User login
A primer on cannabis for cosmeceuticals: The endocannabinoid system
In the United States, 31 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam have legalized medical marijuana, which is also permitted for recreational use in 9 states, as well as in the District of Columbia. However, marijuana, derived from Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, is regulated as a schedule I drug in the United States at the federal level. (Some believe that the federal status may change in the coming year as a result of the Democratic Party’s takeover in the House of Representatives.1)
Cannabis species contain hundreds of various substances, of which the cannabinoids are the most studied. More than 113 biologically active chemical compounds are found within the class of cannabinoids and their derivatives,2 which have been used for centuries in natural medicine.3 The legal status of marijuana has long hampered scientific research of cannabinoids. Nevertheless, the number of studies focusing on the therapeutic potential of these compounds has steadily risen as the legal landscape of marijuana has evolved.
Findings over the last 20 years have shown that cannabinoids present in C. sativa exhibit anti-inflammatory activity and suppress the proliferation of multiple tumorigenic cell lines, some of which are moderated through cannabinoid (CB) receptors.4 In addition to anti-inflammatory properties, .3 Recent research has demonstrated that CB receptors are present in human skin.4
The endocannabinoid system has emerged as an intriguing area of research, as we’ve come to learn about its convoluted role in human anatomy and health. It features a pervasive network of endogenous ligands, enzymes, and receptors, which exogenous substances (including phytocannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoids) can activate.5 Data from recent studies indicate that the endocannabinoid system plays a significant role in cutaneous homeostasis, as it regulates proliferation, differentiation, and inflammatory mediator release.5 Further, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, pruritus, and wound healing have been identified in recent research as cutaneous concerns in which the use of cannabinoids may be of benefit.6,7 We must also consider reports that cannabinoids can slow human hair growth and that some constituents may spur the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines.8,9This column will briefly address potential confusion over the psychoactive aspects of cannabis, which are related to particular constituents of cannabis and specific CB receptors, and focus on the endocannabinoid system.
Psychoactive or not?
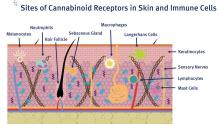
C. sativa confers biological activity through its influence on the G-protein-coupled receptor types CB1 and CB2,10 which pervade human skin epithelium.11 CB1 receptors are found in greatest supply in the central nervous system, especially the basal ganglia, cerebellum, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex, where their activation yields psychoactivity.2,5,12,13 Stimulation of CB1 receptors in the skin – where they are present in differentiated keratinocytes, hair follicle cells, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons14 – diminishes pain and pruritus, controls keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, inhibits hair follicle growth, and regulates the release of damage-induced keratins and inflammatory mediators to maintain cutaneous homeostasis.11,14,15
CB2 receptors are expressed in the immune system, particularly monocytes, macrophages, as well as B and T cells, and in peripheral tissues including the spleen, tonsils, thymus gland, bone, and, notably, the skin.2,16 Stimulation of CB2 receptors in the skin – where they are found in keratinocytes, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons – fosters sebum production, regulates pain sensation, hinders keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, and suppresses cutaneous inflammatory responses.14,15
The best known, or most notorious, component of exogenous cannabinoids is delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta9-THC or simply THC), which is a natural psychoactive constituent in marijuana.3 In fact, of the five primary cannabinoids derived from marijuana, including cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and THC, only THC imparts psychoactive effects.17
CBD is thought to exhibit anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities.18 THC has been found to have the capacity to induce cancer cell apoptosis and block angiogenesis,19 and is thought to have immunomodulatory potential, partly acting through the G-protein-coupled CB1 and CB2 receptors but also yielding effects not related to these receptors.20In a 2014 survey of medical cannabis users, a statistically significant preference for C. indica (which contains higher CBD and lower THC levels) was observed for pain management, sedation, and sleep, while C. sativa was associated with euphoria and improving energy.21
The endocannabinoid system and skin health
The endogenous cannabinoid or endocannabinoid system includes cannabinoid receptors, associated endogenous ligands (such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide [anandamide or AEA], 2-arachidonoyl glycerol [2-AG], and N-palmitoylethanolamide [PEA], a fatty acid amide that enhances AEA activity),2 and enzymes involved in endocannabinoid production and decay.11,15,22,23 Research in recent years appears to support the notion that the endocannabinoid system plays an important role in skin health, as its dysregulation has been linked to atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, scleroderma, and skin cancer. Data indicate that exogenous and endogenous cannabinoids influence the endocannabinoid system through cannabinoid receptors, transient receptor potential channels (TRPs), and peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors (PPARs). Río et al. suggest that the dynamism of the endocannabinoid system buttresses the targeting of multiple endpoints for therapeutic success with cannabinoids rather than the one-disease-one-target approach.24 Endogenous cannabinoids, such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, are now thought to be significant mediators in the skin.3 Further, endocannabinoids have been shown to deliver analgesia to the skin, at the spinal and supraspinal levels.25
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Tubaro et al. used the Croton oil mouse ear dermatitis assay to study the in vivo topical anti-inflammatory effects of seven phytocannabinoids and their related cannabivarins (nonpsychoactive cannabinoids). They found that anti-inflammatory activity was derived from the involvement of the cannabinoid receptors as well as the inflammatory endpoints that the phytocannabinoids targeted.26
In 2013, Gaffal et al. explored the anti-inflammatory activity of topical THC in dinitrofluorobenzene-mediated allergic contact dermatitis independent of CB1/2 receptors by using wild-type and CB1/2 receptor-deficient mice. The researchers found that topically applied THC reduced contact allergic ear edema and myeloid immune cell infiltration in both groups of mice. They concluded that such a decline in inflammation resulted from mitigating the keratinocyte-derived proinflammatory mediators that direct myeloid immune cell infiltration independent of CB1/2 receptors, and positions cannabinoids well for future use in treating inflammatory cutaneous conditions.20
Literature reviews
In a 2018 literature review on the uses of cannabinoids for cutaneous disorders, Eagleston et al. determined that preclinical data on cannabinoids reveal the potential to treat acne, allergic contact dermatitis, asteatotic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, Kaposi sarcoma, pruritus, psoriasis, skin cancer, and the skin symptoms of systemic sclerosis. They caution, though, that more preclinical work is necessary along with randomized, controlled trials with sufficiently large sample sizes to establish the safety and efficacy of cannabinoids to treat skin conditions.27
A literature review by Marks and Friedman published later that year on the therapeutic potential of phytocannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids in managing skin disorders revealed the same findings regarding the cutaneous conditions associated with these compounds. The authors noted, though, that while the preponderance of articles highlight the efficacy of cannabinoids in treating inflammatory and neoplastic cutaneous conditions, some reports indicate proinflammatory and proneoplastic activities of cannabinoids. Like Eagleston et al., they call for additional studies.28
Conclusion
As in many botanical agents that I cover in this column, cannabis is associated with numerous medical benefits. I am encouraged to see expanding legalization of medical marijuana and increased research into its reputedly broad potential to improve human health. Anecdotally, I have heard stunning reports from patients about amelioration of joint and back pain as well as relief from other inflammatory symptoms. Discovery and elucidation of the endogenous cannabinoid system is a recent development. Research on its functions and roles in cutaneous health has followed suit and is steadily increasing. Particular skin conditions for which cannabis and cannabinoids may be indicated will be the focus of the next column.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann wrote two textbooks: “Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002), and “Cosmeceuticals and Cosmetic Ingredients” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2014), and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers, “The Skin Type Solution” (New York: Bantam Dell, 2006). Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Evolus, Galderma, and Revance. She is the founder and CEO of Skin Type Solutions Franchise Systems LLC. Write to her at [email protected]
References
1. Higdon J. Why 2019 could be marijuana’s biggest year yet. Politico Magazine. Jan 21, 2019.
2. Singh D et al. Clin Dermatol. 2018 May-Jun;36(3):399-419.
3. Kupczyk P et al. Exp Dermatol. 2009 Aug;18(8):669-79.
4. Wilkinson JD et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2007 Feb;45(2):87-92.
5. Milando R et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019 April;20(2):167-80.
6. Robinson E et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018 Dec 1;17(12):1273-8.
7. Mounessa JS et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Jul;77(1):188-90.
8. Liszewski W et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Sep;77(3):e87-e88.
9. Telek A et al. FASEB J. 2007 Nov;21(13):3534-41.
10. Wollenberg A et al. Br J Dermatol. 2014 Jul;170 Suppl 1:7-11.
11. Ramot Y et al. PeerJ. 2013 Feb 19;1:e40.
12. Schlicker E et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001 Nov;22(11):565-72.
13. Christie MJ et al. Nature. 2001 Mar 29;410(6828):527-30.
14. Ibid.
15. Bíró T et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Aug;30(8):411-20.
16. Pacher P et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2006 Sep;58(3):389-462.
17. Shalaby M et al. Pract Dermatol. 2018 Jan;68-70.
18. Chelliah MP et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jul;35(4):e224-e227.
19. Glodde N et al. Life Sci. 2015 Oct 1;138:35-40.
20. Gaffal E et al. Allergy. 2013 Aug;68(8):994-1000.
21. Pearce DD et al. J Altern Complement Med. 2014 Oct;20(10):787:91.
22. Leonti M et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 15;79(12):1815-26.
23. Trusler AR et al. Dermatitis. 2017 Jan/Feb;28(1):22-32.
24. Río CD et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Nov;157:122-133.
25. Chuquilin M et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Feb;74(2):197-212.
26. Tubaro A et al. Fitoterapia. 2010 Oct;81(7):816-9.
27. Eagleston LRM et al. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Jun 15;24(6).
28. Marks DH et al. Skin Therapy Lett. 2018 Nov;23(6):1-5.
In the United States, 31 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam have legalized medical marijuana, which is also permitted for recreational use in 9 states, as well as in the District of Columbia. However, marijuana, derived from Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, is regulated as a schedule I drug in the United States at the federal level. (Some believe that the federal status may change in the coming year as a result of the Democratic Party’s takeover in the House of Representatives.1)
Cannabis species contain hundreds of various substances, of which the cannabinoids are the most studied. More than 113 biologically active chemical compounds are found within the class of cannabinoids and their derivatives,2 which have been used for centuries in natural medicine.3 The legal status of marijuana has long hampered scientific research of cannabinoids. Nevertheless, the number of studies focusing on the therapeutic potential of these compounds has steadily risen as the legal landscape of marijuana has evolved.
