User login
New guideline for in-hospital care of diabetes says use CGMs
Goal-directed glycemic management – which may include new technologies for glucose monitoring – for non–critically ill hospitalized patients who have diabetes or newly recognized hyperglycemia can improve outcomes, according to a new practice guideline from the Endocrine Society.
Even though roughly 35% of hospitalized patients have diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia, there is “wide variability in glycemic management in clinical practice,” writing panel chair Mary Korytkowski, MD, from the University of Pittsburgh, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society. “These patients get admitted to every patient service in the hospital, meaning that every clinical service will encounter this group of patients, and their glycemic management can have a major effect on their outcomes. Both short term and long term.”
This guideline provides strategies “to achieve previously recommended glycemic goals while also reducing the risk for hypoglycemia, and this includes inpatient use of insulin pump therapy or continuous glucose monitoring [CGM] devices, among others,” she said.
It also includes “recommendations for preoperative glycemic goals as well as when the use of correctional insulin – well known as sliding scale insulin – may be appropriate” and when it is not.
The document, which replaces a 2012 guideline, was published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
A multidisciplinary panel developed the document over the last 3 years to answer 10 clinical practice questions related to management of non–critically ill hospitalized patients with diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia.
Use of CGM devices in hospital
The first recommendation is: “In adults with insulin-treated diabetes hospitalized for noncritical illness who are at high risk of hypoglycemia, we suggest the use of real-time [CGM] with confirmatory bedside point-of-care blood glucose monitoring for adjustments in insulin dosing rather than point-of-care blood glucose rather than testing alone in hospital settings where resources and training are available.” (Conditional recommendation. Low certainty of evidence).
“We were actually very careful in terms of looking at the data” for use of CGMs, Dr. Korytkowski said in an interview.
Although CGMs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the outpatient setting, and that’s becoming the standard of care there, they are not yet approved for in-hospital use.
However, the FDA granted an emergency allowance for use of CGMs in hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic.
That was “when everyone was scrambling for what to do,” Dr. Korytkowski noted. “There was a shortage of personal protective equipment and a real interest in trying to limit the amount of exposure of healthcare personnel in some of these really critically ill patients for whom intravenous insulin therapy was used to control their glucose level.”
On March 1, the FDA granted Breakthrough Devices Designation for Dexcom CGM use in the hospital setting.
The new guideline suggests CGM be used to detect trends in glycemic management, with insulin dosing decisions made with point-of-care glucose measure (the standard of care).
To implement CGM for glycemic management in hospitals, Dr. Korytkowski said, would require “extensive staff and nursing education to have people with expertise available to provide support to nursing personnel who are both placing these devices, changing these devices, looking at trends, and then knowing when to remove them for certain procedures such as MRI or radiologic procedures.”
“We know that not all hospitals may be readily available to use these devices,” she said. “It is an area of active research. But the use of these devices during the pandemic, in both critical care and non–critical care setting has really provided us with a lot of information that was used to formulate this suggestion in the guideline.”
The document addresses the following areas: CGM, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump therapy, inpatient diabetes education, prespecified preoperative glycemic targets, use of neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin for glucocorticoid or enteral nutrition-associated hyperglycemia, noninsulin therapies, preoperative carbohydrate-containing oral fluids, carbohydrate counting for prandial (mealtime) insulin dosing, and correctional and scheduled (basal or basal bolus) insulin therapies.
Nine key recommendations
Dr. Korytkowski identified nine key recommendations:
- CGM systems can help guide glycemic management with reduced risk for hypoglycemia.
- Patients experiencing glucocorticoid- or enteral nutrition–associated hyperglycemia require scheduled insulin therapy to address anticipated glucose excursions.
- Selected patients using insulin pump therapy prior to a hospital admission can continue to use these devices in the hospital if they have the mental and physical capacity to do so with knowledgeable hospital personnel.
- Diabetes self-management education provided to hospitalized patients can promote improved glycemic control following discharge with reductions in the risk for hospital readmission. “We know that is recommended for patients in the outpatient setting but often they do not get this,” she said. “We were able to observe that this can also impact long-term outcomes “
- Patients with diabetes scheduled for elective surgery may have improved postoperative outcomes when preoperative hemoglobin A1c is 8% or less and preoperative blood glucose is less than 180 mg/dL. “This recommendation answers the question: ‘Where should glycemic goals be for people who are undergoing surgery?’ ”
- Providing preoperative carbohydrate-containing beverages to patients with known diabetes is not recommended.
- Patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or well-managed diabetes on noninsulin therapy may be treated with correctional insulin alone as initial therapy at hospital admission.
- Some noninsulin diabetes therapies can be used in combination with correction insulin for patients with type 2 diabetes who have mild hyperglycemia.
- Correctional insulin – “otherwise known as sliding-scale insulin” – can be used as initial therapy for patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or type 2 diabetes treated with noninsulin therapy prior to hospital admission.
- Scheduled insulin therapy is preferred for patients experiencing persistent blood glucose values greater than 180 mg/dL and is recommended for patients using insulin therapy prior to admission.
The guideline writers’ hopes
“We hope that this guideline will resolve debates” about appropriate preoperative glycemic management and when sliding-scale insulin can be used and should not be used, said Dr. Korytkowski.
The authors also hope that “it will stimulate research funding for this very important aspect of diabetes care, and that hospitals will recognize the importance of having access to knowledgeable diabetes care and education specialists who can provide staff education regarding inpatient glycemic management, provide oversight for patients using insulin pump therapy or CGM devices, and empower hospital nurses to provide diabetes [self-management] education prior to patient discharge.”
Claire Pegg, the patient representative on the panel, hopes “that this guideline serves as the beginning of a conversation that will allow inpatient caregivers to provide individualized care to patients – some of whom may be self-sufficient with their glycemic management and others who need additional assistance.”
Development of the guideline was funded by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Korytkowski has reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Goal-directed glycemic management – which may include new technologies for glucose monitoring – for non–critically ill hospitalized patients who have diabetes or newly recognized hyperglycemia can improve outcomes, according to a new practice guideline from the Endocrine Society.
Even though roughly 35% of hospitalized patients have diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia, there is “wide variability in glycemic management in clinical practice,” writing panel chair Mary Korytkowski, MD, from the University of Pittsburgh, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society. “These patients get admitted to every patient service in the hospital, meaning that every clinical service will encounter this group of patients, and their glycemic management can have a major effect on their outcomes. Both short term and long term.”
This guideline provides strategies “to achieve previously recommended glycemic goals while also reducing the risk for hypoglycemia, and this includes inpatient use of insulin pump therapy or continuous glucose monitoring [CGM] devices, among others,” she said.
It also includes “recommendations for preoperative glycemic goals as well as when the use of correctional insulin – well known as sliding scale insulin – may be appropriate” and when it is not.
The document, which replaces a 2012 guideline, was published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
A multidisciplinary panel developed the document over the last 3 years to answer 10 clinical practice questions related to management of non–critically ill hospitalized patients with diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia.
Use of CGM devices in hospital
The first recommendation is: “In adults with insulin-treated diabetes hospitalized for noncritical illness who are at high risk of hypoglycemia, we suggest the use of real-time [CGM] with confirmatory bedside point-of-care blood glucose monitoring for adjustments in insulin dosing rather than point-of-care blood glucose rather than testing alone in hospital settings where resources and training are available.” (Conditional recommendation. Low certainty of evidence).
“We were actually very careful in terms of looking at the data” for use of CGMs, Dr. Korytkowski said in an interview.
Although CGMs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the outpatient setting, and that’s becoming the standard of care there, they are not yet approved for in-hospital use.
However, the FDA granted an emergency allowance for use of CGMs in hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic.
That was “when everyone was scrambling for what to do,” Dr. Korytkowski noted. “There was a shortage of personal protective equipment and a real interest in trying to limit the amount of exposure of healthcare personnel in some of these really critically ill patients for whom intravenous insulin therapy was used to control their glucose level.”
On March 1, the FDA granted Breakthrough Devices Designation for Dexcom CGM use in the hospital setting.
The new guideline suggests CGM be used to detect trends in glycemic management, with insulin dosing decisions made with point-of-care glucose measure (the standard of care).
To implement CGM for glycemic management in hospitals, Dr. Korytkowski said, would require “extensive staff and nursing education to have people with expertise available to provide support to nursing personnel who are both placing these devices, changing these devices, looking at trends, and then knowing when to remove them for certain procedures such as MRI or radiologic procedures.”
“We know that not all hospitals may be readily available to use these devices,” she said. “It is an area of active research. But the use of these devices during the pandemic, in both critical care and non–critical care setting has really provided us with a lot of information that was used to formulate this suggestion in the guideline.”
The document addresses the following areas: CGM, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump therapy, inpatient diabetes education, prespecified preoperative glycemic targets, use of neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin for glucocorticoid or enteral nutrition-associated hyperglycemia, noninsulin therapies, preoperative carbohydrate-containing oral fluids, carbohydrate counting for prandial (mealtime) insulin dosing, and correctional and scheduled (basal or basal bolus) insulin therapies.
Nine key recommendations
Dr. Korytkowski identified nine key recommendations:
- CGM systems can help guide glycemic management with reduced risk for hypoglycemia.
- Patients experiencing glucocorticoid- or enteral nutrition–associated hyperglycemia require scheduled insulin therapy to address anticipated glucose excursions.
- Selected patients using insulin pump therapy prior to a hospital admission can continue to use these devices in the hospital if they have the mental and physical capacity to do so with knowledgeable hospital personnel.
- Diabetes self-management education provided to hospitalized patients can promote improved glycemic control following discharge with reductions in the risk for hospital readmission. “We know that is recommended for patients in the outpatient setting but often they do not get this,” she said. “We were able to observe that this can also impact long-term outcomes “
- Patients with diabetes scheduled for elective surgery may have improved postoperative outcomes when preoperative hemoglobin A1c is 8% or less and preoperative blood glucose is less than 180 mg/dL. “This recommendation answers the question: ‘Where should glycemic goals be for people who are undergoing surgery?’ ”
- Providing preoperative carbohydrate-containing beverages to patients with known diabetes is not recommended.
- Patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or well-managed diabetes on noninsulin therapy may be treated with correctional insulin alone as initial therapy at hospital admission.
- Some noninsulin diabetes therapies can be used in combination with correction insulin for patients with type 2 diabetes who have mild hyperglycemia.
- Correctional insulin – “otherwise known as sliding-scale insulin” – can be used as initial therapy for patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or type 2 diabetes treated with noninsulin therapy prior to hospital admission.
- Scheduled insulin therapy is preferred for patients experiencing persistent blood glucose values greater than 180 mg/dL and is recommended for patients using insulin therapy prior to admission.
The guideline writers’ hopes
“We hope that this guideline will resolve debates” about appropriate preoperative glycemic management and when sliding-scale insulin can be used and should not be used, said Dr. Korytkowski.
The authors also hope that “it will stimulate research funding for this very important aspect of diabetes care, and that hospitals will recognize the importance of having access to knowledgeable diabetes care and education specialists who can provide staff education regarding inpatient glycemic management, provide oversight for patients using insulin pump therapy or CGM devices, and empower hospital nurses to provide diabetes [self-management] education prior to patient discharge.”
Claire Pegg, the patient representative on the panel, hopes “that this guideline serves as the beginning of a conversation that will allow inpatient caregivers to provide individualized care to patients – some of whom may be self-sufficient with their glycemic management and others who need additional assistance.”
Development of the guideline was funded by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Korytkowski has reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Goal-directed glycemic management – which may include new technologies for glucose monitoring – for non–critically ill hospitalized patients who have diabetes or newly recognized hyperglycemia can improve outcomes, according to a new practice guideline from the Endocrine Society.
Even though roughly 35% of hospitalized patients have diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia, there is “wide variability in glycemic management in clinical practice,” writing panel chair Mary Korytkowski, MD, from the University of Pittsburgh, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society. “These patients get admitted to every patient service in the hospital, meaning that every clinical service will encounter this group of patients, and their glycemic management can have a major effect on their outcomes. Both short term and long term.”
This guideline provides strategies “to achieve previously recommended glycemic goals while also reducing the risk for hypoglycemia, and this includes inpatient use of insulin pump therapy or continuous glucose monitoring [CGM] devices, among others,” she said.
It also includes “recommendations for preoperative glycemic goals as well as when the use of correctional insulin – well known as sliding scale insulin – may be appropriate” and when it is not.
The document, which replaces a 2012 guideline, was published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
A multidisciplinary panel developed the document over the last 3 years to answer 10 clinical practice questions related to management of non–critically ill hospitalized patients with diabetes or newly discovered hyperglycemia.
Use of CGM devices in hospital
The first recommendation is: “In adults with insulin-treated diabetes hospitalized for noncritical illness who are at high risk of hypoglycemia, we suggest the use of real-time [CGM] with confirmatory bedside point-of-care blood glucose monitoring for adjustments in insulin dosing rather than point-of-care blood glucose rather than testing alone in hospital settings where resources and training are available.” (Conditional recommendation. Low certainty of evidence).
“We were actually very careful in terms of looking at the data” for use of CGMs, Dr. Korytkowski said in an interview.
Although CGMs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the outpatient setting, and that’s becoming the standard of care there, they are not yet approved for in-hospital use.
However, the FDA granted an emergency allowance for use of CGMs in hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic.
That was “when everyone was scrambling for what to do,” Dr. Korytkowski noted. “There was a shortage of personal protective equipment and a real interest in trying to limit the amount of exposure of healthcare personnel in some of these really critically ill patients for whom intravenous insulin therapy was used to control their glucose level.”
On March 1, the FDA granted Breakthrough Devices Designation for Dexcom CGM use in the hospital setting.
The new guideline suggests CGM be used to detect trends in glycemic management, with insulin dosing decisions made with point-of-care glucose measure (the standard of care).
To implement CGM for glycemic management in hospitals, Dr. Korytkowski said, would require “extensive staff and nursing education to have people with expertise available to provide support to nursing personnel who are both placing these devices, changing these devices, looking at trends, and then knowing when to remove them for certain procedures such as MRI or radiologic procedures.”
“We know that not all hospitals may be readily available to use these devices,” she said. “It is an area of active research. But the use of these devices during the pandemic, in both critical care and non–critical care setting has really provided us with a lot of information that was used to formulate this suggestion in the guideline.”
The document addresses the following areas: CGM, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump therapy, inpatient diabetes education, prespecified preoperative glycemic targets, use of neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin for glucocorticoid or enteral nutrition-associated hyperglycemia, noninsulin therapies, preoperative carbohydrate-containing oral fluids, carbohydrate counting for prandial (mealtime) insulin dosing, and correctional and scheduled (basal or basal bolus) insulin therapies.
Nine key recommendations
Dr. Korytkowski identified nine key recommendations:
- CGM systems can help guide glycemic management with reduced risk for hypoglycemia.
- Patients experiencing glucocorticoid- or enteral nutrition–associated hyperglycemia require scheduled insulin therapy to address anticipated glucose excursions.
- Selected patients using insulin pump therapy prior to a hospital admission can continue to use these devices in the hospital if they have the mental and physical capacity to do so with knowledgeable hospital personnel.
- Diabetes self-management education provided to hospitalized patients can promote improved glycemic control following discharge with reductions in the risk for hospital readmission. “We know that is recommended for patients in the outpatient setting but often they do not get this,” she said. “We were able to observe that this can also impact long-term outcomes “
- Patients with diabetes scheduled for elective surgery may have improved postoperative outcomes when preoperative hemoglobin A1c is 8% or less and preoperative blood glucose is less than 180 mg/dL. “This recommendation answers the question: ‘Where should glycemic goals be for people who are undergoing surgery?’ ”
- Providing preoperative carbohydrate-containing beverages to patients with known diabetes is not recommended.
- Patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or well-managed diabetes on noninsulin therapy may be treated with correctional insulin alone as initial therapy at hospital admission.
- Some noninsulin diabetes therapies can be used in combination with correction insulin for patients with type 2 diabetes who have mild hyperglycemia.
- Correctional insulin – “otherwise known as sliding-scale insulin” – can be used as initial therapy for patients with newly recognized hyperglycemia or type 2 diabetes treated with noninsulin therapy prior to hospital admission.
- Scheduled insulin therapy is preferred for patients experiencing persistent blood glucose values greater than 180 mg/dL and is recommended for patients using insulin therapy prior to admission.
The guideline writers’ hopes
“We hope that this guideline will resolve debates” about appropriate preoperative glycemic management and when sliding-scale insulin can be used and should not be used, said Dr. Korytkowski.
The authors also hope that “it will stimulate research funding for this very important aspect of diabetes care, and that hospitals will recognize the importance of having access to knowledgeable diabetes care and education specialists who can provide staff education regarding inpatient glycemic management, provide oversight for patients using insulin pump therapy or CGM devices, and empower hospital nurses to provide diabetes [self-management] education prior to patient discharge.”
Claire Pegg, the patient representative on the panel, hopes “that this guideline serves as the beginning of a conversation that will allow inpatient caregivers to provide individualized care to patients – some of whom may be self-sufficient with their glycemic management and others who need additional assistance.”
Development of the guideline was funded by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Korytkowski has reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ENDO 2022
Opioid use in the elderly a dementia risk factor?
in new findings that suggest exposure to these drugs may be another modifiable risk factor for dementia.
“Clinicians and others may want to consider that opioid exposure in those aged 75-80 increases dementia risk, and to balance the potential benefits of opioid use in old age with adverse side effects,” said Stephen Z. Levine, PhD, professor, department of community mental health, University of Haifa (Israel).
The study was published online in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Widespread use
Evidence points to a relatively high rate of opioid prescriptions among older adults. A Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report noted 19.2% of the U.S. adult population filled an opioid prescription in 2018, with the rate in those over 65 double that of adults aged 20-24 years (25% vs. 11.2%).
Disorders and illnesses for which opioids might be prescribed, including cancer and some pain conditions, “are far more prevalent in old age than at a younger age,” said Dr. Levine.
This high rate of opioid use underscores the need to consider the risks of opioid use in old age, said Dr. Levine. “Unfortunately, studies of the association between opioid use and dementia risk in old age are few, and their results are inconsistent.”
The study included 91,307 Israeli citizens aged 60 and over without dementia who were enrolled in the Meuhedet Healthcare Services, a nonprofit health maintenance organization (HMO) serving 14% of the country’s population. Meuhedet has maintained an up-to-date dementia registry since 2002.
The average age of the study sample was 68.29 years at the start of the study (in 2012).
