User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
Powered by CHEST Physician, Clinician Reviews, MDedge Family Medicine, Internal Medicine News, and The Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management.
WHO calls for pause on booster doses
The World Health Organization is calling on wealthy nations to wait to give their citizens booster doses of COVID-19 vaccines until at least the end of September to give more people in other countries a chance to get a first dose of these lifesaving shots.
WHO Director-General Tedros Ghebreyesus, PhD, said that more than 80% of the 4 billion vaccine doses given around the world had been distributed to high-income countries, though they represent less than half the world’s population.
“I understand the concern of all governments to protect their people from the Delta variant,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said. “But we cannot accept countries that have already used most of the global supply of vaccines using even more of it, while the world’s most vulnerable people remain unprotected.”
So far, high-income countries have given about 100 vaccine doses for every 100 people, while low-income countries have given just 1.5 doses for every 100 people.
“Which means, in some of the most vulnerable countries in the world with the weakest health systems, health care workers are working without protection. … the older populations remain at high risk,” said Bruce Aylward, MD, the WHO’s senior adviser on organizational change.
But not everyone agrees.
Leana Wen, MD, a visiting professor at the Milken Institute School of Public Health at George Washington University, Washington, said there are doses already in the United States that won’t last long enough to be sent elsewhere.
“Yes, we need to get vaccines to the world (which also includes helping with distribution, not just supply), but there are doses expiring here in the U.S.,” she said on Twitter. “Why not allow those immunosuppressed to receive them?”
Israel became the first country to start giving some residents booster shots on Sunday, offering extra doses to seniors who are more than 5 months past their last vaccinations. On Monday, Germany announced it would also give booster doses to vulnerable patients, such as nursing home residents, beginning in September.
Dr. Aylward said the moratorium was all about “trying to put a hold on those policies until and unless we get the rest of the world caught up.”
He said it’s clear from the emergence of variant after variant that if we don’t stop the transmission of the virus around the world, the pandemic will continue to put pressure on the vaccines, making them less and less effective.
“We cannot get out of it unless the whole world gets out of it together,” Dr. Aylward said.
“We need an urgent reversal, from the majority of vaccines going to high-income countries, to the majority going to low-income countries,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said, asking leaders of high-income countries to wait on distributing booster doses until at least 10% of the world’s population is vaccinated.
“To make that happen, we need everyone’s cooperation, especially the handful of countries and companies that control the global supply of vaccines,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The World Health Organization is calling on wealthy nations to wait to give their citizens booster doses of COVID-19 vaccines until at least the end of September to give more people in other countries a chance to get a first dose of these lifesaving shots.
WHO Director-General Tedros Ghebreyesus, PhD, said that more than 80% of the 4 billion vaccine doses given around the world had been distributed to high-income countries, though they represent less than half the world’s population.
“I understand the concern of all governments to protect their people from the Delta variant,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said. “But we cannot accept countries that have already used most of the global supply of vaccines using even more of it, while the world’s most vulnerable people remain unprotected.”
So far, high-income countries have given about 100 vaccine doses for every 100 people, while low-income countries have given just 1.5 doses for every 100 people.
“Which means, in some of the most vulnerable countries in the world with the weakest health systems, health care workers are working without protection. … the older populations remain at high risk,” said Bruce Aylward, MD, the WHO’s senior adviser on organizational change.
But not everyone agrees.
Leana Wen, MD, a visiting professor at the Milken Institute School of Public Health at George Washington University, Washington, said there are doses already in the United States that won’t last long enough to be sent elsewhere.
“Yes, we need to get vaccines to the world (which also includes helping with distribution, not just supply), but there are doses expiring here in the U.S.,” she said on Twitter. “Why not allow those immunosuppressed to receive them?”
Israel became the first country to start giving some residents booster shots on Sunday, offering extra doses to seniors who are more than 5 months past their last vaccinations. On Monday, Germany announced it would also give booster doses to vulnerable patients, such as nursing home residents, beginning in September.
Dr. Aylward said the moratorium was all about “trying to put a hold on those policies until and unless we get the rest of the world caught up.”
He said it’s clear from the emergence of variant after variant that if we don’t stop the transmission of the virus around the world, the pandemic will continue to put pressure on the vaccines, making them less and less effective.
“We cannot get out of it unless the whole world gets out of it together,” Dr. Aylward said.
“We need an urgent reversal, from the majority of vaccines going to high-income countries, to the majority going to low-income countries,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said, asking leaders of high-income countries to wait on distributing booster doses until at least 10% of the world’s population is vaccinated.
“To make that happen, we need everyone’s cooperation, especially the handful of countries and companies that control the global supply of vaccines,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The World Health Organization is calling on wealthy nations to wait to give their citizens booster doses of COVID-19 vaccines until at least the end of September to give more people in other countries a chance to get a first dose of these lifesaving shots.
WHO Director-General Tedros Ghebreyesus, PhD, said that more than 80% of the 4 billion vaccine doses given around the world had been distributed to high-income countries, though they represent less than half the world’s population.
“I understand the concern of all governments to protect their people from the Delta variant,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said. “But we cannot accept countries that have already used most of the global supply of vaccines using even more of it, while the world’s most vulnerable people remain unprotected.”
So far, high-income countries have given about 100 vaccine doses for every 100 people, while low-income countries have given just 1.5 doses for every 100 people.
“Which means, in some of the most vulnerable countries in the world with the weakest health systems, health care workers are working without protection. … the older populations remain at high risk,” said Bruce Aylward, MD, the WHO’s senior adviser on organizational change.
But not everyone agrees.
Leana Wen, MD, a visiting professor at the Milken Institute School of Public Health at George Washington University, Washington, said there are doses already in the United States that won’t last long enough to be sent elsewhere.
“Yes, we need to get vaccines to the world (which also includes helping with distribution, not just supply), but there are doses expiring here in the U.S.,” she said on Twitter. “Why not allow those immunosuppressed to receive them?”
Israel became the first country to start giving some residents booster shots on Sunday, offering extra doses to seniors who are more than 5 months past their last vaccinations. On Monday, Germany announced it would also give booster doses to vulnerable patients, such as nursing home residents, beginning in September.
Dr. Aylward said the moratorium was all about “trying to put a hold on those policies until and unless we get the rest of the world caught up.”
He said it’s clear from the emergence of variant after variant that if we don’t stop the transmission of the virus around the world, the pandemic will continue to put pressure on the vaccines, making them less and less effective.
“We cannot get out of it unless the whole world gets out of it together,” Dr. Aylward said.
“We need an urgent reversal, from the majority of vaccines going to high-income countries, to the majority going to low-income countries,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said, asking leaders of high-income countries to wait on distributing booster doses until at least 10% of the world’s population is vaccinated.
“To make that happen, we need everyone’s cooperation, especially the handful of countries and companies that control the global supply of vaccines,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Will the Delta variant peak and then burn out?
When the Delta variant of the coronavirus was first identified in India in December 2020, the threat may have seemed too remote to trigger worry in the United States, although the horror of it ripping through the country was soon hard to ignore.
Within months, the Delta variant had spread to more than 98 countries, including Scotland, the United Kingdom, Israel, and now, of course, the United States. The CDC said this week the Delta variant now accounts for 93% of all COVID cases.
Fueled by Delta, COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths are increasing in nearly all states, according to the latest CDC data. After the 7-day average number of cases dipped by June 22 to about 11,000, it rose by Aug. 3 to more than 85,000.
Some experts are heartened by the recent decrease in COVID-19 cases in the United Kingdom and India, both hard-hit with the Delta variant. COVID-19 cases in India peaked at more than 400,000 a day in May; by Aug. 2, that had dropped to about 30,500 daily.
Andy Slavitt, former Biden White House senior adviser for COVID-19 response, tweeted July 26 that, if the Delta variant acted the same in the United Kingdom as in India, it would have a quick rise and a quick drop.
The prediction seems to have come true. As of Aug. 3, U.K. cases have dropped to 7,467, compared with more than 46,800 July 19.
So the question of the summer has become: “When will Delta burn out here?”
Like other pandemic predictions, these are all over the board. Here are five predictions about when COVID cases will peak, then fall. They range from less than 2 weeks to more than 2 months:
- Mid-August: Among the most optimistic predictions of when the Delta-driven COVID-19 cases will decline is from Scott Gottlieb, MD, former FDA director. He told CNBC on July 28 that he would expect cases to decline in 2-3 weeks – so by August 11.
- Mid-August to mid-September: Ali Mokdad, PhD, chief strategy officer for population health at the University of Washington, Seattle, said that, “right now for the U.S. as a country, cases will peak mid-August” and then decline. He is citing projections by the university’s Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. In its “most likely” scenario, it predicts COVID deaths will peak at about 1,000 daily by mid-September, then decline. (As of Aug. 3, daily deaths averaged 371.)
- September: “I am hoping we get over this Delta hump [by then],” says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape. “But sometimes, I am too much of an optimist.”
- Mid-October: Experts at the COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub, a consortium of researchers from leading institutions who consult with the CDC, said the Delta-fueled pandemic will steadily increase through summer and fall, with a mid-October peak.
- Unclear: Because cases are underestimated, “I think it is unclear when we will see a peak of Delta,” says Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore. He predicts a decline in cases as “more people get infected and develop natural immunity.”
The predictions are based on different scenarios, such as most likely or worst case. Factors such as personal behaviors, public mandates, and vaccination rates could all alter the projections.
What a difference vaccination may make
An uptick in vaccinations could change all the models and predictions, experts agree. As of Aug. 3, almost half (49.7%) of the total U.S. population was fully vaccinated, the CDC said. (And 80.1% of those 65 and over were.)
