User login
What makes teens choose to use sunscreen?
a cornerstone of skin cancer prevention, according to results from a systematic review.
“We know that skin cancer is one of the most common malignancies in the world, and sun protection methods such as sunscreen make it highly preventable,” first author Carly R. Stevens, a student at Tulane University, New Orleans, said in an interview. “This study demonstrates the adolescent populations that are most vulnerable to sun damage and how we can help mitigate their risk of developing skin cancer through education methods, such as Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students.”
Ms. Stevens and coauthors presented the findings during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
To investigate predictors of sunscreen use among high school students, they searched PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science using the terms (“sunscreen” or “SPF” or “sun protection”) and (“high school” or “teen” or “teenager” or “adolescent”) and limited the analysis to English studies reporting data on sunscreen use in U.S. high school students up to November 2021.
A total of 20 studies were included in the final review. The study populations ranged in number from 208 to 24,645. Of 11 studies that examined gender, all showed increased sunscreen use in females compared with males. Of five studies that examined age, all showed increased sunscreen use in younger adolescents, compared with their older counterparts.
Of four studies that examined the role of ethnicity on sunscreen use, White students were more likely to use sunscreen, compared with their peers of other ethnicities. “This may be due to perceived sun sensitivity, as [these four studies] also showed increased sunscreen use in populations that believed were more susceptible to sun damage,” the researchers wrote in their abstract.
In other findings, two studies that examined perceived self-efficacy concluded that higher levels of sunscreen use correlated with higher self-efficacy, while four studies concluded that high school students were more likely to use sunscreen if their parents encouraged them the wear it or if the parent used it themselves.
“With 40%-50% of ultraviolet damage being done before the age of 20, it’s crucial that we find ways to educate adolescents on the importance of sunscreen use and target those populations who were found to rarely use sunscreen in our study,” Ms. Stevens said.
In one outreach program, Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students (SPOTS), medical students visit middle and high schools to educate them about the importance of practicing sun protection. The program began as a collaboration between Saint Louis University and Washington University in St. Louis, but has expanded nationwide. Ms. Stevens described SPOTS as “a great way for medical students to present the information to middle and high school students in a way that is engaging and interactive.”
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
a cornerstone of skin cancer prevention, according to results from a systematic review.
“We know that skin cancer is one of the most common malignancies in the world, and sun protection methods such as sunscreen make it highly preventable,” first author Carly R. Stevens, a student at Tulane University, New Orleans, said in an interview. “This study demonstrates the adolescent populations that are most vulnerable to sun damage and how we can help mitigate their risk of developing skin cancer through education methods, such as Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students.”
Ms. Stevens and coauthors presented the findings during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
To investigate predictors of sunscreen use among high school students, they searched PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science using the terms (“sunscreen” or “SPF” or “sun protection”) and (“high school” or “teen” or “teenager” or “adolescent”) and limited the analysis to English studies reporting data on sunscreen use in U.S. high school students up to November 2021.
A total of 20 studies were included in the final review. The study populations ranged in number from 208 to 24,645. Of 11 studies that examined gender, all showed increased sunscreen use in females compared with males. Of five studies that examined age, all showed increased sunscreen use in younger adolescents, compared with their older counterparts.
Of four studies that examined the role of ethnicity on sunscreen use, White students were more likely to use sunscreen, compared with their peers of other ethnicities. “This may be due to perceived sun sensitivity, as [these four studies] also showed increased sunscreen use in populations that believed were more susceptible to sun damage,” the researchers wrote in their abstract.
In other findings, two studies that examined perceived self-efficacy concluded that higher levels of sunscreen use correlated with higher self-efficacy, while four studies concluded that high school students were more likely to use sunscreen if their parents encouraged them the wear it or if the parent used it themselves.
“With 40%-50% of ultraviolet damage being done before the age of 20, it’s crucial that we find ways to educate adolescents on the importance of sunscreen use and target those populations who were found to rarely use sunscreen in our study,” Ms. Stevens said.
In one outreach program, Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students (SPOTS), medical students visit middle and high schools to educate them about the importance of practicing sun protection. The program began as a collaboration between Saint Louis University and Washington University in St. Louis, but has expanded nationwide. Ms. Stevens described SPOTS as “a great way for medical students to present the information to middle and high school students in a way that is engaging and interactive.”
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
a cornerstone of skin cancer prevention, according to results from a systematic review.
“We know that skin cancer is one of the most common malignancies in the world, and sun protection methods such as sunscreen make it highly preventable,” first author Carly R. Stevens, a student at Tulane University, New Orleans, said in an interview. “This study demonstrates the adolescent populations that are most vulnerable to sun damage and how we can help mitigate their risk of developing skin cancer through education methods, such as Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students.”
Ms. Stevens and coauthors presented the findings during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
To investigate predictors of sunscreen use among high school students, they searched PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science using the terms (“sunscreen” or “SPF” or “sun protection”) and (“high school” or “teen” or “teenager” or “adolescent”) and limited the analysis to English studies reporting data on sunscreen use in U.S. high school students up to November 2021.
A total of 20 studies were included in the final review. The study populations ranged in number from 208 to 24,645. Of 11 studies that examined gender, all showed increased sunscreen use in females compared with males. Of five studies that examined age, all showed increased sunscreen use in younger adolescents, compared with their older counterparts.
Of four studies that examined the role of ethnicity on sunscreen use, White students were more likely to use sunscreen, compared with their peers of other ethnicities. “This may be due to perceived sun sensitivity, as [these four studies] also showed increased sunscreen use in populations that believed were more susceptible to sun damage,” the researchers wrote in their abstract.
In other findings, two studies that examined perceived self-efficacy concluded that higher levels of sunscreen use correlated with higher self-efficacy, while four studies concluded that high school students were more likely to use sunscreen if their parents encouraged them the wear it or if the parent used it themselves.
“With 40%-50% of ultraviolet damage being done before the age of 20, it’s crucial that we find ways to educate adolescents on the importance of sunscreen use and target those populations who were found to rarely use sunscreen in our study,” Ms. Stevens said.
In one outreach program, Sun Protection Outreach Teaching by Students (SPOTS), medical students visit middle and high schools to educate them about the importance of practicing sun protection. The program began as a collaboration between Saint Louis University and Washington University in St. Louis, but has expanded nationwide. Ms. Stevens described SPOTS as “a great way for medical students to present the information to middle and high school students in a way that is engaging and interactive.”
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
FROM SPD 2023
USPSTF maintains ‘insufficient evidence’ for lipid disorder screenings in kids and teens
The group’s final recommendation and corresponding evidence report were published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, following a draft recommendation in January.
The organization reached a similar conclusion following its evaluation in 2016.
“There’s just not enough evidence to determine whether or not screening all children for high cholesterol improves their heart health into adulthood,” said Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, a USPSTF member and a professor in the department of family medicine at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “We’re calling for additional research on the effectiveness of screening for and treatment of high cholesterol in children and adolescents to prevent heart attacks, strokes, and death in adulthood.”
The task force recommended other evidence-based strategies to promote heart health, such as screening for obesity and interventions to prevent tobacco use.
The recommendation was the result of a review of 43 studies from MEDLINE and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials through May 16, 2022. No randomized controlled trial directly addressed the effectiveness or harms of lipid screening for children and adolescents. The task force continued to use article alerts and targeted journal searches through March 24, 2023.
Conditions such as familial hypercholesterolemia and multifactorial dyslipidemia can cause abnormally high lipid levels in children, potentially leading to premature cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and death in adulthood. According to the USPSTF, the prevalence of FH in U.S. children and adolescents ranges from 0.2% to 0.4% (one in every 250-500 youth). Multifactorial dyslipidemia is more common – the prevalence in children and adolescents ranges from 7.1% to 9.4%.
In an editorial response to the task force’s statement, the authors, including Sarah D. de Ferranti, MD, department of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, question the impact of not screening children to identify FH and other conditions and caution against the subsequent delay in treatment.
“Treating FH during childhood slows the progression of vascular finding in atherosclerosis,” the authors write.
They note that the recommendation “leaves a void for clinicians seeking to provide care for patients today” while additional research is conducted.
Sarah Nosal, MD, a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said that despite the lack of a recommendation, primary care clinicians can still encourage proper nutrition and physical activity for patients.
Dr. Nosal said that even without clear recommendations from the USPSTF, in the rare case of a patient with a family history of FH, she would order a lipid test and discuss treatment plans with the patient and family, if needed.
“We really don’t want to do tests that we don’t know what to do with the information,” she said.
One USPSTF member reported receiving grants from Healthwise, a nonprofit organization, outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The group’s final recommendation and corresponding evidence report were published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, following a draft recommendation in January.
The organization reached a similar conclusion following its evaluation in 2016.
“There’s just not enough evidence to determine whether or not screening all children for high cholesterol improves their heart health into adulthood,” said Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, a USPSTF member and a professor in the department of family medicine at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “We’re calling for additional research on the effectiveness of screening for and treatment of high cholesterol in children and adolescents to prevent heart attacks, strokes, and death in adulthood.”
The task force recommended other evidence-based strategies to promote heart health, such as screening for obesity and interventions to prevent tobacco use.
The recommendation was the result of a review of 43 studies from MEDLINE and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials through May 16, 2022. No randomized controlled trial directly addressed the effectiveness or harms of lipid screening for children and adolescents. The task force continued to use article alerts and targeted journal searches through March 24, 2023.
Conditions such as familial hypercholesterolemia and multifactorial dyslipidemia can cause abnormally high lipid levels in children, potentially leading to premature cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and death in adulthood. According to the USPSTF, the prevalence of FH in U.S. children and adolescents ranges from 0.2% to 0.4% (one in every 250-500 youth). Multifactorial dyslipidemia is more common – the prevalence in children and adolescents ranges from 7.1% to 9.4%.
In an editorial response to the task force’s statement, the authors, including Sarah D. de Ferranti, MD, department of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, question the impact of not screening children to identify FH and other conditions and caution against the subsequent delay in treatment.
“Treating FH during childhood slows the progression of vascular finding in atherosclerosis,” the authors write.
They note that the recommendation “leaves a void for clinicians seeking to provide care for patients today” while additional research is conducted.
Sarah Nosal, MD, a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said that despite the lack of a recommendation, primary care clinicians can still encourage proper nutrition and physical activity for patients.
Dr. Nosal said that even without clear recommendations from the USPSTF, in the rare case of a patient with a family history of FH, she would order a lipid test and discuss treatment plans with the patient and family, if needed.
“We really don’t want to do tests that we don’t know what to do with the information,” she said.
One USPSTF member reported receiving grants from Healthwise, a nonprofit organization, outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The group’s final recommendation and corresponding evidence report were published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, following a draft recommendation in January.
The organization reached a similar conclusion following its evaluation in 2016.
“There’s just not enough evidence to determine whether or not screening all children for high cholesterol improves their heart health into adulthood,” said Katrina Donahue, MD, MPH, a USPSTF member and a professor in the department of family medicine at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “We’re calling for additional research on the effectiveness of screening for and treatment of high cholesterol in children and adolescents to prevent heart attacks, strokes, and death in adulthood.”
The task force recommended other evidence-based strategies to promote heart health, such as screening for obesity and interventions to prevent tobacco use.
The recommendation was the result of a review of 43 studies from MEDLINE and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials through May 16, 2022. No randomized controlled trial directly addressed the effectiveness or harms of lipid screening for children and adolescents. The task force continued to use article alerts and targeted journal searches through March 24, 2023.
Conditions such as familial hypercholesterolemia and multifactorial dyslipidemia can cause abnormally high lipid levels in children, potentially leading to premature cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and death in adulthood. According to the USPSTF, the prevalence of FH in U.S. children and adolescents ranges from 0.2% to 0.4% (one in every 250-500 youth). Multifactorial dyslipidemia is more common – the prevalence in children and adolescents ranges from 7.1% to 9.4%.
In an editorial response to the task force’s statement, the authors, including Sarah D. de Ferranti, MD, department of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, question the impact of not screening children to identify FH and other conditions and caution against the subsequent delay in treatment.
“Treating FH during childhood slows the progression of vascular finding in atherosclerosis,” the authors write.
They note that the recommendation “leaves a void for clinicians seeking to provide care for patients today” while additional research is conducted.
Sarah Nosal, MD, a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said that despite the lack of a recommendation, primary care clinicians can still encourage proper nutrition and physical activity for patients.
Dr. Nosal said that even without clear recommendations from the USPSTF, in the rare case of a patient with a family history of FH, she would order a lipid test and discuss treatment plans with the patient and family, if needed.
“We really don’t want to do tests that we don’t know what to do with the information,” she said.
One USPSTF member reported receiving grants from Healthwise, a nonprofit organization, outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Camp Discovery: A place for children to be comfortable in their own skin
The talent show, the grand finale of the 1-week camp, was nearly 7 years ago, but Emily Haygood of Houston, now 17 and about to start her senior year, remembers it in detail. She sang “Death of a Bachelor,” an R&B pop song and Billboard No. 1 hit at the time about a former bachelor who had happily married. These days, she said, if she watched the video of her 10-year-old singing self, “I would probably throw up.” But she still treasures the audience response, “having all those people I’d gotten close to cheer for me.”
Emily was at , but share one feature: they are the kind of dermatologic issues that can make doing everyday kid or teen activities like swimming difficult and can elicit mean comments from classmates and other would-be friends.

Emily was first diagnosed with atopic dermatitis at age 4, her mother, Amber Haygood, says. By age 9, it had become severe. Emily remembers being teased some in elementary school. “I did feel bad a lot of the time, when asked insensitive questions.” Her mother still bristles that adults often could be cruel, too.
But at Camp Discovery, those issues were nonexistent. “Camp was so cool,” Emily said. Besides the usual camp activities, it had things that “normal” camp didn’t, like other kids who didn’t stare at your skin condition or make fun of it.
30th anniversary season begins
This year is the 30th anniversary of Camp Discovery. Sessions began July 23 and continue through Aug. 18, with locations in Crosslake, Minn.; Hebron, Conn.; and Millville, Pa., in addition to Burton, Tex. About 300 campers will attend this year, according to the AAD, and 6,151 campers have attended from 1993 to 2022.
The 1-week camp accepts youth with conditions ranging from eczema and psoriasis to vitiligo, alopecia, epidermolysis bullosa, and ichthyosis, according to the academy. A dermatologist first refers a child, downloading and completing the referral form and sending it to the academy.
The 1-week session, including travel, is free for the campers, thanks to donors. As a nonprofit and membership-based organization, the AAD does not release the detailed financial information about the operating budget for the camp. Dermatologists, nurses, and counselors volunteer their time.
In his presidential address at the AAD’s annual meeting in March, outgoing president Mark D. Kaufmann, MD, of the department of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, referred to camp volunteering as an antidote to professional burnout. Remembering why as a dermatologist one entered the profession can be one solution, he said, and described his own recent 3-day volunteer stint at the camp.
“Those 3 magical days, being with kids as they discovered they weren’t alone in the world, sharing their experiences and ideas, reminded me why I became a physician in the first place,” he told the audience of meeting attendees. He vowed to expand the program, with a goal of having every dermatology resident attend Camp Discovery.
Mental health effects of skin conditions
Much research has focused on the mental health fallout from living with chronic skin conditions, and even young children can be adversely affected. In one review of the literature, researchers concluded that pediatric skin disease, including acne, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis, can affect quality of life, carry stigma, and lead to bullying and eventually even suicidal behavior. Another study, published earlier this year, found that atopic dermatitis affected children’s quality of life, impacting sleep and leading to feelings of being ashamed.
“It’s not necessarily about what their skin condition is and more about the psychosocial impact,’’ said Samantha Hill, MD, a pediatric and general dermatologist in Lynchburg, Va., who is the medical director of Camp Discovery in Minnesota this year.
Camp activities, reactions
The overriding theme of camp is allowing all the youth to be “just one of the kids at camp,” Dr. Hill said in an interview. “They come to do all kinds of things they don’t do in normal life because people don’t give them the credit to [be able to] do it.”
Every year, she said, “I tell my staff we are in the business of making things happen, so if there is a kid bandaged head to toe [because of a skin condition] and they want to go tubing and get in the lake, we figure out how to make it happen. We have done that multiple times.”