In Israel, opioids are prescribed for a 30-day period. In this study, opioid exposure was defined as opioid medication fills covering 60 days (or two prescriptions) within a 120-day interval.
The primary outcome was incident dementia during follow-up from Jan. 1, 2013 to Oct. 30, 2017. The analysis controlled for a number of factors, including age, sex, smoking status, health conditions such as arthritis, depression, diabetes, osteoporosis, cognitive decline, vitamin deficiencies, cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and hospitalizations for falls.
Researchers also accounted for the competing risk of mortality.
During the study, 3.1% of subjects were exposed to opioids at a mean age of 73.94 years, and 5.8% of subjects developed dementia at an average age of 78.07 years.
Increased dementia risk
The risk of incident dementia was significantly increased in those exposed to opioids versus unexposed individuals in the 75- to 80-year age group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.39; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.92; z statistic = 2.02; P < .05).
The authors noted the effect size for opioid exposure in this elderly age group is like other potentially modifiable risk factors for dementia, including body mass index and smoking.
The current study could not determine the biological explanation for the increased dementia risk among older opioid users. “Causal notions are challenging in observational studies and should be viewed with caution,” Dr. Levine noted.
However, a plausible mechanism highlighted in the literature is that opioids promote apoptosis of microglia and neurons that contribute to neurodegenerative diseases, he said.
The study included 14 sensitivity analyses, including those that looked at females, subjects older than 70, smokers, and groups with and without comorbid health conditions. The only sensitivity analysis that didn’t have similar findings to the primary analysis looked at dementia risk restricted to subjects without a vitamin deficiency.
“It’s reassuring that 13 or 14 sensitivity analyses found a significant association between opioid exposure and dementia risk,” said Dr. Levine.
Some prior studies did not show an association between opioid exposure and dementia risk. One possible reason for the discrepancy with the current findings is that the previous research didn’t account for age-specific opioid use effects, or the competing risk of mortality, said Dr. Levine.
Clinicians have a number of potential alternatives to opioids to treat various conditions including acetaminophen, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, amine reuptake inhibitors (ARIs), membrane stabilizers, muscle relaxants, topical capsaicin, botulinum toxin, cannabinoids, and steroids.
A limitation of the study was that it didn’t adjust for all possible comorbid health conditions, including vascular conditions, or for use of benzodiazepines, and surgical procedures.
In addition, since up to 50% of dementia cases are undetected, it’s possible some in the unexposed opioid group may actually have undiagnosed dementia, thereby reducing the effect sizes in the results.
Reverse causality is also a possibility as the neuropathological process associated with dementia could have started prior to opioid exposure. In addition, the results are limited to prolonged opioid exposure.
Interpret with caution
Commenting on the study, David Knopman, MD, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., whose research involves late-life cognitive disorders, was skeptical.
“On the face of it, the fact that an association was seen only in one narrow age range – 75+ to 80 years – ought to raise serious suspicion about the reliability and validity of the claim that opioid use is a risk factor for dementia, he said.
Although the researchers performed several sensitivity analyses, including accounting for mortality, “pharmacoepidemiological studies are terribly sensitive to residual biases” related to physician and patient choices related to medication use, added Dr. Knopman.
The claim that opioids are a dementia risk “should be viewed with great caution” and should not influence use of opioids where they’re truly indicated, he said.
“It would be a great pity if patients with pain requiring opioids avoid them because of fears about dementia based on the dubious relationship between age and opioid use.”
Dr. Levine and Dr. Knopman report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in new findings that suggest exposure to these drugs may be another modifiable risk factor for dementia.
“Clinicians and others may want to consider that opioid exposure in those aged 75-80 increases dementia risk, and to balance the potential benefits of opioid use in old age with adverse side effects,” said Stephen Z. Levine, PhD, professor, department of community mental health, University of Haifa (Israel).
The study was published online in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Widespread use
Evidence points to a relatively high rate of opioid prescriptions among older adults. A Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report noted 19.2% of the U.S. adult population filled an opioid prescription in 2018, with the rate in those over 65 double that of adults aged 20-24 years (25% vs. 11.2%).
Disorders and illnesses for which opioids might be prescribed, including cancer and some pain conditions, “are far more prevalent in old age than at a younger age,” said Dr. Levine.
This high rate of opioid use underscores the need to consider the risks of opioid use in old age, said Dr. Levine. “Unfortunately, studies of the association between opioid use and dementia risk in old age are few, and their results are inconsistent.”
The study included 91,307 Israeli citizens aged 60 and over without dementia who were enrolled in the Meuhedet Healthcare Services, a nonprofit health maintenance organization (HMO) serving 14% of the country’s population. Meuhedet has maintained an up-to-date dementia registry since 2002.
The average age of the study sample was 68.29 years at the start of the study (in 2012).
In Israel, opioids are prescribed for a 30-day period. In this study, opioid exposure was defined as opioid medication fills covering 60 days (or two prescriptions) within a 120-day interval.
The primary outcome was incident dementia during follow-up from Jan. 1, 2013 to Oct. 30, 2017. The analysis controlled for a number of factors, including age, sex, smoking status, health conditions such as arthritis, depression, diabetes, osteoporosis, cognitive decline, vitamin deficiencies, cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and hospitalizations for falls.
Researchers also accounted for the competing risk of mortality.
During the study, 3.1% of subjects were exposed to opioids at a mean age of 73.94 years, and 5.8% of subjects developed dementia at an average age of 78.07 years.
Increased dementia risk
The risk of incident dementia was significantly increased in those exposed to opioids versus unexposed individuals in the 75- to 80-year age group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.39; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.92; z statistic = 2.02; P < .05).
The authors noted the effect size for opioid exposure in this elderly age group is like other potentially modifiable risk factors for dementia, including body mass index and smoking.
The current study could not determine the biological explanation for the increased dementia risk among older opioid users. “Causal notions are challenging in observational studies and should be viewed with caution,” Dr. Levine noted.
However, a plausible mechanism highlighted in the literature is that opioids promote apoptosis of microglia and neurons that contribute to neurodegenerative diseases, he said.
The study included 14 sensitivity analyses, including those that looked at females, subjects older than 70, smokers, and groups with and without comorbid health conditions. The only sensitivity analysis that didn’t have similar findings to the primary analysis looked at dementia risk restricted to subjects without a vitamin deficiency.
“It’s reassuring that 13 or 14 sensitivity analyses found a significant association between opioid exposure and dementia risk,” said Dr. Levine.
Some prior studies did not show an association between opioid exposure and dementia risk. One possible reason for the discrepancy with the current findings is that the previous research didn’t account for age-specific opioid use effects, or the competing risk of mortality, said Dr. Levine.
Clinicians have a number of potential alternatives to opioids to treat various conditions including acetaminophen, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, amine reuptake inhibitors (ARIs), membrane stabilizers, muscle relaxants, topical capsaicin, botulinum toxin, cannabinoids, and steroids.
A limitation of the study was that it didn’t adjust for all possible comorbid health conditions, including vascular conditions, or for use of benzodiazepines, and surgical procedures.
In addition, since up to 50% of dementia cases are undetected, it’s possible some in the unexposed opioid group may actually have undiagnosed dementia, thereby reducing the effect sizes in the results.
Reverse causality is also a possibility as the neuropathological process associated with dementia could have started prior to opioid exposure. In addition, the results are limited to prolonged opioid exposure.
Interpret with caution
Commenting on the study, David Knopman, MD, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., whose research involves late-life cognitive disorders, was skeptical.
“On the face of it, the fact that an association was seen only in one narrow age range – 75+ to 80 years – ought to raise serious suspicion about the reliability and validity of the claim that opioid use is a risk factor for dementia, he said.
Although the researchers performed several sensitivity analyses, including accounting for mortality, “pharmacoepidemiological studies are terribly sensitive to residual biases” related to physician and patient choices related to medication use, added Dr. Knopman.
The claim that opioids are a dementia risk “should be viewed with great caution” and should not influence use of opioids where they’re truly indicated, he said.
“It would be a great pity if patients with pain requiring opioids avoid them because of fears about dementia based on the dubious relationship between age and opioid use.”
Dr. Levine and Dr. Knopman report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in new findings that suggest exposure to these drugs may be another modifiable risk factor for dementia.
“Clinicians and others may want to consider that opioid exposure in those aged 75-80 increases dementia risk, and to balance the potential benefits of opioid use in old age with adverse side effects,” said Stephen Z. Levine, PhD, professor, department of community mental health, University of Haifa (Israel).
The study was published online in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Widespread use
Evidence points to a relatively high rate of opioid prescriptions among older adults. A Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report noted 19.2% of the U.S. adult population filled an opioid prescription in 2018, with the rate in those over 65 double that of adults aged 20-24 years (25% vs. 11.2%).
Disorders and illnesses for which opioids might be prescribed, including cancer and some pain conditions, “are far more prevalent in old age than at a younger age,” said Dr. Levine.
This high rate of opioid use underscores the need to consider the risks of opioid use in old age, said Dr. Levine. “Unfortunately, studies of the association between opioid use and dementia risk in old age are few, and their results are inconsistent.”
The study included 91,307 Israeli citizens aged 60 and over without dementia who were enrolled in the Meuhedet Healthcare Services, a nonprofit health maintenance organization (HMO) serving 14% of the country’s population. Meuhedet has maintained an up-to-date dementia registry since 2002.
The average age of the study sample was 68.29 years at the start of the study (in 2012).
In Israel, opioids are prescribed for a 30-day period. In this study, opioid exposure was defined as opioid medication fills covering 60 days (or two prescriptions) within a 120-day interval.
The primary outcome was incident dementia during follow-up from Jan. 1, 2013 to Oct. 30, 2017. The analysis controlled for a number of factors, including age, sex, smoking status, health conditions such as arthritis, depression, diabetes, osteoporosis, cognitive decline, vitamin deficiencies, cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and hospitalizations for falls.
Researchers also accounted for the competing risk of mortality.
During the study, 3.1% of subjects were exposed to opioids at a mean age of 73.94 years, and 5.8% of subjects developed dementia at an average age of 78.07 years.
Increased dementia risk
The risk of incident dementia was significantly increased in those exposed to opioids versus unexposed individuals in the 75- to 80-year age group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.39; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.92; z statistic = 2.02; P < .05).
The authors noted the effect size for opioid exposure in this elderly age group is like other potentially modifiable risk factors for dementia, including body mass index and smoking.
The current study could not determine the biological explanation for the increased dementia risk among older opioid users. “Causal notions are challenging in observational studies and should be viewed with caution,” Dr. Levine noted.
However, a plausible mechanism highlighted in the literature is that opioids promote apoptosis of microglia and neurons that contribute to neurodegenerative diseases, he said.
The study included 14 sensitivity analyses, including those that looked at females, subjects older than 70, smokers, and groups with and without comorbid health conditions. The only sensitivity analysis that didn’t have similar findings to the primary analysis looked at dementia risk restricted to subjects without a vitamin deficiency.
“It’s reassuring that 13 or 14 sensitivity analyses found a significant association between opioid exposure and dementia risk,” said Dr. Levine.
Some prior studies did not show an association between opioid exposure and dementia risk. One possible reason for the discrepancy with the current findings is that the previous research didn’t account for age-specific opioid use effects, or the competing risk of mortality, said Dr. Levine.
Clinicians have a number of potential alternatives to opioids to treat various conditions including acetaminophen, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, amine reuptake inhibitors (ARIs), membrane stabilizers, muscle relaxants, topical capsaicin, botulinum toxin, cannabinoids, and steroids.
A limitation of the study was that it didn’t adjust for all possible comorbid health conditions, including vascular conditions, or for use of benzodiazepines, and surgical procedures.
In addition, since up to 50% of dementia cases are undetected, it’s possible some in the unexposed opioid group may actually have undiagnosed dementia, thereby reducing the effect sizes in the results.
Reverse causality is also a possibility as the neuropathological process associated with dementia could have started prior to opioid exposure. In addition, the results are limited to prolonged opioid exposure.
Interpret with caution
Commenting on the study, David Knopman, MD, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., whose research involves late-life cognitive disorders, was skeptical.
“On the face of it, the fact that an association was seen only in one narrow age range – 75+ to 80 years – ought to raise serious suspicion about the reliability and validity of the claim that opioid use is a risk factor for dementia, he said.
Although the researchers performed several sensitivity analyses, including accounting for mortality, “pharmacoepidemiological studies are terribly sensitive to residual biases” related to physician and patient choices related to medication use, added Dr. Knopman.
The claim that opioids are a dementia risk “should be viewed with great caution” and should not influence use of opioids where they’re truly indicated, he said.
“It would be a great pity if patients with pain requiring opioids avoid them because of fears about dementia based on the dubious relationship between age and opioid use.”
Dr. Levine and Dr. Knopman report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GERIATRIC PSYCHIATRY
Collagen ‘tile’ delivers postsurgical radiation in glioblastoma
and spares healthy tissue, new research suggests.
The results showed inserting a collagen matrix containing radioactive seeds into the brain postsurgery did not impede wound healing. It also showed a favorable safety profile, researchers note.
Benefits for patients undergoing this GammaTile (GT) intervention include not having to wait weeks to receive radiation treatment, which in turn improves their quality of life, said study investigator Clark C. Chen, MD, PhD, chair, department of neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis.
“These initial results are highly promising and offer hope for patients afflicted with an otherwise devastating disease,” Dr. Chen said in an interview.
If replicated in larger trials, GT therapy “could define a new standard of care, and there would really be no reason why patients shouldn’t get this therapy,” he added.
This is the first clinical series describing GT use since its approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for recurrent brain cancer.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS) and were published recently in Neuro-Oncology Advances.
Radioactive seeds
GT therapy is a version of brachytherapy where radioactive sources are placed adjacent to cancerous tissue. It consists of radioactive seeds embedded with a collagen tile.
The neurosurgeon inserts these “tiles” immediately after tumor removal to cover the entire resection cavity, Dr. Chen said. The tiles maintain the cavity architecture to prevent radiation “hot spots” associated with cavity collapse.
Dr. Chen noted the therapy is “short range,” with most of the radiation delivered within 8 millimeters of the radioactive seeds.
The radiation lasts for about a month and the collagen tiles are eventually absorbed within the body. “You put in the tiles and you don’t need to do anything more,” Dr. Chen said.
GT has a number of advantages. Unlike with traditional brachytherapy, the collagen tile provides a buffer around the radiation sources, allowing delivery of the optimal radiation dose while preserving healthy tissue.
It also avoids the up-to-6-weeks patients have to wait postsurgery to get external beam radiation therapy. “If you start radiation too early, it actually compromises wound healing, and in the meantime the tumor is growing,” said Dr. Chen.
“I have several patients where I removed a large tumor and within that 6-week period, the tumor came back entirely,” he added.
With the gamma-tile, however, radiation from the seeds kills the tumor while the body heals.
Safety profile
The study included 22 patients (mean age, 57.7 years; 15 men, 7 women) with wild-type isocitrate dehydrogenase glioblastoma. They were all having surgery for recurrent tumors.
“One of the most challenging aspects of glioblastomas is that not only do the tumors come back, they come back immediately adjacent to where you have done the surgery, and for many patients this is demoralizing,” Dr. Chen said.
Six participants had 0 6 -Methylguanine-DNA methyltranferase (MGMT) methylated glioblastoma, while the others had unmethylated MGMT.
The mean follow-up from initial diagnosis was 733 days (2 years).
Results showed one patient had to be readmitted to the hospital for hydrocephalus, but there were no re-admissions within 30 days attributable to GT.
Despite participants having undergone a second and third resection through the same surgical incision, there were no wound infections. “One of the concerns of giving radiation right after surgery is it can compromise wound healing, and this is why you wait 6 weeks,” Dr. Chen noted.
He stressed that no patient in the study suffered from adverse radiation effects that required medical or surgical intervention.
As the radiation is so short-range, hair loss and skin irritation are not side effects of GT, he added.
“The radiation is inside the brain and highly targeted, so it doesn’t hit hair follicles,” said Dr. Chen. “As best as I can observe in these patients, I did not see toxicity associated with radiation.”
One and done
Among the 22 participants, 18 had neurologic symptoms at baseline. There were no new neurologic deficits that developed after GT placement.
In addition, GT therapy improved “local control” — preventing the tumor from growing back at the site of the surgery. The local control was 86% at 6 months and 81% at 12 months.
The median progression-free survival was about 8 months. The median overall survival was 20 months (about 600 days) for the unmethylated MGMT group and 37.4 months (about 1120 days) for the methylated group.
Outcomes compared favorably to an independent glioblastoma cohort of similar patients who did not receive GT treatment during the study period, Dr. Chen noted.
“This therapy can potentially redefine how we treat glioblastoma patients whose cancer came back,” he said.
A study limitation was that it did not include quality-of-life data, which makes it challenging to assess the therapy’s overall impact, Dr. Chen said. However, he added that from his experience, patients very much appreciate not having to repeatedly take time off work for clinic or hospital visits to receive radiation treatments.
“One of the beauties of this therapy is it’s a one-and-done deal,” he said.
Interesting, timely
Commenting for this news organization, William T. Curry Jr, MD, co-director at MassGeneral Neuroscience and director of neurosurgical oncology at Mass General Cancer Center, Boston, called the study “interesting and timely.”
These new data “underscore that GT is safe in patients that have undergone gross total resection of recurrent glioblastoma and that rates of progression free survival may exceed those treated with resection alone,” said Dr. Curry, who was not involved with the research.
“Surgeons are excited about anything that has the potential to improve outcomes for patients with this very challenging disease, and it is wonderful to be able to offer hope and survival tools to patients,” he added.
However, Dr. Curry noted there are challenges and potential biases when studying survival in cancer patients without conducting a randomization process. The investigators “admit to methodological flaws inherent in the single-arm design in a patient population with recurrent glioblastoma not treated uniformly,” he said.
In addition, he noted overall survival may not have been related to the GT intervention. “Multicenter randomization is probably required to get to the bottom of the survival advantage in different subsets of glioblastoma patients,” Dr. Curry said.
Further research is needed to confirm the efficacy, appropriate indications, and timing of the intervention, but “I would support a randomized multicenter study in patients undergoing near gross total resection of recurrent glioblastoma,” he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Chen and Dr. Curry have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and spares healthy tissue, new research suggests.
The results showed inserting a collagen matrix containing radioactive seeds into the brain postsurgery did not impede wound healing. It also showed a favorable safety profile, researchers note.
