User login
Salt pills for patients with acute decompensated heart failure?
Restriction of dietary salt to alleviate or prevent volume overload in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is common hospital practice, but without a solid evidence base. A trial testing whether taking salt pills might have benefits for patients with ADHF undergoing intensive diuresis, therefore, may seem a bit counterintuitive.
In just such a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, the approach made no difference to weight loss on diuresis, a proxy for volume reduction, or to serum creatinine levels in ADHF patients receiving high-dose intravenous diuretic therapy.
The patients consumed the extra salt during their intravenous therapy in the form of tablets providing 6 g sodium chloride daily on top of their hospital-provided, low-sodium meals.
During that time, serum sodium levels remained stable for the 34 patients assigned to the salt tablets but dropped significantly in the 31 given placebo pills.
They lost about the same weight, averages of 4 kg and 4.6 kg (8.8-10 lb), respectively, and their urine output was also similar. Patients who took the salt tablets showed less of an increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) at both 96 hours and at discharge.
The findings “challenge the routine practice of sodium chloride restriction in acute heart failure, something done thousands of times a day, millions of times a year,” Robert A. Montgomery, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said when presenting the study at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The trial, called OSPREY-AHF (Oral Sodium to Preserve Renal Efficiency in Acute Heart Failure), also may encourage a shift in ADHF management from a preoccupation with salt restriction to focus more on fighting fluid retention.
OSPREY-HF took on “an established practice that doesn’t have much high-quality evidentiary support,” one guided primarily by consensus and observational data, Montgomery said in an interview.
There are also potential downsides to dietary sodium restriction, including some that may complicate or block ADHF therapies.
“Low-sodium diets can be associated with decreased caloric intake and nutritional quality,” Dr. Montgomery observed. And observational studies suggest that “patients who are on a low sodium diet can develop increased neurohormonal activation. The kidney is not sensing salt, and so starts ramping up the hormones,” which promotes diuretic resistance.
But emerging evidence also suggests “that giving sodium chloride in the form of hypertonic saline can help patients who are diuretic resistant.” The intervention, which appears to attenuate the neurohormonal activation associated with high-dose intravenous diuretics, Dr. Montgomery noted, helped inspire the design of OSPREY-AHF.
Edema consists of “a gallon of water and a pinch of salt, so we really should stop being so salt-centric and think much more about water as the problem in decompensated heart failure,” said John G.F. Cleland, MD, PhD, during the question-and-answer period after Montgomery’s presentation. Dr. Cleland, of the University of Glasgow Institute of Health and Wellbeing, is not connected to OSPREY-AHF.
“I think that maybe we overinterpret how important salt is” as a focus of volume management in ADHF, offered David Lanfear, MD, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, who is also not part of the study.
OSPREY-AHF was well conducted but applies to a “very specific” clinical setting, Dr. Lanfear said in an interview. “These people are getting aggressive diuresis, a big dose and continuous infusion. It’s not everybody that has heart failure.”
Although the study was small, “I think it will fuel interest in this area and, probably, further investigation,” he said. The trial on its own won’t change practice, “but it will raise some eyebrows.”
The trial included patients with ADHF who have been “admitted to a cardiovascular medicine floor, not the intensive care unit” and were receiving at least 10 mg per hour of furosemide. It excluded any who were “hypernatremic or severely hyponatremic,” said Dr. Montgomery when presenting the study. They were required to have an initial estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of at least 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
The patients were randomly assigned double blind at a single center to receive tablets providing 2 g sodium chloride or placebo pills – 34 and 31 patients, respectively – three times daily during intravenous diuresis.
At 96 hours, the two groups showed no difference in change in creatinine levels or change in weight, both primary endpoints. Nor did they differ in urine output or change in eGFR. But serum sodium levels fell further, and BUN levels went up more in those given placebo.
The two groups showed no differences in hospital length of stay, use of renal replacement therapy at 90 days, ICU time during the index hospitalization, 30-day readmission, or 90-day mortality – although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical outcomes, Dr. Montgomery reported.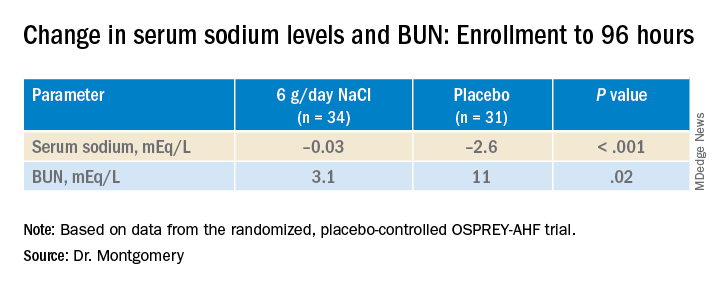
"We have patients who complain about their sodium-restricted diet, we have patients that have cachexia, who have a lot of complaints about provider-ordered meals and recommendations,” Dr. Montgomery explained in an interview.
Clinicians provide education and invest a lot of effort into getting patients with heart failure to start and maintain a low-sodium diet, he said. “But a low-sodium diet, in prior studies – and our study adds to this – is not a lever that actually seems to positively or adversely affect patients.”
Dr. Montgomery pointed to the recently published SODIUM-HF trial comparing low-sodium and unrestricted-sodium diets in outpatients with heart failure. It saw no clinical benefit from the low-sodium intervention.
Until studies show, potentially, that sodium restriction in hospitalized patients with heart failure makes a clinical difference, Dr. Montgomery said, “I’d say we should invest our time in things that we know are the most helpful, like getting them on guideline-directed medical therapy, when instead we spend an enormous amount of time counseling on and enforcing dietary restriction.”
Support for this study was provided by Cleveland Clinic Heart Vascular and Thoracic Institute’s Wilson Grant and Kaufman Center for Heart Failure Treatment and Recovery Grant. Dr. Lanfear disclosed research support from SomaLogic and Lilly; consulting for Abbott Laboratories, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Martin Pharmaceuticals, and Amgen; and serving on advisory panels for Illumina and Cytokinetics. Dr. Montgomery and Dr. Cleland disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Restriction of dietary salt to alleviate or prevent volume overload in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is common hospital practice, but without a solid evidence base. A trial testing whether taking salt pills might have benefits for patients with ADHF undergoing intensive diuresis, therefore, may seem a bit counterintuitive.
In just such a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, the approach made no difference to weight loss on diuresis, a proxy for volume reduction, or to serum creatinine levels in ADHF patients receiving high-dose intravenous diuretic therapy.
The patients consumed the extra salt during their intravenous therapy in the form of tablets providing 6 g sodium chloride daily on top of their hospital-provided, low-sodium meals.
During that time, serum sodium levels remained stable for the 34 patients assigned to the salt tablets but dropped significantly in the 31 given placebo pills.
They lost about the same weight, averages of 4 kg and 4.6 kg (8.8-10 lb), respectively, and their urine output was also similar. Patients who took the salt tablets showed less of an increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) at both 96 hours and at discharge.
The findings “challenge the routine practice of sodium chloride restriction in acute heart failure, something done thousands of times a day, millions of times a year,” Robert A. Montgomery, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said when presenting the study at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The trial, called OSPREY-AHF (Oral Sodium to Preserve Renal Efficiency in Acute Heart Failure), also may encourage a shift in ADHF management from a preoccupation with salt restriction to focus more on fighting fluid retention.
OSPREY-HF took on “an established practice that doesn’t have much high-quality evidentiary support,” one guided primarily by consensus and observational data, Montgomery said in an interview.
There are also potential downsides to dietary sodium restriction, including some that may complicate or block ADHF therapies.
“Low-sodium diets can be associated with decreased caloric intake and nutritional quality,” Dr. Montgomery observed. And observational studies suggest that “patients who are on a low sodium diet can develop increased neurohormonal activation. The kidney is not sensing salt, and so starts ramping up the hormones,” which promotes diuretic resistance.
But emerging evidence also suggests “that giving sodium chloride in the form of hypertonic saline can help patients who are diuretic resistant.” The intervention, which appears to attenuate the neurohormonal activation associated with high-dose intravenous diuretics, Dr. Montgomery noted, helped inspire the design of OSPREY-AHF.
Edema consists of “a gallon of water and a pinch of salt, so we really should stop being so salt-centric and think much more about water as the problem in decompensated heart failure,” said John G.F. Cleland, MD, PhD, during the question-and-answer period after Montgomery’s presentation. Dr. Cleland, of the University of Glasgow Institute of Health and Wellbeing, is not connected to OSPREY-AHF.
“I think that maybe we overinterpret how important salt is” as a focus of volume management in ADHF, offered David Lanfear, MD, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, who is also not part of the study.
OSPREY-AHF was well conducted but applies to a “very specific” clinical setting, Dr. Lanfear said in an interview. “These people are getting aggressive diuresis, a big dose and continuous infusion. It’s not everybody that has heart failure.”
Although the study was small, “I think it will fuel interest in this area and, probably, further investigation,” he said. The trial on its own won’t change practice, “but it will raise some eyebrows.”
The trial included patients with ADHF who have been “admitted to a cardiovascular medicine floor, not the intensive care unit” and were receiving at least 10 mg per hour of furosemide. It excluded any who were “hypernatremic or severely hyponatremic,” said Dr. Montgomery when presenting the study. They were required to have an initial estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of at least 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
The patients were randomly assigned double blind at a single center to receive tablets providing 2 g sodium chloride or placebo pills – 34 and 31 patients, respectively – three times daily during intravenous diuresis.
At 96 hours, the two groups showed no difference in change in creatinine levels or change in weight, both primary endpoints. Nor did they differ in urine output or change in eGFR. But serum sodium levels fell further, and BUN levels went up more in those given placebo.
The two groups showed no differences in hospital length of stay, use of renal replacement therapy at 90 days, ICU time during the index hospitalization, 30-day readmission, or 90-day mortality – although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical outcomes, Dr. Montgomery reported.
"We have patients who complain about their sodium-restricted diet, we have patients that have cachexia, who have a lot of complaints about provider-ordered meals and recommendations,” Dr. Montgomery explained in an interview.
Clinicians provide education and invest a lot of effort into getting patients with heart failure to start and maintain a low-sodium diet, he said. “But a low-sodium diet, in prior studies – and our study adds to this – is not a lever that actually seems to positively or adversely affect patients.”
Dr. Montgomery pointed to the recently published SODIUM-HF trial comparing low-sodium and unrestricted-sodium diets in outpatients with heart failure. It saw no clinical benefit from the low-sodium intervention.
Until studies show, potentially, that sodium restriction in hospitalized patients with heart failure makes a clinical difference, Dr. Montgomery said, “I’d say we should invest our time in things that we know are the most helpful, like getting them on guideline-directed medical therapy, when instead we spend an enormous amount of time counseling on and enforcing dietary restriction.”
Support for this study was provided by Cleveland Clinic Heart Vascular and Thoracic Institute’s Wilson Grant and Kaufman Center for Heart Failure Treatment and Recovery Grant. Dr. Lanfear disclosed research support from SomaLogic and Lilly; consulting for Abbott Laboratories, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Martin Pharmaceuticals, and Amgen; and serving on advisory panels for Illumina and Cytokinetics. Dr. Montgomery and Dr. Cleland disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Restriction of dietary salt to alleviate or prevent volume overload in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is common hospital practice, but without a solid evidence base. A trial testing whether taking salt pills might have benefits for patients with ADHF undergoing intensive diuresis, therefore, may seem a bit counterintuitive.
In just such a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, the approach made no difference to weight loss on diuresis, a proxy for volume reduction, or to serum creatinine levels in ADHF patients receiving high-dose intravenous diuretic therapy.
The patients consumed the extra salt during their intravenous therapy in the form of tablets providing 6 g sodium chloride daily on top of their hospital-provided, low-sodium meals.
During that time, serum sodium levels remained stable for the 34 patients assigned to the salt tablets but dropped significantly in the 31 given placebo pills.
They lost about the same weight, averages of 4 kg and 4.6 kg (8.8-10 lb), respectively, and their urine output was also similar. Patients who took the salt tablets showed less of an increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) at both 96 hours and at discharge.
The findings “challenge the routine practice of sodium chloride restriction in acute heart failure, something done thousands of times a day, millions of times a year,” Robert A. Montgomery, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said when presenting the study at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The trial, called OSPREY-AHF (Oral Sodium to Preserve Renal Efficiency in Acute Heart Failure), also may encourage a shift in ADHF management from a preoccupation with salt restriction to focus more on fighting fluid retention.
OSPREY-HF took on “an established practice that doesn’t have much high-quality evidentiary support,” one guided primarily by consensus and observational data, Montgomery said in an interview.
There are also potential downsides to dietary sodium restriction, including some that may complicate or block ADHF therapies.
“Low-sodium diets can be associated with decreased caloric intake and nutritional quality,” Dr. Montgomery observed. And observational studies suggest that “patients who are on a low sodium diet can develop increased neurohormonal activation. The kidney is not sensing salt, and so starts ramping up the hormones,” which promotes diuretic resistance.
