User login
Children and COVID: Hospitalizations provide a tale of two sources
New cases of COVID-19 in children largely held steady over the Thanksgiving holiday, but hospital admissions are telling a somewhat different story.
New pediatric COVID cases for the week ending on Thanksgiving (11/18-11/24) were up by 5.3% over the previous week, but in the most recent week (11/25-12/1) new cases dropped by 2.6%, according to state data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
In both weeks, though, the total case count stayed below 30,000 – a streak that has now lasted 8 weeks – so the actual number of weekly cases remained fairly low, the AAP/CHA weekly report indicates.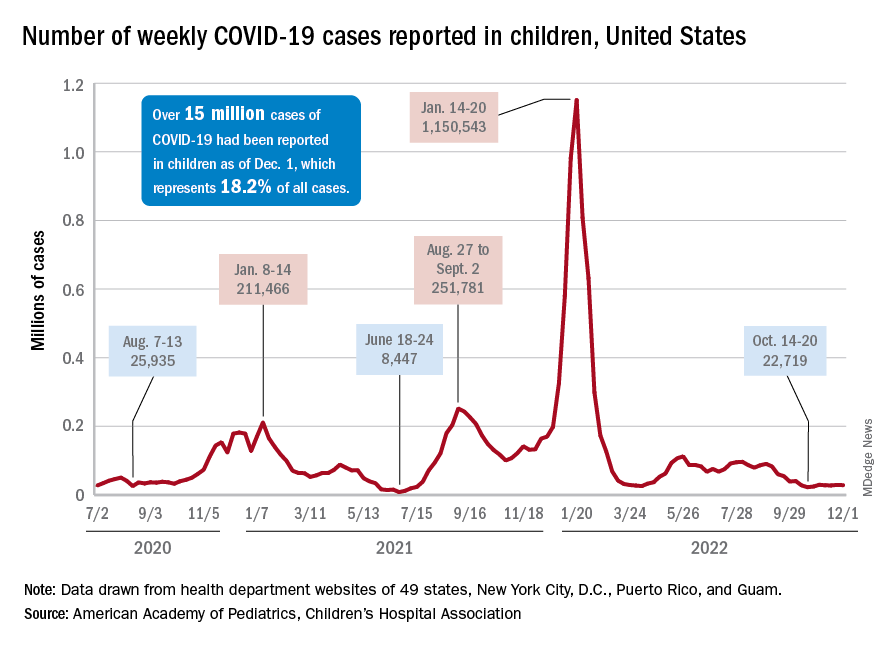
The nation’s emergency departments also experienced a small Thanksgiving bump, as the proportion of visits with diagnosed COVID went from 1.0% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years on Nov. 14 to 2.0% on Nov. 27, just 3 days after the official holiday, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The rate was down to 1.5% on Dec. 1, and similar patterns can be seen for children aged 12-15 and 16-17 years.
New hospital admissions, on the other hand, seem to be following a different path, at least according to the CDC. The hospitalization rate for children aged 0-17 years bottomed out at 0.16 new admissions per 100,000 population back on Oct. 21 and has climbed fairly steadily since then. It was up to 0.20 per 100,000 by Nov. 14, had reached 0.22 per 100,000 on Thanksgiving day (11/24), and then continued to 0.26 per 100,000 by Dec. 2, the latest date for which CDC data are available.
The hospitalization story, however, offers yet another twist. The New York Times, using data from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, reports that new COVID-related admissions have held steady at 1.0 per 100,000 since Nov. 18. The rate is much higher than has been reported by the CDC, but no increase can be seen in recent weeks among children, which is not the case for Americans overall, Medscape recently reported.
New cases of COVID-19 in children largely held steady over the Thanksgiving holiday, but hospital admissions are telling a somewhat different story.
New pediatric COVID cases for the week ending on Thanksgiving (11/18-11/24) were up by 5.3% over the previous week, but in the most recent week (11/25-12/1) new cases dropped by 2.6%, according to state data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
In both weeks, though, the total case count stayed below 30,000 – a streak that has now lasted 8 weeks – so the actual number of weekly cases remained fairly low, the AAP/CHA weekly report indicates.
The nation’s emergency departments also experienced a small Thanksgiving bump, as the proportion of visits with diagnosed COVID went from 1.0% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years on Nov. 14 to 2.0% on Nov. 27, just 3 days after the official holiday, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The rate was down to 1.5% on Dec. 1, and similar patterns can be seen for children aged 12-15 and 16-17 years.
New hospital admissions, on the other hand, seem to be following a different path, at least according to the CDC. The hospitalization rate for children aged 0-17 years bottomed out at 0.16 new admissions per 100,000 population back on Oct. 21 and has climbed fairly steadily since then. It was up to 0.20 per 100,000 by Nov. 14, had reached 0.22 per 100,000 on Thanksgiving day (11/24), and then continued to 0.26 per 100,000 by Dec. 2, the latest date for which CDC data are available.
The hospitalization story, however, offers yet another twist. The New York Times, using data from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, reports that new COVID-related admissions have held steady at 1.0 per 100,000 since Nov. 18. The rate is much higher than has been reported by the CDC, but no increase can be seen in recent weeks among children, which is not the case for Americans overall, Medscape recently reported.
New cases of COVID-19 in children largely held steady over the Thanksgiving holiday, but hospital admissions are telling a somewhat different story.
New pediatric COVID cases for the week ending on Thanksgiving (11/18-11/24) were up by 5.3% over the previous week, but in the most recent week (11/25-12/1) new cases dropped by 2.6%, according to state data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
In both weeks, though, the total case count stayed below 30,000 – a streak that has now lasted 8 weeks – so the actual number of weekly cases remained fairly low, the AAP/CHA weekly report indicates.
The nation’s emergency departments also experienced a small Thanksgiving bump, as the proportion of visits with diagnosed COVID went from 1.0% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years on Nov. 14 to 2.0% on Nov. 27, just 3 days after the official holiday, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The rate was down to 1.5% on Dec. 1, and similar patterns can be seen for children aged 12-15 and 16-17 years.
New hospital admissions, on the other hand, seem to be following a different path, at least according to the CDC. The hospitalization rate for children aged 0-17 years bottomed out at 0.16 new admissions per 100,000 population back on Oct. 21 and has climbed fairly steadily since then. It was up to 0.20 per 100,000 by Nov. 14, had reached 0.22 per 100,000 on Thanksgiving day (11/24), and then continued to 0.26 per 100,000 by Dec. 2, the latest date for which CDC data are available.
The hospitalization story, however, offers yet another twist. The New York Times, using data from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, reports that new COVID-related admissions have held steady at 1.0 per 100,000 since Nov. 18. The rate is much higher than has been reported by the CDC, but no increase can be seen in recent weeks among children, which is not the case for Americans overall, Medscape recently reported.
FDA OKs first fecal microbiota therapy for recurrent C. difficile
Rebyota (fecal microbiota, live-jslm), from Ferring Pharmaceuticals, is intended for use after an individual has completed antibiotic treatment for recurrent CDI. It is not indicated for the first occurrence of CDI.
“Recurrent CDI impacts an individual’s quality of life and can also potentially be life-threatening,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director, FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a statement announcing approval.
As the first FDA-approved fecal microbiota product, this approval “represents an important milestone, as it provides an additional approved option to prevent recurrent CDI,” Dr. Marks added.
A panel of FDA advisors recommended approval of Rebyota in September.
The application for Rebyota received priority review and had orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designation.
A vicious cycle
Treatment options for recurrent CDI are limited. It’s been estimated that up to one-third of CDI cases recur, and people who suffer a recurrent bout of CDI are at a significantly higher risk for further infections.
Following the first recurrence, up to two-thirds of patients may experience a subsequent recurrence. Antibiotics used to treat CDI may contribute to a cycle of recurrence by altering the gut flora. The administration of fecal microbiota helps restore the gut flora to prevent further episodes of CDI.
“This is a major milestone in the translation of gut microbiome science to clinical solutions for patients,” Phillip I. Tarr, MD, chair of the American Gastroenterological Association’s Center for Gut Microbiome Research and Education Scientific Advisory Board, said in a written statement issued by the AGA. “This accomplishment is based on decades of work on the gut microbiome by gastroenterologists and collaborators. AGA applauds FDA for recognizing the demonstrated and conceptual merit of microbiota-based therapies.”
Rebyota is a microbiota-based live biotherapeutic prepared from human stool collected from prescreened, qualified donors. It comes prepackaged in a single dose that is administered rectally.
The safety and efficacy of Rebyota were assessed in five clinical trials with more than 1,000 participants, the company notes in a press release.
In one trial, following a standard course of antibiotics, a one-time treatment with Rebyota was successful for three-quarters of participants at 8 weeks.
The treatment also prevented additional bouts; 84% of these initial responders remaining free of CDI at 6 months.
Two-thirds of participants reported treatment-emergent adverse events. Most events were mild to moderate in severity. Diarrhea and abdominal pain were the most common.
The data, from the ongoing PUNCH CD3-OLS study, were presented in October at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology and were published simultaneously in the journal Drugs.
“This is a positive adjunct to our current therapies for C. difficile in terms of trying to knock it out once a standard course of antibiotics has been administered,” Lisa Malter, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor of medicine at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
Dr. Malter acknowledged that, because it’s delivered rectally, there could be “some hesitation” on the patient’s part to undergo the therapy.
However, C. difficile can be “excruciating” for patients, and they “may be more than willing to take [this agent] because it gets them feeling better,” said Dr. Malter said, who reported no relevant financial relationships.