Findings over the last 20 years have shown that cannabinoids present in C. sativa exhibit anti-inflammatory activity and suppress the proliferation of multiple tumorigenic cell lines, some of which are moderated through cannabinoid (CB) receptors.4 In addition to anti-inflammatory properties, .3 Recent research has demonstrated that CB receptors are present in human skin.4
The endocannabinoid system has emerged as an intriguing area of research, as we’ve come to learn about its convoluted role in human anatomy and health. It features a pervasive network of endogenous ligands, enzymes, and receptors, which exogenous substances (including phytocannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoids) can activate.5 Data from recent studies indicate that the endocannabinoid system plays a significant role in cutaneous homeostasis, as it regulates proliferation, differentiation, and inflammatory mediator release.5 Further, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, pruritus, and wound healing have been identified in recent research as cutaneous concerns in which the use of cannabinoids may be of benefit.6,7 We must also consider reports that cannabinoids can slow human hair growth and that some constituents may spur the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines.8,9This column will briefly address potential confusion over the psychoactive aspects of cannabis, which are related to particular constituents of cannabis and specific CB receptors, and focus on the endocannabinoid system.
Psychoactive or not?
C. sativa confers biological activity through its influence on the G-protein-coupled receptor types CB1 and CB2,10 which pervade human skin epithelium.11 CB1 receptors are found in greatest supply in the central nervous system, especially the basal ganglia, cerebellum, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex, where their activation yields psychoactivity.2,5,12,13 Stimulation of CB1 receptors in the skin – where they are present in differentiated keratinocytes, hair follicle cells, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons14 – diminishes pain and pruritus, controls keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, inhibits hair follicle growth, and regulates the release of damage-induced keratins and inflammatory mediators to maintain cutaneous homeostasis.11,14,15
CB2 receptors are expressed in the immune system, particularly monocytes, macrophages, as well as B and T cells, and in peripheral tissues including the spleen, tonsils, thymus gland, bone, and, notably, the skin.2,16 Stimulation of CB2 receptors in the skin – where they are found in keratinocytes, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons – fosters sebum production, regulates pain sensation, hinders keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, and suppresses cutaneous inflammatory responses.14,15
The best known, or most notorious, component of exogenous cannabinoids is delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta9-THC or simply THC), which is a natural psychoactive constituent in marijuana.3 In fact, of the five primary cannabinoids derived from marijuana, including cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and THC, only THC imparts psychoactive effects.17
CBD is thought to exhibit anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities.18 THC has been found to have the capacity to induce cancer cell apoptosis and block angiogenesis,19 and is thought to have immunomodulatory potential, partly acting through the G-protein-coupled CB1 and CB2 receptors but also yielding effects not related to these receptors.20In a 2014 survey of medical cannabis users, a statistically significant preference for C. indica (which contains higher CBD and lower THC levels) was observed for pain management, sedation, and sleep, while C. sativa was associated with euphoria and improving energy.21
The endocannabinoid system and skin health
The endogenous cannabinoid or endocannabinoid system includes cannabinoid receptors, associated endogenous ligands (such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide [anandamide or AEA], 2-arachidonoyl glycerol [2-AG], and N-palmitoylethanolamide [PEA], a fatty acid amide that enhances AEA activity),2 and enzymes involved in endocannabinoid production and decay.11,15,22,23 Research in recent years appears to support the notion that the endocannabinoid system plays an important role in skin health, as its dysregulation has been linked to atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, scleroderma, and skin cancer. Data indicate that exogenous and endogenous cannabinoids influence the endocannabinoid system through cannabinoid receptors, transient receptor potential channels (TRPs), and peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors (PPARs). Río et al. suggest that the dynamism of the endocannabinoid system buttresses the targeting of multiple endpoints for therapeutic success with cannabinoids rather than the one-disease-one-target approach.24 Endogenous cannabinoids, such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, are now thought to be significant mediators in the skin.3 Further, endocannabinoids have been shown to deliver analgesia to the skin, at the spinal and supraspinal levels.25
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Tubaro et al. used the Croton oil mouse ear dermatitis assay to study the in vivo topical anti-inflammatory effects of seven phytocannabinoids and their related cannabivarins (nonpsychoactive cannabinoids). They found that anti-inflammatory activity was derived from the involvement of the cannabinoid receptors as well as the inflammatory endpoints that the phytocannabinoids targeted.26
In 2013, Gaffal et al. explored the anti-inflammatory activity of topical THC in dinitrofluorobenzene-mediated allergic contact dermatitis independent of CB1/2 receptors by using wild-type and CB1/2 receptor-deficient mice. The researchers found that topically applied THC reduced contact allergic ear edema and myeloid immune cell infiltration in both groups of mice. They concluded that such a decline in inflammation resulted from mitigating the keratinocyte-derived proinflammatory mediators that direct myeloid immune cell infiltration independent of CB1/2 receptors, and positions cannabinoids well for future use in treating inflammatory cutaneous conditions.20
Literature reviews
In a 2018 literature review on the uses of cannabinoids for cutaneous disorders, Eagleston et al. determined that preclinical data on cannabinoids reveal the potential to treat acne, allergic contact dermatitis, asteatotic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, Kaposi sarcoma, pruritus, psoriasis, skin cancer, and the skin symptoms of systemic sclerosis. They caution, though, that more preclinical work is necessary along with randomized, controlled trials with sufficiently large sample sizes to establish the safety and efficacy of cannabinoids to treat skin conditions.27
A literature review by Marks and Friedman published later that year on the therapeutic potential of phytocannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids in managing skin disorders revealed the same findings regarding the cutaneous conditions associated with these compounds. The authors noted, though, that while the preponderance of articles highlight the efficacy of cannabinoids in treating inflammatory and neoplastic cutaneous conditions, some reports indicate proinflammatory and proneoplastic activities of cannabinoids. Like Eagleston et al., they call for additional studies.28
Conclusion
As in many botanical agents that I cover in this column, cannabis is associated with numerous medical benefits. I am encouraged to see expanding legalization of medical marijuana and increased research into its reputedly broad potential to improve human health. Anecdotally, I have heard stunning reports from patients about amelioration of joint and back pain as well as relief from other inflammatory symptoms. Discovery and elucidation of the endogenous cannabinoid system is a recent development. Research on its functions and roles in cutaneous health has followed suit and is steadily increasing. Particular skin conditions for which cannabis and cannabinoids may be indicated will be the focus of the next column.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann wrote two textbooks: “Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002), and “Cosmeceuticals and Cosmetic Ingredients” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2014), and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers, “The Skin Type Solution” (New York: Bantam Dell, 2006). Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Evolus, Galderma, and Revance. She is the founder and CEO of Skin Type Solutions Franchise Systems LLC. Write to her at [email protected]
References
1. Higdon J. Why 2019 could be marijuana’s biggest year yet. Politico Magazine. Jan 21, 2019.
2. Singh D et al. Clin Dermatol. 2018 May-Jun;36(3):399-419.
3. Kupczyk P et al. Exp Dermatol. 2009 Aug;18(8):669-79.
4. Wilkinson JD et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2007 Feb;45(2):87-92.
5. Milando R et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019 April;20(2):167-80.
6. Robinson E et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018 Dec 1;17(12):1273-8.
7. Mounessa JS et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Jul;77(1):188-90.
8. Liszewski W et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Sep;77(3):e87-e88.
9. Telek A et al. FASEB J. 2007 Nov;21(13):3534-41.
10. Wollenberg A et al. Br J Dermatol. 2014 Jul;170 Suppl 1:7-11.
11. Ramot Y et al. PeerJ. 2013 Feb 19;1:e40.
12. Schlicker E et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001 Nov;22(11):565-72.
13. Christie MJ et al. Nature. 2001 Mar 29;410(6828):527-30.
14. Ibid.
15. Bíró T et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Aug;30(8):411-20.
16. Pacher P et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2006 Sep;58(3):389-462.
17. Shalaby M et al. Pract Dermatol. 2018 Jan;68-70.
18. Chelliah MP et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jul;35(4):e224-e227.
19. Glodde N et al. Life Sci. 2015 Oct 1;138:35-40.
20. Gaffal E et al. Allergy. 2013 Aug;68(8):994-1000.
21. Pearce DD et al. J Altern Complement Med. 2014 Oct;20(10):787:91.
22. Leonti M et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 15;79(12):1815-26.
23. Trusler AR et al. Dermatitis. 2017 Jan/Feb;28(1):22-32.
24. Río CD et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Nov;157:122-133.
25. Chuquilin M et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Feb;74(2):197-212.
26. Tubaro A et al. Fitoterapia. 2010 Oct;81(7):816-9.
27. Eagleston LRM et al. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Jun 15;24(6).
28. Marks DH et al. Skin Therapy Lett. 2018 Nov;23(6):1-5.
In the United States, 31 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam have legalized medical marijuana, which is also permitted for recreational use in 9 states, as well as in the District of Columbia. However, marijuana, derived from Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, is regulated as a schedule I drug in the United States at the federal level. (Some believe that the federal status may change in the coming year as a result of the Democratic Party’s takeover in the House of Representatives.1)
Cannabis species contain hundreds of various substances, of which the cannabinoids are the most studied. More than 113 biologically active chemical compounds are found within the class of cannabinoids and their derivatives,2 which have been used for centuries in natural medicine.3 The legal status of marijuana has long hampered scientific research of cannabinoids. Nevertheless, the number of studies focusing on the therapeutic potential of these compounds has steadily risen as the legal landscape of marijuana has evolved.
Findings over the last 20 years have shown that cannabinoids present in C. sativa exhibit anti-inflammatory activity and suppress the proliferation of multiple tumorigenic cell lines, some of which are moderated through cannabinoid (CB) receptors.4 In addition to anti-inflammatory properties, .3 Recent research has demonstrated that CB receptors are present in human skin.4
The endocannabinoid system has emerged as an intriguing area of research, as we’ve come to learn about its convoluted role in human anatomy and health. It features a pervasive network of endogenous ligands, enzymes, and receptors, which exogenous substances (including phytocannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoids) can activate.5 Data from recent studies indicate that the endocannabinoid system plays a significant role in cutaneous homeostasis, as it regulates proliferation, differentiation, and inflammatory mediator release.5 Further, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, pruritus, and wound healing have been identified in recent research as cutaneous concerns in which the use of cannabinoids may be of benefit.6,7 We must also consider reports that cannabinoids can slow human hair growth and that some constituents may spur the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines.8,9This column will briefly address potential confusion over the psychoactive aspects of cannabis, which are related to particular constituents of cannabis and specific CB receptors, and focus on the endocannabinoid system.
Psychoactive or not?
