User login
Antiepileptic drugs tied to increased Parkinson’s disease risk
, new research suggests.
Drawing on data from the UK Biobank, investigators compared more than 1,400 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with matched control persons and found a considerably higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease among those who had taken AEDs in comparison with those who had not. There was a trend linking a greater number of AED prescriptions and multiple AEDs associated with a greater risk for Parkinson’s disease.
“We observed an association between the most commonly prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the U.K. and Parkinson’s disease using data from UK Biobank,” said senior author Alastair Noyce, PhD, professor of neurology and neuroepidemiology and honorary consultant neurologist, Queen Mary University of London.
“This is the first time that a comprehensive study of the link between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has been undertaken,” said Dr. Noyce.
He added that the findings have no immediate clinical implications, “but further research is definitely needed, [as] this is an interesting observation made in a research setting.”
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Plausible, but unclear link
Recent observational studies have found a “temporal association” between epilepsy and incident Parkinson’s disease, but the mechanism underlying this association is “unclear,” the authors wrote.
It is “plausible” that AEDs “may account for some or all of the apparent association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease” and that movement disorders are potential side effects of AEDs, but the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has “not been well studied,” so it remains “unclear” whether AEDs play a role in the association.
“We have previously reported an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease in several different datasets. Here, we wanted to see if it could be explained by an association with the drugs used to treat epilepsy rather than epilepsy per se,” Dr. Noyce explained.
Are AEDs the culprit?
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank, a longitudinal cohort study with more than 500,000 participants, as well as linked primary care medication data to conduct a nested case-control study to investigate this potential association. Participants ranged in age from 40 to 69 years and were recruited between 2006 and 2010.
The researchers compared 1,433 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with 8,598 control persons who were matched in a 6:1 ratio for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status (median [interquartile range] age, 71 [65-75] years; 60.9% men; 97.5% White).
Of those with Parkinson’s disease, 4.3% had been prescribed an AED prior to the date of their being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, compared with 2.5% in the control group; 4.4% had been diagnosed with epilepsy, compared with 1% of the control persons.
The strongest evidence was for the association between lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and sodium valproate and Parkinson’s disease. There was “weaker evidence” for carbamazepine, although all the AEDs were associated with a higher risk of Parkinson’s disease.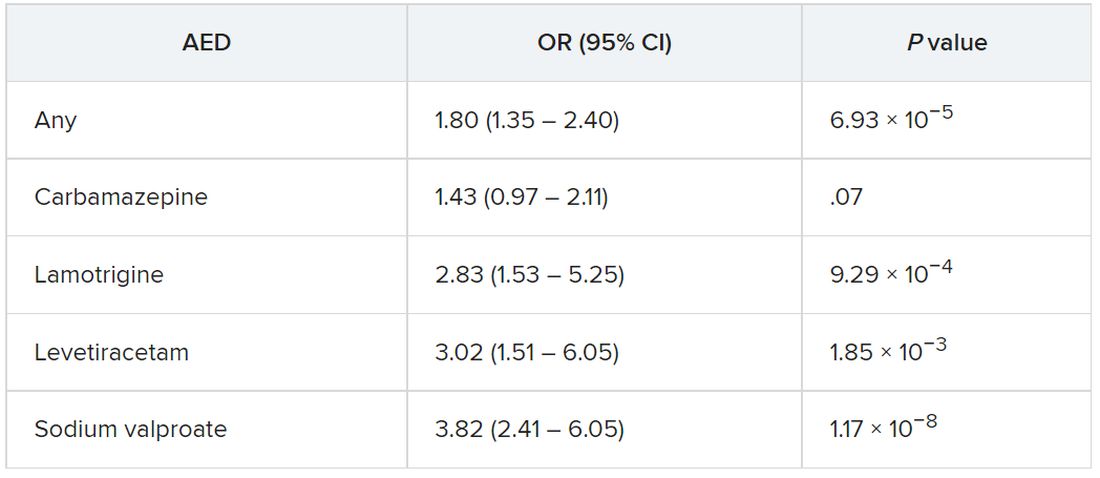
The odds of incident Parkinson’s disease were higher among those who were prescribed one or more AEDs and among individuals who were issued a higher number of prescriptions, the authors reported.
It is possible that it is the epilepsy itself that is associated with the risk of Parkinson’s disease, rather than the drugs, and that “likely explains part of the association we are seeing,” said Dr. Noyce.
“The bottom line is that more research into the links between epilepsy – and drugs used to treat epilepsy – and Parkinson’s disease is needed,” he said.
Moreover, “only with time will we work out whether the findings hold any real clinical relevance,” he added.
Alternative explanations
Commenting on the research, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer, American Parkinson Disease Association, said, “It has been established in prior research that there is an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.” The current study “shows that having had a prescription written for one of four antiepileptic medications was associated with subsequently receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.”
Although one possible conclusion is that the AEDs themselves increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, “there seem to be other alternative explanations as to why a person who had been prescribed AEDs has an increased risk of receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Gilbert, an associate professor of neurology at Bellevue Hospital Center, New York, who was not involved with the current study.
For example, pre-motor changes in the brain of persons with Parkinson’s disease “may increase the risk of requiring an AED by potentially increasing the risk of having a seizure,” and “changes in the brain caused by the seizures for which AEDs are prescribed may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.”
Moreover, psychiatric changes related to Parkinson’s disease may have led to the prescription for AEDs, because at least two of the AEDs are also prescribed for mood stabilization, Dr. Gilbert suggested.
“An unanswered question that the paper acknowledges is, what about people who receive AEDs for reasons other than seizures? Do they also have an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease? This would be an interesting population to focus on because it would remove the link between AEDs and seizure and focus on the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Gilbert said.
She emphasized that people who take AEDs for seizures “should not jump to the conclusion that they must come off these medications so as not to increase their risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.” She noted that having seizures “can be dangerous – injuries can occur during a seizure, and if a seizure can’t be stopped or a number occur in rapid succession, brain injury may result.”
For these reasons, people with “a tendency to have seizures need to protect themselves with AEDs” and “should certainly reach out to their neurologists with any questions,” Dr. Gilbert said.
The Preventive Neurology Unit is funded by Barts Charity. The Apocrita High Performance Cluster facility, supported by Queen Mary University London Research–IT Services, was used for this research. Dr. Noyce has received grants from Barts Charity, Parkinson’s UK, Cure Parkinson’s, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, Innovate UK, Solvemed, and Alchemab and personal fees from AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Zambon, BIAL, uMedeor, Alchemab, Britannia, and Charco Neurotech outside the submitted work. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original article. Dr. Gilbert reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
Drawing on data from the UK Biobank, investigators compared more than 1,400 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with matched control persons and found a considerably higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease among those who had taken AEDs in comparison with those who had not. There was a trend linking a greater number of AED prescriptions and multiple AEDs associated with a greater risk for Parkinson’s disease.
“We observed an association between the most commonly prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the U.K. and Parkinson’s disease using data from UK Biobank,” said senior author Alastair Noyce, PhD, professor of neurology and neuroepidemiology and honorary consultant neurologist, Queen Mary University of London.
“This is the first time that a comprehensive study of the link between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has been undertaken,” said Dr. Noyce.
He added that the findings have no immediate clinical implications, “but further research is definitely needed, [as] this is an interesting observation made in a research setting.”
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Plausible, but unclear link
Recent observational studies have found a “temporal association” between epilepsy and incident Parkinson’s disease, but the mechanism underlying this association is “unclear,” the authors wrote.
It is “plausible” that AEDs “may account for some or all of the apparent association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease” and that movement disorders are potential side effects of AEDs, but the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has “not been well studied,” so it remains “unclear” whether AEDs play a role in the association.
“We have previously reported an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease in several different datasets. Here, we wanted to see if it could be explained by an association with the drugs used to treat epilepsy rather than epilepsy per se,” Dr. Noyce explained.
Are AEDs the culprit?
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank, a longitudinal cohort study with more than 500,000 participants, as well as linked primary care medication data to conduct a nested case-control study to investigate this potential association. Participants ranged in age from 40 to 69 years and were recruited between 2006 and 2010.
The researchers compared 1,433 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with 8,598 control persons who were matched in a 6:1 ratio for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status (median [interquartile range] age, 71 [65-75] years; 60.9% men; 97.5% White).
Of those with Parkinson’s disease, 4.3% had been prescribed an AED prior to the date of their being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, compared with 2.5% in the control group; 4.4% had been diagnosed with epilepsy, compared with 1% of the control persons.
The strongest evidence was for the association between lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and sodium valproate and Parkinson’s disease. There was “weaker evidence” for carbamazepine, although all the AEDs were associated with a higher risk of Parkinson’s disease.
The odds of incident Parkinson’s disease were higher among those who were prescribed one or more AEDs and among individuals who were issued a higher number of prescriptions, the authors reported.
It is possible that it is the epilepsy itself that is associated with the risk of Parkinson’s disease, rather than the drugs, and that “likely explains part of the association we are seeing,” said Dr. Noyce.
“The bottom line is that more research into the links between epilepsy – and drugs used to treat epilepsy – and Parkinson’s disease is needed,” he said.
Moreover, “only with time will we work out whether the findings hold any real clinical relevance,” he added.
Alternative explanations
Commenting on the research, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer, American Parkinson Disease Association, said, “It has been established in prior research that there is an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.” The current study “shows that having had a prescription written for one of four antiepileptic medications was associated with subsequently receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.”
Although one possible conclusion is that the AEDs themselves increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, “there seem to be other alternative explanations as to why a person who had been prescribed AEDs has an increased risk of receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Gilbert, an associate professor of neurology at Bellevue Hospital Center, New York, who was not involved with the current study.
For example, pre-motor changes in the brain of persons with Parkinson’s disease “may increase the risk of requiring an AED by potentially increasing the risk of having a seizure,” and “changes in the brain caused by the seizures for which AEDs are prescribed may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.”
Moreover, psychiatric changes related to Parkinson’s disease may have led to the prescription for AEDs, because at least two of the AEDs are also prescribed for mood stabilization, Dr. Gilbert suggested.
“An unanswered question that the paper acknowledges is, what about people who receive AEDs for reasons other than seizures? Do they also have an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease? This would be an interesting population to focus on because it would remove the link between AEDs and seizure and focus on the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Gilbert said.
She emphasized that people who take AEDs for seizures “should not jump to the conclusion that they must come off these medications so as not to increase their risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.” She noted that having seizures “can be dangerous – injuries can occur during a seizure, and if a seizure can’t be stopped or a number occur in rapid succession, brain injury may result.”
For these reasons, people with “a tendency to have seizures need to protect themselves with AEDs” and “should certainly reach out to their neurologists with any questions,” Dr. Gilbert said.
The Preventive Neurology Unit is funded by Barts Charity. The Apocrita High Performance Cluster facility, supported by Queen Mary University London Research–IT Services, was used for this research. Dr. Noyce has received grants from Barts Charity, Parkinson’s UK, Cure Parkinson’s, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, Innovate UK, Solvemed, and Alchemab and personal fees from AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Zambon, BIAL, uMedeor, Alchemab, Britannia, and Charco Neurotech outside the submitted work. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original article. Dr. Gilbert reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
Drawing on data from the UK Biobank, investigators compared more than 1,400 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with matched control persons and found a considerably higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease among those who had taken AEDs in comparison with those who had not. There was a trend linking a greater number of AED prescriptions and multiple AEDs associated with a greater risk for Parkinson’s disease.
“We observed an association between the most commonly prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the U.K. and Parkinson’s disease using data from UK Biobank,” said senior author Alastair Noyce, PhD, professor of neurology and neuroepidemiology and honorary consultant neurologist, Queen Mary University of London.
“This is the first time that a comprehensive study of the link between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has been undertaken,” said Dr. Noyce.
He added that the findings have no immediate clinical implications, “but further research is definitely needed, [as] this is an interesting observation made in a research setting.”
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Plausible, but unclear link
Recent observational studies have found a “temporal association” between epilepsy and incident Parkinson’s disease, but the mechanism underlying this association is “unclear,” the authors wrote.
It is “plausible” that AEDs “may account for some or all of the apparent association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease” and that movement disorders are potential side effects of AEDs, but the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has “not been well studied,” so it remains “unclear” whether AEDs play a role in the association.
“We have previously reported an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease in several different datasets. Here, we wanted to see if it could be explained by an association with the drugs used to treat epilepsy rather than epilepsy per se,” Dr. Noyce explained.
Are AEDs the culprit?
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank, a longitudinal cohort study with more than 500,000 participants, as well as linked primary care medication data to conduct a nested case-control study to investigate this potential association. Participants ranged in age from 40 to 69 years and were recruited between 2006 and 2010.
The researchers compared 1,433 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with 8,598 control persons who were matched in a 6:1 ratio for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status (median [interquartile range] age, 71 [65-75] years; 60.9% men; 97.5% White).
Of those with Parkinson’s disease, 4.3% had been prescribed an AED prior to the date of their being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, compared with 2.5% in the control group; 4.4% had been diagnosed with epilepsy, compared with 1% of the control persons.
The strongest evidence was for the association between lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and sodium valproate and Parkinson’s disease. There was “weaker evidence” for carbamazepine, although all the AEDs were associated with a higher risk of Parkinson’s disease.
The odds of incident Parkinson’s disease were higher among those who were prescribed one or more AEDs and among individuals who were issued a higher number of prescriptions, the authors reported.
It is possible that it is the epilepsy itself that is associated with the risk of Parkinson’s disease, rather than the drugs, and that “likely explains part of the association we are seeing,” said Dr. Noyce.
“The bottom line is that more research into the links between epilepsy – and drugs used to treat epilepsy – and Parkinson’s disease is needed,” he said.
Moreover, “only with time will we work out whether the findings hold any real clinical relevance,” he added.
Alternative explanations
Commenting on the research, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer, American Parkinson Disease Association, said, “It has been established in prior research that there is an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.” The current study “shows that having had a prescription written for one of four antiepileptic medications was associated with subsequently receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.”
Although one possible conclusion is that the AEDs themselves increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, “there seem to be other alternative explanations as to why a person who had been prescribed AEDs has an increased risk of receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Gilbert, an associate professor of neurology at Bellevue Hospital Center, New York, who was not involved with the current study.
For example, pre-motor changes in the brain of persons with Parkinson’s disease “may increase the risk of requiring an AED by potentially increasing the risk of having a seizure,” and “changes in the brain caused by the seizures for which AEDs are prescribed may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.”
Moreover, psychiatric changes related to Parkinson’s disease may have led to the prescription for AEDs, because at least two of the AEDs are also prescribed for mood stabilization, Dr. Gilbert suggested.
“An unanswered question that the paper acknowledges is, what about people who receive AEDs for reasons other than seizures? Do they also have an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease? This would be an interesting population to focus on because it would remove the link between AEDs and seizure and focus on the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Gilbert said.
She emphasized that people who take AEDs for seizures “should not jump to the conclusion that they must come off these medications so as not to increase their risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.” She noted that having seizures “can be dangerous – injuries can occur during a seizure, and if a seizure can’t be stopped or a number occur in rapid succession, brain injury may result.”
For these reasons, people with “a tendency to have seizures need to protect themselves with AEDs” and “should certainly reach out to their neurologists with any questions,” Dr. Gilbert said.
The Preventive Neurology Unit is funded by Barts Charity. The Apocrita High Performance Cluster facility, supported by Queen Mary University London Research–IT Services, was used for this research. Dr. Noyce has received grants from Barts Charity, Parkinson’s UK, Cure Parkinson’s, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, Innovate UK, Solvemed, and Alchemab and personal fees from AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Zambon, BIAL, uMedeor, Alchemab, Britannia, and Charco Neurotech outside the submitted work. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original article. Dr. Gilbert reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Stem cell transplant superior to DMTs for secondary progressive MS
new research suggests.
Results from a retrospective study show that more than 60% of patients with SPMS who received AHSCT were free from disability progression at 5 years. Also for these patients, improvement was more likely to be maintained for years after treatment.
The investigators noted that patients with secondary progressive disease often show little benefit from other DMTs, so interest in other treatments is high. While AHSCT is known to offer good results for patients with relapsing remitting MS, studies of its efficacy for SPMS have yielded conflicting results.
The new findings suggest it may be time to take another look at this therapy for patients with active, more severe disease, the researchers wrote.
“AHSCT may become a treatment option in secondary progressive MS patients with inflammatory activity who have failed available treatments,” said coinvestigator Matilde Inglese, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Genoa (Italy).
“Patients selection is very important to ensure the best treatment response and minimize safety issues, including transplant-related mortality,” Dr. Inglese added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Class III evidence
In the retrospective, propensity-matching study, researchers used two Italian registries to identify 79 patients who were treated off label with AHSCT and 1,975 patients who received another therapy.
Other DMTs included in the control-group analysis were beta-interferons, azathioprine, glatiramer acetate, mitoxantrone, fingolimod, natalizumab, methotrexate, teriflunomide, cyclophosphamide, dimethyl fumarate, or alemtuzumab.
Results showed that time to first disability progression was significantly longer for patients who had received transplants (hazard ratio, 0.5; P = .005); 61.7% of the AHSCT group were free of disability progression at 5 years versus 46.3% of the control group.
Among patients who received AHSCT, relapse rates were lower in comparison with those who received other DMTs (P < .001), and disability scores were lower over 10 years (P < .001).
The transplant group was also significantly more likely than the other-DMTs group to achieve sustained improvement in disability 3 years after treatment (34.7% vs. 4.6%; P < .001).
“This study provides Class III evidence that autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplants prolonged the time to confirmed disability progression compared to other disease-modifying therapies,” the investigators wrote.
Extends the treatment population
Commenting on the study, Jeff Cohen, MD, director of experimental therapeutics at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, said the research “extends the population for which hematopoietic stem cell transplant should be considered.”
