User login
AAP approves 2023 child and adolescent immunization schedule
The American Academy of Pediatrics said it supports the Recommended Childhood and Adolescent Immunization Schedule: United States, 2023.
In a policy statement published online in the journal Pediatrics, the AAP said the updated recommendations do not include major changes from those released in 2022 by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In one small shift, COVID-19 is now addressed in the main text instead of being relegated to the notes section.
“And a new vaccine – Priorix [GlaxoSmithKline] – has been added for MMR [measles, mumps, rubella], so now there are two available,” Sean T. O’Leary, MD, MPH, chair of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases, told this news organization. “There’s also a second pneumococcal conjugate vaccine listed, PCV15, and this and PCV13 can essentially be used interchangeably.”
Minor updates to the schedule, reflected on the cover page, relate to vaccines for COVID-19, dengue fever, and pneumococcal disease, added Dr. O’Leary, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora.
The committee also changed layouts to improve the usability of the schedule. Updated annually, the guidance provides a table on recommended pediatric immunizations from birth to age 18 years, and catch-up recommendations for children aged 4 months to 18 years who start their vaccinations late or are more than 1 month behind the recommended age for vaccine administration.
“We hope this annual update will encourage clinicians to make sure all their patients are up to date on their routine vaccinations,” Dr. O’Leary said. “It’s an opportunity to develop strategies to improve vaccination rates.”
The 2023 schedule follows news from the CDC that kindergarten vaccination rates declined during the 2021-2022 school year. Only 93% of kindergarteners obtained full vaccinations, representing a drop of 1 percentage point from the year before and 2 percentage points from the 2019-2020 school year.
The dip in coverage has been attributed to disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. AAP advises health care professionals to urge families to make sure their child’s vaccines are current.
Among other additions:
In Table 1
- MMR: Second vaccine added (Priorix, GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals)
- Pneumococcal disease: second conjugate vaccine, PCV15, added (Vaxneuvance, Merck Sharp & Dohme).
- COVID-19: New row added.
- Dengue: Text changed from “Seropositive in endemic areas only” to “Seropositive in endemic dengue areas.”
- Inactivated polio vaccine: “See Notes” added to the column for children aged 18 years.
In Table 2
- PCV: Dose 3 to dose 4 interval revised to align with ACIP’s recommendation for dose 4. This dose is necessary only for children ages 12-59 months regardless of risk, or age 60-71 months with any risk who received three doses before age 12 months.
A parent-friendly vaccine schedule for children and adolescents is available on the CDC’s website.
“Vaccines are essential for the health of our whole society, including children and adolescents,” Dr. O’Leary said in a press release from AAP. “These schedules provide a road map [that] parents and pediatricians can follow to help children get the vaccines they need so their immune systems will be ready to recognize and resist diseases.”
As previously, the 2023 schedule was adjusted to ensure consistency between the formats of the childhood/adolescent and adult immunization guidance. A meeting of stakeholder organizations in October 2022 harmonized the two formats.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Academy of Pediatrics said it supports the Recommended Childhood and Adolescent Immunization Schedule: United States, 2023.
In a policy statement published online in the journal Pediatrics, the AAP said the updated recommendations do not include major changes from those released in 2022 by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In one small shift, COVID-19 is now addressed in the main text instead of being relegated to the notes section.
“And a new vaccine – Priorix [GlaxoSmithKline] – has been added for MMR [measles, mumps, rubella], so now there are two available,” Sean T. O’Leary, MD, MPH, chair of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases, told this news organization. “There’s also a second pneumococcal conjugate vaccine listed, PCV15, and this and PCV13 can essentially be used interchangeably.”
Minor updates to the schedule, reflected on the cover page, relate to vaccines for COVID-19, dengue fever, and pneumococcal disease, added Dr. O’Leary, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora.
The committee also changed layouts to improve the usability of the schedule. Updated annually, the guidance provides a table on recommended pediatric immunizations from birth to age 18 years, and catch-up recommendations for children aged 4 months to 18 years who start their vaccinations late or are more than 1 month behind the recommended age for vaccine administration.
“We hope this annual update will encourage clinicians to make sure all their patients are up to date on their routine vaccinations,” Dr. O’Leary said. “It’s an opportunity to develop strategies to improve vaccination rates.”
The 2023 schedule follows news from the CDC that kindergarten vaccination rates declined during the 2021-2022 school year. Only 93% of kindergarteners obtained full vaccinations, representing a drop of 1 percentage point from the year before and 2 percentage points from the 2019-2020 school year.
The dip in coverage has been attributed to disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. AAP advises health care professionals to urge families to make sure their child’s vaccines are current.
Among other additions:
In Table 1
- MMR: Second vaccine added (Priorix, GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals)
- Pneumococcal disease: second conjugate vaccine, PCV15, added (Vaxneuvance, Merck Sharp & Dohme).
- COVID-19: New row added.
- Dengue: Text changed from “Seropositive in endemic areas only” to “Seropositive in endemic dengue areas.”
- Inactivated polio vaccine: “See Notes” added to the column for children aged 18 years.
In Table 2
- PCV: Dose 3 to dose 4 interval revised to align with ACIP’s recommendation for dose 4. This dose is necessary only for children ages 12-59 months regardless of risk, or age 60-71 months with any risk who received three doses before age 12 months.
A parent-friendly vaccine schedule for children and adolescents is available on the CDC’s website.
“Vaccines are essential for the health of our whole society, including children and adolescents,” Dr. O’Leary said in a press release from AAP. “These schedules provide a road map [that] parents and pediatricians can follow to help children get the vaccines they need so their immune systems will be ready to recognize and resist diseases.”
As previously, the 2023 schedule was adjusted to ensure consistency between the formats of the childhood/adolescent and adult immunization guidance. A meeting of stakeholder organizations in October 2022 harmonized the two formats.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Academy of Pediatrics said it supports the Recommended Childhood and Adolescent Immunization Schedule: United States, 2023.
In a policy statement published online in the journal Pediatrics, the AAP said the updated recommendations do not include major changes from those released in 2022 by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In one small shift, COVID-19 is now addressed in the main text instead of being relegated to the notes section.
“And a new vaccine – Priorix [GlaxoSmithKline] – has been added for MMR [measles, mumps, rubella], so now there are two available,” Sean T. O’Leary, MD, MPH, chair of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases, told this news organization. “There’s also a second pneumococcal conjugate vaccine listed, PCV15, and this and PCV13 can essentially be used interchangeably.”
Minor updates to the schedule, reflected on the cover page, relate to vaccines for COVID-19, dengue fever, and pneumococcal disease, added Dr. O’Leary, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora.
The committee also changed layouts to improve the usability of the schedule. Updated annually, the guidance provides a table on recommended pediatric immunizations from birth to age 18 years, and catch-up recommendations for children aged 4 months to 18 years who start their vaccinations late or are more than 1 month behind the recommended age for vaccine administration.
“We hope this annual update will encourage clinicians to make sure all their patients are up to date on their routine vaccinations,” Dr. O’Leary said. “It’s an opportunity to develop strategies to improve vaccination rates.”
The 2023 schedule follows news from the CDC that kindergarten vaccination rates declined during the 2021-2022 school year. Only 93% of kindergarteners obtained full vaccinations, representing a drop of 1 percentage point from the year before and 2 percentage points from the 2019-2020 school year.
The dip in coverage has been attributed to disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. AAP advises health care professionals to urge families to make sure their child’s vaccines are current.
Among other additions:
In Table 1
- MMR: Second vaccine added (Priorix, GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals)
- Pneumococcal disease: second conjugate vaccine, PCV15, added (Vaxneuvance, Merck Sharp & Dohme).
- COVID-19: New row added.
- Dengue: Text changed from “Seropositive in endemic areas only” to “Seropositive in endemic dengue areas.”
- Inactivated polio vaccine: “See Notes” added to the column for children aged 18 years.
In Table 2
- PCV: Dose 3 to dose 4 interval revised to align with ACIP’s recommendation for dose 4. This dose is necessary only for children ages 12-59 months regardless of risk, or age 60-71 months with any risk who received three doses before age 12 months.
A parent-friendly vaccine schedule for children and adolescents is available on the CDC’s website.
