User login
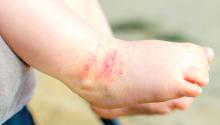
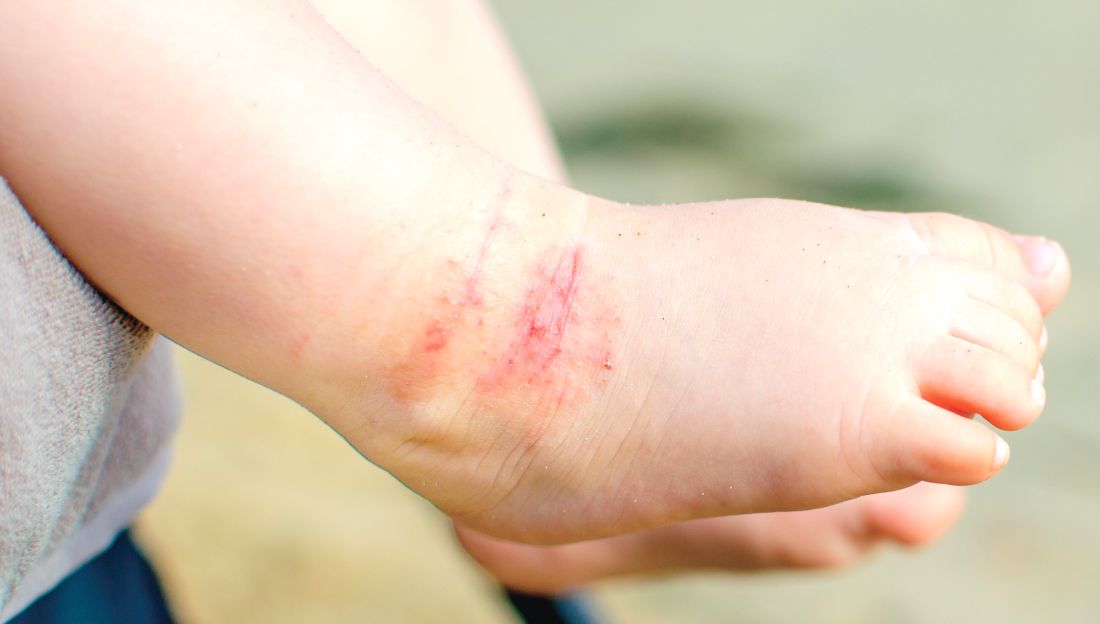
Parental atopic dermatitis, asthma linked to risk of AD in offspring
of life, an analysis of a large birth cohort found.
“The prevalence of AD in children has increased dramatically in recent years, and most studies reporting the impact of parental atopic history on AD are based on older data,” wrote the study authors, led by Cathal O’Connor, MD. “Given the recent interest in early intervention to prevent AD and other allergic diseases, enhanced early identification of infants at risk of AD is increasingly important.”
The detailed analysis of AD risk associated with parental atopy in early life “may help to risk stratify infants to optimize early interventions for prevention or early treatment of AD,” they wrote.
The study was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
For the analysis, Dr. O’Connor of the department of pediatrics and child health at University College Cork (Ireland) and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of the Cork Babies After Scope: Evaluating the Longitudinal Impact Using Neurological and Nutritional Endpoints (BASELINE) Birth Cohort Study.
The study recruited 2,183 healthy first-born babies between August 2009 and October 2011 to examine the effects of environmental factors during pregnancy and infancy on childhood health and development. Skin barrier assessments were performed at birth, 2 months, 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months using a validated open chamber system to measure transepidermal water loss.
Parental atopy was self-reported at 2 months. Parents were asked at 2 months if the infant had an “itchy rash on the face or in the folds of the arms or legs,” as a screening question for AD. Experienced health care personnel used UK Working Party criteria to diagnose AD at 6, 12, and 24 months.
Complete data on AD status was available for 1,505 children in the cohort. Dr. O’Connor and colleagues calculated an overall AD prevalence of 18.6% at 6 months, 15.2% at 12 months, and 16.5% at 24 months.
Overall prevalence of AD was highest at 6 months. The study showed a similar or slightly higher impact of paternal atopy on offspring AD development, compared to maternal atopy.
Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that the odds of AD were 1.57 at 6 months and 1.66 at 12 months for maternal AD; 1.90 at 6 months and 1.85 at 24 months for paternal AD; 1.76 at 6 months and 1.75 at 12 months for maternal asthma; and 1.70 at 6 months, 1.86 at 12 months, and 1.99 at 24 months for paternal asthma.
“Parental allergic rhinitis was not associated with AD in offspring in the first 2 years, except for maternal rhinitis at 24 months [an adjusted odds ratio of 1.79],” the authors wrote. “The genetic predisposition to allergic rhinitis, given the key role of aeroallergen sensitization in its pathogenesis, may not be associated with early onset AD, but may have a greater impact in later onset or persistent AD.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it was a secondary data analysis, and that parental AD, asthma, and rhinitis were self-reported, “which may reduce reliability and may contribute to the differences seen between the impact of maternal and paternal reported atopy on offspring,” they wrote. “Data on siblings were not captured, as participants in the study were first-born children. Filaggrin mutational analysis was not performed, which would have provided richer detail.”
Kelly M. Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study confirms the well-known association between parental atopy and the risk of atopy in offspring, which has been shown in several studies dating back decades.
“The authors try to parse risk based on maternal or paternal or biparental history of AD and/or asthma and/or rhinitis, but this type of nuanced analysis when diagnosis is based solely on parental report may be an over-reach,” she said.
“Given that this data supports the association between parental atopy and risk of AD in infants at various time points, the clinically relevant immediate next question is how can we leverage this knowledge to prevent onset of AD in infants at risk?” she said. “To date, interventions such as early introduction of emollients have been evaluated with mixed results.”
A recent Cochrane analysis concluded that, based on available data, skin care interventions such as emollient use during the first year of life in otherwise healthy infants is probably not effective for preventing eczema and may increase risk of skin infection.
“Effects of skin care interventions on risk of asthma are also uncertain,” said Dr. Cordoro, who is also chief of the division of pediatric dermatology at UCSF.
“In sum, this study offers additional data in support of the link between atopy in parents and offspring,” she said. “Understanding how to mitigate risk and prevent atopy requires unraveling of the complex interplay between genetic, environmental, immunologic, microbial and other factors. For now, dermatologists are unable to make broad evidence-based recommendations for otherwise healthy (i.e., with normal skin) but at-risk infants in terms of approaches to skin care that might prevent eczema and asthma.”
of life, an analysis of a large birth cohort found.
“The prevalence of AD in children has increased dramatically in recent years, and most studies reporting the impact of parental atopic history on AD are based on older data,” wrote the study authors, led by Cathal O’Connor, MD. “Given the recent interest in early intervention to prevent AD and other allergic diseases, enhanced early identification of infants at risk of AD is increasingly important.”
The detailed analysis of AD risk associated with parental atopy in early life “may help to risk stratify infants to optimize early interventions for prevention or early treatment of AD,” they wrote.
The study was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
For the analysis, Dr. O’Connor of the department of pediatrics and child health at University College Cork (Ireland) and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of the Cork Babies After Scope: Evaluating the Longitudinal Impact Using Neurological and Nutritional Endpoints (BASELINE) Birth Cohort Study.
The study recruited 2,183 healthy first-born babies between August 2009 and October 2011 to examine the effects of environmental factors during pregnancy and infancy on childhood health and development. Skin barrier assessments were performed at birth, 2 months, 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months using a validated open chamber system to measure transepidermal water loss.
Parental atopy was self-reported at 2 months. Parents were asked at 2 months if the infant had an “itchy rash on the face or in the folds of the arms or legs,” as a screening question for AD. Experienced health care personnel used UK Working Party criteria to diagnose AD at 6, 12, and 24 months.
Complete data on AD status was available for 1,505 children in the cohort. Dr. O’Connor and colleagues calculated an overall AD prevalence of 18.6% at 6 months, 15.2% at 12 months, and 16.5% at 24 months.
Overall prevalence of AD was highest at 6 months. The study showed a similar or slightly higher impact of paternal atopy on offspring AD development, compared to maternal atopy.
Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that the odds of AD were 1.57 at 6 months and 1.66 at 12 months for maternal AD; 1.90 at 6 months and 1.85 at 24 months for paternal AD; 1.76 at 6 months and 1.75 at 12 months for maternal asthma; and 1.70 at 6 months, 1.86 at 12 months, and 1.99 at 24 months for paternal asthma.
“Parental allergic rhinitis was not associated with AD in offspring in the first 2 years, except for maternal rhinitis at 24 months [an adjusted odds ratio of 1.79],” the authors wrote. “The genetic predisposition to allergic rhinitis, given the key role of aeroallergen sensitization in its pathogenesis, may not be associated with early onset AD, but may have a greater impact in later onset or persistent AD.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it was a secondary data analysis, and that parental AD, asthma, and rhinitis were self-reported, “which may reduce reliability and may contribute to the differences seen between the impact of maternal and paternal reported atopy on offspring,” they wrote. “Data on siblings were not captured, as participants in the study were first-born children. Filaggrin mutational analysis was not performed, which would have provided richer detail.”
Kelly M. Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study confirms the well-known association between parental atopy and the risk of atopy in offspring, which has been shown in several studies dating back decades.
“The authors try to parse risk based on maternal or paternal or biparental history of AD and/or asthma and/or rhinitis, but this type of nuanced analysis when diagnosis is based solely on parental report may be an over-reach,” she said.
“Given that this data supports the association between parental atopy and risk of AD in infants at various time points, the clinically relevant immediate next question is how can we leverage this knowledge to prevent onset of AD in infants at risk?” she said. “To date, interventions such as early introduction of emollients have been evaluated with mixed results.”
A recent Cochrane analysis concluded that, based on available data, skin care interventions such as emollient use during the first year of life in otherwise healthy infants is probably not effective for preventing eczema and may increase risk of skin infection.
“Effects of skin care interventions on risk of asthma are also uncertain,” said Dr. Cordoro, who is also chief of the division of pediatric dermatology at UCSF.
“In sum, this study offers additional data in support of the link between atopy in parents and offspring,” she said. “Understanding how to mitigate risk and prevent atopy requires unraveling of the complex interplay between genetic, environmental, immunologic, microbial and other factors. For now, dermatologists are unable to make broad evidence-based recommendations for otherwise healthy (i.e., with normal skin) but at-risk infants in terms of approaches to skin care that might prevent eczema and asthma.”
of life, an analysis of a large birth cohort found.
“The prevalence of AD in children has increased dramatically in recent years, and most studies reporting the impact of parental atopic history on AD are based on older data,” wrote the study authors, led by Cathal O’Connor, MD. “Given the recent interest in early intervention to prevent AD and other allergic diseases, enhanced early identification of infants at risk of AD is increasingly important.”
The detailed analysis of AD risk associated with parental atopy in early life “may help to risk stratify infants to optimize early interventions for prevention or early treatment of AD,” they wrote.
The study was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
For the analysis, Dr. O’Connor of the department of pediatrics and child health at University College Cork (Ireland) and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of the Cork Babies After Scope: Evaluating the Longitudinal Impact Using Neurological and Nutritional Endpoints (BASELINE) Birth Cohort Study.
The study recruited 2,183 healthy first-born babies between August 2009 and October 2011 to examine the effects of environmental factors during pregnancy and infancy on childhood health and development. Skin barrier assessments were performed at birth, 2 months, 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months using a validated open chamber system to measure transepidermal water loss.
Parental atopy was self-reported at 2 months. Parents were asked at 2 months if the infant had an “itchy rash on the face or in the folds of the arms or legs,” as a screening question for AD. Experienced health care personnel used UK Working Party criteria to diagnose AD at 6, 12, and 24 months.
Complete data on AD status was available for 1,505 children in the cohort. Dr. O’Connor and colleagues calculated an overall AD prevalence of 18.6% at 6 months, 15.2% at 12 months, and 16.5% at 24 months.
Overall prevalence of AD was highest at 6 months. The study showed a similar or slightly higher impact of paternal atopy on offspring AD development, compared to maternal atopy.
Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that the odds of AD were 1.57 at 6 months and 1.66 at 12 months for maternal AD; 1.90 at 6 months and 1.85 at 24 months for paternal AD; 1.76 at 6 months and 1.75 at 12 months for maternal asthma; and 1.70 at 6 months, 1.86 at 12 months, and 1.99 at 24 months for paternal asthma.
“Parental allergic rhinitis was not associated with AD in offspring in the first 2 years, except for maternal rhinitis at 24 months [an adjusted odds ratio of 1.79],” the authors wrote. “The genetic predisposition to allergic rhinitis, given the key role of aeroallergen sensitization in its pathogenesis, may not be associated with early onset AD, but may have a greater impact in later onset or persistent AD.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it was a secondary data analysis, and that parental AD, asthma, and rhinitis were self-reported, “which may reduce reliability and may contribute to the differences seen between the impact of maternal and paternal reported atopy on offspring,” they wrote. “Data on siblings were not captured, as participants in the study were first-born children. Filaggrin mutational analysis was not performed, which would have provided richer detail.”
Kelly M. Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study confirms the well-known association between parental atopy and the risk of atopy in offspring, which has been shown in several studies dating back decades.
“The authors try to parse risk based on maternal or paternal or biparental history of AD and/or asthma and/or rhinitis, but this type of nuanced analysis when diagnosis is based solely on parental report may be an over-reach,” she said.
“Given that this data supports the association between parental atopy and risk of AD in infants at various time points, the clinically relevant immediate next question is how can we leverage this knowledge to prevent onset of AD in infants at risk?” she said. “To date, interventions such as early introduction of emollients have been evaluated with mixed results.”
A recent Cochrane analysis concluded that, based on available data, skin care interventions such as emollient use during the first year of life in otherwise healthy infants is probably not effective for preventing eczema and may increase risk of skin infection.
“Effects of skin care interventions on risk of asthma are also uncertain,” said Dr. Cordoro, who is also chief of the division of pediatric dermatology at UCSF.
“In sum, this study offers additional data in support of the link between atopy in parents and offspring,” she said. “Understanding how to mitigate risk and prevent atopy requires unraveling of the complex interplay between genetic, environmental, immunologic, microbial and other factors. For now, dermatologists are unable to make broad evidence-based recommendations for otherwise healthy (i.e., with normal skin) but at-risk infants in terms of approaches to skin care that might prevent eczema and asthma.”
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Pooled safety data analysis of tralokinumab reported
The most , according to a review published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
These findings underscore the mechanistic elegance of interleukin (IL)-13 inhibition and highlight potential advantages of flexible dosing, according to the study’s lead author, Eric Simpson, MD, MCR. Overall, the pooled analysis of safety data from five phase 2 and 3 trials shows that “blockade of a single cytokine provides excellent short- and long-term safety, which is useful for a severe chronic disease,” said Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
Most patients with AD require years of treatment. “So for clinicians to confidently report to patients the low rates of serious adverse events (AEs) and lack of immune suppression side-effect profile is very encouraging for both the provider and patient,” Dr. Simpson said, noting there were no new signals or concerning short-term AEs.
Tralokinumab (Adbry), an IL-13 antagonist administered subcutaneously, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults in December 2021.
Minor differences vs. placebo
In the pooled analysis involving 1,605 patients treated for 16 weeks with tralokinumab and 680 who received placebo, frequency of any AE was 65.7% and 67.2%, respectively. Severe AEs occurred in 4.6% and 6.3% of patients, respectively.
The most common AE overall was AD, which occurred less often in tralokinumab-treated patients (15.4%) than those on placebo (26.2%). Other common AEs that occurred more frequently with tralokinumab included viral upper respiratory tract infections (15.7% vs. 12.2%), upper respiratory tract infections (URTI, 5.6% vs. 4.8%), conjunctivitis (5.4% vs. 1.9%), and injection-site reactions (3.5% vs. 0.3%).
AEs that occurred less often with tralokinumab than placebo included skin infections (3.7% vs. 9.2%, respectively) and infected dermatitis (1.6% vs. 6.4%).
Regarding safety areas of special interest, eye disorders classified as conjunctivitis, keratoconjunctivitis, or keratitis occurred more commonly with tralokinumab (7.9%) than placebo (3.4%). Most eye disorders were mild or moderate and resolved during the study. During maintenance treatment up to 52 weeks, AE rates mirrored those in the initial treatment period and did not increase with treatment duration.
In fact, Dr. Simpson said, the low rate of AEs that are known to accompany type 2 blockade, such as conjunctivitis, do not increase but rather appear to drop with longer-term use. The fact that skin infections were reduced vs. placebo and decreased over time suggests that long-term IL-13 blockade with tralokinumab positively impacts skin infections, a well-known comorbidity in uncontrolled AD, he added.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, who was asked to comment on the study, said, “These findings provide additional data supporting the safety and tolerability of tralokinumab and support my personal real-world experience with tralokinumab as a safe and effective biologic therapy for patients with moderate to severe AD.”
Dr. Chovatiya is assistant professor, director of the Center for Eczema and Itch, and medical director of clinical trials at Northwestern University in Chicago.
Four-week dosing
Consistent with ECZTRA 3, the rates of URTIs and conjunctivitis were lower with maintenance dosing 300 mg every 4 weeks, consideration of which is approved for responders weighing less than 220 pounds, vs. 300 mg every 2 weeks. Specifically, 6.7% of patients on every 4-week dosing schedule experienced URTIs, vs. 9.4% on the every 2-week dosing schedule and 7% of those on the every 2-week dosing schedule plus optional topical corticosteroids. Corresponding figures for conjunctivitis were 3%, 5%, and 5.6%, respectively.
“Four-week dosing is a possibility in your patients with a good clinical response at 16 weeks,” Dr. Simpson said. Advantages include improved convenience for patients, he added, and this analysis shows that dosing every 4 weeks may improve tolerability, with a lower rate of conjunctivitis.
Although it is difficult to directly compare review data to other studies, said Dr. Chovatiya, findings also suggest that tralokinumab may be associated with reduced infections and conjunctivitis compared with other advanced AD therapies. Head-to-head trials and real-world studies are needed to better understand comparative safety, he added.
Some patients will lose a degree of response with the 4-week dosing schedule, Dr. Simpson said. In ECZTRA 1 and 2, 55.9% of patients who achieved investigator global assessment (IGA) scores of 0 or 1 after 16 weeks of dosing every 2 weeks maintained this response level through week 52, vs. 42.4% of responders who switched from dosing every 2 weeks to every 4 weeks after week 16. But according to data that Dr. Simpson recently presented, 95% of patients switched to monthly dosing who relapsed and returned to dosing every 2 weeks regained their original response level within approximately 4 weeks.
In his personal practice, Dr. Simpson has prescribed tralokinumab for patients with AD for up to a year. However, he and fellow investigators have been following much larger populations for more than 2 years and are planning additional publications. “Safety data will continue to accrue” said Dr. Simpson, “but I don’t expect any surprises.”
The clinical trials were sponsored by MedImmune (phase 2b) and LEO Pharma ( ECZTRA phase 3 trials), which also sponsored the review. Dr. Simpson reports grants and personal fees from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya has been an advisory board member, consultant, investigator, and speaker for numerous pharmaceutical companies including LEO Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The most , according to a review published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
These findings underscore the mechanistic elegance of interleukin (IL)-13 inhibition and highlight potential advantages of flexible dosing, according to the study’s lead author, Eric Simpson, MD, MCR. Overall, the pooled analysis of safety data from five phase 2 and 3 trials shows that “blockade of a single cytokine provides excellent short- and long-term safety, which is useful for a severe chronic disease,” said Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
Most patients with AD require years of treatment. “So for clinicians to confidently report to patients the low rates of serious adverse events (AEs) and lack of immune suppression side-effect profile is very encouraging for both the provider and patient,” Dr. Simpson said, noting there were no new signals or concerning short-term AEs.
Tralokinumab (Adbry), an IL-13 antagonist administered subcutaneously, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults in December 2021.
Minor differences vs. placebo
In the pooled analysis involving 1,605 patients treated for 16 weeks with tralokinumab and 680 who received placebo, frequency of any AE was 65.7% and 67.2%, respectively. Severe AEs occurred in 4.6% and 6.3% of patients, respectively.
The most common AE overall was AD, which occurred less often in tralokinumab-treated patients (15.4%) than those on placebo (26.2%). Other common AEs that occurred more frequently with tralokinumab included viral upper respiratory tract infections (15.7% vs. 12.2%), upper respiratory tract infections (URTI, 5.6% vs. 4.8%), conjunctivitis (5.4% vs. 1.9%), and injection-site reactions (3.5% vs. 0.3%).
AEs that occurred less often with tralokinumab than placebo included skin infections (3.7% vs. 9.2%, respectively) and infected dermatitis (1.6% vs. 6.4%).
Regarding safety areas of special interest, eye disorders classified as conjunctivitis, keratoconjunctivitis, or keratitis occurred more commonly with tralokinumab (7.9%) than placebo (3.4%). Most eye disorders were mild or moderate and resolved during the study. During maintenance treatment up to 52 weeks, AE rates mirrored those in the initial treatment period and did not increase with treatment duration.
In fact, Dr. Simpson said, the low rate of AEs that are known to accompany type 2 blockade, such as conjunctivitis, do not increase but rather appear to drop with longer-term use. The fact that skin infections were reduced vs. placebo and decreased over time suggests that long-term IL-13 blockade with tralokinumab positively impacts skin infections, a well-known comorbidity in uncontrolled AD, he added.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, who was asked to comment on the study, said, “These findings provide additional data supporting the safety and tolerability of tralokinumab and support my personal real-world experience with tralokinumab as a safe and effective biologic therapy for patients with moderate to severe AD.”
Dr. Chovatiya is assistant professor, director of the Center for Eczema and Itch, and medical director of clinical trials at Northwestern University in Chicago.
Four-week dosing
Consistent with ECZTRA 3, the rates of URTIs and conjunctivitis were lower with maintenance dosing 300 mg every 4 weeks, consideration of which is approved for responders weighing less than 220 pounds, vs. 300 mg every 2 weeks. Specifically, 6.7% of patients on every 4-week dosing schedule experienced URTIs, vs. 9.4% on the every 2-week dosing schedule and 7% of those on the every 2-week dosing schedule plus optional topical corticosteroids. Corresponding figures for conjunctivitis were 3%, 5%, and 5.6%, respectively.
“Four-week dosing is a possibility in your patients with a good clinical response at 16 weeks,” Dr. Simpson said. Advantages include improved convenience for patients, he added, and this analysis shows that dosing every 4 weeks may improve tolerability, with a lower rate of conjunctivitis.
Although it is difficult to directly compare review data to other studies, said Dr. Chovatiya, findings also suggest that tralokinumab may be associated with reduced infections and conjunctivitis compared with other advanced AD therapies. Head-to-head trials and real-world studies are needed to better understand comparative safety, he added.
Some patients will lose a degree of response with the 4-week dosing schedule, Dr. Simpson said. In ECZTRA 1 and 2, 55.9% of patients who achieved investigator global assessment (IGA) scores of 0 or 1 after 16 weeks of dosing every 2 weeks maintained this response level through week 52, vs. 42.4% of responders who switched from dosing every 2 weeks to every 4 weeks after week 16. But according to data that Dr. Simpson recently presented, 95% of patients switched to monthly dosing who relapsed and returned to dosing every 2 weeks regained their original response level within approximately 4 weeks.
In his personal practice, Dr. Simpson has prescribed tralokinumab for patients with AD for up to a year. However, he and fellow investigators have been following much larger populations for more than 2 years and are planning additional publications. “Safety data will continue to accrue” said Dr. Simpson, “but I don’t expect any surprises.”
The clinical trials were sponsored by MedImmune (phase 2b) and LEO Pharma ( ECZTRA phase 3 trials), which also sponsored the review. Dr. Simpson reports grants and personal fees from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya has been an advisory board member, consultant, investigator, and speaker for numerous pharmaceutical companies including LEO Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The most , according to a review published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
These findings underscore the mechanistic elegance of interleukin (IL)-13 inhibition and highlight potential advantages of flexible dosing, according to the study’s lead author, Eric Simpson, MD, MCR. Overall, the pooled analysis of safety data from five phase 2 and 3 trials shows that “blockade of a single cytokine provides excellent short- and long-term safety, which is useful for a severe chronic disease,” said Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
Most patients with AD require years of treatment. “So for clinicians to confidently report to patients the low rates of serious adverse events (AEs) and lack of immune suppression side-effect profile is very encouraging for both the provider and patient,” Dr. Simpson said, noting there were no new signals or concerning short-term AEs.
Tralokinumab (Adbry), an IL-13 antagonist administered subcutaneously, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults in December 2021.
Minor differences vs. placebo
In the pooled analysis involving 1,605 patients treated for 16 weeks with tralokinumab and 680 who received placebo, frequency of any AE was 65.7% and 67.2%, respectively. Severe AEs occurred in 4.6% and 6.3% of patients, respectively.
The most common AE overall was AD, which occurred less often in tralokinumab-treated patients (15.4%) than those on placebo (26.2%). Other common AEs that occurred more frequently with tralokinumab included viral upper respiratory tract infections (15.7% vs. 12.2%), upper respiratory tract infections (URTI, 5.6% vs. 4.8%), conjunctivitis (5.4% vs. 1.9%), and injection-site reactions (3.5% vs. 0.3%).
AEs that occurred less often with tralokinumab than placebo included skin infections (3.7% vs. 9.2%, respectively) and infected dermatitis (1.6% vs. 6.4%).
Regarding safety areas of special interest, eye disorders classified as conjunctivitis, keratoconjunctivitis, or keratitis occurred more commonly with tralokinumab (7.9%) than placebo (3.4%). Most eye disorders were mild or moderate and resolved during the study. During maintenance treatment up to 52 weeks, AE rates mirrored those in the initial treatment period and did not increase with treatment duration.
In fact, Dr. Simpson said, the low rate of AEs that are known to accompany type 2 blockade, such as conjunctivitis, do not increase but rather appear to drop with longer-term use. The fact that skin infections were reduced vs. placebo and decreased over time suggests that long-term IL-13 blockade with tralokinumab positively impacts skin infections, a well-known comorbidity in uncontrolled AD, he added.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, who was asked to comment on the study, said, “These findings provide additional data supporting the safety and tolerability of tralokinumab and support my personal real-world experience with tralokinumab as a safe and effective biologic therapy for patients with moderate to severe AD.”
Dr. Chovatiya is assistant professor, director of the Center for Eczema and Itch, and medical director of clinical trials at Northwestern University in Chicago.
Four-week dosing
Consistent with ECZTRA 3, the rates of URTIs and conjunctivitis were lower with maintenance dosing 300 mg every 4 weeks, consideration of which is approved for responders weighing less than 220 pounds, vs. 300 mg every 2 weeks. Specifically, 6.7% of patients on every 4-week dosing schedule experienced URTIs, vs. 9.4% on the every 2-week dosing schedule and 7% of those on the every 2-week dosing schedule plus optional topical corticosteroids. Corresponding figures for conjunctivitis were 3%, 5%, and 5.6%, respectively.
“Four-week dosing is a possibility in your patients with a good clinical response at 16 weeks,” Dr. Simpson said. Advantages include improved convenience for patients, he added, and this analysis shows that dosing every 4 weeks may improve tolerability, with a lower rate of conjunctivitis.
Although it is difficult to directly compare review data to other studies, said Dr. Chovatiya, findings also suggest that tralokinumab may be associated with reduced infections and conjunctivitis compared with other advanced AD therapies. Head-to-head trials and real-world studies are needed to better understand comparative safety, he added.
Some patients will lose a degree of response with the 4-week dosing schedule, Dr. Simpson said. In ECZTRA 1 and 2, 55.9% of patients who achieved investigator global assessment (IGA) scores of 0 or 1 after 16 weeks of dosing every 2 weeks maintained this response level through week 52, vs. 42.4% of responders who switched from dosing every 2 weeks to every 4 weeks after week 16. But according to data that Dr. Simpson recently presented, 95% of patients switched to monthly dosing who relapsed and returned to dosing every 2 weeks regained their original response level within approximately 4 weeks.
In his personal practice, Dr. Simpson has prescribed tralokinumab for patients with AD for up to a year. However, he and fellow investigators have been following much larger populations for more than 2 years and are planning additional publications. “Safety data will continue to accrue” said Dr. Simpson, “but I don’t expect any surprises.”
The clinical trials were sponsored by MedImmune (phase 2b) and LEO Pharma ( ECZTRA phase 3 trials), which also sponsored the review. Dr. Simpson reports grants and personal fees from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya has been an advisory board member, consultant, investigator, and speaker for numerous pharmaceutical companies including LEO Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
Saururus chinensis
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
Janus Kinase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Military Considerations
The atopic dermatitis (AD) therapeutic landscape is changing considerably with the advent of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. Several JAK inhibitors recently have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, building off years of foundational research aimed at elucidating the downstream effects of the JAK–signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway and its role in AD pathogenesis. Agents within this promising new class of drugs have performed well vs placebo in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials. This article reviews relevant trial efficacy and safety data of several JAK inhibitors as well as the implications of the use of these medications in AD patients, with specific considerations unique to active-duty military personnel.
Background on JAK Inhibitors
The hematopoietin superfamily of cytokine receptors encompasses a broad group that includes receptors for immune (eg, IL-2, IL-4, IFN-γ), hematopoietic (eg, erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor), and nonimmune (eg, prolactin, leptin, growth hormone) cytokines. These cytokines signal via the JAK-STAT pathway. The hematopoietin family of cytokine receptors lacks intrinsic enzymatic activity, and as a result, they rely on JAK enzymes to transmit their signals intracellularly after cytokine binding to the receptor.1 Janus, of Roman mythology, was the god of doorways and archways and was commonly depicted with 2 heads. Janus kinases were named for their 2 “faces,” the kinase domain with its adjacent regulatory kinaselike domains.2 The binding of a cytokine to its receptor triggers engagement of the receptor by JAKs, leading to phosphorylation of both the JAKs and the receptor. Subsequent recruitment and phosphorylation of STAT proteins occurs. Following STAT phosphorylation, the STAT proteins dissociate, dimerize, and translocate to the nucleus, where they enact changes in cell behavior through transcriptional effects.1
Humans possess only 4 JAKs. Janus kinase 1, JAK2, and tyrosine kinase 2 are widely expressed, whereas JAK3 expression is largely limited to immune cells. Thus, there is notable overlap in the use of the 4 JAKs among the relatively larger number of various cytokines that utilize them to propagate intracellular signaling.1 Janus kinase 1 is important for signaling of receptors activated by a variety of interleukins, as well as IFN-α, IFN-β, and IFN-γ. Janus kinase 2 is important for signaling for the hormonelike cytokines erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, growth hormone, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, IL-3, and IL-5. Janus kinase 3 is important for hematopoietic cell proliferation and function.1
JAK Inhibitors and Atopic Dermatitis
Topical treatments, including corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors, are considered the standard-of-care therapy for most patients with AD; however, their clinical benefit often is limited by their anatomic use restrictions and local adverse events, including skin atrophy, striae, and application-site reactions such as stinging and burning.3 As a result, long-term application of these drugs, particularly in sensitive areas, is not recommended owing to safety/tolerability issues.3 Systemic immunomodulatory medications are indicated for patients with AD who do not achieve adequate disease control with topical treatments and/or phototherapy or for patients with severely impaired quality of life.4
Janus kinase inhibitors have several key benefits over biologics: oral and topical bioavailability, predictable pharmacokinetics, nonimmunogenicity, and dosing flexibility.4 Janus kinase 1 is central to the cell signaling of many cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of AD that comprise the T-helper lymphocytes type 2 axis: IL-4, IL-13, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Janus kinase signaling also may mediate itch responses by acting directly on sensory nerve fibers. Consequently, the substantial reduction in pruritus seen in many studies of JAK inhibitors is thought to be in part due to the effects on sensory nerve fibers in the skin and the blockade of early itch signaling in response to IL-4, IL-13, and IL-31.5
Abrocitinib is a JAK1 inhibitor with a similar side effect profile to upadacitinib. Both agents were approved by the FDA for the treatment of refractory moderate to severe AD on January 14, 2022.6 These are second-generation (also referred to as selective) oral JAK inhibitors with much greater inhibitory potency for JAK1 than for JAK2, JAK3, or tyrosine kinase 2, thereby reducing the risk for hematopoietic effects associated with JAK2 inhibition. The approval of abrocitinib stemmed from the phase 3 clinical trial JAK1 Atopic Dermatitis Efficacy and Safety (JADE)-MONO-1 (N=387),7 its replicate trial JADE-MONO-2 (N=391),8 and the JADE COMPARE trial.9 The JADE-MONO trials were multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies that enrolled patients 12 years and older with moderate to severe AD.7,8 Treatment groups consisted of 100-mg and 200-mg doses and were evaluated with the placebo group for their ability to achieve an investigator global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1 and eczema area and severity index 75 (EASI-75) at 12 weeks.7,8 Sixty-three percent of patients in the 200-mg group, 40% in the 100-mg group, and 12% in the placebo group reached the EASI-75 end point, and the differences in these response rates were statistically significant vs placebo (100 mg: 27.9% [95% CI, 17.4-38.3], P<.0001; 200 mg: 51.0% [95% CI, 40.5-61.5], P<.0001). Notably, 44% of patients using the 200-mg dose achieved almost complete or complete resolution of AD (IGA responders, improvement of ≥2 and IGA score of 0 or 1 at 12 weeks).7 In JADE-MONO-2, EASI-75 also was achieved significantly more frequently in the treatment groups compared with the placebo group at 12 weeks (200 mg: 61.0%; 100 mg: 44.5%; placebo: 10.4%; P<.001 vs placebo).8 Adjunctive therapy with topical corticosteroids was prohibited in both studies. A dose-dependent decrease in platelets was seen in both trials, as in the phase 2 trial that preceded them.10
The primary end point of the JADE COMPARE trial was to evaluate the efficacy of abrocitinib as compared with placebo at 12 weeks in adult patients with moderate to severe AD and in the setting of concomitant topical corticosteroid therapy.9 One of several secondary end points of this study compared the ability of dupilumab vs abrocitinib and placebo treatment groups to achieve itch reduction at 2 weeks, defined as 4-point improvement or more from baseline in the score on the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (NRS), a well‐defined, reliable, sensitive, and valid scale for evaluating worst itch intensity in adults with moderate to severe AD.9,11 The primary end point was the same as in the other phase 3 studies and was met in the JADE COMPARE trial by all treatment arms. An EASI-75 was seen in 70.3% of patients treated with 200 mg of abrocitinib, 58.7% in the 100-mg abrocitinib group, 58.1% in the dupilumab group, and 27.1% in the placebo group (P<.001 for both abrocitinib doses vs placebo). Only the 200-mg dose of abrocitinib demonstrated superior itch response at week 2 compared with dupilumab (22.1% response rate difference [95% CI, 13.5-30.7; P<.001]). Both abrocitinib groups failed to demonstrate significant differences compared with dupilumab with respect to other secondary end points to include IGA response and EASI-75 at week 16.9
The most frequently reported treatment-associated adverse events were nausea, nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and headache, and the percentages were similar among trial groups.9 Acne was more frequently reported in the abrocitinib groups compared with placebo and the dupilumab group, and conjunctivitis was more frequently reported in the dupilumab group. Herpesvirus cutaneous infections were rare in the abrocitinib groups, as were other serious infections. No deaths, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), or venous thromboembolic events (VTEs) occurred during the trial. Dose-dependent increases in creatinine phosphokinase were seen in the abrocitinib groups, whereas dose-dependent decreases were seen in platelet counts, with no patient demonstrating a platelet count below 75,000/mm3 during the study.9 Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels increased in a dose-dependent manner as well, but the ratios of low-density lipoprotein to high-density lipoprotein were unchanged.9 The results of a phase 3, 92-week extension study, JADE EXTEND, were recently published and demonstrated a role for abrocitinib as a treatment for patients with moderate to severe AD, regardless of prior dupilumab response status.12
Upadacitinib, another selective JAK1 inhibitor, was approved following data from 2 replicate double-blind, phase 3, randomized, controlled trials—Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2.13 Results demonstrated that monotherapy with once-daily upadacitinib 15 mg or 30 mg is an effective and well-tolerated treatment option for patients with moderate to severe AD vs placebo. All coprimary end points at week 16 were achieved in the upadacitinib groups in both trials. Acne, upper respiratory tract infections, nasopharyngitis, headache, and increase in serum creatinine phosphokinase levels were the most frequently reported adverse events. Rates of herpes zoster infection in upadacitinib groups were low.13
In the subsequent phase 3 AD Up trial, researchers evaluated the safety and efficacy of combination therapy with topical corticosteroids in patients aged 12 to 75 years.14 Upadacitinib groups again achieved the identical coprimary end points that were present in the Measure Up trials13 as well as all key secondary end points.14 Additionally, significant differences in secondary end points, such as a 4-point improvement in the Worst Pruritus NRS vs placebo, were noticed in both upadacitinib treatment groups as early as 1 week into the study (P<.0001), with maintenance of the effect through to week 16 (P<.0001).14 AD Up was followed by the Heads Up trial, a 24-week, phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled trial comparing safety and efficacy of upadacitinib with dupilumab among 692 adults with moderate to severe AD.15 At week 16, a higher percentage of patients in the upadacitinib group achieved EASI-75 vs the dupilumab group (71.0% vs 61.1%, respectively; P=.006). The difference noted at week 2 was even more impressive, with 43.7% of patients in the upadacitinib treatment group achieving EASI-75 compared with 17.4% in the dupilumab group (P<.001). No new safety-related events were registered compared with the already available data for both drugs.15
Ruxolitinib (RUX) is a topical JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor that was FDA approved in September 2021 for the treatment of AD.16 In a phase 2 clinical trial of 307 adult patients with 3% to 20% body surface area (BSA) affected with AD, significant reductions in itch NRS scores were observed within 36 hours after the first application of RUX cream 1.5% twice daily (-1.8 vs -0.2, P<.0001).17 These decreases were noted within the first 2 weeks of treatment for all the RUX cream regimens and were sustained through to week 8, the end of the double-blind period. At 4 weeks, change in itch from baseline was significantly reduced in the RUX 1.5% twice-daily group compared with the triamcinolone ointment 0.1% group (−4 vs −2.5, P=.003). During the open-label treatment period from 8 to 12 weeks, all patients who switched to RUX cream 1.5% twice daily noted further reductions in itch, and those who continued it demonstrated additional improvement.17
The recent FDA approval was further backed by positive phase 3 trial data from the TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 studies.18 Patients in these trials were aged 12 years and older and had AD for 2 or more years with an IGA score of 2 or 3 and 3% to 20% affected BSA. Patients were randomized to twice-daily RUX cream 0.75%, RUX cream 1.5%, or vehicle cream, and the primary end point was an IGA score of 0 or 1 and an improvement of 2 or more points from baseline at week 8. Significantly more patients achieved IGA treatment success with RUX cream 0.75% (TRuE-AD1, 50.0%; TRuE-AD2, 39.0%) and RUX cream 1.5% (TRuE-AD1, 53.8%; TRuE-AD2, 51.3%) vs vehicle (TRuE-AD1, 15.1%; TRuE-AD2, 7.6%; P<.0001) at week 8. The RUX groups experienced dramatically reduced itch compared with vehicle, with a mean reduction of approximately 3 points on the NRS at 8 weeks. Additionally, statistically significant itch reductions vs vehicle were reported within 12 hours of first application of RUX cream 1.5% (P<.05). Application-site reactions including stinging and burning occurred in less than 1% of patients, and none were considered clinically significant. Mean plasma concentrations of RUX were monitored during the phase 2 and 3 AD studies and did not lead to any clinically meaningful changes in hematologic parameters. The low bioavailability following topical application of RUX cream (6% in the TRuE-AD studies) allows for a targeted delivery of the active drug to lesional skin while reducing the safety issues associated with oral administration of JAK inhibitors.18
Baricitinib is a predominantly JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor that was the first JAK inhibitor to be approved for the treatment of moderate to severe AD in the European Union and Japan.19 Although the FDA’s decision on baricitinib has lagged behind market competitors, in 2 phase 3 clinical trials, BREEZE-AD1 and BREEZE-AD2, baricitinib demonstrated benefit over placebo on clinically important measures of disease severity. The primary end point—the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 or 1 with an improvement of 2 or more points from baseline at week 16—was met by both tested doses of baricitinib (2 mg and 4 mg) vs placebo in BREEZE-AD1 (2 mg, P≤.05; 4 mg, P≤.001) and BREEZE-AD2 (2 mg, P≤.05; 4 mg, P≤.001). In addition, baricitinib 4 mg consistently demonstrated significant benefit over placebo on other clinically important measures of disease severity at week 16 to include itch (BREEZE-AD1 and BREEZE-AD2, P≤.001), sleep disturbance (BREEZE-AD1, P≤.01; BREEZE-AD2, P≤.001), and skin pain (BREEZE-AD1, P≤.01; BREEZE-AD2, P≤.001). Nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infections, creatine phosphokinase elevations, and headaches were the most frequently reported adverse events. During the 16-week treatment period in these trials, no deaths, MACEs, or VTEs occurred.19 Similar results were seen in a long-term extension study, BREEZE-AD3.20 The combination of baricitinib and topical corticosteroids were evaluated in 2 additional phase 3 trials, BREEZE-AD421 and BREEZE-AD7.22 Although only baricitinib 4 mg met the primary end point of EASI-75 at week 16 in both trials, both dosing regimens plus topical corticosteroids demonstrated notable reduction in multiple clinical and quality-of-life indices prior to week 2 when compared with placebo plus topical corticosteroids.22,23
AD in Military Service Members
Atopic dermatitis is a common condition in the general population, with a prevalence of 7.3% (95% CI, 5.9-8.8) in a recent study of American adults.24 Historically, the burden of AD that would be expected among active-duty military service members given the prevalence among the general population has not been observed, in part because of the disqualifying nature of AD for enlistment.25 The Department of Defense Instruction 6130.03, Volume 1, Medical Standards for Military Service: Appointment, Enlistment, or Induction stipulates that a history of AD or eczema after the twelfth birthday or history of residual or recurrent lesions in characteristic areas (ie, face, neck, antecubital or popliteal fossae, occasionally wrists and hands) is disqualifying.26 Specific military services possess additional standards that further define limits within the aforementioned Department of Defense instruction.25 Additionally, there are service-specific policies in place that mandate medical evaluation boards to determine fitness for continued service in the event the condition interferes with the member’s ability to perform their duties. Insection 4.2 of the U.S. Navy Aeromedical Reference and Waiver Guide, further restrictions for aviation personnel are delineated: “Depending on the location of lesions, there can be interference with the wearing of flight gear. The symptoms, particularly itching, can be distracting in flight. Patients with atopic dermatitis are more susceptible to contact dermatitis due to irritants found in a military environment.” Ultimately, the document stipulates that symptom severity and the requirement for therapy will determine the aeromedical disposition. It specifically states that “[p]atients controlled on topical therapy over small areas and patients who are asymptomatic on stable doses of loratadine (Claritin) OR fexofenadine (Allegra) may be considered for waiver,” and “intermittent use of topical steroids over a limited area is compatible with waiver.”27 It follows that limited use of topical JAK inhibitors, such as RUX, would be compatible with a waiver, given the favorable side effect profile and requirement for use in patients with 20% or lower affected BSA.16 This is just one example of duty-specific and service-specific medical standards that exist that could impact the use of both topical and oral JAK inhibitors.
Use of oral JAK inhibitors in active-duty service members is less ideal for multiple reasons. A large randomized safety clinical trial of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who received tofacitinib and methotrexate was required by the FDA to evaluate the risk of MACEs, malignancy, and infections associated with JAK inhibitor treatment. Data from this trial showed a dose-dependent increased risk for MACEs, all-cause mortality, and thrombosis at both doses of tofacitinib compared with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and a non–dose-dependent increased risk for malignancy excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer.28 In contrast to the MACE and VTE data from patients with diseases other than AD treated with JAK inhibitors, there has been only 1 patient who developed a pulmonary embolism while being treated with baricitinib 4 mg.22,29 Downstream effects from the above study were label recommendations to reserve the medicines for patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to 1 or more tumor necrosis factor blockers and to carefully consider risks vs benefits in patients, in particular current or prior smokers, those with other cardiovascular risk factors or a history of VTE, and those with a malignancy history other than already treated nonmelanoma skin cancer.28
There are consistent observations of laboratory abnormalities with JAK inhibitors, as discussed above, to include creatine phosphokinase elevation and cytopenias.30 Although existing data demonstrate that cytopenias are less of a concern in the AD population compared with the rheumatoid arthritis population, baseline and periodic laboratory monitoring are still recommended. In general, pretreatment laboratory assessment prior to initiating an oral JAK inhibitor should consist of a complete blood cell count with differential, complete metabolic panel, tuberculosis screening, chronic hepatitis panel, HIV screening, and a fasting lipid panel.2 The feasibility of obtaining these laboratory measurements in an operational setting or sea-going platform is limited, but many deployed locations and naval vessels possess the laboratory capability to perform a complete blood cell count and complete metabolic panel. Overall tolerability of oral JAK inhibitors in the treatment of AD appears favorable based on studies that were mostly 16 weeks in duration. Few recent longer-term studies have confirmed this side effect profile, but additional studies are needed.
Final Thoughts
Janus kinase inhibitors are a promising therapeutic class with multiple recently FDA-approved agents for the treatment of moderate to severe AD, with new agents on the horizon. Available efficacy data are promising and balanced by a favorable safety profile in clinical trials to date. The oral and topical bioavailability of JAK inhibitors makes them attractive alternatives to existing therapies. The rapidity of itch reduction and AD improvement demonstrated in multiple trials has the potential to decrease the length of limited-duty assignments, potentially returning treated service members to full-duty status more expeditiously. Other applications include use of these medications in scenarios where injectable medications are either unavailable or unsupported.
In the active-duty population, both the condition and/or the treatment may be duty limiting. Service members with AD who require more than topical treatment may require a medical evaluation board to determine if they are still fit to serve. The deployed environment routinely exacerbates AD and exposes service members to infections and environments where immunosuppression can create more risks than in the general population. Nonbiologic medications, which do not require refrigeration, are an exciting option for our patients with AD, including those actively serving or considering serving in the military. However, all factors in any patient’s life should be considered. Therefore, it is important for the nonmilitary dermatologist to work with local military physicians and the patient to determine the optimal treatment regimen to result in the best possible outcome.
- Damsky W, Peterson D, Ramseier J, et al. The emerging role of Janus kinase inhibitors in the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:814-826.
- Gadina M, Le MT, Schwartz DM, et al. Janus kinases to jakinibs: from basic insights to clinical practice. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019;58(suppl 1):i4-i6.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 2, management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132.
- Cartron AM, Nguyen TH, Roh YS, et al. Janus kinase inhibitors for atopic dermatitis: a promising treatment modality. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46:820-824.
- Oetjen LK, Mack MR, Feng J, et al. Sensory neurons co-opt classical immune signaling pathways to mediate chronic itch. Cell. 2017;171:217-228.e13.
- U.S. FDA approves Pfizer’s CIBINQO® (abrocitinib) for adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [press release]. January 14, 2022. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/us-fda-approves-pfizers-cibinqor-abrocitinib-adults
- Simpson EL, Sinclair R, Forman S, et al. Efficacy and safety of abrocitinib in adults and adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (JADE MONO-1): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2020;396:255-266.
- Silverberg JI, Simpson EL, Thyssen JP, et al. Efficacy and safety of abrocitinib in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:863-873.
- Bieber T, Simpson EL, Silverberg JI, et al. Abrocitinib versus placebo or dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1101-1112.
- Gooderham MJ, Forman SB, Bissonnette R, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral Janus kinase 1 inhibitor abrocitinib for patients with atopic dermatitis: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1371-1379. Published correction appears in JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:104.
- Yosipovitch G, Reaney M, Mastey V, et al. Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale: psychometric validation and responder definition for assessing itch in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:761-769.
- Shi VY, Bhutani T, Fonacier L, et al. Phase 3 efficacy and safety of abrocitinib in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis after switching from dupilumab (JADE EXTEND). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:351-358.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021;397:2151-2168.
- Reich K, Teixeira HD, de Bruin-Weller M, et al. Safety and efficacy of upadacitinib in combination with topical corticosteroids in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD Up): results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:2169-2181.
- Blauvelt A, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib vs dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1047-1055. Published correction appears in JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:219.
- FDA approves Opzelura. Drugs.com. September 21, 2021. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://www.drugs.com/newdrugs/fda-approves-opzelura-ruxolitinib-cream-atopic-dermatitis-ad-5666.html
- Kim BS, Sun K, Papp K, et al. Effects of ruxolitinib cream on pruritus and quality of life in atopic dermatitis: results from a phase 2, randomized, doseranging, vehicle- and active-controlled study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1305-1313.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib cream for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 2 phase 3, randomized, double-blind studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:863-872.
- Simpson EL, Lacour JP, Spelman L, et al. Baricitinib in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis and inadequate response to topical corticosteroids: results from two randomized monotherapy phase III trials. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:242-255.
- Silverberg JI, Simpson EL, Wollenberg A, et al. Long-term efficacy of baricitinib in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis who were treatment responders or partial responders: an extension study of 2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:691-699.
- Lilly and Incyte announce top-line results from phase 3 study (BREEZE-AD4) of oral selective JAK inhibitor baricitinib in combination with topical corticosteroids in patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis not controlled with cyclosporine. January 27, 2020. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lilly-and-incyte-announce-top-line-results-phase-3-study-breeze
- Reich K, Kabashima K, Peris K, et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib combined with topical corticosteroids for treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:1333-1343.
- Wollenberg A, Nakahara T, Maari C, et al. Impact of baricitinib in combination with topical steroids on atopic dermatitis symptoms, quality of life and functioning in adult patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis from the BREEZE-AD7 phase 3 randomized trial. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:1543-1552.
- Chiesa Fuxench ZC, Block JK, Boguniewicz M, et al. Atopic dermatitis in America study: a cross-sectional study examining the prevalence and disease burden of atopic dermatitis in the US adult population. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:583-590.
- Jeter J, Bowen C. Atopic dermatitis and implications for military service. Mil Med. 2019;184:E177-E182.
- Department of Defense. Medical standards for military service: appointment, enlistment, or induction. DoD Instruction 6130.03. Vol 1. May 6, 2022. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.esd.whs.mil/Portals/54/Documents/DD/issuances/dodi/613003_v1p.PDF?ver=9NsVi30gsHBBsRhMLcyVVQ%3d%3d
- Dermatitis. In: U.S. Navy Aeromedical Reference and Waiver Guide. Navy Medicine Operational Training Command and Naval Aerospace Medical Institute. August 11, 2021. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.med.navy.mil/Portals/62/Documents/NMFSC/NMOTC/NAMI/ARWG/Waiver%20Guide/ARWG%20COMPLETE_210811.pdf?ver=_pLPzFrtl8E2swFESnN4rA%3D%3D
- FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. FDA Drug Safety Podcast. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Updated January 14, 2022. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-drug-safety-podcasts/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death
- Chang PH, Huang SF, Chang PS, et al. Safety considerations of systemic Janus kinase inhibitors in atopic dermatitis applications. J Dermatol. 2021;48:1631-1639.
- Wood H, Chandler A, Nezamololama N, et al. Safety of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in the short-term treatment of atopic dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:746-754.
The atopic dermatitis (AD) therapeutic landscape is changing considerably with the advent of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. Several JAK inhibitors recently have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, building off years of foundational research aimed at elucidating the downstream effects of the JAK–signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway and its role in AD pathogenesis. Agents within this promising new class of drugs have performed well vs placebo in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials. This article reviews relevant trial efficacy and safety data of several JAK inhibitors as well as the implications of the use of these medications in AD patients, with specific considerations unique to active-duty military personnel.