The AGA will continue to follow the long-term effectiveness and safety of patients receiving Rebyota, fecal microbiota transplant, and other microbiota-based therapies through its FMT National Registry, according to the AGA statement.
Full prescribing information for Rebyota is available online.
For more information about CDI and FMT, visit patient.gastro.org.
Rebyota (fecal microbiota, live-jslm), from Ferring Pharmaceuticals, is intended for use after an individual has completed antibiotic treatment for recurrent CDI. It is not indicated for the first occurrence of CDI.
“Recurrent CDI impacts an individual’s quality of life and can also potentially be life-threatening,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director, FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a statement announcing approval.
As the first FDA-approved fecal microbiota product, this approval “represents an important milestone, as it provides an additional approved option to prevent recurrent CDI,” Dr. Marks added.
A panel of FDA advisors recommended approval of Rebyota in September.
The application for Rebyota received priority review and had orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designation.
A vicious cycle
Treatment options for recurrent CDI are limited. It’s been estimated that up to one-third of CDI cases recur, and people who suffer a recurrent bout of CDI are at a significantly higher risk for further infections.
Following the first recurrence, up to two-thirds of patients may experience a subsequent recurrence. Antibiotics used to treat CDI may contribute to a cycle of recurrence by altering the gut flora. The administration of fecal microbiota helps restore the gut flora to prevent further episodes of CDI.
“This is a major milestone in the translation of gut microbiome science to clinical solutions for patients,” Phillip I. Tarr, MD, chair of the American Gastroenterological Association’s Center for Gut Microbiome Research and Education Scientific Advisory Board, said in a written statement issued by the AGA. “This accomplishment is based on decades of work on the gut microbiome by gastroenterologists and collaborators. AGA applauds FDA for recognizing the demonstrated and conceptual merit of microbiota-based therapies.”
Rebyota is a microbiota-based live biotherapeutic prepared from human stool collected from prescreened, qualified donors. It comes prepackaged in a single dose that is administered rectally.
The safety and efficacy of Rebyota were assessed in five clinical trials with more than 1,000 participants, the company notes in a press release.
In one trial, following a standard course of antibiotics, a one-time treatment with Rebyota was successful for three-quarters of participants at 8 weeks.
The treatment also prevented additional bouts; 84% of these initial responders remaining free of CDI at 6 months.
Two-thirds of participants reported treatment-emergent adverse events. Most events were mild to moderate in severity. Diarrhea and abdominal pain were the most common.
The data, from the ongoing PUNCH CD3-OLS study, were presented in October at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology and were published simultaneously in the journal Drugs.
“This is a positive adjunct to our current therapies for C. difficile in terms of trying to knock it out once a standard course of antibiotics has been administered,” Lisa Malter, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor of medicine at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
Dr. Malter acknowledged that, because it’s delivered rectally, there could be “some hesitation” on the patient’s part to undergo the therapy.
However, C. difficile can be “excruciating” for patients, and they “may be more than willing to take [this agent] because it gets them feeling better,” said Dr. Malter said, who reported no relevant financial relationships.
The AGA will continue to follow the long-term effectiveness and safety of patients receiving Rebyota, fecal microbiota transplant, and other microbiota-based therapies through its FMT National Registry, according to the AGA statement.
Full prescribing information for Rebyota is available online.
For more information about CDI and FMT, visit patient.gastro.org.
Rebyota (fecal microbiota, live-jslm), from Ferring Pharmaceuticals, is intended for use after an individual has completed antibiotic treatment for recurrent CDI. It is not indicated for the first occurrence of CDI.
“Recurrent CDI impacts an individual’s quality of life and can also potentially be life-threatening,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director, FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a statement announcing approval.
As the first FDA-approved fecal microbiota product, this approval “represents an important milestone, as it provides an additional approved option to prevent recurrent CDI,” Dr. Marks added.
A panel of FDA advisors recommended approval of Rebyota in September.
The application for Rebyota received priority review and had orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designation.
A vicious cycle
Treatment options for recurrent CDI are limited. It’s been estimated that up to one-third of CDI cases recur, and people who suffer a recurrent bout of CDI are at a significantly higher risk for further infections.
Following the first recurrence, up to two-thirds of patients may experience a subsequent recurrence. Antibiotics used to treat CDI may contribute to a cycle of recurrence by altering the gut flora. The administration of fecal microbiota helps restore the gut flora to prevent further episodes of CDI.
“This is a major milestone in the translation of gut microbiome science to clinical solutions for patients,” Phillip I. Tarr, MD, chair of the American Gastroenterological Association’s Center for Gut Microbiome Research and Education Scientific Advisory Board, said in a written statement issued by the AGA. “This accomplishment is based on decades of work on the gut microbiome by gastroenterologists and collaborators. AGA applauds FDA for recognizing the demonstrated and conceptual merit of microbiota-based therapies.”
Rebyota is a microbiota-based live biotherapeutic prepared from human stool collected from prescreened, qualified donors. It comes prepackaged in a single dose that is administered rectally.
The safety and efficacy of Rebyota were assessed in five clinical trials with more than 1,000 participants, the company notes in a press release.
In one trial, following a standard course of antibiotics, a one-time treatment with Rebyota was successful for three-quarters of participants at 8 weeks.
The treatment also prevented additional bouts; 84% of these initial responders remaining free of CDI at 6 months.
Two-thirds of participants reported treatment-emergent adverse events. Most events were mild to moderate in severity. Diarrhea and abdominal pain were the most common.
The data, from the ongoing PUNCH CD3-OLS study, were presented in October at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology and were published simultaneously in the journal Drugs.
“This is a positive adjunct to our current therapies for C. difficile in terms of trying to knock it out once a standard course of antibiotics has been administered,” Lisa Malter, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor of medicine at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
Dr. Malter acknowledged that, because it’s delivered rectally, there could be “some hesitation” on the patient’s part to undergo the therapy.
However, C. difficile can be “excruciating” for patients, and they “may be more than willing to take [this agent] because it gets them feeling better,” said Dr. Malter said, who reported no relevant financial relationships.
The AGA will continue to follow the long-term effectiveness and safety of patients receiving Rebyota, fecal microbiota transplant, and other microbiota-based therapies through its FMT National Registry, according to the AGA statement.
Full prescribing information for Rebyota is available online.
For more information about CDI and FMT, visit patient.gastro.org.
FDA OKs first fecal transplant therapy for recurrent C. difficile
Rebyota (fecal microbiota, live-jslm), from Ferring Pharmaceuticals, is intended for use after an individual has completed antibiotic treatment for recurrent CDI. It is not indicated for the first occurrence of CDI.
“Recurrent CDI impacts an individual’s quality of life and can also potentially be life-threatening,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director, FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a statement announcing approval.
As the first FDA-approved fecal microbiota product, this approval “represents an important milestone, as it provides an additional approved option to prevent recurrent CDI,” Dr. Marks added.
A panel of FDA advisors recommended approval of Rebyota in September.
The application for Rebyota received priority review and had orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designation.
A vicious cycle
Treatment options for recurrent CDI are limited. It’s been estimated that up to one-third of CDI cases recur, and people who suffer a recurrent bout of CDI are at a significantly higher risk for further infections.
Following the first recurrence, up to two-thirds of patients may experience a subsequent recurrence. Antibiotics used to treat CDI may contribute to a cycle of recurrence by altering the gut flora. The administration of fecal microbiota helps restore the gut flora to prevent further episodes of CDI.
Rebyota is a microbiota-based live biotherapeutic prepared from human stool collected from prescreened, qualified donors. It comes prepackaged in a single dose that is administered rectally.
The safety and efficacy of Rebyota were assessed in five clinical trials with more than 1,000 participants, the company notes in a press release.
In one trial, following a standard course of antibiotics, a one-time treatment with Rebyota was successful for three-quarters of participants at 8 weeks.
The treatment also prevented additional bouts; 84% of these initial responders remaining free of CDI at 6 months.
Two-thirds of participants reported treatment-emergent adverse events. Most events were mild to moderate in severity. Diarrhea and abdominal pain were the most common.
The data, from the ongoing PUNCH CD3-OLS study, were presented in October at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology and were published simultaneously in the journal Drugs.
“This is a positive adjunct to our current therapies for C. difficile in terms of trying to knock it out once a standard course of antibiotics has been administered,” Lisa Malter, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor of medicine at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
Dr. Malter acknowledged that because it’s delivered rectally, there could be “some hesitation” on the patient’s part to undergo the therapy.
However, C. difficile can be “excruciating” for patients, and they “may be more than willing to take [this agent] because it gets them feeling better,” Dr. Malter said.
Full prescribing information for Rebyota is available online.
Dr. Malter reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rebyota (fecal microbiota, live-jslm), from Ferring Pharmaceuticals, is intended for use after an individual has completed antibiotic treatment for recurrent CDI. It is not indicated for the first occurrence of CDI.
“Recurrent CDI impacts an individual’s quality of life and can also potentially be life-threatening,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director, FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a statement announcing approval.
As the first FDA-approved fecal microbiota product, this approval “represents an important milestone, as it provides an additional approved option to prevent recurrent CDI,” Dr. Marks added.
A panel of FDA advisors recommended approval of Rebyota in September.
The application for Rebyota received priority review and had orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designation.
A vicious cycle
Treatment options for recurrent CDI are limited. It’s been estimated that up to one-third of CDI cases recur, and people who suffer a recurrent bout of CDI are at a significantly higher risk for further infections.
Following the first recurrence, up to two-thirds of patients may experience a subsequent recurrence. Antibiotics used to treat CDI may contribute to a cycle of recurrence by altering the gut flora. The administration of fecal microbiota helps restore the gut flora to prevent further episodes of CDI.