Benefits for patients undergoing this GammaTile (GT) intervention include not having to wait weeks to receive radiation treatment, which in turn improves their quality of life, said study investigator Clark C. Chen, MD, PhD, chair, department of neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis.
“These initial results are highly promising and offer hope for patients afflicted with an otherwise devastating disease,” Dr. Chen said in an interview.
If replicated in larger trials, GT therapy “could define a new standard of care, and there would really be no reason why patients shouldn’t get this therapy,” he added.
This is the first clinical series describing GT use since its approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for recurrent brain cancer.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS) and were published recently in Neuro-Oncology Advances.
Radioactive seeds
GT therapy is a version of brachytherapy where radioactive sources are placed adjacent to cancerous tissue. It consists of radioactive seeds embedded with a collagen tile.
The neurosurgeon inserts these “tiles” immediately after tumor removal to cover the entire resection cavity, Dr. Chen said. The tiles maintain the cavity architecture to prevent radiation “hot spots” associated with cavity collapse.
Dr. Chen noted the therapy is “short range,” with most of the radiation delivered within 8 millimeters of the radioactive seeds.
The radiation lasts for about a month and the collagen tiles are eventually absorbed within the body. “You put in the tiles and you don’t need to do anything more,” Dr. Chen said.
GT has a number of advantages. Unlike with traditional brachytherapy, the collagen tile provides a buffer around the radiation sources, allowing delivery of the optimal radiation dose while preserving healthy tissue.
It also avoids the up-to-6-weeks patients have to wait postsurgery to get external beam radiation therapy. “If you start radiation too early, it actually compromises wound healing, and in the meantime the tumor is growing,” said Dr. Chen.
“I have several patients where I removed a large tumor and within that 6-week period, the tumor came back entirely,” he added.
With the gamma-tile, however, radiation from the seeds kills the tumor while the body heals.
Safety profile
The study included 22 patients (mean age, 57.7 years; 15 men, 7 women) with wild-type isocitrate dehydrogenase glioblastoma. They were all having surgery for recurrent tumors.
“One of the most challenging aspects of glioblastomas is that not only do the tumors come back, they come back immediately adjacent to where you have done the surgery, and for many patients this is demoralizing,” Dr. Chen said.
Six participants had 0 6 -Methylguanine-DNA methyltranferase (MGMT) methylated glioblastoma, while the others had unmethylated MGMT.
The mean follow-up from initial diagnosis was 733 days (2 years).
Results showed one patient had to be readmitted to the hospital for hydrocephalus, but there were no re-admissions within 30 days attributable to GT.
Despite participants having undergone a second and third resection through the same surgical incision, there were no wound infections. “One of the concerns of giving radiation right after surgery is it can compromise wound healing, and this is why you wait 6 weeks,” Dr. Chen noted.
He stressed that no patient in the study suffered from adverse radiation effects that required medical or surgical intervention.
As the radiation is so short-range, hair loss and skin irritation are not side effects of GT, he added.
“The radiation is inside the brain and highly targeted, so it doesn’t hit hair follicles,” said Dr. Chen. “As best as I can observe in these patients, I did not see toxicity associated with radiation.”
One and done
Among the 22 participants, 18 had neurologic symptoms at baseline. There were no new neurologic deficits that developed after GT placement.
In addition, GT therapy improved “local control” — preventing the tumor from growing back at the site of the surgery. The local control was 86% at 6 months and 81% at 12 months.
The median progression-free survival was about 8 months. The median overall survival was 20 months (about 600 days) for the unmethylated MGMT group and 37.4 months (about 1120 days) for the methylated group.
Outcomes compared favorably to an independent glioblastoma cohort of similar patients who did not receive GT treatment during the study period, Dr. Chen noted.
“This therapy can potentially redefine how we treat glioblastoma patients whose cancer came back,” he said.
A study limitation was that it did not include quality-of-life data, which makes it challenging to assess the therapy’s overall impact, Dr. Chen said. However, he added that from his experience, patients very much appreciate not having to repeatedly take time off work for clinic or hospital visits to receive radiation treatments.
“One of the beauties of this therapy is it’s a one-and-done deal,” he said.
Interesting, timely
Commenting for this news organization, William T. Curry Jr, MD, co-director at MassGeneral Neuroscience and director of neurosurgical oncology at Mass General Cancer Center, Boston, called the study “interesting and timely.”
These new data “underscore that GT is safe in patients that have undergone gross total resection of recurrent glioblastoma and that rates of progression free survival may exceed those treated with resection alone,” said Dr. Curry, who was not involved with the research.
“Surgeons are excited about anything that has the potential to improve outcomes for patients with this very challenging disease, and it is wonderful to be able to offer hope and survival tools to patients,” he added.
However, Dr. Curry noted there are challenges and potential biases when studying survival in cancer patients without conducting a randomization process. The investigators “admit to methodological flaws inherent in the single-arm design in a patient population with recurrent glioblastoma not treated uniformly,” he said.
In addition, he noted overall survival may not have been related to the GT intervention. “Multicenter randomization is probably required to get to the bottom of the survival advantage in different subsets of glioblastoma patients,” Dr. Curry said.
Further research is needed to confirm the efficacy, appropriate indications, and timing of the intervention, but “I would support a randomized multicenter study in patients undergoing near gross total resection of recurrent glioblastoma,” he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Chen and Dr. Curry have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and spares healthy tissue, new research suggests.
The results showed inserting a collagen matrix containing radioactive seeds into the brain postsurgery did not impede wound healing. It also showed a favorable safety profile, researchers note.
Benefits for patients undergoing this GammaTile (GT) intervention include not having to wait weeks to receive radiation treatment, which in turn improves their quality of life, said study investigator Clark C. Chen, MD, PhD, chair, department of neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis.
“These initial results are highly promising and offer hope for patients afflicted with an otherwise devastating disease,” Dr. Chen said in an interview.
If replicated in larger trials, GT therapy “could define a new standard of care, and there would really be no reason why patients shouldn’t get this therapy,” he added.
This is the first clinical series describing GT use since its approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for recurrent brain cancer.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS) and were published recently in Neuro-Oncology Advances.
Radioactive seeds
GT therapy is a version of brachytherapy where radioactive sources are placed adjacent to cancerous tissue. It consists of radioactive seeds embedded with a collagen tile.
The neurosurgeon inserts these “tiles” immediately after tumor removal to cover the entire resection cavity, Dr. Chen said. The tiles maintain the cavity architecture to prevent radiation “hot spots” associated with cavity collapse.
Dr. Chen noted the therapy is “short range,” with most of the radiation delivered within 8 millimeters of the radioactive seeds.
The radiation lasts for about a month and the collagen tiles are eventually absorbed within the body. “You put in the tiles and you don’t need to do anything more,” Dr. Chen said.
GT has a number of advantages. Unlike with traditional brachytherapy, the collagen tile provides a buffer around the radiation sources, allowing delivery of the optimal radiation dose while preserving healthy tissue.
It also avoids the up-to-6-weeks patients have to wait postsurgery to get external beam radiation therapy. “If you start radiation too early, it actually compromises wound healing, and in the meantime the tumor is growing,” said Dr. Chen.
“I have several patients where I removed a large tumor and within that 6-week period, the tumor came back entirely,” he added.
With the gamma-tile, however, radiation from the seeds kills the tumor while the body heals.
Safety profile
The study included 22 patients (mean age, 57.7 years; 15 men, 7 women) with wild-type isocitrate dehydrogenase glioblastoma. They were all having surgery for recurrent tumors.
“One of the most challenging aspects of glioblastomas is that not only do the tumors come back, they come back immediately adjacent to where you have done the surgery, and for many patients this is demoralizing,” Dr. Chen said.
Six participants had 0 6 -Methylguanine-DNA methyltranferase (MGMT) methylated glioblastoma, while the others had unmethylated MGMT.
The mean follow-up from initial diagnosis was 733 days (2 years).
Results showed one patient had to be readmitted to the hospital for hydrocephalus, but there were no re-admissions within 30 days attributable to GT.
Despite participants having undergone a second and third resection through the same surgical incision, there were no wound infections. “One of the concerns of giving radiation right after surgery is it can compromise wound healing, and this is why you wait 6 weeks,” Dr. Chen noted.
He stressed that no patient in the study suffered from adverse radiation effects that required medical or surgical intervention.
As the radiation is so short-range, hair loss and skin irritation are not side effects of GT, he added.
“The radiation is inside the brain and highly targeted, so it doesn’t hit hair follicles,” said Dr. Chen. “As best as I can observe in these patients, I did not see toxicity associated with radiation.”
One and done
Among the 22 participants, 18 had neurologic symptoms at baseline. There were no new neurologic deficits that developed after GT placement.
In addition, GT therapy improved “local control” — preventing the tumor from growing back at the site of the surgery. The local control was 86% at 6 months and 81% at 12 months.
The median progression-free survival was about 8 months. The median overall survival was 20 months (about 600 days) for the unmethylated MGMT group and 37.4 months (about 1120 days) for the methylated group.
Outcomes compared favorably to an independent glioblastoma cohort of similar patients who did not receive GT treatment during the study period, Dr. Chen noted.
“This therapy can potentially redefine how we treat glioblastoma patients whose cancer came back,” he said.
A study limitation was that it did not include quality-of-life data, which makes it challenging to assess the therapy’s overall impact, Dr. Chen said. However, he added that from his experience, patients very much appreciate not having to repeatedly take time off work for clinic or hospital visits to receive radiation treatments.
“One of the beauties of this therapy is it’s a one-and-done deal,” he said.
Interesting, timely
Commenting for this news organization, William T. Curry Jr, MD, co-director at MassGeneral Neuroscience and director of neurosurgical oncology at Mass General Cancer Center, Boston, called the study “interesting and timely.”
These new data “underscore that GT is safe in patients that have undergone gross total resection of recurrent glioblastoma and that rates of progression free survival may exceed those treated with resection alone,” said Dr. Curry, who was not involved with the research.
“Surgeons are excited about anything that has the potential to improve outcomes for patients with this very challenging disease, and it is wonderful to be able to offer hope and survival tools to patients,” he added.
However, Dr. Curry noted there are challenges and potential biases when studying survival in cancer patients without conducting a randomization process. The investigators “admit to methodological flaws inherent in the single-arm design in a patient population with recurrent glioblastoma not treated uniformly,” he said.
In addition, he noted overall survival may not have been related to the GT intervention. “Multicenter randomization is probably required to get to the bottom of the survival advantage in different subsets of glioblastoma patients,” Dr. Curry said.
Further research is needed to confirm the efficacy, appropriate indications, and timing of the intervention, but “I would support a randomized multicenter study in patients undergoing near gross total resection of recurrent glioblastoma,” he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Chen and Dr. Curry have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AANS 2022
ADA updates on finerenone, SGLT2 inhibitors, and race-based eGFR
As it gears up for the first in-person scientific sessions for 3 years, the American Diabetes Association has issued an addendum to its most recent annual clinical practice recommendations published in December 2021, the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes, based on recent trial evidence and consensus.
The update informs clinicians about:
- The effect of the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid antagonist (Kerendia) on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
- The effect of a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor on heart failure and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The National Kidney Foundation and the American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation to remove race in the formula for calculating estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
“This is the fifth year that we are able to update the Standards of Care after it has been published through our Living Standards of Care updates, making it possible to give diabetes care providers the most important information and the latest evidence relevant to their practice,” Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, ADA chief scientific and medical officer, said in a press release from the organization.
The addendum, entitled, “Living Standards of Care,” updates Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” and Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management” of the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes.
The amendments were approved by the ADA Professional Practice Committee, which is responsible for developing the Standards of Care. The American College of Cardiology reviewed and endorsed the section on CVD and risk management.
The Living Standards Update was published online in Diabetes Care.
CVD and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “For patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease treated with maximum tolerated doses of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers, addition of finerenone should be considered to improve cardiovascular outcomes and reduce the risk of chronic kidney disease progression. A”
- “Patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease should be considered for treatment with finerenone to reduce cardiovascular outcomes and the risk of chronic kidney disease progression.”
- “In patients with type 2 diabetes and established heart failure with either preserved or reduced ejection fraction, an SGLT2 inhibitor [with proven benefit in this patient population] is recommended to reduce risk of worsening heart failure, hospitalizations for heart failure, and cardiovascular death. ”
In the section “Statin Treatment,” the addendum no longer states that “a prospective trial of a newer fibrate ... is ongoing,” because that trial investigating pemafibrate (Kowa), a novel selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha modulator (or fibrate), has been discontinued.
Chronic kidney disease and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “Traditionally, eGFR is calculated from serum creatinine using a validated formula. The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation is preferred. ... Historically, a correction factor for muscle mass was included in a modified equation for African Americans; however, due to various issues with inequities, it was decided to the equation such that it applies to all. Hence, a committee was convened, resulting in the recommendation for immediate implementation of the CKD-EPI creatinine equation refit without the race variable in all laboratories in the U.S.” (This is based on an National Kidney Foundation and American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation.)
- “Additionally, increased use of cystatin C, especially to confirm estimated GFR in adults who are at risk for or have chronic kidney disease, because combining filtration markers (creatinine and cystatin C) is more accurate and would support better clinical decisions than either marker alone.”
Evidence from clinical trials
The update is based on findings from the following clinical trials:
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIDELIO-DKD)
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Clinical Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIGARO-DKD)
- FIDELITY, a prespecified pooled analysis of FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD
- Empagliflozin Outcome Trial in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction (EMPEROR-Preserved)
- Effects of Dapagliflozin on Biomarkers, Symptoms and Functional Status in Patients with PRESERVED Ejection Fraction Heart Failure (PRESERVED-HF)
- Pemafibrate to Reduce Cardiovascular Outcomes by Reducing Triglycerides in Patients with Diabetes (PROMINENT).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As it gears up for the first in-person scientific sessions for 3 years, the American Diabetes Association has issued an addendum to its most recent annual clinical practice recommendations published in December 2021, the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes, based on recent trial evidence and consensus.
The update informs clinicians about:
- The effect of the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid antagonist (Kerendia) on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
- The effect of a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor on heart failure and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The National Kidney Foundation and the American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation to remove race in the formula for calculating estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
“This is the fifth year that we are able to update the Standards of Care after it has been published through our Living Standards of Care updates, making it possible to give diabetes care providers the most important information and the latest evidence relevant to their practice,” Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, ADA chief scientific and medical officer, said in a press release from the organization.
The addendum, entitled, “Living Standards of Care,” updates Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” and Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management” of the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes.
The amendments were approved by the ADA Professional Practice Committee, which is responsible for developing the Standards of Care. The American College of Cardiology reviewed and endorsed the section on CVD and risk management.
The Living Standards Update was published online in Diabetes Care.
CVD and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “For patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease treated with maximum tolerated doses of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers, addition of finerenone should be considered to improve cardiovascular outcomes and reduce the risk of chronic kidney disease progression. A”
- “Patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease should be considered for treatment with finerenone to reduce cardiovascular outcomes and the risk of chronic kidney disease progression.”
- “In patients with type 2 diabetes and established heart failure with either preserved or reduced ejection fraction, an SGLT2 inhibitor [with proven benefit in this patient population] is recommended to reduce risk of worsening heart failure, hospitalizations for heart failure, and cardiovascular death. ”
In the section “Statin Treatment,” the addendum no longer states that “a prospective trial of a newer fibrate ... is ongoing,” because that trial investigating pemafibrate (Kowa), a novel selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha modulator (or fibrate), has been discontinued.
Chronic kidney disease and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “Traditionally, eGFR is calculated from serum creatinine using a validated formula. The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation is preferred. ... Historically, a correction factor for muscle mass was included in a modified equation for African Americans; however, due to various issues with inequities, it was decided to the equation such that it applies to all. Hence, a committee was convened, resulting in the recommendation for immediate implementation of the CKD-EPI creatinine equation refit without the race variable in all laboratories in the U.S.” (This is based on an National Kidney Foundation and American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation.)
- “Additionally, increased use of cystatin C, especially to confirm estimated GFR in adults who are at risk for or have chronic kidney disease, because combining filtration markers (creatinine and cystatin C) is more accurate and would support better clinical decisions than either marker alone.”
Evidence from clinical trials
The update is based on findings from the following clinical trials:
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIDELIO-DKD)
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Clinical Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIGARO-DKD)
- FIDELITY, a prespecified pooled analysis of FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD
- Empagliflozin Outcome Trial in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction (EMPEROR-Preserved)
- Effects of Dapagliflozin on Biomarkers, Symptoms and Functional Status in Patients with PRESERVED Ejection Fraction Heart Failure (PRESERVED-HF)
- Pemafibrate to Reduce Cardiovascular Outcomes by Reducing Triglycerides in Patients with Diabetes (PROMINENT).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As it gears up for the first in-person scientific sessions for 3 years, the American Diabetes Association has issued an addendum to its most recent annual clinical practice recommendations published in December 2021, the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes, based on recent trial evidence and consensus.
The update informs clinicians about:
- The effect of the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid antagonist (Kerendia) on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
- The effect of a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor on heart failure and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The National Kidney Foundation and the American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation to remove race in the formula for calculating estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
“This is the fifth year that we are able to update the Standards of Care after it has been published through our Living Standards of Care updates, making it possible to give diabetes care providers the most important information and the latest evidence relevant to their practice,” Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, ADA chief scientific and medical officer, said in a press release from the organization.
The addendum, entitled, “Living Standards of Care,” updates Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” and Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management” of the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes.
The amendments were approved by the ADA Professional Practice Committee, which is responsible for developing the Standards of Care. The American College of Cardiology reviewed and endorsed the section on CVD and risk management.
The Living Standards Update was published online in Diabetes Care.
CVD and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “For patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease treated with maximum tolerated doses of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers, addition of finerenone should be considered to improve cardiovascular outcomes and reduce the risk of chronic kidney disease progression. A”
- “Patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease should be considered for treatment with finerenone to reduce cardiovascular outcomes and the risk of chronic kidney disease progression.”
- “In patients with type 2 diabetes and established heart failure with either preserved or reduced ejection fraction, an SGLT2 inhibitor [with proven benefit in this patient population] is recommended to reduce risk of worsening heart failure, hospitalizations for heart failure, and cardiovascular death. ”
In the section “Statin Treatment,” the addendum no longer states that “a prospective trial of a newer fibrate ... is ongoing,” because that trial investigating pemafibrate (Kowa), a novel selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha modulator (or fibrate), has been discontinued.
