User login
Social determinants of health may drive CVD risk in Black Americans
Investigators analyzed 20 years of data on over 50,500 U.S. adults drawn from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) and found that, in the overall population, body mass index and hemoglobin A1c were significantly increased between 1999 and 2018, while serum total cholesterol and cigarette smoking were significantly decreased. Mean systolic blood pressure decreased between 1999 and 2010, but then increased after 2010.
The mean age- and sex-adjusted estimated 10-year risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) was consistently higher in Black participants vs. White participants, but the difference was attenuated after further adjusting for education, income, home ownership, employment, health insurance, and access to health care.
“These findings are helpful to guide the development of national public health policies for targeted interventions aimed at eliminating health disparities,” Jiang He, MD, PhD, Joseph S. Copes Chair and professor of epidemiology, Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, New Orleans, said in an interview.
“Interventions on social determinants of cardiovascular health should be tested in rigorous designed intervention trials,” said Dr. He, director of the Tulane University Translational Science Institute.
The study was published online Oct. 5 in JAMA.
‘Flattened’ CVD mortality?
Recent data show that the CVD mortality rate flattened, while the total number of cardiovascular deaths increased in the U.S. general population from 2010 to 2018, “but the reasons for this deceleration in the decline of CVD mortality are not entirely understood,” Dr. He said.
Moreover, “racial and ethnic differences in CVD mortality persist in the U.S. general population [but] the secular trends of cardiovascular risk factors among U.S. subpopulations with various racial and ethnic backgrounds and socioeconomic status are [also] not well understood,” he added. The effects of social determinants of health, such as education, income, home ownership, employment, health insurance, and access to health care on racial/ethnic differences in CVD risk, “are not well documented.”
To investigate these questions, the researchers drew on data from NHANES, a series of cross-sectional surveys in nationally representative samples of the U.S. population aged 20 years and older. The surveys are conducted in 2-year cycles and include data from 10 cycles conducted from 1999-2000 to 2017-2018 (n = 50,571, mean age 49.0-51.8 years; 48.2%-51.3% female).
Every 2 years, participants provided sociodemographic information, including age, race/ethnicity, sex, education, income, employment, housing, health insurance, and access to health care, as well as medical history and medication use. They underwent a physical examination that included weight and height, blood pressure, lipid levels, plasma glucose, and hemoglobin A1c.
Social determinants of health
Between 1999-2000 and 2017-2018, age- and sex-adjusted mean BMI and hemoglobin A1c increased, while mean serum total cholesterol and prevalence of smoking decreased (all P < .001).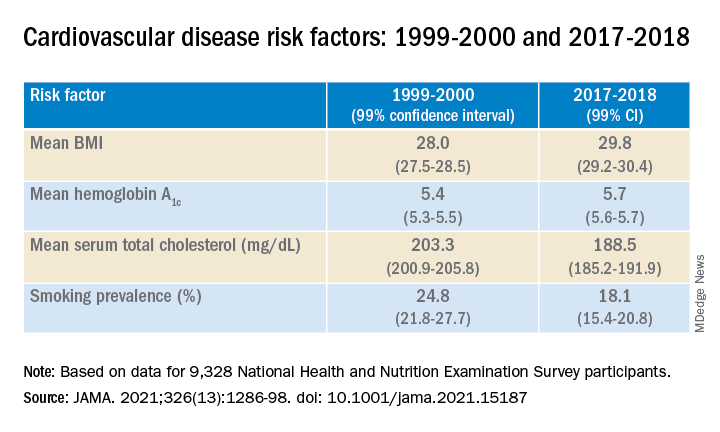
Age- and sex-adjusted 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk decreased from 7.6% (6.9%-8.2%) in 1999-2000 to 6.5% (6.1%-6.8%) in 2011-2012, with no significant changes thereafter.
When the researchers looked at specific racial and ethnic groups, they found that age- and sex-adjusted BMI, systolic BP, and hemoglobin A1c were “consistently higher” in non-Hispanic Black participants compared with non-Hispanic White participants, but total cholesterol was lower (all P < .001).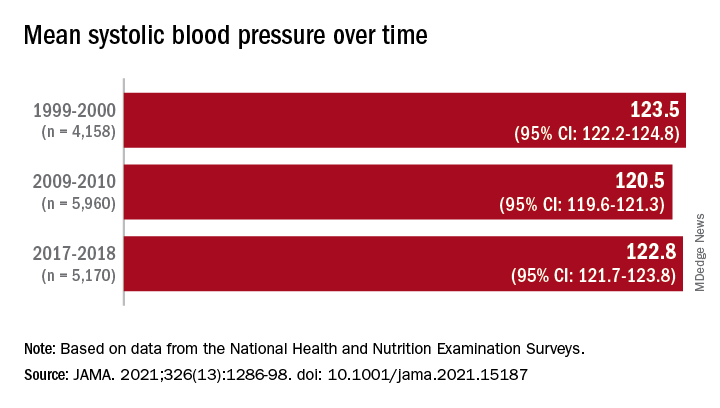
Participants with at least a college education or high family income had “consistently lower levels” of cardiovascular risk factors. And although the mean age- and sex-adjusted 10-year risk for ASCVD was significantly higher in non-Hispanic Black vs. non-Hispanic White participants (difference, 1.4% [1.0%-1.7%] in 1999-2008 and 2.0% [1.7%-2.4%] in 2009-2018), the difference was attenuated (by –0.3% in 1999-2008 and 0.7% in 2009-2018) after the researchers further adjusted for education, income, home ownership, employment, health insurance, and access to health care.
The differences in cardiovascular risk factors between Black and White participants “may have been moderated by social determinants of health,” the authors noted.
Provide appropriate education
Commenting on the study in an interview, Mary Ann McLaughlin, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine, cardiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, pointed out that two important cardiovascular risk factors associated with being overweight – hypertension and diabetes – remained higher in the Black population compared with the White population in this analysis.
“Physicians and health care systems should provide appropriate education and resources regarding risk factor modification regarding diet, exercise, and blood pressure control,” advised Dr. McLaughlin, who was not involved with the study.
“Importantly, smoking rates and cholesterol levels are lower in the Black population, compared to the White population, when adjusted for many important socioeconomic factors,” she pointed out.
Dr. McLaughlin added that other “important social determinants of health, such as neighborhood and access to healthy food, were not measured and should be addressed by physicians when optimizing cardiovascular risk.”
The research reported in this publication was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. One of the researchers, Joshua D. Bundy, PhD, was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. He and the other coauthors and Dr. McLaughlin reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators analyzed 20 years of data on over 50,500 U.S. adults drawn from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) and found that, in the overall population, body mass index and hemoglobin A1c were significantly increased between 1999 and 2018, while serum total cholesterol and cigarette smoking were significantly decreased. Mean systolic blood pressure decreased between 1999 and 2010, but then increased after 2010.
The mean age- and sex-adjusted estimated 10-year risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) was consistently higher in Black participants vs. White participants, but the difference was attenuated after further adjusting for education, income, home ownership, employment, health insurance, and access to health care.
“These findings are helpful to guide the development of national public health policies for targeted interventions aimed at eliminating health disparities,” Jiang He, MD, PhD, Joseph S. Copes Chair and professor of epidemiology, Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, New Orleans, said in an interview.
“Interventions on social determinants of cardiovascular health should be tested in rigorous designed intervention trials,” said Dr. He, director of the Tulane University Translational Science Institute.
The study was published online Oct. 5 in JAMA.
‘Flattened’ CVD mortality?
Recent data show that the CVD mortality rate flattened, while the total number of cardiovascular deaths increased in the U.S. general population from 2010 to 2018, “but the reasons for this deceleration in the decline of CVD mortality are not entirely understood,” Dr. He said.
Moreover, “racial and ethnic differences in CVD mortality persist in the U.S. general population [but] the secular trends of cardiovascular risk factors among U.S. subpopulations with various racial and ethnic backgrounds and socioeconomic status are [also] not well understood,” he added. The effects of social determinants of health, such as education, income, home ownership, employment, health insurance, and access to health care on racial/ethnic differences in CVD risk, “are not well documented.”
To investigate these questions, the researchers drew on data from NHANES, a series of cross-sectional surveys in nationally representative samples of the U.S. population aged 20 years and older. The surveys are conducted in 2-year cycles and include data from 10 cycles conducted from 1999-2000 to 2017-2018 (n = 50,571, mean age 49.0-51.8 years; 48.2%-51.3% female).
Every 2 years, participants provided sociodemographic information, including age, race/ethnicity, sex, education, income, employment, housing, health insurance, and access to health care, as well as medical history and medication use. They underwent a physical examination that included weight and height, blood pressure, lipid levels, plasma glucose, and hemoglobin A1c.
Social determinants of health
Between 1999-2000 and 2017-2018, age- and sex-adjusted mean BMI and hemoglobin A1c increased, while mean serum total cholesterol and prevalence of smoking decreased (all P < .001).
Age- and sex-adjusted 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk decreased from 7.6% (6.9%-8.2%) in 1999-2000 to 6.5% (6.1%-6.8%) in 2011-2012, with no significant changes thereafter.
When the researchers looked at specific racial and ethnic groups, they found that age- and sex-adjusted BMI, systolic BP, and hemoglobin A1c were “consistently higher” in non-Hispanic Black participants compared with non-Hispanic White participants, but total cholesterol was lower (all P < .001).
Participants with at least a college education or high family income had “consistently lower levels” of cardiovascular risk factors. And although the mean age- and sex-adjusted 10-year risk for ASCVD was significantly higher in non-Hispanic Black vs. non-Hispanic White participants (difference, 1.4% [1.0%-1.7%] in 1999-2008 and 2.0% [1.7%-2.4%] in 2009-2018), the difference was attenuated (by –0.3% in 1999-2008 and 0.7% in 2009-2018) after the researchers further adjusted for education, income, home ownership, employment, health insurance, and access to health care.
The differences in cardiovascular risk factors between Black and White participants “may have been moderated by social determinants of health,” the authors noted.
Provide appropriate education
Commenting on the study in an interview, Mary Ann McLaughlin, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine, cardiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, pointed out that two important cardiovascular risk factors associated with being overweight – hypertension and diabetes – remained higher in the Black population compared with the White population in this analysis.
“Physicians and health care systems should provide appropriate education and resources regarding risk factor modification regarding diet, exercise, and blood pressure control,” advised Dr. McLaughlin, who was not involved with the study.
“Importantly, smoking rates and cholesterol levels are lower in the Black population, compared to the White population, when adjusted for many important socioeconomic factors,” she pointed out.
Dr. McLaughlin added that other “important social determinants of health, such as neighborhood and access to healthy food, were not measured and should be addressed by physicians when optimizing cardiovascular risk.”
The research reported in this publication was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. One of the researchers, Joshua D. Bundy, PhD, was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. He and the other coauthors and Dr. McLaughlin reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators analyzed 20 years of data on over 50,500 U.S. adults drawn from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) and found that, in the overall population, body mass index and hemoglobin A1c were significantly increased between 1999 and 2018, while serum total cholesterol and cigarette smoking were significantly decreased. Mean systolic blood pressure decreased between 1999 and 2010, but then increased after 2010.
The mean age- and sex-adjusted estimated 10-year risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) was consistently higher in Black participants vs. White participants, but the difference was attenuated after further adjusting for education, income, home ownership, employment, health insurance, and access to health care.
“These findings are helpful to guide the development of national public health policies for targeted interventions aimed at eliminating health disparities,” Jiang He, MD, PhD, Joseph S. Copes Chair and professor of epidemiology, Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, New Orleans, said in an interview.
“Interventions on social determinants of cardiovascular health should be tested in rigorous designed intervention trials,” said Dr. He, director of the Tulane University Translational Science Institute.
The study was published online Oct. 5 in JAMA.
‘Flattened’ CVD mortality?
Recent data show that the CVD mortality rate flattened, while the total number of cardiovascular deaths increased in the U.S. general population from 2010 to 2018, “but the reasons for this deceleration in the decline of CVD mortality are not entirely understood,” Dr. He said.
Moreover, “racial and ethnic differences in CVD mortality persist in the U.S. general population [but] the secular trends of cardiovascular risk factors among U.S. subpopulations with various racial and ethnic backgrounds and socioeconomic status are [also] not well understood,” he added. The effects of social determinants of health, such as education, income, home ownership, employment, health insurance, and access to health care on racial/ethnic differences in CVD risk, “are not well documented.”
To investigate these questions, the researchers drew on data from NHANES, a series of cross-sectional surveys in nationally representative samples of the U.S. population aged 20 years and older. The surveys are conducted in 2-year cycles and include data from 10 cycles conducted from 1999-2000 to 2017-2018 (n = 50,571, mean age 49.0-51.8 years; 48.2%-51.3% female).
Every 2 years, participants provided sociodemographic information, including age, race/ethnicity, sex, education, income, employment, housing, health insurance, and access to health care, as well as medical history and medication use. They underwent a physical examination that included weight and height, blood pressure, lipid levels, plasma glucose, and hemoglobin A1c.
Social determinants of health
Between 1999-2000 and 2017-2018, age- and sex-adjusted mean BMI and hemoglobin A1c increased, while mean serum total cholesterol and prevalence of smoking decreased (all P < .001).
Age- and sex-adjusted 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk decreased from 7.6% (6.9%-8.2%) in 1999-2000 to 6.5% (6.1%-6.8%) in 2011-2012, with no significant changes thereafter.
When the researchers looked at specific racial and ethnic groups, they found that age- and sex-adjusted BMI, systolic BP, and hemoglobin A1c were “consistently higher” in non-Hispanic Black participants compared with non-Hispanic White participants, but total cholesterol was lower (all P < .001).
Participants with at least a college education or high family income had “consistently lower levels” of cardiovascular risk factors. And although the mean age- and sex-adjusted 10-year risk for ASCVD was significantly higher in non-Hispanic Black vs. non-Hispanic White participants (difference, 1.4% [1.0%-1.7%] in 1999-2008 and 2.0% [1.7%-2.4%] in 2009-2018), the difference was attenuated (by –0.3% in 1999-2008 and 0.7% in 2009-2018) after the researchers further adjusted for education, income, home ownership, employment, health insurance, and access to health care.
The differences in cardiovascular risk factors between Black and White participants “may have been moderated by social determinants of health,” the authors noted.
Provide appropriate education
Commenting on the study in an interview, Mary Ann McLaughlin, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine, cardiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, pointed out that two important cardiovascular risk factors associated with being overweight – hypertension and diabetes – remained higher in the Black population compared with the White population in this analysis.
“Physicians and health care systems should provide appropriate education and resources regarding risk factor modification regarding diet, exercise, and blood pressure control,” advised Dr. McLaughlin, who was not involved with the study.
“Importantly, smoking rates and cholesterol levels are lower in the Black population, compared to the White population, when adjusted for many important socioeconomic factors,” she pointed out.
Dr. McLaughlin added that other “important social determinants of health, such as neighborhood and access to healthy food, were not measured and should be addressed by physicians when optimizing cardiovascular risk.”
The research reported in this publication was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. One of the researchers, Joshua D. Bundy, PhD, was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. He and the other coauthors and Dr. McLaughlin reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Beloved psychiatrist dies at 102
Respected psychiatrist and psychoanalyst Irwin Marcus, MD, died on October 3. He was 102. Dedicated to his profession, Dr. Marcus was seeing patients until earlier this year. His long and illustrious career included creating and founding programs and organizations wherever he saw a need.
Among his many professional accomplishments, Dr. Marcus helped found the child and adolescent psychiatry program at Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, and was one of the founders and a past president of the New Orleans Psychoanalytic Institute.
Dr. Marcus was also former chairman of the psychiatric department at Touro Infirmary and clinical professor emeritus at Louisiana State University Medical School, both in New Orleans.
“He initiated a number of traditions that are still important to us – community outreach, treating underserved youth, and strong interdisciplinary relationships,” Charles H. Zeanah, Jr., MD, current Mary Peters Sellars-Polchow chair of psychiatry at Tulane, told this news organization.
Dr. Marcus also continued to treat adult patients by phone and at his home until mid-June of this year. He had also started writing a children’s book.
It was his “tremendous work ethic” and creativity that kept him working past the age of 100, his wife, Angela Hill, a former news anchor, said in an interview.
Even vision loss resulting from macular degeneration and long-standing hearing problems did not stop him, she noted.
“He was always thinking creatively; he was always thinking intellectually,” said Ms. Hill. “That was, to me, the marvel of him.”
Wartime service, brain-trauma clinic
Born in Chicago in 1919, Dr. Marcus studied first at the Illinois Institute of Technology before transferring to the University of Illinois School of Medicine.
Neurosurgery was an early interest, and Dr. Marcus undertook his medical residency at Cook County Hospital in Chicago. The day after the bombing of Pearl Harbor, he enlisted in the U.S. Army.
During World War II, Dr. Marcus served in the Army Medical Corps and treated brain injuries and other wounds before he was badly injured himself and had to return to the United States for treatment.
After his recovery, he worked at an army medical facility in El Paso, Texas. On the basis of his earlier experiences, he founded a clinic there to diagnose and treat brain trauma.
After the war, Dr. Marcus continued his studies at Columbia University’s College of Physicians and Surgeons, in New York. Soon, his focus became psychiatry, child psychiatry, and psychoanalysis.
In 1951, Dr. Marcus accepted a position at Tulane. He created the Family Study Unit there the following year. Dr. Zeanah noted that the original name was chosen out of concern over the stigma associated with the term “child psychiatry.”
However, the environment changed relatively quickly, and the unit soon became known as Tulane Child Psychiatry.
Research, books, helmet patent
Dr. Marcus received Tulane’s first research grant in child psychiatry from the National Institute of Mental Health to investigate the potential mechanisms behind accident-prone children. That interest was inspired by his own clinical experience.
The findings, which were published in Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, showed that being accident prone was a nonspecific response to stressors from multiple sources, including a temperamental disposition, parent-child conflict, and family conflict.
To provide care to young patients, Dr. Marcus collaborated with the Children’s Bureau, the Jewish Children’s Home, the German Protestant’s Orphan Asylum, and Associated Catholic Charities.
‘He saved my life’
In 2002, Dr. Marcus participated in the 50th anniversary celebration of Tulane’s child psychiatry program. He returned in 2009 for what would be his final grand rounds presentation, which included an inspiring interview with Dr. Zeanah.
“He talked about the early history of child psychiatry, the things that he’d been trying to do, and some of the challenges that he faced,” Dr. Zeanah said.
Dr. Marcus’s former patients often told Ms. Hill how much he had helped them, she said.
“A couple walked up at a restaurant, and both of them said, ‘He saved our family.’”
Throughout his professional life, Dr. Marcus continued to strive toward growth and providing aid, she added.
“That is the bottom line of Irwin Marcus: All of his work was to help,” said Ms. Hill.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.
Respected psychiatrist and psychoanalyst Irwin Marcus, MD, died on October 3. He was 102. Dedicated to his profession, Dr. Marcus was seeing patients until earlier this year. His long and illustrious career included creating and founding programs and organizations wherever he saw a need.
Among his many professional accomplishments, Dr. Marcus helped found the child and adolescent psychiatry program at Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, and was one of the founders and a past president of the New Orleans Psychoanalytic Institute.
Dr. Marcus was also former chairman of the psychiatric department at Touro Infirmary and clinical professor emeritus at Louisiana State University Medical School, both in New Orleans.
“He initiated a number of traditions that are still important to us – community outreach, treating underserved youth, and strong interdisciplinary relationships,” Charles H. Zeanah, Jr., MD, current Mary Peters Sellars-Polchow chair of psychiatry at Tulane, told this news organization.
Dr. Marcus also continued to treat adult patients by phone and at his home until mid-June of this year. He had also started writing a children’s book.
It was his “tremendous work ethic” and creativity that kept him working past the age of 100, his wife, Angela Hill, a former news anchor, said in an interview.
Even vision loss resulting from macular degeneration and long-standing hearing problems did not stop him, she noted.
“He was always thinking creatively; he was always thinking intellectually,” said Ms. Hill. “That was, to me, the marvel of him.”
Wartime service, brain-trauma clinic
Born in Chicago in 1919, Dr. Marcus studied first at the Illinois Institute of Technology before transferring to the University of Illinois School of Medicine.
Neurosurgery was an early interest, and Dr. Marcus undertook his medical residency at Cook County Hospital in Chicago. The day after the bombing of Pearl Harbor, he enlisted in the U.S. Army.
During World War II, Dr. Marcus served in the Army Medical Corps and treated brain injuries and other wounds before he was badly injured himself and had to return to the United States for treatment.
After his recovery, he worked at an army medical facility in El Paso, Texas. On the basis of his earlier experiences, he founded a clinic there to diagnose and treat brain trauma.
After the war, Dr. Marcus continued his studies at Columbia University’s College of Physicians and Surgeons, in New York. Soon, his focus became psychiatry, child psychiatry, and psychoanalysis.
In 1951, Dr. Marcus accepted a position at Tulane. He created the Family Study Unit there the following year. Dr. Zeanah noted that the original name was chosen out of concern over the stigma associated with the term “child psychiatry.”
However, the environment changed relatively quickly, and the unit soon became known as Tulane Child Psychiatry.