Rebyota is a microbiota-based live biotherapeutic prepared from human stool collected from prescreened, qualified donors. It comes prepackaged in a single dose that is administered rectally.
The safety and efficacy of Rebyota were assessed in five clinical trials with more than 1,000 participants, the company notes in a press release.
In one trial, following a standard course of antibiotics, a one-time treatment with Rebyota was successful for three-quarters of participants at 8 weeks.
The treatment also prevented additional bouts; 84% of these initial responders remaining free of CDI at 6 months.
Two-thirds of participants reported treatment-emergent adverse events. Most events were mild to moderate in severity. Diarrhea and abdominal pain were the most common.
The data, from the ongoing PUNCH CD3-OLS study, were presented in October at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology and were published simultaneously in the journal Drugs.
“This is a positive adjunct to our current therapies for C. difficile in terms of trying to knock it out once a standard course of antibiotics has been administered,” Lisa Malter, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor of medicine at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
Dr. Malter acknowledged that because it’s delivered rectally, there could be “some hesitation” on the patient’s part to undergo the therapy.
However, C. difficile can be “excruciating” for patients, and they “may be more than willing to take [this agent] because it gets them feeling better,” Dr. Malter said.
Full prescribing information for Rebyota is available online.
Dr. Malter reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rebyota (fecal microbiota, live-jslm), from Ferring Pharmaceuticals, is intended for use after an individual has completed antibiotic treatment for recurrent CDI. It is not indicated for the first occurrence of CDI.
“Recurrent CDI impacts an individual’s quality of life and can also potentially be life-threatening,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director, FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a statement announcing approval.
As the first FDA-approved fecal microbiota product, this approval “represents an important milestone, as it provides an additional approved option to prevent recurrent CDI,” Dr. Marks added.
A panel of FDA advisors recommended approval of Rebyota in September.
The application for Rebyota received priority review and had orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designation.
A vicious cycle
Treatment options for recurrent CDI are limited. It’s been estimated that up to one-third of CDI cases recur, and people who suffer a recurrent bout of CDI are at a significantly higher risk for further infections.
Following the first recurrence, up to two-thirds of patients may experience a subsequent recurrence. Antibiotics used to treat CDI may contribute to a cycle of recurrence by altering the gut flora. The administration of fecal microbiota helps restore the gut flora to prevent further episodes of CDI.
Rebyota is a microbiota-based live biotherapeutic prepared from human stool collected from prescreened, qualified donors. It comes prepackaged in a single dose that is administered rectally.
The safety and efficacy of Rebyota were assessed in five clinical trials with more than 1,000 participants, the company notes in a press release.
In one trial, following a standard course of antibiotics, a one-time treatment with Rebyota was successful for three-quarters of participants at 8 weeks.
The treatment also prevented additional bouts; 84% of these initial responders remaining free of CDI at 6 months.
Two-thirds of participants reported treatment-emergent adverse events. Most events were mild to moderate in severity. Diarrhea and abdominal pain were the most common.
The data, from the ongoing PUNCH CD3-OLS study, were presented in October at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology and were published simultaneously in the journal Drugs.
“This is a positive adjunct to our current therapies for C. difficile in terms of trying to knock it out once a standard course of antibiotics has been administered,” Lisa Malter, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor of medicine at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
Dr. Malter acknowledged that because it’s delivered rectally, there could be “some hesitation” on the patient’s part to undergo the therapy.
However, C. difficile can be “excruciating” for patients, and they “may be more than willing to take [this agent] because it gets them feeling better,” Dr. Malter said.
Full prescribing information for Rebyota is available online.
Dr. Malter reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. flu activity already at mid-season levels
according to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, 6% of all outpatient visits were because of flu or flu-like illness for the week of Nov. 13-19, up from 5.8% the previous week, the CDC’s Influenza Division said in its weekly FluView report.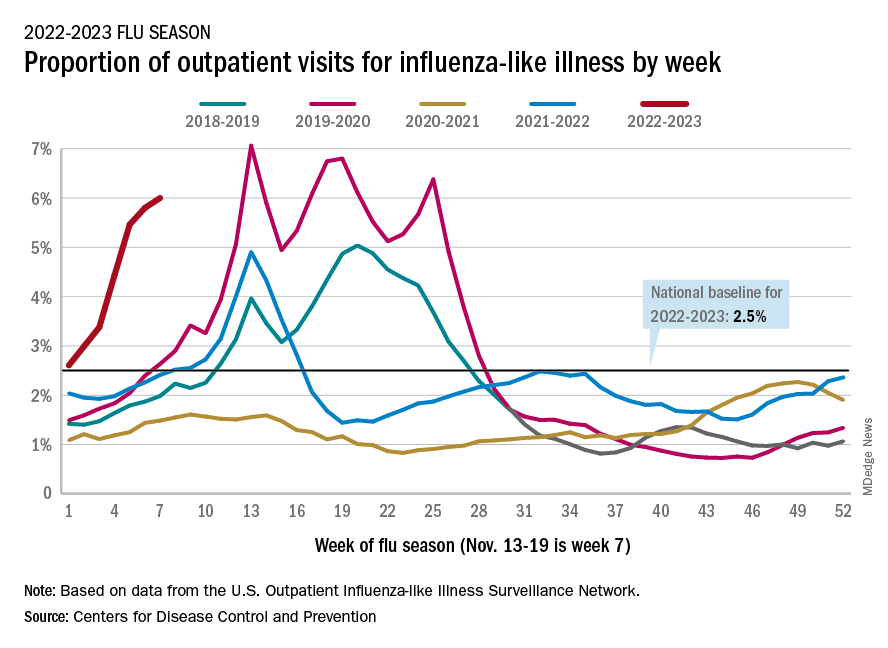
Those figures are the highest recorded in November since 2009, but the peak of the 2009-10 flu season occurred even earlier – the week of Oct. 18-24 – and the rate of flu-like illness had already dropped to just over 4.0% by Nov. 15-21 that year and continued to drop thereafter.
Although COVID-19 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are included in the data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the agency did note that “seasonal influenza activity is elevated across the country” and estimated that “there have been at least 6.2 million illnesses, 53,000 hospitalizations, and 2,900 deaths from flu” during the 2022-23 season.
Total flu deaths include 11 reported in children as of Nov. 19, and children ages 0-4 had a higher proportion of visits for flu like-illness than other age groups.
The agency also said the cumulative hospitalization rate of 11.3 per 100,000 population “is higher than the rate observed in [the corresponding week of] every previous season since 2010-2011.” Adults 65 years and older have the highest cumulative rate, 25.9 per 100,000, for this year, compared with 20.7 for children 0-4; 11.1 for adults 50-64; 10.3 for children 5-17; and 5.6 for adults 18-49 years old, the CDC said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, 6% of all outpatient visits were because of flu or flu-like illness for the week of Nov. 13-19, up from 5.8% the previous week, the CDC’s Influenza Division said in its weekly FluView report.
Those figures are the highest recorded in November since 2009, but the peak of the 2009-10 flu season occurred even earlier – the week of Oct. 18-24 – and the rate of flu-like illness had already dropped to just over 4.0% by Nov. 15-21 that year and continued to drop thereafter.
Although COVID-19 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are included in the data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the agency did note that “seasonal influenza activity is elevated across the country” and estimated that “there have been at least 6.2 million illnesses, 53,000 hospitalizations, and 2,900 deaths from flu” during the 2022-23 season.
Total flu deaths include 11 reported in children as of Nov. 19, and children ages 0-4 had a higher proportion of visits for flu like-illness than other age groups.
The agency also said the cumulative hospitalization rate of 11.3 per 100,000 population “is higher than the rate observed in [the corresponding week of] every previous season since 2010-2011.” Adults 65 years and older have the highest cumulative rate, 25.9 per 100,000, for this year, compared with 20.7 for children 0-4; 11.1 for adults 50-64; 10.3 for children 5-17; and 5.6 for adults 18-49 years old, the CDC said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, 6% of all outpatient visits were because of flu or flu-like illness for the week of Nov. 13-19, up from 5.8% the previous week, the CDC’s Influenza Division said in its weekly FluView report.
Those figures are the highest recorded in November since 2009, but the peak of the 2009-10 flu season occurred even earlier – the week of Oct. 18-24 – and the rate of flu-like illness had already dropped to just over 4.0% by Nov. 15-21 that year and continued to drop thereafter.
Although COVID-19 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are included in the data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the agency did note that “seasonal influenza activity is elevated across the country” and estimated that “there have been at least 6.2 million illnesses, 53,000 hospitalizations, and 2,900 deaths from flu” during the 2022-23 season.
Total flu deaths include 11 reported in children as of Nov. 19, and children ages 0-4 had a higher proportion of visits for flu like-illness than other age groups.
The agency also said the cumulative hospitalization rate of 11.3 per 100,000 population “is higher than the rate observed in [the corresponding week of] every previous season since 2010-2011.” Adults 65 years and older have the highest cumulative rate, 25.9 per 100,000, for this year, compared with 20.7 for children 0-4; 11.1 for adults 50-64; 10.3 for children 5-17; and 5.6 for adults 18-49 years old, the CDC said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA alert: ‘Substantial’ hypocalcemia risk with denosumab use in dialysis patients
The Food and Drug Administration issued an alert on Nov. 22 that cited preliminary evidence for a “substantial risk” for severe and symptomatic hypocalcemia and serious outcomes related to abnormally low calcium levels in people being treated with dialysis and receiving the osteoporosis medication denosumab (Prolia), including hospitalization and death.