Chronic kidney disease and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “Traditionally, eGFR is calculated from serum creatinine using a validated formula. The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation is preferred. ... Historically, a correction factor for muscle mass was included in a modified equation for African Americans; however, due to various issues with inequities, it was decided to the equation such that it applies to all. Hence, a committee was convened, resulting in the recommendation for immediate implementation of the CKD-EPI creatinine equation refit without the race variable in all laboratories in the U.S.” (This is based on an National Kidney Foundation and American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation.)
- “Additionally, increased use of cystatin C, especially to confirm estimated GFR in adults who are at risk for or have chronic kidney disease, because combining filtration markers (creatinine and cystatin C) is more accurate and would support better clinical decisions than either marker alone.”
Evidence from clinical trials
The update is based on findings from the following clinical trials:
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIDELIO-DKD)
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Clinical Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIGARO-DKD)
- FIDELITY, a prespecified pooled analysis of FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD
- Empagliflozin Outcome Trial in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction (EMPEROR-Preserved)
- Effects of Dapagliflozin on Biomarkers, Symptoms and Functional Status in Patients with PRESERVED Ejection Fraction Heart Failure (PRESERVED-HF)
- Pemafibrate to Reduce Cardiovascular Outcomes by Reducing Triglycerides in Patients with Diabetes (PROMINENT).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETES CARE
‘Genetic’ height linked to peripheral neuropathy and certain skin and bone infections
, according to a study published in PLOS Genetics.
Prior studies have investigated height as a risk factor for chronic diseases, such as a higher risk for atrial fibrillation and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. It’s been consistently difficult, however, to eliminate the confounding influences of diet, socioeconomics, lifestyle behaviors, and other environmental factors that may interfere with a person’s reaching their expected height based on their genes.
This study, however, was able to better parse those differences by using Mendelian randomization within the comprehensive clinical and genetic dataset of a national health care system biobank. Mendelian randomization uses “genetic instruments for exposures of interest under the assumption that genotype is less susceptible to confounding than measured exposures,” the authors explained. The findings confirmed previously suspected associations between height and a range of cardiovascular and metabolic conditions as well as revealing new associations with several other conditions.
Prior associations confirmed, new associations uncovered
The results confirmed that being tall is linked to a higher risk of atrial fibrillation and varicose veins, and a lower risk of coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. The study also uncovered new associations between greater height and a higher risk of peripheral neuropathy, which is caused by damage to nerves on the extremities, as well as skin and bone infections, such as leg and foot ulcers.
The meta-analysis “identified five additional traits associated with genetically-predicted height,” wrote Sridharan Raghavan, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, and colleagues. “Two were genitourinary conditions – erectile dysfunction and urinary retention – that can be associated with neuropathy, and a third was a phecode for nonspecific skin disorders that may be related to skin infections – consistent with the race/ethnicity stratified results.”
Removing potential confounders
F. Perry Wilson, MD, associate professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was not involved in the study, said the findings were not particularly surprising overall, but it’s striking that the researchers had ”such a large cohort with such detailed electronic health records allowing for the comparison of genetic height with a variety of clinical outcomes.” He also noted the study’s strength in using Mendelian randomization so that the exposure is the predicted genetic height instead of a person’s measured height.
“This is key, since lots of things affect actual height – nutrition is an important one that could certainly be linked to disease as well,” Dr. Wilson said. ”By using genetic height, the authors remove these potential confounders. Since genetic height is “assigned” at birth (or conception), there is little opportunity for confounding. Of course, it is possible that some of the gene variants used to predict genetic height actually do something else, such as make you seek out less nutritious meals, but by and large this is how these types of studies need to be done.”
Height may impact over 100 clinical traits
The study relied on data from the U.S. Veteran Affairs Million Veteran Program with 222,300 non-Hispanic White and 58,151 non-Hispanic Black participants. The researchers first estimated the likelihood of participants’ genetic height based on 3,290 genetic variants determined to affect genetic height in a recent European-ancestry genome-wide meta-analysis. Then they compared these estimates with participants’ actual height in the VA medical record, adjusting for age, sex, and other genetic characteristics.
In doing so, the researchers found 345 clinical traits that were associated with the actual measured height in White participants plus another 17 clinical trials linked to actual measured height in Black participants. An overall 127 of these clinical traits were significantly associated with White participants’ genetically predicted height, and two of them were significantly associated with Black participants’ genetically predicted height.
In analyzing all these data together, the researchers were largely able to separate out those associations between genetically predicted height and certain health conditions from those associations between health conditions and a person’s actual measured height. They also determined that including body mass index as a covariate had little impact on the results. The researchers conducted the appropriate statistical correction to ensure the use of so many variables did not result in spurious statistical significance in some associations.
“Using genetic methods applied to the VA Million Veteran Program, we found evidence that adult height may impact over 100 clinical traits, including several conditions associated with poor outcomes and quality of life – peripheral neuropathy, lower extremity ulcers, and chronic venous insufficiency. We conclude that height may be an unrecognized nonmodifiable risk factor for several common conditions in adults.”
Height linked with health conditions
Genetically predicted height predicted a reduced risk of hyperlipidemia and hypertension independent of coronary heart disease, the analysis revealed. Genetically predicted height was also linked to an approximately 51% increased risk of atrial fibrillation in participants without coronary heart disease but, paradoxically, only a 39% increased risk in those with coronary heart disease, despite coronary heart disease being a risk factor for atrial fibrillation. Genetically predicted height was also associated with a greater risk of varicose veins in the legs and deep vein thrombosis.
Another novel association uncovered by the analysis was between women’s genetically predicted height and both asthma and nonspecific peripheral nerve disorders. “Whether these associations reflect differences by sex in disease pathophysiology related to height may warrant exploration in a sample with better balance between men and women,” the authors wrote. “In sum, our results suggest that an individual’s height may warrant consideration as a nonmodifiable predictor for several common conditions, particularly those affecting peripheral/distal extremities that are most physically impacted by tall stature.”
A substantial limitation of the study was its homogeneity of participants, who were 92% male with an average height of 176 cm and an average BMI of 30.1. The Black participants tended to be younger, with an average age of 58 compared with 64 years in the White participants, but the groups were otherwise similar in height and weight.* The database included data from Hispanic participants, but the researchers excluded these data because of the small sample size.
The smaller dataset for Black participants was a limitation as well as the fact that the genome-wide association study the researchers relied on came from a European population, which may not be as accurate in people with other ancestry, Dr. Wilson said. The bigger limitation, however, is what the findings’ clinical relevance is.
What does it all mean?
“Genetic height is in your genes – there is nothing to be done about it – so it is more of academic interest than clinical interest,” Dr. Wilson said. It’s not even clear whether incorporating a person’s height – actual or genetically predicted, if it could be easily determined for each person – into risk calculators. ”To know whether it would be beneficial to use height (or genetic height) as a risk factor, you’d need to examine each condition of interest, adjusting for all known risk factors, to see if height improved the prediction,” Dr. Wilson said. “I suspect for most conditions, the well-known risk factors would swamp height. For example, high genetic height might truly increase risk for neuropathy. But diabetes might increase the risk so much more that height is not particularly relevant.”
On the other hand, the fact that height in general has any potential influence at all on disease risk may inspire physicians to consider other risk factors in especially tall individuals.
”Physicians may find it interesting that we have some confirmation that height does increase the risk of certain conditions,” Dr. Wilson said. “While this is unlikely to dramatically change practice, they may be a bit more diligent in looking for other relevant risk factors for the diseases found in this study in their very tall patients.”
The research was funded by the U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs, the Boettcher Foundation’s Webb-Waring Biomedical Research Program, the National Institutes of Health, and a Linda Pechenik Montague Investigator award. One study coauthor is a full-time employee of Novartis Institutes of Biomedical Research. The other authors and Dr. Wilson had no disclosures.
*Correction, 6/29/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the average age of Black participants.
, according to a study published in PLOS Genetics.
Prior studies have investigated height as a risk factor for chronic diseases, such as a higher risk for atrial fibrillation and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. It’s been consistently difficult, however, to eliminate the confounding influences of diet, socioeconomics, lifestyle behaviors, and other environmental factors that may interfere with a person’s reaching their expected height based on their genes.
This study, however, was able to better parse those differences by using Mendelian randomization within the comprehensive clinical and genetic dataset of a national health care system biobank. Mendelian randomization uses “genetic instruments for exposures of interest under the assumption that genotype is less susceptible to confounding than measured exposures,” the authors explained. The findings confirmed previously suspected associations between height and a range of cardiovascular and metabolic conditions as well as revealing new associations with several other conditions.
Prior associations confirmed, new associations uncovered
The results confirmed that being tall is linked to a higher risk of atrial fibrillation and varicose veins, and a lower risk of coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. The study also uncovered new associations between greater height and a higher risk of peripheral neuropathy, which is caused by damage to nerves on the extremities, as well as skin and bone infections, such as leg and foot ulcers.
The meta-analysis “identified five additional traits associated with genetically-predicted height,” wrote Sridharan Raghavan, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, and colleagues. “Two were genitourinary conditions – erectile dysfunction and urinary retention – that can be associated with neuropathy, and a third was a phecode for nonspecific skin disorders that may be related to skin infections – consistent with the race/ethnicity stratified results.”
Removing potential confounders
F. Perry Wilson, MD, associate professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was not involved in the study, said the findings were not particularly surprising overall, but it’s striking that the researchers had ”such a large cohort with such detailed electronic health records allowing for the comparison of genetic height with a variety of clinical outcomes.” He also noted the study’s strength in using Mendelian randomization so that the exposure is the predicted genetic height instead of a person’s measured height.
“This is key, since lots of things affect actual height – nutrition is an important one that could certainly be linked to disease as well,” Dr. Wilson said. ”By using genetic height, the authors remove these potential confounders. Since genetic height is “assigned” at birth (or conception), there is little opportunity for confounding. Of course, it is possible that some of the gene variants used to predict genetic height actually do something else, such as make you seek out less nutritious meals, but by and large this is how these types of studies need to be done.”
Height may impact over 100 clinical traits
The study relied on data from the U.S. Veteran Affairs Million Veteran Program with 222,300 non-Hispanic White and 58,151 non-Hispanic Black participants. The researchers first estimated the likelihood of participants’ genetic height based on 3,290 genetic variants determined to affect genetic height in a recent European-ancestry genome-wide meta-analysis. Then they compared these estimates with participants’ actual height in the VA medical record, adjusting for age, sex, and other genetic characteristics.
In doing so, the researchers found 345 clinical traits that were associated with the actual measured height in White participants plus another 17 clinical trials linked to actual measured height in Black participants. An overall 127 of these clinical traits were significantly associated with White participants’ genetically predicted height, and two of them were significantly associated with Black participants’ genetically predicted height.
In analyzing all these data together, the researchers were largely able to separate out those associations between genetically predicted height and certain health conditions from those associations between health conditions and a person’s actual measured height. They also determined that including body mass index as a covariate had little impact on the results. The researchers conducted the appropriate statistical correction to ensure the use of so many variables did not result in spurious statistical significance in some associations.
“Using genetic methods applied to the VA Million Veteran Program, we found evidence that adult height may impact over 100 clinical traits, including several conditions associated with poor outcomes and quality of life – peripheral neuropathy, lower extremity ulcers, and chronic venous insufficiency. We conclude that height may be an unrecognized nonmodifiable risk factor for several common conditions in adults.”
Height linked with health conditions
Genetically predicted height predicted a reduced risk of hyperlipidemia and hypertension independent of coronary heart disease, the analysis revealed. Genetically predicted height was also linked to an approximately 51% increased risk of atrial fibrillation in participants without coronary heart disease but, paradoxically, only a 39% increased risk in those with coronary heart disease, despite coronary heart disease being a risk factor for atrial fibrillation. Genetically predicted height was also associated with a greater risk of varicose veins in the legs and deep vein thrombosis.
Another novel association uncovered by the analysis was between women’s genetically predicted height and both asthma and nonspecific peripheral nerve disorders. “Whether these associations reflect differences by sex in disease pathophysiology related to height may warrant exploration in a sample with better balance between men and women,” the authors wrote. “In sum, our results suggest that an individual’s height may warrant consideration as a nonmodifiable predictor for several common conditions, particularly those affecting peripheral/distal extremities that are most physically impacted by tall stature.”
A substantial limitation of the study was its homogeneity of participants, who were 92% male with an average height of 176 cm and an average BMI of 30.1. The Black participants tended to be younger, with an average age of 58 compared with 64 years in the White participants, but the groups were otherwise similar in height and weight.* The database included data from Hispanic participants, but the researchers excluded these data because of the small sample size.
The smaller dataset for Black participants was a limitation as well as the fact that the genome-wide association study the researchers relied on came from a European population, which may not be as accurate in people with other ancestry, Dr. Wilson said. The bigger limitation, however, is what the findings’ clinical relevance is.
What does it all mean?
“Genetic height is in your genes – there is nothing to be done about it – so it is more of academic interest than clinical interest,” Dr. Wilson said. It’s not even clear whether incorporating a person’s height – actual or genetically predicted, if it could be easily determined for each person – into risk calculators. ”To know whether it would be beneficial to use height (or genetic height) as a risk factor, you’d need to examine each condition of interest, adjusting for all known risk factors, to see if height improved the prediction,” Dr. Wilson said. “I suspect for most conditions, the well-known risk factors would swamp height. For example, high genetic height might truly increase risk for neuropathy. But diabetes might increase the risk so much more that height is not particularly relevant.”
On the other hand, the fact that height in general has any potential influence at all on disease risk may inspire physicians to consider other risk factors in especially tall individuals.
”Physicians may find it interesting that we have some confirmation that height does increase the risk of certain conditions,” Dr. Wilson said. “While this is unlikely to dramatically change practice, they may be a bit more diligent in looking for other relevant risk factors for the diseases found in this study in their very tall patients.”
The research was funded by the U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs, the Boettcher Foundation’s Webb-Waring Biomedical Research Program, the National Institutes of Health, and a Linda Pechenik Montague Investigator award. One study coauthor is a full-time employee of Novartis Institutes of Biomedical Research. The other authors and Dr. Wilson had no disclosures.
*Correction, 6/29/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the average age of Black participants.
, according to a study published in PLOS Genetics.
Prior studies have investigated height as a risk factor for chronic diseases, such as a higher risk for atrial fibrillation and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. It’s been consistently difficult, however, to eliminate the confounding influences of diet, socioeconomics, lifestyle behaviors, and other environmental factors that may interfere with a person’s reaching their expected height based on their genes.
This study, however, was able to better parse those differences by using Mendelian randomization within the comprehensive clinical and genetic dataset of a national health care system biobank. Mendelian randomization uses “genetic instruments for exposures of interest under the assumption that genotype is less susceptible to confounding than measured exposures,” the authors explained. The findings confirmed previously suspected associations between height and a range of cardiovascular and metabolic conditions as well as revealing new associations with several other conditions.
Prior associations confirmed, new associations uncovered
The results confirmed that being tall is linked to a higher risk of atrial fibrillation and varicose veins, and a lower risk of coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. The study also uncovered new associations between greater height and a higher risk of peripheral neuropathy, which is caused by damage to nerves on the extremities, as well as skin and bone infections, such as leg and foot ulcers.
The meta-analysis “identified five additional traits associated with genetically-predicted height,” wrote Sridharan Raghavan, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, and colleagues. “Two were genitourinary conditions – erectile dysfunction and urinary retention – that can be associated with neuropathy, and a third was a phecode for nonspecific skin disorders that may be related to skin infections – consistent with the race/ethnicity stratified results.”
Removing potential confounders
F. Perry Wilson, MD, associate professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was not involved in the study, said the findings were not particularly surprising overall, but it’s striking that the researchers had ”such a large cohort with such detailed electronic health records allowing for the comparison of genetic height with a variety of clinical outcomes.” He also noted the study’s strength in using Mendelian randomization so that the exposure is the predicted genetic height instead of a person’s measured height.
“This is key, since lots of things affect actual height – nutrition is an important one that could certainly be linked to disease as well,” Dr. Wilson said. ”By using genetic height, the authors remove these potential confounders. Since genetic height is “assigned” at birth (or conception), there is little opportunity for confounding. Of course, it is possible that some of the gene variants used to predict genetic height actually do something else, such as make you seek out less nutritious meals, but by and large this is how these types of studies need to be done.”
Height may impact over 100 clinical traits
The study relied on data from the U.S. Veteran Affairs Million Veteran Program with 222,300 non-Hispanic White and 58,151 non-Hispanic Black participants. The researchers first estimated the likelihood of participants’ genetic height based on 3,290 genetic variants determined to affect genetic height in a recent European-ancestry genome-wide meta-analysis. Then they compared these estimates with participants’ actual height in the VA medical record, adjusting for age, sex, and other genetic characteristics.
In doing so, the researchers found 345 clinical traits that were associated with the actual measured height in White participants plus another 17 clinical trials linked to actual measured height in Black participants. An overall 127 of these clinical traits were significantly associated with White participants’ genetically predicted height, and two of them were significantly associated with Black participants’ genetically predicted height.
In analyzing all these data together, the researchers were largely able to separate out those associations between genetically predicted height and certain health conditions from those associations between health conditions and a person’s actual measured height. They also determined that including body mass index as a covariate had little impact on the results. The researchers conducted the appropriate statistical correction to ensure the use of so many variables did not result in spurious statistical significance in some associations.
“Using genetic methods applied to the VA Million Veteran Program, we found evidence that adult height may impact over 100 clinical traits, including several conditions associated with poor outcomes and quality of life – peripheral neuropathy, lower extremity ulcers, and chronic venous insufficiency. We conclude that height may be an unrecognized nonmodifiable risk factor for several common conditions in adults.”
Height linked with health conditions
Genetically predicted height predicted a reduced risk of hyperlipidemia and hypertension independent of coronary heart disease, the analysis revealed. Genetically predicted height was also linked to an approximately 51% increased risk of atrial fibrillation in participants without coronary heart disease but, paradoxically, only a 39% increased risk in those with coronary heart disease, despite coronary heart disease being a risk factor for atrial fibrillation. Genetically predicted height was also associated with a greater risk of varicose veins in the legs and deep vein thrombosis.
Another novel association uncovered by the analysis was between women’s genetically predicted height and both asthma and nonspecific peripheral nerve disorders. “Whether these associations reflect differences by sex in disease pathophysiology related to height may warrant exploration in a sample with better balance between men and women,” the authors wrote. “In sum, our results suggest that an individual’s height may warrant consideration as a nonmodifiable predictor for several common conditions, particularly those affecting peripheral/distal extremities that are most physically impacted by tall stature.”