Background on JAK Inhibitors
The hematopoietin superfamily of cytokine receptors encompasses a broad group that includes receptors for immune (eg, IL-2, IL-4, IFN-γ), hematopoietic (eg, erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor), and nonimmune (eg, prolactin, leptin, growth hormone) cytokines. These cytokines signal via the JAK-STAT pathway. The hematopoietin family of cytokine receptors lacks intrinsic enzymatic activity, and as a result, they rely on JAK enzymes to transmit their signals intracellularly after cytokine binding to the receptor.1 Janus, of Roman mythology, was the god of doorways and archways and was commonly depicted with 2 heads. Janus kinases were named for their 2 “faces,” the kinase domain with its adjacent regulatory kinaselike domains.2 The binding of a cytokine to its receptor triggers engagement of the receptor by JAKs, leading to phosphorylation of both the JAKs and the receptor. Subsequent recruitment and phosphorylation of STAT proteins occurs. Following STAT phosphorylation, the STAT proteins dissociate, dimerize, and translocate to the nucleus, where they enact changes in cell behavior through transcriptional effects.1
Humans possess only 4 JAKs. Janus kinase 1, JAK2, and tyrosine kinase 2 are widely expressed, whereas JAK3 expression is largely limited to immune cells. Thus, there is notable overlap in the use of the 4 JAKs among the relatively larger number of various cytokines that utilize them to propagate intracellular signaling.1 Janus kinase 1 is important for signaling of receptors activated by a variety of interleukins, as well as IFN-α, IFN-β, and IFN-γ. Janus kinase 2 is important for signaling for the hormonelike cytokines erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, growth hormone, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, IL-3, and IL-5. Janus kinase 3 is important for hematopoietic cell proliferation and function.1
JAK Inhibitors and Atopic Dermatitis
Topical treatments, including corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors, are considered the standard-of-care therapy for most patients with AD; however, their clinical benefit often is limited by their anatomic use restrictions and local adverse events, including skin atrophy, striae, and application-site reactions such as stinging and burning.3 As a result, long-term application of these drugs, particularly in sensitive areas, is not recommended owing to safety/tolerability issues.3 Systemic immunomodulatory medications are indicated for patients with AD who do not achieve adequate disease control with topical treatments and/or phototherapy or for patients with severely impaired quality of life.4
Janus kinase inhibitors have several key benefits over biologics: oral and topical bioavailability, predictable pharmacokinetics, nonimmunogenicity, and dosing flexibility.4 Janus kinase 1 is central to the cell signaling of many cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of AD that comprise the T-helper lymphocytes type 2 axis: IL-4, IL-13, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Janus kinase signaling also may mediate itch responses by acting directly on sensory nerve fibers. Consequently, the substantial reduction in pruritus seen in many studies of JAK inhibitors is thought to be in part due to the effects on sensory nerve fibers in the skin and the blockade of early itch signaling in response to IL-4, IL-13, and IL-31.5
Abrocitinib is a JAK1 inhibitor with a similar side effect profile to upadacitinib. Both agents were approved by the FDA for the treatment of refractory moderate to severe AD on January 14, 2022.6 These are second-generation (also referred to as selective) oral JAK inhibitors with much greater inhibitory potency for JAK1 than for JAK2, JAK3, or tyrosine kinase 2, thereby reducing the risk for hematopoietic effects associated with JAK2 inhibition. The approval of abrocitinib stemmed from the phase 3 clinical trial JAK1 Atopic Dermatitis Efficacy and Safety (JADE)-MONO-1 (N=387),7 its replicate trial JADE-MONO-2 (N=391),8 and the JADE COMPARE trial.9 The JADE-MONO trials were multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies that enrolled patients 12 years and older with moderate to severe AD.7,8 Treatment groups consisted of 100-mg and 200-mg doses and were evaluated with the placebo group for their ability to achieve an investigator global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1 and eczema area and severity index 75 (EASI-75) at 12 weeks.7,8 Sixty-three percent of patients in the 200-mg group, 40% in the 100-mg group, and 12% in the placebo group reached the EASI-75 end point, and the differences in these response rates were statistically significant vs placebo (100 mg: 27.9% [95% CI, 17.4-38.3], P<.0001; 200 mg: 51.0% [95% CI, 40.5-61.5], P<.0001). Notably, 44% of patients using the 200-mg dose achieved almost complete or complete resolution of AD (IGA responders, improvement of ≥2 and IGA score of 0 or 1 at 12 weeks).7 In JADE-MONO-2, EASI-75 also was achieved significantly more frequently in the treatment groups compared with the placebo group at 12 weeks (200 mg: 61.0%; 100 mg: 44.5%; placebo: 10.4%; P<.001 vs placebo).8 Adjunctive therapy with topical corticosteroids was prohibited in both studies. A dose-dependent decrease in platelets was seen in both trials, as in the phase 2 trial that preceded them.10
The primary end point of the JADE COMPARE trial was to evaluate the efficacy of abrocitinib as compared with placebo at 12 weeks in adult patients with moderate to severe AD and in the setting of concomitant topical corticosteroid therapy.9 One of several secondary end points of this study compared the ability of dupilumab vs abrocitinib and placebo treatment groups to achieve itch reduction at 2 weeks, defined as 4-point improvement or more from baseline in the score on the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (NRS), a well‐defined, reliable, sensitive, and valid scale for evaluating worst itch intensity in adults with moderate to severe AD.9,11 The primary end point was the same as in the other phase 3 studies and was met in the JADE COMPARE trial by all treatment arms. An EASI-75 was seen in 70.3% of patients treated with 200 mg of abrocitinib, 58.7% in the 100-mg abrocitinib group, 58.1% in the dupilumab group, and 27.1% in the placebo group (P<.001 for both abrocitinib doses vs placebo). Only the 200-mg dose of abrocitinib demonstrated superior itch response at week 2 compared with dupilumab (22.1% response rate difference [95% CI, 13.5-30.7; P<.001]). Both abrocitinib groups failed to demonstrate significant differences compared with dupilumab with respect to other secondary end points to include IGA response and EASI-75 at week 16.9
The most frequently reported treatment-associated adverse events were nausea, nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and headache, and the percentages were similar among trial groups.9 Acne was more frequently reported in the abrocitinib groups compared with placebo and the dupilumab group, and conjunctivitis was more frequently reported in the dupilumab group. Herpesvirus cutaneous infections were rare in the abrocitinib groups, as were other serious infections. No deaths, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), or venous thromboembolic events (VTEs) occurred during the trial. Dose-dependent increases in creatinine phosphokinase were seen in the abrocitinib groups, whereas dose-dependent decreases were seen in platelet counts, with no patient demonstrating a platelet count below 75,000/mm3 during the study.9 Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels increased in a dose-dependent manner as well, but the ratios of low-density lipoprotein to high-density lipoprotein were unchanged.9 The results of a phase 3, 92-week extension study, JADE EXTEND, were recently published and demonstrated a role for abrocitinib as a treatment for patients with moderate to severe AD, regardless of prior dupilumab response status.12
Upadacitinib, another selective JAK1 inhibitor, was approved following data from 2 replicate double-blind, phase 3, randomized, controlled trials—Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2.13 Results demonstrated that monotherapy with once-daily upadacitinib 15 mg or 30 mg is an effective and well-tolerated treatment option for patients with moderate to severe AD vs placebo. All coprimary end points at week 16 were achieved in the upadacitinib groups in both trials. Acne, upper respiratory tract infections, nasopharyngitis, headache, and increase in serum creatinine phosphokinase levels were the most frequently reported adverse events. Rates of herpes zoster infection in upadacitinib groups were low.13
In the subsequent phase 3 AD Up trial, researchers evaluated the safety and efficacy of combination therapy with topical corticosteroids in patients aged 12 to 75 years.14 Upadacitinib groups again achieved the identical coprimary end points that were present in the Measure Up trials13 as well as all key secondary end points.14 Additionally, significant differences in secondary end points, such as a 4-point improvement in the Worst Pruritus NRS vs placebo, were noticed in both upadacitinib treatment groups as early as 1 week into the study (P<.0001), with maintenance of the effect through to week 16 (P<.0001).14 AD Up was followed by the Heads Up trial, a 24-week, phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled trial comparing safety and efficacy of upadacitinib with dupilumab among 692 adults with moderate to severe AD.15 At week 16, a higher percentage of patients in the upadacitinib group achieved EASI-75 vs the dupilumab group (71.0% vs 61.1%, respectively; P=.006). The difference noted at week 2 was even more impressive, with 43.7% of patients in the upadacitinib treatment group achieving EASI-75 compared with 17.4% in the dupilumab group (P<.001). No new safety-related events were registered compared with the already available data for both drugs.15
Ruxolitinib (RUX) is a topical JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor that was FDA approved in September 2021 for the treatment of AD.16 In a phase 2 clinical trial of 307 adult patients with 3% to 20% body surface area (BSA) affected with AD, significant reductions in itch NRS scores were observed within 36 hours after the first application of RUX cream 1.5% twice daily (-1.8 vs -0.2, P<.0001).17 These decreases were noted within the first 2 weeks of treatment for all the RUX cream regimens and were sustained through to week 8, the end of the double-blind period. At 4 weeks, change in itch from baseline was significantly reduced in the RUX 1.5% twice-daily group compared with the triamcinolone ointment 0.1% group (−4 vs −2.5, P=.003). During the open-label treatment period from 8 to 12 weeks, all patients who switched to RUX cream 1.5% twice daily noted further reductions in itch, and those who continued it demonstrated additional improvement.17
The recent FDA approval was further backed by positive phase 3 trial data from the TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 studies.18 Patients in these trials were aged 12 years and older and had AD for 2 or more years with an IGA score of 2 or 3 and 3% to 20% affected BSA. Patients were randomized to twice-daily RUX cream 0.75%, RUX cream 1.5%, or vehicle cream, and the primary end point was an IGA score of 0 or 1 and an improvement of 2 or more points from baseline at week 8. Significantly more patients achieved IGA treatment success with RUX cream 0.75% (TRuE-AD1, 50.0%; TRuE-AD2, 39.0%) and RUX cream 1.5% (TRuE-AD1, 53.8%; TRuE-AD2, 51.3%) vs vehicle (TRuE-AD1, 15.1%; TRuE-AD2, 7.6%; P<.0001) at week 8. The RUX groups experienced dramatically reduced itch compared with vehicle, with a mean reduction of approximately 3 points on the NRS at 8 weeks. Additionally, statistically significant itch reductions vs vehicle were reported within 12 hours of first application of RUX cream 1.5% (P<.05). Application-site reactions including stinging and burning occurred in less than 1% of patients, and none were considered clinically significant. Mean plasma concentrations of RUX were monitored during the phase 2 and 3 AD studies and did not lead to any clinically meaningful changes in hematologic parameters. The low bioavailability following topical application of RUX cream (6% in the TRuE-AD studies) allows for a targeted delivery of the active drug to lesional skin while reducing the safety issues associated with oral administration of JAK inhibitors.18
Baricitinib is a predominantly JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor that was the first JAK inhibitor to be approved for the treatment of moderate to severe AD in the European Union and Japan.19 Although the FDA’s decision on baricitinib has lagged behind market competitors, in 2 phase 3 clinical trials, BREEZE-AD1 and BREEZE-AD2, baricitinib demonstrated benefit over placebo on clinically important measures of disease severity. The primary end point—the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 or 1 with an improvement of 2 or more points from baseline at week 16—was met by both tested doses of baricitinib (2 mg and 4 mg) vs placebo in BREEZE-AD1 (2 mg, P≤.05; 4 mg, P≤.001) and BREEZE-AD2 (2 mg, P≤.05; 4 mg, P≤.001). In addition, baricitinib 4 mg consistently demonstrated significant benefit over placebo on other clinically important measures of disease severity at week 16 to include itch (BREEZE-AD1 and BREEZE-AD2, P≤.001), sleep disturbance (BREEZE-AD1, P≤.01; BREEZE-AD2, P≤.001), and skin pain (BREEZE-AD1, P≤.01; BREEZE-AD2, P≤.001). Nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infections, creatine phosphokinase elevations, and headaches were the most frequently reported adverse events. During the 16-week treatment period in these trials, no deaths, MACEs, or VTEs occurred.19 Similar results were seen in a long-term extension study, BREEZE-AD3.20 The combination of baricitinib and topical corticosteroids were evaluated in 2 additional phase 3 trials, BREEZE-AD421 and BREEZE-AD7.22 Although only baricitinib 4 mg met the primary end point of EASI-75 at week 16 in both trials, both dosing regimens plus topical corticosteroids demonstrated notable reduction in multiple clinical and quality-of-life indices prior to week 2 when compared with placebo plus topical corticosteroids.22,23
AD in Military Service Members
Atopic dermatitis is a common condition in the general population, with a prevalence of 7.3% (95% CI, 5.9-8.8) in a recent study of American adults.24 Historically, the burden of AD that would be expected among active-duty military service members given the prevalence among the general population has not been observed, in part because of the disqualifying nature of AD for enlistment.25 The Department of Defense Instruction 6130.03, Volume 1, Medical Standards for Military Service: Appointment, Enlistment, or Induction stipulates that a history of AD or eczema after the twelfth birthday or history of residual or recurrent lesions in characteristic areas (ie, face, neck, antecubital or popliteal fossae, occasionally wrists and hands) is disqualifying.26 Specific military services possess additional standards that further define limits within the aforementioned Department of Defense instruction.25 Additionally, there are service-specific policies in place that mandate medical evaluation boards to determine fitness for continued service in the event the condition interferes with the member’s ability to perform their duties. Insection 4.2 of the U.S. Navy Aeromedical Reference and Waiver Guide, further restrictions for aviation personnel are delineated: “Depending on the location of lesions, there can be interference with the wearing of flight gear. The symptoms, particularly itching, can be distracting in flight. Patients with atopic dermatitis are more susceptible to contact dermatitis due to irritants found in a military environment.” Ultimately, the document stipulates that symptom severity and the requirement for therapy will determine the aeromedical disposition. It specifically states that “[p]atients controlled on topical therapy over small areas and patients who are asymptomatic on stable doses of loratadine (Claritin) OR fexofenadine (Allegra) may be considered for waiver,” and “intermittent use of topical steroids over a limited area is compatible with waiver.”27 It follows that limited use of topical JAK inhibitors, such as RUX, would be compatible with a waiver, given the favorable side effect profile and requirement for use in patients with 20% or lower affected BSA.16 This is just one example of duty-specific and service-specific medical standards that exist that could impact the use of both topical and oral JAK inhibitors.
Use of oral JAK inhibitors in active-duty service members is less ideal for multiple reasons. A large randomized safety clinical trial of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who received tofacitinib and methotrexate was required by the FDA to evaluate the risk of MACEs, malignancy, and infections associated with JAK inhibitor treatment. Data from this trial showed a dose-dependent increased risk for MACEs, all-cause mortality, and thrombosis at both doses of tofacitinib compared with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and a non–dose-dependent increased risk for malignancy excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer.28 In contrast to the MACE and VTE data from patients with diseases other than AD treated with JAK inhibitors, there has been only 1 patient who developed a pulmonary embolism while being treated with baricitinib 4 mg.22,29 Downstream effects from the above study were label recommendations to reserve the medicines for patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to 1 or more tumor necrosis factor blockers and to carefully consider risks vs benefits in patients, in particular current or prior smokers, those with other cardiovascular risk factors or a history of VTE, and those with a malignancy history other than already treated nonmelanoma skin cancer.28
There are consistent observations of laboratory abnormalities with JAK inhibitors, as discussed above, to include creatine phosphokinase elevation and cytopenias.30 Although existing data demonstrate that cytopenias are less of a concern in the AD population compared with the rheumatoid arthritis population, baseline and periodic laboratory monitoring are still recommended. In general, pretreatment laboratory assessment prior to initiating an oral JAK inhibitor should consist of a complete blood cell count with differential, complete metabolic panel, tuberculosis screening, chronic hepatitis panel, HIV screening, and a fasting lipid panel.2 The feasibility of obtaining these laboratory measurements in an operational setting or sea-going platform is limited, but many deployed locations and naval vessels possess the laboratory capability to perform a complete blood cell count and complete metabolic panel. Overall tolerability of oral JAK inhibitors in the treatment of AD appears favorable based on studies that were mostly 16 weeks in duration. Few recent longer-term studies have confirmed this side effect profile, but additional studies are needed.
Final Thoughts
Janus kinase inhibitors are a promising therapeutic class with multiple recently FDA-approved agents for the treatment of moderate to severe AD, with new agents on the horizon. Available efficacy data are promising and balanced by a favorable safety profile in clinical trials to date. The oral and topical bioavailability of JAK inhibitors makes them attractive alternatives to existing therapies. The rapidity of itch reduction and AD improvement demonstrated in multiple trials has the potential to decrease the length of limited-duty assignments, potentially returning treated service members to full-duty status more expeditiously. Other applications include use of these medications in scenarios where injectable medications are either unavailable or unsupported.
In the active-duty population, both the condition and/or the treatment may be duty limiting. Service members with AD who require more than topical treatment may require a medical evaluation board to determine if they are still fit to serve. The deployed environment routinely exacerbates AD and exposes service members to infections and environments where immunosuppression can create more risks than in the general population. Nonbiologic medications, which do not require refrigeration, are an exciting option for our patients with AD, including those actively serving or considering serving in the military. However, all factors in any patient’s life should be considered. Therefore, it is important for the nonmilitary dermatologist to work with local military physicians and the patient to determine the optimal treatment regimen to result in the best possible outcome.
The atopic dermatitis (AD) therapeutic landscape is changing considerably with the advent of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. Several JAK inhibitors recently have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, building off years of foundational research aimed at elucidating the downstream effects of the JAK–signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway and its role in AD pathogenesis. Agents within this promising new class of drugs have performed well vs placebo in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials. This article reviews relevant trial efficacy and safety data of several JAK inhibitors as well as the implications of the use of these medications in AD patients, with specific considerations unique to active-duty military personnel.
Background on JAK Inhibitors
The hematopoietin superfamily of cytokine receptors encompasses a broad group that includes receptors for immune (eg, IL-2, IL-4, IFN-γ), hematopoietic (eg, erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor), and nonimmune (eg, prolactin, leptin, growth hormone) cytokines. These cytokines signal via the JAK-STAT pathway. The hematopoietin family of cytokine receptors lacks intrinsic enzymatic activity, and as a result, they rely on JAK enzymes to transmit their signals intracellularly after cytokine binding to the receptor.1 Janus, of Roman mythology, was the god of doorways and archways and was commonly depicted with 2 heads. Janus kinases were named for their 2 “faces,” the kinase domain with its adjacent regulatory kinaselike domains.2 The binding of a cytokine to its receptor triggers engagement of the receptor by JAKs, leading to phosphorylation of both the JAKs and the receptor. Subsequent recruitment and phosphorylation of STAT proteins occurs. Following STAT phosphorylation, the STAT proteins dissociate, dimerize, and translocate to the nucleus, where they enact changes in cell behavior through transcriptional effects.1
Humans possess only 4 JAKs. Janus kinase 1, JAK2, and tyrosine kinase 2 are widely expressed, whereas JAK3 expression is largely limited to immune cells. Thus, there is notable overlap in the use of the 4 JAKs among the relatively larger number of various cytokines that utilize them to propagate intracellular signaling.1 Janus kinase 1 is important for signaling of receptors activated by a variety of interleukins, as well as IFN-α, IFN-β, and IFN-γ. Janus kinase 2 is important for signaling for the hormonelike cytokines erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, growth hormone, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, IL-3, and IL-5. Janus kinase 3 is important for hematopoietic cell proliferation and function.1
JAK Inhibitors and Atopic Dermatitis
Topical treatments, including corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors, are considered the standard-of-care therapy for most patients with AD; however, their clinical benefit often is limited by their anatomic use restrictions and local adverse events, including skin atrophy, striae, and application-site reactions such as stinging and burning.3 As a result, long-term application of these drugs, particularly in sensitive areas, is not recommended owing to safety/tolerability issues.3 Systemic immunomodulatory medications are indicated for patients with AD who do not achieve adequate disease control with topical treatments and/or phototherapy or for patients with severely impaired quality of life.4
Janus kinase inhibitors have several key benefits over biologics: oral and topical bioavailability, predictable pharmacokinetics, nonimmunogenicity, and dosing flexibility.4 Janus kinase 1 is central to the cell signaling of many cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of AD that comprise the T-helper lymphocytes type 2 axis: IL-4, IL-13, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Janus kinase signaling also may mediate itch responses by acting directly on sensory nerve fibers. Consequently, the substantial reduction in pruritus seen in many studies of JAK inhibitors is thought to be in part due to the effects on sensory nerve fibers in the skin and the blockade of early itch signaling in response to IL-4, IL-13, and IL-31.5
Abrocitinib is a JAK1 inhibitor with a similar side effect profile to upadacitinib. Both agents were approved by the FDA for the treatment of refractory moderate to severe AD on January 14, 2022.6 These are second-generation (also referred to as selective) oral JAK inhibitors with much greater inhibitory potency for JAK1 than for JAK2, JAK3, or tyrosine kinase 2, thereby reducing the risk for hematopoietic effects associated with JAK2 inhibition. The approval of abrocitinib stemmed from the phase 3 clinical trial JAK1 Atopic Dermatitis Efficacy and Safety (JADE)-MONO-1 (N=387),7 its replicate trial JADE-MONO-2 (N=391),8 and the JADE COMPARE trial.9 The JADE-MONO trials were multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies that enrolled patients 12 years and older with moderate to severe AD.7,8 Treatment groups consisted of 100-mg and 200-mg doses and were evaluated with the placebo group for their ability to achieve an investigator global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1 and eczema area and severity index 75 (EASI-75) at 12 weeks.7,8 Sixty-three percent of patients in the 200-mg group, 40% in the 100-mg group, and 12% in the placebo group reached the EASI-75 end point, and the differences in these response rates were statistically significant vs placebo (100 mg: 27.9% [95% CI, 17.4-38.3], P<.0001; 200 mg: 51.0% [95% CI, 40.5-61.5], P<.0001). Notably, 44% of patients using the 200-mg dose achieved almost complete or complete resolution of AD (IGA responders, improvement of ≥2 and IGA score of 0 or 1 at 12 weeks).7 In JADE-MONO-2, EASI-75 also was achieved significantly more frequently in the treatment groups compared with the placebo group at 12 weeks (200 mg: 61.0%; 100 mg: 44.5%; placebo: 10.4%; P<.001 vs placebo).8 Adjunctive therapy with topical corticosteroids was prohibited in both studies. A dose-dependent decrease in platelets was seen in both trials, as in the phase 2 trial that preceded them.10