Research, books, helmet patent
Dr. Marcus received Tulane’s first research grant in child psychiatry from the National Institute of Mental Health to investigate the potential mechanisms behind accident-prone children. That interest was inspired by his own clinical experience.
The findings, which were published in Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, showed that being accident prone was a nonspecific response to stressors from multiple sources, including a temperamental disposition, parent-child conflict, and family conflict.
To provide care to young patients, Dr. Marcus collaborated with the Children’s Bureau, the Jewish Children’s Home, the German Protestant’s Orphan Asylum, and Associated Catholic Charities.
‘He saved my life’
In 2002, Dr. Marcus participated in the 50th anniversary celebration of Tulane’s child psychiatry program. He returned in 2009 for what would be his final grand rounds presentation, which included an inspiring interview with Dr. Zeanah.
“He talked about the early history of child psychiatry, the things that he’d been trying to do, and some of the challenges that he faced,” Dr. Zeanah said.
Dr. Marcus’s former patients often told Ms. Hill how much he had helped them, she said.
“A couple walked up at a restaurant, and both of them said, ‘He saved our family.’”
Throughout his professional life, Dr. Marcus continued to strive toward growth and providing aid, she added.
“That is the bottom line of Irwin Marcus: All of his work was to help,” said Ms. Hill.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.
Respected psychiatrist and psychoanalyst Irwin Marcus, MD, died on October 3. He was 102. Dedicated to his profession, Dr. Marcus was seeing patients until earlier this year. His long and illustrious career included creating and founding programs and organizations wherever he saw a need.
Among his many professional accomplishments, Dr. Marcus helped found the child and adolescent psychiatry program at Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, and was one of the founders and a past president of the New Orleans Psychoanalytic Institute.
Dr. Marcus was also former chairman of the psychiatric department at Touro Infirmary and clinical professor emeritus at Louisiana State University Medical School, both in New Orleans.
“He initiated a number of traditions that are still important to us – community outreach, treating underserved youth, and strong interdisciplinary relationships,” Charles H. Zeanah, Jr., MD, current Mary Peters Sellars-Polchow chair of psychiatry at Tulane, told this news organization.
Dr. Marcus also continued to treat adult patients by phone and at his home until mid-June of this year. He had also started writing a children’s book.
It was his “tremendous work ethic” and creativity that kept him working past the age of 100, his wife, Angela Hill, a former news anchor, said in an interview.
Even vision loss resulting from macular degeneration and long-standing hearing problems did not stop him, she noted.
“He was always thinking creatively; he was always thinking intellectually,” said Ms. Hill. “That was, to me, the marvel of him.”
Wartime service, brain-trauma clinic
Born in Chicago in 1919, Dr. Marcus studied first at the Illinois Institute of Technology before transferring to the University of Illinois School of Medicine.
Neurosurgery was an early interest, and Dr. Marcus undertook his medical residency at Cook County Hospital in Chicago. The day after the bombing of Pearl Harbor, he enlisted in the U.S. Army.
During World War II, Dr. Marcus served in the Army Medical Corps and treated brain injuries and other wounds before he was badly injured himself and had to return to the United States for treatment.
After his recovery, he worked at an army medical facility in El Paso, Texas. On the basis of his earlier experiences, he founded a clinic there to diagnose and treat brain trauma.
After the war, Dr. Marcus continued his studies at Columbia University’s College of Physicians and Surgeons, in New York. Soon, his focus became psychiatry, child psychiatry, and psychoanalysis.
In 1951, Dr. Marcus accepted a position at Tulane. He created the Family Study Unit there the following year. Dr. Zeanah noted that the original name was chosen out of concern over the stigma associated with the term “child psychiatry.”
However, the environment changed relatively quickly, and the unit soon became known as Tulane Child Psychiatry.
Research, books, helmet patent
Dr. Marcus received Tulane’s first research grant in child psychiatry from the National Institute of Mental Health to investigate the potential mechanisms behind accident-prone children. That interest was inspired by his own clinical experience.
The findings, which were published in Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, showed that being accident prone was a nonspecific response to stressors from multiple sources, including a temperamental disposition, parent-child conflict, and family conflict.
To provide care to young patients, Dr. Marcus collaborated with the Children’s Bureau, the Jewish Children’s Home, the German Protestant’s Orphan Asylum, and Associated Catholic Charities.
‘He saved my life’
In 2002, Dr. Marcus participated in the 50th anniversary celebration of Tulane’s child psychiatry program. He returned in 2009 for what would be his final grand rounds presentation, which included an inspiring interview with Dr. Zeanah.
“He talked about the early history of child psychiatry, the things that he’d been trying to do, and some of the challenges that he faced,” Dr. Zeanah said.
Dr. Marcus’s former patients often told Ms. Hill how much he had helped them, she said.
“A couple walked up at a restaurant, and both of them said, ‘He saved our family.’”
Throughout his professional life, Dr. Marcus continued to strive toward growth and providing aid, she added.
“That is the bottom line of Irwin Marcus: All of his work was to help,” said Ms. Hill.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.
Good news, bad news for buprenorphine in opioid use disorder
Misuse of buprenorphine in the United States by patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) dropped sharply between 2015 and 2019, new research shows.
Analyses of data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health also showed that about 50% of the patients with OUD were not receiving substance use treatment – and that some may be misusing buprenorphine in an effort to self-treat their addiction.
Interestingly, there was no association between buprenorphine misuse and income among those with OUD or with race, ethnicity, or insurance status regardless of OUD status, which bucks commonly held perceptions of those with the disorder.
Overall, the findings “underscore the need to pursue actions that expand access to buprenorphine-based OUD treatment, to develop strategies to monitor and reduce buprenorphine misuse, and to address associated conditions,” the investigators, led by Beth Han, MD, PhD, National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), write.
The study was published online October 15 in JAMA Network Open.
Opioid deaths
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data Of those deaths, 69,710 involved opioids.
Buprenorphine, a medication approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat OUD, has been shown to reduce opioid cravings and withdrawal symptoms and lower overdose risk.
The new survey included responses from 214,505 adults. Of these, 51.7% were women, 45.5% were age 50 years or older, and 63.9% were non-Hispanic White.
Responses were collected between 2015-2019 as part of an annual survey administered annually by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
Misuse was defined as any use outside the prescribed amount, frequency, duration, or indication.
In 2019, hydrocodone, oxycodone, codeine, and tramadol were the most misused prescription opioid products. An estimated 2.4 million adults used buprenorphine, with 1.7 million reporting no misuse in the past 12 months.
While buprenorphine misuse was stable between 2015 and 2019 among individuals without OUD, misuse declined significantly among those with OUD – from 20.5% in 2015 to 15.9% in 2019 (P = .04).
A different picture of misuse
The demographic data reveals a picture of buprenorphine misuse that researchers note is quite different from common perceptions about people with substance use.
Those with OUD who misused buprenorphine were more likely to be non-Hispanic White (82.9% vs. 73.6%, respectively) and less likely to live in large metropolitan areas (47.7% vs. 58.1%).
Among participants with OUD, buprenorphine misuse was significantly associated with age, especially in those between 24 and 34 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.9; 95% confidence interval, 1.4-5.8) and between 35 and 49 years (aOR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.2-4.5).
It was also significantly associated with living in nonmetropolitan areas (aOR, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.0-3.0) and having past-year polysubstance use and use disorders (aOR, 3.9; 95% CI, 1.3-11.2); but negatively associated with past-year treatment for illicit drug use–only treatment (aOR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.3-0.7).
There was no significant association between buprenorphine misuse and income in participants with OUD or with race, ethnicity, or insurance status, regardless of OUD status.
“Perceptions that persons of racial and ethnic minority groups and people living in poverty are more likely to misuse their medication are incorrect,” the researchers write.
“Nevertheless, these factors have been found to be important factors associated with opioid harms and receipt of buprenorphine treatment,” they add.
Between 2015 and 2017, the largest increase in opioid-related drug overdose deaths was among Black people aged 25 to 34, and the largest increase involving synthetic opioids was among Hispanic individuals aged 45 to 54. At the same time, White people were more likely to receive buprenorphine treatment for OUD.
‘Don’t exaggerate concerns’
Among survey participants with OUD, 57% of those who had misused buprenorphine in the past year had received no substance use treatment. Among those with OUD who had not misused the drug in the past year, 49% had received no treatment for their addiction.
The most common reason for buprenorphine misuse cited by those with OUD was “because I am hooked” (27.3%), which researchers said suggests people may be taking buprenorphine without a prescription to self-treat their OUD.
The investigators note that although buprenorphine is inexpensive and effective, clinicians currently must receive a federal waiver to prescribe it to more than 30 patients at a time.
Concern over potential misuse may be one reason some clinicians have been reluctant to complete the training process. However, the study results showed misuse rates of other opioids, including oxycodone and hydrocodone, were higher than those reported for buprenorphine.
“Many other prescription opioids are misused at much higher rates,” co-investigator Wilson Compton, MD, MPE, deputy director of NIDA, told this news organization.
“While there are concerns about all of them, we want to make sure that people don’t exaggerate the concerns – and understanding that oxycodone and hydrocodone are so much more frequently misused is important,” added Dr. Compton.
Symptom of inadequate access?
Commenting on the research, Bobby Mukkamala, MD, chair of the American Medical Association Board of Trustees, said individuals who misuse buprenorphine “commonly do so to alleviate uncontrolled pain or symptoms of withdrawal.”
“So-called misuse of buprenorphine is a symptom of inadequate access to physicians to treat opioid use disorder,” said Dr. Mukkamala, who also chairs the AMA Substance Use and Pain Care Task Force.
A 2020 study from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services showed 40% of U.S. counties have no clinicians with a federal waiver permitting them to prescribe buprenorphine in an office setting.
In April, the HHS released new practice guidelines that allow certain practitioners licensed under state law who have a valid Drug Enforcement Administration registration to treat up to 30 patients with buprenorphine without having to complete requirements related to training, counseling, and other ancillary services known as an “X-waiver.”
The move was welcomed by many in the field, but Dr. Mukkamala said the agency did not go far enough.
“The AMA supports removing the federal X-waiver requirement to help destigmatize the provision of buprenorphine as well as remove the many administrative barriers that come with the federal requirement,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Misuse of buprenorphine in the United States by patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) dropped sharply between 2015 and 2019, new research shows.
Analyses of data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health also showed that about 50% of the patients with OUD were not receiving substance use treatment – and that some may be misusing buprenorphine in an effort to self-treat their addiction.
Interestingly, there was no association between buprenorphine misuse and income among those with OUD or with race, ethnicity, or insurance status regardless of OUD status, which bucks commonly held perceptions of those with the disorder.
Overall, the findings “underscore the need to pursue actions that expand access to buprenorphine-based OUD treatment, to develop strategies to monitor and reduce buprenorphine misuse, and to address associated conditions,” the investigators, led by Beth Han, MD, PhD, National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), write.
The study was published online October 15 in JAMA Network Open.
Opioid deaths
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data Of those deaths, 69,710 involved opioids.
Buprenorphine, a medication approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat OUD, has been shown to reduce opioid cravings and withdrawal symptoms and lower overdose risk.
The new survey included responses from 214,505 adults. Of these, 51.7% were women, 45.5% were age 50 years or older, and 63.9% were non-Hispanic White.
Responses were collected between 2015-2019 as part of an annual survey administered annually by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
Misuse was defined as any use outside the prescribed amount, frequency, duration, or indication.
In 2019, hydrocodone, oxycodone, codeine, and tramadol were the most misused prescription opioid products. An estimated 2.4 million adults used buprenorphine, with 1.7 million reporting no misuse in the past 12 months.
While buprenorphine misuse was stable between 2015 and 2019 among individuals without OUD, misuse declined significantly among those with OUD – from 20.5% in 2015 to 15.9% in 2019 (P = .04).
A different picture of misuse
The demographic data reveals a picture of buprenorphine misuse that researchers note is quite different from common perceptions about people with substance use.
Those with OUD who misused buprenorphine were more likely to be non-Hispanic White (82.9% vs. 73.6%, respectively) and less likely to live in large metropolitan areas (47.7% vs. 58.1%).
Among participants with OUD, buprenorphine misuse was significantly associated with age, especially in those between 24 and 34 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.9; 95% confidence interval, 1.4-5.8) and between 35 and 49 years (aOR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.2-4.5).
It was also significantly associated with living in nonmetropolitan areas (aOR, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.0-3.0) and having past-year polysubstance use and use disorders (aOR, 3.9; 95% CI, 1.3-11.2); but negatively associated with past-year treatment for illicit drug use–only treatment (aOR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.3-0.7).
There was no significant association between buprenorphine misuse and income in participants with OUD or with race, ethnicity, or insurance status, regardless of OUD status.
“Perceptions that persons of racial and ethnic minority groups and people living in poverty are more likely to misuse their medication are incorrect,” the researchers write.
“Nevertheless, these factors have been found to be important factors associated with opioid harms and receipt of buprenorphine treatment,” they add.
Between 2015 and 2017, the largest increase in opioid-related drug overdose deaths was among Black people aged 25 to 34, and the largest increase involving synthetic opioids was among Hispanic individuals aged 45 to 54. At the same time, White people were more likely to receive buprenorphine treatment for OUD.
‘Don’t exaggerate concerns’
Among survey participants with OUD, 57% of those who had misused buprenorphine in the past year had received no substance use treatment. Among those with OUD who had not misused the drug in the past year, 49% had received no treatment for their addiction.
The most common reason for buprenorphine misuse cited by those with OUD was “because I am hooked” (27.3%), which researchers said suggests people may be taking buprenorphine without a prescription to self-treat their OUD.
The investigators note that although buprenorphine is inexpensive and effective, clinicians currently must receive a federal waiver to prescribe it to more than 30 patients at a time.
Concern over potential misuse may be one reason some clinicians have been reluctant to complete the training process. However, the study results showed misuse rates of other opioids, including oxycodone and hydrocodone, were higher than those reported for buprenorphine.
“Many other prescription opioids are misused at much higher rates,” co-investigator Wilson Compton, MD, MPE, deputy director of NIDA, told this news organization.
“While there are concerns about all of them, we want to make sure that people don’t exaggerate the concerns – and understanding that oxycodone and hydrocodone are so much more frequently misused is important,” added Dr. Compton.
Symptom of inadequate access?
Commenting on the research, Bobby Mukkamala, MD, chair of the American Medical Association Board of Trustees, said individuals who misuse buprenorphine “commonly do so to alleviate uncontrolled pain or symptoms of withdrawal.”
“So-called misuse of buprenorphine is a symptom of inadequate access to physicians to treat opioid use disorder,” said Dr. Mukkamala, who also chairs the AMA Substance Use and Pain Care Task Force.
A 2020 study from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services showed 40% of U.S. counties have no clinicians with a federal waiver permitting them to prescribe buprenorphine in an office setting.
In April, the HHS released new practice guidelines that allow certain practitioners licensed under state law who have a valid Drug Enforcement Administration registration to treat up to 30 patients with buprenorphine without having to complete requirements related to training, counseling, and other ancillary services known as an “X-waiver.”
The move was welcomed by many in the field, but Dr. Mukkamala said the agency did not go far enough.
“The AMA supports removing the federal X-waiver requirement to help destigmatize the provision of buprenorphine as well as remove the many administrative barriers that come with the federal requirement,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Misuse of buprenorphine in the United States by patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) dropped sharply between 2015 and 2019, new research shows.
Analyses of data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health also showed that about 50% of the patients with OUD were not receiving substance use treatment – and that some may be misusing buprenorphine in an effort to self-treat their addiction.
Interestingly, there was no association between buprenorphine misuse and income among those with OUD or with race, ethnicity, or insurance status regardless of OUD status, which bucks commonly held perceptions of those with the disorder.
Overall, the findings “underscore the need to pursue actions that expand access to buprenorphine-based OUD treatment, to develop strategies to monitor and reduce buprenorphine misuse, and to address associated conditions,” the investigators, led by Beth Han, MD, PhD, National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), write.
The study was published online October 15 in JAMA Network Open.
Opioid deaths
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data Of those deaths, 69,710 involved opioids.
Buprenorphine, a medication approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat OUD, has been shown to reduce opioid cravings and withdrawal symptoms and lower overdose risk.
The new survey included responses from 214,505 adults. Of these, 51.7% were women, 45.5% were age 50 years or older, and 63.9% were non-Hispanic White.
Responses were collected between 2015-2019 as part of an annual survey administered annually by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
Misuse was defined as any use outside the prescribed amount, frequency, duration, or indication.
In 2019, hydrocodone, oxycodone, codeine, and tramadol were the most misused prescription opioid products. An estimated 2.4 million adults used buprenorphine, with 1.7 million reporting no misuse in the past 12 months.
While buprenorphine misuse was stable between 2015 and 2019 among individuals without OUD, misuse declined significantly among those with OUD – from 20.5% in 2015 to 15.9% in 2019 (P = .04).
A different picture of misuse
The demographic data reveals a picture of buprenorphine misuse that researchers note is quite different from common perceptions about people with substance use.
Those with OUD who misused buprenorphine were more likely to be non-Hispanic White (82.9% vs. 73.6%, respectively) and less likely to live in large metropolitan areas (47.7% vs. 58.1%).
Among participants with OUD, buprenorphine misuse was significantly associated with age, especially in those between 24 and 34 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.9; 95% confidence interval, 1.4-5.8) and between 35 and 49 years (aOR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.2-4.5).
It was also significantly associated with living in nonmetropolitan areas (aOR, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.0-3.0) and having past-year polysubstance use and use disorders (aOR, 3.9; 95% CI, 1.3-11.2); but negatively associated with past-year treatment for illicit drug use–only treatment (aOR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.3-0.7).
There was no significant association between buprenorphine misuse and income in participants with OUD or with race, ethnicity, or insurance status, regardless of OUD status.
“Perceptions that persons of racial and ethnic minority groups and people living in poverty are more likely to misuse their medication are incorrect,” the researchers write.
“Nevertheless, these factors have been found to be important factors associated with opioid harms and receipt of buprenorphine treatment,” they add.
Between 2015 and 2017, the largest increase in opioid-related drug overdose deaths was among Black people aged 25 to 34, and the largest increase involving synthetic opioids was among Hispanic individuals aged 45 to 54. At the same time, White people were more likely to receive buprenorphine treatment for OUD.
‘Don’t exaggerate concerns’
Among survey participants with OUD, 57% of those who had misused buprenorphine in the past year had received no substance use treatment. Among those with OUD who had not misused the drug in the past year, 49% had received no treatment for their addiction.
The most common reason for buprenorphine misuse cited by those with OUD was “because I am hooked” (27.3%), which researchers said suggests people may be taking buprenorphine without a prescription to self-treat their OUD.
The investigators note that although buprenorphine is inexpensive and effective, clinicians currently must receive a federal waiver to prescribe it to more than 30 patients at a time.
Concern over potential misuse may be one reason some clinicians have been reluctant to complete the training process. However, the study results showed misuse rates of other opioids, including oxycodone and hydrocodone, were higher than those reported for buprenorphine.
“Many other prescription opioids are misused at much higher rates,” co-investigator Wilson Compton, MD, MPE, deputy director of NIDA, told this news organization.
“While there are concerns about all of them, we want to make sure that people don’t exaggerate the concerns – and understanding that oxycodone and hydrocodone are so much more frequently misused is important,” added Dr. Compton.
Symptom of inadequate access?
Commenting on the research, Bobby Mukkamala, MD, chair of the American Medical Association Board of Trustees, said individuals who misuse buprenorphine “commonly do so to alleviate uncontrolled pain or symptoms of withdrawal.”
“So-called misuse of buprenorphine is a symptom of inadequate access to physicians to treat opioid use disorder,” said Dr. Mukkamala, who also chairs the AMA Substance Use and Pain Care Task Force.
A 2020 study from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services showed 40% of U.S. counties have no clinicians with a federal waiver permitting them to prescribe buprenorphine in an office setting.
In April, the HHS released new practice guidelines that allow certain practitioners licensed under state law who have a valid Drug Enforcement Administration registration to treat up to 30 patients with buprenorphine without having to complete requirements related to training, counseling, and other ancillary services known as an “X-waiver.”
The move was welcomed by many in the field, but Dr. Mukkamala said the agency did not go far enough.
“The AMA supports removing the federal X-waiver requirement to help destigmatize the provision of buprenorphine as well as remove the many administrative barriers that come with the federal requirement,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antithrombotic therapy not warranted in COVID-19 outpatients
Antithrombotic therapy in clinically stable, nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients does not offer protection against adverse cardiovascular or pulmonary events, new randomized clinical trial results suggest.
Antithrombotic therapy has proven useful in acutely ill inpatients with COVID-19, but in this study, treatment with aspirin or apixaban (Eliquis) did not reduce the rate of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary causes in patients ill with COVID-19 but who were not hospitalized.
“Among symptomatic, clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19, treatment with aspirin or apixaban compared with placebo did not reduce the rate of a composite clinical outcome,” the authors conclude. “However, the study was terminated after enrollment of 9% of participants because of a primary event rate lower than anticipated.”
The study, which was led by Jean M. Connors, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online October 11 in JAMA.
The ACTIV-4B Outpatient Thrombosis Prevention Trial was a randomized, adaptive, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that sought to compare anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy among 7,000 symptomatic but clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19.