A substantial limitation of the study was its homogeneity of participants, who were 92% male with an average height of 176 cm and an average BMI of 30.1. The Black participants tended to be younger, with an average age of 58 compared with 64 years in the White participants, but the groups were otherwise similar in height and weight.* The database included data from Hispanic participants, but the researchers excluded these data because of the small sample size.
The smaller dataset for Black participants was a limitation as well as the fact that the genome-wide association study the researchers relied on came from a European population, which may not be as accurate in people with other ancestry, Dr. Wilson said. The bigger limitation, however, is what the findings’ clinical relevance is.
What does it all mean?
“Genetic height is in your genes – there is nothing to be done about it – so it is more of academic interest than clinical interest,” Dr. Wilson said. It’s not even clear whether incorporating a person’s height – actual or genetically predicted, if it could be easily determined for each person – into risk calculators. ”To know whether it would be beneficial to use height (or genetic height) as a risk factor, you’d need to examine each condition of interest, adjusting for all known risk factors, to see if height improved the prediction,” Dr. Wilson said. “I suspect for most conditions, the well-known risk factors would swamp height. For example, high genetic height might truly increase risk for neuropathy. But diabetes might increase the risk so much more that height is not particularly relevant.”
On the other hand, the fact that height in general has any potential influence at all on disease risk may inspire physicians to consider other risk factors in especially tall individuals.
”Physicians may find it interesting that we have some confirmation that height does increase the risk of certain conditions,” Dr. Wilson said. “While this is unlikely to dramatically change practice, they may be a bit more diligent in looking for other relevant risk factors for the diseases found in this study in their very tall patients.”
The research was funded by the U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs, the Boettcher Foundation’s Webb-Waring Biomedical Research Program, the National Institutes of Health, and a Linda Pechenik Montague Investigator award. One study coauthor is a full-time employee of Novartis Institutes of Biomedical Research. The other authors and Dr. Wilson had no disclosures.
*Correction, 6/29/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the average age of Black participants.
FROM PLOS GENETICS
‘Sit less, move more’ to reduce stroke risk
in a population-based study of middle aged and older adults.
The study also found relatively short periods of moderate to vigorous exercise were associated with reduced stroke risk.
“Our results suggest there are a number of ways to reduce stroke risk simply by moving about,” said lead author Steven P. Hooker, PhD, San Diego State University. “This could be with short periods of moderate to vigorous activity each day, longer periods of light activity, or just sedentary for shorter periods of time. All these things can make a difference.”
Dr. Hooker explained that, while it has been found previously that moderate to vigorous exercise reduces stroke risk, this study gives more information on light-intensity activities and sedentary behavior and the risk of stroke.
“Our results suggest that you don’t have to be a chronic exerciser to reduce stroke risk. Replacing sedentary time with light-intensity activity will be beneficial. Just go for a short walk, get up from your desk and move around the house at regular intervals. That can help to reduce stroke risk,” Dr. Hooker said.
“Our message is basically to sit less and move more,” he added.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study involved 7,607 U.S. individuals without a history of stroke, with oversampling from the southeastern “Stroke Belt,” who were participating in the REGARDS cohort study.
The participants wore an accelerometer to measure physical activity and sedentary behavior for 7 consecutive days. The mean age of the individuals was 63 years; 54% were female, 32% were Black.
Over a mean follow-up of 7.4 years, 286 incident stroke cases occurred.
Results showed that increased levels of physical activity were associated with reduced risk of stroke.
For moderate to vigorous activity, compared with participants in the lowest tertile, those in the highest tertile of total daily time in moderate to vigorous activity had a 43% lower risk of stroke.
In the current study, the amount of moderate to vigorous activity associated with a significant reduction in stroke risk was approximately 25 minutes per day (3 hours per week).
Dr. Hooker noted that moderate to vigorous activity included things such as brisk walking, jogging, bike riding, swimming, or playing tennis or soccer. “Doing such activities for just 25 minutes per day reduced risk of stroke by 43%. This is very doable. Just commuting to work by bicycle would cover you here,” he said.
In terms of light-intensity activity, individuals who did 4-5 hours of light activities each day had a 26% reduced risk for first stroke, compared with those doing less than 3 hours of such light activities.
Dr. Hooker explained that examples of light activity included household chores, such as vacuuming, washing dishes, or going for a gentle stroll. “These activities do not require heaving breathing, increased heart rate or breaking into a sweat. They are activities of daily living and relatively easy to engage in.”
But he pointed out that the 4-5 hours of light activity every day linked to a reduction in stroke risk may be more difficult to achieve than the 25 minutes of moderate to vigorous activity, saying: “You have to have some intentionality here.”
Long bouts of sedentary time are harmful
The study also showed that sedentary time was associated with a higher risk for stroke.
The authors noted that time spent in sedentary behavior is of interest because most adults spend most of their awake time being physically inactive.
They report that participants in the highest tertile of sedentary time (more than 13 hours/day) exhibited a 44% increase in risk of stroke, compared with those in the lowest tertile (less than 11 hours/day), and the association remained significant when adjusted for several covariates, including moderate to vigorous activity.
“Even when controlling for the amount of other physical activity, sedentary behavior is still highly associated with risk of stroke. So even if you are active, long bouts of sedentary behavior are harmful,” Dr. Hooker commented.
They also found that longer bouts of sedentary time (more than 17 minutes at a time) were associated with a 54% higher risk of stroke than shorter bouts (less than 8 minutes).
“This suggests that breaking up periods of sedentary behavior into shorter bouts would be beneficial,” Dr. Hooker said.
“If you are going to spend the evening on the couch watching television, try to stand up and walk around every few minutes. Same for if you are sitting at a computer all day – try having a standing workstation, or at least take regular breaks to walk around,” he added.
This research was supported by grants from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging. Additional funding was provided by an unrestricted grant from the Coca-Cola Company. The authors report no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a population-based study of middle aged and older adults.
The study also found relatively short periods of moderate to vigorous exercise were associated with reduced stroke risk.
“Our results suggest there are a number of ways to reduce stroke risk simply by moving about,” said lead author Steven P. Hooker, PhD, San Diego State University. “This could be with short periods of moderate to vigorous activity each day, longer periods of light activity, or just sedentary for shorter periods of time. All these things can make a difference.”
Dr. Hooker explained that, while it has been found previously that moderate to vigorous exercise reduces stroke risk, this study gives more information on light-intensity activities and sedentary behavior and the risk of stroke.
“Our results suggest that you don’t have to be a chronic exerciser to reduce stroke risk. Replacing sedentary time with light-intensity activity will be beneficial. Just go for a short walk, get up from your desk and move around the house at regular intervals. That can help to reduce stroke risk,” Dr. Hooker said.
“Our message is basically to sit less and move more,” he added.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study involved 7,607 U.S. individuals without a history of stroke, with oversampling from the southeastern “Stroke Belt,” who were participating in the REGARDS cohort study.
The participants wore an accelerometer to measure physical activity and sedentary behavior for 7 consecutive days. The mean age of the individuals was 63 years; 54% were female, 32% were Black.
Over a mean follow-up of 7.4 years, 286 incident stroke cases occurred.
Results showed that increased levels of physical activity were associated with reduced risk of stroke.
For moderate to vigorous activity, compared with participants in the lowest tertile, those in the highest tertile of total daily time in moderate to vigorous activity had a 43% lower risk of stroke.
In the current study, the amount of moderate to vigorous activity associated with a significant reduction in stroke risk was approximately 25 minutes per day (3 hours per week).
Dr. Hooker noted that moderate to vigorous activity included things such as brisk walking, jogging, bike riding, swimming, or playing tennis or soccer. “Doing such activities for just 25 minutes per day reduced risk of stroke by 43%. This is very doable. Just commuting to work by bicycle would cover you here,” he said.
In terms of light-intensity activity, individuals who did 4-5 hours of light activities each day had a 26% reduced risk for first stroke, compared with those doing less than 3 hours of such light activities.
Dr. Hooker explained that examples of light activity included household chores, such as vacuuming, washing dishes, or going for a gentle stroll. “These activities do not require heaving breathing, increased heart rate or breaking into a sweat. They are activities of daily living and relatively easy to engage in.”
But he pointed out that the 4-5 hours of light activity every day linked to a reduction in stroke risk may be more difficult to achieve than the 25 minutes of moderate to vigorous activity, saying: “You have to have some intentionality here.”
Long bouts of sedentary time are harmful
The study also showed that sedentary time was associated with a higher risk for stroke.
The authors noted that time spent in sedentary behavior is of interest because most adults spend most of their awake time being physically inactive.
They report that participants in the highest tertile of sedentary time (more than 13 hours/day) exhibited a 44% increase in risk of stroke, compared with those in the lowest tertile (less than 11 hours/day), and the association remained significant when adjusted for several covariates, including moderate to vigorous activity.
“Even when controlling for the amount of other physical activity, sedentary behavior is still highly associated with risk of stroke. So even if you are active, long bouts of sedentary behavior are harmful,” Dr. Hooker commented.
They also found that longer bouts of sedentary time (more than 17 minutes at a time) were associated with a 54% higher risk of stroke than shorter bouts (less than 8 minutes).
“This suggests that breaking up periods of sedentary behavior into shorter bouts would be beneficial,” Dr. Hooker said.
“If you are going to spend the evening on the couch watching television, try to stand up and walk around every few minutes. Same for if you are sitting at a computer all day – try having a standing workstation, or at least take regular breaks to walk around,” he added.
This research was supported by grants from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging. Additional funding was provided by an unrestricted grant from the Coca-Cola Company. The authors report no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a population-based study of middle aged and older adults.
The study also found relatively short periods of moderate to vigorous exercise were associated with reduced stroke risk.
“Our results suggest there are a number of ways to reduce stroke risk simply by moving about,” said lead author Steven P. Hooker, PhD, San Diego State University. “This could be with short periods of moderate to vigorous activity each day, longer periods of light activity, or just sedentary for shorter periods of time. All these things can make a difference.”
Dr. Hooker explained that, while it has been found previously that moderate to vigorous exercise reduces stroke risk, this study gives more information on light-intensity activities and sedentary behavior and the risk of stroke.
“Our results suggest that you don’t have to be a chronic exerciser to reduce stroke risk. Replacing sedentary time with light-intensity activity will be beneficial. Just go for a short walk, get up from your desk and move around the house at regular intervals. That can help to reduce stroke risk,” Dr. Hooker said.
“Our message is basically to sit less and move more,” he added.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study involved 7,607 U.S. individuals without a history of stroke, with oversampling from the southeastern “Stroke Belt,” who were participating in the REGARDS cohort study.
The participants wore an accelerometer to measure physical activity and sedentary behavior for 7 consecutive days. The mean age of the individuals was 63 years; 54% were female, 32% were Black.
Over a mean follow-up of 7.4 years, 286 incident stroke cases occurred.
Results showed that increased levels of physical activity were associated with reduced risk of stroke.
For moderate to vigorous activity, compared with participants in the lowest tertile, those in the highest tertile of total daily time in moderate to vigorous activity had a 43% lower risk of stroke.
In the current study, the amount of moderate to vigorous activity associated with a significant reduction in stroke risk was approximately 25 minutes per day (3 hours per week).
Dr. Hooker noted that moderate to vigorous activity included things such as brisk walking, jogging, bike riding, swimming, or playing tennis or soccer. “Doing such activities for just 25 minutes per day reduced risk of stroke by 43%. This is very doable. Just commuting to work by bicycle would cover you here,” he said.
In terms of light-intensity activity, individuals who did 4-5 hours of light activities each day had a 26% reduced risk for first stroke, compared with those doing less than 3 hours of such light activities.
Dr. Hooker explained that examples of light activity included household chores, such as vacuuming, washing dishes, or going for a gentle stroll. “These activities do not require heaving breathing, increased heart rate or breaking into a sweat. They are activities of daily living and relatively easy to engage in.”
But he pointed out that the 4-5 hours of light activity every day linked to a reduction in stroke risk may be more difficult to achieve than the 25 minutes of moderate to vigorous activity, saying: “You have to have some intentionality here.”
Long bouts of sedentary time are harmful
The study also showed that sedentary time was associated with a higher risk for stroke.
The authors noted that time spent in sedentary behavior is of interest because most adults spend most of their awake time being physically inactive.
They report that participants in the highest tertile of sedentary time (more than 13 hours/day) exhibited a 44% increase in risk of stroke, compared with those in the lowest tertile (less than 11 hours/day), and the association remained significant when adjusted for several covariates, including moderate to vigorous activity.
“Even when controlling for the amount of other physical activity, sedentary behavior is still highly associated with risk of stroke. So even if you are active, long bouts of sedentary behavior are harmful,” Dr. Hooker commented.
They also found that longer bouts of sedentary time (more than 17 minutes at a time) were associated with a 54% higher risk of stroke than shorter bouts (less than 8 minutes).
“This suggests that breaking up periods of sedentary behavior into shorter bouts would be beneficial,” Dr. Hooker said.
“If you are going to spend the evening on the couch watching television, try to stand up and walk around every few minutes. Same for if you are sitting at a computer all day – try having a standing workstation, or at least take regular breaks to walk around,” he added.
This research was supported by grants from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging. Additional funding was provided by an unrestricted grant from the Coca-Cola Company. The authors report no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Blood-based assay may offer new way of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease
A novel blood-based assay could one day be used to diagnose Parkinson’s disease and possibly other chronic inflammatory conditions, according to investigators. In addition to being highly accurate, the assay, which detects changes in expression of cytochrome P450s, is faster and easier to perform than other Parkinson’s disease assays under investigation, reported lead author Kohei Ihara, PhD, of Kobe University, Japan, and colleagues.
“Effective diagnostic systems and biomarkers for patients without subjective motor symptoms have not yet been established,” the investigators wrote in Nature Scientific Reports. “Consequently, the poor diagnostic options for Parkinson’s disease delay the development of therapeutic approaches and medication. Therefore, the development of efficient diagnostic systems and biomarkers is crucial for overcoming Parkinson’s disease.”
According to Dr. Ihara and colleagues, various cytochrome P450 expression patterns and associated serum metabolites correlate with chronic conditions, making them possible markers of disease. To detect these changes, they developed the present assay. It relies upon recombinant P450s expressed on the surface of Escherichia coli. By mixing the E. coli with serum and Vivid, a fluorescent substrate, the investigators can measure “the inhibition rate of the Vivid decomposition reaction” that was driven by “serum metabolites associated with P450s,” revealing underlying expression and, if present, disease.
After some promising initial experiments with mouse models of ulcerative colitis and diabetes, Dr. Ihara and colleagues focused on a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Evaluating inhibition rates associated with four P450s revealed area-under-the-curve (AUC) values of 0.814-0.914. Two of those P450s were also associated with progression of disease symptoms.
“Therefore, we concluded that the P450 inhibition assay could discriminate between Parkinson’s disease model rats and control rats,” the investigators wrote.
Next, the investigators tested the approach with a case-control study involving 20 patients with Parkinson’s disease and 20 healthy volunteers. Twelve P450s were analyzed, three of which revealed significant differences between patients with Parkinson’s disease and controls, with AUCs ranging from 0.740-0.775. Each of the three P450 enzymes also correlated significantly with stage of disease on the Hoehn & Yahr scale, although severity and frequency of symptoms were not reported.
To increase accuracy of the technique, the investigators developed a logistic regression model using two of the three P450s, generating an AUC of 0.910. Further testing showed that the P450 inhibition assay could distinguish between patients with Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, as well as other chronic inflammatory diseases.
“The P450 inhibition assay is easier to perform and is faster than other assays because this assay does not require pretreatment, such as purification of exosomes, and it involves a single enzymatic reaction,” the investigators wrote, suggesting that the assay may be suitable for real-world diagnosis.
‘Promising’ findings need replication
According to Douglas Galasko, MD, a neurologist and professor of neurosciences at UC San Diego Health, the reported accuracy of the assay “seems spectacular,” and the findings are “promising,” but they need to be replicated, “particularly in early-stage patients where the diagnosis [of Parkinson’s disease] is more difficult and important to make.” In practice, the assay would likely see greatest usage for “early diagnosis or diagnosis of unusual or challenging cases,” so accuracy testing needs to be conducted in this setting, he said.
Dr. Galasko, who was not involved in the study, predicted that liquid biopsy for detecting Parkinson’s disease is unlikely to hit the clinic floor anytime soon. “We’re not really close with blood-based biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease,” he said, “unlike the situation for Alzheimer’s disease, where there are several promising blood-based biomarkers.”
For diagnosing Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Galasko suggested that assays using skin biopsies to measure alpha-synuclein accumulation may be closer to approval.
The study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 20K20223 and the Sumitomo Electric Industries Group Corporate Social Responsibility Foundation. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A novel blood-based assay could one day be used to diagnose Parkinson’s disease and possibly other chronic inflammatory conditions, according to investigators. In addition to being highly accurate, the assay, which detects changes in expression of cytochrome P450s, is faster and easier to perform than other Parkinson’s disease assays under investigation, reported lead author Kohei Ihara, PhD, of Kobe University, Japan, and colleagues.
“Effective diagnostic systems and biomarkers for patients without subjective motor symptoms have not yet been established,” the investigators wrote in Nature Scientific Reports. “Consequently, the poor diagnostic options for Parkinson’s disease delay the development of therapeutic approaches and medication. Therefore, the development of efficient diagnostic systems and biomarkers is crucial for overcoming Parkinson’s disease.”
According to Dr. Ihara and colleagues, various cytochrome P450 expression patterns and associated serum metabolites correlate with chronic conditions, making them possible markers of disease. To detect these changes, they developed the present assay. It relies upon recombinant P450s expressed on the surface of Escherichia coli. By mixing the E. coli with serum and Vivid, a fluorescent substrate, the investigators can measure “the inhibition rate of the Vivid decomposition reaction” that was driven by “serum metabolites associated with P450s,” revealing underlying expression and, if present, disease.
After some promising initial experiments with mouse models of ulcerative colitis and diabetes, Dr. Ihara and colleagues focused on a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Evaluating inhibition rates associated with four P450s revealed area-under-the-curve (AUC) values of 0.814-0.914. Two of those P450s were also associated with progression of disease symptoms.
“Therefore, we concluded that the P450 inhibition assay could discriminate between Parkinson’s disease model rats and control rats,” the investigators wrote.