Newcomers are initially nervous, Dr. Hill acknowledged, but in time let their guard down. Returnees are a different story. “When kids who have been at camp before arrive, you can see them start breathing again, looking for their friends. You can see them relax right before your eyes.”
“The single most empowering thing is the realization you are not alone,” said Meena Julapalli, MD, a Houston dermatologist who is a medical team member and long-time volunteer at Camp Discovery. That, she said, and “You get to be a kid, and you don’t have to have people staring at you.”
Dr. Julapalli remembers one of her patients with keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness (KID) syndrome. “She needed more than what I could offer,” she said. “She needed camp.” At camp, the organizers found a counselor who knew sign language to accompany her. At first, she was quiet and didn’t smile much. By the end of the week, as she was about to observe her birthday, things changed. After breakfast, she was led to the stage, where fellow campers began singing – and signing the song they had just learned.
Camp staff gets it
Allyson Garin, who was diagnosed with vitiligo at age 6 months, is a camp program director at Camp Discovery in Crosslake, Minn. She first went to camp in 1990 at age 11, returning until she “aged out” at 16, then worked as a counselor. She gets it when campers tell her they hear rude comments about their skin conditions.
“I remember being in swimming pools, in lines at fairgrounds or amusement parks,” she said in an interview, “and hearing people say, ‘Don’t touch her,’ ’’ fearing contagion, perhaps. “People would make jokes about cows, since they are spotted,” she said, or people would simply step back.
All those years ago, her mother found out about the camp and decided to figure out how to get her there. She got there, and she met a fellow camper with vitiligo, and they became pen pals. “We still talk,” she said.
Meeting someone with the same skin condition, she said, isn’t just about commiserating. “There is a lot of information sharing,” on topics such as best treatments, strategies, and other conversations.
Other lessons
While campers can feel comfortable around others who also have skin conditions, and understand, the lesson extends beyond that, Ms. Garin said. “It gave me a perspective,” she said of her camp experience. “I always felt, ‘Woe is me.’ ” But when she met others with, as she said, conditions “way worse than vitiligo, it really grounds you.”
Dr. Hill agreed. Campers get the benefit of others accepting and including them, but also practicing that same attitude toward fellow campers, she said. “It insures that we are providing this environment of inclusion, but that they are practicing it as well. They need to practice it like everyone else.”
Getting parents on board
The idea of camp, especially for those at the younger end of the 8- to 16-years age range accepted for Camp Discovery, can take some getting used to for some parents. Ms. Haygood, Emily’s mother, relates to that. Her daughter’s dermatologist at the time, who is now retired, had first suggested the camp. Her first reaction? “I am not sending my chronically ill child to camp with strangers.” She also acknowledged that she, like other parents of children with a chronic illness, can be a helicopter parent.
Then, she noticed that Emily seemed interested, so she got more information, finding out that it was staffed by doctors. It all sounded good, she said, and the social interaction, she knew, would be beneficial. “Then my husband was a no,” she said, concerned about their daughter being with strangers. “Eventually he came around,” Ms. Haygood said. All along, Emily said, “it seemed fun. I was probably trying to talk them into it.” She admits she was very nervous at first, but calmed down when she realized her own dermatologist was going to be there.
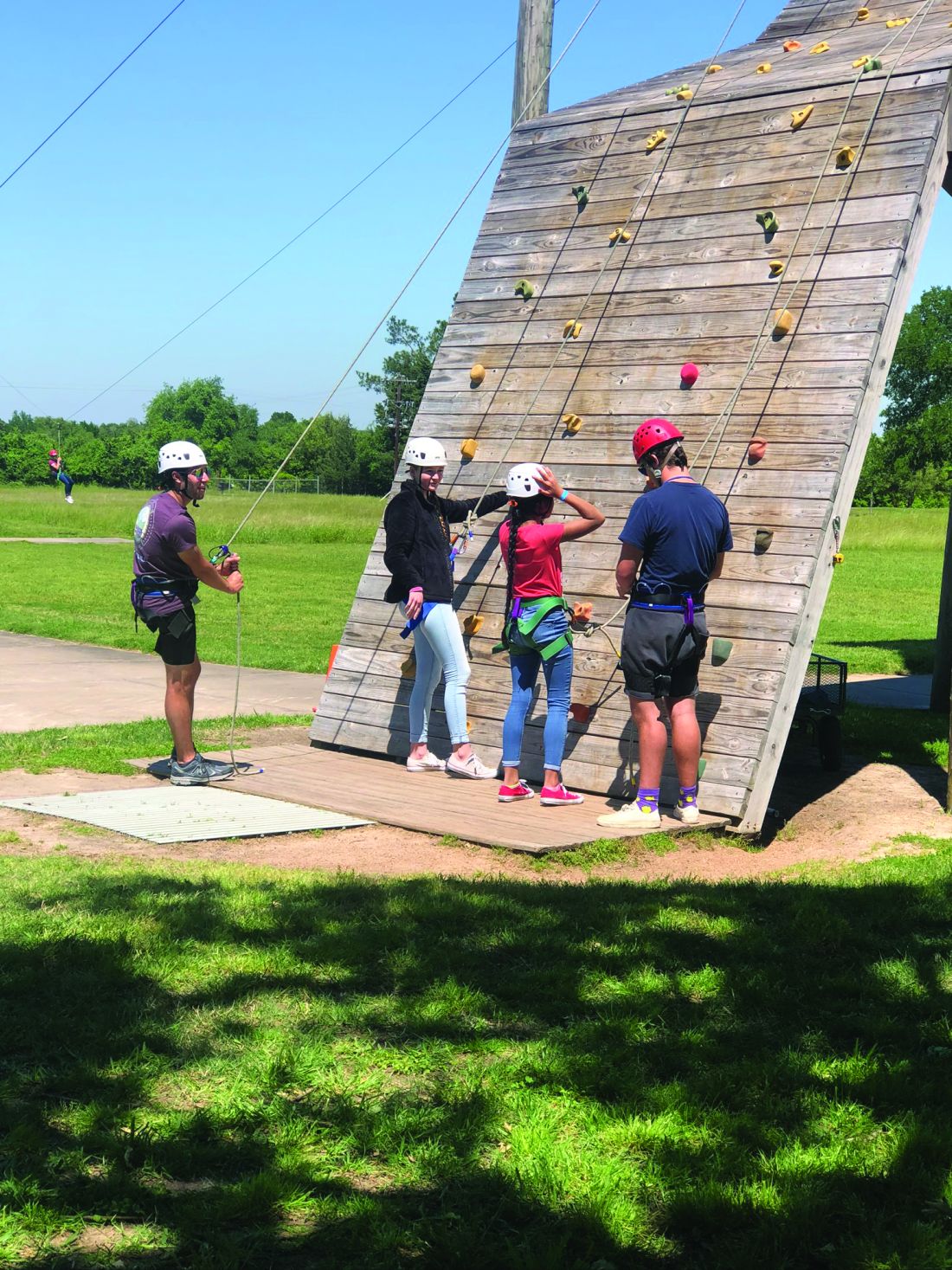
Vanessa Hadley of Spring, Tex., was on board the moment she heard about Camp Discovery. “I just thought it was amazing,” she said. Her daughter Isabelle, 13, has been to the camp. “She has alopecia areata and severe eczema,” Ms. Hadley said. Now, Isabelle is returning to camp and coaching her sister Penelope, 8, who has eczema and mild alopecia and is a first-timer this summer.
One tip the 8-year-old has learned so far: Turn to your counselor for support if you’re nervous. That worked, Isabelle said, the first year when she was wary of the zipline – then surprised herself and conquered it.
Dr. Hill and Dr. Julapalli have no disclosures.
The talent show, the grand finale of the 1-week camp, was nearly 7 years ago, but Emily Haygood of Houston, now 17 and about to start her senior year, remembers it in detail. She sang “Death of a Bachelor,” an R&B pop song and Billboard No. 1 hit at the time about a former bachelor who had happily married. These days, she said, if she watched the video of her 10-year-old singing self, “I would probably throw up.” But she still treasures the audience response, “having all those people I’d gotten close to cheer for me.”
Emily was at , but share one feature: they are the kind of dermatologic issues that can make doing everyday kid or teen activities like swimming difficult and can elicit mean comments from classmates and other would-be friends.

Emily was first diagnosed with atopic dermatitis at age 4, her mother, Amber Haygood, says. By age 9, it had become severe. Emily remembers being teased some in elementary school. “I did feel bad a lot of the time, when asked insensitive questions.” Her mother still bristles that adults often could be cruel, too.
But at Camp Discovery, those issues were nonexistent. “Camp was so cool,” Emily said. Besides the usual camp activities, it had things that “normal” camp didn’t, like other kids who didn’t stare at your skin condition or make fun of it.
30th anniversary season begins
This year is the 30th anniversary of Camp Discovery. Sessions began July 23 and continue through Aug. 18, with locations in Crosslake, Minn.; Hebron, Conn.; and Millville, Pa., in addition to Burton, Tex. About 300 campers will attend this year, according to the AAD, and 6,151 campers have attended from 1993 to 2022.
The 1-week camp accepts youth with conditions ranging from eczema and psoriasis to vitiligo, alopecia, epidermolysis bullosa, and ichthyosis, according to the academy. A dermatologist first refers a child, downloading and completing the referral form and sending it to the academy.
The 1-week session, including travel, is free for the campers, thanks to donors. As a nonprofit and membership-based organization, the AAD does not release the detailed financial information about the operating budget for the camp. Dermatologists, nurses, and counselors volunteer their time.
In his presidential address at the AAD’s annual meeting in March, outgoing president Mark D. Kaufmann, MD, of the department of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, referred to camp volunteering as an antidote to professional burnout. Remembering why as a dermatologist one entered the profession can be one solution, he said, and described his own recent 3-day volunteer stint at the camp.
“Those 3 magical days, being with kids as they discovered they weren’t alone in the world, sharing their experiences and ideas, reminded me why I became a physician in the first place,” he told the audience of meeting attendees. He vowed to expand the program, with a goal of having every dermatology resident attend Camp Discovery.
Mental health effects of skin conditions
Much research has focused on the mental health fallout from living with chronic skin conditions, and even young children can be adversely affected. In one review of the literature, researchers concluded that pediatric skin disease, including acne, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis, can affect quality of life, carry stigma, and lead to bullying and eventually even suicidal behavior. Another study, published earlier this year, found that atopic dermatitis affected children’s quality of life, impacting sleep and leading to feelings of being ashamed.
“It’s not necessarily about what their skin condition is and more about the psychosocial impact,’’ said Samantha Hill, MD, a pediatric and general dermatologist in Lynchburg, Va., who is the medical director of Camp Discovery in Minnesota this year.
Camp activities, reactions
The overriding theme of camp is allowing all the youth to be “just one of the kids at camp,” Dr. Hill said in an interview. “They come to do all kinds of things they don’t do in normal life because people don’t give them the credit to [be able to] do it.”
Every year, she said, “I tell my staff we are in the business of making things happen, so if there is a kid bandaged head to toe [because of a skin condition] and they want to go tubing and get in the lake, we figure out how to make it happen. We have done that multiple times.”
Newcomers are initially nervous, Dr. Hill acknowledged, but in time let their guard down. Returnees are a different story. “When kids who have been at camp before arrive, you can see them start breathing again, looking for their friends. You can see them relax right before your eyes.”
“The single most empowering thing is the realization you are not alone,” said Meena Julapalli, MD, a Houston dermatologist who is a medical team member and long-time volunteer at Camp Discovery. That, she said, and “You get to be a kid, and you don’t have to have people staring at you.”
Dr. Julapalli remembers one of her patients with keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness (KID) syndrome. “She needed more than what I could offer,” she said. “She needed camp.” At camp, the organizers found a counselor who knew sign language to accompany her. At first, she was quiet and didn’t smile much. By the end of the week, as she was about to observe her birthday, things changed. After breakfast, she was led to the stage, where fellow campers began singing – and signing the song they had just learned.
Camp staff gets it
Allyson Garin, who was diagnosed with vitiligo at age 6 months, is a camp program director at Camp Discovery in Crosslake, Minn. She first went to camp in 1990 at age 11, returning until she “aged out” at 16, then worked as a counselor. She gets it when campers tell her they hear rude comments about their skin conditions.
“I remember being in swimming pools, in lines at fairgrounds or amusement parks,” she said in an interview, “and hearing people say, ‘Don’t touch her,’ ’’ fearing contagion, perhaps. “People would make jokes about cows, since they are spotted,” she said, or people would simply step back.
All those years ago, her mother found out about the camp and decided to figure out how to get her there. She got there, and she met a fellow camper with vitiligo, and they became pen pals. “We still talk,” she said.
Meeting someone with the same skin condition, she said, isn’t just about commiserating. “There is a lot of information sharing,” on topics such as best treatments, strategies, and other conversations.
Other lessons
While campers can feel comfortable around others who also have skin conditions, and understand, the lesson extends beyond that, Ms. Garin said. “It gave me a perspective,” she said of her camp experience. “I always felt, ‘Woe is me.’ ” But when she met others with, as she said, conditions “way worse than vitiligo, it really grounds you.”
Dr. Hill agreed. Campers get the benefit of others accepting and including them, but also practicing that same attitude toward fellow campers, she said. “It insures that we are providing this environment of inclusion, but that they are practicing it as well. They need to practice it like everyone else.”
Getting parents on board
The idea of camp, especially for those at the younger end of the 8- to 16-years age range accepted for Camp Discovery, can take some getting used to for some parents. Ms. Haygood, Emily’s mother, relates to that. Her daughter’s dermatologist at the time, who is now retired, had first suggested the camp. Her first reaction? “I am not sending my chronically ill child to camp with strangers.” She also acknowledged that she, like other parents of children with a chronic illness, can be a helicopter parent.
Then, she noticed that Emily seemed interested, so she got more information, finding out that it was staffed by doctors. It all sounded good, she said, and the social interaction, she knew, would be beneficial. “Then my husband was a no,” she said, concerned about their daughter being with strangers. “Eventually he came around,” Ms. Haygood said. All along, Emily said, “it seemed fun. I was probably trying to talk them into it.” She admits she was very nervous at first, but calmed down when she realized her own dermatologist was going to be there.
Vanessa Hadley of Spring, Tex., was on board the moment she heard about Camp Discovery. “I just thought it was amazing,” she said. Her daughter Isabelle, 13, has been to the camp. “She has alopecia areata and severe eczema,” Ms. Hadley said. Now, Isabelle is returning to camp and coaching her sister Penelope, 8, who has eczema and mild alopecia and is a first-timer this summer.
One tip the 8-year-old has learned so far: Turn to your counselor for support if you’re nervous. That worked, Isabelle said, the first year when she was wary of the zipline – then surprised herself and conquered it.
Dr. Hill and Dr. Julapalli have no disclosures.
The talent show, the grand finale of the 1-week camp, was nearly 7 years ago, but Emily Haygood of Houston, now 17 and about to start her senior year, remembers it in detail. She sang “Death of a Bachelor,” an R&B pop song and Billboard No. 1 hit at the time about a former bachelor who had happily married. These days, she said, if she watched the video of her 10-year-old singing self, “I would probably throw up.” But she still treasures the audience response, “having all those people I’d gotten close to cheer for me.”
Emily was at , but share one feature: they are the kind of dermatologic issues that can make doing everyday kid or teen activities like swimming difficult and can elicit mean comments from classmates and other would-be friends.

Emily was first diagnosed with atopic dermatitis at age 4, her mother, Amber Haygood, says. By age 9, it had become severe. Emily remembers being teased some in elementary school. “I did feel bad a lot of the time, when asked insensitive questions.” Her mother still bristles that adults often could be cruel, too.
But at Camp Discovery, those issues were nonexistent. “Camp was so cool,” Emily said. Besides the usual camp activities, it had things that “normal” camp didn’t, like other kids who didn’t stare at your skin condition or make fun of it.
30th anniversary season begins
This year is the 30th anniversary of Camp Discovery. Sessions began July 23 and continue through Aug. 18, with locations in Crosslake, Minn.; Hebron, Conn.; and Millville, Pa., in addition to Burton, Tex. About 300 campers will attend this year, according to the AAD, and 6,151 campers have attended from 1993 to 2022.
The 1-week camp accepts youth with conditions ranging from eczema and psoriasis to vitiligo, alopecia, epidermolysis bullosa, and ichthyosis, according to the academy. A dermatologist first refers a child, downloading and completing the referral form and sending it to the academy.
The 1-week session, including travel, is free for the campers, thanks to donors. As a nonprofit and membership-based organization, the AAD does not release the detailed financial information about the operating budget for the camp. Dermatologists, nurses, and counselors volunteer their time.
In his presidential address at the AAD’s annual meeting in March, outgoing president Mark D. Kaufmann, MD, of the department of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, referred to camp volunteering as an antidote to professional burnout. Remembering why as a dermatologist one entered the profession can be one solution, he said, and described his own recent 3-day volunteer stint at the camp.
“Those 3 magical days, being with kids as they discovered they weren’t alone in the world, sharing their experiences and ideas, reminded me why I became a physician in the first place,” he told the audience of meeting attendees. He vowed to expand the program, with a goal of having every dermatology resident attend Camp Discovery.
Mental health effects of skin conditions
Much research has focused on the mental health fallout from living with chronic skin conditions, and even young children can be adversely affected. In one review of the literature, researchers concluded that pediatric skin disease, including acne, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis, can affect quality of life, carry stigma, and lead to bullying and eventually even suicidal behavior. Another study, published earlier this year, found that atopic dermatitis affected children’s quality of life, impacting sleep and leading to feelings of being ashamed.
“It’s not necessarily about what their skin condition is and more about the psychosocial impact,’’ said Samantha Hill, MD, a pediatric and general dermatologist in Lynchburg, Va., who is the medical director of Camp Discovery in Minnesota this year.
Camp activities, reactions
The overriding theme of camp is allowing all the youth to be “just one of the kids at camp,” Dr. Hill said in an interview. “They come to do all kinds of things they don’t do in normal life because people don’t give them the credit to [be able to] do it.”
Every year, she said, “I tell my staff we are in the business of making things happen, so if there is a kid bandaged head to toe [because of a skin condition] and they want to go tubing and get in the lake, we figure out how to make it happen. We have done that multiple times.”
Newcomers are initially nervous, Dr. Hill acknowledged, but in time let their guard down. Returnees are a different story. “When kids who have been at camp before arrive, you can see them start breathing again, looking for their friends. You can see them relax right before your eyes.”
“The single most empowering thing is the realization you are not alone,” said Meena Julapalli, MD, a Houston dermatologist who is a medical team member and long-time volunteer at Camp Discovery. That, she said, and “You get to be a kid, and you don’t have to have people staring at you.”
Dr. Julapalli remembers one of her patients with keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness (KID) syndrome. “She needed more than what I could offer,” she said. “She needed camp.” At camp, the organizers found a counselor who knew sign language to accompany her. At first, she was quiet and didn’t smile much. By the end of the week, as she was about to observe her birthday, things changed. After breakfast, she was led to the stage, where fellow campers began singing – and signing the song they had just learned.
Camp staff gets it
Allyson Garin, who was diagnosed with vitiligo at age 6 months, is a camp program director at Camp Discovery in Crosslake, Minn. She first went to camp in 1990 at age 11, returning until she “aged out” at 16, then worked as a counselor. She gets it when campers tell her they hear rude comments about their skin conditions.
“I remember being in swimming pools, in lines at fairgrounds or amusement parks,” she said in an interview, “and hearing people say, ‘Don’t touch her,’ ’’ fearing contagion, perhaps. “People would make jokes about cows, since they are spotted,” she said, or people would simply step back.
All those years ago, her mother found out about the camp and decided to figure out how to get her there. She got there, and she met a fellow camper with vitiligo, and they became pen pals. “We still talk,” she said.
Meeting someone with the same skin condition, she said, isn’t just about commiserating. “There is a lot of information sharing,” on topics such as best treatments, strategies, and other conversations.
Other lessons
While campers can feel comfortable around others who also have skin conditions, and understand, the lesson extends beyond that, Ms. Garin said. “It gave me a perspective,” she said of her camp experience. “I always felt, ‘Woe is me.’ ” But when she met others with, as she said, conditions “way worse than vitiligo, it really grounds you.”
Dr. Hill agreed. Campers get the benefit of others accepting and including them, but also practicing that same attitude toward fellow campers, she said. “It insures that we are providing this environment of inclusion, but that they are practicing it as well. They need to practice it like everyone else.”
Getting parents on board
The idea of camp, especially for those at the younger end of the 8- to 16-years age range accepted for Camp Discovery, can take some getting used to for some parents. Ms. Haygood, Emily’s mother, relates to that. Her daughter’s dermatologist at the time, who is now retired, had first suggested the camp. Her first reaction? “I am not sending my chronically ill child to camp with strangers.” She also acknowledged that she, like other parents of children with a chronic illness, can be a helicopter parent.
Then, she noticed that Emily seemed interested, so she got more information, finding out that it was staffed by doctors. It all sounded good, she said, and the social interaction, she knew, would be beneficial. “Then my husband was a no,” she said, concerned about their daughter being with strangers. “Eventually he came around,” Ms. Haygood said. All along, Emily said, “it seemed fun. I was probably trying to talk them into it.” She admits she was very nervous at first, but calmed down when she realized her own dermatologist was going to be there.
Vanessa Hadley of Spring, Tex., was on board the moment she heard about Camp Discovery. “I just thought it was amazing,” she said. Her daughter Isabelle, 13, has been to the camp. “She has alopecia areata and severe eczema,” Ms. Hadley said. Now, Isabelle is returning to camp and coaching her sister Penelope, 8, who has eczema and mild alopecia and is a first-timer this summer.
One tip the 8-year-old has learned so far: Turn to your counselor for support if you’re nervous. That worked, Isabelle said, the first year when she was wary of the zipline – then surprised herself and conquered it.
Dr. Hill and Dr. Julapalli have no disclosures.
Novel tool accurately predicts suicide after self-harm
Investigators have developed and validated a new risk calculator to help predict death by suicide in the 6-12 months after an episode of nonfatal self-harm, new research shows.
A study led by Seena Fazel, MBChB, MD, University of Oxford, England, suggests the Oxford Suicide Assessment Tool for Self-harm (OxSATS) may help guide treatment decisions and target resources to those most in need, the researchers note.
“Many tools use only simple high/low categories, whereas OxSATS includes probability scores, which align more closely with risk calculators in cardiovascular medicine, such as the Framingham Risk Score, and prognostic models in cancer medicine, which provide 5-year survival probabilities. This potentially allows OxSATS to inform clinical decision-making more directly,” Dr. Fazel told this news organization.
The findings were published online in BMJ Mental Health.
Targeted tool
Self-harm is associated with a 1-year risk of suicide that is 20 times higher than that of the general population. Given that about 16 million people self-harm annually, the impact at a population level is potentially quite large, the researchers note.
Current structured approaches to gauge suicide risk among those who have engaged in self-harm are based on tools developed for other purposes and symptom checklists. “Their poor to moderate performance is therefore not unexpected,” Dr. Fazel told this news organization.
In contrast, OxSATS was specifically developed to predict suicide mortality after self-harm.
Dr. Fazel’s group evaluated data on 53,172 Swedish individuals aged 10 years and older who sought emergency medical care after episodes of self-harm.
The development cohort included 37,523 individuals. Of these, 391 died by suicide within 12 months. The validation cohort included 15,649 individuals; of these people, 178 died by suicide within 12 months.
The final OxSATS model includes 11 predictors related to age and sex, as well as variables related to substance misuse, mental health, and treatment and history of self-harm.
“The performance of the model in external validation was good, with c-index at 6 and 12 months of 0.77,” the researchers note.
Using a cutoff threshold of 1%, the OxSATS correctly identified 68% of those who died by suicide within 6 months, while 71% of those who didn’t die were correctly classified as being at low risk. The figures for risk prediction at 12 months were 82% and 54%, respectively.
The OxSATS has been made into a simple online tool with probability scores for suicide at 6 and 12 months after an episode of self-harm, but without linkage to interventions. A tool on its own is unlikely to improve outcomes, said Dr. Fazel.
“However,” he added, “it can improve consistency in the assessment process, especially in busy clinical settings where people from different professional backgrounds and experience undertake such assessments. It can also highlight the role of modifiable risk factors and provide an opportunity to transparently discuss risk with patients and their carers.”
Valuable work
Reached for comment, Igor Galynker, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said that this is a “very solid study with a very large sample size and solid statistical analysis.”
Another strength of the research is the outcome of suicide death versus suicide attempt or suicidal ideation. “In that respect, it is a valuable paper,” Dr. Galynker, who directs the Mount Sinai Beth Israel Suicide Research Laboratory, told this news organization.
He noted that there are no new risk factors in the model. Rather, the model contains the typical risk factors for suicide, which include male sex, substance misuse, past suicide attempt, and psychiatric diagnosis.
“The strongest risk factor in the model is self-harm by hanging, strangulation, or suffocation, which has been shown before and is therefore unsurprising,” said Dr. Galynker.
In general, the risk factors included in the model are often part of administrative tools for suicide risk assessment, said Dr. Galynker, but the OxSATS “seems easier to use because it has 11 items only.”
Broadly speaking, individuals with mental illness and past suicide attempt, past self-harm, alcohol use, and other risk factors “should be treated proactively with suicide prevention measures,” he told this news organization.
As previously reported, Dr. Galynker and colleagues have developed the Abbreviated Suicide Crisis Syndrome Checklist (A-SCS-C), a novel tool to help identify which suicidal patients who present to the emergency department should be admitted to hospital and which patients can be safely discharged.
Funding for the study was provided by Wellcome Trust and the Swedish Research Council. Dr. Fazel and Dr. Galynker have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators have developed and validated a new risk calculator to help predict death by suicide in the 6-12 months after an episode of nonfatal self-harm, new research shows.
A study led by Seena Fazel, MBChB, MD, University of Oxford, England, suggests the Oxford Suicide Assessment Tool for Self-harm (OxSATS) may help guide treatment decisions and target resources to those most in need, the researchers note.
“Many tools use only simple high/low categories, whereas OxSATS includes probability scores, which align more closely with risk calculators in cardiovascular medicine, such as the Framingham Risk Score, and prognostic models in cancer medicine, which provide 5-year survival probabilities. This potentially allows OxSATS to inform clinical decision-making more directly,” Dr. Fazel told this news organization.
The findings were published online in BMJ Mental Health.
Targeted tool
Self-harm is associated with a 1-year risk of suicide that is 20 times higher than that of the general population. Given that about 16 million people self-harm annually, the impact at a population level is potentially quite large, the researchers note.
Current structured approaches to gauge suicide risk among those who have engaged in self-harm are based on tools developed for other purposes and symptom checklists. “Their poor to moderate performance is therefore not unexpected,” Dr. Fazel told this news organization.
In contrast, OxSATS was specifically developed to predict suicide mortality after self-harm.
Dr. Fazel’s group evaluated data on 53,172 Swedish individuals aged 10 years and older who sought emergency medical care after episodes of self-harm.
The development cohort included 37,523 individuals. Of these, 391 died by suicide within 12 months. The validation cohort included 15,649 individuals; of these people, 178 died by suicide within 12 months.
The final OxSATS model includes 11 predictors related to age and sex, as well as variables related to substance misuse, mental health, and treatment and history of self-harm.
“The performance of the model in external validation was good, with c-index at 6 and 12 months of 0.77,” the researchers note.
Using a cutoff threshold of 1%, the OxSATS correctly identified 68% of those who died by suicide within 6 months, while 71% of those who didn’t die were correctly classified as being at low risk. The figures for risk prediction at 12 months were 82% and 54%, respectively.
The OxSATS has been made into a simple online tool with probability scores for suicide at 6 and 12 months after an episode of self-harm, but without linkage to interventions. A tool on its own is unlikely to improve outcomes, said Dr. Fazel.
“However,” he added, “it can improve consistency in the assessment process, especially in busy clinical settings where people from different professional backgrounds and experience undertake such assessments. It can also highlight the role of modifiable risk factors and provide an opportunity to transparently discuss risk with patients and their carers.”
Valuable work
Reached for comment, Igor Galynker, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said that this is a “very solid study with a very large sample size and solid statistical analysis.”
Another strength of the research is the outcome of suicide death versus suicide attempt or suicidal ideation. “In that respect, it is a valuable paper,” Dr. Galynker, who directs the Mount Sinai Beth Israel Suicide Research Laboratory, told this news organization.
He noted that there are no new risk factors in the model. Rather, the model contains the typical risk factors for suicide, which include male sex, substance misuse, past suicide attempt, and psychiatric diagnosis.
“The strongest risk factor in the model is self-harm by hanging, strangulation, or suffocation, which has been shown before and is therefore unsurprising,” said Dr. Galynker.
In general, the risk factors included in the model are often part of administrative tools for suicide risk assessment, said Dr. Galynker, but the OxSATS “seems easier to use because it has 11 items only.”
Broadly speaking, individuals with mental illness and past suicide attempt, past self-harm, alcohol use, and other risk factors “should be treated proactively with suicide prevention measures,” he told this news organization.
As previously reported, Dr. Galynker and colleagues have developed the Abbreviated Suicide Crisis Syndrome Checklist (A-SCS-C), a novel tool to help identify which suicidal patients who present to the emergency department should be admitted to hospital and which patients can be safely discharged.
Funding for the study was provided by Wellcome Trust and the Swedish Research Council. Dr. Fazel and Dr. Galynker have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators have developed and validated a new risk calculator to help predict death by suicide in the 6-12 months after an episode of nonfatal self-harm, new research shows.
A study led by Seena Fazel, MBChB, MD, University of Oxford, England, suggests the Oxford Suicide Assessment Tool for Self-harm (OxSATS) may help guide treatment decisions and target resources to those most in need, the researchers note.
“Many tools use only simple high/low categories, whereas OxSATS includes probability scores, which align more closely with risk calculators in cardiovascular medicine, such as the Framingham Risk Score, and prognostic models in cancer medicine, which provide 5-year survival probabilities. This potentially allows OxSATS to inform clinical decision-making more directly,” Dr. Fazel told this news organization.
The findings were published online in BMJ Mental Health.
Targeted tool
Self-harm is associated with a 1-year risk of suicide that is 20 times higher than that of the general population. Given that about 16 million people self-harm annually, the impact at a population level is potentially quite large, the researchers note.
Current structured approaches to gauge suicide risk among those who have engaged in self-harm are based on tools developed for other purposes and symptom checklists. “Their poor to moderate performance is therefore not unexpected,” Dr. Fazel told this news organization.
In contrast, OxSATS was specifically developed to predict suicide mortality after self-harm.
Dr. Fazel’s group evaluated data on 53,172 Swedish individuals aged 10 years and older who sought emergency medical care after episodes of self-harm.
The development cohort included 37,523 individuals. Of these, 391 died by suicide within 12 months. The validation cohort included 15,649 individuals; of these people, 178 died by suicide within 12 months.
The final OxSATS model includes 11 predictors related to age and sex, as well as variables related to substance misuse, mental health, and treatment and history of self-harm.
“The performance of the model in external validation was good, with c-index at 6 and 12 months of 0.77,” the researchers note.
Using a cutoff threshold of 1%, the OxSATS correctly identified 68% of those who died by suicide within 6 months, while 71% of those who didn’t die were correctly classified as being at low risk. The figures for risk prediction at 12 months were 82% and 54%, respectively.
The OxSATS has been made into a simple online tool with probability scores for suicide at 6 and 12 months after an episode of self-harm, but without linkage to interventions. A tool on its own is unlikely to improve outcomes, said Dr. Fazel.
“However,” he added, “it can improve consistency in the assessment process, especially in busy clinical settings where people from different professional backgrounds and experience undertake such assessments. It can also highlight the role of modifiable risk factors and provide an opportunity to transparently discuss risk with patients and their carers.”
Valuable work
Reached for comment, Igor Galynker, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said that this is a “very solid study with a very large sample size and solid statistical analysis.”
Another strength of the research is the outcome of suicide death versus suicide attempt or suicidal ideation. “In that respect, it is a valuable paper,” Dr. Galynker, who directs the Mount Sinai Beth Israel Suicide Research Laboratory, told this news organization.
