User login
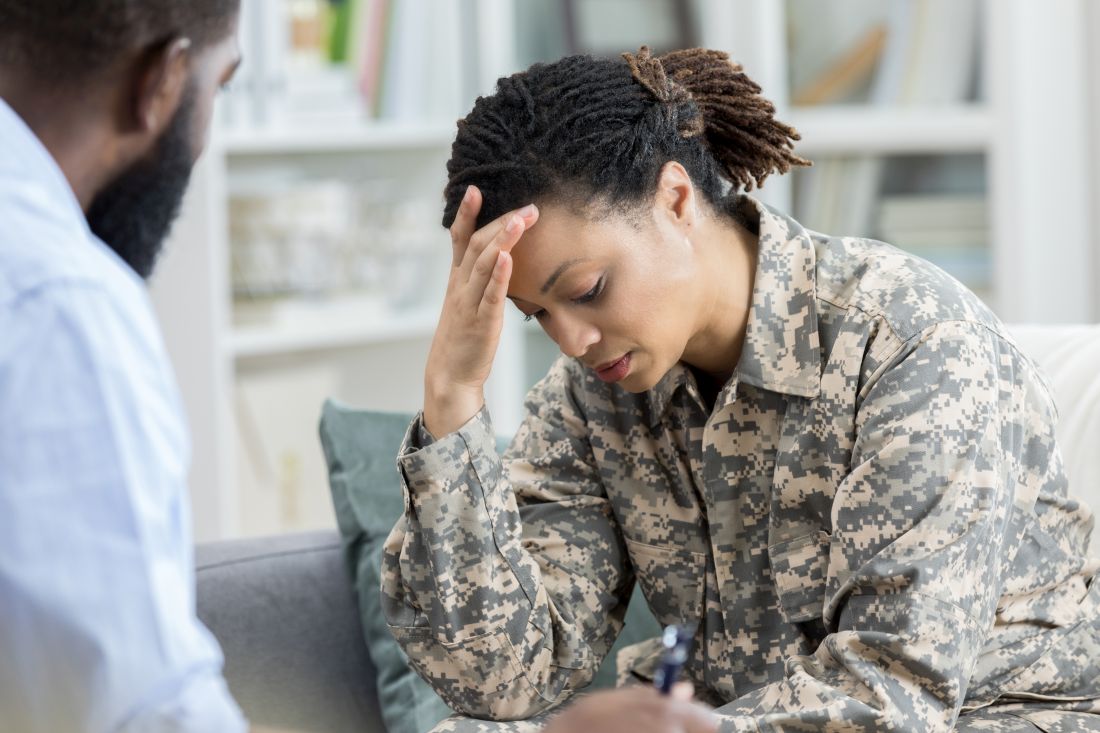
How to engage soldiers, veterans in psychiatric treatment
Deployments in places such as Afghanistan and Iraq, and traumatic events such as the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks affect everyone, but military personnel and veterans face unique circumstances that can present challenges to treatment. Much progress has been made in recent years in treating people with posttraumatic stress disorder and helping them recover after traumatic events.
To explore some of those changes and challenges, this news organization interviewed Col. (Ret.) Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, MPH, who retired from the Army in 2010 after assignments and missions that took her to Korea, Somalia, Iraq, and Cuba, about her approaches to treating soldiers and veterans.
Dr. Ritchie is chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, and a professor of psychiatry at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences in Bethesda, Md., and at Georgetown University and George Washington University, both in Washington.
She is the author of 250 publications, including the book, “Forensic and Ethical Issues in Military Behavioral Health” (Fort Sam Houston, Tex.: Borden Institute, 2015). In addition, Dr. Ritchie is coeditor of “Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Related Diseases in Combat Veterans” (New York: Springer, 2015) and “Psychiatrists in Combat, Clinicians Experience in the War Zone” (New York: Springer, 2017).
Question: What are some of the interventions available in the aftermath of traumatic events?
Answer: What we thought the standard of care should be after a traumatic event was to have what’s called a critical incident stress debriefing (CISD). It was basically getting the members of the group who had been traumatized by a school shooting or plane crash, or the Oklahoma City bombing, getting them all together literally a few hours after the event, and having them tell what happened. And the idea is to get it all out. But what we discovered is that this could actually make people worse, because you’d be hearing not only about your own trauma, but other people’s traumas, and that it was too soon for the event.
So prior to 9/11, we had organized a conference, which was held in October 2001, just a month after 9/11. At that conference, we worked on mass violence and early intervention, which is the name of the book that came out from the (National Institute of Mental Health) as a result. It focused on basic principles of safety and security and communication, and knowing where your family was, rather than reliving the trauma. Now, we did think that sometimes you could have a CISD that would be helpful, but only when it was people who knew each other well, like an ED group who would work with each other or soldiers who served together.
Q: What was your involvement in the aftermath of the Sept. 11 attacks?
A: At the time of 9/11, I was assigned at the Pentagon, but I wasn’t there. When the plane hit, I was actually across the river at the Navy’s Bureau of Medicine and Surgery. And then for the next 3 weeks, all I did was work at the Pentagon. We used some of these principles of early intervention but not focusing on telling us what happened right afterward. We focused on how the service members and their families were coping in the here and now, and how they could support each other.
We knew that soldiers would not come out of their offices to go to a therapist. They are too strong for that. So, we did what was called “therapy by walking around.” We went to the service members’ offices.
There was also a Family Assistance Center. That was for the families of the people who died. And that was very helpful because you had all the services there in one place – medical care, mental health care, therapy dogs, massage, the people who collected the DNA to identify remains. You had it in one place, the Sheraton in Crystal City, Va.. That has become a model now, especially for mass transportation fatalities. There are a lot more in the literature about Family Assistance Centers now, mainly formed by the National Transportation Safety Board.
Right after 9/11, we went to war in Afghanistan, and later in Iraq, and we had a lot of soldiers who developed both PTSD and traumatic brain injury (TBI). One of the good things that the military can do is they can really innovate with both medical treatment and mental health treatment because they don’t have to ask for an insurance company to pay for it. So for some years, starting in about 2004, Congress allocated a large sum of money every year to the Department of Defense to focus on treatment for PTSD and TBI.
And as a result of that, a couple of things happened. One was that the treatments that we had, we were able to study much better, exposure therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy. We were able to do large trials, and then we continued with the use of medications when necessary. There are only two (Food and Drug Administration)–approved medicines for the treatment of PTSD: sertraline and paroxetine, but many others are used.
We also learned what didn’t work and what soldiers would not take. Most of these medications have sexual side effects. If you’re a young, healthy soldier, you really don’t want to be taking something that causes you erectile dysfunction, or in women a loss of libido. So many people wouldn’t take these therapies. As for exposure therapy, if you got into it and completed the program, usually your PTSD symptoms went down. But many people couldn’t complete it. In the exposure therapy, you’re talking about whatever trauma you’ve been through – maybe your best friend died next to you, and you don’t want to talk about that all the time.
When I talk to patients about this, I say the first bucket is medication, the second bucket is therapy, and the third bucket is everything else. And everything else includes meditation, yoga, exercise, and it also involves working with animals. There are programs where you’re paired with a service dog, who helps calm you down, and you feel protected.
One of my favorites is called Warrior Canine Connection, where a soldier with PTSD trains a puppy to become a service animal. And in the training of the dog, you have to learn to control your emotions, you have to modulate your voice, you have to appear calm. Often soldiers have a background that they’re familiar with animals, especially dogs. So that’s been very successful.
A couple of other (treatments) to mention one is called stellate ganglion block, where a little lidocaine is injected into the back of the cervical spine. It was used initially for pain control, and they found that it was actually very helpful for PTSD. Another thing we’ve learned is that pain and PTSD often go hand in hand, because if you’re in pain, you’ll be feeling awful, you won’t sleep well, you’ll have more nightmares. But if you can control both of them together, then that’s going to help.
Q: One issue that veterans may face is moral injury. Can you talk about that?
A: Moral injury is a term that was first used after Vietnam. Moral injury is not a psychiatric diagnosis. It is feelings of shame and guilt that can be very corrosive and can lead to suicide. It overlaps with PTSD. You feel either you’ve let yourself down, or the government has let you down. And this can be very corrosive. Another thing that could happen is, say, you switched your tour of duty with a buddy, and he got killed and you didn’t. A very common scenario is you’re manning a checkpoint, and a car comes at you and doesn’t stop like it’s supposed to. You do what you’ve been trained to do, which is open fire, and check on the car afterward. And there’s four little kids and their parents in the car all dead. And that is something that even though that was your sort of duty, that it still eats at you because you have kids the same age as the ones who were dead in the car.
You can still have these feelings of shame and guilt, and it will often bleed into your relationships with your family. And that can lead to distance and divorce, which is a further risk factor for suicide.
Q: Are there are any specific treatments that have been designed for moral injury, different from PTSD or other conditions?
A: The Armed Services has set up a number of intensive programs at different places, and each is a little bit different. They usually integrate moral injury in with some of the other treatments. There was one at Fort Bliss, Tex., that had reiki; they had art therapy. And they had the chaplains working on moral injury. So there’s no medical treatment for it, but there certainly is talking about it, and for some people to go to a chaplain can be very helpful.
There’s a Military Health System Centers of Excellence, which is a place by the new Walter Reed on the campus, they have a marvelous wall full of masks. And the masks have been painted by soldiers with usually a combination of PTSD, TBI, and although it’s not an official psychiatric diagnosis, moral injury. They’re able to draw and paint. Another thing that’s been used quite a bit as writing therapy, and journaling, and just writing down how you feel about something, because you can do that without retraumatizing anybody else, except perhaps if you are working with a therapist.
Q: For therapists who are treating soldiers, veterans, are there specific challenges that they should be aware of? Are these patients maybe different from the patients that they might otherwise see? Are there specific pieces of advice as to how to engage them?
A: There are a few things that are different. One is that many people in the military are not used to talking about their feelings. And that’s especially if you’ve got a young man who only grunts and says: “Hooah!” That is going to be hard to break through. And that’s why some of these other ways of reaching somebody is very effective. Also, the military likes to have physical activity; they’re usually not comfortable sitting in a chair. If you’re a civilian psychiatrist, I don’t expect you to go bungee jumping with your patients. But what I’d recommend is that you recommend to your patients that they stay active.
Another thing about veterans is that they like to be self-sufficient. They really don’t like to ask for help, although they might ask for help for their buddy. After the Pentagon and 9/11, when I was working with senior officers, they never needed any help. No, but their buddy over here might, so I could help them in the guise of providing care for their buddy in a group setting. We could work with everybody and enhance cohesion, morale, bonding, “we’re all in this together” type of feeling.
I think one thing that’s really improved is that there is less stigma around PTSD. People are more willing to present for help, and some people have called PTSD the Purple Heart of mental disorders. People don’t feel like it’s as bad as having depression or anxiety. Even though PTSD often has depression and anxiety components to it – they run hand in hand – still, it’s sort of more honorable if you’ve been at war and have gotten PTSD.
Q: How have you been faring yourself, in the face of the 9/11 anniversary and recent events in Afghanistan?
A: (The Sept. 11 weekend) was very sad for me – and a lot of my colleagues [with] the combination of the 20th anniversary of 9/11, and the recent development. Fortunately, I have friends and people I can talk to. I walked with a colleague of mine who was in the Army. I’m following my own rule of the three buckets, so we took a walk around the hospital center for about 45 minutes, and we have five fish ponds here. And we went and looked at the fish, and talked to the fish. At the National Rehab Hospital, they were playing the guitar. So there’s are a variety of things that people can do.
Deployments in places such as Afghanistan and Iraq, and traumatic events such as the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks affect everyone, but military personnel and veterans face unique circumstances that can present challenges to treatment. Much progress has been made in recent years in treating people with posttraumatic stress disorder and helping them recover after traumatic events.
To explore some of those changes and challenges, this news organization interviewed Col. (Ret.) Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, MPH, who retired from the Army in 2010 after assignments and missions that took her to Korea, Somalia, Iraq, and Cuba, about her approaches to treating soldiers and veterans.
Dr. Ritchie is chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, and a professor of psychiatry at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences in Bethesda, Md., and at Georgetown University and George Washington University, both in Washington.
She is the author of 250 publications, including the book, “Forensic and Ethical Issues in Military Behavioral Health” (Fort Sam Houston, Tex.: Borden Institute, 2015). In addition, Dr. Ritchie is coeditor of “Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Related Diseases in Combat Veterans” (New York: Springer, 2015) and “Psychiatrists in Combat, Clinicians Experience in the War Zone” (New York: Springer, 2017).
Question: What are some of the interventions available in the aftermath of traumatic events?
Answer: What we thought the standard of care should be after a traumatic event was to have what’s called a critical incident stress debriefing (CISD). It was basically getting the members of the group who had been traumatized by a school shooting or plane crash, or the Oklahoma City bombing, getting them all together literally a few hours after the event, and having them tell what happened. And the idea is to get it all out. But what we discovered is that this could actually make people worse, because you’d be hearing not only about your own trauma, but other people’s traumas, and that it was too soon for the event.
So prior to 9/11, we had organized a conference, which was held in October 2001, just a month after 9/11. At that conference, we worked on mass violence and early intervention, which is the name of the book that came out from the (National Institute of Mental Health) as a result. It focused on basic principles of safety and security and communication, and knowing where your family was, rather than reliving the trauma. Now, we did think that sometimes you could have a CISD that would be helpful, but only when it was people who knew each other well, like an ED group who would work with each other or soldiers who served together.
Q: What was your involvement in the aftermath of the Sept. 11 attacks?
A: At the time of 9/11, I was assigned at the Pentagon, but I wasn’t there. When the plane hit, I was actually across the river at the Navy’s Bureau of Medicine and Surgery. And then for the next 3 weeks, all I did was work at the Pentagon. We used some of these principles of early intervention but not focusing on telling us what happened right afterward. We focused on how the service members and their families were coping in the here and now, and how they could support each other.
We knew that soldiers would not come out of their offices to go to a therapist. They are too strong for that. So, we did what was called “therapy by walking around.” We went to the service members’ offices.
There was also a Family Assistance Center. That was for the families of the people who died. And that was very helpful because you had all the services there in one place – medical care, mental health care, therapy dogs, massage, the people who collected the DNA to identify remains. You had it in one place, the Sheraton in Crystal City, Va.. That has become a model now, especially for mass transportation fatalities. There are a lot more in the literature about Family Assistance Centers now, mainly formed by the National Transportation Safety Board.
Right after 9/11, we went to war in Afghanistan, and later in Iraq, and we had a lot of soldiers who developed both PTSD and traumatic brain injury (TBI). One of the good things that the military can do is they can really innovate with both medical treatment and mental health treatment because they don’t have to ask for an insurance company to pay for it. So for some years, starting in about 2004, Congress allocated a large sum of money every year to the Department of Defense to focus on treatment for PTSD and TBI.
And as a result of that, a couple of things happened. One was that the treatments that we had, we were able to study much better, exposure therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy. We were able to do large trials, and then we continued with the use of medications when necessary. There are only two (Food and Drug Administration)–approved medicines for the treatment of PTSD: sertraline and paroxetine, but many others are used.
We also learned what didn’t work and what soldiers would not take. Most of these medications have sexual side effects. If you’re a young, healthy soldier, you really don’t want to be taking something that causes you erectile dysfunction, or in women a loss of libido. So many people wouldn’t take these therapies. As for exposure therapy, if you got into it and completed the program, usually your PTSD symptoms went down. But many people couldn’t complete it. In the exposure therapy, you’re talking about whatever trauma you’ve been through – maybe your best friend died next to you, and you don’t want to talk about that all the time.
When I talk to patients about this, I say the first bucket is medication, the second bucket is therapy, and the third bucket is everything else. And everything else includes meditation, yoga, exercise, and it also involves working with animals. There are programs where you’re paired with a service dog, who helps calm you down, and you feel protected.
One of my favorites is called Warrior Canine Connection, where a soldier with PTSD trains a puppy to become a service animal. And in the training of the dog, you have to learn to control your emotions, you have to modulate your voice, you have to appear calm. Often soldiers have a background that they’re familiar with animals, especially dogs. So that’s been very successful.
A couple of other (treatments) to mention one is called stellate ganglion block, where a little lidocaine is injected into the back of the cervical spine. It was used initially for pain control, and they found that it was actually very helpful for PTSD. Another thing we’ve learned is that pain and PTSD often go hand in hand, because if you’re in pain, you’ll be feeling awful, you won’t sleep well, you’ll have more nightmares. But if you can control both of them together, then that’s going to help.
Q: One issue that veterans may face is moral injury. Can you talk about that?
A: Moral injury is a term that was first used after Vietnam. Moral injury is not a psychiatric diagnosis. It is feelings of shame and guilt that can be very corrosive and can lead to suicide. It overlaps with PTSD. You feel either you’ve let yourself down, or the government has let you down. And this can be very corrosive. Another thing that could happen is, say, you switched your tour of duty with a buddy, and he got killed and you didn’t. A very common scenario is you’re manning a checkpoint, and a car comes at you and doesn’t stop like it’s supposed to. You do what you’ve been trained to do, which is open fire, and check on the car afterward. And there’s four little kids and their parents in the car all dead. And that is something that even though that was your sort of duty, that it still eats at you because you have kids the same age as the ones who were dead in the car.
You can still have these feelings of shame and guilt, and it will often bleed into your relationships with your family. And that can lead to distance and divorce, which is a further risk factor for suicide.
Q: Are there are any specific treatments that have been designed for moral injury, different from PTSD or other conditions?
A: The Armed Services has set up a number of intensive programs at different places, and each is a little bit different. They usually integrate moral injury in with some of the other treatments. There was one at Fort Bliss, Tex., that had reiki; they had art therapy. And they had the chaplains working on moral injury. So there’s no medical treatment for it, but there certainly is talking about it, and for some people to go to a chaplain can be very helpful.
There’s a Military Health System Centers of Excellence, which is a place by the new Walter Reed on the campus, they have a marvelous wall full of masks. And the masks have been painted by soldiers with usually a combination of PTSD, TBI, and although it’s not an official psychiatric diagnosis, moral injury. They’re able to draw and paint. Another thing that’s been used quite a bit as writing therapy, and journaling, and just writing down how you feel about something, because you can do that without retraumatizing anybody else, except perhaps if you are working with a therapist.
Q: For therapists who are treating soldiers, veterans, are there specific challenges that they should be aware of? Are these patients maybe different from the patients that they might otherwise see? Are there specific pieces of advice as to how to engage them?
A: There are a few things that are different. One is that many people in the military are not used to talking about their feelings. And that’s especially if you’ve got a young man who only grunts and says: “Hooah!” That is going to be hard to break through. And that’s why some of these other ways of reaching somebody is very effective. Also, the military likes to have physical activity; they’re usually not comfortable sitting in a chair. If you’re a civilian psychiatrist, I don’t expect you to go bungee jumping with your patients. But what I’d recommend is that you recommend to your patients that they stay active.
Another thing about veterans is that they like to be self-sufficient. They really don’t like to ask for help, although they might ask for help for their buddy. After the Pentagon and 9/11, when I was working with senior officers, they never needed any help. No, but their buddy over here might, so I could help them in the guise of providing care for their buddy in a group setting. We could work with everybody and enhance cohesion, morale, bonding, “we’re all in this together” type of feeling.
I think one thing that’s really improved is that there is less stigma around PTSD. People are more willing to present for help, and some people have called PTSD the Purple Heart of mental disorders. People don’t feel like it’s as bad as having depression or anxiety. Even though PTSD often has depression and anxiety components to it – they run hand in hand – still, it’s sort of more honorable if you’ve been at war and have gotten PTSD.
