User login
FALCON airs PFS edge for fulvestrant in ER+ breast cancer
COPENHAGEN – Fulvestrant continues to show superiority over anastrozole in treatment of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, particularly in women with lower-volume disease, reported investigators in the phase III FALCON trial.
At a median follow-up of 25 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) for women assigned to receive the selective estrogen-receptor degrader fulvestrant (Faslodex) was 16.6 months, compared with 13.8 months for women assigned to receive the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole (Arimidex), reported Matthew J. Ellis, PhD, of the Lester and Sue Smith Breast Center at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston.
“These results are consistent with data from the FIRST study and confirm that fulvestrant is more efficacious than anastrozole in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who have not received prior endocrine therapy,” he said at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
The benefit of fulvestrant appeared to be only among patients who did not have visceral metastases, however.
In the FIRST study, results of which were reported at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium in 2014, median overall survival at a median follow-up of 48.8 months was 54.1 months in patients on fulvestrant, vs. 48.4 months with anastrozole (hazard ratio [HR] 0.70, P = .04). The median PFS durations were 23.4 months vs. 13.1 months, respectively (HR 0.66, P = .01).
The FALCON (Fulvestrant and Anastrozole Compared in Hormonal Therapy-Naive Advanced Breast Cancer) trial was a phase III study designed to confirm the PFS benefit seen with fulvestrant in the earlier trial.
Postmenopausal women with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer positive for the estrogen and/or progesterone receptor and negative for HER2 who had not previously received endocrine therapy were enrolled. They were randomly assigned to receive fulvestrant 500 mg intramuscularly on days 0, 14, and 28 then every 28 days plus an anastrozole placebo (232 patients), or oral anastrozole 1 mg daily plus fulvestrant placebo (230 patients).
Women with life-threatening visceral metastases, systemic estrogen-containing hormone replacement therapy within 6 months of randomization, or prior systemic treatment for breast cancer other than one line of chemotherapy or radiotherapy within 28 days of randomization (except radiation for control of bone pain) were excluded.
As noted, the primary endpoint of PFS was 16.6 months in the fulvestrant arm vs. 13.8 months in the anastrozole arm, translating into an HR for progression on fulvestrant of 0.797 (P = .0486).
Among the 208 patients with no visceral disease, median PFS with fulvestrant was 22.3 months, vs. 13.8 months (HR 0.59, P less than .01). In contrast, among the 254 patients with visceral disease, the respective median PFS durations were 13.8 and 15.9 months (nonsignificant).
For the secondary endpoint of overall survival, at 31% maturity (longest follow-up out to 39 months), there was no significant difference between the study arms.
There were also no significant differences in the secondary endpoints of overall response rate (among patients with measurable disease at baseline), clinical benefit rate, median duration of response, median duration of clinical benefit, or median time to deterioration of total score on the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–Breast (FACT-B) patient-reported outcomes instrument.
Only estimated duration of response (11.4 vs. 7.5 months) and estimated duration of clinical benefit (21.9 vs. 17.5 months) were significantly better with fulvestrant (P less than .001 for each).
Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 22.4% vs. 17.7%. Deaths from adverse events occurred in six patients on fulvestrant vs. seven on anastrozole. None of these deaths were considered to be related.
The FALCON results, which showed a benefit for fulvestrant only for those patients without visceral disease, point to a need for investigating whether patients with visceral metastases should receive other therapies, but this observation is hypothesis-generating only, said invited discussant Peter Schmid, MD, PhD, of Barts Cancer Institute at St. Bartholomew’s Hospital at Queen Mary University of London.
COPENHAGEN – Fulvestrant continues to show superiority over anastrozole in treatment of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, particularly in women with lower-volume disease, reported investigators in the phase III FALCON trial.
At a median follow-up of 25 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) for women assigned to receive the selective estrogen-receptor degrader fulvestrant (Faslodex) was 16.6 months, compared with 13.8 months for women assigned to receive the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole (Arimidex), reported Matthew J. Ellis, PhD, of the Lester and Sue Smith Breast Center at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston.
“These results are consistent with data from the FIRST study and confirm that fulvestrant is more efficacious than anastrozole in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who have not received prior endocrine therapy,” he said at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
The benefit of fulvestrant appeared to be only among patients who did not have visceral metastases, however.
In the FIRST study, results of which were reported at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium in 2014, median overall survival at a median follow-up of 48.8 months was 54.1 months in patients on fulvestrant, vs. 48.4 months with anastrozole (hazard ratio [HR] 0.70, P = .04). The median PFS durations were 23.4 months vs. 13.1 months, respectively (HR 0.66, P = .01).
The FALCON (Fulvestrant and Anastrozole Compared in Hormonal Therapy-Naive Advanced Breast Cancer) trial was a phase III study designed to confirm the PFS benefit seen with fulvestrant in the earlier trial.
Postmenopausal women with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer positive for the estrogen and/or progesterone receptor and negative for HER2 who had not previously received endocrine therapy were enrolled. They were randomly assigned to receive fulvestrant 500 mg intramuscularly on days 0, 14, and 28 then every 28 days plus an anastrozole placebo (232 patients), or oral anastrozole 1 mg daily plus fulvestrant placebo (230 patients).
Women with life-threatening visceral metastases, systemic estrogen-containing hormone replacement therapy within 6 months of randomization, or prior systemic treatment for breast cancer other than one line of chemotherapy or radiotherapy within 28 days of randomization (except radiation for control of bone pain) were excluded.
As noted, the primary endpoint of PFS was 16.6 months in the fulvestrant arm vs. 13.8 months in the anastrozole arm, translating into an HR for progression on fulvestrant of 0.797 (P = .0486).
Among the 208 patients with no visceral disease, median PFS with fulvestrant was 22.3 months, vs. 13.8 months (HR 0.59, P less than .01). In contrast, among the 254 patients with visceral disease, the respective median PFS durations were 13.8 and 15.9 months (nonsignificant).
For the secondary endpoint of overall survival, at 31% maturity (longest follow-up out to 39 months), there was no significant difference between the study arms.
There were also no significant differences in the secondary endpoints of overall response rate (among patients with measurable disease at baseline), clinical benefit rate, median duration of response, median duration of clinical benefit, or median time to deterioration of total score on the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–Breast (FACT-B) patient-reported outcomes instrument.
Only estimated duration of response (11.4 vs. 7.5 months) and estimated duration of clinical benefit (21.9 vs. 17.5 months) were significantly better with fulvestrant (P less than .001 for each).
Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 22.4% vs. 17.7%. Deaths from adverse events occurred in six patients on fulvestrant vs. seven on anastrozole. None of these deaths were considered to be related.
The FALCON results, which showed a benefit for fulvestrant only for those patients without visceral disease, point to a need for investigating whether patients with visceral metastases should receive other therapies, but this observation is hypothesis-generating only, said invited discussant Peter Schmid, MD, PhD, of Barts Cancer Institute at St. Bartholomew’s Hospital at Queen Mary University of London.
COPENHAGEN – Fulvestrant continues to show superiority over anastrozole in treatment of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, particularly in women with lower-volume disease, reported investigators in the phase III FALCON trial.
At a median follow-up of 25 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) for women assigned to receive the selective estrogen-receptor degrader fulvestrant (Faslodex) was 16.6 months, compared with 13.8 months for women assigned to receive the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole (Arimidex), reported Matthew J. Ellis, PhD, of the Lester and Sue Smith Breast Center at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston.
“These results are consistent with data from the FIRST study and confirm that fulvestrant is more efficacious than anastrozole in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who have not received prior endocrine therapy,” he said at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
The benefit of fulvestrant appeared to be only among patients who did not have visceral metastases, however.
In the FIRST study, results of which were reported at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium in 2014, median overall survival at a median follow-up of 48.8 months was 54.1 months in patients on fulvestrant, vs. 48.4 months with anastrozole (hazard ratio [HR] 0.70, P = .04). The median PFS durations were 23.4 months vs. 13.1 months, respectively (HR 0.66, P = .01).
The FALCON (Fulvestrant and Anastrozole Compared in Hormonal Therapy-Naive Advanced Breast Cancer) trial was a phase III study designed to confirm the PFS benefit seen with fulvestrant in the earlier trial.
Postmenopausal women with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer positive for the estrogen and/or progesterone receptor and negative for HER2 who had not previously received endocrine therapy were enrolled. They were randomly assigned to receive fulvestrant 500 mg intramuscularly on days 0, 14, and 28 then every 28 days plus an anastrozole placebo (232 patients), or oral anastrozole 1 mg daily plus fulvestrant placebo (230 patients).
Women with life-threatening visceral metastases, systemic estrogen-containing hormone replacement therapy within 6 months of randomization, or prior systemic treatment for breast cancer other than one line of chemotherapy or radiotherapy within 28 days of randomization (except radiation for control of bone pain) were excluded.
As noted, the primary endpoint of PFS was 16.6 months in the fulvestrant arm vs. 13.8 months in the anastrozole arm, translating into an HR for progression on fulvestrant of 0.797 (P = .0486).
Among the 208 patients with no visceral disease, median PFS with fulvestrant was 22.3 months, vs. 13.8 months (HR 0.59, P less than .01). In contrast, among the 254 patients with visceral disease, the respective median PFS durations were 13.8 and 15.9 months (nonsignificant).
For the secondary endpoint of overall survival, at 31% maturity (longest follow-up out to 39 months), there was no significant difference between the study arms.
There were also no significant differences in the secondary endpoints of overall response rate (among patients with measurable disease at baseline), clinical benefit rate, median duration of response, median duration of clinical benefit, or median time to deterioration of total score on the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–Breast (FACT-B) patient-reported outcomes instrument.
Only estimated duration of response (11.4 vs. 7.5 months) and estimated duration of clinical benefit (21.9 vs. 17.5 months) were significantly better with fulvestrant (P less than .001 for each).
Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 22.4% vs. 17.7%. Deaths from adverse events occurred in six patients on fulvestrant vs. seven on anastrozole. None of these deaths were considered to be related.
The FALCON results, which showed a benefit for fulvestrant only for those patients without visceral disease, point to a need for investigating whether patients with visceral metastases should receive other therapies, but this observation is hypothesis-generating only, said invited discussant Peter Schmid, MD, PhD, of Barts Cancer Institute at St. Bartholomew’s Hospital at Queen Mary University of London.
AT ESMO 2016
Key clinical point: The selective estrogen receptor degrader fulvestrant continues to offer improved progression-free survival (PFS) compared with the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole.
Major finding: At a median 25 months’ follow-up, median PFS was 16.6 months for fulvestrant vs. 13.8 months for anastrozole.
Data source: Randomized phase III trial of 462 women with endocrine therapy–naive locally advanced metastatic hormone receptor–positive breast cancer.
Disclosures: FALCON was sponsored by AstraZeneca. Dr. Ellis reported consulting for AstraZeneca, and Dr. Schmid reported honoraria or consultation fees from the company.
Missed Adult Vaccines Cost U.S. Nearly $9 Billion in 2015
Just how important are adult vaccines? According to a new study from Health Affairs missed vaccines cost the U.S. economy $8.95 billion in 2015. “This review not only estimated the direct costs and productivity losses due to inpatient and outpatient visits associated with vaccine-preventable diseases…but [it also] examined this across all vaccines recommended for US adults,” authors Sachiko Ozawa, Allison Portnoy, Hiwote Getaneh, Samantha Clark, Maria Knoll, David Bishai, H. Keri Yang, and Pallavi D. Patwardhan explained.
“Low rates of vaccine uptake lead to costs to individuals and society in terms of deaths and disabilities, which are avoidable, and they create economic losses from doctor visits, hospitalizations, and lost income,” the authors argued. “To identify the magnitude of this problem, we calculated the current economic burden that is attributable to vaccine-preventable diseases among US adults.
Not surprisingly, preventable influenza exacted the highest cost, estimated to be $5.8 billion. Pneumococcal disease was second, with an estimated cost of $1.9 billion, followed by herpes zoster ($782 million), human papillomavirus, and hepatitis B ($173 million).
Researchers were from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, in Boston, Massachusetts, MRDC in New York City, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, in Baltimore, Maryland, and Merck. This study was funded by Merck. The study “highlights the need for US adults to better appreciate the value of vaccines to prevent economic burden,” they said.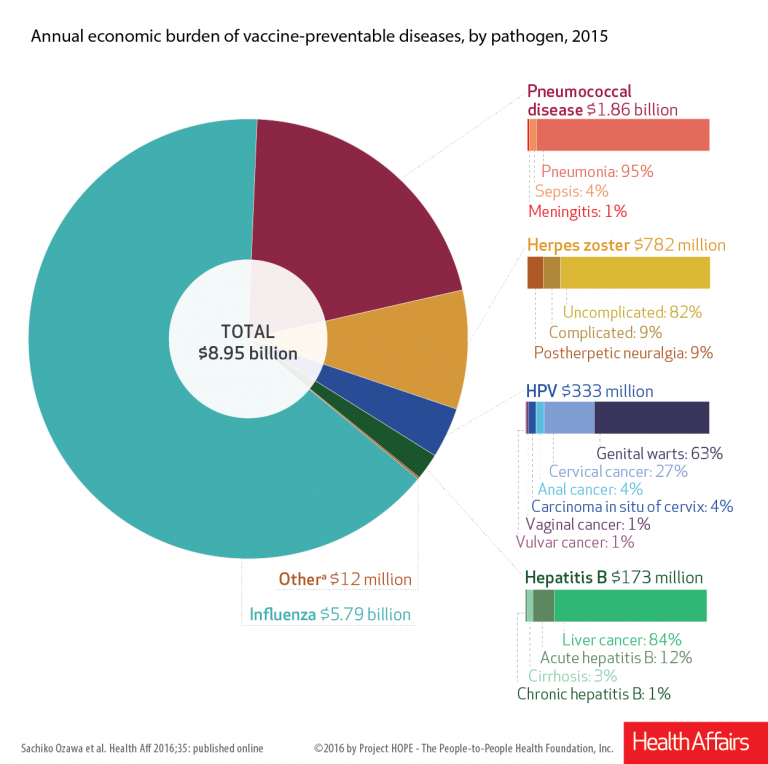
Just how important are adult vaccines? According to a new study from Health Affairs missed vaccines cost the U.S. economy $8.95 billion in 2015. “This review not only estimated the direct costs and productivity losses due to inpatient and outpatient visits associated with vaccine-preventable diseases…but [it also] examined this across all vaccines recommended for US adults,” authors Sachiko Ozawa, Allison Portnoy, Hiwote Getaneh, Samantha Clark, Maria Knoll, David Bishai, H. Keri Yang, and Pallavi D. Patwardhan explained.
“Low rates of vaccine uptake lead to costs to individuals and society in terms of deaths and disabilities, which are avoidable, and they create economic losses from doctor visits, hospitalizations, and lost income,” the authors argued. “To identify the magnitude of this problem, we calculated the current economic burden that is attributable to vaccine-preventable diseases among US adults.
Not surprisingly, preventable influenza exacted the highest cost, estimated to be $5.8 billion. Pneumococcal disease was second, with an estimated cost of $1.9 billion, followed by herpes zoster ($782 million), human papillomavirus, and hepatitis B ($173 million).
Researchers were from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, in Boston, Massachusetts, MRDC in New York City, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, in Baltimore, Maryland, and Merck. This study was funded by Merck. The study “highlights the need for US adults to better appreciate the value of vaccines to prevent economic burden,” they said.