He noted that there are no new risk factors in the model. Rather, the model contains the typical risk factors for suicide, which include male sex, substance misuse, past suicide attempt, and psychiatric diagnosis.
“The strongest risk factor in the model is self-harm by hanging, strangulation, or suffocation, which has been shown before and is therefore unsurprising,” said Dr. Galynker.
In general, the risk factors included in the model are often part of administrative tools for suicide risk assessment, said Dr. Galynker, but the OxSATS “seems easier to use because it has 11 items only.”
Broadly speaking, individuals with mental illness and past suicide attempt, past self-harm, alcohol use, and other risk factors “should be treated proactively with suicide prevention measures,” he told this news organization.
As previously reported, Dr. Galynker and colleagues have developed the Abbreviated Suicide Crisis Syndrome Checklist (A-SCS-C), a novel tool to help identify which suicidal patients who present to the emergency department should be admitted to hospital and which patients can be safely discharged.
Funding for the study was provided by Wellcome Trust and the Swedish Research Council. Dr. Fazel and Dr. Galynker have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CGM alarm fatigue in youth?
Teenagers with diabetes who use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) employ a wide variety of alarm settings to alert them when their blood sugar may be too high or too low. But sometimes those thresholds generate too many alarms – which in turn might lead patients to ignore the devices, according to a study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“These alarms alert people with diabetes and their caregivers of pending glycemic changes. However, little work has been done studying CGM alarm settings in pediatric clinical populations,” said Victoria Ochs, BS, a medical student at the Indiana University, Indianapolis, who helped conduct the study.
Ms. Ochs and colleagues analyzed 2 weeks of real-time CGM alarm settings from 150 children with diabetes treated at Indiana. Their average age was 14 years; 47% were female, 89% of were White, 9.5% were Black, and 1.5% were Asian. Approximately half the patients used insulin pumps (51%) in addition to the monitoring devices.
For both alarms that indicated blood sugar was too low or too high, settings among the children often varied widely from thresholds recommended by the University of Colorado’s Barbara Davis Center for Diabetes, Aurora. Those thresholds are 70 mg/dL of glucose for low and 180 mg/dL for high glucose. At Indiana, the median alert level for low was set to 74 mg/dL (range: 60-100), while the median for high was 242 mg/dL (range: 120-400).
“If we have it set at 100, what exactly is the purpose of that? Is it just to make you more anxious that you’re going to drop low at some point?” asked Cari Berget, MPH, RN, CDE, who specializes in pediatric diabetes at the University of Colorado, speaking of the low blood sugar alarm. Setting this alarm at 70 md/dL instead could lead to concrete action when it does go off – such as consuming carbohydrates to boost blood sugar, she said.
“Alarms should result in action most of the time,” said Ms. Berget, associate director of Colorado’s PANTHER program, which established the alarm thresholds used in the Indiana study. Alarm setting is not one-size-fits-all, Ms. Berget noted: Some people might want 70 mg/dL to warn of low blood sugar, whereas others prefer 75 or 80 mg/dL.
As for alerts about hyperglycemia, Ms. Berget said patients often exceed the high range of 180 mg/dL immediately after a meal. Ideally these sugars will subside on their own within 3 hours, a process aided by insulin shots or pumps. Setting a threshold for high blood sugar too low, such as 120 mg/dL, could result in ceaseless alarms even if the person is not at risk for harm.
“If you receive an alarm and there’s no action for you to take, then we need to change how we’re setting these alarms,” Ms. Berget said. She advised parents and children to be thoughtful about setting their CGM alarm thresholds to be most useful to them.
Ms. Ochs said in some cases families have CGM devices shipped directly to their homes and never consult with anyone about optimal alarm settings.
“It would be useful to talk to families about what baseline information they had,” Ms. Ochs told this news organization. “It would be nice to talk to diabetes educators, and I think it would be nice to talk to physicians.”
Ms. Ochs reports no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Berget has consulted for Dexcom and Insulet.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Teenagers with diabetes who use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) employ a wide variety of alarm settings to alert them when their blood sugar may be too high or too low. But sometimes those thresholds generate too many alarms – which in turn might lead patients to ignore the devices, according to a study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“These alarms alert people with diabetes and their caregivers of pending glycemic changes. However, little work has been done studying CGM alarm settings in pediatric clinical populations,” said Victoria Ochs, BS, a medical student at the Indiana University, Indianapolis, who helped conduct the study.
Ms. Ochs and colleagues analyzed 2 weeks of real-time CGM alarm settings from 150 children with diabetes treated at Indiana. Their average age was 14 years; 47% were female, 89% of were White, 9.5% were Black, and 1.5% were Asian. Approximately half the patients used insulin pumps (51%) in addition to the monitoring devices.
For both alarms that indicated blood sugar was too low or too high, settings among the children often varied widely from thresholds recommended by the University of Colorado’s Barbara Davis Center for Diabetes, Aurora. Those thresholds are 70 mg/dL of glucose for low and 180 mg/dL for high glucose. At Indiana, the median alert level for low was set to 74 mg/dL (range: 60-100), while the median for high was 242 mg/dL (range: 120-400).
“If we have it set at 100, what exactly is the purpose of that? Is it just to make you more anxious that you’re going to drop low at some point?” asked Cari Berget, MPH, RN, CDE, who specializes in pediatric diabetes at the University of Colorado, speaking of the low blood sugar alarm. Setting this alarm at 70 md/dL instead could lead to concrete action when it does go off – such as consuming carbohydrates to boost blood sugar, she said.
“Alarms should result in action most of the time,” said Ms. Berget, associate director of Colorado’s PANTHER program, which established the alarm thresholds used in the Indiana study. Alarm setting is not one-size-fits-all, Ms. Berget noted: Some people might want 70 mg/dL to warn of low blood sugar, whereas others prefer 75 or 80 mg/dL.
As for alerts about hyperglycemia, Ms. Berget said patients often exceed the high range of 180 mg/dL immediately after a meal. Ideally these sugars will subside on their own within 3 hours, a process aided by insulin shots or pumps. Setting a threshold for high blood sugar too low, such as 120 mg/dL, could result in ceaseless alarms even if the person is not at risk for harm.
“If you receive an alarm and there’s no action for you to take, then we need to change how we’re setting these alarms,” Ms. Berget said. She advised parents and children to be thoughtful about setting their CGM alarm thresholds to be most useful to them.
Ms. Ochs said in some cases families have CGM devices shipped directly to their homes and never consult with anyone about optimal alarm settings.
“It would be useful to talk to families about what baseline information they had,” Ms. Ochs told this news organization. “It would be nice to talk to diabetes educators, and I think it would be nice to talk to physicians.”
Ms. Ochs reports no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Berget has consulted for Dexcom and Insulet.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Teenagers with diabetes who use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) employ a wide variety of alarm settings to alert them when their blood sugar may be too high or too low. But sometimes those thresholds generate too many alarms – which in turn might lead patients to ignore the devices, according to a study presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“These alarms alert people with diabetes and their caregivers of pending glycemic changes. However, little work has been done studying CGM alarm settings in pediatric clinical populations,” said Victoria Ochs, BS, a medical student at the Indiana University, Indianapolis, who helped conduct the study.
Ms. Ochs and colleagues analyzed 2 weeks of real-time CGM alarm settings from 150 children with diabetes treated at Indiana. Their average age was 14 years; 47% were female, 89% of were White, 9.5% were Black, and 1.5% were Asian. Approximately half the patients used insulin pumps (51%) in addition to the monitoring devices.
For both alarms that indicated blood sugar was too low or too high, settings among the children often varied widely from thresholds recommended by the University of Colorado’s Barbara Davis Center for Diabetes, Aurora. Those thresholds are 70 mg/dL of glucose for low and 180 mg/dL for high glucose. At Indiana, the median alert level for low was set to 74 mg/dL (range: 60-100), while the median for high was 242 mg/dL (range: 120-400).
“If we have it set at 100, what exactly is the purpose of that? Is it just to make you more anxious that you’re going to drop low at some point?” asked Cari Berget, MPH, RN, CDE, who specializes in pediatric diabetes at the University of Colorado, speaking of the low blood sugar alarm. Setting this alarm at 70 md/dL instead could lead to concrete action when it does go off – such as consuming carbohydrates to boost blood sugar, she said.
“Alarms should result in action most of the time,” said Ms. Berget, associate director of Colorado’s PANTHER program, which established the alarm thresholds used in the Indiana study. Alarm setting is not one-size-fits-all, Ms. Berget noted: Some people might want 70 mg/dL to warn of low blood sugar, whereas others prefer 75 or 80 mg/dL.
As for alerts about hyperglycemia, Ms. Berget said patients often exceed the high range of 180 mg/dL immediately after a meal. Ideally these sugars will subside on their own within 3 hours, a process aided by insulin shots or pumps. Setting a threshold for high blood sugar too low, such as 120 mg/dL, could result in ceaseless alarms even if the person is not at risk for harm.
“If you receive an alarm and there’s no action for you to take, then we need to change how we’re setting these alarms,” Ms. Berget said. She advised parents and children to be thoughtful about setting their CGM alarm thresholds to be most useful to them.
Ms. Ochs said in some cases families have CGM devices shipped directly to their homes and never consult with anyone about optimal alarm settings.
“It would be useful to talk to families about what baseline information they had,” Ms. Ochs told this news organization. “It would be nice to talk to diabetes educators, and I think it would be nice to talk to physicians.”
Ms. Ochs reports no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Berget has consulted for Dexcom and Insulet.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Young girls, women are at high risk of iron deficiency: Study
, which can lead to fatigue and increase the risk of many health problems, according to a new study.
Researchers also found that 6 in every 100 of the girls and young women had extremely low iron levels, known as iron-deficiency anemia, which impacts the blood’s ability to carry oxygen throughout the body.
The findings suggest that current screening guidelines for iron levels in girls and women may be flawed, resulting in missed chances to get a simple blood test that can diagnose the easy-to-treat condition. Iron supplements are often prescribed as a treatment.
The study was published in JAMA and included 12 years of data for a total of nearly 3,500 girls and women aged 12-21 years.
In addition to shortness of breath and fatigue, other symptoms of iron deficiency anemia are:
- Pale skin
- Cold hands and feet
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Unusual cravings for nonfood items such as ice, dirt, or paper.
The Cleveland Clinic says the most common causes of iron-deficiency anemia are those that involve blood loss, including heavy menstrual periods. The body gets iron from food, and not getting enough iron from food, as can happen from eating a vegan or vegetarian diet, can also lead to deficiency.
In this latest study, researchers found that young women and girls’ likelihood to have iron deficiency or iron-deficiency anemia were significantly linked to race and ethnicity, poverty status, access to sufficient or quality food (also called food insecurity), and body mass index. Black and Hispanic girls and women were more likely to have iron level problems, compared with White girls and women. Black girls and women were four times more likely to have iron-deficiency anemia, compared with White girls and women.
The authors did not discuss potential causes and suggested further study is needed to identify risk factors of iron deficiency in girls and young women.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
, which can lead to fatigue and increase the risk of many health problems, according to a new study.
Researchers also found that 6 in every 100 of the girls and young women had extremely low iron levels, known as iron-deficiency anemia, which impacts the blood’s ability to carry oxygen throughout the body.
The findings suggest that current screening guidelines for iron levels in girls and women may be flawed, resulting in missed chances to get a simple blood test that can diagnose the easy-to-treat condition. Iron supplements are often prescribed as a treatment.
The study was published in JAMA and included 12 years of data for a total of nearly 3,500 girls and women aged 12-21 years.
In addition to shortness of breath and fatigue, other symptoms of iron deficiency anemia are:
- Pale skin
- Cold hands and feet
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Unusual cravings for nonfood items such as ice, dirt, or paper.
The Cleveland Clinic says the most common causes of iron-deficiency anemia are those that involve blood loss, including heavy menstrual periods. The body gets iron from food, and not getting enough iron from food, as can happen from eating a vegan or vegetarian diet, can also lead to deficiency.
In this latest study, researchers found that young women and girls’ likelihood to have iron deficiency or iron-deficiency anemia were significantly linked to race and ethnicity, poverty status, access to sufficient or quality food (also called food insecurity), and body mass index. Black and Hispanic girls and women were more likely to have iron level problems, compared with White girls and women. Black girls and women were four times more likely to have iron-deficiency anemia, compared with White girls and women.
The authors did not discuss potential causes and suggested further study is needed to identify risk factors of iron deficiency in girls and young women.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
, which can lead to fatigue and increase the risk of many health problems, according to a new study.
Researchers also found that 6 in every 100 of the girls and young women had extremely low iron levels, known as iron-deficiency anemia, which impacts the blood’s ability to carry oxygen throughout the body.
The findings suggest that current screening guidelines for iron levels in girls and women may be flawed, resulting in missed chances to get a simple blood test that can diagnose the easy-to-treat condition. Iron supplements are often prescribed as a treatment.
The study was published in JAMA and included 12 years of data for a total of nearly 3,500 girls and women aged 12-21 years.
In addition to shortness of breath and fatigue, other symptoms of iron deficiency anemia are:
- Pale skin
- Cold hands and feet
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Unusual cravings for nonfood items such as ice, dirt, or paper.
The Cleveland Clinic says the most common causes of iron-deficiency anemia are those that involve blood loss, including heavy menstrual periods. The body gets iron from food, and not getting enough iron from food, as can happen from eating a vegan or vegetarian diet, can also lead to deficiency.
In this latest study, researchers found that young women and girls’ likelihood to have iron deficiency or iron-deficiency anemia were significantly linked to race and ethnicity, poverty status, access to sufficient or quality food (also called food insecurity), and body mass index. Black and Hispanic girls and women were more likely to have iron level problems, compared with White girls and women. Black girls and women were four times more likely to have iron-deficiency anemia, compared with White girls and women.
The authors did not discuss potential causes and suggested further study is needed to identify risk factors of iron deficiency in girls and young women.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM JAMA
Limiting social media use in youths brings challenges, benefits
Amelia Kennedy, 19, of Royersford, Pa., a point guard on the Catholic University of America, Washington, basketball team who will begin her sophomore year in the fall, uses TikTok, Snapchat, Instagram, and YouTube regularly.
How regularly? She estimates 7 hours a day and about 9 on weekends. She’s aware of the time-wasting potential. “If my mom says, ‘Do dishes,’ and I say, ‘5 more minutes,’ it can be longer,’’ she said.
Now imagine the challenge of cutting that 7 or 9 hours a day of social media use down to 30 minutes.
A very tall order, considering a 2022 Pew Research Center survey of more than 1,300 teens found 35% are “nearly constantly” on at least one of the top five social media platforms: YouTube, TikTok, Instagram, Snapchat, and Facebook.
Researchers from Iowa State University, Ames, recently took on that daunting challenge, limiting a group of students to only 30 minutes of social media a day to see what happens. Two weeks into the study, the students reported improvement in psychological well-being and other important measures, including sleep quality, compared with a control group assigned to continue using social media as usual.
And the dreaded FOMO, or fear of missing out, didn’t happen, the researchers said. At the end, the students were rethinking their social media use and feeling positive about it.
As social media becomes more common and youth mental health more endangered, experts are sounding the alarm. In late May, U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, issued an advisory on social media and youth mental health, calling for tech companies to do better, policymakers to strengthen safety, and researchers to get more information, among other actions.
After that, the Biden administration took actions including the launch of a task force on kids’ online health and safety. The American Psychological Association has issued recommendations on social media use in youths. And the Social Media Victims Law Center in Seattle has sued numerous social media companies for online activity resulting in death and other tragedies.
While experts acknowledge that much more research is needed to sort out how to balance social media’s risks and benefits to preserve youth mental health and prevent such disasters, the new Iowa State study, as well as other recent research, suggests that
Goal: 30 minutes a day
In the Iowa State study, 230 undergraduate students were assigned to one of two groups, with 99 in the 30-minute-a-day social media use group and 131 in the “usual” or control group, which made no changes. For those in the intervention group, “we sent a daily reminder email,” said Ella Faulhaber, a PhD candidate at Iowa State and the study’s lead author. It simply reminded them to limit social medial use to the 30-minute maximum.
At the study start and end, all participants provided a screenshot of their weekly social media usage time. The researchers gave both groups a battery of tests to assess anxiety, depression, loneliness, fear of missing out, and negative and positive feelings.
“By limiting their social media time, that resulted in less anxiety, less depression, less FOMO, fewer negative emotions, and greater positive emotions,” said Douglas Gentile, PhD, a distinguished professor of psychology at Iowa State and a study coauthor. “We know that it is the limiting [of] the social media that is causing that.”
Ms. Faulhaber recalled one participant who mentioned having trouble at first adjusting to the 30-minute time frame, but once sleep improved, it was easier to stick to that guidance. Another who gave up phone use at bedtime found: “Instead of looking at my phone, it was much easier to go straight to bed.”
Sleep improvements, of course, affect many parts of physical and mental health, Dr. Gentile said. And the study also showed that even with reduced screen time, “we can still get the benefit of being connected.” Those who didn’t make the 30-minute mark, but cut back, got benefits, too, the researchers said.
‘Youth are aware’
Self-monitoring works, agreed Jane Harness, DO, an adjunct clinical assistant professor of psychiatry at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, because “having that insight is often the first step.”
In a study she conducted, Dr. Harness aimed to gather youths’ insights about how their social media use affected them. With her colleagues, she asked more than 1,100 youths, aged 14-24, what advice they would give to those new to social media, if they ever felt they needed to change social media habits, and if they have deleted or considered deleting social media accounts.
From the 871 responses, Harness found that youths were especially concerned about safety online, that most had thought about deleting a social media app and some had, and that youths were more likely to say they wanted to change the amount of time spent on social media, compared with the content they view.
“Users responded with great advice for each other,” she said. “Safety was brought up,” with users reminding others to keep accounts private and to be aware of location tracking links and content that seems to promote eating disorders, suicide, and other harms.
In the study report, Dr. Harness concluded: “Youth are aware of ways in which social media could be negatively impacting them and they have employed methods to modulate their use because of this awareness.”
Less FOMO, less anxiety
In an earlier study, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, researchers had 143 college students self-monitor social media for a week, then randomly assigned them either to a group told to limit Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat use to 10 minutes per platform, per day, or to a group told to use social media as usual for 3 weeks.
At the end of the study, the researchers evaluated both groups and found “significant reductions in loneliness and depression over 3 weeks’’ in the limited-use group, compared with the usual-use group, according to study researcher Melissa G. Hunt, PhD, associate director of clinical training at the University of Pennsylvania.
And both groups showed declines in anxiety and fear of missing out, suggesting a benefit tied to self-monitoring itself, she said.
While Dr. Hunt’s study focused on 30 minutes a day, she said “about an hour a day seems to be the sweet spot for maximizing the positive effects of connecting, but limiting the negative effects of social media use.”
She also suggested that smartphones have no place in middle or high school classrooms. Instead, they should be on lockdown during classes.
“Parents need to set real limits of cellphone use during meals and in bedrooms,” Dr. Hunt said. At mealtime, for instance, all phones should be absent from the table. And after 10 p.m., “all family phones remain in the kitchen.”
Be ‘more mindful’
These recent study findings about self-monitoring and limiting social media time may not work the same for everyone, especially among those who aren’t as motivated, said psychiatrist Elizabeth Ortiz-Schwartz, MD, team lead for the adolescent inpatient unit at Silver Hill Hospital in New Canaan, Conn.
But “the bigger take-home piece is that being intentional and attempting to decrease the use in these individuals, even if they were not always successful, was clearly beneficial,” she said.
As we await clearer guidelines about what is the “right” amount of use in terms of social media content and time, Dr. Ortiz-Schwartz said, “becoming more mindful and aware of the risks and benefits can hopefully help individuals become more mindful and deliberate about its use.”
Real-world strategies
Max Schwandt, 23, is an outlier, but a happy one. He works as a sales clerk at a Los Angeles–area recreational gear shop, and he uses no social media. Why not? “It takes up too much time,” he explained. As simple as that.
But for many other teens and young adults, the struggle to stay off social media is real.
Amelia Kennedy, the Catholic University of America student, is trying to reduce her screen time. One way is to track it on her phone. These days, her summer job at a restaurant serving breakfast gets her up early. “If I have to work, I still go on my phone, but not that long.” And once at work, she only has time for quick checks between work responsibilities. “I definitely am more productive,” she said about days when she has work.
Last December, Lauren Young, 25, whose father was a researcher on the Iowa State study, was finishing law school at Georgetown University, Washington, and decided to take a break from social media for the entire month. “I can’t say I was always successful in avoiding it,” she said. But cutting down greatly “made me a lot more present in my day-to-day life, and it was easier to concentrate.”
She could even get through a meal, out with friends, without her phone, keeping it in her purse. That was a definite change from the norm. “I noticed I would go out to dinner and the standard for people my age is having the phone on the table. If you are being polite, you turn it over.”
During her social media “blackout,” Ms. Young had deleted TikTok, Instagram, and Facebook apps. Then, when she graduated, she had to reinstall to post a picture. But now, she is back to minimal social media use.
“I’m studying for the bar, so it’s kind of necessary, but it always makes me happier.” She figures she can always text family and friends if necessary, instead of posting. “I felt for a while I was missing out on things, but not now,” she said.
Others, including Sarah Goldstein, 22, of Chatsworth, Calif., a supermarket courtesy clerk who is thinking of returning to college, said she has developed a healthier attitude toward social media as she has gotten older.
“In middle and early high school, I would see parties, things I wasn’t invited to, on Snapchat and Instagram.” While she realized there could be legitimate reasons for not being included, she said it was easy to internalize those feelings of being left out.
These days, she said she doesn’t let it affect her mental health that way. She enjoys social media – especially TikTok and Instagram – for its benefits. “It kills time, gives you something to watch, can make you laugh and feel like you have a connection with other people.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Amelia Kennedy, 19, of Royersford, Pa., a point guard on the Catholic University of America, Washington, basketball team who will begin her sophomore year in the fall, uses TikTok, Snapchat, Instagram, and YouTube regularly.
How regularly? She estimates 7 hours a day and about 9 on weekends. She’s aware of the time-wasting potential. “If my mom says, ‘Do dishes,’ and I say, ‘5 more minutes,’ it can be longer,’’ she said.
Now imagine the challenge of cutting that 7 or 9 hours a day of social media use down to 30 minutes.
A very tall order, considering a 2022 Pew Research Center survey of more than 1,300 teens found 35% are “nearly constantly” on at least one of the top five social media platforms: YouTube, TikTok, Instagram, Snapchat, and Facebook.
Researchers from Iowa State University, Ames, recently took on that daunting challenge, limiting a group of students to only 30 minutes of social media a day to see what happens. Two weeks into the study, the students reported improvement in psychological well-being and other important measures, including sleep quality, compared with a control group assigned to continue using social media as usual.
And the dreaded FOMO, or fear of missing out, didn’t happen, the researchers said. At the end, the students were rethinking their social media use and feeling positive about it.
As social media becomes more common and youth mental health more endangered, experts are sounding the alarm. In late May, U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, issued an advisory on social media and youth mental health, calling for tech companies to do better, policymakers to strengthen safety, and researchers to get more information, among other actions.
After that, the Biden administration took actions including the launch of a task force on kids’ online health and safety. The American Psychological Association has issued recommendations on social media use in youths. And the Social Media Victims Law Center in Seattle has sued numerous social media companies for online activity resulting in death and other tragedies.
While experts acknowledge that much more research is needed to sort out how to balance social media’s risks and benefits to preserve youth mental health and prevent such disasters, the new Iowa State study, as well as other recent research, suggests that
Goal: 30 minutes a day
In the Iowa State study, 230 undergraduate students were assigned to one of two groups, with 99 in the 30-minute-a-day social media use group and 131 in the “usual” or control group, which made no changes. For those in the intervention group, “we sent a daily reminder email,” said Ella Faulhaber, a PhD candidate at Iowa State and the study’s lead author. It simply reminded them to limit social medial use to the 30-minute maximum.
At the study start and end, all participants provided a screenshot of their weekly social media usage time. The researchers gave both groups a battery of tests to assess anxiety, depression, loneliness, fear of missing out, and negative and positive feelings.
“By limiting their social media time, that resulted in less anxiety, less depression, less FOMO, fewer negative emotions, and greater positive emotions,” said Douglas Gentile, PhD, a distinguished professor of psychology at Iowa State and a study coauthor. “We know that it is the limiting [of] the social media that is causing that.”
Ms. Faulhaber recalled one participant who mentioned having trouble at first adjusting to the 30-minute time frame, but once sleep improved, it was easier to stick to that guidance. Another who gave up phone use at bedtime found: “Instead of looking at my phone, it was much easier to go straight to bed.”
Sleep improvements, of course, affect many parts of physical and mental health, Dr. Gentile said. And the study also showed that even with reduced screen time, “we can still get the benefit of being connected.” Those who didn’t make the 30-minute mark, but cut back, got benefits, too, the researchers said.
‘Youth are aware’
Self-monitoring works, agreed Jane Harness, DO, an adjunct clinical assistant professor of psychiatry at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, because “having that insight is often the first step.”
In a study she conducted, Dr. Harness aimed to gather youths’ insights about how their social media use affected them. With her colleagues, she asked more than 1,100 youths, aged 14-24, what advice they would give to those new to social media, if they ever felt they needed to change social media habits, and if they have deleted or considered deleting social media accounts.
From the 871 responses, Harness found that youths were especially concerned about safety online, that most had thought about deleting a social media app and some had, and that youths were more likely to say they wanted to change the amount of time spent on social media, compared with the content they view.
“Users responded with great advice for each other,” she said. “Safety was brought up,” with users reminding others to keep accounts private and to be aware of location tracking links and content that seems to promote eating disorders, suicide, and other harms.
In the study report, Dr. Harness concluded: “Youth are aware of ways in which social media could be negatively impacting them and they have employed methods to modulate their use because of this awareness.”
Less FOMO, less anxiety
In an earlier study, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, researchers had 143 college students self-monitor social media for a week, then randomly assigned them either to a group told to limit Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat use to 10 minutes per platform, per day, or to a group told to use social media as usual for 3 weeks.
At the end of the study, the researchers evaluated both groups and found “significant reductions in loneliness and depression over 3 weeks’’ in the limited-use group, compared with the usual-use group, according to study researcher Melissa G. Hunt, PhD, associate director of clinical training at the University of Pennsylvania.
And both groups showed declines in anxiety and fear of missing out, suggesting a benefit tied to self-monitoring itself, she said.
While Dr. Hunt’s study focused on 30 minutes a day, she said “about an hour a day seems to be the sweet spot for maximizing the positive effects of connecting, but limiting the negative effects of social media use.”
She also suggested that smartphones have no place in middle or high school classrooms. Instead, they should be on lockdown during classes.
“Parents need to set real limits of cellphone use during meals and in bedrooms,” Dr. Hunt said. At mealtime, for instance, all phones should be absent from the table. And after 10 p.m., “all family phones remain in the kitchen.”
Be ‘more mindful’
These recent study findings about self-monitoring and limiting social media time may not work the same for everyone, especially among those who aren’t as motivated, said psychiatrist Elizabeth Ortiz-Schwartz, MD, team lead for the adolescent inpatient unit at Silver Hill Hospital in New Canaan, Conn.
But “the bigger take-home piece is that being intentional and attempting to decrease the use in these individuals, even if they were not always successful, was clearly beneficial,” she said.
As we await clearer guidelines about what is the “right” amount of use in terms of social media content and time, Dr. Ortiz-Schwartz said, “becoming more mindful and aware of the risks and benefits can hopefully help individuals become more mindful and deliberate about its use.”
Real-world strategies
Max Schwandt, 23, is an outlier, but a happy one. He works as a sales clerk at a Los Angeles–area recreational gear shop, and he uses no social media. Why not? “It takes up too much time,” he explained. As simple as that.
But for many other teens and young adults, the struggle to stay off social media is real.
Amelia Kennedy, the Catholic University of America student, is trying to reduce her screen time. One way is to track it on her phone. These days, her summer job at a restaurant serving breakfast gets her up early. “If I have to work, I still go on my phone, but not that long.” And once at work, she only has time for quick checks between work responsibilities. “I definitely am more productive,” she said about days when she has work.
Last December, Lauren Young, 25, whose father was a researcher on the Iowa State study, was finishing law school at Georgetown University, Washington, and decided to take a break from social media for the entire month. “I can’t say I was always successful in avoiding it,” she said. But cutting down greatly “made me a lot more present in my day-to-day life, and it was easier to concentrate.”
She could even get through a meal, out with friends, without her phone, keeping it in her purse. That was a definite change from the norm. “I noticed I would go out to dinner and the standard for people my age is having the phone on the table. If you are being polite, you turn it over.”
During her social media “blackout,” Ms. Young had deleted TikTok, Instagram, and Facebook apps. Then, when she graduated, she had to reinstall to post a picture. But now, she is back to minimal social media use.
“I’m studying for the bar, so it’s kind of necessary, but it always makes me happier.” She figures she can always text family and friends if necessary, instead of posting. “I felt for a while I was missing out on things, but not now,” she said.
Others, including Sarah Goldstein, 22, of Chatsworth, Calif., a supermarket courtesy clerk who is thinking of returning to college, said she has developed a healthier attitude toward social media as she has gotten older.
“In middle and early high school, I would see parties, things I wasn’t invited to, on Snapchat and Instagram.” While she realized there could be legitimate reasons for not being included, she said it was easy to internalize those feelings of being left out.
These days, she said she doesn’t let it affect her mental health that way. She enjoys social media – especially TikTok and Instagram – for its benefits. “It kills time, gives you something to watch, can make you laugh and feel like you have a connection with other people.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Amelia Kennedy, 19, of Royersford, Pa., a point guard on the Catholic University of America, Washington, basketball team who will begin her sophomore year in the fall, uses TikTok, Snapchat, Instagram, and YouTube regularly.
How regularly? She estimates 7 hours a day and about 9 on weekends. She’s aware of the time-wasting potential. “If my mom says, ‘Do dishes,’ and I say, ‘5 more minutes,’ it can be longer,’’ she said.
Now imagine the challenge of cutting that 7 or 9 hours a day of social media use down to 30 minutes.
A very tall order, considering a 2022 Pew Research Center survey of more than 1,300 teens found 35% are “nearly constantly” on at least one of the top five social media platforms: YouTube, TikTok, Instagram, Snapchat, and Facebook.
Researchers from Iowa State University, Ames, recently took on that daunting challenge, limiting a group of students to only 30 minutes of social media a day to see what happens. Two weeks into the study, the students reported improvement in psychological well-being and other important measures, including sleep quality, compared with a control group assigned to continue using social media as usual.
And the dreaded FOMO, or fear of missing out, didn’t happen, the researchers said. At the end, the students were rethinking their social media use and feeling positive about it.
As social media becomes more common and youth mental health more endangered, experts are sounding the alarm. In late May, U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, issued an advisory on social media and youth mental health, calling for tech companies to do better, policymakers to strengthen safety, and researchers to get more information, among other actions.
After that, the Biden administration took actions including the launch of a task force on kids’ online health and safety. The American Psychological Association has issued recommendations on social media use in youths. And the Social Media Victims Law Center in Seattle has sued numerous social media companies for online activity resulting in death and other tragedies.
While experts acknowledge that much more research is needed to sort out how to balance social media’s risks and benefits to preserve youth mental health and prevent such disasters, the new Iowa State study, as well as other recent research, suggests that
Goal: 30 minutes a day
In the Iowa State study, 230 undergraduate students were assigned to one of two groups, with 99 in the 30-minute-a-day social media use group and 131 in the “usual” or control group, which made no changes. For those in the intervention group, “we sent a daily reminder email,” said Ella Faulhaber, a PhD candidate at Iowa State and the study’s lead author. It simply reminded them to limit social medial use to the 30-minute maximum.
At the study start and end, all participants provided a screenshot of their weekly social media usage time. The researchers gave both groups a battery of tests to assess anxiety, depression, loneliness, fear of missing out, and negative and positive feelings.
“By limiting their social media time, that resulted in less anxiety, less depression, less FOMO, fewer negative emotions, and greater positive emotions,” said Douglas Gentile, PhD, a distinguished professor of psychology at Iowa State and a study coauthor. “We know that it is the limiting [of] the social media that is causing that.”
Ms. Faulhaber recalled one participant who mentioned having trouble at first adjusting to the 30-minute time frame, but once sleep improved, it was easier to stick to that guidance. Another who gave up phone use at bedtime found: “Instead of looking at my phone, it was much easier to go straight to bed.”
Sleep improvements, of course, affect many parts of physical and mental health, Dr. Gentile said. And the study also showed that even with reduced screen time, “we can still get the benefit of being connected.” Those who didn’t make the 30-minute mark, but cut back, got benefits, too, the researchers said.
‘Youth are aware’
Self-monitoring works, agreed Jane Harness, DO, an adjunct clinical assistant professor of psychiatry at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, because “having that insight is often the first step.”
In a study she conducted, Dr. Harness aimed to gather youths’ insights about how their social media use affected them. With her colleagues, she asked more than 1,100 youths, aged 14-24, what advice they would give to those new to social media, if they ever felt they needed to change social media habits, and if they have deleted or considered deleting social media accounts.
From the 871 responses, Harness found that youths were especially concerned about safety online, that most had thought about deleting a social media app and some had, and that youths were more likely to say they wanted to change the amount of time spent on social media, compared with the content they view.
“Users responded with great advice for each other,” she said. “Safety was brought up,” with users reminding others to keep accounts private and to be aware of location tracking links and content that seems to promote eating disorders, suicide, and other harms.
In the study report, Dr. Harness concluded: “Youth are aware of ways in which social media could be negatively impacting them and they have employed methods to modulate their use because of this awareness.”
Less FOMO, less anxiety
In an earlier study, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, researchers had 143 college students self-monitor social media for a week, then randomly assigned them either to a group told to limit Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat use to 10 minutes per platform, per day, or to a group told to use social media as usual for 3 weeks.
At the end of the study, the researchers evaluated both groups and found “significant reductions in loneliness and depression over 3 weeks’’ in the limited-use group, compared with the usual-use group, according to study researcher Melissa G. Hunt, PhD, associate director of clinical training at the University of Pennsylvania.
And both groups showed declines in anxiety and fear of missing out, suggesting a benefit tied to self-monitoring itself, she said.
While Dr. Hunt’s study focused on 30 minutes a day, she said “about an hour a day seems to be the sweet spot for maximizing the positive effects of connecting, but limiting the negative effects of social media use.”
She also suggested that smartphones have no place in middle or high school classrooms. Instead, they should be on lockdown during classes.
“Parents need to set real limits of cellphone use during meals and in bedrooms,” Dr. Hunt said. At mealtime, for instance, all phones should be absent from the table. And after 10 p.m., “all family phones remain in the kitchen.”
Be ‘more mindful’
These recent study findings about self-monitoring and limiting social media time may not work the same for everyone, especially among those who aren’t as motivated, said psychiatrist Elizabeth Ortiz-Schwartz, MD, team lead for the adolescent inpatient unit at Silver Hill Hospital in New Canaan, Conn.
But “the bigger take-home piece is that being intentional and attempting to decrease the use in these individuals, even if they were not always successful, was clearly beneficial,” she said.
As we await clearer guidelines about what is the “right” amount of use in terms of social media content and time, Dr. Ortiz-Schwartz said, “becoming more mindful and aware of the risks and benefits can hopefully help individuals become more mindful and deliberate about its use.”
Real-world strategies
Max Schwandt, 23, is an outlier, but a happy one. He works as a sales clerk at a Los Angeles–area recreational gear shop, and he uses no social media. Why not? “It takes up too much time,” he explained. As simple as that.
But for many other teens and young adults, the struggle to stay off social media is real.
Amelia Kennedy, the Catholic University of America student, is trying to reduce her screen time. One way is to track it on her phone. These days, her summer job at a restaurant serving breakfast gets her up early. “If I have to work, I still go on my phone, but not that long.” And once at work, she only has time for quick checks between work responsibilities. “I definitely am more productive,” she said about days when she has work.
Last December, Lauren Young, 25, whose father was a researcher on the Iowa State study, was finishing law school at Georgetown University, Washington, and decided to take a break from social media for the entire month. “I can’t say I was always successful in avoiding it,” she said. But cutting down greatly “made me a lot more present in my day-to-day life, and it was easier to concentrate.”
She could even get through a meal, out with friends, without her phone, keeping it in her purse. That was a definite change from the norm. “I noticed I would go out to dinner and the standard for people my age is having the phone on the table. If you are being polite, you turn it over.”
During her social media “blackout,” Ms. Young had deleted TikTok, Instagram, and Facebook apps. Then, when she graduated, she had to reinstall to post a picture. But now, she is back to minimal social media use.
“I’m studying for the bar, so it’s kind of necessary, but it always makes me happier.” She figures she can always text family and friends if necessary, instead of posting. “I felt for a while I was missing out on things, but not now,” she said.
Others, including Sarah Goldstein, 22, of Chatsworth, Calif., a supermarket courtesy clerk who is thinking of returning to college, said she has developed a healthier attitude toward social media as she has gotten older.
“In middle and early high school, I would see parties, things I wasn’t invited to, on Snapchat and Instagram.” While she realized there could be legitimate reasons for not being included, she said it was easy to internalize those feelings of being left out.
These days, she said she doesn’t let it affect her mental health that way. She enjoys social media – especially TikTok and Instagram – for its benefits. “It kills time, gives you something to watch, can make you laugh and feel like you have a connection with other people.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
HPV rates skyrocket despite safe, effective vaccine
An epidemic of sexually transmitted HPV is now swirling around the United States and the United Kingdom, with some serious cases leading to oropharyngeal cancer, which can affect the back of the throat, tonsils, and tongue.
HPV is the leading cause (70%) of this oropharyngeal cancer, according to the CDC. It is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the nation, and around 3.6% of women and 10% of men report oral HPV specifically. But over the past decade, oropharyngeal cases have been steadily falling a little under 4% and 2%, respectively, according to the National Cancer Institute.
HPV is often undetectable and can clear up within a few months. But unfortunately for some, serious disease, such as throat cancer, can develop.
Studies show the HPV vaccine to be extremely effective in lowering sexually transmitted HPV cases. Yet, only 54.5% of young people aged 13-15 have taken the recommended two to three doses, according to the National Cancer Institute.
Why aren’t more young people taking the vaccine?
Low public awareness of the dangers of HPV may be behind young people’s poor vaccination rates, according to Teresa Lee, MD, of the Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia. “For example, while the link with head and neck cancers has been well-studied, the FDA labeling was not changed to reflect this as an indication until 2020,” she said.
Other reasons can include one’s socioeconomic background, poor health literacy, cultural or religious stigmas around vaccines, and lack of quality, low-cost health care, says Emmanuel Aguh, MD, a board-certified family medicine physician. “Some individuals and families are still resistant to vaccines and the noted lack of uptake.”
Doctors and other health care professionals should also be sure to tell patients of all ages about the risks of HPV infection and how well the vaccine works, Dr. Lee said. “Not everyone who is now eligible may have been offered the vaccine as a child, and the first time young adults may receive counseling on this subject may not be until they are entering a very busy period of their lives with many responsibilities – when it may be hard to fit in things like health maintenance.”
How safe is the HPV vaccine?
The Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have studied the HPV vaccine for years to find out how safe it is and how well it works, Dr. Aguh said. No major side effects have been reported, and the most common side effect is soreness where you get the shot (which is normal after most vaccines). Some dizziness and fainting in adolescents can also occur, so young people are usually asked to sit or lie down during the shot and for 15 minutes afterward, he said.
“Serious adverse events have not been reported at higher rates than expected following HPV vaccination, meaning there is no clear evidence they are related to the vaccine,” Dr. Lee said. “The vaccine is highly effective in decreasing rates of detectable infection with the high-risk HPV strains responsible for HPV-associated cancers.”
The HPV vaccine is largely recommended for people aged 9-26, and sometimes up to age 45, depending on the individual, Dr. Aguh said. If you are over 26, talk to your doctor about whether you should consider getting the vaccine.
“It is usually given in two doses for complete protection if taken before the 15th birthday,” Dr. Aguh said. “If taken afterward, or in those with a weak immune system, they might require three doses to be fully protected.”
The vaccine produces antibodies that can stop HPV from infecting cells and lowers your chances of catching an HPV-related cancer, such as throat cancer or cancer of the cervix, he said.
While the vaccine is not guaranteed to protect you from the more than 100 strains of HPV, it can protect you from HPV 16 and HPV 18 – two high-risk strains that cause around 70% of cervical cancers.
What is fueling the rise of HPV cases?
A misconception that oral sex is somehow a “safe and risk-free” alternative to anal or vaginal sex could be one reason, Dr. Aguh said.
“It is important to know that, with oral sex, you are exposed to many of the risks associated with vaginal intercourse, especially if you do not take any measures to protect yourself and/or your partner,” Dr. Aguh said. “[With oral sex] it is possible to end up contracting an infection like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and even HPV, leading to an increased risk of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancers.”
A lack of public awareness of what can cause throat cancer could also explain this phenomenon. The number of people you have oral sex with, along with the age you begin sexual activity, can greatly determine your risk of the disease, according to Dr. Lee. She echoes a report by Hisham Mehanna, PhD, in The Conversation.
“For oropharyngeal cancer, the main risk factor is the number of lifetime sexual partners, especially oral sex,” wrote Dr. Mehanna, a professor at the Institute of Cancer and Genomic Sciences at the University of Birmingham (England). “Those with six or more lifetime oral-sex partners are 8.5 times more likely to develop oropharyngeal cancer than those who do not practice oral sex.”
What are symptoms of oropharyngeal cancer?
Labored breathing or swallowing, a cough that won’t go away, and crackling or hoarseness of your voice could all be signs of throat cancer. Other symptoms include earaches, swelling of the head or neck, and enlarged lymph nodes, among others, Dr. Aguh said.
“The signs and symptoms of HPV-related throat cancers can be difficult to identify and recognize, as they can be vague and are also associated with other medical conditions. Sometimes, there are no signs at all, or they are not easily noticeable due to the location,” he said.
You should go see your doctor if you have any of these ailments for an extended period.
How to reduce your risk
In addition to having six or more oral-sex partners, smoking and drinking heavily could also raise your risk of throat cancer, said Dr. Lee. Proper dental health – like seeing your dentist regularly and practicing proper oral hygiene – can also shave your risk.
“[Good dental health] can help not just with head and neck cancer risk, but with many other inflammation-related diseases,” Dr. Lee said.
Using dental dams and condoms can also be a good method of protection, Dr. Aguh said. A dental dam is a stretchy sheet of latex, or polyurethane plastic, in the shape of a square that is made for blocking body fluid to lower your risk of contracting an STD via oral sex.
Keep in mind: Even with these protections, make sure you and your partner discuss each other’s sexual history, any prior or current STDs and their preferred protection from STDs, said Dr. Aguh.
If you or your partner is being treated for an STD, consider opting out of oral sex and consulting a doctor.
The HPV vaccine is another common method of protection. The shot is “approved for prevention of nine of the most high-risk strains of HPV,” or those that are most commonly linked to cancer, according to Dr. Lee. The vaccine “reduces the frequency of infection” with these viruses, which can ultimately lower the risk of cancers linked to HPV, including cervical, anal, and vulvar and vaginal cancers, she said.
“The best time to receive treatment for prevention of disease is prior to onset of sexual intercourse,” said Dr. Lee.
To get your HPV vaccine, head to your family doctor, school- or community-based health center, or state health department, suggests the CDC.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
An epidemic of sexually transmitted HPV is now swirling around the United States and the United Kingdom, with some serious cases leading to oropharyngeal cancer, which can affect the back of the throat, tonsils, and tongue.
HPV is the leading cause (70%) of this oropharyngeal cancer, according to the CDC. It is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the nation, and around 3.6% of women and 10% of men report oral HPV specifically. But over the past decade, oropharyngeal cases have been steadily falling a little under 4% and 2%, respectively, according to the National Cancer Institute.
HPV is often undetectable and can clear up within a few months. But unfortunately for some, serious disease, such as throat cancer, can develop.
Studies show the HPV vaccine to be extremely effective in lowering sexually transmitted HPV cases. Yet, only 54.5% of young people aged 13-15 have taken the recommended two to three doses, according to the National Cancer Institute.
Why aren’t more young people taking the vaccine?
Low public awareness of the dangers of HPV may be behind young people’s poor vaccination rates, according to Teresa Lee, MD, of the Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia. “For example, while the link with head and neck cancers has been well-studied, the FDA labeling was not changed to reflect this as an indication until 2020,” she said.
Other reasons can include one’s socioeconomic background, poor health literacy, cultural or religious stigmas around vaccines, and lack of quality, low-cost health care, says Emmanuel Aguh, MD, a board-certified family medicine physician. “Some individuals and families are still resistant to vaccines and the noted lack of uptake.”
Doctors and other health care professionals should also be sure to tell patients of all ages about the risks of HPV infection and how well the vaccine works, Dr. Lee said. “Not everyone who is now eligible may have been offered the vaccine as a child, and the first time young adults may receive counseling on this subject may not be until they are entering a very busy period of their lives with many responsibilities – when it may be hard to fit in things like health maintenance.”
How safe is the HPV vaccine?
The Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have studied the HPV vaccine for years to find out how safe it is and how well it works, Dr. Aguh said. No major side effects have been reported, and the most common side effect is soreness where you get the shot (which is normal after most vaccines). Some dizziness and fainting in adolescents can also occur, so young people are usually asked to sit or lie down during the shot and for 15 minutes afterward, he said.
“Serious adverse events have not been reported at higher rates than expected following HPV vaccination, meaning there is no clear evidence they are related to the vaccine,” Dr. Lee said. “The vaccine is highly effective in decreasing rates of detectable infection with the high-risk HPV strains responsible for HPV-associated cancers.”
The HPV vaccine is largely recommended for people aged 9-26, and sometimes up to age 45, depending on the individual, Dr. Aguh said. If you are over 26, talk to your doctor about whether you should consider getting the vaccine.
“It is usually given in two doses for complete protection if taken before the 15th birthday,” Dr. Aguh said. “If taken afterward, or in those with a weak immune system, they might require three doses to be fully protected.”
The vaccine produces antibodies that can stop HPV from infecting cells and lowers your chances of catching an HPV-related cancer, such as throat cancer or cancer of the cervix, he said.
While the vaccine is not guaranteed to protect you from the more than 100 strains of HPV, it can protect you from HPV 16 and HPV 18 – two high-risk strains that cause around 70% of cervical cancers.
What is fueling the rise of HPV cases?
A misconception that oral sex is somehow a “safe and risk-free” alternative to anal or vaginal sex could be one reason, Dr. Aguh said.
“It is important to know that, with oral sex, you are exposed to many of the risks associated with vaginal intercourse, especially if you do not take any measures to protect yourself and/or your partner,” Dr. Aguh said. “[With oral sex] it is possible to end up contracting an infection like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and even HPV, leading to an increased risk of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancers.”
A lack of public awareness of what can cause throat cancer could also explain this phenomenon. The number of people you have oral sex with, along with the age you begin sexual activity, can greatly determine your risk of the disease, according to Dr. Lee. She echoes a report by Hisham Mehanna, PhD, in The Conversation.
“For oropharyngeal cancer, the main risk factor is the number of lifetime sexual partners, especially oral sex,” wrote Dr. Mehanna, a professor at the Institute of Cancer and Genomic Sciences at the University of Birmingham (England). “Those with six or more lifetime oral-sex partners are 8.5 times more likely to develop oropharyngeal cancer than those who do not practice oral sex.”
What are symptoms of oropharyngeal cancer?
Labored breathing or swallowing, a cough that won’t go away, and crackling or hoarseness of your voice could all be signs of throat cancer. Other symptoms include earaches, swelling of the head or neck, and enlarged lymph nodes, among others, Dr. Aguh said.
“The signs and symptoms of HPV-related throat cancers can be difficult to identify and recognize, as they can be vague and are also associated with other medical conditions. Sometimes, there are no signs at all, or they are not easily noticeable due to the location,” he said.
You should go see your doctor if you have any of these ailments for an extended period.
How to reduce your risk
In addition to having six or more oral-sex partners, smoking and drinking heavily could also raise your risk of throat cancer, said Dr. Lee. Proper dental health – like seeing your dentist regularly and practicing proper oral hygiene – can also shave your risk.