But that’s a long way from the 70% or 80% figure often cited to reach herd immunity. Recently, Ricardo Franco, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said at a briefing by the Infectious Diseases Society of America that the infectiousness of the Delta variant may mean the herd immunity threshold is actually closer to 90%.
Dr. Mokdad estimates that by Nov. 1, based on the current rate of infections, 64% of people in the United States will be immune to a variant like Delta, taking into account those already infected and those vaccinated against COVID-19.
Justin Lessler, PhD, a University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill epidemiologist involved in the modeling hub, says if enough people get vaccinated, it could stop the Delta variant in its tracks. But that percentage is high.
“I am relatively confident that if we could get 90% or more of the eligible population vaccinated that we would see the epidemic begin to recede,” he says.
It’s a huge leap from 50%, or even 64%, to 90%. Could the Delta surge really motivate that many people to head to a vaccination site?
That’s hard to predict, Dr. Topol said. Some unvaccinated people may feel like soldiers in a foxhole, especially if they are in hard-hit states like Louisiana, and rush to get the vaccine as soon as possible. Others, hearing about the “breakthrough” cases in the vaccinated, may dig in their heels and ask: “Why bother?” as they mistakenly conclude that the vaccine has not done its job.
Roles of public policy, individual behavior
Besides an increase in vaccinations, individual behaviors and mandates can change the scenario. Doctors can remind even vaccinated patients that behaviors such as social distancing and masks still matter, experts said.
“Don’t ‘stress test’ your vaccine, “ Dr. Topol said.
The vaccines against COVID are good but not perfect and, he notes, they offer less protection if many months have passed since the vaccines were given.
The best advice now, Dr. Topol said, is: “Don’t be inside without a mask.”
Even if outdoors, depending on how close others are and the level of the conversation, a mask might be wise, he says.
Dr. Mokdad finds that “when cases go up, people put on their best behavior,” such as going back to masks and social distancing.
“Unfortunately, we have two countries,” he said, referring to the way public health measures and mandates vary from state to state.
Once the Delta variant subsides, what’s next?
It’s not a matter of if there is another variant on the heels of Delta, but when, Dr. Topol and other experts said. A new variant, Lambda, was first identified in Peru in August 2020 but now makes up about 90% of the country’s infections.
There’s also Delta-plus, just found in two people in South Korea.
Future variants could be even more transmissible than Delta, “which would be a horror show,” Dr. Topol said. “This [Delta] is by far the worst version. The virus is going to keep evolving. It is not done with us.”
On the horizon: Variant-proof vaccines
What’s needed to tackle the next variant is another approach to vaccine development, according to Dr. Topol and his colleague, Dennis R. Burton, a professor of immunology and microbiology at Scripps Research Institute.
Writing a commentary in Nature published in 2021, the two propose using a special class of protective antibodies, known as broadly neutralizing antibodies, to develop these vaccines. The success of the current COVID-19 vaccines is likely because of the vaccine’s ability to prompt the body to make protective neutralizing antibodies. These proteins bind to the viruses and prevent them from infecting the body’s cells.
The broadly neutralizing antibodies, however, can act against many different strains of related viruses, Dr. Topol and Mr. Burton wrote. Using this approach, which is already under study, scientists could make vaccines that would be effective against a family of viruses. The goal: to stop future outbreaks from becoming epidemics and then pandemics.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
When the Delta variant of the coronavirus was first identified in India in December 2020, the threat may have seemed too remote to trigger worry in the United States, although the horror of it ripping through the country was soon hard to ignore.
Within months, the Delta variant had spread to more than 98 countries, including Scotland, the United Kingdom, Israel, and now, of course, the United States. The CDC said this week the Delta variant now accounts for 93% of all COVID cases.
Fueled by Delta, COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths are increasing in nearly all states, according to the latest CDC data. After the 7-day average number of cases dipped by June 22 to about 11,000, it rose by Aug. 3 to more than 85,000.
Some experts are heartened by the recent decrease in COVID-19 cases in the United Kingdom and India, both hard-hit with the Delta variant. COVID-19 cases in India peaked at more than 400,000 a day in May; by Aug. 2, that had dropped to about 30,500 daily.
Andy Slavitt, former Biden White House senior adviser for COVID-19 response, tweeted July 26 that, if the Delta variant acted the same in the United Kingdom as in India, it would have a quick rise and a quick drop.
The prediction seems to have come true. As of Aug. 3, U.K. cases have dropped to 7,467, compared with more than 46,800 July 19.
So the question of the summer has become: “When will Delta burn out here?”
Like other pandemic predictions, these are all over the board. Here are five predictions about when COVID cases will peak, then fall. They range from less than 2 weeks to more than 2 months:
- Mid-August: Among the most optimistic predictions of when the Delta-driven COVID-19 cases will decline is from Scott Gottlieb, MD, former FDA director. He told CNBC on July 28 that he would expect cases to decline in 2-3 weeks – so by August 11.
- Mid-August to mid-September: Ali Mokdad, PhD, chief strategy officer for population health at the University of Washington, Seattle, said that, “right now for the U.S. as a country, cases will peak mid-August” and then decline. He is citing projections by the university’s Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. In its “most likely” scenario, it predicts COVID deaths will peak at about 1,000 daily by mid-September, then decline. (As of Aug. 3, daily deaths averaged 371.)
- September: “I am hoping we get over this Delta hump [by then],” says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape. “But sometimes, I am too much of an optimist.”
- Mid-October: Experts at the COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub, a consortium of researchers from leading institutions who consult with the CDC, said the Delta-fueled pandemic will steadily increase through summer and fall, with a mid-October peak.
- Unclear: Because cases are underestimated, “I think it is unclear when we will see a peak of Delta,” says Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore. He predicts a decline in cases as “more people get infected and develop natural immunity.”
The predictions are based on different scenarios, such as most likely or worst case. Factors such as personal behaviors, public mandates, and vaccination rates could all alter the projections.
What a difference vaccination may make
An uptick in vaccinations could change all the models and predictions, experts agree. As of Aug. 3, almost half (49.7%) of the total U.S. population was fully vaccinated, the CDC said. (And 80.1% of those 65 and over were.)
But that’s a long way from the 70% or 80% figure often cited to reach herd immunity. Recently, Ricardo Franco, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said at a briefing by the Infectious Diseases Society of America that the infectiousness of the Delta variant may mean the herd immunity threshold is actually closer to 90%.
Dr. Mokdad estimates that by Nov. 1, based on the current rate of infections, 64% of people in the United States will be immune to a variant like Delta, taking into account those already infected and those vaccinated against COVID-19.
Justin Lessler, PhD, a University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill epidemiologist involved in the modeling hub, says if enough people get vaccinated, it could stop the Delta variant in its tracks. But that percentage is high.
“I am relatively confident that if we could get 90% or more of the eligible population vaccinated that we would see the epidemic begin to recede,” he says.
It’s a huge leap from 50%, or even 64%, to 90%. Could the Delta surge really motivate that many people to head to a vaccination site?
That’s hard to predict, Dr. Topol said. Some unvaccinated people may feel like soldiers in a foxhole, especially if they are in hard-hit states like Louisiana, and rush to get the vaccine as soon as possible. Others, hearing about the “breakthrough” cases in the vaccinated, may dig in their heels and ask: “Why bother?” as they mistakenly conclude that the vaccine has not done its job.
Roles of public policy, individual behavior
Besides an increase in vaccinations, individual behaviors and mandates can change the scenario. Doctors can remind even vaccinated patients that behaviors such as social distancing and masks still matter, experts said.
“Don’t ‘stress test’ your vaccine, “ Dr. Topol said.
The vaccines against COVID are good but not perfect and, he notes, they offer less protection if many months have passed since the vaccines were given.
The best advice now, Dr. Topol said, is: “Don’t be inside without a mask.”
Even if outdoors, depending on how close others are and the level of the conversation, a mask might be wise, he says.
Dr. Mokdad finds that “when cases go up, people put on their best behavior,” such as going back to masks and social distancing.
“Unfortunately, we have two countries,” he said, referring to the way public health measures and mandates vary from state to state.
Once the Delta variant subsides, what’s next?
It’s not a matter of if there is another variant on the heels of Delta, but when, Dr. Topol and other experts said. A new variant, Lambda, was first identified in Peru in August 2020 but now makes up about 90% of the country’s infections.
There’s also Delta-plus, just found in two people in South Korea.
Future variants could be even more transmissible than Delta, “which would be a horror show,” Dr. Topol said. “This [Delta] is by far the worst version. The virus is going to keep evolving. It is not done with us.”
On the horizon: Variant-proof vaccines
What’s needed to tackle the next variant is another approach to vaccine development, according to Dr. Topol and his colleague, Dennis R. Burton, a professor of immunology and microbiology at Scripps Research Institute.
Writing a commentary in Nature published in 2021, the two propose using a special class of protective antibodies, known as broadly neutralizing antibodies, to develop these vaccines. The success of the current COVID-19 vaccines is likely because of the vaccine’s ability to prompt the body to make protective neutralizing antibodies. These proteins bind to the viruses and prevent them from infecting the body’s cells.
The broadly neutralizing antibodies, however, can act against many different strains of related viruses, Dr. Topol and Mr. Burton wrote. Using this approach, which is already under study, scientists could make vaccines that would be effective against a family of viruses. The goal: to stop future outbreaks from becoming epidemics and then pandemics.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
When the Delta variant of the coronavirus was first identified in India in December 2020, the threat may have seemed too remote to trigger worry in the United States, although the horror of it ripping through the country was soon hard to ignore.
Within months, the Delta variant had spread to more than 98 countries, including Scotland, the United Kingdom, Israel, and now, of course, the United States. The CDC said this week the Delta variant now accounts for 93% of all COVID cases.