In its alert, the FDA advised clinicians to make sure that people on dialysis who receive Prolia ingest adequate calcium and vitamin D supplementation and undergo frequent blood calcium monitoring, “possibly more often than is already being conducted,” which “may help decrease the likelihood or severity of these risks.”
The agency also called on clinicians to “advise patients on dialysis to immediately seek help if they experience symptoms of hypocalcemia,” such as unusual tingling or numbness in the hands, arms, legs, or feet; painful muscle spasms or cramps; voice box or lung spasms causing difficulty breathing; vomiting; seizures; or irregular heart rhythm.
The FDA had a similar message for people being treated with dialysis who are also receiving Prolia. The alert advised patients to watch for these symptoms and to tell their health care provider if they occur. The agency also advised patients who are undergoing dialysis and receiving Prolia to not stop the agent on their own, without first discussing this step with their care provider.
The FDA also advised providers and patients to contact the agency about episodes of side effects from Prolia (or other medications) via the FDA’s MedWatch program.
Frequent and serious
The FDA explained it issued the alert because of “the frequency and seriousness” of the risk for hypocalcemia and resulting complications. The agency noted that the risk seems most acute for people on dialysis who also receive Prolia, but the risk may also extend to people with advanced kidney disease who are not being treated with hemodialysis.
The alert stemmed from “interim results” in an ongoing safety study of Prolia that the FDA required the agent’s manufacturer, Amgen, to run when the agency first approved denosumab for U.S. marketing in 2010. The FDA said its review of these interim results suggested an increased risk of hypocalcemia with Prolia in patients with advanced kidney disease.
In addition, adverse event reports submitted to the FDA suggested in a separate, internal study that patients on dialysis treated with Prolia are at “substantial risk for severe and symptomatic hypocalcemia, including hospitalization and death.”
The alert explained that “because of the frequency and seriousness of these risks, we are alerting healthcare professionals and patients about them and that we are continuing to evaluate this potential safety issue with Prolia use in patients with advanced kidney disease, particularly those on dialysis.” The FDA added that “we will communicate our final conclusions and recommendations when we have completed our review or have more information to share.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration issued an alert on Nov. 22 that cited preliminary evidence for a “substantial risk” for severe and symptomatic hypocalcemia and serious outcomes related to abnormally low calcium levels in people being treated with dialysis and receiving the osteoporosis medication denosumab (Prolia), including hospitalization and death.
In its alert, the FDA advised clinicians to make sure that people on dialysis who receive Prolia ingest adequate calcium and vitamin D supplementation and undergo frequent blood calcium monitoring, “possibly more often than is already being conducted,” which “may help decrease the likelihood or severity of these risks.”
The agency also called on clinicians to “advise patients on dialysis to immediately seek help if they experience symptoms of hypocalcemia,” such as unusual tingling or numbness in the hands, arms, legs, or feet; painful muscle spasms or cramps; voice box or lung spasms causing difficulty breathing; vomiting; seizures; or irregular heart rhythm.
The FDA had a similar message for people being treated with dialysis who are also receiving Prolia. The alert advised patients to watch for these symptoms and to tell their health care provider if they occur. The agency also advised patients who are undergoing dialysis and receiving Prolia to not stop the agent on their own, without first discussing this step with their care provider.
The FDA also advised providers and patients to contact the agency about episodes of side effects from Prolia (or other medications) via the FDA’s MedWatch program.
Frequent and serious
The FDA explained it issued the alert because of “the frequency and seriousness” of the risk for hypocalcemia and resulting complications. The agency noted that the risk seems most acute for people on dialysis who also receive Prolia, but the risk may also extend to people with advanced kidney disease who are not being treated with hemodialysis.
The alert stemmed from “interim results” in an ongoing safety study of Prolia that the FDA required the agent’s manufacturer, Amgen, to run when the agency first approved denosumab for U.S. marketing in 2010. The FDA said its review of these interim results suggested an increased risk of hypocalcemia with Prolia in patients with advanced kidney disease.
In addition, adverse event reports submitted to the FDA suggested in a separate, internal study that patients on dialysis treated with Prolia are at “substantial risk for severe and symptomatic hypocalcemia, including hospitalization and death.”
The alert explained that “because of the frequency and seriousness of these risks, we are alerting healthcare professionals and patients about them and that we are continuing to evaluate this potential safety issue with Prolia use in patients with advanced kidney disease, particularly those on dialysis.” The FDA added that “we will communicate our final conclusions and recommendations when we have completed our review or have more information to share.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration issued an alert on Nov. 22 that cited preliminary evidence for a “substantial risk” for severe and symptomatic hypocalcemia and serious outcomes related to abnormally low calcium levels in people being treated with dialysis and receiving the osteoporosis medication denosumab (Prolia), including hospitalization and death.
In its alert, the FDA advised clinicians to make sure that people on dialysis who receive Prolia ingest adequate calcium and vitamin D supplementation and undergo frequent blood calcium monitoring, “possibly more often than is already being conducted,” which “may help decrease the likelihood or severity of these risks.”
The agency also called on clinicians to “advise patients on dialysis to immediately seek help if they experience symptoms of hypocalcemia,” such as unusual tingling or numbness in the hands, arms, legs, or feet; painful muscle spasms or cramps; voice box or lung spasms causing difficulty breathing; vomiting; seizures; or irregular heart rhythm.
The FDA had a similar message for people being treated with dialysis who are also receiving Prolia. The alert advised patients to watch for these symptoms and to tell their health care provider if they occur. The agency also advised patients who are undergoing dialysis and receiving Prolia to not stop the agent on their own, without first discussing this step with their care provider.
The FDA also advised providers and patients to contact the agency about episodes of side effects from Prolia (or other medications) via the FDA’s MedWatch program.
Frequent and serious
The FDA explained it issued the alert because of “the frequency and seriousness” of the risk for hypocalcemia and resulting complications. The agency noted that the risk seems most acute for people on dialysis who also receive Prolia, but the risk may also extend to people with advanced kidney disease who are not being treated with hemodialysis.
The alert stemmed from “interim results” in an ongoing safety study of Prolia that the FDA required the agent’s manufacturer, Amgen, to run when the agency first approved denosumab for U.S. marketing in 2010. The FDA said its review of these interim results suggested an increased risk of hypocalcemia with Prolia in patients with advanced kidney disease.
In addition, adverse event reports submitted to the FDA suggested in a separate, internal study that patients on dialysis treated with Prolia are at “substantial risk for severe and symptomatic hypocalcemia, including hospitalization and death.”
The alert explained that “because of the frequency and seriousness of these risks, we are alerting healthcare professionals and patients about them and that we are continuing to evaluate this potential safety issue with Prolia use in patients with advanced kidney disease, particularly those on dialysis.” The FDA added that “we will communicate our final conclusions and recommendations when we have completed our review or have more information to share.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
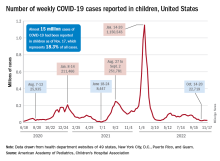
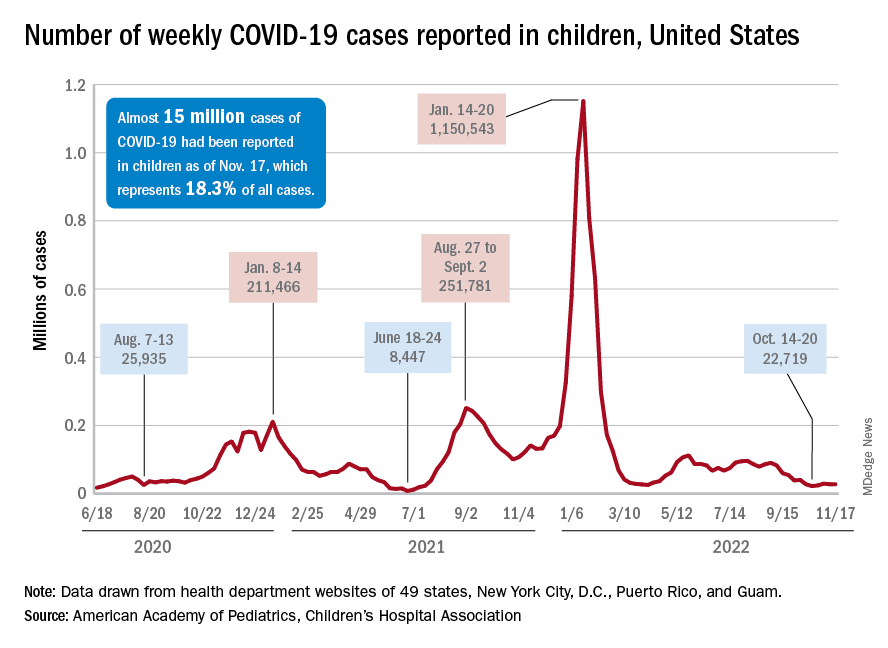
Children and COVID: Weekly cases maintain a low-level plateau
A less-than-1% decrease in weekly COVID-19 cases in children demonstrated continued stability in the pandemic situation as the nation heads into the holiday season.
the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in the latest edition of their joint COVID report.
New cases for the week of Nov. 11-17 totaled 27,899, down by 0.9% from the previous week and just 4 weeks removed from the lowest total of the year: 22,719 for Oct. 14-20. There have been just under 15 million cases of COVID-19 in children since the pandemic began, and children represent 18.3% of cases in all ages, the AAP and CHA reported.