Q: How have you been faring yourself, in the face of the 9/11 anniversary and recent events in Afghanistan?
A: (The Sept. 11 weekend) was very sad for me – and a lot of my colleagues [with] the combination of the 20th anniversary of 9/11, and the recent development. Fortunately, I have friends and people I can talk to. I walked with a colleague of mine who was in the Army. I’m following my own rule of the three buckets, so we took a walk around the hospital center for about 45 minutes, and we have five fish ponds here. And we went and looked at the fish, and talked to the fish. At the National Rehab Hospital, they were playing the guitar. So there’s are a variety of things that people can do.
Deployments in places such as Afghanistan and Iraq, and traumatic events such as the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks affect everyone, but military personnel and veterans face unique circumstances that can present challenges to treatment. Much progress has been made in recent years in treating people with posttraumatic stress disorder and helping them recover after traumatic events.
To explore some of those changes and challenges, this news organization interviewed Col. (Ret.) Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, MPH, who retired from the Army in 2010 after assignments and missions that took her to Korea, Somalia, Iraq, and Cuba, about her approaches to treating soldiers and veterans.
Dr. Ritchie is chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, and a professor of psychiatry at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences in Bethesda, Md., and at Georgetown University and George Washington University, both in Washington.
She is the author of 250 publications, including the book, “Forensic and Ethical Issues in Military Behavioral Health” (Fort Sam Houston, Tex.: Borden Institute, 2015). In addition, Dr. Ritchie is coeditor of “Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Related Diseases in Combat Veterans” (New York: Springer, 2015) and “Psychiatrists in Combat, Clinicians Experience in the War Zone” (New York: Springer, 2017).
Question: What are some of the interventions available in the aftermath of traumatic events?
Answer: What we thought the standard of care should be after a traumatic event was to have what’s called a critical incident stress debriefing (CISD). It was basically getting the members of the group who had been traumatized by a school shooting or plane crash, or the Oklahoma City bombing, getting them all together literally a few hours after the event, and having them tell what happened. And the idea is to get it all out. But what we discovered is that this could actually make people worse, because you’d be hearing not only about your own trauma, but other people’s traumas, and that it was too soon for the event.
So prior to 9/11, we had organized a conference, which was held in October 2001, just a month after 9/11. At that conference, we worked on mass violence and early intervention, which is the name of the book that came out from the (National Institute of Mental Health) as a result. It focused on basic principles of safety and security and communication, and knowing where your family was, rather than reliving the trauma. Now, we did think that sometimes you could have a CISD that would be helpful, but only when it was people who knew each other well, like an ED group who would work with each other or soldiers who served together.
Q: What was your involvement in the aftermath of the Sept. 11 attacks?
A: At the time of 9/11, I was assigned at the Pentagon, but I wasn’t there. When the plane hit, I was actually across the river at the Navy’s Bureau of Medicine and Surgery. And then for the next 3 weeks, all I did was work at the Pentagon. We used some of these principles of early intervention but not focusing on telling us what happened right afterward. We focused on how the service members and their families were coping in the here and now, and how they could support each other.
We knew that soldiers would not come out of their offices to go to a therapist. They are too strong for that. So, we did what was called “therapy by walking around.” We went to the service members’ offices.
There was also a Family Assistance Center. That was for the families of the people who died. And that was very helpful because you had all the services there in one place – medical care, mental health care, therapy dogs, massage, the people who collected the DNA to identify remains. You had it in one place, the Sheraton in Crystal City, Va.. That has become a model now, especially for mass transportation fatalities. There are a lot more in the literature about Family Assistance Centers now, mainly formed by the National Transportation Safety Board.
Right after 9/11, we went to war in Afghanistan, and later in Iraq, and we had a lot of soldiers who developed both PTSD and traumatic brain injury (TBI). One of the good things that the military can do is they can really innovate with both medical treatment and mental health treatment because they don’t have to ask for an insurance company to pay for it. So for some years, starting in about 2004, Congress allocated a large sum of money every year to the Department of Defense to focus on treatment for PTSD and TBI.
And as a result of that, a couple of things happened. One was that the treatments that we had, we were able to study much better, exposure therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy. We were able to do large trials, and then we continued with the use of medications when necessary. There are only two (Food and Drug Administration)–approved medicines for the treatment of PTSD: sertraline and paroxetine, but many others are used.
We also learned what didn’t work and what soldiers would not take. Most of these medications have sexual side effects. If you’re a young, healthy soldier, you really don’t want to be taking something that causes you erectile dysfunction, or in women a loss of libido. So many people wouldn’t take these therapies. As for exposure therapy, if you got into it and completed the program, usually your PTSD symptoms went down. But many people couldn’t complete it. In the exposure therapy, you’re talking about whatever trauma you’ve been through – maybe your best friend died next to you, and you don’t want to talk about that all the time.
When I talk to patients about this, I say the first bucket is medication, the second bucket is therapy, and the third bucket is everything else. And everything else includes meditation, yoga, exercise, and it also involves working with animals. There are programs where you’re paired with a service dog, who helps calm you down, and you feel protected.
One of my favorites is called Warrior Canine Connection, where a soldier with PTSD trains a puppy to become a service animal. And in the training of the dog, you have to learn to control your emotions, you have to modulate your voice, you have to appear calm. Often soldiers have a background that they’re familiar with animals, especially dogs. So that’s been very successful.
A couple of other (treatments) to mention one is called stellate ganglion block, where a little lidocaine is injected into the back of the cervical spine. It was used initially for pain control, and they found that it was actually very helpful for PTSD. Another thing we’ve learned is that pain and PTSD often go hand in hand, because if you’re in pain, you’ll be feeling awful, you won’t sleep well, you’ll have more nightmares. But if you can control both of them together, then that’s going to help.
Q: One issue that veterans may face is moral injury. Can you talk about that?
A: Moral injury is a term that was first used after Vietnam. Moral injury is not a psychiatric diagnosis. It is feelings of shame and guilt that can be very corrosive and can lead to suicide. It overlaps with PTSD. You feel either you’ve let yourself down, or the government has let you down. And this can be very corrosive. Another thing that could happen is, say, you switched your tour of duty with a buddy, and he got killed and you didn’t. A very common scenario is you’re manning a checkpoint, and a car comes at you and doesn’t stop like it’s supposed to. You do what you’ve been trained to do, which is open fire, and check on the car afterward. And there’s four little kids and their parents in the car all dead. And that is something that even though that was your sort of duty, that it still eats at you because you have kids the same age as the ones who were dead in the car.
You can still have these feelings of shame and guilt, and it will often bleed into your relationships with your family. And that can lead to distance and divorce, which is a further risk factor for suicide.
Q: Are there are any specific treatments that have been designed for moral injury, different from PTSD or other conditions?
A: The Armed Services has set up a number of intensive programs at different places, and each is a little bit different. They usually integrate moral injury in with some of the other treatments. There was one at Fort Bliss, Tex., that had reiki; they had art therapy. And they had the chaplains working on moral injury. So there’s no medical treatment for it, but there certainly is talking about it, and for some people to go to a chaplain can be very helpful.
There’s a Military Health System Centers of Excellence, which is a place by the new Walter Reed on the campus, they have a marvelous wall full of masks. And the masks have been painted by soldiers with usually a combination of PTSD, TBI, and although it’s not an official psychiatric diagnosis, moral injury. They’re able to draw and paint. Another thing that’s been used quite a bit as writing therapy, and journaling, and just writing down how you feel about something, because you can do that without retraumatizing anybody else, except perhaps if you are working with a therapist.
Q: For therapists who are treating soldiers, veterans, are there specific challenges that they should be aware of? Are these patients maybe different from the patients that they might otherwise see? Are there specific pieces of advice as to how to engage them?
A: There are a few things that are different. One is that many people in the military are not used to talking about their feelings. And that’s especially if you’ve got a young man who only grunts and says: “Hooah!” That is going to be hard to break through. And that’s why some of these other ways of reaching somebody is very effective. Also, the military likes to have physical activity; they’re usually not comfortable sitting in a chair. If you’re a civilian psychiatrist, I don’t expect you to go bungee jumping with your patients. But what I’d recommend is that you recommend to your patients that they stay active.
Another thing about veterans is that they like to be self-sufficient. They really don’t like to ask for help, although they might ask for help for their buddy. After the Pentagon and 9/11, when I was working with senior officers, they never needed any help. No, but their buddy over here might, so I could help them in the guise of providing care for their buddy in a group setting. We could work with everybody and enhance cohesion, morale, bonding, “we’re all in this together” type of feeling.
I think one thing that’s really improved is that there is less stigma around PTSD. People are more willing to present for help, and some people have called PTSD the Purple Heart of mental disorders. People don’t feel like it’s as bad as having depression or anxiety. Even though PTSD often has depression and anxiety components to it – they run hand in hand – still, it’s sort of more honorable if you’ve been at war and have gotten PTSD.
Q: How have you been faring yourself, in the face of the 9/11 anniversary and recent events in Afghanistan?
A: (The Sept. 11 weekend) was very sad for me – and a lot of my colleagues [with] the combination of the 20th anniversary of 9/11, and the recent development. Fortunately, I have friends and people I can talk to. I walked with a colleague of mine who was in the Army. I’m following my own rule of the three buckets, so we took a walk around the hospital center for about 45 minutes, and we have five fish ponds here. And we went and looked at the fish, and talked to the fish. At the National Rehab Hospital, they were playing the guitar. So there’s are a variety of things that people can do.
Residency programs need greater focus on BPD treatment
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) has suffered from underdiagnosis, in part because not enough clinicians know how to handle patients with BPD. “They don’t have the tools to know how to manage these situations effectively,” Lois W. Choi-Kain, MEd, MD, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., said in an interview.
As a result, the clinician avoids the BPD patient, who feels demeaned and never finds the capacity to get better.
Psychiatry training in residency tends to emphasize biomedical treatments and does not focus enough on learning psychotherapy and other psychosocial treatments, according to Eric M. Plakun, MD, DLFAPA, FACPsych, medical director/CEO of the Austen Riggs Center in Stockbridge, Mass.
“This is where I see the need for a greater psychotherapy teaching focus in residency, along with teaching of general principles for working with patients with BPD,” said Dr. Plakun.
In his last phase of his career, BPD pioneer John G. Gunderson, MD, worked with Dr. Choi-Kain to train clinicians on general psychiatric management (GPM), which employs a sensitive, nonattacking approach to diffuse and calm situations with BPD patients.
As interest grows in combining GPM with manual treatments, GPM alone offers a more accessible approach for therapist and patient, said Dr. Choi-Kain, who has been trying to promote its use and do research on its techniques.
“It’s trying to boil it down to make it simple,” she said. As much as evidence-based, manualized approaches have advanced the field, they’re just not that widely available, she said.
Orchestrating treatments such as dialectical behavior therapy and mentalization-based therapy takes a lot of specialization, noted Dr. Choi-Kain. “And because of the amount of work that it involves for both the clinician and the patient, it decreases the capacity that clinicians and systems have to offer treatment to a wider number of patients.”
Learning a manualized treatment for BPD is asking a lot from residents, agreed Dr. Plakun. “Those who want more immersion in treating these patients can pursue further training in residency electives, in postresidency graduate medical education programs or through psychoanalytic training.”
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) has suffered from underdiagnosis, in part because not enough clinicians know how to handle patients with BPD. “They don’t have the tools to know how to manage these situations effectively,” Lois W. Choi-Kain, MEd, MD, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., said in an interview.
As a result, the clinician avoids the BPD patient, who feels demeaned and never finds the capacity to get better.
Psychiatry training in residency tends to emphasize biomedical treatments and does not focus enough on learning psychotherapy and other psychosocial treatments, according to Eric M. Plakun, MD, DLFAPA, FACPsych, medical director/CEO of the Austen Riggs Center in Stockbridge, Mass.
“This is where I see the need for a greater psychotherapy teaching focus in residency, along with teaching of general principles for working with patients with BPD,” said Dr. Plakun.
In his last phase of his career, BPD pioneer John G. Gunderson, MD, worked with Dr. Choi-Kain to train clinicians on general psychiatric management (GPM), which employs a sensitive, nonattacking approach to diffuse and calm situations with BPD patients.
As interest grows in combining GPM with manual treatments, GPM alone offers a more accessible approach for therapist and patient, said Dr. Choi-Kain, who has been trying to promote its use and do research on its techniques.
“It’s trying to boil it down to make it simple,” she said. As much as evidence-based, manualized approaches have advanced the field, they’re just not that widely available, she said.
Orchestrating treatments such as dialectical behavior therapy and mentalization-based therapy takes a lot of specialization, noted Dr. Choi-Kain. “And because of the amount of work that it involves for both the clinician and the patient, it decreases the capacity that clinicians and systems have to offer treatment to a wider number of patients.”
Learning a manualized treatment for BPD is asking a lot from residents, agreed Dr. Plakun. “Those who want more immersion in treating these patients can pursue further training in residency electives, in postresidency graduate medical education programs or through psychoanalytic training.”
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) has suffered from underdiagnosis, in part because not enough clinicians know how to handle patients with BPD. “They don’t have the tools to know how to manage these situations effectively,” Lois W. Choi-Kain, MEd, MD, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass., said in an interview.
As a result, the clinician avoids the BPD patient, who feels demeaned and never finds the capacity to get better.
Psychiatry training in residency tends to emphasize biomedical treatments and does not focus enough on learning psychotherapy and other psychosocial treatments, according to Eric M. Plakun, MD, DLFAPA, FACPsych, medical director/CEO of the Austen Riggs Center in Stockbridge, Mass.
“This is where I see the need for a greater psychotherapy teaching focus in residency, along with teaching of general principles for working with patients with BPD,” said Dr. Plakun.
In his last phase of his career, BPD pioneer John G. Gunderson, MD, worked with Dr. Choi-Kain to train clinicians on general psychiatric management (GPM), which employs a sensitive, nonattacking approach to diffuse and calm situations with BPD patients.
As interest grows in combining GPM with manual treatments, GPM alone offers a more accessible approach for therapist and patient, said Dr. Choi-Kain, who has been trying to promote its use and do research on its techniques.
“It’s trying to boil it down to make it simple,” she said. As much as evidence-based, manualized approaches have advanced the field, they’re just not that widely available, she said.
Orchestrating treatments such as dialectical behavior therapy and mentalization-based therapy takes a lot of specialization, noted Dr. Choi-Kain. “And because of the amount of work that it involves for both the clinician and the patient, it decreases the capacity that clinicians and systems have to offer treatment to a wider number of patients.”
Learning a manualized treatment for BPD is asking a lot from residents, agreed Dr. Plakun. “Those who want more immersion in treating these patients can pursue further training in residency electives, in postresidency graduate medical education programs or through psychoanalytic training.”
A new name for BPD?
Michael A. Cummings, MD, has never liked the term “borderline personality disorder” (BPD). In his view, it’s a misnomer and needs to be changed.
“What is it bordering on? It’s not bordering on something, it’s a disorder on its own,” said Dr. Cummings of the department of psychiatry at the University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD grew out of the concept that patients were bordering on something, perhaps becoming bipolar. “In many ways, I don’t think it is even a personality disorder. It appears to be an inherent temperament that evolves into an inability to regulate mood.”
In his view, this puts it in the category of a mood dysregulation disorder.
Changing the label would not necessarily improve treatment, he added. However, transitioning from a pejorative to a more neutral label could make it easier for people to say, “this is just a type of mood disorder. It’s not necessarily easy, but it’s workable,” said Dr. Cummings.
Others in the field contend that the term fits the condition. BPD “describes how it encompasses a lot of complex psychological difficulties, undermining functioning of patients in a specific way,” said Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass. The disorder was identified because of its relationship with other known psychiatric disorders, said Dr. Choi-Kain. “There’s an element of BPD that borders on mood disorders because moods are so unstable with BPD. It also borders on trauma-related disorders. It borders on psychotic disorders because there’s sometimes stress-induced experiences of losing contact with realistic thinking.”
If anything needs to change, it’s the attitude toward the disorder, not the name. “I don’t think the term itself is pejorative. But I think that associations with the term have been very stigmatizing. For a long time, there was an attitude that these patients could not be treated or had negative therapeutic reactions.”
Data suggest that these patients are highly prevalent in clinical settings. “And I interpret that as them seeking the care that they need rather than resisting care or not responding to care,” said Dr. Choi-Kain.
Michael A. Cummings, MD, has never liked the term “borderline personality disorder” (BPD). In his view, it’s a misnomer and needs to be changed.
“What is it bordering on? It’s not bordering on something, it’s a disorder on its own,” said Dr. Cummings of the department of psychiatry at the University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD grew out of the concept that patients were bordering on something, perhaps becoming bipolar. “In many ways, I don’t think it is even a personality disorder. It appears to be an inherent temperament that evolves into an inability to regulate mood.”
In his view, this puts it in the category of a mood dysregulation disorder.
Changing the label would not necessarily improve treatment, he added. However, transitioning from a pejorative to a more neutral label could make it easier for people to say, “this is just a type of mood disorder. It’s not necessarily easy, but it’s workable,” said Dr. Cummings.
Others in the field contend that the term fits the condition. BPD “describes how it encompasses a lot of complex psychological difficulties, undermining functioning of patients in a specific way,” said Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass. The disorder was identified because of its relationship with other known psychiatric disorders, said Dr. Choi-Kain. “There’s an element of BPD that borders on mood disorders because moods are so unstable with BPD. It also borders on trauma-related disorders. It borders on psychotic disorders because there’s sometimes stress-induced experiences of losing contact with realistic thinking.”
If anything needs to change, it’s the attitude toward the disorder, not the name. “I don’t think the term itself is pejorative. But I think that associations with the term have been very stigmatizing. For a long time, there was an attitude that these patients could not be treated or had negative therapeutic reactions.”
Data suggest that these patients are highly prevalent in clinical settings. “And I interpret that as them seeking the care that they need rather than resisting care or not responding to care,” said Dr. Choi-Kain.
Michael A. Cummings, MD, has never liked the term “borderline personality disorder” (BPD). In his view, it’s a misnomer and needs to be changed.
“What is it bordering on? It’s not bordering on something, it’s a disorder on its own,” said Dr. Cummings of the department of psychiatry at the University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD grew out of the concept that patients were bordering on something, perhaps becoming bipolar. “In many ways, I don’t think it is even a personality disorder. It appears to be an inherent temperament that evolves into an inability to regulate mood.”
In his view, this puts it in the category of a mood dysregulation disorder.
Changing the label would not necessarily improve treatment, he added. However, transitioning from a pejorative to a more neutral label could make it easier for people to say, “this is just a type of mood disorder. It’s not necessarily easy, but it’s workable,” said Dr. Cummings.
Others in the field contend that the term fits the condition. BPD “describes how it encompasses a lot of complex psychological difficulties, undermining functioning of patients in a specific way,” said Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass. The disorder was identified because of its relationship with other known psychiatric disorders, said Dr. Choi-Kain. “There’s an element of BPD that borders on mood disorders because moods are so unstable with BPD. It also borders on trauma-related disorders. It borders on psychotic disorders because there’s sometimes stress-induced experiences of losing contact with realistic thinking.”
If anything needs to change, it’s the attitude toward the disorder, not the name. “I don’t think the term itself is pejorative. But I think that associations with the term have been very stigmatizing. For a long time, there was an attitude that these patients could not be treated or had negative therapeutic reactions.”
Data suggest that these patients are highly prevalent in clinical settings. “And I interpret that as them seeking the care that they need rather than resisting care or not responding to care,” said Dr. Choi-Kain.
Trust is key in treating borderline personality disorder
Difficulties associated with treating borderline personality disorder (BPD) make for an uneasy alliance between patient and clinician. Deep-seated anxiety and trust issues often lead to patients skipping visits or raging at those who treat them, leaving clinicians frustrated and ready to give up or relying on a pill to make the patient better.
John M. Oldham, MD, MS, recalls one patient he almost lost, a woman who was struggling with aggressive behavior. Initially cooperative and punctual, the patient gradually became distrustful, grilling Dr. Oldham on his training and credentials. “As the questions continued, she slipped from being very cooperative to being enraged and attacking me,” said Dr. Oldham, Distinguished Emeritus Professor in the Menninger department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College in Houston.
Dr. Oldham eventually drew her back in by earning her trust. “There’s no magic to this,” he acknowledged. “You try to be as alert and informed and vigilant for anything you say that produces a negative or concerning reaction in the patient.”
This interactive approach to BPD treatment has been gaining traction in a profession that often looks to medications to alleviate specific symptoms. It’s so effective that it sometimes even surprises the patient, Dr. Oldham noted. “When you approach them like this, they can begin to settle down,” which was the case with the female patient he once treated.
About 1.4% of the U.S. population has BPD, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. Conceptualized by the late John G. Gunderson, MD, BPD initially was seen as floating on the borderline between psychosis and neurosis. Clinicians now understand that this isn’t the case. The patients need, as Dr. Gunderson once pointed out, constant vigilance because of attachment issues and childhood trauma.
A stable therapeutic alliance between patient and physician, sometimes in combination with evidence-based therapies, is a formula for success, some experts say.
A misunderstood condition
Although there is some degree of heritable risk, BPD patients are often the product of an invalidating environment in childhood. “As kids, we’re guided and nurtured by caring adults to provide models of reasonable, trustworthy behavior. If those role models are missing or just so inconsistent and unpredictable, the patient doesn’t end up with a sturdy self-image. Instead, they’re adrift, trying to figure out who will be helpful and be a meaningful, trustworthy companion and adviser,” Dr. Oldham said.
Emotional or affective instability and impulsivity, sometimes impulsive aggression, often characterize their condition. “Brain-imaging studies have revealed that certain nerve pathways that are necessary to regulate emotions are impoverished in patients with BPD,” Dr. Oldham said.
An analogy is a car going too fast, with a runaway engine that’s running too hot – and the brakes don’t work, he added.
“People think these patients are trying to create big drama, that they’re putting on a big show. That’s not accurate,” he continued. These patients don’t have the ability to stop the trigger that leads to their emotional storms. They also don’t have the ability to regulate themselves. “We may say, it’s a beautiful day outside, but I still have to go to work. Someone with BPD may say: It’s a beautiful day; I’m going to the beach,” Dr. Oldham explained.
A person with BPD might sound coherent when arguing with someone else. But their words are driven by the storm they can’t turn off.
This can lead to their own efforts to turn off the intensity. They might become self-injurious or push other people away. It’s one of the ironies of this condition because BPD patients desperately want to trust others but are scared to do so. “They look for any little signal – that someone else will hurt, disappoint, or leave them. Eventually their relationships unravel,” Dr. Oldham saod.
For some, suicide is sometimes a final solution.
Those traits make it difficult for a therapist to connect with a patient. “This is a very difficult group of people to treat and to establish treatment,” said Michael A. Cummings, MD, of the department of psychiatry at University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD patients tend to idealize people who are attempting to help them. When they become frustrated or disappointed in some way, “they then devalue the caregiver or the treatment and not infrequently, fall out of treatment,” Dr. Cummings said. It can be a very taxing experience, particularly for younger, less experienced therapists.
Medication only goes so far
Psychiatrists tend to look at BPD patients as receptor sites for molecules, assessing symptoms they can prescribe for, Eric M. Plakun, MD, DLFAPA, FACPsych, medical director/CEO of the Austen Riggs Center in Stockbridge, Mass., said in an interview.
Yet, BPD is not a molecular problem, principally. It’s an interpersonal disorder. When BPD is a co-occurring disorder, as is often the case, the depressive, anxiety, or other disorder can mask the BPD, he added, citing his 2018 paper on tensions in psychiatry between the biomedical and biopsychosocial models (Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2018 Jun;41[2]:237-48).
In one longitudinal study (J Pers Disord. 2005 Oct;19[5]:487-504), the presence of BPD strongly predicted the persistence of depression. BPD comorbid with depression is often a recipe for treatment-resistant depression, which results in higher costs, more utilization of resources, and higher suicide rates. Too often, psychiatrists diagnose the depression but miss the BPD. They keep trying molecular approaches with prescription drugs – even though it’s really the interpersonal issues of BPD that need to be addressed, said Dr. Plakun, who is a member of the Group for the Advancement of Psychiatry’s Psychotherapy Committee, and founder and past leader of the American Psychiatric Association’s Psychotherapy Caucus.
Medication can be helpful as a short-term adjunctive therapy. Long term, it’s not a sustainable approach, said Dr. Oldham. “If a patient is in a particularly stressful period, in the middle of a stormy breakup or having a depressive episode or talking about suicide, a time-limited course of an antidepressant may be helpful,” he said. They could also benefit from an anxiety-related drug or medication to help them sleep.
What you don’t want is for the patient to start relying on medications to help them feel better. The problem is, many are suffering so much that they’ll go to their primary care doctor and say, “I’m suffering from anxiety,” and get an antianxiety drug. Or they’re depressed or in pain and end up with a cocktail of medications. “And that’s just going to make matters worse,” Dr. Oldham said.
Psychotherapy as a first-line approach
APA practice guidelines and others worldwide have all come to the same conclusion about BPD. , who chaired an APA committee that developed an evidence-based practice guideline for patients with BPD.
Psychotherapy keeps the patient from firing you, he asserted. “Because of the lack of trust, they push away. They’re very scared, and this fear also applies to therapist. The goal is to help the patient learn to trust you. To do that, you need to develop a strong therapeutic alliance.”
In crafting the APA’s practice guideline, Dr. Oldham and his colleagues studied a variety of approaches, including mentalization-based therapy (MBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), which was developed by Marsha Linehan, PhD. Since then, other approaches have demonstrated efficacy in randomized clinical trials, including schema-based therapy (SBT), cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and transference-focused psychotherapy (TFP).
Those treatments might complement the broader goal of establishing a strong alliance with the patient, Dr. Oldham said. Manualized approaches can help prepackage a program that allows clinicians and patients to look at their problems in an objective, nonpejorative way, Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute at McLean Hospital in Belmont, Mass., said in an interview. DBT, for example, focuses on emotion dysregulation. MBT addresses how the patient sees themselves through others and their interactions with others. “It destigmatizes a problem as a clinical entity rather than an interpersonal problem between the patient and the clinician,” Dr. Choi-Kain said.
The choice of approach depends on several factors: the patient’s needs and preferences, and the therapist’s skills and experience, said Dr. Oldham. Some patients don’t do well with DBT because it involves a lot of homework and didactic work. Others do better with TFP because they want to understand what drives their behavior.
Dr. Cummings recalled how one of his patients used TFP to look inward and heal.
He first met the patient when she was in her early 30s. “She had made some progress, but I remember she was still struggling mightily with relationship issues and with identifying her role in relationships,” he said. The patient was becoming increasingly aware that she was going to end up alone and didn’t want that as an outcome.
Adapting to a TFP model, “she worked very hard trying to understand herself as she related to other people, understanding her own emotional volatility, and some of her proneness to behavioral problems,” Dr. Cummings said. The patient also had to learn how to negotiate her relationships to the point where she didn’t end up destroying them and alienating people.
Customizing the treatment
Physicians can choose from one of these manualized forms of treatment to see what’s appropriate and what works for the patient. “You can individualize the treatment, borrowing from these approaches and shaping it based on what your patient needs,” Dr. Oldham recommended.
Recently, the field of psychiatry has seen the benefits of combining manualized, evidence-based approaches with general psychiatric management (GPM), a method conceived by Dr. Gunderson. GPM “reflects a sensitive understanding of mental illness, offering ‘non attacking’ or collaborative work with the patient and a sensitive recognition of appropriate interventions or corrections to help the patient stay in treatment,” said Dr. Oldham.
It aims to conceptualize BPD in a clinically objective way, medicalizing the disorder so it’s something that the patient has, rather than something he or she is, explained Dr. Choi-Kain, who worked with Dr. Gunderson to train clinicians on using this approach. Using a framework that’s compatible with good medical practices, the clinician tries to define the problem together with the patient, “really assessing whether or not the treatment works, setting goals, managing safety, and trying to promote functioning, something we need to pay more attention to with BPD,” she said.
For these patients, the goal is to have positive, corrective experiences in the real world, reinforcing their hopes and what they’re capable of, and an interface with the world that makes them feel like contributors, she said.
Cycle of rupture and repair
Many people with BPD struggle with the desire to find and feel love, but also deal with their rage and hate. Hence, therapists must prepare themselves for the experience of sometimes being hated, said Dr. Plakun. The patient needs to feel they’re in a safe enough space to express those feelings, activating a cycle of “rupture and repair,” he continued.
The key in working with these patients is to avoid any language that will make them feel attacked or criticized, said Dr. Oldham.
A patient may get furious and say “I don’t know what you’re talking about. I didn’t say that.” When in truth, the psychiatrist is flat accurate about what the patient said. Instead of arguing with the patient, a physician can back up and say: “Help me understand what you’re feeling right now. What did I say that made you feel that you couldn’t trust me? Help me understand you. I may have made a mistake,” he advised.
Trust is a key ingredient in an alliance-based intervention for suicidal patients with BPD that Dr. Plakun has frequently written about. A bond he had with a deeply suicidal patient helped her overcome her grief and come to terms with an abusive childhood.
“She had a horrible history of abuse and had BPD and bipolar disorder. Even controlled with medications her life was still awful. She contemplated suicide relentlessly.” Working through her history of sexual abuse, the patient discovered that much of what she and clinicians thought of as a depressive illness was in fact intense grief about the irreparable damage that had taken place during childhood.
Through their work she was able to mourn, and her depression and BPD improved.
Developing a trusting relationship with the patient isn’t a starting point; it’s the goal, he emphasized.
“You don’t prescribe trust to someone. It’s earned.” Through the shared journey of therapy, as the patient suffers from inevitable injuries and ruptures and as the therapist reveals his or her imperfections, opportunities arise to nonjudgmentally examine and repair ruptures. This lead to gains in trust, he said.
It’s not just about genes
Many in the psychiatric and psychological communities tend to develop a very nihilistic view of BPD patients, observed Dr. Cummings. “They’ll say: ‘Oh, well, it’s hopeless. There’s nothing that can be done.’ That isn’t true,” he said.
Epidemiologic studies of these individuals have shown that many of these patients no longer meet the diagnostic criteria for BPD by the time they reach middle age. This means they get better over time, noted Dr. Cummings.
Dr. Plakun’s hope is that the field will evolve in a direction that recognizes the importance of psychosocial treatments like psychotherapy, in addition to biomedical treatments. The drive to medicate still exists, which can contribute to underdiagnosis and undertreatment of BPD, he said. “Although there are manualized, evidence-based treatments, few clinicians learn even one of these for BPD, not to mention those for other disorders.”
In 1996, Francis S. Collins, MD, PhD, the current director of the National Institutes of Health, predicted that the decoding of the human genome would transform treatment of medical and mental disorders [and] “that we would discover the ways in which genes equal disease,” said Dr. Plakun. What the science has since shown, is genes by environmental interaction lead to disease and health.
Nature and nurture both matter. “And I don’t think we’re paying enough attention to the nurture side,” Dr. Plakun said.
The solution is a return to a biopsychosocial model, recognizing that psychotherapy is an essential part of treatment of BPD and other conditions, and an essential clinician skill, he said.
Dr. Oldham is coeditor of the “Textbook of Personality Disorders”, 3rd edition (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2021).Dr. Choi-Kain is coeditor with Dr. Gunderson of “Applications of Good Psychiatric Management for Borderline Personality Disorder: A Practical Guide” (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2019).
Dr. Cummings and Dr. Plakun had no disclosures.
Difficulties associated with treating borderline personality disorder (BPD) make for an uneasy alliance between patient and clinician. Deep-seated anxiety and trust issues often lead to patients skipping visits or raging at those who treat them, leaving clinicians frustrated and ready to give up or relying on a pill to make the patient better.
John M. Oldham, MD, MS, recalls one patient he almost lost, a woman who was struggling with aggressive behavior. Initially cooperative and punctual, the patient gradually became distrustful, grilling Dr. Oldham on his training and credentials. “As the questions continued, she slipped from being very cooperative to being enraged and attacking me,” said Dr. Oldham, Distinguished Emeritus Professor in the Menninger department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College in Houston.
Dr. Oldham eventually drew her back in by earning her trust. “There’s no magic to this,” he acknowledged. “You try to be as alert and informed and vigilant for anything you say that produces a negative or concerning reaction in the patient.”
This interactive approach to BPD treatment has been gaining traction in a profession that often looks to medications to alleviate specific symptoms. It’s so effective that it sometimes even surprises the patient, Dr. Oldham noted. “When you approach them like this, they can begin to settle down,” which was the case with the female patient he once treated.
About 1.4% of the U.S. population has BPD, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. Conceptualized by the late John G. Gunderson, MD, BPD initially was seen as floating on the borderline between psychosis and neurosis. Clinicians now understand that this isn’t the case. The patients need, as Dr. Gunderson once pointed out, constant vigilance because of attachment issues and childhood trauma.
A stable therapeutic alliance between patient and physician, sometimes in combination with evidence-based therapies, is a formula for success, some experts say.
A misunderstood condition
Although there is some degree of heritable risk, BPD patients are often the product of an invalidating environment in childhood. “As kids, we’re guided and nurtured by caring adults to provide models of reasonable, trustworthy behavior. If those role models are missing or just so inconsistent and unpredictable, the patient doesn’t end up with a sturdy self-image. Instead, they’re adrift, trying to figure out who will be helpful and be a meaningful, trustworthy companion and adviser,” Dr. Oldham said.
Emotional or affective instability and impulsivity, sometimes impulsive aggression, often characterize their condition. “Brain-imaging studies have revealed that certain nerve pathways that are necessary to regulate emotions are impoverished in patients with BPD,” Dr. Oldham said.
An analogy is a car going too fast, with a runaway engine that’s running too hot – and the brakes don’t work, he added.
“People think these patients are trying to create big drama, that they’re putting on a big show. That’s not accurate,” he continued. These patients don’t have the ability to stop the trigger that leads to their emotional storms. They also don’t have the ability to regulate themselves. “We may say, it’s a beautiful day outside, but I still have to go to work. Someone with BPD may say: It’s a beautiful day; I’m going to the beach,” Dr. Oldham explained.
A person with BPD might sound coherent when arguing with someone else. But their words are driven by the storm they can’t turn off.
This can lead to their own efforts to turn off the intensity. They might become self-injurious or push other people away. It’s one of the ironies of this condition because BPD patients desperately want to trust others but are scared to do so. “They look for any little signal – that someone else will hurt, disappoint, or leave them. Eventually their relationships unravel,” Dr. Oldham saod.
For some, suicide is sometimes a final solution.
Those traits make it difficult for a therapist to connect with a patient. “This is a very difficult group of people to treat and to establish treatment,” said Michael A. Cummings, MD, of the department of psychiatry at University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD patients tend to idealize people who are attempting to help them. When they become frustrated or disappointed in some way, “they then devalue the caregiver or the treatment and not infrequently, fall out of treatment,” Dr. Cummings said. It can be a very taxing experience, particularly for younger, less experienced therapists.
Medication only goes so far
Psychiatrists tend to look at BPD patients as receptor sites for molecules, assessing symptoms they can prescribe for, Eric M. Plakun, MD, DLFAPA, FACPsych, medical director/CEO of the Austen Riggs Center in Stockbridge, Mass., said in an interview.
Yet, BPD is not a molecular problem, principally. It’s an interpersonal disorder. When BPD is a co-occurring disorder, as is often the case, the depressive, anxiety, or other disorder can mask the BPD, he added, citing his 2018 paper on tensions in psychiatry between the biomedical and biopsychosocial models (Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2018 Jun;41[2]:237-48).
In one longitudinal study (J Pers Disord. 2005 Oct;19[5]:487-504), the presence of BPD strongly predicted the persistence of depression. BPD comorbid with depression is often a recipe for treatment-resistant depression, which results in higher costs, more utilization of resources, and higher suicide rates. Too often, psychiatrists diagnose the depression but miss the BPD. They keep trying molecular approaches with prescription drugs – even though it’s really the interpersonal issues of BPD that need to be addressed, said Dr. Plakun, who is a member of the Group for the Advancement of Psychiatry’s Psychotherapy Committee, and founder and past leader of the American Psychiatric Association’s Psychotherapy Caucus.
Medication can be helpful as a short-term adjunctive therapy. Long term, it’s not a sustainable approach, said Dr. Oldham. “If a patient is in a particularly stressful period, in the middle of a stormy breakup or having a depressive episode or talking about suicide, a time-limited course of an antidepressant may be helpful,” he said. They could also benefit from an anxiety-related drug or medication to help them sleep.
What you don’t want is for the patient to start relying on medications to help them feel better. The problem is, many are suffering so much that they’ll go to their primary care doctor and say, “I’m suffering from anxiety,” and get an antianxiety drug. Or they’re depressed or in pain and end up with a cocktail of medications. “And that’s just going to make matters worse,” Dr. Oldham said.
Psychotherapy as a first-line approach
APA practice guidelines and others worldwide have all come to the same conclusion about BPD. , who chaired an APA committee that developed an evidence-based practice guideline for patients with BPD.
Psychotherapy keeps the patient from firing you, he asserted. “Because of the lack of trust, they push away. They’re very scared, and this fear also applies to therapist. The goal is to help the patient learn to trust you. To do that, you need to develop a strong therapeutic alliance.”
In crafting the APA’s practice guideline, Dr. Oldham and his colleagues studied a variety of approaches, including mentalization-based therapy (MBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), which was developed by Marsha Linehan, PhD. Since then, other approaches have demonstrated efficacy in randomized clinical trials, including schema-based therapy (SBT), cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and transference-focused psychotherapy (TFP).
Those treatments might complement the broader goal of establishing a strong alliance with the patient, Dr. Oldham said. Manualized approaches can help prepackage a program that allows clinicians and patients to look at their problems in an objective, nonpejorative way, Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute at McLean Hospital in Belmont, Mass., said in an interview. DBT, for example, focuses on emotion dysregulation. MBT addresses how the patient sees themselves through others and their interactions with others. “It destigmatizes a problem as a clinical entity rather than an interpersonal problem between the patient and the clinician,” Dr. Choi-Kain said.
The choice of approach depends on several factors: the patient’s needs and preferences, and the therapist’s skills and experience, said Dr. Oldham. Some patients don’t do well with DBT because it involves a lot of homework and didactic work. Others do better with TFP because they want to understand what drives their behavior.
Dr. Cummings recalled how one of his patients used TFP to look inward and heal.
He first met the patient when she was in her early 30s. “She had made some progress, but I remember she was still struggling mightily with relationship issues and with identifying her role in relationships,” he said. The patient was becoming increasingly aware that she was going to end up alone and didn’t want that as an outcome.