“Vaccines are essential for the health of our whole society, including children and adolescents,” Dr. O’Leary said in a press release from AAP. “These schedules provide a road map [that] parents and pediatricians can follow to help children get the vaccines they need so their immune systems will be ready to recognize and resist diseases.”
As previously, the 2023 schedule was adjusted to ensure consistency between the formats of the childhood/adolescent and adult immunization guidance. A meeting of stakeholder organizations in October 2022 harmonized the two formats.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PEDIATRICS
FDA OKs sacituzumab govitecan for HR+ metastatic breast cancer
for patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic hormone receptor (HR)–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer after endocrine-based therapy and at least two additional systemic therapies for metastatic disease.
Label expansion for the Trop-2–directed antibody-drug conjugate was based on the TROPICS-02 trial, which randomized 543 adults 1:1 to either sacituzumab govitecan 10 mg/kg IV on days 1 and 8 of a 21-day cycle or single agent chemotherapy, most often eribulin but also vinorelbine, gemcitabine, or capecitabine.
Median progression free survival was 5.5 months with sacituzumab govitecan versus 4 months with single agent chemotherapy (hazard ratio, 0.66; P = .0003). Median overall survival was 14.4 months in the sacituzumab govitecan group versus 11.2 months with chemotherapy (HR, 0.79), according to an FDA press release announcing the approval.
In a Gilead press release, Hope Rugo, MD, a breast cancer specialist at the University of California, San Francisco, and principal investigator for TROPICS-02, said the approval “is significant for the breast cancer community. We have had limited options to offer patients after endocrine-based therapy and chemotherapy, and to see a clinically meaningful survival benefit of more than 3 months with a quality-of-life benefit for these women is exceptional.”
The most common adverse events associated with sacituzumab govitecan in the trial, occurring in a quarter or more of participants, were decreased leukocyte count, decreased neutrophil count, decreased hemoglobin, decreased lymphocyte count, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, alopecia, glucose elevation, constipation, and decreased albumin.
Labeling for the agent carries a boxedwarning of severe or life-threatening neutropenia and severe diarrhea.
The recommended dose is the trial dose: 10 mg/kg IV on days 1 and 8 of 21-day cycles until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Sacituzumab govitecan was previously approved for unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer after two or more prior systemic therapies and locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer after platinum-based chemotherapy and either a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
for patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic hormone receptor (HR)–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer after endocrine-based therapy and at least two additional systemic therapies for metastatic disease.
Label expansion for the Trop-2–directed antibody-drug conjugate was based on the TROPICS-02 trial, which randomized 543 adults 1:1 to either sacituzumab govitecan 10 mg/kg IV on days 1 and 8 of a 21-day cycle or single agent chemotherapy, most often eribulin but also vinorelbine, gemcitabine, or capecitabine.
Median progression free survival was 5.5 months with sacituzumab govitecan versus 4 months with single agent chemotherapy (hazard ratio, 0.66; P = .0003). Median overall survival was 14.4 months in the sacituzumab govitecan group versus 11.2 months with chemotherapy (HR, 0.79), according to an FDA press release announcing the approval.
In a Gilead press release, Hope Rugo, MD, a breast cancer specialist at the University of California, San Francisco, and principal investigator for TROPICS-02, said the approval “is significant for the breast cancer community. We have had limited options to offer patients after endocrine-based therapy and chemotherapy, and to see a clinically meaningful survival benefit of more than 3 months with a quality-of-life benefit for these women is exceptional.”
The most common adverse events associated with sacituzumab govitecan in the trial, occurring in a quarter or more of participants, were decreased leukocyte count, decreased neutrophil count, decreased hemoglobin, decreased lymphocyte count, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, alopecia, glucose elevation, constipation, and decreased albumin.
Labeling for the agent carries a boxedwarning of severe or life-threatening neutropenia and severe diarrhea.
The recommended dose is the trial dose: 10 mg/kg IV on days 1 and 8 of 21-day cycles until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Sacituzumab govitecan was previously approved for unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer after two or more prior systemic therapies and locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer after platinum-based chemotherapy and either a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
for patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic hormone receptor (HR)–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer after endocrine-based therapy and at least two additional systemic therapies for metastatic disease.
Label expansion for the Trop-2–directed antibody-drug conjugate was based on the TROPICS-02 trial, which randomized 543 adults 1:1 to either sacituzumab govitecan 10 mg/kg IV on days 1 and 8 of a 21-day cycle or single agent chemotherapy, most often eribulin but also vinorelbine, gemcitabine, or capecitabine.
Median progression free survival was 5.5 months with sacituzumab govitecan versus 4 months with single agent chemotherapy (hazard ratio, 0.66; P = .0003). Median overall survival was 14.4 months in the sacituzumab govitecan group versus 11.2 months with chemotherapy (HR, 0.79), according to an FDA press release announcing the approval.
In a Gilead press release, Hope Rugo, MD, a breast cancer specialist at the University of California, San Francisco, and principal investigator for TROPICS-02, said the approval “is significant for the breast cancer community. We have had limited options to offer patients after endocrine-based therapy and chemotherapy, and to see a clinically meaningful survival benefit of more than 3 months with a quality-of-life benefit for these women is exceptional.”
The most common adverse events associated with sacituzumab govitecan in the trial, occurring in a quarter or more of participants, were decreased leukocyte count, decreased neutrophil count, decreased hemoglobin, decreased lymphocyte count, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, alopecia, glucose elevation, constipation, and decreased albumin.
Labeling for the agent carries a boxedwarning of severe or life-threatening neutropenia and severe diarrhea.
The recommended dose is the trial dose: 10 mg/kg IV on days 1 and 8 of 21-day cycles until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Sacituzumab govitecan was previously approved for unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer after two or more prior systemic therapies and locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer after platinum-based chemotherapy and either a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Massive rise in drug overdose deaths driven by opioids
The 376% represents the change in age-adjusted overdose deaths per 100,000 population, which went from 6.9 in 2001 to 32.4 in 2021, as the total number of deaths rose from 19,394 to 106,699 (450%) over that time period, the NCHS said in a recent data brief. That total made 2021 the first year ever with more than 100,000 overdose deaths.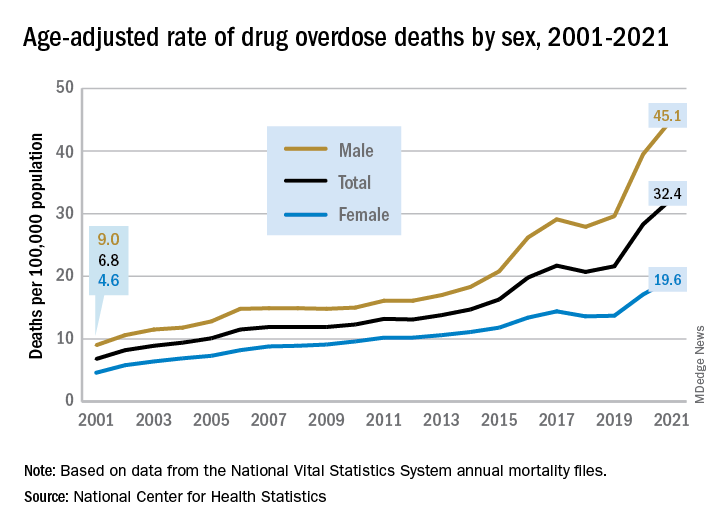
Since the age-adjusted rate stood at 21.6 per 100,000 in 2019, that means 42% of the total increase over 20 years actually occurred in 2020 and 2021. The number of deaths increased by about 36,000 over those 2 years, accounting for 41% of the total annual increase from 2001 to 2021, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System mortality files.
The overdose death rate was significantly higher for males than females for all of the years from 2001 to 2021, with males seeing an increase from 9.0 to 45.1 per 100,000 and females going from 4.6 to 19.6 deaths per 100,000. In the single year from 2020 to 2021, the age-adjusted rate was up by 14% for males and 15% for females, the mortality-file data show.
Analysis by age showed an even larger effect in some groups from 2020 to 2021. Drug overdose deaths jumped 28% among adults aged 65 years and older, more than any other group, and by 21% in those aged 55-64 years, according to the NCHS.
The only age group for which deaths didn’t increase significantly from 2020 to 2021 was 15- to 24-year-olds, whose rate rose by just 3%. The age group with the highest rate in both 2020 and 2021, however, was the 35- to 44-year-olds: 53.9 and 62.0 overdose deaths per 100,000, respectively, for an increase of 15%, the NCHS said in the report.