Next, the investigators tested the approach with a case-control study involving 20 patients with Parkinson’s disease and 20 healthy volunteers. Twelve P450s were analyzed, three of which revealed significant differences between patients with Parkinson’s disease and controls, with AUCs ranging from 0.740-0.775. Each of the three P450 enzymes also correlated significantly with stage of disease on the Hoehn & Yahr scale, although severity and frequency of symptoms were not reported.
To increase accuracy of the technique, the investigators developed a logistic regression model using two of the three P450s, generating an AUC of 0.910. Further testing showed that the P450 inhibition assay could distinguish between patients with Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, as well as other chronic inflammatory diseases.
“The P450 inhibition assay is easier to perform and is faster than other assays because this assay does not require pretreatment, such as purification of exosomes, and it involves a single enzymatic reaction,” the investigators wrote, suggesting that the assay may be suitable for real-world diagnosis.
‘Promising’ findings need replication
According to Douglas Galasko, MD, a neurologist and professor of neurosciences at UC San Diego Health, the reported accuracy of the assay “seems spectacular,” and the findings are “promising,” but they need to be replicated, “particularly in early-stage patients where the diagnosis [of Parkinson’s disease] is more difficult and important to make.” In practice, the assay would likely see greatest usage for “early diagnosis or diagnosis of unusual or challenging cases,” so accuracy testing needs to be conducted in this setting, he said.
Dr. Galasko, who was not involved in the study, predicted that liquid biopsy for detecting Parkinson’s disease is unlikely to hit the clinic floor anytime soon. “We’re not really close with blood-based biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease,” he said, “unlike the situation for Alzheimer’s disease, where there are several promising blood-based biomarkers.”
For diagnosing Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Galasko suggested that assays using skin biopsies to measure alpha-synuclein accumulation may be closer to approval.
The study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 20K20223 and the Sumitomo Electric Industries Group Corporate Social Responsibility Foundation. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A novel blood-based assay could one day be used to diagnose Parkinson’s disease and possibly other chronic inflammatory conditions, according to investigators. In addition to being highly accurate, the assay, which detects changes in expression of cytochrome P450s, is faster and easier to perform than other Parkinson’s disease assays under investigation, reported lead author Kohei Ihara, PhD, of Kobe University, Japan, and colleagues.
“Effective diagnostic systems and biomarkers for patients without subjective motor symptoms have not yet been established,” the investigators wrote in Nature Scientific Reports. “Consequently, the poor diagnostic options for Parkinson’s disease delay the development of therapeutic approaches and medication. Therefore, the development of efficient diagnostic systems and biomarkers is crucial for overcoming Parkinson’s disease.”
According to Dr. Ihara and colleagues, various cytochrome P450 expression patterns and associated serum metabolites correlate with chronic conditions, making them possible markers of disease. To detect these changes, they developed the present assay. It relies upon recombinant P450s expressed on the surface of Escherichia coli. By mixing the E. coli with serum and Vivid, a fluorescent substrate, the investigators can measure “the inhibition rate of the Vivid decomposition reaction” that was driven by “serum metabolites associated with P450s,” revealing underlying expression and, if present, disease.
After some promising initial experiments with mouse models of ulcerative colitis and diabetes, Dr. Ihara and colleagues focused on a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Evaluating inhibition rates associated with four P450s revealed area-under-the-curve (AUC) values of 0.814-0.914. Two of those P450s were also associated with progression of disease symptoms.
“Therefore, we concluded that the P450 inhibition assay could discriminate between Parkinson’s disease model rats and control rats,” the investigators wrote.
Next, the investigators tested the approach with a case-control study involving 20 patients with Parkinson’s disease and 20 healthy volunteers. Twelve P450s were analyzed, three of which revealed significant differences between patients with Parkinson’s disease and controls, with AUCs ranging from 0.740-0.775. Each of the three P450 enzymes also correlated significantly with stage of disease on the Hoehn & Yahr scale, although severity and frequency of symptoms were not reported.
To increase accuracy of the technique, the investigators developed a logistic regression model using two of the three P450s, generating an AUC of 0.910. Further testing showed that the P450 inhibition assay could distinguish between patients with Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, as well as other chronic inflammatory diseases.
“The P450 inhibition assay is easier to perform and is faster than other assays because this assay does not require pretreatment, such as purification of exosomes, and it involves a single enzymatic reaction,” the investigators wrote, suggesting that the assay may be suitable for real-world diagnosis.
‘Promising’ findings need replication
According to Douglas Galasko, MD, a neurologist and professor of neurosciences at UC San Diego Health, the reported accuracy of the assay “seems spectacular,” and the findings are “promising,” but they need to be replicated, “particularly in early-stage patients where the diagnosis [of Parkinson’s disease] is more difficult and important to make.” In practice, the assay would likely see greatest usage for “early diagnosis or diagnosis of unusual or challenging cases,” so accuracy testing needs to be conducted in this setting, he said.
Dr. Galasko, who was not involved in the study, predicted that liquid biopsy for detecting Parkinson’s disease is unlikely to hit the clinic floor anytime soon. “We’re not really close with blood-based biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease,” he said, “unlike the situation for Alzheimer’s disease, where there are several promising blood-based biomarkers.”
For diagnosing Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Galasko suggested that assays using skin biopsies to measure alpha-synuclein accumulation may be closer to approval.
The study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 20K20223 and the Sumitomo Electric Industries Group Corporate Social Responsibility Foundation. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM NATURE SCIENTIFIC REPORTS
ADA prioritizes heart failure in patients with diabetes
All U.S. patients with diabetes should undergo annual biomarker testing to allow for early diagnosis of progressive but presymptomatic heart failure, and treatment with an agent from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class should expand among such patients to include everyone with stage B heart failure (“pre–heart failure”) or more advanced stages.
That’s a recommendation from an American Diabetes Association consensus report published June 1 in Diabetes Care.
The report notes that until now, “implementation of available strategies to detect asymptomatic heart failure [in patients with diabetes] has been suboptimal.” The remedy for this is that, “among individuals with diabetes, measurement of a natriuretic peptide or high-sensitivity cardiac troponin is recommended on at least a yearly basis to identify the earliest heart failure stages and to implement strategies to prevent transition to symptomatic heart failure.”
Written by a 10-member panel, chaired by Rodica Pop-Busui, MD, PhD, and endorsed by the American College of Cardiology, the document also set threshold for levels of these biomarkers that are diagnostic for a more advanced stage (stage B) of heart failure in patients with diabetes but without heart failure symptoms:
- A B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) level of ≥50 pg/mL;
- An N-terminal pro-BNP level of ≥125 pg/mL; or
- Any high sensitivity cardiac troponin value that’s above the usual upper reference limit set at >99th percentile.
‘Inexpensive’ biomarker testing
“Addition of relatively inexpensive biomarker testing as part of the standard of care may help to refine heart failure risk prediction in individuals with diabetes,” the report says.
“Substantial data indicate the ability of these biomarkers to identify those in stage A or B [heart failure] at highest risk of progressing to symptomatic heart failure or death,” and this identification is useful because “the risk in such individuals may be lowered through targeted intervention or multidisciplinary care.”
It is “impossible to understate the importance of early recognition of heart failure” in patients with heart failure, the authors declare. However, the report also cautions that, “using biomarkers to identify and in turn reduce risk for heart failure should always be done within the context of a thoughtful clinical evaluation, supported by all information available.”
The report, written during March 2021 – March 2022, cites the high prevalence and increasing incidence of heart failure in patients with diabetes as the rationale for the new recommendations.
For a person with diabetes who receives a heart failure diagnosis, the report details several management steps, starting with an evaluation for obstructive coronary artery disease, given the strong link between diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
It highlights the importance of interventions that involve nutrition, smoking avoidance, minimized alcohol intake, exercise, weight loss, and relevant social determinants of health, but focuses in greater detail on a range of pharmacologic interventions. These include treatment of hypertension for people with early-stage heart failure with an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker, a thiazide-type diuretic, and a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, such as spironolactone or the newer, nonsteroidal agent finerenone for patients with diabetic kidney disease.
Dr. Busui of the division of metabolism, endocrinology, and diabetes at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues cite recent recommendations for using guidelines-directed medical therapy to treat patients with more advanced, symptomatic stages of heart failure, including heart failure with reduced or with preserved ejection fraction.
‘Prioritize’ the SGLT2-inhibitor class
The consensus report also summarizes the roles for agents in the various classes of antidiabetes drugs now available, with particular emphasis on the role for the SGLT2-inhibitor class.
SGLT2 inhibitors “are recommended for all individuals with [diabetes and] heart failure,” it says. “This consensus recommends prioritizing the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in individuals with stage B heart failure, and that SGLT2 inhibitors be an expected element of care in all individuals with diabetes and symptomatic heart failure.”
Other agents for glycemic control that receive endorsement from the report are those in the glucagonlike peptide 1 receptor agonist class. “Despite the lack of conclusive evidence of direct heart failure risk reduction” with this class, it gets a “should be considered” designation, based on its positive effects on weight loss, blood pressure, and atherothrombotic disease.
Similar acknowledgment of potential benefit in a “should be considered” role goes to metformin. But the report turned a thumb down for both the class of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors and the thiazolidinedione class, and said that agents from the insulin and sulfonylurea classes should be used “judiciously.”
The report did not identify any commercial funding. Several of the writing committee members listed personal commercial disclosures.
All U.S. patients with diabetes should undergo annual biomarker testing to allow for early diagnosis of progressive but presymptomatic heart failure, and treatment with an agent from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class should expand among such patients to include everyone with stage B heart failure (“pre–heart failure”) or more advanced stages.
That’s a recommendation from an American Diabetes Association consensus report published June 1 in Diabetes Care.
The report notes that until now, “implementation of available strategies to detect asymptomatic heart failure [in patients with diabetes] has been suboptimal.” The remedy for this is that, “among individuals with diabetes, measurement of a natriuretic peptide or high-sensitivity cardiac troponin is recommended on at least a yearly basis to identify the earliest heart failure stages and to implement strategies to prevent transition to symptomatic heart failure.”
Written by a 10-member panel, chaired by Rodica Pop-Busui, MD, PhD, and endorsed by the American College of Cardiology, the document also set threshold for levels of these biomarkers that are diagnostic for a more advanced stage (stage B) of heart failure in patients with diabetes but without heart failure symptoms:
- A B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) level of ≥50 pg/mL;
- An N-terminal pro-BNP level of ≥125 pg/mL; or
- Any high sensitivity cardiac troponin value that’s above the usual upper reference limit set at >99th percentile.
‘Inexpensive’ biomarker testing
“Addition of relatively inexpensive biomarker testing as part of the standard of care may help to refine heart failure risk prediction in individuals with diabetes,” the report says.
“Substantial data indicate the ability of these biomarkers to identify those in stage A or B [heart failure] at highest risk of progressing to symptomatic heart failure or death,” and this identification is useful because “the risk in such individuals may be lowered through targeted intervention or multidisciplinary care.”
It is “impossible to understate the importance of early recognition of heart failure” in patients with heart failure, the authors declare. However, the report also cautions that, “using biomarkers to identify and in turn reduce risk for heart failure should always be done within the context of a thoughtful clinical evaluation, supported by all information available.”
The report, written during March 2021 – March 2022, cites the high prevalence and increasing incidence of heart failure in patients with diabetes as the rationale for the new recommendations.
For a person with diabetes who receives a heart failure diagnosis, the report details several management steps, starting with an evaluation for obstructive coronary artery disease, given the strong link between diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
It highlights the importance of interventions that involve nutrition, smoking avoidance, minimized alcohol intake, exercise, weight loss, and relevant social determinants of health, but focuses in greater detail on a range of pharmacologic interventions. These include treatment of hypertension for people with early-stage heart failure with an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker, a thiazide-type diuretic, and a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, such as spironolactone or the newer, nonsteroidal agent finerenone for patients with diabetic kidney disease.
Dr. Busui of the division of metabolism, endocrinology, and diabetes at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues cite recent recommendations for using guidelines-directed medical therapy to treat patients with more advanced, symptomatic stages of heart failure, including heart failure with reduced or with preserved ejection fraction.
‘Prioritize’ the SGLT2-inhibitor class
The consensus report also summarizes the roles for agents in the various classes of antidiabetes drugs now available, with particular emphasis on the role for the SGLT2-inhibitor class.
SGLT2 inhibitors “are recommended for all individuals with [diabetes and] heart failure,” it says. “This consensus recommends prioritizing the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in individuals with stage B heart failure, and that SGLT2 inhibitors be an expected element of care in all individuals with diabetes and symptomatic heart failure.”
Other agents for glycemic control that receive endorsement from the report are those in the glucagonlike peptide 1 receptor agonist class. “Despite the lack of conclusive evidence of direct heart failure risk reduction” with this class, it gets a “should be considered” designation, based on its positive effects on weight loss, blood pressure, and atherothrombotic disease.
Similar acknowledgment of potential benefit in a “should be considered” role goes to metformin. But the report turned a thumb down for both the class of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors and the thiazolidinedione class, and said that agents from the insulin and sulfonylurea classes should be used “judiciously.”
The report did not identify any commercial funding. Several of the writing committee members listed personal commercial disclosures.
All U.S. patients with diabetes should undergo annual biomarker testing to allow for early diagnosis of progressive but presymptomatic heart failure, and treatment with an agent from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class should expand among such patients to include everyone with stage B heart failure (“pre–heart failure”) or more advanced stages.
That’s a recommendation from an American Diabetes Association consensus report published June 1 in Diabetes Care.
The report notes that until now, “implementation of available strategies to detect asymptomatic heart failure [in patients with diabetes] has been suboptimal.” The remedy for this is that, “among individuals with diabetes, measurement of a natriuretic peptide or high-sensitivity cardiac troponin is recommended on at least a yearly basis to identify the earliest heart failure stages and to implement strategies to prevent transition to symptomatic heart failure.”
Written by a 10-member panel, chaired by Rodica Pop-Busui, MD, PhD, and endorsed by the American College of Cardiology, the document also set threshold for levels of these biomarkers that are diagnostic for a more advanced stage (stage B) of heart failure in patients with diabetes but without heart failure symptoms:
- A B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) level of ≥50 pg/mL;
- An N-terminal pro-BNP level of ≥125 pg/mL; or
- Any high sensitivity cardiac troponin value that’s above the usual upper reference limit set at >99th percentile.
‘Inexpensive’ biomarker testing
“Addition of relatively inexpensive biomarker testing as part of the standard of care may help to refine heart failure risk prediction in individuals with diabetes,” the report says.
“Substantial data indicate the ability of these biomarkers to identify those in stage A or B [heart failure] at highest risk of progressing to symptomatic heart failure or death,” and this identification is useful because “the risk in such individuals may be lowered through targeted intervention or multidisciplinary care.”
It is “impossible to understate the importance of early recognition of heart failure” in patients with heart failure, the authors declare. However, the report also cautions that, “using biomarkers to identify and in turn reduce risk for heart failure should always be done within the context of a thoughtful clinical evaluation, supported by all information available.”
The report, written during March 2021 – March 2022, cites the high prevalence and increasing incidence of heart failure in patients with diabetes as the rationale for the new recommendations.
For a person with diabetes who receives a heart failure diagnosis, the report details several management steps, starting with an evaluation for obstructive coronary artery disease, given the strong link between diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
It highlights the importance of interventions that involve nutrition, smoking avoidance, minimized alcohol intake, exercise, weight loss, and relevant social determinants of health, but focuses in greater detail on a range of pharmacologic interventions. These include treatment of hypertension for people with early-stage heart failure with an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker, a thiazide-type diuretic, and a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, such as spironolactone or the newer, nonsteroidal agent finerenone for patients with diabetic kidney disease.
Dr. Busui of the division of metabolism, endocrinology, and diabetes at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues cite recent recommendations for using guidelines-directed medical therapy to treat patients with more advanced, symptomatic stages of heart failure, including heart failure with reduced or with preserved ejection fraction.
‘Prioritize’ the SGLT2-inhibitor class
The consensus report also summarizes the roles for agents in the various classes of antidiabetes drugs now available, with particular emphasis on the role for the SGLT2-inhibitor class.
SGLT2 inhibitors “are recommended for all individuals with [diabetes and] heart failure,” it says. “This consensus recommends prioritizing the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in individuals with stage B heart failure, and that SGLT2 inhibitors be an expected element of care in all individuals with diabetes and symptomatic heart failure.”
Other agents for glycemic control that receive endorsement from the report are those in the glucagonlike peptide 1 receptor agonist class. “Despite the lack of conclusive evidence of direct heart failure risk reduction” with this class, it gets a “should be considered” designation, based on its positive effects on weight loss, blood pressure, and atherothrombotic disease.
Similar acknowledgment of potential benefit in a “should be considered” role goes to metformin. But the report turned a thumb down for both the class of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors and the thiazolidinedione class, and said that agents from the insulin and sulfonylurea classes should be used “judiciously.”
The report did not identify any commercial funding. Several of the writing committee members listed personal commercial disclosures.
FROM DIABETES CARE
Hearing, vision loss combo a colossal risk for cognitive decline
The combination of hearing loss and vision loss is linked to an eightfold increased risk of cognitive impairment, new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data on more than 5 million U.S. seniors. Adjusted results show that participants with hearing impairment alone had more than twice the odds of also having cognitive impairment, while those with vision impairment alone had more than triple the odds of cognitive impairment.
However, those with dual sensory impairment (DSI) had an eightfold higher risk for cognitive impairment.
In addition, half of the participants with DSI also had cognitive impairment. Of those with cognitive impairment, 16% had DSI, compared with only about 2% of their peers without cognitive impairment.
“The findings of the present study may inform interventions that can support older people with concurrent sensory impairment and cognitive impairment,” said lead author Esme Fuller-Thomson, PhD, professor, Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work, University of Toronto.
“Special attention, in particular, should be given to those aged 65-74 who have serious hearing and/or vision impairment [because], if the relationship with dementia is found to be causal, such interventions can potentially mitigate the development of cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Fuller-Thomson, who is also director of the Institute for Life Course and Aging and a professor in the department of family and community medicine and faculty of nursing, all at the University of Toronto.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports.
Sensory isolation
Hearing and vision impairment increase with age; it is estimated that one-third of U.S. adults between the ages of 65 and 74 experience hearing loss, and 4% experience vision impairment, the investigators note.
“The link between dual hearing loss and seeing loss and mental health problems such as depression and social isolation have been well researched, but we were very interested in the link between dual sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Additionally, “there have been several studies in the past decade linking hearing loss to dementia and cognitive decline, but less attention has been paid to cognitive problems among those with DSI, despite this group being particularly isolated,” she said. Existing research into DSI suggests an association with cognitive decline; the current investigators sought to expand on this previous work.