Adapting to a TFP model, “she worked very hard trying to understand herself as she related to other people, understanding her own emotional volatility, and some of her proneness to behavioral problems,” Dr. Cummings said. The patient also had to learn how to negotiate her relationships to the point where she didn’t end up destroying them and alienating people.
Customizing the treatment
Physicians can choose from one of these manualized forms of treatment to see what’s appropriate and what works for the patient. “You can individualize the treatment, borrowing from these approaches and shaping it based on what your patient needs,” Dr. Oldham recommended.
Recently, the field of psychiatry has seen the benefits of combining manualized, evidence-based approaches with general psychiatric management (GPM), a method conceived by Dr. Gunderson. GPM “reflects a sensitive understanding of mental illness, offering ‘non attacking’ or collaborative work with the patient and a sensitive recognition of appropriate interventions or corrections to help the patient stay in treatment,” said Dr. Oldham.
It aims to conceptualize BPD in a clinically objective way, medicalizing the disorder so it’s something that the patient has, rather than something he or she is, explained Dr. Choi-Kain, who worked with Dr. Gunderson to train clinicians on using this approach. Using a framework that’s compatible with good medical practices, the clinician tries to define the problem together with the patient, “really assessing whether or not the treatment works, setting goals, managing safety, and trying to promote functioning, something we need to pay more attention to with BPD,” she said.
For these patients, the goal is to have positive, corrective experiences in the real world, reinforcing their hopes and what they’re capable of, and an interface with the world that makes them feel like contributors, she said.
Cycle of rupture and repair
Many people with BPD struggle with the desire to find and feel love, but also deal with their rage and hate. Hence, therapists must prepare themselves for the experience of sometimes being hated, said Dr. Plakun. The patient needs to feel they’re in a safe enough space to express those feelings, activating a cycle of “rupture and repair,” he continued.
The key in working with these patients is to avoid any language that will make them feel attacked or criticized, said Dr. Oldham.
A patient may get furious and say “I don’t know what you’re talking about. I didn’t say that.” When in truth, the psychiatrist is flat accurate about what the patient said. Instead of arguing with the patient, a physician can back up and say: “Help me understand what you’re feeling right now. What did I say that made you feel that you couldn’t trust me? Help me understand you. I may have made a mistake,” he advised.
Trust is a key ingredient in an alliance-based intervention for suicidal patients with BPD that Dr. Plakun has frequently written about. A bond he had with a deeply suicidal patient helped her overcome her grief and come to terms with an abusive childhood.
“She had a horrible history of abuse and had BPD and bipolar disorder. Even controlled with medications her life was still awful. She contemplated suicide relentlessly.” Working through her history of sexual abuse, the patient discovered that much of what she and clinicians thought of as a depressive illness was in fact intense grief about the irreparable damage that had taken place during childhood.
Through their work she was able to mourn, and her depression and BPD improved.
Developing a trusting relationship with the patient isn’t a starting point; it’s the goal, he emphasized.
“You don’t prescribe trust to someone. It’s earned.” Through the shared journey of therapy, as the patient suffers from inevitable injuries and ruptures and as the therapist reveals his or her imperfections, opportunities arise to nonjudgmentally examine and repair ruptures. This lead to gains in trust, he said.
It’s not just about genes
Many in the psychiatric and psychological communities tend to develop a very nihilistic view of BPD patients, observed Dr. Cummings. “They’ll say: ‘Oh, well, it’s hopeless. There’s nothing that can be done.’ That isn’t true,” he said.
Epidemiologic studies of these individuals have shown that many of these patients no longer meet the diagnostic criteria for BPD by the time they reach middle age. This means they get better over time, noted Dr. Cummings.
Dr. Plakun’s hope is that the field will evolve in a direction that recognizes the importance of psychosocial treatments like psychotherapy, in addition to biomedical treatments. The drive to medicate still exists, which can contribute to underdiagnosis and undertreatment of BPD, he said. “Although there are manualized, evidence-based treatments, few clinicians learn even one of these for BPD, not to mention those for other disorders.”
In 1996, Francis S. Collins, MD, PhD, the current director of the National Institutes of Health, predicted that the decoding of the human genome would transform treatment of medical and mental disorders [and] “that we would discover the ways in which genes equal disease,” said Dr. Plakun. What the science has since shown, is genes by environmental interaction lead to disease and health.
Nature and nurture both matter. “And I don’t think we’re paying enough attention to the nurture side,” Dr. Plakun said.
The solution is a return to a biopsychosocial model, recognizing that psychotherapy is an essential part of treatment of BPD and other conditions, and an essential clinician skill, he said.
Dr. Oldham is coeditor of the “Textbook of Personality Disorders”, 3rd edition (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2021).Dr. Choi-Kain is coeditor with Dr. Gunderson of “Applications of Good Psychiatric Management for Borderline Personality Disorder: A Practical Guide” (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2019).
Dr. Cummings and Dr. Plakun had no disclosures.
Difficulties associated with treating borderline personality disorder (BPD) make for an uneasy alliance between patient and clinician. Deep-seated anxiety and trust issues often lead to patients skipping visits or raging at those who treat them, leaving clinicians frustrated and ready to give up or relying on a pill to make the patient better.
John M. Oldham, MD, MS, recalls one patient he almost lost, a woman who was struggling with aggressive behavior. Initially cooperative and punctual, the patient gradually became distrustful, grilling Dr. Oldham on his training and credentials. “As the questions continued, she slipped from being very cooperative to being enraged and attacking me,” said Dr. Oldham, Distinguished Emeritus Professor in the Menninger department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College in Houston.
Dr. Oldham eventually drew her back in by earning her trust. “There’s no magic to this,” he acknowledged. “You try to be as alert and informed and vigilant for anything you say that produces a negative or concerning reaction in the patient.”
This interactive approach to BPD treatment has been gaining traction in a profession that often looks to medications to alleviate specific symptoms. It’s so effective that it sometimes even surprises the patient, Dr. Oldham noted. “When you approach them like this, they can begin to settle down,” which was the case with the female patient he once treated.
About 1.4% of the U.S. population has BPD, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. Conceptualized by the late John G. Gunderson, MD, BPD initially was seen as floating on the borderline between psychosis and neurosis. Clinicians now understand that this isn’t the case. The patients need, as Dr. Gunderson once pointed out, constant vigilance because of attachment issues and childhood trauma.
A stable therapeutic alliance between patient and physician, sometimes in combination with evidence-based therapies, is a formula for success, some experts say.
A misunderstood condition
Although there is some degree of heritable risk, BPD patients are often the product of an invalidating environment in childhood. “As kids, we’re guided and nurtured by caring adults to provide models of reasonable, trustworthy behavior. If those role models are missing or just so inconsistent and unpredictable, the patient doesn’t end up with a sturdy self-image. Instead, they’re adrift, trying to figure out who will be helpful and be a meaningful, trustworthy companion and adviser,” Dr. Oldham said.
Emotional or affective instability and impulsivity, sometimes impulsive aggression, often characterize their condition. “Brain-imaging studies have revealed that certain nerve pathways that are necessary to regulate emotions are impoverished in patients with BPD,” Dr. Oldham said.
An analogy is a car going too fast, with a runaway engine that’s running too hot – and the brakes don’t work, he added.
“People think these patients are trying to create big drama, that they’re putting on a big show. That’s not accurate,” he continued. These patients don’t have the ability to stop the trigger that leads to their emotional storms. They also don’t have the ability to regulate themselves. “We may say, it’s a beautiful day outside, but I still have to go to work. Someone with BPD may say: It’s a beautiful day; I’m going to the beach,” Dr. Oldham explained.
A person with BPD might sound coherent when arguing with someone else. But their words are driven by the storm they can’t turn off.
This can lead to their own efforts to turn off the intensity. They might become self-injurious or push other people away. It’s one of the ironies of this condition because BPD patients desperately want to trust others but are scared to do so. “They look for any little signal – that someone else will hurt, disappoint, or leave them. Eventually their relationships unravel,” Dr. Oldham saod.
For some, suicide is sometimes a final solution.
Those traits make it difficult for a therapist to connect with a patient. “This is a very difficult group of people to treat and to establish treatment,” said Michael A. Cummings, MD, of the department of psychiatry at University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD patients tend to idealize people who are attempting to help them. When they become frustrated or disappointed in some way, “they then devalue the caregiver or the treatment and not infrequently, fall out of treatment,” Dr. Cummings said. It can be a very taxing experience, particularly for younger, less experienced therapists.
Medication only goes so far
Psychiatrists tend to look at BPD patients as receptor sites for molecules, assessing symptoms they can prescribe for, Eric M. Plakun, MD, DLFAPA, FACPsych, medical director/CEO of the Austen Riggs Center in Stockbridge, Mass., said in an interview.
Yet, BPD is not a molecular problem, principally. It’s an interpersonal disorder. When BPD is a co-occurring disorder, as is often the case, the depressive, anxiety, or other disorder can mask the BPD, he added, citing his 2018 paper on tensions in psychiatry between the biomedical and biopsychosocial models (Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2018 Jun;41[2]:237-48).
In one longitudinal study (J Pers Disord. 2005 Oct;19[5]:487-504), the presence of BPD strongly predicted the persistence of depression. BPD comorbid with depression is often a recipe for treatment-resistant depression, which results in higher costs, more utilization of resources, and higher suicide rates. Too often, psychiatrists diagnose the depression but miss the BPD. They keep trying molecular approaches with prescription drugs – even though it’s really the interpersonal issues of BPD that need to be addressed, said Dr. Plakun, who is a member of the Group for the Advancement of Psychiatry’s Psychotherapy Committee, and founder and past leader of the American Psychiatric Association’s Psychotherapy Caucus.
Medication can be helpful as a short-term adjunctive therapy. Long term, it’s not a sustainable approach, said Dr. Oldham. “If a patient is in a particularly stressful period, in the middle of a stormy breakup or having a depressive episode or talking about suicide, a time-limited course of an antidepressant may be helpful,” he said. They could also benefit from an anxiety-related drug or medication to help them sleep.
What you don’t want is for the patient to start relying on medications to help them feel better. The problem is, many are suffering so much that they’ll go to their primary care doctor and say, “I’m suffering from anxiety,” and get an antianxiety drug. Or they’re depressed or in pain and end up with a cocktail of medications. “And that’s just going to make matters worse,” Dr. Oldham said.
Psychotherapy as a first-line approach
APA practice guidelines and others worldwide have all come to the same conclusion about BPD. , who chaired an APA committee that developed an evidence-based practice guideline for patients with BPD.
Psychotherapy keeps the patient from firing you, he asserted. “Because of the lack of trust, they push away. They’re very scared, and this fear also applies to therapist. The goal is to help the patient learn to trust you. To do that, you need to develop a strong therapeutic alliance.”
In crafting the APA’s practice guideline, Dr. Oldham and his colleagues studied a variety of approaches, including mentalization-based therapy (MBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), which was developed by Marsha Linehan, PhD. Since then, other approaches have demonstrated efficacy in randomized clinical trials, including schema-based therapy (SBT), cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and transference-focused psychotherapy (TFP).
Those treatments might complement the broader goal of establishing a strong alliance with the patient, Dr. Oldham said. Manualized approaches can help prepackage a program that allows clinicians and patients to look at their problems in an objective, nonpejorative way, Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute at McLean Hospital in Belmont, Mass., said in an interview. DBT, for example, focuses on emotion dysregulation. MBT addresses how the patient sees themselves through others and their interactions with others. “It destigmatizes a problem as a clinical entity rather than an interpersonal problem between the patient and the clinician,” Dr. Choi-Kain said.
The choice of approach depends on several factors: the patient’s needs and preferences, and the therapist’s skills and experience, said Dr. Oldham. Some patients don’t do well with DBT because it involves a lot of homework and didactic work. Others do better with TFP because they want to understand what drives their behavior.
Dr. Cummings recalled how one of his patients used TFP to look inward and heal.
He first met the patient when she was in her early 30s. “She had made some progress, but I remember she was still struggling mightily with relationship issues and with identifying her role in relationships,” he said. The patient was becoming increasingly aware that she was going to end up alone and didn’t want that as an outcome.
Adapting to a TFP model, “she worked very hard trying to understand herself as she related to other people, understanding her own emotional volatility, and some of her proneness to behavioral problems,” Dr. Cummings said. The patient also had to learn how to negotiate her relationships to the point where she didn’t end up destroying them and alienating people.
Customizing the treatment
Physicians can choose from one of these manualized forms of treatment to see what’s appropriate and what works for the patient. “You can individualize the treatment, borrowing from these approaches and shaping it based on what your patient needs,” Dr. Oldham recommended.
Recently, the field of psychiatry has seen the benefits of combining manualized, evidence-based approaches with general psychiatric management (GPM), a method conceived by Dr. Gunderson. GPM “reflects a sensitive understanding of mental illness, offering ‘non attacking’ or collaborative work with the patient and a sensitive recognition of appropriate interventions or corrections to help the patient stay in treatment,” said Dr. Oldham.
It aims to conceptualize BPD in a clinically objective way, medicalizing the disorder so it’s something that the patient has, rather than something he or she is, explained Dr. Choi-Kain, who worked with Dr. Gunderson to train clinicians on using this approach. Using a framework that’s compatible with good medical practices, the clinician tries to define the problem together with the patient, “really assessing whether or not the treatment works, setting goals, managing safety, and trying to promote functioning, something we need to pay more attention to with BPD,” she said.
For these patients, the goal is to have positive, corrective experiences in the real world, reinforcing their hopes and what they’re capable of, and an interface with the world that makes them feel like contributors, she said.
Cycle of rupture and repair
Many people with BPD struggle with the desire to find and feel love, but also deal with their rage and hate. Hence, therapists must prepare themselves for the experience of sometimes being hated, said Dr. Plakun. The patient needs to feel they’re in a safe enough space to express those feelings, activating a cycle of “rupture and repair,” he continued.
The key in working with these patients is to avoid any language that will make them feel attacked or criticized, said Dr. Oldham.
A patient may get furious and say “I don’t know what you’re talking about. I didn’t say that.” When in truth, the psychiatrist is flat accurate about what the patient said. Instead of arguing with the patient, a physician can back up and say: “Help me understand what you’re feeling right now. What did I say that made you feel that you couldn’t trust me? Help me understand you. I may have made a mistake,” he advised.
Trust is a key ingredient in an alliance-based intervention for suicidal patients with BPD that Dr. Plakun has frequently written about. A bond he had with a deeply suicidal patient helped her overcome her grief and come to terms with an abusive childhood.
“She had a horrible history of abuse and had BPD and bipolar disorder. Even controlled with medications her life was still awful. She contemplated suicide relentlessly.” Working through her history of sexual abuse, the patient discovered that much of what she and clinicians thought of as a depressive illness was in fact intense grief about the irreparable damage that had taken place during childhood.
Through their work she was able to mourn, and her depression and BPD improved.
Developing a trusting relationship with the patient isn’t a starting point; it’s the goal, he emphasized.
“You don’t prescribe trust to someone. It’s earned.” Through the shared journey of therapy, as the patient suffers from inevitable injuries and ruptures and as the therapist reveals his or her imperfections, opportunities arise to nonjudgmentally examine and repair ruptures. This lead to gains in trust, he said.
It’s not just about genes
Many in the psychiatric and psychological communities tend to develop a very nihilistic view of BPD patients, observed Dr. Cummings. “They’ll say: ‘Oh, well, it’s hopeless. There’s nothing that can be done.’ That isn’t true,” he said.
Epidemiologic studies of these individuals have shown that many of these patients no longer meet the diagnostic criteria for BPD by the time they reach middle age. This means they get better over time, noted Dr. Cummings.
Dr. Plakun’s hope is that the field will evolve in a direction that recognizes the importance of psychosocial treatments like psychotherapy, in addition to biomedical treatments. The drive to medicate still exists, which can contribute to underdiagnosis and undertreatment of BPD, he said. “Although there are manualized, evidence-based treatments, few clinicians learn even one of these for BPD, not to mention those for other disorders.”
In 1996, Francis S. Collins, MD, PhD, the current director of the National Institutes of Health, predicted that the decoding of the human genome would transform treatment of medical and mental disorders [and] “that we would discover the ways in which genes equal disease,” said Dr. Plakun. What the science has since shown, is genes by environmental interaction lead to disease and health.
Nature and nurture both matter. “And I don’t think we’re paying enough attention to the nurture side,” Dr. Plakun said.
The solution is a return to a biopsychosocial model, recognizing that psychotherapy is an essential part of treatment of BPD and other conditions, and an essential clinician skill, he said.
Dr. Oldham is coeditor of the “Textbook of Personality Disorders”, 3rd edition (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2021).Dr. Choi-Kain is coeditor with Dr. Gunderson of “Applications of Good Psychiatric Management for Borderline Personality Disorder: A Practical Guide” (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2019).
Dr. Cummings and Dr. Plakun had no disclosures.
‘Empathy fatigue’ in clinicians rises with latest COVID-19 surge
Heidi Erickson, MD, is tired. As a pulmonary and critical care physician at Hennepin Healthcare in Minneapolis, she has been providing care for patients with COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic.
It was exhausting from the beginning, as she and her colleagues scrambled to understand how to deal with this new disease. But lately, she has noticed a different kind of exhaustion arising from the knowledge that with vaccines widely available, the latest surge was preventable.
Her intensive care unit is currently as full as it has ever been with COVID-19 patients, many of them young adults and most of them unvaccinated. After the recent death of one patient, an unvaccinated man with teenage children, she had to face his family’s questions about why ivermectin, an antiparasitic medication that was falsely promoted as a COVID-19 treatment, was not administered.
“I’m fatigued because I’m working more than ever, but more people don’t have to die,” Dr. Erickson said in an interview . “It’s been very hard physically, mentally, emotionally.”
Amid yet another surge in COVID-19 cases around the United States, clinicians are speaking out about their growing frustration with this preventable crisis.
Some are using the terms “empathy fatigue” and “compassion fatigue” – a sense that they are losing empathy for unvaccinated individuals who are fueling the pandemic.
Dr. Erickson says she is frustrated not by individual patients but by a system that has allowed disinformation to proliferate. Experts say these types of feelings fit into a widespread pattern of physician burnout that has taken a new turn at this stage of the pandemic.
Paradoxical choices
Empathy is a cornerstone of what clinicians do, and the ability to understand and share a patient’s feelings is an essential skill for providing effective care, says Kaz Nelson, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Practitioners face paradoxical situations all the time, she notes. These include individuals who break bones and go skydiving again, people who have high cholesterol but continue to eat fried foods, and those with advanced lung cancer who continue to smoke.
To treat patients with compassion, practitioners learn to set aside judgment by acknowledging the complexity of human behavior. They may lament the addictive nature of nicotine and advertising that targets children, for example, while still listening and caring.
Empathy requires high-level brain function, but as stress levels rise, brain function that drives empathy tends to shut down. It’s a survival mechanism, Dr. Nelson says.
When health care workers feel overwhelmed, trapped, or threatened by patients demanding unproven treatments or by ICUs with more patients than ventilators, they may experience a fight-or-flight response that makes them defensive, frustrated, angry, or uncaring, notes Mona Masood, DO, a Philadelphia-area psychiatrist and founder of Physician Support Line, a free mental health hotline for doctors.
Some clinicians have taken to Twitter and other social media platforms to post about these types of experiences.
These feelings, which have been brewing for months, have been exacerbated by the complexity of the current situation. Clinicians see a disconnect between what is and what could be, Dr. Nelson notes.