Although previous studies did not show a benefit for patients with severe progressive MS, participants in the current study had secondary progressive MS and superimposed relapse activity, said Dr. Cohen, who was not involved with the research.
“We think that indicates a greater likelihood of benefit” from AHSCT, he noted. “The fact that someone has overt progression or somewhat more severe disability doesn’t preclude the use of stem cell transplant.”
Dr. Cohen pointed out, however, that the study is not without limitations. The exclusion of patients taking B-cell therapies from the SPMS control group raises the question of whether similar results would come from a comparison with AHSCT.
In addition, Dr. Cohen noted there are safety concerns about the therapy, which has yielded higher transplant-related mortality among patients with SPMS – although only one patient in the current study died following the transplant.
Still, the findings are promising, Dr. Cohen added.
“I think as more data accumulate that supports its benefit and reasonable safety in a variety of populations, we’ll see it used more,” he said.
The study was funded by the Italian Multiple Sclerosis Foundation. Dr. Inglese has received fees for consultation from Roche, Genzyme, Merck, Biogen, and Novartis. Dr. Cohen reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Results from a retrospective study show that more than 60% of patients with SPMS who received AHSCT were free from disability progression at 5 years. Also for these patients, improvement was more likely to be maintained for years after treatment.
The investigators noted that patients with secondary progressive disease often show little benefit from other DMTs, so interest in other treatments is high. While AHSCT is known to offer good results for patients with relapsing remitting MS, studies of its efficacy for SPMS have yielded conflicting results.
The new findings suggest it may be time to take another look at this therapy for patients with active, more severe disease, the researchers wrote.
“AHSCT may become a treatment option in secondary progressive MS patients with inflammatory activity who have failed available treatments,” said coinvestigator Matilde Inglese, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Genoa (Italy).
“Patients selection is very important to ensure the best treatment response and minimize safety issues, including transplant-related mortality,” Dr. Inglese added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Class III evidence
In the retrospective, propensity-matching study, researchers used two Italian registries to identify 79 patients who were treated off label with AHSCT and 1,975 patients who received another therapy.
Other DMTs included in the control-group analysis were beta-interferons, azathioprine, glatiramer acetate, mitoxantrone, fingolimod, natalizumab, methotrexate, teriflunomide, cyclophosphamide, dimethyl fumarate, or alemtuzumab.
Results showed that time to first disability progression was significantly longer for patients who had received transplants (hazard ratio, 0.5; P = .005); 61.7% of the AHSCT group were free of disability progression at 5 years versus 46.3% of the control group.
Among patients who received AHSCT, relapse rates were lower in comparison with those who received other DMTs (P < .001), and disability scores were lower over 10 years (P < .001).
The transplant group was also significantly more likely than the other-DMTs group to achieve sustained improvement in disability 3 years after treatment (34.7% vs. 4.6%; P < .001).
“This study provides Class III evidence that autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplants prolonged the time to confirmed disability progression compared to other disease-modifying therapies,” the investigators wrote.
Extends the treatment population
Commenting on the study, Jeff Cohen, MD, director of experimental therapeutics at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, said the research “extends the population for which hematopoietic stem cell transplant should be considered.”
Although previous studies did not show a benefit for patients with severe progressive MS, participants in the current study had secondary progressive MS and superimposed relapse activity, said Dr. Cohen, who was not involved with the research.
“We think that indicates a greater likelihood of benefit” from AHSCT, he noted. “The fact that someone has overt progression or somewhat more severe disability doesn’t preclude the use of stem cell transplant.”
Dr. Cohen pointed out, however, that the study is not without limitations. The exclusion of patients taking B-cell therapies from the SPMS control group raises the question of whether similar results would come from a comparison with AHSCT.
In addition, Dr. Cohen noted there are safety concerns about the therapy, which has yielded higher transplant-related mortality among patients with SPMS – although only one patient in the current study died following the transplant.
Still, the findings are promising, Dr. Cohen added.
“I think as more data accumulate that supports its benefit and reasonable safety in a variety of populations, we’ll see it used more,” he said.
The study was funded by the Italian Multiple Sclerosis Foundation. Dr. Inglese has received fees for consultation from Roche, Genzyme, Merck, Biogen, and Novartis. Dr. Cohen reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Results from a retrospective study show that more than 60% of patients with SPMS who received AHSCT were free from disability progression at 5 years. Also for these patients, improvement was more likely to be maintained for years after treatment.
The investigators noted that patients with secondary progressive disease often show little benefit from other DMTs, so interest in other treatments is high. While AHSCT is known to offer good results for patients with relapsing remitting MS, studies of its efficacy for SPMS have yielded conflicting results.
The new findings suggest it may be time to take another look at this therapy for patients with active, more severe disease, the researchers wrote.
“AHSCT may become a treatment option in secondary progressive MS patients with inflammatory activity who have failed available treatments,” said coinvestigator Matilde Inglese, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Genoa (Italy).
“Patients selection is very important to ensure the best treatment response and minimize safety issues, including transplant-related mortality,” Dr. Inglese added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Class III evidence
In the retrospective, propensity-matching study, researchers used two Italian registries to identify 79 patients who were treated off label with AHSCT and 1,975 patients who received another therapy.
Other DMTs included in the control-group analysis were beta-interferons, azathioprine, glatiramer acetate, mitoxantrone, fingolimod, natalizumab, methotrexate, teriflunomide, cyclophosphamide, dimethyl fumarate, or alemtuzumab.
Results showed that time to first disability progression was significantly longer for patients who had received transplants (hazard ratio, 0.5; P = .005); 61.7% of the AHSCT group were free of disability progression at 5 years versus 46.3% of the control group.
Among patients who received AHSCT, relapse rates were lower in comparison with those who received other DMTs (P < .001), and disability scores were lower over 10 years (P < .001).
The transplant group was also significantly more likely than the other-DMTs group to achieve sustained improvement in disability 3 years after treatment (34.7% vs. 4.6%; P < .001).
“This study provides Class III evidence that autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplants prolonged the time to confirmed disability progression compared to other disease-modifying therapies,” the investigators wrote.
Extends the treatment population
Commenting on the study, Jeff Cohen, MD, director of experimental therapeutics at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, said the research “extends the population for which hematopoietic stem cell transplant should be considered.”
Although previous studies did not show a benefit for patients with severe progressive MS, participants in the current study had secondary progressive MS and superimposed relapse activity, said Dr. Cohen, who was not involved with the research.
“We think that indicates a greater likelihood of benefit” from AHSCT, he noted. “The fact that someone has overt progression or somewhat more severe disability doesn’t preclude the use of stem cell transplant.”
Dr. Cohen pointed out, however, that the study is not without limitations. The exclusion of patients taking B-cell therapies from the SPMS control group raises the question of whether similar results would come from a comparison with AHSCT.
In addition, Dr. Cohen noted there are safety concerns about the therapy, which has yielded higher transplant-related mortality among patients with SPMS – although only one patient in the current study died following the transplant.
Still, the findings are promising, Dr. Cohen added.
“I think as more data accumulate that supports its benefit and reasonable safety in a variety of populations, we’ll see it used more,” he said.
The study was funded by the Italian Multiple Sclerosis Foundation. Dr. Inglese has received fees for consultation from Roche, Genzyme, Merck, Biogen, and Novartis. Dr. Cohen reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Prodromal Parkinson’s disease tied to significant functional impairment
new research shows.
The new findings come from a large case-control study that analyzed Medicare claims data to evaluate functional limitations in prodromal Parkinson’s disease, leading the investigators to suggest prodromal Parkinson’s disease should be recognized as a distinct disease stage.
“It’s increasingly recognized as a stage of Parkinson’s and there is an argument here for that,” said lead investigator Cameron Miller-Patterson, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond. “Because we’re finding that people with prodromal Parkinson’s disease may have functional limitations, identifying them sooner and getting them the appropriate symptomatic therapy could be helpful.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Improving quality of life
Individuals with prodromal Parkinson’s disease have symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, but not enough to meet diagnostic criteria. However, all patients with prodromal Parkinson’s disease eventually meet that threshold.
To evaluate whether functional limitations are present in individuals with Parkinson’s disease prior to diagnosis versus the general population, researchers analyzed Medicare-linked data on 6,674 individuals aged 65 years and older who participated in the National Health and Aging Trends Study, a longitudinal survey in the United States. Survey questions evaluated dexterity, eating, mobility, mood, pain, sleep, speech, strength, and vision.
Patients with incident Parkinson’s disease were defined as having two or more Medicare diagnoses. Controls were defined as those with Medicare eligibility at baseline and 2 or more years prior, with no diagnosis.
Compared with individuals who never had Parkinson’s disease, those who eventually received a diagnosis were less likely to report being able to walk 6 blocks (odds ratio, 0.34; 95% confidence interval, 0.15-0.82), stand independently from kneeling (OR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.11-0.85) or lift a heavy object overhead (OR, 0.36; 95% CI, 0.15-0.87). They were also more likely to report imbalance (OR, 2.77; 95% CI, 1.24-6.20) 3 years prior to diagnosis.
“Generally, we don’t start treating people until we see them in the clinic and give them a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Miller-Patterson said. “If we identify them earlier, even before diagnosis, we may be able to improve their quality of life by treating them sooner.”
Serving patients better
Better recognition of prodromal Parkinson’s disease could also help identify participants for clinical trials of therapeutics that could slow disease progression, something that is beyond the ability of currently approved medications.
This, and growing support for distinguishing prodromal Parkinson’s disease as an official stage of Parkinson’s disease, makes findings such as these both timely and important, the authors of an accompanying commentary wrote .
“The recognition of a prodromal period has been viewed as potentially critical to the success of disease-modifying interventions, on the argument that it may be too late to enact meaningful clinical change once symptoms clinically manifest given the degree of neurodegeneration already present,” Ian O. Bledsoe, MD, Weill Institute for Neurosciences, University of California, San Francisco, and coauthors wrote.
One limitation, however, is that the study design didn’t allow researchers to determine if individuals with eventual Parkinson’s disease who reported parkinsonian symptoms had prodromal Parkinson’s disease or undiagnosed disease. The answer would clarify whether prodromal Parkinson’s disease is more common than previously thought or if Parkinson’s disease diagnosis is often delayed for years – or both.
“Despite the limitations of this study, its broader point and importance remain: People appear to have some markers of functional decline before they are diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease,” the editorialists wrote. “Additionally, motor dysfunction may arise at an earlier time point in the disease than we typically think. There is a potential opportunity to serve this population better.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Miller-Patterson reported receiving other NIH grants during the course of the study. Dr. Bledsoe reported personal fees from Boston Scientific, Amneal Pharmaceuticals, IDEO, Accorda, Humancraft.com, and Putnam Associates, as well as grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and Dystonia Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
The new findings come from a large case-control study that analyzed Medicare claims data to evaluate functional limitations in prodromal Parkinson’s disease, leading the investigators to suggest prodromal Parkinson’s disease should be recognized as a distinct disease stage.
“It’s increasingly recognized as a stage of Parkinson’s and there is an argument here for that,” said lead investigator Cameron Miller-Patterson, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond. “Because we’re finding that people with prodromal Parkinson’s disease may have functional limitations, identifying them sooner and getting them the appropriate symptomatic therapy could be helpful.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Improving quality of life
Individuals with prodromal Parkinson’s disease have symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, but not enough to meet diagnostic criteria. However, all patients with prodromal Parkinson’s disease eventually meet that threshold.
To evaluate whether functional limitations are present in individuals with Parkinson’s disease prior to diagnosis versus the general population, researchers analyzed Medicare-linked data on 6,674 individuals aged 65 years and older who participated in the National Health and Aging Trends Study, a longitudinal survey in the United States. Survey questions evaluated dexterity, eating, mobility, mood, pain, sleep, speech, strength, and vision.
Patients with incident Parkinson’s disease were defined as having two or more Medicare diagnoses. Controls were defined as those with Medicare eligibility at baseline and 2 or more years prior, with no diagnosis.
Compared with individuals who never had Parkinson’s disease, those who eventually received a diagnosis were less likely to report being able to walk 6 blocks (odds ratio, 0.34; 95% confidence interval, 0.15-0.82), stand independently from kneeling (OR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.11-0.85) or lift a heavy object overhead (OR, 0.36; 95% CI, 0.15-0.87). They were also more likely to report imbalance (OR, 2.77; 95% CI, 1.24-6.20) 3 years prior to diagnosis.
“Generally, we don’t start treating people until we see them in the clinic and give them a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Miller-Patterson said. “If we identify them earlier, even before diagnosis, we may be able to improve their quality of life by treating them sooner.”
Serving patients better
Better recognition of prodromal Parkinson’s disease could also help identify participants for clinical trials of therapeutics that could slow disease progression, something that is beyond the ability of currently approved medications.
This, and growing support for distinguishing prodromal Parkinson’s disease as an official stage of Parkinson’s disease, makes findings such as these both timely and important, the authors of an accompanying commentary wrote .
“The recognition of a prodromal period has been viewed as potentially critical to the success of disease-modifying interventions, on the argument that it may be too late to enact meaningful clinical change once symptoms clinically manifest given the degree of neurodegeneration already present,” Ian O. Bledsoe, MD, Weill Institute for Neurosciences, University of California, San Francisco, and coauthors wrote.
One limitation, however, is that the study design didn’t allow researchers to determine if individuals with eventual Parkinson’s disease who reported parkinsonian symptoms had prodromal Parkinson’s disease or undiagnosed disease. The answer would clarify whether prodromal Parkinson’s disease is more common than previously thought or if Parkinson’s disease diagnosis is often delayed for years – or both.
“Despite the limitations of this study, its broader point and importance remain: People appear to have some markers of functional decline before they are diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease,” the editorialists wrote. “Additionally, motor dysfunction may arise at an earlier time point in the disease than we typically think. There is a potential opportunity to serve this population better.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Miller-Patterson reported receiving other NIH grants during the course of the study. Dr. Bledsoe reported personal fees from Boston Scientific, Amneal Pharmaceuticals, IDEO, Accorda, Humancraft.com, and Putnam Associates, as well as grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and Dystonia Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
The new findings come from a large case-control study that analyzed Medicare claims data to evaluate functional limitations in prodromal Parkinson’s disease, leading the investigators to suggest prodromal Parkinson’s disease should be recognized as a distinct disease stage.
“It’s increasingly recognized as a stage of Parkinson’s and there is an argument here for that,” said lead investigator Cameron Miller-Patterson, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond. “Because we’re finding that people with prodromal Parkinson’s disease may have functional limitations, identifying them sooner and getting them the appropriate symptomatic therapy could be helpful.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Improving quality of life
Individuals with prodromal Parkinson’s disease have symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, but not enough to meet diagnostic criteria. However, all patients with prodromal Parkinson’s disease eventually meet that threshold.
To evaluate whether functional limitations are present in individuals with Parkinson’s disease prior to diagnosis versus the general population, researchers analyzed Medicare-linked data on 6,674 individuals aged 65 years and older who participated in the National Health and Aging Trends Study, a longitudinal survey in the United States. Survey questions evaluated dexterity, eating, mobility, mood, pain, sleep, speech, strength, and vision.
Patients with incident Parkinson’s disease were defined as having two or more Medicare diagnoses. Controls were defined as those with Medicare eligibility at baseline and 2 or more years prior, with no diagnosis.
Compared with individuals who never had Parkinson’s disease, those who eventually received a diagnosis were less likely to report being able to walk 6 blocks (odds ratio, 0.34; 95% confidence interval, 0.15-0.82), stand independently from kneeling (OR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.11-0.85) or lift a heavy object overhead (OR, 0.36; 95% CI, 0.15-0.87). They were also more likely to report imbalance (OR, 2.77; 95% CI, 1.24-6.20) 3 years prior to diagnosis.
“Generally, we don’t start treating people until we see them in the clinic and give them a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Miller-Patterson said. “If we identify them earlier, even before diagnosis, we may be able to improve their quality of life by treating them sooner.”
Serving patients better
Better recognition of prodromal Parkinson’s disease could also help identify participants for clinical trials of therapeutics that could slow disease progression, something that is beyond the ability of currently approved medications.
This, and growing support for distinguishing prodromal Parkinson’s disease as an official stage of Parkinson’s disease, makes findings such as these both timely and important, the authors of an accompanying commentary wrote .
“The recognition of a prodromal period has been viewed as potentially critical to the success of disease-modifying interventions, on the argument that it may be too late to enact meaningful clinical change once symptoms clinically manifest given the degree of neurodegeneration already present,” Ian O. Bledsoe, MD, Weill Institute for Neurosciences, University of California, San Francisco, and coauthors wrote.
One limitation, however, is that the study design didn’t allow researchers to determine if individuals with eventual Parkinson’s disease who reported parkinsonian symptoms had prodromal Parkinson’s disease or undiagnosed disease. The answer would clarify whether prodromal Parkinson’s disease is more common than previously thought or if Parkinson’s disease diagnosis is often delayed for years – or both.
“Despite the limitations of this study, its broader point and importance remain: People appear to have some markers of functional decline before they are diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease,” the editorialists wrote. “Additionally, motor dysfunction may arise at an earlier time point in the disease than we typically think. There is a potential opportunity to serve this population better.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Miller-Patterson reported receiving other NIH grants during the course of the study. Dr. Bledsoe reported personal fees from Boston Scientific, Amneal Pharmaceuticals, IDEO, Accorda, Humancraft.com, and Putnam Associates, as well as grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and Dystonia Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Cluster headache tied to high risk of mental and neurologic disorders
, leading to significant disability and absenteeism, new research shows.
Results from a Swedish register-based study also showed that patients with cluster headache had a sixfold increased risk for central nervous system disorders and a twofold increased risk for musculoskeletal disorders.
Although cluster headaches are often more prevalent in men, researchers found that multimorbidity rates were significantly higher in women. In addition, rates of external injuries were significantly higher among individuals with cluster headache than among persons without cluster headache.