But emerging evidence also suggests “that giving sodium chloride in the form of hypertonic saline can help patients who are diuretic resistant.” The intervention, which appears to attenuate the neurohormonal activation associated with high-dose intravenous diuretics, Dr. Montgomery noted, helped inspire the design of OSPREY-AHF.
Edema consists of “a gallon of water and a pinch of salt, so we really should stop being so salt-centric and think much more about water as the problem in decompensated heart failure,” said John G.F. Cleland, MD, PhD, during the question-and-answer period after Montgomery’s presentation. Dr. Cleland, of the University of Glasgow Institute of Health and Wellbeing, is not connected to OSPREY-AHF.
“I think that maybe we overinterpret how important salt is” as a focus of volume management in ADHF, offered David Lanfear, MD, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, who is also not part of the study.
OSPREY-AHF was well conducted but applies to a “very specific” clinical setting, Dr. Lanfear said in an interview. “These people are getting aggressive diuresis, a big dose and continuous infusion. It’s not everybody that has heart failure.”
Although the study was small, “I think it will fuel interest in this area and, probably, further investigation,” he said. The trial on its own won’t change practice, “but it will raise some eyebrows.”
The trial included patients with ADHF who have been “admitted to a cardiovascular medicine floor, not the intensive care unit” and were receiving at least 10 mg per hour of furosemide. It excluded any who were “hypernatremic or severely hyponatremic,” said Dr. Montgomery when presenting the study. They were required to have an initial estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of at least 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
The patients were randomly assigned double blind at a single center to receive tablets providing 2 g sodium chloride or placebo pills – 34 and 31 patients, respectively – three times daily during intravenous diuresis.
At 96 hours, the two groups showed no difference in change in creatinine levels or change in weight, both primary endpoints. Nor did they differ in urine output or change in eGFR. But serum sodium levels fell further, and BUN levels went up more in those given placebo.
The two groups showed no differences in hospital length of stay, use of renal replacement therapy at 90 days, ICU time during the index hospitalization, 30-day readmission, or 90-day mortality – although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical outcomes, Dr. Montgomery reported.
"We have patients who complain about their sodium-restricted diet, we have patients that have cachexia, who have a lot of complaints about provider-ordered meals and recommendations,” Dr. Montgomery explained in an interview.
Clinicians provide education and invest a lot of effort into getting patients with heart failure to start and maintain a low-sodium diet, he said. “But a low-sodium diet, in prior studies – and our study adds to this – is not a lever that actually seems to positively or adversely affect patients.”
Dr. Montgomery pointed to the recently published SODIUM-HF trial comparing low-sodium and unrestricted-sodium diets in outpatients with heart failure. It saw no clinical benefit from the low-sodium intervention.
Until studies show, potentially, that sodium restriction in hospitalized patients with heart failure makes a clinical difference, Dr. Montgomery said, “I’d say we should invest our time in things that we know are the most helpful, like getting them on guideline-directed medical therapy, when instead we spend an enormous amount of time counseling on and enforcing dietary restriction.”
Support for this study was provided by Cleveland Clinic Heart Vascular and Thoracic Institute’s Wilson Grant and Kaufman Center for Heart Failure Treatment and Recovery Grant. Dr. Lanfear disclosed research support from SomaLogic and Lilly; consulting for Abbott Laboratories, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Martin Pharmaceuticals, and Amgen; and serving on advisory panels for Illumina and Cytokinetics. Dr. Montgomery and Dr. Cleland disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HFSA 2022
Newer drugs not cost effective for first-line diabetes therapy
To be cost effective, compared with metformin, for initial therapy for type 2 diabetes, prices for a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist would have to fall by at least 70% and at least 90%, respectively, according to estimates.
The study, modeled on U.S. patients, by Jin G. Choi, MD, and colleagues, was published online Oct. 3 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The researchers simulated the lifetime incidence, prevalence, mortality, and costs associated with three different first-line treatment strategies – metformin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, or a GLP-1 agonist – in U.S. patients with untreated type 2 diabetes.
Compared with patients who received initial treatment with metformin, those who received one of the newer drugs had 4.4% to 5.2% lower lifetime rates of congestive heart failure, ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
However, to be cost-effective at under $150,000 per quality-adjusted life-years (QALY), SGLT2 inhibitors would need to cost less than $5 a day ($1,800 a year), and GLP-1 agonists would have to cost less than $6 a day ($2,100 a year), a lot less than now.
Knowing how expensive these drugs are, “I am not surprised” that the model predicts that the price would have to drop so much to make them cost-effective, compared with first-line treatment with metformin, senior author Neda Laiteerapong, MD, said in an interview.
“But I am disappointed,” she said, because these drugs are very effective, and if the prices were lower, more people could benefit.
“In the interest of improving access to high-quality care in the United States, our study results indicate the need to reduce SGLT2 inhibitor and GLP-1 receptor agonist medication costs substantially for patients with type 2 [diabetes] to improve health outcomes and prevent exacerbating diabetes health disparities,” the researchers conclude.
One way that the newer drugs might be more widely affordable is if the government became involved, possibly by passing a law similar to the Affordable Insulin Now Act, speculated Dr. Laiteerapong, who is associate director at the Center for Chronic Disease Research and Policy, University of Chicago.
‘Current prices too high to encourage first-line adoption’
Guidelines recommend the use of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists as second-line therapies for patients with type 2 diabetes, but it has not been clear if clinical benefits would outweigh costs for use as first-line therapies.
“Although clinical trials have demonstrated the clinical effectiveness of these newer drugs, they are hundreds of times more expensive than other ... diabetes drugs,” the researchers note.
On the other hand, costs may fall in the coming years when these new drugs come off-patent.
The current study was designed to help inform future clinical guidelines.
The researchers created a population simulation model based on the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study, Outcomes Model version 2 (UKPDS OM2) for diabetes-related complications and mortality, with added information about hypoglycemic events, quality of life, and U.S. costs.
The researchers also identified a nationally representative sample of people who would be eligible to start first-line diabetes therapy when their A1c reached 7% for the model.
Using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data (2013-2016), the researchers identified about 7.3 million U.S. adults aged 18 and older with self-reported diabetes or an A1c greater than 6.5% with no reported use of diabetes medications.
Patients were an average age of 55, and 55% were women. They had had diabetes for an average of 4.2 years, and 36% had a history of diabetes complications.
The model projected that patients would have an improved life expectancy of 3.0 and 3.4 months from first-line SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists, respectively, compared with initial therapy with metformin due to reduced rates of macrovascular disease.
“However, the current drug costs would be too high to encourage their adoption as first-line for usual clinical practice,” the researchers report.
‘Disparities could remain for decades’
Generic SGLT2 inhibitors could enter the marketplace shortly, because one of two dapagliflozin patents expired in October 2020 and approval for generic alternatives has been sought from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Dr. Choi and colleagues note.
However, it could still take decades for medication prices to drop low enough to become affordable, the group cautions. For example, a generic GLP-1 agonist became available in 2017, but costs remain high.
“Without external incentives,” the group writes, “limited access to these drug classes will likely persist (for example, due to higher copays or requirements for prior authorizations), as will further diabetes disparities – for decades into the future – because of differential access to care due to insurance (for example, private vs. public), which often tracks race and ethnicity.”
The study was supported by the American Diabetes Association. Dr. Choi was supported by a National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging grant. Dr. Laiteerapong and other co-authors are members of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Chicago Center for Diabetes Translation Research at the University of Chicago. Dr. Choi and Dr. Laiteerapong have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To be cost effective, compared with metformin, for initial therapy for type 2 diabetes, prices for a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist would have to fall by at least 70% and at least 90%, respectively, according to estimates.
The study, modeled on U.S. patients, by Jin G. Choi, MD, and colleagues, was published online Oct. 3 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The researchers simulated the lifetime incidence, prevalence, mortality, and costs associated with three different first-line treatment strategies – metformin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, or a GLP-1 agonist – in U.S. patients with untreated type 2 diabetes.
Compared with patients who received initial treatment with metformin, those who received one of the newer drugs had 4.4% to 5.2% lower lifetime rates of congestive heart failure, ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
However, to be cost-effective at under $150,000 per quality-adjusted life-years (QALY), SGLT2 inhibitors would need to cost less than $5 a day ($1,800 a year), and GLP-1 agonists would have to cost less than $6 a day ($2,100 a year), a lot less than now.
Knowing how expensive these drugs are, “I am not surprised” that the model predicts that the price would have to drop so much to make them cost-effective, compared with first-line treatment with metformin, senior author Neda Laiteerapong, MD, said in an interview.
“But I am disappointed,” she said, because these drugs are very effective, and if the prices were lower, more people could benefit.
“In the interest of improving access to high-quality care in the United States, our study results indicate the need to reduce SGLT2 inhibitor and GLP-1 receptor agonist medication costs substantially for patients with type 2 [diabetes] to improve health outcomes and prevent exacerbating diabetes health disparities,” the researchers conclude.
One way that the newer drugs might be more widely affordable is if the government became involved, possibly by passing a law similar to the Affordable Insulin Now Act, speculated Dr. Laiteerapong, who is associate director at the Center for Chronic Disease Research and Policy, University of Chicago.
‘Current prices too high to encourage first-line adoption’
Guidelines recommend the use of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists as second-line therapies for patients with type 2 diabetes, but it has not been clear if clinical benefits would outweigh costs for use as first-line therapies.
“Although clinical trials have demonstrated the clinical effectiveness of these newer drugs, they are hundreds of times more expensive than other ... diabetes drugs,” the researchers note.
On the other hand, costs may fall in the coming years when these new drugs come off-patent.
The current study was designed to help inform future clinical guidelines.
The researchers created a population simulation model based on the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study, Outcomes Model version 2 (UKPDS OM2) for diabetes-related complications and mortality, with added information about hypoglycemic events, quality of life, and U.S. costs.
The researchers also identified a nationally representative sample of people who would be eligible to start first-line diabetes therapy when their A1c reached 7% for the model.
Using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data (2013-2016), the researchers identified about 7.3 million U.S. adults aged 18 and older with self-reported diabetes or an A1c greater than 6.5% with no reported use of diabetes medications.
Patients were an average age of 55, and 55% were women. They had had diabetes for an average of 4.2 years, and 36% had a history of diabetes complications.
The model projected that patients would have an improved life expectancy of 3.0 and 3.4 months from first-line SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists, respectively, compared with initial therapy with metformin due to reduced rates of macrovascular disease.
“However, the current drug costs would be too high to encourage their adoption as first-line for usual clinical practice,” the researchers report.
‘Disparities could remain for decades’
Generic SGLT2 inhibitors could enter the marketplace shortly, because one of two dapagliflozin patents expired in October 2020 and approval for generic alternatives has been sought from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Dr. Choi and colleagues note.
However, it could still take decades for medication prices to drop low enough to become affordable, the group cautions. For example, a generic GLP-1 agonist became available in 2017, but costs remain high.
“Without external incentives,” the group writes, “limited access to these drug classes will likely persist (for example, due to higher copays or requirements for prior authorizations), as will further diabetes disparities – for decades into the future – because of differential access to care due to insurance (for example, private vs. public), which often tracks race and ethnicity.”
The study was supported by the American Diabetes Association. Dr. Choi was supported by a National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging grant. Dr. Laiteerapong and other co-authors are members of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Chicago Center for Diabetes Translation Research at the University of Chicago. Dr. Choi and Dr. Laiteerapong have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To be cost effective, compared with metformin, for initial therapy for type 2 diabetes, prices for a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist would have to fall by at least 70% and at least 90%, respectively, according to estimates.
The study, modeled on U.S. patients, by Jin G. Choi, MD, and colleagues, was published online Oct. 3 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The researchers simulated the lifetime incidence, prevalence, mortality, and costs associated with three different first-line treatment strategies – metformin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, or a GLP-1 agonist – in U.S. patients with untreated type 2 diabetes.
Compared with patients who received initial treatment with metformin, those who received one of the newer drugs had 4.4% to 5.2% lower lifetime rates of congestive heart failure, ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
However, to be cost-effective at under $150,000 per quality-adjusted life-years (QALY), SGLT2 inhibitors would need to cost less than $5 a day ($1,800 a year), and GLP-1 agonists would have to cost less than $6 a day ($2,100 a year), a lot less than now.
Knowing how expensive these drugs are, “I am not surprised” that the model predicts that the price would have to drop so much to make them cost-effective, compared with first-line treatment with metformin, senior author Neda Laiteerapong, MD, said in an interview.
“But I am disappointed,” she said, because these drugs are very effective, and if the prices were lower, more people could benefit.
“In the interest of improving access to high-quality care in the United States, our study results indicate the need to reduce SGLT2 inhibitor and GLP-1 receptor agonist medication costs substantially for patients with type 2 [diabetes] to improve health outcomes and prevent exacerbating diabetes health disparities,” the researchers conclude.
One way that the newer drugs might be more widely affordable is if the government became involved, possibly by passing a law similar to the Affordable Insulin Now Act, speculated Dr. Laiteerapong, who is associate director at the Center for Chronic Disease Research and Policy, University of Chicago.
‘Current prices too high to encourage first-line adoption’
Guidelines recommend the use of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists as second-line therapies for patients with type 2 diabetes, but it has not been clear if clinical benefits would outweigh costs for use as first-line therapies.
“Although clinical trials have demonstrated the clinical effectiveness of these newer drugs, they are hundreds of times more expensive than other ... diabetes drugs,” the researchers note.
On the other hand, costs may fall in the coming years when these new drugs come off-patent.
The current study was designed to help inform future clinical guidelines.
The researchers created a population simulation model based on the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study, Outcomes Model version 2 (UKPDS OM2) for diabetes-related complications and mortality, with added information about hypoglycemic events, quality of life, and U.S. costs.
The researchers also identified a nationally representative sample of people who would be eligible to start first-line diabetes therapy when their A1c reached 7% for the model.
Using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data (2013-2016), the researchers identified about 7.3 million U.S. adults aged 18 and older with self-reported diabetes or an A1c greater than 6.5% with no reported use of diabetes medications.
Patients were an average age of 55, and 55% were women. They had had diabetes for an average of 4.2 years, and 36% had a history of diabetes complications.
The model projected that patients would have an improved life expectancy of 3.0 and 3.4 months from first-line SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists, respectively, compared with initial therapy with metformin due to reduced rates of macrovascular disease.
“However, the current drug costs would be too high to encourage their adoption as first-line for usual clinical practice,” the researchers report.
‘Disparities could remain for decades’
Generic SGLT2 inhibitors could enter the marketplace shortly, because one of two dapagliflozin patents expired in October 2020 and approval for generic alternatives has been sought from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Dr. Choi and colleagues note.
However, it could still take decades for medication prices to drop low enough to become affordable, the group cautions. For example, a generic GLP-1 agonist became available in 2017, but costs remain high.
“Without external incentives,” the group writes, “limited access to these drug classes will likely persist (for example, due to higher copays or requirements for prior authorizations), as will further diabetes disparities – for decades into the future – because of differential access to care due to insurance (for example, private vs. public), which often tracks race and ethnicity.”
The study was supported by the American Diabetes Association. Dr. Choi was supported by a National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging grant. Dr. Laiteerapong and other co-authors are members of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Chicago Center for Diabetes Translation Research at the University of Chicago. Dr. Choi and Dr. Laiteerapong have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Retinal imaging can predict cardiovascular mortality
according to a new study using data from the UK Biobank Eye and Vision Consortium and the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC)–Norfolk study.
The researchers, from St. George’s University of London, Cambridge University, Kingston University, Moorfields Eye Hospital, and University College London, developed a method of artificial intelligence (AI)–enabled imaging of the retina’s vascular network that could accurately predict CVD and death, without the need for blood tests or blood pressure measurement.
The system “paves the way for a highly effective, noninvasive screening test for people at medium to high risk of circulatory disease that doesn’t have to be done in a clinic,” they said. “In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.” Optometry specialists welcomed the prospect and hailed it as “an exciting development.”
Retinal vessels give an accurate early indicator of CVD
The study, published online in the British Journal of Ophthalmology, was based on previous research showing that the width of retinal arterioles and venules seen on retinal imaging may provide an accurate early indicator of CVD, whereas current risk prediction frameworks aren’t always reliable in identifying people who will go on to develop or die of circulatory diseases.
The researchers developed a fully automated AI-enabled algorithm, called Quantitative Analysis of Retinal vessels Topology and Size (QUARTZ), to assess the potential of retinal vasculature imaging plus known risk factors to predict vascular health and death. They applied QUARTZ to retinal images from 88,052 UK Biobank participants aged 40-69 years, looking specifically at the width, vessel area, and degree of tortuosity of the retinal microvasculature, to develop prediction models for stroke, heart attack, and death from circulatory disease.
They then applied these models to the retinal images of 7,411 participants, aged 48-92 years, in the EPIC-Norfolk study. They then compared the performance of QUARTZ with the widely used Framingham Risk Scores framework.
The participants in the two studies were tracked for an average of 7.7 and 9.1 years, respectively, during which time there were 327 circulatory disease deaths among 64,144 UK Biobank participants (average age, 56.8 years) and 201 circulatory deaths among 5,862 EPIC-Norfolk participants (average age, 67.6 years).
Vessel characteristics important predictors of CVD mortality
Results from the QUARTZ models showed that in all participants, arteriolar and venular width, venular tortuosity, and width variation were important predictors of circulatory disease death. In addition, in women, but not in men, arteriolar and venular area were separate factors that contributed to risk prediction.
Overall, the predictive models, based on age, smoking, and medical history (antihypertensive or cholesterol lowering medication, diabetes, and history of stroke or MI) as well as retinal vasculature, captured between half and two-thirds of circulatory disease deaths in those most at risk, the authors said.
Compared with Framingham Risk Scores (FRS), the retinal vasculature (RV) models captured about 5% more cases of stroke in UK Biobank men, 8% more cases in UK Biobank women, and 3% more cases among EPIC-Norfolk men most at risk, but nearly 2% fewer cases among EPIC-Norfolk women. However, the team said that, while adding RV to FRS resulted in only marginal changes in prediction of stroke or MI, a simpler noninvasive risk score based on age, sex, smoking status, medical history, and RV “yielded comparable performance to FRS, without the need for blood sampling or BP measurement.”
Vasculometry low cost, noninvasive and with high street availability
They concluded: “Retinal imaging is established within clinic and hospital eye care and in optometric practices in the U.S. and U.K. AI-enabled vasculometry risk prediction is fully automated, low cost, noninvasive and has the potential for reaching a higher proportion of the population in the community because of “high street” availability and because blood sampling or sphygmomanometry are not needed.
“[Retinal vasculature] is a microvascular marker, hence offers better prediction for circulatory mortality and stroke, compared with MI, which is more macrovascular, except perhaps in women.
“In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.”
In the United Kingdom, for example, it could be included in the primary care NHS Health Check for those aged 41-74 years, they suggested. In addition, “high street” retinal scanning could directly feed into primary medical services and help achieve greater screening coverage for older age groups, who are likely to attend an optometric practice for visual correction, especially with the onset of presbyopia. “This would offer a novel approach to identify those at high risk of circulatory mortality, which is not currently screened for,” the team said.
Test could help to identify high-risk individuals
In a linked editorial, Ify Mordi, MD, and Emanuele Trucco, MD, of the University of Dundee (Scotland), said that CVD remains a significant cause of mortality and morbidity and the most common cause of death worldwide, accounting for a quarter of all U.K. deaths – and its burden is increasing. “Identification of individuals at high risk is particularly important,” they said, but current clinical risk scores to identify those at risk “are unfortunately not perfect,” so miss some of those who might benefit from preventative therapy.
“The retina is the only location that allows non-invasive direct visualisation of the vasculature, potentially providing a rich source of information.” In the new study, the measurements derived with the software tool, QUARTZ, were significantly associated with CVD, they said, with similar predictive performance to the Framingham clinical risk score.
“The results strengthen the evidence from several similar studies that the retina can be a useful and potentially disruptive source of information for CVD risk in personalised medicine.” However, a number of questions remain about how this knowledge could be integrated into clinical care, including who would conduct such a retinal screening program and who would act on the findings?
The editorial concluded: “What is now needed is for ophthalmologists, cardiologists, primary care physicians, and computer scientists to work together to design studies to determine whether using this information improves clinical outcome, and, if so, to work with regulatory bodies, scientific societies and healthcare systems to optimize clinical work flows and enable practical implementation in routine practice.”
‘Exciting development that could improve outcomes’
Asked to comment, Farah Topia, clinical and regulatory adviser at the Association of Optometrists, said: “This is an exciting development that could improve outcomes for many patients by enabling earlier detection of serious health risks. Patients attend optometric practice for a variety of reasons and this interaction could be used to a greater extent to help detect disease earlier. With optometrists available on every High Street, in the heart of communities, it’s an element of primary care that can be accessed quickly and easily, and optometrists are also already trained to have health and lifestyle discussion with patients.”
She added: “Retinal photographs are regularly taken when patients visit an optometrist, so being able to further enhance this process using AI is exciting.
“We look forward to seeing how this area develops and how optometrists can work together with other healthcare sectors to improve patient outcomes and ease the burden the NHS currently faces.”
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council Population and Systems Medicine Board and the British Heart Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
according to a new study using data from the UK Biobank Eye and Vision Consortium and the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC)–Norfolk study.
The researchers, from St. George’s University of London, Cambridge University, Kingston University, Moorfields Eye Hospital, and University College London, developed a method of artificial intelligence (AI)–enabled imaging of the retina’s vascular network that could accurately predict CVD and death, without the need for blood tests or blood pressure measurement.
The system “paves the way for a highly effective, noninvasive screening test for people at medium to high risk of circulatory disease that doesn’t have to be done in a clinic,” they said. “In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.” Optometry specialists welcomed the prospect and hailed it as “an exciting development.”
Retinal vessels give an accurate early indicator of CVD
The study, published online in the British Journal of Ophthalmology, was based on previous research showing that the width of retinal arterioles and venules seen on retinal imaging may provide an accurate early indicator of CVD, whereas current risk prediction frameworks aren’t always reliable in identifying people who will go on to develop or die of circulatory diseases.
The researchers developed a fully automated AI-enabled algorithm, called Quantitative Analysis of Retinal vessels Topology and Size (QUARTZ), to assess the potential of retinal vasculature imaging plus known risk factors to predict vascular health and death. They applied QUARTZ to retinal images from 88,052 UK Biobank participants aged 40-69 years, looking specifically at the width, vessel area, and degree of tortuosity of the retinal microvasculature, to develop prediction models for stroke, heart attack, and death from circulatory disease.
They then applied these models to the retinal images of 7,411 participants, aged 48-92 years, in the EPIC-Norfolk study. They then compared the performance of QUARTZ with the widely used Framingham Risk Scores framework.
The participants in the two studies were tracked for an average of 7.7 and 9.1 years, respectively, during which time there were 327 circulatory disease deaths among 64,144 UK Biobank participants (average age, 56.8 years) and 201 circulatory deaths among 5,862 EPIC-Norfolk participants (average age, 67.6 years).
Vessel characteristics important predictors of CVD mortality
Results from the QUARTZ models showed that in all participants, arteriolar and venular width, venular tortuosity, and width variation were important predictors of circulatory disease death. In addition, in women, but not in men, arteriolar and venular area were separate factors that contributed to risk prediction.
Overall, the predictive models, based on age, smoking, and medical history (antihypertensive or cholesterol lowering medication, diabetes, and history of stroke or MI) as well as retinal vasculature, captured between half and two-thirds of circulatory disease deaths in those most at risk, the authors said.
Compared with Framingham Risk Scores (FRS), the retinal vasculature (RV) models captured about 5% more cases of stroke in UK Biobank men, 8% more cases in UK Biobank women, and 3% more cases among EPIC-Norfolk men most at risk, but nearly 2% fewer cases among EPIC-Norfolk women. However, the team said that, while adding RV to FRS resulted in only marginal changes in prediction of stroke or MI, a simpler noninvasive risk score based on age, sex, smoking status, medical history, and RV “yielded comparable performance to FRS, without the need for blood sampling or BP measurement.”
Vasculometry low cost, noninvasive and with high street availability
They concluded: “Retinal imaging is established within clinic and hospital eye care and in optometric practices in the U.S. and U.K. AI-enabled vasculometry risk prediction is fully automated, low cost, noninvasive and has the potential for reaching a higher proportion of the population in the community because of “high street” availability and because blood sampling or sphygmomanometry are not needed.
“[Retinal vasculature] is a microvascular marker, hence offers better prediction for circulatory mortality and stroke, compared with MI, which is more macrovascular, except perhaps in women.
“In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.”
In the United Kingdom, for example, it could be included in the primary care NHS Health Check for those aged 41-74 years, they suggested. In addition, “high street” retinal scanning could directly feed into primary medical services and help achieve greater screening coverage for older age groups, who are likely to attend an optometric practice for visual correction, especially with the onset of presbyopia. “This would offer a novel approach to identify those at high risk of circulatory mortality, which is not currently screened for,” the team said.
Test could help to identify high-risk individuals
In a linked editorial, Ify Mordi, MD, and Emanuele Trucco, MD, of the University of Dundee (Scotland), said that CVD remains a significant cause of mortality and morbidity and the most common cause of death worldwide, accounting for a quarter of all U.K. deaths – and its burden is increasing. “Identification of individuals at high risk is particularly important,” they said, but current clinical risk scores to identify those at risk “are unfortunately not perfect,” so miss some of those who might benefit from preventative therapy.
“The retina is the only location that allows non-invasive direct visualisation of the vasculature, potentially providing a rich source of information.” In the new study, the measurements derived with the software tool, QUARTZ, were significantly associated with CVD, they said, with similar predictive performance to the Framingham clinical risk score.
“The results strengthen the evidence from several similar studies that the retina can be a useful and potentially disruptive source of information for CVD risk in personalised medicine.” However, a number of questions remain about how this knowledge could be integrated into clinical care, including who would conduct such a retinal screening program and who would act on the findings?
