Part of the discrepancy can blamed on the fact there is no official, widely accepted definition of long COVID. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has said it means patients who experience “new, returning, or ongoing health problems 4 or more weeks after an initial infection” the coronavirus. The UCLA study, meanwhile, included patients still having symptoms 60-90 days after infection.
Still, the UCLA research team looked at demographics and clinical characteristics in an attempt to develop effective treatments.
People with a history of hospitalization, diabetes, and higher body mass index were most likely to develop long COVID, the researchers said. The kind of insurance the patients had also seemed to be a factor, though the researchers didn’t offer a reason why.
“Surprisingly, patients with commercial insurance had double the likelihood of developing [long COVID] compared to patients with Medicaid,” they wrote. “This association will be important to explore further to understand if insurance status in this group is representing unmeasured demographic factors or exposures.”
Older age and socioeconomic status were not associated with long COVID in the study – a surprise because those characteristics are often linked with severe illness and higher risk of death from COVID-19.
Weaknesses in the study included the subjective nature of how patients rated their symptoms and the limited number of symptoms evaluated.
“This study illustrates the need to follow diverse patient populations ... to understand the long COVID disease trajectory and evaluate how individual factors such as preexisting comorbidities, sociodemographic factors, vaccination status and virus variant type affect type and persistence of long COVID symptoms,” said Sun Yoo, MD, health sciences assistant clinical professor at UCLA.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
University of California, Los Angeles, researchers said in a study published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
The UCLA researchers studied 1,038 people enrolled in the UCLA COVID Ambulatory Program between April 2020 and February 2021 and found that 309 developed long COVID.
A long-COVID diagnosis came if a patient answering a questionnaire reported persistent symptoms 60-90 days after they were infected or hospitalized. The most persistent symptoms were fatigue (31%) and shortness of breath (15%) in hospitalized participants. Among outpatients, 16% reported losing sense of smell.
The study’s findings differ from earlier research. The University of California, Davis, for example, estimated that 10% of COVID-19 patients develop long-haul symptoms. A 2021 study from Penn State University found that more than half of worldwide COVID-19 patients would develop long COVID.
Part of the discrepancy can blamed on the fact there is no official, widely accepted definition of long COVID. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has said it means patients who experience “new, returning, or ongoing health problems 4 or more weeks after an initial infection” the coronavirus. The UCLA study, meanwhile, included patients still having symptoms 60-90 days after infection.
Still, the UCLA research team looked at demographics and clinical characteristics in an attempt to develop effective treatments.
People with a history of hospitalization, diabetes, and higher body mass index were most likely to develop long COVID, the researchers said. The kind of insurance the patients had also seemed to be a factor, though the researchers didn’t offer a reason why.
“Surprisingly, patients with commercial insurance had double the likelihood of developing [long COVID] compared to patients with Medicaid,” they wrote. “This association will be important to explore further to understand if insurance status in this group is representing unmeasured demographic factors or exposures.”
Older age and socioeconomic status were not associated with long COVID in the study – a surprise because those characteristics are often linked with severe illness and higher risk of death from COVID-19.
Weaknesses in the study included the subjective nature of how patients rated their symptoms and the limited number of symptoms evaluated.
“This study illustrates the need to follow diverse patient populations ... to understand the long COVID disease trajectory and evaluate how individual factors such as preexisting comorbidities, sociodemographic factors, vaccination status and virus variant type affect type and persistence of long COVID symptoms,” said Sun Yoo, MD, health sciences assistant clinical professor at UCLA.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
University of California, Los Angeles, researchers said in a study published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
The UCLA researchers studied 1,038 people enrolled in the UCLA COVID Ambulatory Program between April 2020 and February 2021 and found that 309 developed long COVID.
A long-COVID diagnosis came if a patient answering a questionnaire reported persistent symptoms 60-90 days after they were infected or hospitalized. The most persistent symptoms were fatigue (31%) and shortness of breath (15%) in hospitalized participants. Among outpatients, 16% reported losing sense of smell.
The study’s findings differ from earlier research. The University of California, Davis, for example, estimated that 10% of COVID-19 patients develop long-haul symptoms. A 2021 study from Penn State University found that more than half of worldwide COVID-19 patients would develop long COVID.
Part of the discrepancy can blamed on the fact there is no official, widely accepted definition of long COVID. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has said it means patients who experience “new, returning, or ongoing health problems 4 or more weeks after an initial infection” the coronavirus. The UCLA study, meanwhile, included patients still having symptoms 60-90 days after infection.
Still, the UCLA research team looked at demographics and clinical characteristics in an attempt to develop effective treatments.
People with a history of hospitalization, diabetes, and higher body mass index were most likely to develop long COVID, the researchers said. The kind of insurance the patients had also seemed to be a factor, though the researchers didn’t offer a reason why.
“Surprisingly, patients with commercial insurance had double the likelihood of developing [long COVID] compared to patients with Medicaid,” they wrote. “This association will be important to explore further to understand if insurance status in this group is representing unmeasured demographic factors or exposures.”
Older age and socioeconomic status were not associated with long COVID in the study – a surprise because those characteristics are often linked with severe illness and higher risk of death from COVID-19.
Weaknesses in the study included the subjective nature of how patients rated their symptoms and the limited number of symptoms evaluated.
“This study illustrates the need to follow diverse patient populations ... to understand the long COVID disease trajectory and evaluate how individual factors such as preexisting comorbidities, sociodemographic factors, vaccination status and virus variant type affect type and persistence of long COVID symptoms,” said Sun Yoo, MD, health sciences assistant clinical professor at UCLA.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE