User login
Empowering Culture Change and Safety on the Journey to Zero Harm With Huddle Cards
Empowering Culture Change and Safety on the Journey to Zero Harm With Huddle Cards
Safety event reporting plays a vital role in fostering a culture of safety within a health care organization. The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has shifted its focus from eradicating medical errors to minimizing or eliminating harm to patients.1 The National Center for Patient Safety’s objective is to prevent recurring errors by identifying and addressing systemic problems that may have been overlooked.2
Taking inspiration from industries known for high reliability, such as aviation and nuclear power, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) patient safety program aims to identify and eliminate system vulnerabilities, such as medical errors. Learning from near misses, which occur more frequently than actual adverse events, is a crucial part of this process.3 By addressing these issues, the VHA can establish safer systems and encourage continuous identification of potential problems with proactive resolution.
All staff should participate actively in event reporting, which involves documenting and communicating details, outcomes, and relevant data about an event to understand what occurred, evaluate success, identify areas for improvement, and inform future decisions. This helps identify system weaknesses, create opportunities to standardize procedures and enhance patient care.
At the high complexity Central Texas Veterans Health Care System (CTVHCS), the fiscal year (FY) 2023 All Employee Survey (AES) found that staff members require additional education and awareness regarding the reporting of patient safety concerns.4 The survey highlighted areas such as lack of education on reporting, doubts about the effectiveness of reporting, confusion about the process after a report is made, and insufficient feedback.
BACKGROUND
To improve the culture of safety and address deficiencies noted in the AES, the CTVHCS patient safety (PS) and high reliability organization (HRO) teams partnered to develop a quality improvement initiative to increase staff understanding of safety event reporting and strengthen the safety culture. The PS and HRO teams developed an innovative education model that integrates Joint Patient Safety Reporting System (JPSR) education into huddles.
This initiative, called the JPSR Huddle Card Toolkit, sought to assess the impact of the toolkit on staff knowledge and behaviors related to patient safety event reporting. The toolkit consisted of educational materials encompassing 6 key areas: (1) reporting incidents; (2) close calls and near misses; (3) identification of root causes; (4) understanding the life cycle of a JPSR; (5) celebrating achievements; and (6) distinguishing between facts and fiction. Each JPSR huddle card included discussion points for the facilitator and was formatted on a 5 × 7-inch card (Figure 1). Topics were addressed during weekly safety huddles conducted in the pilot unit over a 6-week period. To evaluate its effectiveness, a pilot unit was selected and distributed an anonymous questionnaire paired with the JPSR huddle card toolkit to measure staff responses.

The pilot was conducted from November 2023 to January 2024. The participating pilot unit was a 10-bed critical care unit with 42 full-time employees. Nursing leadership, quality safety, and value personnel, and the Veterans Integrated Services Network (VISN) PS Team reviewed and approved the pilot.
Reporting of adverse events and near misses provides an opportunity to learn about latent systems errors.2 In 2018, the VHA began using the JPSR to standardize the capture and data management on medical errors and close calls across the Defense Health Administration (DHA) and VHA.1 The JPSR software is a joint application of the VHA and DHA. It improves the identification and documentation of patient safety-related events for VA medical centers, military hospitals and clinics, active-duty personnel, veterans and their families.
Event reporting is a key element in advancing high reliability and achieving zero preventable harm.1 Teams use these data to identify organizational patient safety trends and preempt common safety issues. All data are protected under 38 USC §5705 and 10 USC §1102.5 The JPSR single-source system standardizes the collection of core data points and increases collaboration between the DHA and VHA. This partnership increases insight into safety-related incidents, allowing for earlier detection and prevention of patient harm or injury incidents.
Numerous studies consistently commend huddles for their effectiveness in promoting teamwork and their positive impact on patient safety.6-8 Huddles facilitate connections between employees who may not typically interact, provide opportunities for discussions, and serve as a platform to encourage employees to voice their opinions. By fostering these interactions, huddles empower employees and create an environment for shared understanding, building trust, and promoting continuous learning.8
OBSERVATIONS
The JPSR huddle card initiative aimed to improve understanding of the JPSR process and promote knowledge and attitudes about patient safety and event reporting, while emphasizing shared responsibility. The goals focused on effective communication, respect for expertise, awareness of operational nuances, voicing concerns, and ensuring zero harm.
The facilitator initiated huddles by announcing their start to cultivate a constructive outcome.8 The JPSR huddle cards used a structured format designed to foster engagement and understanding of the topic. Each card begins with a factual statement or an open-ended question to gauge participants’ awareness or understanding. It then provides essential facts, principles, and relevant information to deepen knowledge. The card concludes with a discussion question, allowing facilitators to assess shared learning and encourage group reflection. This format promotes active participation and ensures that key concepts are both introduced and reinforced through dialogue.
The PS team standardized the format for all huddle cards, allowing 5 to 10 minutes for discussing training materials, receiving feedback, and concluding with a discussion question and call to action. Prior to each huddle, the facilitator would read a scripted remark that reviewed the objectives and ground rules for an effective huddle.
The PS and HRO teams promoted interactive discussions and welcomed ongoing feedback. Huddles provided a psychologically safe environment where individuals were encouraged to voice their thoughts and ideas.
Each weekly huddle card addressed a different patient safety topic. The Week 1 huddle card focuses on event reporting for safety improvement. The card outlines the purpose of JPSR as a tool to identify, manage, and analyze safety events to reduce preventable harm. The card emphasizes 3 core principles: (1) acknowledging mistakes, recognizing that errors happen; (2) no blame, no shame (encouraging a no-blame just culture to raise concerns); and (3) continuous improvement (committing to ongoing learning and prevention). It provides guidance on event details entry, advising staff to include facts in an SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Response) format, avoid assumptions, and exclude personal identifiers. Tips include entering only relevant facts to help reviewers understand the incident. The card ends with discussion questions on reporting barriers and potential improvements in event reporting practices.
The Week 2 huddle card focuses on understanding and reporting near miss events, also known as close calls or good catches. A near miss is an incident where a potential hazard was identified and prevented before it reached the patient, avoiding harm due to timely intervention. The card emphasizes the importance of identifying these events to understand weaknesses and proactively reduce risks. Examples of near misses include discovering expired medication before use, catching a potential wrong-site surgery, and noticing incorrect medication dosages. Staff are encouraged to develop a mindset for anticipating and solving risks. The card ends with a discussion asking participants to share examples of near misses in their area.
The Week 3 huddle card covers root causes in preventing errors. The card highlights that errors in health care often stem from flawed processes rather than individual faults. By identifying root causes, systemic weaknesses can be addressed to reduce mistakes and build more error-tolerant and robust systems. All staff are advised to adopt a mindset of continuous improvement, error trapping behaviors and problem-solving. It concludes with discussion questions prompting reflection on assumptions and identifying weaknesses when something goes wrong.
The Week 4 huddle card covers the life of a JPSR, detailing that after entry JPSR events are viewed by the highest leadership levels at the morning report, and that lessons learned are distributed through frontline managers and chiefs in a monthly report to be shared with frontline staff. Additionally, JPSR trends are shared during monthly HRO safety forums. These practices promote a culture of safety through open communication and problem-solving. Staff and leaders are encouraged to prioritize safety daily. Discussion prompts ask team members if they had seen positive changes from JPSR reporting and what they would like leadership to communicate after investigations.
The Week 5 huddle card covers celebrating safety event reporting called Cue the Confetti. The VHA emphasizes recognizing staff who report safety events as part of their commitment to zero harm. By celebrating these contributions, the VHA fosters respect, joy, and satisfaction in the work. Staff are encouraged to nominate colleagues for recognition, reinforcing a supportive environment. Prompts invite teams to discuss how they celebrate JPSR reporting and how they’d like to enhance this culture of appreciation.
The Week 6 huddle card covers common misconceptions about JPSR. Key facts include that JPSRs are confidential, not for disciplinary action, and can be submitted by any staff member at any time. Only PS can view reporter identities for clarification purposes. The card concludes with prompts to ensure staff know how to access JPSR support and resources.
Measuring the impact on staff was essential to assess effectiveness and gather data for program improvement. To evaluate the impact of the huddle cards on the staff, the team provided a voluntary and anonymous 9 question survey (Figure 2). The survey was completed before the pilot began and again at the end of Week 6.
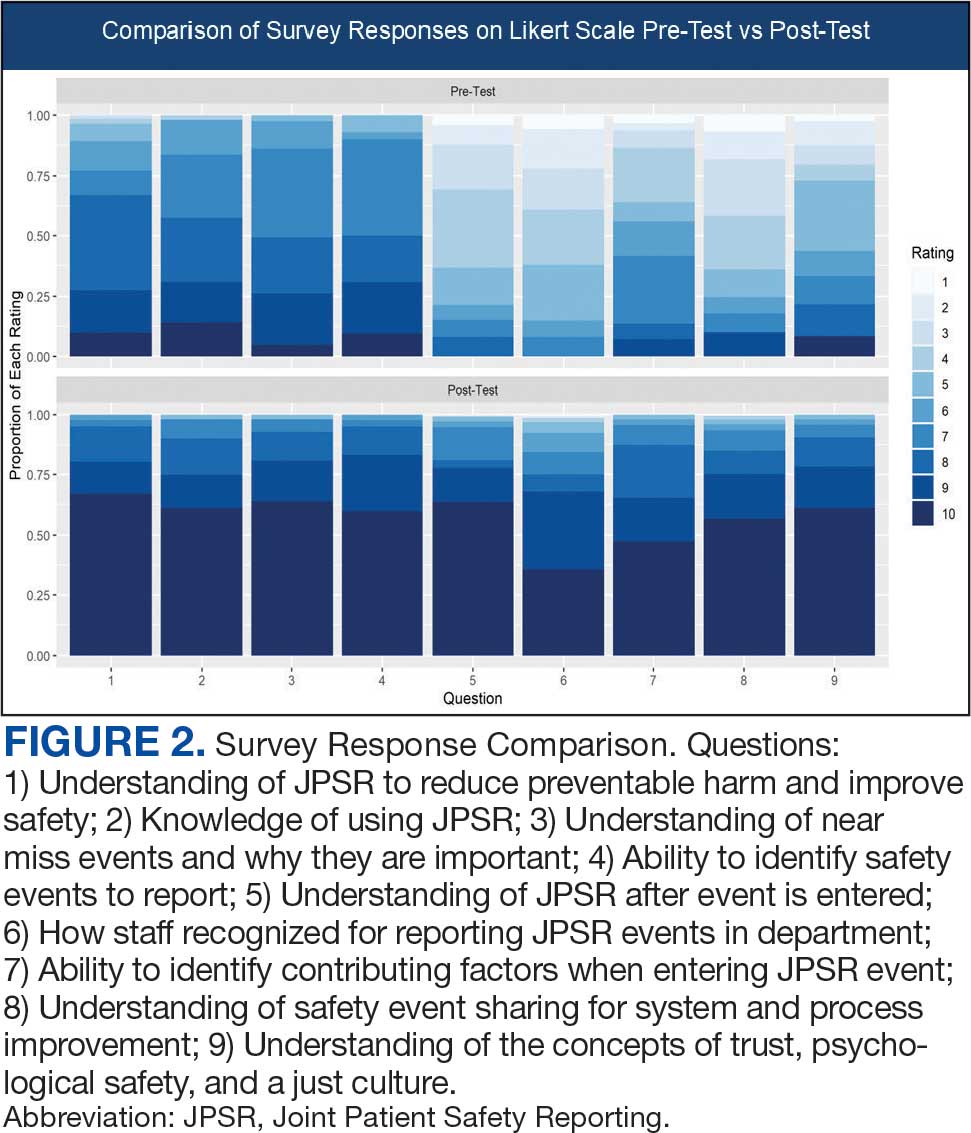
Questions 1 through 5 and 7 through 9 pertained to participants’ perceived knowledge and understanding of aspects of the JPSR. Perceived improvement among intensive care unit (ICU) participants ranged from 15% to 53%. There was a positive increase associated with every question with the top improvements: question 8, “How do you rate your understanding of how we share safety events for system and process improvement?” (53.4% increase); question 5, “How do you rate your understanding of what happens to a JPSR after it is entered?” (51.9% increase), and question 9, “How do you rate your understanding of the concepts of trust, psychological safety and a just culture?” (47.8% increase).