Just how important are adult vaccines? According to a new study from Health Affairs missed vaccines cost the U.S. economy $8.95 billion in 2015. “This review not only estimated the direct costs and productivity losses due to inpatient and outpatient visits associated with vaccine-preventable diseases…but [it also] examined this across all vaccines recommended for US adults,” authors Sachiko Ozawa, Allison Portnoy, Hiwote Getaneh, Samantha Clark, Maria Knoll, David Bishai, H. Keri Yang, and Pallavi D. Patwardhan explained.
“Low rates of vaccine uptake lead to costs to individuals and society in terms of deaths and disabilities, which are avoidable, and they create economic losses from doctor visits, hospitalizations, and lost income,” the authors argued. “To identify the magnitude of this problem, we calculated the current economic burden that is attributable to vaccine-preventable diseases among US adults.
Not surprisingly, preventable influenza exacted the highest cost, estimated to be $5.8 billion. Pneumococcal disease was second, with an estimated cost of $1.9 billion, followed by herpes zoster ($782 million), human papillomavirus, and hepatitis B ($173 million).
Researchers were from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, in Boston, Massachusetts, MRDC in New York City, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, in Baltimore, Maryland, and Merck. This study was funded by Merck. The study “highlights the need for US adults to better appreciate the value of vaccines to prevent economic burden,” they said.
Earlier ischemic stroke presentation may sometimes mean delayed tPA
BALTIMORE – Going to the hospital soon after the development of symptoms of acute ischemic stroke may not guarantee quick treatment.
A study of 1,865 patients treated within the past decade at a large urban comprehensive stroke center has revealed delayed treatment with tissue plasminogen activator, compared with patients who came to the emergency room hours after symptom development, Dr. Kyle C. Rossi said at the annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
Treatment with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) within 3 hours after the first symptoms of acute ischemic stroke definitely improves long-term outcomes, but meeting this target time remains a challenge. Patients who present to the emergency room soon after symptom development would seemingly have an advantage, yet Dr. Rossi’s preliminary scrutiny of patient records at Mount Sinai raised doubts about this and prompted the present study.
The hypothesis was that cases with a shorter time between symptom development and diagnosis of stroke (last known well-to-stroke code time, or LKW-to-code) will have a longer time between diagnosis and tPA administration (code-to-tPA), “possibly due to the perception on the part of evaluating physicians of sufficient remaining time before the end of the tPA window.”
The researchers examined patient records from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association’s “Get with the Guidelines” stroke program, a voluntary observational registry for patients with acute stroke. Of the 1,865 ischemic stroke patients treated during 2009-2015, 122 who received intravenous tPA were allocated to three LKW-to-code groups: within an hour (38 patients), within the next hour (49 patients), or 2 hours or more (35 patients).
The patients tended to be in their late 60s. Just over half were female, and about 40% were white.
Overall, the average LKW-to-code time was 91 ± 48 minutes and the average code-to-tPA time was 67 ± 26 minutes.
Average code-to-tPA times were 80, 67, and 52 minutes, respectively, for the three groups (P less than .0001). On average, it took 28 minutes longer to give tPA to patients who presented within an hour than to patients presenting 2 hours or longer after their first stroke symptom. There was an increase in code-to-tPA time of 1 minute for every decrease in LKW-to-code time of 4 minutes (P less than .0001).
The delay in the time to treat patients who arrive sooner after development of stroke symptoms may result from a decision made by the evaluating neurologist to conduct additional testing prior to administering tPA. Sometimes other staff may be unaware of the decision to delay treatment, according to Dr. Rossi and his colleagues.
“Absolutely, folks coming in soon after symptoms develop should be treated early. But treatment needs to balance rapid delivery with adequate testing. Sometimes, when there is some time to spare before the optimum treatment window closes we can do a more thorough examination and address lingering questions,” Dr. Rossi said.
The decision to get more information about the patient’s condition reflects the goal to give tPA as soon as safely possible to the right patients. While laudable, the study highlights that the timing of treatment can be improved.
Dr. Rossi reported having no financial disclosures.
BALTIMORE – Going to the hospital soon after the development of symptoms of acute ischemic stroke may not guarantee quick treatment.
A study of 1,865 patients treated within the past decade at a large urban comprehensive stroke center has revealed delayed treatment with tissue plasminogen activator, compared with patients who came to the emergency room hours after symptom development, Dr. Kyle C. Rossi said at the annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
Treatment with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) within 3 hours after the first symptoms of acute ischemic stroke definitely improves long-term outcomes, but meeting this target time remains a challenge. Patients who present to the emergency room soon after symptom development would seemingly have an advantage, yet Dr. Rossi’s preliminary scrutiny of patient records at Mount Sinai raised doubts about this and prompted the present study.
The hypothesis was that cases with a shorter time between symptom development and diagnosis of stroke (last known well-to-stroke code time, or LKW-to-code) will have a longer time between diagnosis and tPA administration (code-to-tPA), “possibly due to the perception on the part of evaluating physicians of sufficient remaining time before the end of the tPA window.”
The researchers examined patient records from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association’s “Get with the Guidelines” stroke program, a voluntary observational registry for patients with acute stroke. Of the 1,865 ischemic stroke patients treated during 2009-2015, 122 who received intravenous tPA were allocated to three LKW-to-code groups: within an hour (38 patients), within the next hour (49 patients), or 2 hours or more (35 patients).
The patients tended to be in their late 60s. Just over half were female, and about 40% were white.
Overall, the average LKW-to-code time was 91 ± 48 minutes and the average code-to-tPA time was 67 ± 26 minutes.
Average code-to-tPA times were 80, 67, and 52 minutes, respectively, for the three groups (P less than .0001). On average, it took 28 minutes longer to give tPA to patients who presented within an hour than to patients presenting 2 hours or longer after their first stroke symptom. There was an increase in code-to-tPA time of 1 minute for every decrease in LKW-to-code time of 4 minutes (P less than .0001).
The delay in the time to treat patients who arrive sooner after development of stroke symptoms may result from a decision made by the evaluating neurologist to conduct additional testing prior to administering tPA. Sometimes other staff may be unaware of the decision to delay treatment, according to Dr. Rossi and his colleagues.
“Absolutely, folks coming in soon after symptoms develop should be treated early. But treatment needs to balance rapid delivery with adequate testing. Sometimes, when there is some time to spare before the optimum treatment window closes we can do a more thorough examination and address lingering questions,” Dr. Rossi said.
The decision to get more information about the patient’s condition reflects the goal to give tPA as soon as safely possible to the right patients. While laudable, the study highlights that the timing of treatment can be improved.
Dr. Rossi reported having no financial disclosures.
BALTIMORE – Going to the hospital soon after the development of symptoms of acute ischemic stroke may not guarantee quick treatment.
A study of 1,865 patients treated within the past decade at a large urban comprehensive stroke center has revealed delayed treatment with tissue plasminogen activator, compared with patients who came to the emergency room hours after symptom development, Dr. Kyle C. Rossi said at the annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
Treatment with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) within 3 hours after the first symptoms of acute ischemic stroke definitely improves long-term outcomes, but meeting this target time remains a challenge. Patients who present to the emergency room soon after symptom development would seemingly have an advantage, yet Dr. Rossi’s preliminary scrutiny of patient records at Mount Sinai raised doubts about this and prompted the present study.
The hypothesis was that cases with a shorter time between symptom development and diagnosis of stroke (last known well-to-stroke code time, or LKW-to-code) will have a longer time between diagnosis and tPA administration (code-to-tPA), “possibly due to the perception on the part of evaluating physicians of sufficient remaining time before the end of the tPA window.”
The researchers examined patient records from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association’s “Get with the Guidelines” stroke program, a voluntary observational registry for patients with acute stroke. Of the 1,865 ischemic stroke patients treated during 2009-2015, 122 who received intravenous tPA were allocated to three LKW-to-code groups: within an hour (38 patients), within the next hour (49 patients), or 2 hours or more (35 patients).
The patients tended to be in their late 60s. Just over half were female, and about 40% were white.
Overall, the average LKW-to-code time was 91 ± 48 minutes and the average code-to-tPA time was 67 ± 26 minutes.
Average code-to-tPA times were 80, 67, and 52 minutes, respectively, for the three groups (P less than .0001). On average, it took 28 minutes longer to give tPA to patients who presented within an hour than to patients presenting 2 hours or longer after their first stroke symptom. There was an increase in code-to-tPA time of 1 minute for every decrease in LKW-to-code time of 4 minutes (P less than .0001).
The delay in the time to treat patients who arrive sooner after development of stroke symptoms may result from a decision made by the evaluating neurologist to conduct additional testing prior to administering tPA. Sometimes other staff may be unaware of the decision to delay treatment, according to Dr. Rossi and his colleagues.
“Absolutely, folks coming in soon after symptoms develop should be treated early. But treatment needs to balance rapid delivery with adequate testing. Sometimes, when there is some time to spare before the optimum treatment window closes we can do a more thorough examination and address lingering questions,” Dr. Rossi said.
The decision to get more information about the patient’s condition reflects the goal to give tPA as soon as safely possible to the right patients. While laudable, the study highlights that the timing of treatment can be improved.
Dr. Rossi reported having no financial disclosures.
AT ANA 2016
Key clinical point:
Major finding: TPA was delivered 28 minutes longer on average for patients presenting less than 1 hour after stroke symptoms, compared with patients presenting more than 2 hours after.
Data source: Analysis of 1,865 patients with acute ischemic stroke in the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association’s “Get with the Guidelines” stroke program who were diagnosed at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York.
Disclosures: Dr. Rossi reported having no financial disclosures.
Novel Messenger RNA Vaccine in Development for Zika
A novel anti-Zika vaccine based on messenger RNA (mRNA) technology received financial backing from HHS. Moderna Therapeutics, Cambridge, Massachusetts, will get $8.2 million to accelerate the development of the vaccine.
Messenger RNA carries specific genetic codes to parts of the cell. The vaccine uses mRNA containing the genetic sequence of the Zika virus to generate an immune response.
This technology produces vaccine faster than other methods, which require the growth and purification of an attenuated or inactivated virus, HHS says. Moderna also is designing the vaccine to be easy to administer by not requiring any specialized delivery devices.
Under the initial 4-year agreement, HHS’ Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) will support a phase 1 clinical trial, toxicology studies, vaccine formulation, and manufacturing. If additional funding is identified the agreement could be extended to 5 years, with a total of $125.5 million to cover phase 2 and 3 clinical trials and large-scale manufacturing.
The funding is part of an obligated $85 million BARDA “reprogrammed” for Zika work. The funds are also being used to develop other Zika vaccines, blood screening tests, and pathogen reduction technologies.
A novel anti-Zika vaccine based on messenger RNA (mRNA) technology received financial backing from HHS. Moderna Therapeutics, Cambridge, Massachusetts, will get $8.2 million to accelerate the development of the vaccine.
Messenger RNA carries specific genetic codes to parts of the cell. The vaccine uses mRNA containing the genetic sequence of the Zika virus to generate an immune response.
This technology produces vaccine faster than other methods, which require the growth and purification of an attenuated or inactivated virus, HHS says. Moderna also is designing the vaccine to be easy to administer by not requiring any specialized delivery devices.
Under the initial 4-year agreement, HHS’ Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) will support a phase 1 clinical trial, toxicology studies, vaccine formulation, and manufacturing. If additional funding is identified the agreement could be extended to 5 years, with a total of $125.5 million to cover phase 2 and 3 clinical trials and large-scale manufacturing.
The funding is part of an obligated $85 million BARDA “reprogrammed” for Zika work. The funds are also being used to develop other Zika vaccines, blood screening tests, and pathogen reduction technologies.
A novel anti-Zika vaccine based on messenger RNA (mRNA) technology received financial backing from HHS. Moderna Therapeutics, Cambridge, Massachusetts, will get $8.2 million to accelerate the development of the vaccine.
Messenger RNA carries specific genetic codes to parts of the cell. The vaccine uses mRNA containing the genetic sequence of the Zika virus to generate an immune response.
This technology produces vaccine faster than other methods, which require the growth and purification of an attenuated or inactivated virus, HHS says. Moderna also is designing the vaccine to be easy to administer by not requiring any specialized delivery devices.
Under the initial 4-year agreement, HHS’ Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) will support a phase 1 clinical trial, toxicology studies, vaccine formulation, and manufacturing. If additional funding is identified the agreement could be extended to 5 years, with a total of $125.5 million to cover phase 2 and 3 clinical trials and large-scale manufacturing.
The funding is part of an obligated $85 million BARDA “reprogrammed” for Zika work. The funds are also being used to develop other Zika vaccines, blood screening tests, and pathogen reduction technologies.
Psychiatric patients face inordinately long wait times in emergency departments
Individuals with psychiatric conditions are facing increasingly longer wait times in emergency departments across the country, including children, according to a pair of studies presented by the American College of Emergency Physicians.
“I really started doing this research because of my clinical experience,” explained Suzanne Catherine Lippert, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and the lead author of both studies during an Oct. 17 conference call, saying that seeing patients sit in the ED for days prompted her to finally look into this issue.
Patients with bipolar disorder had the highest likelihood of waiting more than 24 hours in the ED, with an odds ratio of 3.7 (95% confidence interval, 1.5-9.4). This was followed by patients with a diagnosis of psychosis, a dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders, multiple psychiatric diagnoses, or depression. The most common diagnoses were substance abuse, anxiety, and depression, which constituted 41%, 26%, and 23% of the diagnoses, respectively. Patients with psychosis were admitted 34% of the time and transferred 24% of the time; those who self-harmed were admitted 33% of the time and transferred 29% of the time; and patients with bipolar disorder were admitted 29% of the time and transferred 40% of the time. Patients who had either two or three diagnoses were admitted 9% and 10% of the time, respectively.
“Further investigation of the systems affecting these patients, including placement of involuntary holds, availability of ED psychiatric consultants, or outpatient resources would delineate potential intervention points for the care of these vulnerable patients,” Dr. Lippert and her coauthors wrote.
The second study looked at the differences in waiting for care at EDs between psychiatric patients and medical patients. Length of stay was defined the same way it was in the previous study, with disposition meaning either “discharge, admission to medical or psychiatric bed, [or] transfer to any acute facility.” Length of stay was divided into the same three categories as the previous study, too.
Psychiatric patients were more likely than were medical patients to wait more than 6 hours for disposition, regardless of what the disposition itself ended up being, by a rate of 23% vs. 10%. Similarly, 7% of psychiatric patients vs. just 2.3% of medical patients had to wait longer than 12 hours in the ED, while 1.3% of psychiatric had to wait longer than 24 hours, compared with only 0.5% of medical patients. The average length of stay was significantly longer for psychiatric patients: 194 minutes vs. 138 minutes for medical patients (P less than .01).
Additionally, psychiatric patients were more likely to be uninsured, with 22% not having insurance, compared with 15% of medical patients being uninsured. Furthermore, 4.6% of the psychiatric patients’ previous visit to the ED had been within the prior 72 hours, compared with 3.6% of medical patients. A total of 21% of psychiatric patients required admittance, compared with 13% of medical patients, while 11% of psychiatric patients were transferred, compared with just 1.4% of medical patients.
“These results compel us to further investigate the potential causes of prolonged length of stay in psychiatric patients and to further characterize the population of psychiatric patients most at risk of prolonged stays,” Dr. Lippert and her coinvestigators concluded.
ACEP President Rebecca B. Parker, MD, chimed in during the conference call, explaining that a survey of more than 1,700 emergency physicians revealed some “troubling” findings about the state of emergency departments over the last year.
The nation’s dwindling mental health resources are having a direct impact on patients having psychiatric emergencies, including children,” Dr. Parker explained. “These patients are waiting longer for care, especially those patients who require hospitalization.”
Findings of the survey indicate that 48% of ED physicians witness psychiatric patients being “boarded” in their EDs at least once a day while they wait for a bed. Additionally, less than 17% of respondents said their ED has a psychiatrist on call to respond to psychiatric emergencies, with 11.7% responding that they have no psychiatrist on call to deal with such emergencies. And 52% of respondents said the mental health system in their community has gotten noticeably worse in just the last year.
In a separate statement, Dr. Parker voiced outrage about the situation. “Psychiatric patients wait in the emergency department for hours and even days for a bed, which delays the psychiatric care they so desperately need,” she said. “It also leads to delays in care and diminished resources for other emergency patients. The emergency department has become the dumping ground for these vulnerable patients who have been abandoned by every other part of the health care system.”
ACEP presented the findings during its annual meeting in Las Vegas. No funding sources for these studies were disclosed; Dr. Lippert did not report any financial disclosures.
Individuals with psychiatric conditions are facing increasingly longer wait times in emergency departments across the country, including children, according to a pair of studies presented by the American College of Emergency Physicians.
“I really started doing this research because of my clinical experience,” explained Suzanne Catherine Lippert, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and the lead author of both studies during an Oct. 17 conference call, saying that seeing patients sit in the ED for days prompted her to finally look into this issue.
Patients with bipolar disorder had the highest likelihood of waiting more than 24 hours in the ED, with an odds ratio of 3.7 (95% confidence interval, 1.5-9.4). This was followed by patients with a diagnosis of psychosis, a dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders, multiple psychiatric diagnoses, or depression. The most common diagnoses were substance abuse, anxiety, and depression, which constituted 41%, 26%, and 23% of the diagnoses, respectively. Patients with psychosis were admitted 34% of the time and transferred 24% of the time; those who self-harmed were admitted 33% of the time and transferred 29% of the time; and patients with bipolar disorder were admitted 29% of the time and transferred 40% of the time. Patients who had either two or three diagnoses were admitted 9% and 10% of the time, respectively.
“Further investigation of the systems affecting these patients, including placement of involuntary holds, availability of ED psychiatric consultants, or outpatient resources would delineate potential intervention points for the care of these vulnerable patients,” Dr. Lippert and her coauthors wrote.
The second study looked at the differences in waiting for care at EDs between psychiatric patients and medical patients. Length of stay was defined the same way it was in the previous study, with disposition meaning either “discharge, admission to medical or psychiatric bed, [or] transfer to any acute facility.” Length of stay was divided into the same three categories as the previous study, too.
Psychiatric patients were more likely than were medical patients to wait more than 6 hours for disposition, regardless of what the disposition itself ended up being, by a rate of 23% vs. 10%. Similarly, 7% of psychiatric patients vs. just 2.3% of medical patients had to wait longer than 12 hours in the ED, while 1.3% of psychiatric had to wait longer than 24 hours, compared with only 0.5% of medical patients. The average length of stay was significantly longer for psychiatric patients: 194 minutes vs. 138 minutes for medical patients (P less than .01).
Additionally, psychiatric patients were more likely to be uninsured, with 22% not having insurance, compared with 15% of medical patients being uninsured. Furthermore, 4.6% of the psychiatric patients’ previous visit to the ED had been within the prior 72 hours, compared with 3.6% of medical patients. A total of 21% of psychiatric patients required admittance, compared with 13% of medical patients, while 11% of psychiatric patients were transferred, compared with just 1.4% of medical patients.
“These results compel us to further investigate the potential causes of prolonged length of stay in psychiatric patients and to further characterize the population of psychiatric patients most at risk of prolonged stays,” Dr. Lippert and her coinvestigators concluded.
ACEP President Rebecca B. Parker, MD, chimed in during the conference call, explaining that a survey of more than 1,700 emergency physicians revealed some “troubling” findings about the state of emergency departments over the last year.
The nation’s dwindling mental health resources are having a direct impact on patients having psychiatric emergencies, including children,” Dr. Parker explained. “These patients are waiting longer for care, especially those patients who require hospitalization.”
Findings of the survey indicate that 48% of ED physicians witness psychiatric patients being “boarded” in their EDs at least once a day while they wait for a bed. Additionally, less than 17% of respondents said their ED has a psychiatrist on call to respond to psychiatric emergencies, with 11.7% responding that they have no psychiatrist on call to deal with such emergencies. And 52% of respondents said the mental health system in their community has gotten noticeably worse in just the last year.
In a separate statement, Dr. Parker voiced outrage about the situation. “Psychiatric patients wait in the emergency department for hours and even days for a bed, which delays the psychiatric care they so desperately need,” she said. “It also leads to delays in care and diminished resources for other emergency patients. The emergency department has become the dumping ground for these vulnerable patients who have been abandoned by every other part of the health care system.”
ACEP presented the findings during its annual meeting in Las Vegas. No funding sources for these studies were disclosed; Dr. Lippert did not report any financial disclosures.
Individuals with psychiatric conditions are facing increasingly longer wait times in emergency departments across the country, including children, according to a pair of studies presented by the American College of Emergency Physicians.
“I really started doing this research because of my clinical experience,” explained Suzanne Catherine Lippert, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and the lead author of both studies during an Oct. 17 conference call, saying that seeing patients sit in the ED for days prompted her to finally look into this issue.
Patients with bipolar disorder had the highest likelihood of waiting more than 24 hours in the ED, with an odds ratio of 3.7 (95% confidence interval, 1.5-9.4). This was followed by patients with a diagnosis of psychosis, a dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders, multiple psychiatric diagnoses, or depression. The most common diagnoses were substance abuse, anxiety, and depression, which constituted 41%, 26%, and 23% of the diagnoses, respectively. Patients with psychosis were admitted 34% of the time and transferred 24% of the time; those who self-harmed were admitted 33% of the time and transferred 29% of the time; and patients with bipolar disorder were admitted 29% of the time and transferred 40% of the time. Patients who had either two or three diagnoses were admitted 9% and 10% of the time, respectively.
“Further investigation of the systems affecting these patients, including placement of involuntary holds, availability of ED psychiatric consultants, or outpatient resources would delineate potential intervention points for the care of these vulnerable patients,” Dr. Lippert and her coauthors wrote.
The second study looked at the differences in waiting for care at EDs between psychiatric patients and medical patients. Length of stay was defined the same way it was in the previous study, with disposition meaning either “discharge, admission to medical or psychiatric bed, [or] transfer to any acute facility.” Length of stay was divided into the same three categories as the previous study, too.
Psychiatric patients were more likely than were medical patients to wait more than 6 hours for disposition, regardless of what the disposition itself ended up being, by a rate of 23% vs. 10%. Similarly, 7% of psychiatric patients vs. just 2.3% of medical patients had to wait longer than 12 hours in the ED, while 1.3% of psychiatric had to wait longer than 24 hours, compared with only 0.5% of medical patients. The average length of stay was significantly longer for psychiatric patients: 194 minutes vs. 138 minutes for medical patients (P less than .01).
Additionally, psychiatric patients were more likely to be uninsured, with 22% not having insurance, compared with 15% of medical patients being uninsured. Furthermore, 4.6% of the psychiatric patients’ previous visit to the ED had been within the prior 72 hours, compared with 3.6% of medical patients. A total of 21% of psychiatric patients required admittance, compared with 13% of medical patients, while 11% of psychiatric patients were transferred, compared with just 1.4% of medical patients.
“These results compel us to further investigate the potential causes of prolonged length of stay in psychiatric patients and to further characterize the population of psychiatric patients most at risk of prolonged stays,” Dr. Lippert and her coinvestigators concluded.
ACEP President Rebecca B. Parker, MD, chimed in during the conference call, explaining that a survey of more than 1,700 emergency physicians revealed some “troubling” findings about the state of emergency departments over the last year.
The nation’s dwindling mental health resources are having a direct impact on patients having psychiatric emergencies, including children,” Dr. Parker explained. “These patients are waiting longer for care, especially those patients who require hospitalization.”
Findings of the survey indicate that 48% of ED physicians witness psychiatric patients being “boarded” in their EDs at least once a day while they wait for a bed. Additionally, less than 17% of respondents said their ED has a psychiatrist on call to respond to psychiatric emergencies, with 11.7% responding that they have no psychiatrist on call to deal with such emergencies. And 52% of respondents said the mental health system in their community has gotten noticeably worse in just the last year.
In a separate statement, Dr. Parker voiced outrage about the situation. “Psychiatric patients wait in the emergency department for hours and even days for a bed, which delays the psychiatric care they so desperately need,” she said. “It also leads to delays in care and diminished resources for other emergency patients. The emergency department has become the dumping ground for these vulnerable patients who have been abandoned by every other part of the health care system.”
ACEP presented the findings during its annual meeting in Las Vegas. No funding sources for these studies were disclosed; Dr. Lippert did not report any financial disclosures.
FROM AN ACEP TELECONFERENCE
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Higher percentages of psychiatric patients have to wait more than a day before disposition, compared with medical patients.
Data source: Two retrospective reviews of more than 65 million ED visits in the NHAMCS database from 2001-2011.
Disclosures: No funding sources or disclosures were reported.
Addressing sex and gender inequality in biomedical research
in two general areas. Not only are biologic sex and gender insufficiently reported within research studies, but women are also underrepresented as basic and clinical researchers in academic medicine. While these issues may seem unrelated, addressing both will diversify knowledge and interdisciplinary research teams, as well as improve the value of the science produced and ultimately the quality of health care provided.
In 1986, the National Institutes of Health instituted a policy urging the inclusion of women as subjects in clinical trials. This policy became law when Congress passed the NIH Revitalization Act of 1993, which requires that NIH-supported clinical research include women and minorities as subjects “in approximately equal numbers of both sexes … unless different proportions are appropriate because of known prevalence, incidence, morbidity, mortality rates, or expected intervention effect.” Women of childbearing potential cannot be routinely excluded without a strong scientific rationale.
Despite these initiatives, evidence suggests that sex/gender is still not sufficiently considered as a biologic variable in federally funded research, and studies oftentimes fail to account for the cultural and societal influences of gender in health outcomes. Women comprise more than half of clinical trial participants, yet 75% of federally funded studies published in 2009 failed to report any outcomes by sex/gender. Recent events, such as the Food and Drug Administration’s updated Ambien dosage recommendation for men versus women, demonstrate the harmful effects of failing to account for sex as a biologic variable.
In recognition of the slow progress, the NIH required that research grants submitted after Jan. 25, 2016, address biologic sex within their research design and added reviewer criteria related to consideration of biologic sex in the research proposal. Ensuring enhanced inclusion, analysis, and reporting of sex and gender goes beyond NIH policy to include NIH enforcement of its own policies. In addition, journal editors should add review criteria related to sex and gender, and researchers themselves should examine potential sex/gender differences in their research.
The NIH and ORWH have implemented various programs to diversify the sciences; however, change has been less than desired. Studies indicate that females have lower publication rates throughout their careers, and are less likely to receive an R01 than men, despite reporting equal likelihood of applying for R01 awards. Additionally, the intraorganizational and network reach of female scientists is smaller than that of men, hindering opportunities for collaboration and publication. Even in the instance of equally qualified men and women conducting comparable work, investigators find differential pay between male and female researchers, as well as differential promotion to leadership positions. These factors, both in part caused by and exacerbated by unconscious or implicit interpersonal and institutional biases, lead to higher female attrition within the sciences and academia.
Addressing disparities and promoting greater inclusion includes unmasking unconscious bias and putting greater efforts toward mentoring and leadership initiatives for women. Only by partnering efforts to increase inclusion of sex/gender within research design with efforts to diversify the biomedical workforce can we adequately consider the role of sex and gender in biomedical research.
Dr. Geller is the G. William Arends Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the University of Illinois College of Medicine, and the Director of the UIC Center for Research on Women and Gender. Ms. Koch is a senior research specialist at the Center for Research on Women and Gender. They reported having no financial disclosures.
in two general areas. Not only are biologic sex and gender insufficiently reported within research studies, but women are also underrepresented as basic and clinical researchers in academic medicine. While these issues may seem unrelated, addressing both will diversify knowledge and interdisciplinary research teams, as well as improve the value of the science produced and ultimately the quality of health care provided.
In 1986, the National Institutes of Health instituted a policy urging the inclusion of women as subjects in clinical trials. This policy became law when Congress passed the NIH Revitalization Act of 1993, which requires that NIH-supported clinical research include women and minorities as subjects “in approximately equal numbers of both sexes … unless different proportions are appropriate because of known prevalence, incidence, morbidity, mortality rates, or expected intervention effect.” Women of childbearing potential cannot be routinely excluded without a strong scientific rationale.
Despite these initiatives, evidence suggests that sex/gender is still not sufficiently considered as a biologic variable in federally funded research, and studies oftentimes fail to account for the cultural and societal influences of gender in health outcomes. Women comprise more than half of clinical trial participants, yet 75% of federally funded studies published in 2009 failed to report any outcomes by sex/gender. Recent events, such as the Food and Drug Administration’s updated Ambien dosage recommendation for men versus women, demonstrate the harmful effects of failing to account for sex as a biologic variable.
In recognition of the slow progress, the NIH required that research grants submitted after Jan. 25, 2016, address biologic sex within their research design and added reviewer criteria related to consideration of biologic sex in the research proposal. Ensuring enhanced inclusion, analysis, and reporting of sex and gender goes beyond NIH policy to include NIH enforcement of its own policies. In addition, journal editors should add review criteria related to sex and gender, and researchers themselves should examine potential sex/gender differences in their research.
The NIH and ORWH have implemented various programs to diversify the sciences; however, change has been less than desired. Studies indicate that females have lower publication rates throughout their careers, and are less likely to receive an R01 than men, despite reporting equal likelihood of applying for R01 awards. Additionally, the intraorganizational and network reach of female scientists is smaller than that of men, hindering opportunities for collaboration and publication. Even in the instance of equally qualified men and women conducting comparable work, investigators find differential pay between male and female researchers, as well as differential promotion to leadership positions. These factors, both in part caused by and exacerbated by unconscious or implicit interpersonal and institutional biases, lead to higher female attrition within the sciences and academia.
Addressing disparities and promoting greater inclusion includes unmasking unconscious bias and putting greater efforts toward mentoring and leadership initiatives for women. Only by partnering efforts to increase inclusion of sex/gender within research design with efforts to diversify the biomedical workforce can we adequately consider the role of sex and gender in biomedical research.
Dr. Geller is the G. William Arends Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the University of Illinois College of Medicine, and the Director of the UIC Center for Research on Women and Gender. Ms. Koch is a senior research specialist at the Center for Research on Women and Gender. They reported having no financial disclosures.
in two general areas. Not only are biologic sex and gender insufficiently reported within research studies, but women are also underrepresented as basic and clinical researchers in academic medicine. While these issues may seem unrelated, addressing both will diversify knowledge and interdisciplinary research teams, as well as improve the value of the science produced and ultimately the quality of health care provided.
In 1986, the National Institutes of Health instituted a policy urging the inclusion of women as subjects in clinical trials. This policy became law when Congress passed the NIH Revitalization Act of 1993, which requires that NIH-supported clinical research include women and minorities as subjects “in approximately equal numbers of both sexes … unless different proportions are appropriate because of known prevalence, incidence, morbidity, mortality rates, or expected intervention effect.” Women of childbearing potential cannot be routinely excluded without a strong scientific rationale.
Despite these initiatives, evidence suggests that sex/gender is still not sufficiently considered as a biologic variable in federally funded research, and studies oftentimes fail to account for the cultural and societal influences of gender in health outcomes. Women comprise more than half of clinical trial participants, yet 75% of federally funded studies published in 2009 failed to report any outcomes by sex/gender. Recent events, such as the Food and Drug Administration’s updated Ambien dosage recommendation for men versus women, demonstrate the harmful effects of failing to account for sex as a biologic variable.
In recognition of the slow progress, the NIH required that research grants submitted after Jan. 25, 2016, address biologic sex within their research design and added reviewer criteria related to consideration of biologic sex in the research proposal. Ensuring enhanced inclusion, analysis, and reporting of sex and gender goes beyond NIH policy to include NIH enforcement of its own policies. In addition, journal editors should add review criteria related to sex and gender, and researchers themselves should examine potential sex/gender differences in their research.
The NIH and ORWH have implemented various programs to diversify the sciences; however, change has been less than desired. Studies indicate that females have lower publication rates throughout their careers, and are less likely to receive an R01 than men, despite reporting equal likelihood of applying for R01 awards. Additionally, the intraorganizational and network reach of female scientists is smaller than that of men, hindering opportunities for collaboration and publication. Even in the instance of equally qualified men and women conducting comparable work, investigators find differential pay between male and female researchers, as well as differential promotion to leadership positions. These factors, both in part caused by and exacerbated by unconscious or implicit interpersonal and institutional biases, lead to higher female attrition within the sciences and academia.
Addressing disparities and promoting greater inclusion includes unmasking unconscious bias and putting greater efforts toward mentoring and leadership initiatives for women. Only by partnering efforts to increase inclusion of sex/gender within research design with efforts to diversify the biomedical workforce can we adequately consider the role of sex and gender in biomedical research.
Dr. Geller is the G. William Arends Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the University of Illinois College of Medicine, and the Director of the UIC Center for Research on Women and Gender. Ms. Koch is a senior research specialist at the Center for Research on Women and Gender. They reported having no financial disclosures.
Recurrent Cerebriform Connective Tissue Nevus on the Foot of a Patient With Proteus Syndrome
To the Editor:
A 12-year-old girl presented with discomfort and walking limitation caused by cutaneous masses on the plantar aspects of the feet with associated bone abnormalities that had started as several flesh-colored papules on the plantar surface of both feet at the age of 1 year. Over time the lesions gradually enlarged and formed irregular masses, more prominently on the right foot. At the age of 6 years, surgical correction was performed due to increased walking impairment and a skin examination that suggested connective tissue nevus. The results were good. However, the local tissue overgrowth recurred after 1 year. Slowly growing lesions were found at the surgical site, which necessitated hospitalization. Her medical history was negative for other disease. There was no family history of similar skin conditions and her parents were nonconsanguineous.
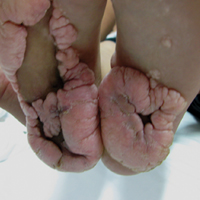
Physical examination revealed malnutrition and poor development in height as well as difficulty walking. She also had moderate scoliosis with a curve to the left. Dermatological examination showed multiple reddish cerebriform hyperplasia in both plantar areas; the right side was more severely involved (Figure 1A). There was macrodactyly of 2 toes on the right foot (Figure 1B). All results of routine blood examinations were within reference range. There were no abnormalities noted in the abdominal ultrasound and cardiac examinations. Plain radiographs of the spine and feet demonstrated scoliosis and exostosis on the calcaneus and bottom of the scaphoid. Histopathologic examination of tissue from the plantar cerebriform hyperplasia revealed hyperkeratosis, slight acanthosis and papillomatosis in the epidermis, and dense collagen bands and sparse elastic fibers in the dermis (Figure 2).
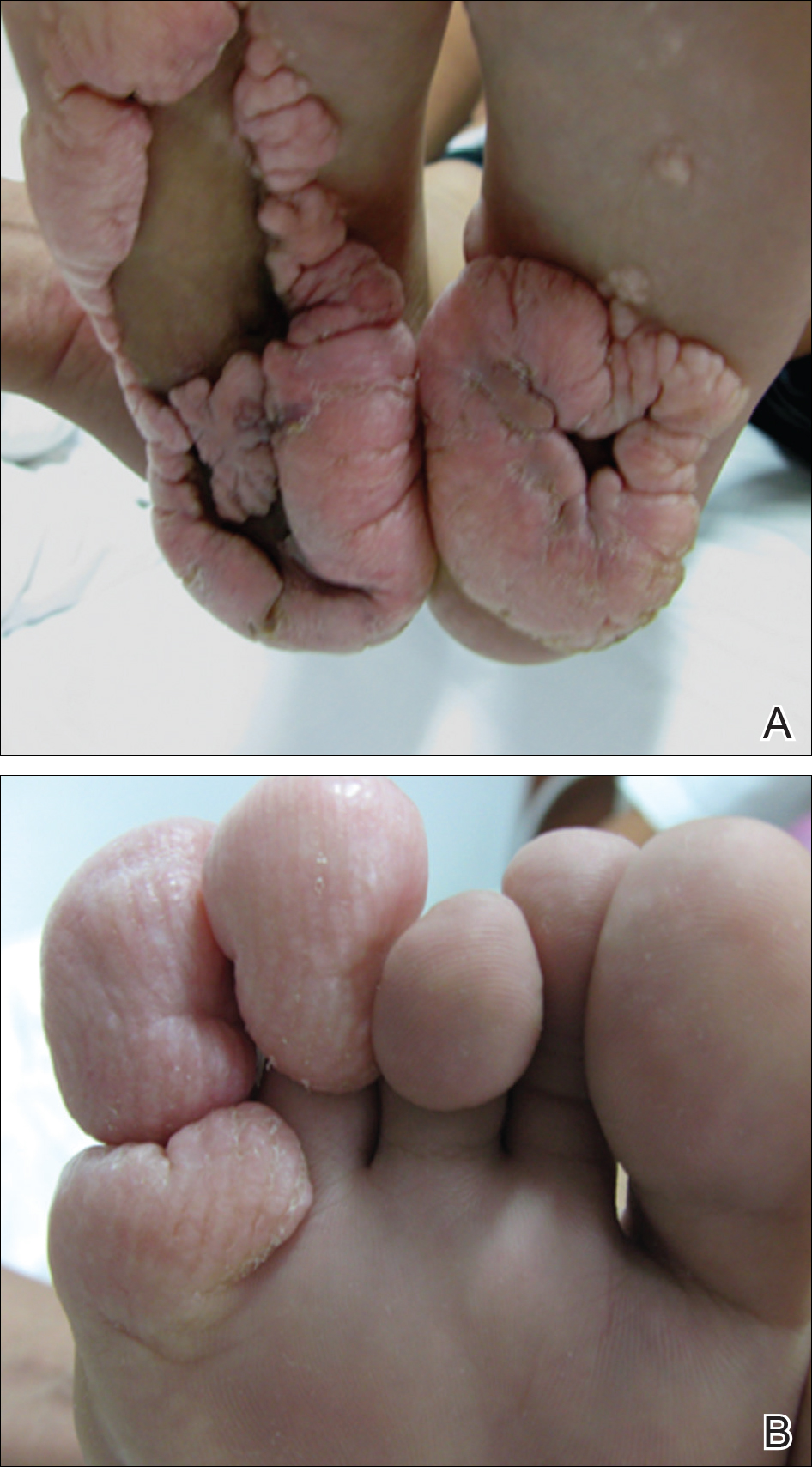

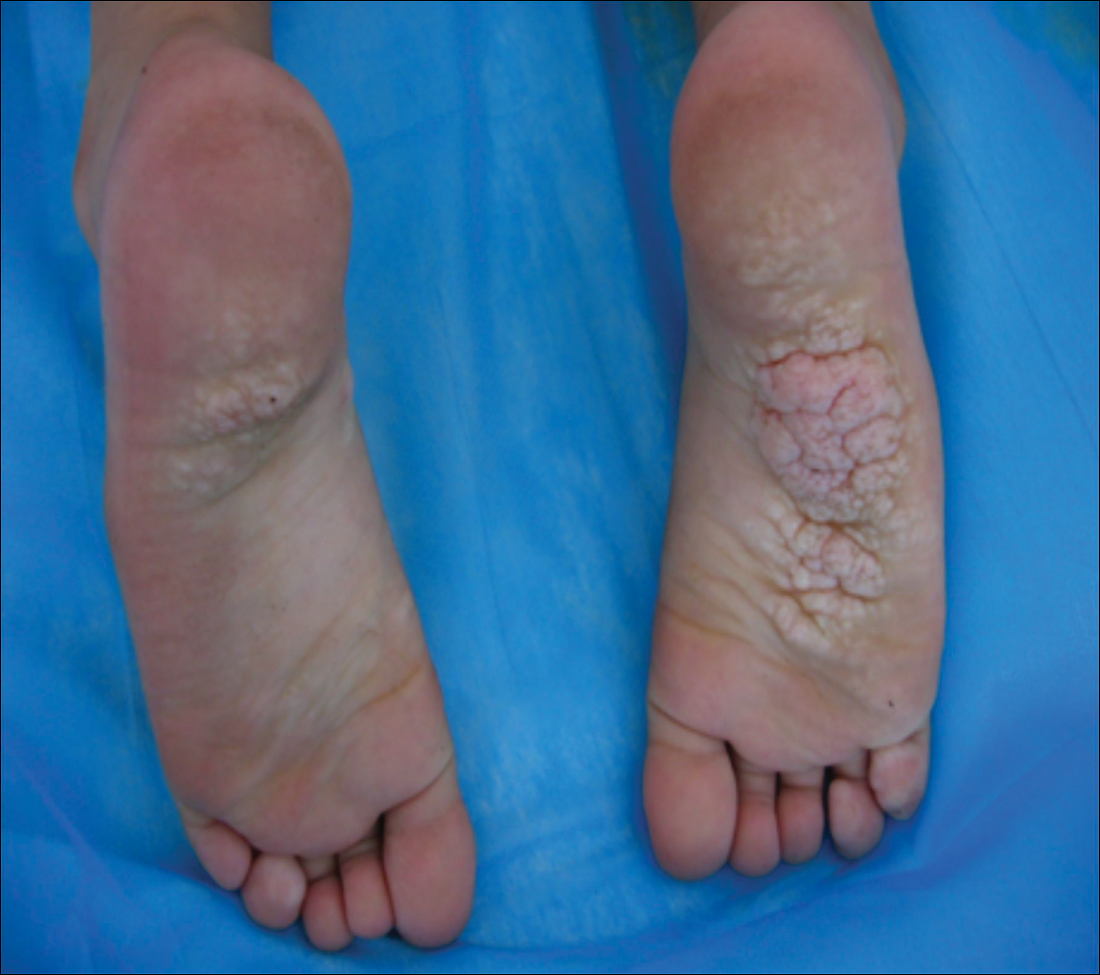
Given the clinical and radiologic manifestation, the diagnosis of Proteus syndrome (PS) was established. After taking into account the severe discomfort and the success of the first surgery, we performed a resection and full-thickness skin graft surgery once again. The feet recovered without any discomfort in daily life. The appearance of the skin graft area was normal 1 year following surgery (Figure 3). She was treated with spinal plate fixation at another institution, progressed well for 2 years, and was subsequently lost to follow-up.
Proteus syndrome is a multisystem disorder with a difficult diagnosis due to the variability of its manifestations. The worldwide incidence of this rare disorder is less than 1 per 1 million individuals, and it is thought to be caused by a somatic genetic alteration.1 Clinical characteristics include bone abnormalities, vascular malformations, dysregulation of fatty tissue, linear verrucous epidermal nevus, and cerebriform connective tissue nevus (CCTN). Although CCTN is not a common finding in patients with PS, it is considered a fairly specific sign with the greatest impact for the diagnosis of PS.2
The general feature of PS--asymmetric disproportionate overgrowth of tissues--appears at 6 to 18 months of age, which makes it challenging to diagnose disease earlier. The CCTN in our patient was present since 1 year of age.
To make a diagnosis of PS, one must have all the general criteria and various specific criteria. The revised diagnostic criteria for PS are given in the Table.3 According to the diagnostic criteria, our patient fulfilled the mandatory general criteria and had plantar CCTN, epidermal nevus, and dysregulated adipose tissue. The CCTN has notable diagnostic value in mildly affected patients, as it is absent in diseases included in the differential diagnosis such as neurofibromatosis, Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome, Maffucci syndrome, and Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome. Hemihyperplasia-multiple lipomatosis syndrome and CLOVES (congenital, lipomatous overgrowth, vascular malformations, epidermal nevi, and scoliosis/spinal/skeletal anomalies) syndrome also can present on the plantar surfaces, and lesions may be overgrown at birth but are softer and compressible, have wrinkles instead of deep folds, and tend to grow with the child rather than disproportionately as in PS.4
The epidermal nevi and vascular malformations generally do not spread or increase in number. In contrast, CCTN in PS grows throughout childhood but tends to remain stable in adulthood.4 Postponing surgical treatment until skin lesions stabilize appears to be the best option. However, for practical purposes, surgical intervention may be required at an earlier phase to address the severe functional and cosmetic consequences. Some patients require multiple orthopedic procedures over the ensuing years or decades to control the hyperplasia.3 New CCTN that developed from the prior surgical incision, macrodactyly of the fourth and fifth right toes, and scoliosis appeared when the patient came to our clinic for retreatment 1 year after the initial presentation. The asymmetrical and disproportionate overgrowth of tissues had moderately accelerated in that period. Considering the increasingly impaired walking, we performed a second surgery. On follow-up visits, the patient expressed improvement in daily life.

Studies had been performed to clarify the genetic bases of PS, and the somatic activating mutation in AKT1 (AKT serine/threonine kinase 1) was reported to be the cause of the disease.5,6 Germline PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog) mutations have been identified in some patients with overgrowth abnormalities of PS. However, given the misdiagnosis of PS with PTEN mutations and the notion that a gene alone cannot result in PS, the loss-of-function mutations of LEMD3 that have been reported in familial cutaneous collagenomas also may be related to the abnormal growth of connective and bone tissues that are typical of PS.7,8 Lindhurst et al5 concluded that PS is caused by a somatic activating mutation in AKT1, which proved the hypothesis of somatic mosaicism and implicated activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway in the characteristic clinical findings of overgrowth and tumor susceptibility in this disorder. AKT1 is activated by loss-of-function mutations in PTEN, which explains why patients with these mutations (eg, those with the segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation, epidermal nevus, SOLAMEN [segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation, and epidermal nevus] syndrome) and patients with activating mutations in AKT1 (eg, those with PS) have overlapping but distinct clinical manifestations. Molecular genetic testing may be useful to confirm the diagnosis in individuals who meet clinical criteria and to establish the diagnosis in individuals with clinical findings that are ambiguous or mild. Further studies are necessary to progress the understanding and management of PS, which will require cooperation of geneticists, surgeons, and other specialists.
- Popescu MD, Burnei G, Draghici L, et al. Proteus syndrome: a difficult diagnosis and management plan. J Med Life. 2014;7:563-566.
- Schepis C, Greco D, Siragusa M, et al. Cerebriform plantar hyperplasia: the major cutaneous feature of Proteus syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:374-376.
- Biesecker L. The challenges of Proteus syndrome: diagnosis and management. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006;14:1151-1157.
- Beachkofsky TM, Sapp JC, Biesecker LG, et al. Progressive overgrowth of the cerebriform connective tissue nevus in patients with Proteus syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:799-804.
- Lindhurst MJ, Sapp JC, Teer JK, et al. A mosaic activating mutation in AKT1 associated with the Proteus syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:611-619.
- Wieland I, Tinschert S, Zenker M. High-level somatic mosaicism of AKT1 c.49G>A mutation in skin scrapings from epidermal nevi enables non-invasive molecular diagnosis in patients with Proteus syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2013;161A:889-891.
- Cohen MJ, Turner JT, Biesecker LG. Proteus syndrome: misdiagnosis with PTEN mutations. Am J Med Genet A. 2003;122A:323-324.
- Di Stefani A, Gabellini M, Ferlosio A, et al. Cerebriform plantar hyperplasia: the clinico-pathological hallmark of Proteus syndrome. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:580-581.
To the Editor:
A 12-year-old girl presented with discomfort and walking limitation caused by cutaneous masses on the plantar aspects of the feet with associated bone abnormalities that had started as several flesh-colored papules on the plantar surface of both feet at the age of 1 year. Over time the lesions gradually enlarged and formed irregular masses, more prominently on the right foot. At the age of 6 years, surgical correction was performed due to increased walking impairment and a skin examination that suggested connective tissue nevus. The results were good. However, the local tissue overgrowth recurred after 1 year. Slowly growing lesions were found at the surgical site, which necessitated hospitalization. Her medical history was negative for other disease. There was no family history of similar skin conditions and her parents were nonconsanguineous.
Physical examination revealed malnutrition and poor development in height as well as difficulty walking. She also had moderate scoliosis with a curve to the left. Dermatological examination showed multiple reddish cerebriform hyperplasia in both plantar areas; the right side was more severely involved (Figure 1A). There was macrodactyly of 2 toes on the right foot (Figure 1B). All results of routine blood examinations were within reference range. There were no abnormalities noted in the abdominal ultrasound and cardiac examinations. Plain radiographs of the spine and feet demonstrated scoliosis and exostosis on the calcaneus and bottom of the scaphoid. Histopathologic examination of tissue from the plantar cerebriform hyperplasia revealed hyperkeratosis, slight acanthosis and papillomatosis in the epidermis, and dense collagen bands and sparse elastic fibers in the dermis (Figure 2).


Given the clinical and radiologic manifestation, the diagnosis of Proteus syndrome (PS) was established. After taking into account the severe discomfort and the success of the first surgery, we performed a resection and full-thickness skin graft surgery once again. The feet recovered without any discomfort in daily life. The appearance of the skin graft area was normal 1 year following surgery (Figure 3). She was treated with spinal plate fixation at another institution, progressed well for 2 years, and was subsequently lost to follow-up.

Proteus syndrome is a multisystem disorder with a difficult diagnosis due to the variability of its manifestations. The worldwide incidence of this rare disorder is less than 1 per 1 million individuals, and it is thought to be caused by a somatic genetic alteration.1 Clinical characteristics include bone abnormalities, vascular malformations, dysregulation of fatty tissue, linear verrucous epidermal nevus, and cerebriform connective tissue nevus (CCTN). Although CCTN is not a common finding in patients with PS, it is considered a fairly specific sign with the greatest impact for the diagnosis of PS.2
The general feature of PS--asymmetric disproportionate overgrowth of tissues--appears at 6 to 18 months of age, which makes it challenging to diagnose disease earlier. The CCTN in our patient was present since 1 year of age.
To make a diagnosis of PS, one must have all the general criteria and various specific criteria. The revised diagnostic criteria for PS are given in the Table.3 According to the diagnostic criteria, our patient fulfilled the mandatory general criteria and had plantar CCTN, epidermal nevus, and dysregulated adipose tissue. The CCTN has notable diagnostic value in mildly affected patients, as it is absent in diseases included in the differential diagnosis such as neurofibromatosis, Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome, Maffucci syndrome, and Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome. Hemihyperplasia-multiple lipomatosis syndrome and CLOVES (congenital, lipomatous overgrowth, vascular malformations, epidermal nevi, and scoliosis/spinal/skeletal anomalies) syndrome also can present on the plantar surfaces, and lesions may be overgrown at birth but are softer and compressible, have wrinkles instead of deep folds, and tend to grow with the child rather than disproportionately as in PS.4
The epidermal nevi and vascular malformations generally do not spread or increase in number. In contrast, CCTN in PS grows throughout childhood but tends to remain stable in adulthood.4 Postponing surgical treatment until skin lesions stabilize appears to be the best option. However, for practical purposes, surgical intervention may be required at an earlier phase to address the severe functional and cosmetic consequences. Some patients require multiple orthopedic procedures over the ensuing years or decades to control the hyperplasia.3 New CCTN that developed from the prior surgical incision, macrodactyly of the fourth and fifth right toes, and scoliosis appeared when the patient came to our clinic for retreatment 1 year after the initial presentation. The asymmetrical and disproportionate overgrowth of tissues had moderately accelerated in that period. Considering the increasingly impaired walking, we performed a second surgery. On follow-up visits, the patient expressed improvement in daily life.

Studies had been performed to clarify the genetic bases of PS, and the somatic activating mutation in AKT1 (AKT serine/threonine kinase 1) was reported to be the cause of the disease.5,6 Germline PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog) mutations have been identified in some patients with overgrowth abnormalities of PS. However, given the misdiagnosis of PS with PTEN mutations and the notion that a gene alone cannot result in PS, the loss-of-function mutations of LEMD3 that have been reported in familial cutaneous collagenomas also may be related to the abnormal growth of connective and bone tissues that are typical of PS.7,8 Lindhurst et al5 concluded that PS is caused by a somatic activating mutation in AKT1, which proved the hypothesis of somatic mosaicism and implicated activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway in the characteristic clinical findings of overgrowth and tumor susceptibility in this disorder. AKT1 is activated by loss-of-function mutations in PTEN, which explains why patients with these mutations (eg, those with the segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation, epidermal nevus, SOLAMEN [segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation, and epidermal nevus] syndrome) and patients with activating mutations in AKT1 (eg, those with PS) have overlapping but distinct clinical manifestations. Molecular genetic testing may be useful to confirm the diagnosis in individuals who meet clinical criteria and to establish the diagnosis in individuals with clinical findings that are ambiguous or mild. Further studies are necessary to progress the understanding and management of PS, which will require cooperation of geneticists, surgeons, and other specialists.
To the Editor:
A 12-year-old girl presented with discomfort and walking limitation caused by cutaneous masses on the plantar aspects of the feet with associated bone abnormalities that had started as several flesh-colored papules on the plantar surface of both feet at the age of 1 year. Over time the lesions gradually enlarged and formed irregular masses, more prominently on the right foot. At the age of 6 years, surgical correction was performed due to increased walking impairment and a skin examination that suggested connective tissue nevus. The results were good. However, the local tissue overgrowth recurred after 1 year. Slowly growing lesions were found at the surgical site, which necessitated hospitalization. Her medical history was negative for other disease. There was no family history of similar skin conditions and her parents were nonconsanguineous.
Physical examination revealed malnutrition and poor development in height as well as difficulty walking. She also had moderate scoliosis with a curve to the left. Dermatological examination showed multiple reddish cerebriform hyperplasia in both plantar areas; the right side was more severely involved (Figure 1A). There was macrodactyly of 2 toes on the right foot (Figure 1B). All results of routine blood examinations were within reference range. There were no abnormalities noted in the abdominal ultrasound and cardiac examinations. Plain radiographs of the spine and feet demonstrated scoliosis and exostosis on the calcaneus and bottom of the scaphoid. Histopathologic examination of tissue from the plantar cerebriform hyperplasia revealed hyperkeratosis, slight acanthosis and papillomatosis in the epidermis, and dense collagen bands and sparse elastic fibers in the dermis (Figure 2).


Given the clinical and radiologic manifestation, the diagnosis of Proteus syndrome (PS) was established. After taking into account the severe discomfort and the success of the first surgery, we performed a resection and full-thickness skin graft surgery once again. The feet recovered without any discomfort in daily life. The appearance of the skin graft area was normal 1 year following surgery (Figure 3). She was treated with spinal plate fixation at another institution, progressed well for 2 years, and was subsequently lost to follow-up.

Proteus syndrome is a multisystem disorder with a difficult diagnosis due to the variability of its manifestations. The worldwide incidence of this rare disorder is less than 1 per 1 million individuals, and it is thought to be caused by a somatic genetic alteration.1 Clinical characteristics include bone abnormalities, vascular malformations, dysregulation of fatty tissue, linear verrucous epidermal nevus, and cerebriform connective tissue nevus (CCTN). Although CCTN is not a common finding in patients with PS, it is considered a fairly specific sign with the greatest impact for the diagnosis of PS.2
The general feature of PS--asymmetric disproportionate overgrowth of tissues--appears at 6 to 18 months of age, which makes it challenging to diagnose disease earlier. The CCTN in our patient was present since 1 year of age.
To make a diagnosis of PS, one must have all the general criteria and various specific criteria. The revised diagnostic criteria for PS are given in the Table.3 According to the diagnostic criteria, our patient fulfilled the mandatory general criteria and had plantar CCTN, epidermal nevus, and dysregulated adipose tissue. The CCTN has notable diagnostic value in mildly affected patients, as it is absent in diseases included in the differential diagnosis such as neurofibromatosis, Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome, Maffucci syndrome, and Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome. Hemihyperplasia-multiple lipomatosis syndrome and CLOVES (congenital, lipomatous overgrowth, vascular malformations, epidermal nevi, and scoliosis/spinal/skeletal anomalies) syndrome also can present on the plantar surfaces, and lesions may be overgrown at birth but are softer and compressible, have wrinkles instead of deep folds, and tend to grow with the child rather than disproportionately as in PS.4
The epidermal nevi and vascular malformations generally do not spread or increase in number. In contrast, CCTN in PS grows throughout childhood but tends to remain stable in adulthood.4 Postponing surgical treatment until skin lesions stabilize appears to be the best option. However, for practical purposes, surgical intervention may be required at an earlier phase to address the severe functional and cosmetic consequences. Some patients require multiple orthopedic procedures over the ensuing years or decades to control the hyperplasia.3 New CCTN that developed from the prior surgical incision, macrodactyly of the fourth and fifth right toes, and scoliosis appeared when the patient came to our clinic for retreatment 1 year after the initial presentation. The asymmetrical and disproportionate overgrowth of tissues had moderately accelerated in that period. Considering the increasingly impaired walking, we performed a second surgery. On follow-up visits, the patient expressed improvement in daily life.

Studies had been performed to clarify the genetic bases of PS, and the somatic activating mutation in AKT1 (AKT serine/threonine kinase 1) was reported to be the cause of the disease.5,6 Germline PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog) mutations have been identified in some patients with overgrowth abnormalities of PS. However, given the misdiagnosis of PS with PTEN mutations and the notion that a gene alone cannot result in PS, the loss-of-function mutations of LEMD3 that have been reported in familial cutaneous collagenomas also may be related to the abnormal growth of connective and bone tissues that are typical of PS.7,8 Lindhurst et al5 concluded that PS is caused by a somatic activating mutation in AKT1, which proved the hypothesis of somatic mosaicism and implicated activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway in the characteristic clinical findings of overgrowth and tumor susceptibility in this disorder. AKT1 is activated by loss-of-function mutations in PTEN, which explains why patients with these mutations (eg, those with the segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation, epidermal nevus, SOLAMEN [segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation, and epidermal nevus] syndrome) and patients with activating mutations in AKT1 (eg, those with PS) have overlapping but distinct clinical manifestations. Molecular genetic testing may be useful to confirm the diagnosis in individuals who meet clinical criteria and to establish the diagnosis in individuals with clinical findings that are ambiguous or mild. Further studies are necessary to progress the understanding and management of PS, which will require cooperation of geneticists, surgeons, and other specialists.
- Popescu MD, Burnei G, Draghici L, et al. Proteus syndrome: a difficult diagnosis and management plan. J Med Life. 2014;7:563-566.
- Schepis C, Greco D, Siragusa M, et al. Cerebriform plantar hyperplasia: the major cutaneous feature of Proteus syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:374-376.
- Biesecker L. The challenges of Proteus syndrome: diagnosis and management. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006;14:1151-1157.
- Beachkofsky TM, Sapp JC, Biesecker LG, et al. Progressive overgrowth of the cerebriform connective tissue nevus in patients with Proteus syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:799-804.
- Lindhurst MJ, Sapp JC, Teer JK, et al. A mosaic activating mutation in AKT1 associated with the Proteus syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:611-619.
- Wieland I, Tinschert S, Zenker M. High-level somatic mosaicism of AKT1 c.49G>A mutation in skin scrapings from epidermal nevi enables non-invasive molecular diagnosis in patients with Proteus syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2013;161A:889-891.
- Cohen MJ, Turner JT, Biesecker LG. Proteus syndrome: misdiagnosis with PTEN mutations. Am J Med Genet A. 2003;122A:323-324.
- Di Stefani A, Gabellini M, Ferlosio A, et al. Cerebriform plantar hyperplasia: the clinico-pathological hallmark of Proteus syndrome. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:580-581.
- Popescu MD, Burnei G, Draghici L, et al. Proteus syndrome: a difficult diagnosis and management plan. J Med Life. 2014;7:563-566.
- Schepis C, Greco D, Siragusa M, et al. Cerebriform plantar hyperplasia: the major cutaneous feature of Proteus syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:374-376.
- Biesecker L. The challenges of Proteus syndrome: diagnosis and management. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006;14:1151-1157.
- Beachkofsky TM, Sapp JC, Biesecker LG, et al. Progressive overgrowth of the cerebriform connective tissue nevus in patients with Proteus syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:799-804.
- Lindhurst MJ, Sapp JC, Teer JK, et al. A mosaic activating mutation in AKT1 associated with the Proteus syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:611-619.
- Wieland I, Tinschert S, Zenker M. High-level somatic mosaicism of AKT1 c.49G>A mutation in skin scrapings from epidermal nevi enables non-invasive molecular diagnosis in patients with Proteus syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2013;161A:889-891.
- Cohen MJ, Turner JT, Biesecker LG. Proteus syndrome: misdiagnosis with PTEN mutations. Am J Med Genet A. 2003;122A:323-324.
- Di Stefani A, Gabellini M, Ferlosio A, et al. Cerebriform plantar hyperplasia: the clinico-pathological hallmark of Proteus syndrome. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:580-581.
Practice Points
- Proteus syndrome (PS) is a rare mosaic condition characterized by progressive overgrowth of skin, connective tissue, brain tissue, and other tissues.
- A somatic activating mutation of the AKT1 gene has been identified as a cause for developing PS.
- Distinct cutaneous features, including cerebriform connective tissue nevi (CCTN), epidermal nevi, vascular malformations, and adipose abnormalities, can alert the dermatologist to the underlying condition before the onset of asymmetric skeletal overgrowth.
- The CCTN in PS grows throughout childhood but tends to remain stable in adulthood. Postponing surgical treatment until skin lesions stabilize appears to be the best option. However, for practical purposes, surgical intervention may be required at an earlier phase to address the severe functional and cosmetic consequences.
Young patients suffer most from PBC
Youth is no ally when it comes to primary biliary cholangitis, according to a review of 1,990 patients in the United Kingdom–PBC cohort, the largest primary biliary cholangitis cohort in the world.
The investigators previously found that younger patients are less likely to respond to the mainstay treatment, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), and more likely to eventually need a liver transplant and die from the chronic autoimmune disease. Their new study found that they also suffer most from symptoms and have the lowest quality of life.
There was a linear relationship between age and quality of life (QoL) in this study of 1,990 primary biliary cholangitis patients; people who presented at age 20 had more than a 50% chance of reporting a poor QoL, while those presenting at age 70 had less than a 30% chance.
Overall perception of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)-related QoL and individual severity of all symptoms, as is true with UDCA response, were strongly related to the age of onset of disease, with younger presenting patients experiencing the greatest impact. Each 10-year increase in presentation age was associated with a 14% decrease in the risk of poor QoL (OR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.75–0.98; P less than .05), after adjustment for gender, disease severity, UDCA response, and disease duration. Presentations before the age of, perhaps, 50 years signal the need for greater vigilance (Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Nov;44[10]:1039-50).
The findings challenge “the view that PBC is a relatively benign condition of typically older people with limited clinical impact.” The biology “or natural history of PBC may differ between different patient groups, with younger-presenting patients having a more aggressive or materially different form of the disease.” Alternatively, the “enhanced symptom impact in younger patients may be [due to] age-related differences in [the expectation] of chronic disease, personal coping skills, and support networks,” said Jessica Dyson, MBBS, of Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne (England), and her associates.
QoL was most affected by social isolation. “Addressing and treating this single aspect could improve global quality of life significantly... Approaches could range from simple counseling to alert patients to the potential for social isolation, to the development of support groups, to the development of newer digital approaches to social networking through social media,” Dr. Dyson and her colleagues said.
Fatigue, anxiety, and depression also were especially vexing for younger patients, and could “be related to fear of the future and ability to cope, uncertainty as to disease prognosis, and frustration at limitations to life quality,” they said.
“Specifically targeting fatigue is likely to pay dividends,” but “there are currently no therapies able to do that.” However, “a more sociological approach targeting social isolation and the depression and anxiety which may accompany it are very viable approaches.” The findings should help guide future intervention trials, the team said.
QoL was assessed by the PBC-40, a 40 item questionnaire about fatigue; itch; and emotional, social, cognitive, and general symptoms. Each item is scored from 1 to 5, with higher scores indicating greater symptom severity.
The team used the results to assign patients a global QoL score from 1-5 points; scores of 1-3 indicated neutral or good QoL, while 4-5 signaled poor QoL. Overall, two-thirds of patients reported neutral/good scores, and a third had poor scores.
Meanwhile, patients doing well had a median of 18 of 50 possible points on the PBC-40 social score, while those not doing well had a median score of 34 points.
Patients in the study, 91% of whom were women, presented at a median age of 55 years, but 493 presented before the age of 50.
This research was supported by the British Medical Research Council and the National Institute for Health Research, among others. Dr. Dyson had no disclosures, but other authors reported relationships with a range of pharmaceutical companies, including Abbvie, GSK, Intercept, Novartis, and Pfizer.
Youth is no ally when it comes to primary biliary cholangitis, according to a review of 1,990 patients in the United Kingdom–PBC cohort, the largest primary biliary cholangitis cohort in the world.
The investigators previously found that younger patients are less likely to respond to the mainstay treatment, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), and more likely to eventually need a liver transplant and die from the chronic autoimmune disease. Their new study found that they also suffer most from symptoms and have the lowest quality of life.
There was a linear relationship between age and quality of life (QoL) in this study of 1,990 primary biliary cholangitis patients; people who presented at age 20 had more than a 50% chance of reporting a poor QoL, while those presenting at age 70 had less than a 30% chance.
Overall perception of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)-related QoL and individual severity of all symptoms, as is true with UDCA response, were strongly related to the age of onset of disease, with younger presenting patients experiencing the greatest impact. Each 10-year increase in presentation age was associated with a 14% decrease in the risk of poor QoL (OR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.75–0.98; P less than .05), after adjustment for gender, disease severity, UDCA response, and disease duration. Presentations before the age of, perhaps, 50 years signal the need for greater vigilance (Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Nov;44[10]:1039-50).
The findings challenge “the view that PBC is a relatively benign condition of typically older people with limited clinical impact.” The biology “or natural history of PBC may differ between different patient groups, with younger-presenting patients having a more aggressive or materially different form of the disease.” Alternatively, the “enhanced symptom impact in younger patients may be [due to] age-related differences in [the expectation] of chronic disease, personal coping skills, and support networks,” said Jessica Dyson, MBBS, of Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne (England), and her associates.
QoL was most affected by social isolation. “Addressing and treating this single aspect could improve global quality of life significantly... Approaches could range from simple counseling to alert patients to the potential for social isolation, to the development of support groups, to the development of newer digital approaches to social networking through social media,” Dr. Dyson and her colleagues said.
Fatigue, anxiety, and depression also were especially vexing for younger patients, and could “be related to fear of the future and ability to cope, uncertainty as to disease prognosis, and frustration at limitations to life quality,” they said.
“Specifically targeting fatigue is likely to pay dividends,” but “there are currently no therapies able to do that.” However, “a more sociological approach targeting social isolation and the depression and anxiety which may accompany it are very viable approaches.” The findings should help guide future intervention trials, the team said.
QoL was assessed by the PBC-40, a 40 item questionnaire about fatigue; itch; and emotional, social, cognitive, and general symptoms. Each item is scored from 1 to 5, with higher scores indicating greater symptom severity.
The team used the results to assign patients a global QoL score from 1-5 points; scores of 1-3 indicated neutral or good QoL, while 4-5 signaled poor QoL. Overall, two-thirds of patients reported neutral/good scores, and a third had poor scores.
Meanwhile, patients doing well had a median of 18 of 50 possible points on the PBC-40 social score, while those not doing well had a median score of 34 points.
Patients in the study, 91% of whom were women, presented at a median age of 55 years, but 493 presented before the age of 50.
This research was supported by the British Medical Research Council and the National Institute for Health Research, among others. Dr. Dyson had no disclosures, but other authors reported relationships with a range of pharmaceutical companies, including Abbvie, GSK, Intercept, Novartis, and Pfizer.
Youth is no ally when it comes to primary biliary cholangitis, according to a review of 1,990 patients in the United Kingdom–PBC cohort, the largest primary biliary cholangitis cohort in the world.
The investigators previously found that younger patients are less likely to respond to the mainstay treatment, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), and more likely to eventually need a liver transplant and die from the chronic autoimmune disease. Their new study found that they also suffer most from symptoms and have the lowest quality of life.
There was a linear relationship between age and quality of life (QoL) in this study of 1,990 primary biliary cholangitis patients; people who presented at age 20 had more than a 50% chance of reporting a poor QoL, while those presenting at age 70 had less than a 30% chance.
Overall perception of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)-related QoL and individual severity of all symptoms, as is true with UDCA response, were strongly related to the age of onset of disease, with younger presenting patients experiencing the greatest impact. Each 10-year increase in presentation age was associated with a 14% decrease in the risk of poor QoL (OR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.75–0.98; P less than .05), after adjustment for gender, disease severity, UDCA response, and disease duration. Presentations before the age of, perhaps, 50 years signal the need for greater vigilance (Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Nov;44[10]:1039-50).
The findings challenge “the view that PBC is a relatively benign condition of typically older people with limited clinical impact.” The biology “or natural history of PBC may differ between different patient groups, with younger-presenting patients having a more aggressive or materially different form of the disease.” Alternatively, the “enhanced symptom impact in younger patients may be [due to] age-related differences in [the expectation] of chronic disease, personal coping skills, and support networks,” said Jessica Dyson, MBBS, of Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne (England), and her associates.
QoL was most affected by social isolation. “Addressing and treating this single aspect could improve global quality of life significantly... Approaches could range from simple counseling to alert patients to the potential for social isolation, to the development of support groups, to the development of newer digital approaches to social networking through social media,” Dr. Dyson and her colleagues said.
Fatigue, anxiety, and depression also were especially vexing for younger patients, and could “be related to fear of the future and ability to cope, uncertainty as to disease prognosis, and frustration at limitations to life quality,” they said.
“Specifically targeting fatigue is likely to pay dividends,” but “there are currently no therapies able to do that.” However, “a more sociological approach targeting social isolation and the depression and anxiety which may accompany it are very viable approaches.” The findings should help guide future intervention trials, the team said.
QoL was assessed by the PBC-40, a 40 item questionnaire about fatigue; itch; and emotional, social, cognitive, and general symptoms. Each item is scored from 1 to 5, with higher scores indicating greater symptom severity.
The team used the results to assign patients a global QoL score from 1-5 points; scores of 1-3 indicated neutral or good QoL, while 4-5 signaled poor QoL. Overall, two-thirds of patients reported neutral/good scores, and a third had poor scores.
Meanwhile, patients doing well had a median of 18 of 50 possible points on the PBC-40 social score, while those not doing well had a median score of 34 points.
Patients in the study, 91% of whom were women, presented at a median age of 55 years, but 493 presented before the age of 50.
This research was supported by the British Medical Research Council and the National Institute for Health Research, among others. Dr. Dyson had no disclosures, but other authors reported relationships with a range of pharmaceutical companies, including Abbvie, GSK, Intercept, Novartis, and Pfizer.
FROM ALIMENTARY PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: There was a linear relationship between age and quality of life (QoL) in patients with primary biliary cholangitis, with younger presenting patients having the poorest QoL. Each 10-year increase in presentation age was associated with a 14% decrease in the risk of poor QoL.
Data source: Review of 1,990 patients in the United Kingdom–PBC cohort.
Disclosures: The work was funded by the British Medical Research Council and the National Institute for Health Research, among others. Dr. Dyson had no disclosures, but other authors reported relationships with a range of pharmaceutical companies, including Abbvie, GSK, Intercept, and Novartis.
Claimed missteps lead to brain damage: $53M award
Claimed missteps lead to brain damage: $53M award
At 2:00 AM, a woman at 40 weeks’ gestation went to a hospital because she felt a decrease in fetal movement. At birth, the baby was not breathing. He was rushed to the neonatal intensive care unit where he was resuscitated and placed on life support. He remained in critical care for 4 weeks. The child has cerebral palsy and cannot walk, talk, or care for himself. He will need 24-hour care for the rest of his life.
PARENT’S CLAIM:
The lawsuit cited 20 alleged missteps by physicians and nurses, including failure to: react to abnormal fetal heart-rate patterns that indicated fetal distress, perform a timely cesarean delivery, and follow a chain of command. During the 12 hours that the mother was in labor at the hospital, nurses and physicians allegedly ignored her. Although the fetal heart-rate monitor showed fetal distress, the mother continued to lie unattended. At 12:40 PM, physicians called for cesarean delivery due to fetal distress, but it took an hour for the child to be born.
The negligence of the hospital staff and delay in delivery caused hypoxia, resulting in cerebral palsy. All medical records from the hospital’s neonatal clinic show that he suffered hypoxia at birth.
HOSPITAL’S DEFENSE:
The mother and child were treated for an infection, which is a recognized cause of cerebral palsy. The child was born with normal blood oxygen levels. His injury occurred before the mother came to the hospital.
VERDICT:
A $53 million Illinois verdict was returned. The hospital applied for a mistrial based on allegedly inflammatory comments by the prosecuting attorney, but that was dismissed.
Birth trauma: $2.75M settlement
A woman had her first prenatal visit at 21 weeks’ gestation. Her advanced maternal age (39 years) and poor health history, including prior delivery of a baby with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), put her at risk; her prenatal care was transferred to a high-risk clinic.
At her next prenatal visit, records noted that the mother’s job required excessive standing, that she tested positive for marijuana, and that she was at risk for IUGR. Notes did not say that the mother was informed of her IUGR risk nor was a plan created for additional testing to monitor IUGR.
Ultrasonography (US) performed at 25 weeks’ gestation estimated that the baby’s weight was in the 11th- to 12th-week percentile. Amniotic fluid volume was noted as normal.
The mother missed her next appointment but returned at 28 weeks’ gestation, when she reported a headache and was found to have high blood pressure. US revealed normal fetal heart anatomy but amniotic fluid volume was noted to have decreased since the first US. The mother missed the next several appointments.
When she presented at 33 weeks’ gestation, her blood pressure was 160/97 mm Hg, fetal heart-rate tones were normal, and there was positive fetal movement. Fundal height measurement revealed a 3-cm discrepancy in date and size, suggesting a small baby, decreased amniotic fluid, or both. The ObGyn ordered testing for the next day. When a nonstress test performed from 8:44 AM to 9:10 AM was nonreassuring, the mother was ordered to immediately go to the hospital. She did not arrive at the hospital until 11:13 AM, when she was placed on fetal heart-rate monitor; test results were nonreassuring. At 11:30 AM, US revealed IUGR and oligohydramnios. An urgent cesarean delivery was performed and the baby was born at 11:56 AM.
The child’s Apgar scores were 4 and 9 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. The baby developed white matter brain damage and grade III and IV intraventricular hemorrhages due to hypoxia, ischemia, and metabolic acidosis. A maternal drug screen was positive for marijuana. Placental pathology revealed multiple abnormalities including placental infarcts involving approximately 50% of placental tissue, abnormal vascular changes, intervillous fibrin deposition, and chronic villitis.
At trial, the child had developmental delays, cognitive defects, learning disabilities, and breakthrough seizures.
PARENT’S CLAIM:
The mother claimed that the high-risk clinic was negligent. A plan should have been put into place at her first visit to monitor for IUGR based on her history. She was not advised of her risk of having another IUGR baby. Fundal height measurement, US to test for IUGR, or assessments of fetal heart-rate tones and fetal movement were not performed regularly. If a nonstress test had been performed earlier than 33 weeks’ gestation, she might have been admitted to the hospital for monitoring and earlier delivery, resulting in a healthier baby.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The mother was noncompliant and missed most of her prenatal appointments. She also continued to smoke marijuana throughout her pregnancy although she was told to stop. When the mother arrived at the prenatal clinic at 33 weeks’ gestation, tests were ordered and delivery occurred in a timely fashion. Any problems suffered by the child were a result of prematurity and damage that occurred during the 5 weeks of missed prenatal appointments.
VERDICT:
A $2.75M Missouri settlement was reached.
Who should have delivered the baby?
A mother’s prenatal care was managed by her family practitioner (FP). The mother went to the FP for induction of labor, but it was unsuccessful. Three days later, the baby was delivered by the FP and began having seizures a few minutes after birth. The child is quadriplegic and has severe cerebral palsy.