Fueled by Delta, COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths are increasing in nearly all states, according to the latest CDC data. After the 7-day average number of cases dipped by June 22 to about 11,000, it rose by Aug. 3 to more than 85,000.
Some experts are heartened by the recent decrease in COVID-19 cases in the United Kingdom and India, both hard-hit with the Delta variant. COVID-19 cases in India peaked at more than 400,000 a day in May; by Aug. 2, that had dropped to about 30,500 daily.
Andy Slavitt, former Biden White House senior adviser for COVID-19 response, tweeted July 26 that, if the Delta variant acted the same in the United Kingdom as in India, it would have a quick rise and a quick drop.
The prediction seems to have come true. As of Aug. 3, U.K. cases have dropped to 7,467, compared with more than 46,800 July 19.
So the question of the summer has become: “When will Delta burn out here?”
Like other pandemic predictions, these are all over the board. Here are five predictions about when COVID cases will peak, then fall. They range from less than 2 weeks to more than 2 months:
- Mid-August: Among the most optimistic predictions of when the Delta-driven COVID-19 cases will decline is from Scott Gottlieb, MD, former FDA director. He told CNBC on July 28 that he would expect cases to decline in 2-3 weeks – so by August 11.
- Mid-August to mid-September: Ali Mokdad, PhD, chief strategy officer for population health at the University of Washington, Seattle, said that, “right now for the U.S. as a country, cases will peak mid-August” and then decline. He is citing projections by the university’s Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. In its “most likely” scenario, it predicts COVID deaths will peak at about 1,000 daily by mid-September, then decline. (As of Aug. 3, daily deaths averaged 371.)
- September: “I am hoping we get over this Delta hump [by then],” says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape. “But sometimes, I am too much of an optimist.”
- Mid-October: Experts at the COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub, a consortium of researchers from leading institutions who consult with the CDC, said the Delta-fueled pandemic will steadily increase through summer and fall, with a mid-October peak.
- Unclear: Because cases are underestimated, “I think it is unclear when we will see a peak of Delta,” says Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore. He predicts a decline in cases as “more people get infected and develop natural immunity.”
The predictions are based on different scenarios, such as most likely or worst case. Factors such as personal behaviors, public mandates, and vaccination rates could all alter the projections.
What a difference vaccination may make
An uptick in vaccinations could change all the models and predictions, experts agree. As of Aug. 3, almost half (49.7%) of the total U.S. population was fully vaccinated, the CDC said. (And 80.1% of those 65 and over were.)
But that’s a long way from the 70% or 80% figure often cited to reach herd immunity. Recently, Ricardo Franco, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said at a briefing by the Infectious Diseases Society of America that the infectiousness of the Delta variant may mean the herd immunity threshold is actually closer to 90%.
Dr. Mokdad estimates that by Nov. 1, based on the current rate of infections, 64% of people in the United States will be immune to a variant like Delta, taking into account those already infected and those vaccinated against COVID-19.
Justin Lessler, PhD, a University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill epidemiologist involved in the modeling hub, says if enough people get vaccinated, it could stop the Delta variant in its tracks. But that percentage is high.
“I am relatively confident that if we could get 90% or more of the eligible population vaccinated that we would see the epidemic begin to recede,” he says.
It’s a huge leap from 50%, or even 64%, to 90%. Could the Delta surge really motivate that many people to head to a vaccination site?
That’s hard to predict, Dr. Topol said. Some unvaccinated people may feel like soldiers in a foxhole, especially if they are in hard-hit states like Louisiana, and rush to get the vaccine as soon as possible. Others, hearing about the “breakthrough” cases in the vaccinated, may dig in their heels and ask: “Why bother?” as they mistakenly conclude that the vaccine has not done its job.
Roles of public policy, individual behavior
Besides an increase in vaccinations, individual behaviors and mandates can change the scenario. Doctors can remind even vaccinated patients that behaviors such as social distancing and masks still matter, experts said.
“Don’t ‘stress test’ your vaccine, “ Dr. Topol said.
The vaccines against COVID are good but not perfect and, he notes, they offer less protection if many months have passed since the vaccines were given.
The best advice now, Dr. Topol said, is: “Don’t be inside without a mask.”
Even if outdoors, depending on how close others are and the level of the conversation, a mask might be wise, he says.
Dr. Mokdad finds that “when cases go up, people put on their best behavior,” such as going back to masks and social distancing.
“Unfortunately, we have two countries,” he said, referring to the way public health measures and mandates vary from state to state.
Once the Delta variant subsides, what’s next?
It’s not a matter of if there is another variant on the heels of Delta, but when, Dr. Topol and other experts said. A new variant, Lambda, was first identified in Peru in August 2020 but now makes up about 90% of the country’s infections.
There’s also Delta-plus, just found in two people in South Korea.
Future variants could be even more transmissible than Delta, “which would be a horror show,” Dr. Topol said. “This [Delta] is by far the worst version. The virus is going to keep evolving. It is not done with us.”
On the horizon: Variant-proof vaccines
What’s needed to tackle the next variant is another approach to vaccine development, according to Dr. Topol and his colleague, Dennis R. Burton, a professor of immunology and microbiology at Scripps Research Institute.
Writing a commentary in Nature published in 2021, the two propose using a special class of protective antibodies, known as broadly neutralizing antibodies, to develop these vaccines. The success of the current COVID-19 vaccines is likely because of the vaccine’s ability to prompt the body to make protective neutralizing antibodies. These proteins bind to the viruses and prevent them from infecting the body’s cells.
The broadly neutralizing antibodies, however, can act against many different strains of related viruses, Dr. Topol and Mr. Burton wrote. Using this approach, which is already under study, scientists could make vaccines that would be effective against a family of viruses. The goal: to stop future outbreaks from becoming epidemics and then pandemics.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Increases in new COVID cases among children far outpace vaccinations
New COVID-19 cases in children soared by almost 86% over the course of just 1 week, while the number of 12- to 17-year-old children who have received at least one dose of vaccine rose by 5.4%, according to two separate sources.
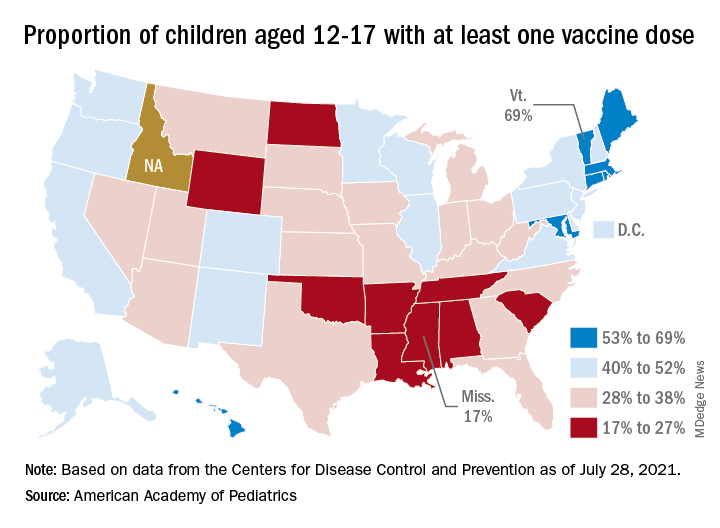
Meanwhile, the increase over the past 2 weeks – from 23,551 new cases for July 16-22 to almost 72,000 – works out to almost 205%, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Children represented 19.0% of the cases reported during the week of July 23-29, and they have made up 14.3% of all cases since the pandemic began, with the total number of cases in children now approaching 4.2 million, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. About 22% of the U.S. population is under the age of 18 years.
As of Aug. 2, just over 9.8 million children aged 12-17 years had received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, which was up by about 500,000, or 5.4%, from a week earlier, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Children aged 16-17 have reached a notable milestone on the journey that started with vaccine approval in December: 50.2% have gotten at least one dose and 40.3% are fully vaccinated. Among children aged 12-15 years, the proportion with at least one dose of vaccine is up to 39.5%, compared with 37.1% the previous week, while 29.0% are fully vaccinated (27.8% the week before), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The national rates for child vaccination, however, tend to hide the disparities between states. There is a gap between Mississippi (lowest), where just 17% of children aged 12-17 years have gotten at least one dose, and Vermont (highest), which is up to 69%. Vermont also has the highest rate of vaccine completion (60%), while Alabama and Mississippi have the lowest (10%), according to a solo report from the AAP.
New COVID-19 cases in children soared by almost 86% over the course of just 1 week, while the number of 12- to 17-year-old children who have received at least one dose of vaccine rose by 5.4%, according to two separate sources.

Meanwhile, the increase over the past 2 weeks – from 23,551 new cases for July 16-22 to almost 72,000 – works out to almost 205%, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Children represented 19.0% of the cases reported during the week of July 23-29, and they have made up 14.3% of all cases since the pandemic began, with the total number of cases in children now approaching 4.2 million, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. About 22% of the U.S. population is under the age of 18 years.
As of Aug. 2, just over 9.8 million children aged 12-17 years had received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, which was up by about 500,000, or 5.4%, from a week earlier, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Children aged 16-17 have reached a notable milestone on the journey that started with vaccine approval in December: 50.2% have gotten at least one dose and 40.3% are fully vaccinated. Among children aged 12-15 years, the proportion with at least one dose of vaccine is up to 39.5%, compared with 37.1% the previous week, while 29.0% are fully vaccinated (27.8% the week before), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The national rates for child vaccination, however, tend to hide the disparities between states. There is a gap between Mississippi (lowest), where just 17% of children aged 12-17 years have gotten at least one dose, and Vermont (highest), which is up to 69%. Vermont also has the highest rate of vaccine completion (60%), while Alabama and Mississippi have the lowest (10%), according to a solo report from the AAP.