The drugs now involved in overdose deaths are most often opioids, a change from 2001. That year, opioids were involved in 49% of all overdose deaths, but by 2021 that share had increased to 75%. The trend for opioid-related deaths almost matches that of overall deaths over the 20-year span, and the significantly increasing trend that began for all overdose deaths in 2013 closely follows that of synthetic opioids such as fentanyl and tramadol, the report shows.
Overdose deaths involving cocaine and psychostimulants such as methamphetamine, amphetamine, and methylphenidate also show similar increases. The cocaine-related death rate rose 22% from 2020 to 2021 and is up by 421% since 2012, while the corresponding increases for psychostimulant deaths were 33% and 2,400%, the NCHS said.
The 376% represents the change in age-adjusted overdose deaths per 100,000 population, which went from 6.9 in 2001 to 32.4 in 2021, as the total number of deaths rose from 19,394 to 106,699 (450%) over that time period, the NCHS said in a recent data brief. That total made 2021 the first year ever with more than 100,000 overdose deaths.
Since the age-adjusted rate stood at 21.6 per 100,000 in 2019, that means 42% of the total increase over 20 years actually occurred in 2020 and 2021. The number of deaths increased by about 36,000 over those 2 years, accounting for 41% of the total annual increase from 2001 to 2021, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System mortality files.
The overdose death rate was significantly higher for males than females for all of the years from 2001 to 2021, with males seeing an increase from 9.0 to 45.1 per 100,000 and females going from 4.6 to 19.6 deaths per 100,000. In the single year from 2020 to 2021, the age-adjusted rate was up by 14% for males and 15% for females, the mortality-file data show.
Analysis by age showed an even larger effect in some groups from 2020 to 2021. Drug overdose deaths jumped 28% among adults aged 65 years and older, more than any other group, and by 21% in those aged 55-64 years, according to the NCHS.
The only age group for which deaths didn’t increase significantly from 2020 to 2021 was 15- to 24-year-olds, whose rate rose by just 3%. The age group with the highest rate in both 2020 and 2021, however, was the 35- to 44-year-olds: 53.9 and 62.0 overdose deaths per 100,000, respectively, for an increase of 15%, the NCHS said in the report.
The drugs now involved in overdose deaths are most often opioids, a change from 2001. That year, opioids were involved in 49% of all overdose deaths, but by 2021 that share had increased to 75%. The trend for opioid-related deaths almost matches that of overall deaths over the 20-year span, and the significantly increasing trend that began for all overdose deaths in 2013 closely follows that of synthetic opioids such as fentanyl and tramadol, the report shows.
Overdose deaths involving cocaine and psychostimulants such as methamphetamine, amphetamine, and methylphenidate also show similar increases. The cocaine-related death rate rose 22% from 2020 to 2021 and is up by 421% since 2012, while the corresponding increases for psychostimulant deaths were 33% and 2,400%, the NCHS said.
The 376% represents the change in age-adjusted overdose deaths per 100,000 population, which went from 6.9 in 2001 to 32.4 in 2021, as the total number of deaths rose from 19,394 to 106,699 (450%) over that time period, the NCHS said in a recent data brief. That total made 2021 the first year ever with more than 100,000 overdose deaths.
Since the age-adjusted rate stood at 21.6 per 100,000 in 2019, that means 42% of the total increase over 20 years actually occurred in 2020 and 2021. The number of deaths increased by about 36,000 over those 2 years, accounting for 41% of the total annual increase from 2001 to 2021, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System mortality files.
The overdose death rate was significantly higher for males than females for all of the years from 2001 to 2021, with males seeing an increase from 9.0 to 45.1 per 100,000 and females going from 4.6 to 19.6 deaths per 100,000. In the single year from 2020 to 2021, the age-adjusted rate was up by 14% for males and 15% for females, the mortality-file data show.
Analysis by age showed an even larger effect in some groups from 2020 to 2021. Drug overdose deaths jumped 28% among adults aged 65 years and older, more than any other group, and by 21% in those aged 55-64 years, according to the NCHS.
The only age group for which deaths didn’t increase significantly from 2020 to 2021 was 15- to 24-year-olds, whose rate rose by just 3%. The age group with the highest rate in both 2020 and 2021, however, was the 35- to 44-year-olds: 53.9 and 62.0 overdose deaths per 100,000, respectively, for an increase of 15%, the NCHS said in the report.
The drugs now involved in overdose deaths are most often opioids, a change from 2001. That year, opioids were involved in 49% of all overdose deaths, but by 2021 that share had increased to 75%. The trend for opioid-related deaths almost matches that of overall deaths over the 20-year span, and the significantly increasing trend that began for all overdose deaths in 2013 closely follows that of synthetic opioids such as fentanyl and tramadol, the report shows.
Overdose deaths involving cocaine and psychostimulants such as methamphetamine, amphetamine, and methylphenidate also show similar increases. The cocaine-related death rate rose 22% from 2020 to 2021 and is up by 421% since 2012, while the corresponding increases for psychostimulant deaths were 33% and 2,400%, the NCHS said.
Children and COVID: Weekly cases may have doubled in early January
Although new COVID-19 cases in children, as measured by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association, have remained fairly steady in recent months, data from the Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention suggest that weekly cases took a big jump in early January.
For the most recent week covered . New cases for the first 2 weeks of the year – 31,000 for the week of Dec. 30 to Jan. 5 and 26,000 during Jan. 6-12 – were consistent with the AAP/CHA assertion that “weekly reported child cases have plateaued at an average of about 32,000 cases ... over the past 4 months.”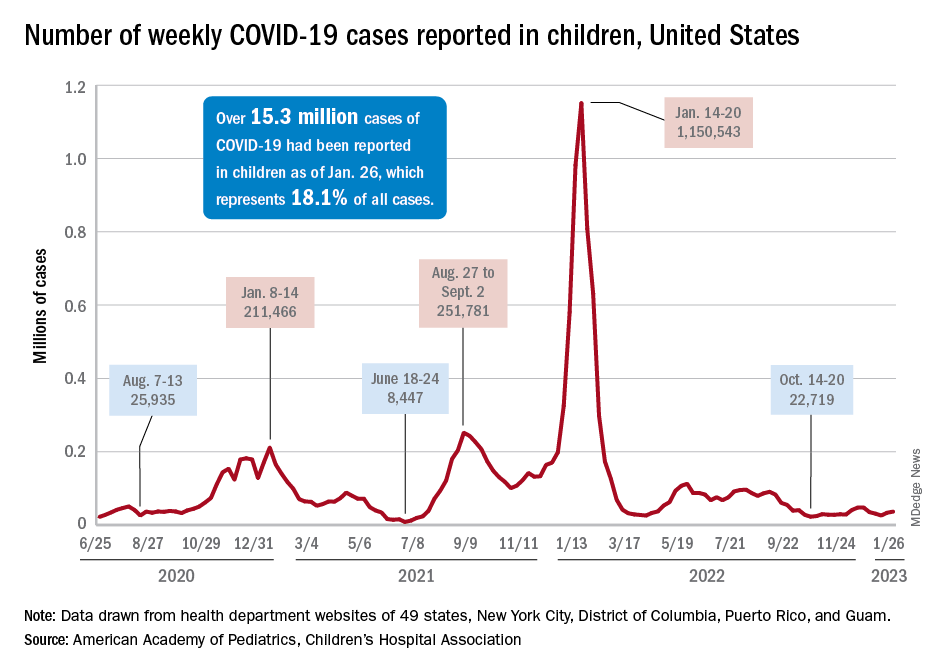
The CDC data, however, show that new cases doubled during the week of Jan. 1-7 to over 65,000, compared with the end of December, and stayed at that level for Jan. 8-14, and since CDC figures are subject to a 6-week reporting delay, the final numbers are likely to be even higher. The composition by age changed somewhat between the 2 weeks, though, as those aged 0-4 years went from almost half of all cases in the first week down to 40% in the second, while cases rose for children aged 5-11 and 12-15, based on data from the COVID-19 response team.