“Prior to vaccines, there weren’t other options, and so we had toxic stress and we had fatigue, but we could still maintain little bits of empathy by saying, ‘You know, people didn’t choose to get infected, and we are in a pandemic.’ We could kind of hate the virus. Now with access to vaccines, that last connection to empathy is removed for many people,” she says.
Self-preservation vs. empathy
Compassion fatigue or empathy fatigue is just one reaction to feeling completely maxed out and overstressed, Dr. Nelson says. Anger at society, such as what Dr. Erickson experienced, is another response.
Practitioners may also feel as if they are just going through the motions of their job, or they might disassociate, ceasing to feel that their patients are human. Plenty of doctors and nurses have cried in their cars after shifts and have posted tearful videos on social media.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Masood says, physicians who called the support hotline expressed sadness and grief. Now, she had her colleagues hear frustration and anger, along with guilt and shame for having feelings they believe they shouldn’t be having, especially toward patients. They may feel unprofessional or worse – unworthy of being physicians, she says.
One recent caller to the hotline was a long-time ICU physician who had been told so many times by patients that ivermectin was the only medicine that would cure them that he began to doubt himself, says Dr. Masood. This caller needed to be reassured by another physician that he was doing the right thing.
Another emergency department physician told Dr. Masood about a young child who had arrived at the hospital with COVID-19 symptoms. When asked whether the family had been exposed to anyone with COVID-19, the child’s parent lied so that they could be triaged faster.
The physician, who needed to step away from the situation, reached out to Dr. Masood to express her frustration so that she wouldn’t “let it out” on the patient.
“It’s hard to have empathy for people who, for all intents and purposes, are very self-centered,” Dr. Masood says. “We’re at a place where we’re having to choose between self-preservation and empathy.”
How to cope
To help practitioners cope, Dr. Masood offers words that describe what they’re experiencing. She often hears clinicians say things such as, “This is a type of burnout that I feel to my bones,” or “This makes me want to quit,” or “I feel like I’m at the end of my rope.”
She encourages them to consider the terms “empathy fatigue,” and “moral injury” in order to reconcile how their sense of responsibility to take care of people is compromised by factors outside of their control.
It is not shameful to acknowledge that they experience emotions, including difficult ones such as frustration, anger, sadness, and anxiety, Dr. Masood adds.
Being frustrated with a patient doesn’t make someone a bad doctor, and admitting those emotions is the first step toward dealing with them, she says.
before they cause a sense of callousness or other consequences that become harder to heal from as time goes on.
“We’re trained to just go, go, go and sometimes not pause and check in,” she says. Clinicians who open up are likely to find they are not the only ones feeling tired or frustrated right now, she adds.
“Connect with peers and colleagues, because chances are, they can relate,” Dr. Nelson says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heidi Erickson, MD, is tired. As a pulmonary and critical care physician at Hennepin Healthcare in Minneapolis, she has been providing care for patients with COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic.
It was exhausting from the beginning, as she and her colleagues scrambled to understand how to deal with this new disease. But lately, she has noticed a different kind of exhaustion arising from the knowledge that with vaccines widely available, the latest surge was preventable.
Her intensive care unit is currently as full as it has ever been with COVID-19 patients, many of them young adults and most of them unvaccinated. After the recent death of one patient, an unvaccinated man with teenage children, she had to face his family’s questions about why ivermectin, an antiparasitic medication that was falsely promoted as a COVID-19 treatment, was not administered.
“I’m fatigued because I’m working more than ever, but more people don’t have to die,” Dr. Erickson said in an interview . “It’s been very hard physically, mentally, emotionally.”
Amid yet another surge in COVID-19 cases around the United States, clinicians are speaking out about their growing frustration with this preventable crisis.
Some are using the terms “empathy fatigue” and “compassion fatigue” – a sense that they are losing empathy for unvaccinated individuals who are fueling the pandemic.
Dr. Erickson says she is frustrated not by individual patients but by a system that has allowed disinformation to proliferate. Experts say these types of feelings fit into a widespread pattern of physician burnout that has taken a new turn at this stage of the pandemic.
Paradoxical choices
Empathy is a cornerstone of what clinicians do, and the ability to understand and share a patient’s feelings is an essential skill for providing effective care, says Kaz Nelson, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Practitioners face paradoxical situations all the time, she notes. These include individuals who break bones and go skydiving again, people who have high cholesterol but continue to eat fried foods, and those with advanced lung cancer who continue to smoke.
To treat patients with compassion, practitioners learn to set aside judgment by acknowledging the complexity of human behavior. They may lament the addictive nature of nicotine and advertising that targets children, for example, while still listening and caring.
Empathy requires high-level brain function, but as stress levels rise, brain function that drives empathy tends to shut down. It’s a survival mechanism, Dr. Nelson says.
When health care workers feel overwhelmed, trapped, or threatened by patients demanding unproven treatments or by ICUs with more patients than ventilators, they may experience a fight-or-flight response that makes them defensive, frustrated, angry, or uncaring, notes Mona Masood, DO, a Philadelphia-area psychiatrist and founder of Physician Support Line, a free mental health hotline for doctors.
Some clinicians have taken to Twitter and other social media platforms to post about these types of experiences.
These feelings, which have been brewing for months, have been exacerbated by the complexity of the current situation. Clinicians see a disconnect between what is and what could be, Dr. Nelson notes.
“Prior to vaccines, there weren’t other options, and so we had toxic stress and we had fatigue, but we could still maintain little bits of empathy by saying, ‘You know, people didn’t choose to get infected, and we are in a pandemic.’ We could kind of hate the virus. Now with access to vaccines, that last connection to empathy is removed for many people,” she says.
Self-preservation vs. empathy
Compassion fatigue or empathy fatigue is just one reaction to feeling completely maxed out and overstressed, Dr. Nelson says. Anger at society, such as what Dr. Erickson experienced, is another response.
Practitioners may also feel as if they are just going through the motions of their job, or they might disassociate, ceasing to feel that their patients are human. Plenty of doctors and nurses have cried in their cars after shifts and have posted tearful videos on social media.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Masood says, physicians who called the support hotline expressed sadness and grief. Now, she had her colleagues hear frustration and anger, along with guilt and shame for having feelings they believe they shouldn’t be having, especially toward patients. They may feel unprofessional or worse – unworthy of being physicians, she says.
One recent caller to the hotline was a long-time ICU physician who had been told so many times by patients that ivermectin was the only medicine that would cure them that he began to doubt himself, says Dr. Masood. This caller needed to be reassured by another physician that he was doing the right thing.
Another emergency department physician told Dr. Masood about a young child who had arrived at the hospital with COVID-19 symptoms. When asked whether the family had been exposed to anyone with COVID-19, the child’s parent lied so that they could be triaged faster.
The physician, who needed to step away from the situation, reached out to Dr. Masood to express her frustration so that she wouldn’t “let it out” on the patient.
“It’s hard to have empathy for people who, for all intents and purposes, are very self-centered,” Dr. Masood says. “We’re at a place where we’re having to choose between self-preservation and empathy.”
How to cope
To help practitioners cope, Dr. Masood offers words that describe what they’re experiencing. She often hears clinicians say things such as, “This is a type of burnout that I feel to my bones,” or “This makes me want to quit,” or “I feel like I’m at the end of my rope.”
She encourages them to consider the terms “empathy fatigue,” and “moral injury” in order to reconcile how their sense of responsibility to take care of people is compromised by factors outside of their control.
It is not shameful to acknowledge that they experience emotions, including difficult ones such as frustration, anger, sadness, and anxiety, Dr. Masood adds.
Being frustrated with a patient doesn’t make someone a bad doctor, and admitting those emotions is the first step toward dealing with them, she says.
before they cause a sense of callousness or other consequences that become harder to heal from as time goes on.
“We’re trained to just go, go, go and sometimes not pause and check in,” she says. Clinicians who open up are likely to find they are not the only ones feeling tired or frustrated right now, she adds.
“Connect with peers and colleagues, because chances are, they can relate,” Dr. Nelson says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heidi Erickson, MD, is tired. As a pulmonary and critical care physician at Hennepin Healthcare in Minneapolis, she has been providing care for patients with COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic.
It was exhausting from the beginning, as she and her colleagues scrambled to understand how to deal with this new disease. But lately, she has noticed a different kind of exhaustion arising from the knowledge that with vaccines widely available, the latest surge was preventable.
Her intensive care unit is currently as full as it has ever been with COVID-19 patients, many of them young adults and most of them unvaccinated. After the recent death of one patient, an unvaccinated man with teenage children, she had to face his family’s questions about why ivermectin, an antiparasitic medication that was falsely promoted as a COVID-19 treatment, was not administered.
“I’m fatigued because I’m working more than ever, but more people don’t have to die,” Dr. Erickson said in an interview . “It’s been very hard physically, mentally, emotionally.”
Amid yet another surge in COVID-19 cases around the United States, clinicians are speaking out about their growing frustration with this preventable crisis.
Some are using the terms “empathy fatigue” and “compassion fatigue” – a sense that they are losing empathy for unvaccinated individuals who are fueling the pandemic.
Dr. Erickson says she is frustrated not by individual patients but by a system that has allowed disinformation to proliferate. Experts say these types of feelings fit into a widespread pattern of physician burnout that has taken a new turn at this stage of the pandemic.
Paradoxical choices
Empathy is a cornerstone of what clinicians do, and the ability to understand and share a patient’s feelings is an essential skill for providing effective care, says Kaz Nelson, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Practitioners face paradoxical situations all the time, she notes. These include individuals who break bones and go skydiving again, people who have high cholesterol but continue to eat fried foods, and those with advanced lung cancer who continue to smoke.
To treat patients with compassion, practitioners learn to set aside judgment by acknowledging the complexity of human behavior. They may lament the addictive nature of nicotine and advertising that targets children, for example, while still listening and caring.
Empathy requires high-level brain function, but as stress levels rise, brain function that drives empathy tends to shut down. It’s a survival mechanism, Dr. Nelson says.
When health care workers feel overwhelmed, trapped, or threatened by patients demanding unproven treatments or by ICUs with more patients than ventilators, they may experience a fight-or-flight response that makes them defensive, frustrated, angry, or uncaring, notes Mona Masood, DO, a Philadelphia-area psychiatrist and founder of Physician Support Line, a free mental health hotline for doctors.
Some clinicians have taken to Twitter and other social media platforms to post about these types of experiences.
These feelings, which have been brewing for months, have been exacerbated by the complexity of the current situation. Clinicians see a disconnect between what is and what could be, Dr. Nelson notes.
“Prior to vaccines, there weren’t other options, and so we had toxic stress and we had fatigue, but we could still maintain little bits of empathy by saying, ‘You know, people didn’t choose to get infected, and we are in a pandemic.’ We could kind of hate the virus. Now with access to vaccines, that last connection to empathy is removed for many people,” she says.
Self-preservation vs. empathy
Compassion fatigue or empathy fatigue is just one reaction to feeling completely maxed out and overstressed, Dr. Nelson says. Anger at society, such as what Dr. Erickson experienced, is another response.
Practitioners may also feel as if they are just going through the motions of their job, or they might disassociate, ceasing to feel that their patients are human. Plenty of doctors and nurses have cried in their cars after shifts and have posted tearful videos on social media.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Masood says, physicians who called the support hotline expressed sadness and grief. Now, she had her colleagues hear frustration and anger, along with guilt and shame for having feelings they believe they shouldn’t be having, especially toward patients. They may feel unprofessional or worse – unworthy of being physicians, she says.
One recent caller to the hotline was a long-time ICU physician who had been told so many times by patients that ivermectin was the only medicine that would cure them that he began to doubt himself, says Dr. Masood. This caller needed to be reassured by another physician that he was doing the right thing.
Another emergency department physician told Dr. Masood about a young child who had arrived at the hospital with COVID-19 symptoms. When asked whether the family had been exposed to anyone with COVID-19, the child’s parent lied so that they could be triaged faster.
The physician, who needed to step away from the situation, reached out to Dr. Masood to express her frustration so that she wouldn’t “let it out” on the patient.
“It’s hard to have empathy for people who, for all intents and purposes, are very self-centered,” Dr. Masood says. “We’re at a place where we’re having to choose between self-preservation and empathy.”
How to cope
To help practitioners cope, Dr. Masood offers words that describe what they’re experiencing. She often hears clinicians say things such as, “This is a type of burnout that I feel to my bones,” or “This makes me want to quit,” or “I feel like I’m at the end of my rope.”
She encourages them to consider the terms “empathy fatigue,” and “moral injury” in order to reconcile how their sense of responsibility to take care of people is compromised by factors outside of their control.
It is not shameful to acknowledge that they experience emotions, including difficult ones such as frustration, anger, sadness, and anxiety, Dr. Masood adds.
Being frustrated with a patient doesn’t make someone a bad doctor, and admitting those emotions is the first step toward dealing with them, she says.
before they cause a sense of callousness or other consequences that become harder to heal from as time goes on.
“We’re trained to just go, go, go and sometimes not pause and check in,” she says. Clinicians who open up are likely to find they are not the only ones feeling tired or frustrated right now, she adds.
“Connect with peers and colleagues, because chances are, they can relate,” Dr. Nelson says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Online mental health treatment: Is this the answer we’ve been waiting for?
If you haven’t noticed yet, there has been an explosion of new online companies specializing in slicing off some little sliver of health care and leaving traditional medicine to take care of the rest of the patient. Lately, many of these startups involve mental health care, traditionally a difficult area to make profitable unless one caters just to the wealthy. Many pediatricians have been unsure exactly what to make of these new efforts. Are these the rescuers we’ve been waiting for to fill what seems like an enormous and growing unmet need? Are they just another means to extract money from desperate people and leave the real work to someone else? Something in-between? This article outlines some points to consider when evaluating this new frontier.
Case vignette
A 12-year-old girl presents with her parents for an annual exam. She has been struggling with her mood and anxiety over the past 2 years along with occasional superficial cutting. You have started treatment with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and have recommended that she see a mental health professional but the parents report that one attempt with a therapist was a poor fit and nobody in the area seems to be accepting new patients. The parents state that they saw an advertisement on TV for a company that offers online psychotherapy by video appointments or text. They think this might be an option to pursue but are a little skeptical of the whole idea. They look for your opinion on this topic.
Most of these companies operate by having subscribers pay a monthly fee for different levels of services such as videoconference therapy sessions, supportive text messages, or even some psychopharmacological care. Many also offer the ability to switch rapidly between clinicians if you don’t like the one you have.
These arrangements sound great as the world grows increasingly comfortable with online communication and the mental health needs of children and adolescents increase with the seemingly endless COVID pandemic. Further, research generally finds that online mental health treatment is just as effective as services delivered in person, although the data on therapy by text are less robust.
Nevertheless, a lot of skepticism remains about online mental health treatment, particularly among those involved in more traditionally delivered mental health care. Some of the concerns that often get brought up include the following:
- Cost. Most of these online groups, especially the big national companies, don’t interact directly with insurance companies, leaving a lot of out-of-pocket expenses or the need for families to work things out directly with their insurance provider.
- Care fragmentation. In many ways, the online mental health care surge seems at odds with the growing “integrated care” movement that is trying to embed more behavioral care within primary care practices. From this lens, outsourcing someone’s mental health treatment to a therapist across the country that the patient has never actually met seems like a step in the wrong direction. Further, concerns arise about how much these folks will know about local resources in the community.
- The corporate model in mental health care. While being able to shop for a therapist like you would for a pillow sounds great on the surface, there are many times where a patient may need to be supportively confronted by their therapist or told no when asking about things like certain medications. The “customer is always right” principle often falls short when it comes to good mental health treatment.
- Depth and type of treatment. It is probably fair to say that most online therapy could be described as supportive psychotherapy. This type of therapy can be quite helpful for many but may lack the depth or specific techniques that some people need. For youth, some of the most effective types of psychotherapy, like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be harder to find, and implement, online.
- Emergencies. While many online companies claim to offer round-the-clock support for paying customers, they can quickly punt to “call your doctor” or even “call 911” if there is any real mental health crisis.
Balancing these potential benefits and pitfalls of online therapy, here are a few questions your patients may want to consider before signing onto a long-term contract with an online therapy company.
- Would the online clinician have any knowledge of my community? In some cases, this may not matter that much, while for others it could be quite important.
- What happens in an emergency? Would the regular online therapist be available to help through a crisis or would things revert back to local resources?
- What about privacy and collaboration? Effective communication between a patient’s primary care clinician and their therapist can be crucial to good care, and asking the patient always to be the intermediary can be fraught with difficulty.
- How long is the contract? Just like those gym memberships, these companies bank on individuals who sign up but then don’t really use the service.
- What kind of training do the therapists at the site have? Is it possible to receive specific types of therapy, like CBT or parent training? Otherwise, pediatricians might be quite likely to hear back from the family wondering about medications after therapy “isn’t helping.”
Overall, mental health treatment delivered by telehealth is here to stay whether we like it or not. For some families, it is likely to provide new access to services not easily obtainable locally, while for others it could end up being a costly and ineffective enterprise. For families who use these services, a key challenge for pediatricians that may be important to overcome is finding a way for these clinicians to integrate into the overall medical team rather than being a detached island unto themselves.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and associate professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, Burlington. Follow him on Twitter @PediPsych. His book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows About the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood” (New York: Oxford University Press, 2021). Email him at [email protected].
If you haven’t noticed yet, there has been an explosion of new online companies specializing in slicing off some little sliver of health care and leaving traditional medicine to take care of the rest of the patient. Lately, many of these startups involve mental health care, traditionally a difficult area to make profitable unless one caters just to the wealthy. Many pediatricians have been unsure exactly what to make of these new efforts. Are these the rescuers we’ve been waiting for to fill what seems like an enormous and growing unmet need? Are they just another means to extract money from desperate people and leave the real work to someone else? Something in-between? This article outlines some points to consider when evaluating this new frontier.
Case vignette
A 12-year-old girl presents with her parents for an annual exam. She has been struggling with her mood and anxiety over the past 2 years along with occasional superficial cutting. You have started treatment with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and have recommended that she see a mental health professional but the parents report that one attempt with a therapist was a poor fit and nobody in the area seems to be accepting new patients. The parents state that they saw an advertisement on TV for a company that offers online psychotherapy by video appointments or text. They think this might be an option to pursue but are a little skeptical of the whole idea. They look for your opinion on this topic.
Most of these companies operate by having subscribers pay a monthly fee for different levels of services such as videoconference therapy sessions, supportive text messages, or even some psychopharmacological care. Many also offer the ability to switch rapidly between clinicians if you don’t like the one you have.
These arrangements sound great as the world grows increasingly comfortable with online communication and the mental health needs of children and adolescents increase with the seemingly endless COVID pandemic. Further, research generally finds that online mental health treatment is just as effective as services delivered in person, although the data on therapy by text are less robust.
Nevertheless, a lot of skepticism remains about online mental health treatment, particularly among those involved in more traditionally delivered mental health care. Some of the concerns that often get brought up include the following:
- Cost. Most of these online groups, especially the big national companies, don’t interact directly with insurance companies, leaving a lot of out-of-pocket expenses or the need for families to work things out directly with their insurance provider.
- Care fragmentation. In many ways, the online mental health care surge seems at odds with the growing “integrated care” movement that is trying to embed more behavioral care within primary care practices. From this lens, outsourcing someone’s mental health treatment to a therapist across the country that the patient has never actually met seems like a step in the wrong direction. Further, concerns arise about how much these folks will know about local resources in the community.