“The findings very clearly indicate that cluster headache patients suffer from other health issues as well and that they are at risk of having longer periods of times when they cannot work,” said lead investigator Caroline Ran, PhD, a research specialist in the department of neuroscience at the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm.
“It’s really important for clinicians to look at cluster headache from a broader perspective and make sure that patients are followed up so that they don’t risk ending up in a situation where they have several comorbidities,” Dr. Ran added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
‘Striking’ finding
Cluster headache is one of the most severe and debilitating types of headache. It causes intense pain behind the eyes, which has been described as being worse than pain associated with childbirth or kidney stones.
Attacks can occur multiple times in a single day and can last up to 3 hours. Cluster headache is rare, occurring in about 1 in 1,000 individuals, and is more common in men. Underdiagnosis is common – especially in women.
The study drew on two Swedish population-based registries and included 3,240 patients with cluster headache aged 16-64 years and 16,200 matched control persons. The analysis covered medical visits from 2001 to 2010.
Results showed that 91.9% of participants with cluster headache had some type of multimorbidity. By comparison, 77.6% of the control group had some type of multimorbidity (odds ratio, 3.26; P < .0001).
Prior studies have shown a higher incidence of mental health and behavioral disorders among patients with cluster headache. However, when the researchers removed those conditions along with external injuries from the dataset, patients with headache were still significantly more likely to have multiple co-occurring illnesses (86.7% vs. 68.8%; OR, 2.95; P < .0001).
The most common comorbid conditions in the overall cluster headache group were diseases of the nervous system (OR, 5.9; 95% CI, 5.46 -6.42); 51.8% of the cluster headache group reported these disorders, compared with just 15.4% of the control group.
Diseases of the eye, the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal systems, and connective tissue were also significantly more common among patients with cluster headache.
“For each diagnosis that we investigated, we found a higher incidence in the cluster headache group, and we thought this was a very striking finding and worth discussing in the clinical setting that these patients are at risk of general ill health,” Dr. Ran said.
Risky behavior?
Another novel finding was the higher rate of external injuries among the cluster headache group, compared with the control group. The finding seems to back up the theory that patients with cluster headache are more likely to engage in risky behaviors, the researchers noted.
In the cluster headache group, external injuries were reported by 47.1% of men and 41% of women, versus 34.9% and 26.0%, respectively, in the control group.
“Now we can also show that cluster headache patients have more injuries and that is totally unrelated to the biological health of the individuals, so that could also indicate higher risk taking,” Dr. Ran said.
Overall multimorbidity rates and diagnoses in each medical category except external injury were higher among women with cluster headache than men with headaches. In addition, the mean number of days on sick leave and disability pension was higher among women with cluster headache than among men with cluster headache (83.71 days vs. 52.56 days).
Overall, the mean number of sickness absence and disability pension net days in 2010 was nearly twice as high in the cluster headache group as in the control group (63.15 days vs. 34.08 days).
Removing mental and behavioral health disorders from the mix did not lower those numbers.
“Our numbers indicate that the mental health issues that are related to cluster headache might not impact their work situation as much as the other comorbidities,” Dr. Ran said.
Struggle is real
Commenting on the findings, Heidi Schwarz, MD, professor of clinical neurology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, called the study a “valuable contribution” to the field and to the treatment of cluster headache.
“It’s a good study that addresses factors that really need to be considered as you take care of these patients,” said Dr. Schwarz, who was not involved with the research.
“The most salient features of this is that cluster headache is quite disabling, and if you add a comorbidity to it, it’s even more disabling,” she said.
Dr. Schwarz noted that cluster headache is often misdiagnosed as migraine or is overlooked altogether, especially in women. These data underscore that, although cluster headache is more common in men, it affects women too and could lead to even greater disability.
“This has a direct impact on patient quality of life, and in the end, that really should be what we’re looking to enhance,” Dr. Schwarz said. “When a patient with cluster comes in and they tell you they’re really struggling, believe them because it’s quite real.”
The findings also fill a gap in the literature and offer the kind of data that could not be collected in the United States, she noted. Sweden provides paid sick time for all workers aged 16 and older and offers a disability pension to all workers whose ability to work is temporarily or permanently inhibited because of illness or injury.
“You will never get this kind of data in the United States because this kind of data comes from two datasets that are extremely inclusive and detailed in a society, Sweden, where they have a social support system,” Dr. Schwarz said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Brain Foundation, and Mellby Gård, Region Stockholm, Märta Lundkvist stiftelse and Karolinska Institutet research funds. Dr. Ran and Dr. Schwarz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, leading to significant disability and absenteeism, new research shows.
Results from a Swedish register-based study also showed that patients with cluster headache had a sixfold increased risk for central nervous system disorders and a twofold increased risk for musculoskeletal disorders.
Although cluster headaches are often more prevalent in men, researchers found that multimorbidity rates were significantly higher in women. In addition, rates of external injuries were significantly higher among individuals with cluster headache than among persons without cluster headache.
“The findings very clearly indicate that cluster headache patients suffer from other health issues as well and that they are at risk of having longer periods of times when they cannot work,” said lead investigator Caroline Ran, PhD, a research specialist in the department of neuroscience at the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm.
“It’s really important for clinicians to look at cluster headache from a broader perspective and make sure that patients are followed up so that they don’t risk ending up in a situation where they have several comorbidities,” Dr. Ran added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
‘Striking’ finding
Cluster headache is one of the most severe and debilitating types of headache. It causes intense pain behind the eyes, which has been described as being worse than pain associated with childbirth or kidney stones.
Attacks can occur multiple times in a single day and can last up to 3 hours. Cluster headache is rare, occurring in about 1 in 1,000 individuals, and is more common in men. Underdiagnosis is common – especially in women.
The study drew on two Swedish population-based registries and included 3,240 patients with cluster headache aged 16-64 years and 16,200 matched control persons. The analysis covered medical visits from 2001 to 2010.
Results showed that 91.9% of participants with cluster headache had some type of multimorbidity. By comparison, 77.6% of the control group had some type of multimorbidity (odds ratio, 3.26; P < .0001).
Prior studies have shown a higher incidence of mental health and behavioral disorders among patients with cluster headache. However, when the researchers removed those conditions along with external injuries from the dataset, patients with headache were still significantly more likely to have multiple co-occurring illnesses (86.7% vs. 68.8%; OR, 2.95; P < .0001).
The most common comorbid conditions in the overall cluster headache group were diseases of the nervous system (OR, 5.9; 95% CI, 5.46 -6.42); 51.8% of the cluster headache group reported these disorders, compared with just 15.4% of the control group.
Diseases of the eye, the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal systems, and connective tissue were also significantly more common among patients with cluster headache.
“For each diagnosis that we investigated, we found a higher incidence in the cluster headache group, and we thought this was a very striking finding and worth discussing in the clinical setting that these patients are at risk of general ill health,” Dr. Ran said.
Risky behavior?
Another novel finding was the higher rate of external injuries among the cluster headache group, compared with the control group. The finding seems to back up the theory that patients with cluster headache are more likely to engage in risky behaviors, the researchers noted.
In the cluster headache group, external injuries were reported by 47.1% of men and 41% of women, versus 34.9% and 26.0%, respectively, in the control group.
“Now we can also show that cluster headache patients have more injuries and that is totally unrelated to the biological health of the individuals, so that could also indicate higher risk taking,” Dr. Ran said.
Overall multimorbidity rates and diagnoses in each medical category except external injury were higher among women with cluster headache than men with headaches. In addition, the mean number of days on sick leave and disability pension was higher among women with cluster headache than among men with cluster headache (83.71 days vs. 52.56 days).
Overall, the mean number of sickness absence and disability pension net days in 2010 was nearly twice as high in the cluster headache group as in the control group (63.15 days vs. 34.08 days).
Removing mental and behavioral health disorders from the mix did not lower those numbers.
“Our numbers indicate that the mental health issues that are related to cluster headache might not impact their work situation as much as the other comorbidities,” Dr. Ran said.
Struggle is real
Commenting on the findings, Heidi Schwarz, MD, professor of clinical neurology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, called the study a “valuable contribution” to the field and to the treatment of cluster headache.
“It’s a good study that addresses factors that really need to be considered as you take care of these patients,” said Dr. Schwarz, who was not involved with the research.
“The most salient features of this is that cluster headache is quite disabling, and if you add a comorbidity to it, it’s even more disabling,” she said.
Dr. Schwarz noted that cluster headache is often misdiagnosed as migraine or is overlooked altogether, especially in women. These data underscore that, although cluster headache is more common in men, it affects women too and could lead to even greater disability.
“This has a direct impact on patient quality of life, and in the end, that really should be what we’re looking to enhance,” Dr. Schwarz said. “When a patient with cluster comes in and they tell you they’re really struggling, believe them because it’s quite real.”
The findings also fill a gap in the literature and offer the kind of data that could not be collected in the United States, she noted. Sweden provides paid sick time for all workers aged 16 and older and offers a disability pension to all workers whose ability to work is temporarily or permanently inhibited because of illness or injury.
“You will never get this kind of data in the United States because this kind of data comes from two datasets that are extremely inclusive and detailed in a society, Sweden, where they have a social support system,” Dr. Schwarz said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Brain Foundation, and Mellby Gård, Region Stockholm, Märta Lundkvist stiftelse and Karolinska Institutet research funds. Dr. Ran and Dr. Schwarz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, leading to significant disability and absenteeism, new research shows.
Results from a Swedish register-based study also showed that patients with cluster headache had a sixfold increased risk for central nervous system disorders and a twofold increased risk for musculoskeletal disorders.
Although cluster headaches are often more prevalent in men, researchers found that multimorbidity rates were significantly higher in women. In addition, rates of external injuries were significantly higher among individuals with cluster headache than among persons without cluster headache.
“The findings very clearly indicate that cluster headache patients suffer from other health issues as well and that they are at risk of having longer periods of times when they cannot work,” said lead investigator Caroline Ran, PhD, a research specialist in the department of neuroscience at the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm.
“It’s really important for clinicians to look at cluster headache from a broader perspective and make sure that patients are followed up so that they don’t risk ending up in a situation where they have several comorbidities,” Dr. Ran added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
‘Striking’ finding
Cluster headache is one of the most severe and debilitating types of headache. It causes intense pain behind the eyes, which has been described as being worse than pain associated with childbirth or kidney stones.
Attacks can occur multiple times in a single day and can last up to 3 hours. Cluster headache is rare, occurring in about 1 in 1,000 individuals, and is more common in men. Underdiagnosis is common – especially in women.
The study drew on two Swedish population-based registries and included 3,240 patients with cluster headache aged 16-64 years and 16,200 matched control persons. The analysis covered medical visits from 2001 to 2010.
Results showed that 91.9% of participants with cluster headache had some type of multimorbidity. By comparison, 77.6% of the control group had some type of multimorbidity (odds ratio, 3.26; P < .0001).
Prior studies have shown a higher incidence of mental health and behavioral disorders among patients with cluster headache. However, when the researchers removed those conditions along with external injuries from the dataset, patients with headache were still significantly more likely to have multiple co-occurring illnesses (86.7% vs. 68.8%; OR, 2.95; P < .0001).
The most common comorbid conditions in the overall cluster headache group were diseases of the nervous system (OR, 5.9; 95% CI, 5.46 -6.42); 51.8% of the cluster headache group reported these disorders, compared with just 15.4% of the control group.
Diseases of the eye, the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal systems, and connective tissue were also significantly more common among patients with cluster headache.
“For each diagnosis that we investigated, we found a higher incidence in the cluster headache group, and we thought this was a very striking finding and worth discussing in the clinical setting that these patients are at risk of general ill health,” Dr. Ran said.
Risky behavior?
Another novel finding was the higher rate of external injuries among the cluster headache group, compared with the control group. The finding seems to back up the theory that patients with cluster headache are more likely to engage in risky behaviors, the researchers noted.
In the cluster headache group, external injuries were reported by 47.1% of men and 41% of women, versus 34.9% and 26.0%, respectively, in the control group.
“Now we can also show that cluster headache patients have more injuries and that is totally unrelated to the biological health of the individuals, so that could also indicate higher risk taking,” Dr. Ran said.
Overall multimorbidity rates and diagnoses in each medical category except external injury were higher among women with cluster headache than men with headaches. In addition, the mean number of days on sick leave and disability pension was higher among women with cluster headache than among men with cluster headache (83.71 days vs. 52.56 days).
Overall, the mean number of sickness absence and disability pension net days in 2010 was nearly twice as high in the cluster headache group as in the control group (63.15 days vs. 34.08 days).
Removing mental and behavioral health disorders from the mix did not lower those numbers.
“Our numbers indicate that the mental health issues that are related to cluster headache might not impact their work situation as much as the other comorbidities,” Dr. Ran said.
Struggle is real
Commenting on the findings, Heidi Schwarz, MD, professor of clinical neurology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, called the study a “valuable contribution” to the field and to the treatment of cluster headache.
“It’s a good study that addresses factors that really need to be considered as you take care of these patients,” said Dr. Schwarz, who was not involved with the research.
“The most salient features of this is that cluster headache is quite disabling, and if you add a comorbidity to it, it’s even more disabling,” she said.
Dr. Schwarz noted that cluster headache is often misdiagnosed as migraine or is overlooked altogether, especially in women. These data underscore that, although cluster headache is more common in men, it affects women too and could lead to even greater disability.
“This has a direct impact on patient quality of life, and in the end, that really should be what we’re looking to enhance,” Dr. Schwarz said. “When a patient with cluster comes in and they tell you they’re really struggling, believe them because it’s quite real.”
The findings also fill a gap in the literature and offer the kind of data that could not be collected in the United States, she noted. Sweden provides paid sick time for all workers aged 16 and older and offers a disability pension to all workers whose ability to work is temporarily or permanently inhibited because of illness or injury.
“You will never get this kind of data in the United States because this kind of data comes from two datasets that are extremely inclusive and detailed in a society, Sweden, where they have a social support system,” Dr. Schwarz said.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Brain Foundation, and Mellby Gård, Region Stockholm, Märta Lundkvist stiftelse and Karolinska Institutet research funds. Dr. Ran and Dr. Schwarz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Annual U.S. Parkinson’s disease incidence 50% higher than earlier estimates
according to new research that investigators say highlights the growing strain on clinical services and the need for more research funding.
In an analysis of five databases and more than 15 million people, about 60,000-90,000 individuals older than 45 years are estimated to be diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease each year – which is far more than the previous estimate of around 40,000-60,000 new cases annually.
This is the latest study to update decades-old epidemiologic data on Parkinson’s disease incidence and prevalence. Previous incidence rates came from small, single-population studies that are now more than 25 years old.
“In the advocacy community, we’ve been earnest about the impact of people living with Parkinson’s disease, and what we really lacked was sufficient data to be able to demonstrate the urgency of our need,” said study coinvestigator James Beck, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Parkinson’s Foundation, New York.
“We wanted to revise these numbers, highlight that they are larger than people anticipated, and use it as a call to action to change the approach we have toward Parkinson’s,” Dr. Beck said.
The findings were published online in NPJ Parkinson’s Disease.
Updating an outdated model
The study builds on the Parkinson’s Prevalence Project, a 2018 initiative that used a new model to calculate Parkinson’s disease prevalence. Before then, federal prevalence data was based on a 40-year-old study of just 26 Parkinson’s disease cases in one small county in rural Mississippi.
Dr. Beck and others used a more sophisticated model, using data from five separate cohort studies. They estimated the total number of patients living with Parkinson’s disease in the United States to be 930,000, which is far higher than the 650,000 the old model predicted.
Researchers then moved on to the current project, developing a new method to estimate Parkinson’s disease incidence.
The project included 2012 data on more than 15 million individuals in the United States and Canada. The investigators drew from three large insurance databases (Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Ontario Health Care, and Medicare) and two long-term epidemiologic studies (the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study and the Rochester Epidemiology Project).
On the basis of their analysis, the investigators proposed a working Parkinson’s disease incident rate estimate of 47-77 cases per 100,000 people aged 45 years or older. Limiting the analysis to those aged 65 or older raised the incidence to 108-212 per 100,000 people.
That translates to 60,000-95,000 new cases each year among adults aged 45 years or older. Using the Medicare administrative database alone for this same time period suggests an annual incidence of nearly 90,000 for individuals aged 65 or older.
“The numbers we’re proposing are conservative,” Dr. Beck said. “The true numbers are probably north of 90,000.”
Incidence rates increased with age and were higher in men. The researchers also identified clusters of counties with higher incidence rates in parts of the country called the “Parkinson’s belt.”
That geographic area mirrors the Rust Belt and includes parts of the Northeastern and Midwestern United States with a long history of industrial manufacturing that used heavy metals and industrial solvents, which are environmental factors linked to risk for Parkinson’s disease.
Cases were also higher in southern California, southeastern Texas, and Florida – agricultural regions with high pesticide use, which is also a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease. Central Pennsylvania also had higher incidence rates.
Why the increase?
The increase in cases could be the result of the more comprehensive estimation model used, the researchers noted. Or it could be improved detection, the aging population, a rise in sedentary lifestyles, increased exposure to environmental risk factors, or even the sharp decline in smoking in the United States, as some studies have shown that smokers have a lower Parkinson’s disease risk.
“The short answer is, we don’t know; and the long answer is, it’s all the above,” Dr. Beck said.
Although about 15% of Parkinson’s disease cases have a genetic basis, the cause is unknown in the majority of cases. In addition, diagnosis is difficult because there is no blood test or scan that detects the disease.
“Diagnosis requires a skilled clinician with real familiarity with Parkinson’s. And we have a real shortage of neurologists in this country to not only be able to diagnose but also to treat the condition,” Dr. Beck said.
That was one motivation for doing the study: to highlight what experts say is a pending clinical crisis for patients with Parkinson’s disease, he added.
The investigators also wanted to raise awareness about the scope of the disorder – not just about prevalence and incidence but also what those data mean for the health care industry, research aims, drug development and health care coverage, and policies.