C. sativa confers biological activity through its influence on the G-protein-coupled receptor types CB1 and CB2,10 which pervade human skin epithelium.11 CB1 receptors are found in greatest supply in the central nervous system, especially the basal ganglia, cerebellum, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex, where their activation yields psychoactivity.2,5,12,13 Stimulation of CB1 receptors in the skin – where they are present in differentiated keratinocytes, hair follicle cells, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons14 – diminishes pain and pruritus, controls keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, inhibits hair follicle growth, and regulates the release of damage-induced keratins and inflammatory mediators to maintain cutaneous homeostasis.11,14,15
CB2 receptors are expressed in the immune system, particularly monocytes, macrophages, as well as B and T cells, and in peripheral tissues including the spleen, tonsils, thymus gland, bone, and, notably, the skin.2,16 Stimulation of CB2 receptors in the skin – where they are found in keratinocytes, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons – fosters sebum production, regulates pain sensation, hinders keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, and suppresses cutaneous inflammatory responses.14,15
The best known, or most notorious, component of exogenous cannabinoids is delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta9-THC or simply THC), which is a natural psychoactive constituent in marijuana.3 In fact, of the five primary cannabinoids derived from marijuana, including cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and THC, only THC imparts psychoactive effects.17
CBD is thought to exhibit anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities.18 THC has been found to have the capacity to induce cancer cell apoptosis and block angiogenesis,19 and is thought to have immunomodulatory potential, partly acting through the G-protein-coupled CB1 and CB2 receptors but also yielding effects not related to these receptors.20In a 2014 survey of medical cannabis users, a statistically significant preference for C. indica (which contains higher CBD and lower THC levels) was observed for pain management, sedation, and sleep, while C. sativa was associated with euphoria and improving energy.21
The endocannabinoid system and skin health
The endogenous cannabinoid or endocannabinoid system includes cannabinoid receptors, associated endogenous ligands (such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide [anandamide or AEA], 2-arachidonoyl glycerol [2-AG], and N-palmitoylethanolamide [PEA], a fatty acid amide that enhances AEA activity),2 and enzymes involved in endocannabinoid production and decay.11,15,22,23 Research in recent years appears to support the notion that the endocannabinoid system plays an important role in skin health, as its dysregulation has been linked to atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, scleroderma, and skin cancer. Data indicate that exogenous and endogenous cannabinoids influence the endocannabinoid system through cannabinoid receptors, transient receptor potential channels (TRPs), and peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors (PPARs). Río et al. suggest that the dynamism of the endocannabinoid system buttresses the targeting of multiple endpoints for therapeutic success with cannabinoids rather than the one-disease-one-target approach.24 Endogenous cannabinoids, such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, are now thought to be significant mediators in the skin.3 Further, endocannabinoids have been shown to deliver analgesia to the skin, at the spinal and supraspinal levels.25
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Tubaro et al. used the Croton oil mouse ear dermatitis assay to study the in vivo topical anti-inflammatory effects of seven phytocannabinoids and their related cannabivarins (nonpsychoactive cannabinoids). They found that anti-inflammatory activity was derived from the involvement of the cannabinoid receptors as well as the inflammatory endpoints that the phytocannabinoids targeted.26
In 2013, Gaffal et al. explored the anti-inflammatory activity of topical THC in dinitrofluorobenzene-mediated allergic contact dermatitis independent of CB1/2 receptors by using wild-type and CB1/2 receptor-deficient mice. The researchers found that topically applied THC reduced contact allergic ear edema and myeloid immune cell infiltration in both groups of mice. They concluded that such a decline in inflammation resulted from mitigating the keratinocyte-derived proinflammatory mediators that direct myeloid immune cell infiltration independent of CB1/2 receptors, and positions cannabinoids well for future use in treating inflammatory cutaneous conditions.20
Literature reviews
In a 2018 literature review on the uses of cannabinoids for cutaneous disorders, Eagleston et al. determined that preclinical data on cannabinoids reveal the potential to treat acne, allergic contact dermatitis, asteatotic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, Kaposi sarcoma, pruritus, psoriasis, skin cancer, and the skin symptoms of systemic sclerosis. They caution, though, that more preclinical work is necessary along with randomized, controlled trials with sufficiently large sample sizes to establish the safety and efficacy of cannabinoids to treat skin conditions.27
A literature review by Marks and Friedman published later that year on the therapeutic potential of phytocannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids in managing skin disorders revealed the same findings regarding the cutaneous conditions associated with these compounds. The authors noted, though, that while the preponderance of articles highlight the efficacy of cannabinoids in treating inflammatory and neoplastic cutaneous conditions, some reports indicate proinflammatory and proneoplastic activities of cannabinoids. Like Eagleston et al., they call for additional studies.28
Conclusion
As in many botanical agents that I cover in this column, cannabis is associated with numerous medical benefits. I am encouraged to see expanding legalization of medical marijuana and increased research into its reputedly broad potential to improve human health. Anecdotally, I have heard stunning reports from patients about amelioration of joint and back pain as well as relief from other inflammatory symptoms. Discovery and elucidation of the endogenous cannabinoid system is a recent development. Research on its functions and roles in cutaneous health has followed suit and is steadily increasing. Particular skin conditions for which cannabis and cannabinoids may be indicated will be the focus of the next column.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann wrote two textbooks: “Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002), and “Cosmeceuticals and Cosmetic Ingredients” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2014), and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers, “The Skin Type Solution” (New York: Bantam Dell, 2006). Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Evolus, Galderma, and Revance. She is the founder and CEO of Skin Type Solutions Franchise Systems LLC. Write to her at [email protected]
References
1. Higdon J. Why 2019 could be marijuana’s biggest year yet. Politico Magazine. Jan 21, 2019.
2. Singh D et al. Clin Dermatol. 2018 May-Jun;36(3):399-419.
3. Kupczyk P et al. Exp Dermatol. 2009 Aug;18(8):669-79.
4. Wilkinson JD et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2007 Feb;45(2):87-92.
5. Milando R et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019 April;20(2):167-80.
6. Robinson E et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018 Dec 1;17(12):1273-8.
7. Mounessa JS et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Jul;77(1):188-90.
8. Liszewski W et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Sep;77(3):e87-e88.
9. Telek A et al. FASEB J. 2007 Nov;21(13):3534-41.
10. Wollenberg A et al. Br J Dermatol. 2014 Jul;170 Suppl 1:7-11.
11. Ramot Y et al. PeerJ. 2013 Feb 19;1:e40.
12. Schlicker E et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001 Nov;22(11):565-72.
13. Christie MJ et al. Nature. 2001 Mar 29;410(6828):527-30.
14. Ibid.
15. Bíró T et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Aug;30(8):411-20.
16. Pacher P et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2006 Sep;58(3):389-462.
17. Shalaby M et al. Pract Dermatol. 2018 Jan;68-70.
18. Chelliah MP et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jul;35(4):e224-e227.
19. Glodde N et al. Life Sci. 2015 Oct 1;138:35-40.
20. Gaffal E et al. Allergy. 2013 Aug;68(8):994-1000.
21. Pearce DD et al. J Altern Complement Med. 2014 Oct;20(10):787:91.
22. Leonti M et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 15;79(12):1815-26.
23. Trusler AR et al. Dermatitis. 2017 Jan/Feb;28(1):22-32.
24. Río CD et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Nov;157:122-133.
25. Chuquilin M et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Feb;74(2):197-212.
26. Tubaro A et al. Fitoterapia. 2010 Oct;81(7):816-9.
27. Eagleston LRM et al. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Jun 15;24(6).
28. Marks DH et al. Skin Therapy Lett. 2018 Nov;23(6):1-5.
Ventricular Arrhythmia Due to MS Treatment
Fingolimod, a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, has been used to treat > 55,000 patients in the US, according to the manufacturer (Gilenya/Novartis). It is believed to work by keeping lymphocytes from migrating into the CNS, sequestering them in the lymph nodes.
Although it has been found effective in randomized controlled trials, fingolimod is also known to have a wide range of adverse effects (AEs), including some that are serious and even life-threatening, such as bradycardia and atrioventricular block. The drug is contraindicated for patients who have had myocardial infarction, unstable angina, or heart failure, among other conditions. Ventricular tachycardia has been reported only once, but clinicians from Hurley Medical Center in Flint, Michigan, suggest that it may actually be an underrecognized cause of sudden death.
They describe the case of their patient, a 63-year-old woman with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis and hypertension who was about to start fingolomod. She underwent a basal ECG to be cleared before starting treatment. She received her first dose of fingolimod at the cardiology office, was monitored for 6 hours, and went home with a surface-mounted Holter monitor.
Two weeks later, she was in the emergency department because the monitor had captured ventricular tachycardia, and she was reporting palpitations.
Lab work was normal; the echocardiogram was normal. Cardiac monitoring showed no other evidence of cardiac arrhythmias. Her only other medication was amlodipine. The fingolimod was held back. She was observed for4 days then discharged in a stable condition. Her clinicians followed her for 2 months but the arrhythmia did not return.
Although this patient had no further arrhythmias, the authors warn that serious outcomes are possible. They urge health care practitioners to let patients know of this potential AE and advise them to report symptoms such as palpitations immediately.
Fingolimod, a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, has been used to treat > 55,000 patients in the US, according to the manufacturer (Gilenya/Novartis). It is believed to work by keeping lymphocytes from migrating into the CNS, sequestering them in the lymph nodes.
Although it has been found effective in randomized controlled trials, fingolimod is also known to have a wide range of adverse effects (AEs), including some that are serious and even life-threatening, such as bradycardia and atrioventricular block. The drug is contraindicated for patients who have had myocardial infarction, unstable angina, or heart failure, among other conditions. Ventricular tachycardia has been reported only once, but clinicians from Hurley Medical Center in Flint, Michigan, suggest that it may actually be an underrecognized cause of sudden death.
They describe the case of their patient, a 63-year-old woman with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis and hypertension who was about to start fingolomod. She underwent a basal ECG to be cleared before starting treatment. She received her first dose of fingolimod at the cardiology office, was monitored for 6 hours, and went home with a surface-mounted Holter monitor.
Two weeks later, she was in the emergency department because the monitor had captured ventricular tachycardia, and she was reporting palpitations.
Lab work was normal; the echocardiogram was normal. Cardiac monitoring showed no other evidence of cardiac arrhythmias. Her only other medication was amlodipine. The fingolimod was held back. She was observed for4 days then discharged in a stable condition. Her clinicians followed her for 2 months but the arrhythmia did not return.
Although this patient had no further arrhythmias, the authors warn that serious outcomes are possible. They urge health care practitioners to let patients know of this potential AE and advise them to report symptoms such as palpitations immediately.
Fingolimod, a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, has been used to treat > 55,000 patients in the US, according to the manufacturer (Gilenya/Novartis). It is believed to work by keeping lymphocytes from migrating into the CNS, sequestering them in the lymph nodes.
Although it has been found effective in randomized controlled trials, fingolimod is also known to have a wide range of adverse effects (AEs), including some that are serious and even life-threatening, such as bradycardia and atrioventricular block. The drug is contraindicated for patients who have had myocardial infarction, unstable angina, or heart failure, among other conditions. Ventricular tachycardia has been reported only once, but clinicians from Hurley Medical Center in Flint, Michigan, suggest that it may actually be an underrecognized cause of sudden death.
They describe the case of their patient, a 63-year-old woman with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis and hypertension who was about to start fingolomod. She underwent a basal ECG to be cleared before starting treatment. She received her first dose of fingolimod at the cardiology office, was monitored for 6 hours, and went home with a surface-mounted Holter monitor.
Two weeks later, she was in the emergency department because the monitor had captured ventricular tachycardia, and she was reporting palpitations.