New COVID-19 cases in children soared by almost 86% over the course of just 1 week, while the number of 12- to 17-year-old children who have received at least one dose of vaccine rose by 5.4%, according to two separate sources.

Meanwhile, the increase over the past 2 weeks – from 23,551 new cases for July 16-22 to almost 72,000 – works out to almost 205%, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Children represented 19.0% of the cases reported during the week of July 23-29, and they have made up 14.3% of all cases since the pandemic began, with the total number of cases in children now approaching 4.2 million, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. About 22% of the U.S. population is under the age of 18 years.
As of Aug. 2, just over 9.8 million children aged 12-17 years had received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, which was up by about 500,000, or 5.4%, from a week earlier, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Children aged 16-17 have reached a notable milestone on the journey that started with vaccine approval in December: 50.2% have gotten at least one dose and 40.3% are fully vaccinated. Among children aged 12-15 years, the proportion with at least one dose of vaccine is up to 39.5%, compared with 37.1% the previous week, while 29.0% are fully vaccinated (27.8% the week before), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The national rates for child vaccination, however, tend to hide the disparities between states. There is a gap between Mississippi (lowest), where just 17% of children aged 12-17 years have gotten at least one dose, and Vermont (highest), which is up to 69%. Vermont also has the highest rate of vaccine completion (60%), while Alabama and Mississippi have the lowest (10%), according to a solo report from the AAP.
Indoor masking needed in almost 70% of U.S. counties: CDC data
In announcing new guidance on July 27, the CDC said vaccinated people should wear face masks in indoor public places with “high” or “substantial” community transmission rates of COVID-19.
Data from the CDC shows that designation covers 69.3% of all counties in the United States – 52.2% (1,680 counties) with high community transmission rates and 17.1% (551 counties) with substantial rates.
A county has “high transmission” if it reports 100 or more weekly cases per 100,000 residents or a 10% or higher test positivity rate in the last 7 days, the CDC said. “Substantial transmission” means a county reports 50-99 weekly cases per 100,000 residents or has a positivity rate between 8% and 9.9% in the last 7 days.
About 23% of U.S. counties had moderate rates of community transmission, and 7.67% had low rates.
To find out the transmission rate in your county, go to the CDC COVID data tracker.
Smithsonian requiring masks again
The Smithsonian now requires all visitors over age 2, regardless of vaccination status, to wear face masks indoors and in all museum spaces.
The Smithsonian said in a news release that fully vaccinated visitors won’t have to wear masks at the National Zoo or outdoor gardens for museums.
The new rule goes into effect Aug. 6. It reverses a rule that said fully vaccinated visitors didn’t have to wear masks indoors beginning June 28.
Indoor face masks will be required throughout the District of Columbia beginning July 31., D.C. Mayor Muriel Bowser.
House Republicans protest face mask policy
About 40 maskless Republican members of the U.S. House of Representatives filed onto the Senate floor on July 29 to protest a new rule requiring House members to wear face masks, the Hill reported.
Congress’s attending doctor said in a memo that the 435 members of the House, plus workers, must wear masks indoors, but not the 100 members of the Senate. The Senate is a smaller body and has had better mask compliance than the House.
Rep. Ronny Jackson (R-Tex.), told the Hill that Republicans wanted to show “what it was like on the floor of the Senate versus the floor of the House. Obviously, it’s vastly different.”
Among the group of Republicans who filed onto the Senate floor were Rep. Lauren Boebert of Colorado, Rep. Matt Gaetz and Rep. Byron Donalds of Florida, Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene of Georgia, Rep. Chip Roy and Rep. Louie Gohmert of Texas, Rep. Madison Cawthorn of North Carolina, Rep. Warren Davidson of Ohio, and Rep. Andy Biggs of Arizona.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In announcing new guidance on July 27, the CDC said vaccinated people should wear face masks in indoor public places with “high” or “substantial” community transmission rates of COVID-19.
Data from the CDC shows that designation covers 69.3% of all counties in the United States – 52.2% (1,680 counties) with high community transmission rates and 17.1% (551 counties) with substantial rates.
A county has “high transmission” if it reports 100 or more weekly cases per 100,000 residents or a 10% or higher test positivity rate in the last 7 days, the CDC said. “Substantial transmission” means a county reports 50-99 weekly cases per 100,000 residents or has a positivity rate between 8% and 9.9% in the last 7 days.
About 23% of U.S. counties had moderate rates of community transmission, and 7.67% had low rates.
To find out the transmission rate in your county, go to the CDC COVID data tracker.
Smithsonian requiring masks again
The Smithsonian now requires all visitors over age 2, regardless of vaccination status, to wear face masks indoors and in all museum spaces.
The Smithsonian said in a news release that fully vaccinated visitors won’t have to wear masks at the National Zoo or outdoor gardens for museums.
The new rule goes into effect Aug. 6. It reverses a rule that said fully vaccinated visitors didn’t have to wear masks indoors beginning June 28.
Indoor face masks will be required throughout the District of Columbia beginning July 31., D.C. Mayor Muriel Bowser.
House Republicans protest face mask policy
About 40 maskless Republican members of the U.S. House of Representatives filed onto the Senate floor on July 29 to protest a new rule requiring House members to wear face masks, the Hill reported.
Congress’s attending doctor said in a memo that the 435 members of the House, plus workers, must wear masks indoors, but not the 100 members of the Senate. The Senate is a smaller body and has had better mask compliance than the House.
Rep. Ronny Jackson (R-Tex.), told the Hill that Republicans wanted to show “what it was like on the floor of the Senate versus the floor of the House. Obviously, it’s vastly different.”
Among the group of Republicans who filed onto the Senate floor were Rep. Lauren Boebert of Colorado, Rep. Matt Gaetz and Rep. Byron Donalds of Florida, Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene of Georgia, Rep. Chip Roy and Rep. Louie Gohmert of Texas, Rep. Madison Cawthorn of North Carolina, Rep. Warren Davidson of Ohio, and Rep. Andy Biggs of Arizona.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In announcing new guidance on July 27, the CDC said vaccinated people should wear face masks in indoor public places with “high” or “substantial” community transmission rates of COVID-19.
Data from the CDC shows that designation covers 69.3% of all counties in the United States – 52.2% (1,680 counties) with high community transmission rates and 17.1% (551 counties) with substantial rates.
A county has “high transmission” if it reports 100 or more weekly cases per 100,000 residents or a 10% or higher test positivity rate in the last 7 days, the CDC said. “Substantial transmission” means a county reports 50-99 weekly cases per 100,000 residents or has a positivity rate between 8% and 9.9% in the last 7 days.
About 23% of U.S. counties had moderate rates of community transmission, and 7.67% had low rates.
To find out the transmission rate in your county, go to the CDC COVID data tracker.
Smithsonian requiring masks again
The Smithsonian now requires all visitors over age 2, regardless of vaccination status, to wear face masks indoors and in all museum spaces.
The Smithsonian said in a news release that fully vaccinated visitors won’t have to wear masks at the National Zoo or outdoor gardens for museums.
The new rule goes into effect Aug. 6. It reverses a rule that said fully vaccinated visitors didn’t have to wear masks indoors beginning June 28.
Indoor face masks will be required throughout the District of Columbia beginning July 31., D.C. Mayor Muriel Bowser.
House Republicans protest face mask policy
About 40 maskless Republican members of the U.S. House of Representatives filed onto the Senate floor on July 29 to protest a new rule requiring House members to wear face masks, the Hill reported.
Congress’s attending doctor said in a memo that the 435 members of the House, plus workers, must wear masks indoors, but not the 100 members of the Senate. The Senate is a smaller body and has had better mask compliance than the House.
Rep. Ronny Jackson (R-Tex.), told the Hill that Republicans wanted to show “what it was like on the floor of the Senate versus the floor of the House. Obviously, it’s vastly different.”
Among the group of Republicans who filed onto the Senate floor were Rep. Lauren Boebert of Colorado, Rep. Matt Gaetz and Rep. Byron Donalds of Florida, Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene of Georgia, Rep. Chip Roy and Rep. Louie Gohmert of Texas, Rep. Madison Cawthorn of North Carolina, Rep. Warren Davidson of Ohio, and Rep. Andy Biggs of Arizona.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
‘War has changed’: CDC says Delta as contagious as chicken pox
Internal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention documents support the high transmission rate of the Delta variant and put the risk in easier to understand terms.
In addition, the agency released a new study that shows that breakthrough infections in the vaccinated make people about as contagious as those who are unvaccinated. The new report, published July 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), also reveals that the Delta variant likely causes more severe COVID-19 illness.
Given these recent findings, the internal CDC slide show advises that the agency should “acknowledge the war has changed.”
A ‘pivotal discovery’
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, said in a statement that the MMWR report demonstrates “that [D]elta infection resulted in similarly high SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in vaccinated and unvaccinated people.
“High viral loads suggest an increased risk of transmission and raised concern that, unlike with other variants, vaccinated people infected with [D]elta can transmit the virus,” she added. “This finding is concerning and was a pivotal discovery leading to CDC’s updated mask recommendation.”
The investigators analyzed 469 COVID-19 cases reported in Massachusetts residents July 3 through 17, 2021. The infections were associated with an outbreak following multiple events and large gatherings in Provincetown in that state’s easternmost Barnstable County, also known as Cape Cod.
Notably, 346 infections, or 74%, of the cases occurred in fully vaccinated individuals. This group had a median age of 42, and 87% were male. Also, 79% of the breakthrough infections were symptomatic.
Researchers also identified the Delta variant in 90% of 133 specimens collected for analysis. Furthermore, viral loads were about the same between samples taken from people who were fully vaccinated and those who were not.
Four of the five people hospitalized were fully vaccinated. No deaths were reported.