In a 2020 study, the same researchers calculated a cost of $52 billion per year for medical and nonmedical costs related to Parkinson’s disease, which works out to about $26,000 per year per patient. That figure is expected to surpass $79 billion by 2030.
“This is an urgent condition for many people who live with the disease. And to the extent we can get our country to recognize that and really make the investment now, this is an area where a stitch in time saves nine,” Dr. Beck said.
“If we can invest some money now, we have a chance to really make a difference in the future,” he added.
‘Groundbreaking’ findings
Commenting on the findings, Jori Fleisher, MD, MSCE, associate professor of neurological sciences at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, called the results “groundbreaking” and said that they validate what clinicians have been seeing in real-world practice.
“The findings reflect what a lot of us in practice have been appreciating anecdotally, which is that it seems that Parkinson’s is being diagnosed more frequently and that the incidence has been rising,” said Dr. Fleisher, who was not involved with the study.
She noted that the use of multiple datasets is one element of the methodology that makes the data so significant.
“There has been great work out of individual centers; but no matter how good your study methods are within that one population, you’re drawing conclusions based on that one population,” Dr. Fleisher said.
This research, together with the previous work by the group on prevalence data, could go a long way toward raising awareness about the scope of Parkinson’s disease in the United States – which could lead to earlier diagnosis, more research funding, and increased attention on the need for more clinicians who specialize in movement disorders, she added.
“This should increase research funding across the spectrum, including everything from the basic science to translational research, clinical research and implementation, and health services research,” Dr. Fleisher said.
The study was supported by the Parkinson’s Foundation, The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, and the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Beck and Dr. Fleisher reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to new research that investigators say highlights the growing strain on clinical services and the need for more research funding.
In an analysis of five databases and more than 15 million people, about 60,000-90,000 individuals older than 45 years are estimated to be diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease each year – which is far more than the previous estimate of around 40,000-60,000 new cases annually.
This is the latest study to update decades-old epidemiologic data on Parkinson’s disease incidence and prevalence. Previous incidence rates came from small, single-population studies that are now more than 25 years old.
“In the advocacy community, we’ve been earnest about the impact of people living with Parkinson’s disease, and what we really lacked was sufficient data to be able to demonstrate the urgency of our need,” said study coinvestigator James Beck, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Parkinson’s Foundation, New York.
“We wanted to revise these numbers, highlight that they are larger than people anticipated, and use it as a call to action to change the approach we have toward Parkinson’s,” Dr. Beck said.
The findings were published online in NPJ Parkinson’s Disease.
Updating an outdated model
The study builds on the Parkinson’s Prevalence Project, a 2018 initiative that used a new model to calculate Parkinson’s disease prevalence. Before then, federal prevalence data was based on a 40-year-old study of just 26 Parkinson’s disease cases in one small county in rural Mississippi.
Dr. Beck and others used a more sophisticated model, using data from five separate cohort studies. They estimated the total number of patients living with Parkinson’s disease in the United States to be 930,000, which is far higher than the 650,000 the old model predicted.
Researchers then moved on to the current project, developing a new method to estimate Parkinson’s disease incidence.
The project included 2012 data on more than 15 million individuals in the United States and Canada. The investigators drew from three large insurance databases (Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Ontario Health Care, and Medicare) and two long-term epidemiologic studies (the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study and the Rochester Epidemiology Project).
On the basis of their analysis, the investigators proposed a working Parkinson’s disease incident rate estimate of 47-77 cases per 100,000 people aged 45 years or older. Limiting the analysis to those aged 65 or older raised the incidence to 108-212 per 100,000 people.
That translates to 60,000-95,000 new cases each year among adults aged 45 years or older. Using the Medicare administrative database alone for this same time period suggests an annual incidence of nearly 90,000 for individuals aged 65 or older.
“The numbers we’re proposing are conservative,” Dr. Beck said. “The true numbers are probably north of 90,000.”
Incidence rates increased with age and were higher in men. The researchers also identified clusters of counties with higher incidence rates in parts of the country called the “Parkinson’s belt.”
That geographic area mirrors the Rust Belt and includes parts of the Northeastern and Midwestern United States with a long history of industrial manufacturing that used heavy metals and industrial solvents, which are environmental factors linked to risk for Parkinson’s disease.
Cases were also higher in southern California, southeastern Texas, and Florida – agricultural regions with high pesticide use, which is also a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease. Central Pennsylvania also had higher incidence rates.
Why the increase?
The increase in cases could be the result of the more comprehensive estimation model used, the researchers noted. Or it could be improved detection, the aging population, a rise in sedentary lifestyles, increased exposure to environmental risk factors, or even the sharp decline in smoking in the United States, as some studies have shown that smokers have a lower Parkinson’s disease risk.
“The short answer is, we don’t know; and the long answer is, it’s all the above,” Dr. Beck said.
Although about 15% of Parkinson’s disease cases have a genetic basis, the cause is unknown in the majority of cases. In addition, diagnosis is difficult because there is no blood test or scan that detects the disease.
“Diagnosis requires a skilled clinician with real familiarity with Parkinson’s. And we have a real shortage of neurologists in this country to not only be able to diagnose but also to treat the condition,” Dr. Beck said.
That was one motivation for doing the study: to highlight what experts say is a pending clinical crisis for patients with Parkinson’s disease, he added.
The investigators also wanted to raise awareness about the scope of the disorder – not just about prevalence and incidence but also what those data mean for the health care industry, research aims, drug development and health care coverage, and policies.
In a 2020 study, the same researchers calculated a cost of $52 billion per year for medical and nonmedical costs related to Parkinson’s disease, which works out to about $26,000 per year per patient. That figure is expected to surpass $79 billion by 2030.
“This is an urgent condition for many people who live with the disease. And to the extent we can get our country to recognize that and really make the investment now, this is an area where a stitch in time saves nine,” Dr. Beck said.
“If we can invest some money now, we have a chance to really make a difference in the future,” he added.
‘Groundbreaking’ findings
Commenting on the findings, Jori Fleisher, MD, MSCE, associate professor of neurological sciences at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, called the results “groundbreaking” and said that they validate what clinicians have been seeing in real-world practice.
“The findings reflect what a lot of us in practice have been appreciating anecdotally, which is that it seems that Parkinson’s is being diagnosed more frequently and that the incidence has been rising,” said Dr. Fleisher, who was not involved with the study.
She noted that the use of multiple datasets is one element of the methodology that makes the data so significant.
“There has been great work out of individual centers; but no matter how good your study methods are within that one population, you’re drawing conclusions based on that one population,” Dr. Fleisher said.
This research, together with the previous work by the group on prevalence data, could go a long way toward raising awareness about the scope of Parkinson’s disease in the United States – which could lead to earlier diagnosis, more research funding, and increased attention on the need for more clinicians who specialize in movement disorders, she added.
“This should increase research funding across the spectrum, including everything from the basic science to translational research, clinical research and implementation, and health services research,” Dr. Fleisher said.
The study was supported by the Parkinson’s Foundation, The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, and the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Beck and Dr. Fleisher reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to new research that investigators say highlights the growing strain on clinical services and the need for more research funding.
In an analysis of five databases and more than 15 million people, about 60,000-90,000 individuals older than 45 years are estimated to be diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease each year – which is far more than the previous estimate of around 40,000-60,000 new cases annually.
This is the latest study to update decades-old epidemiologic data on Parkinson’s disease incidence and prevalence. Previous incidence rates came from small, single-population studies that are now more than 25 years old.
“In the advocacy community, we’ve been earnest about the impact of people living with Parkinson’s disease, and what we really lacked was sufficient data to be able to demonstrate the urgency of our need,” said study coinvestigator James Beck, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Parkinson’s Foundation, New York.
“We wanted to revise these numbers, highlight that they are larger than people anticipated, and use it as a call to action to change the approach we have toward Parkinson’s,” Dr. Beck said.
The findings were published online in NPJ Parkinson’s Disease.
Updating an outdated model
The study builds on the Parkinson’s Prevalence Project, a 2018 initiative that used a new model to calculate Parkinson’s disease prevalence. Before then, federal prevalence data was based on a 40-year-old study of just 26 Parkinson’s disease cases in one small county in rural Mississippi.
Dr. Beck and others used a more sophisticated model, using data from five separate cohort studies. They estimated the total number of patients living with Parkinson’s disease in the United States to be 930,000, which is far higher than the 650,000 the old model predicted.
Researchers then moved on to the current project, developing a new method to estimate Parkinson’s disease incidence.
The project included 2012 data on more than 15 million individuals in the United States and Canada. The investigators drew from three large insurance databases (Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Ontario Health Care, and Medicare) and two long-term epidemiologic studies (the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study and the Rochester Epidemiology Project).
On the basis of their analysis, the investigators proposed a working Parkinson’s disease incident rate estimate of 47-77 cases per 100,000 people aged 45 years or older. Limiting the analysis to those aged 65 or older raised the incidence to 108-212 per 100,000 people.
That translates to 60,000-95,000 new cases each year among adults aged 45 years or older. Using the Medicare administrative database alone for this same time period suggests an annual incidence of nearly 90,000 for individuals aged 65 or older.
“The numbers we’re proposing are conservative,” Dr. Beck said. “The true numbers are probably north of 90,000.”
Incidence rates increased with age and were higher in men. The researchers also identified clusters of counties with higher incidence rates in parts of the country called the “Parkinson’s belt.”
That geographic area mirrors the Rust Belt and includes parts of the Northeastern and Midwestern United States with a long history of industrial manufacturing that used heavy metals and industrial solvents, which are environmental factors linked to risk for Parkinson’s disease.
Cases were also higher in southern California, southeastern Texas, and Florida – agricultural regions with high pesticide use, which is also a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease. Central Pennsylvania also had higher incidence rates.
Why the increase?
The increase in cases could be the result of the more comprehensive estimation model used, the researchers noted. Or it could be improved detection, the aging population, a rise in sedentary lifestyles, increased exposure to environmental risk factors, or even the sharp decline in smoking in the United States, as some studies have shown that smokers have a lower Parkinson’s disease risk.
“The short answer is, we don’t know; and the long answer is, it’s all the above,” Dr. Beck said.
Although about 15% of Parkinson’s disease cases have a genetic basis, the cause is unknown in the majority of cases. In addition, diagnosis is difficult because there is no blood test or scan that detects the disease.
“Diagnosis requires a skilled clinician with real familiarity with Parkinson’s. And we have a real shortage of neurologists in this country to not only be able to diagnose but also to treat the condition,” Dr. Beck said.
That was one motivation for doing the study: to highlight what experts say is a pending clinical crisis for patients with Parkinson’s disease, he added.
The investigators also wanted to raise awareness about the scope of the disorder – not just about prevalence and incidence but also what those data mean for the health care industry, research aims, drug development and health care coverage, and policies.
In a 2020 study, the same researchers calculated a cost of $52 billion per year for medical and nonmedical costs related to Parkinson’s disease, which works out to about $26,000 per year per patient. That figure is expected to surpass $79 billion by 2030.
“This is an urgent condition for many people who live with the disease. And to the extent we can get our country to recognize that and really make the investment now, this is an area where a stitch in time saves nine,” Dr. Beck said.
“If we can invest some money now, we have a chance to really make a difference in the future,” he added.
‘Groundbreaking’ findings
Commenting on the findings, Jori Fleisher, MD, MSCE, associate professor of neurological sciences at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, called the results “groundbreaking” and said that they validate what clinicians have been seeing in real-world practice.
“The findings reflect what a lot of us in practice have been appreciating anecdotally, which is that it seems that Parkinson’s is being diagnosed more frequently and that the incidence has been rising,” said Dr. Fleisher, who was not involved with the study.
She noted that the use of multiple datasets is one element of the methodology that makes the data so significant.
“There has been great work out of individual centers; but no matter how good your study methods are within that one population, you’re drawing conclusions based on that one population,” Dr. Fleisher said.
This research, together with the previous work by the group on prevalence data, could go a long way toward raising awareness about the scope of Parkinson’s disease in the United States – which could lead to earlier diagnosis, more research funding, and increased attention on the need for more clinicians who specialize in movement disorders, she added.
“This should increase research funding across the spectrum, including everything from the basic science to translational research, clinical research and implementation, and health services research,” Dr. Fleisher said.
The study was supported by the Parkinson’s Foundation, The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, and the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Beck and Dr. Fleisher reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NPJ PARKINSON’S DISEASE
Four-gene signature linked to increased PML risk
a team of European and U.S. investigators reported.
The four-gene signature could be used to screen patients who are currently taking or are candidates for drugs know to increase risk for PML, a rare but frequently lethal demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system, according to Eli Hatchwell, MD, PhD, from Population BIO UK in Oxfordshire, England, and colleagues.
“Due to the seriousness of a PML diagnosis – particularly because it often leads to life-threatening outcomes and the lack of treatment options once it develops – it would seem unethical not to test individuals considering immunosuppressive therapies with PML risk for our top four variants, and advising those with a positive result to consider an alternative therapy or treatment strategy,” they wrote in a study published in Frontiers in Neurology.
Benign virus, bad disease
PML is caused by reactivation of the otherwise benign JC virus (JCV), also known as human polyomavirus 2. (The “J” and “C” in the virus’ common name stand for John Cunningham, a man with Hodgkin lymphoma from whose brain the virus was first isolated, in 1971.)
The estimated prevalence of JCV infection ranges from 40% to 70% of the population worldwide, although PML itself is rare, with an incidence of approximately 1 in 200,000.
PML is a complication of treatment with targeted monoclonal antibodies, such as natalizumab (Tysabri), rituximab (Rituxan), alemtuzumab (Campath; Lemtrada), and other agents with immunosuppressive properties, such as dimethyl fumarate and mycophenolate mofetil.
In addition, PML can occur among patients with diseases that disrupt or inhibit natural immunity, such as HIV/AIDS, hematologic cancers, and autoimmune diseases.
Predisposing variants suspected
Dr. Hatchwell and colleagues hypothesized that some patients may have rare genetic variants in immune-system genes that predispose them to increased risk for PML. The researchers had previously shown an association between PML and 19 genetic risk variants among 184 patients with PML.
In the current study, they looked at variants in an additional 152 patients with PML who served as a validation sample. Of the 19 risk variants they had previously identified, the investigators narrowed the field down to 4 variants in both population controls and in a matched control set consisting of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who were positive for JCV and who were on therapy with a PML-linked drug for at least 2 years.
The four variants they identified, all linked to immune viral defense, were C8B, 1-57409459-C-A, rs139498867; LY9 (a checkpoint regulator also known as SLAMF3), 1-160769595-AG-A, rs763811636; FCN2, 9-137779251-G-A, rs76267164; and STXBP2, 19-7712287-G-C, rs35490401.
In all, 10.9% of patients with PML carried at least one of the variants.
The investigators reported that carriers of any one of the variants has a nearly ninefold risk for developing PML after exposure to a PML-linked drug compared with non-carriers with similar drug exposures (odds ratio, 8.7; P < .001).
“Measures of clinical validity and utility compare favorably to other genetic risk tests, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 screening for breast cancer risk and HLA-B_15:02 pharmacogenetic screening for pharmacovigilance of carbamazepine to prevent Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis,” the authors noted.
Screening? Maybe
In a press release, Lawrence Steinman, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, who was not involved in the study, stated that “preventative screening for these variants should become part of the standard of care. I wish we had more powerful tools like this for other therapies.”
But another neurologist who was not involved in the study commented that the finding, while “exciting” as a confirmation study, is not as yet practice changing.
“It does give us very good confidence that these four genes are indeed risk factors that increase the risk of this brain infection by quite a bit, so that makes it very exciting,” said Robert Fox, MD, from the Neurological Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
“Indeed, we are trying to risk-stratify patients to try to reduce the risk of PML in the patients treated with our MS drugs. So for natalizumab we risk stratify by testing them for JC virus serology. Half of people don’t have it and we say ‘OK, you’re good to go.’ With other drugs like Tecfidera – dimethyl fumarate – we follow their lymphocyte counts, so when their lymphocyte counts drop too low we say ‘OK, you need to come off the drug because of the risk of PML,’ ” he said in an interview.
The four-gene signature, however, only identifies about 11% of patients with PML, which is not a sufficiently large enough effect to be clinically useful. For example, the risk for PML in patients treated with natalizumab is about 1%, and if the test can only detect enhanced risk in about 11% of those patients, the risk would drop from 1% to 0.9%, which “doesn’t really the move needle much,” he pointed out.
Dr. Fox also noted that neurologists now have a large formulary of drugs to offer their patients, including agents (such as interferon-beta and corticosteroids that are not associated with increased risk for PML).
The study was funded by Emerald Lake Safety and Population Bio. Dr. Hatchwell and several coauthors are employees of the respective companies, and several are inventors of genetic screening methods for PML. Dr. Steiman has disclosed consulting for TG Therapeutics. Dr. Fox reported consulting for manufacturers of MS therapies.
a team of European and U.S. investigators reported.
The four-gene signature could be used to screen patients who are currently taking or are candidates for drugs know to increase risk for PML, a rare but frequently lethal demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system, according to Eli Hatchwell, MD, PhD, from Population BIO UK in Oxfordshire, England, and colleagues.
“Due to the seriousness of a PML diagnosis – particularly because it often leads to life-threatening outcomes and the lack of treatment options once it develops – it would seem unethical not to test individuals considering immunosuppressive therapies with PML risk for our top four variants, and advising those with a positive result to consider an alternative therapy or treatment strategy,” they wrote in a study published in Frontiers in Neurology.
Benign virus, bad disease
PML is caused by reactivation of the otherwise benign JC virus (JCV), also known as human polyomavirus 2. (The “J” and “C” in the virus’ common name stand for John Cunningham, a man with Hodgkin lymphoma from whose brain the virus was first isolated, in 1971.)
The estimated prevalence of JCV infection ranges from 40% to 70% of the population worldwide, although PML itself is rare, with an incidence of approximately 1 in 200,000.