The editorial concluded: “What is now needed is for ophthalmologists, cardiologists, primary care physicians, and computer scientists to work together to design studies to determine whether using this information improves clinical outcome, and, if so, to work with regulatory bodies, scientific societies and healthcare systems to optimize clinical work flows and enable practical implementation in routine practice.”
‘Exciting development that could improve outcomes’
Asked to comment, Farah Topia, clinical and regulatory adviser at the Association of Optometrists, said: “This is an exciting development that could improve outcomes for many patients by enabling earlier detection of serious health risks. Patients attend optometric practice for a variety of reasons and this interaction could be used to a greater extent to help detect disease earlier. With optometrists available on every High Street, in the heart of communities, it’s an element of primary care that can be accessed quickly and easily, and optometrists are also already trained to have health and lifestyle discussion with patients.”
She added: “Retinal photographs are regularly taken when patients visit an optometrist, so being able to further enhance this process using AI is exciting.
“We look forward to seeing how this area develops and how optometrists can work together with other healthcare sectors to improve patient outcomes and ease the burden the NHS currently faces.”
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council Population and Systems Medicine Board and the British Heart Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
according to a new study using data from the UK Biobank Eye and Vision Consortium and the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC)–Norfolk study.
The researchers, from St. George’s University of London, Cambridge University, Kingston University, Moorfields Eye Hospital, and University College London, developed a method of artificial intelligence (AI)–enabled imaging of the retina’s vascular network that could accurately predict CVD and death, without the need for blood tests or blood pressure measurement.
The system “paves the way for a highly effective, noninvasive screening test for people at medium to high risk of circulatory disease that doesn’t have to be done in a clinic,” they said. “In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.” Optometry specialists welcomed the prospect and hailed it as “an exciting development.”
Retinal vessels give an accurate early indicator of CVD
The study, published online in the British Journal of Ophthalmology, was based on previous research showing that the width of retinal arterioles and venules seen on retinal imaging may provide an accurate early indicator of CVD, whereas current risk prediction frameworks aren’t always reliable in identifying people who will go on to develop or die of circulatory diseases.
The researchers developed a fully automated AI-enabled algorithm, called Quantitative Analysis of Retinal vessels Topology and Size (QUARTZ), to assess the potential of retinal vasculature imaging plus known risk factors to predict vascular health and death. They applied QUARTZ to retinal images from 88,052 UK Biobank participants aged 40-69 years, looking specifically at the width, vessel area, and degree of tortuosity of the retinal microvasculature, to develop prediction models for stroke, heart attack, and death from circulatory disease.
They then applied these models to the retinal images of 7,411 participants, aged 48-92 years, in the EPIC-Norfolk study. They then compared the performance of QUARTZ with the widely used Framingham Risk Scores framework.
The participants in the two studies were tracked for an average of 7.7 and 9.1 years, respectively, during which time there were 327 circulatory disease deaths among 64,144 UK Biobank participants (average age, 56.8 years) and 201 circulatory deaths among 5,862 EPIC-Norfolk participants (average age, 67.6 years).
Vessel characteristics important predictors of CVD mortality
Results from the QUARTZ models showed that in all participants, arteriolar and venular width, venular tortuosity, and width variation were important predictors of circulatory disease death. In addition, in women, but not in men, arteriolar and venular area were separate factors that contributed to risk prediction.
Overall, the predictive models, based on age, smoking, and medical history (antihypertensive or cholesterol lowering medication, diabetes, and history of stroke or MI) as well as retinal vasculature, captured between half and two-thirds of circulatory disease deaths in those most at risk, the authors said.
Compared with Framingham Risk Scores (FRS), the retinal vasculature (RV) models captured about 5% more cases of stroke in UK Biobank men, 8% more cases in UK Biobank women, and 3% more cases among EPIC-Norfolk men most at risk, but nearly 2% fewer cases among EPIC-Norfolk women. However, the team said that, while adding RV to FRS resulted in only marginal changes in prediction of stroke or MI, a simpler noninvasive risk score based on age, sex, smoking status, medical history, and RV “yielded comparable performance to FRS, without the need for blood sampling or BP measurement.”
Vasculometry low cost, noninvasive and with high street availability
They concluded: “Retinal imaging is established within clinic and hospital eye care and in optometric practices in the U.S. and U.K. AI-enabled vasculometry risk prediction is fully automated, low cost, noninvasive and has the potential for reaching a higher proportion of the population in the community because of “high street” availability and because blood sampling or sphygmomanometry are not needed.
“[Retinal vasculature] is a microvascular marker, hence offers better prediction for circulatory mortality and stroke, compared with MI, which is more macrovascular, except perhaps in women.
“In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.”
In the United Kingdom, for example, it could be included in the primary care NHS Health Check for those aged 41-74 years, they suggested. In addition, “high street” retinal scanning could directly feed into primary medical services and help achieve greater screening coverage for older age groups, who are likely to attend an optometric practice for visual correction, especially with the onset of presbyopia. “This would offer a novel approach to identify those at high risk of circulatory mortality, which is not currently screened for,” the team said.
Test could help to identify high-risk individuals
In a linked editorial, Ify Mordi, MD, and Emanuele Trucco, MD, of the University of Dundee (Scotland), said that CVD remains a significant cause of mortality and morbidity and the most common cause of death worldwide, accounting for a quarter of all U.K. deaths – and its burden is increasing. “Identification of individuals at high risk is particularly important,” they said, but current clinical risk scores to identify those at risk “are unfortunately not perfect,” so miss some of those who might benefit from preventative therapy.
“The retina is the only location that allows non-invasive direct visualisation of the vasculature, potentially providing a rich source of information.” In the new study, the measurements derived with the software tool, QUARTZ, were significantly associated with CVD, they said, with similar predictive performance to the Framingham clinical risk score.
“The results strengthen the evidence from several similar studies that the retina can be a useful and potentially disruptive source of information for CVD risk in personalised medicine.” However, a number of questions remain about how this knowledge could be integrated into clinical care, including who would conduct such a retinal screening program and who would act on the findings?
The editorial concluded: “What is now needed is for ophthalmologists, cardiologists, primary care physicians, and computer scientists to work together to design studies to determine whether using this information improves clinical outcome, and, if so, to work with regulatory bodies, scientific societies and healthcare systems to optimize clinical work flows and enable practical implementation in routine practice.”
‘Exciting development that could improve outcomes’
Asked to comment, Farah Topia, clinical and regulatory adviser at the Association of Optometrists, said: “This is an exciting development that could improve outcomes for many patients by enabling earlier detection of serious health risks. Patients attend optometric practice for a variety of reasons and this interaction could be used to a greater extent to help detect disease earlier. With optometrists available on every High Street, in the heart of communities, it’s an element of primary care that can be accessed quickly and easily, and optometrists are also already trained to have health and lifestyle discussion with patients.”
She added: “Retinal photographs are regularly taken when patients visit an optometrist, so being able to further enhance this process using AI is exciting.
“We look forward to seeing how this area develops and how optometrists can work together with other healthcare sectors to improve patient outcomes and ease the burden the NHS currently faces.”
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council Population and Systems Medicine Board and the British Heart Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
Food insecurity a growing problem for many with CVD
A growing number of Americans with cardiovascular disease (CVD) have limited or uncertain access to food, results of a new study suggest.
An analysis of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) representing more than 300 million American adults found that, overall, 38.1% of people with cardiovascular disease were food insecure in 2017-2019.
Twenty years earlier, that rate was 16.3%.
“What really stood out from our study is how frequent food insecurity is among people with cardiovascular disease, compared to those without cardiovascular disease,” lead author, Eric J. Brandt, MD, MHS, a cardiologist at the University of Michigan Health Frankel Cardiovascular Center, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
“We believe that the relationship between food insecurity and cardiovascular disease is bidirectional. Food insecurity puts people at risk for cardiovascular disease, which then makes them vulnerable to events like myocardial infarction or stroke, which in turn may make them less able to work, thereby worsening their financial situation and increasing their vulnerability to food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt said.
For the analysis, Dr. Brandt and his team used an analytic sample of 57,517 adults to represent 312 million non-institutionalized adults in the United States.
Overall, 6,770 individuals (11.8%) in the analytic sample reported food insecurity.
Food insecurity was more prevalent among Hispanic people (n = 1,938, 24.0%) and non-Hispanic Black people (n = 1,202, 18.2%), compared with non-Hispanic Asian people (n = 100, 8.0%), and non-Hispanic White people (n = 3,221, 8.5%).
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the sample was 7.9% (n = 4,527).
Hypertension was the most prevalent CVD risk factor, reported in 49.6% of the sample. This was followed by obesity in 33.2%, dyslipidemia in 30.8%, and diabetes in 11.2%.
The findings were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
“All cardiovascular disease and cardiometabolic diseases except coronary artery disease were more prevalent among those with food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt noted.
“The results of our study are especially timely, as the White House just hosted its first conference on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health in over 50 years. Food insecurity is a focus of that conference. In the last few years, especially in relation to the pandemic, there has been expansion of some of the federal programs to prevent food insecurity. I would like to see a continued effort to solve this,” he said.
Dr. Brandt added that he hopes clinicians will be more cognizant of the problem of food insecurity and other social determinants of health when they see their patients.
“If someone is not going to be able to afford the food on their table, they’re probably not going to pay for their medications. Recognizing these social determinants in the clinical setting and helping our patients access local resources may address the underlying factors contributing to heart disease,” he said.
Uphill battle
Johanna Contreras, MD, advanced heart failure and transplant cardiologist at the Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, treats food insecure cardiovascular patients in her practice and tries to educate them about good nutrition. But it is an uphill battle.
“A lot of my patients live in the South Bronx. They have hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and there are no grocery stores where they can buy fresh vegetables. I talk to them about eating healthy. They tell me it’s impossible. The stores only have pre-packaged foods. So even in the South Bronx, even though it is in New York, it is very hard to get fresh food. And when it is available, it is very expensive,” Dr. Contreras told this news organization.
“Fresh pineapples can cost $8. A fast-food burger costs $3. So that is what they buy: It’s what they can afford. Even the store managers don’t want to stock fresh produce because it can spoil. They open stores, like Whole Foods, but in the more affluent neighborhoods. They should open one in poor neighborhoods,” she said.
Dr. Contreras says she spends much of her time educating her patients about good nutrition. She asks them to keep a food diary and analyzes the results at each visit.
“I look at what they eat, and I try to see how I can use this information in a good way. I advise them to use frozen foods, and avoid canned, because it is a lot healthier. I am pragmatic, because I know that if I tell my patients to eat salmon, for example, they aren’t going to be able to afford it, if they can even access it.”
She also informs them about relatively healthy fast-food choices.
“I tell them to order 100% fruit juice, water, or milk when they go to McDonalds or other fast-food places. So I think this study is very important. Food insecurity is a very important component of cardiovascular disease, and unfortunately, minority communities are where this occurs.”
Dr. Brandt and Dr. Contreras report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A growing number of Americans with cardiovascular disease (CVD) have limited or uncertain access to food, results of a new study suggest.
An analysis of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) representing more than 300 million American adults found that, overall, 38.1% of people with cardiovascular disease were food insecure in 2017-2019.
Twenty years earlier, that rate was 16.3%.
“What really stood out from our study is how frequent food insecurity is among people with cardiovascular disease, compared to those without cardiovascular disease,” lead author, Eric J. Brandt, MD, MHS, a cardiologist at the University of Michigan Health Frankel Cardiovascular Center, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
“We believe that the relationship between food insecurity and cardiovascular disease is bidirectional. Food insecurity puts people at risk for cardiovascular disease, which then makes them vulnerable to events like myocardial infarction or stroke, which in turn may make them less able to work, thereby worsening their financial situation and increasing their vulnerability to food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt said.
For the analysis, Dr. Brandt and his team used an analytic sample of 57,517 adults to represent 312 million non-institutionalized adults in the United States.
Overall, 6,770 individuals (11.8%) in the analytic sample reported food insecurity.
Food insecurity was more prevalent among Hispanic people (n = 1,938, 24.0%) and non-Hispanic Black people (n = 1,202, 18.2%), compared with non-Hispanic Asian people (n = 100, 8.0%), and non-Hispanic White people (n = 3,221, 8.5%).
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the sample was 7.9% (n = 4,527).
Hypertension was the most prevalent CVD risk factor, reported in 49.6% of the sample. This was followed by obesity in 33.2%, dyslipidemia in 30.8%, and diabetes in 11.2%.
The findings were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
“All cardiovascular disease and cardiometabolic diseases except coronary artery disease were more prevalent among those with food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt noted.
“The results of our study are especially timely, as the White House just hosted its first conference on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health in over 50 years. Food insecurity is a focus of that conference. In the last few years, especially in relation to the pandemic, there has been expansion of some of the federal programs to prevent food insecurity. I would like to see a continued effort to solve this,” he said.
Dr. Brandt added that he hopes clinicians will be more cognizant of the problem of food insecurity and other social determinants of health when they see their patients.