Conditions look favorable for that plateau to continue, despite the upcoming holidays, White House COVID-19 coordinator Ashish Jha said recently. “We are in a very different place and we will remain in a different place,” Dr. Jha said, according to STAT News. “We are now at a point where I believe if you’re up to date on your vaccines, you have access to treatments ... there really should be no restrictions on people’s activities.”
One possible spoiler, an apparent spike in COVID-related hospitalizations in children we reported last week, seems to have been a false alarm. The rate of new admissions for Nov. 11, which preliminary data suggested was 0.48 per 100,000 population, has now been revised with more solid data to 0.20 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We continue to monitor the recent increases in admissions among children. Some of these may be admissions with COVID-19, not because of COVID-19. Co-infections are being noted in our surveillance systems for hospitalizations among children; as much as 10% of admissions or higher have viruses codetected (RSV, influenza, enterovirus/rhinovirus, and other respiratory viruses),” a CDC spokesperson told this news organization.
For children aged 0-17 years, the current 7-day (Nov. 13-19) average number of new admissions with confirmed COVID is 129 per day, down from 147 for the previous 7-day average. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, are largely holding steady. The latest 7-day averages available (Nov. 18) – 1.0% for children aged 0-11 years, 0.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds, and 0.8% in 16- to 17-year-olds – are the same or within a tenth of a percent of the rates recorded on Oct. 18, CDC data show.
New vaccinations for the week of Nov. 10-16 were down just slightly for children under age 5 years and for those aged 5-11 years, with a larger drop seen among 12- to 17-year-olds, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. So far, 7.9% of all children under age 5 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have 39.1% of 5 to 11-year-olds and 71.5% of those aged 12-17years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
A less-than-1% decrease in weekly COVID-19 cases in children demonstrated continued stability in the pandemic situation as the nation heads into the holiday season.
the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in the latest edition of their joint COVID report.
New cases for the week of Nov. 11-17 totaled 27,899, down by 0.9% from the previous week and just 4 weeks removed from the lowest total of the year: 22,719 for Oct. 14-20. There have been just under 15 million cases of COVID-19 in children since the pandemic began, and children represent 18.3% of cases in all ages, the AAP and CHA reported.
Conditions look favorable for that plateau to continue, despite the upcoming holidays, White House COVID-19 coordinator Ashish Jha said recently. “We are in a very different place and we will remain in a different place,” Dr. Jha said, according to STAT News. “We are now at a point where I believe if you’re up to date on your vaccines, you have access to treatments ... there really should be no restrictions on people’s activities.”
One possible spoiler, an apparent spike in COVID-related hospitalizations in children we reported last week, seems to have been a false alarm. The rate of new admissions for Nov. 11, which preliminary data suggested was 0.48 per 100,000 population, has now been revised with more solid data to 0.20 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We continue to monitor the recent increases in admissions among children. Some of these may be admissions with COVID-19, not because of COVID-19. Co-infections are being noted in our surveillance systems for hospitalizations among children; as much as 10% of admissions or higher have viruses codetected (RSV, influenza, enterovirus/rhinovirus, and other respiratory viruses),” a CDC spokesperson told this news organization.
For children aged 0-17 years, the current 7-day (Nov. 13-19) average number of new admissions with confirmed COVID is 129 per day, down from 147 for the previous 7-day average. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, are largely holding steady. The latest 7-day averages available (Nov. 18) – 1.0% for children aged 0-11 years, 0.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds, and 0.8% in 16- to 17-year-olds – are the same or within a tenth of a percent of the rates recorded on Oct. 18, CDC data show.
New vaccinations for the week of Nov. 10-16 were down just slightly for children under age 5 years and for those aged 5-11 years, with a larger drop seen among 12- to 17-year-olds, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. So far, 7.9% of all children under age 5 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have 39.1% of 5 to 11-year-olds and 71.5% of those aged 12-17years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
A less-than-1% decrease in weekly COVID-19 cases in children demonstrated continued stability in the pandemic situation as the nation heads into the holiday season.
the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in the latest edition of their joint COVID report.
New cases for the week of Nov. 11-17 totaled 27,899, down by 0.9% from the previous week and just 4 weeks removed from the lowest total of the year: 22,719 for Oct. 14-20. There have been just under 15 million cases of COVID-19 in children since the pandemic began, and children represent 18.3% of cases in all ages, the AAP and CHA reported.
Conditions look favorable for that plateau to continue, despite the upcoming holidays, White House COVID-19 coordinator Ashish Jha said recently. “We are in a very different place and we will remain in a different place,” Dr. Jha said, according to STAT News. “We are now at a point where I believe if you’re up to date on your vaccines, you have access to treatments ... there really should be no restrictions on people’s activities.”
One possible spoiler, an apparent spike in COVID-related hospitalizations in children we reported last week, seems to have been a false alarm. The rate of new admissions for Nov. 11, which preliminary data suggested was 0.48 per 100,000 population, has now been revised with more solid data to 0.20 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We continue to monitor the recent increases in admissions among children. Some of these may be admissions with COVID-19, not because of COVID-19. Co-infections are being noted in our surveillance systems for hospitalizations among children; as much as 10% of admissions or higher have viruses codetected (RSV, influenza, enterovirus/rhinovirus, and other respiratory viruses),” a CDC spokesperson told this news organization.
For children aged 0-17 years, the current 7-day (Nov. 13-19) average number of new admissions with confirmed COVID is 129 per day, down from 147 for the previous 7-day average. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, are largely holding steady. The latest 7-day averages available (Nov. 18) – 1.0% for children aged 0-11 years, 0.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds, and 0.8% in 16- to 17-year-olds – are the same or within a tenth of a percent of the rates recorded on Oct. 18, CDC data show.
New vaccinations for the week of Nov. 10-16 were down just slightly for children under age 5 years and for those aged 5-11 years, with a larger drop seen among 12- to 17-year-olds, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. So far, 7.9% of all children under age 5 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have 39.1% of 5 to 11-year-olds and 71.5% of those aged 12-17years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
FDA approves first-ever agent to delay type 1 diabetes onset
“Today’s approval of a first-in-class therapy adds an important new treatment option for certain at-risk patients,” said John Sharretts, MD, director of the Division of Diabetes, Lipid Disorders, and Obesity in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “The drug’s potential to delay clinical diagnosis of type 1 diabetes may provide patients with months to years without the burdens of disease.”
The agent, which interferes with T-cell-mediated autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells, is the first disease-modifying therapy for impeding progression of type 1 diabetes. It is administered by intravenous infusion once daily for 14 consecutive days.
The specific indication is “to delay the onset of stage 3 type 1 diabetes in adults and pediatric patients 8 years and older who currently have stage 2 type 1 diabetes.” In type 1 diabetes staging, adopted in 2015, stage 1 is defined as the presence of beta cell autoimmunity with two or more islet autoantibodies with normoglycemia, stage 2 is beta-cell autoimmunity with dysglycemia yet asymptomatic, and stage 3 is the onset of symptomatic type 1 diabetes.
Stage 2 type 1 diabetes is associated with a nearly 100% lifetime risk of progression to clinical (stage 3) type 1 diabetes and a 75% risk of developing the condition within 5 years.
The FDA had previously rejected teplizumab for this indication in July 2021, despite a prior endorsement from an advisory panel in May 2021.
Now, with the FDA approval, Provention Bio cofounder and CEO Ashleigh Palmer said in a statement, “This is a historic occasion for the T1D community and a paradigm shifting breakthrough ... It cannot be emphasized enough how precious a delay in the onset of stage 3 T1D can be from a patient and family perspective; more time to live without and, when necessary, prepare for the burdens, complications, and risks associated with stage 3 disease.”
T1D onset delayed by 2 years
In 2019, a pivotal phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled trial involving 76 at-risk children and adults aged 8 years and older showed that a single 14-day treatment of daily intravenous infusions of teplizumab in 44 patients resulted in a significant median 2-year delay to onset of clinical type 1 diabetes compared with 32 who received placebo.
Those “game changer” data were presented at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) annual meeting in June 2019 and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Three-year data were presented at the June 2020 ADA meeting and published in March 2021 in Science Translational Medicine, by Emily K. Sims, MD, department of pediatrics, Indiana University, Indianapolis, and colleagues.
At a median follow-up of 923 days, 50% of those randomly assigned to teplizumab remained diabetes free, compared with 22% of those who received placebo infusions (hazard ratio, 0.457; P = .01). The teplizumab group had a greater average C-peptide area under the curve compared with placebo, reflecting improved beta-cell function (1.96 vs. 1.68 pmol/mL; P = .006).
C-peptide levels declined over time in the placebo group but stabilized in those receiving teplizumab (P = .0015).
“The mid-range time from randomization to stage 3 type 1 diabetes diagnosis was 50 months for the patients who received Tzield and 25 months for those who received a placebo. This represents a statistically significant delay in the development of stage 3 type 1 diabetes,” according to the FDA statement.
The most common side effects of Tzield include lymphopenia (73% teplizumab vs. 6% placebo), rash (36% vs. 0%), leukopenia (221% vs. 0%), and headache (11% vs. 6%). Label warnings and precautions include monitoring for cytokine release syndrome, risk for serious infections, and avoidance of live, inactivated, and mRNA vaccines.
This approval is likely to accelerate discussion about universal autoantibody screening. Currently, most individuals identified as having preclinical type 1 diabetes are first-degree relatives of people with type 1 diabetes identified through the federally funded TrialNet program. In December 2020, the type 1 diabetes research and advocacy organization JDRF began offering a $55 home blood test to screen for the antibodies, and other screening programs have been launched in the United States and Europe.
Previous studies have examined cost-effectiveness of universal screening in children and the optimal ages that such screening should take place.