PML is a complication of treatment with targeted monoclonal antibodies, such as natalizumab (Tysabri), rituximab (Rituxan), alemtuzumab (Campath; Lemtrada), and other agents with immunosuppressive properties, such as dimethyl fumarate and mycophenolate mofetil.
In addition, PML can occur among patients with diseases that disrupt or inhibit natural immunity, such as HIV/AIDS, hematologic cancers, and autoimmune diseases.
Predisposing variants suspected
Dr. Hatchwell and colleagues hypothesized that some patients may have rare genetic variants in immune-system genes that predispose them to increased risk for PML. The researchers had previously shown an association between PML and 19 genetic risk variants among 184 patients with PML.
In the current study, they looked at variants in an additional 152 patients with PML who served as a validation sample. Of the 19 risk variants they had previously identified, the investigators narrowed the field down to 4 variants in both population controls and in a matched control set consisting of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who were positive for JCV and who were on therapy with a PML-linked drug for at least 2 years.
The four variants they identified, all linked to immune viral defense, were C8B, 1-57409459-C-A, rs139498867; LY9 (a checkpoint regulator also known as SLAMF3), 1-160769595-AG-A, rs763811636; FCN2, 9-137779251-G-A, rs76267164; and STXBP2, 19-7712287-G-C, rs35490401.
In all, 10.9% of patients with PML carried at least one of the variants.
The investigators reported that carriers of any one of the variants has a nearly ninefold risk for developing PML after exposure to a PML-linked drug compared with non-carriers with similar drug exposures (odds ratio, 8.7; P < .001).
“Measures of clinical validity and utility compare favorably to other genetic risk tests, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 screening for breast cancer risk and HLA-B_15:02 pharmacogenetic screening for pharmacovigilance of carbamazepine to prevent Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis,” the authors noted.
Screening? Maybe
In a press release, Lawrence Steinman, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, who was not involved in the study, stated that “preventative screening for these variants should become part of the standard of care. I wish we had more powerful tools like this for other therapies.”
But another neurologist who was not involved in the study commented that the finding, while “exciting” as a confirmation study, is not as yet practice changing.
“It does give us very good confidence that these four genes are indeed risk factors that increase the risk of this brain infection by quite a bit, so that makes it very exciting,” said Robert Fox, MD, from the Neurological Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
“Indeed, we are trying to risk-stratify patients to try to reduce the risk of PML in the patients treated with our MS drugs. So for natalizumab we risk stratify by testing them for JC virus serology. Half of people don’t have it and we say ‘OK, you’re good to go.’ With other drugs like Tecfidera – dimethyl fumarate – we follow their lymphocyte counts, so when their lymphocyte counts drop too low we say ‘OK, you need to come off the drug because of the risk of PML,’ ” he said in an interview.
The four-gene signature, however, only identifies about 11% of patients with PML, which is not a sufficiently large enough effect to be clinically useful. For example, the risk for PML in patients treated with natalizumab is about 1%, and if the test can only detect enhanced risk in about 11% of those patients, the risk would drop from 1% to 0.9%, which “doesn’t really the move needle much,” he pointed out.
Dr. Fox also noted that neurologists now have a large formulary of drugs to offer their patients, including agents (such as interferon-beta and corticosteroids that are not associated with increased risk for PML).
The study was funded by Emerald Lake Safety and Population Bio. Dr. Hatchwell and several coauthors are employees of the respective companies, and several are inventors of genetic screening methods for PML. Dr. Steiman has disclosed consulting for TG Therapeutics. Dr. Fox reported consulting for manufacturers of MS therapies.
a team of European and U.S. investigators reported.
The four-gene signature could be used to screen patients who are currently taking or are candidates for drugs know to increase risk for PML, a rare but frequently lethal demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system, according to Eli Hatchwell, MD, PhD, from Population BIO UK in Oxfordshire, England, and colleagues.
“Due to the seriousness of a PML diagnosis – particularly because it often leads to life-threatening outcomes and the lack of treatment options once it develops – it would seem unethical not to test individuals considering immunosuppressive therapies with PML risk for our top four variants, and advising those with a positive result to consider an alternative therapy or treatment strategy,” they wrote in a study published in Frontiers in Neurology.
Benign virus, bad disease
PML is caused by reactivation of the otherwise benign JC virus (JCV), also known as human polyomavirus 2. (The “J” and “C” in the virus’ common name stand for John Cunningham, a man with Hodgkin lymphoma from whose brain the virus was first isolated, in 1971.)
The estimated prevalence of JCV infection ranges from 40% to 70% of the population worldwide, although PML itself is rare, with an incidence of approximately 1 in 200,000.
PML is a complication of treatment with targeted monoclonal antibodies, such as natalizumab (Tysabri), rituximab (Rituxan), alemtuzumab (Campath; Lemtrada), and other agents with immunosuppressive properties, such as dimethyl fumarate and mycophenolate mofetil.
In addition, PML can occur among patients with diseases that disrupt or inhibit natural immunity, such as HIV/AIDS, hematologic cancers, and autoimmune diseases.
Predisposing variants suspected
Dr. Hatchwell and colleagues hypothesized that some patients may have rare genetic variants in immune-system genes that predispose them to increased risk for PML. The researchers had previously shown an association between PML and 19 genetic risk variants among 184 patients with PML.
In the current study, they looked at variants in an additional 152 patients with PML who served as a validation sample. Of the 19 risk variants they had previously identified, the investigators narrowed the field down to 4 variants in both population controls and in a matched control set consisting of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who were positive for JCV and who were on therapy with a PML-linked drug for at least 2 years.
The four variants they identified, all linked to immune viral defense, were C8B, 1-57409459-C-A, rs139498867; LY9 (a checkpoint regulator also known as SLAMF3), 1-160769595-AG-A, rs763811636; FCN2, 9-137779251-G-A, rs76267164; and STXBP2, 19-7712287-G-C, rs35490401.
In all, 10.9% of patients with PML carried at least one of the variants.
The investigators reported that carriers of any one of the variants has a nearly ninefold risk for developing PML after exposure to a PML-linked drug compared with non-carriers with similar drug exposures (odds ratio, 8.7; P < .001).
“Measures of clinical validity and utility compare favorably to other genetic risk tests, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 screening for breast cancer risk and HLA-B_15:02 pharmacogenetic screening for pharmacovigilance of carbamazepine to prevent Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis,” the authors noted.
Screening? Maybe
In a press release, Lawrence Steinman, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, who was not involved in the study, stated that “preventative screening for these variants should become part of the standard of care. I wish we had more powerful tools like this for other therapies.”
But another neurologist who was not involved in the study commented that the finding, while “exciting” as a confirmation study, is not as yet practice changing.
“It does give us very good confidence that these four genes are indeed risk factors that increase the risk of this brain infection by quite a bit, so that makes it very exciting,” said Robert Fox, MD, from the Neurological Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
“Indeed, we are trying to risk-stratify patients to try to reduce the risk of PML in the patients treated with our MS drugs. So for natalizumab we risk stratify by testing them for JC virus serology. Half of people don’t have it and we say ‘OK, you’re good to go.’ With other drugs like Tecfidera – dimethyl fumarate – we follow their lymphocyte counts, so when their lymphocyte counts drop too low we say ‘OK, you need to come off the drug because of the risk of PML,’ ” he said in an interview.
The four-gene signature, however, only identifies about 11% of patients with PML, which is not a sufficiently large enough effect to be clinically useful. For example, the risk for PML in patients treated with natalizumab is about 1%, and if the test can only detect enhanced risk in about 11% of those patients, the risk would drop from 1% to 0.9%, which “doesn’t really the move needle much,” he pointed out.
Dr. Fox also noted that neurologists now have a large formulary of drugs to offer their patients, including agents (such as interferon-beta and corticosteroids that are not associated with increased risk for PML).
The study was funded by Emerald Lake Safety and Population Bio. Dr. Hatchwell and several coauthors are employees of the respective companies, and several are inventors of genetic screening methods for PML. Dr. Steiman has disclosed consulting for TG Therapeutics. Dr. Fox reported consulting for manufacturers of MS therapies.
FROM FRONTIERS IN NEUROLOGY
Strong two-way link between epilepsy and depression
, with implications for diagnosis and patient care. The findings “strongly support previous observations of a bidirectional association between these two brain disorders,” said Eva Bølling-Ladegaard, MD, a PhD student, department of clinical medicine (Neurology), Aarhus (Denmark) University.
“We add to the existing evidence in temporal range, showing that the increased risks of depression following epilepsy, and vice versa, are sustained over a much more extended time period than previously shown; that is, 20 years on both sides of receiving a diagnosis of the index disorder,” Ms. Bølling-Ladegaard said.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Epilepsy then depression
The researchers examined the magnitude and long-term temporal association between epilepsy and depression. They compared the risk of the two brain disorders following another chronic disorder (asthma) in a nationwide, register-based, matched cohort study.
In a population of more than 8.7 million people, they identified 139,014 persons with epilepsy (54% males; median age at diagnosis, 43 years), 219,990 with depression (37% males; median age at diagnosis, 43 years), and 358,821 with asthma (49% males; median age at diagnosis, 29 years).
The rate of developing depression was increased nearly twofold among people with epilepsy compared with the matched population who did not have epilepsy (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.88; 95% confidence interval, 1.82-1.95).
The rate of depression was highest during the first months and years after epilepsy diagnosis. It declined over time, yet remained significantly elevated throughout the 20+ years of observation.
The cumulative incidence of depression at 5 and 35 years’ follow-up in the epilepsy cohort was 1.37% and 6.05%, respectively, compared with 0.59% and 3.92% in the reference population.
The highest rate of depression after epilepsy was among individuals aged 40-59 years, and the lowest was among those aged 0-19 years at first epilepsy diagnosis.
Depression then epilepsy
The rate of developing epilepsy was increased more than twofold among patients with incident depression compared with the matched population who were without depression (aHR, 2.35; 95% CI, 2.25-2.44).
As in the opposite analysis, the rate of epilepsy was highest during the first months and years after depression diagnosis and declined over time.
The cumulative incidence of epilepsy at 5 and 35 years after depression diagnosis was 1.10% and 4.19%, respectively, compared with 0.32% and 2.06% in the reference population.
The rate of epilepsy was highest among those aged 0-19 years at time of first depression diagnosis and was lowest among those aged 80+ at first depression diagnosis.
For comparison, after asthma diagnosis, rates of depression and epilepsy were increased 1.63-fold (95% CI, 1.59-1.67) and 1.48-fold (95% CI, 1.44-1.53), respectively, compared with matched individuals without asthma.
Using admission with seizures as a proxy for treatment failure, the researchers observed an increased risk of treatment failure among people with epilepsy who were diagnosed with depression.
“Our results support previous findings indicating worse seizure outcomes in people with epilepsy and coexisting depression,” said Ms. Bølling-Ladegaard.
“Increased clinical awareness of the association between epilepsy and depression is therefore needed in order to increase the proportion of patients that receive appropriate treatment and improve outcomes for these patient groups,” she said.
Clinical implications
Reached for comment, Zulfi Haneef, MBBS, MD, associate professor of neurology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, noted that the link between epilepsy and depression is “well-known.”
“However, typically one thinks of epilepsy as leading to depression, not vice versa. Here they show the risk of epilepsy following depression to be high (highest of the risks given), which is thought provoking. However, association does not imply causation,” Dr. Haneef said.
“Prima facie, there is no biological rationale for depression to lead to epilepsy,” he said. He noted that some antidepressants can reduce the seizure threshold.
The findings do have implications for care, he said.
“For neurologists, this is another study that exhorts them to screen for depression and treat adequately in all patients with epilepsy,” Dr. Haneef said.
“For psychiatrists, this study may give guidance to watch more carefully for seizures in patients with depression, especially when using antidepressant medications that induce seizures.
“For the general public with either epilepsy or depression, it would help them be aware about this bidirectional association,” Dr. Haneef said.
The study was funded by the Lundbeck Foundation, the Danish Epilepsy Association, and the Novo Nordisk Foundation. Ms. Bølling-Ladegaard and Dr. Haneef have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, with implications for diagnosis and patient care. The findings “strongly support previous observations of a bidirectional association between these two brain disorders,” said Eva Bølling-Ladegaard, MD, a PhD student, department of clinical medicine (Neurology), Aarhus (Denmark) University.
“We add to the existing evidence in temporal range, showing that the increased risks of depression following epilepsy, and vice versa, are sustained over a much more extended time period than previously shown; that is, 20 years on both sides of receiving a diagnosis of the index disorder,” Ms. Bølling-Ladegaard said.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Epilepsy then depression
The researchers examined the magnitude and long-term temporal association between epilepsy and depression. They compared the risk of the two brain disorders following another chronic disorder (asthma) in a nationwide, register-based, matched cohort study.
In a population of more than 8.7 million people, they identified 139,014 persons with epilepsy (54% males; median age at diagnosis, 43 years), 219,990 with depression (37% males; median age at diagnosis, 43 years), and 358,821 with asthma (49% males; median age at diagnosis, 29 years).
The rate of developing depression was increased nearly twofold among people with epilepsy compared with the matched population who did not have epilepsy (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.88; 95% confidence interval, 1.82-1.95).
The rate of depression was highest during the first months and years after epilepsy diagnosis. It declined over time, yet remained significantly elevated throughout the 20+ years of observation.
The cumulative incidence of depression at 5 and 35 years’ follow-up in the epilepsy cohort was 1.37% and 6.05%, respectively, compared with 0.59% and 3.92% in the reference population.
The highest rate of depression after epilepsy was among individuals aged 40-59 years, and the lowest was among those aged 0-19 years at first epilepsy diagnosis.
Depression then epilepsy
The rate of developing epilepsy was increased more than twofold among patients with incident depression compared with the matched population who were without depression (aHR, 2.35; 95% CI, 2.25-2.44).
As in the opposite analysis, the rate of epilepsy was highest during the first months and years after depression diagnosis and declined over time.
The cumulative incidence of epilepsy at 5 and 35 years after depression diagnosis was 1.10% and 4.19%, respectively, compared with 0.32% and 2.06% in the reference population.
The rate of epilepsy was highest among those aged 0-19 years at time of first depression diagnosis and was lowest among those aged 80+ at first depression diagnosis.
For comparison, after asthma diagnosis, rates of depression and epilepsy were increased 1.63-fold (95% CI, 1.59-1.67) and 1.48-fold (95% CI, 1.44-1.53), respectively, compared with matched individuals without asthma.
Using admission with seizures as a proxy for treatment failure, the researchers observed an increased risk of treatment failure among people with epilepsy who were diagnosed with depression.
“Our results support previous findings indicating worse seizure outcomes in people with epilepsy and coexisting depression,” said Ms. Bølling-Ladegaard.
“Increased clinical awareness of the association between epilepsy and depression is therefore needed in order to increase the proportion of patients that receive appropriate treatment and improve outcomes for these patient groups,” she said.
Clinical implications
Reached for comment, Zulfi Haneef, MBBS, MD, associate professor of neurology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, noted that the link between epilepsy and depression is “well-known.”
“However, typically one thinks of epilepsy as leading to depression, not vice versa. Here they show the risk of epilepsy following depression to be high (highest of the risks given), which is thought provoking. However, association does not imply causation,” Dr. Haneef said.
“Prima facie, there is no biological rationale for depression to lead to epilepsy,” he said. He noted that some antidepressants can reduce the seizure threshold.
The findings do have implications for care, he said.
“For neurologists, this is another study that exhorts them to screen for depression and treat adequately in all patients with epilepsy,” Dr. Haneef said.
“For psychiatrists, this study may give guidance to watch more carefully for seizures in patients with depression, especially when using antidepressant medications that induce seizures.
“For the general public with either epilepsy or depression, it would help them be aware about this bidirectional association,” Dr. Haneef said.
The study was funded by the Lundbeck Foundation, the Danish Epilepsy Association, and the Novo Nordisk Foundation. Ms. Bølling-Ladegaard and Dr. Haneef have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, with implications for diagnosis and patient care. The findings “strongly support previous observations of a bidirectional association between these two brain disorders,” said Eva Bølling-Ladegaard, MD, a PhD student, department of clinical medicine (Neurology), Aarhus (Denmark) University.
“We add to the existing evidence in temporal range, showing that the increased risks of depression following epilepsy, and vice versa, are sustained over a much more extended time period than previously shown; that is, 20 years on both sides of receiving a diagnosis of the index disorder,” Ms. Bølling-Ladegaard said.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Epilepsy then depression
The researchers examined the magnitude and long-term temporal association between epilepsy and depression. They compared the risk of the two brain disorders following another chronic disorder (asthma) in a nationwide, register-based, matched cohort study.
In a population of more than 8.7 million people, they identified 139,014 persons with epilepsy (54% males; median age at diagnosis, 43 years), 219,990 with depression (37% males; median age at diagnosis, 43 years), and 358,821 with asthma (49% males; median age at diagnosis, 29 years).
The rate of developing depression was increased nearly twofold among people with epilepsy compared with the matched population who did not have epilepsy (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.88; 95% confidence interval, 1.82-1.95).
The rate of depression was highest during the first months and years after epilepsy diagnosis. It declined over time, yet remained significantly elevated throughout the 20+ years of observation.
The cumulative incidence of depression at 5 and 35 years’ follow-up in the epilepsy cohort was 1.37% and 6.05%, respectively, compared with 0.59% and 3.92% in the reference population.
The highest rate of depression after epilepsy was among individuals aged 40-59 years, and the lowest was among those aged 0-19 years at first epilepsy diagnosis.
Depression then epilepsy
The rate of developing epilepsy was increased more than twofold among patients with incident depression compared with the matched population who were without depression (aHR, 2.35; 95% CI, 2.25-2.44).
As in the opposite analysis, the rate of epilepsy was highest during the first months and years after depression diagnosis and declined over time.
The cumulative incidence of epilepsy at 5 and 35 years after depression diagnosis was 1.10% and 4.19%, respectively, compared with 0.32% and 2.06% in the reference population.