The publication of these results was highly anticipated following the CDC’s updated mask recommendations on July 27.
Outside the scope of the MMWR report is the total number of cases associated with the outbreak, including visitors from outside Massachusetts, which now approach 900 infections, NBC Boston reported.
‘Very sobering’ data
“The new information from the CDC around the [D]elta variant is very sobering,” David Hirschwerk, MD, infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said in an interview.
“The CDC is trying to convey and present this uncertain situation clearly to the public based on new, accumulated data,” he said. For example, given the evidence for higher contagiousness of the Delta variant, Dr. Hirschwerk added, “there will be situations where vaccinated people get infected, because the amount of the virus overwhelms the immune protection.
“What is new that is concerning is that people who are vaccinated still have the potential to transmit the virus to the same degree,” he said.
The MMWR study “helps us better understand the question related to whether or not a person who has completed a COVID-19 series can spread the infection,” agreed Michelle Barron, MD, a professor in the division of infectious disease at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
“The message is that, because the [D]elta variant is much more contagious than the original strain, unvaccinated persons need to get vaccinated because it is nearly impossible to avoid the virus indefinitely,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, infectious diseases specialist and epidemiologist at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said when asked to comment.
The new data highlight “that vaccinated persons, if they become sick, should still seek COVID-19 testing and should still isolate, as they are likely contagious,” Dr. Lin added.
More contagious than other infections
The internal CDC slide presentation also puts the new transmission risk in simple terms. Saying that the Delta variant is about as contagious as chicken pox, for example, immediately brings back vivid memories for some of staying indoors and away from friends during childhood or teenage outbreaks.
“A lot of people will remember getting chicken pox and then having their siblings get it shortly thereafter,” Dr. Barron said. “The only key thing to note is that this does not mean that the COVID-19 [D]elta variant mechanism of spread is the same as chicken pox and Ebola. The primary means of spread of COVID-19, even the Delta variant, is via droplets.”
This also means each person infected with the Delta variant could infect an average of eight or nine others.
In contrast, the original strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus was about as infectious as the common cold. In other words, someone was likely to infect about two other people on average.
In addition to the cold, the CDC notes that the Delta variant is now more contagious than Ebola, the seasonal flu, or small pox.
These Delta variant comparisons are one tangible way of explaining why the CDC on July 27 recommended a return to masking in schools and other indoor spaces for people – vaccinated and unvaccinated – in about 70% of the counties across the United States.
In comparing the Delta variant with other infections, “I think the CDC is trying to help people understand a little bit better the situation we now face since the information is so new. We are in a very different position now than just a few weeks ago, and it is hard for people to accept this,” Dr. Hirschwerk said.
The Delta variant is so different that the CDC considers it almost acting like a new virus altogether.
The CDC’s internal documents were first released by The Washington Post on July 29. The slides cite communication challenges for the agency to continue promoting vaccination while also acknowledging that breakthrough cases are occurring and therefore the fully vaccinated, in some instances, are likely infecting others.
Moving back to science talk, the CDC used the recent outbreak in Barnstable County as an example. The cycle threshold, or Ct values, a measure of viral load, were about the same between 80 vaccinated people linked to the outbreak who had a mean Ct value of 21.9, compared with 65 other unvaccinated people with a Ct of 21.5.
Many experts are quick to note that vaccination remains essential, in part because a vaccinated person also walks around with a much lower risk for severe outcomes, hospitalization, and death. In the internal slide show, the CDC points out that vaccination reduces the risk for infection threefold.
“Even with this high amount of virus, [the Delta variant] did not necessarily make the vaccinated individuals as sick,” Dr. Barron said.
In her statement, Dr. Walensky credited collaboration with the Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of Public Health and the CDC for the new data. She also thanked the residents of Barnstable County for participating in interviews done by contact tracers and their willingness to get tested and adhere to safety protocols after learning of their exposure.
Next moves by CDC?
The agency notes that next steps include consideration of prevention measures such as vaccine mandates for healthcare professionals to protect vulnerable populations, universal masking for source control and prevention, and reconsidering other community mitigation strategies.
Asked if this potential policy is appropriate and feasible, Dr. Lin said, “Yes, I believe that every person working in health care should be vaccinated for COVID-19, and it is feasible.”
Dr. Barron agreed as well. “We as health care providers choose to work in health care, and we should be doing everything feasible to ensure that we are protecting our patients and keeping our coworkers safe.”
“Whether you are a health care professional or not, I would urge everyone to get the COVID-19 vaccine, especially as cases across the country continue to rise,” Dr. Hirschwerk said. “Unequivocally vaccines protect you from the virus.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Internal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention documents support the high transmission rate of the Delta variant and put the risk in easier to understand terms.
In addition, the agency released a new study that shows that breakthrough infections in the vaccinated make people about as contagious as those who are unvaccinated. The new report, published July 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), also reveals that the Delta variant likely causes more severe COVID-19 illness.
Given these recent findings, the internal CDC slide show advises that the agency should “acknowledge the war has changed.”
A ‘pivotal discovery’
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, said in a statement that the MMWR report demonstrates “that [D]elta infection resulted in similarly high SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in vaccinated and unvaccinated people.
“High viral loads suggest an increased risk of transmission and raised concern that, unlike with other variants, vaccinated people infected with [D]elta can transmit the virus,” she added. “This finding is concerning and was a pivotal discovery leading to CDC’s updated mask recommendation.”
The investigators analyzed 469 COVID-19 cases reported in Massachusetts residents July 3 through 17, 2021. The infections were associated with an outbreak following multiple events and large gatherings in Provincetown in that state’s easternmost Barnstable County, also known as Cape Cod.
Notably, 346 infections, or 74%, of the cases occurred in fully vaccinated individuals. This group had a median age of 42, and 87% were male. Also, 79% of the breakthrough infections were symptomatic.
Researchers also identified the Delta variant in 90% of 133 specimens collected for analysis. Furthermore, viral loads were about the same between samples taken from people who were fully vaccinated and those who were not.
Four of the five people hospitalized were fully vaccinated. No deaths were reported.
The publication of these results was highly anticipated following the CDC’s updated mask recommendations on July 27.
Outside the scope of the MMWR report is the total number of cases associated with the outbreak, including visitors from outside Massachusetts, which now approach 900 infections, NBC Boston reported.
‘Very sobering’ data
“The new information from the CDC around the [D]elta variant is very sobering,” David Hirschwerk, MD, infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said in an interview.
“The CDC is trying to convey and present this uncertain situation clearly to the public based on new, accumulated data,” he said. For example, given the evidence for higher contagiousness of the Delta variant, Dr. Hirschwerk added, “there will be situations where vaccinated people get infected, because the amount of the virus overwhelms the immune protection.
“What is new that is concerning is that people who are vaccinated still have the potential to transmit the virus to the same degree,” he said.
The MMWR study “helps us better understand the question related to whether or not a person who has completed a COVID-19 series can spread the infection,” agreed Michelle Barron, MD, a professor in the division of infectious disease at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
“The message is that, because the [D]elta variant is much more contagious than the original strain, unvaccinated persons need to get vaccinated because it is nearly impossible to avoid the virus indefinitely,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, infectious diseases specialist and epidemiologist at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said when asked to comment.
The new data highlight “that vaccinated persons, if they become sick, should still seek COVID-19 testing and should still isolate, as they are likely contagious,” Dr. Lin added.
More contagious than other infections
The internal CDC slide presentation also puts the new transmission risk in simple terms. Saying that the Delta variant is about as contagious as chicken pox, for example, immediately brings back vivid memories for some of staying indoors and away from friends during childhood or teenage outbreaks.
“A lot of people will remember getting chicken pox and then having their siblings get it shortly thereafter,” Dr. Barron said. “The only key thing to note is that this does not mean that the COVID-19 [D]elta variant mechanism of spread is the same as chicken pox and Ebola. The primary means of spread of COVID-19, even the Delta variant, is via droplets.”
This also means each person infected with the Delta variant could infect an average of eight or nine others.
In contrast, the original strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus was about as infectious as the common cold. In other words, someone was likely to infect about two other people on average.
In addition to the cold, the CDC notes that the Delta variant is now more contagious than Ebola, the seasonal flu, or small pox.
These Delta variant comparisons are one tangible way of explaining why the CDC on July 27 recommended a return to masking in schools and other indoor spaces for people – vaccinated and unvaccinated – in about 70% of the counties across the United States.
In comparing the Delta variant with other infections, “I think the CDC is trying to help people understand a little bit better the situation we now face since the information is so new. We are in a very different position now than just a few weeks ago, and it is hard for people to accept this,” Dr. Hirschwerk said.
The Delta variant is so different that the CDC considers it almost acting like a new virus altogether.
The CDC’s internal documents were first released by The Washington Post on July 29. The slides cite communication challenges for the agency to continue promoting vaccination while also acknowledging that breakthrough cases are occurring and therefore the fully vaccinated, in some instances, are likely infecting others.
Moving back to science talk, the CDC used the recent outbreak in Barnstable County as an example. The cycle threshold, or Ct values, a measure of viral load, were about the same between 80 vaccinated people linked to the outbreak who had a mean Ct value of 21.9, compared with 65 other unvaccinated people with a Ct of 21.5.
Many experts are quick to note that vaccination remains essential, in part because a vaccinated person also walks around with a much lower risk for severe outcomes, hospitalization, and death. In the internal slide show, the CDC points out that vaccination reduces the risk for infection threefold.
“Even with this high amount of virus, [the Delta variant] did not necessarily make the vaccinated individuals as sick,” Dr. Barron said.
In her statement, Dr. Walensky credited collaboration with the Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of Public Health and the CDC for the new data. She also thanked the residents of Barnstable County for participating in interviews done by contact tracers and their willingness to get tested and adhere to safety protocols after learning of their exposure.