- The corporate model in mental health care. While being able to shop for a therapist like you would for a pillow sounds great on the surface, there are many times where a patient may need to be supportively confronted by their therapist or told no when asking about things like certain medications. The “customer is always right” principle often falls short when it comes to good mental health treatment.
- Depth and type of treatment. It is probably fair to say that most online therapy could be described as supportive psychotherapy. This type of therapy can be quite helpful for many but may lack the depth or specific techniques that some people need. For youth, some of the most effective types of psychotherapy, like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be harder to find, and implement, online.
- Emergencies. While many online companies claim to offer round-the-clock support for paying customers, they can quickly punt to “call your doctor” or even “call 911” if there is any real mental health crisis.
Balancing these potential benefits and pitfalls of online therapy, here are a few questions your patients may want to consider before signing onto a long-term contract with an online therapy company.
- Would the online clinician have any knowledge of my community? In some cases, this may not matter that much, while for others it could be quite important.
- What happens in an emergency? Would the regular online therapist be available to help through a crisis or would things revert back to local resources?
- What about privacy and collaboration? Effective communication between a patient’s primary care clinician and their therapist can be crucial to good care, and asking the patient always to be the intermediary can be fraught with difficulty.
- How long is the contract? Just like those gym memberships, these companies bank on individuals who sign up but then don’t really use the service.
- What kind of training do the therapists at the site have? Is it possible to receive specific types of therapy, like CBT or parent training? Otherwise, pediatricians might be quite likely to hear back from the family wondering about medications after therapy “isn’t helping.”
Overall, mental health treatment delivered by telehealth is here to stay whether we like it or not. For some families, it is likely to provide new access to services not easily obtainable locally, while for others it could end up being a costly and ineffective enterprise. For families who use these services, a key challenge for pediatricians that may be important to overcome is finding a way for these clinicians to integrate into the overall medical team rather than being a detached island unto themselves.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and associate professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, Burlington. Follow him on Twitter @PediPsych. His book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows About the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood” (New York: Oxford University Press, 2021). Email him at [email protected].
If you haven’t noticed yet, there has been an explosion of new online companies specializing in slicing off some little sliver of health care and leaving traditional medicine to take care of the rest of the patient. Lately, many of these startups involve mental health care, traditionally a difficult area to make profitable unless one caters just to the wealthy. Many pediatricians have been unsure exactly what to make of these new efforts. Are these the rescuers we’ve been waiting for to fill what seems like an enormous and growing unmet need? Are they just another means to extract money from desperate people and leave the real work to someone else? Something in-between? This article outlines some points to consider when evaluating this new frontier.
Case vignette
A 12-year-old girl presents with her parents for an annual exam. She has been struggling with her mood and anxiety over the past 2 years along with occasional superficial cutting. You have started treatment with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and have recommended that she see a mental health professional but the parents report that one attempt with a therapist was a poor fit and nobody in the area seems to be accepting new patients. The parents state that they saw an advertisement on TV for a company that offers online psychotherapy by video appointments or text. They think this might be an option to pursue but are a little skeptical of the whole idea. They look for your opinion on this topic.
Most of these companies operate by having subscribers pay a monthly fee for different levels of services such as videoconference therapy sessions, supportive text messages, or even some psychopharmacological care. Many also offer the ability to switch rapidly between clinicians if you don’t like the one you have.
These arrangements sound great as the world grows increasingly comfortable with online communication and the mental health needs of children and adolescents increase with the seemingly endless COVID pandemic. Further, research generally finds that online mental health treatment is just as effective as services delivered in person, although the data on therapy by text are less robust.
Nevertheless, a lot of skepticism remains about online mental health treatment, particularly among those involved in more traditionally delivered mental health care. Some of the concerns that often get brought up include the following:
- Cost. Most of these online groups, especially the big national companies, don’t interact directly with insurance companies, leaving a lot of out-of-pocket expenses or the need for families to work things out directly with their insurance provider.
- Care fragmentation. In many ways, the online mental health care surge seems at odds with the growing “integrated care” movement that is trying to embed more behavioral care within primary care practices. From this lens, outsourcing someone’s mental health treatment to a therapist across the country that the patient has never actually met seems like a step in the wrong direction. Further, concerns arise about how much these folks will know about local resources in the community.
- The corporate model in mental health care. While being able to shop for a therapist like you would for a pillow sounds great on the surface, there are many times where a patient may need to be supportively confronted by their therapist or told no when asking about things like certain medications. The “customer is always right” principle often falls short when it comes to good mental health treatment.
- Depth and type of treatment. It is probably fair to say that most online therapy could be described as supportive psychotherapy. This type of therapy can be quite helpful for many but may lack the depth or specific techniques that some people need. For youth, some of the most effective types of psychotherapy, like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be harder to find, and implement, online.
- Emergencies. While many online companies claim to offer round-the-clock support for paying customers, they can quickly punt to “call your doctor” or even “call 911” if there is any real mental health crisis.
Balancing these potential benefits and pitfalls of online therapy, here are a few questions your patients may want to consider before signing onto a long-term contract with an online therapy company.
- Would the online clinician have any knowledge of my community? In some cases, this may not matter that much, while for others it could be quite important.
- What happens in an emergency? Would the regular online therapist be available to help through a crisis or would things revert back to local resources?
- What about privacy and collaboration? Effective communication between a patient’s primary care clinician and their therapist can be crucial to good care, and asking the patient always to be the intermediary can be fraught with difficulty.
- How long is the contract? Just like those gym memberships, these companies bank on individuals who sign up but then don’t really use the service.
- What kind of training do the therapists at the site have? Is it possible to receive specific types of therapy, like CBT or parent training? Otherwise, pediatricians might be quite likely to hear back from the family wondering about medications after therapy “isn’t helping.”
Overall, mental health treatment delivered by telehealth is here to stay whether we like it or not. For some families, it is likely to provide new access to services not easily obtainable locally, while for others it could end up being a costly and ineffective enterprise. For families who use these services, a key challenge for pediatricians that may be important to overcome is finding a way for these clinicians to integrate into the overall medical team rather than being a detached island unto themselves.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and associate professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, Burlington. Follow him on Twitter @PediPsych. His book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows About the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood” (New York: Oxford University Press, 2021). Email him at [email protected].
The role of probiotics in mental health
In 1950, at Staten Island’s Sea View Hospital, a group of patients with terminal tuberculosis were given a new antibiotic called isoniazid, which caused some unexpected side effects. The patients reported euphoria, mental stimulation, and improved sleep, and even began socializing with more vigor. The press was all over the case, writing about the sick “dancing in the halls tho’ they had holes in their lungs.” Soon doctors started prescribing isoniazid as the first-ever antidepressant.
The Sea View Hospital experiment was an early hint that changing the composition of the gut microbiome – in this case, via antibiotics – might affect our mental health. Yet only in the last 2 decades has research into connections between what we ingest and psychiatric disorders really taken off. In 2004, a landmark study showed that germ-free mice (born in such sterile conditions that they lacked a microbiome) had an exaggerated stress response. The effects were reversed, however, if the mice were fed a bacterial strain, Bifidobacterium infantis, a probiotic. This sparked academic interest, and thousands of research papers followed.
According to Stephen Ilardi, PhD, a clinical psychologist at the University of Kansas, Lawrence, focusing on the etiology and treatment of depression, now is the “time of exciting discovery” in the field of probiotics and psychiatric disorders, although, admittedly, a lot still remains unknown.
Gut microbiome profiles in mental health disorders
We humans have about 100 trillion microbes residing in our guts. Some of these are archaea, some fungi, some protozoans and even viruses, but most are bacteria. Things like diet, sleep, and stress can all impact the composition of our gut microbiome. When the microbiome differs considerably from the typical, doctors and researchers describe it as dysbiosis, or imbalance. Studies have uncovered dysbiosis in patients with depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.
“I think there is now pretty good evidence that the gut microbiome is actually an important factor in a number of psychiatric disorders,” says Allan Young, MBChB, clinical psychiatrist at King’s College London. The gut microbiome composition does seem to differ between psychiatric patients and the healthy. In depression, for example, a recent review of nine studies found an increase on the genus level in Streptococcus and Oscillibacter and low abundance of Lactobacillus and Coprococcus, among others. In generalized anxiety disorder, meanwhile, there appears to be an increase in Fusobacteria and Escherichia/Shigella .
For Dr. Ilardi, the next important question is whether there are plausible mechanisms that could explain how gut microbiota may influence brain function. And, it appears there are.
“The microbes in the gut can release neurotransmitters into blood that cross into the brain and influence brain function. They can release hormones into the blood that again cross into the brain. They’ve got a lot of tricks up their sleeve,” he says.
One particularly important pathway runs through the vagus nerve – the longest nerve that emerges directly from the brain, connecting it to the gut. Another is the immune pathway. Gut bacteria can interact with immune cells and reduce cytokine production, which in turn can reduce systemic inflammation. Inflammatory processes have been implicated in both depression and bipolar disorder. What’s more, gut microbes can upregulate the expression of a protein called BDNF – brain-derived neurotrophic factor – which helps the development and survival of nerve cells in the brain.
Probiotics’ promise varies for different conditions
As the pathways by which gut dysbiosis may influence psychiatric disorders become clearer, the next logical step is to try to influence the composition of the microbiome to prevent and treat depression, anxiety, or schizophrenia. That’s where probiotics come in.
The evidence for the effects of probiotics – live microorganisms which, when ingested in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit – so far is the strongest for depression, says Viktoriya Nikolova, MRes, MSc, a PhD student and researcher at King’s College London. In their 2021 meta-analysis of seven trials, Mr. Nikolova and colleagues revealed that probiotics can significantly reduce depressive symptoms after just 8 weeks. There was a caveat, however – the probiotics only worked when used in addition to an approved antidepressant. Another meta-analysis, published in 2018, also showed that probiotics, when compared with placebo, improve mood in people with depressive symptoms (here, no antidepressant treatment was necessary).
Roumen Milev, MD, PhD, a neuroscientist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and coauthor of a review on probiotics and depression published in the Annals of General Psychiatry, warns, however, that the research is still in its infancy. “,” he says.
When it comes to using probiotics to relieve anxiety, “the evidence in the animal literature is really compelling,” says Dr. Ilardi. Human studies are less convincing, however, which Dr. Dr. Ilardi showed in his 2018 review and meta-analysis involving 743 animals and 1,527 humans. “Studies are small for the most part, and some of them aren’t terribly well conducted, and they often use very low doses of probiotics,” he says. One of the larger double-blind and placebo-controlled trials showed that supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum helps reduce stress and anxiety, while the levels of proinflammatory cytokines go down. Another meta-analysis, published in June, revealed that, when it comes to reducing stress and anxiety in youth, the results are mixed.
Evidence of probiotics’ efficiency in schizophrenia is emerging, yet also limited. A 2019 review concluded that currently available results only “hint” at a possibility that probiotics could make a difference in schizophrenia. Similarly, a 2020 review summed up that the role of probiotics in bipolar disorder “remains unclear and underexplored.”
Better studies, remaining questions
Apart from small samples, one issue with research on probiotics is that they generally tend to use varied doses of different strains of bacteria, or even multistrain mixtures, making it tough to compare results. Although there are hundreds of species of bacteria in the human gut, only a few have been evaluated for their antidepressant or antianxiety effects.
“To make it even worse, it’s almost certainly the case that depending on a person’s actual genetics or maybe their epigenetics, a strain that is helpful for one person may not be helpful for another. There is almost certainly no one-size-fits-all probiotic formulation,” says Dr. Ilardi.
Another critical question that remains to be answered is that of potential side effects.
“Probiotics are often seen as food supplements, so they don’t follow under the same regulations as drugs would,” says Mr. Nikolova. “They don’t necessarily have to follow the pattern of drug trials in many countries, which means that the monitoring of side effects is not the requirement.”
That’s something that worries King’s College psychiatrist Young too. “If you are giving it to modulate how the brain works, you could potentially induce psychiatric symptoms or a psychiatric disorder. There could be allergic reactions. There could be lots of different things,” he says.
When you search the web for “probiotics,” chances are you will come across sites boasting amazing effects that such products can have on cardiovascular heath, the immune system, and yes, mental well-being. Many also sell various probiotic supplements “formulated” for your gut health or improved moods. However, many such commercially available strains have never been actually tested in clinical trials. What’s more, according to Kathrin Cohen Kadosh, PhD, a neuroscientist at University of Surrey (England), “it is not always clear whether the different strains actually reach the gut intact.”
For now, considering the limited research evidence, a safer bet is to try to improve gut health through consumption of fermented foods that naturally contain probiotics, such as miso, kefir, or sauerkraut. Alternatively, you could reach for prebiotics, such as foods containing fiber (prebiotics enhance the growth of beneficial gut microbes). This, Dr. Kadosh says, could be “a gentler way of improving gut health” than popping a pill. Whether an improved mental well-being might follow still remains to be seen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 1950, at Staten Island’s Sea View Hospital, a group of patients with terminal tuberculosis were given a new antibiotic called isoniazid, which caused some unexpected side effects. The patients reported euphoria, mental stimulation, and improved sleep, and even began socializing with more vigor. The press was all over the case, writing about the sick “dancing in the halls tho’ they had holes in their lungs.” Soon doctors started prescribing isoniazid as the first-ever antidepressant.
The Sea View Hospital experiment was an early hint that changing the composition of the gut microbiome – in this case, via antibiotics – might affect our mental health. Yet only in the last 2 decades has research into connections between what we ingest and psychiatric disorders really taken off. In 2004, a landmark study showed that germ-free mice (born in such sterile conditions that they lacked a microbiome) had an exaggerated stress response. The effects were reversed, however, if the mice were fed a bacterial strain, Bifidobacterium infantis, a probiotic. This sparked academic interest, and thousands of research papers followed.
According to Stephen Ilardi, PhD, a clinical psychologist at the University of Kansas, Lawrence, focusing on the etiology and treatment of depression, now is the “time of exciting discovery” in the field of probiotics and psychiatric disorders, although, admittedly, a lot still remains unknown.
Gut microbiome profiles in mental health disorders
We humans have about 100 trillion microbes residing in our guts. Some of these are archaea, some fungi, some protozoans and even viruses, but most are bacteria. Things like diet, sleep, and stress can all impact the composition of our gut microbiome. When the microbiome differs considerably from the typical, doctors and researchers describe it as dysbiosis, or imbalance. Studies have uncovered dysbiosis in patients with depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.
“I think there is now pretty good evidence that the gut microbiome is actually an important factor in a number of psychiatric disorders,” says Allan Young, MBChB, clinical psychiatrist at King’s College London. The gut microbiome composition does seem to differ between psychiatric patients and the healthy. In depression, for example, a recent review of nine studies found an increase on the genus level in Streptococcus and Oscillibacter and low abundance of Lactobacillus and Coprococcus, among others. In generalized anxiety disorder, meanwhile, there appears to be an increase in Fusobacteria and Escherichia/Shigella .
For Dr. Ilardi, the next important question is whether there are plausible mechanisms that could explain how gut microbiota may influence brain function. And, it appears there are.
“The microbes in the gut can release neurotransmitters into blood that cross into the brain and influence brain function. They can release hormones into the blood that again cross into the brain. They’ve got a lot of tricks up their sleeve,” he says.
One particularly important pathway runs through the vagus nerve – the longest nerve that emerges directly from the brain, connecting it to the gut. Another is the immune pathway. Gut bacteria can interact with immune cells and reduce cytokine production, which in turn can reduce systemic inflammation. Inflammatory processes have been implicated in both depression and bipolar disorder. What’s more, gut microbes can upregulate the expression of a protein called BDNF – brain-derived neurotrophic factor – which helps the development and survival of nerve cells in the brain.
Probiotics’ promise varies for different conditions
As the pathways by which gut dysbiosis may influence psychiatric disorders become clearer, the next logical step is to try to influence the composition of the microbiome to prevent and treat depression, anxiety, or schizophrenia. That’s where probiotics come in.
The evidence for the effects of probiotics – live microorganisms which, when ingested in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit – so far is the strongest for depression, says Viktoriya Nikolova, MRes, MSc, a PhD student and researcher at King’s College London. In their 2021 meta-analysis of seven trials, Mr. Nikolova and colleagues revealed that probiotics can significantly reduce depressive symptoms after just 8 weeks. There was a caveat, however – the probiotics only worked when used in addition to an approved antidepressant. Another meta-analysis, published in 2018, also showed that probiotics, when compared with placebo, improve mood in people with depressive symptoms (here, no antidepressant treatment was necessary).
Roumen Milev, MD, PhD, a neuroscientist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and coauthor of a review on probiotics and depression published in the Annals of General Psychiatry, warns, however, that the research is still in its infancy. “,” he says.
When it comes to using probiotics to relieve anxiety, “the evidence in the animal literature is really compelling,” says Dr. Ilardi. Human studies are less convincing, however, which Dr. Dr. Ilardi showed in his 2018 review and meta-analysis involving 743 animals and 1,527 humans. “Studies are small for the most part, and some of them aren’t terribly well conducted, and they often use very low doses of probiotics,” he says. One of the larger double-blind and placebo-controlled trials showed that supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum helps reduce stress and anxiety, while the levels of proinflammatory cytokines go down. Another meta-analysis, published in June, revealed that, when it comes to reducing stress and anxiety in youth, the results are mixed.
Evidence of probiotics’ efficiency in schizophrenia is emerging, yet also limited. A 2019 review concluded that currently available results only “hint” at a possibility that probiotics could make a difference in schizophrenia. Similarly, a 2020 review summed up that the role of probiotics in bipolar disorder “remains unclear and underexplored.”
Better studies, remaining questions
Apart from small samples, one issue with research on probiotics is that they generally tend to use varied doses of different strains of bacteria, or even multistrain mixtures, making it tough to compare results. Although there are hundreds of species of bacteria in the human gut, only a few have been evaluated for their antidepressant or antianxiety effects.
“To make it even worse, it’s almost certainly the case that depending on a person’s actual genetics or maybe their epigenetics, a strain that is helpful for one person may not be helpful for another. There is almost certainly no one-size-fits-all probiotic formulation,” says Dr. Ilardi.
Another critical question that remains to be answered is that of potential side effects.
“Probiotics are often seen as food supplements, so they don’t follow under the same regulations as drugs would,” says Mr. Nikolova. “They don’t necessarily have to follow the pattern of drug trials in many countries, which means that the monitoring of side effects is not the requirement.”
That’s something that worries King’s College psychiatrist Young too. “If you are giving it to modulate how the brain works, you could potentially induce psychiatric symptoms or a psychiatric disorder. There could be allergic reactions. There could be lots of different things,” he says.
When you search the web for “probiotics,” chances are you will come across sites boasting amazing effects that such products can have on cardiovascular heath, the immune system, and yes, mental well-being. Many also sell various probiotic supplements “formulated” for your gut health or improved moods. However, many such commercially available strains have never been actually tested in clinical trials. What’s more, according to Kathrin Cohen Kadosh, PhD, a neuroscientist at University of Surrey (England), “it is not always clear whether the different strains actually reach the gut intact.”
For now, considering the limited research evidence, a safer bet is to try to improve gut health through consumption of fermented foods that naturally contain probiotics, such as miso, kefir, or sauerkraut. Alternatively, you could reach for prebiotics, such as foods containing fiber (prebiotics enhance the growth of beneficial gut microbes). This, Dr. Kadosh says, could be “a gentler way of improving gut health” than popping a pill. Whether an improved mental well-being might follow still remains to be seen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 1950, at Staten Island’s Sea View Hospital, a group of patients with terminal tuberculosis were given a new antibiotic called isoniazid, which caused some unexpected side effects. The patients reported euphoria, mental stimulation, and improved sleep, and even began socializing with more vigor. The press was all over the case, writing about the sick “dancing in the halls tho’ they had holes in their lungs.” Soon doctors started prescribing isoniazid as the first-ever antidepressant.