The rate of epilepsy was highest among those aged 0-19 years at time of first depression diagnosis and was lowest among those aged 80+ at first depression diagnosis.
For comparison, after asthma diagnosis, rates of depression and epilepsy were increased 1.63-fold (95% CI, 1.59-1.67) and 1.48-fold (95% CI, 1.44-1.53), respectively, compared with matched individuals without asthma.
Using admission with seizures as a proxy for treatment failure, the researchers observed an increased risk of treatment failure among people with epilepsy who were diagnosed with depression.
“Our results support previous findings indicating worse seizure outcomes in people with epilepsy and coexisting depression,” said Ms. Bølling-Ladegaard.
“Increased clinical awareness of the association between epilepsy and depression is therefore needed in order to increase the proportion of patients that receive appropriate treatment and improve outcomes for these patient groups,” she said.
Clinical implications
Reached for comment, Zulfi Haneef, MBBS, MD, associate professor of neurology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, noted that the link between epilepsy and depression is “well-known.”
“However, typically one thinks of epilepsy as leading to depression, not vice versa. Here they show the risk of epilepsy following depression to be high (highest of the risks given), which is thought provoking. However, association does not imply causation,” Dr. Haneef said.
“Prima facie, there is no biological rationale for depression to lead to epilepsy,” he said. He noted that some antidepressants can reduce the seizure threshold.
The findings do have implications for care, he said.
“For neurologists, this is another study that exhorts them to screen for depression and treat adequately in all patients with epilepsy,” Dr. Haneef said.
“For psychiatrists, this study may give guidance to watch more carefully for seizures in patients with depression, especially when using antidepressant medications that induce seizures.
“For the general public with either epilepsy or depression, it would help them be aware about this bidirectional association,” Dr. Haneef said.
The study was funded by the Lundbeck Foundation, the Danish Epilepsy Association, and the Novo Nordisk Foundation. Ms. Bølling-Ladegaard and Dr. Haneef have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
High drug costs exclude most neurology patients from cutting-edge treatment
, new research shows.
“Our study of people with neurologic conditions found that fewer than 20% were being treated with new medications,” study author Brian C. Callaghan, MD, with University of Michigan Health in Ann Arbor, said in a statement.
“For new, high-cost medications that have similar effectiveness to older drugs, limited use is likely appropriate. However, future studies are needed to look into whether the high costs are barriers to those new medications that can really make a difference for people living with neurologic disease,” Dr. Callaghan said.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Most expensive drugs
Using insurance claims data, the investigators compared the utilization and costs of new-to-market drugs from 2014 to 2018 with those for existing guideline-supported medications for treating 11 neurologic conditions.
The new drugs included:
- erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab for migraine.
- ocrelizumab and peginterferon beta-1a for multiple sclerosis (MS).
- pimavanserin and safinamide for Parkinson’s disease.
- droxidopa for orthostatic hypertension.
- eculizumab for myasthenia gravis (MG).
- edaravone for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
- deutetrabenazine and valbenazine for Huntington’s disease and tardive dyskinesia.
- patisiran and inotersen for transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR).
- eteplirsen and deflazacort for Duchenne disease.
- nusinersen for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
Utilization of new drugs was modest – they accounted for one in five prescriptions for every condition except tardive dyskinesia (32% for valbenazine), the researchers noted.
Mean out-of-pocket costs were significantly higher for the new medications, although there was large variability among individual drugs.
The two most expensive drugs were edaravone, for ALS, with a mean out-of-pocket cost of $713 for a 30-day supply, and eculizumab, for MG, which costs $91 per month.
“For new-to-market medications, the distribution of out-of-pocket costs were highly variable and the trends over time were unpredictable compared with existing guideline-supported medications,” the authors reported.
They noted that potential reasons for low utilization of newer agents include delay in provider uptake and prescriber and/or patient avoidance because of high cost.
Given that most of the new neurologic agents offer little advantage compared with existing treatments – exceptions being new drugs for SMA and ATTR – drug costs should be a key consideration in prescribing decisions, Dr. Callaghan and colleagues concluded.
One limitation of the study is that follow-up time was short for some of the recently approved medications. Another limitation is that the number of people in the study who had rare diseases was small.
Revolution in neurotherapeutics
“We are living in a time when new treatments bring hope to people with neurologic diseases and disorders,” Orly Avitzur, MD, president of the American Academy of Neurology, said in a statement.
“However, even existing prescription medication can be expensive and drug prices continue to rise. In order for neurologists to provide people with the highest quality care, it is imperative that new drugs are accessible and affordable to the people who need them,” Dr. Avitzur added.
Writing in a linked editorial, A. Gordon Smith, MD, professor and chair, department of neurology, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said there is a revolution in neurotherapeutics, with particularly robust growth in new drug approvals for orphan diseases (those affecting < 200,000 Americans).
“This study adds to a growing literature indicating rising drug prices are a threat to the health care system. No matter how effective a disease-modifying therapy may be, if a patient cannot afford the cost, it doesn’t work,” Dr. Smith wrote.
He added that neurologists must be “diligent in assessing for financial toxicity and appropriately tailor individual treatment recommendations. We must insist on development of point-of-care tools to accurately estimate each patient’s potential financial toxicity including RTBT [real-time benefit tools].
“Neurologists’ primary obligation is to the individual patient, but we are also compelled to support access to high-quality care for all people, which requires advocacy for appropriate policy reforms to ensure value based and fair drug pricing and treatment success,” Dr. Smith added.
The study was funded by the American Academy of Neurology Health Services Research Subcommittee. Dr. Callaghan consults for a PCORI grant, DynaMed, receives research support from the American Academy of Neurology, and performs medical/legal consultations, including consultations for the Vaccine Injury Compensation Program. Dr. Smith has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
“Our study of people with neurologic conditions found that fewer than 20% were being treated with new medications,” study author Brian C. Callaghan, MD, with University of Michigan Health in Ann Arbor, said in a statement.
“For new, high-cost medications that have similar effectiveness to older drugs, limited use is likely appropriate. However, future studies are needed to look into whether the high costs are barriers to those new medications that can really make a difference for people living with neurologic disease,” Dr. Callaghan said.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Most expensive drugs
Using insurance claims data, the investigators compared the utilization and costs of new-to-market drugs from 2014 to 2018 with those for existing guideline-supported medications for treating 11 neurologic conditions.
The new drugs included:
- erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab for migraine.
- ocrelizumab and peginterferon beta-1a for multiple sclerosis (MS).
- pimavanserin and safinamide for Parkinson’s disease.
- droxidopa for orthostatic hypertension.
- eculizumab for myasthenia gravis (MG).
- edaravone for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
- deutetrabenazine and valbenazine for Huntington’s disease and tardive dyskinesia.
- patisiran and inotersen for transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR).
- eteplirsen and deflazacort for Duchenne disease.
- nusinersen for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
Utilization of new drugs was modest – they accounted for one in five prescriptions for every condition except tardive dyskinesia (32% for valbenazine), the researchers noted.
Mean out-of-pocket costs were significantly higher for the new medications, although there was large variability among individual drugs.
The two most expensive drugs were edaravone, for ALS, with a mean out-of-pocket cost of $713 for a 30-day supply, and eculizumab, for MG, which costs $91 per month.
“For new-to-market medications, the distribution of out-of-pocket costs were highly variable and the trends over time were unpredictable compared with existing guideline-supported medications,” the authors reported.
They noted that potential reasons for low utilization of newer agents include delay in provider uptake and prescriber and/or patient avoidance because of high cost.
Given that most of the new neurologic agents offer little advantage compared with existing treatments – exceptions being new drugs for SMA and ATTR – drug costs should be a key consideration in prescribing decisions, Dr. Callaghan and colleagues concluded.
One limitation of the study is that follow-up time was short for some of the recently approved medications. Another limitation is that the number of people in the study who had rare diseases was small.
Revolution in neurotherapeutics
“We are living in a time when new treatments bring hope to people with neurologic diseases and disorders,” Orly Avitzur, MD, president of the American Academy of Neurology, said in a statement.
“However, even existing prescription medication can be expensive and drug prices continue to rise. In order for neurologists to provide people with the highest quality care, it is imperative that new drugs are accessible and affordable to the people who need them,” Dr. Avitzur added.
Writing in a linked editorial, A. Gordon Smith, MD, professor and chair, department of neurology, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said there is a revolution in neurotherapeutics, with particularly robust growth in new drug approvals for orphan diseases (those affecting < 200,000 Americans).
“This study adds to a growing literature indicating rising drug prices are a threat to the health care system. No matter how effective a disease-modifying therapy may be, if a patient cannot afford the cost, it doesn’t work,” Dr. Smith wrote.
He added that neurologists must be “diligent in assessing for financial toxicity and appropriately tailor individual treatment recommendations. We must insist on development of point-of-care tools to accurately estimate each patient’s potential financial toxicity including RTBT [real-time benefit tools].
“Neurologists’ primary obligation is to the individual patient, but we are also compelled to support access to high-quality care for all people, which requires advocacy for appropriate policy reforms to ensure value based and fair drug pricing and treatment success,” Dr. Smith added.
The study was funded by the American Academy of Neurology Health Services Research Subcommittee. Dr. Callaghan consults for a PCORI grant, DynaMed, receives research support from the American Academy of Neurology, and performs medical/legal consultations, including consultations for the Vaccine Injury Compensation Program. Dr. Smith has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
“Our study of people with neurologic conditions found that fewer than 20% were being treated with new medications,” study author Brian C. Callaghan, MD, with University of Michigan Health in Ann Arbor, said in a statement.
“For new, high-cost medications that have similar effectiveness to older drugs, limited use is likely appropriate. However, future studies are needed to look into whether the high costs are barriers to those new medications that can really make a difference for people living with neurologic disease,” Dr. Callaghan said.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Most expensive drugs
Using insurance claims data, the investigators compared the utilization and costs of new-to-market drugs from 2014 to 2018 with those for existing guideline-supported medications for treating 11 neurologic conditions.
The new drugs included:
- erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab for migraine.
- ocrelizumab and peginterferon beta-1a for multiple sclerosis (MS).
- pimavanserin and safinamide for Parkinson’s disease.
- droxidopa for orthostatic hypertension.
- eculizumab for myasthenia gravis (MG).
- edaravone for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
- deutetrabenazine and valbenazine for Huntington’s disease and tardive dyskinesia.
- patisiran and inotersen for transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR).
- eteplirsen and deflazacort for Duchenne disease.
- nusinersen for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
Utilization of new drugs was modest – they accounted for one in five prescriptions for every condition except tardive dyskinesia (32% for valbenazine), the researchers noted.
Mean out-of-pocket costs were significantly higher for the new medications, although there was large variability among individual drugs.
The two most expensive drugs were edaravone, for ALS, with a mean out-of-pocket cost of $713 for a 30-day supply, and eculizumab, for MG, which costs $91 per month.
“For new-to-market medications, the distribution of out-of-pocket costs were highly variable and the trends over time were unpredictable compared with existing guideline-supported medications,” the authors reported.
They noted that potential reasons for low utilization of newer agents include delay in provider uptake and prescriber and/or patient avoidance because of high cost.
Given that most of the new neurologic agents offer little advantage compared with existing treatments – exceptions being new drugs for SMA and ATTR – drug costs should be a key consideration in prescribing decisions, Dr. Callaghan and colleagues concluded.
One limitation of the study is that follow-up time was short for some of the recently approved medications. Another limitation is that the number of people in the study who had rare diseases was small.
Revolution in neurotherapeutics
“We are living in a time when new treatments bring hope to people with neurologic diseases and disorders,” Orly Avitzur, MD, president of the American Academy of Neurology, said in a statement.
“However, even existing prescription medication can be expensive and drug prices continue to rise. In order for neurologists to provide people with the highest quality care, it is imperative that new drugs are accessible and affordable to the people who need them,” Dr. Avitzur added.
Writing in a linked editorial, A. Gordon Smith, MD, professor and chair, department of neurology, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said there is a revolution in neurotherapeutics, with particularly robust growth in new drug approvals for orphan diseases (those affecting < 200,000 Americans).
“This study adds to a growing literature indicating rising drug prices are a threat to the health care system. No matter how effective a disease-modifying therapy may be, if a patient cannot afford the cost, it doesn’t work,” Dr. Smith wrote.
He added that neurologists must be “diligent in assessing for financial toxicity and appropriately tailor individual treatment recommendations. We must insist on development of point-of-care tools to accurately estimate each patient’s potential financial toxicity including RTBT [real-time benefit tools].
“Neurologists’ primary obligation is to the individual patient, but we are also compelled to support access to high-quality care for all people, which requires advocacy for appropriate policy reforms to ensure value based and fair drug pricing and treatment success,” Dr. Smith added.
The study was funded by the American Academy of Neurology Health Services Research Subcommittee. Dr. Callaghan consults for a PCORI grant, DynaMed, receives research support from the American Academy of Neurology, and performs medical/legal consultations, including consultations for the Vaccine Injury Compensation Program. Dr. Smith has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
New framework for MS diagnosis and treatment proposed
The goal is to eventually move away from the current system, which classifies MS based on disease progression into distinct relapsing-remitting, secondary progressive, and primary progressive subtypes.
Members of the International Advisory Committee on Clinical Trials in Multiple Sclerosis, which developed the framework, note the new framework is based on underlying biology of disease and acknowledges the different trajectories of individual patients. “The categorization of patients into distinct subtypes or stages is artificial,” said framework coauthor Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of experimental therapeutics, Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research, Cleveland Clinic. “The rationale for the new framework was recent studies demonstrating that the biologic processes that underlie relapses and progression are present to varying degrees throughout the disease course, representing a continuum.”
The proposal was published online in The Lancet Neurology.
A more responsive system
Since the current MS classification, dubbed the Lublin-Reingold descriptors, was introduced, there have been calls for a different system that is more responsive to biological changes inherent in MS. The committee, which is jointly sponsored by the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis and the U.S. National Multiple Sclerosis Society, responded by clarifying clinical course descriptions published in 1996 and 2013. The proposed framework grew out of that process.
“One of the main points is the concept that patients don’t evolve into secondary progressive MS,” Dr. Cohen said. “The processes that underlie progression and the findings of proxy measures of progression are present from the earliest stages of the disease.”
In its report, the committee reviews current data on the pathophysiology of injury and compensatory mechanisms in MS, presenting findings that suggest disease progression is caused not by a single disease mechanism, but from a combination of several processes that vary from patient to patient.
Current research studies highlighted in the report include those focused on mechanisms of injury, such as acute and chronic inflammation, myelin loss, nerve fiber and neuron loss, and mitochondrial dysfunction. How the body responds to that injury is likely to determine how MS evolves in each patient, the committee wrote.
Studies point to a range of factors that influence how MS manifests and progresses, including patients’ age at onset, biological sex, genes, race, ethnicity, comorbid health conditions, health behaviors, therapies, and social and environmental exposures.
Potential for better treatments
Any new framework for classifying the disease in the future would enable the development and approval of more biologically based treatment approaches, Dr. Cohen said. “One anticipated advantage of the new framework is that treatments should be evaluated based on their efficacy on biologic processes, not in artificial categories of patients.”
Dr. Cohen and other committee members acknowledged that developing the framework is just a first step in what would likely be a long and complicated process. “This proposal is among many initiatives that the committee has supported over the years as part of its overarching aim to constantly improve, update, and enhance clinical trial design and inform clinical care delivery for people living with MS and their health care teams,” committee chair Ruth Ann Marrie, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Clinic at the University of Manitoba Health Sciences Center, Winnipeg, said in a press release.
Commenting on the proposal, Tony Reder, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Chicago Medicine, said the paper offers a “good framework for all trialists attempting to go beyond the usual markers.”
The time is right for reclassifying MS
The authors “have good reasons to propose the need for a new mechanism-driven framework to define MS progression,” wrote Takashi Yamamura, MD, PhD, director and chief of the Neuroimmunology Section and director of Multiple Sclerosis Center, National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry, Kodaira, Tokyo, Japan, in an accompanying commentary.
Adopting biologically based definitions of MS progression will be challenging to implement, the authors admitted. The current subtype classification is woven into clinical care and research models and is the basis for regulatory approval of new therapeutics. Replacing it will take time and require external validation in the clinic and the lab.
“Although the goal is distant and many obstacles might arise (such as reaching a consensus between physicians, academia, and stakeholders), the time seems right to launch initiatives to reframe the classification of MS subtypes,” Dr. Yamamura added.
The study was supported by the German Research Foundation and the Intramural Research Program of NINDS. Dr. Cohen reported personal compensation for consulting for Biogen, Convelo, EMD Serono, Gossamer Bio, Mylan, and PSI. Dr. Yamamura has received support from AMED-CREST, Novartis, and Chiome Bioscience, and speaker honoraria from Novartis, Biogen, Chugai, Alexion, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, and Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The goal is to eventually move away from the current system, which classifies MS based on disease progression into distinct relapsing-remitting, secondary progressive, and primary progressive subtypes.
Members of the International Advisory Committee on Clinical Trials in Multiple Sclerosis, which developed the framework, note the new framework is based on underlying biology of disease and acknowledges the different trajectories of individual patients. “The categorization of patients into distinct subtypes or stages is artificial,” said framework coauthor Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of experimental therapeutics, Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research, Cleveland Clinic. “The rationale for the new framework was recent studies demonstrating that the biologic processes that underlie relapses and progression are present to varying degrees throughout the disease course, representing a continuum.”
The proposal was published online in The Lancet Neurology.
A more responsive system
Since the current MS classification, dubbed the Lublin-Reingold descriptors, was introduced, there have been calls for a different system that is more responsive to biological changes inherent in MS. The committee, which is jointly sponsored by the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis and the U.S. National Multiple Sclerosis Society, responded by clarifying clinical course descriptions published in 1996 and 2013. The proposed framework grew out of that process.
“One of the main points is the concept that patients don’t evolve into secondary progressive MS,” Dr. Cohen said. “The processes that underlie progression and the findings of proxy measures of progression are present from the earliest stages of the disease.”