The primary end point of the JADE COMPARE trial was to evaluate the efficacy of abrocitinib as compared with placebo at 12 weeks in adult patients with moderate to severe AD and in the setting of concomitant topical corticosteroid therapy.9 One of several secondary end points of this study compared the ability of dupilumab vs abrocitinib and placebo treatment groups to achieve itch reduction at 2 weeks, defined as 4-point improvement or more from baseline in the score on the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (NRS), a well‐defined, reliable, sensitive, and valid scale for evaluating worst itch intensity in adults with moderate to severe AD.9,11 The primary end point was the same as in the other phase 3 studies and was met in the JADE COMPARE trial by all treatment arms. An EASI-75 was seen in 70.3% of patients treated with 200 mg of abrocitinib, 58.7% in the 100-mg abrocitinib group, 58.1% in the dupilumab group, and 27.1% in the placebo group (P<.001 for both abrocitinib doses vs placebo). Only the 200-mg dose of abrocitinib demonstrated superior itch response at week 2 compared with dupilumab (22.1% response rate difference [95% CI, 13.5-30.7; P<.001]). Both abrocitinib groups failed to demonstrate significant differences compared with dupilumab with respect to other secondary end points to include IGA response and EASI-75 at week 16.9
The most frequently reported treatment-associated adverse events were nausea, nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and headache, and the percentages were similar among trial groups.9 Acne was more frequently reported in the abrocitinib groups compared with placebo and the dupilumab group, and conjunctivitis was more frequently reported in the dupilumab group. Herpesvirus cutaneous infections were rare in the abrocitinib groups, as were other serious infections. No deaths, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), or venous thromboembolic events (VTEs) occurred during the trial. Dose-dependent increases in creatinine phosphokinase were seen in the abrocitinib groups, whereas dose-dependent decreases were seen in platelet counts, with no patient demonstrating a platelet count below 75,000/mm3 during the study.9 Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels increased in a dose-dependent manner as well, but the ratios of low-density lipoprotein to high-density lipoprotein were unchanged.9 The results of a phase 3, 92-week extension study, JADE EXTEND, were recently published and demonstrated a role for abrocitinib as a treatment for patients with moderate to severe AD, regardless of prior dupilumab response status.12
Upadacitinib, another selective JAK1 inhibitor, was approved following data from 2 replicate double-blind, phase 3, randomized, controlled trials—Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2.13 Results demonstrated that monotherapy with once-daily upadacitinib 15 mg or 30 mg is an effective and well-tolerated treatment option for patients with moderate to severe AD vs placebo. All coprimary end points at week 16 were achieved in the upadacitinib groups in both trials. Acne, upper respiratory tract infections, nasopharyngitis, headache, and increase in serum creatinine phosphokinase levels were the most frequently reported adverse events. Rates of herpes zoster infection in upadacitinib groups were low.13
In the subsequent phase 3 AD Up trial, researchers evaluated the safety and efficacy of combination therapy with topical corticosteroids in patients aged 12 to 75 years.14 Upadacitinib groups again achieved the identical coprimary end points that were present in the Measure Up trials13 as well as all key secondary end points.14 Additionally, significant differences in secondary end points, such as a 4-point improvement in the Worst Pruritus NRS vs placebo, were noticed in both upadacitinib treatment groups as early as 1 week into the study (P<.0001), with maintenance of the effect through to week 16 (P<.0001).14 AD Up was followed by the Heads Up trial, a 24-week, phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled trial comparing safety and efficacy of upadacitinib with dupilumab among 692 adults with moderate to severe AD.15 At week 16, a higher percentage of patients in the upadacitinib group achieved EASI-75 vs the dupilumab group (71.0% vs 61.1%, respectively; P=.006). The difference noted at week 2 was even more impressive, with 43.7% of patients in the upadacitinib treatment group achieving EASI-75 compared with 17.4% in the dupilumab group (P<.001). No new safety-related events were registered compared with the already available data for both drugs.15
Ruxolitinib (RUX) is a topical JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor that was FDA approved in September 2021 for the treatment of AD.16 In a phase 2 clinical trial of 307 adult patients with 3% to 20% body surface area (BSA) affected with AD, significant reductions in itch NRS scores were observed within 36 hours after the first application of RUX cream 1.5% twice daily (-1.8 vs -0.2, P<.0001).17 These decreases were noted within the first 2 weeks of treatment for all the RUX cream regimens and were sustained through to week 8, the end of the double-blind period. At 4 weeks, change in itch from baseline was significantly reduced in the RUX 1.5% twice-daily group compared with the triamcinolone ointment 0.1% group (−4 vs −2.5, P=.003). During the open-label treatment period from 8 to 12 weeks, all patients who switched to RUX cream 1.5% twice daily noted further reductions in itch, and those who continued it demonstrated additional improvement.17
The recent FDA approval was further backed by positive phase 3 trial data from the TRuE-AD1 and TRuE-AD2 studies.18 Patients in these trials were aged 12 years and older and had AD for 2 or more years with an IGA score of 2 or 3 and 3% to 20% affected BSA. Patients were randomized to twice-daily RUX cream 0.75%, RUX cream 1.5%, or vehicle cream, and the primary end point was an IGA score of 0 or 1 and an improvement of 2 or more points from baseline at week 8. Significantly more patients achieved IGA treatment success with RUX cream 0.75% (TRuE-AD1, 50.0%; TRuE-AD2, 39.0%) and RUX cream 1.5% (TRuE-AD1, 53.8%; TRuE-AD2, 51.3%) vs vehicle (TRuE-AD1, 15.1%; TRuE-AD2, 7.6%; P<.0001) at week 8. The RUX groups experienced dramatically reduced itch compared with vehicle, with a mean reduction of approximately 3 points on the NRS at 8 weeks. Additionally, statistically significant itch reductions vs vehicle were reported within 12 hours of first application of RUX cream 1.5% (P<.05). Application-site reactions including stinging and burning occurred in less than 1% of patients, and none were considered clinically significant. Mean plasma concentrations of RUX were monitored during the phase 2 and 3 AD studies and did not lead to any clinically meaningful changes in hematologic parameters. The low bioavailability following topical application of RUX cream (6% in the TRuE-AD studies) allows for a targeted delivery of the active drug to lesional skin while reducing the safety issues associated with oral administration of JAK inhibitors.18
Baricitinib is a predominantly JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor that was the first JAK inhibitor to be approved for the treatment of moderate to severe AD in the European Union and Japan.19 Although the FDA’s decision on baricitinib has lagged behind market competitors, in 2 phase 3 clinical trials, BREEZE-AD1 and BREEZE-AD2, baricitinib demonstrated benefit over placebo on clinically important measures of disease severity. The primary end point—the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 or 1 with an improvement of 2 or more points from baseline at week 16—was met by both tested doses of baricitinib (2 mg and 4 mg) vs placebo in BREEZE-AD1 (2 mg, P≤.05; 4 mg, P≤.001) and BREEZE-AD2 (2 mg, P≤.05; 4 mg, P≤.001). In addition, baricitinib 4 mg consistently demonstrated significant benefit over placebo on other clinically important measures of disease severity at week 16 to include itch (BREEZE-AD1 and BREEZE-AD2, P≤.001), sleep disturbance (BREEZE-AD1, P≤.01; BREEZE-AD2, P≤.001), and skin pain (BREEZE-AD1, P≤.01; BREEZE-AD2, P≤.001). Nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infections, creatine phosphokinase elevations, and headaches were the most frequently reported adverse events. During the 16-week treatment period in these trials, no deaths, MACEs, or VTEs occurred.19 Similar results were seen in a long-term extension study, BREEZE-AD3.20 The combination of baricitinib and topical corticosteroids were evaluated in 2 additional phase 3 trials, BREEZE-AD421 and BREEZE-AD7.22 Although only baricitinib 4 mg met the primary end point of EASI-75 at week 16 in both trials, both dosing regimens plus topical corticosteroids demonstrated notable reduction in multiple clinical and quality-of-life indices prior to week 2 when compared with placebo plus topical corticosteroids.22,23
AD in Military Service Members
Atopic dermatitis is a common condition in the general population, with a prevalence of 7.3% (95% CI, 5.9-8.8) in a recent study of American adults.24 Historically, the burden of AD that would be expected among active-duty military service members given the prevalence among the general population has not been observed, in part because of the disqualifying nature of AD for enlistment.25 The Department of Defense Instruction 6130.03, Volume 1, Medical Standards for Military Service: Appointment, Enlistment, or Induction stipulates that a history of AD or eczema after the twelfth birthday or history of residual or recurrent lesions in characteristic areas (ie, face, neck, antecubital or popliteal fossae, occasionally wrists and hands) is disqualifying.26 Specific military services possess additional standards that further define limits within the aforementioned Department of Defense instruction.25 Additionally, there are service-specific policies in place that mandate medical evaluation boards to determine fitness for continued service in the event the condition interferes with the member’s ability to perform their duties. Insection 4.2 of the U.S. Navy Aeromedical Reference and Waiver Guide, further restrictions for aviation personnel are delineated: “Depending on the location of lesions, there can be interference with the wearing of flight gear. The symptoms, particularly itching, can be distracting in flight. Patients with atopic dermatitis are more susceptible to contact dermatitis due to irritants found in a military environment.” Ultimately, the document stipulates that symptom severity and the requirement for therapy will determine the aeromedical disposition. It specifically states that “[p]atients controlled on topical therapy over small areas and patients who are asymptomatic on stable doses of loratadine (Claritin) OR fexofenadine (Allegra) may be considered for waiver,” and “intermittent use of topical steroids over a limited area is compatible with waiver.”27 It follows that limited use of topical JAK inhibitors, such as RUX, would be compatible with a waiver, given the favorable side effect profile and requirement for use in patients with 20% or lower affected BSA.16 This is just one example of duty-specific and service-specific medical standards that exist that could impact the use of both topical and oral JAK inhibitors.
Use of oral JAK inhibitors in active-duty service members is less ideal for multiple reasons. A large randomized safety clinical trial of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who received tofacitinib and methotrexate was required by the FDA to evaluate the risk of MACEs, malignancy, and infections associated with JAK inhibitor treatment. Data from this trial showed a dose-dependent increased risk for MACEs, all-cause mortality, and thrombosis at both doses of tofacitinib compared with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and a non–dose-dependent increased risk for malignancy excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer.28 In contrast to the MACE and VTE data from patients with diseases other than AD treated with JAK inhibitors, there has been only 1 patient who developed a pulmonary embolism while being treated with baricitinib 4 mg.22,29 Downstream effects from the above study were label recommendations to reserve the medicines for patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to 1 or more tumor necrosis factor blockers and to carefully consider risks vs benefits in patients, in particular current or prior smokers, those with other cardiovascular risk factors or a history of VTE, and those with a malignancy history other than already treated nonmelanoma skin cancer.28
There are consistent observations of laboratory abnormalities with JAK inhibitors, as discussed above, to include creatine phosphokinase elevation and cytopenias.30 Although existing data demonstrate that cytopenias are less of a concern in the AD population compared with the rheumatoid arthritis population, baseline and periodic laboratory monitoring are still recommended. In general, pretreatment laboratory assessment prior to initiating an oral JAK inhibitor should consist of a complete blood cell count with differential, complete metabolic panel, tuberculosis screening, chronic hepatitis panel, HIV screening, and a fasting lipid panel.2 The feasibility of obtaining these laboratory measurements in an operational setting or sea-going platform is limited, but many deployed locations and naval vessels possess the laboratory capability to perform a complete blood cell count and complete metabolic panel. Overall tolerability of oral JAK inhibitors in the treatment of AD appears favorable based on studies that were mostly 16 weeks in duration. Few recent longer-term studies have confirmed this side effect profile, but additional studies are needed.
Final Thoughts
Janus kinase inhibitors are a promising therapeutic class with multiple recently FDA-approved agents for the treatment of moderate to severe AD, with new agents on the horizon. Available efficacy data are promising and balanced by a favorable safety profile in clinical trials to date. The oral and topical bioavailability of JAK inhibitors makes them attractive alternatives to existing therapies. The rapidity of itch reduction and AD improvement demonstrated in multiple trials has the potential to decrease the length of limited-duty assignments, potentially returning treated service members to full-duty status more expeditiously. Other applications include use of these medications in scenarios where injectable medications are either unavailable or unsupported.
In the active-duty population, both the condition and/or the treatment may be duty limiting. Service members with AD who require more than topical treatment may require a medical evaluation board to determine if they are still fit to serve. The deployed environment routinely exacerbates AD and exposes service members to infections and environments where immunosuppression can create more risks than in the general population. Nonbiologic medications, which do not require refrigeration, are an exciting option for our patients with AD, including those actively serving or considering serving in the military. However, all factors in any patient’s life should be considered. Therefore, it is important for the nonmilitary dermatologist to work with local military physicians and the patient to determine the optimal treatment regimen to result in the best possible outcome.
- Damsky W, Peterson D, Ramseier J, et al. The emerging role of Janus kinase inhibitors in the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:814-826.
- Gadina M, Le MT, Schwartz DM, et al. Janus kinases to jakinibs: from basic insights to clinical practice. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019;58(suppl 1):i4-i6.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 2, management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132.
- Cartron AM, Nguyen TH, Roh YS, et al. Janus kinase inhibitors for atopic dermatitis: a promising treatment modality. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46:820-824.
- Oetjen LK, Mack MR, Feng J, et al. Sensory neurons co-opt classical immune signaling pathways to mediate chronic itch. Cell. 2017;171:217-228.e13.
- U.S. FDA approves Pfizer’s CIBINQO® (abrocitinib) for adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [press release]. January 14, 2022. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/us-fda-approves-pfizers-cibinqor-abrocitinib-adults
- Simpson EL, Sinclair R, Forman S, et al. Efficacy and safety of abrocitinib in adults and adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (JADE MONO-1): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2020;396:255-266.
- Silverberg JI, Simpson EL, Thyssen JP, et al. Efficacy and safety of abrocitinib in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:863-873.
- Bieber T, Simpson EL, Silverberg JI, et al. Abrocitinib versus placebo or dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1101-1112.
- Gooderham MJ, Forman SB, Bissonnette R, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral Janus kinase 1 inhibitor abrocitinib for patients with atopic dermatitis: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1371-1379. Published correction appears in JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:104.
- Yosipovitch G, Reaney M, Mastey V, et al. Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale: psychometric validation and responder definition for assessing itch in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:761-769.
- Shi VY, Bhutani T, Fonacier L, et al. Phase 3 efficacy and safety of abrocitinib in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis after switching from dupilumab (JADE EXTEND). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:351-358.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021;397:2151-2168.
- Reich K, Teixeira HD, de Bruin-Weller M, et al. Safety and efficacy of upadacitinib in combination with topical corticosteroids in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD Up): results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:2169-2181.
- Blauvelt A, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib vs dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1047-1055. Published correction appears in JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:219.
- FDA approves Opzelura. Drugs.com. September 21, 2021. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://www.drugs.com/newdrugs/fda-approves-opzelura-ruxolitinib-cream-atopic-dermatitis-ad-5666.html
- Kim BS, Sun K, Papp K, et al. Effects of ruxolitinib cream on pruritus and quality of life in atopic dermatitis: results from a phase 2, randomized, doseranging, vehicle- and active-controlled study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1305-1313.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib cream for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 2 phase 3, randomized, double-blind studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:863-872.
- Simpson EL, Lacour JP, Spelman L, et al. Baricitinib in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis and inadequate response to topical corticosteroids: results from two randomized monotherapy phase III trials. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:242-255.
- Silverberg JI, Simpson EL, Wollenberg A, et al. Long-term efficacy of baricitinib in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis who were treatment responders or partial responders: an extension study of 2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:691-699.
- Lilly and Incyte announce top-line results from phase 3 study (BREEZE-AD4) of oral selective JAK inhibitor baricitinib in combination with topical corticosteroids in patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis not controlled with cyclosporine. January 27, 2020. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lilly-and-incyte-announce-top-line-results-phase-3-study-breeze
- Reich K, Kabashima K, Peris K, et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib combined with topical corticosteroids for treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:1333-1343.
- Wollenberg A, Nakahara T, Maari C, et al. Impact of baricitinib in combination with topical steroids on atopic dermatitis symptoms, quality of life and functioning in adult patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis from the BREEZE-AD7 phase 3 randomized trial. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:1543-1552.
- Chiesa Fuxench ZC, Block JK, Boguniewicz M, et al. Atopic dermatitis in America study: a cross-sectional study examining the prevalence and disease burden of atopic dermatitis in the US adult population. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:583-590.
- Jeter J, Bowen C. Atopic dermatitis and implications for military service. Mil Med. 2019;184:E177-E182.
- Department of Defense. Medical standards for military service: appointment, enlistment, or induction. DoD Instruction 6130.03. Vol 1. May 6, 2022. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.esd.whs.mil/Portals/54/Documents/DD/issuances/dodi/613003_v1p.PDF?ver=9NsVi30gsHBBsRhMLcyVVQ%3d%3d
- Dermatitis. In: U.S. Navy Aeromedical Reference and Waiver Guide. Navy Medicine Operational Training Command and Naval Aerospace Medical Institute. August 11, 2021. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.med.navy.mil/Portals/62/Documents/NMFSC/NMOTC/NAMI/ARWG/Waiver%20Guide/ARWG%20COMPLETE_210811.pdf?ver=_pLPzFrtl8E2swFESnN4rA%3D%3D
- FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. FDA Drug Safety Podcast. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Updated January 14, 2022. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-drug-safety-podcasts/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death
- Chang PH, Huang SF, Chang PS, et al. Safety considerations of systemic Janus kinase inhibitors in atopic dermatitis applications. J Dermatol. 2021;48:1631-1639.
- Wood H, Chandler A, Nezamololama N, et al. Safety of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in the short-term treatment of atopic dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:746-754.
- Damsky W, Peterson D, Ramseier J, et al. The emerging role of Janus kinase inhibitors in the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147:814-826.
- Gadina M, Le MT, Schwartz DM, et al. Janus kinases to jakinibs: from basic insights to clinical practice. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019;58(suppl 1):i4-i6.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 2, management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132.
- Cartron AM, Nguyen TH, Roh YS, et al. Janus kinase inhibitors for atopic dermatitis: a promising treatment modality. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46:820-824.
- Oetjen LK, Mack MR, Feng J, et al. Sensory neurons co-opt classical immune signaling pathways to mediate chronic itch. Cell. 2017;171:217-228.e13.
- U.S. FDA approves Pfizer’s CIBINQO® (abrocitinib) for adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis [press release]. January 14, 2022. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/us-fda-approves-pfizers-cibinqor-abrocitinib-adults
- Simpson EL, Sinclair R, Forman S, et al. Efficacy and safety of abrocitinib in adults and adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (JADE MONO-1): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2020;396:255-266.
- Silverberg JI, Simpson EL, Thyssen JP, et al. Efficacy and safety of abrocitinib in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:863-873.
- Bieber T, Simpson EL, Silverberg JI, et al. Abrocitinib versus placebo or dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1101-1112.
- Gooderham MJ, Forman SB, Bissonnette R, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral Janus kinase 1 inhibitor abrocitinib for patients with atopic dermatitis: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1371-1379. Published correction appears in JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:104.
- Yosipovitch G, Reaney M, Mastey V, et al. Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale: psychometric validation and responder definition for assessing itch in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:761-769.
- Shi VY, Bhutani T, Fonacier L, et al. Phase 3 efficacy and safety of abrocitinib in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis after switching from dupilumab (JADE EXTEND). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:351-358.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021;397:2151-2168.
- Reich K, Teixeira HD, de Bruin-Weller M, et al. Safety and efficacy of upadacitinib in combination with topical corticosteroids in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD Up): results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:2169-2181.
- Blauvelt A, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib vs dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1047-1055. Published correction appears in JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:219.
- FDA approves Opzelura. Drugs.com. September 21, 2021. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://www.drugs.com/newdrugs/fda-approves-opzelura-ruxolitinib-cream-atopic-dermatitis-ad-5666.html
- Kim BS, Sun K, Papp K, et al. Effects of ruxolitinib cream on pruritus and quality of life in atopic dermatitis: results from a phase 2, randomized, doseranging, vehicle- and active-controlled study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1305-1313.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib cream for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 2 phase 3, randomized, double-blind studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:863-872.
- Simpson EL, Lacour JP, Spelman L, et al. Baricitinib in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis and inadequate response to topical corticosteroids: results from two randomized monotherapy phase III trials. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:242-255.
- Silverberg JI, Simpson EL, Wollenberg A, et al. Long-term efficacy of baricitinib in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis who were treatment responders or partial responders: an extension study of 2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:691-699.
- Lilly and Incyte announce top-line results from phase 3 study (BREEZE-AD4) of oral selective JAK inhibitor baricitinib in combination with topical corticosteroids in patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis not controlled with cyclosporine. January 27, 2020. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lilly-and-incyte-announce-top-line-results-phase-3-study-breeze
- Reich K, Kabashima K, Peris K, et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib combined with topical corticosteroids for treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:1333-1343.