The trial was conducted at 52 sites in the U.S. between Sept. 2020 and June 2021, with final follow-up this past August 5, and involved minimal face-to-face interactions with study participants.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to aspirin (81 mg orally once daily; n = 164 patients), prophylactic-dose apixaban (2.5 mg orally twice daily; n = 165), therapeutic-dose apixaban (5 mg orally twice daily; n = 164), or placebo (n = 164) for 45 days.
The primary endpoint was a composite of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary cause.
The trial was terminated early this past June by the independent data monitoring committee because of lower than anticipated event rates. At the time, just 657 symptomatic outpatients with COVID-19 had been enrolled.
The median age of the study participants was 54 years (Interquartile Range [IQR] 46-59); 59% were women.
The median time from diagnosis to randomization was 7 days, and the median time from randomization to initiation of study medications was 3 days.
The trial’s primary efficacy and safety analyses were restricted to patients who received at least one dose of trial medication, for a final number of 558 patients.
Among these patients, the primary endpoint occurred in 1 patient (0.7%) in the aspirin group, 1 patient (0.7%) in the 2.5 mg apixaban group, 2 patients (1.4%) in the 5-mg apixaban group, and 1 patient (0.7%) in the placebo group.
The researchers found that the absolute risk reductions compared with placebo for the primary outcome were 0.0% (95% confidence interval not calculable) in the aspirin group, 0.7% (95% confidence interval, -2.1% to 4.1%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 1.4% (95% CI, -1.5% to 5%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
No major bleeding events were reported.
The absolute risk differences compared with placebo for clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding events were 2% (95% CI, -2.7% to 6.8%) in the aspirin group, 4.5% (95% CI, -0.7% to 10.2%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 6.9% (95% CI, 1.4% to 12.9%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
Safety and efficacy results were similar in all randomly assigned patients.
The researchers speculated that a combination of two demographic shifts over time may have led to the lower than anticipated rate of events in ACTIV-4B.
“First, the threshold for hospital admission has markedly declined since the beginning of the pandemic, such that hospitalization is no longer limited almost exclusively to those with severe pulmonary distress likely to require mechanical ventilation,” they write. “As a result, the severity of illness among individuals with COVID-19 and destined for outpatient care has declined.”
“Second, at least within the U.S., where the trial was conducted, individuals currently being infected with SARS-CoV-2 tend to be younger and have fewer comorbidities when compared with individuals with incident infection at the onset of the pandemic,” they add.
Further, COVID-19 testing was quite limited early in the pandemic, they note, “and it is possible that the anticipated event rates based on data from registries available at that time were overestimated because the denominator (that is, the number of infected individuals overall) was essentially unknown.”
Robust evidence
“The ACTIV-4B trial is the first randomized trial to generate robust evidence about the effects of antithrombotic therapy in outpatients with COVID-19,” Otavio Berwanger, MD, PhD, director of the Academic Research Organization, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, Sao Paulo-SP, Brazil, told this news organization.
“It should be noted that this was a well-designed trial with low risk of bias. On the other hand, the main limitation is the low number of events and, consequently, the limited statistical power,” said Dr. Berwanger, who wrote an accompanying editorial.
The ACTIV-4B trial has immediate implications for clinical practice, he added.
“In this sense, considering the neutral results for major cardiopulmonary outcomes, the use of aspirin or apixaban for the management of outpatients with COVID-19 should not be recommended.”
ACTIV-4B also provides useful information for the steering committees of other ongoing trials of antithrombotic therapy for patients with COVID-19 who are not hospitalized, Dr. Berwanger added.
“In this sense, probably issues like statistical power, outcome choices, recruitment feasibility, and even futility would need to be revisited. And finally, lessons learned from the implementation of an innovative, pragmatic, and decentralized trial design represent an important legacy for future trials in cardiovascular diseases and other common conditions,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Connors reports financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Abbott, Alnylam, Takeda, Roche, and Sanofi. Dr. Berwanger reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Amgen, Servier, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bayer, Novartis, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antithrombotic therapy in clinically stable, nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients does not offer protection against adverse cardiovascular or pulmonary events, new randomized clinical trial results suggest.
Antithrombotic therapy has proven useful in acutely ill inpatients with COVID-19, but in this study, treatment with aspirin or apixaban (Eliquis) did not reduce the rate of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary causes in patients ill with COVID-19 but who were not hospitalized.
“Among symptomatic, clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19, treatment with aspirin or apixaban compared with placebo did not reduce the rate of a composite clinical outcome,” the authors conclude. “However, the study was terminated after enrollment of 9% of participants because of a primary event rate lower than anticipated.”
The study, which was led by Jean M. Connors, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online October 11 in JAMA.
The ACTIV-4B Outpatient Thrombosis Prevention Trial was a randomized, adaptive, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that sought to compare anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy among 7,000 symptomatic but clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19.
The trial was conducted at 52 sites in the U.S. between Sept. 2020 and June 2021, with final follow-up this past August 5, and involved minimal face-to-face interactions with study participants.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to aspirin (81 mg orally once daily; n = 164 patients), prophylactic-dose apixaban (2.5 mg orally twice daily; n = 165), therapeutic-dose apixaban (5 mg orally twice daily; n = 164), or placebo (n = 164) for 45 days.
The primary endpoint was a composite of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary cause.
The trial was terminated early this past June by the independent data monitoring committee because of lower than anticipated event rates. At the time, just 657 symptomatic outpatients with COVID-19 had been enrolled.
The median age of the study participants was 54 years (Interquartile Range [IQR] 46-59); 59% were women.
The median time from diagnosis to randomization was 7 days, and the median time from randomization to initiation of study medications was 3 days.
The trial’s primary efficacy and safety analyses were restricted to patients who received at least one dose of trial medication, for a final number of 558 patients.
Among these patients, the primary endpoint occurred in 1 patient (0.7%) in the aspirin group, 1 patient (0.7%) in the 2.5 mg apixaban group, 2 patients (1.4%) in the 5-mg apixaban group, and 1 patient (0.7%) in the placebo group.
The researchers found that the absolute risk reductions compared with placebo for the primary outcome were 0.0% (95% confidence interval not calculable) in the aspirin group, 0.7% (95% confidence interval, -2.1% to 4.1%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 1.4% (95% CI, -1.5% to 5%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
No major bleeding events were reported.
The absolute risk differences compared with placebo for clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding events were 2% (95% CI, -2.7% to 6.8%) in the aspirin group, 4.5% (95% CI, -0.7% to 10.2%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 6.9% (95% CI, 1.4% to 12.9%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
Safety and efficacy results were similar in all randomly assigned patients.
The researchers speculated that a combination of two demographic shifts over time may have led to the lower than anticipated rate of events in ACTIV-4B.
“First, the threshold for hospital admission has markedly declined since the beginning of the pandemic, such that hospitalization is no longer limited almost exclusively to those with severe pulmonary distress likely to require mechanical ventilation,” they write. “As a result, the severity of illness among individuals with COVID-19 and destined for outpatient care has declined.”
“Second, at least within the U.S., where the trial was conducted, individuals currently being infected with SARS-CoV-2 tend to be younger and have fewer comorbidities when compared with individuals with incident infection at the onset of the pandemic,” they add.
Further, COVID-19 testing was quite limited early in the pandemic, they note, “and it is possible that the anticipated event rates based on data from registries available at that time were overestimated because the denominator (that is, the number of infected individuals overall) was essentially unknown.”
Robust evidence
“The ACTIV-4B trial is the first randomized trial to generate robust evidence about the effects of antithrombotic therapy in outpatients with COVID-19,” Otavio Berwanger, MD, PhD, director of the Academic Research Organization, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, Sao Paulo-SP, Brazil, told this news organization.
“It should be noted that this was a well-designed trial with low risk of bias. On the other hand, the main limitation is the low number of events and, consequently, the limited statistical power,” said Dr. Berwanger, who wrote an accompanying editorial.
The ACTIV-4B trial has immediate implications for clinical practice, he added.
“In this sense, considering the neutral results for major cardiopulmonary outcomes, the use of aspirin or apixaban for the management of outpatients with COVID-19 should not be recommended.”
ACTIV-4B also provides useful information for the steering committees of other ongoing trials of antithrombotic therapy for patients with COVID-19 who are not hospitalized, Dr. Berwanger added.
“In this sense, probably issues like statistical power, outcome choices, recruitment feasibility, and even futility would need to be revisited. And finally, lessons learned from the implementation of an innovative, pragmatic, and decentralized trial design represent an important legacy for future trials in cardiovascular diseases and other common conditions,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Connors reports financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Abbott, Alnylam, Takeda, Roche, and Sanofi. Dr. Berwanger reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Amgen, Servier, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bayer, Novartis, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antithrombotic therapy in clinically stable, nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients does not offer protection against adverse cardiovascular or pulmonary events, new randomized clinical trial results suggest.
Antithrombotic therapy has proven useful in acutely ill inpatients with COVID-19, but in this study, treatment with aspirin or apixaban (Eliquis) did not reduce the rate of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary causes in patients ill with COVID-19 but who were not hospitalized.
“Among symptomatic, clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19, treatment with aspirin or apixaban compared with placebo did not reduce the rate of a composite clinical outcome,” the authors conclude. “However, the study was terminated after enrollment of 9% of participants because of a primary event rate lower than anticipated.”
The study, which was led by Jean M. Connors, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online October 11 in JAMA.
The ACTIV-4B Outpatient Thrombosis Prevention Trial was a randomized, adaptive, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that sought to compare anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy among 7,000 symptomatic but clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19.
The trial was conducted at 52 sites in the U.S. between Sept. 2020 and June 2021, with final follow-up this past August 5, and involved minimal face-to-face interactions with study participants.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to aspirin (81 mg orally once daily; n = 164 patients), prophylactic-dose apixaban (2.5 mg orally twice daily; n = 165), therapeutic-dose apixaban (5 mg orally twice daily; n = 164), or placebo (n = 164) for 45 days.
The primary endpoint was a composite of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary cause.
The trial was terminated early this past June by the independent data monitoring committee because of lower than anticipated event rates. At the time, just 657 symptomatic outpatients with COVID-19 had been enrolled.
The median age of the study participants was 54 years (Interquartile Range [IQR] 46-59); 59% were women.
The median time from diagnosis to randomization was 7 days, and the median time from randomization to initiation of study medications was 3 days.
The trial’s primary efficacy and safety analyses were restricted to patients who received at least one dose of trial medication, for a final number of 558 patients.
Among these patients, the primary endpoint occurred in 1 patient (0.7%) in the aspirin group, 1 patient (0.7%) in the 2.5 mg apixaban group, 2 patients (1.4%) in the 5-mg apixaban group, and 1 patient (0.7%) in the placebo group.
The researchers found that the absolute risk reductions compared with placebo for the primary outcome were 0.0% (95% confidence interval not calculable) in the aspirin group, 0.7% (95% confidence interval, -2.1% to 4.1%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 1.4% (95% CI, -1.5% to 5%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
No major bleeding events were reported.
The absolute risk differences compared with placebo for clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding events were 2% (95% CI, -2.7% to 6.8%) in the aspirin group, 4.5% (95% CI, -0.7% to 10.2%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 6.9% (95% CI, 1.4% to 12.9%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
Safety and efficacy results were similar in all randomly assigned patients.
The researchers speculated that a combination of two demographic shifts over time may have led to the lower than anticipated rate of events in ACTIV-4B.
“First, the threshold for hospital admission has markedly declined since the beginning of the pandemic, such that hospitalization is no longer limited almost exclusively to those with severe pulmonary distress likely to require mechanical ventilation,” they write. “As a result, the severity of illness among individuals with COVID-19 and destined for outpatient care has declined.”
“Second, at least within the U.S., where the trial was conducted, individuals currently being infected with SARS-CoV-2 tend to be younger and have fewer comorbidities when compared with individuals with incident infection at the onset of the pandemic,” they add.
Further, COVID-19 testing was quite limited early in the pandemic, they note, “and it is possible that the anticipated event rates based on data from registries available at that time were overestimated because the denominator (that is, the number of infected individuals overall) was essentially unknown.”
Robust evidence
“The ACTIV-4B trial is the first randomized trial to generate robust evidence about the effects of antithrombotic therapy in outpatients with COVID-19,” Otavio Berwanger, MD, PhD, director of the Academic Research Organization, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, Sao Paulo-SP, Brazil, told this news organization.
“It should be noted that this was a well-designed trial with low risk of bias. On the other hand, the main limitation is the low number of events and, consequently, the limited statistical power,” said Dr. Berwanger, who wrote an accompanying editorial.
The ACTIV-4B trial has immediate implications for clinical practice, he added.
“In this sense, considering the neutral results for major cardiopulmonary outcomes, the use of aspirin or apixaban for the management of outpatients with COVID-19 should not be recommended.”
ACTIV-4B also provides useful information for the steering committees of other ongoing trials of antithrombotic therapy for patients with COVID-19 who are not hospitalized, Dr. Berwanger added.
“In this sense, probably issues like statistical power, outcome choices, recruitment feasibility, and even futility would need to be revisited. And finally, lessons learned from the implementation of an innovative, pragmatic, and decentralized trial design represent an important legacy for future trials in cardiovascular diseases and other common conditions,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Connors reports financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Abbott, Alnylam, Takeda, Roche, and Sanofi. Dr. Berwanger reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Amgen, Servier, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bayer, Novartis, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Flesh-Colored Papule in the Nose of a Child
The Diagnosis: Striated Muscle Hamartoma
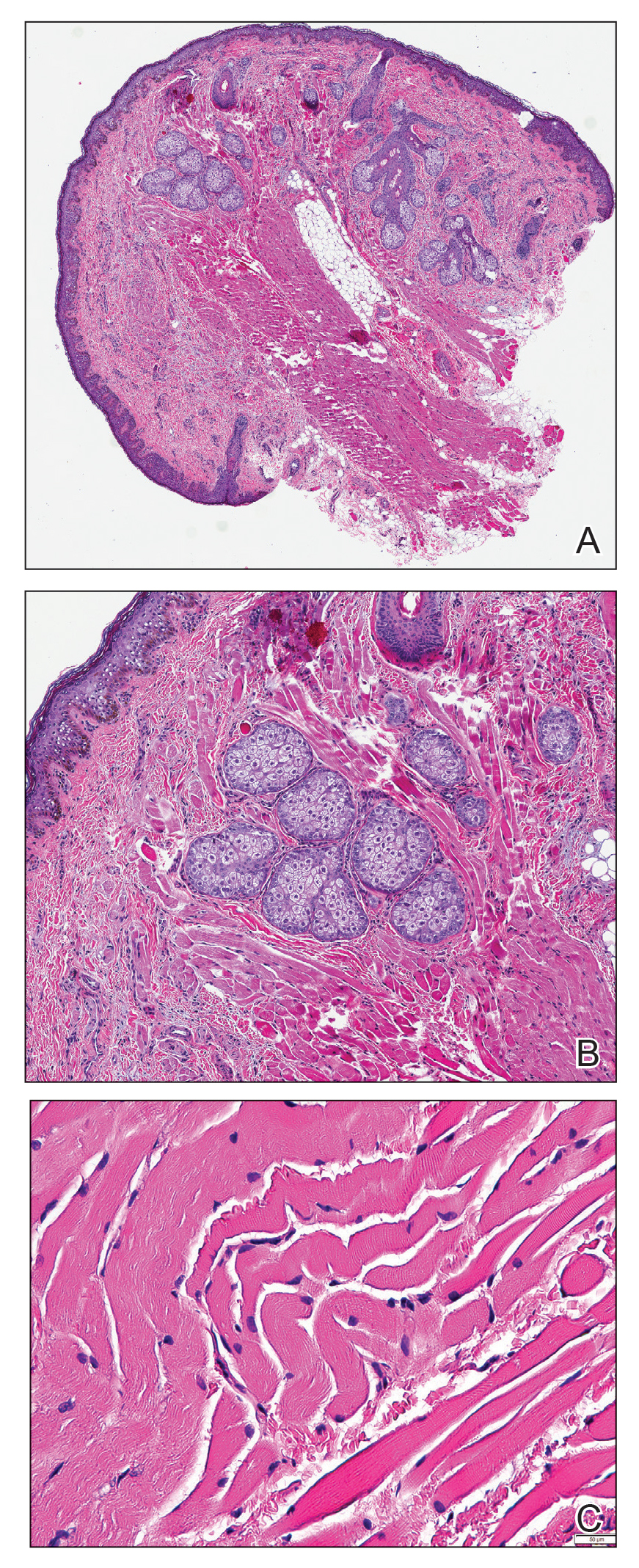
Histopathologic evaluation revealed a dome-shaped papule with a center composed of mature striated muscle bundles, vellus hairs, sebaceous lobules, and nerve twigs (Figure) consistent with a diagnosis of striated muscle hamartoma (SMH).
Striated muscle hamartoma was first described in 1986 by Hendrick et al1 with 2 cases in neonates. Biopsies of the lesions taken from the upper lip and sternum showed a characteristic histology consisting of dermal striated muscle fibers and nerve bundles in the central core of the papules associated with a marked number of adnexa. In 1989, the diagnosis of rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma was described, which showed similar findings.2 Cases reported since these entities were discovered have used the terms striated muscle hamartoma and rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma interchangeably.3
Most commonly found on the head and neck, SMH has now been observed in diverse locations including the sternum, hallux, vagina, and oral cavity.1-15 Many reported cases describe lesions around or in the nose.4,7,8 Multiple congenital anomalies have been described alongside SMH and may be associated with this entity including amniotic bands, cleft lip and palate, coloboma, and Delleman syndrome.1,3,4 Almost all of the lesions present as a sessile or pedunculated papule, polyp, nodule, or plaque measuring from 0.3 cm up to 4.9 cm and typically are present since birth.3,5,15 However, there are a few cases of lesions presenting in adults with no prior history.5,6,15
Microscopically, SMH is defined by a dermal lesion with a core comprised of mature skeletal muscle admixed with adipose tissue, adnexa, nerve bundles, and fibrovascular tissue.1 There are other entities that should be considered before making the diagnosis of SMH. Other hamartomas such as accessory tragus, connective tissue nevus, fibrous hamartoma of infancy, and nevus lipomatosis may present similarly; however, these lesions classically lack skeletal muscle. Benign triton tumors, or neuromuscular hamartomas, are rare lesions composed of skeletal muscle and abundant, intimately associated neural tissue. Neuromuscular hamartomas frequently involve large nerves.16 Rhabdomyomas also should be considered. Adult rhabdomyomas are composed of eosinophilic polygonal cells with granular cytoplasm and occasional cross-striations. Fetal rhabdomyomas have multiple histologic types and are defined by a variable myxoid stroma, eosinophilic spindled cells, and rhabdomyocytes in various stages of maturity. Genital rhabdomyomas histopathologically appear similar to fetal rhabdomyomas but are confined to the genital region. The skeletal muscle present in rhabdomyomas typically is less differentiated.17 TMature skeletal bundles should be a dominant component of the lesion before diagnosing SMH.
Typically presenting as congenital lesions in the head and neck region, papules with a dermal core of mature skeletal muscle associated with adnexa and nerve twigs should prompt consideration of a diagnosis of SMH or rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. These lesions are benign and usually are cured with complete excision.
- Hendrick SJ, Sanchez RL, Blackwell SJ, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma: description of two cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986;3:153-157.
- Mills AE. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 1989;1:58-63.
- Rosenberg AS, Kirk J, Morgan MB. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: an unusual dermal entity with a report of two cases and a review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2002;29:238-243.
- Sánchez RL, Raimer SS. Clinical and histologic features of striated muscle hamartoma: possible relationship to Delleman’s syndrome. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:40-46.
- Chang CP, Chen GS. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: a plaque-type variant in an adult. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2005;21:185-188.
- Harris MA, Dutton JJ, Proia AD. Striated muscle hamartoma of the eyelid in an adult woman. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;24:492-494.
- Nakanishi H, Hashimoto I, Takiwaki H, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma of the nostril. J Dermatol. 1995;22:504-507.
- Farris PE, Manning S, Veatch F. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:73-75.
- Grilli R, Escalonilla P, Soriano ML, et al. The so-called striated muscle hamartoma is a hamartoma of cutaneous adnexa and mesenchyme, but not of striated muscle. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:390.
- Sampat K, Cheesman E, Siminas S. Perianal rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017;99:E193-E195.
- Brinster NK, Farmer ER. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting on a digit. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:61-63.
- Han SH, Song HJ, Hong WK, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of the vagina. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:753-755.
- De la Sotta P, Salomone C, González S. Rhabdomyomatous (mesenchymal) hamartoma of the tongue: report of a case. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36:58-59.
- Magro G, Di Benedetto A, Sanges G, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of oral cavity: an unusual location for such a rare lesion. Virchows Arch. 2005;446:346-347.
- Wang Y, Zhao H, Yue X, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting as a big subcutaneous mass on the neck: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2014;8:410.
- Amita K, Shankar SV, Nischal KC, et al. Benign triton tumor: a rare entity in head and neck region. Korean J Pathol. 2013;47:74-76.
- Walsh S, Hurt M. Cutaneous fetal rhabdomyoma: a case report and historical review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:485-491.