The survey analysis was not able to track individual changes. As a result, the findings reflect an overall change for the entire study group. Moreover, the questions assessed participants’ perceived knowledge rather than actual knowledge gained. It is important to note that there may be a significant gap between the actual knowledge gained and how participants perceive it. Additionally, improvement in knowledge and comprehension does not necessarily translate into behavior changes.
CONCLUSIONS
The use of JPSR huddle cards and direct engagement with staff during safety huddles yielded positive outcomes. On average, participants demonstrated higher scores in posttest questions compared to pretest questions. The posttest scores were consistently higher than the pretest scores, showing an average increase of around 2 standard deviations across all questions. This indicates an improvement in participants’ perceived knowledge and comprehension of the JPSR material.
During the pilot implementation of the huddle cards, there was a notable improvement in team member engagement. The structured format of the cards facilitated focused and meaningful discussions during safety huddles, encouraging open dialogue and fostering a culture of safety. Team members actively participated in identifying potential risks, sharing observations, and proposing actionable solutions, which reflected an enhanced sense of ownership regarding safety practices.
The support dialogue facilitated by the huddle cards highlighted the significance of mutual accountability and a collective commitment to achieving zero harm. This collaborative environment strengthened trust among team members and underscored the importance of shared vigilance in preventing adverse events. The pilot demonstrated the potential of huddle cards as an essential tool for enhancing team-based safety initiatives and promoting a culture of high reliability within the organization.
The total number of JPSR events in the ICU rose from 156 in FY 23 to 170 in FY 24. Adverse events increased from 19 to 31, while close calls saw a slight uptick from 137 to 139. Despite the overall rise in adverse events, a detailed analysis indicated that incidents of moderate harm decreased from 4 in FY 23 to 2 in FY 24. Furthermore, there was 1 reported case of death or severe harm in FY 23, which decreased to 0 in FY 24. This trend is consistent with the overarching objective of a high-reliability organization to achieve zero harm.
The next step is to expand this initiative across CTVHCS. This initiative aims to make this an annual education for all areas. The JPSR huddle card toolkit will be formatted by the media department for easy printing and retrieval. Leaders within units, clinics, and services will be empowered to facilitate the sessions in their safety huddles and reap the same outcomes as in the pilot. CTVHCS PS will monitor the effectiveness of this through ongoing CTVHCS patient safety rounding and future AES.
- Essen K, Villalobos C, Sculli GL, Steinbach L. Establishing a just culture: implications for the Veterans Health Administration journey to high reliability. Fed Pract. 2024;41:290-297. doi:10.12788/fp.0512
- Louis MY, Hussain LR, Dhanraj DN, et al. Improving patient safety event reporting among residents and teaching faculty. Ochsner J. 2016;16:73-80.
- Pimental CB, Snow AL, Carnes SL, et al. Huddles and their effectiveness at the frontlines of clinical care: a scoping review. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36:2772-2783. doi:10.1007/s11606-021-06632-9
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Appendix C: Nature of Veterans Health Administration Facilities Management (Engineering) Tasks and Staffing. Facilities Staffing Requirements for the Veterans Health Administration-Resource Planning and Methodology for the Future. National Academies Press. 2020:105-116. Accessed August 11, 2025. https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/25454/chapter/11
- Woodier N, Burnett C, Moppett I. The value of learning from near misses to improve patient safety: a scoping review. J Patient Saf. 2023;19:42-47. doi:10.1097/pts.0000000000001078
- Ismail A, Khalid SNM. Patient safety culture and its determinants among healthcare professionals at a cluster hospital in Malaysia: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e060546. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-060546
- Ngo J, Lau D, Ploquin J, Receveur T, Stassen K, Del Castilho C. Improving incident reporting among physicians at south health campus hospital. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11:e001945. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001945
- Oweidat I, Al-Mugheed K, Alsenany SA, et al. Awareness of reporting practices and barriers to incident reporting among nurses. BMC Nurs. 2023;22:231. doi:10.1186/s12912-023-01376-9
Safety event reporting plays a vital role in fostering a culture of safety within a health care organization. The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has shifted its focus from eradicating medical errors to minimizing or eliminating harm to patients.1 The National Center for Patient Safety’s objective is to prevent recurring errors by identifying and addressing systemic problems that may have been overlooked.2
Taking inspiration from industries known for high reliability, such as aviation and nuclear power, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) patient safety program aims to identify and eliminate system vulnerabilities, such as medical errors. Learning from near misses, which occur more frequently than actual adverse events, is a crucial part of this process.3 By addressing these issues, the VHA can establish safer systems and encourage continuous identification of potential problems with proactive resolution.
All staff should participate actively in event reporting, which involves documenting and communicating details, outcomes, and relevant data about an event to understand what occurred, evaluate success, identify areas for improvement, and inform future decisions. This helps identify system weaknesses, create opportunities to standardize procedures and enhance patient care.
At the high complexity Central Texas Veterans Health Care System (CTVHCS), the fiscal year (FY) 2023 All Employee Survey (AES) found that staff members require additional education and awareness regarding the reporting of patient safety concerns.4 The survey highlighted areas such as lack of education on reporting, doubts about the effectiveness of reporting, confusion about the process after a report is made, and insufficient feedback.
BACKGROUND
To improve the culture of safety and address deficiencies noted in the AES, the CTVHCS patient safety (PS) and high reliability organization (HRO) teams partnered to develop a quality improvement initiative to increase staff understanding of safety event reporting and strengthen the safety culture. The PS and HRO teams developed an innovative education model that integrates Joint Patient Safety Reporting System (JPSR) education into huddles.
This initiative, called the JPSR Huddle Card Toolkit, sought to assess the impact of the toolkit on staff knowledge and behaviors related to patient safety event reporting. The toolkit consisted of educational materials encompassing 6 key areas: (1) reporting incidents; (2) close calls and near misses; (3) identification of root causes; (4) understanding the life cycle of a JPSR; (5) celebrating achievements; and (6) distinguishing between facts and fiction. Each JPSR huddle card included discussion points for the facilitator and was formatted on a 5 × 7-inch card (Figure 1). Topics were addressed during weekly safety huddles conducted in the pilot unit over a 6-week period. To evaluate its effectiveness, a pilot unit was selected and distributed an anonymous questionnaire paired with the JPSR huddle card toolkit to measure staff responses.

The pilot was conducted from November 2023 to January 2024. The participating pilot unit was a 10-bed critical care unit with 42 full-time employees. Nursing leadership, quality safety, and value personnel, and the Veterans Integrated Services Network (VISN) PS Team reviewed and approved the pilot.
Reporting of adverse events and near misses provides an opportunity to learn about latent systems errors.2 In 2018, the VHA began using the JPSR to standardize the capture and data management on medical errors and close calls across the Defense Health Administration (DHA) and VHA.1 The JPSR software is a joint application of the VHA and DHA. It improves the identification and documentation of patient safety-related events for VA medical centers, military hospitals and clinics, active-duty personnel, veterans and their families.
Event reporting is a key element in advancing high reliability and achieving zero preventable harm.1 Teams use these data to identify organizational patient safety trends and preempt common safety issues. All data are protected under 38 USC §5705 and 10 USC §1102.5 The JPSR single-source system standardizes the collection of core data points and increases collaboration between the DHA and VHA. This partnership increases insight into safety-related incidents, allowing for earlier detection and prevention of patient harm or injury incidents.
Numerous studies consistently commend huddles for their effectiveness in promoting teamwork and their positive impact on patient safety.6-8 Huddles facilitate connections between employees who may not typically interact, provide opportunities for discussions, and serve as a platform to encourage employees to voice their opinions. By fostering these interactions, huddles empower employees and create an environment for shared understanding, building trust, and promoting continuous learning.8
OBSERVATIONS
The JPSR huddle card initiative aimed to improve understanding of the JPSR process and promote knowledge and attitudes about patient safety and event reporting, while emphasizing shared responsibility. The goals focused on effective communication, respect for expertise, awareness of operational nuances, voicing concerns, and ensuring zero harm.
The facilitator initiated huddles by announcing their start to cultivate a constructive outcome.8 The JPSR huddle cards used a structured format designed to foster engagement and understanding of the topic. Each card begins with a factual statement or an open-ended question to gauge participants’ awareness or understanding. It then provides essential facts, principles, and relevant information to deepen knowledge. The card concludes with a discussion question, allowing facilitators to assess shared learning and encourage group reflection. This format promotes active participation and ensures that key concepts are both introduced and reinforced through dialogue.
The PS team standardized the format for all huddle cards, allowing 5 to 10 minutes for discussing training materials, receiving feedback, and concluding with a discussion question and call to action. Prior to each huddle, the facilitator would read a scripted remark that reviewed the objectives and ground rules for an effective huddle.
The PS and HRO teams promoted interactive discussions and welcomed ongoing feedback. Huddles provided a psychologically safe environment where individuals were encouraged to voice their thoughts and ideas.
Each weekly huddle card addressed a different patient safety topic. The Week 1 huddle card focuses on event reporting for safety improvement. The card outlines the purpose of JPSR as a tool to identify, manage, and analyze safety events to reduce preventable harm. The card emphasizes 3 core principles: (1) acknowledging mistakes, recognizing that errors happen; (2) no blame, no shame (encouraging a no-blame just culture to raise concerns); and (3) continuous improvement (committing to ongoing learning and prevention). It provides guidance on event details entry, advising staff to include facts in an SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Response) format, avoid assumptions, and exclude personal identifiers. Tips include entering only relevant facts to help reviewers understand the incident. The card ends with discussion questions on reporting barriers and potential improvements in event reporting practices.
The Week 2 huddle card focuses on understanding and reporting near miss events, also known as close calls or good catches. A near miss is an incident where a potential hazard was identified and prevented before it reached the patient, avoiding harm due to timely intervention. The card emphasizes the importance of identifying these events to understand weaknesses and proactively reduce risks. Examples of near misses include discovering expired medication before use, catching a potential wrong-site surgery, and noticing incorrect medication dosages. Staff are encouraged to develop a mindset for anticipating and solving risks. The card ends with a discussion asking participants to share examples of near misses in their area.
The Week 3 huddle card covers root causes in preventing errors. The card highlights that errors in health care often stem from flawed processes rather than individual faults. By identifying root causes, systemic weaknesses can be addressed to reduce mistakes and build more error-tolerant and robust systems. All staff are advised to adopt a mindset of continuous improvement, error trapping behaviors and problem-solving. It concludes with discussion questions prompting reflection on assumptions and identifying weaknesses when something goes wrong.
The Week 4 huddle card covers the life of a JPSR, detailing that after entry JPSR events are viewed by the highest leadership levels at the morning report, and that lessons learned are distributed through frontline managers and chiefs in a monthly report to be shared with frontline staff. Additionally, JPSR trends are shared during monthly HRO safety forums. These practices promote a culture of safety through open communication and problem-solving. Staff and leaders are encouraged to prioritize safety daily. Discussion prompts ask team members if they had seen positive changes from JPSR reporting and what they would like leadership to communicate after investigations.