- Wollenberg A, Nakahara T, Maari C, et al. Impact of baricitinib in combination with topical steroids on atopic dermatitis symptoms, quality of life and functioning in adult patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis from the BREEZE-AD7 phase 3 randomized trial. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:1543-1552.
- Chiesa Fuxench ZC, Block JK, Boguniewicz M, et al. Atopic dermatitis in America study: a cross-sectional study examining the prevalence and disease burden of atopic dermatitis in the US adult population. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:583-590.
- Jeter J, Bowen C. Atopic dermatitis and implications for military service. Mil Med. 2019;184:E177-E182.
- Department of Defense. Medical standards for military service: appointment, enlistment, or induction. DoD Instruction 6130.03. Vol 1. May 6, 2022. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.esd.whs.mil/Portals/54/Documents/DD/issuances/dodi/613003_v1p.PDF?ver=9NsVi30gsHBBsRhMLcyVVQ%3d%3d
- Dermatitis. In: U.S. Navy Aeromedical Reference and Waiver Guide. Navy Medicine Operational Training Command and Naval Aerospace Medical Institute. August 11, 2021. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.med.navy.mil/Portals/62/Documents/NMFSC/NMOTC/NAMI/ARWG/Waiver%20Guide/ARWG%20COMPLETE_210811.pdf?ver=_pLPzFrtl8E2swFESnN4rA%3D%3D
- FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. FDA Drug Safety Podcast. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Updated January 14, 2022. Accessed November 18, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-drug-safety-podcasts/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death
- Chang PH, Huang SF, Chang PS, et al. Safety considerations of systemic Janus kinase inhibitors in atopic dermatitis applications. J Dermatol. 2021;48:1631-1639.
- Wood H, Chandler A, Nezamololama N, et al. Safety of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in the short-term treatment of atopic dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:746-754.
Practice Points
- Oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are novel therapies available for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD), with multiple recently approved agents within the class.
- Recommended laboratory monitoring during treatment with oral JAK inhibitors may limit the use of these medications in the active-duty military population or in those with special-duty assignments.
- The oral and topical bioavailability of these medications makes them a more feasible option for deploying service members or for those requiring flexible dosing.
- The rapid improvement in AD seen in multiple trials of oral JAK inhibitors suggests these agents could prove useful in management of acute AD flares, especially in military environments, where injectable agents are either unavailable or unsupported.
Commentary: Prevention in AD, December 2022
We are in the golden age of atopic dermatitis (AD) drug development. We are fortunate to have numerous topicals, oral systemics, and biologics recently approved or in late-stage clinical development. Yet, we are still lacking effective strategies for primary prevention of incident AD and secondary prevention of AD exacerbations.
Kottner and colleagues published the results from the ADAPI study of 150 infants who were at an enhanced risk for AD. The children were randomly assigned to receive either a skincare regimen that was standardized or unstandardized skincare preferred by parents. They found that in the first year of life, the overall cumulative incidence rate of AD was similar between standardized skincare and skincare preferred by parents (P = .999).
Bradshaw and colleagues also published results from the BEEP study (a 5-year prospective study) of 1394 infants who were at high risk for AD. The children were randomly assigned to receive either emollient for the first year plus standard skincare or standard skincare alone. They found a similar proportion of children were clinically diagnosed with AD between 12 and 60 months in the emollient plus skincare group vs skincare alone group (31% vs 28%; adjusted relative risk 1.10; 95% CI 0.93-1.30). Unfortunately, the results from both studies are consistent with earlier results from BEEP, as well as other studies, and did not show that early application of emollients successfully prevent AD.
The use of applying emollients for primary prevention is unclear. However, proactive application of topical corticosteroids (TCS) and other topical nonsteroidal agents is well accepted in AD treatment guidelines for secondary prevention of AD exacerbations.1 Although, a recent study from Kamiya and colleagues suggested that proactive application of topical corticosteroids may not work as well as we think. They conducted an open-label, active-controlled, parallel-group study of 49 pediatric patients with moderate to severe AD who achieved remission with potent TCS. The children were then randomly assigned to receive proactive therapy with or discontinuation of TCS. The authors found no significant decrease in relapse rates with proactive vs no proactive treatment groups (8.33% vs 20.0%; P = .0859). I don't think these results will change our guidelines. But I do think these results raise important questions about the myriad aspects of proactive therapy that require appropriate counseling, including frequency of application per week (1-3 times), choice of therapies (corticosteroid or nonsteroidal agent), additional emollient use, bathing practice, etc. I personally would strongly recommend use of proactive therapy in clinical practice, but these results highlight that it is not a magic bullet for all patients either.
Additional Reference
- Boguniewicz M, Fonacier L, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Atopic dermatitis yardstick: practical recommendations for an evolving therapeutic landscape. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;120:10-22.e2. Doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2017.10.039
We are in the golden age of atopic dermatitis (AD) drug development. We are fortunate to have numerous topicals, oral systemics, and biologics recently approved or in late-stage clinical development. Yet, we are still lacking effective strategies for primary prevention of incident AD and secondary prevention of AD exacerbations.
Kottner and colleagues published the results from the ADAPI study of 150 infants who were at an enhanced risk for AD. The children were randomly assigned to receive either a skincare regimen that was standardized or unstandardized skincare preferred by parents. They found that in the first year of life, the overall cumulative incidence rate of AD was similar between standardized skincare and skincare preferred by parents (P = .999).
Bradshaw and colleagues also published results from the BEEP study (a 5-year prospective study) of 1394 infants who were at high risk for AD. The children were randomly assigned to receive either emollient for the first year plus standard skincare or standard skincare alone. They found a similar proportion of children were clinically diagnosed with AD between 12 and 60 months in the emollient plus skincare group vs skincare alone group (31% vs 28%; adjusted relative risk 1.10; 95% CI 0.93-1.30). Unfortunately, the results from both studies are consistent with earlier results from BEEP, as well as other studies, and did not show that early application of emollients successfully prevent AD.
The use of applying emollients for primary prevention is unclear. However, proactive application of topical corticosteroids (TCS) and other topical nonsteroidal agents is well accepted in AD treatment guidelines for secondary prevention of AD exacerbations.1 Although, a recent study from Kamiya and colleagues suggested that proactive application of topical corticosteroids may not work as well as we think. They conducted an open-label, active-controlled, parallel-group study of 49 pediatric patients with moderate to severe AD who achieved remission with potent TCS. The children were then randomly assigned to receive proactive therapy with or discontinuation of TCS. The authors found no significant decrease in relapse rates with proactive vs no proactive treatment groups (8.33% vs 20.0%; P = .0859). I don't think these results will change our guidelines. But I do think these results raise important questions about the myriad aspects of proactive therapy that require appropriate counseling, including frequency of application per week (1-3 times), choice of therapies (corticosteroid or nonsteroidal agent), additional emollient use, bathing practice, etc. I personally would strongly recommend use of proactive therapy in clinical practice, but these results highlight that it is not a magic bullet for all patients either.
Additional Reference
- Boguniewicz M, Fonacier L, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Atopic dermatitis yardstick: practical recommendations for an evolving therapeutic landscape. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;120:10-22.e2. Doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2017.10.039
We are in the golden age of atopic dermatitis (AD) drug development. We are fortunate to have numerous topicals, oral systemics, and biologics recently approved or in late-stage clinical development. Yet, we are still lacking effective strategies for primary prevention of incident AD and secondary prevention of AD exacerbations.
Kottner and colleagues published the results from the ADAPI study of 150 infants who were at an enhanced risk for AD. The children were randomly assigned to receive either a skincare regimen that was standardized or unstandardized skincare preferred by parents. They found that in the first year of life, the overall cumulative incidence rate of AD was similar between standardized skincare and skincare preferred by parents (P = .999).
Bradshaw and colleagues also published results from the BEEP study (a 5-year prospective study) of 1394 infants who were at high risk for AD. The children were randomly assigned to receive either emollient for the first year plus standard skincare or standard skincare alone. They found a similar proportion of children were clinically diagnosed with AD between 12 and 60 months in the emollient plus skincare group vs skincare alone group (31% vs 28%; adjusted relative risk 1.10; 95% CI 0.93-1.30). Unfortunately, the results from both studies are consistent with earlier results from BEEP, as well as other studies, and did not show that early application of emollients successfully prevent AD.
The use of applying emollients for primary prevention is unclear. However, proactive application of topical corticosteroids (TCS) and other topical nonsteroidal agents is well accepted in AD treatment guidelines for secondary prevention of AD exacerbations.1 Although, a recent study from Kamiya and colleagues suggested that proactive application of topical corticosteroids may not work as well as we think. They conducted an open-label, active-controlled, parallel-group study of 49 pediatric patients with moderate to severe AD who achieved remission with potent TCS. The children were then randomly assigned to receive proactive therapy with or discontinuation of TCS. The authors found no significant decrease in relapse rates with proactive vs no proactive treatment groups (8.33% vs 20.0%; P = .0859). I don't think these results will change our guidelines. But I do think these results raise important questions about the myriad aspects of proactive therapy that require appropriate counseling, including frequency of application per week (1-3 times), choice of therapies (corticosteroid or nonsteroidal agent), additional emollient use, bathing practice, etc. I personally would strongly recommend use of proactive therapy in clinical practice, but these results highlight that it is not a magic bullet for all patients either.
Additional Reference
- Boguniewicz M, Fonacier L, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Atopic dermatitis yardstick: practical recommendations for an evolving therapeutic landscape. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;120:10-22.e2. Doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2017.10.039
Brepocitinib improves symptoms of mild to moderate AD in phase 2b trial
compared with a group that received vehicle, in a recently published study..
The investigators said that brepocitinib, an investigational dual tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) and Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) inhibitor, was effective and well tolerated in patients with mild to moderate AD based on improvements in multiple measures, including Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) total score and Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) responder rates. Brepocitinib also reduced pruritus symptoms as early as 2 days after the start of treatment, they noted.
“This study supports the further evaluation of topical brepocitinib as a novel treatment for mild to moderate AD,” Megan N. Landis, MD, of the department of medicine at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and colleagues wrote in the study published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
They evaluated brepocitinib in a phase 2b, double-blind, dose-ranging study where 292 patients were randomized to receive brepocitinib once daily (brepocitinib 0.1%, 0.3%, 1.0%, 3.0%) or twice daily (brepocitinib 0.3%, 1.0%), or vehicle for 6 weeks. At 6 weeks, the researchers assessed EASI total score as a primary outcome, an IGA score of 0 or 1 as a secondary outcome. The mean age of the patients was 40 years (range, 13-74), almost 60% were White, 17.5% were Black, and about 20% were Asian.
Compared with the corresponding once-daily vehicle group (least squares mean reduction of –44.4; 90% confidence interval, –57.3 to –31.6) and the twice-daily vehicle group (LSM, –47.6; 90% CI, –57.5 to –37.7) , the brepocitinib 1% once-daily group (LSM, –70.1; 90% CI, –82.1 to –58.0) and twice-daily group (LSM, –75.0; 90% CI, –83.8 to –66.2) had significant percentage reductions in EASI total score compared with baseline at 6 weeks. Patients in the other brepocitinib dose groups had nonsignificant reductions in EASI from baseline.
Regarding secondary outcomes, a significantly higher percentage of patients in five of the six active treatment groups achieved an IGA score of 0 or 1 and at least a 2-point reduction in IGA score in the once-daily brepocitinib 0.1% group (29.7%; 90% CI, 18.5%-43.3%), 0.3% group (33.3%; 90% CI, 21.3%-47.0%), 1.0% group (40.5%; 90% CI, 28.0%-54.4%), 3.0% group (44.4%; 90% CI, 30.2%-59.1%), and brepocitinib 0.3% twice-daily group (33.3%; 90% CI, 21.3%-47.0%) compared with the once-daily (10.8%; 90% CI, 4.8%-22.2%) and twice-daily (13.9%; 90% CI, 6.9%-25.4%) vehicle groups.
The study authors noted that 37.0% of patients overall experienced treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs), with most TEAEs occurring in the once-daily vehicle (48.6%), twice-daily vehicle (47.2%), and brepocitinib 0.1% (45.9%) groups. Adverse events were not considered dose dependent, and no group had any serious TEAEs or deaths.
Nasopharyngitis and worsening AD were the most common TEAEs reported, with about 8% of those in the vehicle groups experiencing worsening AD.
Brepocitinib is also currently being developed as a treatment for dermatomyositis, systemic lupus erythematosus, hidradenitis suppurativa, and noninfectious uveitis by Priovant Therapeutics, a company founded by Pfizer and Roivant Sciences.
In September 2021, the Food and Drug Administration approved topical ruxolitinib cream for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis aged 12 years and older, the first topical JAK inhibitor approved for AD.
This study was sponsored by Pfizer. The authors reported personal and institutional relationships in the form of investigator positions, fees, honoraria, research grants, employee positions, and holding stock or shares for a variety of pharmaceutical, life science, and biotechnology companies.
compared with a group that received vehicle, in a recently published study..
The investigators said that brepocitinib, an investigational dual tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) and Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) inhibitor, was effective and well tolerated in patients with mild to moderate AD based on improvements in multiple measures, including Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) total score and Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) responder rates. Brepocitinib also reduced pruritus symptoms as early as 2 days after the start of treatment, they noted.
“This study supports the further evaluation of topical brepocitinib as a novel treatment for mild to moderate AD,” Megan N. Landis, MD, of the department of medicine at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and colleagues wrote in the study published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
They evaluated brepocitinib in a phase 2b, double-blind, dose-ranging study where 292 patients were randomized to receive brepocitinib once daily (brepocitinib 0.1%, 0.3%, 1.0%, 3.0%) or twice daily (brepocitinib 0.3%, 1.0%), or vehicle for 6 weeks. At 6 weeks, the researchers assessed EASI total score as a primary outcome, an IGA score of 0 or 1 as a secondary outcome. The mean age of the patients was 40 years (range, 13-74), almost 60% were White, 17.5% were Black, and about 20% were Asian.
Compared with the corresponding once-daily vehicle group (least squares mean reduction of –44.4; 90% confidence interval, –57.3 to –31.6) and the twice-daily vehicle group (LSM, –47.6; 90% CI, –57.5 to –37.7) , the brepocitinib 1% once-daily group (LSM, –70.1; 90% CI, –82.1 to –58.0) and twice-daily group (LSM, –75.0; 90% CI, –83.8 to –66.2) had significant percentage reductions in EASI total score compared with baseline at 6 weeks. Patients in the other brepocitinib dose groups had nonsignificant reductions in EASI from baseline.
Regarding secondary outcomes, a significantly higher percentage of patients in five of the six active treatment groups achieved an IGA score of 0 or 1 and at least a 2-point reduction in IGA score in the once-daily brepocitinib 0.1% group (29.7%; 90% CI, 18.5%-43.3%), 0.3% group (33.3%; 90% CI, 21.3%-47.0%), 1.0% group (40.5%; 90% CI, 28.0%-54.4%), 3.0% group (44.4%; 90% CI, 30.2%-59.1%), and brepocitinib 0.3% twice-daily group (33.3%; 90% CI, 21.3%-47.0%) compared with the once-daily (10.8%; 90% CI, 4.8%-22.2%) and twice-daily (13.9%; 90% CI, 6.9%-25.4%) vehicle groups.
The study authors noted that 37.0% of patients overall experienced treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs), with most TEAEs occurring in the once-daily vehicle (48.6%), twice-daily vehicle (47.2%), and brepocitinib 0.1% (45.9%) groups. Adverse events were not considered dose dependent, and no group had any serious TEAEs or deaths.
Nasopharyngitis and worsening AD were the most common TEAEs reported, with about 8% of those in the vehicle groups experiencing worsening AD.
Brepocitinib is also currently being developed as a treatment for dermatomyositis, systemic lupus erythematosus, hidradenitis suppurativa, and noninfectious uveitis by Priovant Therapeutics, a company founded by Pfizer and Roivant Sciences.
In September 2021, the Food and Drug Administration approved topical ruxolitinib cream for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis aged 12 years and older, the first topical JAK inhibitor approved for AD.
This study was sponsored by Pfizer. The authors reported personal and institutional relationships in the form of investigator positions, fees, honoraria, research grants, employee positions, and holding stock or shares for a variety of pharmaceutical, life science, and biotechnology companies.
compared with a group that received vehicle, in a recently published study..
The investigators said that brepocitinib, an investigational dual tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) and Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) inhibitor, was effective and well tolerated in patients with mild to moderate AD based on improvements in multiple measures, including Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) total score and Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) responder rates. Brepocitinib also reduced pruritus symptoms as early as 2 days after the start of treatment, they noted.
“This study supports the further evaluation of topical brepocitinib as a novel treatment for mild to moderate AD,” Megan N. Landis, MD, of the department of medicine at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and colleagues wrote in the study published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
They evaluated brepocitinib in a phase 2b, double-blind, dose-ranging study where 292 patients were randomized to receive brepocitinib once daily (brepocitinib 0.1%, 0.3%, 1.0%, 3.0%) or twice daily (brepocitinib 0.3%, 1.0%), or vehicle for 6 weeks. At 6 weeks, the researchers assessed EASI total score as a primary outcome, an IGA score of 0 or 1 as a secondary outcome. The mean age of the patients was 40 years (range, 13-74), almost 60% were White, 17.5% were Black, and about 20% were Asian.
Compared with the corresponding once-daily vehicle group (least squares mean reduction of –44.4; 90% confidence interval, –57.3 to –31.6) and the twice-daily vehicle group (LSM, –47.6; 90% CI, –57.5 to –37.7) , the brepocitinib 1% once-daily group (LSM, –70.1; 90% CI, –82.1 to –58.0) and twice-daily group (LSM, –75.0; 90% CI, –83.8 to –66.2) had significant percentage reductions in EASI total score compared with baseline at 6 weeks. Patients in the other brepocitinib dose groups had nonsignificant reductions in EASI from baseline.
Regarding secondary outcomes, a significantly higher percentage of patients in five of the six active treatment groups achieved an IGA score of 0 or 1 and at least a 2-point reduction in IGA score in the once-daily brepocitinib 0.1% group (29.7%; 90% CI, 18.5%-43.3%), 0.3% group (33.3%; 90% CI, 21.3%-47.0%), 1.0% group (40.5%; 90% CI, 28.0%-54.4%), 3.0% group (44.4%; 90% CI, 30.2%-59.1%), and brepocitinib 0.3% twice-daily group (33.3%; 90% CI, 21.3%-47.0%) compared with the once-daily (10.8%; 90% CI, 4.8%-22.2%) and twice-daily (13.9%; 90% CI, 6.9%-25.4%) vehicle groups.
The study authors noted that 37.0% of patients overall experienced treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs), with most TEAEs occurring in the once-daily vehicle (48.6%), twice-daily vehicle (47.2%), and brepocitinib 0.1% (45.9%) groups. Adverse events were not considered dose dependent, and no group had any serious TEAEs or deaths.
Nasopharyngitis and worsening AD were the most common TEAEs reported, with about 8% of those in the vehicle groups experiencing worsening AD.
Brepocitinib is also currently being developed as a treatment for dermatomyositis, systemic lupus erythematosus, hidradenitis suppurativa, and noninfectious uveitis by Priovant Therapeutics, a company founded by Pfizer and Roivant Sciences.