Next moves by CDC?
The agency notes that next steps include consideration of prevention measures such as vaccine mandates for healthcare professionals to protect vulnerable populations, universal masking for source control and prevention, and reconsidering other community mitigation strategies.
Asked if this potential policy is appropriate and feasible, Dr. Lin said, “Yes, I believe that every person working in health care should be vaccinated for COVID-19, and it is feasible.”
Dr. Barron agreed as well. “We as health care providers choose to work in health care, and we should be doing everything feasible to ensure that we are protecting our patients and keeping our coworkers safe.”
“Whether you are a health care professional or not, I would urge everyone to get the COVID-19 vaccine, especially as cases across the country continue to rise,” Dr. Hirschwerk said. “Unequivocally vaccines protect you from the virus.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Internal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention documents support the high transmission rate of the Delta variant and put the risk in easier to understand terms.
In addition, the agency released a new study that shows that breakthrough infections in the vaccinated make people about as contagious as those who are unvaccinated. The new report, published July 30 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), also reveals that the Delta variant likely causes more severe COVID-19 illness.
Given these recent findings, the internal CDC slide show advises that the agency should “acknowledge the war has changed.”
A ‘pivotal discovery’
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, said in a statement that the MMWR report demonstrates “that [D]elta infection resulted in similarly high SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in vaccinated and unvaccinated people.
“High viral loads suggest an increased risk of transmission and raised concern that, unlike with other variants, vaccinated people infected with [D]elta can transmit the virus,” she added. “This finding is concerning and was a pivotal discovery leading to CDC’s updated mask recommendation.”
The investigators analyzed 469 COVID-19 cases reported in Massachusetts residents July 3 through 17, 2021. The infections were associated with an outbreak following multiple events and large gatherings in Provincetown in that state’s easternmost Barnstable County, also known as Cape Cod.
Notably, 346 infections, or 74%, of the cases occurred in fully vaccinated individuals. This group had a median age of 42, and 87% were male. Also, 79% of the breakthrough infections were symptomatic.
Researchers also identified the Delta variant in 90% of 133 specimens collected for analysis. Furthermore, viral loads were about the same between samples taken from people who were fully vaccinated and those who were not.
Four of the five people hospitalized were fully vaccinated. No deaths were reported.
The publication of these results was highly anticipated following the CDC’s updated mask recommendations on July 27.
Outside the scope of the MMWR report is the total number of cases associated with the outbreak, including visitors from outside Massachusetts, which now approach 900 infections, NBC Boston reported.
‘Very sobering’ data
“The new information from the CDC around the [D]elta variant is very sobering,” David Hirschwerk, MD, infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said in an interview.
“The CDC is trying to convey and present this uncertain situation clearly to the public based on new, accumulated data,” he said. For example, given the evidence for higher contagiousness of the Delta variant, Dr. Hirschwerk added, “there will be situations where vaccinated people get infected, because the amount of the virus overwhelms the immune protection.
“What is new that is concerning is that people who are vaccinated still have the potential to transmit the virus to the same degree,” he said.
The MMWR study “helps us better understand the question related to whether or not a person who has completed a COVID-19 series can spread the infection,” agreed Michelle Barron, MD, a professor in the division of infectious disease at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
“The message is that, because the [D]elta variant is much more contagious than the original strain, unvaccinated persons need to get vaccinated because it is nearly impossible to avoid the virus indefinitely,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, infectious diseases specialist and epidemiologist at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said when asked to comment.
The new data highlight “that vaccinated persons, if they become sick, should still seek COVID-19 testing and should still isolate, as they are likely contagious,” Dr. Lin added.
More contagious than other infections
The internal CDC slide presentation also puts the new transmission risk in simple terms. Saying that the Delta variant is about as contagious as chicken pox, for example, immediately brings back vivid memories for some of staying indoors and away from friends during childhood or teenage outbreaks.
“A lot of people will remember getting chicken pox and then having their siblings get it shortly thereafter,” Dr. Barron said. “The only key thing to note is that this does not mean that the COVID-19 [D]elta variant mechanism of spread is the same as chicken pox and Ebola. The primary means of spread of COVID-19, even the Delta variant, is via droplets.”
This also means each person infected with the Delta variant could infect an average of eight or nine others.
In contrast, the original strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus was about as infectious as the common cold. In other words, someone was likely to infect about two other people on average.
In addition to the cold, the CDC notes that the Delta variant is now more contagious than Ebola, the seasonal flu, or small pox.
These Delta variant comparisons are one tangible way of explaining why the CDC on July 27 recommended a return to masking in schools and other indoor spaces for people – vaccinated and unvaccinated – in about 70% of the counties across the United States.
In comparing the Delta variant with other infections, “I think the CDC is trying to help people understand a little bit better the situation we now face since the information is so new. We are in a very different position now than just a few weeks ago, and it is hard for people to accept this,” Dr. Hirschwerk said.
The Delta variant is so different that the CDC considers it almost acting like a new virus altogether.
The CDC’s internal documents were first released by The Washington Post on July 29. The slides cite communication challenges for the agency to continue promoting vaccination while also acknowledging that breakthrough cases are occurring and therefore the fully vaccinated, in some instances, are likely infecting others.
Moving back to science talk, the CDC used the recent outbreak in Barnstable County as an example. The cycle threshold, or Ct values, a measure of viral load, were about the same between 80 vaccinated people linked to the outbreak who had a mean Ct value of 21.9, compared with 65 other unvaccinated people with a Ct of 21.5.
Many experts are quick to note that vaccination remains essential, in part because a vaccinated person also walks around with a much lower risk for severe outcomes, hospitalization, and death. In the internal slide show, the CDC points out that vaccination reduces the risk for infection threefold.
“Even with this high amount of virus, [the Delta variant] did not necessarily make the vaccinated individuals as sick,” Dr. Barron said.
In her statement, Dr. Walensky credited collaboration with the Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of Public Health and the CDC for the new data. She also thanked the residents of Barnstable County for participating in interviews done by contact tracers and their willingness to get tested and adhere to safety protocols after learning of their exposure.
Next moves by CDC?
The agency notes that next steps include consideration of prevention measures such as vaccine mandates for healthcare professionals to protect vulnerable populations, universal masking for source control and prevention, and reconsidering other community mitigation strategies.
Asked if this potential policy is appropriate and feasible, Dr. Lin said, “Yes, I believe that every person working in health care should be vaccinated for COVID-19, and it is feasible.”
Dr. Barron agreed as well. “We as health care providers choose to work in health care, and we should be doing everything feasible to ensure that we are protecting our patients and keeping our coworkers safe.”
“Whether you are a health care professional or not, I would urge everyone to get the COVID-19 vaccine, especially as cases across the country continue to rise,” Dr. Hirschwerk said. “Unequivocally vaccines protect you from the virus.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC to show vaccinated people infected with Delta remain contagious
and infect others, the New York Times reported on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the New York Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data shows people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on Jul 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak on Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and infect others, the New York Times reported on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the New York Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data shows people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on Jul 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak on Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and infect others, the New York Times reported on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the New York Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data shows people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on Jul 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak on Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Bronchitis the leader at putting children in the hospital
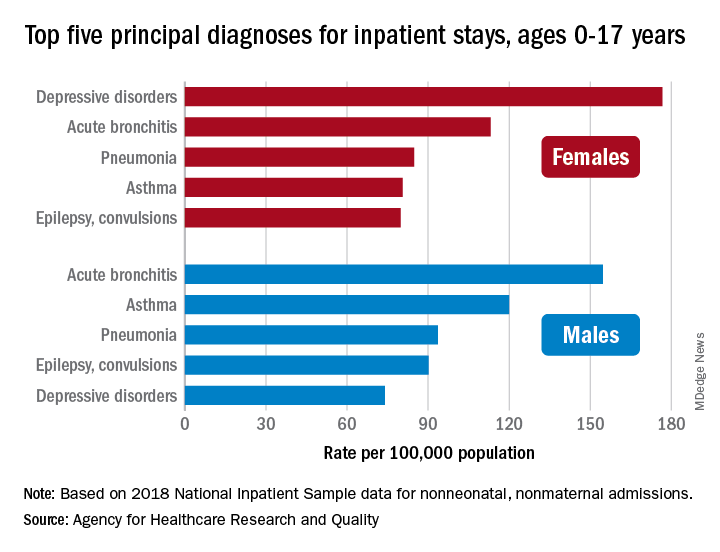
About 7% (99,000) of the 1.47 million nonmaternal, nonneonatal hospital stays in children aged 0-17 years involved a primary diagnosis of acute bronchitis in 2018, representing the leading cause of admissions in boys (154.7 stays per 100,000 population) and the second-leading diagnosis in girls (113.1 stays per 100,000), Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and Marc Roemer, MS, said in a statistical brief.
Depressive disorders were the most common primary diagnosis in girls, with a rate of 176.7 stays per 100,000, and the second-leading diagnosis overall, although the rate was less than half that (74.0 per 100,000) in boys. Two other respiratory conditions, asthma and pneumonia, were among the top five for both girls and boys, as was epilepsy, they reported.
The combined rate for all diagnoses was slightly higher for boys, 2,051 per 100,000, compared with 1,922 for girls, they said based on data from the National Inpatient Sample.
“Identifying the most frequent primary conditions for which patients are admitted to the hospital is important to the implementation and improvement of health care delivery, quality initiatives, and health policy,” said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Mr. Roemer of the AHRQ.

About 7% (99,000) of the 1.47 million nonmaternal, nonneonatal hospital stays in children aged 0-17 years involved a primary diagnosis of acute bronchitis in 2018, representing the leading cause of admissions in boys (154.7 stays per 100,000 population) and the second-leading diagnosis in girls (113.1 stays per 100,000), Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and Marc Roemer, MS, said in a statistical brief.