The Week 5 huddle card covers celebrating safety event reporting called Cue the Confetti. The VHA emphasizes recognizing staff who report safety events as part of their commitment to zero harm. By celebrating these contributions, the VHA fosters respect, joy, and satisfaction in the work. Staff are encouraged to nominate colleagues for recognition, reinforcing a supportive environment. Prompts invite teams to discuss how they celebrate JPSR reporting and how they’d like to enhance this culture of appreciation.
The Week 6 huddle card covers common misconceptions about JPSR. Key facts include that JPSRs are confidential, not for disciplinary action, and can be submitted by any staff member at any time. Only PS can view reporter identities for clarification purposes. The card concludes with prompts to ensure staff know how to access JPSR support and resources.
Measuring the impact on staff was essential to assess effectiveness and gather data for program improvement. To evaluate the impact of the huddle cards on the staff, the team provided a voluntary and anonymous 9 question survey (Figure 2). The survey was completed before the pilot began and again at the end of Week 6.

Questions 1 through 5 and 7 through 9 pertained to participants’ perceived knowledge and understanding of aspects of the JPSR. Perceived improvement among intensive care unit (ICU) participants ranged from 15% to 53%. There was a positive increase associated with every question with the top improvements: question 8, “How do you rate your understanding of how we share safety events for system and process improvement?” (53.4% increase); question 5, “How do you rate your understanding of what happens to a JPSR after it is entered?” (51.9% increase), and question 9, “How do you rate your understanding of the concepts of trust, psychological safety and a just culture?” (47.8% increase).
The survey analysis was not able to track individual changes. As a result, the findings reflect an overall change for the entire study group. Moreover, the questions assessed participants’ perceived knowledge rather than actual knowledge gained. It is important to note that there may be a significant gap between the actual knowledge gained and how participants perceive it. Additionally, improvement in knowledge and comprehension does not necessarily translate into behavior changes.
CONCLUSIONS
The use of JPSR huddle cards and direct engagement with staff during safety huddles yielded positive outcomes. On average, participants demonstrated higher scores in posttest questions compared to pretest questions. The posttest scores were consistently higher than the pretest scores, showing an average increase of around 2 standard deviations across all questions. This indicates an improvement in participants’ perceived knowledge and comprehension of the JPSR material.
During the pilot implementation of the huddle cards, there was a notable improvement in team member engagement. The structured format of the cards facilitated focused and meaningful discussions during safety huddles, encouraging open dialogue and fostering a culture of safety. Team members actively participated in identifying potential risks, sharing observations, and proposing actionable solutions, which reflected an enhanced sense of ownership regarding safety practices.
The support dialogue facilitated by the huddle cards highlighted the significance of mutual accountability and a collective commitment to achieving zero harm. This collaborative environment strengthened trust among team members and underscored the importance of shared vigilance in preventing adverse events. The pilot demonstrated the potential of huddle cards as an essential tool for enhancing team-based safety initiatives and promoting a culture of high reliability within the organization.
The total number of JPSR events in the ICU rose from 156 in FY 23 to 170 in FY 24. Adverse events increased from 19 to 31, while close calls saw a slight uptick from 137 to 139. Despite the overall rise in adverse events, a detailed analysis indicated that incidents of moderate harm decreased from 4 in FY 23 to 2 in FY 24. Furthermore, there was 1 reported case of death or severe harm in FY 23, which decreased to 0 in FY 24. This trend is consistent with the overarching objective of a high-reliability organization to achieve zero harm.
The next step is to expand this initiative across CTVHCS. This initiative aims to make this an annual education for all areas. The JPSR huddle card toolkit will be formatted by the media department for easy printing and retrieval. Leaders within units, clinics, and services will be empowered to facilitate the sessions in their safety huddles and reap the same outcomes as in the pilot. CTVHCS PS will monitor the effectiveness of this through ongoing CTVHCS patient safety rounding and future AES.
Safety event reporting plays a vital role in fostering a culture of safety within a health care organization. The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has shifted its focus from eradicating medical errors to minimizing or eliminating harm to patients.1 The National Center for Patient Safety’s objective is to prevent recurring errors by identifying and addressing systemic problems that may have been overlooked.2
Taking inspiration from industries known for high reliability, such as aviation and nuclear power, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) patient safety program aims to identify and eliminate system vulnerabilities, such as medical errors. Learning from near misses, which occur more frequently than actual adverse events, is a crucial part of this process.3 By addressing these issues, the VHA can establish safer systems and encourage continuous identification of potential problems with proactive resolution.
All staff should participate actively in event reporting, which involves documenting and communicating details, outcomes, and relevant data about an event to understand what occurred, evaluate success, identify areas for improvement, and inform future decisions. This helps identify system weaknesses, create opportunities to standardize procedures and enhance patient care.
At the high complexity Central Texas Veterans Health Care System (CTVHCS), the fiscal year (FY) 2023 All Employee Survey (AES) found that staff members require additional education and awareness regarding the reporting of patient safety concerns.4 The survey highlighted areas such as lack of education on reporting, doubts about the effectiveness of reporting, confusion about the process after a report is made, and insufficient feedback.
BACKGROUND
To improve the culture of safety and address deficiencies noted in the AES, the CTVHCS patient safety (PS) and high reliability organization (HRO) teams partnered to develop a quality improvement initiative to increase staff understanding of safety event reporting and strengthen the safety culture. The PS and HRO teams developed an innovative education model that integrates Joint Patient Safety Reporting System (JPSR) education into huddles.
This initiative, called the JPSR Huddle Card Toolkit, sought to assess the impact of the toolkit on staff knowledge and behaviors related to patient safety event reporting. The toolkit consisted of educational materials encompassing 6 key areas: (1) reporting incidents; (2) close calls and near misses; (3) identification of root causes; (4) understanding the life cycle of a JPSR; (5) celebrating achievements; and (6) distinguishing between facts and fiction. Each JPSR huddle card included discussion points for the facilitator and was formatted on a 5 × 7-inch card (Figure 1). Topics were addressed during weekly safety huddles conducted in the pilot unit over a 6-week period. To evaluate its effectiveness, a pilot unit was selected and distributed an anonymous questionnaire paired with the JPSR huddle card toolkit to measure staff responses.

The pilot was conducted from November 2023 to January 2024. The participating pilot unit was a 10-bed critical care unit with 42 full-time employees. Nursing leadership, quality safety, and value personnel, and the Veterans Integrated Services Network (VISN) PS Team reviewed and approved the pilot.
Reporting of adverse events and near misses provides an opportunity to learn about latent systems errors.2 In 2018, the VHA began using the JPSR to standardize the capture and data management on medical errors and close calls across the Defense Health Administration (DHA) and VHA.1 The JPSR software is a joint application of the VHA and DHA. It improves the identification and documentation of patient safety-related events for VA medical centers, military hospitals and clinics, active-duty personnel, veterans and their families.
Event reporting is a key element in advancing high reliability and achieving zero preventable harm.1 Teams use these data to identify organizational patient safety trends and preempt common safety issues. All data are protected under 38 USC §5705 and 10 USC §1102.5 The JPSR single-source system standardizes the collection of core data points and increases collaboration between the DHA and VHA. This partnership increases insight into safety-related incidents, allowing for earlier detection and prevention of patient harm or injury incidents.
Numerous studies consistently commend huddles for their effectiveness in promoting teamwork and their positive impact on patient safety.6-8 Huddles facilitate connections between employees who may not typically interact, provide opportunities for discussions, and serve as a platform to encourage employees to voice their opinions. By fostering these interactions, huddles empower employees and create an environment for shared understanding, building trust, and promoting continuous learning.8
OBSERVATIONS
The JPSR huddle card initiative aimed to improve understanding of the JPSR process and promote knowledge and attitudes about patient safety and event reporting, while emphasizing shared responsibility. The goals focused on effective communication, respect for expertise, awareness of operational nuances, voicing concerns, and ensuring zero harm.
The facilitator initiated huddles by announcing their start to cultivate a constructive outcome.8 The JPSR huddle cards used a structured format designed to foster engagement and understanding of the topic. Each card begins with a factual statement or an open-ended question to gauge participants’ awareness or understanding. It then provides essential facts, principles, and relevant information to deepen knowledge. The card concludes with a discussion question, allowing facilitators to assess shared learning and encourage group reflection. This format promotes active participation and ensures that key concepts are both introduced and reinforced through dialogue.
The PS team standardized the format for all huddle cards, allowing 5 to 10 minutes for discussing training materials, receiving feedback, and concluding with a discussion question and call to action. Prior to each huddle, the facilitator would read a scripted remark that reviewed the objectives and ground rules for an effective huddle.
The PS and HRO teams promoted interactive discussions and welcomed ongoing feedback. Huddles provided a psychologically safe environment where individuals were encouraged to voice their thoughts and ideas.
Each weekly huddle card addressed a different patient safety topic. The Week 1 huddle card focuses on event reporting for safety improvement. The card outlines the purpose of JPSR as a tool to identify, manage, and analyze safety events to reduce preventable harm. The card emphasizes 3 core principles: (1) acknowledging mistakes, recognizing that errors happen; (2) no blame, no shame (encouraging a no-blame just culture to raise concerns); and (3) continuous improvement (committing to ongoing learning and prevention). It provides guidance on event details entry, advising staff to include facts in an SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Response) format, avoid assumptions, and exclude personal identifiers. Tips include entering only relevant facts to help reviewers understand the incident. The card ends with discussion questions on reporting barriers and potential improvements in event reporting practices.
The Week 2 huddle card focuses on understanding and reporting near miss events, also known as close calls or good catches. A near miss is an incident where a potential hazard was identified and prevented before it reached the patient, avoiding harm due to timely intervention. The card emphasizes the importance of identifying these events to understand weaknesses and proactively reduce risks. Examples of near misses include discovering expired medication before use, catching a potential wrong-site surgery, and noticing incorrect medication dosages. Staff are encouraged to develop a mindset for anticipating and solving risks. The card ends with a discussion asking participants to share examples of near misses in their area.
The Week 3 huddle card covers root causes in preventing errors. The card highlights that errors in health care often stem from flawed processes rather than individual faults. By identifying root causes, systemic weaknesses can be addressed to reduce mistakes and build more error-tolerant and robust systems. All staff are advised to adopt a mindset of continuous improvement, error trapping behaviors and problem-solving. It concludes with discussion questions prompting reflection on assumptions and identifying weaknesses when something goes wrong.
The Week 4 huddle card covers the life of a JPSR, detailing that after entry JPSR events are viewed by the highest leadership levels at the morning report, and that lessons learned are distributed through frontline managers and chiefs in a monthly report to be shared with frontline staff. Additionally, JPSR trends are shared during monthly HRO safety forums. These practices promote a culture of safety through open communication and problem-solving. Staff and leaders are encouraged to prioritize safety daily. Discussion prompts ask team members if they had seen positive changes from JPSR reporting and what they would like leadership to communicate after investigations.
The Week 5 huddle card covers celebrating safety event reporting called Cue the Confetti. The VHA emphasizes recognizing staff who report safety events as part of their commitment to zero harm. By celebrating these contributions, the VHA fosters respect, joy, and satisfaction in the work. Staff are encouraged to nominate colleagues for recognition, reinforcing a supportive environment. Prompts invite teams to discuss how they celebrate JPSR reporting and how they’d like to enhance this culture of appreciation.
The Week 6 huddle card covers common misconceptions about JPSR. Key facts include that JPSRs are confidential, not for disciplinary action, and can be submitted by any staff member at any time. Only PS can view reporter identities for clarification purposes. The card concludes with prompts to ensure staff know how to access JPSR support and resources.
Measuring the impact on staff was essential to assess effectiveness and gather data for program improvement. To evaluate the impact of the huddle cards on the staff, the team provided a voluntary and anonymous 9 question survey (Figure 2). The survey was completed before the pilot began and again at the end of Week 6.

Questions 1 through 5 and 7 through 9 pertained to participants’ perceived knowledge and understanding of aspects of the JPSR. Perceived improvement among intensive care unit (ICU) participants ranged from 15% to 53%. There was a positive increase associated with every question with the top improvements: question 8, “How do you rate your understanding of how we share safety events for system and process improvement?” (53.4% increase); question 5, “How do you rate your understanding of what happens to a JPSR after it is entered?” (51.9% increase), and question 9, “How do you rate your understanding of the concepts of trust, psychological safety and a just culture?” (47.8% increase).
The survey analysis was not able to track individual changes. As a result, the findings reflect an overall change for the entire study group. Moreover, the questions assessed participants’ perceived knowledge rather than actual knowledge gained. It is important to note that there may be a significant gap between the actual knowledge gained and how participants perceive it. Additionally, improvement in knowledge and comprehension does not necessarily translate into behavior changes.
CONCLUSIONS
The use of JPSR huddle cards and direct engagement with staff during safety huddles yielded positive outcomes. On average, participants demonstrated higher scores in posttest questions compared to pretest questions. The posttest scores were consistently higher than the pretest scores, showing an average increase of around 2 standard deviations across all questions. This indicates an improvement in participants’ perceived knowledge and comprehension of the JPSR material.
During the pilot implementation of the huddle cards, there was a notable improvement in team member engagement. The structured format of the cards facilitated focused and meaningful discussions during safety huddles, encouraging open dialogue and fostering a culture of safety. Team members actively participated in identifying potential risks, sharing observations, and proposing actionable solutions, which reflected an enhanced sense of ownership regarding safety practices.
The support dialogue facilitated by the huddle cards highlighted the significance of mutual accountability and a collective commitment to achieving zero harm. This collaborative environment strengthened trust among team members and underscored the importance of shared vigilance in preventing adverse events. The pilot demonstrated the potential of huddle cards as an essential tool for enhancing team-based safety initiatives and promoting a culture of high reliability within the organization.
The total number of JPSR events in the ICU rose from 156 in FY 23 to 170 in FY 24. Adverse events increased from 19 to 31, while close calls saw a slight uptick from 137 to 139. Despite the overall rise in adverse events, a detailed analysis indicated that incidents of moderate harm decreased from 4 in FY 23 to 2 in FY 24. Furthermore, there was 1 reported case of death or severe harm in FY 23, which decreased to 0 in FY 24. This trend is consistent with the overarching objective of a high-reliability organization to achieve zero harm.
The next step is to expand this initiative across CTVHCS. This initiative aims to make this an annual education for all areas. The JPSR huddle card toolkit will be formatted by the media department for easy printing and retrieval. Leaders within units, clinics, and services will be empowered to facilitate the sessions in their safety huddles and reap the same outcomes as in the pilot. CTVHCS PS will monitor the effectiveness of this through ongoing CTVHCS patient safety rounding and future AES.
- Essen K, Villalobos C, Sculli GL, Steinbach L. Establishing a just culture: implications for the Veterans Health Administration journey to high reliability. Fed Pract. 2024;41:290-297. doi:10.12788/fp.0512
- Louis MY, Hussain LR, Dhanraj DN, et al. Improving patient safety event reporting among residents and teaching faculty. Ochsner J. 2016;16:73-80.
- Pimental CB, Snow AL, Carnes SL, et al. Huddles and their effectiveness at the frontlines of clinical care: a scoping review. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36:2772-2783. doi:10.1007/s11606-021-06632-9
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Appendix C: Nature of Veterans Health Administration Facilities Management (Engineering) Tasks and Staffing. Facilities Staffing Requirements for the Veterans Health Administration-Resource Planning and Methodology for the Future. National Academies Press. 2020:105-116. Accessed August 11, 2025. https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/25454/chapter/11
- Woodier N, Burnett C, Moppett I. The value of learning from near misses to improve patient safety: a scoping review. J Patient Saf. 2023;19:42-47. doi:10.1097/pts.0000000000001078
- Ismail A, Khalid SNM. Patient safety culture and its determinants among healthcare professionals at a cluster hospital in Malaysia: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e060546. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-060546
- Ngo J, Lau D, Ploquin J, Receveur T, Stassen K, Del Castilho C. Improving incident reporting among physicians at south health campus hospital. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11:e001945. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001945
- Oweidat I, Al-Mugheed K, Alsenany SA, et al. Awareness of reporting practices and barriers to incident reporting among nurses. BMC Nurs. 2023;22:231. doi:10.1186/s12912-023-01376-9
- Essen K, Villalobos C, Sculli GL, Steinbach L. Establishing a just culture: implications for the Veterans Health Administration journey to high reliability. Fed Pract. 2024;41:290-297. doi:10.12788/fp.0512
- Louis MY, Hussain LR, Dhanraj DN, et al. Improving patient safety event reporting among residents and teaching faculty. Ochsner J. 2016;16:73-80.
- Pimental CB, Snow AL, Carnes SL, et al. Huddles and their effectiveness at the frontlines of clinical care: a scoping review. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36:2772-2783. doi:10.1007/s11606-021-06632-9
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Appendix C: Nature of Veterans Health Administration Facilities Management (Engineering) Tasks and Staffing. Facilities Staffing Requirements for the Veterans Health Administration-Resource Planning and Methodology for the Future. National Academies Press. 2020:105-116. Accessed August 11, 2025. https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/25454/chapter/11
- Woodier N, Burnett C, Moppett I. The value of learning from near misses to improve patient safety: a scoping review. J Patient Saf. 2023;19:42-47. doi:10.1097/pts.0000000000001078
- Ismail A, Khalid SNM. Patient safety culture and its determinants among healthcare professionals at a cluster hospital in Malaysia: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e060546. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-060546
- Ngo J, Lau D, Ploquin J, Receveur T, Stassen K, Del Castilho C. Improving incident reporting among physicians at south health campus hospital. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11:e001945. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001945
- Oweidat I, Al-Mugheed K, Alsenany SA, et al. Awareness of reporting practices and barriers to incident reporting among nurses. BMC Nurs. 2023;22:231. doi:10.1186/s12912-023-01376-9
Empowering Culture Change and Safety on the Journey to Zero Harm With Huddle Cards
Empowering Culture Change and Safety on the Journey to Zero Harm With Huddle Cards
Enhancing Veteran Health Research: A Quality Improvement Initiative to Optimize Biorepository Efficiency
Purpose
Biorepositories are critical to scientific research within the VA. They offer high-quality, well-characterized biospecimens linked to clinical, demographic, and molecular data. Biorepositories support studies on disease mechanisms, personalized therapies, and emerging infectious diseases by systematically collecting, processing, storing, and distributing biological materials, including tissue, blood, and DNA samples. Within the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), biorepositories provide essential support to clinical and translational research on service- related conditions such as PTSD, traumatic brain injury, cancers, and toxic exposures. While the need for harmonized quality processes and resource allocation has long been acknowledged within the biorepository community (Siwek, 2015), each biorepository operates independently, limiting scalability and standardization. This quality improvement project describes a collaboration between two VA biorepository sites supporting a national genomic study investigating disease risk and treatment outcomes. The project aimed to expand capacity, improve processing times, and enhance quality control. Each site mirrors the other’s functions, including receiving, accessioning, processing, storing, and shipping biospecimens, and serves as a contingency site to strengthen operational resilience.
Methods
To address space limitations and improve processing efficiency, one site implemented a custom rack design, expanding storage capacity per freezer. Robotic workflows were optimized, reducing biospecimen processing time. An in-process quality control step was introduced to identify data discrepancies earlier in the workflow, reducing investigation time and supporting overall data integrity. Efficiency was measured by the increase in storage capacity and decreased processing time. Descriptive statistics were used to evaluate changes in performance. Metrics were monitored over twelve months and compared against baseline data.
Results
Following implementation, storage capacity per freezer increased by 20%, and specimen processing time decreased by 30%. The new quality control checkpoint reduced investigation times by 98%, resulting in a more streamlined workflow. These improvements enhanced coordination between sites and improved support for ongoing studies.
Conclusions
This effort demonstrates that collaboration between biorepositories can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce turnaround times, and support high-quality research. Strengthening infrastructure through joint initiatives enables more effective support of large-scale clinical studies and contributes to improved outcomes for Veterans. These findings may also inform process improvements at other VA research facilities.
Purpose
Biorepositories are critical to scientific research within the VA. They offer high-quality, well-characterized biospecimens linked to clinical, demographic, and molecular data. Biorepositories support studies on disease mechanisms, personalized therapies, and emerging infectious diseases by systematically collecting, processing, storing, and distributing biological materials, including tissue, blood, and DNA samples. Within the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), biorepositories provide essential support to clinical and translational research on service- related conditions such as PTSD, traumatic brain injury, cancers, and toxic exposures. While the need for harmonized quality processes and resource allocation has long been acknowledged within the biorepository community (Siwek, 2015), each biorepository operates independently, limiting scalability and standardization. This quality improvement project describes a collaboration between two VA biorepository sites supporting a national genomic study investigating disease risk and treatment outcomes. The project aimed to expand capacity, improve processing times, and enhance quality control. Each site mirrors the other’s functions, including receiving, accessioning, processing, storing, and shipping biospecimens, and serves as a contingency site to strengthen operational resilience.
Methods
To address space limitations and improve processing efficiency, one site implemented a custom rack design, expanding storage capacity per freezer. Robotic workflows were optimized, reducing biospecimen processing time. An in-process quality control step was introduced to identify data discrepancies earlier in the workflow, reducing investigation time and supporting overall data integrity. Efficiency was measured by the increase in storage capacity and decreased processing time. Descriptive statistics were used to evaluate changes in performance. Metrics were monitored over twelve months and compared against baseline data.
Results
Following implementation, storage capacity per freezer increased by 20%, and specimen processing time decreased by 30%. The new quality control checkpoint reduced investigation times by 98%, resulting in a more streamlined workflow. These improvements enhanced coordination between sites and improved support for ongoing studies.
Conclusions
This effort demonstrates that collaboration between biorepositories can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce turnaround times, and support high-quality research. Strengthening infrastructure through joint initiatives enables more effective support of large-scale clinical studies and contributes to improved outcomes for Veterans. These findings may also inform process improvements at other VA research facilities.
Purpose
Biorepositories are critical to scientific research within the VA. They offer high-quality, well-characterized biospecimens linked to clinical, demographic, and molecular data. Biorepositories support studies on disease mechanisms, personalized therapies, and emerging infectious diseases by systematically collecting, processing, storing, and distributing biological materials, including tissue, blood, and DNA samples. Within the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), biorepositories provide essential support to clinical and translational research on service- related conditions such as PTSD, traumatic brain injury, cancers, and toxic exposures. While the need for harmonized quality processes and resource allocation has long been acknowledged within the biorepository community (Siwek, 2015), each biorepository operates independently, limiting scalability and standardization. This quality improvement project describes a collaboration between two VA biorepository sites supporting a national genomic study investigating disease risk and treatment outcomes. The project aimed to expand capacity, improve processing times, and enhance quality control. Each site mirrors the other’s functions, including receiving, accessioning, processing, storing, and shipping biospecimens, and serves as a contingency site to strengthen operational resilience.
Methods
To address space limitations and improve processing efficiency, one site implemented a custom rack design, expanding storage capacity per freezer. Robotic workflows were optimized, reducing biospecimen processing time. An in-process quality control step was introduced to identify data discrepancies earlier in the workflow, reducing investigation time and supporting overall data integrity. Efficiency was measured by the increase in storage capacity and decreased processing time. Descriptive statistics were used to evaluate changes in performance. Metrics were monitored over twelve months and compared against baseline data.
Results
Following implementation, storage capacity per freezer increased by 20%, and specimen processing time decreased by 30%. The new quality control checkpoint reduced investigation times by 98%, resulting in a more streamlined workflow. These improvements enhanced coordination between sites and improved support for ongoing studies.
Conclusions
This effort demonstrates that collaboration between biorepositories can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce turnaround times, and support high-quality research. Strengthening infrastructure through joint initiatives enables more effective support of large-scale clinical studies and contributes to improved outcomes for Veterans. These findings may also inform process improvements at other VA research facilities.
Enhancing Coding Accuracy at the Hematology/Oncology Clinic: Is It Time to Hire a Dedicated Coder?
Background
Accurate clinical coding that reflects all diagnoses and problems addressed during a patient encounter is essential for the cancer program’s data quality, research initiatives, and securing VERA (Veterans Equitable Resource Allocation) funding. However, providers often face barriers such as limited time during patient visits and difficulty navigating Electronic health record (EHR) systems. These challenges lead to inaccurate coding, which undermines downstream data integrity. This quality improvement (QI) study aimed to identify these barriers and implement an intervention to improve coding accuracy, while also assessing the financial implications of improved documentation.
Methods
This QI study was conducted at the Albany Stratton VA Medical Center, focusing on hematology/ oncology outpatient encounters. A baseline chart audit of diagnosis codes from June 2023 revealed an accuracy rate of 69.8%. To address this, an intervention was implemented in which dedicated coders were assigned to support attending physicians in coding for over a two-week period. These coders reviewed and corrected diagnosis codes in real-time. A follow-up audit conducted after the intervention showed an improved coding accuracy of 82%.
Discussion/Implications
Coding remains a timeconsuming task for providers, made more difficult by EHR systems that are not user-friendly. This study demonstrated that involving dedicated coders significantly improves documentation accuracy—from 69% to 82%. In addition to data quality, the financial benefits are notable. A projected annual return on investment of $216,094 was calculated, based on an internal analysis showing that in a sample of 124 patients, 10% could have qualified for higher VERA funding based on accurate coding, generating an estimated $17,427 in additional reimbursement per patient. This cost-benefit ratio supports the recommendation to staff dedicated coders. Other interventions were also utilised, such as updating the national encounter form and auto-populating documentation in Dragon software, but had limited impact and did not directly address diagnosis accuracy respectively.
Conclusions
Targeted interventions improved coding accuracy, but sustainability remains a challenge due to time and system limitations. Future efforts should focus on hiring full-time coders. These steps can further enhance coding quality and potentially increase hospital revenue.
Background
Accurate clinical coding that reflects all diagnoses and problems addressed during a patient encounter is essential for the cancer program’s data quality, research initiatives, and securing VERA (Veterans Equitable Resource Allocation) funding. However, providers often face barriers such as limited time during patient visits and difficulty navigating Electronic health record (EHR) systems. These challenges lead to inaccurate coding, which undermines downstream data integrity. This quality improvement (QI) study aimed to identify these barriers and implement an intervention to improve coding accuracy, while also assessing the financial implications of improved documentation.
Methods
This QI study was conducted at the Albany Stratton VA Medical Center, focusing on hematology/ oncology outpatient encounters. A baseline chart audit of diagnosis codes from June 2023 revealed an accuracy rate of 69.8%. To address this, an intervention was implemented in which dedicated coders were assigned to support attending physicians in coding for over a two-week period. These coders reviewed and corrected diagnosis codes in real-time. A follow-up audit conducted after the intervention showed an improved coding accuracy of 82%.
Discussion/Implications
Coding remains a timeconsuming task for providers, made more difficult by EHR systems that are not user-friendly. This study demonstrated that involving dedicated coders significantly improves documentation accuracy—from 69% to 82%. In addition to data quality, the financial benefits are notable. A projected annual return on investment of $216,094 was calculated, based on an internal analysis showing that in a sample of 124 patients, 10% could have qualified for higher VERA funding based on accurate coding, generating an estimated $17,427 in additional reimbursement per patient. This cost-benefit ratio supports the recommendation to staff dedicated coders. Other interventions were also utilised, such as updating the national encounter form and auto-populating documentation in Dragon software, but had limited impact and did not directly address diagnosis accuracy respectively.
Conclusions
Targeted interventions improved coding accuracy, but sustainability remains a challenge due to time and system limitations. Future efforts should focus on hiring full-time coders. These steps can further enhance coding quality and potentially increase hospital revenue.
Background
Accurate clinical coding that reflects all diagnoses and problems addressed during a patient encounter is essential for the cancer program’s data quality, research initiatives, and securing VERA (Veterans Equitable Resource Allocation) funding. However, providers often face barriers such as limited time during patient visits and difficulty navigating Electronic health record (EHR) systems. These challenges lead to inaccurate coding, which undermines downstream data integrity. This quality improvement (QI) study aimed to identify these barriers and implement an intervention to improve coding accuracy, while also assessing the financial implications of improved documentation.
Methods
This QI study was conducted at the Albany Stratton VA Medical Center, focusing on hematology/ oncology outpatient encounters. A baseline chart audit of diagnosis codes from June 2023 revealed an accuracy rate of 69.8%. To address this, an intervention was implemented in which dedicated coders were assigned to support attending physicians in coding for over a two-week period. These coders reviewed and corrected diagnosis codes in real-time. A follow-up audit conducted after the intervention showed an improved coding accuracy of 82%.
Discussion/Implications
Coding remains a timeconsuming task for providers, made more difficult by EHR systems that are not user-friendly. This study demonstrated that involving dedicated coders significantly improves documentation accuracy—from 69% to 82%. In addition to data quality, the financial benefits are notable. A projected annual return on investment of $216,094 was calculated, based on an internal analysis showing that in a sample of 124 patients, 10% could have qualified for higher VERA funding based on accurate coding, generating an estimated $17,427 in additional reimbursement per patient. This cost-benefit ratio supports the recommendation to staff dedicated coders. Other interventions were also utilised, such as updating the national encounter form and auto-populating documentation in Dragon software, but had limited impact and did not directly address diagnosis accuracy respectively.
Conclusions
Targeted interventions improved coding accuracy, but sustainability remains a challenge due to time and system limitations. Future efforts should focus on hiring full-time coders. These steps can further enhance coding quality and potentially increase hospital revenue.
Evaluating the Implementation of 60-minute Iron Dextran Infusions at a Rural Health Center
Background
Due to risk for infusion-related reactions (IRR), administration of iron dextran requires an initial test dose with an extended monitoring period and subsequent doses given as a slow infusion over 2-3 hours. Safe use of a 60-minute iron dextran infusion protocol has been demonstrated previously at fully staffed academic teaching institutions. This study sought to determine the impact on patient safety and infusion clinic efficiency after implementing a 60-minute iron dextran administration protocol at a small, rural facility utilizing a decentralized clinical model.
Methods
This single-site, prospective, interventional study was conducted at a rural level 1C Veterans Affairs secondary care facility. The Hematology/Oncology clinic staffing includes one onsite clinical pharmacy practitioner (CPP) and advanced practice nurse. Remote providers complete patient encounters through video and telehealth modalities. A 60-minute iron dextran infusion service line agreement was designed by the Hematology/Oncology CPP and approved by the facility prior to data collection. The protocol included administration of a test dose and 15-minute monitoring period for treatment naïve patients. Pre-medications were allowed at the discretion of the ordering providers. All patients who received iron dextran between May 31, 2024 and April 14, 2025 per protocol were included in data analysis and results were stratified by treatment naïve and pre-treated patients. Outcomes included the proportion of patients experiencing any grade of IRR based on the Common Criteria for Adverse Events Version 5.0, and the average duration of administration. Descriptive statistics were used for safety and efficiency outcomes.
Results
Eighty patients received 103 iron dextran infusions and were included for analysis. Pre-medications were administered for 16 of the 103 (15.5%) included infusions. Two patients experienced grade 1 IRR (nausea) on 4 occasions (3.8%) which quickly resolved with intravenous ondansetron, and full iron dextran doses were received. The mean infusion time was 94 minutes in the treatment naïve cohort vs 71 minutes in the pre-treated cohort.
Conclusions
This study suggests a Hematology/ Oncology CPP developed iron dextran 60-minute infusion protocol may be safely and efficiently administered for qualifying patients in a decentralized, rural healthcare setting.
Background
Due to risk for infusion-related reactions (IRR), administration of iron dextran requires an initial test dose with an extended monitoring period and subsequent doses given as a slow infusion over 2-3 hours. Safe use of a 60-minute iron dextran infusion protocol has been demonstrated previously at fully staffed academic teaching institutions. This study sought to determine the impact on patient safety and infusion clinic efficiency after implementing a 60-minute iron dextran administration protocol at a small, rural facility utilizing a decentralized clinical model.
Methods
This single-site, prospective, interventional study was conducted at a rural level 1C Veterans Affairs secondary care facility. The Hematology/Oncology clinic staffing includes one onsite clinical pharmacy practitioner (CPP) and advanced practice nurse. Remote providers complete patient encounters through video and telehealth modalities. A 60-minute iron dextran infusion service line agreement was designed by the Hematology/Oncology CPP and approved by the facility prior to data collection. The protocol included administration of a test dose and 15-minute monitoring period for treatment naïve patients. Pre-medications were allowed at the discretion of the ordering providers. All patients who received iron dextran between May 31, 2024 and April 14, 2025 per protocol were included in data analysis and results were stratified by treatment naïve and pre-treated patients. Outcomes included the proportion of patients experiencing any grade of IRR based on the Common Criteria for Adverse Events Version 5.0, and the average duration of administration. Descriptive statistics were used for safety and efficiency outcomes.
Results
Eighty patients received 103 iron dextran infusions and were included for analysis. Pre-medications were administered for 16 of the 103 (15.5%) included infusions. Two patients experienced grade 1 IRR (nausea) on 4 occasions (3.8%) which quickly resolved with intravenous ondansetron, and full iron dextran doses were received. The mean infusion time was 94 minutes in the treatment naïve cohort vs 71 minutes in the pre-treated cohort.
Conclusions
This study suggests a Hematology/ Oncology CPP developed iron dextran 60-minute infusion protocol may be safely and efficiently administered for qualifying patients in a decentralized, rural healthcare setting.
Background
Due to risk for infusion-related reactions (IRR), administration of iron dextran requires an initial test dose with an extended monitoring period and subsequent doses given as a slow infusion over 2-3 hours. Safe use of a 60-minute iron dextran infusion protocol has been demonstrated previously at fully staffed academic teaching institutions. This study sought to determine the impact on patient safety and infusion clinic efficiency after implementing a 60-minute iron dextran administration protocol at a small, rural facility utilizing a decentralized clinical model.
Methods
This single-site, prospective, interventional study was conducted at a rural level 1C Veterans Affairs secondary care facility. The Hematology/Oncology clinic staffing includes one onsite clinical pharmacy practitioner (CPP) and advanced practice nurse. Remote providers complete patient encounters through video and telehealth modalities. A 60-minute iron dextran infusion service line agreement was designed by the Hematology/Oncology CPP and approved by the facility prior to data collection. The protocol included administration of a test dose and 15-minute monitoring period for treatment naïve patients. Pre-medications were allowed at the discretion of the ordering providers. All patients who received iron dextran between May 31, 2024 and April 14, 2025 per protocol were included in data analysis and results were stratified by treatment naïve and pre-treated patients. Outcomes included the proportion of patients experiencing any grade of IRR based on the Common Criteria for Adverse Events Version 5.0, and the average duration of administration. Descriptive statistics were used for safety and efficiency outcomes.