Emergency department visits for January do not show a corresponding increase. ED visits among children aged 0-11 years with COVID-19, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, declined over the course of the month, as did visits for 16- and 17-year-olds, while those aged 12-15 started the month at 1.4% and were at 1.4% on Jan. 27, with a slight dip down to 1.2% in between, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Daily hospitalizations for children aged 0-17 also declined through mid-January and did not reflect the jump in new cases.
Meanwhile, vaccinated children are still in the minority: 57% of those under age 18 have received no COVID vaccine yet, the AAP said in a separate report. Just 7.4% of children under age 2 years had received at least one dose as of Jan. 25, as had 10.1% of those aged 2-4 years, 39.6% of 5- to 11-year-olds and 71.8% of those 12-17 years old, according to the CDC, with corresponding figures for completion of the primary series at 3.5%, 5.3%, 32.5%, and 61.5%.
Although new COVID-19 cases in children, as measured by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association, have remained fairly steady in recent months, data from the Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention suggest that weekly cases took a big jump in early January.
For the most recent week covered . New cases for the first 2 weeks of the year – 31,000 for the week of Dec. 30 to Jan. 5 and 26,000 during Jan. 6-12 – were consistent with the AAP/CHA assertion that “weekly reported child cases have plateaued at an average of about 32,000 cases ... over the past 4 months.”
The CDC data, however, show that new cases doubled during the week of Jan. 1-7 to over 65,000, compared with the end of December, and stayed at that level for Jan. 8-14, and since CDC figures are subject to a 6-week reporting delay, the final numbers are likely to be even higher. The composition by age changed somewhat between the 2 weeks, though, as those aged 0-4 years went from almost half of all cases in the first week down to 40% in the second, while cases rose for children aged 5-11 and 12-15, based on data from the COVID-19 response team.
Emergency department visits for January do not show a corresponding increase. ED visits among children aged 0-11 years with COVID-19, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, declined over the course of the month, as did visits for 16- and 17-year-olds, while those aged 12-15 started the month at 1.4% and were at 1.4% on Jan. 27, with a slight dip down to 1.2% in between, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Daily hospitalizations for children aged 0-17 also declined through mid-January and did not reflect the jump in new cases.
Meanwhile, vaccinated children are still in the minority: 57% of those under age 18 have received no COVID vaccine yet, the AAP said in a separate report. Just 7.4% of children under age 2 years had received at least one dose as of Jan. 25, as had 10.1% of those aged 2-4 years, 39.6% of 5- to 11-year-olds and 71.8% of those 12-17 years old, according to the CDC, with corresponding figures for completion of the primary series at 3.5%, 5.3%, 32.5%, and 61.5%.
Although new COVID-19 cases in children, as measured by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association, have remained fairly steady in recent months, data from the Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention suggest that weekly cases took a big jump in early January.
For the most recent week covered . New cases for the first 2 weeks of the year – 31,000 for the week of Dec. 30 to Jan. 5 and 26,000 during Jan. 6-12 – were consistent with the AAP/CHA assertion that “weekly reported child cases have plateaued at an average of about 32,000 cases ... over the past 4 months.”
The CDC data, however, show that new cases doubled during the week of Jan. 1-7 to over 65,000, compared with the end of December, and stayed at that level for Jan. 8-14, and since CDC figures are subject to a 6-week reporting delay, the final numbers are likely to be even higher. The composition by age changed somewhat between the 2 weeks, though, as those aged 0-4 years went from almost half of all cases in the first week down to 40% in the second, while cases rose for children aged 5-11 and 12-15, based on data from the COVID-19 response team.
Emergency department visits for January do not show a corresponding increase. ED visits among children aged 0-11 years with COVID-19, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, declined over the course of the month, as did visits for 16- and 17-year-olds, while those aged 12-15 started the month at 1.4% and were at 1.4% on Jan. 27, with a slight dip down to 1.2% in between, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Daily hospitalizations for children aged 0-17 also declined through mid-January and did not reflect the jump in new cases.
Meanwhile, vaccinated children are still in the minority: 57% of those under age 18 have received no COVID vaccine yet, the AAP said in a separate report. Just 7.4% of children under age 2 years had received at least one dose as of Jan. 25, as had 10.1% of those aged 2-4 years, 39.6% of 5- to 11-year-olds and 71.8% of those 12-17 years old, according to the CDC, with corresponding figures for completion of the primary series at 3.5%, 5.3%, 32.5%, and 61.5%.
Children and COVID: ED visits and hospitalizations start to fall again
Emergency department visits and hospitalizations for COVID-19 in children appear to be following the declining trend set by weekly cases since early December, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
. New cases took a different path that had the weekly total falling through November before taking a big jump during the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 – the count doubled from 30,000 the previous week to 63,000 – and then decreased again, the CDC reported.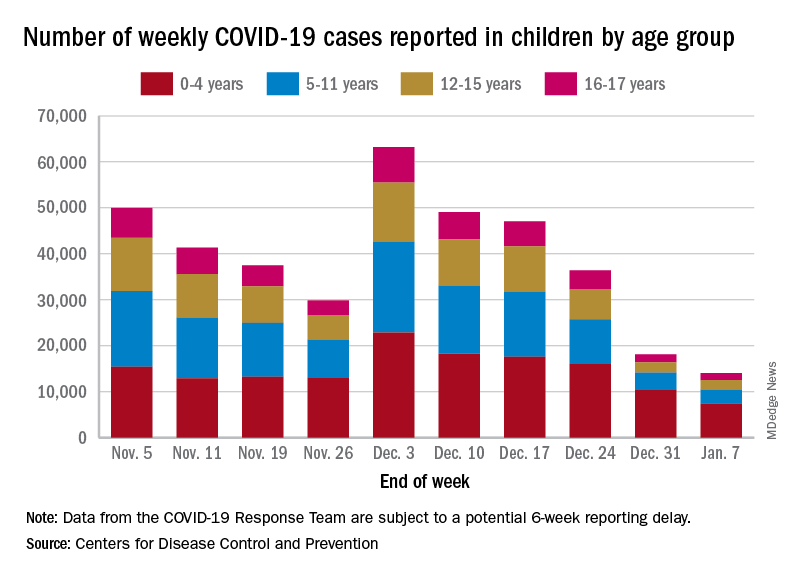
The proportion of ED visits with COVID, which was down to 1.0% of all ED visits (7-day average) for children aged 0-4 years on Nov. 4, was up to 3.2% on Jan. 3 but slipped to 2.5% as of Jan. 10. The patterns for older children are similar, with some differences in timing and lower peaks (1.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.9% for those aged 16-17), according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The trend for new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID showed a similar rise through December, and the latest data for the very beginning of January suggest an even faster drop, although there is more of a reporting lag with hospitalization data, compared with ED visits, the CDC noted.
The most current data (Dec. 30 to Jan. 5) available from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association show less volatility in the number of weekly cases through November and December, with the peak being about 48,000 in mid-December. The AAP/CHA totals for the last 2 weeks, however, were both higher than the CDC’s corresponding counts, which are more preliminary and subject to revision.
The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 16.7 million – about 17.2% of all cases – as of Jan. 11, with 1,981 deaths reported so far. The AAP and CHA are not tracking deaths, but their case total as of Jan. 5 was 15.2 million, which represents 18.1% of cases in all ages. The AAP/CHA report is based on data reported publicly by an ever-decreasing number of states and territories.
Emergency department visits and hospitalizations for COVID-19 in children appear to be following the declining trend set by weekly cases since early December, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
. New cases took a different path that had the weekly total falling through November before taking a big jump during the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 – the count doubled from 30,000 the previous week to 63,000 – and then decreased again, the CDC reported.
The proportion of ED visits with COVID, which was down to 1.0% of all ED visits (7-day average) for children aged 0-4 years on Nov. 4, was up to 3.2% on Jan. 3 but slipped to 2.5% as of Jan. 10. The patterns for older children are similar, with some differences in timing and lower peaks (1.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.9% for those aged 16-17), according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The trend for new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID showed a similar rise through December, and the latest data for the very beginning of January suggest an even faster drop, although there is more of a reporting lag with hospitalization data, compared with ED visits, the CDC noted.
The most current data (Dec. 30 to Jan. 5) available from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association show less volatility in the number of weekly cases through November and December, with the peak being about 48,000 in mid-December. The AAP/CHA totals for the last 2 weeks, however, were both higher than the CDC’s corresponding counts, which are more preliminary and subject to revision.