Depressive disorders were the most common primary diagnosis in girls, with a rate of 176.7 stays per 100,000, and the second-leading diagnosis overall, although the rate was less than half that (74.0 per 100,000) in boys. Two other respiratory conditions, asthma and pneumonia, were among the top five for both girls and boys, as was epilepsy, they reported.
The combined rate for all diagnoses was slightly higher for boys, 2,051 per 100,000, compared with 1,922 for girls, they said based on data from the National Inpatient Sample.
“Identifying the most frequent primary conditions for which patients are admitted to the hospital is important to the implementation and improvement of health care delivery, quality initiatives, and health policy,” said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Mr. Roemer of the AHRQ.

About 7% (99,000) of the 1.47 million nonmaternal, nonneonatal hospital stays in children aged 0-17 years involved a primary diagnosis of acute bronchitis in 2018, representing the leading cause of admissions in boys (154.7 stays per 100,000 population) and the second-leading diagnosis in girls (113.1 stays per 100,000), Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and Marc Roemer, MS, said in a statistical brief.
Depressive disorders were the most common primary diagnosis in girls, with a rate of 176.7 stays per 100,000, and the second-leading diagnosis overall, although the rate was less than half that (74.0 per 100,000) in boys. Two other respiratory conditions, asthma and pneumonia, were among the top five for both girls and boys, as was epilepsy, they reported.
The combined rate for all diagnoses was slightly higher for boys, 2,051 per 100,000, compared with 1,922 for girls, they said based on data from the National Inpatient Sample.
“Identifying the most frequent primary conditions for which patients are admitted to the hospital is important to the implementation and improvement of health care delivery, quality initiatives, and health policy,” said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Mr. Roemer of the AHRQ.
‘A few mutations away’: The threat of a vaccine-proof variant
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, made a dire prediction during a media briefing this week that, if we weren’t already living within the reality of the COVID-19 pandemic, would sound more like a pitch for a movie about a dystopian future.
“For the amount of virus circulating in this country right now largely among unvaccinated people, the largest concern that we in public health and science are worried about is that the virus … [becomes] a very transmissible virus that has the potential to evade our vaccines in terms of how it protects us from severe disease and death,” Dr. Walensky told reporters on July 27.
A new, more elusive variant could be “just a few mutations away,” she said.
“That’s a very prescient comment,” Lewis Nelson, MD, professor and clinical chair of emergency medicine and chief of the division of medical toxicology at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, told this news organization.
“We’ve gone through a few mutations already that have been named, and each one of them gets a little more transmissible,” he said. “That’s normal, natural selection and what you would expect to happen as viruses mutate from one strain to another.”
“What we’ve mostly seen this virus do is evolve to become more infectious,” said Stuart Ray, MD, when also asked to comment. “That is the remarkable feature of Delta – that it is so infectious.”
He said that the SARS-CoV-2 has evolved largely as expected, at least so far. “The potential for this virus to mutate has been something that has been a concern from early on.”
“The viral evolution is a bit like a ticking clock. The more we allow infections to occur, the more likely changes will occur. When we have lots of people infected, we give more chances to the virus to diversify and then adapt to selective pressures,” said Dr. Ray, vice-chair of medicine for data integrity and analytics and professor in the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore.
Dr. Nelson said.
If this occurs, he added, “we will have an ineffective vaccine, essentially. And we’ll be back to where we were last March with a brand-new disease.”
Technology to the rescue?
The flexibility of mRNA vaccines is one potential solution. These vaccines could be more easily and quickly adapted to respond to a new, more vaccine-elusive variant.
“That’s absolutely reassuring,” Dr. Nelson said. For example, if a mutation changes the spike protein and vaccines no longer recognize it, a manufacturer could identify the new protein and incorporate that in a new mRNA vaccine.
“The problem is that some people are not taking the current vaccine,” he added. “I’m not sure what is going to make them take the next vaccine.”
Nothing appears certain
When asked how likely a new strain of SARS-CoV-2 could emerge that gets around vaccine protection, Dr. Nelson said, “I think [what] we’ve learned so far there is no way to predict anything” about this pandemic.
“The best way to prevent the virus from mutating is to prevent hosts, people, from getting sick with it,” he said. “That’s why it’s so important people should get immunized and wear masks.”
Both Dr. Nelson and Dr. Ray pointed out that it is in the best interest of the virus to evolve to be more transmissible and spread to more people. In contrast, a virus that causes people to get so sick that they isolate or die, thus halting transmission, works against viruses surviving evolutionarily.
Some viruses also mutate to become milder over time, but that has not been the case with SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Ray said.
Mutations not the only concern
Viruses have another mechanism that produces new strains, and it works even more quickly than mutations. Recombination, as it’s known, can occur when a person is infected with two different strains of the same virus. If the two versions enter the same cell, the viruses can swap genetic material and produce a third, altogether different strain.
Recombination has already been seen with influenza strains, where H and N genetic segments are swapped to yield H1N1, H1N2, and H3N2 versions of the flu, for example.
“In the early days of SARS-CoV-2 there was so little diversity that recombination did not matter,” Dr. Ray said. However, there are now distinct lineages of the virus circulating globally. If two of these lineages swap segments “this would make a very new viral sequence in one step without having to mutate to gain those differences.”
“The more diverse the strains that are circulating, the bigger a possibility this is,” Dr. Ray said.
Protected, for now
Dr. Walensky’s sober warning came at the same time the CDC released new guidance calling for the wearing of masks indoors in schools and in any location in the country where COVID-19 cases surpass 50 people per 100,000, also known as substantial or high transmission areas.
On a positive note, Dr. Walensky said: “Right now, fortunately, we are not there. The vaccines operate really well in protecting us from severe disease and death.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, made a dire prediction during a media briefing this week that, if we weren’t already living within the reality of the COVID-19 pandemic, would sound more like a pitch for a movie about a dystopian future.
“For the amount of virus circulating in this country right now largely among unvaccinated people, the largest concern that we in public health and science are worried about is that the virus … [becomes] a very transmissible virus that has the potential to evade our vaccines in terms of how it protects us from severe disease and death,” Dr. Walensky told reporters on July 27.
A new, more elusive variant could be “just a few mutations away,” she said.
“That’s a very prescient comment,” Lewis Nelson, MD, professor and clinical chair of emergency medicine and chief of the division of medical toxicology at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, told this news organization.
“We’ve gone through a few mutations already that have been named, and each one of them gets a little more transmissible,” he said. “That’s normal, natural selection and what you would expect to happen as viruses mutate from one strain to another.”
“What we’ve mostly seen this virus do is evolve to become more infectious,” said Stuart Ray, MD, when also asked to comment. “That is the remarkable feature of Delta – that it is so infectious.”
He said that the SARS-CoV-2 has evolved largely as expected, at least so far. “The potential for this virus to mutate has been something that has been a concern from early on.”
“The viral evolution is a bit like a ticking clock. The more we allow infections to occur, the more likely changes will occur. When we have lots of people infected, we give more chances to the virus to diversify and then adapt to selective pressures,” said Dr. Ray, vice-chair of medicine for data integrity and analytics and professor in the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore.
Dr. Nelson said.
If this occurs, he added, “we will have an ineffective vaccine, essentially. And we’ll be back to where we were last March with a brand-new disease.”
Technology to the rescue?
The flexibility of mRNA vaccines is one potential solution. These vaccines could be more easily and quickly adapted to respond to a new, more vaccine-elusive variant.
“That’s absolutely reassuring,” Dr. Nelson said. For example, if a mutation changes the spike protein and vaccines no longer recognize it, a manufacturer could identify the new protein and incorporate that in a new mRNA vaccine.
“The problem is that some people are not taking the current vaccine,” he added. “I’m not sure what is going to make them take the next vaccine.”
Nothing appears certain
When asked how likely a new strain of SARS-CoV-2 could emerge that gets around vaccine protection, Dr. Nelson said, “I think [what] we’ve learned so far there is no way to predict anything” about this pandemic.
“The best way to prevent the virus from mutating is to prevent hosts, people, from getting sick with it,” he said. “That’s why it’s so important people should get immunized and wear masks.”
Both Dr. Nelson and Dr. Ray pointed out that it is in the best interest of the virus to evolve to be more transmissible and spread to more people. In contrast, a virus that causes people to get so sick that they isolate or die, thus halting transmission, works against viruses surviving evolutionarily.
Some viruses also mutate to become milder over time, but that has not been the case with SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Ray said.
Mutations not the only concern
Viruses have another mechanism that produces new strains, and it works even more quickly than mutations. Recombination, as it’s known, can occur when a person is infected with two different strains of the same virus. If the two versions enter the same cell, the viruses can swap genetic material and produce a third, altogether different strain.
Recombination has already been seen with influenza strains, where H and N genetic segments are swapped to yield H1N1, H1N2, and H3N2 versions of the flu, for example.
“In the early days of SARS-CoV-2 there was so little diversity that recombination did not matter,” Dr. Ray said. However, there are now distinct lineages of the virus circulating globally. If two of these lineages swap segments “this would make a very new viral sequence in one step without having to mutate to gain those differences.”
“The more diverse the strains that are circulating, the bigger a possibility this is,” Dr. Ray said.
Protected, for now
Dr. Walensky’s sober warning came at the same time the CDC released new guidance calling for the wearing of masks indoors in schools and in any location in the country where COVID-19 cases surpass 50 people per 100,000, also known as substantial or high transmission areas.
On a positive note, Dr. Walensky said: “Right now, fortunately, we are not there. The vaccines operate really well in protecting us from severe disease and death.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, made a dire prediction during a media briefing this week that, if we weren’t already living within the reality of the COVID-19 pandemic, would sound more like a pitch for a movie about a dystopian future.