The Diagnosis: Striated Muscle Hamartoma
Histopathologic evaluation revealed a dome-shaped papule with a center composed of mature striated muscle bundles, vellus hairs, sebaceous lobules, and nerve twigs (Figure) consistent with a diagnosis of striated muscle hamartoma (SMH).

Striated muscle hamartoma was first described in 1986 by Hendrick et al1 with 2 cases in neonates. Biopsies of the lesions taken from the upper lip and sternum showed a characteristic histology consisting of dermal striated muscle fibers and nerve bundles in the central core of the papules associated with a marked number of adnexa. In 1989, the diagnosis of rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma was described, which showed similar findings.2 Cases reported since these entities were discovered have used the terms striated muscle hamartoma and rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma interchangeably.3
Most commonly found on the head and neck, SMH has now been observed in diverse locations including the sternum, hallux, vagina, and oral cavity.1-15 Many reported cases describe lesions around or in the nose.4,7,8 Multiple congenital anomalies have been described alongside SMH and may be associated with this entity including amniotic bands, cleft lip and palate, coloboma, and Delleman syndrome.1,3,4 Almost all of the lesions present as a sessile or pedunculated papule, polyp, nodule, or plaque measuring from 0.3 cm up to 4.9 cm and typically are present since birth.3,5,15 However, there are a few cases of lesions presenting in adults with no prior history.5,6,15
Microscopically, SMH is defined by a dermal lesion with a core comprised of mature skeletal muscle admixed with adipose tissue, adnexa, nerve bundles, and fibrovascular tissue.1 There are other entities that should be considered before making the diagnosis of SMH. Other hamartomas such as accessory tragus, connective tissue nevus, fibrous hamartoma of infancy, and nevus lipomatosis may present similarly; however, these lesions classically lack skeletal muscle. Benign triton tumors, or neuromuscular hamartomas, are rare lesions composed of skeletal muscle and abundant, intimately associated neural tissue. Neuromuscular hamartomas frequently involve large nerves.16 Rhabdomyomas also should be considered. Adult rhabdomyomas are composed of eosinophilic polygonal cells with granular cytoplasm and occasional cross-striations. Fetal rhabdomyomas have multiple histologic types and are defined by a variable myxoid stroma, eosinophilic spindled cells, and rhabdomyocytes in various stages of maturity. Genital rhabdomyomas histopathologically appear similar to fetal rhabdomyomas but are confined to the genital region. The skeletal muscle present in rhabdomyomas typically is less differentiated.17 TMature skeletal bundles should be a dominant component of the lesion before diagnosing SMH.
Typically presenting as congenital lesions in the head and neck region, papules with a dermal core of mature skeletal muscle associated with adnexa and nerve twigs should prompt consideration of a diagnosis of SMH or rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. These lesions are benign and usually are cured with complete excision.
The Diagnosis: Striated Muscle Hamartoma
Histopathologic evaluation revealed a dome-shaped papule with a center composed of mature striated muscle bundles, vellus hairs, sebaceous lobules, and nerve twigs (Figure) consistent with a diagnosis of striated muscle hamartoma (SMH).

Striated muscle hamartoma was first described in 1986 by Hendrick et al1 with 2 cases in neonates. Biopsies of the lesions taken from the upper lip and sternum showed a characteristic histology consisting of dermal striated muscle fibers and nerve bundles in the central core of the papules associated with a marked number of adnexa. In 1989, the diagnosis of rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma was described, which showed similar findings.2 Cases reported since these entities were discovered have used the terms striated muscle hamartoma and rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma interchangeably.3
Most commonly found on the head and neck, SMH has now been observed in diverse locations including the sternum, hallux, vagina, and oral cavity.1-15 Many reported cases describe lesions around or in the nose.4,7,8 Multiple congenital anomalies have been described alongside SMH and may be associated with this entity including amniotic bands, cleft lip and palate, coloboma, and Delleman syndrome.1,3,4 Almost all of the lesions present as a sessile or pedunculated papule, polyp, nodule, or plaque measuring from 0.3 cm up to 4.9 cm and typically are present since birth.3,5,15 However, there are a few cases of lesions presenting in adults with no prior history.5,6,15
Microscopically, SMH is defined by a dermal lesion with a core comprised of mature skeletal muscle admixed with adipose tissue, adnexa, nerve bundles, and fibrovascular tissue.1 There are other entities that should be considered before making the diagnosis of SMH. Other hamartomas such as accessory tragus, connective tissue nevus, fibrous hamartoma of infancy, and nevus lipomatosis may present similarly; however, these lesions classically lack skeletal muscle. Benign triton tumors, or neuromuscular hamartomas, are rare lesions composed of skeletal muscle and abundant, intimately associated neural tissue. Neuromuscular hamartomas frequently involve large nerves.16 Rhabdomyomas also should be considered. Adult rhabdomyomas are composed of eosinophilic polygonal cells with granular cytoplasm and occasional cross-striations. Fetal rhabdomyomas have multiple histologic types and are defined by a variable myxoid stroma, eosinophilic spindled cells, and rhabdomyocytes in various stages of maturity. Genital rhabdomyomas histopathologically appear similar to fetal rhabdomyomas but are confined to the genital region. The skeletal muscle present in rhabdomyomas typically is less differentiated.17 TMature skeletal bundles should be a dominant component of the lesion before diagnosing SMH.
Typically presenting as congenital lesions in the head and neck region, papules with a dermal core of mature skeletal muscle associated with adnexa and nerve twigs should prompt consideration of a diagnosis of SMH or rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. These lesions are benign and usually are cured with complete excision.
- Hendrick SJ, Sanchez RL, Blackwell SJ, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma: description of two cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986;3:153-157.
- Mills AE. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 1989;1:58-63.
- Rosenberg AS, Kirk J, Morgan MB. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: an unusual dermal entity with a report of two cases and a review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2002;29:238-243.
- Sánchez RL, Raimer SS. Clinical and histologic features of striated muscle hamartoma: possible relationship to Delleman’s syndrome. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:40-46.
- Chang CP, Chen GS. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: a plaque-type variant in an adult. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2005;21:185-188.
- Harris MA, Dutton JJ, Proia AD. Striated muscle hamartoma of the eyelid in an adult woman. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;24:492-494.
- Nakanishi H, Hashimoto I, Takiwaki H, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma of the nostril. J Dermatol. 1995;22:504-507.
- Farris PE, Manning S, Veatch F. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:73-75.
- Grilli R, Escalonilla P, Soriano ML, et al. The so-called striated muscle hamartoma is a hamartoma of cutaneous adnexa and mesenchyme, but not of striated muscle. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:390.
- Sampat K, Cheesman E, Siminas S. Perianal rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017;99:E193-E195.
- Brinster NK, Farmer ER. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting on a digit. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:61-63.
- Han SH, Song HJ, Hong WK, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of the vagina. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:753-755.
- De la Sotta P, Salomone C, González S. Rhabdomyomatous (mesenchymal) hamartoma of the tongue: report of a case. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36:58-59.
- Magro G, Di Benedetto A, Sanges G, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of oral cavity: an unusual location for such a rare lesion. Virchows Arch. 2005;446:346-347.
- Wang Y, Zhao H, Yue X, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting as a big subcutaneous mass on the neck: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2014;8:410.
- Amita K, Shankar SV, Nischal KC, et al. Benign triton tumor: a rare entity in head and neck region. Korean J Pathol. 2013;47:74-76.
- Walsh S, Hurt M. Cutaneous fetal rhabdomyoma: a case report and historical review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:485-491.
- Hendrick SJ, Sanchez RL, Blackwell SJ, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma: description of two cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986;3:153-157.
- Mills AE. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 1989;1:58-63.
- Rosenberg AS, Kirk J, Morgan MB. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: an unusual dermal entity with a report of two cases and a review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2002;29:238-243.
- Sánchez RL, Raimer SS. Clinical and histologic features of striated muscle hamartoma: possible relationship to Delleman’s syndrome. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:40-46.
- Chang CP, Chen GS. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: a plaque-type variant in an adult. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2005;21:185-188.
- Harris MA, Dutton JJ, Proia AD. Striated muscle hamartoma of the eyelid in an adult woman. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;24:492-494.
- Nakanishi H, Hashimoto I, Takiwaki H, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma of the nostril. J Dermatol. 1995;22:504-507.
- Farris PE, Manning S, Veatch F. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:73-75.
- Grilli R, Escalonilla P, Soriano ML, et al. The so-called striated muscle hamartoma is a hamartoma of cutaneous adnexa and mesenchyme, but not of striated muscle. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:390.
- Sampat K, Cheesman E, Siminas S. Perianal rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017;99:E193-E195.
- Brinster NK, Farmer ER. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting on a digit. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:61-63.
- Han SH, Song HJ, Hong WK, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of the vagina. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:753-755.
- De la Sotta P, Salomone C, González S. Rhabdomyomatous (mesenchymal) hamartoma of the tongue: report of a case. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36:58-59.
- Magro G, Di Benedetto A, Sanges G, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of oral cavity: an unusual location for such a rare lesion. Virchows Arch. 2005;446:346-347.
- Wang Y, Zhao H, Yue X, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting as a big subcutaneous mass on the neck: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2014;8:410.
- Amita K, Shankar SV, Nischal KC, et al. Benign triton tumor: a rare entity in head and neck region. Korean J Pathol. 2013;47:74-76.
- Walsh S, Hurt M. Cutaneous fetal rhabdomyoma: a case report and historical review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:485-491.
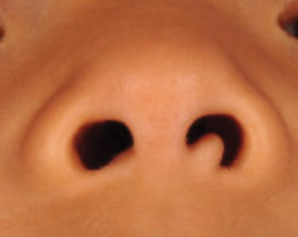
A 4-year-old girl presented to our clinic with an asymptomatic flesh-colored papule in the left nostril. The lesion had been present since birth and grew in relation to the patient with no rapid changes. There had been no pigmentation changes and no bleeding, pain, or itching. The patient’s birth and developmental history were normal. Physical examination revealed a singular, 10×5-mm, flesh-colored, pedunculated mass on the left nasal sill. There were no additional lesions present. An excisional biopsy was performed and submitted for pathologic diagnosis.
Convenience, not outcomes may drive robot-assisted surgeries
“The problem in minimally invasive surgery, especially in cancer surgery, is that the concept has been flip-flopped,” said Hooman Noorchashm, MD, PhD, a retired cardiothoracic surgeon turned patient advocate. “The main purpose of surgery should be removal of diseased tissue or repair of damaged tissue with adequate safety. The size of the incision on that triage scheme is secondary.”
In 2013, Dr. Noorchashm’s wife, Amy Reed, MD, an anesthesiologist, had a hysterectomy for treatment of severe uterine fibroids. The surgery was performed with a laparoscopic power morcellator, which led to the dissemination of cells from a previously undetected abdominal lesion. She was later diagnosed with stage 4 leiomyosarcoma and died in May 2017.
Dr. Noorchashm said the problem with robotic surgery isn’t the technology itself or how it’s used, but why it’s used in the first place. “Not only was there an extreme level of laxity with respect to the malignant potential of fibroids, but also that the size of the incision supersedes the safety of the procedure.”
The ultimate goal of oncologic surgery is to achieve an en bloc resection with clean surgical margins and removal of the tumor intact, Dr. Noorchashm said. The only scientific way of showing the benefits or therapeutic equivalence of new technology is through noninferiority comparison trials.
Robotic surgery inching toward $14 billion in revenue by 2028
Although robotic surgical technology has been in use since the 1990s, the technology is still considered to be its infancy. The first Food and Drug Administration–approved robotics platform, the da Vinci Surgical System (Intuitive Surgical) was approved by the FDA in 2000. And, now, with its patent expiring in 2022, competitors will be developing and launching new products for abdominal and colorectal surgery, partial knee replacements, cardiovascular procedures, head and neck surgery, and spinal procedures.
Robotic surgery is a rapidly expanding area with new product launches announced daily. In August 2021, the market research firm Grand View Research, reported the surgical robot marketplace is projected to reach $14 billion by 2028, up from $3.6 billion this year.
“This new era of robotic-assisted surgery attracts both surgeons and patients. Robotic surgery has reshaped our surgeries over the last 2 decades, and robots are now used in almost in every surgical field. Still, as surgeons, we continue to look – with great interest – to new robotic companies that may be able to provide better robots in a more cost-effective manner,” wrote urologists Ahmad Almujalhem and Koon Ho Rha in a review published in the journal BJUI Compass.
However, the authors wrote that, although the market is competitive, cost remains an issue, as are competing interests. In addition, many companies are creating replicas of existing technologies instead of focusing on new designs and new technology. “Although the da Vinci system propelled many robots to market, there has been no significant improvement in the console,” they added.
The technology is attractive to both surgeons and patients. “Surgeons are attracted to newer technologies, better vision, and easier learning curves. Patients are also attracted to robotic surgery, as this technology is considered state of the art and is associated with reduced pain and scar size,” the authors wrote.
Outcomes depend on many variables
In terms of outcomes, the literature is mixed. It largely depends on a number of variables from the site of surgery, the type of cancer, technology used, and the surgeon’s skill.
Jung Mogg Kim, MD, PhD, a microbiologist with Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea, published a systemic review and meta-analysis of 27 clinical reports in PLoS ONE assessing clinical outcomes. They found that robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery did not result in statistically superior outcomes, compared with conventional laparoscopic surgery, except for lower estimated blood loss with robots. Operative time and total complications rates were “significantly more favorable” with conventional laparoscopic procedures.
Thomas E. Ahlering, MD, a robotic prostatectomy specialist at the University of California, Irvine, explained that the success or failure of robot-assisted surgery can be highly dependent on the body site and tumor type.
“The oncologic outcome, as long as the surgeon is up to speed, is not going to be better, but the goal is to be as good,” he said in an interview.
In most cases, Dr. Ahlering said, the goal of surgery is to remove a viable tumor with clean margins while leaving the organ intact. But in prostate surgery, the goal is to remove the entire organ while trying to preserve urinary continence and sexual function.
“One of the biggest benefits of the robot is that we’re able to use it in a laparoscopic environment meaning that we need a pneumoperitoneum [which] dramatically decreases bleeding. In prostate cancer, the area is so highly vascular that bleeding is a major issue,” he said.
The same benefits of reduced bleeding, improved visualization, and precision are also seen with robotic-assisted surgery for renal cancer, he noted.
He also emphasized that positive surgical margins, while less desirable than complete elimination of malignant cells, is not nearly as dire in prostate cancer as it is in surgery for other malignancies, such as soft-tissue sarcomas.
“The majority of cases are never going to recur, and if they do recur they essentially never lead to metastatic disease to bone, much less to prostate cancer–related death. The only thing they can do is slightly increase the PSA [prostate-specific antigen] recurrence,” he said.
Assuming that outcomes are comparable between an open procedure, conventional laparoscopic procedure, or robot-assisted approach, surgeons “will almost all go for the robot. It’s easier on the surgeon and it’s easier on the system,” Dr. Ahlering said.
In skilled hands for select patients, the use of a carefully researched and well-designed surgical assistive device can result in outcomes that are comparable with those seen in open surgical procedures, with robot-assisted surgery offering the possibility of less perioperative bleeding, lower postoperative morbidity, and faster recovery times.
“In our program we have been using robots to perform robotic radical prostatectomy and nephron-sparing surgery – partial nephrectomy and we’re also using them to perform intracorporeal bowel reconstruction and robotic radical cystectomy,” said Ashutosh Tewari, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Robot-assisted surgery can be used “anywhere where you have to be selective, anywhere where you have to be reconstructive, anywhere where [assisted] vision can help, anywhere where the lack of bleeding will be of help to patients, and anywhere where a smaller incision can achieve the same goals,” Dr. Tewari said in an interview. Dr. Tewari’s Mount Sinai colleagues reported at the 2021 American Urological Association annual meeting, robotic-assisted salvage radical and partial nephrectomies were found to be safe and feasible procedures in patients with metachronous kidney tumors. For patients with early invasive cancer (stage pT1), oncologic outcomes with robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy were similar to those of patients who underwent radical surgery. The authors concluded that salvage robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy “can be considered in this group of patients due to the risk of future recurrences and need to preserve renal function.”
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network guideline for prostate cancer, updated in September 2021, states that “laparoscopic and robot-assisted radical prostatectomy are commonly used and are considered comparable to conventional approaches in experienced hands.”
In 2018, researchers in a multinational comparison trial reported that patients with cervical cancer who were randomly assigned to minimally invasive robot-assisted radical hysterectomy had significantly lower rates of both disease-free survival and overall survival than women randomized to open abdominal radical hysterectomy. The study results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The use of robotically assisted surgical (RAS) devices could possibly create a “shielding layer” between the surgical team and patient reducing the risk of infection, according to Ajmal Zemmar, MD, PhD, FMH, a neurosurgeon with the University of Louisville (Ky.) Dr. Zemmar and colleagues recently published a perspective in Nature Machine Intelligence on trends in the use of surgical robots.
“In the operating theatre, robots can place intravascular lines, intubate the patient and manage the airway. The integration of a robot as a shielding layer, physically separating the health care worker and patient, is a powerful tool to combat the omnipresent fear of pathogen contamination and maintain surgical volumes,” Dr. Zemmar and colleagues wrote.
Surgical vs. clinical outcomes
In July 2021, this news organization reported that clinical trials of RAS for nipple-sparing mastectomy procedures were looking primarily at cosmetic or surgical outcomes and were not collecting cancer outcomes and if they were, it was secondary to cosmetic or surgical outcomes.
The FDA followed up by issuing a safety communication in August warning patients and providers that neither the safety nor efficacy of RAS for use in mastectomy procedures or treatment of breast cancer have been established.
“In addition, the FDA is aware of allegations that clinical studies are being conducted using RAS devices to perform mastectomies for the prevention or treatment of cancer without the FDA oversight required for such significant risk studies,” the communication stated.
Dr. Tewari disclosed relationships with various companies. Dr. Noorchashm had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Ahlering disclosed past funding or other considerations from Intuitive Robotics.
“The problem in minimally invasive surgery, especially in cancer surgery, is that the concept has been flip-flopped,” said Hooman Noorchashm, MD, PhD, a retired cardiothoracic surgeon turned patient advocate. “The main purpose of surgery should be removal of diseased tissue or repair of damaged tissue with adequate safety. The size of the incision on that triage scheme is secondary.”
In 2013, Dr. Noorchashm’s wife, Amy Reed, MD, an anesthesiologist, had a hysterectomy for treatment of severe uterine fibroids. The surgery was performed with a laparoscopic power morcellator, which led to the dissemination of cells from a previously undetected abdominal lesion. She was later diagnosed with stage 4 leiomyosarcoma and died in May 2017.
Dr. Noorchashm said the problem with robotic surgery isn’t the technology itself or how it’s used, but why it’s used in the first place. “Not only was there an extreme level of laxity with respect to the malignant potential of fibroids, but also that the size of the incision supersedes the safety of the procedure.”
The ultimate goal of oncologic surgery is to achieve an en bloc resection with clean surgical margins and removal of the tumor intact, Dr. Noorchashm said. The only scientific way of showing the benefits or therapeutic equivalence of new technology is through noninferiority comparison trials.
Robotic surgery inching toward $14 billion in revenue by 2028
Although robotic surgical technology has been in use since the 1990s, the technology is still considered to be its infancy. The first Food and Drug Administration–approved robotics platform, the da Vinci Surgical System (Intuitive Surgical) was approved by the FDA in 2000. And, now, with its patent expiring in 2022, competitors will be developing and launching new products for abdominal and colorectal surgery, partial knee replacements, cardiovascular procedures, head and neck surgery, and spinal procedures.
Robotic surgery is a rapidly expanding area with new product launches announced daily. In August 2021, the market research firm Grand View Research, reported the surgical robot marketplace is projected to reach $14 billion by 2028, up from $3.6 billion this year.
“This new era of robotic-assisted surgery attracts both surgeons and patients. Robotic surgery has reshaped our surgeries over the last 2 decades, and robots are now used in almost in every surgical field. Still, as surgeons, we continue to look – with great interest – to new robotic companies that may be able to provide better robots in a more cost-effective manner,” wrote urologists Ahmad Almujalhem and Koon Ho Rha in a review published in the journal BJUI Compass.
However, the authors wrote that, although the market is competitive, cost remains an issue, as are competing interests. In addition, many companies are creating replicas of existing technologies instead of focusing on new designs and new technology. “Although the da Vinci system propelled many robots to market, there has been no significant improvement in the console,” they added.
The technology is attractive to both surgeons and patients. “Surgeons are attracted to newer technologies, better vision, and easier learning curves. Patients are also attracted to robotic surgery, as this technology is considered state of the art and is associated with reduced pain and scar size,” the authors wrote.
Outcomes depend on many variables
In terms of outcomes, the literature is mixed. It largely depends on a number of variables from the site of surgery, the type of cancer, technology used, and the surgeon’s skill.
Jung Mogg Kim, MD, PhD, a microbiologist with Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea, published a systemic review and meta-analysis of 27 clinical reports in PLoS ONE assessing clinical outcomes. They found that robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery did not result in statistically superior outcomes, compared with conventional laparoscopic surgery, except for lower estimated blood loss with robots. Operative time and total complications rates were “significantly more favorable” with conventional laparoscopic procedures.