Lab work was normal; the echocardiogram was normal. Cardiac monitoring showed no other evidence of cardiac arrhythmias. Her only other medication was amlodipine. The fingolimod was held back. She was observed for4 days then discharged in a stable condition. Her clinicians followed her for 2 months but the arrhythmia did not return.
Although this patient had no further arrhythmias, the authors warn that serious outcomes are possible. They urge health care practitioners to let patients know of this potential AE and advise them to report symptoms such as palpitations immediately.
CMS plan will incentivize generic drug use
Patients will still be able to use drug manufacturer coupons and pay less at the pharmacy counter, but the money they spend won’t be applied to their out-of-pocket maximum if they choose the brand-name drug with coupon instead of the lower-cost generic.
The change will affect insurance plans offered in the individual market, small-group, large-group, and self-insured–group health plans.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services backed away from implementing two other generic drug provisions based on feedback on its draft proposal.
The provisions would have allowed insurers to remove brand-name drugs from a formulary midyear when a generic became available or move the drug to a higher tier, and allowed insurers to not count certain drug copayments toward the annual limits if the patient selected a brand-name drug when a generic was available.
“Based on issues raised by commenters, we are not finalizing these proposals,” CMS officials said.
Insurers “making mid-year formulary changes [should] only be permitted to move the brand-name drug to a different cost-sharing tier for the remainder of the plan year. [They] should not be allowed to remove a safe brand-name drug from the formulary until the time of plan renewal,” the American College of Physicians recommended in Feb. 12 comments on the proposal.
The final rule on Notice of Benefit and Payment Parameters for the 2020 benefit year also aims to provide more stability and lower premiums in the exchanges, according to CMS officials.
“The rule issued today will give consumers immediate premium relief by reducing the exchange user fees in the federally facilitated exchanges and state-based exchanges using the federal platform for 2020 thanks to successful efforts to improve the efficiency of the exchange,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a statement.
CMS finalized a proposal to lower exchange user fees by 0.5%, fees that are generally passed on to consumers through premiums.
Other provisions cover exchange-related calculations, including how subsidies for exchange enrollees are calculated and how much enrollees are expected to contribute to benchmark plan premiums, which decreased slightly to 8.24%, down 0.07%, according to a CMS fact sheet.
For the out-of-pocket maximum, CMS said it “finalized a maximum annual limitation on cost sharing of $8,150 for self-only coverage and $16,300 for other than self-only coverage for the 2020 benefit year. This represents an approximately 3.16% increase above the 2019 parameters of $7,900 for self-only coverage and $15,800 for other than self-only coverage.”
Patients will still be able to use drug manufacturer coupons and pay less at the pharmacy counter, but the money they spend won’t be applied to their out-of-pocket maximum if they choose the brand-name drug with coupon instead of the lower-cost generic.
The change will affect insurance plans offered in the individual market, small-group, large-group, and self-insured–group health plans.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services backed away from implementing two other generic drug provisions based on feedback on its draft proposal.
The provisions would have allowed insurers to remove brand-name drugs from a formulary midyear when a generic became available or move the drug to a higher tier, and allowed insurers to not count certain drug copayments toward the annual limits if the patient selected a brand-name drug when a generic was available.
“Based on issues raised by commenters, we are not finalizing these proposals,” CMS officials said.
Insurers “making mid-year formulary changes [should] only be permitted to move the brand-name drug to a different cost-sharing tier for the remainder of the plan year. [They] should not be allowed to remove a safe brand-name drug from the formulary until the time of plan renewal,” the American College of Physicians recommended in Feb. 12 comments on the proposal.
The final rule on Notice of Benefit and Payment Parameters for the 2020 benefit year also aims to provide more stability and lower premiums in the exchanges, according to CMS officials.
“The rule issued today will give consumers immediate premium relief by reducing the exchange user fees in the federally facilitated exchanges and state-based exchanges using the federal platform for 2020 thanks to successful efforts to improve the efficiency of the exchange,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a statement.
CMS finalized a proposal to lower exchange user fees by 0.5%, fees that are generally passed on to consumers through premiums.
Other provisions cover exchange-related calculations, including how subsidies for exchange enrollees are calculated and how much enrollees are expected to contribute to benchmark plan premiums, which decreased slightly to 8.24%, down 0.07%, according to a CMS fact sheet.
For the out-of-pocket maximum, CMS said it “finalized a maximum annual limitation on cost sharing of $8,150 for self-only coverage and $16,300 for other than self-only coverage for the 2020 benefit year. This represents an approximately 3.16% increase above the 2019 parameters of $7,900 for self-only coverage and $15,800 for other than self-only coverage.”
Patients will still be able to use drug manufacturer coupons and pay less at the pharmacy counter, but the money they spend won’t be applied to their out-of-pocket maximum if they choose the brand-name drug with coupon instead of the lower-cost generic.
The change will affect insurance plans offered in the individual market, small-group, large-group, and self-insured–group health plans.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services backed away from implementing two other generic drug provisions based on feedback on its draft proposal.
The provisions would have allowed insurers to remove brand-name drugs from a formulary midyear when a generic became available or move the drug to a higher tier, and allowed insurers to not count certain drug copayments toward the annual limits if the patient selected a brand-name drug when a generic was available.
“Based on issues raised by commenters, we are not finalizing these proposals,” CMS officials said.
Insurers “making mid-year formulary changes [should] only be permitted to move the brand-name drug to a different cost-sharing tier for the remainder of the plan year. [They] should not be allowed to remove a safe brand-name drug from the formulary until the time of plan renewal,” the American College of Physicians recommended in Feb. 12 comments on the proposal.
The final rule on Notice of Benefit and Payment Parameters for the 2020 benefit year also aims to provide more stability and lower premiums in the exchanges, according to CMS officials.
“The rule issued today will give consumers immediate premium relief by reducing the exchange user fees in the federally facilitated exchanges and state-based exchanges using the federal platform for 2020 thanks to successful efforts to improve the efficiency of the exchange,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a statement.
CMS finalized a proposal to lower exchange user fees by 0.5%, fees that are generally passed on to consumers through premiums.
Other provisions cover exchange-related calculations, including how subsidies for exchange enrollees are calculated and how much enrollees are expected to contribute to benchmark plan premiums, which decreased slightly to 8.24%, down 0.07%, according to a CMS fact sheet.
For the out-of-pocket maximum, CMS said it “finalized a maximum annual limitation on cost sharing of $8,150 for self-only coverage and $16,300 for other than self-only coverage for the 2020 benefit year. This represents an approximately 3.16% increase above the 2019 parameters of $7,900 for self-only coverage and $15,800 for other than self-only coverage.”
Key clinical point: Patients will be able to use drug manufacturer coupons and pay less at the pharmacy counter, but the money they spend won’t be applied to their out-of-pocket maximum if they choose the brand-name drug with coupon instead of the lower-cost generic.
Major finding: The change will affect insurance plans offered in the individual market, small-group, large-group, and self-insured–group health plans.
Study details: Final rule for the Notice of Benefit and Payment Parameters for the 2020 benefit year
Disclosures: None.
Source: Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act; HHS Notice of Benefit and Payment Parameters for 2020. 45 CFR Parts 146, 147, 148, 153, 155, and 156.
Dr. Douglas Paauw gives updates on antihypertensives, statins, SGLT2 inhibitors
PHILADELPHIA – in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dr. Paauw, professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, began by discussing some of the issues that occurred with antihypertensive drugs in the past year. These included the link between hydrochlorothiazide use and the increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancers, the recalls of many drug lots of angiotensin II receptor blockers, and a study that found an increased risk of lung cancer in people who were taking ACE inhibitors.
He then described the findings of studies that examined the links between statins and muscle pain and other new research on these drugs.
He also warned physicians to be particularity cautious about prescribing sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors to certain kinds of patients.
Dr. Paauw concluded by explaining why clarithromycin is his most hated drug.
Dr. Paauw is also the Rathmann Family Foundation Endowed Chair for Patient-Centered Clinical Education and the medicine clerkship director at the University of Washington.
PHILADELPHIA – in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dr. Paauw, professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, began by discussing some of the issues that occurred with antihypertensive drugs in the past year. These included the link between hydrochlorothiazide use and the increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancers, the recalls of many drug lots of angiotensin II receptor blockers, and a study that found an increased risk of lung cancer in people who were taking ACE inhibitors.
He then described the findings of studies that examined the links between statins and muscle pain and other new research on these drugs.
He also warned physicians to be particularity cautious about prescribing sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors to certain kinds of patients.
Dr. Paauw concluded by explaining why clarithromycin is his most hated drug.
Dr. Paauw is also the Rathmann Family Foundation Endowed Chair for Patient-Centered Clinical Education and the medicine clerkship director at the University of Washington.
PHILADELPHIA – in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dr. Paauw, professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, began by discussing some of the issues that occurred with antihypertensive drugs in the past year. These included the link between hydrochlorothiazide use and the increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancers, the recalls of many drug lots of angiotensin II receptor blockers, and a study that found an increased risk of lung cancer in people who were taking ACE inhibitors.
He then described the findings of studies that examined the links between statins and muscle pain and other new research on these drugs.
He also warned physicians to be particularity cautious about prescribing sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors to certain kinds of patients.
Dr. Paauw concluded by explaining why clarithromycin is his most hated drug.
Dr. Paauw is also the Rathmann Family Foundation Endowed Chair for Patient-Centered Clinical Education and the medicine clerkship director at the University of Washington.
REPORTING FROM INTERNAL MEDICINE 2019
Study highlights lack of data on transgender leukemia patients
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – Researchers have shown they can identify transgender leukemia patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches, but some transgender patients may be overlooked with this method.
The researchers’ work also highlights how little we know about transgender patients with leukemia and other cancers.
Alison Alpert, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, and her colleagues conducted this research and presented their findings in a poster at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
“There’s almost no data about transgender people with cancer ... in terms of prevalence or anything else,” Dr. Alpert noted. “And because we don’t know which patients with cancer are transgender, we can’t begin to answer any of the other big questions for patients.”
Specifically, it’s unclear what kinds of cancer transgender patients have, if there are health disparities among transgender patients, if it is safe to continue hormone therapy during cancer treatment, and if it is possible to do transition-related surgeries in the context of cancer care.
With this in mind, Dr. Alpert and her colleagues set out to identify transgender patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches. The team analyzed data on patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes enrolled in five Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) trials.
Of the 1,748 patients analyzed, six (0.3%) had a gender-karyotype mismatch. Five patients had a 46,XY karyotype and identified as female, and one patient had a 46,XX karyotype and identified as male.
“Some transgender patients have their gender identity accurately reflected in the electronic medical record, [but] some transgender patients probably don’t,” Dr. Alpert noted. “So we identified some, but probably not all, and probably not even most, transgender patients with leukemia in this cohort.”
All six of the transgender patients identified had AML, and all were white. They ranged in age from 18 to 57 years. Four patients had achieved a complete response to therapy, and two had refractory disease.