Results
Eighty patients received 103 iron dextran infusions and were included for analysis. Pre-medications were administered for 16 of the 103 (15.5%) included infusions. Two patients experienced grade 1 IRR (nausea) on 4 occasions (3.8%) which quickly resolved with intravenous ondansetron, and full iron dextran doses were received. The mean infusion time was 94 minutes in the treatment naïve cohort vs 71 minutes in the pre-treated cohort.
Conclusions
This study suggests a Hematology/ Oncology CPP developed iron dextran 60-minute infusion protocol may be safely and efficiently administered for qualifying patients in a decentralized, rural healthcare setting.
Improving Palliative Care Referrals through Education of Hematology/Oncology Fellows: A QI Initiative
Purpose/Background
Palliative care referrals are recommended for patients with advanced or metastatic cancer to enhance patient and caregiver outcomes. However, challenges like delays or lack of referrals hinder implementation. This study identified rate of palliative care referrals at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital in Tampa, Florida; explored potential barriers to referral, and implemented targeted interventions to improve referral rates and patient outcomes.
Methods
A Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle was used for this quality improvement project. Data was collected from electronic medical record, focusing on consult dates, patient demographics, and reasons for seeking palliative care. Pre-intervention surveys were administered to Hematology-Oncology fellows at the institution to identify barriers to referral. Following a root cause analysis, a targeted intervention was developed, focusing on educational programs for fellows for streamlined referral processes.
Results
Before the intervention, monthly average for palliative care consults was low (3-8, typically 5). Pre-intervention surveys revealed that fellows lacked knowledge about palliative care resources, which contributed to low referral rates. To address this issue, a didactic session led by a palliative care specialist was conducted for the fellows in the fellowship program. This session provided education on the role of palliative care, how to initiate referrals, and the benefits of early involvement of palliative care teams in oncology patient management. Post-intervention surveys showed a marked improvement in fellows’ confidence regarding identification of patients suitable for palliative care. Following the session, 90% (9/10) of fellows reported being “very likely” to consult palliative care more often and 80% (8/10) indicated they were “very likely” to initiate palliative care discussions earlier in patient’s disease trajectory, with the remaining 20% (2/10) reporting a neutral stance. All fellows (100%) agreed that earlier palliative care involvement improves patient outcomes.
Implications/Significance
This PDSA cycle demonstrated that targeted education for fellows can increase awareness of palliative care resources and improve referral rates. Future work will focus on reassessing usage of palliative care consults post-intervention to evaluate effects of fellows’ education of appropriate palliative care consultation, make necessary interventions based on data and further evaluate the long-term impact on patient outcomes at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
Purpose/Background
Palliative care referrals are recommended for patients with advanced or metastatic cancer to enhance patient and caregiver outcomes. However, challenges like delays or lack of referrals hinder implementation. This study identified rate of palliative care referrals at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital in Tampa, Florida; explored potential barriers to referral, and implemented targeted interventions to improve referral rates and patient outcomes.
Methods
A Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle was used for this quality improvement project. Data was collected from electronic medical record, focusing on consult dates, patient demographics, and reasons for seeking palliative care. Pre-intervention surveys were administered to Hematology-Oncology fellows at the institution to identify barriers to referral. Following a root cause analysis, a targeted intervention was developed, focusing on educational programs for fellows for streamlined referral processes.
Results
Before the intervention, monthly average for palliative care consults was low (3-8, typically 5). Pre-intervention surveys revealed that fellows lacked knowledge about palliative care resources, which contributed to low referral rates. To address this issue, a didactic session led by a palliative care specialist was conducted for the fellows in the fellowship program. This session provided education on the role of palliative care, how to initiate referrals, and the benefits of early involvement of palliative care teams in oncology patient management. Post-intervention surveys showed a marked improvement in fellows’ confidence regarding identification of patients suitable for palliative care. Following the session, 90% (9/10) of fellows reported being “very likely” to consult palliative care more often and 80% (8/10) indicated they were “very likely” to initiate palliative care discussions earlier in patient’s disease trajectory, with the remaining 20% (2/10) reporting a neutral stance. All fellows (100%) agreed that earlier palliative care involvement improves patient outcomes.
Implications/Significance
This PDSA cycle demonstrated that targeted education for fellows can increase awareness of palliative care resources and improve referral rates. Future work will focus on reassessing usage of palliative care consults post-intervention to evaluate effects of fellows’ education of appropriate palliative care consultation, make necessary interventions based on data and further evaluate the long-term impact on patient outcomes at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
Purpose/Background
Palliative care referrals are recommended for patients with advanced or metastatic cancer to enhance patient and caregiver outcomes. However, challenges like delays or lack of referrals hinder implementation. This study identified rate of palliative care referrals at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital in Tampa, Florida; explored potential barriers to referral, and implemented targeted interventions to improve referral rates and patient outcomes.
Methods
A Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle was used for this quality improvement project. Data was collected from electronic medical record, focusing on consult dates, patient demographics, and reasons for seeking palliative care. Pre-intervention surveys were administered to Hematology-Oncology fellows at the institution to identify barriers to referral. Following a root cause analysis, a targeted intervention was developed, focusing on educational programs for fellows for streamlined referral processes.
Results
Before the intervention, monthly average for palliative care consults was low (3-8, typically 5). Pre-intervention surveys revealed that fellows lacked knowledge about palliative care resources, which contributed to low referral rates. To address this issue, a didactic session led by a palliative care specialist was conducted for the fellows in the fellowship program. This session provided education on the role of palliative care, how to initiate referrals, and the benefits of early involvement of palliative care teams in oncology patient management. Post-intervention surveys showed a marked improvement in fellows’ confidence regarding identification of patients suitable for palliative care. Following the session, 90% (9/10) of fellows reported being “very likely” to consult palliative care more often and 80% (8/10) indicated they were “very likely” to initiate palliative care discussions earlier in patient’s disease trajectory, with the remaining 20% (2/10) reporting a neutral stance. All fellows (100%) agreed that earlier palliative care involvement improves patient outcomes.
Implications/Significance
This PDSA cycle demonstrated that targeted education for fellows can increase awareness of palliative care resources and improve referral rates. Future work will focus on reassessing usage of palliative care consults post-intervention to evaluate effects of fellows’ education of appropriate palliative care consultation, make necessary interventions based on data and further evaluate the long-term impact on patient outcomes at James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
Optimizing Symptom Management in VA Oncology: A Workflow-Based Quality Improvement Initiative
Background
Enhancing symptom assessment and management of patients undergoing cancer treatment presents several challenges, ranging from workflow integration to application of evidenced-based interventions (Minteer, et al., 2023). Previously, our team conducted a VA mixed-methods study and identified a lack of standardized approaches for symptom assessment, lack of technology support to optimize workflows, and the need for adaptable workflows that reflect both facility and patient preferences. In response, the National Oncology Program Office at Palo Alto VA (PAVA) launched the Proactive Patient-Centered Care Program (PPP) to address these care gaps and develop a feasible, replicable, sustainable workflow to guide broader VA-wide implementation based on prior work conducted by the PAVA team (Banks, et al., 2024).
Methods
Prior to launch, the PPP team engaged oncology leadership in VISN21 and VISN22. Long Beach VA (LBVA) was selected as the initial pilot implementation site. A multidisciplinary group from PAVA and LBVA comprised of oncology and palliative care clinicians, nurses, pharmacists, a lay health worker, and project manager guided the workflow adaptations. To support scalability and sustainability, the Empowering Learning, Innovation, and experiences through Implementation of health Informatics (ELIXIR) team designed an electronic health record agnostic technology-enabled tool to support workflow. The group met weekly to bi-monthly over 5 months, virtually and two in-person sessions, to map current practices, co-develop workflows, and identify key decisions regarding patient eligibility criteria, frequency of symptom assessments, triage responsibilities, escalation protocols, and closed-loop communication processes.
Results
A technology-enabled workflow was developed to deploy proactive symptom assessment and management across VA oncology sites with streamlined coordination between peer support staff and clinicians along with technology to support timely interventions.
Conclusions
Process improvement for symptom management requires on the ground adaptation even within an integrated health system like the VA. This initiative underscores the need for multidisciplinary collaboration, sustainability, and technology integration to support long-term intervention fidelity and scalability. The workflow developed will guide the PPP program’s expansion to LBVA, with patient enrollment beginning May 2025. The approach used to develop this workflow will serve as a model for standardizing supportive care processes across the VA to account for local needs.
Background
Enhancing symptom assessment and management of patients undergoing cancer treatment presents several challenges, ranging from workflow integration to application of evidenced-based interventions (Minteer, et al., 2023). Previously, our team conducted a VA mixed-methods study and identified a lack of standardized approaches for symptom assessment, lack of technology support to optimize workflows, and the need for adaptable workflows that reflect both facility and patient preferences. In response, the National Oncology Program Office at Palo Alto VA (PAVA) launched the Proactive Patient-Centered Care Program (PPP) to address these care gaps and develop a feasible, replicable, sustainable workflow to guide broader VA-wide implementation based on prior work conducted by the PAVA team (Banks, et al., 2024).
Methods
Prior to launch, the PPP team engaged oncology leadership in VISN21 and VISN22. Long Beach VA (LBVA) was selected as the initial pilot implementation site. A multidisciplinary group from PAVA and LBVA comprised of oncology and palliative care clinicians, nurses, pharmacists, a lay health worker, and project manager guided the workflow adaptations. To support scalability and sustainability, the Empowering Learning, Innovation, and experiences through Implementation of health Informatics (ELIXIR) team designed an electronic health record agnostic technology-enabled tool to support workflow. The group met weekly to bi-monthly over 5 months, virtually and two in-person sessions, to map current practices, co-develop workflows, and identify key decisions regarding patient eligibility criteria, frequency of symptom assessments, triage responsibilities, escalation protocols, and closed-loop communication processes.
Results
A technology-enabled workflow was developed to deploy proactive symptom assessment and management across VA oncology sites with streamlined coordination between peer support staff and clinicians along with technology to support timely interventions.
Conclusions
Process improvement for symptom management requires on the ground adaptation even within an integrated health system like the VA. This initiative underscores the need for multidisciplinary collaboration, sustainability, and technology integration to support long-term intervention fidelity and scalability. The workflow developed will guide the PPP program’s expansion to LBVA, with patient enrollment beginning May 2025. The approach used to develop this workflow will serve as a model for standardizing supportive care processes across the VA to account for local needs.
Background
Enhancing symptom assessment and management of patients undergoing cancer treatment presents several challenges, ranging from workflow integration to application of evidenced-based interventions (Minteer, et al., 2023). Previously, our team conducted a VA mixed-methods study and identified a lack of standardized approaches for symptom assessment, lack of technology support to optimize workflows, and the need for adaptable workflows that reflect both facility and patient preferences. In response, the National Oncology Program Office at Palo Alto VA (PAVA) launched the Proactive Patient-Centered Care Program (PPP) to address these care gaps and develop a feasible, replicable, sustainable workflow to guide broader VA-wide implementation based on prior work conducted by the PAVA team (Banks, et al., 2024).
Methods
Prior to launch, the PPP team engaged oncology leadership in VISN21 and VISN22. Long Beach VA (LBVA) was selected as the initial pilot implementation site. A multidisciplinary group from PAVA and LBVA comprised of oncology and palliative care clinicians, nurses, pharmacists, a lay health worker, and project manager guided the workflow adaptations. To support scalability and sustainability, the Empowering Learning, Innovation, and experiences through Implementation of health Informatics (ELIXIR) team designed an electronic health record agnostic technology-enabled tool to support workflow. The group met weekly to bi-monthly over 5 months, virtually and two in-person sessions, to map current practices, co-develop workflows, and identify key decisions regarding patient eligibility criteria, frequency of symptom assessments, triage responsibilities, escalation protocols, and closed-loop communication processes.