PARENTS’ CLAIM:
The FP was negligent in managing labor and delivery. She should have called an ObGyn to manage the labor. She failed to monitor fetal heart-rate tracings and failed to order an emergency cesarean delivery. The FP mismanaged the baby’s condition upon delivery and seizures started.
PHYSICIAN’S DEFENSE:
The FP properly managed the delivery and postdelivery complications. The brain injury had nothing to do with the birth; it was instead caused by a stroke disorder that occurred 3 to 7 days before delivery.
VERDICT:
A Minnesota defense verdict was returned.
Undiagnosed H1N1 influenza (swine flu) during pregnancy; mother and child die: $16.7M verdict
At 7 months’ gestation, a 27-year-old woman presented to a clinic on June 26 with a runny nose, congestion, cough, wheezing, chills, and sweats. The physician noted concern about proteinuria and that the patient reported chills and sweats, but that he was uncertain as to the symptoms’ cause. He recommended that she see her ObGyn immediately and report to the emergency department (ED) if symptoms worsened. The patient called her ObGyn to report having a temperature between 94˚F and 103˚F and taking acetaminophen. The next day, she saw a nurse practitioner in the ObGyn’s office who documented that the patient was not given antiviral medication.
On June 29, the patient was still feeling ill and went to the ED. Although a physician planned to discharge her, an ObGyn nurse recognized that the patient was too ill to leave and had her admitted.
The patient’s condition worsened overnight and she was transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU), where she was intubated and put on a ventilator. Medical notes read “as whether influenza was present was unclear…Tamiflu will be started, but the efficacy of it this late into a possible influenza episode is extremely questionable.” ICU physicians believed that the best option was to deliver the child. After the patient’s husband gave permission, the child was born by cesarean delivery. The mother never regained full consciousness and remained in a medically induced coma. She died on August 11 after the family decided to remove life support.
After being given the diagnosis of intrauterine hypoxia, the child remained in intensive care for several weeks and then was discharged home. Seven months later, the father found his daughter in bed, not breathing, which physicians believed was an episode of sudden infant death syndrome. The father performed CPR and rushed her to the hospital. Physicians tried twice to take the child off the ventilator, but she could not breathe without assistance. On February 21, life support was removed and the child died.
ESTATES’ CLAIM:
The clinic and its physician were negligent for failing to recognize that the mother had influenza; she presented with classic flu symptoms during a worldwide pandemic. In the several months before the patient’s visit, the clinic had received notices from health authorities alerting medical professionals to the dangers of H1N1 influenza, or Swine Flu. The clinic also had received, before the patient’s visit, information warning of an elevated risk of H1N1 to pregnant women, with instructions to administer oseltamivir phosphate (Tamiflu) to any pregnant woman suspected of having influenza.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The clinic and physician denied negligence, claiming that treatment of the mother was appropriate.
VERDICT:
A $16.7 million Washington verdict was returned.
Mother claims to being uninformed of antiepileptics’ risks
A woman with epilepsy gave birth to a child with physical and cognitive birth defects.
PARENT’S CLAIM:
The mother claimed that, although she was of child-bearing age, she had never been informed of the risk of birth defects associated with taking an antiepileptic medication. Had she known of the risk, she would not have chosen to conceive. The physicians should have prescribed a different antiepileptic drug.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The clinic’s physicians met the standard of care in prescribing the drug. They properly informed the mother of the risks of taking the antiepileptic drug during pregnancy. The patient was allergic to all other antiepileptic drugs available at the time, so an alternative was not available.
VERDICT:
An Illinois defense verdict was returned for the clinic.
Mother has stroke during delivery: $3M settlement
A 42-year-old woman had a hemorrhagic stroke during the delivery of her first child. She remained hospitalized for observation with a medical plan to insert a drain if her condition worsened. Initially she did well, but she then began to have episodes of decreased consciousness and loss of function and later became unresponsive. Her physicians then undertook an emergency procedure to attempt to drain blood from her brain, but the surgical measure did not prevent her from incurring significant cognitive and physical injuries.
PATIENT’S CLAIM:
The agreed-upon medical plan of treatment was not followed, resulting in severe brain damage to the patient.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The case was settled during the trial.
VERDICT:
A $3 million Massachusetts settlement was reached.
Did delayed cesarean cause cognitive defects?
When fetal distress was detected, the nurse called the patient’s ObGyn at 12:30 AM. The ObGyn arrived at the hospital at 12:48 AM, ordered a cesarean delivery at 12:56 AM, and the baby was born at 1:20 AM.
PARENTS’ CLAIM:
The ObGyn was negligent for not calling for the hospital’s on-duty resident physician to become involved in the case when the nurse phoned at 12:30 AM. If the ObGyn had done so, cesarean delivery would have been ordered and completed earlier, which would have averted the child’s injuries, including cognitive and physical impairments.
PHYSICIAN’S DEFENSE:
The ObGyn asserted that, based on the information provided to her, there was no reason to request the resident’s involvement. An earlier cesarean delivery was not necessary based on fetal heart-rate monitoring strip results. The ObGyn acted in a timely manner when calling for cesarean delivery. There was no concrete evidence that any alleged delay caused the child’s injuries.
VERDICT:
An Illinois defense verdict was returned.
These cases were selected by the editors of OBG Management from Medical Malpractice Verdicts, Settlements & Experts, with permission of the editor, Lewis Laska (www.verdictslaska.com). The information available to the editors about the cases presented here is sometimes incomplete. Moreover, the cases may or may not have merit. Nevertheless, these cases represent the types of clinical situations that typically result in litigation and are meant to illustrate nationwide variation in jury verdicts and awards.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to [email protected]. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
Claimed missteps lead to brain damage: $53M award
At 2:00 AM, a woman at 40 weeks’ gestation went to a hospital because she felt a decrease in fetal movement. At birth, the baby was not breathing. He was rushed to the neonatal intensive care unit where he was resuscitated and placed on life support. He remained in critical care for 4 weeks. The child has cerebral palsy and cannot walk, talk, or care for himself. He will need 24-hour care for the rest of his life.
PARENT’S CLAIM:
The lawsuit cited 20 alleged missteps by physicians and nurses, including failure to: react to abnormal fetal heart-rate patterns that indicated fetal distress, perform a timely cesarean delivery, and follow a chain of command. During the 12 hours that the mother was in labor at the hospital, nurses and physicians allegedly ignored her. Although the fetal heart-rate monitor showed fetal distress, the mother continued to lie unattended. At 12:40 PM, physicians called for cesarean delivery due to fetal distress, but it took an hour for the child to be born.
The negligence of the hospital staff and delay in delivery caused hypoxia, resulting in cerebral palsy. All medical records from the hospital’s neonatal clinic show that he suffered hypoxia at birth.
HOSPITAL’S DEFENSE:
The mother and child were treated for an infection, which is a recognized cause of cerebral palsy. The child was born with normal blood oxygen levels. His injury occurred before the mother came to the hospital.
VERDICT:
A $53 million Illinois verdict was returned. The hospital applied for a mistrial based on allegedly inflammatory comments by the prosecuting attorney, but that was dismissed.
Birth trauma: $2.75M settlement
A woman had her first prenatal visit at 21 weeks’ gestation. Her advanced maternal age (39 years) and poor health history, including prior delivery of a baby with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), put her at risk; her prenatal care was transferred to a high-risk clinic.
At her next prenatal visit, records noted that the mother’s job required excessive standing, that she tested positive for marijuana, and that she was at risk for IUGR. Notes did not say that the mother was informed of her IUGR risk nor was a plan created for additional testing to monitor IUGR.
Ultrasonography (US) performed at 25 weeks’ gestation estimated that the baby’s weight was in the 11th- to 12th-week percentile. Amniotic fluid volume was noted as normal.
The mother missed her next appointment but returned at 28 weeks’ gestation, when she reported a headache and was found to have high blood pressure. US revealed normal fetal heart anatomy but amniotic fluid volume was noted to have decreased since the first US. The mother missed the next several appointments.
When she presented at 33 weeks’ gestation, her blood pressure was 160/97 mm Hg, fetal heart-rate tones were normal, and there was positive fetal movement. Fundal height measurement revealed a 3-cm discrepancy in date and size, suggesting a small baby, decreased amniotic fluid, or both. The ObGyn ordered testing for the next day. When a nonstress test performed from 8:44 AM to 9:10 AM was nonreassuring, the mother was ordered to immediately go to the hospital. She did not arrive at the hospital until 11:13 AM, when she was placed on fetal heart-rate monitor; test results were nonreassuring. At 11:30 AM, US revealed IUGR and oligohydramnios. An urgent cesarean delivery was performed and the baby was born at 11:56 AM.
The child’s Apgar scores were 4 and 9 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. The baby developed white matter brain damage and grade III and IV intraventricular hemorrhages due to hypoxia, ischemia, and metabolic acidosis. A maternal drug screen was positive for marijuana. Placental pathology revealed multiple abnormalities including placental infarcts involving approximately 50% of placental tissue, abnormal vascular changes, intervillous fibrin deposition, and chronic villitis.
At trial, the child had developmental delays, cognitive defects, learning disabilities, and breakthrough seizures.
PARENT’S CLAIM:
The mother claimed that the high-risk clinic was negligent. A plan should have been put into place at her first visit to monitor for IUGR based on her history. She was not advised of her risk of having another IUGR baby. Fundal height measurement, US to test for IUGR, or assessments of fetal heart-rate tones and fetal movement were not performed regularly. If a nonstress test had been performed earlier than 33 weeks’ gestation, she might have been admitted to the hospital for monitoring and earlier delivery, resulting in a healthier baby.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The mother was noncompliant and missed most of her prenatal appointments. She also continued to smoke marijuana throughout her pregnancy although she was told to stop. When the mother arrived at the prenatal clinic at 33 weeks’ gestation, tests were ordered and delivery occurred in a timely fashion. Any problems suffered by the child were a result of prematurity and damage that occurred during the 5 weeks of missed prenatal appointments.
VERDICT:
A $2.75M Missouri settlement was reached.
Who should have delivered the baby?
A mother’s prenatal care was managed by her family practitioner (FP). The mother went to the FP for induction of labor, but it was unsuccessful. Three days later, the baby was delivered by the FP and began having seizures a few minutes after birth. The child is quadriplegic and has severe cerebral palsy.
PARENTS’ CLAIM:
The FP was negligent in managing labor and delivery. She should have called an ObGyn to manage the labor. She failed to monitor fetal heart-rate tracings and failed to order an emergency cesarean delivery. The FP mismanaged the baby’s condition upon delivery and seizures started.
PHYSICIAN’S DEFENSE:
The FP properly managed the delivery and postdelivery complications. The brain injury had nothing to do with the birth; it was instead caused by a stroke disorder that occurred 3 to 7 days before delivery.
VERDICT:
A Minnesota defense verdict was returned.
Undiagnosed H1N1 influenza (swine flu) during pregnancy; mother and child die: $16.7M verdict
At 7 months’ gestation, a 27-year-old woman presented to a clinic on June 26 with a runny nose, congestion, cough, wheezing, chills, and sweats. The physician noted concern about proteinuria and that the patient reported chills and sweats, but that he was uncertain as to the symptoms’ cause. He recommended that she see her ObGyn immediately and report to the emergency department (ED) if symptoms worsened. The patient called her ObGyn to report having a temperature between 94˚F and 103˚F and taking acetaminophen. The next day, she saw a nurse practitioner in the ObGyn’s office who documented that the patient was not given antiviral medication.
On June 29, the patient was still feeling ill and went to the ED. Although a physician planned to discharge her, an ObGyn nurse recognized that the patient was too ill to leave and had her admitted.
The patient’s condition worsened overnight and she was transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU), where she was intubated and put on a ventilator. Medical notes read “as whether influenza was present was unclear…Tamiflu will be started, but the efficacy of it this late into a possible influenza episode is extremely questionable.” ICU physicians believed that the best option was to deliver the child. After the patient’s husband gave permission, the child was born by cesarean delivery. The mother never regained full consciousness and remained in a medically induced coma. She died on August 11 after the family decided to remove life support.
After being given the diagnosis of intrauterine hypoxia, the child remained in intensive care for several weeks and then was discharged home. Seven months later, the father found his daughter in bed, not breathing, which physicians believed was an episode of sudden infant death syndrome. The father performed CPR and rushed her to the hospital. Physicians tried twice to take the child off the ventilator, but she could not breathe without assistance. On February 21, life support was removed and the child died.
ESTATES’ CLAIM:
The clinic and its physician were negligent for failing to recognize that the mother had influenza; she presented with classic flu symptoms during a worldwide pandemic. In the several months before the patient’s visit, the clinic had received notices from health authorities alerting medical professionals to the dangers of H1N1 influenza, or Swine Flu. The clinic also had received, before the patient’s visit, information warning of an elevated risk of H1N1 to pregnant women, with instructions to administer oseltamivir phosphate (Tamiflu) to any pregnant woman suspected of having influenza.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The clinic and physician denied negligence, claiming that treatment of the mother was appropriate.
VERDICT:
A $16.7 million Washington verdict was returned.
Mother claims to being uninformed of antiepileptics’ risks
A woman with epilepsy gave birth to a child with physical and cognitive birth defects.
PARENT’S CLAIM:
The mother claimed that, although she was of child-bearing age, she had never been informed of the risk of birth defects associated with taking an antiepileptic medication. Had she known of the risk, she would not have chosen to conceive. The physicians should have prescribed a different antiepileptic drug.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The clinic’s physicians met the standard of care in prescribing the drug. They properly informed the mother of the risks of taking the antiepileptic drug during pregnancy. The patient was allergic to all other antiepileptic drugs available at the time, so an alternative was not available.
VERDICT:
An Illinois defense verdict was returned for the clinic.
Mother has stroke during delivery: $3M settlement
A 42-year-old woman had a hemorrhagic stroke during the delivery of her first child. She remained hospitalized for observation with a medical plan to insert a drain if her condition worsened. Initially she did well, but she then began to have episodes of decreased consciousness and loss of function and later became unresponsive. Her physicians then undertook an emergency procedure to attempt to drain blood from her brain, but the surgical measure did not prevent her from incurring significant cognitive and physical injuries.
PATIENT’S CLAIM:
The agreed-upon medical plan of treatment was not followed, resulting in severe brain damage to the patient.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The case was settled during the trial.
VERDICT:
A $3 million Massachusetts settlement was reached.
Did delayed cesarean cause cognitive defects?
When fetal distress was detected, the nurse called the patient’s ObGyn at 12:30 AM. The ObGyn arrived at the hospital at 12:48 AM, ordered a cesarean delivery at 12:56 AM, and the baby was born at 1:20 AM.
PARENTS’ CLAIM:
The ObGyn was negligent for not calling for the hospital’s on-duty resident physician to become involved in the case when the nurse phoned at 12:30 AM. If the ObGyn had done so, cesarean delivery would have been ordered and completed earlier, which would have averted the child’s injuries, including cognitive and physical impairments.
PHYSICIAN’S DEFENSE:
The ObGyn asserted that, based on the information provided to her, there was no reason to request the resident’s involvement. An earlier cesarean delivery was not necessary based on fetal heart-rate monitoring strip results. The ObGyn acted in a timely manner when calling for cesarean delivery. There was no concrete evidence that any alleged delay caused the child’s injuries.
VERDICT:
An Illinois defense verdict was returned.