Four patients, including one who was refractory, were still alive at last follow-up. The remaining two patients, including one who had achieved a complete response, had died.
The transgender patients identified in this analysis represent a very small percentage of the population studied, Dr. Alpert noted. Therefore, the researchers could not draw any conclusions about transgender patients with AML.
“Mostly, what we did was, we pointed out how little information we have,” Dr. Alpert said. “Oncologists don’t routinely collect gender identity information, and this information doesn’t exist in cooperative group databases either.”
“But going forward, what probably really needs to happen is that oncologists need to ask their patients whether they are transgender or not. And then, ideally, consent forms for large cooperative groups like SWOG would include gender identity data, and then we would be able to answer some of our other questions and better counsel our patients.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues are hoping to gain insights regarding transgender patients with lymphoma as well. The researchers are analyzing the lymphoma database at the University of Rochester Medical Center, which includes about 2,200 patients.
The team is attempting to identify transgender lymphoma patients using gender-karyotype mismatch as well as other methods, including assessing patients’ medication and surgical histories, determining whether patients have any aliases, and looking for the word “transgender” in patient charts.
“Given that the country is finally starting to talk about transgender patients, their health disparities, and their needs and experiences, it’s really time that we start collecting this data,” Dr. Alpert said.
“[I]f we are able to start to collect this data, it can help us build relationships with our patients, improve their care and outcomes, and, hopefully, be able to better counsel them about hormones and surgery.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is organized by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – Researchers have shown they can identify transgender leukemia patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches, but some transgender patients may be overlooked with this method.
The researchers’ work also highlights how little we know about transgender patients with leukemia and other cancers.
Alison Alpert, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, and her colleagues conducted this research and presented their findings in a poster at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
“There’s almost no data about transgender people with cancer ... in terms of prevalence or anything else,” Dr. Alpert noted. “And because we don’t know which patients with cancer are transgender, we can’t begin to answer any of the other big questions for patients.”
Specifically, it’s unclear what kinds of cancer transgender patients have, if there are health disparities among transgender patients, if it is safe to continue hormone therapy during cancer treatment, and if it is possible to do transition-related surgeries in the context of cancer care.
With this in mind, Dr. Alpert and her colleagues set out to identify transgender patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches. The team analyzed data on patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes enrolled in five Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) trials.
Of the 1,748 patients analyzed, six (0.3%) had a gender-karyotype mismatch. Five patients had a 46,XY karyotype and identified as female, and one patient had a 46,XX karyotype and identified as male.
“Some transgender patients have their gender identity accurately reflected in the electronic medical record, [but] some transgender patients probably don’t,” Dr. Alpert noted. “So we identified some, but probably not all, and probably not even most, transgender patients with leukemia in this cohort.”
All six of the transgender patients identified had AML, and all were white. They ranged in age from 18 to 57 years. Four patients had achieved a complete response to therapy, and two had refractory disease.
Four patients, including one who was refractory, were still alive at last follow-up. The remaining two patients, including one who had achieved a complete response, had died.
The transgender patients identified in this analysis represent a very small percentage of the population studied, Dr. Alpert noted. Therefore, the researchers could not draw any conclusions about transgender patients with AML.
“Mostly, what we did was, we pointed out how little information we have,” Dr. Alpert said. “Oncologists don’t routinely collect gender identity information, and this information doesn’t exist in cooperative group databases either.”
“But going forward, what probably really needs to happen is that oncologists need to ask their patients whether they are transgender or not. And then, ideally, consent forms for large cooperative groups like SWOG would include gender identity data, and then we would be able to answer some of our other questions and better counsel our patients.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues are hoping to gain insights regarding transgender patients with lymphoma as well. The researchers are analyzing the lymphoma database at the University of Rochester Medical Center, which includes about 2,200 patients.
The team is attempting to identify transgender lymphoma patients using gender-karyotype mismatch as well as other methods, including assessing patients’ medication and surgical histories, determining whether patients have any aliases, and looking for the word “transgender” in patient charts.
“Given that the country is finally starting to talk about transgender patients, their health disparities, and their needs and experiences, it’s really time that we start collecting this data,” Dr. Alpert said.
“[I]f we are able to start to collect this data, it can help us build relationships with our patients, improve their care and outcomes, and, hopefully, be able to better counsel them about hormones and surgery.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is organized by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – Researchers have shown they can identify transgender leukemia patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches, but some transgender patients may be overlooked with this method.
The researchers’ work also highlights how little we know about transgender patients with leukemia and other cancers.
Alison Alpert, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, and her colleagues conducted this research and presented their findings in a poster at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
“There’s almost no data about transgender people with cancer ... in terms of prevalence or anything else,” Dr. Alpert noted. “And because we don’t know which patients with cancer are transgender, we can’t begin to answer any of the other big questions for patients.”
Specifically, it’s unclear what kinds of cancer transgender patients have, if there are health disparities among transgender patients, if it is safe to continue hormone therapy during cancer treatment, and if it is possible to do transition-related surgeries in the context of cancer care.
With this in mind, Dr. Alpert and her colleagues set out to identify transgender patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches. The team analyzed data on patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes enrolled in five Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) trials.
Of the 1,748 patients analyzed, six (0.3%) had a gender-karyotype mismatch. Five patients had a 46,XY karyotype and identified as female, and one patient had a 46,XX karyotype and identified as male.
“Some transgender patients have their gender identity accurately reflected in the electronic medical record, [but] some transgender patients probably don’t,” Dr. Alpert noted. “So we identified some, but probably not all, and probably not even most, transgender patients with leukemia in this cohort.”
All six of the transgender patients identified had AML, and all were white. They ranged in age from 18 to 57 years. Four patients had achieved a complete response to therapy, and two had refractory disease.
Four patients, including one who was refractory, were still alive at last follow-up. The remaining two patients, including one who had achieved a complete response, had died.
The transgender patients identified in this analysis represent a very small percentage of the population studied, Dr. Alpert noted. Therefore, the researchers could not draw any conclusions about transgender patients with AML.
“Mostly, what we did was, we pointed out how little information we have,” Dr. Alpert said. “Oncologists don’t routinely collect gender identity information, and this information doesn’t exist in cooperative group databases either.”
“But going forward, what probably really needs to happen is that oncologists need to ask their patients whether they are transgender or not. And then, ideally, consent forms for large cooperative groups like SWOG would include gender identity data, and then we would be able to answer some of our other questions and better counsel our patients.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues are hoping to gain insights regarding transgender patients with lymphoma as well. The researchers are analyzing the lymphoma database at the University of Rochester Medical Center, which includes about 2,200 patients.
The team is attempting to identify transgender lymphoma patients using gender-karyotype mismatch as well as other methods, including assessing patients’ medication and surgical histories, determining whether patients have any aliases, and looking for the word “transgender” in patient charts.
“Given that the country is finally starting to talk about transgender patients, their health disparities, and their needs and experiences, it’s really time that we start collecting this data,” Dr. Alpert said.
“[I]f we are able to start to collect this data, it can help us build relationships with our patients, improve their care and outcomes, and, hopefully, be able to better counsel them about hormones and surgery.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is organized by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
REPORTING FROM ALF 2019
ALF 2019 showcases evolving treatment of AML
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – The evolving treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) was highlighted at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
In a video interview, Martin Tallman, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, discussed several meeting presentations on the treatment of AML.
In his presentation, Craig Jordan, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, explained how the combination of venetoclax and azacitidine appears to target leukemic stem cells in AML.
Courtney DiNardo, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, presented information on novel agents for AML, including antibody-drug conjugates; bispecific therapies; checkpoint inhibitors; and inhibitors of IDH1/2, MCL1, and MDM2.
Richard Larson, MD, of the University of Chicago, explored the possibility of an individualized approach to postremission therapy in AML.
Frederick Appelbaum, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, showed that various maintenance therapies given after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) have not proven beneficial for AML patients.
Richard Jones, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, presented data showing that post-HSCT cyclophosphamide has made haploidentical transplants safer and more effective for AML patients.
And James Ferrara, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, detailed research showing that biomarkers of graft-versus-host disease can predict nonrelapse mortality after HSCT.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – The evolving treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) was highlighted at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
In a video interview, Martin Tallman, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, discussed several meeting presentations on the treatment of AML.
In his presentation, Craig Jordan, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, explained how the combination of venetoclax and azacitidine appears to target leukemic stem cells in AML.
Courtney DiNardo, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, presented information on novel agents for AML, including antibody-drug conjugates; bispecific therapies; checkpoint inhibitors; and inhibitors of IDH1/2, MCL1, and MDM2.
Richard Larson, MD, of the University of Chicago, explored the possibility of an individualized approach to postremission therapy in AML.
Frederick Appelbaum, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, showed that various maintenance therapies given after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) have not proven beneficial for AML patients.
Richard Jones, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, presented data showing that post-HSCT cyclophosphamide has made haploidentical transplants safer and more effective for AML patients.
And James Ferrara, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, detailed research showing that biomarkers of graft-versus-host disease can predict nonrelapse mortality after HSCT.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – The evolving treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) was highlighted at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
In a video interview, Martin Tallman, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, discussed several meeting presentations on the treatment of AML.
In his presentation, Craig Jordan, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, explained how the combination of venetoclax and azacitidine appears to target leukemic stem cells in AML.
Courtney DiNardo, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, presented information on novel agents for AML, including antibody-drug conjugates; bispecific therapies; checkpoint inhibitors; and inhibitors of IDH1/2, MCL1, and MDM2.
Richard Larson, MD, of the University of Chicago, explored the possibility of an individualized approach to postremission therapy in AML.
Frederick Appelbaum, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, showed that various maintenance therapies given after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) have not proven beneficial for AML patients.
Richard Jones, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, presented data showing that post-HSCT cyclophosphamide has made haploidentical transplants safer and more effective for AML patients.
And James Ferrara, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, detailed research showing that biomarkers of graft-versus-host disease can predict nonrelapse mortality after HSCT.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
REPORTING FROM ALF 2019
Medical societies endorse tiered certification for U.S. heart-valve care
The centerpiece of the integrated model is a certification process that would designate appropriate hospitals as “Comprehensive (Level I)” or “Primary (Level II)” valve centers to serve as the designated U.S. sites for performing repair or replacement of aortic and mitral valves by transcatheter or open-surgery procedures.
The consensus document, written by a panel of mostly interventional cardiologists or heart surgeons and published in Journal of the American College of Cardiology, cited the success of similar accreditation and tiered systems that have become fixtures in United States for the delivery of care for trauma, stroke, cancer, bariatric surgery, and percutaneous coronary intervention for acute ST-segment elevation MI.
The focus of the consensus document is to “initiate a discussion regarding whether a regionalized, tiered system of care for patients with [valvular heart disease (VHD)] that accounts for the differences in valve center expertise, experience, and resources constitutes a more rational delivery model than one left to expand continuously without direction,” the panel wrote.