In its report, the committee reviews current data on the pathophysiology of injury and compensatory mechanisms in MS, presenting findings that suggest disease progression is caused not by a single disease mechanism, but from a combination of several processes that vary from patient to patient.
Current research studies highlighted in the report include those focused on mechanisms of injury, such as acute and chronic inflammation, myelin loss, nerve fiber and neuron loss, and mitochondrial dysfunction. How the body responds to that injury is likely to determine how MS evolves in each patient, the committee wrote.
Studies point to a range of factors that influence how MS manifests and progresses, including patients’ age at onset, biological sex, genes, race, ethnicity, comorbid health conditions, health behaviors, therapies, and social and environmental exposures.
Potential for better treatments
Any new framework for classifying the disease in the future would enable the development and approval of more biologically based treatment approaches, Dr. Cohen said. “One anticipated advantage of the new framework is that treatments should be evaluated based on their efficacy on biologic processes, not in artificial categories of patients.”
Dr. Cohen and other committee members acknowledged that developing the framework is just a first step in what would likely be a long and complicated process. “This proposal is among many initiatives that the committee has supported over the years as part of its overarching aim to constantly improve, update, and enhance clinical trial design and inform clinical care delivery for people living with MS and their health care teams,” committee chair Ruth Ann Marrie, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Clinic at the University of Manitoba Health Sciences Center, Winnipeg, said in a press release.
Commenting on the proposal, Tony Reder, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Chicago Medicine, said the paper offers a “good framework for all trialists attempting to go beyond the usual markers.”
The time is right for reclassifying MS
The authors “have good reasons to propose the need for a new mechanism-driven framework to define MS progression,” wrote Takashi Yamamura, MD, PhD, director and chief of the Neuroimmunology Section and director of Multiple Sclerosis Center, National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry, Kodaira, Tokyo, Japan, in an accompanying commentary.
Adopting biologically based definitions of MS progression will be challenging to implement, the authors admitted. The current subtype classification is woven into clinical care and research models and is the basis for regulatory approval of new therapeutics. Replacing it will take time and require external validation in the clinic and the lab.
“Although the goal is distant and many obstacles might arise (such as reaching a consensus between physicians, academia, and stakeholders), the time seems right to launch initiatives to reframe the classification of MS subtypes,” Dr. Yamamura added.
The study was supported by the German Research Foundation and the Intramural Research Program of NINDS. Dr. Cohen reported personal compensation for consulting for Biogen, Convelo, EMD Serono, Gossamer Bio, Mylan, and PSI. Dr. Yamamura has received support from AMED-CREST, Novartis, and Chiome Bioscience, and speaker honoraria from Novartis, Biogen, Chugai, Alexion, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, and Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The goal is to eventually move away from the current system, which classifies MS based on disease progression into distinct relapsing-remitting, secondary progressive, and primary progressive subtypes.
Members of the International Advisory Committee on Clinical Trials in Multiple Sclerosis, which developed the framework, note the new framework is based on underlying biology of disease and acknowledges the different trajectories of individual patients. “The categorization of patients into distinct subtypes or stages is artificial,” said framework coauthor Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of experimental therapeutics, Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research, Cleveland Clinic. “The rationale for the new framework was recent studies demonstrating that the biologic processes that underlie relapses and progression are present to varying degrees throughout the disease course, representing a continuum.”
The proposal was published online in The Lancet Neurology.
A more responsive system
Since the current MS classification, dubbed the Lublin-Reingold descriptors, was introduced, there have been calls for a different system that is more responsive to biological changes inherent in MS. The committee, which is jointly sponsored by the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis and the U.S. National Multiple Sclerosis Society, responded by clarifying clinical course descriptions published in 1996 and 2013. The proposed framework grew out of that process.
“One of the main points is the concept that patients don’t evolve into secondary progressive MS,” Dr. Cohen said. “The processes that underlie progression and the findings of proxy measures of progression are present from the earliest stages of the disease.”
In its report, the committee reviews current data on the pathophysiology of injury and compensatory mechanisms in MS, presenting findings that suggest disease progression is caused not by a single disease mechanism, but from a combination of several processes that vary from patient to patient.
Current research studies highlighted in the report include those focused on mechanisms of injury, such as acute and chronic inflammation, myelin loss, nerve fiber and neuron loss, and mitochondrial dysfunction. How the body responds to that injury is likely to determine how MS evolves in each patient, the committee wrote.
Studies point to a range of factors that influence how MS manifests and progresses, including patients’ age at onset, biological sex, genes, race, ethnicity, comorbid health conditions, health behaviors, therapies, and social and environmental exposures.
Potential for better treatments
Any new framework for classifying the disease in the future would enable the development and approval of more biologically based treatment approaches, Dr. Cohen said. “One anticipated advantage of the new framework is that treatments should be evaluated based on their efficacy on biologic processes, not in artificial categories of patients.”
Dr. Cohen and other committee members acknowledged that developing the framework is just a first step in what would likely be a long and complicated process. “This proposal is among many initiatives that the committee has supported over the years as part of its overarching aim to constantly improve, update, and enhance clinical trial design and inform clinical care delivery for people living with MS and their health care teams,” committee chair Ruth Ann Marrie, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Clinic at the University of Manitoba Health Sciences Center, Winnipeg, said in a press release.
Commenting on the proposal, Tony Reder, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Chicago Medicine, said the paper offers a “good framework for all trialists attempting to go beyond the usual markers.”
The time is right for reclassifying MS
The authors “have good reasons to propose the need for a new mechanism-driven framework to define MS progression,” wrote Takashi Yamamura, MD, PhD, director and chief of the Neuroimmunology Section and director of Multiple Sclerosis Center, National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry, Kodaira, Tokyo, Japan, in an accompanying commentary.
Adopting biologically based definitions of MS progression will be challenging to implement, the authors admitted. The current subtype classification is woven into clinical care and research models and is the basis for regulatory approval of new therapeutics. Replacing it will take time and require external validation in the clinic and the lab.
“Although the goal is distant and many obstacles might arise (such as reaching a consensus between physicians, academia, and stakeholders), the time seems right to launch initiatives to reframe the classification of MS subtypes,” Dr. Yamamura added.
The study was supported by the German Research Foundation and the Intramural Research Program of NINDS. Dr. Cohen reported personal compensation for consulting for Biogen, Convelo, EMD Serono, Gossamer Bio, Mylan, and PSI. Dr. Yamamura has received support from AMED-CREST, Novartis, and Chiome Bioscience, and speaker honoraria from Novartis, Biogen, Chugai, Alexion, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, and Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET NEUROLOGY
Advancing health equity in neurology is essential to patient care
Black and Latinx older adults are up to three times as likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease than non-Latinx White adults and tend to experience onset at a younger age with more severe symptoms, according to Monica Rivera-Mindt, PhD, a professor of psychology at Fordham University and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Looking ahead, that means by 2030, nearly 40% of the 8.4 million Americans affected by Alzheimer’s disease will be Black and/or Latinx, she said. These facts were among the stark disparities in health care outcomes Dr. Rivera-Mindt discussed in her presentation on brain health equity at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
Dr. Rivera-Mindt’s presentation opened the ANA’s plenary session on health disparities and inequities. The plenary, “Advancing Neurologic Equity: Challenges and Paths Forward,” did not simply enumerate racial and ethnic disparities that exist with various neurological conditions. Rather it went beyond the discussion of what disparities exist into understanding the roots of them as well as tips, tools, and resources that can aid clinicians in addressing or ameliorating them.
Roy Hamilton, MD, an associate professor of neurology and physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said. “If clinicians are unaware of these disparities or don’t have any sense of how to start to address or think about them, then they’re really missing out on an important component of their education as persons who take care of patients with brain disorders.”
Dr. Hamilton, who organized the plenary, noted that awareness of these disparities is crucial to comprehensively caring for patients.
Missed opportunities
“We’re talking about disadvantages that are structural and large scale, but those disadvantages play themselves out in the individual encounter,” Dr. Hamilton said. “When physicians see patients, they have to treat the whole patient in front of them,” which means being aware of the risks and factors that could affect a patient’s clinical presentation. “Being aware of disparities has practical impacts on physician judgment,” he said.
For example, recent research in multiple sclerosis (MS) has highlighted how clinicians may be missing diagnosis of this condition in non-White populations because the condition has been regarded for so long as a “White person’s” disease, Dr. Hamilton said. In non-White patients exhibiting MS symptoms, then, clinicians may have been less likely to consider MS as a possibility, thereby delaying diagnosis and treatment.
Those patterns may partly explain why the mortality rate for MS is greater in Black patients, who also show more rapid neurodegeneration than White patients with MS, Lilyana Amezcua, MD, an associate professor of neurology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, reported in the plenary’s second presentation.
Transgender issues
The third session, presented by Nicole Rosendale, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the San Francisco General Hospital neurology inpatient services, examined disparities in neurology within the LGBTQ+ community through representative case studies and then offered specific ways that neurologists could make their practices more inclusive and equitable for sexual and gender minorities.
Her first case study was a 52-year-old man who presented with new-onset seizures, right hemiparesis, and aphasia. A brain biopsy consistent with adenocarcinoma eventually led his physician to discover he had metastatic breast cancer. It turned out the man was transgender and, despite a family history of breast cancer, hadn’t been advised to get breast cancer screenings.
“Breast cancer was not initially on the differential as no one had identified that the patient was transmasculine,” Dr. Rosendale said. A major challenge to providing care to transgender patients is a dearth of data on risks and screening recommendations. Another barrier is low knowledge of LGBTQ+ health among neurologists, Dr. Rosendale said while sharing findings from her 2019 study on the topic and calling for more research in LGBTQ+ populations.
Dr. Rosendale’s second case study dealt with a nonbinary patient who suffered from debilitating headaches for decades, first because they lacked access to health insurance and then because negative experiences with providers dissuaded them from seeking care. In data from the Center for American Progress she shared, 8% of LGB respondents and 22% of transgender respondents said they had avoided or delayed care because of fear of discrimination or mistreatment.
“So it’s not only access but also what experiences people are having when they go in and whether they’re actually even getting access to care or being taken care of,” Dr. Rosendale said. Other findings from the CAP found that:
- 8% of LGB patients and 29% of transgender patients reported having a clinician refuse to see them.
- 6% of LGB patients and 12% of transgender patients reported that a clinician refused to give them health care.
- 9% of LGB patients and 21% of transgender patients experienced harsh or abusive language during a health care experience.
- 7% of LGB patients and nearly a third (29%) of transgender patients experienced unwanted physical contact, such as fondling or sexual assault.
Reducing the disparities
Adys Mendizabal, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the Institute of Society and Genetics at the University of California, Los Angeles, who attended the presentation, was grateful to see how the various lectures enriched the discussion beyond stating the fact of racial/ethnic disparities and dug into the nuances on how to think about and address these disparities. She particularly appreciated discussion about the need to go out of the way to recruit diverse patient populations for clinical trials while also providing them care.
“It is definitely complicated, but it’s not impossible for an individual neurologist or an individual department to do something to reduce some of the disparities,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It starts with just knowing that they exist and being aware of some of the things that may be impacting care for a particular patient.”
Tools to counter disparity
In the final presentation, Amy Kind, MD, PhD, the associate dean for social health sciences and programs at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, rounded out the discussion by exploring social determinants of health and their influence on outcomes.
“Social determinants impact brain health, and brain health is not distributed equally,” Dr. Kind told attendees. “We have known this for decades, yet disparities persist.”
Dr. Kind described the “exposome,” a “measure of all the exposures of an individual in a lifetime and how those exposures relate to health,” according to the CDC, and then introduced a tool clinicians can use to better understand social determinants of health in specific geographic areas. The Neighborhood Atlas, which Dr. Kind described in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2018, measures 17 social determinants across small population-sensitive areas and provides an area deprivation index. A high area deprivation index is linked to a range of negative outcomes, including reshopitalization, later diagnoses, less comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, increased risk of postsurgical complications, and decreased life expectancy.
“One of the things that really stood out to me about Dr. Kind’s discussion of the use of the area deprivation index was the fact that understanding and quantifying these kinds of risks and exposures is the vehicle for creating the kinds of social changes, including policy changes, that will actually lead to addressing and mitigating some of these lifelong risks and exposures,” Dr. Hamilton said. “It is implausible to think that a specific group of people would be genetically more susceptible to basically every disease that we know,” he added. “It makes much more sense to think that groups of individuals have been subjected systematically to conditions that impair health in a variety of ways.”
Not just race, ethnicity, sex, and gender
Following the four presentations from researchers in health inequities was an Emerging Scholar presentation in which Jay B. Lusk, an MD/MBA candidate at Duke University, Durham, N.C., shared new research findings on the role of neighborhood disadvantage in predicting mortality from coma, stroke, and other neurologic conditions. His findings revealed that living in a neighborhood with greater deprivation substantially increased risk of mortality even after accounting for individual wealth and demographics.
Maria Eugenia Diaz-Ortiz, PhD, of the department of neurology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said she found the five presentations to be an excellent introduction to people like herself who are in the earlier stages of learning about health equity research.
“I think they introduced various important concepts and frameworks and provided tools for people who don’t know about them,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “Then they asked important questions and provided some solutions to them.”
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz also appreciated seemingly minor but actually important details in how the speakers presented themselves, such as Dr. Rivera-Mindt opening with a land acknowledgment and her disclosures of “positionality.” The former recognized the traditional Native American custodians of the land on which she lives and works, and the latter revealed details about her as an individual – such as being the Afro-Latinx daughter of immigrants yet being cisgender, able-bodied, and U.S.-born – that show where she falls on the axis of adversity and axis of privilege.
Implications for research
The biggest takeaway for Dr. Diaz-Ortiz, however, came from the first Q&A session when someone asked how to increase underrepresented populations in dementia research. Dr. Rivera-Mindt described her experience engaging these communities by employing “community-based participatory research practices, which involves making yourself a part of the community and making the community active participants in the research,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “It’s an evidence-based approach that has been shown to increase participation in research not only in her work but in the work of others.”
Preaching to the choir
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz was pleased overall with the plenary but disappointed in its placement at the end of the meeting, when attendance is always lower as attendees head home.
“The people who stayed were people who already know and recognize the value of health equity work, so I think that was a missed opportunity where the session could have been included on day one or two to boost attendance and also to educate like a broader group of neurologists,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said in an interview.
Dr. Mendizabal felt similarly, appreciating the plenary but noting it was “definitely overdue” and that it should not be the last session. Instead, sessions on health equity should be as easy as possible to attend to bring in larger audiences. “Perhaps having that session on a Saturday or Sunday would have a higher likelihood of greater attendance than on a Tuesday,” she said. That said, Dr. Mendizabal also noticed that greater attention to health care disparities was woven into many other sessions throughout the conference, which is “the best way of addressing health equity instead of trying to just designate a session,” she said.
Dr. Mendizabal hopes that plenaries like this one and the weaving of health equity issues into presentations throughout neurology conferences continue.
“After the racial reckoning in 2020, there was a big impetus and a big wave of energy in addressing health disparities in the field, and I hope that that momentum is not starting to wane,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It’s important because not talking about is not going to make this issue go away.”
Dr. Hamilton agreed that it is important that the conversation continue and that physicians recognize the importance of understanding health care disparities and determinants of health, regardless of where they fall on the political spectrum or whether they choose to get involved in policy or advocacy.
“Irrespective of whether you think race or ethnicity or socioeconomic status are political issues or not, it is the case that you’re obligated to have an objective understanding of the factors that contribute to your patient’s health and as points of intervention,” Dr. Hamilton said. “So even if you don’t want to sit down and jot off that email to your senator, you still have to take these factors into account when you’re treating the person who’s sitting right in front of you, and that’s not political. That’s the promise of being a physician.”
Dr. Amezcua has received personal compensation for consulting, speaking, or serving on steering committees or advisory boards for Biogen Idec, Novartis, Genentech, and EMD Serono, and she has received research support from Biogen Idec and Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation. Dr. Kind reported support from the Alzheimer’s Association. Dr. Diaz-Ortiz is coinventor of a provisional patent submitted by the University of Pennsylvania that relates to a potential therapeutic in Parkinson’s disease. Mr. Lusk reported fellowship support from American Heart Association and travel support from the American Neurological Association. No other speakers or sources had relevant disclosures.
Black and Latinx older adults are up to three times as likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease than non-Latinx White adults and tend to experience onset at a younger age with more severe symptoms, according to Monica Rivera-Mindt, PhD, a professor of psychology at Fordham University and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Looking ahead, that means by 2030, nearly 40% of the 8.4 million Americans affected by Alzheimer’s disease will be Black and/or Latinx, she said. These facts were among the stark disparities in health care outcomes Dr. Rivera-Mindt discussed in her presentation on brain health equity at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
Dr. Rivera-Mindt’s presentation opened the ANA’s plenary session on health disparities and inequities. The plenary, “Advancing Neurologic Equity: Challenges and Paths Forward,” did not simply enumerate racial and ethnic disparities that exist with various neurological conditions. Rather it went beyond the discussion of what disparities exist into understanding the roots of them as well as tips, tools, and resources that can aid clinicians in addressing or ameliorating them.
Roy Hamilton, MD, an associate professor of neurology and physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said. “If clinicians are unaware of these disparities or don’t have any sense of how to start to address or think about them, then they’re really missing out on an important component of their education as persons who take care of patients with brain disorders.”
Dr. Hamilton, who organized the plenary, noted that awareness of these disparities is crucial to comprehensively caring for patients.
Missed opportunities
“We’re talking about disadvantages that are structural and large scale, but those disadvantages play themselves out in the individual encounter,” Dr. Hamilton said. “When physicians see patients, they have to treat the whole patient in front of them,” which means being aware of the risks and factors that could affect a patient’s clinical presentation. “Being aware of disparities has practical impacts on physician judgment,” he said.