“If someone is not going to be able to afford the food on their table, they’re probably not going to pay for their medications. Recognizing these social determinants in the clinical setting and helping our patients access local resources may address the underlying factors contributing to heart disease,” he said.
Uphill battle
Johanna Contreras, MD, advanced heart failure and transplant cardiologist at the Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, treats food insecure cardiovascular patients in her practice and tries to educate them about good nutrition. But it is an uphill battle.
“A lot of my patients live in the South Bronx. They have hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and there are no grocery stores where they can buy fresh vegetables. I talk to them about eating healthy. They tell me it’s impossible. The stores only have pre-packaged foods. So even in the South Bronx, even though it is in New York, it is very hard to get fresh food. And when it is available, it is very expensive,” Dr. Contreras told this news organization.
“Fresh pineapples can cost $8. A fast-food burger costs $3. So that is what they buy: It’s what they can afford. Even the store managers don’t want to stock fresh produce because it can spoil. They open stores, like Whole Foods, but in the more affluent neighborhoods. They should open one in poor neighborhoods,” she said.
Dr. Contreras says she spends much of her time educating her patients about good nutrition. She asks them to keep a food diary and analyzes the results at each visit.
“I look at what they eat, and I try to see how I can use this information in a good way. I advise them to use frozen foods, and avoid canned, because it is a lot healthier. I am pragmatic, because I know that if I tell my patients to eat salmon, for example, they aren’t going to be able to afford it, if they can even access it.”
She also informs them about relatively healthy fast-food choices.
“I tell them to order 100% fruit juice, water, or milk when they go to McDonalds or other fast-food places. So I think this study is very important. Food insecurity is a very important component of cardiovascular disease, and unfortunately, minority communities are where this occurs.”
Dr. Brandt and Dr. Contreras report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A growing number of Americans with cardiovascular disease (CVD) have limited or uncertain access to food, results of a new study suggest.
An analysis of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) representing more than 300 million American adults found that, overall, 38.1% of people with cardiovascular disease were food insecure in 2017-2019.
Twenty years earlier, that rate was 16.3%.
“What really stood out from our study is how frequent food insecurity is among people with cardiovascular disease, compared to those without cardiovascular disease,” lead author, Eric J. Brandt, MD, MHS, a cardiologist at the University of Michigan Health Frankel Cardiovascular Center, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
“We believe that the relationship between food insecurity and cardiovascular disease is bidirectional. Food insecurity puts people at risk for cardiovascular disease, which then makes them vulnerable to events like myocardial infarction or stroke, which in turn may make them less able to work, thereby worsening their financial situation and increasing their vulnerability to food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt said.
For the analysis, Dr. Brandt and his team used an analytic sample of 57,517 adults to represent 312 million non-institutionalized adults in the United States.
Overall, 6,770 individuals (11.8%) in the analytic sample reported food insecurity.
Food insecurity was more prevalent among Hispanic people (n = 1,938, 24.0%) and non-Hispanic Black people (n = 1,202, 18.2%), compared with non-Hispanic Asian people (n = 100, 8.0%), and non-Hispanic White people (n = 3,221, 8.5%).
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the sample was 7.9% (n = 4,527).
Hypertension was the most prevalent CVD risk factor, reported in 49.6% of the sample. This was followed by obesity in 33.2%, dyslipidemia in 30.8%, and diabetes in 11.2%.
The findings were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
“All cardiovascular disease and cardiometabolic diseases except coronary artery disease were more prevalent among those with food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt noted.
“The results of our study are especially timely, as the White House just hosted its first conference on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health in over 50 years. Food insecurity is a focus of that conference. In the last few years, especially in relation to the pandemic, there has been expansion of some of the federal programs to prevent food insecurity. I would like to see a continued effort to solve this,” he said.
Dr. Brandt added that he hopes clinicians will be more cognizant of the problem of food insecurity and other social determinants of health when they see their patients.
“If someone is not going to be able to afford the food on their table, they’re probably not going to pay for their medications. Recognizing these social determinants in the clinical setting and helping our patients access local resources may address the underlying factors contributing to heart disease,” he said.
Uphill battle
Johanna Contreras, MD, advanced heart failure and transplant cardiologist at the Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, treats food insecure cardiovascular patients in her practice and tries to educate them about good nutrition. But it is an uphill battle.
“A lot of my patients live in the South Bronx. They have hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and there are no grocery stores where they can buy fresh vegetables. I talk to them about eating healthy. They tell me it’s impossible. The stores only have pre-packaged foods. So even in the South Bronx, even though it is in New York, it is very hard to get fresh food. And when it is available, it is very expensive,” Dr. Contreras told this news organization.
“Fresh pineapples can cost $8. A fast-food burger costs $3. So that is what they buy: It’s what they can afford. Even the store managers don’t want to stock fresh produce because it can spoil. They open stores, like Whole Foods, but in the more affluent neighborhoods. They should open one in poor neighborhoods,” she said.
Dr. Contreras says she spends much of her time educating her patients about good nutrition. She asks them to keep a food diary and analyzes the results at each visit.
“I look at what they eat, and I try to see how I can use this information in a good way. I advise them to use frozen foods, and avoid canned, because it is a lot healthier. I am pragmatic, because I know that if I tell my patients to eat salmon, for example, they aren’t going to be able to afford it, if they can even access it.”
She also informs them about relatively healthy fast-food choices.
“I tell them to order 100% fruit juice, water, or milk when they go to McDonalds or other fast-food places. So I think this study is very important. Food insecurity is a very important component of cardiovascular disease, and unfortunately, minority communities are where this occurs.”
Dr. Brandt and Dr. Contreras report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Similar transplant outcomes with hearts donated after circulatory death
Transplantation of hearts donated after circulatory death (DCD) is associated with short-term clinical outcomes similar to those of hearts donated after brain death (DBD), except for transient posttransplant right heart dysfunction, a single-center analysis suggests.
The right-heart dysfunction resolved by 3 weeks post transplant, and recipient mortality was similar for those receiving DCD and DBD, which is considered standard of care (SOC).
Furthermore, the median waiting list time was significantly shorter for DCD recipients than for SOC recipients (17 vs. 70 days).
The authors suggest that use of DCD hearts could expand the donor pool by as much as 30%.
“Now that we and others have demonstrated the safety of this technique, I believe it is our obligation as a transplant community to use these organs and not allow them to be wasted,” David A. D’Alessandro, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, told this news organization.
“I will caution that DCD heart transplantation is labor intensive, and there is a learning curve which can potentially put patients at risk,” he added. “It is vitally important, therefore, that we learn from each other’s experiences to flatten this curve.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Similar outcomes
Dr. D’Alessandro and colleagues compared the hemodynamic and clinical profiles of 47 DCD hearts with 166 SOC hearts implanted at Massachusetts General Hospital between 2016 and 2022. DCD hearts were maintained with use of a proprietary warm perfusion circuit organ care system (OCS, TransMedics).
Baseline characteristics were similar between the groups, except the DCD heart recipients were younger (mean age, 55 vs. 59); they were less likely to be an inpatient at the time of transplant (26% vs. 49%); and they had lower pulmonary vascular resistance (1.73 WU vs. 2.26 WU).
The median time from DCD consent to transplant was significantly shorter than for SOC hearts (17 vs. 70 days). However, there was a higher, though not statistically significant, incidence of severe primary graft dysfunction at 24 hours post transplant with DCD (10.6% vs. SOC 3.6%), leading five DCD recipients (10.6%) and nine SOC recipients (5.4%) to receive venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Right heart function was significantly impaired in DCD vs. SOC recipients 1 week post transplant, with higher median right atrial pressure (10 mm Hg vs. 7 mm Hg); higher right atrial pressure to pulmonary capillary wedge pressure ratio (0.64 vs. 0.57); and lower pulmonary arterial pulsatility index (1.66 vs. 2.52).
However, by 3 weeks post transplant, right heart function was similar between the groups, as was mortality at 30 days (0 vs. 2%) and 1 year (3% vs. 8%).
Furthermore, hospital length of stay following transplant, intensive care unit length of stay, ICU readmissions, and 30-day readmissions were similar between the groups.
“We and others will continue to push the boundaries of this technique to understand if we can safely extend the warm ischemic time, which could make additional organs available,” Dr. D’Alessandro said. “We will also be exploring additional ways to monitor and assess organ health and viability ex situ and potential avenues of treatment which could repair and optimize organ function.
“A successful DCD heart transplant program requires institutional and team commitment,” he added, “and there are clinical nuances which should be appreciated to minimize patient risks associated with the obligate learning curve.”
Ulrich P. Jorde, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center in New York, author of a related editorial, concluded that heart donation after circulatory death “promises significant expansion of the donor pool and will lead to many lives saved” and that “the current investigation is a timely and important contribution to this effort”.
However, he noted, “it must be acknowledged that donation after cardiac death has evoked significant controversy regarding the ethics of this approach,” particularly when using a technique called normothermic regional perfusion (NRP), in which, after declaration of death and ligation of cerebral vessels, the heart is resuscitated in situ using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, as opposed to the proprietary warm perfusion OCS used in this study.
“Central to this discussion is the definition of death and its irreversibility,” Dr. Jorde noted. “In contrast to DBD, where brain death protocols are well established and accepted by societies across the globe, DCD protocol rules, e.g., standoff times after complete cessation of circulation, continue to vary even within national jurisdictions. Such variability and incomplete standardization of practice is particularly important when the organ is resuscitated in situ using normothermic regional perfusion.
“The International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation has recently provided a framework within which donation after cardiac death, with or without the use of NRP, can be conducted to comply with ethical and legal norms and regulations, acknowledging that such norms and regulations may differ between societies,” he wrote. “To advance the field, and to ensure ongoing trust in the transplantation system, it is of critical importance that such discussions are held publicly and transparently.”
More ‘dry runs’
“Donor heart allographs are safe for our patients with heart failure if procured and transplanted in an organized and protocolized manner,” Philip J. Spencer, MD, a cardiovascular and transplant surgeon at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told this news organization. “As the techniques are adopted globally, our patients will benefit.”
Nevertheless, like Dr. D’Alessandro, he noted that procurement of DCD hearts is more labor intensive. “A program and its patients must be willing to accept a higher number of ‘dry runs,’ which occurs when the team is sent for an organ and the donor does not progress to circulatory death in a time and manner appropriate for safe organ recovery.
“There is no doubt that being open to these organs will increase the patient’s chances of receiving a donor heart in a shorter period of time,” he said. “However, the experience of a dry run, or multiple, can be emotionally and financially stressful for the patient and the program.”
No commercial funding or relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transplantation of hearts donated after circulatory death (DCD) is associated with short-term clinical outcomes similar to those of hearts donated after brain death (DBD), except for transient posttransplant right heart dysfunction, a single-center analysis suggests.
The right-heart dysfunction resolved by 3 weeks post transplant, and recipient mortality was similar for those receiving DCD and DBD, which is considered standard of care (SOC).
Furthermore, the median waiting list time was significantly shorter for DCD recipients than for SOC recipients (17 vs. 70 days).
The authors suggest that use of DCD hearts could expand the donor pool by as much as 30%.
“Now that we and others have demonstrated the safety of this technique, I believe it is our obligation as a transplant community to use these organs and not allow them to be wasted,” David A. D’Alessandro, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, told this news organization.
“I will caution that DCD heart transplantation is labor intensive, and there is a learning curve which can potentially put patients at risk,” he added. “It is vitally important, therefore, that we learn from each other’s experiences to flatten this curve.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Similar outcomes
Dr. D’Alessandro and colleagues compared the hemodynamic and clinical profiles of 47 DCD hearts with 166 SOC hearts implanted at Massachusetts General Hospital between 2016 and 2022. DCD hearts were maintained with use of a proprietary warm perfusion circuit organ care system (OCS, TransMedics).
Baseline characteristics were similar between the groups, except the DCD heart recipients were younger (mean age, 55 vs. 59); they were less likely to be an inpatient at the time of transplant (26% vs. 49%); and they had lower pulmonary vascular resistance (1.73 WU vs. 2.26 WU).
The median time from DCD consent to transplant was significantly shorter than for SOC hearts (17 vs. 70 days). However, there was a higher, though not statistically significant, incidence of severe primary graft dysfunction at 24 hours post transplant with DCD (10.6% vs. SOC 3.6%), leading five DCD recipients (10.6%) and nine SOC recipients (5.4%) to receive venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Right heart function was significantly impaired in DCD vs. SOC recipients 1 week post transplant, with higher median right atrial pressure (10 mm Hg vs. 7 mm Hg); higher right atrial pressure to pulmonary capillary wedge pressure ratio (0.64 vs. 0.57); and lower pulmonary arterial pulsatility index (1.66 vs. 2.52).
However, by 3 weeks post transplant, right heart function was similar between the groups, as was mortality at 30 days (0 vs. 2%) and 1 year (3% vs. 8%).
Furthermore, hospital length of stay following transplant, intensive care unit length of stay, ICU readmissions, and 30-day readmissions were similar between the groups.