“[Good dental health] can help not just with head and neck cancer risk, but with many other inflammation-related diseases,” Dr. Lee said.
Using dental dams and condoms can also be a good method of protection, Dr. Aguh said. A dental dam is a stretchy sheet of latex, or polyurethane plastic, in the shape of a square that is made for blocking body fluid to lower your risk of contracting an STD via oral sex.
Keep in mind: Even with these protections, make sure you and your partner discuss each other’s sexual history, any prior or current STDs and their preferred protection from STDs, said Dr. Aguh.
If you or your partner is being treated for an STD, consider opting out of oral sex and consulting a doctor.
The HPV vaccine is another common method of protection. The shot is “approved for prevention of nine of the most high-risk strains of HPV,” or those that are most commonly linked to cancer, according to Dr. Lee. The vaccine “reduces the frequency of infection” with these viruses, which can ultimately lower the risk of cancers linked to HPV, including cervical, anal, and vulvar and vaginal cancers, she said.
“The best time to receive treatment for prevention of disease is prior to onset of sexual intercourse,” said Dr. Lee.
To get your HPV vaccine, head to your family doctor, school- or community-based health center, or state health department, suggests the CDC.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
An epidemic of sexually transmitted HPV is now swirling around the United States and the United Kingdom, with some serious cases leading to oropharyngeal cancer, which can affect the back of the throat, tonsils, and tongue.
HPV is the leading cause (70%) of this oropharyngeal cancer, according to the CDC. It is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the nation, and around 3.6% of women and 10% of men report oral HPV specifically. But over the past decade, oropharyngeal cases have been steadily falling a little under 4% and 2%, respectively, according to the National Cancer Institute.
HPV is often undetectable and can clear up within a few months. But unfortunately for some, serious disease, such as throat cancer, can develop.
Studies show the HPV vaccine to be extremely effective in lowering sexually transmitted HPV cases. Yet, only 54.5% of young people aged 13-15 have taken the recommended two to three doses, according to the National Cancer Institute.
Why aren’t more young people taking the vaccine?
Low public awareness of the dangers of HPV may be behind young people’s poor vaccination rates, according to Teresa Lee, MD, of the Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia. “For example, while the link with head and neck cancers has been well-studied, the FDA labeling was not changed to reflect this as an indication until 2020,” she said.
Other reasons can include one’s socioeconomic background, poor health literacy, cultural or religious stigmas around vaccines, and lack of quality, low-cost health care, says Emmanuel Aguh, MD, a board-certified family medicine physician. “Some individuals and families are still resistant to vaccines and the noted lack of uptake.”
Doctors and other health care professionals should also be sure to tell patients of all ages about the risks of HPV infection and how well the vaccine works, Dr. Lee said. “Not everyone who is now eligible may have been offered the vaccine as a child, and the first time young adults may receive counseling on this subject may not be until they are entering a very busy period of their lives with many responsibilities – when it may be hard to fit in things like health maintenance.”
How safe is the HPV vaccine?
The Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have studied the HPV vaccine for years to find out how safe it is and how well it works, Dr. Aguh said. No major side effects have been reported, and the most common side effect is soreness where you get the shot (which is normal after most vaccines). Some dizziness and fainting in adolescents can also occur, so young people are usually asked to sit or lie down during the shot and for 15 minutes afterward, he said.
“Serious adverse events have not been reported at higher rates than expected following HPV vaccination, meaning there is no clear evidence they are related to the vaccine,” Dr. Lee said. “The vaccine is highly effective in decreasing rates of detectable infection with the high-risk HPV strains responsible for HPV-associated cancers.”
The HPV vaccine is largely recommended for people aged 9-26, and sometimes up to age 45, depending on the individual, Dr. Aguh said. If you are over 26, talk to your doctor about whether you should consider getting the vaccine.
“It is usually given in two doses for complete protection if taken before the 15th birthday,” Dr. Aguh said. “If taken afterward, or in those with a weak immune system, they might require three doses to be fully protected.”
The vaccine produces antibodies that can stop HPV from infecting cells and lowers your chances of catching an HPV-related cancer, such as throat cancer or cancer of the cervix, he said.
While the vaccine is not guaranteed to protect you from the more than 100 strains of HPV, it can protect you from HPV 16 and HPV 18 – two high-risk strains that cause around 70% of cervical cancers.
What is fueling the rise of HPV cases?
A misconception that oral sex is somehow a “safe and risk-free” alternative to anal or vaginal sex could be one reason, Dr. Aguh said.
“It is important to know that, with oral sex, you are exposed to many of the risks associated with vaginal intercourse, especially if you do not take any measures to protect yourself and/or your partner,” Dr. Aguh said. “[With oral sex] it is possible to end up contracting an infection like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and even HPV, leading to an increased risk of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancers.”
A lack of public awareness of what can cause throat cancer could also explain this phenomenon. The number of people you have oral sex with, along with the age you begin sexual activity, can greatly determine your risk of the disease, according to Dr. Lee. She echoes a report by Hisham Mehanna, PhD, in The Conversation.
“For oropharyngeal cancer, the main risk factor is the number of lifetime sexual partners, especially oral sex,” wrote Dr. Mehanna, a professor at the Institute of Cancer and Genomic Sciences at the University of Birmingham (England). “Those with six or more lifetime oral-sex partners are 8.5 times more likely to develop oropharyngeal cancer than those who do not practice oral sex.”
What are symptoms of oropharyngeal cancer?
Labored breathing or swallowing, a cough that won’t go away, and crackling or hoarseness of your voice could all be signs of throat cancer. Other symptoms include earaches, swelling of the head or neck, and enlarged lymph nodes, among others, Dr. Aguh said.
“The signs and symptoms of HPV-related throat cancers can be difficult to identify and recognize, as they can be vague and are also associated with other medical conditions. Sometimes, there are no signs at all, or they are not easily noticeable due to the location,” he said.
You should go see your doctor if you have any of these ailments for an extended period.
How to reduce your risk
In addition to having six or more oral-sex partners, smoking and drinking heavily could also raise your risk of throat cancer, said Dr. Lee. Proper dental health – like seeing your dentist regularly and practicing proper oral hygiene – can also shave your risk.
“[Good dental health] can help not just with head and neck cancer risk, but with many other inflammation-related diseases,” Dr. Lee said.
Using dental dams and condoms can also be a good method of protection, Dr. Aguh said. A dental dam is a stretchy sheet of latex, or polyurethane plastic, in the shape of a square that is made for blocking body fluid to lower your risk of contracting an STD via oral sex.
Keep in mind: Even with these protections, make sure you and your partner discuss each other’s sexual history, any prior or current STDs and their preferred protection from STDs, said Dr. Aguh.
If you or your partner is being treated for an STD, consider opting out of oral sex and consulting a doctor.
The HPV vaccine is another common method of protection. The shot is “approved for prevention of nine of the most high-risk strains of HPV,” or those that are most commonly linked to cancer, according to Dr. Lee. The vaccine “reduces the frequency of infection” with these viruses, which can ultimately lower the risk of cancers linked to HPV, including cervical, anal, and vulvar and vaginal cancers, she said.
“The best time to receive treatment for prevention of disease is prior to onset of sexual intercourse,” said Dr. Lee.
To get your HPV vaccine, head to your family doctor, school- or community-based health center, or state health department, suggests the CDC.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
Migraine device expands treatment possibilities
AUSTIN, TEX – Migraine treatment and prevention is challenging in any population, but some present even more difficulties. Pregnant women and pediatric patients are two such groups where physicians and patients may be hesitant to use drugs.
Neuromodulation devices are proven alternatives to medical interventions, and the remote electrical neuromodulation device Nerivio (Theranica) was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for acute treatment of migraine patients aged 12 and over in 2021. In March 2023, the agency expanded the clearance to include prevention of migration in adolescents aged 12 and over as well as adults.
Two studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed The latter study yielded similar findings to adults and was used by FDA in its decision to expand the device’s indication in adolescents in 2023, according to Teshamae Monteith, MD, who presented the study at a poster session.
The device, worn on the arm, allows the user to modulate the intensity of the stimulation so that it activates nociceptive pain receptors, but not in a painful way. “Each [patient] raises the intensity until it feels strong, yet comfortable, and when that happens, they activate the nociceptive receptors and the arm sends a signal all the way back up to the brainstem, where the pain control area is. Activating it causes the release of neurotransmitters that inhibit pain. That inhibition is a global pain inhibition mechanism, which causes inhibition of the migraine pain, and also the symptoms associated with migraine like photophobia and vomiting,” said Alit Stark-Inbar, PhD, who presented the study of treatment of pregnant women during a poster session.
Declining treatment days over time in adolescents
Dr. Monteith’s team studied high-frequency remote electrical neuromodulation device use in adolescents who had migraine on 10 days or more per month. They also required at least three treatment days in months 2 and 3 to control for the possibility that patients might stop using the device because they couldn’t afford it or for some reason other than efficacy or because their migraines went away.
The study included 83 adolescents aged 12-17 (mean, 15.9 years, 89% female). In the first month of use, the mean number of migraine treatment days was 12.6, which dropped to 9.0 in month 2 (P < .001), and 7.4 in month 3 (P < .001 from month 2). At 2 hours after treatment, 61.9% had pain relief, 24.5% had freedom from pain, 67.4% had functional disability relief, and 41.3% had functional disability freedom.
“It parallels the findings of the randomized, sham-controlled study in adults. The safety profile was excellent with just one person complaining of minor discomfort of the arm that resolved after treatment. The combination of the exceedingly safe profile and the likelihood of efficacy based on using monthly migraine treatment days as a proxy, the FDA decided to clear this for an adolescent indication,” said Dr. Monteith, associate professor of clinical neurology and chief of the headache division at the University of Miami.
The device design is convenient, according to Dr. Monteith. “The arm is just an easy place to stimulate. It’s a wearable device, and it’s 45 minutes [of treatment] and it’s app controlled. You know adolescents like their technology. They can track their symptoms here, and there’s some biobehavioral power to this because they can do biobehavioral exercises in addition to receiving the simulation,” she said.
The fact that the device is discrete is also an advantage for adolescents in school. “You have to go to the nurse to get your medication versus a device, you can just put it on, it’s easy, no one sees it, and no one’s making fun of you,” said Dr. Monteith.
Advantages for adolescents
The device offers a useful alternative to medication, according to Alan M. Rapoport, MD, who was asked for comment on the adolescent study. “I’d rather not give medication and certainly not preventive medication to an adolescent,” he said. He noted that over-the-counter acute care migraine medications such as aspirin or acetaminophen and combination medications with caffeine, as well as prescription medications such as triptans, “all have possible side effects, and when used to an increased extent can even cause medication overuse headache, increasing the severity and frequency of headache and migraine days per month,” Dr. Rapoport said. Using an effective device with almost no side effects is preferable to any of these acute care medications, especially if there are several headaches a month,” he said. Some newer medications that block calcitonin gene-related peptide might be quite effective when they are approved for adolescents, and should have few adverse events, he added.
In the past, Dr. Rapoport has favored biofeedback training for acute and especially preventive treatment of migraine in adolescents. “[Remote electrical neuromodulation] seems to do just as well, children enjoy it, and it’s easier for a patient to do at home,” said Dr. Rapoport.
Biofeedback training is usually taught to patients by a PhD psychologist. Once the patients have been on the biofeedback equipment and learn the techniques, they can practice on their own at home without equipment. “This new device treatment using Nerivio for acute care and prevention of migraine in adults and children 12 and older, where they can easily apply the device in almost any situation, whether they are at home or possibly even in school or out and about, looks very promising,” said Dr. Rapoport. It is quite effective and has almost no adverse events, which is what you really want, especially for adolescents,” he said.
Also asked to comment on the study of remote electrical neuromodulation use in adolescents, Abraham Avi Ashkenazi, MD, director of the Headache Clinic at Shaare Zedek Medical Center in Jerusalem, who attended the session, was enthusiastic, and said he has begun using it in his own practice. “It shows that remote electrical neuromodulation can not only be effective for the acute migraine attack, but also has a potential preventive effect on future migraine attacks. [This] actually makes sense, because we know that the more migraine attacks a person has, the more likely they are to progress to a more chronic form of the disease,” he said in an interview.
Asked what distinguishes REN from other neuromodulation therapies such as vagus nerve stimulation or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), Dr. Ashkenazi said: “It’s just a different way of modulating the brain system via a different mechanism. In both ways, though, the advantage is that there are literally no adverse effects, as opposed to drug treatment.”
An alternative during pregnancy
Adolescents aren’t the only population where there is reluctance to use medication. Physicians have been prescribing the device for pregnant women, who are reluctant to take medication due to concerns effects on the fetus. However, pregnant women were not included in the pivotal studies. “They expect it to be safe. This study was done in order to validate that assumption. We reached out to women who either used the device during pregnancy or women from the same database who started it using afterwards, but did not use it during the pregnancy,” said Dr. Stark-Inbar, vice president of medical information at Theranica.
The study included 140 women, 59 in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 81 controls. The primary endpoint was gestational age, which was 38 weeks and 5 days in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 39 weeks among controls (P = .150). There were no significant between-group differences with respect to newborn birth weight, miscarriage rate, preterm birth rate, birth defect rate, developmental milestone rate, or emergency department visit rate.
Dr. Monteith and Dr. Ashkenazi have no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Rapoport advises AbbVie, Biohaven, Cala Health, Dr. Reddy’s, Pfizer, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, and Theranica. He is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Dr. Reddy’s, Impel, Pfizer and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. Dr. Rapoport is the editor-in-chief of Neurology Reviews and on the editorial board of CNS Drugs.
AUSTIN, TEX – Migraine treatment and prevention is challenging in any population, but some present even more difficulties. Pregnant women and pediatric patients are two such groups where physicians and patients may be hesitant to use drugs.
Neuromodulation devices are proven alternatives to medical interventions, and the remote electrical neuromodulation device Nerivio (Theranica) was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for acute treatment of migraine patients aged 12 and over in 2021. In March 2023, the agency expanded the clearance to include prevention of migration in adolescents aged 12 and over as well as adults.
Two studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed The latter study yielded similar findings to adults and was used by FDA in its decision to expand the device’s indication in adolescents in 2023, according to Teshamae Monteith, MD, who presented the study at a poster session.
The device, worn on the arm, allows the user to modulate the intensity of the stimulation so that it activates nociceptive pain receptors, but not in a painful way. “Each [patient] raises the intensity until it feels strong, yet comfortable, and when that happens, they activate the nociceptive receptors and the arm sends a signal all the way back up to the brainstem, where the pain control area is. Activating it causes the release of neurotransmitters that inhibit pain. That inhibition is a global pain inhibition mechanism, which causes inhibition of the migraine pain, and also the symptoms associated with migraine like photophobia and vomiting,” said Alit Stark-Inbar, PhD, who presented the study of treatment of pregnant women during a poster session.
Declining treatment days over time in adolescents
Dr. Monteith’s team studied high-frequency remote electrical neuromodulation device use in adolescents who had migraine on 10 days or more per month. They also required at least three treatment days in months 2 and 3 to control for the possibility that patients might stop using the device because they couldn’t afford it or for some reason other than efficacy or because their migraines went away.
The study included 83 adolescents aged 12-17 (mean, 15.9 years, 89% female). In the first month of use, the mean number of migraine treatment days was 12.6, which dropped to 9.0 in month 2 (P < .001), and 7.4 in month 3 (P < .001 from month 2). At 2 hours after treatment, 61.9% had pain relief, 24.5% had freedom from pain, 67.4% had functional disability relief, and 41.3% had functional disability freedom.
“It parallels the findings of the randomized, sham-controlled study in adults. The safety profile was excellent with just one person complaining of minor discomfort of the arm that resolved after treatment. The combination of the exceedingly safe profile and the likelihood of efficacy based on using monthly migraine treatment days as a proxy, the FDA decided to clear this for an adolescent indication,” said Dr. Monteith, associate professor of clinical neurology and chief of the headache division at the University of Miami.
The device design is convenient, according to Dr. Monteith. “The arm is just an easy place to stimulate. It’s a wearable device, and it’s 45 minutes [of treatment] and it’s app controlled. You know adolescents like their technology. They can track their symptoms here, and there’s some biobehavioral power to this because they can do biobehavioral exercises in addition to receiving the simulation,” she said.