“For the amount of virus circulating in this country right now largely among unvaccinated people, the largest concern that we in public health and science are worried about is that the virus … [becomes] a very transmissible virus that has the potential to evade our vaccines in terms of how it protects us from severe disease and death,” Dr. Walensky told reporters on July 27.
A new, more elusive variant could be “just a few mutations away,” she said.
“That’s a very prescient comment,” Lewis Nelson, MD, professor and clinical chair of emergency medicine and chief of the division of medical toxicology at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, told this news organization.
“We’ve gone through a few mutations already that have been named, and each one of them gets a little more transmissible,” he said. “That’s normal, natural selection and what you would expect to happen as viruses mutate from one strain to another.”
“What we’ve mostly seen this virus do is evolve to become more infectious,” said Stuart Ray, MD, when also asked to comment. “That is the remarkable feature of Delta – that it is so infectious.”
He said that the SARS-CoV-2 has evolved largely as expected, at least so far. “The potential for this virus to mutate has been something that has been a concern from early on.”
“The viral evolution is a bit like a ticking clock. The more we allow infections to occur, the more likely changes will occur. When we have lots of people infected, we give more chances to the virus to diversify and then adapt to selective pressures,” said Dr. Ray, vice-chair of medicine for data integrity and analytics and professor in the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore.
Dr. Nelson said.
If this occurs, he added, “we will have an ineffective vaccine, essentially. And we’ll be back to where we were last March with a brand-new disease.”
Technology to the rescue?
The flexibility of mRNA vaccines is one potential solution. These vaccines could be more easily and quickly adapted to respond to a new, more vaccine-elusive variant.
“That’s absolutely reassuring,” Dr. Nelson said. For example, if a mutation changes the spike protein and vaccines no longer recognize it, a manufacturer could identify the new protein and incorporate that in a new mRNA vaccine.
“The problem is that some people are not taking the current vaccine,” he added. “I’m not sure what is going to make them take the next vaccine.”
Nothing appears certain
When asked how likely a new strain of SARS-CoV-2 could emerge that gets around vaccine protection, Dr. Nelson said, “I think [what] we’ve learned so far there is no way to predict anything” about this pandemic.
“The best way to prevent the virus from mutating is to prevent hosts, people, from getting sick with it,” he said. “That’s why it’s so important people should get immunized and wear masks.”
Both Dr. Nelson and Dr. Ray pointed out that it is in the best interest of the virus to evolve to be more transmissible and spread to more people. In contrast, a virus that causes people to get so sick that they isolate or die, thus halting transmission, works against viruses surviving evolutionarily.
Some viruses also mutate to become milder over time, but that has not been the case with SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Ray said.
Mutations not the only concern
Viruses have another mechanism that produces new strains, and it works even more quickly than mutations. Recombination, as it’s known, can occur when a person is infected with two different strains of the same virus. If the two versions enter the same cell, the viruses can swap genetic material and produce a third, altogether different strain.
Recombination has already been seen with influenza strains, where H and N genetic segments are swapped to yield H1N1, H1N2, and H3N2 versions of the flu, for example.
“In the early days of SARS-CoV-2 there was so little diversity that recombination did not matter,” Dr. Ray said. However, there are now distinct lineages of the virus circulating globally. If two of these lineages swap segments “this would make a very new viral sequence in one step without having to mutate to gain those differences.”
“The more diverse the strains that are circulating, the bigger a possibility this is,” Dr. Ray said.
Protected, for now
Dr. Walensky’s sober warning came at the same time the CDC released new guidance calling for the wearing of masks indoors in schools and in any location in the country where COVID-19 cases surpass 50 people per 100,000, also known as substantial or high transmission areas.
On a positive note, Dr. Walensky said: “Right now, fortunately, we are not there. The vaccines operate really well in protecting us from severe disease and death.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vaccinated people infected with Delta remain contagious
, The New York Times reported late on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data show people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on July 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak in Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
, The New York Times reported late on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data show people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on July 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak in Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
, The New York Times reported late on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data show people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on July 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak in Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
Pfizer vaccine protection wanes after 6 months, study finds
, according to a new study.
The July 28 preprint report of the study, which has not been peer reviewed, suggests a gradual “declining trend in vaccine efficacy” over 6 months after two doses of the Pfizer vaccine in more than 45,000 people worldwide.
The study finds overall effectiveness falls from 96% to 84%.
At the same time, a third booster dose of the Pfizer vaccine increases neutralizing antibody levels against the Delta variant by more than five times, compared to levels after just a second dose in people aged 18-55 years, new data from Pfizer shows.
The third-dose immune response appears even more robust – more than 11 times higher than the second shot – among people aged 65-85 years.
The company noted this could mean an estimated 100-fold increase in Delta variant protection after a third dose. These new findings are outlined in a Pfizer second-quarter 2021 earnings report, which notes that the data are submitted for publication in a medical journal.
The data come from a relatively small number of people studied. There were 11 people in the 18- to 55-year-old group and 12 people in the 65- to 85-year-old group.
“These preliminary data are very encouraging as Delta continues to spread,” Mikael Dolsten, MD, chief scientific officer and president of the Worldwide Research, Development, and Medical organization at Pfizer, said during prepared remarks on a company earnings call July 28, CNN reported.
Availability of a third dose of any of the current COVID-19 vaccines would require amendment of the Food and Drug Administration’s emergency use authorization, or full FDA approval for the vaccine.
The possibility of a third dose authorization or approval has not been without controversy. For example, when Pfizer announced intentions to file for FDA authorization of a booster dose on July 8, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the FDA, and the National Institutes of Health were quick to issue a joint statement saying they would decide when the timing is right for Americans to have a third immunization. The agencies stated, in part, “We are prepared for booster doses if and when the science demonstrates that they are needed.”
In addition, the World Health Organization said at a media briefing on July 12 that rich countries should prioritize sharing of COVID-19 vaccine supplies to other countries in need worldwide before allocating doses for a booster shot for its own residents.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study.
The July 28 preprint report of the study, which has not been peer reviewed, suggests a gradual “declining trend in vaccine efficacy” over 6 months after two doses of the Pfizer vaccine in more than 45,000 people worldwide.
The study finds overall effectiveness falls from 96% to 84%.
At the same time, a third booster dose of the Pfizer vaccine increases neutralizing antibody levels against the Delta variant by more than five times, compared to levels after just a second dose in people aged 18-55 years, new data from Pfizer shows.
The third-dose immune response appears even more robust – more than 11 times higher than the second shot – among people aged 65-85 years.
The company noted this could mean an estimated 100-fold increase in Delta variant protection after a third dose. These new findings are outlined in a Pfizer second-quarter 2021 earnings report, which notes that the data are submitted for publication in a medical journal.
The data come from a relatively small number of people studied. There were 11 people in the 18- to 55-year-old group and 12 people in the 65- to 85-year-old group.
“These preliminary data are very encouraging as Delta continues to spread,” Mikael Dolsten, MD, chief scientific officer and president of the Worldwide Research, Development, and Medical organization at Pfizer, said during prepared remarks on a company earnings call July 28, CNN reported.
Availability of a third dose of any of the current COVID-19 vaccines would require amendment of the Food and Drug Administration’s emergency use authorization, or full FDA approval for the vaccine.
The possibility of a third dose authorization or approval has not been without controversy. For example, when Pfizer announced intentions to file for FDA authorization of a booster dose on July 8, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the FDA, and the National Institutes of Health were quick to issue a joint statement saying they would decide when the timing is right for Americans to have a third immunization. The agencies stated, in part, “We are prepared for booster doses if and when the science demonstrates that they are needed.”
In addition, the World Health Organization said at a media briefing on July 12 that rich countries should prioritize sharing of COVID-19 vaccine supplies to other countries in need worldwide before allocating doses for a booster shot for its own residents.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study.
The July 28 preprint report of the study, which has not been peer reviewed, suggests a gradual “declining trend in vaccine efficacy” over 6 months after two doses of the Pfizer vaccine in more than 45,000 people worldwide.
The study finds overall effectiveness falls from 96% to 84%.
At the same time, a third booster dose of the Pfizer vaccine increases neutralizing antibody levels against the Delta variant by more than five times, compared to levels after just a second dose in people aged 18-55 years, new data from Pfizer shows.
The third-dose immune response appears even more robust – more than 11 times higher than the second shot – among people aged 65-85 years.
The company noted this could mean an estimated 100-fold increase in Delta variant protection after a third dose. These new findings are outlined in a Pfizer second-quarter 2021 earnings report, which notes that the data are submitted for publication in a medical journal.
The data come from a relatively small number of people studied. There were 11 people in the 18- to 55-year-old group and 12 people in the 65- to 85-year-old group.
“These preliminary data are very encouraging as Delta continues to spread,” Mikael Dolsten, MD, chief scientific officer and president of the Worldwide Research, Development, and Medical organization at Pfizer, said during prepared remarks on a company earnings call July 28, CNN reported.
Availability of a third dose of any of the current COVID-19 vaccines would require amendment of the Food and Drug Administration’s emergency use authorization, or full FDA approval for the vaccine.
The possibility of a third dose authorization or approval has not been without controversy. For example, when Pfizer announced intentions to file for FDA authorization of a booster dose on July 8, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the FDA, and the National Institutes of Health were quick to issue a joint statement saying they would decide when the timing is right for Americans to have a third immunization. The agencies stated, in part, “We are prepared for booster doses if and when the science demonstrates that they are needed.”
In addition, the World Health Organization said at a media briefing on July 12 that rich countries should prioritize sharing of COVID-19 vaccine supplies to other countries in need worldwide before allocating doses for a booster shot for its own residents.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.