To do so, they used merged data from 10 consecutive waves from 2008 to 2017 of the American Community Survey (ACS), which was conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. The ACS is a nationally representative sample of 3.5 million randomly selected U.S. addresses and includes community-dwelling adults and those residing in institutional settings.
Participants aged 65 or older (n = 5,405,135; 56.4% women) were asked yes/no questions regarding serious cognitive impairment, hearing impairment, and vision impairment. A proxy, such as a family member or nursing home staff member, provided answers for individuals not capable of self-report.
Potential confounding variables included age, race/ethnicity, sex, education, and household income.
Potential mechanisms
Results showed that, among those with cognitive impairment, there was a higher prevalence of hearing impairment, vision impairment, and DSI than among their peers without cognitive impairment; in addition, a lower percentage of these persons had no sensory impairment (P < .001).
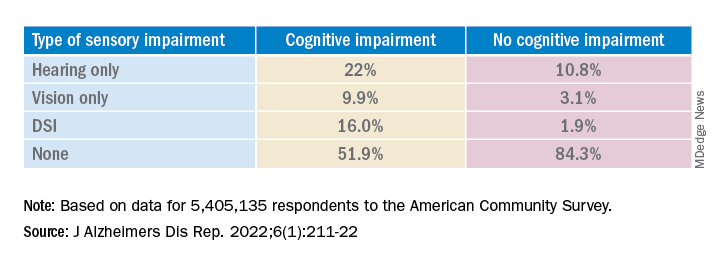
The prevalence of DSI climbed with age, from 1.5% for respondents aged 65-74 years to 2.6% for those aged 75-84 and to 10.8% in those 85 years and older.
Individuals with higher levels of poverty also had higher levels of DSI. Among those who had not completed high school, the prevalence of DSI was higher, compared with high school or university graduates (6.3% vs. 3.1% and 1.85, respectively).
After controlling for age, race, education, and income, the researchers found “substantially” higher odds of cognitive impairment in those with vs. those without sensory impairments.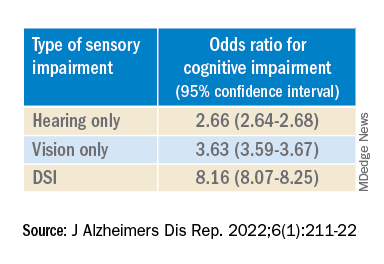
“The magnitude of the odds of cognitive impairment by sensory impairment was greatest for the youngest cohort (age 65-74) and lowest for the oldest cohort (age 85+),” the investigators wrote. Among participants in the youngest cohort, there was a “dose-response relationship” for those with hearing impairment only, visual impairment only, and DSI.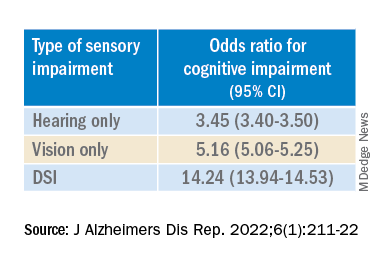
Because the study was observational, it “does not provide sufficient information to determine the reasons behind the observed link between sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said. However, there are “several potential causal mechanisms [that] warrant future research.”
The “sensory deprivation hypothesis” suggests that DSI could cause cognitive deterioration because of decreased auditory and visual input. The “resource allocation hypothesis” posits that hearing- or vision-impaired older adults “may use more cognitive resources to accommodate for sensory deficits, allocating fewer cognitive resources for higher-order memory processes,” the researchers wrote. Hearing impairment “may also lead to social disengagement among older adults, hastening cognitive decline due to isolation and lack of stimulation,” they added.
Reverse causality is also possible. In the “cognitive load on perception” hypothesis, cognitive decline may lead to declines in hearing and vision because of “decreased resources for sensory processing.”
In addition, the association may be noncausal. “The ‘common cause hypothesis’ theorizes that sensory impairment and cognitive impairment may be due to shared age-related degeneration of the central nervous system ... or frailty,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Parallel findings
The results are similar to those from a study conducted by Phillip Hwang, PhD, of the department of anatomy and neurobiology, Boston University, and colleagues that was published online in JAMA Network Open.
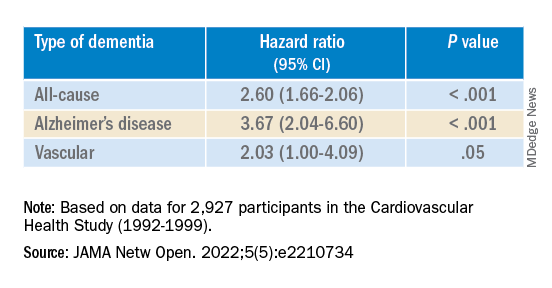
They analyzed data on 8 years of follow-up of 2,927 participants in the Cardiovascular Health Study (mean age, 74.6 years; 58.2% women).
Compared with no sensory impairment, DSI was associated with increased risk for all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, but not with vascular dementia.
“Future work in health care guidelines could consider incorporating screening of sensory impairment in older adults as part of risk assessment for dementia,” Nicholas Reed, AuD, and Esther Oh, MD, PhD, both of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Accurate testing
Commenting on both studies, Heather Whitson, MD, professor of medicine (geriatrics) and ophthalmology and director at the Duke University Center for the Study of Aging and Human Development, Durham, N.C., said both “add further strength to the evidence base, which has really converged in the last few years to support that there is a link between sensory health and cognitive health.”
However, “we still don’t know whether hearing/vision loss causes cognitive decline, though there are plausible ways that sensory loss could affect cognitive abilities like memory, language, and executive function,” she said
Dr. Whitson, who was not involved with the research, is also codirector of the Duke/University of North Carolina Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and the Durham VA Medical Center.
“The big question is whether we can improve patients’ cognitive performance by treating or accommodating their sensory impairments,” she said. “If safe and feasible things like hearing aids or cataract surgery improve cognitive health, even a little bit, it would be a huge benefit to society, because sensory loss is very common, and there are many treatment options,” Dr. Whitson added.
Dr. Fuller-Thomson emphasized that practitioners should “consider the full impact of sensory impairment on cognitive testing methods, as both auditory and visual testing methods may fail to take hearing and vision impairment into account.”
Thus, “when performing cognitive tests on older adults with sensory impairments, practitioners should ensure they are communicating audibly and/or using visual speech cues for hearing-impaired individuals, eliminating items from cognitive tests that rely on vision for those who are visually impaired, and using physical cues for individuals with hearing or dual sensory impairment, as this can help increase the accuracy of testing and prevent confounding,” she said.
The study by Fuller-Thomson et al. was funded by a donation from Janis Rotman. Its investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. The study by Hwang et al. was funded by contracts from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Hwang reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Reed received grants from the National Institute on Aging during the conduct of the study and has served on the advisory board of Neosensory outside the submitted work. Dr. Oh and Dr. Whitson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The combination of hearing loss and vision loss is linked to an eightfold increased risk of cognitive impairment, new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data on more than 5 million U.S. seniors. Adjusted results show that participants with hearing impairment alone had more than twice the odds of also having cognitive impairment, while those with vision impairment alone had more than triple the odds of cognitive impairment.
However, those with dual sensory impairment (DSI) had an eightfold higher risk for cognitive impairment.
In addition, half of the participants with DSI also had cognitive impairment. Of those with cognitive impairment, 16% had DSI, compared with only about 2% of their peers without cognitive impairment.
“The findings of the present study may inform interventions that can support older people with concurrent sensory impairment and cognitive impairment,” said lead author Esme Fuller-Thomson, PhD, professor, Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work, University of Toronto.
“Special attention, in particular, should be given to those aged 65-74 who have serious hearing and/or vision impairment [because], if the relationship with dementia is found to be causal, such interventions can potentially mitigate the development of cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Fuller-Thomson, who is also director of the Institute for Life Course and Aging and a professor in the department of family and community medicine and faculty of nursing, all at the University of Toronto.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports.
Sensory isolation
Hearing and vision impairment increase with age; it is estimated that one-third of U.S. adults between the ages of 65 and 74 experience hearing loss, and 4% experience vision impairment, the investigators note.
“The link between dual hearing loss and seeing loss and mental health problems such as depression and social isolation have been well researched, but we were very interested in the link between dual sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Additionally, “there have been several studies in the past decade linking hearing loss to dementia and cognitive decline, but less attention has been paid to cognitive problems among those with DSI, despite this group being particularly isolated,” she said. Existing research into DSI suggests an association with cognitive decline; the current investigators sought to expand on this previous work.
To do so, they used merged data from 10 consecutive waves from 2008 to 2017 of the American Community Survey (ACS), which was conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. The ACS is a nationally representative sample of 3.5 million randomly selected U.S. addresses and includes community-dwelling adults and those residing in institutional settings.
Participants aged 65 or older (n = 5,405,135; 56.4% women) were asked yes/no questions regarding serious cognitive impairment, hearing impairment, and vision impairment. A proxy, such as a family member or nursing home staff member, provided answers for individuals not capable of self-report.
Potential confounding variables included age, race/ethnicity, sex, education, and household income.
Potential mechanisms
Results showed that, among those with cognitive impairment, there was a higher prevalence of hearing impairment, vision impairment, and DSI than among their peers without cognitive impairment; in addition, a lower percentage of these persons had no sensory impairment (P < .001).

The prevalence of DSI climbed with age, from 1.5% for respondents aged 65-74 years to 2.6% for those aged 75-84 and to 10.8% in those 85 years and older.
Individuals with higher levels of poverty also had higher levels of DSI. Among those who had not completed high school, the prevalence of DSI was higher, compared with high school or university graduates (6.3% vs. 3.1% and 1.85, respectively).
After controlling for age, race, education, and income, the researchers found “substantially” higher odds of cognitive impairment in those with vs. those without sensory impairments.
“The magnitude of the odds of cognitive impairment by sensory impairment was greatest for the youngest cohort (age 65-74) and lowest for the oldest cohort (age 85+),” the investigators wrote. Among participants in the youngest cohort, there was a “dose-response relationship” for those with hearing impairment only, visual impairment only, and DSI.
Because the study was observational, it “does not provide sufficient information to determine the reasons behind the observed link between sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said. However, there are “several potential causal mechanisms [that] warrant future research.”
The “sensory deprivation hypothesis” suggests that DSI could cause cognitive deterioration because of decreased auditory and visual input. The “resource allocation hypothesis” posits that hearing- or vision-impaired older adults “may use more cognitive resources to accommodate for sensory deficits, allocating fewer cognitive resources for higher-order memory processes,” the researchers wrote. Hearing impairment “may also lead to social disengagement among older adults, hastening cognitive decline due to isolation and lack of stimulation,” they added.
Reverse causality is also possible. In the “cognitive load on perception” hypothesis, cognitive decline may lead to declines in hearing and vision because of “decreased resources for sensory processing.”
In addition, the association may be noncausal. “The ‘common cause hypothesis’ theorizes that sensory impairment and cognitive impairment may be due to shared age-related degeneration of the central nervous system ... or frailty,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Parallel findings
The results are similar to those from a study conducted by Phillip Hwang, PhD, of the department of anatomy and neurobiology, Boston University, and colleagues that was published online in JAMA Network Open.

They analyzed data on 8 years of follow-up of 2,927 participants in the Cardiovascular Health Study (mean age, 74.6 years; 58.2% women).
Compared with no sensory impairment, DSI was associated with increased risk for all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, but not with vascular dementia.
“Future work in health care guidelines could consider incorporating screening of sensory impairment in older adults as part of risk assessment for dementia,” Nicholas Reed, AuD, and Esther Oh, MD, PhD, both of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Accurate testing
Commenting on both studies, Heather Whitson, MD, professor of medicine (geriatrics) and ophthalmology and director at the Duke University Center for the Study of Aging and Human Development, Durham, N.C., said both “add further strength to the evidence base, which has really converged in the last few years to support that there is a link between sensory health and cognitive health.”
However, “we still don’t know whether hearing/vision loss causes cognitive decline, though there are plausible ways that sensory loss could affect cognitive abilities like memory, language, and executive function,” she said
Dr. Whitson, who was not involved with the research, is also codirector of the Duke/University of North Carolina Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and the Durham VA Medical Center.
“The big question is whether we can improve patients’ cognitive performance by treating or accommodating their sensory impairments,” she said. “If safe and feasible things like hearing aids or cataract surgery improve cognitive health, even a little bit, it would be a huge benefit to society, because sensory loss is very common, and there are many treatment options,” Dr. Whitson added.
Dr. Fuller-Thomson emphasized that practitioners should “consider the full impact of sensory impairment on cognitive testing methods, as both auditory and visual testing methods may fail to take hearing and vision impairment into account.”
Thus, “when performing cognitive tests on older adults with sensory impairments, practitioners should ensure they are communicating audibly and/or using visual speech cues for hearing-impaired individuals, eliminating items from cognitive tests that rely on vision for those who are visually impaired, and using physical cues for individuals with hearing or dual sensory impairment, as this can help increase the accuracy of testing and prevent confounding,” she said.
The study by Fuller-Thomson et al. was funded by a donation from Janis Rotman. Its investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. The study by Hwang et al. was funded by contracts from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Hwang reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Reed received grants from the National Institute on Aging during the conduct of the study and has served on the advisory board of Neosensory outside the submitted work. Dr. Oh and Dr. Whitson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The combination of hearing loss and vision loss is linked to an eightfold increased risk of cognitive impairment, new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data on more than 5 million U.S. seniors. Adjusted results show that participants with hearing impairment alone had more than twice the odds of also having cognitive impairment, while those with vision impairment alone had more than triple the odds of cognitive impairment.
However, those with dual sensory impairment (DSI) had an eightfold higher risk for cognitive impairment.
In addition, half of the participants with DSI also had cognitive impairment. Of those with cognitive impairment, 16% had DSI, compared with only about 2% of their peers without cognitive impairment.
“The findings of the present study may inform interventions that can support older people with concurrent sensory impairment and cognitive impairment,” said lead author Esme Fuller-Thomson, PhD, professor, Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work, University of Toronto.
“Special attention, in particular, should be given to those aged 65-74 who have serious hearing and/or vision impairment [because], if the relationship with dementia is found to be causal, such interventions can potentially mitigate the development of cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Fuller-Thomson, who is also director of the Institute for Life Course and Aging and a professor in the department of family and community medicine and faculty of nursing, all at the University of Toronto.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports.
Sensory isolation
Hearing and vision impairment increase with age; it is estimated that one-third of U.S. adults between the ages of 65 and 74 experience hearing loss, and 4% experience vision impairment, the investigators note.
“The link between dual hearing loss and seeing loss and mental health problems such as depression and social isolation have been well researched, but we were very interested in the link between dual sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Additionally, “there have been several studies in the past decade linking hearing loss to dementia and cognitive decline, but less attention has been paid to cognitive problems among those with DSI, despite this group being particularly isolated,” she said. Existing research into DSI suggests an association with cognitive decline; the current investigators sought to expand on this previous work.
To do so, they used merged data from 10 consecutive waves from 2008 to 2017 of the American Community Survey (ACS), which was conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. The ACS is a nationally representative sample of 3.5 million randomly selected U.S. addresses and includes community-dwelling adults and those residing in institutional settings.
Participants aged 65 or older (n = 5,405,135; 56.4% women) were asked yes/no questions regarding serious cognitive impairment, hearing impairment, and vision impairment. A proxy, such as a family member or nursing home staff member, provided answers for individuals not capable of self-report.
Potential confounding variables included age, race/ethnicity, sex, education, and household income.
Potential mechanisms
Results showed that, among those with cognitive impairment, there was a higher prevalence of hearing impairment, vision impairment, and DSI than among their peers without cognitive impairment; in addition, a lower percentage of these persons had no sensory impairment (P < .001).

The prevalence of DSI climbed with age, from 1.5% for respondents aged 65-74 years to 2.6% for those aged 75-84 and to 10.8% in those 85 years and older.
Individuals with higher levels of poverty also had higher levels of DSI. Among those who had not completed high school, the prevalence of DSI was higher, compared with high school or university graduates (6.3% vs. 3.1% and 1.85, respectively).
After controlling for age, race, education, and income, the researchers found “substantially” higher odds of cognitive impairment in those with vs. those without sensory impairments.
“The magnitude of the odds of cognitive impairment by sensory impairment was greatest for the youngest cohort (age 65-74) and lowest for the oldest cohort (age 85+),” the investigators wrote. Among participants in the youngest cohort, there was a “dose-response relationship” for those with hearing impairment only, visual impairment only, and DSI.
Because the study was observational, it “does not provide sufficient information to determine the reasons behind the observed link between sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said. However, there are “several potential causal mechanisms [that] warrant future research.”
The “sensory deprivation hypothesis” suggests that DSI could cause cognitive deterioration because of decreased auditory and visual input. The “resource allocation hypothesis” posits that hearing- or vision-impaired older adults “may use more cognitive resources to accommodate for sensory deficits, allocating fewer cognitive resources for higher-order memory processes,” the researchers wrote. Hearing impairment “may also lead to social disengagement among older adults, hastening cognitive decline due to isolation and lack of stimulation,” they added.
Reverse causality is also possible. In the “cognitive load on perception” hypothesis, cognitive decline may lead to declines in hearing and vision because of “decreased resources for sensory processing.”
In addition, the association may be noncausal. “The ‘common cause hypothesis’ theorizes that sensory impairment and cognitive impairment may be due to shared age-related degeneration of the central nervous system ... or frailty,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Parallel findings
The results are similar to those from a study conducted by Phillip Hwang, PhD, of the department of anatomy and neurobiology, Boston University, and colleagues that was published online in JAMA Network Open.

They analyzed data on 8 years of follow-up of 2,927 participants in the Cardiovascular Health Study (mean age, 74.6 years; 58.2% women).
Compared with no sensory impairment, DSI was associated with increased risk for all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, but not with vascular dementia.
“Future work in health care guidelines could consider incorporating screening of sensory impairment in older adults as part of risk assessment for dementia,” Nicholas Reed, AuD, and Esther Oh, MD, PhD, both of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Accurate testing
Commenting on both studies, Heather Whitson, MD, professor of medicine (geriatrics) and ophthalmology and director at the Duke University Center for the Study of Aging and Human Development, Durham, N.C., said both “add further strength to the evidence base, which has really converged in the last few years to support that there is a link between sensory health and cognitive health.”