Under the proposal, a key component of every designated valve center would be a multidisciplinary clinical team, staffed at minimum with an interventional cardiologist, a cardiac surgeon, echocardiographic and radiographic imaging specialists, a specialist in heart failure, a person with valve expertise, nurse practitioners, a cardiovascular anesthesiologist, a program navigator, and a data manager. Valve centers also would need to enroll patients in registries, perform research, education, and training, and collect data using carefully selected performance metrics.
The document addresses case-volume minimums, a topic that’s been tricky for leaders in the heart-valve field to reconcile as they try to balance volume thresholds against having valve procedures readily available and convenient for rural or remote patients.
“The primary motivation behind volume recommendations is not to exclude centers but rather to serve as one metric in the identification of centers that are most capable of providing certain services,” the consensus statement explained. “Volumes alone are not necessarily the best surrogate for quality, but a volume-outcome association does exist for many cardiac procedures.”
Recent proof of this relationship for transcatheter aortic valve replacement appeared in an article published earlier in April; the article reviewed 30-day mortality outcomes for more than 113,000 U.S. patients who underwent this procedure and showed that centers with the lowest procedure volumes also had the highest mortality rate (New Engl J Med. 2019 April 3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1901109).
But the document also qualified its support of and the role for volume minimums, highlighting that case volume is an inadequate surrogate for program quality, especially when considered in isolation. “The proposed concept of system care for VHD patients is not conceived to deny individuals and institutions the opportunity to provide services, nor should it be perceived to impede the ability of a committed center to achieve its strategic goals. Rather, it is intended to focus more on outcomes and not simply on procedural volumes.”
The launch by the Joint Commission of a Comprehensive Cardiac Advanced Certification program in January 2017, which included VHD care, is a step toward that goal, but “there is a great deal of detailed work ahead to realize the goal of this proposal,” according to the consensus document.
The consensus statement was issued by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, the American College of Cardiology, the American Society of Echocardiography, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons.
SOURCE: Nishimura RA et al. J Amer Coll Cardiol. 2019 April 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.007.
The centerpiece of the integrated model is a certification process that would designate appropriate hospitals as “Comprehensive (Level I)” or “Primary (Level II)” valve centers to serve as the designated U.S. sites for performing repair or replacement of aortic and mitral valves by transcatheter or open-surgery procedures.
The consensus document, written by a panel of mostly interventional cardiologists or heart surgeons and published in Journal of the American College of Cardiology, cited the success of similar accreditation and tiered systems that have become fixtures in United States for the delivery of care for trauma, stroke, cancer, bariatric surgery, and percutaneous coronary intervention for acute ST-segment elevation MI.
The focus of the consensus document is to “initiate a discussion regarding whether a regionalized, tiered system of care for patients with [valvular heart disease (VHD)] that accounts for the differences in valve center expertise, experience, and resources constitutes a more rational delivery model than one left to expand continuously without direction,” the panel wrote.
Under the proposal, a key component of every designated valve center would be a multidisciplinary clinical team, staffed at minimum with an interventional cardiologist, a cardiac surgeon, echocardiographic and radiographic imaging specialists, a specialist in heart failure, a person with valve expertise, nurse practitioners, a cardiovascular anesthesiologist, a program navigator, and a data manager. Valve centers also would need to enroll patients in registries, perform research, education, and training, and collect data using carefully selected performance metrics.
The document addresses case-volume minimums, a topic that’s been tricky for leaders in the heart-valve field to reconcile as they try to balance volume thresholds against having valve procedures readily available and convenient for rural or remote patients.
“The primary motivation behind volume recommendations is not to exclude centers but rather to serve as one metric in the identification of centers that are most capable of providing certain services,” the consensus statement explained. “Volumes alone are not necessarily the best surrogate for quality, but a volume-outcome association does exist for many cardiac procedures.”
Recent proof of this relationship for transcatheter aortic valve replacement appeared in an article published earlier in April; the article reviewed 30-day mortality outcomes for more than 113,000 U.S. patients who underwent this procedure and showed that centers with the lowest procedure volumes also had the highest mortality rate (New Engl J Med. 2019 April 3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1901109).
But the document also qualified its support of and the role for volume minimums, highlighting that case volume is an inadequate surrogate for program quality, especially when considered in isolation. “The proposed concept of system care for VHD patients is not conceived to deny individuals and institutions the opportunity to provide services, nor should it be perceived to impede the ability of a committed center to achieve its strategic goals. Rather, it is intended to focus more on outcomes and not simply on procedural volumes.”
The launch by the Joint Commission of a Comprehensive Cardiac Advanced Certification program in January 2017, which included VHD care, is a step toward that goal, but “there is a great deal of detailed work ahead to realize the goal of this proposal,” according to the consensus document.
The consensus statement was issued by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, the American College of Cardiology, the American Society of Echocardiography, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons.
SOURCE: Nishimura RA et al. J Amer Coll Cardiol. 2019 April 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.007.
The centerpiece of the integrated model is a certification process that would designate appropriate hospitals as “Comprehensive (Level I)” or “Primary (Level II)” valve centers to serve as the designated U.S. sites for performing repair or replacement of aortic and mitral valves by transcatheter or open-surgery procedures.
The consensus document, written by a panel of mostly interventional cardiologists or heart surgeons and published in Journal of the American College of Cardiology, cited the success of similar accreditation and tiered systems that have become fixtures in United States for the delivery of care for trauma, stroke, cancer, bariatric surgery, and percutaneous coronary intervention for acute ST-segment elevation MI.
The focus of the consensus document is to “initiate a discussion regarding whether a regionalized, tiered system of care for patients with [valvular heart disease (VHD)] that accounts for the differences in valve center expertise, experience, and resources constitutes a more rational delivery model than one left to expand continuously without direction,” the panel wrote.
Under the proposal, a key component of every designated valve center would be a multidisciplinary clinical team, staffed at minimum with an interventional cardiologist, a cardiac surgeon, echocardiographic and radiographic imaging specialists, a specialist in heart failure, a person with valve expertise, nurse practitioners, a cardiovascular anesthesiologist, a program navigator, and a data manager. Valve centers also would need to enroll patients in registries, perform research, education, and training, and collect data using carefully selected performance metrics.
The document addresses case-volume minimums, a topic that’s been tricky for leaders in the heart-valve field to reconcile as they try to balance volume thresholds against having valve procedures readily available and convenient for rural or remote patients.
“The primary motivation behind volume recommendations is not to exclude centers but rather to serve as one metric in the identification of centers that are most capable of providing certain services,” the consensus statement explained. “Volumes alone are not necessarily the best surrogate for quality, but a volume-outcome association does exist for many cardiac procedures.”
Recent proof of this relationship for transcatheter aortic valve replacement appeared in an article published earlier in April; the article reviewed 30-day mortality outcomes for more than 113,000 U.S. patients who underwent this procedure and showed that centers with the lowest procedure volumes also had the highest mortality rate (New Engl J Med. 2019 April 3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1901109).
But the document also qualified its support of and the role for volume minimums, highlighting that case volume is an inadequate surrogate for program quality, especially when considered in isolation. “The proposed concept of system care for VHD patients is not conceived to deny individuals and institutions the opportunity to provide services, nor should it be perceived to impede the ability of a committed center to achieve its strategic goals. Rather, it is intended to focus more on outcomes and not simply on procedural volumes.”
The launch by the Joint Commission of a Comprehensive Cardiac Advanced Certification program in January 2017, which included VHD care, is a step toward that goal, but “there is a great deal of detailed work ahead to realize the goal of this proposal,” according to the consensus document.
The consensus statement was issued by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, the American College of Cardiology, the American Society of Echocardiography, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons.
SOURCE: Nishimura RA et al. J Amer Coll Cardiol. 2019 April 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.007.
FROM JACC
Low-dose IL-2 found effective in SLE
SAN FRANCISCO – , according to the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the novel therapy.
Of note, more than half of the study participants with lupus nephritis experienced complete remission of their renal impairment, and another quarter had partial remission, Jing He, MD, PhD, reported at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus.
The mechanism of benefit appears to be the same as previously shown for low-dose interleukin-2 in patients with chronic graft versus host disease refractory to glucocorticoids (N Engl J Med. 2011 Dec 1;365[22]:2055-66): expansion of the deficient population of T regulatory cells, which is a hallmark of both inflammatory diseases.
“Low-dose IL-2 can reinstate the imbalance of T regulatory/T effector cells and improve immune homeostasis, which is critical in clinical remission of SLE,” said Dr. He of Peking University People’s Hospital in Beijing.
For nearly 20 years it has been known that SLE is characterized by very low levels of endogenous IL-2. Dr. He was lead author of the first proof-of-concept study, which showed low-dose subcutaneous IL-2 therapy resulted in markedly reduced SLE disease activity accompanied by expansion of the T regulatory cell population and suppression of follicular helper T cells and IL-17–producing helper T cells (Nat Med. 2016 Sep;22[9]:991-3). However, that was a small, single-center, uncontrolled study, so she and her coworkers have now carried out a 60-patient, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial. In addition to hydroxychloroquine and other standard background medications, the patients in the active treatment arm received 1 million IU of IL-2 every other day for 2 weeks, followed by a 2-week hiatus, for a total of three courses.
At week 24 – 12 weeks after the last injection – the IL-2 recipients showed significantly greater improvement on numerous endpoints.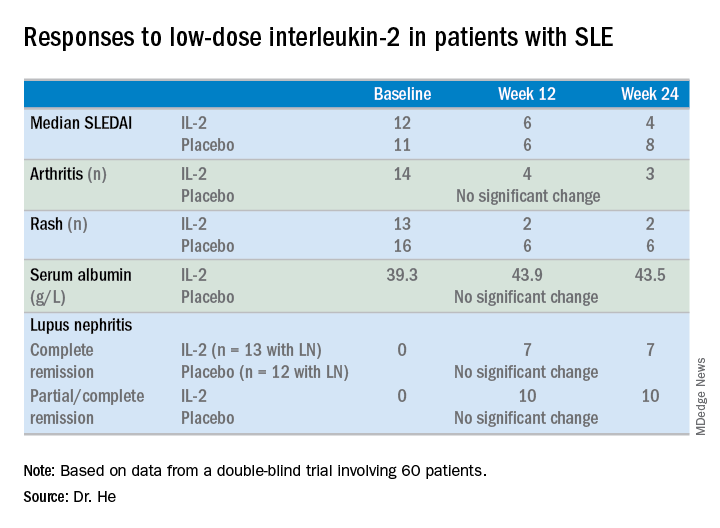
For example, the median SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) in the IL-2 group improved from 12 at baseline to 6 at week 12 and to 4 at week 24.
The marked improvement in renal impairment in the IL-2 recipients with lupus nephritis at baseline was accompanied by a significant increase in serum albumin and reduced 24-hour urinary protein, compared with controls.
The treatment was safe, with no increase in infections, severe or otherwise, and indeed with no serious adverse events of any kind, although nine patients in the IL-2 group experienced mild injection site reactions and three developed flu-like symptoms.