Results
A technology-enabled workflow was developed to deploy proactive symptom assessment and management across VA oncology sites with streamlined coordination between peer support staff and clinicians along with technology to support timely interventions.
Conclusions
Process improvement for symptom management requires on the ground adaptation even within an integrated health system like the VA. This initiative underscores the need for multidisciplinary collaboration, sustainability, and technology integration to support long-term intervention fidelity and scalability. The workflow developed will guide the PPP program’s expansion to LBVA, with patient enrollment beginning May 2025. The approach used to develop this workflow will serve as a model for standardizing supportive care processes across the VA to account for local needs.
Implementation of Consult Template Optimizes Hematology E-Consult Evaluation
Purpose/Background
The purpose of this project was to understand how implementing a consult template could optimize hematology E-consult evaluation. At the Tampa VA, providers can submit hematology E-consults for interpretation of lab abnormalities and management recommendations that do not require an in-person hematology evaluation. Previously, submission of an E-consult did not require prerequisite labs or imaging or for lab parameters to be met, leading to an increased number of hematology E-consults and subsequently, lower efficiency for hematologists.
Methods
A hematology E-consult template was created through collaboration between the hematology/ oncology and ambulatory care sections, which lists specific diagnoses and required parameters/workup needed for each diagnosis prior to submission of the E-consult. If those criteria were not met, the consult was cancelled. A representative sample of one month pre- and post-implementation data was analyzed.
Results
The E-consult template was implemented in September 2024. From April to August 2024, the average number of E-consults per month was 243, averaging at 11.0 per day, while from October 2024 to February 2025, the average number of E-consults per month was 146.4, averaging at 6.6 per day. In August 2024, the leading reasons for consult were anemia (77), leukocytosis (26), and thrombocytopenia (24). That month, there were 15 consult cancellations, with the primary reason being the patient was established in clinic (9). In October 2024, the leading reasons for consult were anemia (39), leukocytosis (14), and thrombocytopenia (13). That month, there were 34 consult cancellations, with the primary reason being that hematology advised a clinic consultation rather than an E-consult (10).
Implications/Significance
These data reveal that the hematology E-consult template was associated with a decreased number of E-consults per day and per month. Implementation of the hematology E-consult template allows the hematology consultants to focus on interpretation of lab results and providing management recommendations, as opposed to providing standard of care diagnostic recommendations. It also serves as an educational tool to referring providers, to understand appropriate indications for hematology E-consultation. Lastly, the template has created increased efficiency in providing hematology recommendations and ultimately, improved timely care for our veterans.
Purpose/Background
The purpose of this project was to understand how implementing a consult template could optimize hematology E-consult evaluation. At the Tampa VA, providers can submit hematology E-consults for interpretation of lab abnormalities and management recommendations that do not require an in-person hematology evaluation. Previously, submission of an E-consult did not require prerequisite labs or imaging or for lab parameters to be met, leading to an increased number of hematology E-consults and subsequently, lower efficiency for hematologists.
Methods
A hematology E-consult template was created through collaboration between the hematology/ oncology and ambulatory care sections, which lists specific diagnoses and required parameters/workup needed for each diagnosis prior to submission of the E-consult. If those criteria were not met, the consult was cancelled. A representative sample of one month pre- and post-implementation data was analyzed.
Results
The E-consult template was implemented in September 2024. From April to August 2024, the average number of E-consults per month was 243, averaging at 11.0 per day, while from October 2024 to February 2025, the average number of E-consults per month was 146.4, averaging at 6.6 per day. In August 2024, the leading reasons for consult were anemia (77), leukocytosis (26), and thrombocytopenia (24). That month, there were 15 consult cancellations, with the primary reason being the patient was established in clinic (9). In October 2024, the leading reasons for consult were anemia (39), leukocytosis (14), and thrombocytopenia (13). That month, there were 34 consult cancellations, with the primary reason being that hematology advised a clinic consultation rather than an E-consult (10).
Implications/Significance
These data reveal that the hematology E-consult template was associated with a decreased number of E-consults per day and per month. Implementation of the hematology E-consult template allows the hematology consultants to focus on interpretation of lab results and providing management recommendations, as opposed to providing standard of care diagnostic recommendations. It also serves as an educational tool to referring providers, to understand appropriate indications for hematology E-consultation. Lastly, the template has created increased efficiency in providing hematology recommendations and ultimately, improved timely care for our veterans.
Purpose/Background
The purpose of this project was to understand how implementing a consult template could optimize hematology E-consult evaluation. At the Tampa VA, providers can submit hematology E-consults for interpretation of lab abnormalities and management recommendations that do not require an in-person hematology evaluation. Previously, submission of an E-consult did not require prerequisite labs or imaging or for lab parameters to be met, leading to an increased number of hematology E-consults and subsequently, lower efficiency for hematologists.
Methods
A hematology E-consult template was created through collaboration between the hematology/ oncology and ambulatory care sections, which lists specific diagnoses and required parameters/workup needed for each diagnosis prior to submission of the E-consult. If those criteria were not met, the consult was cancelled. A representative sample of one month pre- and post-implementation data was analyzed.
Results
The E-consult template was implemented in September 2024. From April to August 2024, the average number of E-consults per month was 243, averaging at 11.0 per day, while from October 2024 to February 2025, the average number of E-consults per month was 146.4, averaging at 6.6 per day. In August 2024, the leading reasons for consult were anemia (77), leukocytosis (26), and thrombocytopenia (24). That month, there were 15 consult cancellations, with the primary reason being the patient was established in clinic (9). In October 2024, the leading reasons for consult were anemia (39), leukocytosis (14), and thrombocytopenia (13). That month, there were 34 consult cancellations, with the primary reason being that hematology advised a clinic consultation rather than an E-consult (10).
Implications/Significance
These data reveal that the hematology E-consult template was associated with a decreased number of E-consults per day and per month. Implementation of the hematology E-consult template allows the hematology consultants to focus on interpretation of lab results and providing management recommendations, as opposed to providing standard of care diagnostic recommendations. It also serves as an educational tool to referring providers, to understand appropriate indications for hematology E-consultation. Lastly, the template has created increased efficiency in providing hematology recommendations and ultimately, improved timely care for our veterans.
Enhancing Workforce Practices to Achieve Commission on Cancer Accreditation
Background
The American College of Surgeons’ Commission on Cancer (CoC) Accreditation requires establishment of a comprehensive cancer program, multi-disciplinary tumor boards, active cancer registry, quality improvement activities and cancer research.
Methods
In 2022, the Tibor Rubin VA Medical Center (TRVAMC) set out to obtain accreditation through enhancing workforce practices. Changes in workforce practices included (1) leadership engagement; (2) acquisition of staff; (3) enhancing staff efficiency and (4) inter-departmental collaboration, leading to CoC accreditation in August 2024. executive leadership team (ELT) buy-in was essential. ELT engagement included communicating the benefits of accreditation, alignment with organizational mission and values, protected time for Cancer Committee members, Chief of Staff presence in Cancer Committee, commitment to recruiting new staff, and membership in the Medical Executive Council to voice cancer program needs. New staff included a cancer program manager, cancer case conference RN care coordinator, certified oncology data specialist and survivorship nurse practitioner. Staff development included structured and focused training. Enhancing staff efficiency included developing standards of work with clear delineation of duties (delegation of specific CoC standards), decentralizing decision making, a shared governance council, and weekly Cancer Program meetings. These changes allowed staff members to be active, autonomous decision-making participants, and increased efficiency. Inter-departmental collaboration involved Hematology/Oncology, Surgery, Radiation Oncology, Pharmacy, Nutrition, Pathology, Palliative Care, Rehabilitation, Chaplaincy and Cancer Research, with key individuals serving as Cancer Committee members. Each department set performance goals and metrics. Each employee’s contribution was rated in annual performance reviews.
Results
TRVAMC thus elevated cancer care delivery standards through structured workforce practices within the framework of CoC standards required for accreditation. Additionally, the accreditation process achieved desirable and measurable outcomes, e.g. 100% growth in oncology dietitian referrals, 75% increase in early palliative care referrals (TRVAMC ranked in the top 5 in the US), and more than 200 patients enrolled in cancer clinical trials (TRVAMC was the highest enrolling VA in the US to NCI trials in 2024).
Conclusions
Our model demonstrates how strategic improvements in healthcare workforce practices at a VA can directly contribute to sustained improvements in quality and delivery of cancer care services.
Background
The American College of Surgeons’ Commission on Cancer (CoC) Accreditation requires establishment of a comprehensive cancer program, multi-disciplinary tumor boards, active cancer registry, quality improvement activities and cancer research.
Methods
In 2022, the Tibor Rubin VA Medical Center (TRVAMC) set out to obtain accreditation through enhancing workforce practices. Changes in workforce practices included (1) leadership engagement; (2) acquisition of staff; (3) enhancing staff efficiency and (4) inter-departmental collaboration, leading to CoC accreditation in August 2024. executive leadership team (ELT) buy-in was essential. ELT engagement included communicating the benefits of accreditation, alignment with organizational mission and values, protected time for Cancer Committee members, Chief of Staff presence in Cancer Committee, commitment to recruiting new staff, and membership in the Medical Executive Council to voice cancer program needs. New staff included a cancer program manager, cancer case conference RN care coordinator, certified oncology data specialist and survivorship nurse practitioner. Staff development included structured and focused training. Enhancing staff efficiency included developing standards of work with clear delineation of duties (delegation of specific CoC standards), decentralizing decision making, a shared governance council, and weekly Cancer Program meetings. These changes allowed staff members to be active, autonomous decision-making participants, and increased efficiency. Inter-departmental collaboration involved Hematology/Oncology, Surgery, Radiation Oncology, Pharmacy, Nutrition, Pathology, Palliative Care, Rehabilitation, Chaplaincy and Cancer Research, with key individuals serving as Cancer Committee members. Each department set performance goals and metrics. Each employee’s contribution was rated in annual performance reviews.
Results
TRVAMC thus elevated cancer care delivery standards through structured workforce practices within the framework of CoC standards required for accreditation. Additionally, the accreditation process achieved desirable and measurable outcomes, e.g. 100% growth in oncology dietitian referrals, 75% increase in early palliative care referrals (TRVAMC ranked in the top 5 in the US), and more than 200 patients enrolled in cancer clinical trials (TRVAMC was the highest enrolling VA in the US to NCI trials in 2024).
Conclusions
Our model demonstrates how strategic improvements in healthcare workforce practices at a VA can directly contribute to sustained improvements in quality and delivery of cancer care services.
Background
The American College of Surgeons’ Commission on Cancer (CoC) Accreditation requires establishment of a comprehensive cancer program, multi-disciplinary tumor boards, active cancer registry, quality improvement activities and cancer research.
Methods
In 2022, the Tibor Rubin VA Medical Center (TRVAMC) set out to obtain accreditation through enhancing workforce practices. Changes in workforce practices included (1) leadership engagement; (2) acquisition of staff; (3) enhancing staff efficiency and (4) inter-departmental collaboration, leading to CoC accreditation in August 2024. executive leadership team (ELT) buy-in was essential. ELT engagement included communicating the benefits of accreditation, alignment with organizational mission and values, protected time for Cancer Committee members, Chief of Staff presence in Cancer Committee, commitment to recruiting new staff, and membership in the Medical Executive Council to voice cancer program needs. New staff included a cancer program manager, cancer case conference RN care coordinator, certified oncology data specialist and survivorship nurse practitioner. Staff development included structured and focused training. Enhancing staff efficiency included developing standards of work with clear delineation of duties (delegation of specific CoC standards), decentralizing decision making, a shared governance council, and weekly Cancer Program meetings. These changes allowed staff members to be active, autonomous decision-making participants, and increased efficiency. Inter-departmental collaboration involved Hematology/Oncology, Surgery, Radiation Oncology, Pharmacy, Nutrition, Pathology, Palliative Care, Rehabilitation, Chaplaincy and Cancer Research, with key individuals serving as Cancer Committee members. Each department set performance goals and metrics. Each employee’s contribution was rated in annual performance reviews.