“We and others will continue to push the boundaries of this technique to understand if we can safely extend the warm ischemic time, which could make additional organs available,” Dr. D’Alessandro said. “We will also be exploring additional ways to monitor and assess organ health and viability ex situ and potential avenues of treatment which could repair and optimize organ function.
“A successful DCD heart transplant program requires institutional and team commitment,” he added, “and there are clinical nuances which should be appreciated to minimize patient risks associated with the obligate learning curve.”
Ulrich P. Jorde, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center in New York, author of a related editorial, concluded that heart donation after circulatory death “promises significant expansion of the donor pool and will lead to many lives saved” and that “the current investigation is a timely and important contribution to this effort”.
However, he noted, “it must be acknowledged that donation after cardiac death has evoked significant controversy regarding the ethics of this approach,” particularly when using a technique called normothermic regional perfusion (NRP), in which, after declaration of death and ligation of cerebral vessels, the heart is resuscitated in situ using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, as opposed to the proprietary warm perfusion OCS used in this study.
“Central to this discussion is the definition of death and its irreversibility,” Dr. Jorde noted. “In contrast to DBD, where brain death protocols are well established and accepted by societies across the globe, DCD protocol rules, e.g., standoff times after complete cessation of circulation, continue to vary even within national jurisdictions. Such variability and incomplete standardization of practice is particularly important when the organ is resuscitated in situ using normothermic regional perfusion.
“The International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation has recently provided a framework within which donation after cardiac death, with or without the use of NRP, can be conducted to comply with ethical and legal norms and regulations, acknowledging that such norms and regulations may differ between societies,” he wrote. “To advance the field, and to ensure ongoing trust in the transplantation system, it is of critical importance that such discussions are held publicly and transparently.”
More ‘dry runs’
“Donor heart allographs are safe for our patients with heart failure if procured and transplanted in an organized and protocolized manner,” Philip J. Spencer, MD, a cardiovascular and transplant surgeon at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told this news organization. “As the techniques are adopted globally, our patients will benefit.”
Nevertheless, like Dr. D’Alessandro, he noted that procurement of DCD hearts is more labor intensive. “A program and its patients must be willing to accept a higher number of ‘dry runs,’ which occurs when the team is sent for an organ and the donor does not progress to circulatory death in a time and manner appropriate for safe organ recovery.
“There is no doubt that being open to these organs will increase the patient’s chances of receiving a donor heart in a shorter period of time,” he said. “However, the experience of a dry run, or multiple, can be emotionally and financially stressful for the patient and the program.”
No commercial funding or relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transplantation of hearts donated after circulatory death (DCD) is associated with short-term clinical outcomes similar to those of hearts donated after brain death (DBD), except for transient posttransplant right heart dysfunction, a single-center analysis suggests.
The right-heart dysfunction resolved by 3 weeks post transplant, and recipient mortality was similar for those receiving DCD and DBD, which is considered standard of care (SOC).
Furthermore, the median waiting list time was significantly shorter for DCD recipients than for SOC recipients (17 vs. 70 days).
The authors suggest that use of DCD hearts could expand the donor pool by as much as 30%.
“Now that we and others have demonstrated the safety of this technique, I believe it is our obligation as a transplant community to use these organs and not allow them to be wasted,” David A. D’Alessandro, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, told this news organization.
“I will caution that DCD heart transplantation is labor intensive, and there is a learning curve which can potentially put patients at risk,” he added. “It is vitally important, therefore, that we learn from each other’s experiences to flatten this curve.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Similar outcomes
Dr. D’Alessandro and colleagues compared the hemodynamic and clinical profiles of 47 DCD hearts with 166 SOC hearts implanted at Massachusetts General Hospital between 2016 and 2022. DCD hearts were maintained with use of a proprietary warm perfusion circuit organ care system (OCS, TransMedics).
Baseline characteristics were similar between the groups, except the DCD heart recipients were younger (mean age, 55 vs. 59); they were less likely to be an inpatient at the time of transplant (26% vs. 49%); and they had lower pulmonary vascular resistance (1.73 WU vs. 2.26 WU).
The median time from DCD consent to transplant was significantly shorter than for SOC hearts (17 vs. 70 days). However, there was a higher, though not statistically significant, incidence of severe primary graft dysfunction at 24 hours post transplant with DCD (10.6% vs. SOC 3.6%), leading five DCD recipients (10.6%) and nine SOC recipients (5.4%) to receive venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Right heart function was significantly impaired in DCD vs. SOC recipients 1 week post transplant, with higher median right atrial pressure (10 mm Hg vs. 7 mm Hg); higher right atrial pressure to pulmonary capillary wedge pressure ratio (0.64 vs. 0.57); and lower pulmonary arterial pulsatility index (1.66 vs. 2.52).
However, by 3 weeks post transplant, right heart function was similar between the groups, as was mortality at 30 days (0 vs. 2%) and 1 year (3% vs. 8%).
Furthermore, hospital length of stay following transplant, intensive care unit length of stay, ICU readmissions, and 30-day readmissions were similar between the groups.
“We and others will continue to push the boundaries of this technique to understand if we can safely extend the warm ischemic time, which could make additional organs available,” Dr. D’Alessandro said. “We will also be exploring additional ways to monitor and assess organ health and viability ex situ and potential avenues of treatment which could repair and optimize organ function.
“A successful DCD heart transplant program requires institutional and team commitment,” he added, “and there are clinical nuances which should be appreciated to minimize patient risks associated with the obligate learning curve.”
Ulrich P. Jorde, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center in New York, author of a related editorial, concluded that heart donation after circulatory death “promises significant expansion of the donor pool and will lead to many lives saved” and that “the current investigation is a timely and important contribution to this effort”.
However, he noted, “it must be acknowledged that donation after cardiac death has evoked significant controversy regarding the ethics of this approach,” particularly when using a technique called normothermic regional perfusion (NRP), in which, after declaration of death and ligation of cerebral vessels, the heart is resuscitated in situ using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, as opposed to the proprietary warm perfusion OCS used in this study.
“Central to this discussion is the definition of death and its irreversibility,” Dr. Jorde noted. “In contrast to DBD, where brain death protocols are well established and accepted by societies across the globe, DCD protocol rules, e.g., standoff times after complete cessation of circulation, continue to vary even within national jurisdictions. Such variability and incomplete standardization of practice is particularly important when the organ is resuscitated in situ using normothermic regional perfusion.
“The International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation has recently provided a framework within which donation after cardiac death, with or without the use of NRP, can be conducted to comply with ethical and legal norms and regulations, acknowledging that such norms and regulations may differ between societies,” he wrote. “To advance the field, and to ensure ongoing trust in the transplantation system, it is of critical importance that such discussions are held publicly and transparently.”
More ‘dry runs’
“Donor heart allographs are safe for our patients with heart failure if procured and transplanted in an organized and protocolized manner,” Philip J. Spencer, MD, a cardiovascular and transplant surgeon at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told this news organization. “As the techniques are adopted globally, our patients will benefit.”
Nevertheless, like Dr. D’Alessandro, he noted that procurement of DCD hearts is more labor intensive. “A program and its patients must be willing to accept a higher number of ‘dry runs,’ which occurs when the team is sent for an organ and the donor does not progress to circulatory death in a time and manner appropriate for safe organ recovery.
“There is no doubt that being open to these organs will increase the patient’s chances of receiving a donor heart in a shorter period of time,” he said. “However, the experience of a dry run, or multiple, can be emotionally and financially stressful for the patient and the program.”
No commercial funding or relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
COVID attacks DNA in heart, unlike flu, study says
, according to a study published in Immunology.
The study looked at the hearts of patients who died from COVID-19, the flu, and other causes. The findings could provide clues about why coronavirus has led to complications such as ongoing heart issues.
“We found a lot of DNA damage that was unique to the COVID-19 patients, which wasn’t present in the flu patients,” Arutha Kulasinghe, one of the lead study authors and a research fellow at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, told the Brisbane Times.
“So in this study, COVID-19 and flu look very different in the way they affect the heart,” he said.
Dr. Kulasinghe and colleagues analyzed the hearts of seven COVID-19 patients, two flu patients, and six patients who died from other causes. They used transcriptomic profiling, which looks at the DNA landscape of an organ, to investigate heart tissue from the patients.
Because of previous studies about heart problems associated with COVID-19, he and colleagues expected to find extreme inflammation in the heart. Instead, they found that inflammation signals had been suppressed in the heart, and markers for DNA damage and repair were much higher. They’re still unsure of the underlying cause.
“The indications here are that there’s DNA damage here, it’s not inflammation,” Dr. Kulasinghe said. “There’s something else going on that we need to figure out.”
The damage was similar to the way chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer appear in the heart, he said, with heart tissue showing DNA damage signals.
Dr. Kulasinghe said he hopes other studies can build on the findings to develop risk models to understand which patients may face a higher risk of serious COVID-19 complications. In turn, this could help doctors provide early treatment. For instance, all seven COVID-19 patients had other chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease.
“Ideally in the future, if you have cardiovascular disease, if you’re obese or have other complications, and you’ve got a signature in your blood that indicates you are at risk of severe disease, then we can risk-stratify patients when they are diagnosed,” he said.
The research is a preliminary step, Dr. Kulasinghe said, because of the small sample size. This type of study is often difficult to conduct because researchers have to wait for the availability of organs, as well as request permission from families for postmortem autopsies and biopsies, to be able to look at the effects on dead tissues.
“Our challenge now is to draw a clinical finding from this, which we can’t at this stage,” he added. “But it’s a really fundamental biological difference we’re observing [between COVID-19 and flu], which we need to validate with larger studies.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a study published in Immunology.
The study looked at the hearts of patients who died from COVID-19, the flu, and other causes. The findings could provide clues about why coronavirus has led to complications such as ongoing heart issues.
“We found a lot of DNA damage that was unique to the COVID-19 patients, which wasn’t present in the flu patients,” Arutha Kulasinghe, one of the lead study authors and a research fellow at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, told the Brisbane Times.
“So in this study, COVID-19 and flu look very different in the way they affect the heart,” he said.
Dr. Kulasinghe and colleagues analyzed the hearts of seven COVID-19 patients, two flu patients, and six patients who died from other causes. They used transcriptomic profiling, which looks at the DNA landscape of an organ, to investigate heart tissue from the patients.
Because of previous studies about heart problems associated with COVID-19, he and colleagues expected to find extreme inflammation in the heart. Instead, they found that inflammation signals had been suppressed in the heart, and markers for DNA damage and repair were much higher. They’re still unsure of the underlying cause.
“The indications here are that there’s DNA damage here, it’s not inflammation,” Dr. Kulasinghe said. “There’s something else going on that we need to figure out.”
The damage was similar to the way chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer appear in the heart, he said, with heart tissue showing DNA damage signals.
Dr. Kulasinghe said he hopes other studies can build on the findings to develop risk models to understand which patients may face a higher risk of serious COVID-19 complications. In turn, this could help doctors provide early treatment. For instance, all seven COVID-19 patients had other chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease.
“Ideally in the future, if you have cardiovascular disease, if you’re obese or have other complications, and you’ve got a signature in your blood that indicates you are at risk of severe disease, then we can risk-stratify patients when they are diagnosed,” he said.
The research is a preliminary step, Dr. Kulasinghe said, because of the small sample size. This type of study is often difficult to conduct because researchers have to wait for the availability of organs, as well as request permission from families for postmortem autopsies and biopsies, to be able to look at the effects on dead tissues.
“Our challenge now is to draw a clinical finding from this, which we can’t at this stage,” he added. “But it’s a really fundamental biological difference we’re observing [between COVID-19 and flu], which we need to validate with larger studies.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a study published in Immunology.
The study looked at the hearts of patients who died from COVID-19, the flu, and other causes. The findings could provide clues about why coronavirus has led to complications such as ongoing heart issues.
“We found a lot of DNA damage that was unique to the COVID-19 patients, which wasn’t present in the flu patients,” Arutha Kulasinghe, one of the lead study authors and a research fellow at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, told the Brisbane Times.
“So in this study, COVID-19 and flu look very different in the way they affect the heart,” he said.
Dr. Kulasinghe and colleagues analyzed the hearts of seven COVID-19 patients, two flu patients, and six patients who died from other causes. They used transcriptomic profiling, which looks at the DNA landscape of an organ, to investigate heart tissue from the patients.
Because of previous studies about heart problems associated with COVID-19, he and colleagues expected to find extreme inflammation in the heart. Instead, they found that inflammation signals had been suppressed in the heart, and markers for DNA damage and repair were much higher. They’re still unsure of the underlying cause.
“The indications here are that there’s DNA damage here, it’s not inflammation,” Dr. Kulasinghe said. “There’s something else going on that we need to figure out.”
The damage was similar to the way chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer appear in the heart, he said, with heart tissue showing DNA damage signals.
Dr. Kulasinghe said he hopes other studies can build on the findings to develop risk models to understand which patients may face a higher risk of serious COVID-19 complications. In turn, this could help doctors provide early treatment. For instance, all seven COVID-19 patients had other chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease.