The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 16.7 million – about 17.2% of all cases – as of Jan. 11, with 1,981 deaths reported so far. The AAP and CHA are not tracking deaths, but their case total as of Jan. 5 was 15.2 million, which represents 18.1% of cases in all ages. The AAP/CHA report is based on data reported publicly by an ever-decreasing number of states and territories.
Emergency department visits and hospitalizations for COVID-19 in children appear to be following the declining trend set by weekly cases since early December, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
. New cases took a different path that had the weekly total falling through November before taking a big jump during the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 – the count doubled from 30,000 the previous week to 63,000 – and then decreased again, the CDC reported.
The proportion of ED visits with COVID, which was down to 1.0% of all ED visits (7-day average) for children aged 0-4 years on Nov. 4, was up to 3.2% on Jan. 3 but slipped to 2.5% as of Jan. 10. The patterns for older children are similar, with some differences in timing and lower peaks (1.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.9% for those aged 16-17), according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The trend for new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID showed a similar rise through December, and the latest data for the very beginning of January suggest an even faster drop, although there is more of a reporting lag with hospitalization data, compared with ED visits, the CDC noted.
The most current data (Dec. 30 to Jan. 5) available from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association show less volatility in the number of weekly cases through November and December, with the peak being about 48,000 in mid-December. The AAP/CHA totals for the last 2 weeks, however, were both higher than the CDC’s corresponding counts, which are more preliminary and subject to revision.
The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 16.7 million – about 17.2% of all cases – as of Jan. 11, with 1,981 deaths reported so far. The AAP and CHA are not tracking deaths, but their case total as of Jan. 5 was 15.2 million, which represents 18.1% of cases in all ages. The AAP/CHA report is based on data reported publicly by an ever-decreasing number of states and territories.
Children and COVID: New cases fell as the old year ended
The end of 2022 saw a drop in new COVID-19 cases in children, even as rates of emergency department visits continued upward trends that began in late October.
New cases for the week of Dec. 23-29 fell for the first time since late November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The AAP/CHA analysis of publicly available state data differs somewhat from figures reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has new cases for the latest available week, Dec.18-24, at just over 27,000 after 3 straight weeks of declines from a count of almost 63,000 for the week ending Nov. 26. The CDC, however, updates previously reported data on a regular basis, so that 27,000 is likely to increase in the coming weeks.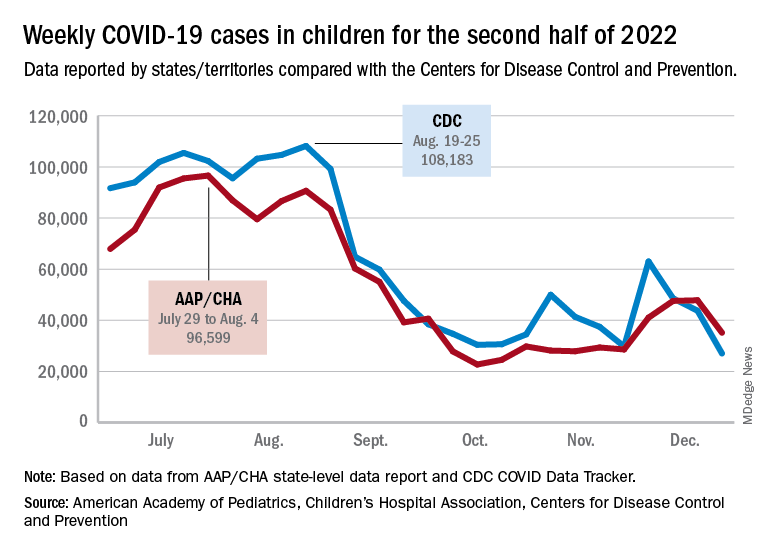
The CDC line on the graph also shows a peak for the week of Oct. 30 to Nov. 5 when new cases reached almost 50,000, compared with almost 30,000 reported for the week of Oct. 28 to Nov. 3 by the AAP and CHA in their report of state-level data. The AAP and CHA put the total number of child COVID cases since the start of the pandemic at 15.2 million as of Dec. 29, while the CDC reports 16.2 million cases as of Dec. 28.
There have been 1,975 deaths from COVID-19 in children aged 0-17 years, according to the CDC, which amounts to just over 0.2% of all COVID deaths for which age group data were available.
CDC data on emergency department visits involving diagnosed COVID-19 have been rising since late October. In children aged 0-11 years, for example, COVID was involved in 1.0% of ED visits (7-day average) as late as Nov. 4, but by Dec. 27 that rate was 2.6%. Children aged 12-15 years went from 0.6% on Oct. 28 to 1.5% on Dec. 27, while 16- to 17-year-olds had ED visit rates of 0.6% on Oct. 19 and 1.7% on Dec. 27, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
New hospital admissions with diagnosed COVID, which had been following the same upward trend as ED visits since late October, halted that rise in children aged 0-17 years and have gone no higher than 0.29 per 100,000 population since Dec. 9, the CDC data show.
The end of 2022 saw a drop in new COVID-19 cases in children, even as rates of emergency department visits continued upward trends that began in late October.
New cases for the week of Dec. 23-29 fell for the first time since late November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The AAP/CHA analysis of publicly available state data differs somewhat from figures reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has new cases for the latest available week, Dec.18-24, at just over 27,000 after 3 straight weeks of declines from a count of almost 63,000 for the week ending Nov. 26. The CDC, however, updates previously reported data on a regular basis, so that 27,000 is likely to increase in the coming weeks.
The CDC line on the graph also shows a peak for the week of Oct. 30 to Nov. 5 when new cases reached almost 50,000, compared with almost 30,000 reported for the week of Oct. 28 to Nov. 3 by the AAP and CHA in their report of state-level data. The AAP and CHA put the total number of child COVID cases since the start of the pandemic at 15.2 million as of Dec. 29, while the CDC reports 16.2 million cases as of Dec. 28.
There have been 1,975 deaths from COVID-19 in children aged 0-17 years, according to the CDC, which amounts to just over 0.2% of all COVID deaths for which age group data were available.
CDC data on emergency department visits involving diagnosed COVID-19 have been rising since late October. In children aged 0-11 years, for example, COVID was involved in 1.0% of ED visits (7-day average) as late as Nov. 4, but by Dec. 27 that rate was 2.6%. Children aged 12-15 years went from 0.6% on Oct. 28 to 1.5% on Dec. 27, while 16- to 17-year-olds had ED visit rates of 0.6% on Oct. 19 and 1.7% on Dec. 27, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
New hospital admissions with diagnosed COVID, which had been following the same upward trend as ED visits since late October, halted that rise in children aged 0-17 years and have gone no higher than 0.29 per 100,000 population since Dec. 9, the CDC data show.
The end of 2022 saw a drop in new COVID-19 cases in children, even as rates of emergency department visits continued upward trends that began in late October.
New cases for the week of Dec. 23-29 fell for the first time since late November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The AAP/CHA analysis of publicly available state data differs somewhat from figures reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has new cases for the latest available week, Dec.18-24, at just over 27,000 after 3 straight weeks of declines from a count of almost 63,000 for the week ending Nov. 26. The CDC, however, updates previously reported data on a regular basis, so that 27,000 is likely to increase in the coming weeks.
The CDC line on the graph also shows a peak for the week of Oct. 30 to Nov. 5 when new cases reached almost 50,000, compared with almost 30,000 reported for the week of Oct. 28 to Nov. 3 by the AAP and CHA in their report of state-level data. The AAP and CHA put the total number of child COVID cases since the start of the pandemic at 15.2 million as of Dec. 29, while the CDC reports 16.2 million cases as of Dec. 28.
There have been 1,975 deaths from COVID-19 in children aged 0-17 years, according to the CDC, which amounts to just over 0.2% of all COVID deaths for which age group data were available.
CDC data on emergency department visits involving diagnosed COVID-19 have been rising since late October. In children aged 0-11 years, for example, COVID was involved in 1.0% of ED visits (7-day average) as late as Nov. 4, but by Dec. 27 that rate was 2.6%. Children aged 12-15 years went from 0.6% on Oct. 28 to 1.5% on Dec. 27, while 16- to 17-year-olds had ED visit rates of 0.6% on Oct. 19 and 1.7% on Dec. 27, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
New hospital admissions with diagnosed COVID, which had been following the same upward trend as ED visits since late October, halted that rise in children aged 0-17 years and have gone no higher than 0.29 per 100,000 population since Dec. 9, the CDC data show.
CDC reports uptick in invasive Strep A infections
Clinicians in the United States are reporting more cases of invasive group A streptococcal infection (iGAS) in children, according to an alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. These infections are rare but can be deadly, and they can affect adults as well as children.
including those with recent or co-occurring viral respiratory infections, the agency advised in a Dec. 22 alert.
In some cases, iGAS manifests as persistent or worsening symptoms after a patient with a known viral infection initially starts to show signs of improvement, according to the agency.
In November, the CDC was notified about a possible increase in cases of pediatric iGAS at a hospital in Colorado. Since then, two surveillance systems – the Infectious Diseases Society of America’s Emerging Infections Network and the CDC’s Active Bacterial Core Surveillance System – have detected potential increases in pediatric iGAS cases in other states.
The uptick has coincided with “increased circulation of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza viruses, SARS-CoV-2, and other respiratory viruses,” the advisory stated. “While the overall number of cases has remained relatively low and iGAS infections remain rare in children, [the] CDC is investigating these reports.”
Not just strep throat
Group A Streptococcus bacteria can cause strep throat and infections in skin and soft tissue. The pathogens also can lead to uncommon but severe diseases, such as sepsis, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, and necrotizing fasciitis, according to the CDC. The severe illnesses “are associated with high mortality rates and require immediate treatment, including appropriate antibiotic therapy,” the agency said.
Groups at higher risk for iGAS include people aged 65 years or older, American Indian and Alaska Native populations, residents of long-term care facilities, those with wounds or skin disease, people who inject drugs, and people experiencing homelessness.
People with medical conditions such as diabetes, cancer, immunosuppression, and chronic kidney, heart, or respiratory disease also are at increased risk.
Invasive strep A infections initially decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic amid measures to reduce the spread of disease, such as masking and social distancing. But since September, monthly cases have exceeded those in 2020 and 2021. “It is too early to determine whether this rise is beyond what would be expected for pre-COVID” seasonal patterns, the CDC said.
Recommendations
Because iGAS can occur after the flu or chickenpox, health care providers should offer influenza and varicella vaccinations to all eligible people who are not up to date with their vaccines.
In addition, clinicians should educate patients about symptoms of iGAS that require urgent medical attention, including necrotizing fasciitis, cellulitis, and toxic shock syndrome.
They also should obtain cultures for suspected cases of iGAS as clinically indicated, follow guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of strep throat, and be aware of alternative ways to treat strep throat in children amid a shortage of amoxicillin suspension.
Researchers have reported more cases of iGAS in the United Kingdom this year, as well. According to the UK Health Security Agency, 74 deaths, including 16 children, in England have been attributed to iGAS since September.
“We know that this is concerning for parents, but I want to stress that while we are seeing an increase in cases in children, this remains very uncommon,” UKHSA Deputy Director Colin Brown said in a news release. “There are lots of winter bugs circulating that can make your child feel unwell that mostly aren’t cause for alarm. However, make sure you talk to a health professional if your child is getting worse after a bout of scarlet fever, a sore throat, or respiratory infection.”
A fever that doesn’t resolve, dehydration, extreme tiredness, and difficulty breathing are signs to watch out for, Dr. Brown said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians in the United States are reporting more cases of invasive group A streptococcal infection (iGAS) in children, according to an alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. These infections are rare but can be deadly, and they can affect adults as well as children.
including those with recent or co-occurring viral respiratory infections, the agency advised in a Dec. 22 alert.
In some cases, iGAS manifests as persistent or worsening symptoms after a patient with a known viral infection initially starts to show signs of improvement, according to the agency.
In November, the CDC was notified about a possible increase in cases of pediatric iGAS at a hospital in Colorado. Since then, two surveillance systems – the Infectious Diseases Society of America’s Emerging Infections Network and the CDC’s Active Bacterial Core Surveillance System – have detected potential increases in pediatric iGAS cases in other states.
The uptick has coincided with “increased circulation of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza viruses, SARS-CoV-2, and other respiratory viruses,” the advisory stated. “While the overall number of cases has remained relatively low and iGAS infections remain rare in children, [the] CDC is investigating these reports.”
Not just strep throat
Group A Streptococcus bacteria can cause strep throat and infections in skin and soft tissue. The pathogens also can lead to uncommon but severe diseases, such as sepsis, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, and necrotizing fasciitis, according to the CDC. The severe illnesses “are associated with high mortality rates and require immediate treatment, including appropriate antibiotic therapy,” the agency said.
Groups at higher risk for iGAS include people aged 65 years or older, American Indian and Alaska Native populations, residents of long-term care facilities, those with wounds or skin disease, people who inject drugs, and people experiencing homelessness.
People with medical conditions such as diabetes, cancer, immunosuppression, and chronic kidney, heart, or respiratory disease also are at increased risk.
Invasive strep A infections initially decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic amid measures to reduce the spread of disease, such as masking and social distancing. But since September, monthly cases have exceeded those in 2020 and 2021. “It is too early to determine whether this rise is beyond what would be expected for pre-COVID” seasonal patterns, the CDC said.
Recommendations
Because iGAS can occur after the flu or chickenpox, health care providers should offer influenza and varicella vaccinations to all eligible people who are not up to date with their vaccines.
In addition, clinicians should educate patients about symptoms of iGAS that require urgent medical attention, including necrotizing fasciitis, cellulitis, and toxic shock syndrome.
They also should obtain cultures for suspected cases of iGAS as clinically indicated, follow guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of strep throat, and be aware of alternative ways to treat strep throat in children amid a shortage of amoxicillin suspension.
Researchers have reported more cases of iGAS in the United Kingdom this year, as well. According to the UK Health Security Agency, 74 deaths, including 16 children, in England have been attributed to iGAS since September.
“We know that this is concerning for parents, but I want to stress that while we are seeing an increase in cases in children, this remains very uncommon,” UKHSA Deputy Director Colin Brown said in a news release. “There are lots of winter bugs circulating that can make your child feel unwell that mostly aren’t cause for alarm. However, make sure you talk to a health professional if your child is getting worse after a bout of scarlet fever, a sore throat, or respiratory infection.”
A fever that doesn’t resolve, dehydration, extreme tiredness, and difficulty breathing are signs to watch out for, Dr. Brown said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians in the United States are reporting more cases of invasive group A streptococcal infection (iGAS) in children, according to an alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. These infections are rare but can be deadly, and they can affect adults as well as children.
including those with recent or co-occurring viral respiratory infections, the agency advised in a Dec. 22 alert.
In some cases, iGAS manifests as persistent or worsening symptoms after a patient with a known viral infection initially starts to show signs of improvement, according to the agency.
In November, the CDC was notified about a possible increase in cases of pediatric iGAS at a hospital in Colorado. Since then, two surveillance systems – the Infectious Diseases Society of America’s Emerging Infections Network and the CDC’s Active Bacterial Core Surveillance System – have detected potential increases in pediatric iGAS cases in other states.
The uptick has coincided with “increased circulation of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza viruses, SARS-CoV-2, and other respiratory viruses,” the advisory stated. “While the overall number of cases has remained relatively low and iGAS infections remain rare in children, [the] CDC is investigating these reports.”
Not just strep throat
Group A Streptococcus bacteria can cause strep throat and infections in skin and soft tissue. The pathogens also can lead to uncommon but severe diseases, such as sepsis, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, and necrotizing fasciitis, according to the CDC. The severe illnesses “are associated with high mortality rates and require immediate treatment, including appropriate antibiotic therapy,” the agency said.
Groups at higher risk for iGAS include people aged 65 years or older, American Indian and Alaska Native populations, residents of long-term care facilities, those with wounds or skin disease, people who inject drugs, and people experiencing homelessness.
People with medical conditions such as diabetes, cancer, immunosuppression, and chronic kidney, heart, or respiratory disease also are at increased risk.
Invasive strep A infections initially decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic amid measures to reduce the spread of disease, such as masking and social distancing. But since September, monthly cases have exceeded those in 2020 and 2021. “It is too early to determine whether this rise is beyond what would be expected for pre-COVID” seasonal patterns, the CDC said.
Recommendations
Because iGAS can occur after the flu or chickenpox, health care providers should offer influenza and varicella vaccinations to all eligible people who are not up to date with their vaccines.
In addition, clinicians should educate patients about symptoms of iGAS that require urgent medical attention, including necrotizing fasciitis, cellulitis, and toxic shock syndrome.
They also should obtain cultures for suspected cases of iGAS as clinically indicated, follow guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of strep throat, and be aware of alternative ways to treat strep throat in children amid a shortage of amoxicillin suspension.
Researchers have reported more cases of iGAS in the United Kingdom this year, as well. According to the UK Health Security Agency, 74 deaths, including 16 children, in England have been attributed to iGAS since September.
“We know that this is concerning for parents, but I want to stress that while we are seeing an increase in cases in children, this remains very uncommon,” UKHSA Deputy Director Colin Brown said in a news release. “There are lots of winter bugs circulating that can make your child feel unwell that mostly aren’t cause for alarm. However, make sure you talk to a health professional if your child is getting worse after a bout of scarlet fever, a sore throat, or respiratory infection.”
A fever that doesn’t resolve, dehydration, extreme tiredness, and difficulty breathing are signs to watch out for, Dr. Brown said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alzheimer’s Association to CMS: Ditch restraints on amyloid drugs
In a letter addressed to CMS administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure, MPP, the association has asked the agency to remove the requirements for “coverage with evidence development” in its national coverage determination for FDA-approved anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies.
The CMS coverage restrictions for anti-amyloid drugs were finalized in April on the basis of data available at the time.
Since then, new data from the CLARITY AD trial “clearly demonstrate a meaningful clinical benefit” from the investigational anti-amyloid agent lecanemab (Eisai/Biogen), Robert Egge, chief public policy officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, told this news organization.
The CLARITY AD results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Lecanemab is currently under accelerated review at the FDA.
The Alzheimer’s Association’s letter to the CMS includes a joint statement signed by more than 200 AD researchers and experts. All agree that the lecanemab results represent “significant new evidence” that necessitates reconsidering the restrictions on anti-amyloid agents.
“CMS has said it would look at new evidence, and now that evidence is here. We believe CMS recognizes this evidence for lecanemab is stronger than that for many treatments Medicare routinely covers,” Mr. Egge said.
‘No time to waste’
“With the timing of accelerated approvals for both lecanemab and donanemab in the next few months, the Alzheimer’s Association wants to ensure, if approved, that patients can access these treatments,” Mr. Egge noted.
“Because revisions to National Coverage Determinations can be a lengthy process, CMS needs to act quickly to minimize delays. People living with Alzheimer’s disease don’t have time to waste,” he added.
The Alzheimer’s Association estimates that every day, more than 2,000 individuals aged 65 or older may transition from mild dementia due to AD to a more advanced stage of the disease in which they may no longer be eligible for lecanemab and the other anti-amyloid agents currently being tested.
“Each day matters when it comes to slowing the progression of this disease,” Joanne Pike, DrPH, president and incoming chief executive officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted in a news release.
“The current CMS policy to severely limit access to these treatments eliminates people’s options, is resulting in continued irreversible disease progression, and contributes to greater health inequities. That’s not acceptable,” Dr. Pike said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a letter addressed to CMS administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure, MPP, the association has asked the agency to remove the requirements for “coverage with evidence development” in its national coverage determination for FDA-approved anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies.
The CMS coverage restrictions for anti-amyloid drugs were finalized in April on the basis of data available at the time.
Since then, new data from the CLARITY AD trial “clearly demonstrate a meaningful clinical benefit” from the investigational anti-amyloid agent lecanemab (Eisai/Biogen), Robert Egge, chief public policy officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, told this news organization.
The CLARITY AD results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Lecanemab is currently under accelerated review at the FDA.
The Alzheimer’s Association’s letter to the CMS includes a joint statement signed by more than 200 AD researchers and experts. All agree that the lecanemab results represent “significant new evidence” that necessitates reconsidering the restrictions on anti-amyloid agents.
“CMS has said it would look at new evidence, and now that evidence is here. We believe CMS recognizes this evidence for lecanemab is stronger than that for many treatments Medicare routinely covers,” Mr. Egge said.
‘No time to waste’
“With the timing of accelerated approvals for both lecanemab and donanemab in the next few months, the Alzheimer’s Association wants to ensure, if approved, that patients can access these treatments,” Mr. Egge noted.
“Because revisions to National Coverage Determinations can be a lengthy process, CMS needs to act quickly to minimize delays. People living with Alzheimer’s disease don’t have time to waste,” he added.
The Alzheimer’s Association estimates that every day, more than 2,000 individuals aged 65 or older may transition from mild dementia due to AD to a more advanced stage of the disease in which they may no longer be eligible for lecanemab and the other anti-amyloid agents currently being tested.
“Each day matters when it comes to slowing the progression of this disease,” Joanne Pike, DrPH, president and incoming chief executive officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted in a news release.
“The current CMS policy to severely limit access to these treatments eliminates people’s options, is resulting in continued irreversible disease progression, and contributes to greater health inequities. That’s not acceptable,” Dr. Pike said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a letter addressed to CMS administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure, MPP, the association has asked the agency to remove the requirements for “coverage with evidence development” in its national coverage determination for FDA-approved anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies.
The CMS coverage restrictions for anti-amyloid drugs were finalized in April on the basis of data available at the time.
Since then, new data from the CLARITY AD trial “clearly demonstrate a meaningful clinical benefit” from the investigational anti-amyloid agent lecanemab (Eisai/Biogen), Robert Egge, chief public policy officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, told this news organization.
The CLARITY AD results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Lecanemab is currently under accelerated review at the FDA.
The Alzheimer’s Association’s letter to the CMS includes a joint statement signed by more than 200 AD researchers and experts. All agree that the lecanemab results represent “significant new evidence” that necessitates reconsidering the restrictions on anti-amyloid agents.
“CMS has said it would look at new evidence, and now that evidence is here. We believe CMS recognizes this evidence for lecanemab is stronger than that for many treatments Medicare routinely covers,” Mr. Egge said.
‘No time to waste’
“With the timing of accelerated approvals for both lecanemab and donanemab in the next few months, the Alzheimer’s Association wants to ensure, if approved, that patients can access these treatments,” Mr. Egge noted.
“Because revisions to National Coverage Determinations can be a lengthy process, CMS needs to act quickly to minimize delays. People living with Alzheimer’s disease don’t have time to waste,” he added.
The Alzheimer’s Association estimates that every day, more than 2,000 individuals aged 65 or older may transition from mild dementia due to AD to a more advanced stage of the disease in which they may no longer be eligible for lecanemab and the other anti-amyloid agents currently being tested.
“Each day matters when it comes to slowing the progression of this disease,” Joanne Pike, DrPH, president and incoming chief executive officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted in a news release.
“The current CMS policy to severely limit access to these treatments eliminates people’s options, is resulting in continued irreversible disease progression, and contributes to greater health inequities. That’s not acceptable,” Dr. Pike said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: New-case counts offer dueling narratives
New COVID-19 cases in children jumped by 66% during the first 2 weeks of December after an 8-week steady period lasting through October and November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
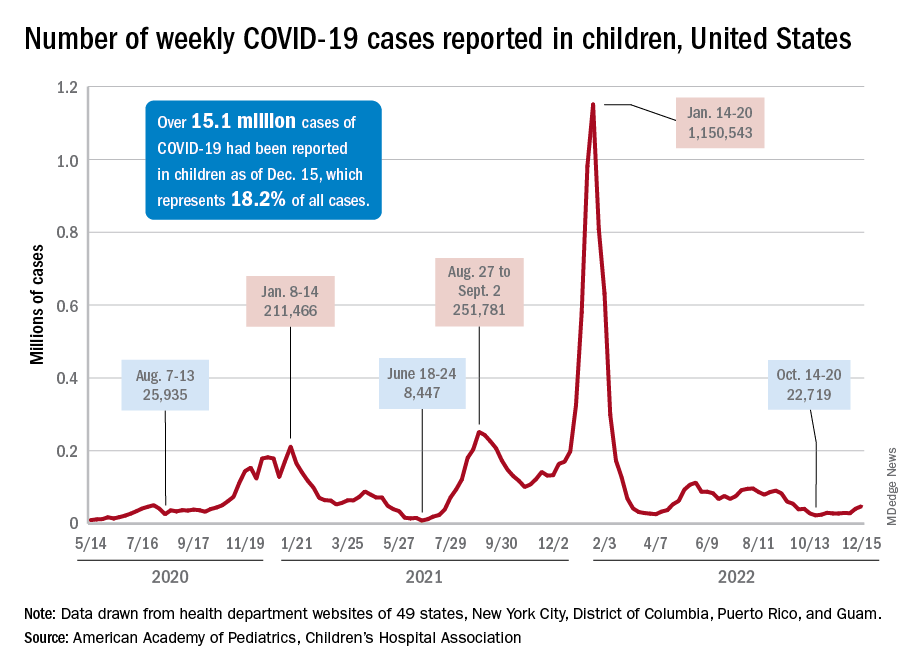
and totaling less than 29,000 for the week of Nov. 25 to Dec. 1. That increase of almost 19,000 cases is the largest over a 2-week period since late July, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report based on data collected from state and territorial health department websites.
[This publication has been following the AAP/CHA report since the summer of 2020 and continues to share the data for the sake of consistency, but it must be noted that a number of states are no longer updating their public COVID dashboards. As a result, there is now a considerable discrepancy between the AAP/CHA weekly figures and those reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has no such limitations on state data.]
The situation involving new cases over the last 2 weeks is quite different from the CDC’s perspective. The agency does not publish a weekly count, instead offering cumulative cases, which stood at almost 16.1 million as of Dec. 14. Calculating a 2-week total puts the new-case count for Dec. 1-14 at 113,572 among children aged 0-17 years. That is higher than the AAP/CHA count (88,629) for roughly the same period, but it is actually lower than the CDC’s figure (161,832) for the last 2 weeks of November.
The CDC data, in other words, suggest that new cases have gone down in the last 2 weeks, while the AAP and CHA, with their somewhat limited perspective, announced that new cases have gone up.
One COVID-related measure from the CDC that is not contradicted by other sources is hospitalization rates, which had climbed from 0.16 new admissions in children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID per 100,000 population on Oct. 22 to 0.29 per 100,000 on Dec. 9. Visits to the emergency department with diagnosed COVID, meanwhile, have been fairly steady so far through December in children, according to the CDC.
New COVID-19 cases in children jumped by 66% during the first 2 weeks of December after an 8-week steady period lasting through October and November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

and totaling less than 29,000 for the week of Nov. 25 to Dec. 1. That increase of almost 19,000 cases is the largest over a 2-week period since late July, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report based on data collected from state and territorial health department websites.
[This publication has been following the AAP/CHA report since the summer of 2020 and continues to share the data for the sake of consistency, but it must be noted that a number of states are no longer updating their public COVID dashboards. As a result, there is now a considerable discrepancy between the AAP/CHA weekly figures and those reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has no such limitations on state data.]
The situation involving new cases over the last 2 weeks is quite different from the CDC’s perspective. The agency does not publish a weekly count, instead offering cumulative cases, which stood at almost 16.1 million as of Dec. 14. Calculating a 2-week total puts the new-case count for Dec. 1-14 at 113,572 among children aged 0-17 years. That is higher than the AAP/CHA count (88,629) for roughly the same period, but it is actually lower than the CDC’s figure (161,832) for the last 2 weeks of November.
The CDC data, in other words, suggest that new cases have gone down in the last 2 weeks, while the AAP and CHA, with their somewhat limited perspective, announced that new cases have gone up.
One COVID-related measure from the CDC that is not contradicted by other sources is hospitalization rates, which had climbed from 0.16 new admissions in children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID per 100,000 population on Oct. 22 to 0.29 per 100,000 on Dec. 9. Visits to the emergency department with diagnosed COVID, meanwhile, have been fairly steady so far through December in children, according to the CDC.
New COVID-19 cases in children jumped by 66% during the first 2 weeks of December after an 8-week steady period lasting through October and November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

and totaling less than 29,000 for the week of Nov. 25 to Dec. 1. That increase of almost 19,000 cases is the largest over a 2-week period since late July, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report based on data collected from state and territorial health department websites.
[This publication has been following the AAP/CHA report since the summer of 2020 and continues to share the data for the sake of consistency, but it must be noted that a number of states are no longer updating their public COVID dashboards. As a result, there is now a considerable discrepancy between the AAP/CHA weekly figures and those reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has no such limitations on state data.]
The situation involving new cases over the last 2 weeks is quite different from the CDC’s perspective. The agency does not publish a weekly count, instead offering cumulative cases, which stood at almost 16.1 million as of Dec. 14. Calculating a 2-week total puts the new-case count for Dec. 1-14 at 113,572 among children aged 0-17 years. That is higher than the AAP/CHA count (88,629) for roughly the same period, but it is actually lower than the CDC’s figure (161,832) for the last 2 weeks of November.
The CDC data, in other words, suggest that new cases have gone down in the last 2 weeks, while the AAP and CHA, with their somewhat limited perspective, announced that new cases have gone up.
One COVID-related measure from the CDC that is not contradicted by other sources is hospitalization rates, which had climbed from 0.16 new admissions in children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID per 100,000 population on Oct. 22 to 0.29 per 100,000 on Dec. 9. Visits to the emergency department with diagnosed COVID, meanwhile, have been fairly steady so far through December in children, according to the CDC.
FDA approves Idacio as eighth adalimumab biosimilar in U.S.
A biosimilar drug to the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor adalimumab, marketed as Idacio (adalimumab-aacf), has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the United States, according to a press release from manufacturer Fresenius Kabi.
Idacio is a citrate-free, low-concentration formulation of adalimumab and is now approved for use for all but three of the indications that currently apply to the reference adalimumab product (Humira): rheumatoid arthritis, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis in adults, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease in adults and children aged 6 years or older, ulcerative colitis in adults, and plaque psoriasis in adults. It does not apply to Humira’s indications for hidradenitis suppurativa, uveitis, or ulcerative colitis in pediatric patients aged 5 years and older.
Idacio is the eighth adalimumab biosimilar to be approved in the United States. Its approval was based on evidence of a similar profile of pharmacokinetics, safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity to Humira.
Idacio was first launched in 2019 and has been marketed in more than 37 countries worldwide, according to Fresenius Kabi. The U.S. launch is scheduled for July, and Idacio will be available as a self-administered prefilled syringe or prefilled pen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A biosimilar drug to the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor adalimumab, marketed as Idacio (adalimumab-aacf), has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the United States, according to a press release from manufacturer Fresenius Kabi.
Idacio is a citrate-free, low-concentration formulation of adalimumab and is now approved for use for all but three of the indications that currently apply to the reference adalimumab product (Humira): rheumatoid arthritis, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis in adults, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease in adults and children aged 6 years or older, ulcerative colitis in adults, and plaque psoriasis in adults. It does not apply to Humira’s indications for hidradenitis suppurativa, uveitis, or ulcerative colitis in pediatric patients aged 5 years and older.
Idacio is the eighth adalimumab biosimilar to be approved in the United States. Its approval was based on evidence of a similar profile of pharmacokinetics, safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity to Humira.
Idacio was first launched in 2019 and has been marketed in more than 37 countries worldwide, according to Fresenius Kabi. The U.S. launch is scheduled for July, and Idacio will be available as a self-administered prefilled syringe or prefilled pen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A biosimilar drug to the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor adalimumab, marketed as Idacio (adalimumab-aacf), has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the United States, according to a press release from manufacturer Fresenius Kabi.
Idacio is a citrate-free, low-concentration formulation of adalimumab and is now approved for use for all but three of the indications that currently apply to the reference adalimumab product (Humira): rheumatoid arthritis, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis in adults, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease in adults and children aged 6 years or older, ulcerative colitis in adults, and plaque psoriasis in adults. It does not apply to Humira’s indications for hidradenitis suppurativa, uveitis, or ulcerative colitis in pediatric patients aged 5 years and older.
Idacio is the eighth adalimumab biosimilar to be approved in the United States. Its approval was based on evidence of a similar profile of pharmacokinetics, safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity to Humira.
Idacio was first launched in 2019 and has been marketed in more than 37 countries worldwide, according to Fresenius Kabi. The U.S. launch is scheduled for July, and Idacio will be available as a self-administered prefilled syringe or prefilled pen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.