In October, Provention Bio announced a co-promotion agreement with Sanofi for the U.S. launch of Tzield for delay in onset of clinical T1D in at-risk individuals. Provention Bio offers financial assistance options (e.g., copay assistance) to eligible patients for out-of-pocket costs.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Today’s approval of a first-in-class therapy adds an important new treatment option for certain at-risk patients,” said John Sharretts, MD, director of the Division of Diabetes, Lipid Disorders, and Obesity in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “The drug’s potential to delay clinical diagnosis of type 1 diabetes may provide patients with months to years without the burdens of disease.”
The agent, which interferes with T-cell-mediated autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells, is the first disease-modifying therapy for impeding progression of type 1 diabetes. It is administered by intravenous infusion once daily for 14 consecutive days.
The specific indication is “to delay the onset of stage 3 type 1 diabetes in adults and pediatric patients 8 years and older who currently have stage 2 type 1 diabetes.” In type 1 diabetes staging, adopted in 2015, stage 1 is defined as the presence of beta cell autoimmunity with two or more islet autoantibodies with normoglycemia, stage 2 is beta-cell autoimmunity with dysglycemia yet asymptomatic, and stage 3 is the onset of symptomatic type 1 diabetes.
Stage 2 type 1 diabetes is associated with a nearly 100% lifetime risk of progression to clinical (stage 3) type 1 diabetes and a 75% risk of developing the condition within 5 years.
The FDA had previously rejected teplizumab for this indication in July 2021, despite a prior endorsement from an advisory panel in May 2021.
Now, with the FDA approval, Provention Bio cofounder and CEO Ashleigh Palmer said in a statement, “This is a historic occasion for the T1D community and a paradigm shifting breakthrough ... It cannot be emphasized enough how precious a delay in the onset of stage 3 T1D can be from a patient and family perspective; more time to live without and, when necessary, prepare for the burdens, complications, and risks associated with stage 3 disease.”
T1D onset delayed by 2 years
In 2019, a pivotal phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled trial involving 76 at-risk children and adults aged 8 years and older showed that a single 14-day treatment of daily intravenous infusions of teplizumab in 44 patients resulted in a significant median 2-year delay to onset of clinical type 1 diabetes compared with 32 who received placebo.
Those “game changer” data were presented at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) annual meeting in June 2019 and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Three-year data were presented at the June 2020 ADA meeting and published in March 2021 in Science Translational Medicine, by Emily K. Sims, MD, department of pediatrics, Indiana University, Indianapolis, and colleagues.
At a median follow-up of 923 days, 50% of those randomly assigned to teplizumab remained diabetes free, compared with 22% of those who received placebo infusions (hazard ratio, 0.457; P = .01). The teplizumab group had a greater average C-peptide area under the curve compared with placebo, reflecting improved beta-cell function (1.96 vs. 1.68 pmol/mL; P = .006).
C-peptide levels declined over time in the placebo group but stabilized in those receiving teplizumab (P = .0015).
“The mid-range time from randomization to stage 3 type 1 diabetes diagnosis was 50 months for the patients who received Tzield and 25 months for those who received a placebo. This represents a statistically significant delay in the development of stage 3 type 1 diabetes,” according to the FDA statement.
The most common side effects of Tzield include lymphopenia (73% teplizumab vs. 6% placebo), rash (36% vs. 0%), leukopenia (221% vs. 0%), and headache (11% vs. 6%). Label warnings and precautions include monitoring for cytokine release syndrome, risk for serious infections, and avoidance of live, inactivated, and mRNA vaccines.
This approval is likely to accelerate discussion about universal autoantibody screening. Currently, most individuals identified as having preclinical type 1 diabetes are first-degree relatives of people with type 1 diabetes identified through the federally funded TrialNet program. In December 2020, the type 1 diabetes research and advocacy organization JDRF began offering a $55 home blood test to screen for the antibodies, and other screening programs have been launched in the United States and Europe.
Previous studies have examined cost-effectiveness of universal screening in children and the optimal ages that such screening should take place.
In October, Provention Bio announced a co-promotion agreement with Sanofi for the U.S. launch of Tzield for delay in onset of clinical T1D in at-risk individuals. Provention Bio offers financial assistance options (e.g., copay assistance) to eligible patients for out-of-pocket costs.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Today’s approval of a first-in-class therapy adds an important new treatment option for certain at-risk patients,” said John Sharretts, MD, director of the Division of Diabetes, Lipid Disorders, and Obesity in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “The drug’s potential to delay clinical diagnosis of type 1 diabetes may provide patients with months to years without the burdens of disease.”
The agent, which interferes with T-cell-mediated autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells, is the first disease-modifying therapy for impeding progression of type 1 diabetes. It is administered by intravenous infusion once daily for 14 consecutive days.
The specific indication is “to delay the onset of stage 3 type 1 diabetes in adults and pediatric patients 8 years and older who currently have stage 2 type 1 diabetes.” In type 1 diabetes staging, adopted in 2015, stage 1 is defined as the presence of beta cell autoimmunity with two or more islet autoantibodies with normoglycemia, stage 2 is beta-cell autoimmunity with dysglycemia yet asymptomatic, and stage 3 is the onset of symptomatic type 1 diabetes.
Stage 2 type 1 diabetes is associated with a nearly 100% lifetime risk of progression to clinical (stage 3) type 1 diabetes and a 75% risk of developing the condition within 5 years.
The FDA had previously rejected teplizumab for this indication in July 2021, despite a prior endorsement from an advisory panel in May 2021.
Now, with the FDA approval, Provention Bio cofounder and CEO Ashleigh Palmer said in a statement, “This is a historic occasion for the T1D community and a paradigm shifting breakthrough ... It cannot be emphasized enough how precious a delay in the onset of stage 3 T1D can be from a patient and family perspective; more time to live without and, when necessary, prepare for the burdens, complications, and risks associated with stage 3 disease.”
T1D onset delayed by 2 years
In 2019, a pivotal phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled trial involving 76 at-risk children and adults aged 8 years and older showed that a single 14-day treatment of daily intravenous infusions of teplizumab in 44 patients resulted in a significant median 2-year delay to onset of clinical type 1 diabetes compared with 32 who received placebo.
Those “game changer” data were presented at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) annual meeting in June 2019 and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Three-year data were presented at the June 2020 ADA meeting and published in March 2021 in Science Translational Medicine, by Emily K. Sims, MD, department of pediatrics, Indiana University, Indianapolis, and colleagues.
At a median follow-up of 923 days, 50% of those randomly assigned to teplizumab remained diabetes free, compared with 22% of those who received placebo infusions (hazard ratio, 0.457; P = .01). The teplizumab group had a greater average C-peptide area under the curve compared with placebo, reflecting improved beta-cell function (1.96 vs. 1.68 pmol/mL; P = .006).
C-peptide levels declined over time in the placebo group but stabilized in those receiving teplizumab (P = .0015).
“The mid-range time from randomization to stage 3 type 1 diabetes diagnosis was 50 months for the patients who received Tzield and 25 months for those who received a placebo. This represents a statistically significant delay in the development of stage 3 type 1 diabetes,” according to the FDA statement.
The most common side effects of Tzield include lymphopenia (73% teplizumab vs. 6% placebo), rash (36% vs. 0%), leukopenia (221% vs. 0%), and headache (11% vs. 6%). Label warnings and precautions include monitoring for cytokine release syndrome, risk for serious infections, and avoidance of live, inactivated, and mRNA vaccines.
This approval is likely to accelerate discussion about universal autoantibody screening. Currently, most individuals identified as having preclinical type 1 diabetes are first-degree relatives of people with type 1 diabetes identified through the federally funded TrialNet program. In December 2020, the type 1 diabetes research and advocacy organization JDRF began offering a $55 home blood test to screen for the antibodies, and other screening programs have been launched in the United States and Europe.
Previous studies have examined cost-effectiveness of universal screening in children and the optimal ages that such screening should take place.
In October, Provention Bio announced a co-promotion agreement with Sanofi for the U.S. launch of Tzield for delay in onset of clinical T1D in at-risk individuals. Provention Bio offers financial assistance options (e.g., copay assistance) to eligible patients for out-of-pocket costs.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Weekly cases continue to hold fairly steady
The incidence of new COVID-19 cases in children seems to have stabilized as the national count remained under 30,000 for the fifth consecutive week, but hospitalization data may indicate some possible turbulence.
Just over 28,000 pediatric cases were reported during the week of Nov. 4-10, a drop of 5.4% from the previous week, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report involving data from state and territorial health departments, several of which are no longer updating their websites.