Thomas E. Ahlering, MD, a robotic prostatectomy specialist at the University of California, Irvine, explained that the success or failure of robot-assisted surgery can be highly dependent on the body site and tumor type.
“The oncologic outcome, as long as the surgeon is up to speed, is not going to be better, but the goal is to be as good,” he said in an interview.
In most cases, Dr. Ahlering said, the goal of surgery is to remove a viable tumor with clean margins while leaving the organ intact. But in prostate surgery, the goal is to remove the entire organ while trying to preserve urinary continence and sexual function.
“One of the biggest benefits of the robot is that we’re able to use it in a laparoscopic environment meaning that we need a pneumoperitoneum [which] dramatically decreases bleeding. In prostate cancer, the area is so highly vascular that bleeding is a major issue,” he said.
The same benefits of reduced bleeding, improved visualization, and precision are also seen with robotic-assisted surgery for renal cancer, he noted.
He also emphasized that positive surgical margins, while less desirable than complete elimination of malignant cells, is not nearly as dire in prostate cancer as it is in surgery for other malignancies, such as soft-tissue sarcomas.
“The majority of cases are never going to recur, and if they do recur they essentially never lead to metastatic disease to bone, much less to prostate cancer–related death. The only thing they can do is slightly increase the PSA [prostate-specific antigen] recurrence,” he said.
Assuming that outcomes are comparable between an open procedure, conventional laparoscopic procedure, or robot-assisted approach, surgeons “will almost all go for the robot. It’s easier on the surgeon and it’s easier on the system,” Dr. Ahlering said.
In skilled hands for select patients, the use of a carefully researched and well-designed surgical assistive device can result in outcomes that are comparable with those seen in open surgical procedures, with robot-assisted surgery offering the possibility of less perioperative bleeding, lower postoperative morbidity, and faster recovery times.
“In our program we have been using robots to perform robotic radical prostatectomy and nephron-sparing surgery – partial nephrectomy and we’re also using them to perform intracorporeal bowel reconstruction and robotic radical cystectomy,” said Ashutosh Tewari, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Robot-assisted surgery can be used “anywhere where you have to be selective, anywhere where you have to be reconstructive, anywhere where [assisted] vision can help, anywhere where the lack of bleeding will be of help to patients, and anywhere where a smaller incision can achieve the same goals,” Dr. Tewari said in an interview. Dr. Tewari’s Mount Sinai colleagues reported at the 2021 American Urological Association annual meeting, robotic-assisted salvage radical and partial nephrectomies were found to be safe and feasible procedures in patients with metachronous kidney tumors. For patients with early invasive cancer (stage pT1), oncologic outcomes with robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy were similar to those of patients who underwent radical surgery. The authors concluded that salvage robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy “can be considered in this group of patients due to the risk of future recurrences and need to preserve renal function.”
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network guideline for prostate cancer, updated in September 2021, states that “laparoscopic and robot-assisted radical prostatectomy are commonly used and are considered comparable to conventional approaches in experienced hands.”
In 2018, researchers in a multinational comparison trial reported that patients with cervical cancer who were randomly assigned to minimally invasive robot-assisted radical hysterectomy had significantly lower rates of both disease-free survival and overall survival than women randomized to open abdominal radical hysterectomy. The study results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The use of robotically assisted surgical (RAS) devices could possibly create a “shielding layer” between the surgical team and patient reducing the risk of infection, according to Ajmal Zemmar, MD, PhD, FMH, a neurosurgeon with the University of Louisville (Ky.) Dr. Zemmar and colleagues recently published a perspective in Nature Machine Intelligence on trends in the use of surgical robots.
“In the operating theatre, robots can place intravascular lines, intubate the patient and manage the airway. The integration of a robot as a shielding layer, physically separating the health care worker and patient, is a powerful tool to combat the omnipresent fear of pathogen contamination and maintain surgical volumes,” Dr. Zemmar and colleagues wrote.
Surgical vs. clinical outcomes
In July 2021, this news organization reported that clinical trials of RAS for nipple-sparing mastectomy procedures were looking primarily at cosmetic or surgical outcomes and were not collecting cancer outcomes and if they were, it was secondary to cosmetic or surgical outcomes.
The FDA followed up by issuing a safety communication in August warning patients and providers that neither the safety nor efficacy of RAS for use in mastectomy procedures or treatment of breast cancer have been established.
“In addition, the FDA is aware of allegations that clinical studies are being conducted using RAS devices to perform mastectomies for the prevention or treatment of cancer without the FDA oversight required for such significant risk studies,” the communication stated.
Dr. Tewari disclosed relationships with various companies. Dr. Noorchashm had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Ahlering disclosed past funding or other considerations from Intuitive Robotics.
“The problem in minimally invasive surgery, especially in cancer surgery, is that the concept has been flip-flopped,” said Hooman Noorchashm, MD, PhD, a retired cardiothoracic surgeon turned patient advocate. “The main purpose of surgery should be removal of diseased tissue or repair of damaged tissue with adequate safety. The size of the incision on that triage scheme is secondary.”
In 2013, Dr. Noorchashm’s wife, Amy Reed, MD, an anesthesiologist, had a hysterectomy for treatment of severe uterine fibroids. The surgery was performed with a laparoscopic power morcellator, which led to the dissemination of cells from a previously undetected abdominal lesion. She was later diagnosed with stage 4 leiomyosarcoma and died in May 2017.
Dr. Noorchashm said the problem with robotic surgery isn’t the technology itself or how it’s used, but why it’s used in the first place. “Not only was there an extreme level of laxity with respect to the malignant potential of fibroids, but also that the size of the incision supersedes the safety of the procedure.”
The ultimate goal of oncologic surgery is to achieve an en bloc resection with clean surgical margins and removal of the tumor intact, Dr. Noorchashm said. The only scientific way of showing the benefits or therapeutic equivalence of new technology is through noninferiority comparison trials.
Robotic surgery inching toward $14 billion in revenue by 2028
Although robotic surgical technology has been in use since the 1990s, the technology is still considered to be its infancy. The first Food and Drug Administration–approved robotics platform, the da Vinci Surgical System (Intuitive Surgical) was approved by the FDA in 2000. And, now, with its patent expiring in 2022, competitors will be developing and launching new products for abdominal and colorectal surgery, partial knee replacements, cardiovascular procedures, head and neck surgery, and spinal procedures.
Robotic surgery is a rapidly expanding area with new product launches announced daily. In August 2021, the market research firm Grand View Research, reported the surgical robot marketplace is projected to reach $14 billion by 2028, up from $3.6 billion this year.
“This new era of robotic-assisted surgery attracts both surgeons and patients. Robotic surgery has reshaped our surgeries over the last 2 decades, and robots are now used in almost in every surgical field. Still, as surgeons, we continue to look – with great interest – to new robotic companies that may be able to provide better robots in a more cost-effective manner,” wrote urologists Ahmad Almujalhem and Koon Ho Rha in a review published in the journal BJUI Compass.
However, the authors wrote that, although the market is competitive, cost remains an issue, as are competing interests. In addition, many companies are creating replicas of existing technologies instead of focusing on new designs and new technology. “Although the da Vinci system propelled many robots to market, there has been no significant improvement in the console,” they added.
The technology is attractive to both surgeons and patients. “Surgeons are attracted to newer technologies, better vision, and easier learning curves. Patients are also attracted to robotic surgery, as this technology is considered state of the art and is associated with reduced pain and scar size,” the authors wrote.
Outcomes depend on many variables
In terms of outcomes, the literature is mixed. It largely depends on a number of variables from the site of surgery, the type of cancer, technology used, and the surgeon’s skill.
Jung Mogg Kim, MD, PhD, a microbiologist with Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea, published a systemic review and meta-analysis of 27 clinical reports in PLoS ONE assessing clinical outcomes. They found that robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery did not result in statistically superior outcomes, compared with conventional laparoscopic surgery, except for lower estimated blood loss with robots. Operative time and total complications rates were “significantly more favorable” with conventional laparoscopic procedures.
Thomas E. Ahlering, MD, a robotic prostatectomy specialist at the University of California, Irvine, explained that the success or failure of robot-assisted surgery can be highly dependent on the body site and tumor type.
“The oncologic outcome, as long as the surgeon is up to speed, is not going to be better, but the goal is to be as good,” he said in an interview.
In most cases, Dr. Ahlering said, the goal of surgery is to remove a viable tumor with clean margins while leaving the organ intact. But in prostate surgery, the goal is to remove the entire organ while trying to preserve urinary continence and sexual function.
“One of the biggest benefits of the robot is that we’re able to use it in a laparoscopic environment meaning that we need a pneumoperitoneum [which] dramatically decreases bleeding. In prostate cancer, the area is so highly vascular that bleeding is a major issue,” he said.
The same benefits of reduced bleeding, improved visualization, and precision are also seen with robotic-assisted surgery for renal cancer, he noted.
He also emphasized that positive surgical margins, while less desirable than complete elimination of malignant cells, is not nearly as dire in prostate cancer as it is in surgery for other malignancies, such as soft-tissue sarcomas.
“The majority of cases are never going to recur, and if they do recur they essentially never lead to metastatic disease to bone, much less to prostate cancer–related death. The only thing they can do is slightly increase the PSA [prostate-specific antigen] recurrence,” he said.
Assuming that outcomes are comparable between an open procedure, conventional laparoscopic procedure, or robot-assisted approach, surgeons “will almost all go for the robot. It’s easier on the surgeon and it’s easier on the system,” Dr. Ahlering said.
In skilled hands for select patients, the use of a carefully researched and well-designed surgical assistive device can result in outcomes that are comparable with those seen in open surgical procedures, with robot-assisted surgery offering the possibility of less perioperative bleeding, lower postoperative morbidity, and faster recovery times.
“In our program we have been using robots to perform robotic radical prostatectomy and nephron-sparing surgery – partial nephrectomy and we’re also using them to perform intracorporeal bowel reconstruction and robotic radical cystectomy,” said Ashutosh Tewari, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Robot-assisted surgery can be used “anywhere where you have to be selective, anywhere where you have to be reconstructive, anywhere where [assisted] vision can help, anywhere where the lack of bleeding will be of help to patients, and anywhere where a smaller incision can achieve the same goals,” Dr. Tewari said in an interview. Dr. Tewari’s Mount Sinai colleagues reported at the 2021 American Urological Association annual meeting, robotic-assisted salvage radical and partial nephrectomies were found to be safe and feasible procedures in patients with metachronous kidney tumors. For patients with early invasive cancer (stage pT1), oncologic outcomes with robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy were similar to those of patients who underwent radical surgery. The authors concluded that salvage robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy “can be considered in this group of patients due to the risk of future recurrences and need to preserve renal function.”
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network guideline for prostate cancer, updated in September 2021, states that “laparoscopic and robot-assisted radical prostatectomy are commonly used and are considered comparable to conventional approaches in experienced hands.”
In 2018, researchers in a multinational comparison trial reported that patients with cervical cancer who were randomly assigned to minimally invasive robot-assisted radical hysterectomy had significantly lower rates of both disease-free survival and overall survival than women randomized to open abdominal radical hysterectomy. The study results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The use of robotically assisted surgical (RAS) devices could possibly create a “shielding layer” between the surgical team and patient reducing the risk of infection, according to Ajmal Zemmar, MD, PhD, FMH, a neurosurgeon with the University of Louisville (Ky.) Dr. Zemmar and colleagues recently published a perspective in Nature Machine Intelligence on trends in the use of surgical robots.
“In the operating theatre, robots can place intravascular lines, intubate the patient and manage the airway. The integration of a robot as a shielding layer, physically separating the health care worker and patient, is a powerful tool to combat the omnipresent fear of pathogen contamination and maintain surgical volumes,” Dr. Zemmar and colleagues wrote.
Surgical vs. clinical outcomes
In July 2021, this news organization reported that clinical trials of RAS for nipple-sparing mastectomy procedures were looking primarily at cosmetic or surgical outcomes and were not collecting cancer outcomes and if they were, it was secondary to cosmetic or surgical outcomes.
The FDA followed up by issuing a safety communication in August warning patients and providers that neither the safety nor efficacy of RAS for use in mastectomy procedures or treatment of breast cancer have been established.
“In addition, the FDA is aware of allegations that clinical studies are being conducted using RAS devices to perform mastectomies for the prevention or treatment of cancer without the FDA oversight required for such significant risk studies,” the communication stated.
Dr. Tewari disclosed relationships with various companies. Dr. Noorchashm had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Ahlering disclosed past funding or other considerations from Intuitive Robotics.
The male biological clock – How to tell the time
For decades, we have recognized the age-related natural decline in female fecundity (the ability to reproduce) after the age of 30 (Maturitas 1988;[Suppl]1:15-22). Advanced maternal age (AMA) has also been demonstrated to increase miscarriage and pregnancies with chromosomal abnormalities, presumably from the increased rate of oocyte aneuploidy. There has been a sixfold increase in the rate of first birth in women aged 35-39 years (NCHS Data Brief 2014;152:1-8). Consequently, over the last decade, women, often before they reach AMA, have turned to elective oocyte cryopreservation for fertility preservation.
Ovarian aging
Ovarian aging occurs through the decline in quality and quantity of oocytes. The former is a reflection of the woman’s chronologic age. Markers of female ovarian aging have been utilized, for the past 3 decades, most commonly by basal follicle stimulating hormone. Currently, to assess the quantity of ovarian follicles, antimüllerian hormone (AMH) and transvaginal ultrasound for ovarian antral follicle count (AFC) are the most accurate indicators (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004:89:2977-81). While ovarian age testing, particularly AMH, has been widely used to assess a woman’s “fertility potential,” it does not reflect her natural fecundity. In a prospective cohort study, AMH levels (ng/mL) divided into < 0.7, 0.7-8.4, and > 8.4, did not affect natural conception in women aged 30-44 who were divided into the categories of <35, 35-37, or 38-44 years (JAMA 2017;318:1367-76). Although AMH does reduce success with IVF, its main value is the inverse correlation when prescribing gonadotropin dosage for controlled ovarian stimulation.
Despite the familiarity with ovarian aging effects on fertility, the male biological clock remains less studied and understood. Over the last 4 decades, paternal age has increased an average of 3.5 years presumably due to delayed child rearing from professional or personal reasons, improved contraception as well as increased divorce, remarriage, and life expectancy (Hum Reprod. 2017;32:2110-6). Nevertheless, we have little data to definitively counsel men on the effects of advanced paternal age (APA) and no consensus on an actual defined age of designation. This month’s article will summarize the current literature on male age and its impact on fertility.
Testicular aging
Men older than 45 years require approximately five times longer to achieve a pregnancy as men less than 25 after adjustment for female age (Fertil Steril. 2003;79:1520-7). The most likely parameter to assess male fertility, other than pregnancy rates, would be the sperm. Sperm counts, beginning at age 41, may decline but concentrations have been shown to increase in older men apparently because of declining semen volume (Ageing Res Rev. 2015;19:22-33). Sperm motility, but not morphology, also declines while genetic alterations of sperm increase with age. The issue of chromosomal abnormalities in sperm from men of advanced age appears to be similar to that in the oocytes of women with AMA. Consequently, both sexes may contribute to embryo aneuploidy resulting in declining fertility and increasing miscarriage.
For all ages, studies have suggested that elevated male body mass index as well as alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking, including e-cigarettes, can lead to impaired sperm production (Hum Reprod Update 2013;19:221-31).
Fertility treatment outcomes
A mainstay of fertility treatment, particularly in men with mild to moderate impairments in semen parameters, is ovulation induction with intrauterine insemination. Male age has been shown to be a significant indicator for pregnancy rates, including those with normal semen parameters (J Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;31:420-3). Men above age 45 contributed to lower pregnancy rates and higher miscarriages during IUI treatment cycles (Reprod BioMed Online 2008;17:392-7).
During IVF cycles, the sperm of men with APA often undergo ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) due to higher fertilization rates compared with standard insemination. However, APA sperm appear to have lower fertilization rates and decreased embryo development to the blastocyst stage during cycles using donor oocytes, although pregnancy outcomes are inconsistent (Trans Androl Urol. 2019;8[Suppl 1]:S22-S30; Fertil Steril. 2008;90:97-103).
Perinatal and children’s health
The offspring from APA men appear to have higher rates of stillbirth, low birth weight, and preterm birth, as well as birth defects. Men older than 40-45 years have twice the risk of an autistic child and three times the risk of schizophrenia in their offspring (Transl Psychiatry 2017;7:e1019; Am J Psychiatry 2002;159:1528-33).
Conclusions
Most of the literature supports negative effects on sperm and reproduction from men with APA. The challenge in deciphering the true role of APA on fertility is that the partner is often of AMA. A consideration to avoid this effect would be sperm cryopreservation at a younger age, similar to the common trend among women. Preimplantation genetic testing of embryos from men with APA is also a potential option to reduce miscarriage and avoid a chromosomally abnormal pregnancy. Ethicists have pondered the impact of APA on parenthood and the detrimental effect of early paternal death on the child. Nevertheless, the effect of APA in reproduction is a vital area to study with the same fervor as AMA (Fertil Steril 2009;92:1772-5).
Dr. Trolice is director of Fertility CARE – The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando. He has no conflicts. Email him at [email protected].
For decades, we have recognized the age-related natural decline in female fecundity (the ability to reproduce) after the age of 30 (Maturitas 1988;[Suppl]1:15-22). Advanced maternal age (AMA) has also been demonstrated to increase miscarriage and pregnancies with chromosomal abnormalities, presumably from the increased rate of oocyte aneuploidy. There has been a sixfold increase in the rate of first birth in women aged 35-39 years (NCHS Data Brief 2014;152:1-8). Consequently, over the last decade, women, often before they reach AMA, have turned to elective oocyte cryopreservation for fertility preservation.
Ovarian aging
Ovarian aging occurs through the decline in quality and quantity of oocytes. The former is a reflection of the woman’s chronologic age. Markers of female ovarian aging have been utilized, for the past 3 decades, most commonly by basal follicle stimulating hormone. Currently, to assess the quantity of ovarian follicles, antimüllerian hormone (AMH) and transvaginal ultrasound for ovarian antral follicle count (AFC) are the most accurate indicators (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004:89:2977-81). While ovarian age testing, particularly AMH, has been widely used to assess a woman’s “fertility potential,” it does not reflect her natural fecundity. In a prospective cohort study, AMH levels (ng/mL) divided into < 0.7, 0.7-8.4, and > 8.4, did not affect natural conception in women aged 30-44 who were divided into the categories of <35, 35-37, or 38-44 years (JAMA 2017;318:1367-76). Although AMH does reduce success with IVF, its main value is the inverse correlation when prescribing gonadotropin dosage for controlled ovarian stimulation.
Despite the familiarity with ovarian aging effects on fertility, the male biological clock remains less studied and understood. Over the last 4 decades, paternal age has increased an average of 3.5 years presumably due to delayed child rearing from professional or personal reasons, improved contraception as well as increased divorce, remarriage, and life expectancy (Hum Reprod. 2017;32:2110-6). Nevertheless, we have little data to definitively counsel men on the effects of advanced paternal age (APA) and no consensus on an actual defined age of designation. This month’s article will summarize the current literature on male age and its impact on fertility.
Testicular aging
Men older than 45 years require approximately five times longer to achieve a pregnancy as men less than 25 after adjustment for female age (Fertil Steril. 2003;79:1520-7). The most likely parameter to assess male fertility, other than pregnancy rates, would be the sperm. Sperm counts, beginning at age 41, may decline but concentrations have been shown to increase in older men apparently because of declining semen volume (Ageing Res Rev. 2015;19:22-33). Sperm motility, but not morphology, also declines while genetic alterations of sperm increase with age. The issue of chromosomal abnormalities in sperm from men of advanced age appears to be similar to that in the oocytes of women with AMA. Consequently, both sexes may contribute to embryo aneuploidy resulting in declining fertility and increasing miscarriage.
For all ages, studies have suggested that elevated male body mass index as well as alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking, including e-cigarettes, can lead to impaired sperm production (Hum Reprod Update 2013;19:221-31).
Fertility treatment outcomes
A mainstay of fertility treatment, particularly in men with mild to moderate impairments in semen parameters, is ovulation induction with intrauterine insemination. Male age has been shown to be a significant indicator for pregnancy rates, including those with normal semen parameters (J Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;31:420-3). Men above age 45 contributed to lower pregnancy rates and higher miscarriages during IUI treatment cycles (Reprod BioMed Online 2008;17:392-7).
During IVF cycles, the sperm of men with APA often undergo ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) due to higher fertilization rates compared with standard insemination. However, APA sperm appear to have lower fertilization rates and decreased embryo development to the blastocyst stage during cycles using donor oocytes, although pregnancy outcomes are inconsistent (Trans Androl Urol. 2019;8[Suppl 1]:S22-S30; Fertil Steril. 2008;90:97-103).
Perinatal and children’s health
The offspring from APA men appear to have higher rates of stillbirth, low birth weight, and preterm birth, as well as birth defects. Men older than 40-45 years have twice the risk of an autistic child and three times the risk of schizophrenia in their offspring (Transl Psychiatry 2017;7:e1019; Am J Psychiatry 2002;159:1528-33).