Dr. He reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study.
SAN FRANCISCO – , according to the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the novel therapy.
Of note, more than half of the study participants with lupus nephritis experienced complete remission of their renal impairment, and another quarter had partial remission, Jing He, MD, PhD, reported at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus.
The mechanism of benefit appears to be the same as previously shown for low-dose interleukin-2 in patients with chronic graft versus host disease refractory to glucocorticoids (N Engl J Med. 2011 Dec 1;365[22]:2055-66): expansion of the deficient population of T regulatory cells, which is a hallmark of both inflammatory diseases.
“Low-dose IL-2 can reinstate the imbalance of T regulatory/T effector cells and improve immune homeostasis, which is critical in clinical remission of SLE,” said Dr. He of Peking University People’s Hospital in Beijing.
For nearly 20 years it has been known that SLE is characterized by very low levels of endogenous IL-2. Dr. He was lead author of the first proof-of-concept study, which showed low-dose subcutaneous IL-2 therapy resulted in markedly reduced SLE disease activity accompanied by expansion of the T regulatory cell population and suppression of follicular helper T cells and IL-17–producing helper T cells (Nat Med. 2016 Sep;22[9]:991-3). However, that was a small, single-center, uncontrolled study, so she and her coworkers have now carried out a 60-patient, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial. In addition to hydroxychloroquine and other standard background medications, the patients in the active treatment arm received 1 million IU of IL-2 every other day for 2 weeks, followed by a 2-week hiatus, for a total of three courses.
At week 24 – 12 weeks after the last injection – the IL-2 recipients showed significantly greater improvement on numerous endpoints.
For example, the median SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) in the IL-2 group improved from 12 at baseline to 6 at week 12 and to 4 at week 24.
The marked improvement in renal impairment in the IL-2 recipients with lupus nephritis at baseline was accompanied by a significant increase in serum albumin and reduced 24-hour urinary protein, compared with controls.
The treatment was safe, with no increase in infections, severe or otherwise, and indeed with no serious adverse events of any kind, although nine patients in the IL-2 group experienced mild injection site reactions and three developed flu-like symptoms.
Dr. He reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study.
SAN FRANCISCO – , according to the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the novel therapy.
Of note, more than half of the study participants with lupus nephritis experienced complete remission of their renal impairment, and another quarter had partial remission, Jing He, MD, PhD, reported at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus.
The mechanism of benefit appears to be the same as previously shown for low-dose interleukin-2 in patients with chronic graft versus host disease refractory to glucocorticoids (N Engl J Med. 2011 Dec 1;365[22]:2055-66): expansion of the deficient population of T regulatory cells, which is a hallmark of both inflammatory diseases.
“Low-dose IL-2 can reinstate the imbalance of T regulatory/T effector cells and improve immune homeostasis, which is critical in clinical remission of SLE,” said Dr. He of Peking University People’s Hospital in Beijing.
For nearly 20 years it has been known that SLE is characterized by very low levels of endogenous IL-2. Dr. He was lead author of the first proof-of-concept study, which showed low-dose subcutaneous IL-2 therapy resulted in markedly reduced SLE disease activity accompanied by expansion of the T regulatory cell population and suppression of follicular helper T cells and IL-17–producing helper T cells (Nat Med. 2016 Sep;22[9]:991-3). However, that was a small, single-center, uncontrolled study, so she and her coworkers have now carried out a 60-patient, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial. In addition to hydroxychloroquine and other standard background medications, the patients in the active treatment arm received 1 million IU of IL-2 every other day for 2 weeks, followed by a 2-week hiatus, for a total of three courses.
At week 24 – 12 weeks after the last injection – the IL-2 recipients showed significantly greater improvement on numerous endpoints.
For example, the median SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) in the IL-2 group improved from 12 at baseline to 6 at week 12 and to 4 at week 24.
The marked improvement in renal impairment in the IL-2 recipients with lupus nephritis at baseline was accompanied by a significant increase in serum albumin and reduced 24-hour urinary protein, compared with controls.
The treatment was safe, with no increase in infections, severe or otherwise, and indeed with no serious adverse events of any kind, although nine patients in the IL-2 group experienced mild injection site reactions and three developed flu-like symptoms.
Dr. He reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study.
REPORTING FROM LUPUS 2019
LUPUS 2019 Congress: Top takeaways

Join us at #MDedgeChats on Tuesday, April 23, 2019, at 7:00 pm EST, for a Twitter discussion in Rheumatology on some of the top studies reported at the LUPUS 2019 Congress in San Francisco, April 5-8. Our special guests are two rheumatologists with expertise in lupus who attended the congress, Jinoos Yazdany, MD, and Gabriela Schmajuk, MD, both with the University of California, San Francisco. They will discuss the ins and outs of the study results presented.
We hope you can join us and invite a colleague, too.
We will discuss the results of the EMBRACE trial, which looks at the efficacy and safety of belimumab (Benlysta) in black patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE); these patients have a higher prevalence of SLE and often higher disease severity but have been poorly represented in past belimumab studies.
We will also chat about the results of a phase 2 trial of baricitinib (Olumiant) in SLE patients.
Finally, we will look at the clinical utility of monitoring hydroxychloroquine levels in SLE patients and how well levels of the drug correlate with disease activity through the results of a meta-analysis of studies that examined these questions.
Topics of conversation
Q1: How does the methodology of the EMBRACE trial differ from past phase 3 belimumab trials?
Q2: How does the EMBRACE trial affect the way you prescribe belimumab?
Q3: Does the hydroxychloroquine level meta-analysis provide persuasive enough evidence to begin measuring it?
Q4: What kinds of interventions show the best evidence for improving hydroxychloroquine adherence?
Q5: Were concerns about the safety of baricitinib in SLE patients reduced by the trial results?
Resources
EMBRACE trial: Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab in Black Race Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
LUPUS 2019 abstract | ClinicalTrials.gov listing
Phase 2 trial of baricitinib in SLE.
LUPUS 2019 abstract | ClinicalTrials.gov listing
Meta-analysis examining the clinical significance of monitoring of hydroxychloroquine levels in SLE.
LUPUS 2019 abstract
From LUPUS 2019:
Belimumab a bust for black SLE patients.
Here’s a top strategy for immunosuppressant discontinuation in SLE.
From EULAR 2018:
Baricitinib shows potential as lupus treatment.
About Dr. Yazdany
Dr. Yazdany is an associate professor in the division of rheumatology, department of medicine at UCSF (@UCSFMedicine). She is a rheumatologist and clinical researcher with expertise in systemic lupus erythematosus and health care quality measurement and improvement. Her clinical activities include seeing patients in the UCSF Lupus Clinic, where she serves as codirector, as well as at San Francisco General Hospital. Dr. Yazdany codirects the Quality and Informatics Lab (quil.ucsf.edu), which uses data to drive improvements in health care delivery and outcomes for people with rheumatic diseases. She also leads ongoing, longitudinal studies of lupus that are investigating health disparities and outcomes in the condition.
About Dr. Schmajuk
Dr. Schmajuk is an Associate Professor in the Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine at UCSF (@UCSFMedicine) and the San Francisco VA Medical Center. She is a rheumatologist and clinical researcher with expertise in systemic #lupus erythematosus, quality of care, and patient safety. Dr. Schmajuk also co-directs the Quality and Informatics Lab (quil.ucsf.edu), which uses data to drive improvements in health care delivery and outcomes for people with rheumatic diseases. She leads studies to develop patient-facing disease dashboards with the goal of improving patient-provider communication for patients with RA and SLE.
Are you new to Twitter chats? We have included simple steps below to help you join and participate in the conversation.

Join us at #MDedgeChats on Tuesday, April 23, 2019, at 7:00 pm EST, for a Twitter discussion in Rheumatology on some of the top studies reported at the LUPUS 2019 Congress in San Francisco, April 5-8. Our special guests are two rheumatologists with expertise in lupus who attended the congress, Jinoos Yazdany, MD, and Gabriela Schmajuk, MD, both with the University of California, San Francisco. They will discuss the ins and outs of the study results presented.
We hope you can join us and invite a colleague, too.
We will discuss the results of the EMBRACE trial, which looks at the efficacy and safety of belimumab (Benlysta) in black patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE); these patients have a higher prevalence of SLE and often higher disease severity but have been poorly represented in past belimumab studies.
We will also chat about the results of a phase 2 trial of baricitinib (Olumiant) in SLE patients.
Finally, we will look at the clinical utility of monitoring hydroxychloroquine levels in SLE patients and how well levels of the drug correlate with disease activity through the results of a meta-analysis of studies that examined these questions.
Topics of conversation
Q1: How does the methodology of the EMBRACE trial differ from past phase 3 belimumab trials?
Q2: How does the EMBRACE trial affect the way you prescribe belimumab?
Q3: Does the hydroxychloroquine level meta-analysis provide persuasive enough evidence to begin measuring it?
Q4: What kinds of interventions show the best evidence for improving hydroxychloroquine adherence?
Q5: Were concerns about the safety of baricitinib in SLE patients reduced by the trial results?
Resources
EMBRACE trial: Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab in Black Race Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
LUPUS 2019 abstract | ClinicalTrials.gov listing
Phase 2 trial of baricitinib in SLE.
LUPUS 2019 abstract | ClinicalTrials.gov listing
Meta-analysis examining the clinical significance of monitoring of hydroxychloroquine levels in SLE.
LUPUS 2019 abstract
From LUPUS 2019:
Belimumab a bust for black SLE patients.
Here’s a top strategy for immunosuppressant discontinuation in SLE.
From EULAR 2018:
Baricitinib shows potential as lupus treatment.
About Dr. Yazdany
Dr. Yazdany is an associate professor in the division of rheumatology, department of medicine at UCSF (@UCSFMedicine). She is a rheumatologist and clinical researcher with expertise in systemic lupus erythematosus and health care quality measurement and improvement. Her clinical activities include seeing patients in the UCSF Lupus Clinic, where she serves as codirector, as well as at San Francisco General Hospital. Dr. Yazdany codirects the Quality and Informatics Lab (quil.ucsf.edu), which uses data to drive improvements in health care delivery and outcomes for people with rheumatic diseases. She also leads ongoing, longitudinal studies of lupus that are investigating health disparities and outcomes in the condition.
About Dr. Schmajuk
Dr. Schmajuk is an Associate Professor in the Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine at UCSF (@UCSFMedicine) and the San Francisco VA Medical Center. She is a rheumatologist and clinical researcher with expertise in systemic #lupus erythematosus, quality of care, and patient safety. Dr. Schmajuk also co-directs the Quality and Informatics Lab (quil.ucsf.edu), which uses data to drive improvements in health care delivery and outcomes for people with rheumatic diseases. She leads studies to develop patient-facing disease dashboards with the goal of improving patient-provider communication for patients with RA and SLE.
Are you new to Twitter chats? We have included simple steps below to help you join and participate in the conversation.