In September 2021, the Food and Drug Administration approved topical ruxolitinib cream for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis aged 12 years and older, the first topical JAK inhibitor approved for AD.
This study was sponsored by Pfizer. The authors reported personal and institutional relationships in the form of investigator positions, fees, honoraria, research grants, employee positions, and holding stock or shares for a variety of pharmaceutical, life science, and biotechnology companies.
FROM BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
Consider gaps in access and knowledge in diagnosis and treatment in skin of color
LAS VEGAS – and patients, Susan C. Taylor, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Additionally, some disparities occur because of gaps in access to health care, said Dr. Taylor, vice chair, diversity, equity and inclusion, in the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who moderated an expert panel discussion of treatment tips for several common dermatologic conditions in skin of color patients.
Atopic dermatitis angles
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is the fourth most common dermatologic complaint in Black patients, based on data from the United States National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. Also, data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey show that Black children are nearly twice as likely as White children to develop AD after controlling for socioeconomic factors, Dr. Taylor said.
When Black patients present with AD, “you may not see the erythema,” said Valerie D. Callender, MD, of Howard University, Washington, who presented on AD. Instead, “you may see more follicular and papular presentations.” Erythema and erythroderma can present as shades of violet, gray, or dark brown in patients with rich skin tones, added Dr. Callender, who practices in Glenn Dale, Md.
Consequently, disease severity can be misinterpreted, she said, noting that data suggest that scoring systems such as the Eczema Area and Severity Index and Scoring Atopic Dermatitis underestimate AD severity in dark skin.
As for treatment, skin of color patients with AD are often as bothered by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) as by active lesions, so treatment should take these concerns into account, Dr. Callender said. Studies evaluating the effectiveness of AD treatments in diverse populations are limited by lack of representation of racial groups in clinical trials and lack of subset analyses by race.
Acne awareness
An important consideration of acne in skin of color patients is that the acne “might not be red, it might just be darker,” said Andrew F. Alexis, MD, vice-chair for diversity and inclusion in the department of dermatology, and professor of clinical dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. A study published in JAMA Dermatology of nearly 30,000 patients with acne from 2007 to 2017 found that non-Hispanic Black patients were more likely than non-Hispanic White patients to see a dermatologist for acne, but Black patients received fewer prescriptions for acne medications than White patients.
The study also showed that Black patients who received prescriptions for acne were more likely to receive topical retinoids and topical antibiotics, and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, spironolactone, or isotretinoin, compared with White patients. Similarly, Asian patients were more likely to receive topical antibiotics and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, compared with White patients.
Other panelists shared some of their best practices for acne in patients with skin of color, including treatment with topical retinoids (for inflammation) and spironolactone, and therapies that address both inflammation and pigmentation, such as salicylic acid and azelaic acid. Dr. Callender also advised asking patients about makeup, as they may not know that many types of makeup used to cover acne are in fact comedogenic.
Melanoma misconceptions
One of the most common misperceptions about melanoma among skin of color patients is that they don’t think they can get it, Dr. Taylor said. Many health care providers don’t think about melanoma in skin of color patients because of the dramatically lower incidence in this population, but as a result, cases may go undiagnosed, and as studies have shown, the mortality rate from melanoma is higher in Black patients.
Consider the palms, soles, nails, and web spaces as possible melanoma sites, Dr. Taylor added.
Educating skin of color patients about melanoma is important, although the incidence is 20 to 30 times lower than in non-Hispanic Whites, said Nada Elbuluk, MD, the founder and director of the University of Southern California Skin of Color Center and Pigmentary Disorders Clinic, Los Angeles. A 2020 editorial published in Cancer Cytopathology pointed out that 1 in 3 Black men or women with a melanoma diagnosis in the United States dies of the disease, compared with 1 in 7 non-Hispanic White men and 1 in 11 non-Hispanic White women with melanoma.
Don’t skip the total body skin exam in these patients, Dr. Elbuluk emphasized. Many patients will only partially undress, and areas such as toes can be missed.
Rosacea review
For patients with skin of color, clinicians need to look for different signs of rosacea than those typically seen in White patients, Dr. Elbuluk said. “The most common presentation of rosacea in skin of color is papulopustular,” and the granulomatous variant.
“These patients will often give you a history of sensitivity to products,” Dr. Elbuluk noted. They may not always have the flushing, but they may report warmth or itching, in addition to product sensitivity.
When considering rosacea in skin of color patients, be sure to have good lighting for close examination, as skin thickening is another subtle sign of rosacea in these patients, she said. Skin thickening “is a very early sign that will present in skin of color with no erythema, so keep that in mind.”
Stinging and burning sensations may be reported by skin of color patients with rosacea. Use patient history to confirm the diagnosis of rosacea, which is often delayed in skin of color patients because of a low index of suspicion, she said.
Psoriasis pointers
Psoriasis in skin of color patients used to be considered rare, “but that is far from true,” Dr. Alexis said. In fact, many cases of psoriasis are undiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed in these patients.
The panelists noted that current guidelines for psoriasis treatment are based on clinical trials composed mainly of White patients, and do not contain specific recommendations for skin of color patients.
Notably, the morphology, location, and color of psoriasis lesions may be different for patients with darker skin, such as thicker plaques and more scaling over larger areas, they said. Also, skin of color patients may experience long-lasting dyspigmentation from psoriasis lesions that have resolved.
When developing a strategy for psoriasis in skin of color patients, consider not only disease severity, but also comorbidities and medications, response (if any) to prior therapies, patient preferences, and quality of life, the panelists said.
Dr. Callender, Dr. Elbuluk, Dr. Taylor, and Dr. Alexis reported conflicts of interest from numerous sources in industry. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – and patients, Susan C. Taylor, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Additionally, some disparities occur because of gaps in access to health care, said Dr. Taylor, vice chair, diversity, equity and inclusion, in the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who moderated an expert panel discussion of treatment tips for several common dermatologic conditions in skin of color patients.
Atopic dermatitis angles
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is the fourth most common dermatologic complaint in Black patients, based on data from the United States National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. Also, data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey show that Black children are nearly twice as likely as White children to develop AD after controlling for socioeconomic factors, Dr. Taylor said.
When Black patients present with AD, “you may not see the erythema,” said Valerie D. Callender, MD, of Howard University, Washington, who presented on AD. Instead, “you may see more follicular and papular presentations.” Erythema and erythroderma can present as shades of violet, gray, or dark brown in patients with rich skin tones, added Dr. Callender, who practices in Glenn Dale, Md.
Consequently, disease severity can be misinterpreted, she said, noting that data suggest that scoring systems such as the Eczema Area and Severity Index and Scoring Atopic Dermatitis underestimate AD severity in dark skin.
As for treatment, skin of color patients with AD are often as bothered by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) as by active lesions, so treatment should take these concerns into account, Dr. Callender said. Studies evaluating the effectiveness of AD treatments in diverse populations are limited by lack of representation of racial groups in clinical trials and lack of subset analyses by race.
Acne awareness
An important consideration of acne in skin of color patients is that the acne “might not be red, it might just be darker,” said Andrew F. Alexis, MD, vice-chair for diversity and inclusion in the department of dermatology, and professor of clinical dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. A study published in JAMA Dermatology of nearly 30,000 patients with acne from 2007 to 2017 found that non-Hispanic Black patients were more likely than non-Hispanic White patients to see a dermatologist for acne, but Black patients received fewer prescriptions for acne medications than White patients.
The study also showed that Black patients who received prescriptions for acne were more likely to receive topical retinoids and topical antibiotics, and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, spironolactone, or isotretinoin, compared with White patients. Similarly, Asian patients were more likely to receive topical antibiotics and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, compared with White patients.
Other panelists shared some of their best practices for acne in patients with skin of color, including treatment with topical retinoids (for inflammation) and spironolactone, and therapies that address both inflammation and pigmentation, such as salicylic acid and azelaic acid. Dr. Callender also advised asking patients about makeup, as they may not know that many types of makeup used to cover acne are in fact comedogenic.
Melanoma misconceptions
One of the most common misperceptions about melanoma among skin of color patients is that they don’t think they can get it, Dr. Taylor said. Many health care providers don’t think about melanoma in skin of color patients because of the dramatically lower incidence in this population, but as a result, cases may go undiagnosed, and as studies have shown, the mortality rate from melanoma is higher in Black patients.
Consider the palms, soles, nails, and web spaces as possible melanoma sites, Dr. Taylor added.
Educating skin of color patients about melanoma is important, although the incidence is 20 to 30 times lower than in non-Hispanic Whites, said Nada Elbuluk, MD, the founder and director of the University of Southern California Skin of Color Center and Pigmentary Disorders Clinic, Los Angeles. A 2020 editorial published in Cancer Cytopathology pointed out that 1 in 3 Black men or women with a melanoma diagnosis in the United States dies of the disease, compared with 1 in 7 non-Hispanic White men and 1 in 11 non-Hispanic White women with melanoma.
Don’t skip the total body skin exam in these patients, Dr. Elbuluk emphasized. Many patients will only partially undress, and areas such as toes can be missed.
Rosacea review
For patients with skin of color, clinicians need to look for different signs of rosacea than those typically seen in White patients, Dr. Elbuluk said. “The most common presentation of rosacea in skin of color is papulopustular,” and the granulomatous variant.
“These patients will often give you a history of sensitivity to products,” Dr. Elbuluk noted. They may not always have the flushing, but they may report warmth or itching, in addition to product sensitivity.
When considering rosacea in skin of color patients, be sure to have good lighting for close examination, as skin thickening is another subtle sign of rosacea in these patients, she said. Skin thickening “is a very early sign that will present in skin of color with no erythema, so keep that in mind.”
Stinging and burning sensations may be reported by skin of color patients with rosacea. Use patient history to confirm the diagnosis of rosacea, which is often delayed in skin of color patients because of a low index of suspicion, she said.
Psoriasis pointers
Psoriasis in skin of color patients used to be considered rare, “but that is far from true,” Dr. Alexis said. In fact, many cases of psoriasis are undiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed in these patients.
The panelists noted that current guidelines for psoriasis treatment are based on clinical trials composed mainly of White patients, and do not contain specific recommendations for skin of color patients.
Notably, the morphology, location, and color of psoriasis lesions may be different for patients with darker skin, such as thicker plaques and more scaling over larger areas, they said. Also, skin of color patients may experience long-lasting dyspigmentation from psoriasis lesions that have resolved.
When developing a strategy for psoriasis in skin of color patients, consider not only disease severity, but also comorbidities and medications, response (if any) to prior therapies, patient preferences, and quality of life, the panelists said.
Dr. Callender, Dr. Elbuluk, Dr. Taylor, and Dr. Alexis reported conflicts of interest from numerous sources in industry. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – and patients, Susan C. Taylor, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Additionally, some disparities occur because of gaps in access to health care, said Dr. Taylor, vice chair, diversity, equity and inclusion, in the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who moderated an expert panel discussion of treatment tips for several common dermatologic conditions in skin of color patients.
Atopic dermatitis angles
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is the fourth most common dermatologic complaint in Black patients, based on data from the United States National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. Also, data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey show that Black children are nearly twice as likely as White children to develop AD after controlling for socioeconomic factors, Dr. Taylor said.
When Black patients present with AD, “you may not see the erythema,” said Valerie D. Callender, MD, of Howard University, Washington, who presented on AD. Instead, “you may see more follicular and papular presentations.” Erythema and erythroderma can present as shades of violet, gray, or dark brown in patients with rich skin tones, added Dr. Callender, who practices in Glenn Dale, Md.
Consequently, disease severity can be misinterpreted, she said, noting that data suggest that scoring systems such as the Eczema Area and Severity Index and Scoring Atopic Dermatitis underestimate AD severity in dark skin.
As for treatment, skin of color patients with AD are often as bothered by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) as by active lesions, so treatment should take these concerns into account, Dr. Callender said. Studies evaluating the effectiveness of AD treatments in diverse populations are limited by lack of representation of racial groups in clinical trials and lack of subset analyses by race.
Acne awareness
An important consideration of acne in skin of color patients is that the acne “might not be red, it might just be darker,” said Andrew F. Alexis, MD, vice-chair for diversity and inclusion in the department of dermatology, and professor of clinical dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. A study published in JAMA Dermatology of nearly 30,000 patients with acne from 2007 to 2017 found that non-Hispanic Black patients were more likely than non-Hispanic White patients to see a dermatologist for acne, but Black patients received fewer prescriptions for acne medications than White patients.
The study also showed that Black patients who received prescriptions for acne were more likely to receive topical retinoids and topical antibiotics, and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, spironolactone, or isotretinoin, compared with White patients. Similarly, Asian patients were more likely to receive topical antibiotics and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, compared with White patients.
Other panelists shared some of their best practices for acne in patients with skin of color, including treatment with topical retinoids (for inflammation) and spironolactone, and therapies that address both inflammation and pigmentation, such as salicylic acid and azelaic acid. Dr. Callender also advised asking patients about makeup, as they may not know that many types of makeup used to cover acne are in fact comedogenic.
Melanoma misconceptions
One of the most common misperceptions about melanoma among skin of color patients is that they don’t think they can get it, Dr. Taylor said. Many health care providers don’t think about melanoma in skin of color patients because of the dramatically lower incidence in this population, but as a result, cases may go undiagnosed, and as studies have shown, the mortality rate from melanoma is higher in Black patients.
Consider the palms, soles, nails, and web spaces as possible melanoma sites, Dr. Taylor added.
Educating skin of color patients about melanoma is important, although the incidence is 20 to 30 times lower than in non-Hispanic Whites, said Nada Elbuluk, MD, the founder and director of the University of Southern California Skin of Color Center and Pigmentary Disorders Clinic, Los Angeles. A 2020 editorial published in Cancer Cytopathology pointed out that 1 in 3 Black men or women with a melanoma diagnosis in the United States dies of the disease, compared with 1 in 7 non-Hispanic White men and 1 in 11 non-Hispanic White women with melanoma.
Don’t skip the total body skin exam in these patients, Dr. Elbuluk emphasized. Many patients will only partially undress, and areas such as toes can be missed.
Rosacea review
For patients with skin of color, clinicians need to look for different signs of rosacea than those typically seen in White patients, Dr. Elbuluk said. “The most common presentation of rosacea in skin of color is papulopustular,” and the granulomatous variant.
“These patients will often give you a history of sensitivity to products,” Dr. Elbuluk noted. They may not always have the flushing, but they may report warmth or itching, in addition to product sensitivity.
When considering rosacea in skin of color patients, be sure to have good lighting for close examination, as skin thickening is another subtle sign of rosacea in these patients, she said. Skin thickening “is a very early sign that will present in skin of color with no erythema, so keep that in mind.”
Stinging and burning sensations may be reported by skin of color patients with rosacea. Use patient history to confirm the diagnosis of rosacea, which is often delayed in skin of color patients because of a low index of suspicion, she said.
Psoriasis pointers
Psoriasis in skin of color patients used to be considered rare, “but that is far from true,” Dr. Alexis said. In fact, many cases of psoriasis are undiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed in these patients.
The panelists noted that current guidelines for psoriasis treatment are based on clinical trials composed mainly of White patients, and do not contain specific recommendations for skin of color patients.
Notably, the morphology, location, and color of psoriasis lesions may be different for patients with darker skin, such as thicker plaques and more scaling over larger areas, they said. Also, skin of color patients may experience long-lasting dyspigmentation from psoriasis lesions that have resolved.
When developing a strategy for psoriasis in skin of color patients, consider not only disease severity, but also comorbidities and medications, response (if any) to prior therapies, patient preferences, and quality of life, the panelists said.
Dr. Callender, Dr. Elbuluk, Dr. Taylor, and Dr. Alexis reported conflicts of interest from numerous sources in industry. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT INNOVATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY
Dupilumab as a Therapeutic Approach in Alopecia Universalis
To the Editor:
Atopic diseases, specifically atopic dermatitis (AD) and alopecia areata (AA), are at the forefront of a new era in dermatology involving molecular-directed therapy. Dupilumab is one specific example, having received US Food and Drug Administration approval in March 2017 for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe AD.1 It currently is being investigated for use in pediatric AD. The most commonly reported side effects associated with the use of dupilumab include headaches, conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, nasopharyngitis, and injection-site reactions.2 We discuss a case of hair regrowth in a patient who was previously diagnosed with AA after treatment with dupilumab for refractory AD.
A 65-year-old White man presented with a history of AD since childhood. Additional medical history included hyperlipidemia; herpes simplex virus infection; asthma; and a diagnosis of AA 6 years prior, which eventually progressed to alopecia universalis. Physical examination demonstrated scattered erythematous lichenified plaques with excoriations involving the arms, legs, and trunk. The patient’s face and scalp were spared of lesions. Complete loss of body hair including the eyelashes and eyebrows also was noted, which was consistent with alopecia universalis.
The patient was started on dupilumab for refractory AD after multiple courses of topical and systemic steroids failed. Prior treatment for AD did not include immunosuppressive or light therapy. The standard dosage of dupilumab was administered, which consisted of a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks. There was no concurrent topical corticosteroid or topical calcineurin inhibitor prescribed. After 1 month of treatment with dupilumab, near-complete resolution of the patient’s AD was noted, and after 10 months of treatment, the patient experienced regrowth of the eyelashes, terminal hairs of the beard area (Figure), and vellus hairs of the eyebrows. This hair regrowth persists today with continued dupilumab treatment, and the patient has experienced no additional side effects.
Multiple retrospective and meta-analysis studies have demonstrated a high occurrence of AD comorbid with AA, which strongly suggests a common pathogenesis.3,4 Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease mediated by IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 of the helper T-cell type 2 (TH2) pathway.1 Dupilumab is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-4Rα, which also is found in IL-13 receptors. Dupilumab prevents TH2 pathway-related downstream signaling effects of both cytokines. Although this effect was originally utilized to suppress the TH2-mediated signaling in AD, our patient and others have demonstrated successful hair regrowth with dupilumab, which likely stems from a similar TH2-related antagonism in AA.5,6
The cause of AA is unknown, but IL-4 and IL-13 of the TH2 pathway have been implicated, which renders support for the therapeutic effect of dupilumab in the treatment of AA. Scalp samples of patients with AA have demonstrated upregulation of TH2, helper T-cell type 1 (TH1), and IL-23 cytokines, suggesting efficacy with the use of anti-TH2, anti-TH1, and anti–IL-23 therapies.7 Polymerase chain reaction testing performed on serum samples in patients with AA displayed marked elevation of TH2 cytokines, notably IL-13, which were reduced following intralesional corticosteroid treatment.8 It also has been demonstrated that multiple TH2-related genes contribute to the genetic susceptibility of developing AA, specifically IL-4 and IL-13.9,10
Prior case reports have shown contradicting effects (dupilumab-induced AA), which are speculated to be caused by a stronger TH1 response from TH2 suppression.11,12 In one report, dupilumab was initiated for AD refractory to multiple topical and oral interventions. New-onset hair loss to the scalp was noted after 18 weeks of therapy. Twenty-six weeks into therapy with dupilumab, full hair regrowth was then reported.11 Despite this report, our patient’s hair regrowth after the use of dupilumab for refractory AD further strengthens support for the use of dupilumab as a potential therapy for alopecia universalis and other lymphocyte-mediated hair loss conditions. However, a large disparity in response time and an overall slower progression of hair regrowth reported in our case separate it from other reports of rapid voluminous hair regrowth.5,6 Our findings support the potential use of dupilumab in the treatment of patients with AA.