Conclusions
Most of the literature supports negative effects on sperm and reproduction from men with APA. The challenge in deciphering the true role of APA on fertility is that the partner is often of AMA. A consideration to avoid this effect would be sperm cryopreservation at a younger age, similar to the common trend among women. Preimplantation genetic testing of embryos from men with APA is also a potential option to reduce miscarriage and avoid a chromosomally abnormal pregnancy. Ethicists have pondered the impact of APA on parenthood and the detrimental effect of early paternal death on the child. Nevertheless, the effect of APA in reproduction is a vital area to study with the same fervor as AMA (Fertil Steril 2009;92:1772-5).
Dr. Trolice is director of Fertility CARE – The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando. He has no conflicts. Email him at [email protected].
For decades, we have recognized the age-related natural decline in female fecundity (the ability to reproduce) after the age of 30 (Maturitas 1988;[Suppl]1:15-22). Advanced maternal age (AMA) has also been demonstrated to increase miscarriage and pregnancies with chromosomal abnormalities, presumably from the increased rate of oocyte aneuploidy. There has been a sixfold increase in the rate of first birth in women aged 35-39 years (NCHS Data Brief 2014;152:1-8). Consequently, over the last decade, women, often before they reach AMA, have turned to elective oocyte cryopreservation for fertility preservation.
Ovarian aging
Ovarian aging occurs through the decline in quality and quantity of oocytes. The former is a reflection of the woman’s chronologic age. Markers of female ovarian aging have been utilized, for the past 3 decades, most commonly by basal follicle stimulating hormone. Currently, to assess the quantity of ovarian follicles, antimüllerian hormone (AMH) and transvaginal ultrasound for ovarian antral follicle count (AFC) are the most accurate indicators (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004:89:2977-81). While ovarian age testing, particularly AMH, has been widely used to assess a woman’s “fertility potential,” it does not reflect her natural fecundity. In a prospective cohort study, AMH levels (ng/mL) divided into < 0.7, 0.7-8.4, and > 8.4, did not affect natural conception in women aged 30-44 who were divided into the categories of <35, 35-37, or 38-44 years (JAMA 2017;318:1367-76). Although AMH does reduce success with IVF, its main value is the inverse correlation when prescribing gonadotropin dosage for controlled ovarian stimulation.
Despite the familiarity with ovarian aging effects on fertility, the male biological clock remains less studied and understood. Over the last 4 decades, paternal age has increased an average of 3.5 years presumably due to delayed child rearing from professional or personal reasons, improved contraception as well as increased divorce, remarriage, and life expectancy (Hum Reprod. 2017;32:2110-6). Nevertheless, we have little data to definitively counsel men on the effects of advanced paternal age (APA) and no consensus on an actual defined age of designation. This month’s article will summarize the current literature on male age and its impact on fertility.
Testicular aging
Men older than 45 years require approximately five times longer to achieve a pregnancy as men less than 25 after adjustment for female age (Fertil Steril. 2003;79:1520-7). The most likely parameter to assess male fertility, other than pregnancy rates, would be the sperm. Sperm counts, beginning at age 41, may decline but concentrations have been shown to increase in older men apparently because of declining semen volume (Ageing Res Rev. 2015;19:22-33). Sperm motility, but not morphology, also declines while genetic alterations of sperm increase with age. The issue of chromosomal abnormalities in sperm from men of advanced age appears to be similar to that in the oocytes of women with AMA. Consequently, both sexes may contribute to embryo aneuploidy resulting in declining fertility and increasing miscarriage.
For all ages, studies have suggested that elevated male body mass index as well as alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking, including e-cigarettes, can lead to impaired sperm production (Hum Reprod Update 2013;19:221-31).
Fertility treatment outcomes
A mainstay of fertility treatment, particularly in men with mild to moderate impairments in semen parameters, is ovulation induction with intrauterine insemination. Male age has been shown to be a significant indicator for pregnancy rates, including those with normal semen parameters (J Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;31:420-3). Men above age 45 contributed to lower pregnancy rates and higher miscarriages during IUI treatment cycles (Reprod BioMed Online 2008;17:392-7).
During IVF cycles, the sperm of men with APA often undergo ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) due to higher fertilization rates compared with standard insemination. However, APA sperm appear to have lower fertilization rates and decreased embryo development to the blastocyst stage during cycles using donor oocytes, although pregnancy outcomes are inconsistent (Trans Androl Urol. 2019;8[Suppl 1]:S22-S30; Fertil Steril. 2008;90:97-103).
Perinatal and children’s health
The offspring from APA men appear to have higher rates of stillbirth, low birth weight, and preterm birth, as well as birth defects. Men older than 40-45 years have twice the risk of an autistic child and three times the risk of schizophrenia in their offspring (Transl Psychiatry 2017;7:e1019; Am J Psychiatry 2002;159:1528-33).
Conclusions
Most of the literature supports negative effects on sperm and reproduction from men with APA. The challenge in deciphering the true role of APA on fertility is that the partner is often of AMA. A consideration to avoid this effect would be sperm cryopreservation at a younger age, similar to the common trend among women. Preimplantation genetic testing of embryos from men with APA is also a potential option to reduce miscarriage and avoid a chromosomally abnormal pregnancy. Ethicists have pondered the impact of APA on parenthood and the detrimental effect of early paternal death on the child. Nevertheless, the effect of APA in reproduction is a vital area to study with the same fervor as AMA (Fertil Steril 2009;92:1772-5).
Dr. Trolice is director of Fertility CARE – The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando. He has no conflicts. Email him at [email protected].
What if your patient refuses to disrobe?
Sterling Ransone Jr., MD, a family physician in Deltaville, Va., knocked on the exam room door and entered to find the patient, a 28-year-old woman, seated on the examination table. She was complaining about a fever, sore throat, and congestion.
Dr. Ransone asked if it was okay for him to lift her shirt and listen to her heart. She shook her head slightly. He decided to listen without removing the clothing, but when he put one hand on her shoulder and the stethoscope on her back, she flinched.
Instead of proceeding with the examination, Dr. Ransone, who is president-elect of the American Academy of Family Physicians, asked the patient whether everything was okay. It turned out that she had been the victim of a sexual assault and did not want a male to remove any clothing or touch her chest or back. Fortunately, Dr. Ransone’s practice had a female partner, who came in and listened to the patient’s chest.
“I’m glad I asked the patient what was going on for her because otherwise, I wouldn’t have known what she was going through,” Dr. Ransone said. “The patient felt respected and safe, and the therapeutic relationship was enhanced instead of compromised.”
Patient dignity is one of Dr. Ransone’s most important professional values. He recounts that during rounds in medical school, the attending and several interns and students crowded into the semiprivate room of an elderly woman who was lying in bed. The attending pulled off the bed covers, leaving the patient exposed while he discussed her case.
“I was mortified for her, and I learned a lot from watching this unfold, just seeing this woman lying naked in front all of these strangers and God,” said Dr. Ransone, physician practice director at Riverside Fishing Bay Family Practice, Deltaville, and assistant clinical professor of family medicine and population health at Virginia Commonwealth University, in Richmond. “I’ve been in practice for 25 years, and making sure the patient feels comfortable and respected is one of my priorities that dates back to that very first encounter.”
Trauma-informed care
Trauma is a common reason why patients feel reluctant to remove their clothing, according to Lauren Radziejewski, DNP, ANP-BC, clinical program manager, Mount Sinai Center for Transgender Medicine and Surgery, New York.
“We teach and endorse trauma-informed care for any type of procedure that is potentially triggering, and I would certainly put any type of care where people have to take off their clothes as potentially triggering,” she said.
Trauma can be caused by many factors. “Traumas of a sexual nature – having been subjected to sexual violence, for example – are the most obvious that come to mind, but any trauma that involves violation and disempowerment, even a nonsexual one, can make people more reluctant to be in a sensitive situation that can be perceived as invasive or disempowering,” Dr. Radziejewski said.
Talk before you touch
There are other reasons, often multiple intersecting reasons, why patients are reluctant to disrobe, according to Alicia Arbaje, MD, MPH, PhD, associate professor of medicine and director of transitional care research at the Center for Transformative Geriatrics Research, division of geriatric medicine and gerontology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. These include culture and religion, generational sensitivities, and body discomfort associated with transitional times in life (e.g., teen or menopausal years).
Some general approaches apply, regardless of the reason for the patient’s discomfort. Others are specific to the patient’s particular problem or concern, Dr. Arbaje said.
“So much of medicine in this day and age is to quickly get down to business, hurry, and move on to the next patient,” said Dr. Arbaje, who also serves as chair of the American Geriatric Society’s Public Education Committee. “But establishing a little bit of a relationship is crucial before beginning the physical exam with any patient, especially with seniors or other patients who might have particular discomforts.”
She advises practitioners to “spend time talking before touching.” In other words, “Find a way to create some kind of meeting, even very briefly, and establish rapport before the patient changes into a gown and before you touch the patient to examine him or her.”
She acknowledged this might be difficult to do in certain clinical settings, but “to whatever extent you can, try to build this extra time and extra step into your workflow.”
She suggested that physicians first meet with the patient in the office or examining room to hear about his or her concerns. If a gown is necessary, the patient can change into one after the physician leaves the room. This builds trust and rapport.
Choice of language is important, especially when talking with older individuals. “Address the patient by their title until you are told not to – Ms. or Mrs. Smith, or Mr. Jones – or ask, ‘How would you like to be addressed?’ And don’t use terms of endearment, like ‘dear’ or ‘sweetie,’ or the plural, such as ‘How are we feeling today?’ “ These are “infantilizing and patronizing” and can impact the patient’s level of comfort with the entire appointment, including undressing and being examined.
Regarding transgender people, “many have experienced sexual violence and inappropriate touching, but even those fortunate enough to have escaped that type of common problem typically have still undergone traumatic experiences just by being transgender, having been socialized incorrectly, misunderstood, or having the ‘wrong’ genitalia,” said Dr. Radziejewski.
Particularly when dealing with a transgender patient, “you have to assume that there may be a history of trauma. Be sensitive to the patient’s discomforts about disrobing, recognize the examination itself as a potential trigger, and take appropriate measures to mitigate the trauma.”
To do this, Dr. Radziejewski gives her patients a “menu of options,” because “when people are navigating the world after trauma, including marginalized identity, they often have a complete loss of control, so the key is to give them as much control as possible every step of the way.”
For example, Dr. Radziejewski might tell a transgender masculine patient, “I’m looking through your chart and see no documented Pap test.” She acknowledges that after explaining why the test is recommended, the patient might be uncomfortable with it. She then makes a series of suggestions that range from being completely noninvasive to more invasive.
“You can say you don’t want it at all, or you can take a swab that I will give you and do it in the bathroom yourself. If you’re more comfortable with a man performing it, I can arrange that, or if you’re more comfortable with someone other than myself – your regular provider – I can arrange that, too.” By the end of the interaction, most patients are comfortable with Dr. Radziejewski performing the exam.
Regarding invasive exams, she recommends setting up an appointment specifically dedicated to that exam, rather than trying to cram a sensitive process into the time allotted for a patent visit, when other topics are also being discussed. “This also reinforces a sense of control,” she said.
This approach is relevant not only for transgender patients but also for any patient who has experienced trauma or some type of shame associated with the body, she said.
Dr. Ransone asks transgender patients what pronoun they would like him to use when he addresses them.
Prior to the examination, talking about what will be done and why further enhances trust, comfort, and rapport.
Who should be present?
Dr. Arbaje suggested that the pre-examination conversation should include a discussion of who the patient would like to have present during the exam. This is particularly relevant with a geriatric patient who might have been brought in by a family member or caregiver.
Similarly, adolescents may not feel comfortable with a parent being present for an examination. To protect the teen’s privacy, Dr. Ransone asks parents to step out. “There are also subjects that adolescents won’t bring up if their parents are there,” he said.
A question that is relevant in many clinical settings is whether the presence of a chaperone enhances or detracts from the patient’s comfort. Although the use of chaperones is recommended by many societies, it is a judgment call whether a chaperone should be present during all examinations – unless the state in which one practices requires it. Seven states mandate the presence of a chaperone during an intimate exam: Alabama, Delaware, Georgia, Montana, New Jersey, Ohio, and Tennessee.
Dr. Ransone utilizes a medical scribe to take notes on patient visits. The nurse or medical assistant who escorts the patient into the exam room informs the patient that a scribe will be in the room but that the patient should feel free to say whether he or she wants to talk about something privately, in which case the scribe will leave.
Dr. Ransone’s scribe is female and serves as the chaperone during an intimate exam of a female patient. “I have assumed, and my established patients know, that there will be a chaperone present, but my patients also know they can ask for the chaperone to step out,” he said. “When that happens, I document the discussion in the patient’s chart for my own legal protection.”
He recommended that practices consider posting signage or including information about chaperones in the practice’s informational brochures regarding policies and procedures.
Armin Brott, MBA, senior editor of Talking About Men’s Health , said that having a chaperone in the room when a female practitioner is examining a male patient – even if the chaperone is male – would be “extremely uncomfortable, weird, and even voyeuristic for the male patient.”
He noted that typically, male physicians use a chaperone when examining a female patient “for their own legal self-protection and maybe to make the female patient more comfortable, but female physicians are typically less concerned about potentially being accused of violating a male patient and typically do not have chaperones.”
Men face unique challenges
Men have “unique needs and challenges” when it comes to healthcare, said Mr. Brott, an advisory board member of the Men’s Health Network.
Mr. Brott cited research showing that men do not seek healthcare as frequently as women do. “So it’s already hard to get men in the door of a doctor, no matter what the provider’s gender is,” he said. Notably, men are even less likely to seek medical care when the clinician is female, owing to discomfort at having to undergo an intimate exam.
“I think that many men have issues about sexuality and of becoming aroused during an exam if it’s a female practitioner doing the exam,” said Mr. Brott. “I’m sure this is something physicians and nurses are accustomed to, but for the patient, it’s extremely embarrassing. The man may worry that he’ll be perceived as making unwanted sexual overtures to the practitioner.”
The way to mitigate these concerns is through communication, according to Mr. Brott. He recalled his own experience during a catherization conducted by a female practitioner he had never met. “She came in and started dealing with me as if I wasn’t even a person. She didn’t say much. It would have helped if she had created some type of human connection and talked to me – something like, ‘I’ve done this a thousand times and here’s what you’ll be feeling,’ or, “Would you like me to describe what I’m doing, or just do it as quickly as possible?’ ”
On another occasion, Mr. Brott underwent a procedure that was performed by two female practitioners, who were more communicative and even brought some light humor to the encounter, “which set me at ease,” he said.
If a man does become aroused, reassurance would be helpful, Mr. Brott said. “You can say something like, ‘Don’t worry, it’s perfectly natural, it happens all the time. Let’s finish up, and I’ll be out of your way as soon as I can.’ ”
Explain at every step of the way
All the experts emphasize the critical importance of continuing to offer explanations throughout the exam, even if the exam has been discussed beforehand.
“During the exam, it’s key to explain what you’re doing each step of the way – especially with seniors, but with other patients too,” said Arbaje. “For example, ‘I’d like you to remove your arms from your shirt so I can examine the joint better.’ Often there’s apprehension about what you’re going to do next. You can also ask, ‘Is there anything I should know before I examine this part of you? How are you doing?’ “ She advised asking the patient for “ongoing feedback. ‘Is this okay? Is this too rough?’ “
This is especially important when conducting a pelvic exam or palpating the patient’s abdomen, which is a more personal area than, say, the knee. Only the body part that is being examined should be uncovered, and it should be re-covered after the exam of that body part is complete and a different body part is to then be examined.
Asking for feedback is especially important, because many older patients have been acculturated not to question physicians and other medical authorities and may suffer a sense of humiliation silently.
Dr. Arbaje noted that feedback can be nonverbal: “For example, wincing or flinching are signs of discomfort you should ask the patient about or empathetically acknowledge.”
Rapport building doesn’t end after the examination
Dr. Arbaje advises physicians to “spend a little more time with the patient after the examination and not just walk out the door, leaving the person as they are, half undressed or in a gown.”
In the case of an older person, this might involve helping patients get their shoes and socks on or helping them get off the table. “Spend some time closing the encounter, not just doing what you need to do and then leaving or leaving it for someone else or family to do, which can be very dehumanizing,” she said. Even a few minutes of human contact beyond the examination can enhance rapport and help the patient feel respected and more comfortable.
Setting the stage: Create a conducive office environment
Setting patients at ease begins well before the patient enters the examination room, experts say. The overall atmosphere of the practice – the professionalism, courtesy, and friendliness of the staff – contributes to a sense of safety that will set the stage for the patient to feel more comfortable disrobing, if necessary, and being examined.
Mr. Brott pointed out that most medical offices tend to be more “female-friendly” in decor, utilizing pastel colors and flower motifs, for example, and displaying women’s magazines in the waiting room. Gender-neutral decor and different types of reading materials might set men at ease. Receptionists and medical staff are often female, and it is helpful for practices to employ male staff to bring the patient into the examination room or check vital signs. “This would go a long way toward making a man feel welcome and comfortable, even if the physician is female,” he said.
Dr. Radziejewski agreed: “If possible, having male and female support staff available will set patients of any gender at their ease.”
The setup of the examination room may contribute to a patient’s level of comfort. In Dr. Ransone’s examination room, the patient faces the door when on the table, and the door is locked during the exam so that no one can enter.
“I think that if patients are facing away from the door, they may feel claustrophobic or trapped, and I don’t want to position myself between the patient and an exit,” Dr. Ransone said. “My exam room happens to have no windows, but I’ve seen situations where the patient is lying on the table, exposed in front of the window, which can feel vulnerable, even if the office is on a high floor and no one can see into the window.”
Dr. Ransone positions the scribe or chaperone to the side, where the patient can see them, but not directly in front, where the examination might be visible to them. “I think it would be more uncomfortable and anxiety provoking knowing that someone is standing behind me and I can’t see them,” he said.
Choosing the best gown ... when necessary
Is it necessary for patients to disrobe and put on a gown — especially in light of the fact that research suggests that wearing a gown can induce psychological distress?
Danielle Ofri, MD, PhD, clinical professor, department of medicine, NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, said that in her practice, patients wear street clothes unless the patient is to undergo a full physical exam.
Even an abdominal exam can be conducted by loosening and slightly lowering the pants. Dr. Ofri stresses that patients should retain full control over how much to expose: “The patient should always take the lead in adjusting or opening clothing for a focused physical exam. And, of course, we always need to ask permission before starting any part of the exam.”
A gown is more conducive for certain exams, such as pelvic or breast exams. Dr. Ransone said that cloth gowns are preferable to paper gowns, which can tear more easily and so lead to unnecessary exposure. Gowns that hang open at the back should be avoided. If that’s the only type available, a second gown can be provided so as to cover the backside.
This is especially important if the examination involves walking across the room – for example, to evaluate gait – or standing on the scale. Alternatively, the patient can be given a sheet to drape over the gown, which can be moved around during the examination.
Dr. Ransome’s own practice uses gowns that fully wrap around the person. “I’ve seen too many people in gowns that are too small, so I make sure the patient has an appropriately sized gown. The extra material also leaves room for draping, while exposing only the part of the body that’s necessary,” he said.
Numerous types of modest gowns are now available, including kimono-type gowns with ties and snaps that allow partial exposure. All the experts encouraged utilizing these or similar types of gowns if possible.
Cultural and religious considerations
It is important for clinicians to be sensitive to cultural and religious factors that might affect patients’ attitudes toward attire and opposite-sex practitioners, said Dr. Ofri, an internist at Bellevue Hospital, New York.
For example, in Islamic and ultra-Orthodox Jewish traditions, certain parts of the body may not be exposed in the presence of a man who is unrelated by blood or marriage. Studies have shown that Hispanic and Asian women have avoided mammography because of embarrassment.
Dr. Arbaje described a 90-year-old patient whose physician ordered a pelvic ultrasound. The ultrasound department conducted the test transvaginally. “The patient, a widow, came from a Catholic background and regarded this as tantamount to ‘cheating’ on her deceased husband, and she felt violated and ashamed,” Dr. Arbaje said.
Dr. Ofri, who is the author of Medicine in Translation: Journeys With My Patients, said that she has Muslim and Orthodox Jewish male patients who allow her to examine their knees but won’t shake her hand because of the prohibition against touching an unrelated woman. Muslim female patients are willing to unsnap their veils because Dr. Ofri is female, but they would be uncomfortable with a male practitioner.
Whenever possible, gender-concordant care should be provided. If that is not possible, patients should be offered the option of not undergoing the examination, unless it’s an emergent situation, Dr. Ofri said. It may be necessary to reschedule the appointment to a time when a same-sex practitioner is available or to refer the patient to another practitioner.
Keeping cultural and religious considerations in mind is important, but there are variations in any given culture or religion. Practitioners should take cues directly from the patient, the experts advise.
Meeting the needs of cognitively impaired patients
Patients who are cognitively impaired have particular needs, Dr. Arbaje says. Many such patients are seniors with dementia, although developmental disabilities, neurodegenerative diseases, and other problems that affect cognition can occur among patients of any age and stage of life.