The Sea View Hospital experiment was an early hint that changing the composition of the gut microbiome – in this case, via antibiotics – might affect our mental health. Yet only in the last 2 decades has research into connections between what we ingest and psychiatric disorders really taken off. In 2004, a landmark study showed that germ-free mice (born in such sterile conditions that they lacked a microbiome) had an exaggerated stress response. The effects were reversed, however, if the mice were fed a bacterial strain, Bifidobacterium infantis, a probiotic. This sparked academic interest, and thousands of research papers followed.
According to Stephen Ilardi, PhD, a clinical psychologist at the University of Kansas, Lawrence, focusing on the etiology and treatment of depression, now is the “time of exciting discovery” in the field of probiotics and psychiatric disorders, although, admittedly, a lot still remains unknown.
Gut microbiome profiles in mental health disorders
We humans have about 100 trillion microbes residing in our guts. Some of these are archaea, some fungi, some protozoans and even viruses, but most are bacteria. Things like diet, sleep, and stress can all impact the composition of our gut microbiome. When the microbiome differs considerably from the typical, doctors and researchers describe it as dysbiosis, or imbalance. Studies have uncovered dysbiosis in patients with depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.
“I think there is now pretty good evidence that the gut microbiome is actually an important factor in a number of psychiatric disorders,” says Allan Young, MBChB, clinical psychiatrist at King’s College London. The gut microbiome composition does seem to differ between psychiatric patients and the healthy. In depression, for example, a recent review of nine studies found an increase on the genus level in Streptococcus and Oscillibacter and low abundance of Lactobacillus and Coprococcus, among others. In generalized anxiety disorder, meanwhile, there appears to be an increase in Fusobacteria and Escherichia/Shigella .
For Dr. Ilardi, the next important question is whether there are plausible mechanisms that could explain how gut microbiota may influence brain function. And, it appears there are.
“The microbes in the gut can release neurotransmitters into blood that cross into the brain and influence brain function. They can release hormones into the blood that again cross into the brain. They’ve got a lot of tricks up their sleeve,” he says.
One particularly important pathway runs through the vagus nerve – the longest nerve that emerges directly from the brain, connecting it to the gut. Another is the immune pathway. Gut bacteria can interact with immune cells and reduce cytokine production, which in turn can reduce systemic inflammation. Inflammatory processes have been implicated in both depression and bipolar disorder. What’s more, gut microbes can upregulate the expression of a protein called BDNF – brain-derived neurotrophic factor – which helps the development and survival of nerve cells in the brain.
Probiotics’ promise varies for different conditions
As the pathways by which gut dysbiosis may influence psychiatric disorders become clearer, the next logical step is to try to influence the composition of the microbiome to prevent and treat depression, anxiety, or schizophrenia. That’s where probiotics come in.
The evidence for the effects of probiotics – live microorganisms which, when ingested in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit – so far is the strongest for depression, says Viktoriya Nikolova, MRes, MSc, a PhD student and researcher at King’s College London. In their 2021 meta-analysis of seven trials, Mr. Nikolova and colleagues revealed that probiotics can significantly reduce depressive symptoms after just 8 weeks. There was a caveat, however – the probiotics only worked when used in addition to an approved antidepressant. Another meta-analysis, published in 2018, also showed that probiotics, when compared with placebo, improve mood in people with depressive symptoms (here, no antidepressant treatment was necessary).
Roumen Milev, MD, PhD, a neuroscientist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and coauthor of a review on probiotics and depression published in the Annals of General Psychiatry, warns, however, that the research is still in its infancy. “,” he says.
When it comes to using probiotics to relieve anxiety, “the evidence in the animal literature is really compelling,” says Dr. Ilardi. Human studies are less convincing, however, which Dr. Dr. Ilardi showed in his 2018 review and meta-analysis involving 743 animals and 1,527 humans. “Studies are small for the most part, and some of them aren’t terribly well conducted, and they often use very low doses of probiotics,” he says. One of the larger double-blind and placebo-controlled trials showed that supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum helps reduce stress and anxiety, while the levels of proinflammatory cytokines go down. Another meta-analysis, published in June, revealed that, when it comes to reducing stress and anxiety in youth, the results are mixed.
Evidence of probiotics’ efficiency in schizophrenia is emerging, yet also limited. A 2019 review concluded that currently available results only “hint” at a possibility that probiotics could make a difference in schizophrenia. Similarly, a 2020 review summed up that the role of probiotics in bipolar disorder “remains unclear and underexplored.”
Better studies, remaining questions
Apart from small samples, one issue with research on probiotics is that they generally tend to use varied doses of different strains of bacteria, or even multistrain mixtures, making it tough to compare results. Although there are hundreds of species of bacteria in the human gut, only a few have been evaluated for their antidepressant or antianxiety effects.
“To make it even worse, it’s almost certainly the case that depending on a person’s actual genetics or maybe their epigenetics, a strain that is helpful for one person may not be helpful for another. There is almost certainly no one-size-fits-all probiotic formulation,” says Dr. Ilardi.
Another critical question that remains to be answered is that of potential side effects.
“Probiotics are often seen as food supplements, so they don’t follow under the same regulations as drugs would,” says Mr. Nikolova. “They don’t necessarily have to follow the pattern of drug trials in many countries, which means that the monitoring of side effects is not the requirement.”
That’s something that worries King’s College psychiatrist Young too. “If you are giving it to modulate how the brain works, you could potentially induce psychiatric symptoms or a psychiatric disorder. There could be allergic reactions. There could be lots of different things,” he says.
When you search the web for “probiotics,” chances are you will come across sites boasting amazing effects that such products can have on cardiovascular heath, the immune system, and yes, mental well-being. Many also sell various probiotic supplements “formulated” for your gut health or improved moods. However, many such commercially available strains have never been actually tested in clinical trials. What’s more, according to Kathrin Cohen Kadosh, PhD, a neuroscientist at University of Surrey (England), “it is not always clear whether the different strains actually reach the gut intact.”
For now, considering the limited research evidence, a safer bet is to try to improve gut health through consumption of fermented foods that naturally contain probiotics, such as miso, kefir, or sauerkraut. Alternatively, you could reach for prebiotics, such as foods containing fiber (prebiotics enhance the growth of beneficial gut microbes). This, Dr. Kadosh says, could be “a gentler way of improving gut health” than popping a pill. Whether an improved mental well-being might follow still remains to be seen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is social media worsening our social fears?
Ping. Here’s a picture of your friends on a trip without you.
Ding. In your inbox, you find an email from your attending dismissing you from a very important project or patient.
Ring. There’s that call from your colleague telling you all about the incredible dinner with some other residents, which you weren’t invited to.
FoMO. Fear of missing out.
FoMO refers to a social anxiety phenomenon fueled by the need or desire to participate in an experience, event, interaction, or investment. It can be conceptualized in two parts: (1) social ostracism and (2) the need to maintain social connectedness through a sense of belonging and/or strong relationships. It is generally characterized by episodic feelings of regret, discontent, social inferiority, and/or loneliness.
Social networking sites and FoMO
Social networking sites (SNS) are a great way for people to connect instantaneously and without borders. However, they may also decrease the quality of intimate connections and relationships. In the current COVID-19 era of Zoom, most of us could agree that face-to-face and in-person communication triumphs over Internet-based interactions. I can attest that Zoom university, endless FaceTime calls, and late-night Netflix parties are not fulfilling my desire for in-person interactions. That is to say, SNS cannot fully compensate for our unmet social needs.
In fact, achieving social compensation through SNS may exacerbate social fears and anxiety disorders, and encourage rumination. For example, a recent systematic review investigating social media use among individuals who are socially anxious and lonely found that both of the foregoing factors may lead to greater negative and inhibitory behavior as a result of social media use. Feelings of inadequacy can lead to a distorted sense of oneself.
Ping. Ding. Ring. In 2021, almost half of people in the United States spend 5-6 hours on their phones daily.
Most of us are one click away from what essentially is a “live stream” of continuous updates on peoples’ lives. With these constant updates, we often start to imagine what we’re missing out on: trips, dinners, parties, and everything under the sun. However, in reality, what we see on social media is only a fraction of true reality. For example, that 10-second video of your friend going hiking cannot begin to sum up the entire day. The 24/7 nature of SNS can often lead to a perversion of the truth and unhealthy self-comparisons.
In this vicious cycle of notifications and constant entertainment, unreasonable expectations are created that adversely impact self-confidence and self-esteem, and may even lead to the emergence of depressive symptoms.
FoMO and negative associations of SNS go hand in hand. While SNS are a powerful tool for connection and information, they have also been reported to negatively impact quality of interactions.
Next time you see a picture, video, or post of a missed event, perhaps it’s best to stop thinking of the “what ifs” and start crafting your own narrative.
Ms Lui completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate. She has received income from Braxia Scientific Corp. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ping. Here’s a picture of your friends on a trip without you.
Ding. In your inbox, you find an email from your attending dismissing you from a very important project or patient.
Ring. There’s that call from your colleague telling you all about the incredible dinner with some other residents, which you weren’t invited to.
FoMO. Fear of missing out.
FoMO refers to a social anxiety phenomenon fueled by the need or desire to participate in an experience, event, interaction, or investment. It can be conceptualized in two parts: (1) social ostracism and (2) the need to maintain social connectedness through a sense of belonging and/or strong relationships. It is generally characterized by episodic feelings of regret, discontent, social inferiority, and/or loneliness.
Social networking sites and FoMO
Social networking sites (SNS) are a great way for people to connect instantaneously and without borders. However, they may also decrease the quality of intimate connections and relationships. In the current COVID-19 era of Zoom, most of us could agree that face-to-face and in-person communication triumphs over Internet-based interactions. I can attest that Zoom university, endless FaceTime calls, and late-night Netflix parties are not fulfilling my desire for in-person interactions. That is to say, SNS cannot fully compensate for our unmet social needs.
In fact, achieving social compensation through SNS may exacerbate social fears and anxiety disorders, and encourage rumination. For example, a recent systematic review investigating social media use among individuals who are socially anxious and lonely found that both of the foregoing factors may lead to greater negative and inhibitory behavior as a result of social media use. Feelings of inadequacy can lead to a distorted sense of oneself.
Ping. Ding. Ring. In 2021, almost half of people in the United States spend 5-6 hours on their phones daily.
Most of us are one click away from what essentially is a “live stream” of continuous updates on peoples’ lives. With these constant updates, we often start to imagine what we’re missing out on: trips, dinners, parties, and everything under the sun. However, in reality, what we see on social media is only a fraction of true reality. For example, that 10-second video of your friend going hiking cannot begin to sum up the entire day. The 24/7 nature of SNS can often lead to a perversion of the truth and unhealthy self-comparisons.
In this vicious cycle of notifications and constant entertainment, unreasonable expectations are created that adversely impact self-confidence and self-esteem, and may even lead to the emergence of depressive symptoms.
FoMO and negative associations of SNS go hand in hand. While SNS are a powerful tool for connection and information, they have also been reported to negatively impact quality of interactions.
Next time you see a picture, video, or post of a missed event, perhaps it’s best to stop thinking of the “what ifs” and start crafting your own narrative.
Ms Lui completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate. She has received income from Braxia Scientific Corp. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ping. Here’s a picture of your friends on a trip without you.
Ding. In your inbox, you find an email from your attending dismissing you from a very important project or patient.
Ring. There’s that call from your colleague telling you all about the incredible dinner with some other residents, which you weren’t invited to.
FoMO. Fear of missing out.
FoMO refers to a social anxiety phenomenon fueled by the need or desire to participate in an experience, event, interaction, or investment. It can be conceptualized in two parts: (1) social ostracism and (2) the need to maintain social connectedness through a sense of belonging and/or strong relationships. It is generally characterized by episodic feelings of regret, discontent, social inferiority, and/or loneliness.
Social networking sites and FoMO
Social networking sites (SNS) are a great way for people to connect instantaneously and without borders. However, they may also decrease the quality of intimate connections and relationships. In the current COVID-19 era of Zoom, most of us could agree that face-to-face and in-person communication triumphs over Internet-based interactions. I can attest that Zoom university, endless FaceTime calls, and late-night Netflix parties are not fulfilling my desire for in-person interactions. That is to say, SNS cannot fully compensate for our unmet social needs.
In fact, achieving social compensation through SNS may exacerbate social fears and anxiety disorders, and encourage rumination. For example, a recent systematic review investigating social media use among individuals who are socially anxious and lonely found that both of the foregoing factors may lead to greater negative and inhibitory behavior as a result of social media use. Feelings of inadequacy can lead to a distorted sense of oneself.
Ping. Ding. Ring. In 2021, almost half of people in the United States spend 5-6 hours on their phones daily.
Most of us are one click away from what essentially is a “live stream” of continuous updates on peoples’ lives. With these constant updates, we often start to imagine what we’re missing out on: trips, dinners, parties, and everything under the sun. However, in reality, what we see on social media is only a fraction of true reality. For example, that 10-second video of your friend going hiking cannot begin to sum up the entire day. The 24/7 nature of SNS can often lead to a perversion of the truth and unhealthy self-comparisons.
In this vicious cycle of notifications and constant entertainment, unreasonable expectations are created that adversely impact self-confidence and self-esteem, and may even lead to the emergence of depressive symptoms.
FoMO and negative associations of SNS go hand in hand. While SNS are a powerful tool for connection and information, they have also been reported to negatively impact quality of interactions.
Next time you see a picture, video, or post of a missed event, perhaps it’s best to stop thinking of the “what ifs” and start crafting your own narrative.
Ms Lui completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate. She has received income from Braxia Scientific Corp. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Office clutter linked to work, life burnout
As people begin to return to offices after working remotely, a new study suggests that clutter on the job is more than just an annoyance to neatniks. It might also be an indicator that employees are unhappy at work, especially if they have upper-level positions.
Researchers surveyed 202 office workers and linked higher perceived levels of clutter to less satisfaction/pleasure from work and more work-related burnout/tension. While the findings don’t confirm which came first – clutter or unhappiness on the job – they do suggest that the office work environment is more than an matter of appearances.
Study lead author Joseph R. Ferrari, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University, Chicago, goes even further and suggests that clutter might undermine well-being. “If someone comes into [a therapist’s office] with lots of clutter, they probably have it at home and work, and it’s hindering their life,” Dr. Ferrari said in an interview. “Having a lot of clutter piles is really not a good thing. It makes you less effective.”
Dr. Ferrari has conducted several studies into clutter. He and colleagues launched the new study, published in the International Journal of Psychological Research and Reviews, to explore the impact of clutter at the office.
“The impact of clutter on employee well-being may affect profit, staff motivation, the buildup of slack/extraneous resources, interpersonal conflict, attitudes about work, and employee behavior,” Dr. Ferrari and colleagues wrote.
The researchers surveyed participants in 290 workers in 2019 and focused on 209 who worked in offices (60% were men, 87% were 45 years old or younger, 65% held a college or advanced degree, and 79% were White). Most were lower-level employees rather than higher-level employees with management responsibilities.
Both upper-and lower-level employees mentioned the same types of clutter most often – paper, office equipment, and trash, such as used coffee cups. The upper-level workers reported more problems with clutter, although this might be because they are more sensitive to it than lower-level workers, Dr. Ferrari said.
The researchers found that “office clutter was significantly negatively related to ... satisfaction/pleasure from work and significantly positively related to a risk for burnout/tension from work.” They also reported that “upper-level workers were significantly more likely to report clutter and being at risk for burnout/tension than lower-level workers.”
Specifically, a technique known as exploratory factor analysis determined that “63% of office clutter behavior can be explained by either satisfaction/pleasure with one’s work or risk for burnout,” Dr. Ferrari said. The findings suggest that clutter leads to negative feelings about work, not the other way around, he said.
The new study does not address whether clutter has positive attributes, as suggested by a 2013 report published in Psychological Science.
Darby Saxbe, PhD, an associate professor of psychology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, who studies work stress, said in an interview that it can be difficult to figure out the direction of causality in a study like this. “Someone who’s overwhelmed might generate more clutter and not have the bandwidth to put things away. If the space is really cluttered, you won’t be able to find things as effectively, or keep track of projects as well, and that will feed more feelings of stress and burnout.”
David Spiegel, MD, Willson Professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Stanford (Calif.) University, agreed.
“The idea of clutter in the environment having a negative effect on mood is interesting, but it is equally likely that clutter reflects burnout, inability to complete tasks and dispose of their remnants,” he said in an interview. “There may be a relationship, and they may interact, but the direction is not clear,” said Dr. Spiegel, who is also director of Stanford’s Center on Stress and Health.
Still, he said, “in these days of Zoom therapy, observing clutter in a patient’s room or office may provide a hint about potential burnout and depression.”
No funding is reported. Dr. Ferrari, Dr. Saxbe, and Dr. Spiegel reported no disclosures.
As people begin to return to offices after working remotely, a new study suggests that clutter on the job is more than just an annoyance to neatniks. It might also be an indicator that employees are unhappy at work, especially if they have upper-level positions.
Researchers surveyed 202 office workers and linked higher perceived levels of clutter to less satisfaction/pleasure from work and more work-related burnout/tension. While the findings don’t confirm which came first – clutter or unhappiness on the job – they do suggest that the office work environment is more than an matter of appearances.
Study lead author Joseph R. Ferrari, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University, Chicago, goes even further and suggests that clutter might undermine well-being. “If someone comes into [a therapist’s office] with lots of clutter, they probably have it at home and work, and it’s hindering their life,” Dr. Ferrari said in an interview. “Having a lot of clutter piles is really not a good thing. It makes you less effective.”
Dr. Ferrari has conducted several studies into clutter. He and colleagues launched the new study, published in the International Journal of Psychological Research and Reviews, to explore the impact of clutter at the office.
“The impact of clutter on employee well-being may affect profit, staff motivation, the buildup of slack/extraneous resources, interpersonal conflict, attitudes about work, and employee behavior,” Dr. Ferrari and colleagues wrote.
The researchers surveyed participants in 290 workers in 2019 and focused on 209 who worked in offices (60% were men, 87% were 45 years old or younger, 65% held a college or advanced degree, and 79% were White). Most were lower-level employees rather than higher-level employees with management responsibilities.
Both upper-and lower-level employees mentioned the same types of clutter most often – paper, office equipment, and trash, such as used coffee cups. The upper-level workers reported more problems with clutter, although this might be because they are more sensitive to it than lower-level workers, Dr. Ferrari said.
The researchers found that “office clutter was significantly negatively related to ... satisfaction/pleasure from work and significantly positively related to a risk for burnout/tension from work.” They also reported that “upper-level workers were significantly more likely to report clutter and being at risk for burnout/tension than lower-level workers.”
Specifically, a technique known as exploratory factor analysis determined that “63% of office clutter behavior can be explained by either satisfaction/pleasure with one’s work or risk for burnout,” Dr. Ferrari said. The findings suggest that clutter leads to negative feelings about work, not the other way around, he said.
The new study does not address whether clutter has positive attributes, as suggested by a 2013 report published in Psychological Science.