“Ideally in the future, if you have cardiovascular disease, if you’re obese or have other complications, and you’ve got a signature in your blood that indicates you are at risk of severe disease, then we can risk-stratify patients when they are diagnosed,” he said.
The research is a preliminary step, Dr. Kulasinghe said, because of the small sample size. This type of study is often difficult to conduct because researchers have to wait for the availability of organs, as well as request permission from families for postmortem autopsies and biopsies, to be able to look at the effects on dead tissues.
“Our challenge now is to draw a clinical finding from this, which we can’t at this stage,” he added. “But it’s a really fundamental biological difference we’re observing [between COVID-19 and flu], which we need to validate with larger studies.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM IMMUNOLOGY
SMART-CHOICE 3-year results support dropping aspirin after PCI
Shortening the duration of dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) and continuing with a P2Y12 inhibitor alone after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was associated with a similar rate of ischemic events but with less bleeding than prolonged DAPT after 3 years of follow-up in the SMART-CHOICE trial.
“The current the investigators, with lead author Ki Hong Choi, MD, division of cardiology, department of medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea, conclude.
The 3-year results from the study were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
The authors explain that although dual therapy with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor after PCI with a drug-eluting stent (DES) is crucial to reduce the risk of ischemic events, it raises concerns about increased risk of bleeding, and the antiplatelet strategy after PCI is currently shifting to reduce the duration of DAPT.
Several recent randomized studies have consistently shown that a short duration of DAPT (1-3 months) followed by P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy had ischemia protection effects comparable with that of DAPT of longer duration, and it was associated with a significantly reduced risk of bleeding events in patients who underwent PCI, they note. However, these studies have so far reported only 1-year outcomes, and long-term results are not yet available.
The SMART-CHOICE trial compared two antiplatelet strategies – 3 months of DAPT followed by long-term P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy (mainly with clopidogrel) or prolonged DAPT for 12 months or longer – in 2,993 patients who had undergone PCI with a drug-eluting stent. Results at 12 months showed a similar rate of ischemic events with both strategies but a lower rate of bleeding in the group that received shortened DAPT.
The SMART-CHOICE investigators now report the 3-year results showing similar outcomes.
At 3 years, the primary endpoint, a composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction, or stroke, had occurred in 6.3% of the shortened DAPT group and 6.1% in the prolonged DAPT group, giving a hazard ratio of 1.06 (95% confidence interval, 0.79-1.44).
But in the shortened DAPT group, the risk of bleeding was reduced. Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) types 2-5 bleeding had occurred in 3.2% of the shortened DAPT group and in 8.2% of the prolonged DAPT group (hazard ratio, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.28-0.55). Major bleeding, BARC types 3-5, occurred in 1.2% of the shortened DAPT group and in 2.4% of the prolonged DAPT group (HR, 0.56; 95% CI 0.31-0.99).
The landmark analyses between 3 months and 3 years and per-protocol analyses showed consistent results.
The researchers point out that this is the first trial to report on the long-term safety and efficacy of P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy as long-term maintenance therapy for stable patients treated with PCI.
“Especially considering that extended DAPT significantly reduced the risks of ischemic events compared with aspirin monotherapy in a couple of trials, comparison between P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy and prolonged DAPT for recurrent ischemic events over a longer period beyond 1 year is of great importance,” they say.
They cite two other trials – HOST-EXAM and GLOBAL LEADERS – which have shown P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy to be superior to aspirin monotherapy in preventing both ischemic and bleeding events during the long-term maintenance period after PCI.
“Combining the results of the current study, HOST-EXAM trial, and landmark analysis of the GLOBAL LEADERS trial, long-term P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy after a minimum period of DAPT might be the most reliable option from among aspirin monotherapy, P2Y12 monotherapy, and extended DAPT for maintenance therapy after stabilizing patients who have undergone PCI with a current-generation DES,” they conclude.
They note that the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions guidelines for coronary artery revascularization newly recommends a shorter course of DAPT followed by P2Y12 monotherapy as a class IIa indication. The recommendation is based on results of five large, randomized clinical trials, including SMART-CHOICE, TWILIGHT, STOPDAPT-2, TICO, and GLOBAL LEADERS.
“The current results of extended follow-up from the SMART-CHOICE trial support evidence of aspirin-dropping strategy with indefinite use of P2Y12 inhibitor after minimum use of DAPT in patients who underwent PCI,” they say.
They point out that two further trials, A-CLOSE in high-risk patients and SMART-CHOICE III, will be helpful to confirm these findings.
P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy ‘attractive concept’
In an accompanying editor’s note, Ajay Kirtane, MD, Columbia University Irving Medical Center/New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York, note that current guidelines recommend 3-6 months of DAPT following PCI with current-generation drug-eluting stents in stable patients and 6-12 months or longer for those with acute coronary syndromes. For patients at higher risk of bleeding, even shorter DAPT durations can be considered on a case-by-case basis.
Historically, the component of DAPT subject to discontinuation decisions was the P2Y12 inhibitor (clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor), but more recent trials have further explored whether discontinuation of the aspirin component of DAPT can mitigate bleeding while preserving anti-ischemic efficacy.
The editorialists explain that the concept of P2Y1-inhibitor monotherapy is attractive because it may optimize antiplatelet effects through a single agent that can avoid the gastrointestinal toxicity of aspirin as well as the increased bleeding that comes with combing multiple antithrombotic agents.
They suggest that the long-term results from the SMART-CHOICE trial “should lead clinicians to consider a strategy of monotherapy after a short period of DAPT as a viable one to mitigate bleeding risk,” although they also point out that SMART-CHOICE was underpowered to rigorously assess ischemic differences, so caution is warranted.
“For patients at greatest risk for recurrent ischemic events, the role of continued DAPT is always an option, but these data (and other consistent trials) give clinicians more options to pursue individualized treatment decisions,” they write.
“To some, the continually moving field of post-PCI antiplatelet therapy has provided too many choices, which can at times be dizzying. To us, every patient is different, and thoughtful evidence-based consideration is increasingly possible for many of our treatment decisions,” they conclude.
The SMART-CHOICE study was supported by unrestricted grants from the Korean Society of Interventional Cardiology, Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Shortening the duration of dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) and continuing with a P2Y12 inhibitor alone after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was associated with a similar rate of ischemic events but with less bleeding than prolonged DAPT after 3 years of follow-up in the SMART-CHOICE trial.
“The current the investigators, with lead author Ki Hong Choi, MD, division of cardiology, department of medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea, conclude.
The 3-year results from the study were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
The authors explain that although dual therapy with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor after PCI with a drug-eluting stent (DES) is crucial to reduce the risk of ischemic events, it raises concerns about increased risk of bleeding, and the antiplatelet strategy after PCI is currently shifting to reduce the duration of DAPT.
Several recent randomized studies have consistently shown that a short duration of DAPT (1-3 months) followed by P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy had ischemia protection effects comparable with that of DAPT of longer duration, and it was associated with a significantly reduced risk of bleeding events in patients who underwent PCI, they note. However, these studies have so far reported only 1-year outcomes, and long-term results are not yet available.
The SMART-CHOICE trial compared two antiplatelet strategies – 3 months of DAPT followed by long-term P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy (mainly with clopidogrel) or prolonged DAPT for 12 months or longer – in 2,993 patients who had undergone PCI with a drug-eluting stent. Results at 12 months showed a similar rate of ischemic events with both strategies but a lower rate of bleeding in the group that received shortened DAPT.
The SMART-CHOICE investigators now report the 3-year results showing similar outcomes.
At 3 years, the primary endpoint, a composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction, or stroke, had occurred in 6.3% of the shortened DAPT group and 6.1% in the prolonged DAPT group, giving a hazard ratio of 1.06 (95% confidence interval, 0.79-1.44).
But in the shortened DAPT group, the risk of bleeding was reduced. Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) types 2-5 bleeding had occurred in 3.2% of the shortened DAPT group and in 8.2% of the prolonged DAPT group (hazard ratio, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.28-0.55). Major bleeding, BARC types 3-5, occurred in 1.2% of the shortened DAPT group and in 2.4% of the prolonged DAPT group (HR, 0.56; 95% CI 0.31-0.99).
The landmark analyses between 3 months and 3 years and per-protocol analyses showed consistent results.
The researchers point out that this is the first trial to report on the long-term safety and efficacy of P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy as long-term maintenance therapy for stable patients treated with PCI.
“Especially considering that extended DAPT significantly reduced the risks of ischemic events compared with aspirin monotherapy in a couple of trials, comparison between P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy and prolonged DAPT for recurrent ischemic events over a longer period beyond 1 year is of great importance,” they say.
They cite two other trials – HOST-EXAM and GLOBAL LEADERS – which have shown P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy to be superior to aspirin monotherapy in preventing both ischemic and bleeding events during the long-term maintenance period after PCI.
“Combining the results of the current study, HOST-EXAM trial, and landmark analysis of the GLOBAL LEADERS trial, long-term P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy after a minimum period of DAPT might be the most reliable option from among aspirin monotherapy, P2Y12 monotherapy, and extended DAPT for maintenance therapy after stabilizing patients who have undergone PCI with a current-generation DES,” they conclude.
They note that the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions guidelines for coronary artery revascularization newly recommends a shorter course of DAPT followed by P2Y12 monotherapy as a class IIa indication. The recommendation is based on results of five large, randomized clinical trials, including SMART-CHOICE, TWILIGHT, STOPDAPT-2, TICO, and GLOBAL LEADERS.
“The current results of extended follow-up from the SMART-CHOICE trial support evidence of aspirin-dropping strategy with indefinite use of P2Y12 inhibitor after minimum use of DAPT in patients who underwent PCI,” they say.
They point out that two further trials, A-CLOSE in high-risk patients and SMART-CHOICE III, will be helpful to confirm these findings.
P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy ‘attractive concept’
In an accompanying editor’s note, Ajay Kirtane, MD, Columbia University Irving Medical Center/New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York, note that current guidelines recommend 3-6 months of DAPT following PCI with current-generation drug-eluting stents in stable patients and 6-12 months or longer for those with acute coronary syndromes. For patients at higher risk of bleeding, even shorter DAPT durations can be considered on a case-by-case basis.
Historically, the component of DAPT subject to discontinuation decisions was the P2Y12 inhibitor (clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor), but more recent trials have further explored whether discontinuation of the aspirin component of DAPT can mitigate bleeding while preserving anti-ischemic efficacy.
The editorialists explain that the concept of P2Y1-inhibitor monotherapy is attractive because it may optimize antiplatelet effects through a single agent that can avoid the gastrointestinal toxicity of aspirin as well as the increased bleeding that comes with combing multiple antithrombotic agents.
They suggest that the long-term results from the SMART-CHOICE trial “should lead clinicians to consider a strategy of monotherapy after a short period of DAPT as a viable one to mitigate bleeding risk,” although they also point out that SMART-CHOICE was underpowered to rigorously assess ischemic differences, so caution is warranted.
“For patients at greatest risk for recurrent ischemic events, the role of continued DAPT is always an option, but these data (and other consistent trials) give clinicians more options to pursue individualized treatment decisions,” they write.
“To some, the continually moving field of post-PCI antiplatelet therapy has provided too many choices, which can at times be dizzying. To us, every patient is different, and thoughtful evidence-based consideration is increasingly possible for many of our treatment decisions,” they conclude.
The SMART-CHOICE study was supported by unrestricted grants from the Korean Society of Interventional Cardiology, Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Shortening the duration of dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) and continuing with a P2Y12 inhibitor alone after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was associated with a similar rate of ischemic events but with less bleeding than prolonged DAPT after 3 years of follow-up in the SMART-CHOICE trial.
“The current the investigators, with lead author Ki Hong Choi, MD, division of cardiology, department of medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea, conclude.
The 3-year results from the study were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
The authors explain that although dual therapy with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor after PCI with a drug-eluting stent (DES) is crucial to reduce the risk of ischemic events, it raises concerns about increased risk of bleeding, and the antiplatelet strategy after PCI is currently shifting to reduce the duration of DAPT.
Several recent randomized studies have consistently shown that a short duration of DAPT (1-3 months) followed by P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy had ischemia protection effects comparable with that of DAPT of longer duration, and it was associated with a significantly reduced risk of bleeding events in patients who underwent PCI, they note. However, these studies have so far reported only 1-year outcomes, and long-term results are not yet available.
The SMART-CHOICE trial compared two antiplatelet strategies – 3 months of DAPT followed by long-term P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy (mainly with clopidogrel) or prolonged DAPT for 12 months or longer – in 2,993 patients who had undergone PCI with a drug-eluting stent. Results at 12 months showed a similar rate of ischemic events with both strategies but a lower rate of bleeding in the group that received shortened DAPT.
The SMART-CHOICE investigators now report the 3-year results showing similar outcomes.
At 3 years, the primary endpoint, a composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction, or stroke, had occurred in 6.3% of the shortened DAPT group and 6.1% in the prolonged DAPT group, giving a hazard ratio of 1.06 (95% confidence interval, 0.79-1.44).