“People with dementia don’t necessarily understand what you’re doing and why you’re touching them. Even people with advanced dementia often retain a sense of modesty and may feel humiliated by an examination,” Dr. Arbaje said.
Dr. Arbaje encourages offering clear explanations of what is being done. The language one uses should be respectful and nonpatronizing, even if the patient does not understand what is being said. However, the bulk of one’s communication should be nonverbal. “Convey gentleness, safety, and reassurance through your tone and touch,” Dr. Arbaje said.
For cognitively impaired patient, it is helpful for a trusted family member or caregiver to be present during the examination, rather than a stranger. Depending on the degree of impairment, it might also be helpful for them to have a familiar object, perhaps a blanket; the odor and texture can convey familiarity and reassurance.
Nonclinical touch can also be reassuring. “We’re often scared of touching a patient because we don’t want to be considered inappropriate, but people who have dementia in later life are often understimulated, in terms of loving and caring touch,” she said. “For people in that situation, touch is typically of a practical or clinical nature – like bathing the person or taking their blood pressure. Providing reassuring touch or having someone else present to do so can help ease the patient’s fear and can be very healing.”
Making your patient’s eyes light up
“I can’t even count how many times I’ve had patients thank me for just explaining things clearly and giving them the right to opt out of wearing a gown or having an examination or procedure,” Dr. Radziejewski said.
“Obviously, I express recommendations, strong recommendations, but people like to know this is a place where they’ll be acknowledged for who they are, where they can feel safe and their dignity will be preserved. That should be the environment for any patient, whatever their culture, religion, age, background, or sexual identity. Offering that type of venue makes their eyes light up and makes all the difference in adherence to my recommendations and feeling empowered to truly care for their health,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sterling Ransone Jr., MD, a family physician in Deltaville, Va., knocked on the exam room door and entered to find the patient, a 28-year-old woman, seated on the examination table. She was complaining about a fever, sore throat, and congestion.
Dr. Ransone asked if it was okay for him to lift her shirt and listen to her heart. She shook her head slightly. He decided to listen without removing the clothing, but when he put one hand on her shoulder and the stethoscope on her back, she flinched.
Instead of proceeding with the examination, Dr. Ransone, who is president-elect of the American Academy of Family Physicians, asked the patient whether everything was okay. It turned out that she had been the victim of a sexual assault and did not want a male to remove any clothing or touch her chest or back. Fortunately, Dr. Ransone’s practice had a female partner, who came in and listened to the patient’s chest.
“I’m glad I asked the patient what was going on for her because otherwise, I wouldn’t have known what she was going through,” Dr. Ransone said. “The patient felt respected and safe, and the therapeutic relationship was enhanced instead of compromised.”
Patient dignity is one of Dr. Ransone’s most important professional values. He recounts that during rounds in medical school, the attending and several interns and students crowded into the semiprivate room of an elderly woman who was lying in bed. The attending pulled off the bed covers, leaving the patient exposed while he discussed her case.
“I was mortified for her, and I learned a lot from watching this unfold, just seeing this woman lying naked in front all of these strangers and God,” said Dr. Ransone, physician practice director at Riverside Fishing Bay Family Practice, Deltaville, and assistant clinical professor of family medicine and population health at Virginia Commonwealth University, in Richmond. “I’ve been in practice for 25 years, and making sure the patient feels comfortable and respected is one of my priorities that dates back to that very first encounter.”
Trauma-informed care
Trauma is a common reason why patients feel reluctant to remove their clothing, according to Lauren Radziejewski, DNP, ANP-BC, clinical program manager, Mount Sinai Center for Transgender Medicine and Surgery, New York.
“We teach and endorse trauma-informed care for any type of procedure that is potentially triggering, and I would certainly put any type of care where people have to take off their clothes as potentially triggering,” she said.
Trauma can be caused by many factors. “Traumas of a sexual nature – having been subjected to sexual violence, for example – are the most obvious that come to mind, but any trauma that involves violation and disempowerment, even a nonsexual one, can make people more reluctant to be in a sensitive situation that can be perceived as invasive or disempowering,” Dr. Radziejewski said.
Talk before you touch
There are other reasons, often multiple intersecting reasons, why patients are reluctant to disrobe, according to Alicia Arbaje, MD, MPH, PhD, associate professor of medicine and director of transitional care research at the Center for Transformative Geriatrics Research, division of geriatric medicine and gerontology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. These include culture and religion, generational sensitivities, and body discomfort associated with transitional times in life (e.g., teen or menopausal years).
Some general approaches apply, regardless of the reason for the patient’s discomfort. Others are specific to the patient’s particular problem or concern, Dr. Arbaje said.
“So much of medicine in this day and age is to quickly get down to business, hurry, and move on to the next patient,” said Dr. Arbaje, who also serves as chair of the American Geriatric Society’s Public Education Committee. “But establishing a little bit of a relationship is crucial before beginning the physical exam with any patient, especially with seniors or other patients who might have particular discomforts.”
She advises practitioners to “spend time talking before touching.” In other words, “Find a way to create some kind of meeting, even very briefly, and establish rapport before the patient changes into a gown and before you touch the patient to examine him or her.”
She acknowledged this might be difficult to do in certain clinical settings, but “to whatever extent you can, try to build this extra time and extra step into your workflow.”
She suggested that physicians first meet with the patient in the office or examining room to hear about his or her concerns. If a gown is necessary, the patient can change into one after the physician leaves the room. This builds trust and rapport.
Choice of language is important, especially when talking with older individuals. “Address the patient by their title until you are told not to – Ms. or Mrs. Smith, or Mr. Jones – or ask, ‘How would you like to be addressed?’ And don’t use terms of endearment, like ‘dear’ or ‘sweetie,’ or the plural, such as ‘How are we feeling today?’ “ These are “infantilizing and patronizing” and can impact the patient’s level of comfort with the entire appointment, including undressing and being examined.
Regarding transgender people, “many have experienced sexual violence and inappropriate touching, but even those fortunate enough to have escaped that type of common problem typically have still undergone traumatic experiences just by being transgender, having been socialized incorrectly, misunderstood, or having the ‘wrong’ genitalia,” said Dr. Radziejewski.
Particularly when dealing with a transgender patient, “you have to assume that there may be a history of trauma. Be sensitive to the patient’s discomforts about disrobing, recognize the examination itself as a potential trigger, and take appropriate measures to mitigate the trauma.”
To do this, Dr. Radziejewski gives her patients a “menu of options,” because “when people are navigating the world after trauma, including marginalized identity, they often have a complete loss of control, so the key is to give them as much control as possible every step of the way.”
For example, Dr. Radziejewski might tell a transgender masculine patient, “I’m looking through your chart and see no documented Pap test.” She acknowledges that after explaining why the test is recommended, the patient might be uncomfortable with it. She then makes a series of suggestions that range from being completely noninvasive to more invasive.
“You can say you don’t want it at all, or you can take a swab that I will give you and do it in the bathroom yourself. If you’re more comfortable with a man performing it, I can arrange that, or if you’re more comfortable with someone other than myself – your regular provider – I can arrange that, too.” By the end of the interaction, most patients are comfortable with Dr. Radziejewski performing the exam.
Regarding invasive exams, she recommends setting up an appointment specifically dedicated to that exam, rather than trying to cram a sensitive process into the time allotted for a patent visit, when other topics are also being discussed. “This also reinforces a sense of control,” she said.
This approach is relevant not only for transgender patients but also for any patient who has experienced trauma or some type of shame associated with the body, she said.
Dr. Ransone asks transgender patients what pronoun they would like him to use when he addresses them.
Prior to the examination, talking about what will be done and why further enhances trust, comfort, and rapport.
Who should be present?
Dr. Arbaje suggested that the pre-examination conversation should include a discussion of who the patient would like to have present during the exam. This is particularly relevant with a geriatric patient who might have been brought in by a family member or caregiver.
Similarly, adolescents may not feel comfortable with a parent being present for an examination. To protect the teen’s privacy, Dr. Ransone asks parents to step out. “There are also subjects that adolescents won’t bring up if their parents are there,” he said.
A question that is relevant in many clinical settings is whether the presence of a chaperone enhances or detracts from the patient’s comfort. Although the use of chaperones is recommended by many societies, it is a judgment call whether a chaperone should be present during all examinations – unless the state in which one practices requires it. Seven states mandate the presence of a chaperone during an intimate exam: Alabama, Delaware, Georgia, Montana, New Jersey, Ohio, and Tennessee.
Dr. Ransone utilizes a medical scribe to take notes on patient visits. The nurse or medical assistant who escorts the patient into the exam room informs the patient that a scribe will be in the room but that the patient should feel free to say whether he or she wants to talk about something privately, in which case the scribe will leave.
Dr. Ransone’s scribe is female and serves as the chaperone during an intimate exam of a female patient. “I have assumed, and my established patients know, that there will be a chaperone present, but my patients also know they can ask for the chaperone to step out,” he said. “When that happens, I document the discussion in the patient’s chart for my own legal protection.”
He recommended that practices consider posting signage or including information about chaperones in the practice’s informational brochures regarding policies and procedures.
Armin Brott, MBA, senior editor of Talking About Men’s Health , said that having a chaperone in the room when a female practitioner is examining a male patient – even if the chaperone is male – would be “extremely uncomfortable, weird, and even voyeuristic for the male patient.”
He noted that typically, male physicians use a chaperone when examining a female patient “for their own legal self-protection and maybe to make the female patient more comfortable, but female physicians are typically less concerned about potentially being accused of violating a male patient and typically do not have chaperones.”
Men face unique challenges
Men have “unique needs and challenges” when it comes to healthcare, said Mr. Brott, an advisory board member of the Men’s Health Network.
Mr. Brott cited research showing that men do not seek healthcare as frequently as women do. “So it’s already hard to get men in the door of a doctor, no matter what the provider’s gender is,” he said. Notably, men are even less likely to seek medical care when the clinician is female, owing to discomfort at having to undergo an intimate exam.
“I think that many men have issues about sexuality and of becoming aroused during an exam if it’s a female practitioner doing the exam,” said Mr. Brott. “I’m sure this is something physicians and nurses are accustomed to, but for the patient, it’s extremely embarrassing. The man may worry that he’ll be perceived as making unwanted sexual overtures to the practitioner.”
The way to mitigate these concerns is through communication, according to Mr. Brott. He recalled his own experience during a catherization conducted by a female practitioner he had never met. “She came in and started dealing with me as if I wasn’t even a person. She didn’t say much. It would have helped if she had created some type of human connection and talked to me – something like, ‘I’ve done this a thousand times and here’s what you’ll be feeling,’ or, “Would you like me to describe what I’m doing, or just do it as quickly as possible?’ ”
On another occasion, Mr. Brott underwent a procedure that was performed by two female practitioners, who were more communicative and even brought some light humor to the encounter, “which set me at ease,” he said.
If a man does become aroused, reassurance would be helpful, Mr. Brott said. “You can say something like, ‘Don’t worry, it’s perfectly natural, it happens all the time. Let’s finish up, and I’ll be out of your way as soon as I can.’ ”
Explain at every step of the way
All the experts emphasize the critical importance of continuing to offer explanations throughout the exam, even if the exam has been discussed beforehand.
“During the exam, it’s key to explain what you’re doing each step of the way – especially with seniors, but with other patients too,” said Arbaje. “For example, ‘I’d like you to remove your arms from your shirt so I can examine the joint better.’ Often there’s apprehension about what you’re going to do next. You can also ask, ‘Is there anything I should know before I examine this part of you? How are you doing?’ “ She advised asking the patient for “ongoing feedback. ‘Is this okay? Is this too rough?’ “
This is especially important when conducting a pelvic exam or palpating the patient’s abdomen, which is a more personal area than, say, the knee. Only the body part that is being examined should be uncovered, and it should be re-covered after the exam of that body part is complete and a different body part is to then be examined.
Asking for feedback is especially important, because many older patients have been acculturated not to question physicians and other medical authorities and may suffer a sense of humiliation silently.
Dr. Arbaje noted that feedback can be nonverbal: “For example, wincing or flinching are signs of discomfort you should ask the patient about or empathetically acknowledge.”
Rapport building doesn’t end after the examination
Dr. Arbaje advises physicians to “spend a little more time with the patient after the examination and not just walk out the door, leaving the person as they are, half undressed or in a gown.”
In the case of an older person, this might involve helping patients get their shoes and socks on or helping them get off the table. “Spend some time closing the encounter, not just doing what you need to do and then leaving or leaving it for someone else or family to do, which can be very dehumanizing,” she said. Even a few minutes of human contact beyond the examination can enhance rapport and help the patient feel respected and more comfortable.
Setting the stage: Create a conducive office environment
Setting patients at ease begins well before the patient enters the examination room, experts say. The overall atmosphere of the practice – the professionalism, courtesy, and friendliness of the staff – contributes to a sense of safety that will set the stage for the patient to feel more comfortable disrobing, if necessary, and being examined.
Mr. Brott pointed out that most medical offices tend to be more “female-friendly” in decor, utilizing pastel colors and flower motifs, for example, and displaying women’s magazines in the waiting room. Gender-neutral decor and different types of reading materials might set men at ease. Receptionists and medical staff are often female, and it is helpful for practices to employ male staff to bring the patient into the examination room or check vital signs. “This would go a long way toward making a man feel welcome and comfortable, even if the physician is female,” he said.
Dr. Radziejewski agreed: “If possible, having male and female support staff available will set patients of any gender at their ease.”
The setup of the examination room may contribute to a patient’s level of comfort. In Dr. Ransone’s examination room, the patient faces the door when on the table, and the door is locked during the exam so that no one can enter.
“I think that if patients are facing away from the door, they may feel claustrophobic or trapped, and I don’t want to position myself between the patient and an exit,” Dr. Ransone said. “My exam room happens to have no windows, but I’ve seen situations where the patient is lying on the table, exposed in front of the window, which can feel vulnerable, even if the office is on a high floor and no one can see into the window.”
Dr. Ransone positions the scribe or chaperone to the side, where the patient can see them, but not directly in front, where the examination might be visible to them. “I think it would be more uncomfortable and anxiety provoking knowing that someone is standing behind me and I can’t see them,” he said.
Choosing the best gown ... when necessary
Is it necessary for patients to disrobe and put on a gown — especially in light of the fact that research suggests that wearing a gown can induce psychological distress?
Danielle Ofri, MD, PhD, clinical professor, department of medicine, NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, said that in her practice, patients wear street clothes unless the patient is to undergo a full physical exam.
Even an abdominal exam can be conducted by loosening and slightly lowering the pants. Dr. Ofri stresses that patients should retain full control over how much to expose: “The patient should always take the lead in adjusting or opening clothing for a focused physical exam. And, of course, we always need to ask permission before starting any part of the exam.”
A gown is more conducive for certain exams, such as pelvic or breast exams. Dr. Ransone said that cloth gowns are preferable to paper gowns, which can tear more easily and so lead to unnecessary exposure. Gowns that hang open at the back should be avoided. If that’s the only type available, a second gown can be provided so as to cover the backside.
This is especially important if the examination involves walking across the room – for example, to evaluate gait – or standing on the scale. Alternatively, the patient can be given a sheet to drape over the gown, which can be moved around during the examination.
Dr. Ransome’s own practice uses gowns that fully wrap around the person. “I’ve seen too many people in gowns that are too small, so I make sure the patient has an appropriately sized gown. The extra material also leaves room for draping, while exposing only the part of the body that’s necessary,” he said.
Numerous types of modest gowns are now available, including kimono-type gowns with ties and snaps that allow partial exposure. All the experts encouraged utilizing these or similar types of gowns if possible.
Cultural and religious considerations
It is important for clinicians to be sensitive to cultural and religious factors that might affect patients’ attitudes toward attire and opposite-sex practitioners, said Dr. Ofri, an internist at Bellevue Hospital, New York.
For example, in Islamic and ultra-Orthodox Jewish traditions, certain parts of the body may not be exposed in the presence of a man who is unrelated by blood or marriage. Studies have shown that Hispanic and Asian women have avoided mammography because of embarrassment.
Dr. Arbaje described a 90-year-old patient whose physician ordered a pelvic ultrasound. The ultrasound department conducted the test transvaginally. “The patient, a widow, came from a Catholic background and regarded this as tantamount to ‘cheating’ on her deceased husband, and she felt violated and ashamed,” Dr. Arbaje said.
Dr. Ofri, who is the author of Medicine in Translation: Journeys With My Patients, said that she has Muslim and Orthodox Jewish male patients who allow her to examine their knees but won’t shake her hand because of the prohibition against touching an unrelated woman. Muslim female patients are willing to unsnap their veils because Dr. Ofri is female, but they would be uncomfortable with a male practitioner.
Whenever possible, gender-concordant care should be provided. If that is not possible, patients should be offered the option of not undergoing the examination, unless it’s an emergent situation, Dr. Ofri said. It may be necessary to reschedule the appointment to a time when a same-sex practitioner is available or to refer the patient to another practitioner.
Keeping cultural and religious considerations in mind is important, but there are variations in any given culture or religion. Practitioners should take cues directly from the patient, the experts advise.
Meeting the needs of cognitively impaired patients
Patients who are cognitively impaired have particular needs, Dr. Arbaje says. Many such patients are seniors with dementia, although developmental disabilities, neurodegenerative diseases, and other problems that affect cognition can occur among patients of any age and stage of life.
“People with dementia don’t necessarily understand what you’re doing and why you’re touching them. Even people with advanced dementia often retain a sense of modesty and may feel humiliated by an examination,” Dr. Arbaje said.
Dr. Arbaje encourages offering clear explanations of what is being done. The language one uses should be respectful and nonpatronizing, even if the patient does not understand what is being said. However, the bulk of one’s communication should be nonverbal. “Convey gentleness, safety, and reassurance through your tone and touch,” Dr. Arbaje said.
For cognitively impaired patient, it is helpful for a trusted family member or caregiver to be present during the examination, rather than a stranger. Depending on the degree of impairment, it might also be helpful for them to have a familiar object, perhaps a blanket; the odor and texture can convey familiarity and reassurance.
Nonclinical touch can also be reassuring. “We’re often scared of touching a patient because we don’t want to be considered inappropriate, but people who have dementia in later life are often understimulated, in terms of loving and caring touch,” she said. “For people in that situation, touch is typically of a practical or clinical nature – like bathing the person or taking their blood pressure. Providing reassuring touch or having someone else present to do so can help ease the patient’s fear and can be very healing.”
Making your patient’s eyes light up
“I can’t even count how many times I’ve had patients thank me for just explaining things clearly and giving them the right to opt out of wearing a gown or having an examination or procedure,” Dr. Radziejewski said.
“Obviously, I express recommendations, strong recommendations, but people like to know this is a place where they’ll be acknowledged for who they are, where they can feel safe and their dignity will be preserved. That should be the environment for any patient, whatever their culture, religion, age, background, or sexual identity. Offering that type of venue makes their eyes light up and makes all the difference in adherence to my recommendations and feeling empowered to truly care for their health,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sterling Ransone Jr., MD, a family physician in Deltaville, Va., knocked on the exam room door and entered to find the patient, a 28-year-old woman, seated on the examination table. She was complaining about a fever, sore throat, and congestion.
Dr. Ransone asked if it was okay for him to lift her shirt and listen to her heart. She shook her head slightly. He decided to listen without removing the clothing, but when he put one hand on her shoulder and the stethoscope on her back, she flinched.
Instead of proceeding with the examination, Dr. Ransone, who is president-elect of the American Academy of Family Physicians, asked the patient whether everything was okay. It turned out that she had been the victim of a sexual assault and did not want a male to remove any clothing or touch her chest or back. Fortunately, Dr. Ransone’s practice had a female partner, who came in and listened to the patient’s chest.
“I’m glad I asked the patient what was going on for her because otherwise, I wouldn’t have known what she was going through,” Dr. Ransone said. “The patient felt respected and safe, and the therapeutic relationship was enhanced instead of compromised.”
Patient dignity is one of Dr. Ransone’s most important professional values. He recounts that during rounds in medical school, the attending and several interns and students crowded into the semiprivate room of an elderly woman who was lying in bed. The attending pulled off the bed covers, leaving the patient exposed while he discussed her case.
“I was mortified for her, and I learned a lot from watching this unfold, just seeing this woman lying naked in front all of these strangers and God,” said Dr. Ransone, physician practice director at Riverside Fishing Bay Family Practice, Deltaville, and assistant clinical professor of family medicine and population health at Virginia Commonwealth University, in Richmond. “I’ve been in practice for 25 years, and making sure the patient feels comfortable and respected is one of my priorities that dates back to that very first encounter.”
Trauma-informed care
Trauma is a common reason why patients feel reluctant to remove their clothing, according to Lauren Radziejewski, DNP, ANP-BC, clinical program manager, Mount Sinai Center for Transgender Medicine and Surgery, New York.
“We teach and endorse trauma-informed care for any type of procedure that is potentially triggering, and I would certainly put any type of care where people have to take off their clothes as potentially triggering,” she said.
Trauma can be caused by many factors. “Traumas of a sexual nature – having been subjected to sexual violence, for example – are the most obvious that come to mind, but any trauma that involves violation and disempowerment, even a nonsexual one, can make people more reluctant to be in a sensitive situation that can be perceived as invasive or disempowering,” Dr. Radziejewski said.