Darby Saxbe, PhD, an associate professor of psychology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, who studies work stress, said in an interview that it can be difficult to figure out the direction of causality in a study like this. “Someone who’s overwhelmed might generate more clutter and not have the bandwidth to put things away. If the space is really cluttered, you won’t be able to find things as effectively, or keep track of projects as well, and that will feed more feelings of stress and burnout.”
David Spiegel, MD, Willson Professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Stanford (Calif.) University, agreed.
“The idea of clutter in the environment having a negative effect on mood is interesting, but it is equally likely that clutter reflects burnout, inability to complete tasks and dispose of their remnants,” he said in an interview. “There may be a relationship, and they may interact, but the direction is not clear,” said Dr. Spiegel, who is also director of Stanford’s Center on Stress and Health.
Still, he said, “in these days of Zoom therapy, observing clutter in a patient’s room or office may provide a hint about potential burnout and depression.”
No funding is reported. Dr. Ferrari, Dr. Saxbe, and Dr. Spiegel reported no disclosures.
As people begin to return to offices after working remotely, a new study suggests that clutter on the job is more than just an annoyance to neatniks. It might also be an indicator that employees are unhappy at work, especially if they have upper-level positions.
Researchers surveyed 202 office workers and linked higher perceived levels of clutter to less satisfaction/pleasure from work and more work-related burnout/tension. While the findings don’t confirm which came first – clutter or unhappiness on the job – they do suggest that the office work environment is more than an matter of appearances.
Study lead author Joseph R. Ferrari, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University, Chicago, goes even further and suggests that clutter might undermine well-being. “If someone comes into [a therapist’s office] with lots of clutter, they probably have it at home and work, and it’s hindering their life,” Dr. Ferrari said in an interview. “Having a lot of clutter piles is really not a good thing. It makes you less effective.”
Dr. Ferrari has conducted several studies into clutter. He and colleagues launched the new study, published in the International Journal of Psychological Research and Reviews, to explore the impact of clutter at the office.
“The impact of clutter on employee well-being may affect profit, staff motivation, the buildup of slack/extraneous resources, interpersonal conflict, attitudes about work, and employee behavior,” Dr. Ferrari and colleagues wrote.
The researchers surveyed participants in 290 workers in 2019 and focused on 209 who worked in offices (60% were men, 87% were 45 years old or younger, 65% held a college or advanced degree, and 79% were White). Most were lower-level employees rather than higher-level employees with management responsibilities.
Both upper-and lower-level employees mentioned the same types of clutter most often – paper, office equipment, and trash, such as used coffee cups. The upper-level workers reported more problems with clutter, although this might be because they are more sensitive to it than lower-level workers, Dr. Ferrari said.
The researchers found that “office clutter was significantly negatively related to ... satisfaction/pleasure from work and significantly positively related to a risk for burnout/tension from work.” They also reported that “upper-level workers were significantly more likely to report clutter and being at risk for burnout/tension than lower-level workers.”
Specifically, a technique known as exploratory factor analysis determined that “63% of office clutter behavior can be explained by either satisfaction/pleasure with one’s work or risk for burnout,” Dr. Ferrari said. The findings suggest that clutter leads to negative feelings about work, not the other way around, he said.
The new study does not address whether clutter has positive attributes, as suggested by a 2013 report published in Psychological Science.
Darby Saxbe, PhD, an associate professor of psychology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, who studies work stress, said in an interview that it can be difficult to figure out the direction of causality in a study like this. “Someone who’s overwhelmed might generate more clutter and not have the bandwidth to put things away. If the space is really cluttered, you won’t be able to find things as effectively, or keep track of projects as well, and that will feed more feelings of stress and burnout.”
David Spiegel, MD, Willson Professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Stanford (Calif.) University, agreed.
“The idea of clutter in the environment having a negative effect on mood is interesting, but it is equally likely that clutter reflects burnout, inability to complete tasks and dispose of their remnants,” he said in an interview. “There may be a relationship, and they may interact, but the direction is not clear,” said Dr. Spiegel, who is also director of Stanford’s Center on Stress and Health.
Still, he said, “in these days of Zoom therapy, observing clutter in a patient’s room or office may provide a hint about potential burnout and depression.”
No funding is reported. Dr. Ferrari, Dr. Saxbe, and Dr. Spiegel reported no disclosures.
FROM THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH AND REVIEWS
CBT via telehealth or in-person: Which is best for insomnia?
Telehealth can be effective for delivering cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) – and is not inferior to in-person treatment, new research suggests.
Results from a study of 60 adults with insomnia disorder showed no significant between-group difference at 3-month follow-up between those assigned to receive in-person CBT-I and those assigned to telehealth CBT-I in regard to change in score on the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI).
In addition, both groups showed significant change compared with a wait-list group, indicating that telehealth was not inferior to the in-person mode of delivery, the investigators note.
“The take-home message is that patients with insomnia can be treated with cognitive-behavioral treatment for insomnia by video telehealth without sacrificing clinical gains,” study investigator Philip Gehrman, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“This fits with the broader telehealth literature that has shown that other forms of therapy can be delivered this way without losing efficacy, so it is likely that telehealth is a viable option for therapy in general,” he said.
The findings were published online August 24 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Telehealth ‘explosion’
Although CBT-I is the recommended intervention for insomnia, “widespread implementation of CBT-I is limited by the lack of clinicians who are trained in this treatment,” the investigators note. There is a “need for strategies to increase access, particularly for patients in areas with few health care providers.”
Telehealth is a promising technology for providing treatment, without the necessity of having the patient and the practitioner in the same place. There has been an “explosion” in its use because of restrictions necessitated by the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the “rapid deployment of telehealth interventions did not allow time to assess this approach in a controlled manner,” so it is possible that this type of communication might reduce treatment efficacy, the investigators note.
Previous research suggests that telehealth psychotherapeutic treatments in general are not inferior to in-person treatments. One study showed that CBT-I delivered via telehealth was noninferior to in-person delivery. However, that study did not include a control group.
“I have been doing telehealth clinical work for about 10 years – so way before the pandemic pushed everything virtual,” Dr. Gehrman said. “But when I would talk about my telehealth work to other providers, I would frequently get asked whether the advantages of telehealth (greater access to care, reduced travel costs) came at a price of lower efficacy.”
Dr. Gehrman said he suspected that telehealth treatment was just as effective and wanted to formally test this impression to see whether he was correct.
The investigators randomly assigned 60 adults (mean age, 32.72 years; mean ISI score, 17.0; 65% women) with insomnia disorder to in-person CBT-I (n = 20), telehealth-delivered CBT-I (n = 21), or to a wait-list control group (n = 19). For the study, insomnia disorder was determined on the basis of DSM-5 criteria.
Most participants had completed college or postgraduate school (43% and 37%, respectively) and did not have many comorbidities.
The primary outcome was change on the ISI. Other assessments included measures of depression, anxiety, work and social adjustment, fatigue, and medical outcomes. Participants also completed a home unattended sleep study using a portable monitor to screen participants for obstructive sleep apnea.
Both types of CBT-I were delivered over 6 to 8 weekly sessions, with 2-week and 3-month post-treatment follow-ups.
An a priori margin of -3.0 points was used in the noninferiority analysis, and all analyses were conducted using mixed-effects models, the authors explain.
Necessary evil?
In the primary noninferiority analyses, the mean change in ISI score from baseline to 3-month follow-up was -7.8 points for in-person CBT-I, -7.5 points for telehealth, and -1.6 for wait list.
The difference between the CBT-I groups was not statistically significant (t 28 = -0.98, P = .33).
“The lower confidence limit of this between-group difference in the mean ISI changes was greater than the a priori margin of -3.0 points, indicating that telehealth treatment was not inferior to in-person treatment,” the investigators write.
Although there were significant improvements on most secondary outcome measures related to mood/anxiety and daytime functioning, the investigators found no group differences.
The findings suggest that the benefits of telehealth, including increased access and reduced travel time, “do not come with a cost of reduced efficacy,” the researchers write.
However, the results “underscore that the use of telehealth during the pandemic is not a ‘necessary evil,’ but rather a means of providing high quality care while reducing risks of exposure,” they write.
Benefits, fidelity maintained
Commenting on the study, J. Todd Arnedt, PhD, professor of psychiatry and neurology and co-director of the Sleep and Circadian Research Laboratory, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said it is “one of the first studies to clearly demonstrate that the benefits and fidelity of CBT for insomnia, which is most commonly delivered in-person, can be maintained with telehealth delivery.”
Dr. Arnedt is also director of the Behavioral Sleep Medicine Program and was not involved in the study. He said the findings “support the use of this modality by providers to expand access to this highly effective but underutilized insomnia treatment.”
Additionally, telehealth delivery of CBT-I “offers a safe and effective alternative to in-person care for improving insomnia and associated daytime consequences and has the potential to reduce health care disparities by increasing availability to underserved communities,” Dr. Arnedt said.
However, the investigators point out that the utility of this approach for underserved communities needs further investigation. A study limitation was that the participants were “generally healthy and well educated.”
In addition, further research is needed to see whether the findings can be generalized to individuals who have “more complicated health or socioeconomic difficulties,” they write.
The study was funded by a grant from the American Sleep Medicine Foundation and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation Clinical Scientist Development Award. Dr. Gehrman has received research funding from Merck, is a consultant to WW, and serves on the scientific advisory board of Eight Sleep. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Arnedt reports no relevant financial relationships but notes that he was the principal investigator of a similar study run in parallel to this one that was also funded by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation at the same time.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth can be effective for delivering cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) – and is not inferior to in-person treatment, new research suggests.
Results from a study of 60 adults with insomnia disorder showed no significant between-group difference at 3-month follow-up between those assigned to receive in-person CBT-I and those assigned to telehealth CBT-I in regard to change in score on the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI).
In addition, both groups showed significant change compared with a wait-list group, indicating that telehealth was not inferior to the in-person mode of delivery, the investigators note.
“The take-home message is that patients with insomnia can be treated with cognitive-behavioral treatment for insomnia by video telehealth without sacrificing clinical gains,” study investigator Philip Gehrman, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“This fits with the broader telehealth literature that has shown that other forms of therapy can be delivered this way without losing efficacy, so it is likely that telehealth is a viable option for therapy in general,” he said.
The findings were published online August 24 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Telehealth ‘explosion’
Although CBT-I is the recommended intervention for insomnia, “widespread implementation of CBT-I is limited by the lack of clinicians who are trained in this treatment,” the investigators note. There is a “need for strategies to increase access, particularly for patients in areas with few health care providers.”
Telehealth is a promising technology for providing treatment, without the necessity of having the patient and the practitioner in the same place. There has been an “explosion” in its use because of restrictions necessitated by the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the “rapid deployment of telehealth interventions did not allow time to assess this approach in a controlled manner,” so it is possible that this type of communication might reduce treatment efficacy, the investigators note.
Previous research suggests that telehealth psychotherapeutic treatments in general are not inferior to in-person treatments. One study showed that CBT-I delivered via telehealth was noninferior to in-person delivery. However, that study did not include a control group.
“I have been doing telehealth clinical work for about 10 years – so way before the pandemic pushed everything virtual,” Dr. Gehrman said. “But when I would talk about my telehealth work to other providers, I would frequently get asked whether the advantages of telehealth (greater access to care, reduced travel costs) came at a price of lower efficacy.”
Dr. Gehrman said he suspected that telehealth treatment was just as effective and wanted to formally test this impression to see whether he was correct.
The investigators randomly assigned 60 adults (mean age, 32.72 years; mean ISI score, 17.0; 65% women) with insomnia disorder to in-person CBT-I (n = 20), telehealth-delivered CBT-I (n = 21), or to a wait-list control group (n = 19). For the study, insomnia disorder was determined on the basis of DSM-5 criteria.
Most participants had completed college or postgraduate school (43% and 37%, respectively) and did not have many comorbidities.
The primary outcome was change on the ISI. Other assessments included measures of depression, anxiety, work and social adjustment, fatigue, and medical outcomes. Participants also completed a home unattended sleep study using a portable monitor to screen participants for obstructive sleep apnea.
Both types of CBT-I were delivered over 6 to 8 weekly sessions, with 2-week and 3-month post-treatment follow-ups.
An a priori margin of -3.0 points was used in the noninferiority analysis, and all analyses were conducted using mixed-effects models, the authors explain.
Necessary evil?
In the primary noninferiority analyses, the mean change in ISI score from baseline to 3-month follow-up was -7.8 points for in-person CBT-I, -7.5 points for telehealth, and -1.6 for wait list.
The difference between the CBT-I groups was not statistically significant (t 28 = -0.98, P = .33).
“The lower confidence limit of this between-group difference in the mean ISI changes was greater than the a priori margin of -3.0 points, indicating that telehealth treatment was not inferior to in-person treatment,” the investigators write.
Although there were significant improvements on most secondary outcome measures related to mood/anxiety and daytime functioning, the investigators found no group differences.
The findings suggest that the benefits of telehealth, including increased access and reduced travel time, “do not come with a cost of reduced efficacy,” the researchers write.
However, the results “underscore that the use of telehealth during the pandemic is not a ‘necessary evil,’ but rather a means of providing high quality care while reducing risks of exposure,” they write.
Benefits, fidelity maintained
Commenting on the study, J. Todd Arnedt, PhD, professor of psychiatry and neurology and co-director of the Sleep and Circadian Research Laboratory, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said it is “one of the first studies to clearly demonstrate that the benefits and fidelity of CBT for insomnia, which is most commonly delivered in-person, can be maintained with telehealth delivery.”
Dr. Arnedt is also director of the Behavioral Sleep Medicine Program and was not involved in the study. He said the findings “support the use of this modality by providers to expand access to this highly effective but underutilized insomnia treatment.”
Additionally, telehealth delivery of CBT-I “offers a safe and effective alternative to in-person care for improving insomnia and associated daytime consequences and has the potential to reduce health care disparities by increasing availability to underserved communities,” Dr. Arnedt said.
However, the investigators point out that the utility of this approach for underserved communities needs further investigation. A study limitation was that the participants were “generally healthy and well educated.”
In addition, further research is needed to see whether the findings can be generalized to individuals who have “more complicated health or socioeconomic difficulties,” they write.
The study was funded by a grant from the American Sleep Medicine Foundation and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation Clinical Scientist Development Award. Dr. Gehrman has received research funding from Merck, is a consultant to WW, and serves on the scientific advisory board of Eight Sleep. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Arnedt reports no relevant financial relationships but notes that he was the principal investigator of a similar study run in parallel to this one that was also funded by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation at the same time.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth can be effective for delivering cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) – and is not inferior to in-person treatment, new research suggests.
Results from a study of 60 adults with insomnia disorder showed no significant between-group difference at 3-month follow-up between those assigned to receive in-person CBT-I and those assigned to telehealth CBT-I in regard to change in score on the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI).
In addition, both groups showed significant change compared with a wait-list group, indicating that telehealth was not inferior to the in-person mode of delivery, the investigators note.
“The take-home message is that patients with insomnia can be treated with cognitive-behavioral treatment for insomnia by video telehealth without sacrificing clinical gains,” study investigator Philip Gehrman, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“This fits with the broader telehealth literature that has shown that other forms of therapy can be delivered this way without losing efficacy, so it is likely that telehealth is a viable option for therapy in general,” he said.
The findings were published online August 24 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Telehealth ‘explosion’
Although CBT-I is the recommended intervention for insomnia, “widespread implementation of CBT-I is limited by the lack of clinicians who are trained in this treatment,” the investigators note. There is a “need for strategies to increase access, particularly for patients in areas with few health care providers.”
Telehealth is a promising technology for providing treatment, without the necessity of having the patient and the practitioner in the same place. There has been an “explosion” in its use because of restrictions necessitated by the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the “rapid deployment of telehealth interventions did not allow time to assess this approach in a controlled manner,” so it is possible that this type of communication might reduce treatment efficacy, the investigators note.
Previous research suggests that telehealth psychotherapeutic treatments in general are not inferior to in-person treatments. One study showed that CBT-I delivered via telehealth was noninferior to in-person delivery. However, that study did not include a control group.
“I have been doing telehealth clinical work for about 10 years – so way before the pandemic pushed everything virtual,” Dr. Gehrman said. “But when I would talk about my telehealth work to other providers, I would frequently get asked whether the advantages of telehealth (greater access to care, reduced travel costs) came at a price of lower efficacy.”
Dr. Gehrman said he suspected that telehealth treatment was just as effective and wanted to formally test this impression to see whether he was correct.
The investigators randomly assigned 60 adults (mean age, 32.72 years; mean ISI score, 17.0; 65% women) with insomnia disorder to in-person CBT-I (n = 20), telehealth-delivered CBT-I (n = 21), or to a wait-list control group (n = 19). For the study, insomnia disorder was determined on the basis of DSM-5 criteria.
Most participants had completed college or postgraduate school (43% and 37%, respectively) and did not have many comorbidities.
The primary outcome was change on the ISI. Other assessments included measures of depression, anxiety, work and social adjustment, fatigue, and medical outcomes. Participants also completed a home unattended sleep study using a portable monitor to screen participants for obstructive sleep apnea.
Both types of CBT-I were delivered over 6 to 8 weekly sessions, with 2-week and 3-month post-treatment follow-ups.
An a priori margin of -3.0 points was used in the noninferiority analysis, and all analyses were conducted using mixed-effects models, the authors explain.
Necessary evil?
In the primary noninferiority analyses, the mean change in ISI score from baseline to 3-month follow-up was -7.8 points for in-person CBT-I, -7.5 points for telehealth, and -1.6 for wait list.
The difference between the CBT-I groups was not statistically significant (t 28 = -0.98, P = .33).
“The lower confidence limit of this between-group difference in the mean ISI changes was greater than the a priori margin of -3.0 points, indicating that telehealth treatment was not inferior to in-person treatment,” the investigators write.
Although there were significant improvements on most secondary outcome measures related to mood/anxiety and daytime functioning, the investigators found no group differences.
The findings suggest that the benefits of telehealth, including increased access and reduced travel time, “do not come with a cost of reduced efficacy,” the researchers write.
However, the results “underscore that the use of telehealth during the pandemic is not a ‘necessary evil,’ but rather a means of providing high quality care while reducing risks of exposure,” they write.
Benefits, fidelity maintained
Commenting on the study, J. Todd Arnedt, PhD, professor of psychiatry and neurology and co-director of the Sleep and Circadian Research Laboratory, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said it is “one of the first studies to clearly demonstrate that the benefits and fidelity of CBT for insomnia, which is most commonly delivered in-person, can be maintained with telehealth delivery.”
Dr. Arnedt is also director of the Behavioral Sleep Medicine Program and was not involved in the study. He said the findings “support the use of this modality by providers to expand access to this highly effective but underutilized insomnia treatment.”
Additionally, telehealth delivery of CBT-I “offers a safe and effective alternative to in-person care for improving insomnia and associated daytime consequences and has the potential to reduce health care disparities by increasing availability to underserved communities,” Dr. Arnedt said.
However, the investigators point out that the utility of this approach for underserved communities needs further investigation. A study limitation was that the participants were “generally healthy and well educated.”
In addition, further research is needed to see whether the findings can be generalized to individuals who have “more complicated health or socioeconomic difficulties,” they write.
The study was funded by a grant from the American Sleep Medicine Foundation and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation Clinical Scientist Development Award. Dr. Gehrman has received research funding from Merck, is a consultant to WW, and serves on the scientific advisory board of Eight Sleep. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Arnedt reports no relevant financial relationships but notes that he was the principal investigator of a similar study run in parallel to this one that was also funded by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation at the same time.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.