These cases were selected by the editors of OBG Management from Medical Malpractice Verdicts, Settlements & Experts, with permission of the editor, Lewis Laska (www.verdictslaska.com). The information available to the editors about the cases presented here is sometimes incomplete. Moreover, the cases may or may not have merit. Nevertheless, these cases represent the types of clinical situations that typically result in litigation and are meant to illustrate nationwide variation in jury verdicts and awards.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to [email protected]. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
Claimed missteps lead to brain damage: $53M award
At 2:00 AM, a woman at 40 weeks’ gestation went to a hospital because she felt a decrease in fetal movement. At birth, the baby was not breathing. He was rushed to the neonatal intensive care unit where he was resuscitated and placed on life support. He remained in critical care for 4 weeks. The child has cerebral palsy and cannot walk, talk, or care for himself. He will need 24-hour care for the rest of his life.
PARENT’S CLAIM:
The lawsuit cited 20 alleged missteps by physicians and nurses, including failure to: react to abnormal fetal heart-rate patterns that indicated fetal distress, perform a timely cesarean delivery, and follow a chain of command. During the 12 hours that the mother was in labor at the hospital, nurses and physicians allegedly ignored her. Although the fetal heart-rate monitor showed fetal distress, the mother continued to lie unattended. At 12:40 PM, physicians called for cesarean delivery due to fetal distress, but it took an hour for the child to be born.
The negligence of the hospital staff and delay in delivery caused hypoxia, resulting in cerebral palsy. All medical records from the hospital’s neonatal clinic show that he suffered hypoxia at birth.
HOSPITAL’S DEFENSE:
The mother and child were treated for an infection, which is a recognized cause of cerebral palsy. The child was born with normal blood oxygen levels. His injury occurred before the mother came to the hospital.
VERDICT:
A $53 million Illinois verdict was returned. The hospital applied for a mistrial based on allegedly inflammatory comments by the prosecuting attorney, but that was dismissed.
Birth trauma: $2.75M settlement
A woman had her first prenatal visit at 21 weeks’ gestation. Her advanced maternal age (39 years) and poor health history, including prior delivery of a baby with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), put her at risk; her prenatal care was transferred to a high-risk clinic.
At her next prenatal visit, records noted that the mother’s job required excessive standing, that she tested positive for marijuana, and that she was at risk for IUGR. Notes did not say that the mother was informed of her IUGR risk nor was a plan created for additional testing to monitor IUGR.
Ultrasonography (US) performed at 25 weeks’ gestation estimated that the baby’s weight was in the 11th- to 12th-week percentile. Amniotic fluid volume was noted as normal.
The mother missed her next appointment but returned at 28 weeks’ gestation, when she reported a headache and was found to have high blood pressure. US revealed normal fetal heart anatomy but amniotic fluid volume was noted to have decreased since the first US. The mother missed the next several appointments.
When she presented at 33 weeks’ gestation, her blood pressure was 160/97 mm Hg, fetal heart-rate tones were normal, and there was positive fetal movement. Fundal height measurement revealed a 3-cm discrepancy in date and size, suggesting a small baby, decreased amniotic fluid, or both. The ObGyn ordered testing for the next day. When a nonstress test performed from 8:44 AM to 9:10 AM was nonreassuring, the mother was ordered to immediately go to the hospital. She did not arrive at the hospital until 11:13 AM, when she was placed on fetal heart-rate monitor; test results were nonreassuring. At 11:30 AM, US revealed IUGR and oligohydramnios. An urgent cesarean delivery was performed and the baby was born at 11:56 AM.
The child’s Apgar scores were 4 and 9 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. The baby developed white matter brain damage and grade III and IV intraventricular hemorrhages due to hypoxia, ischemia, and metabolic acidosis. A maternal drug screen was positive for marijuana. Placental pathology revealed multiple abnormalities including placental infarcts involving approximately 50% of placental tissue, abnormal vascular changes, intervillous fibrin deposition, and chronic villitis.
At trial, the child had developmental delays, cognitive defects, learning disabilities, and breakthrough seizures.
PARENT’S CLAIM:
The mother claimed that the high-risk clinic was negligent. A plan should have been put into place at her first visit to monitor for IUGR based on her history. She was not advised of her risk of having another IUGR baby. Fundal height measurement, US to test for IUGR, or assessments of fetal heart-rate tones and fetal movement were not performed regularly. If a nonstress test had been performed earlier than 33 weeks’ gestation, she might have been admitted to the hospital for monitoring and earlier delivery, resulting in a healthier baby.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The mother was noncompliant and missed most of her prenatal appointments. She also continued to smoke marijuana throughout her pregnancy although she was told to stop. When the mother arrived at the prenatal clinic at 33 weeks’ gestation, tests were ordered and delivery occurred in a timely fashion. Any problems suffered by the child were a result of prematurity and damage that occurred during the 5 weeks of missed prenatal appointments.
VERDICT:
A $2.75M Missouri settlement was reached.
Who should have delivered the baby?
A mother’s prenatal care was managed by her family practitioner (FP). The mother went to the FP for induction of labor, but it was unsuccessful. Three days later, the baby was delivered by the FP and began having seizures a few minutes after birth. The child is quadriplegic and has severe cerebral palsy.
PARENTS’ CLAIM:
The FP was negligent in managing labor and delivery. She should have called an ObGyn to manage the labor. She failed to monitor fetal heart-rate tracings and failed to order an emergency cesarean delivery. The FP mismanaged the baby’s condition upon delivery and seizures started.
PHYSICIAN’S DEFENSE:
The FP properly managed the delivery and postdelivery complications. The brain injury had nothing to do with the birth; it was instead caused by a stroke disorder that occurred 3 to 7 days before delivery.
VERDICT:
A Minnesota defense verdict was returned.
Undiagnosed H1N1 influenza (swine flu) during pregnancy; mother and child die: $16.7M verdict
At 7 months’ gestation, a 27-year-old woman presented to a clinic on June 26 with a runny nose, congestion, cough, wheezing, chills, and sweats. The physician noted concern about proteinuria and that the patient reported chills and sweats, but that he was uncertain as to the symptoms’ cause. He recommended that she see her ObGyn immediately and report to the emergency department (ED) if symptoms worsened. The patient called her ObGyn to report having a temperature between 94˚F and 103˚F and taking acetaminophen. The next day, she saw a nurse practitioner in the ObGyn’s office who documented that the patient was not given antiviral medication.
On June 29, the patient was still feeling ill and went to the ED. Although a physician planned to discharge her, an ObGyn nurse recognized that the patient was too ill to leave and had her admitted.
The patient’s condition worsened overnight and she was transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU), where she was intubated and put on a ventilator. Medical notes read “as whether influenza was present was unclear…Tamiflu will be started, but the efficacy of it this late into a possible influenza episode is extremely questionable.” ICU physicians believed that the best option was to deliver the child. After the patient’s husband gave permission, the child was born by cesarean delivery. The mother never regained full consciousness and remained in a medically induced coma. She died on August 11 after the family decided to remove life support.
After being given the diagnosis of intrauterine hypoxia, the child remained in intensive care for several weeks and then was discharged home. Seven months later, the father found his daughter in bed, not breathing, which physicians believed was an episode of sudden infant death syndrome. The father performed CPR and rushed her to the hospital. Physicians tried twice to take the child off the ventilator, but she could not breathe without assistance. On February 21, life support was removed and the child died.
ESTATES’ CLAIM:
The clinic and its physician were negligent for failing to recognize that the mother had influenza; she presented with classic flu symptoms during a worldwide pandemic. In the several months before the patient’s visit, the clinic had received notices from health authorities alerting medical professionals to the dangers of H1N1 influenza, or Swine Flu. The clinic also had received, before the patient’s visit, information warning of an elevated risk of H1N1 to pregnant women, with instructions to administer oseltamivir phosphate (Tamiflu) to any pregnant woman suspected of having influenza.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The clinic and physician denied negligence, claiming that treatment of the mother was appropriate.
VERDICT:
A $16.7 million Washington verdict was returned.
Mother claims to being uninformed of antiepileptics’ risks
A woman with epilepsy gave birth to a child with physical and cognitive birth defects.
PARENT’S CLAIM:
The mother claimed that, although she was of child-bearing age, she had never been informed of the risk of birth defects associated with taking an antiepileptic medication. Had she known of the risk, she would not have chosen to conceive. The physicians should have prescribed a different antiepileptic drug.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The clinic’s physicians met the standard of care in prescribing the drug. They properly informed the mother of the risks of taking the antiepileptic drug during pregnancy. The patient was allergic to all other antiepileptic drugs available at the time, so an alternative was not available.
VERDICT:
An Illinois defense verdict was returned for the clinic.
Mother has stroke during delivery: $3M settlement
A 42-year-old woman had a hemorrhagic stroke during the delivery of her first child. She remained hospitalized for observation with a medical plan to insert a drain if her condition worsened. Initially she did well, but she then began to have episodes of decreased consciousness and loss of function and later became unresponsive. Her physicians then undertook an emergency procedure to attempt to drain blood from her brain, but the surgical measure did not prevent her from incurring significant cognitive and physical injuries.
PATIENT’S CLAIM:
The agreed-upon medical plan of treatment was not followed, resulting in severe brain damage to the patient.
DEFENDANTS’ DEFENSE:
The case was settled during the trial.
VERDICT:
A $3 million Massachusetts settlement was reached.
Did delayed cesarean cause cognitive defects?
When fetal distress was detected, the nurse called the patient’s ObGyn at 12:30 AM. The ObGyn arrived at the hospital at 12:48 AM, ordered a cesarean delivery at 12:56 AM, and the baby was born at 1:20 AM.
PARENTS’ CLAIM:
The ObGyn was negligent for not calling for the hospital’s on-duty resident physician to become involved in the case when the nurse phoned at 12:30 AM. If the ObGyn had done so, cesarean delivery would have been ordered and completed earlier, which would have averted the child’s injuries, including cognitive and physical impairments.
PHYSICIAN’S DEFENSE:
The ObGyn asserted that, based on the information provided to her, there was no reason to request the resident’s involvement. An earlier cesarean delivery was not necessary based on fetal heart-rate monitoring strip results. The ObGyn acted in a timely manner when calling for cesarean delivery. There was no concrete evidence that any alleged delay caused the child’s injuries.
VERDICT:
An Illinois defense verdict was returned.
These cases were selected by the editors of OBG Management from Medical Malpractice Verdicts, Settlements & Experts, with permission of the editor, Lewis Laska (www.verdictslaska.com). The information available to the editors about the cases presented here is sometimes incomplete. Moreover, the cases may or may not have merit. Nevertheless, these cases represent the types of clinical situations that typically result in litigation and are meant to illustrate nationwide variation in jury verdicts and awards.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to [email protected]. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
FDA Boxed Warnings
The FDA’s MedWatch program safety labeling changes for boxed warnings are compiled quarterly for drugs and therapeutic biologics where important changes have been made to the safety information. You can search these and other label changes in the Drug Safety Labeling Changes (SLC) database, where data are available to the public in downloadable and searchable formats. Boxed warnings are ordinarily used to highlight either adverse reactions so serious in proportion to the potential bene t from the drug that it is essential that it be considered in assessing the risks and bene ts of using the drug; or serious adverse reactions that can be prevented/reduced in frequency or severity by appropriate use of the drug; or FDA approved the drug with restrictions to ensure safe use because FDA concluded that the drug can be safely used only if distribution or use is restricted.
NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS:
Updated Warning May 2016
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use.
• NSAID is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events.
JUXTAPID (lomitapide) capsules:
- Added section to warning May 2016
Prescribe Juxtapid only to patients with a clinical or laboratory diagnosis consistent with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH). The safety and effectiveness of Juxtapid have not been established in patients with hypercholesterolemia who do not have HoFH.
KADCYLA (ado-trastuzumab emtansine) injection, for intravenous:
- Edited and updated warning April 2016
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Exposure to Kadcyla during pregnancy can result in embryo-fetal harm. Advise patients of these risks and the need for effective contraception.
KYNAMRO (mipomersen sodium) solution for subcutaneous injection:
- Added section to warning May 2016
Prescribe Kynamro only to patients with a clinical or laboratory diagnosis consistent with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH). The safety and effectiveness of Kynamro have not been established in patients with hypercholesterolemia who do not have HoFH.
The FDA’s MedWatch program safety labeling changes for boxed warnings are compiled quarterly for drugs and therapeutic biologics where important changes have been made to the safety information. You can search these and other label changes in the Drug Safety Labeling Changes (SLC) database, where data are available to the public in downloadable and searchable formats. Boxed warnings are ordinarily used to highlight either adverse reactions so serious in proportion to the potential bene t from the drug that it is essential that it be considered in assessing the risks and bene ts of using the drug; or serious adverse reactions that can be prevented/reduced in frequency or severity by appropriate use of the drug; or FDA approved the drug with restrictions to ensure safe use because FDA concluded that the drug can be safely used only if distribution or use is restricted.
NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS:
Updated Warning May 2016
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use.
• NSAID is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events.
JUXTAPID (lomitapide) capsules:
- Added section to warning May 2016
Prescribe Juxtapid only to patients with a clinical or laboratory diagnosis consistent with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH). The safety and effectiveness of Juxtapid have not been established in patients with hypercholesterolemia who do not have HoFH.
KADCYLA (ado-trastuzumab emtansine) injection, for intravenous:
- Edited and updated warning April 2016
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Exposure to Kadcyla during pregnancy can result in embryo-fetal harm. Advise patients of these risks and the need for effective contraception.
KYNAMRO (mipomersen sodium) solution for subcutaneous injection:
- Added section to warning May 2016
Prescribe Kynamro only to patients with a clinical or laboratory diagnosis consistent with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH). The safety and effectiveness of Kynamro have not been established in patients with hypercholesterolemia who do not have HoFH.
The FDA’s MedWatch program safety labeling changes for boxed warnings are compiled quarterly for drugs and therapeutic biologics where important changes have been made to the safety information. You can search these and other label changes in the Drug Safety Labeling Changes (SLC) database, where data are available to the public in downloadable and searchable formats. Boxed warnings are ordinarily used to highlight either adverse reactions so serious in proportion to the potential bene t from the drug that it is essential that it be considered in assessing the risks and bene ts of using the drug; or serious adverse reactions that can be prevented/reduced in frequency or severity by appropriate use of the drug; or FDA approved the drug with restrictions to ensure safe use because FDA concluded that the drug can be safely used only if distribution or use is restricted.
NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS:
Updated Warning May 2016
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use.
• NSAID is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events.
JUXTAPID (lomitapide) capsules:
- Added section to warning May 2016
Prescribe Juxtapid only to patients with a clinical or laboratory diagnosis consistent with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH). The safety and effectiveness of Juxtapid have not been established in patients with hypercholesterolemia who do not have HoFH.
KADCYLA (ado-trastuzumab emtansine) injection, for intravenous:
- Edited and updated warning April 2016
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Exposure to Kadcyla during pregnancy can result in embryo-fetal harm. Advise patients of these risks and the need for effective contraception.
KYNAMRO (mipomersen sodium) solution for subcutaneous injection:
- Added section to warning May 2016
Prescribe Kynamro only to patients with a clinical or laboratory diagnosis consistent with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH). The safety and effectiveness of Kynamro have not been established in patients with hypercholesterolemia who do not have HoFH.