Results
TRVAMC thus elevated cancer care delivery standards through structured workforce practices within the framework of CoC standards required for accreditation. Additionally, the accreditation process achieved desirable and measurable outcomes, e.g. 100% growth in oncology dietitian referrals, 75% increase in early palliative care referrals (TRVAMC ranked in the top 5 in the US), and more than 200 patients enrolled in cancer clinical trials (TRVAMC was the highest enrolling VA in the US to NCI trials in 2024).
Conclusions
Our model demonstrates how strategic improvements in healthcare workforce practices at a VA can directly contribute to sustained improvements in quality and delivery of cancer care services.
National Radiation Oncology Program Granular Radiotherapy Information Database
Purpose/Objectives
Radiation oncology treatment planning and delivery systems are predominantly designed as silos, centered around the care of individual patients and generally disconnected from the broader health record. This poses significant challenges for cohort or population scale research, particularly when trying to analyze the nuances and details of treatments. The National Radiation Oncology Program (NROP) sought to design, develop, and implement a platform-agnostic tool to extract clinically meaningful treatment details from DICOM-RT data and applied this in a pilot initiative to centralize data from several VA distinct treatment facilities and merge the resulting dataset with the broader electronic health record to support research and clinical operations.
Methods
Leveraging NROP’s Health Information Gateway Exchange (HINGE) system, we developed the capability to analyze DICOM-RT datasets and output detailed and clinically meaningful radiation treatment information including but not limited to structure-specific dose volume histogram data, individual beam-level treatment details, and verified delivered fraction data. We applied this to historical data from VA facilities participating in NROP’s initial pilot and linked the resulting data with the broader electronic health record on an individual patient level, constituting the Granular Radiotherapy Information Database (GRID).
Results
We demonstrate successful export of clinically meaningful treatment details from a large real-world cohort of VA patients treated between 2012-2024. This constitutes a novel source of authoritative radiation oncology data within the VA CDW. We confirmed the ability to arbitrarily query these cohorts based on both the intrinsic data export as well as its linkages to the broader electronic health record.
Conclusions
This is a proof-of-principle study demonstrating the ability to extract and integrate detailed radiotherapy data with the broader health record, as well as enable unprecedented arbitrary queries at population scale and broad reuse in the VA research and clinical operations.
Purpose/Objectives
Radiation oncology treatment planning and delivery systems are predominantly designed as silos, centered around the care of individual patients and generally disconnected from the broader health record. This poses significant challenges for cohort or population scale research, particularly when trying to analyze the nuances and details of treatments. The National Radiation Oncology Program (NROP) sought to design, develop, and implement a platform-agnostic tool to extract clinically meaningful treatment details from DICOM-RT data and applied this in a pilot initiative to centralize data from several VA distinct treatment facilities and merge the resulting dataset with the broader electronic health record to support research and clinical operations.
Methods
Leveraging NROP’s Health Information Gateway Exchange (HINGE) system, we developed the capability to analyze DICOM-RT datasets and output detailed and clinically meaningful radiation treatment information including but not limited to structure-specific dose volume histogram data, individual beam-level treatment details, and verified delivered fraction data. We applied this to historical data from VA facilities participating in NROP’s initial pilot and linked the resulting data with the broader electronic health record on an individual patient level, constituting the Granular Radiotherapy Information Database (GRID).
Results
We demonstrate successful export of clinically meaningful treatment details from a large real-world cohort of VA patients treated between 2012-2024. This constitutes a novel source of authoritative radiation oncology data within the VA CDW. We confirmed the ability to arbitrarily query these cohorts based on both the intrinsic data export as well as its linkages to the broader electronic health record.
Conclusions
This is a proof-of-principle study demonstrating the ability to extract and integrate detailed radiotherapy data with the broader health record, as well as enable unprecedented arbitrary queries at population scale and broad reuse in the VA research and clinical operations.
Purpose/Objectives
Radiation oncology treatment planning and delivery systems are predominantly designed as silos, centered around the care of individual patients and generally disconnected from the broader health record. This poses significant challenges for cohort or population scale research, particularly when trying to analyze the nuances and details of treatments. The National Radiation Oncology Program (NROP) sought to design, develop, and implement a platform-agnostic tool to extract clinically meaningful treatment details from DICOM-RT data and applied this in a pilot initiative to centralize data from several VA distinct treatment facilities and merge the resulting dataset with the broader electronic health record to support research and clinical operations.
Methods
Leveraging NROP’s Health Information Gateway Exchange (HINGE) system, we developed the capability to analyze DICOM-RT datasets and output detailed and clinically meaningful radiation treatment information including but not limited to structure-specific dose volume histogram data, individual beam-level treatment details, and verified delivered fraction data. We applied this to historical data from VA facilities participating in NROP’s initial pilot and linked the resulting data with the broader electronic health record on an individual patient level, constituting the Granular Radiotherapy Information Database (GRID).
Results
We demonstrate successful export of clinically meaningful treatment details from a large real-world cohort of VA patients treated between 2012-2024. This constitutes a novel source of authoritative radiation oncology data within the VA CDW. We confirmed the ability to arbitrarily query these cohorts based on both the intrinsic data export as well as its linkages to the broader electronic health record.
Conclusions
This is a proof-of-principle study demonstrating the ability to extract and integrate detailed radiotherapy data with the broader health record, as well as enable unprecedented arbitrary queries at population scale and broad reuse in the VA research and clinical operations.
Implementation of a VHA Virtual Oncology Training Pilot Program for Clinical Pharmacists
Purpose/Background
Oncology clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPP) play a critical role in optimizing drug therapy, managing side effects, and ensuring medication adherence. As a specialized clinical area, specific training is needed to ensure quality of care. Oncology pharmacy training programs are commercially available but pose a financial burden and are not specific to the Veterans Health Administration (VHA). A comprehensive, virtual Oncology Bootcamp series was implemented to upskill new oncology pharmacists (or pharmacists seeking to further their understanding of oncology practice), with didactic materials and clinical tools to enhance and standardize quality care delivery.
Methods
This program was comprised of an online platform of 23 one hour-long continuing education accredited sessions, delivered by leading subject matter experts. Pharmacists from two Veteran Integrated Service Networks (VISNs) were invited for the first year of the bootcamp. The curriculum encompassed fundamentals of oncology practice, patient care assessment, chemotherapy protocol review, practice management, and supportive care. Participants also received in-depth training on managing various cancer types, including but not limited to prostate, lung, gastrointestinal and hematologic malignancies. VHA specific information, including utilization of Oncology Clinical Pathways to promote standardized care was included where applicable. The interactive nature of the virtual sessions provided opportunities for real-time discussion and immediate feedback. To measure the impact of this program, a pre and post program evaluation of participants was conducted.
Results
Over the course of the program, more than 40 pharmacists across two VISNs participated in the bootcamp series. Results of the program evaluation showed an increase in self-reported comfort and skill levels in all criteria that were assessed (oncology pharmacotherapy, solid tumor malignancies, hematologic malignancies and oral anti-cancer therapy management). Additionally, 85% of respondents stated the series met their overall goals and over 90% of respondents stated they were either satisfied or very satisfied with the content, speakers and organization of the course.
Implications/Significance
This initiative has established the viability and significance of a highly accessible, VHA pathway specific and Veteran centric platform for oncology pharmacy professional development. Future directions for the program include a broader nationwide audience, increased content coverage and self-paced learning options.
Purpose/Background
Oncology clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPP) play a critical role in optimizing drug therapy, managing side effects, and ensuring medication adherence. As a specialized clinical area, specific training is needed to ensure quality of care. Oncology pharmacy training programs are commercially available but pose a financial burden and are not specific to the Veterans Health Administration (VHA). A comprehensive, virtual Oncology Bootcamp series was implemented to upskill new oncology pharmacists (or pharmacists seeking to further their understanding of oncology practice), with didactic materials and clinical tools to enhance and standardize quality care delivery.
Methods
This program was comprised of an online platform of 23 one hour-long continuing education accredited sessions, delivered by leading subject matter experts. Pharmacists from two Veteran Integrated Service Networks (VISNs) were invited for the first year of the bootcamp. The curriculum encompassed fundamentals of oncology practice, patient care assessment, chemotherapy protocol review, practice management, and supportive care. Participants also received in-depth training on managing various cancer types, including but not limited to prostate, lung, gastrointestinal and hematologic malignancies. VHA specific information, including utilization of Oncology Clinical Pathways to promote standardized care was included where applicable. The interactive nature of the virtual sessions provided opportunities for real-time discussion and immediate feedback. To measure the impact of this program, a pre and post program evaluation of participants was conducted.
Results
Over the course of the program, more than 40 pharmacists across two VISNs participated in the bootcamp series. Results of the program evaluation showed an increase in self-reported comfort and skill levels in all criteria that were assessed (oncology pharmacotherapy, solid tumor malignancies, hematologic malignancies and oral anti-cancer therapy management). Additionally, 85% of respondents stated the series met their overall goals and over 90% of respondents stated they were either satisfied or very satisfied with the content, speakers and organization of the course.
Implications/Significance
This initiative has established the viability and significance of a highly accessible, VHA pathway specific and Veteran centric platform for oncology pharmacy professional development. Future directions for the program include a broader nationwide audience, increased content coverage and self-paced learning options.
Purpose/Background
Oncology clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPP) play a critical role in optimizing drug therapy, managing side effects, and ensuring medication adherence. As a specialized clinical area, specific training is needed to ensure quality of care. Oncology pharmacy training programs are commercially available but pose a financial burden and are not specific to the Veterans Health Administration (VHA). A comprehensive, virtual Oncology Bootcamp series was implemented to upskill new oncology pharmacists (or pharmacists seeking to further their understanding of oncology practice), with didactic materials and clinical tools to enhance and standardize quality care delivery.
Methods
This program was comprised of an online platform of 23 one hour-long continuing education accredited sessions, delivered by leading subject matter experts. Pharmacists from two Veteran Integrated Service Networks (VISNs) were invited for the first year of the bootcamp. The curriculum encompassed fundamentals of oncology practice, patient care assessment, chemotherapy protocol review, practice management, and supportive care. Participants also received in-depth training on managing various cancer types, including but not limited to prostate, lung, gastrointestinal and hematologic malignancies. VHA specific information, including utilization of Oncology Clinical Pathways to promote standardized care was included where applicable. The interactive nature of the virtual sessions provided opportunities for real-time discussion and immediate feedback. To measure the impact of this program, a pre and post program evaluation of participants was conducted.
Results
Over the course of the program, more than 40 pharmacists across two VISNs participated in the bootcamp series. Results of the program evaluation showed an increase in self-reported comfort and skill levels in all criteria that were assessed (oncology pharmacotherapy, solid tumor malignancies, hematologic malignancies and oral anti-cancer therapy management). Additionally, 85% of respondents stated the series met their overall goals and over 90% of respondents stated they were either satisfied or very satisfied with the content, speakers and organization of the course.
Implications/Significance
This initiative has established the viability and significance of a highly accessible, VHA pathway specific and Veteran centric platform for oncology pharmacy professional development. Future directions for the program include a broader nationwide audience, increased content coverage and self-paced learning options.