The fact that the device is discrete is also an advantage for adolescents in school. “You have to go to the nurse to get your medication versus a device, you can just put it on, it’s easy, no one sees it, and no one’s making fun of you,” said Dr. Monteith.
Advantages for adolescents
The device offers a useful alternative to medication, according to Alan M. Rapoport, MD, who was asked for comment on the adolescent study. “I’d rather not give medication and certainly not preventive medication to an adolescent,” he said. He noted that over-the-counter acute care migraine medications such as aspirin or acetaminophen and combination medications with caffeine, as well as prescription medications such as triptans, “all have possible side effects, and when used to an increased extent can even cause medication overuse headache, increasing the severity and frequency of headache and migraine days per month,” Dr. Rapoport said. Using an effective device with almost no side effects is preferable to any of these acute care medications, especially if there are several headaches a month,” he said. Some newer medications that block calcitonin gene-related peptide might be quite effective when they are approved for adolescents, and should have few adverse events, he added.
In the past, Dr. Rapoport has favored biofeedback training for acute and especially preventive treatment of migraine in adolescents. “[Remote electrical neuromodulation] seems to do just as well, children enjoy it, and it’s easier for a patient to do at home,” said Dr. Rapoport.
Biofeedback training is usually taught to patients by a PhD psychologist. Once the patients have been on the biofeedback equipment and learn the techniques, they can practice on their own at home without equipment. “This new device treatment using Nerivio for acute care and prevention of migraine in adults and children 12 and older, where they can easily apply the device in almost any situation, whether they are at home or possibly even in school or out and about, looks very promising,” said Dr. Rapoport. It is quite effective and has almost no adverse events, which is what you really want, especially for adolescents,” he said.
Also asked to comment on the study of remote electrical neuromodulation use in adolescents, Abraham Avi Ashkenazi, MD, director of the Headache Clinic at Shaare Zedek Medical Center in Jerusalem, who attended the session, was enthusiastic, and said he has begun using it in his own practice. “It shows that remote electrical neuromodulation can not only be effective for the acute migraine attack, but also has a potential preventive effect on future migraine attacks. [This] actually makes sense, because we know that the more migraine attacks a person has, the more likely they are to progress to a more chronic form of the disease,” he said in an interview.
Asked what distinguishes REN from other neuromodulation therapies such as vagus nerve stimulation or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), Dr. Ashkenazi said: “It’s just a different way of modulating the brain system via a different mechanism. In both ways, though, the advantage is that there are literally no adverse effects, as opposed to drug treatment.”
An alternative during pregnancy
Adolescents aren’t the only population where there is reluctance to use medication. Physicians have been prescribing the device for pregnant women, who are reluctant to take medication due to concerns effects on the fetus. However, pregnant women were not included in the pivotal studies. “They expect it to be safe. This study was done in order to validate that assumption. We reached out to women who either used the device during pregnancy or women from the same database who started it using afterwards, but did not use it during the pregnancy,” said Dr. Stark-Inbar, vice president of medical information at Theranica.
The study included 140 women, 59 in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 81 controls. The primary endpoint was gestational age, which was 38 weeks and 5 days in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 39 weeks among controls (P = .150). There were no significant between-group differences with respect to newborn birth weight, miscarriage rate, preterm birth rate, birth defect rate, developmental milestone rate, or emergency department visit rate.
Dr. Monteith and Dr. Ashkenazi have no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Rapoport advises AbbVie, Biohaven, Cala Health, Dr. Reddy’s, Pfizer, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, and Theranica. He is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Dr. Reddy’s, Impel, Pfizer and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. Dr. Rapoport is the editor-in-chief of Neurology Reviews and on the editorial board of CNS Drugs.
AUSTIN, TEX – Migraine treatment and prevention is challenging in any population, but some present even more difficulties. Pregnant women and pediatric patients are two such groups where physicians and patients may be hesitant to use drugs.
Neuromodulation devices are proven alternatives to medical interventions, and the remote electrical neuromodulation device Nerivio (Theranica) was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for acute treatment of migraine patients aged 12 and over in 2021. In March 2023, the agency expanded the clearance to include prevention of migration in adolescents aged 12 and over as well as adults.
Two studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed The latter study yielded similar findings to adults and was used by FDA in its decision to expand the device’s indication in adolescents in 2023, according to Teshamae Monteith, MD, who presented the study at a poster session.
The device, worn on the arm, allows the user to modulate the intensity of the stimulation so that it activates nociceptive pain receptors, but not in a painful way. “Each [patient] raises the intensity until it feels strong, yet comfortable, and when that happens, they activate the nociceptive receptors and the arm sends a signal all the way back up to the brainstem, where the pain control area is. Activating it causes the release of neurotransmitters that inhibit pain. That inhibition is a global pain inhibition mechanism, which causes inhibition of the migraine pain, and also the symptoms associated with migraine like photophobia and vomiting,” said Alit Stark-Inbar, PhD, who presented the study of treatment of pregnant women during a poster session.
Declining treatment days over time in adolescents
Dr. Monteith’s team studied high-frequency remote electrical neuromodulation device use in adolescents who had migraine on 10 days or more per month. They also required at least three treatment days in months 2 and 3 to control for the possibility that patients might stop using the device because they couldn’t afford it or for some reason other than efficacy or because their migraines went away.
The study included 83 adolescents aged 12-17 (mean, 15.9 years, 89% female). In the first month of use, the mean number of migraine treatment days was 12.6, which dropped to 9.0 in month 2 (P < .001), and 7.4 in month 3 (P < .001 from month 2). At 2 hours after treatment, 61.9% had pain relief, 24.5% had freedom from pain, 67.4% had functional disability relief, and 41.3% had functional disability freedom.
“It parallels the findings of the randomized, sham-controlled study in adults. The safety profile was excellent with just one person complaining of minor discomfort of the arm that resolved after treatment. The combination of the exceedingly safe profile and the likelihood of efficacy based on using monthly migraine treatment days as a proxy, the FDA decided to clear this for an adolescent indication,” said Dr. Monteith, associate professor of clinical neurology and chief of the headache division at the University of Miami.
The device design is convenient, according to Dr. Monteith. “The arm is just an easy place to stimulate. It’s a wearable device, and it’s 45 minutes [of treatment] and it’s app controlled. You know adolescents like their technology. They can track their symptoms here, and there’s some biobehavioral power to this because they can do biobehavioral exercises in addition to receiving the simulation,” she said.
The fact that the device is discrete is also an advantage for adolescents in school. “You have to go to the nurse to get your medication versus a device, you can just put it on, it’s easy, no one sees it, and no one’s making fun of you,” said Dr. Monteith.
Advantages for adolescents
The device offers a useful alternative to medication, according to Alan M. Rapoport, MD, who was asked for comment on the adolescent study. “I’d rather not give medication and certainly not preventive medication to an adolescent,” he said. He noted that over-the-counter acute care migraine medications such as aspirin or acetaminophen and combination medications with caffeine, as well as prescription medications such as triptans, “all have possible side effects, and when used to an increased extent can even cause medication overuse headache, increasing the severity and frequency of headache and migraine days per month,” Dr. Rapoport said. Using an effective device with almost no side effects is preferable to any of these acute care medications, especially if there are several headaches a month,” he said. Some newer medications that block calcitonin gene-related peptide might be quite effective when they are approved for adolescents, and should have few adverse events, he added.
In the past, Dr. Rapoport has favored biofeedback training for acute and especially preventive treatment of migraine in adolescents. “[Remote electrical neuromodulation] seems to do just as well, children enjoy it, and it’s easier for a patient to do at home,” said Dr. Rapoport.
Biofeedback training is usually taught to patients by a PhD psychologist. Once the patients have been on the biofeedback equipment and learn the techniques, they can practice on their own at home without equipment. “This new device treatment using Nerivio for acute care and prevention of migraine in adults and children 12 and older, where they can easily apply the device in almost any situation, whether they are at home or possibly even in school or out and about, looks very promising,” said Dr. Rapoport. It is quite effective and has almost no adverse events, which is what you really want, especially for adolescents,” he said.
Also asked to comment on the study of remote electrical neuromodulation use in adolescents, Abraham Avi Ashkenazi, MD, director of the Headache Clinic at Shaare Zedek Medical Center in Jerusalem, who attended the session, was enthusiastic, and said he has begun using it in his own practice. “It shows that remote electrical neuromodulation can not only be effective for the acute migraine attack, but also has a potential preventive effect on future migraine attacks. [This] actually makes sense, because we know that the more migraine attacks a person has, the more likely they are to progress to a more chronic form of the disease,” he said in an interview.
Asked what distinguishes REN from other neuromodulation therapies such as vagus nerve stimulation or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), Dr. Ashkenazi said: “It’s just a different way of modulating the brain system via a different mechanism. In both ways, though, the advantage is that there are literally no adverse effects, as opposed to drug treatment.”
An alternative during pregnancy
Adolescents aren’t the only population where there is reluctance to use medication. Physicians have been prescribing the device for pregnant women, who are reluctant to take medication due to concerns effects on the fetus. However, pregnant women were not included in the pivotal studies. “They expect it to be safe. This study was done in order to validate that assumption. We reached out to women who either used the device during pregnancy or women from the same database who started it using afterwards, but did not use it during the pregnancy,” said Dr. Stark-Inbar, vice president of medical information at Theranica.
The study included 140 women, 59 in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 81 controls. The primary endpoint was gestational age, which was 38 weeks and 5 days in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 39 weeks among controls (P = .150). There were no significant between-group differences with respect to newborn birth weight, miscarriage rate, preterm birth rate, birth defect rate, developmental milestone rate, or emergency department visit rate.
Dr. Monteith and Dr. Ashkenazi have no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Rapoport advises AbbVie, Biohaven, Cala Health, Dr. Reddy’s, Pfizer, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, and Theranica. He is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Dr. Reddy’s, Impel, Pfizer and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. Dr. Rapoport is the editor-in-chief of Neurology Reviews and on the editorial board of CNS Drugs.
AT AHS 2023
New cannabis laws, higher binge drinking rates linked
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
Among adolescents, binge drinking, defined as having five or more drinks for men and four or more drinks for women at one time, is associated with poor academic performance, sexual risk, and injury in the short term, as well as the development of alcohol use disorder and academic disengagement in the long term.
Current evidence regarding the association between recreational cannabis laws (RCLs) and binge drinking is limited.
States in which RCLs have been implemented include Colorado, Washington, Alaska, Oregon, Nevada, California, Massachusetts, and Vermont, as well as the District of Columbia.
The study included 817,359 people aged 12 and older who participated in the 2008-2019 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), a nationally representative survey of the U.S. population.
TAKEAWAY:
Overall, states that have not enacted cannabis laws showed consistently lower rates of binge drinking over time among all age groups.
In all states, there were substantial declines in reporting of past-month binge drinking in some age groups – from 17.5% (95% confidence interval, 16.9-18.2) in 2008 to 11.1% (10.4-11.8) in 2019 among those aged 12-20 and a drop from 43.7% (42.4-44.9) to 40.2% (39.1-41.1) among those aged 21-30.
There were overall increases in binge drinking in all states regardless of cannabis laws among individuals aged 31 and older. The most extensive increases were among people aged 31-40 (from 28.1% [95% CI, 26.6-29.6] to 33.3% [32.1-34.6]), followed by participants aged 51 and over (from 13.3% [95% CI, 12.2-14.4] to 16.8% [15.8-17.7]).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings support calls to reinforce health care providers’ discussions about alcohol use with older adults,” particularly in RCL states, the researchers write.
STUDY DETAILS:
The study was conducted out by Priscila Dib Gonçalves, PhD, department of epidemiology, Columbia University School of Public Health, New York, and colleagues. It was published in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
LIMITATIONS:
Alcohol-related measures, including binge drinking, were self-reported, which may introduce recall bias and underreporting. NSDUH binge drinking measures were not adjusted for sex differences from 2008 to 2014, which may result in underreporting of binge drinking in females before 2015. The researchers did not examine cannabis policy provisions, such as cultivation restrictions, pricing control, the tax imposed, and consumption restrictions.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
Among adolescents, binge drinking, defined as having five or more drinks for men and four or more drinks for women at one time, is associated with poor academic performance, sexual risk, and injury in the short term, as well as the development of alcohol use disorder and academic disengagement in the long term.
Current evidence regarding the association between recreational cannabis laws (RCLs) and binge drinking is limited.
States in which RCLs have been implemented include Colorado, Washington, Alaska, Oregon, Nevada, California, Massachusetts, and Vermont, as well as the District of Columbia.
The study included 817,359 people aged 12 and older who participated in the 2008-2019 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), a nationally representative survey of the U.S. population.
TAKEAWAY:
Overall, states that have not enacted cannabis laws showed consistently lower rates of binge drinking over time among all age groups.
In all states, there were substantial declines in reporting of past-month binge drinking in some age groups – from 17.5% (95% confidence interval, 16.9-18.2) in 2008 to 11.1% (10.4-11.8) in 2019 among those aged 12-20 and a drop from 43.7% (42.4-44.9) to 40.2% (39.1-41.1) among those aged 21-30.
There were overall increases in binge drinking in all states regardless of cannabis laws among individuals aged 31 and older. The most extensive increases were among people aged 31-40 (from 28.1% [95% CI, 26.6-29.6] to 33.3% [32.1-34.6]), followed by participants aged 51 and over (from 13.3% [95% CI, 12.2-14.4] to 16.8% [15.8-17.7]).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings support calls to reinforce health care providers’ discussions about alcohol use with older adults,” particularly in RCL states, the researchers write.
STUDY DETAILS:
The study was conducted out by Priscila Dib Gonçalves, PhD, department of epidemiology, Columbia University School of Public Health, New York, and colleagues. It was published in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
LIMITATIONS:
Alcohol-related measures, including binge drinking, were self-reported, which may introduce recall bias and underreporting. NSDUH binge drinking measures were not adjusted for sex differences from 2008 to 2014, which may result in underreporting of binge drinking in females before 2015. The researchers did not examine cannabis policy provisions, such as cultivation restrictions, pricing control, the tax imposed, and consumption restrictions.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
Among adolescents, binge drinking, defined as having five or more drinks for men and four or more drinks for women at one time, is associated with poor academic performance, sexual risk, and injury in the short term, as well as the development of alcohol use disorder and academic disengagement in the long term.
Current evidence regarding the association between recreational cannabis laws (RCLs) and binge drinking is limited.
States in which RCLs have been implemented include Colorado, Washington, Alaska, Oregon, Nevada, California, Massachusetts, and Vermont, as well as the District of Columbia.
The study included 817,359 people aged 12 and older who participated in the 2008-2019 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), a nationally representative survey of the U.S. population.
TAKEAWAY:
Overall, states that have not enacted cannabis laws showed consistently lower rates of binge drinking over time among all age groups.
In all states, there were substantial declines in reporting of past-month binge drinking in some age groups – from 17.5% (95% confidence interval, 16.9-18.2) in 2008 to 11.1% (10.4-11.8) in 2019 among those aged 12-20 and a drop from 43.7% (42.4-44.9) to 40.2% (39.1-41.1) among those aged 21-30.
There were overall increases in binge drinking in all states regardless of cannabis laws among individuals aged 31 and older. The most extensive increases were among people aged 31-40 (from 28.1% [95% CI, 26.6-29.6] to 33.3% [32.1-34.6]), followed by participants aged 51 and over (from 13.3% [95% CI, 12.2-14.4] to 16.8% [15.8-17.7]).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings support calls to reinforce health care providers’ discussions about alcohol use with older adults,” particularly in RCL states, the researchers write.
STUDY DETAILS:
The study was conducted out by Priscila Dib Gonçalves, PhD, department of epidemiology, Columbia University School of Public Health, New York, and colleagues. It was published in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
LIMITATIONS:
Alcohol-related measures, including binge drinking, were self-reported, which may introduce recall bias and underreporting. NSDUH binge drinking measures were not adjusted for sex differences from 2008 to 2014, which may result in underreporting of binge drinking in females before 2015. The researchers did not examine cannabis policy provisions, such as cultivation restrictions, pricing control, the tax imposed, and consumption restrictions.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.