Talk before you touch
There are other reasons, often multiple intersecting reasons, why patients are reluctant to disrobe, according to Alicia Arbaje, MD, MPH, PhD, associate professor of medicine and director of transitional care research at the Center for Transformative Geriatrics Research, division of geriatric medicine and gerontology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. These include culture and religion, generational sensitivities, and body discomfort associated with transitional times in life (e.g., teen or menopausal years).
Some general approaches apply, regardless of the reason for the patient’s discomfort. Others are specific to the patient’s particular problem or concern, Dr. Arbaje said.
“So much of medicine in this day and age is to quickly get down to business, hurry, and move on to the next patient,” said Dr. Arbaje, who also serves as chair of the American Geriatric Society’s Public Education Committee. “But establishing a little bit of a relationship is crucial before beginning the physical exam with any patient, especially with seniors or other patients who might have particular discomforts.”
She advises practitioners to “spend time talking before touching.” In other words, “Find a way to create some kind of meeting, even very briefly, and establish rapport before the patient changes into a gown and before you touch the patient to examine him or her.”
She acknowledged this might be difficult to do in certain clinical settings, but “to whatever extent you can, try to build this extra time and extra step into your workflow.”
She suggested that physicians first meet with the patient in the office or examining room to hear about his or her concerns. If a gown is necessary, the patient can change into one after the physician leaves the room. This builds trust and rapport.
Choice of language is important, especially when talking with older individuals. “Address the patient by their title until you are told not to – Ms. or Mrs. Smith, or Mr. Jones – or ask, ‘How would you like to be addressed?’ And don’t use terms of endearment, like ‘dear’ or ‘sweetie,’ or the plural, such as ‘How are we feeling today?’ “ These are “infantilizing and patronizing” and can impact the patient’s level of comfort with the entire appointment, including undressing and being examined.
Regarding transgender people, “many have experienced sexual violence and inappropriate touching, but even those fortunate enough to have escaped that type of common problem typically have still undergone traumatic experiences just by being transgender, having been socialized incorrectly, misunderstood, or having the ‘wrong’ genitalia,” said Dr. Radziejewski.
Particularly when dealing with a transgender patient, “you have to assume that there may be a history of trauma. Be sensitive to the patient’s discomforts about disrobing, recognize the examination itself as a potential trigger, and take appropriate measures to mitigate the trauma.”
To do this, Dr. Radziejewski gives her patients a “menu of options,” because “when people are navigating the world after trauma, including marginalized identity, they often have a complete loss of control, so the key is to give them as much control as possible every step of the way.”
For example, Dr. Radziejewski might tell a transgender masculine patient, “I’m looking through your chart and see no documented Pap test.” She acknowledges that after explaining why the test is recommended, the patient might be uncomfortable with it. She then makes a series of suggestions that range from being completely noninvasive to more invasive.
“You can say you don’t want it at all, or you can take a swab that I will give you and do it in the bathroom yourself. If you’re more comfortable with a man performing it, I can arrange that, or if you’re more comfortable with someone other than myself – your regular provider – I can arrange that, too.” By the end of the interaction, most patients are comfortable with Dr. Radziejewski performing the exam.
Regarding invasive exams, she recommends setting up an appointment specifically dedicated to that exam, rather than trying to cram a sensitive process into the time allotted for a patent visit, when other topics are also being discussed. “This also reinforces a sense of control,” she said.
This approach is relevant not only for transgender patients but also for any patient who has experienced trauma or some type of shame associated with the body, she said.
Dr. Ransone asks transgender patients what pronoun they would like him to use when he addresses them.
Prior to the examination, talking about what will be done and why further enhances trust, comfort, and rapport.
Who should be present?
Dr. Arbaje suggested that the pre-examination conversation should include a discussion of who the patient would like to have present during the exam. This is particularly relevant with a geriatric patient who might have been brought in by a family member or caregiver.
Similarly, adolescents may not feel comfortable with a parent being present for an examination. To protect the teen’s privacy, Dr. Ransone asks parents to step out. “There are also subjects that adolescents won’t bring up if their parents are there,” he said.
A question that is relevant in many clinical settings is whether the presence of a chaperone enhances or detracts from the patient’s comfort. Although the use of chaperones is recommended by many societies, it is a judgment call whether a chaperone should be present during all examinations – unless the state in which one practices requires it. Seven states mandate the presence of a chaperone during an intimate exam: Alabama, Delaware, Georgia, Montana, New Jersey, Ohio, and Tennessee.
Dr. Ransone utilizes a medical scribe to take notes on patient visits. The nurse or medical assistant who escorts the patient into the exam room informs the patient that a scribe will be in the room but that the patient should feel free to say whether he or she wants to talk about something privately, in which case the scribe will leave.
Dr. Ransone’s scribe is female and serves as the chaperone during an intimate exam of a female patient. “I have assumed, and my established patients know, that there will be a chaperone present, but my patients also know they can ask for the chaperone to step out,” he said. “When that happens, I document the discussion in the patient’s chart for my own legal protection.”
He recommended that practices consider posting signage or including information about chaperones in the practice’s informational brochures regarding policies and procedures.
Armin Brott, MBA, senior editor of Talking About Men’s Health , said that having a chaperone in the room when a female practitioner is examining a male patient – even if the chaperone is male – would be “extremely uncomfortable, weird, and even voyeuristic for the male patient.”
He noted that typically, male physicians use a chaperone when examining a female patient “for their own legal self-protection and maybe to make the female patient more comfortable, but female physicians are typically less concerned about potentially being accused of violating a male patient and typically do not have chaperones.”
Men face unique challenges
Men have “unique needs and challenges” when it comes to healthcare, said Mr. Brott, an advisory board member of the Men’s Health Network.
Mr. Brott cited research showing that men do not seek healthcare as frequently as women do. “So it’s already hard to get men in the door of a doctor, no matter what the provider’s gender is,” he said. Notably, men are even less likely to seek medical care when the clinician is female, owing to discomfort at having to undergo an intimate exam.
“I think that many men have issues about sexuality and of becoming aroused during an exam if it’s a female practitioner doing the exam,” said Mr. Brott. “I’m sure this is something physicians and nurses are accustomed to, but for the patient, it’s extremely embarrassing. The man may worry that he’ll be perceived as making unwanted sexual overtures to the practitioner.”
The way to mitigate these concerns is through communication, according to Mr. Brott. He recalled his own experience during a catherization conducted by a female practitioner he had never met. “She came in and started dealing with me as if I wasn’t even a person. She didn’t say much. It would have helped if she had created some type of human connection and talked to me – something like, ‘I’ve done this a thousand times and here’s what you’ll be feeling,’ or, “Would you like me to describe what I’m doing, or just do it as quickly as possible?’ ”
On another occasion, Mr. Brott underwent a procedure that was performed by two female practitioners, who were more communicative and even brought some light humor to the encounter, “which set me at ease,” he said.
If a man does become aroused, reassurance would be helpful, Mr. Brott said. “You can say something like, ‘Don’t worry, it’s perfectly natural, it happens all the time. Let’s finish up, and I’ll be out of your way as soon as I can.’ ”
Explain at every step of the way
All the experts emphasize the critical importance of continuing to offer explanations throughout the exam, even if the exam has been discussed beforehand.
“During the exam, it’s key to explain what you’re doing each step of the way – especially with seniors, but with other patients too,” said Arbaje. “For example, ‘I’d like you to remove your arms from your shirt so I can examine the joint better.’ Often there’s apprehension about what you’re going to do next. You can also ask, ‘Is there anything I should know before I examine this part of you? How are you doing?’ “ She advised asking the patient for “ongoing feedback. ‘Is this okay? Is this too rough?’ “
This is especially important when conducting a pelvic exam or palpating the patient’s abdomen, which is a more personal area than, say, the knee. Only the body part that is being examined should be uncovered, and it should be re-covered after the exam of that body part is complete and a different body part is to then be examined.
Asking for feedback is especially important, because many older patients have been acculturated not to question physicians and other medical authorities and may suffer a sense of humiliation silently.
Dr. Arbaje noted that feedback can be nonverbal: “For example, wincing or flinching are signs of discomfort you should ask the patient about or empathetically acknowledge.”
Rapport building doesn’t end after the examination
Dr. Arbaje advises physicians to “spend a little more time with the patient after the examination and not just walk out the door, leaving the person as they are, half undressed or in a gown.”
In the case of an older person, this might involve helping patients get their shoes and socks on or helping them get off the table. “Spend some time closing the encounter, not just doing what you need to do and then leaving or leaving it for someone else or family to do, which can be very dehumanizing,” she said. Even a few minutes of human contact beyond the examination can enhance rapport and help the patient feel respected and more comfortable.
Setting the stage: Create a conducive office environment
Setting patients at ease begins well before the patient enters the examination room, experts say. The overall atmosphere of the practice – the professionalism, courtesy, and friendliness of the staff – contributes to a sense of safety that will set the stage for the patient to feel more comfortable disrobing, if necessary, and being examined.
Mr. Brott pointed out that most medical offices tend to be more “female-friendly” in decor, utilizing pastel colors and flower motifs, for example, and displaying women’s magazines in the waiting room. Gender-neutral decor and different types of reading materials might set men at ease. Receptionists and medical staff are often female, and it is helpful for practices to employ male staff to bring the patient into the examination room or check vital signs. “This would go a long way toward making a man feel welcome and comfortable, even if the physician is female,” he said.
Dr. Radziejewski agreed: “If possible, having male and female support staff available will set patients of any gender at their ease.”
The setup of the examination room may contribute to a patient’s level of comfort. In Dr. Ransone’s examination room, the patient faces the door when on the table, and the door is locked during the exam so that no one can enter.
“I think that if patients are facing away from the door, they may feel claustrophobic or trapped, and I don’t want to position myself between the patient and an exit,” Dr. Ransone said. “My exam room happens to have no windows, but I’ve seen situations where the patient is lying on the table, exposed in front of the window, which can feel vulnerable, even if the office is on a high floor and no one can see into the window.”
Dr. Ransone positions the scribe or chaperone to the side, where the patient can see them, but not directly in front, where the examination might be visible to them. “I think it would be more uncomfortable and anxiety provoking knowing that someone is standing behind me and I can’t see them,” he said.
Choosing the best gown ... when necessary
Is it necessary for patients to disrobe and put on a gown — especially in light of the fact that research suggests that wearing a gown can induce psychological distress?
Danielle Ofri, MD, PhD, clinical professor, department of medicine, NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, said that in her practice, patients wear street clothes unless the patient is to undergo a full physical exam.
Even an abdominal exam can be conducted by loosening and slightly lowering the pants. Dr. Ofri stresses that patients should retain full control over how much to expose: “The patient should always take the lead in adjusting or opening clothing for a focused physical exam. And, of course, we always need to ask permission before starting any part of the exam.”
A gown is more conducive for certain exams, such as pelvic or breast exams. Dr. Ransone said that cloth gowns are preferable to paper gowns, which can tear more easily and so lead to unnecessary exposure. Gowns that hang open at the back should be avoided. If that’s the only type available, a second gown can be provided so as to cover the backside.
This is especially important if the examination involves walking across the room – for example, to evaluate gait – or standing on the scale. Alternatively, the patient can be given a sheet to drape over the gown, which can be moved around during the examination.
Dr. Ransome’s own practice uses gowns that fully wrap around the person. “I’ve seen too many people in gowns that are too small, so I make sure the patient has an appropriately sized gown. The extra material also leaves room for draping, while exposing only the part of the body that’s necessary,” he said.
Numerous types of modest gowns are now available, including kimono-type gowns with ties and snaps that allow partial exposure. All the experts encouraged utilizing these or similar types of gowns if possible.
Cultural and religious considerations
It is important for clinicians to be sensitive to cultural and religious factors that might affect patients’ attitudes toward attire and opposite-sex practitioners, said Dr. Ofri, an internist at Bellevue Hospital, New York.
For example, in Islamic and ultra-Orthodox Jewish traditions, certain parts of the body may not be exposed in the presence of a man who is unrelated by blood or marriage. Studies have shown that Hispanic and Asian women have avoided mammography because of embarrassment.
Dr. Arbaje described a 90-year-old patient whose physician ordered a pelvic ultrasound. The ultrasound department conducted the test transvaginally. “The patient, a widow, came from a Catholic background and regarded this as tantamount to ‘cheating’ on her deceased husband, and she felt violated and ashamed,” Dr. Arbaje said.
Dr. Ofri, who is the author of Medicine in Translation: Journeys With My Patients, said that she has Muslim and Orthodox Jewish male patients who allow her to examine their knees but won’t shake her hand because of the prohibition against touching an unrelated woman. Muslim female patients are willing to unsnap their veils because Dr. Ofri is female, but they would be uncomfortable with a male practitioner.
Whenever possible, gender-concordant care should be provided. If that is not possible, patients should be offered the option of not undergoing the examination, unless it’s an emergent situation, Dr. Ofri said. It may be necessary to reschedule the appointment to a time when a same-sex practitioner is available or to refer the patient to another practitioner.
Keeping cultural and religious considerations in mind is important, but there are variations in any given culture or religion. Practitioners should take cues directly from the patient, the experts advise.
Meeting the needs of cognitively impaired patients
Patients who are cognitively impaired have particular needs, Dr. Arbaje says. Many such patients are seniors with dementia, although developmental disabilities, neurodegenerative diseases, and other problems that affect cognition can occur among patients of any age and stage of life.
“People with dementia don’t necessarily understand what you’re doing and why you’re touching them. Even people with advanced dementia often retain a sense of modesty and may feel humiliated by an examination,” Dr. Arbaje said.
Dr. Arbaje encourages offering clear explanations of what is being done. The language one uses should be respectful and nonpatronizing, even if the patient does not understand what is being said. However, the bulk of one’s communication should be nonverbal. “Convey gentleness, safety, and reassurance through your tone and touch,” Dr. Arbaje said.
For cognitively impaired patient, it is helpful for a trusted family member or caregiver to be present during the examination, rather than a stranger. Depending on the degree of impairment, it might also be helpful for them to have a familiar object, perhaps a blanket; the odor and texture can convey familiarity and reassurance.
Nonclinical touch can also be reassuring. “We’re often scared of touching a patient because we don’t want to be considered inappropriate, but people who have dementia in later life are often understimulated, in terms of loving and caring touch,” she said. “For people in that situation, touch is typically of a practical or clinical nature – like bathing the person or taking their blood pressure. Providing reassuring touch or having someone else present to do so can help ease the patient’s fear and can be very healing.”
Making your patient’s eyes light up
“I can’t even count how many times I’ve had patients thank me for just explaining things clearly and giving them the right to opt out of wearing a gown or having an examination or procedure,” Dr. Radziejewski said.
“Obviously, I express recommendations, strong recommendations, but people like to know this is a place where they’ll be acknowledged for who they are, where they can feel safe and their dignity will be preserved. That should be the environment for any patient, whatever their culture, religion, age, background, or sexual identity. Offering that type of venue makes their eyes light up and makes all the difference in adherence to my recommendations and feeling empowered to truly care for their health,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Meta-analysis evaluates 2 secukinumab regimens for PsA
Key clinical point: A dose of 300 mg secukinumab was more effective than 150 mg secukinumab, along with a similar safety profile in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), particularly those who had an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (anti-TNF-IR).
Major finding: At week 24, 20% or higher improvement in American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response (odds ratio [OR] 1.41; P = .01) and resolution of dactylitis (OR 1.42; P = .02) was higher with 300 mg vs. 150 mg secukinumab. The proportion of ACR20 responders was higher with 300 mg vs. 150 mg secukinumab in anti-TNF-IR patients at weeks 24 (OR 1.75; P = .01) and 52 (OR 1.66; P = .01). The risk for adverse events was similar with both doses.
Study details: Findings are from a meta-analysis of 6 studies including 3 randomized controlled trials and 1,141 patients with PsA that compared 300 mg secukinumab (n = 461) vs. 150 mg secukinumab (n = 680).
Disclosures: This study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Zhang KL et al. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021 (Sep 20);76:e2820. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2021/e2820.
Key clinical point: A dose of 300 mg secukinumab was more effective than 150 mg secukinumab, along with a similar safety profile in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), particularly those who had an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (anti-TNF-IR).
Major finding: At week 24, 20% or higher improvement in American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response (odds ratio [OR] 1.41; P = .01) and resolution of dactylitis (OR 1.42; P = .02) was higher with 300 mg vs. 150 mg secukinumab. The proportion of ACR20 responders was higher with 300 mg vs. 150 mg secukinumab in anti-TNF-IR patients at weeks 24 (OR 1.75; P = .01) and 52 (OR 1.66; P = .01). The risk for adverse events was similar with both doses.
Study details: Findings are from a meta-analysis of 6 studies including 3 randomized controlled trials and 1,141 patients with PsA that compared 300 mg secukinumab (n = 461) vs. 150 mg secukinumab (n = 680).
Disclosures: This study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Zhang KL et al. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021 (Sep 20);76:e2820. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2021/e2820.
Key clinical point: A dose of 300 mg secukinumab was more effective than 150 mg secukinumab, along with a similar safety profile in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), particularly those who had an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (anti-TNF-IR).
Major finding: At week 24, 20% or higher improvement in American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response (odds ratio [OR] 1.41; P = .01) and resolution of dactylitis (OR 1.42; P = .02) was higher with 300 mg vs. 150 mg secukinumab. The proportion of ACR20 responders was higher with 300 mg vs. 150 mg secukinumab in anti-TNF-IR patients at weeks 24 (OR 1.75; P = .01) and 52 (OR 1.66; P = .01). The risk for adverse events was similar with both doses.
Study details: Findings are from a meta-analysis of 6 studies including 3 randomized controlled trials and 1,141 patients with PsA that compared 300 mg secukinumab (n = 461) vs. 150 mg secukinumab (n = 680).
Disclosures: This study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Zhang KL et al. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021 (Sep 20);76:e2820. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2021/e2820.
Effect of background methotrexate dose on tofacitinib efficacy in patients with PsA
Key clinical point: In patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), 5 mg tofacitinib twice a day showed numerically better response with background ≥15 mg methotrexate per week. A twice daily dose of 10 mg tofacitinib, however, showed better response with background ≤15 mg methotrexate per week.
Major finding: In the 5 mg tofacitinib group, 51.4% vs. 47.4% of patients receiving background ≥15 mg methotrexate per week vs. ≤15 mg per week achieved American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response at 3 months. However, in the 10 mg tofacitinib group, 54.9% vs. 51.8% of patients receiving ≤15 mg methotrexate per week vs. ≥15 mg per week achieved ACR20. No new safety risks were identified.
Study details: Findings are from pooled, post hoc exploratory analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, OPAL Broaden and OPAL Beyond, including 556 patients with active PsA randomly assigned to tofacitinib (5 mg or 10 mg twice daily) or placebo, with stable methotrexate.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Pfizer. Some of the authors reported ties with various sources, including Pfizer. C Wang and L Takiya declared being employees and shareholders of Pfizer.
Source: Kivitz AJ et al. Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Sep 12. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05894-2.
Key clinical point: In patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), 5 mg tofacitinib twice a day showed numerically better response with background ≥15 mg methotrexate per week. A twice daily dose of 10 mg tofacitinib, however, showed better response with background ≤15 mg methotrexate per week.
Major finding: In the 5 mg tofacitinib group, 51.4% vs. 47.4% of patients receiving background ≥15 mg methotrexate per week vs. ≤15 mg per week achieved American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response at 3 months. However, in the 10 mg tofacitinib group, 54.9% vs. 51.8% of patients receiving ≤15 mg methotrexate per week vs. ≥15 mg per week achieved ACR20. No new safety risks were identified.
Study details: Findings are from pooled, post hoc exploratory analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, OPAL Broaden and OPAL Beyond, including 556 patients with active PsA randomly assigned to tofacitinib (5 mg or 10 mg twice daily) or placebo, with stable methotrexate.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Pfizer. Some of the authors reported ties with various sources, including Pfizer. C Wang and L Takiya declared being employees and shareholders of Pfizer.
Source: Kivitz AJ et al. Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Sep 12. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05894-2.
Key clinical point: In patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), 5 mg tofacitinib twice a day showed numerically better response with background ≥15 mg methotrexate per week. A twice daily dose of 10 mg tofacitinib, however, showed better response with background ≤15 mg methotrexate per week.
Major finding: In the 5 mg tofacitinib group, 51.4% vs. 47.4% of patients receiving background ≥15 mg methotrexate per week vs. ≤15 mg per week achieved American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response at 3 months. However, in the 10 mg tofacitinib group, 54.9% vs. 51.8% of patients receiving ≤15 mg methotrexate per week vs. ≥15 mg per week achieved ACR20. No new safety risks were identified.
Study details: Findings are from pooled, post hoc exploratory analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, OPAL Broaden and OPAL Beyond, including 556 patients with active PsA randomly assigned to tofacitinib (5 mg or 10 mg twice daily) or placebo, with stable methotrexate.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Pfizer. Some of the authors reported ties with various sources, including Pfizer. C Wang and L Takiya declared being employees and shareholders of Pfizer.
Source: Kivitz AJ et al. Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Sep 12. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05894-2.