Join us at #MDedgeChats on Tuesday, April 23, 2019, at 7:00 pm EST, for a Twitter discussion in Rheumatology on some of the top studies reported at the LUPUS 2019 Congress in San Francisco, April 5-8. Our special guests are two rheumatologists with expertise in lupus who attended the congress, Jinoos Yazdany, MD, and Gabriela Schmajuk, MD, both with the University of California, San Francisco. They will discuss the ins and outs of the study results presented.
We hope you can join us and invite a colleague, too.
We will discuss the results of the EMBRACE trial, which looks at the efficacy and safety of belimumab (Benlysta) in black patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE); these patients have a higher prevalence of SLE and often higher disease severity but have been poorly represented in past belimumab studies.
We will also chat about the results of a phase 2 trial of baricitinib (Olumiant) in SLE patients.
Finally, we will look at the clinical utility of monitoring hydroxychloroquine levels in SLE patients and how well levels of the drug correlate with disease activity through the results of a meta-analysis of studies that examined these questions.
Topics of conversation
Q1: How does the methodology of the EMBRACE trial differ from past phase 3 belimumab trials?
Q2: How does the EMBRACE trial affect the way you prescribe belimumab?
Q3: Does the hydroxychloroquine level meta-analysis provide persuasive enough evidence to begin measuring it?
Q4: What kinds of interventions show the best evidence for improving hydroxychloroquine adherence?
Q5: Were concerns about the safety of baricitinib in SLE patients reduced by the trial results?
Resources
EMBRACE trial: Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab in Black Race Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
LUPUS 2019 abstract | ClinicalTrials.gov listing
Phase 2 trial of baricitinib in SLE.
LUPUS 2019 abstract | ClinicalTrials.gov listing
Meta-analysis examining the clinical significance of monitoring of hydroxychloroquine levels in SLE.
LUPUS 2019 abstract
From LUPUS 2019:
Belimumab a bust for black SLE patients.
Here’s a top strategy for immunosuppressant discontinuation in SLE.
From EULAR 2018:
Baricitinib shows potential as lupus treatment.
About Dr. Yazdany
Dr. Yazdany is an associate professor in the division of rheumatology, department of medicine at UCSF (@UCSFMedicine). She is a rheumatologist and clinical researcher with expertise in systemic lupus erythematosus and health care quality measurement and improvement. Her clinical activities include seeing patients in the UCSF Lupus Clinic, where she serves as codirector, as well as at San Francisco General Hospital. Dr. Yazdany codirects the Quality and Informatics Lab (quil.ucsf.edu), which uses data to drive improvements in health care delivery and outcomes for people with rheumatic diseases. She also leads ongoing, longitudinal studies of lupus that are investigating health disparities and outcomes in the condition.
About Dr. Schmajuk
Dr. Schmajuk is an Associate Professor in the Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine at UCSF (@UCSFMedicine) and the San Francisco VA Medical Center. She is a rheumatologist and clinical researcher with expertise in systemic #lupus erythematosus, quality of care, and patient safety. Dr. Schmajuk also co-directs the Quality and Informatics Lab (quil.ucsf.edu), which uses data to drive improvements in health care delivery and outcomes for people with rheumatic diseases. She leads studies to develop patient-facing disease dashboards with the goal of improving patient-provider communication for patients with RA and SLE.
Are you new to Twitter chats? We have included simple steps below to help you join and participate in the conversation.
Dr. Joseph Vassalotti: Cancer risk minimal with ARBs
PHILADELPHIA – according to a senior officer of the National Kidney Foundation.
“I’ve been telling everyone not to stop on their own,” said Joseph A. Vassalotti, MD, chief medical officer for the National Kidney Foundation and associate clinical professor of medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The risk of cardiovascular events acutely and the long-term risk of kidney disease progression is much more concerning to me, if they self-discontinue the ARB, than the small risk of cancer,” Dr. Vassalotti said in a meet-the-professor session at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Put in perspective, the absolute risk of cancer according to the Food and Drug Administration is one new malignancy per 8,000 patients treated with 320 mg of valsartan daily – the highest ARB dose that contained N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), one of several impurities that led to the recent recalls.
Dr. Vassalotti said that so far, he’s been able to avoid switching patients from one ARB to another by working with pharmacies to get the same medication in a different generic brand not affected by the FDA recalls.
He advised caution in switching ARBs, noting a paucity of head-to-head comparative data between ARBs.
“There may be variable effects,” he said.
If switching is thought to be warranted, he said, some extra tests or visits might be needed to ensure avoidance of hyperkalemia, undertreated hypertension, or hypotension.
Dr. Vassalotti encouraged attendees to review a perspective piece in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 Mar 13. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1901657) describing this hypertension “hot potato” resulting from the large-scale voluntary recalls of products containing valsartan, losartan, and irbesartan due to nitrosamine contamination.
Patients may hear about recalls of hypertension drugs, but may not know what products or manufacturers are involved, leaving the burden on clinicians, pharmacies, and health care systems to respond to their concerns, said authors of that perspective piece, led by J. Brian Byrd, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“Recalls may trigger unnecessary concern among many people receiving antihypertensive therapy – and may be ignored by people who take ARBs for heart failure or chronic kidney disease,” wrote Dr. Byrd and his colleagues.
The FDA, which said it has worked with manufacturers to “swiftly” remove ARB drug products with impurity levels above acceptable limits, is now maintaining a list of other currently marketed ARB products that are being tested for impurities.
As of the latest update on April 4, the FDA listed more than 40 products with an overall nitrosamine impurity determination of “not present” and more than 300 additional products for which assessments are not yet complete.
“Essentially, we have a safe list now of ARBs that is being developed,” Dr. Vassalotti said. “So if a patient really wanted to change, I would consult that list, and consider picking one that’s been tested already on that list, and the FDA hopefully will complete testing on all the ARB drugs in the near future.”
Dr. Vassalotti is a consultant with Merck, Janssen, and the U.S. Nephrology Advisory Board.
PHILADELPHIA – according to a senior officer of the National Kidney Foundation.
“I’ve been telling everyone not to stop on their own,” said Joseph A. Vassalotti, MD, chief medical officer for the National Kidney Foundation and associate clinical professor of medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The risk of cardiovascular events acutely and the long-term risk of kidney disease progression is much more concerning to me, if they self-discontinue the ARB, than the small risk of cancer,” Dr. Vassalotti said in a meet-the-professor session at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Put in perspective, the absolute risk of cancer according to the Food and Drug Administration is one new malignancy per 8,000 patients treated with 320 mg of valsartan daily – the highest ARB dose that contained N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), one of several impurities that led to the recent recalls.
Dr. Vassalotti said that so far, he’s been able to avoid switching patients from one ARB to another by working with pharmacies to get the same medication in a different generic brand not affected by the FDA recalls.
He advised caution in switching ARBs, noting a paucity of head-to-head comparative data between ARBs.
“There may be variable effects,” he said.
If switching is thought to be warranted, he said, some extra tests or visits might be needed to ensure avoidance of hyperkalemia, undertreated hypertension, or hypotension.
Dr. Vassalotti encouraged attendees to review a perspective piece in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 Mar 13. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1901657) describing this hypertension “hot potato” resulting from the large-scale voluntary recalls of products containing valsartan, losartan, and irbesartan due to nitrosamine contamination.
Patients may hear about recalls of hypertension drugs, but may not know what products or manufacturers are involved, leaving the burden on clinicians, pharmacies, and health care systems to respond to their concerns, said authors of that perspective piece, led by J. Brian Byrd, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“Recalls may trigger unnecessary concern among many people receiving antihypertensive therapy – and may be ignored by people who take ARBs for heart failure or chronic kidney disease,” wrote Dr. Byrd and his colleagues.
The FDA, which said it has worked with manufacturers to “swiftly” remove ARB drug products with impurity levels above acceptable limits, is now maintaining a list of other currently marketed ARB products that are being tested for impurities.
As of the latest update on April 4, the FDA listed more than 40 products with an overall nitrosamine impurity determination of “not present” and more than 300 additional products for which assessments are not yet complete.
“Essentially, we have a safe list now of ARBs that is being developed,” Dr. Vassalotti said. “So if a patient really wanted to change, I would consult that list, and consider picking one that’s been tested already on that list, and the FDA hopefully will complete testing on all the ARB drugs in the near future.”
Dr. Vassalotti is a consultant with Merck, Janssen, and the U.S. Nephrology Advisory Board.
PHILADELPHIA – according to a senior officer of the National Kidney Foundation.
“I’ve been telling everyone not to stop on their own,” said Joseph A. Vassalotti, MD, chief medical officer for the National Kidney Foundation and associate clinical professor of medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The risk of cardiovascular events acutely and the long-term risk of kidney disease progression is much more concerning to me, if they self-discontinue the ARB, than the small risk of cancer,” Dr. Vassalotti said in a meet-the-professor session at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Put in perspective, the absolute risk of cancer according to the Food and Drug Administration is one new malignancy per 8,000 patients treated with 320 mg of valsartan daily – the highest ARB dose that contained N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), one of several impurities that led to the recent recalls.
Dr. Vassalotti said that so far, he’s been able to avoid switching patients from one ARB to another by working with pharmacies to get the same medication in a different generic brand not affected by the FDA recalls.
He advised caution in switching ARBs, noting a paucity of head-to-head comparative data between ARBs.
“There may be variable effects,” he said.
If switching is thought to be warranted, he said, some extra tests or visits might be needed to ensure avoidance of hyperkalemia, undertreated hypertension, or hypotension.
Dr. Vassalotti encouraged attendees to review a perspective piece in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 Mar 13. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1901657) describing this hypertension “hot potato” resulting from the large-scale voluntary recalls of products containing valsartan, losartan, and irbesartan due to nitrosamine contamination.
Patients may hear about recalls of hypertension drugs, but may not know what products or manufacturers are involved, leaving the burden on clinicians, pharmacies, and health care systems to respond to their concerns, said authors of that perspective piece, led by J. Brian Byrd, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“Recalls may trigger unnecessary concern among many people receiving antihypertensive therapy – and may be ignored by people who take ARBs for heart failure or chronic kidney disease,” wrote Dr. Byrd and his colleagues.
The FDA, which said it has worked with manufacturers to “swiftly” remove ARB drug products with impurity levels above acceptable limits, is now maintaining a list of other currently marketed ARB products that are being tested for impurities.
As of the latest update on April 4, the FDA listed more than 40 products with an overall nitrosamine impurity determination of “not present” and more than 300 additional products for which assessments are not yet complete.
“Essentially, we have a safe list now of ARBs that is being developed,” Dr. Vassalotti said. “So if a patient really wanted to change, I would consult that list, and consider picking one that’s been tested already on that list, and the FDA hopefully will complete testing on all the ARB drugs in the near future.”
Dr. Vassalotti is a consultant with Merck, Janssen, and the U.S. Nephrology Advisory Board.
FROM INTERNAL MEDICINE 2019