However, “we still don’t know whether hearing/vision loss causes cognitive decline, though there are plausible ways that sensory loss could affect cognitive abilities like memory, language, and executive function,” she said
Dr. Whitson, who was not involved with the research, is also codirector of the Duke/University of North Carolina Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and the Durham VA Medical Center.
“The big question is whether we can improve patients’ cognitive performance by treating or accommodating their sensory impairments,” she said. “If safe and feasible things like hearing aids or cataract surgery improve cognitive health, even a little bit, it would be a huge benefit to society, because sensory loss is very common, and there are many treatment options,” Dr. Whitson added.
Dr. Fuller-Thomson emphasized that practitioners should “consider the full impact of sensory impairment on cognitive testing methods, as both auditory and visual testing methods may fail to take hearing and vision impairment into account.”
Thus, “when performing cognitive tests on older adults with sensory impairments, practitioners should ensure they are communicating audibly and/or using visual speech cues for hearing-impaired individuals, eliminating items from cognitive tests that rely on vision for those who are visually impaired, and using physical cues for individuals with hearing or dual sensory impairment, as this can help increase the accuracy of testing and prevent confounding,” she said.
The study by Fuller-Thomson et al. was funded by a donation from Janis Rotman. Its investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. The study by Hwang et al. was funded by contracts from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Hwang reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Reed received grants from the National Institute on Aging during the conduct of the study and has served on the advisory board of Neosensory outside the submitted work. Dr. Oh and Dr. Whitson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE REPORTS
SGLT2 inhibitors as first-line therapy in type 2 diabetes?
Use of sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors rather than metformin as first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes appears to cut the risk for heart failure hospitalization but not myocardial infarction, stroke, or all-cause mortality, a new analysis of real-world data suggests.
Safety findings were similar, except for the fact that genital infections were more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors.
The study was conducted using claims data from two large U.S. insurance databases and Medicare. Propensity score matching was used to account for baseline differences.
The study was conducted by HoJin Shin, BPharm, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues. The findings were published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Those who start SGLT-2 inhibitors as first line show similar risks, compared with metformin in MI, stroke, and all-cause mortality outcomes. Strikingly and consistently, SGLT-2 inhibitors show lower risk for hospitalization for heart failure, which is consistent with the findings from cardiovascular outcomes trials,” Dr. Shin said in an interview.
Just a beginning step, although trial probably wasn’t long enough
However, she added, “I don’t want to overstate anything. ... We aren’t powered enough to investigate who would benefit the most. ... As a pharmacoepidemiologist, I think it’s my duty to provide high-quality evidence so we can actually help physicians and patients make better decisions on their medication. Our current research is just a beginning step.”
Asked to comment, Simeon I. Taylor, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, told this news organization, “This study generally confirmed conclusions from published RCTs [randomized clinical trials]. No real surprises, albeit the conclusions may not fully support some of the most enthusiastic claims for SGLT-2 inhibitors with respect to MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death.”
Indeed, Dr. Taylor noted that only two SGLT-2 inhibitors, canagliflozin and empagliflozin, were shown to have a statistically significant association with decreased major adverse cardiovascular events.
In contrast, neither dapagliflozin nor ertugliflozin showed significant benefit regarding those outcomes.
He also pointed out that those four major SLGT-2 inhibitor cardiovascular outcomes trials were placebo-controlled rather than head-to-head trials in which they were compared to an active comparator such as metformin.
“Viewed in this light, it’s probably not surprising that the present study did not demonstrate a robust benefit for SGLT-2 inhibitors to decrease [major adverse CV events].”
The duration of follow-up in the current study is also a limitation, he added.
“The majority of patients were followed for a year or less. This is probably sufficient to assess the impact of some pharmacological mechanisms, for example, the beneficial impact to decrease risk of heart failure by promoting urinary sodium excretion. However, it’s probably insufficient time to observe a beneficial impact on atherosclerosis. For example, there is typically a lag of several years before statins demonstrate efficacy with respect to adverse cardiovascular events.”
Nevertheless, he said, “it provides strong support for benefit with respect to decreasing risk of hospitalization for heart failure.”
He noted that while metformin is currently significantly cheaper than any SGLT-2 inhibitors, once the latter become available as generics, they will be cheaper, and this will likely have a bearing on prescribing decisions.
“Availability of generic SGLT-2 inhibitors offers potential to transform prescribing patterns for type 2 diabetes,” he noted.
First-line SGLT2 inhibitors versus metformin: Most outcomes similar
The study data came from two commercial U.S. health insurance databases, Optum Clinfomatics Data Mart and IBM Marketscan, and from Medicare fee-for-service enrollees.
From April 2013 through March 2020, a total of 9,334 patients began treatment with first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors; 819,973 patients began taking metformin. After 1:2 propensity score matching for confounders, there were 8,613 participants in the SGLT-2 inhibitor group and 17,226 in the group that began treatment with metformin.
The mean follow-up times were 10.7 months for patients taking SGLT-2 inhibitors and 12.2 months for patients taking metformin.
Incidence rates per 1,000 person-years for the composite of hospitalization for MI, hospitalization for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, or all-cause mortality (MI/stroke/mortality) were 15.0 versus 16.2 for SLGT-2 inhibitors versus metformin, not a significant difference (hazard ratio, 0.96).
However, for the composite of heart failure hospitalization or all-cause mortality, the rates were 18.3 versus 23.5, a significant difference, with an HR of 0.80. The benefit was seen beginning at about 6 months.
Compared with metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors showed a significantly lower risk for heart failure hospitalization (HR, 0.78), a numerically (but not significantly) lower risk for MI (HR, 0.70), and similar risks for stroke, mortality, and MI/stroke/HHF/mortality.
Genital infections were significantly more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors (54.1 vs. 23.7 per 1,000 person-years; HR, 2.19). Other safety measures were similar, including acute kidney injury, bone fractures, severe hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, and lower-limb amputations.
How does cost factor in?
A sensitivity analysis aimed at examining the possible effect of unmeasured socioeconomic status showed no difference in cardiovascular benefit for first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors and metformin, compared with first-line dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, which cost more than metformin; it is not known what effect DPP-4 inhibitors have on the cardiovascular outcomes of interest.
Cost and insurance coverage factor into the benefit/risk calculation. Metformin is far less costly than any of the SGLT-2 inhibitors – roughly $10 to $20 per month, compared with more than $500 a month.
However, “for some fortunate patients with the most generous pharmacy benefit insurance coverage, the out-of-pocket cost of brand name drugs like SGLT-2 inhibitors is substantially lower,” Dr. Taylor noted.
He said that the current study “raises questions about whether the clinical benefits of SGLT-2 inhibitors as initial monotherapy justify the higher price relative to metformin. The data in this paper suggest that the value case for SGLT-2 inhibitors is strongest for patients with the greatest risk to be hospitalized for heart failure.”
Indeed, Dr. Shin said, “Once we get more information, it may just help in extending the coverage from insurance companies and Medicare/Medicaid, to lower the barrier to access.”
Dr. Taylor reiterated that patents on some of the early SGLT-2 inhibitors are expected to expire in the next few years, which would make it possible for generic versions to be approved. “At that point, prices would likely fall, possibly to levels similar to metformin.”
The study was funded by grant support from the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, department of medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, the National Institute on Aging, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Shin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taylor is a consultant for Ionis Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors rather than metformin as first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes appears to cut the risk for heart failure hospitalization but not myocardial infarction, stroke, or all-cause mortality, a new analysis of real-world data suggests.
Safety findings were similar, except for the fact that genital infections were more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors.
The study was conducted using claims data from two large U.S. insurance databases and Medicare. Propensity score matching was used to account for baseline differences.
The study was conducted by HoJin Shin, BPharm, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues. The findings were published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Those who start SGLT-2 inhibitors as first line show similar risks, compared with metformin in MI, stroke, and all-cause mortality outcomes. Strikingly and consistently, SGLT-2 inhibitors show lower risk for hospitalization for heart failure, which is consistent with the findings from cardiovascular outcomes trials,” Dr. Shin said in an interview.
Just a beginning step, although trial probably wasn’t long enough
However, she added, “I don’t want to overstate anything. ... We aren’t powered enough to investigate who would benefit the most. ... As a pharmacoepidemiologist, I think it’s my duty to provide high-quality evidence so we can actually help physicians and patients make better decisions on their medication. Our current research is just a beginning step.”
Asked to comment, Simeon I. Taylor, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, told this news organization, “This study generally confirmed conclusions from published RCTs [randomized clinical trials]. No real surprises, albeit the conclusions may not fully support some of the most enthusiastic claims for SGLT-2 inhibitors with respect to MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death.”
Indeed, Dr. Taylor noted that only two SGLT-2 inhibitors, canagliflozin and empagliflozin, were shown to have a statistically significant association with decreased major adverse cardiovascular events.
In contrast, neither dapagliflozin nor ertugliflozin showed significant benefit regarding those outcomes.
He also pointed out that those four major SLGT-2 inhibitor cardiovascular outcomes trials were placebo-controlled rather than head-to-head trials in which they were compared to an active comparator such as metformin.
“Viewed in this light, it’s probably not surprising that the present study did not demonstrate a robust benefit for SGLT-2 inhibitors to decrease [major adverse CV events].”
The duration of follow-up in the current study is also a limitation, he added.
“The majority of patients were followed for a year or less. This is probably sufficient to assess the impact of some pharmacological mechanisms, for example, the beneficial impact to decrease risk of heart failure by promoting urinary sodium excretion. However, it’s probably insufficient time to observe a beneficial impact on atherosclerosis. For example, there is typically a lag of several years before statins demonstrate efficacy with respect to adverse cardiovascular events.”
Nevertheless, he said, “it provides strong support for benefit with respect to decreasing risk of hospitalization for heart failure.”
He noted that while metformin is currently significantly cheaper than any SGLT-2 inhibitors, once the latter become available as generics, they will be cheaper, and this will likely have a bearing on prescribing decisions.
“Availability of generic SGLT-2 inhibitors offers potential to transform prescribing patterns for type 2 diabetes,” he noted.
First-line SGLT2 inhibitors versus metformin: Most outcomes similar
The study data came from two commercial U.S. health insurance databases, Optum Clinfomatics Data Mart and IBM Marketscan, and from Medicare fee-for-service enrollees.
From April 2013 through March 2020, a total of 9,334 patients began treatment with first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors; 819,973 patients began taking metformin. After 1:2 propensity score matching for confounders, there were 8,613 participants in the SGLT-2 inhibitor group and 17,226 in the group that began treatment with metformin.
The mean follow-up times were 10.7 months for patients taking SGLT-2 inhibitors and 12.2 months for patients taking metformin.
Incidence rates per 1,000 person-years for the composite of hospitalization for MI, hospitalization for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, or all-cause mortality (MI/stroke/mortality) were 15.0 versus 16.2 for SLGT-2 inhibitors versus metformin, not a significant difference (hazard ratio, 0.96).
However, for the composite of heart failure hospitalization or all-cause mortality, the rates were 18.3 versus 23.5, a significant difference, with an HR of 0.80. The benefit was seen beginning at about 6 months.
Compared with metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors showed a significantly lower risk for heart failure hospitalization (HR, 0.78), a numerically (but not significantly) lower risk for MI (HR, 0.70), and similar risks for stroke, mortality, and MI/stroke/HHF/mortality.
Genital infections were significantly more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors (54.1 vs. 23.7 per 1,000 person-years; HR, 2.19). Other safety measures were similar, including acute kidney injury, bone fractures, severe hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, and lower-limb amputations.
How does cost factor in?
A sensitivity analysis aimed at examining the possible effect of unmeasured socioeconomic status showed no difference in cardiovascular benefit for first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors and metformin, compared with first-line dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, which cost more than metformin; it is not known what effect DPP-4 inhibitors have on the cardiovascular outcomes of interest.
Cost and insurance coverage factor into the benefit/risk calculation. Metformin is far less costly than any of the SGLT-2 inhibitors – roughly $10 to $20 per month, compared with more than $500 a month.
However, “for some fortunate patients with the most generous pharmacy benefit insurance coverage, the out-of-pocket cost of brand name drugs like SGLT-2 inhibitors is substantially lower,” Dr. Taylor noted.
He said that the current study “raises questions about whether the clinical benefits of SGLT-2 inhibitors as initial monotherapy justify the higher price relative to metformin. The data in this paper suggest that the value case for SGLT-2 inhibitors is strongest for patients with the greatest risk to be hospitalized for heart failure.”
Indeed, Dr. Shin said, “Once we get more information, it may just help in extending the coverage from insurance companies and Medicare/Medicaid, to lower the barrier to access.”
Dr. Taylor reiterated that patents on some of the early SGLT-2 inhibitors are expected to expire in the next few years, which would make it possible for generic versions to be approved. “At that point, prices would likely fall, possibly to levels similar to metformin.”
The study was funded by grant support from the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, department of medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, the National Institute on Aging, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Shin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taylor is a consultant for Ionis Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors rather than metformin as first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes appears to cut the risk for heart failure hospitalization but not myocardial infarction, stroke, or all-cause mortality, a new analysis of real-world data suggests.
Safety findings were similar, except for the fact that genital infections were more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors.
The study was conducted using claims data from two large U.S. insurance databases and Medicare. Propensity score matching was used to account for baseline differences.
The study was conducted by HoJin Shin, BPharm, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues. The findings were published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Those who start SGLT-2 inhibitors as first line show similar risks, compared with metformin in MI, stroke, and all-cause mortality outcomes. Strikingly and consistently, SGLT-2 inhibitors show lower risk for hospitalization for heart failure, which is consistent with the findings from cardiovascular outcomes trials,” Dr. Shin said in an interview.
Just a beginning step, although trial probably wasn’t long enough
However, she added, “I don’t want to overstate anything. ... We aren’t powered enough to investigate who would benefit the most. ... As a pharmacoepidemiologist, I think it’s my duty to provide high-quality evidence so we can actually help physicians and patients make better decisions on their medication. Our current research is just a beginning step.”
Asked to comment, Simeon I. Taylor, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, told this news organization, “This study generally confirmed conclusions from published RCTs [randomized clinical trials]. No real surprises, albeit the conclusions may not fully support some of the most enthusiastic claims for SGLT-2 inhibitors with respect to MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death.”
Indeed, Dr. Taylor noted that only two SGLT-2 inhibitors, canagliflozin and empagliflozin, were shown to have a statistically significant association with decreased major adverse cardiovascular events.
In contrast, neither dapagliflozin nor ertugliflozin showed significant benefit regarding those outcomes.
He also pointed out that those four major SLGT-2 inhibitor cardiovascular outcomes trials were placebo-controlled rather than head-to-head trials in which they were compared to an active comparator such as metformin.
“Viewed in this light, it’s probably not surprising that the present study did not demonstrate a robust benefit for SGLT-2 inhibitors to decrease [major adverse CV events].”
The duration of follow-up in the current study is also a limitation, he added.
“The majority of patients were followed for a year or less. This is probably sufficient to assess the impact of some pharmacological mechanisms, for example, the beneficial impact to decrease risk of heart failure by promoting urinary sodium excretion. However, it’s probably insufficient time to observe a beneficial impact on atherosclerosis. For example, there is typically a lag of several years before statins demonstrate efficacy with respect to adverse cardiovascular events.”
Nevertheless, he said, “it provides strong support for benefit with respect to decreasing risk of hospitalization for heart failure.”
He noted that while metformin is currently significantly cheaper than any SGLT-2 inhibitors, once the latter become available as generics, they will be cheaper, and this will likely have a bearing on prescribing decisions.
“Availability of generic SGLT-2 inhibitors offers potential to transform prescribing patterns for type 2 diabetes,” he noted.
First-line SGLT2 inhibitors versus metformin: Most outcomes similar
The study data came from two commercial U.S. health insurance databases, Optum Clinfomatics Data Mart and IBM Marketscan, and from Medicare fee-for-service enrollees.
From April 2013 through March 2020, a total of 9,334 patients began treatment with first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors; 819,973 patients began taking metformin. After 1:2 propensity score matching for confounders, there were 8,613 participants in the SGLT-2 inhibitor group and 17,226 in the group that began treatment with metformin.
The mean follow-up times were 10.7 months for patients taking SGLT-2 inhibitors and 12.2 months for patients taking metformin.
Incidence rates per 1,000 person-years for the composite of hospitalization for MI, hospitalization for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, or all-cause mortality (MI/stroke/mortality) were 15.0 versus 16.2 for SLGT-2 inhibitors versus metformin, not a significant difference (hazard ratio, 0.96).
However, for the composite of heart failure hospitalization or all-cause mortality, the rates were 18.3 versus 23.5, a significant difference, with an HR of 0.80. The benefit was seen beginning at about 6 months.
Compared with metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors showed a significantly lower risk for heart failure hospitalization (HR, 0.78), a numerically (but not significantly) lower risk for MI (HR, 0.70), and similar risks for stroke, mortality, and MI/stroke/HHF/mortality.
Genital infections were significantly more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors (54.1 vs. 23.7 per 1,000 person-years; HR, 2.19). Other safety measures were similar, including acute kidney injury, bone fractures, severe hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, and lower-limb amputations.
How does cost factor in?
A sensitivity analysis aimed at examining the possible effect of unmeasured socioeconomic status showed no difference in cardiovascular benefit for first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors and metformin, compared with first-line dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, which cost more than metformin; it is not known what effect DPP-4 inhibitors have on the cardiovascular outcomes of interest.
Cost and insurance coverage factor into the benefit/risk calculation. Metformin is far less costly than any of the SGLT-2 inhibitors – roughly $10 to $20 per month, compared with more than $500 a month.
However, “for some fortunate patients with the most generous pharmacy benefit insurance coverage, the out-of-pocket cost of brand name drugs like SGLT-2 inhibitors is substantially lower,” Dr. Taylor noted.
He said that the current study “raises questions about whether the clinical benefits of SGLT-2 inhibitors as initial monotherapy justify the higher price relative to metformin. The data in this paper suggest that the value case for SGLT-2 inhibitors is strongest for patients with the greatest risk to be hospitalized for heart failure.”
Indeed, Dr. Shin said, “Once we get more information, it may just help in extending the coverage from insurance companies and Medicare/Medicaid, to lower the barrier to access.”
Dr. Taylor reiterated that patents on some of the early SGLT-2 inhibitors are expected to expire in the next few years, which would make it possible for generic versions to be approved. “At that point, prices would likely fall, possibly to levels similar to metformin.”
The study was funded by grant support from the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, department of medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, the National Institute on Aging, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Shin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taylor is a consultant for Ionis Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE