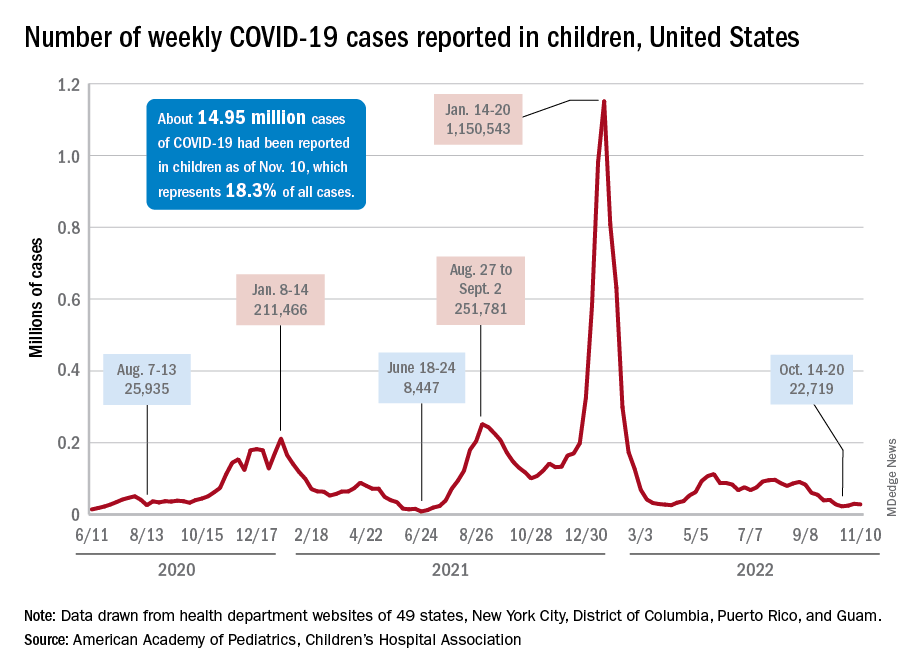
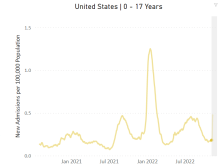
The stability in weekly cases, however, comes in contrast to a very recent and considerable increase in new hospital admissions of children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID-19. That rate, which was 0.18 hospitalizations per 100,000 population on Nov. 7 and 0.19 per 100,000 on Nov. 8 and 9, jumped all the way to 0.34 on Nov. 10 and 0.48 on Nov. 11, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That is the highest rate since the closing days of the Omicron surge in February.
The rate for Nov. 12, the most recent one available, was down slightly to 0.47 admissions per 100,000. There doesn’t seem to be any evidence in the CDC’s data of a similar sudden increase in new hospitalizations among any other age group, and no age group, including children, shows any sign of a recent increase in emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID. (The CDC has not yet responded to our inquiry about this development.)
The two most recent 7-day averages for new admissions in children aged 0-17 show a small increase, but they cover the periods of Oct. 15 to Oct. 31, when there were 126 admissions per day, and Nov. 1 to Nov. 7, when the average went up to 133 per day, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The CDC does not publish a weekly count of new COVID cases, but its latest data on the rate of incident cases seem to agree with the AAP/CHA figures: A gradual decline in all age groups, including children, since the beginning of September.
Vaccinations, on the other hand, bucked their recent trend and increased in the last week. About 43,000 children under age 5 years received their initial dose of COVID vaccine during Nov. 3-9, compared with 30,000 and 33,000 the 2 previous weeks, while 5- to 11-year-olds hit their highest weekly mark (31,000) since late August and 12- to 17-year-olds had their biggest week (27,000) since mid-August, the AAP reported based on CDC data.
The incidence of new COVID-19 cases in children seems to have stabilized as the national count remained under 30,000 for the fifth consecutive week, but hospitalization data may indicate some possible turbulence.
Just over 28,000 pediatric cases were reported during the week of Nov. 4-10, a drop of 5.4% from the previous week, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report involving data from state and territorial health departments, several of which are no longer updating their websites.

The stability in weekly cases, however, comes in contrast to a very recent and considerable increase in new hospital admissions of children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID-19. That rate, which was 0.18 hospitalizations per 100,000 population on Nov. 7 and 0.19 per 100,000 on Nov. 8 and 9, jumped all the way to 0.34 on Nov. 10 and 0.48 on Nov. 11, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That is the highest rate since the closing days of the Omicron surge in February.
The rate for Nov. 12, the most recent one available, was down slightly to 0.47 admissions per 100,000. There doesn’t seem to be any evidence in the CDC’s data of a similar sudden increase in new hospitalizations among any other age group, and no age group, including children, shows any sign of a recent increase in emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID. (The CDC has not yet responded to our inquiry about this development.)
The two most recent 7-day averages for new admissions in children aged 0-17 show a small increase, but they cover the periods of Oct. 15 to Oct. 31, when there were 126 admissions per day, and Nov. 1 to Nov. 7, when the average went up to 133 per day, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The CDC does not publish a weekly count of new COVID cases, but its latest data on the rate of incident cases seem to agree with the AAP/CHA figures: A gradual decline in all age groups, including children, since the beginning of September.
Vaccinations, on the other hand, bucked their recent trend and increased in the last week. About 43,000 children under age 5 years received their initial dose of COVID vaccine during Nov. 3-9, compared with 30,000 and 33,000 the 2 previous weeks, while 5- to 11-year-olds hit their highest weekly mark (31,000) since late August and 12- to 17-year-olds had their biggest week (27,000) since mid-August, the AAP reported based on CDC data.
The incidence of new COVID-19 cases in children seems to have stabilized as the national count remained under 30,000 for the fifth consecutive week, but hospitalization data may indicate some possible turbulence.
Just over 28,000 pediatric cases were reported during the week of Nov. 4-10, a drop of 5.4% from the previous week, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report involving data from state and territorial health departments, several of which are no longer updating their websites.

The stability in weekly cases, however, comes in contrast to a very recent and considerable increase in new hospital admissions of children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID-19. That rate, which was 0.18 hospitalizations per 100,000 population on Nov. 7 and 0.19 per 100,000 on Nov. 8 and 9, jumped all the way to 0.34 on Nov. 10 and 0.48 on Nov. 11, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That is the highest rate since the closing days of the Omicron surge in February.
The rate for Nov. 12, the most recent one available, was down slightly to 0.47 admissions per 100,000. There doesn’t seem to be any evidence in the CDC’s data of a similar sudden increase in new hospitalizations among any other age group, and no age group, including children, shows any sign of a recent increase in emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID. (The CDC has not yet responded to our inquiry about this development.)
The two most recent 7-day averages for new admissions in children aged 0-17 show a small increase, but they cover the periods of Oct. 15 to Oct. 31, when there were 126 admissions per day, and Nov. 1 to Nov. 7, when the average went up to 133 per day, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The CDC does not publish a weekly count of new COVID cases, but its latest data on the rate of incident cases seem to agree with the AAP/CHA figures: A gradual decline in all age groups, including children, since the beginning of September.
Vaccinations, on the other hand, bucked their recent trend and increased in the last week. About 43,000 children under age 5 years received their initial dose of COVID vaccine during Nov. 3-9, compared with 30,000 and 33,000 the 2 previous weeks, while 5- to 11-year-olds hit their highest weekly mark (31,000) since late August and 12- to 17-year-olds had their biggest week (27,000) since mid-August, the AAP reported based on CDC data.
Children and COVID: New cases increase for second straight week
New COVID-19 cases rose among U.S. children for the second consecutive week, while hospitals saw signs of renewed activity on the part of SARS-CoV-2.
, when the count fell to its lowest level in more than a year, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their joint report.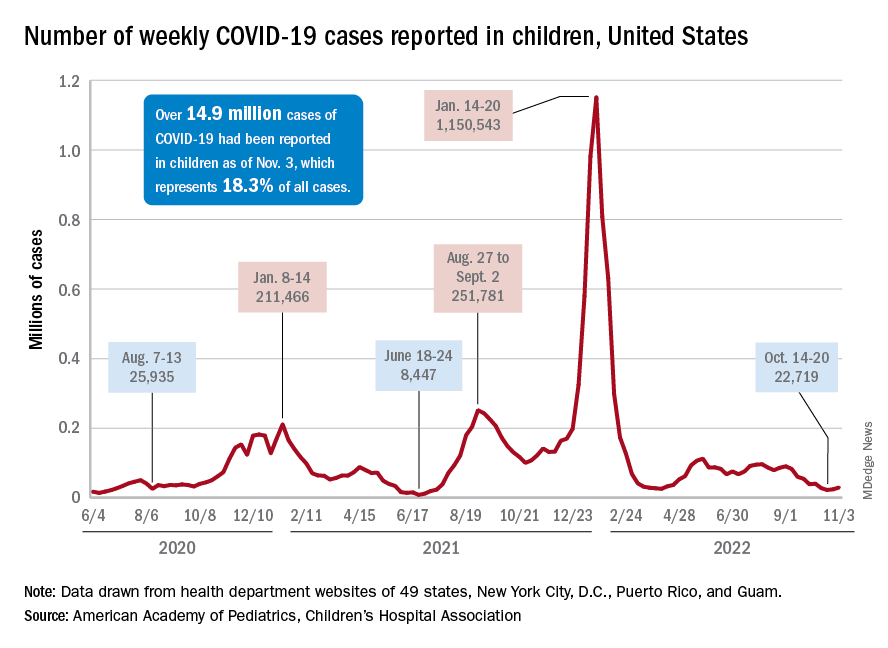
The 7-day average for ED visits with diagnosed COVID was down to just 0.6% of all ED visits for 12- to 15-year-olds as late as Oct. 23 but has moved up to 0.7% since then. Among those aged 16-17 years, the 7-day average was also down to 0.6% for just one day, Oct. 19, but was up to 0.8% as of Nov. 4. So far, though, a similar increase has not yet occurred for ED visits among children aged 0-11 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The trend is discernible, however, when looking at hospitalizations of children with confirmed COVID. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 years was 0.16 per 100,000 population as late as Oct. 23 but ticked up a notch after that and has been 0.17 per 100,000 since, according to the CDC. As with the ED rate, hospitalizations had been steadily declining since late August.
Vaccine initiation continues to slow
During the week of Oct. 27 to Nov. 2, about 30,000 children under 5 years of age received their initial COVID vaccination. A month earlier (Sept. 29 to Oct. 5), that number was about 40,000. A month before that, about 53,000 children aged 0-5 years received their initial dose, the AAP said in a separate vaccination report based on CDC data.
All of that reduced interest adds up to 7.4% of the age group having received at least one dose and just 3.2% being fully vaccinated as of Nov. 2. Among children aged 5-11 years, the corresponding vaccination rates are 38.9% and 31.8%, while those aged 12-17 years are at 71.3% and 61.1%, the CDC said.
Looking at just the first 20 weeks of the vaccination experience for each age group shows that 1.6 million children under 5 years of age had received at least an initial dose, compared with 8.1 million children aged 5-11 years and 8.1 million children aged 12-15, the AAP said.
New COVID-19 cases rose among U.S. children for the second consecutive week, while hospitals saw signs of renewed activity on the part of SARS-CoV-2.
, when the count fell to its lowest level in more than a year, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their joint report.
The 7-day average for ED visits with diagnosed COVID was down to just 0.6% of all ED visits for 12- to 15-year-olds as late as Oct. 23 but has moved up to 0.7% since then. Among those aged 16-17 years, the 7-day average was also down to 0.6% for just one day, Oct. 19, but was up to 0.8% as of Nov. 4. So far, though, a similar increase has not yet occurred for ED visits among children aged 0-11 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The trend is discernible, however, when looking at hospitalizations of children with confirmed COVID. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 years was 0.16 per 100,000 population as late as Oct. 23 but ticked up a notch after that and has been 0.17 per 100,000 since, according to the CDC. As with the ED rate, hospitalizations had been steadily declining since late August.
Vaccine initiation continues to slow
During the week of Oct. 27 to Nov. 2, about 30,000 children under 5 years of age received their initial COVID vaccination. A month earlier (Sept. 29 to Oct. 5), that number was about 40,000. A month before that, about 53,000 children aged 0-5 years received their initial dose, the AAP said in a separate vaccination report based on CDC data.
All of that reduced interest adds up to 7.4% of the age group having received at least one dose and just 3.2% being fully vaccinated as of Nov. 2. Among children aged 5-11 years, the corresponding vaccination rates are 38.9% and 31.8%, while those aged 12-17 years are at 71.3% and 61.1%, the CDC said.
Looking at just the first 20 weeks of the vaccination experience for each age group shows that 1.6 million children under 5 years of age had received at least an initial dose, compared with 8.1 million children aged 5-11 years and 8.1 million children aged 12-15, the AAP said.
New COVID-19 cases rose among U.S. children for the second consecutive week, while hospitals saw signs of renewed activity on the part of SARS-CoV-2.
, when the count fell to its lowest level in more than a year, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their joint report.
The 7-day average for ED visits with diagnosed COVID was down to just 0.6% of all ED visits for 12- to 15-year-olds as late as Oct. 23 but has moved up to 0.7% since then. Among those aged 16-17 years, the 7-day average was also down to 0.6% for just one day, Oct. 19, but was up to 0.8% as of Nov. 4. So far, though, a similar increase has not yet occurred for ED visits among children aged 0-11 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The trend is discernible, however, when looking at hospitalizations of children with confirmed COVID. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 years was 0.16 per 100,000 population as late as Oct. 23 but ticked up a notch after that and has been 0.17 per 100,000 since, according to the CDC. As with the ED rate, hospitalizations had been steadily declining since late August.
Vaccine initiation continues to slow
During the week of Oct. 27 to Nov. 2, about 30,000 children under 5 years of age received their initial COVID vaccination. A month earlier (Sept. 29 to Oct. 5), that number was about 40,000. A month before that, about 53,000 children aged 0-5 years received their initial dose, the AAP said in a separate vaccination report based on CDC data.
All of that reduced interest adds up to 7.4% of the age group having received at least one dose and just 3.2% being fully vaccinated as of Nov. 2. Among children aged 5-11 years, the corresponding vaccination rates are 38.9% and 31.8%, while those aged 12-17 years are at 71.3% and 61.1%, the CDC said.
Looking at just the first 20 weeks of the vaccination experience for each age group shows that 1.6 million children under 5 years of age had received at least an initial dose, compared with 8.1 million children aged 5-11 years and 8.1 million children aged 12-15, the AAP said.
FDA puts REMS requirements on hold to ensure continuity of care
In a Nov. 2 notice on its website, the FDA said it is aware that health care professionals and patients continue to experience ongoing difficulties with the clozapine REMS program, including issues with patient access to clozapine following discharge from inpatient care.
A chief concern is that inpatient pharmacies are only allowed to dispense a 7-days’ supply of clozapine to the patient upon discharge.
To address this issue, the FDA said it will now (temporarily) not object if inpatient pharmacies dispense a days’ supply of clozapine that aligns with the patient’s monitoring frequency.
For example, a 7-days’ supply for weekly monitoring, a 14-days’ supply for twice-monthly monitoring, and a 30-days’ supply for monthly monitoring upon discharge from an inpatient facility.
Clozapine is a second-generation (atypical) antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia that is not well controlled with standard antipsychotics.
While clozapine can be highly effective in some patients, it also carries serious risks, including a decrease in neutrophil count, which can lead to severe neutropenia, serious infections, and death.
As a result, those taking the drug must undergo regular absolute neutrophil count monitoring. Clozapine REMS is intended to maximize the benefits of the drug and minimize risk.
The FDA says it will continue to exercise earlier enforcement discretion regarding the clozapine REMS program announced back in November 2021. This includes allowing pharmacists to dispense clozapine without a REMS dispense authorization and allowing wholesalers to ship clozapine to pharmacies and health care settings without confirming enrollment in the REMS.
“We understand that difficulties with the clozapine REMS program have caused frustration and have led to problems with patient access to clozapine. FDA takes these concerns seriously. Continuity of care, patient access to clozapine, and patient safety are our highest priorities,” the FDA says.
The agency is working closely with the clozapine REMS program administrators to address these challenges and avoid interruptions in patient care.
The FDA encourages pharmacists and prescribers to continue working with the clozapine REMS to complete certification and prescribers to enroll patients in the program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a Nov. 2 notice on its website, the FDA said it is aware that health care professionals and patients continue to experience ongoing difficulties with the clozapine REMS program, including issues with patient access to clozapine following discharge from inpatient care.
A chief concern is that inpatient pharmacies are only allowed to dispense a 7-days’ supply of clozapine to the patient upon discharge.
To address this issue, the FDA said it will now (temporarily) not object if inpatient pharmacies dispense a days’ supply of clozapine that aligns with the patient’s monitoring frequency.
For example, a 7-days’ supply for weekly monitoring, a 14-days’ supply for twice-monthly monitoring, and a 30-days’ supply for monthly monitoring upon discharge from an inpatient facility.
Clozapine is a second-generation (atypical) antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia that is not well controlled with standard antipsychotics.
While clozapine can be highly effective in some patients, it also carries serious risks, including a decrease in neutrophil count, which can lead to severe neutropenia, serious infections, and death.
As a result, those taking the drug must undergo regular absolute neutrophil count monitoring. Clozapine REMS is intended to maximize the benefits of the drug and minimize risk.
The FDA says it will continue to exercise earlier enforcement discretion regarding the clozapine REMS program announced back in November 2021. This includes allowing pharmacists to dispense clozapine without a REMS dispense authorization and allowing wholesalers to ship clozapine to pharmacies and health care settings without confirming enrollment in the REMS.
“We understand that difficulties with the clozapine REMS program have caused frustration and have led to problems with patient access to clozapine. FDA takes these concerns seriously. Continuity of care, patient access to clozapine, and patient safety are our highest priorities,” the FDA says.
The agency is working closely with the clozapine REMS program administrators to address these challenges and avoid interruptions in patient care.
The FDA encourages pharmacists and prescribers to continue working with the clozapine REMS to complete certification and prescribers to enroll patients in the program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a Nov. 2 notice on its website, the FDA said it is aware that health care professionals and patients continue to experience ongoing difficulties with the clozapine REMS program, including issues with patient access to clozapine following discharge from inpatient care.
A chief concern is that inpatient pharmacies are only allowed to dispense a 7-days’ supply of clozapine to the patient upon discharge.
To address this issue, the FDA said it will now (temporarily) not object if inpatient pharmacies dispense a days’ supply of clozapine that aligns with the patient’s monitoring frequency.
For example, a 7-days’ supply for weekly monitoring, a 14-days’ supply for twice-monthly monitoring, and a 30-days’ supply for monthly monitoring upon discharge from an inpatient facility.
Clozapine is a second-generation (atypical) antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia that is not well controlled with standard antipsychotics.
While clozapine can be highly effective in some patients, it also carries serious risks, including a decrease in neutrophil count, which can lead to severe neutropenia, serious infections, and death.
As a result, those taking the drug must undergo regular absolute neutrophil count monitoring. Clozapine REMS is intended to maximize the benefits of the drug and minimize risk.
The FDA says it will continue to exercise earlier enforcement discretion regarding the clozapine REMS program announced back in November 2021. This includes allowing pharmacists to dispense clozapine without a REMS dispense authorization and allowing wholesalers to ship clozapine to pharmacies and health care settings without confirming enrollment in the REMS.
“We understand that difficulties with the clozapine REMS program have caused frustration and have led to problems with patient access to clozapine. FDA takes these concerns seriously. Continuity of care, patient access to clozapine, and patient safety are our highest priorities,” the FDA says.
The agency is working closely with the clozapine REMS program administrators to address these challenges and avoid interruptions in patient care.
The FDA encourages pharmacists and prescribers to continue working with the clozapine REMS to complete certification and prescribers to enroll patients in the program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.