For example, recent research in multiple sclerosis (MS) has highlighted how clinicians may be missing diagnosis of this condition in non-White populations because the condition has been regarded for so long as a “White person’s” disease, Dr. Hamilton said. In non-White patients exhibiting MS symptoms, then, clinicians may have been less likely to consider MS as a possibility, thereby delaying diagnosis and treatment.
Those patterns may partly explain why the mortality rate for MS is greater in Black patients, who also show more rapid neurodegeneration than White patients with MS, Lilyana Amezcua, MD, an associate professor of neurology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, reported in the plenary’s second presentation.
Transgender issues
The third session, presented by Nicole Rosendale, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the San Francisco General Hospital neurology inpatient services, examined disparities in neurology within the LGBTQ+ community through representative case studies and then offered specific ways that neurologists could make their practices more inclusive and equitable for sexual and gender minorities.
Her first case study was a 52-year-old man who presented with new-onset seizures, right hemiparesis, and aphasia. A brain biopsy consistent with adenocarcinoma eventually led his physician to discover he had metastatic breast cancer. It turned out the man was transgender and, despite a family history of breast cancer, hadn’t been advised to get breast cancer screenings.
“Breast cancer was not initially on the differential as no one had identified that the patient was transmasculine,” Dr. Rosendale said. A major challenge to providing care to transgender patients is a dearth of data on risks and screening recommendations. Another barrier is low knowledge of LGBTQ+ health among neurologists, Dr. Rosendale said while sharing findings from her 2019 study on the topic and calling for more research in LGBTQ+ populations.
Dr. Rosendale’s second case study dealt with a nonbinary patient who suffered from debilitating headaches for decades, first because they lacked access to health insurance and then because negative experiences with providers dissuaded them from seeking care. In data from the Center for American Progress she shared, 8% of LGB respondents and 22% of transgender respondents said they had avoided or delayed care because of fear of discrimination or mistreatment.
“So it’s not only access but also what experiences people are having when they go in and whether they’re actually even getting access to care or being taken care of,” Dr. Rosendale said. Other findings from the CAP found that:
- 8% of LGB patients and 29% of transgender patients reported having a clinician refuse to see them.
- 6% of LGB patients and 12% of transgender patients reported that a clinician refused to give them health care.
- 9% of LGB patients and 21% of transgender patients experienced harsh or abusive language during a health care experience.
- 7% of LGB patients and nearly a third (29%) of transgender patients experienced unwanted physical contact, such as fondling or sexual assault.
Reducing the disparities
Adys Mendizabal, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the Institute of Society and Genetics at the University of California, Los Angeles, who attended the presentation, was grateful to see how the various lectures enriched the discussion beyond stating the fact of racial/ethnic disparities and dug into the nuances on how to think about and address these disparities. She particularly appreciated discussion about the need to go out of the way to recruit diverse patient populations for clinical trials while also providing them care.
“It is definitely complicated, but it’s not impossible for an individual neurologist or an individual department to do something to reduce some of the disparities,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It starts with just knowing that they exist and being aware of some of the things that may be impacting care for a particular patient.”
Tools to counter disparity
In the final presentation, Amy Kind, MD, PhD, the associate dean for social health sciences and programs at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, rounded out the discussion by exploring social determinants of health and their influence on outcomes.
“Social determinants impact brain health, and brain health is not distributed equally,” Dr. Kind told attendees. “We have known this for decades, yet disparities persist.”
Dr. Kind described the “exposome,” a “measure of all the exposures of an individual in a lifetime and how those exposures relate to health,” according to the CDC, and then introduced a tool clinicians can use to better understand social determinants of health in specific geographic areas. The Neighborhood Atlas, which Dr. Kind described in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2018, measures 17 social determinants across small population-sensitive areas and provides an area deprivation index. A high area deprivation index is linked to a range of negative outcomes, including reshopitalization, later diagnoses, less comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, increased risk of postsurgical complications, and decreased life expectancy.
“One of the things that really stood out to me about Dr. Kind’s discussion of the use of the area deprivation index was the fact that understanding and quantifying these kinds of risks and exposures is the vehicle for creating the kinds of social changes, including policy changes, that will actually lead to addressing and mitigating some of these lifelong risks and exposures,” Dr. Hamilton said. “It is implausible to think that a specific group of people would be genetically more susceptible to basically every disease that we know,” he added. “It makes much more sense to think that groups of individuals have been subjected systematically to conditions that impair health in a variety of ways.”
Not just race, ethnicity, sex, and gender
Following the four presentations from researchers in health inequities was an Emerging Scholar presentation in which Jay B. Lusk, an MD/MBA candidate at Duke University, Durham, N.C., shared new research findings on the role of neighborhood disadvantage in predicting mortality from coma, stroke, and other neurologic conditions. His findings revealed that living in a neighborhood with greater deprivation substantially increased risk of mortality even after accounting for individual wealth and demographics.
Maria Eugenia Diaz-Ortiz, PhD, of the department of neurology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said she found the five presentations to be an excellent introduction to people like herself who are in the earlier stages of learning about health equity research.
“I think they introduced various important concepts and frameworks and provided tools for people who don’t know about them,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “Then they asked important questions and provided some solutions to them.”
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz also appreciated seemingly minor but actually important details in how the speakers presented themselves, such as Dr. Rivera-Mindt opening with a land acknowledgment and her disclosures of “positionality.” The former recognized the traditional Native American custodians of the land on which she lives and works, and the latter revealed details about her as an individual – such as being the Afro-Latinx daughter of immigrants yet being cisgender, able-bodied, and U.S.-born – that show where she falls on the axis of adversity and axis of privilege.
Implications for research
The biggest takeaway for Dr. Diaz-Ortiz, however, came from the first Q&A session when someone asked how to increase underrepresented populations in dementia research. Dr. Rivera-Mindt described her experience engaging these communities by employing “community-based participatory research practices, which involves making yourself a part of the community and making the community active participants in the research,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “It’s an evidence-based approach that has been shown to increase participation in research not only in her work but in the work of others.”
Preaching to the choir
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz was pleased overall with the plenary but disappointed in its placement at the end of the meeting, when attendance is always lower as attendees head home.
“The people who stayed were people who already know and recognize the value of health equity work, so I think that was a missed opportunity where the session could have been included on day one or two to boost attendance and also to educate like a broader group of neurologists,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said in an interview.
Dr. Mendizabal felt similarly, appreciating the plenary but noting it was “definitely overdue” and that it should not be the last session. Instead, sessions on health equity should be as easy as possible to attend to bring in larger audiences. “Perhaps having that session on a Saturday or Sunday would have a higher likelihood of greater attendance than on a Tuesday,” she said. That said, Dr. Mendizabal also noticed that greater attention to health care disparities was woven into many other sessions throughout the conference, which is “the best way of addressing health equity instead of trying to just designate a session,” she said.
Dr. Mendizabal hopes that plenaries like this one and the weaving of health equity issues into presentations throughout neurology conferences continue.
“After the racial reckoning in 2020, there was a big impetus and a big wave of energy in addressing health disparities in the field, and I hope that that momentum is not starting to wane,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It’s important because not talking about is not going to make this issue go away.”
Dr. Hamilton agreed that it is important that the conversation continue and that physicians recognize the importance of understanding health care disparities and determinants of health, regardless of where they fall on the political spectrum or whether they choose to get involved in policy or advocacy.
“Irrespective of whether you think race or ethnicity or socioeconomic status are political issues or not, it is the case that you’re obligated to have an objective understanding of the factors that contribute to your patient’s health and as points of intervention,” Dr. Hamilton said. “So even if you don’t want to sit down and jot off that email to your senator, you still have to take these factors into account when you’re treating the person who’s sitting right in front of you, and that’s not political. That’s the promise of being a physician.”
Dr. Amezcua has received personal compensation for consulting, speaking, or serving on steering committees or advisory boards for Biogen Idec, Novartis, Genentech, and EMD Serono, and she has received research support from Biogen Idec and Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation. Dr. Kind reported support from the Alzheimer’s Association. Dr. Diaz-Ortiz is coinventor of a provisional patent submitted by the University of Pennsylvania that relates to a potential therapeutic in Parkinson’s disease. Mr. Lusk reported fellowship support from American Heart Association and travel support from the American Neurological Association. No other speakers or sources had relevant disclosures.
Black and Latinx older adults are up to three times as likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease than non-Latinx White adults and tend to experience onset at a younger age with more severe symptoms, according to Monica Rivera-Mindt, PhD, a professor of psychology at Fordham University and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Looking ahead, that means by 2030, nearly 40% of the 8.4 million Americans affected by Alzheimer’s disease will be Black and/or Latinx, she said. These facts were among the stark disparities in health care outcomes Dr. Rivera-Mindt discussed in her presentation on brain health equity at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
Dr. Rivera-Mindt’s presentation opened the ANA’s plenary session on health disparities and inequities. The plenary, “Advancing Neurologic Equity: Challenges and Paths Forward,” did not simply enumerate racial and ethnic disparities that exist with various neurological conditions. Rather it went beyond the discussion of what disparities exist into understanding the roots of them as well as tips, tools, and resources that can aid clinicians in addressing or ameliorating them.
Roy Hamilton, MD, an associate professor of neurology and physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said. “If clinicians are unaware of these disparities or don’t have any sense of how to start to address or think about them, then they’re really missing out on an important component of their education as persons who take care of patients with brain disorders.”
Dr. Hamilton, who organized the plenary, noted that awareness of these disparities is crucial to comprehensively caring for patients.
Missed opportunities
“We’re talking about disadvantages that are structural and large scale, but those disadvantages play themselves out in the individual encounter,” Dr. Hamilton said. “When physicians see patients, they have to treat the whole patient in front of them,” which means being aware of the risks and factors that could affect a patient’s clinical presentation. “Being aware of disparities has practical impacts on physician judgment,” he said.
For example, recent research in multiple sclerosis (MS) has highlighted how clinicians may be missing diagnosis of this condition in non-White populations because the condition has been regarded for so long as a “White person’s” disease, Dr. Hamilton said. In non-White patients exhibiting MS symptoms, then, clinicians may have been less likely to consider MS as a possibility, thereby delaying diagnosis and treatment.
Those patterns may partly explain why the mortality rate for MS is greater in Black patients, who also show more rapid neurodegeneration than White patients with MS, Lilyana Amezcua, MD, an associate professor of neurology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, reported in the plenary’s second presentation.
Transgender issues
The third session, presented by Nicole Rosendale, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the San Francisco General Hospital neurology inpatient services, examined disparities in neurology within the LGBTQ+ community through representative case studies and then offered specific ways that neurologists could make their practices more inclusive and equitable for sexual and gender minorities.
Her first case study was a 52-year-old man who presented with new-onset seizures, right hemiparesis, and aphasia. A brain biopsy consistent with adenocarcinoma eventually led his physician to discover he had metastatic breast cancer. It turned out the man was transgender and, despite a family history of breast cancer, hadn’t been advised to get breast cancer screenings.
“Breast cancer was not initially on the differential as no one had identified that the patient was transmasculine,” Dr. Rosendale said. A major challenge to providing care to transgender patients is a dearth of data on risks and screening recommendations. Another barrier is low knowledge of LGBTQ+ health among neurologists, Dr. Rosendale said while sharing findings from her 2019 study on the topic and calling for more research in LGBTQ+ populations.
Dr. Rosendale’s second case study dealt with a nonbinary patient who suffered from debilitating headaches for decades, first because they lacked access to health insurance and then because negative experiences with providers dissuaded them from seeking care. In data from the Center for American Progress she shared, 8% of LGB respondents and 22% of transgender respondents said they had avoided or delayed care because of fear of discrimination or mistreatment.
“So it’s not only access but also what experiences people are having when they go in and whether they’re actually even getting access to care or being taken care of,” Dr. Rosendale said. Other findings from the CAP found that:
- 8% of LGB patients and 29% of transgender patients reported having a clinician refuse to see them.
- 6% of LGB patients and 12% of transgender patients reported that a clinician refused to give them health care.
- 9% of LGB patients and 21% of transgender patients experienced harsh or abusive language during a health care experience.
- 7% of LGB patients and nearly a third (29%) of transgender patients experienced unwanted physical contact, such as fondling or sexual assault.
Reducing the disparities
Adys Mendizabal, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the Institute of Society and Genetics at the University of California, Los Angeles, who attended the presentation, was grateful to see how the various lectures enriched the discussion beyond stating the fact of racial/ethnic disparities and dug into the nuances on how to think about and address these disparities. She particularly appreciated discussion about the need to go out of the way to recruit diverse patient populations for clinical trials while also providing them care.
“It is definitely complicated, but it’s not impossible for an individual neurologist or an individual department to do something to reduce some of the disparities,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It starts with just knowing that they exist and being aware of some of the things that may be impacting care for a particular patient.”
Tools to counter disparity
In the final presentation, Amy Kind, MD, PhD, the associate dean for social health sciences and programs at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, rounded out the discussion by exploring social determinants of health and their influence on outcomes.
“Social determinants impact brain health, and brain health is not distributed equally,” Dr. Kind told attendees. “We have known this for decades, yet disparities persist.”
Dr. Kind described the “exposome,” a “measure of all the exposures of an individual in a lifetime and how those exposures relate to health,” according to the CDC, and then introduced a tool clinicians can use to better understand social determinants of health in specific geographic areas. The Neighborhood Atlas, which Dr. Kind described in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2018, measures 17 social determinants across small population-sensitive areas and provides an area deprivation index. A high area deprivation index is linked to a range of negative outcomes, including reshopitalization, later diagnoses, less comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, increased risk of postsurgical complications, and decreased life expectancy.
“One of the things that really stood out to me about Dr. Kind’s discussion of the use of the area deprivation index was the fact that understanding and quantifying these kinds of risks and exposures is the vehicle for creating the kinds of social changes, including policy changes, that will actually lead to addressing and mitigating some of these lifelong risks and exposures,” Dr. Hamilton said. “It is implausible to think that a specific group of people would be genetically more susceptible to basically every disease that we know,” he added. “It makes much more sense to think that groups of individuals have been subjected systematically to conditions that impair health in a variety of ways.”
Not just race, ethnicity, sex, and gender
Following the four presentations from researchers in health inequities was an Emerging Scholar presentation in which Jay B. Lusk, an MD/MBA candidate at Duke University, Durham, N.C., shared new research findings on the role of neighborhood disadvantage in predicting mortality from coma, stroke, and other neurologic conditions. His findings revealed that living in a neighborhood with greater deprivation substantially increased risk of mortality even after accounting for individual wealth and demographics.
Maria Eugenia Diaz-Ortiz, PhD, of the department of neurology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said she found the five presentations to be an excellent introduction to people like herself who are in the earlier stages of learning about health equity research.
“I think they introduced various important concepts and frameworks and provided tools for people who don’t know about them,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “Then they asked important questions and provided some solutions to them.”
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz also appreciated seemingly minor but actually important details in how the speakers presented themselves, such as Dr. Rivera-Mindt opening with a land acknowledgment and her disclosures of “positionality.” The former recognized the traditional Native American custodians of the land on which she lives and works, and the latter revealed details about her as an individual – such as being the Afro-Latinx daughter of immigrants yet being cisgender, able-bodied, and U.S.-born – that show where she falls on the axis of adversity and axis of privilege.
Implications for research
The biggest takeaway for Dr. Diaz-Ortiz, however, came from the first Q&A session when someone asked how to increase underrepresented populations in dementia research. Dr. Rivera-Mindt described her experience engaging these communities by employing “community-based participatory research practices, which involves making yourself a part of the community and making the community active participants in the research,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “It’s an evidence-based approach that has been shown to increase participation in research not only in her work but in the work of others.”
Preaching to the choir
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz was pleased overall with the plenary but disappointed in its placement at the end of the meeting, when attendance is always lower as attendees head home.
“The people who stayed were people who already know and recognize the value of health equity work, so I think that was a missed opportunity where the session could have been included on day one or two to boost attendance and also to educate like a broader group of neurologists,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said in an interview.
Dr. Mendizabal felt similarly, appreciating the plenary but noting it was “definitely overdue” and that it should not be the last session. Instead, sessions on health equity should be as easy as possible to attend to bring in larger audiences. “Perhaps having that session on a Saturday or Sunday would have a higher likelihood of greater attendance than on a Tuesday,” she said. That said, Dr. Mendizabal also noticed that greater attention to health care disparities was woven into many other sessions throughout the conference, which is “the best way of addressing health equity instead of trying to just designate a session,” she said.
Dr. Mendizabal hopes that plenaries like this one and the weaving of health equity issues into presentations throughout neurology conferences continue.
“After the racial reckoning in 2020, there was a big impetus and a big wave of energy in addressing health disparities in the field, and I hope that that momentum is not starting to wane,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It’s important because not talking about is not going to make this issue go away.”
Dr. Hamilton agreed that it is important that the conversation continue and that physicians recognize the importance of understanding health care disparities and determinants of health, regardless of where they fall on the political spectrum or whether they choose to get involved in policy or advocacy.
“Irrespective of whether you think race or ethnicity or socioeconomic status are political issues or not, it is the case that you’re obligated to have an objective understanding of the factors that contribute to your patient’s health and as points of intervention,” Dr. Hamilton said. “So even if you don’t want to sit down and jot off that email to your senator, you still have to take these factors into account when you’re treating the person who’s sitting right in front of you, and that’s not political. That’s the promise of being a physician.”
Dr. Amezcua has received personal compensation for consulting, speaking, or serving on steering committees or advisory boards for Biogen Idec, Novartis, Genentech, and EMD Serono, and she has received research support from Biogen Idec and Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation. Dr. Kind reported support from the Alzheimer’s Association. Dr. Diaz-Ortiz is coinventor of a provisional patent submitted by the University of Pennsylvania that relates to a potential therapeutic in Parkinson’s disease. Mr. Lusk reported fellowship support from American Heart Association and travel support from the American Neurological Association. No other speakers or sources had relevant disclosures.
FROM ANA 2022