- Shirly M. Dupilumab: first global approval. Drugs. 2017;77:1115-1121.
- Ou Z, Chen C, Chen A, et al. Adverse events of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a meta-analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;54:303-310.
- Andersen YMF, Egeberg A, Gislason GH, et al. Autoimmune diseases in adults with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:274-280.e1.
- Mohan GC, Silverberg JI. Association of vitiligo and alopecia areata with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;15:522-528.
- Penzi LR, Yasuda M, Manatis-Lornell A, et al. Hair regrowth in a patient with long-standing alopecia totalis and atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1358-1360.
- Alniemi DT, McGevna L. Dupilumab treatment for atopic dermatitis leading to unexpected treatment for alopecia universalis. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:111-112.
- Suárez-Fariñas M, Ungar B, Noda S, et al. Alopecia areata profiling shows TH1, TH2, and IL-23 cytokine activation without parallel TH17/TH22 skewing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1277-1287.
- Fuentes-Duculan J, Gulati N, Bonifacio KM, et al. Biomarkers of alopecia areata disease activity and response to corticosteroid treatment. Exp Dermatol. 2016;25:282-286.
- Jagielska D, Redler S, Brockschmidt FF, et al. Follow-up study of the first genome-wide association scan in alopecia areata: IL13 and KIAA0350 as susceptibility loci supported with genome-wide significance. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:2192-2197.
- Kalkan G, Karakus N, Bas¸ Y, et al. The association between interleukin (IL)-4 gene intron 3 VNTR polymorphism and alopecia areata (AA) in Turkish population. Gene. 2013;527:565-569.
- Flanagan K, Sperling L, Lin J. Drug-induced alopecia after dupilumab therapy. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:54-56.
- Mitchell K, Levitt J. Alopecia areata after dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:143-144.
To the Editor:
Atopic diseases, specifically atopic dermatitis (AD) and alopecia areata (AA), are at the forefront of a new era in dermatology involving molecular-directed therapy. Dupilumab is one specific example, having received US Food and Drug Administration approval in March 2017 for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe AD.1 It currently is being investigated for use in pediatric AD. The most commonly reported side effects associated with the use of dupilumab include headaches, conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, nasopharyngitis, and injection-site reactions.2 We discuss a case of hair regrowth in a patient who was previously diagnosed with AA after treatment with dupilumab for refractory AD.
A 65-year-old White man presented with a history of AD since childhood. Additional medical history included hyperlipidemia; herpes simplex virus infection; asthma; and a diagnosis of AA 6 years prior, which eventually progressed to alopecia universalis. Physical examination demonstrated scattered erythematous lichenified plaques with excoriations involving the arms, legs, and trunk. The patient’s face and scalp were spared of lesions. Complete loss of body hair including the eyelashes and eyebrows also was noted, which was consistent with alopecia universalis.
The patient was started on dupilumab for refractory AD after multiple courses of topical and systemic steroids failed. Prior treatment for AD did not include immunosuppressive or light therapy. The standard dosage of dupilumab was administered, which consisted of a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks. There was no concurrent topical corticosteroid or topical calcineurin inhibitor prescribed. After 1 month of treatment with dupilumab, near-complete resolution of the patient’s AD was noted, and after 10 months of treatment, the patient experienced regrowth of the eyelashes, terminal hairs of the beard area (Figure), and vellus hairs of the eyebrows. This hair regrowth persists today with continued dupilumab treatment, and the patient has experienced no additional side effects.

Multiple retrospective and meta-analysis studies have demonstrated a high occurrence of AD comorbid with AA, which strongly suggests a common pathogenesis.3,4 Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease mediated by IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 of the helper T-cell type 2 (TH2) pathway.1 Dupilumab is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-4Rα, which also is found in IL-13 receptors. Dupilumab prevents TH2 pathway-related downstream signaling effects of both cytokines. Although this effect was originally utilized to suppress the TH2-mediated signaling in AD, our patient and others have demonstrated successful hair regrowth with dupilumab, which likely stems from a similar TH2-related antagonism in AA.5,6
The cause of AA is unknown, but IL-4 and IL-13 of the TH2 pathway have been implicated, which renders support for the therapeutic effect of dupilumab in the treatment of AA. Scalp samples of patients with AA have demonstrated upregulation of TH2, helper T-cell type 1 (TH1), and IL-23 cytokines, suggesting efficacy with the use of anti-TH2, anti-TH1, and anti–IL-23 therapies.7 Polymerase chain reaction testing performed on serum samples in patients with AA displayed marked elevation of TH2 cytokines, notably IL-13, which were reduced following intralesional corticosteroid treatment.8 It also has been demonstrated that multiple TH2-related genes contribute to the genetic susceptibility of developing AA, specifically IL-4 and IL-13.9,10
Prior case reports have shown contradicting effects (dupilumab-induced AA), which are speculated to be caused by a stronger TH1 response from TH2 suppression.11,12 In one report, dupilumab was initiated for AD refractory to multiple topical and oral interventions. New-onset hair loss to the scalp was noted after 18 weeks of therapy. Twenty-six weeks into therapy with dupilumab, full hair regrowth was then reported.11 Despite this report, our patient’s hair regrowth after the use of dupilumab for refractory AD further strengthens support for the use of dupilumab as a potential therapy for alopecia universalis and other lymphocyte-mediated hair loss conditions. However, a large disparity in response time and an overall slower progression of hair regrowth reported in our case separate it from other reports of rapid voluminous hair regrowth.5,6 Our findings support the potential use of dupilumab in the treatment of patients with AA.
To the Editor:
Atopic diseases, specifically atopic dermatitis (AD) and alopecia areata (AA), are at the forefront of a new era in dermatology involving molecular-directed therapy. Dupilumab is one specific example, having received US Food and Drug Administration approval in March 2017 for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe AD.1 It currently is being investigated for use in pediatric AD. The most commonly reported side effects associated with the use of dupilumab include headaches, conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, nasopharyngitis, and injection-site reactions.2 We discuss a case of hair regrowth in a patient who was previously diagnosed with AA after treatment with dupilumab for refractory AD.
A 65-year-old White man presented with a history of AD since childhood. Additional medical history included hyperlipidemia; herpes simplex virus infection; asthma; and a diagnosis of AA 6 years prior, which eventually progressed to alopecia universalis. Physical examination demonstrated scattered erythematous lichenified plaques with excoriations involving the arms, legs, and trunk. The patient’s face and scalp were spared of lesions. Complete loss of body hair including the eyelashes and eyebrows also was noted, which was consistent with alopecia universalis.
The patient was started on dupilumab for refractory AD after multiple courses of topical and systemic steroids failed. Prior treatment for AD did not include immunosuppressive or light therapy. The standard dosage of dupilumab was administered, which consisted of a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks. There was no concurrent topical corticosteroid or topical calcineurin inhibitor prescribed. After 1 month of treatment with dupilumab, near-complete resolution of the patient’s AD was noted, and after 10 months of treatment, the patient experienced regrowth of the eyelashes, terminal hairs of the beard area (Figure), and vellus hairs of the eyebrows. This hair regrowth persists today with continued dupilumab treatment, and the patient has experienced no additional side effects.

Multiple retrospective and meta-analysis studies have demonstrated a high occurrence of AD comorbid with AA, which strongly suggests a common pathogenesis.3,4 Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease mediated by IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 of the helper T-cell type 2 (TH2) pathway.1 Dupilumab is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-4Rα, which also is found in IL-13 receptors. Dupilumab prevents TH2 pathway-related downstream signaling effects of both cytokines. Although this effect was originally utilized to suppress the TH2-mediated signaling in AD, our patient and others have demonstrated successful hair regrowth with dupilumab, which likely stems from a similar TH2-related antagonism in AA.5,6
The cause of AA is unknown, but IL-4 and IL-13 of the TH2 pathway have been implicated, which renders support for the therapeutic effect of dupilumab in the treatment of AA. Scalp samples of patients with AA have demonstrated upregulation of TH2, helper T-cell type 1 (TH1), and IL-23 cytokines, suggesting efficacy with the use of anti-TH2, anti-TH1, and anti–IL-23 therapies.7 Polymerase chain reaction testing performed on serum samples in patients with AA displayed marked elevation of TH2 cytokines, notably IL-13, which were reduced following intralesional corticosteroid treatment.8 It also has been demonstrated that multiple TH2-related genes contribute to the genetic susceptibility of developing AA, specifically IL-4 and IL-13.9,10
Prior case reports have shown contradicting effects (dupilumab-induced AA), which are speculated to be caused by a stronger TH1 response from TH2 suppression.11,12 In one report, dupilumab was initiated for AD refractory to multiple topical and oral interventions. New-onset hair loss to the scalp was noted after 18 weeks of therapy. Twenty-six weeks into therapy with dupilumab, full hair regrowth was then reported.11 Despite this report, our patient’s hair regrowth after the use of dupilumab for refractory AD further strengthens support for the use of dupilumab as a potential therapy for alopecia universalis and other lymphocyte-mediated hair loss conditions. However, a large disparity in response time and an overall slower progression of hair regrowth reported in our case separate it from other reports of rapid voluminous hair regrowth.5,6 Our findings support the potential use of dupilumab in the treatment of patients with AA.
- Shirly M. Dupilumab: first global approval. Drugs. 2017;77:1115-1121.
- Ou Z, Chen C, Chen A, et al. Adverse events of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a meta-analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;54:303-310.
- Andersen YMF, Egeberg A, Gislason GH, et al. Autoimmune diseases in adults with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:274-280.e1.
- Mohan GC, Silverberg JI. Association of vitiligo and alopecia areata with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;15:522-528.
- Penzi LR, Yasuda M, Manatis-Lornell A, et al. Hair regrowth in a patient with long-standing alopecia totalis and atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1358-1360.
- Alniemi DT, McGevna L. Dupilumab treatment for atopic dermatitis leading to unexpected treatment for alopecia universalis. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:111-112.
- Suárez-Fariñas M, Ungar B, Noda S, et al. Alopecia areata profiling shows TH1, TH2, and IL-23 cytokine activation without parallel TH17/TH22 skewing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1277-1287.
- Fuentes-Duculan J, Gulati N, Bonifacio KM, et al. Biomarkers of alopecia areata disease activity and response to corticosteroid treatment. Exp Dermatol. 2016;25:282-286.
- Jagielska D, Redler S, Brockschmidt FF, et al. Follow-up study of the first genome-wide association scan in alopecia areata: IL13 and KIAA0350 as susceptibility loci supported with genome-wide significance. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:2192-2197.
- Kalkan G, Karakus N, Bas¸ Y, et al. The association between interleukin (IL)-4 gene intron 3 VNTR polymorphism and alopecia areata (AA) in Turkish population. Gene. 2013;527:565-569.
- Flanagan K, Sperling L, Lin J. Drug-induced alopecia after dupilumab therapy. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:54-56.
- Mitchell K, Levitt J. Alopecia areata after dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:143-144.
- Shirly M. Dupilumab: first global approval. Drugs. 2017;77:1115-1121.
- Ou Z, Chen C, Chen A, et al. Adverse events of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a meta-analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;54:303-310.
- Andersen YMF, Egeberg A, Gislason GH, et al. Autoimmune diseases in adults with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:274-280.e1.
- Mohan GC, Silverberg JI. Association of vitiligo and alopecia areata with atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;15:522-528.
- Penzi LR, Yasuda M, Manatis-Lornell A, et al. Hair regrowth in a patient with long-standing alopecia totalis and atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1358-1360.
- Alniemi DT, McGevna L. Dupilumab treatment for atopic dermatitis leading to unexpected treatment for alopecia universalis. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:111-112.
- Suárez-Fariñas M, Ungar B, Noda S, et al. Alopecia areata profiling shows TH1, TH2, and IL-23 cytokine activation without parallel TH17/TH22 skewing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1277-1287.
- Fuentes-Duculan J, Gulati N, Bonifacio KM, et al. Biomarkers of alopecia areata disease activity and response to corticosteroid treatment. Exp Dermatol. 2016;25:282-286.
- Jagielska D, Redler S, Brockschmidt FF, et al. Follow-up study of the first genome-wide association scan in alopecia areata: IL13 and KIAA0350 as susceptibility loci supported with genome-wide significance. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:2192-2197.
- Kalkan G, Karakus N, Bas¸ Y, et al. The association between interleukin (IL)-4 gene intron 3 VNTR polymorphism and alopecia areata (AA) in Turkish population. Gene. 2013;527:565-569.
- Flanagan K, Sperling L, Lin J. Drug-induced alopecia after dupilumab therapy. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:54-56.
- Mitchell K, Levitt J. Alopecia areata after dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:143-144.
Practice Points
- Practicing dermatologists should be aware of the shared pathophysiology of alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis and the relief patients with these conditions can experience when treated with dupilumab.
- As molecular-directed biologic therapies emerge in the marketplace, their potential for targeting one atopic disease may offer notable benefits for use in the treatment of other atopic diseases.
Proactive TCS fails to reduce relapse rate in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis
Key clinical point: Although proactive (PA) topical corticosteroid (TCS) therapy did not show lower relapse rates in pediatric patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) in remission, it was more effective against itch and as safe as rank-down (RD) TCS therapy.
Major finding: There was no significant decrease in the relapse rate (8.33% vs 20.0%; P = .0859) in the PA vs RD treatment group; however, at week 4, the mean itching score increased significantly in the RD group (2.5 to 3.6; P = .0438) but not in the PA group (P = .1877). The safety profile was similar in both groups.
Study details: Findings are from an open-label, active-controlled, parallel-group study including 49 pediatric patients with moderate-to-severe AD who had achieved remission with a very strong TCS therapy and were randomly assigned to receive PA or RD TCS therapy.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Torii Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The authors declared receiving payments, honoraria, funds, research grants, or fees from several sources, including Torii Pharmaceutical.
Source: Kamiya K et al. Proactive versus rank-down topical corticosteroid therapy for maintenance of remission in pediatric atopic dermatitis: A randomized, open-label, active-controlled, parallel-group study (Anticipate study). J Clin Med. 2022;11(21):6477 (Oct 31). Doi: 10.3390/jcm11216477
Key clinical point: Although proactive (PA) topical corticosteroid (TCS) therapy did not show lower relapse rates in pediatric patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) in remission, it was more effective against itch and as safe as rank-down (RD) TCS therapy.
Major finding: There was no significant decrease in the relapse rate (8.33% vs 20.0%; P = .0859) in the PA vs RD treatment group; however, at week 4, the mean itching score increased significantly in the RD group (2.5 to 3.6; P = .0438) but not in the PA group (P = .1877). The safety profile was similar in both groups.
Study details: Findings are from an open-label, active-controlled, parallel-group study including 49 pediatric patients with moderate-to-severe AD who had achieved remission with a very strong TCS therapy and were randomly assigned to receive PA or RD TCS therapy.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Torii Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The authors declared receiving payments, honoraria, funds, research grants, or fees from several sources, including Torii Pharmaceutical.
Source: Kamiya K et al. Proactive versus rank-down topical corticosteroid therapy for maintenance of remission in pediatric atopic dermatitis: A randomized, open-label, active-controlled, parallel-group study (Anticipate study). J Clin Med. 2022;11(21):6477 (Oct 31). Doi: 10.3390/jcm11216477
Key clinical point: Although proactive (PA) topical corticosteroid (TCS) therapy did not show lower relapse rates in pediatric patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) in remission, it was more effective against itch and as safe as rank-down (RD) TCS therapy.
Major finding: There was no significant decrease in the relapse rate (8.33% vs 20.0%; P = .0859) in the PA vs RD treatment group; however, at week 4, the mean itching score increased significantly in the RD group (2.5 to 3.6; P = .0438) but not in the PA group (P = .1877). The safety profile was similar in both groups.
Study details: Findings are from an open-label, active-controlled, parallel-group study including 49 pediatric patients with moderate-to-severe AD who had achieved remission with a very strong TCS therapy and were randomly assigned to receive PA or RD TCS therapy.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Torii Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The authors declared receiving payments, honoraria, funds, research grants, or fees from several sources, including Torii Pharmaceutical.
Source: Kamiya K et al. Proactive versus rank-down topical corticosteroid therapy for maintenance of remission in pediatric atopic dermatitis: A randomized, open-label, active-controlled, parallel-group study (Anticipate study). J Clin Med. 2022;11(21):6477 (Oct 31). Doi: 10.3390/jcm11216477
Early application of a standardized skin care product does not prevent atopic dermatitis in predisposed infants
Key clinical point: Regular application of a standardized skin care regimen during the first year of life did not prevent the development of atopic dermatitis (AD) in predisposed infants.
Major finding: In the first year of life, the overall cumulative incidence rate of AD was similar with regular standardized skin care and no predetermined skin care/skin care preferred by parents (odds ratio 1.0; P = .999).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective trial (ADAPI) including 150 infants who were at an enhanced risk of developing AD and were randomly assigned to receive a regular standardized skin care regimen or skin care as preferred by parents.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by HiPP GmbH & Co Vertrieb KG, Germany. Two authors declared being employees of HiPP GmbH & Co Vertrieb KG. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kottner J et al for the ADAPI Study Group. Effectiveness of a standardized skin care regimen to prevent atopic dermatitis in infants at risk for atopy: A randomized, pragmatic, parallel-group study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022 (Oct 29). Doi: 10.1111/jdv.18698
Key clinical point: Regular application of a standardized skin care regimen during the first year of life did not prevent the development of atopic dermatitis (AD) in predisposed infants.
Major finding: In the first year of life, the overall cumulative incidence rate of AD was similar with regular standardized skin care and no predetermined skin care/skin care preferred by parents (odds ratio 1.0; P = .999).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective trial (ADAPI) including 150 infants who were at an enhanced risk of developing AD and were randomly assigned to receive a regular standardized skin care regimen or skin care as preferred by parents.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by HiPP GmbH & Co Vertrieb KG, Germany. Two authors declared being employees of HiPP GmbH & Co Vertrieb KG. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kottner J et al for the ADAPI Study Group. Effectiveness of a standardized skin care regimen to prevent atopic dermatitis in infants at risk for atopy: A randomized, pragmatic, parallel-group study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022 (Oct 29). Doi: 10.1111/jdv.18698
Key clinical point: Regular application of a standardized skin care regimen during the first year of life did not prevent the development of atopic dermatitis (AD) in predisposed infants.
Major finding: In the first year of life, the overall cumulative incidence rate of AD was similar with regular standardized skin care and no predetermined skin care/skin care preferred by parents (odds ratio 1.0; P = .999).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective trial (ADAPI) including 150 infants who were at an enhanced risk of developing AD and were randomly assigned to receive a regular standardized skin care regimen or skin care as preferred by parents.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by HiPP GmbH & Co Vertrieb KG, Germany. Two authors declared being employees of HiPP GmbH & Co Vertrieb KG. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kottner J et al for the ADAPI Study Group. Effectiveness of a standardized skin care regimen to prevent atopic dermatitis in infants at risk for atopy: A randomized, pragmatic, parallel-group study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022 (Oct 29). Doi: 10.1111/jdv.18698