But in the shortened DAPT group, the risk of bleeding was reduced. Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) types 2-5 bleeding had occurred in 3.2% of the shortened DAPT group and in 8.2% of the prolonged DAPT group (hazard ratio, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.28-0.55). Major bleeding, BARC types 3-5, occurred in 1.2% of the shortened DAPT group and in 2.4% of the prolonged DAPT group (HR, 0.56; 95% CI 0.31-0.99).
The landmark analyses between 3 months and 3 years and per-protocol analyses showed consistent results.
The researchers point out that this is the first trial to report on the long-term safety and efficacy of P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy as long-term maintenance therapy for stable patients treated with PCI.
“Especially considering that extended DAPT significantly reduced the risks of ischemic events compared with aspirin monotherapy in a couple of trials, comparison between P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy and prolonged DAPT for recurrent ischemic events over a longer period beyond 1 year is of great importance,” they say.
They cite two other trials – HOST-EXAM and GLOBAL LEADERS – which have shown P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy to be superior to aspirin monotherapy in preventing both ischemic and bleeding events during the long-term maintenance period after PCI.
“Combining the results of the current study, HOST-EXAM trial, and landmark analysis of the GLOBAL LEADERS trial, long-term P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy after a minimum period of DAPT might be the most reliable option from among aspirin monotherapy, P2Y12 monotherapy, and extended DAPT for maintenance therapy after stabilizing patients who have undergone PCI with a current-generation DES,” they conclude.
They note that the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions guidelines for coronary artery revascularization newly recommends a shorter course of DAPT followed by P2Y12 monotherapy as a class IIa indication. The recommendation is based on results of five large, randomized clinical trials, including SMART-CHOICE, TWILIGHT, STOPDAPT-2, TICO, and GLOBAL LEADERS.
“The current results of extended follow-up from the SMART-CHOICE trial support evidence of aspirin-dropping strategy with indefinite use of P2Y12 inhibitor after minimum use of DAPT in patients who underwent PCI,” they say.
They point out that two further trials, A-CLOSE in high-risk patients and SMART-CHOICE III, will be helpful to confirm these findings.
P2Y12-inhibitor monotherapy ‘attractive concept’
In an accompanying editor’s note, Ajay Kirtane, MD, Columbia University Irving Medical Center/New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York, note that current guidelines recommend 3-6 months of DAPT following PCI with current-generation drug-eluting stents in stable patients and 6-12 months or longer for those with acute coronary syndromes. For patients at higher risk of bleeding, even shorter DAPT durations can be considered on a case-by-case basis.
Historically, the component of DAPT subject to discontinuation decisions was the P2Y12 inhibitor (clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor), but more recent trials have further explored whether discontinuation of the aspirin component of DAPT can mitigate bleeding while preserving anti-ischemic efficacy.
The editorialists explain that the concept of P2Y1-inhibitor monotherapy is attractive because it may optimize antiplatelet effects through a single agent that can avoid the gastrointestinal toxicity of aspirin as well as the increased bleeding that comes with combing multiple antithrombotic agents.
They suggest that the long-term results from the SMART-CHOICE trial “should lead clinicians to consider a strategy of monotherapy after a short period of DAPT as a viable one to mitigate bleeding risk,” although they also point out that SMART-CHOICE was underpowered to rigorously assess ischemic differences, so caution is warranted.
“For patients at greatest risk for recurrent ischemic events, the role of continued DAPT is always an option, but these data (and other consistent trials) give clinicians more options to pursue individualized treatment decisions,” they write.
“To some, the continually moving field of post-PCI antiplatelet therapy has provided too many choices, which can at times be dizzying. To us, every patient is different, and thoughtful evidence-based consideration is increasingly possible for many of our treatment decisions,” they conclude.
The SMART-CHOICE study was supported by unrestricted grants from the Korean Society of Interventional Cardiology, Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
How to improve diagnosis of HFpEF, common in diabetes
STOCKHOLM – Recent study results confirm that two agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class can significantly cut the incidence of adverse cardiovascular events in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFpEF), a disease especially common in people with type 2 diabetes, obesity, or both.
And findings from secondary analyses of the studies – including one reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes – show that these SGLT2 inhibitors work as well for cutting incident adverse events (cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure) in patients with HFpEF and diabetes as they do for people with normal blood glucose levels.
But delivering treatment with these proven agents, dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and empagliflozin (Jardiance), first requires diagnosis of HFpEF, a task that clinicians have historically fallen short in accomplishing.
When in 2021, results from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial with empagliflozin and when in September 2022 results from the DELIVER trial with dapagliflozin established the efficacy of these two SGLT2 inhibitors as the first treatments proven to benefit patients with HFpEF, they also raised the stakes for clinicians to be much more diligent and systematic in evaluating people at high risk for developing HFpEF because of having type 2 diabetes or obesity, two of the most potent risk factors for this form of heart failure.
‘Vigilance ... needs to increase’
“Vigilance for HFpEF needs to increase because we can now help these patients,” declared Lars H. Lund, MD, PhD, speaking at the meeting. “Type 2 diabetes dramatically increases the incidence of HFpEF,” and the mechanisms by which it does this are “especially amenable to treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors,” said Dr. Lund, a cardiologist and heart failure specialist at the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm.
HFpEF has a history of going undetected in people with type 2 diabetes, an ironic situation given its high incidence as well as the elevated rate of adverse cardiovascular events when heart failure occurs in patients with type 2 diabetes compared with patients who do not have diabetes.
The key, say experts, is for clinicians to maintain a high index of suspicion for signs and symptoms of heart failure in people with type 2 diabetes and to regularly assess them, starting with just a few simple questions that probe for the presence of dyspnea, exertional fatigue, or both, an approach not widely employed up to now.
Clinicians who care for people with type 2 diabetes must become “alert to thinking about heart failure and alert to asking questions about signs and symptoms” that flag the presence of HFpEF, advised Naveed Sattar, MBChB, PhD, a professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow.
Soon, medical groups will issue guidelines for appropriate assessment for the presence of HFpEF in people with type 2 diabetes, Dr. Sattar predicted in an interview.
A need to probe
“You can’t simply ask patients with type 2 diabetes whether they have shortness of breath or exertional fatigue and stop there,” because often their first response will be no.
“Commonly, patients will initially say they have no dyspnea, but when you probe further, you find symptoms,” noted Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, codirector of Saint Luke’s Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence in Kansas City, Mo.
These people are often sedentary, so they frequently don’t experience shortness of breath at baseline, Dr. Kosiborod said in an interview. In some cases, they may limit their activity because of their exertional intolerance.
Once a person’s suggestive symptoms become known, the next step is to measure the serum level of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), a biomarker considered to be a generally reliable signal of existing heart failure when elevated.
Any value above 125 pg/mL is suggestive of prevalent heart failure and should lead to the next diagnostic step of echocardiography, Dr. Sattar said.
Elevated NT-proBNP has such good positive predictive value for identifying heart failure that it is tempting to use it broadly in people with type 2 diabetes. A 2022 consensus report from the American Diabetes Association says that “measurement of a natriuretic peptide [such as NT-proBNP] or high-sensitivity cardiac troponin is recommended on at least a yearly basis to identify the earliest HF [heart failure] stages and implement strategies to prevent transition to symptomatic HF.”
Test costs require targeting
But because of the relatively high current price for an NT-proBNP test, the cost-benefit ratio for widespread annual testing of all people with type 2 diabetes would be poor, some experts caution.
“Screening everyone may not be the right answer. Hundreds of millions of people worldwide” have type 2 diabetes. “You first need to target evaluation to people with symptoms,” advised Dr. Kosiborod.
He also warned that a low NT-proBNP level does not always rule out HFpEF, especially among people with type 2 diabetes who also have overweight or obesity, because NT-proBNP levels can be “artificially low” in people with obesity.
Other potential aids to diagnosis are assessment scores that researchers have developed, such as the H2FPEF score, which relies on variables that include age, obesity, and the presence of atrial fibrillation and hypertension.
However, this score also requires an echocardiography examination, another test that would have a questionable cost-benefit ratio if performed widely for patients with type 2 diabetes without targeting, Dr. Kosiborod said.
SGLT2 inhibitors benefit HFpEF regardless of glucose levels
A prespecified analysis of the DELIVER results that divided the study cohort on the basis of their glycemic status proved the efficacy of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin for patients with HFpEF regardless of whether or not they had type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, or were normoglycemic at entry into the study, Silvio E. Inzucchi, MD, reported at the EASD meeting.
Treatment with dapagliflozin cut the incidence of the trial’s primary outcome of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure by a significant 18% relative to placebo among all enrolled patients.
The new analysis reported by Dr. Inzucchi showed that treatment was associated with a 23% relative risk reduction among those with normoglycemia, a 13% reduction among those with prediabetes, and a 19% reduction among those with type 2 diabetes, with no signal of a significant difference among the three subgroups.
“There was no statistical interaction between categorical glycemic subgrouping and dapagliflozin’s treatment effect,” concluded Dr. Inzucchi, director of the Yale Medicine Diabetes Center, New Haven, Conn.
He also reported that, among the 6,259 people in the trial with HFpEF, 50% had diabetes, 31% had prediabetes, and a scant 19% had normoglycemia. The finding highlights once again the high prevalence of dysglycemia among people with HFpEF.
Previously, a prespecified secondary analysis of data from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial yielded similar findings for empagliflozin that showed the agent’s efficacy for people with HFpEF across the range of glucose levels.
The DELIVER trial was funded by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). The EMPEROR-Preserved trial was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, the companies that jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Lund has been a consultant to AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim and to numerous other companies, and he is a stockholder in AnaCardio. Dr. Sattar has been a consultant to and has received research support from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim, and he has been a consultant with numerous companies. Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant to and has received research funding from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim and has been a consultant to Eli Lilly and numerous other companies. Dr. Inzucchi has been a consultant to, given talks on behalf of, or served on trial committees for Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Esperion, Lexicon, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and vTv Therapetics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Recent study results confirm that two agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class can significantly cut the incidence of adverse cardiovascular events in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFpEF), a disease especially common in people with type 2 diabetes, obesity, or both.
And findings from secondary analyses of the studies – including one reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes – show that these SGLT2 inhibitors work as well for cutting incident adverse events (cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure) in patients with HFpEF and diabetes as they do for people with normal blood glucose levels.
But delivering treatment with these proven agents, dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and empagliflozin (Jardiance), first requires diagnosis of HFpEF, a task that clinicians have historically fallen short in accomplishing.
When in 2021, results from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial with empagliflozin and when in September 2022 results from the DELIVER trial with dapagliflozin established the efficacy of these two SGLT2 inhibitors as the first treatments proven to benefit patients with HFpEF, they also raised the stakes for clinicians to be much more diligent and systematic in evaluating people at high risk for developing HFpEF because of having type 2 diabetes or obesity, two of the most potent risk factors for this form of heart failure.
‘Vigilance ... needs to increase’
“Vigilance for HFpEF needs to increase because we can now help these patients,” declared Lars H. Lund, MD, PhD, speaking at the meeting. “Type 2 diabetes dramatically increases the incidence of HFpEF,” and the mechanisms by which it does this are “especially amenable to treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors,” said Dr. Lund, a cardiologist and heart failure specialist at the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm.
HFpEF has a history of going undetected in people with type 2 diabetes, an ironic situation given its high incidence as well as the elevated rate of adverse cardiovascular events when heart failure occurs in patients with type 2 diabetes compared with patients who do not have diabetes.
The key, say experts, is for clinicians to maintain a high index of suspicion for signs and symptoms of heart failure in people with type 2 diabetes and to regularly assess them, starting with just a few simple questions that probe for the presence of dyspnea, exertional fatigue, or both, an approach not widely employed up to now.
Clinicians who care for people with type 2 diabetes must become “alert to thinking about heart failure and alert to asking questions about signs and symptoms” that flag the presence of HFpEF, advised Naveed Sattar, MBChB, PhD, a professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow.
Soon, medical groups will issue guidelines for appropriate assessment for the presence of HFpEF in people with type 2 diabetes, Dr. Sattar predicted in an interview.
A need to probe
“You can’t simply ask patients with type 2 diabetes whether they have shortness of breath or exertional fatigue and stop there,” because often their first response will be no.
“Commonly, patients will initially say they have no dyspnea, but when you probe further, you find symptoms,” noted Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, codirector of Saint Luke’s Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence in Kansas City, Mo.
These people are often sedentary, so they frequently don’t experience shortness of breath at baseline, Dr. Kosiborod said in an interview. In some cases, they may limit their activity because of their exertional intolerance.
Once a person’s suggestive symptoms become known, the next step is to measure the serum level of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), a biomarker considered to be a generally reliable signal of existing heart failure when elevated.
Any value above 125 pg/mL is suggestive of prevalent heart failure and should lead to the next diagnostic step of echocardiography, Dr. Sattar said.
Elevated NT-proBNP has such good positive predictive value for identifying heart failure that it is tempting to use it broadly in people with type 2 diabetes. A 2022 consensus report from the American Diabetes Association says that “measurement of a natriuretic peptide [such as NT-proBNP] or high-sensitivity cardiac troponin is recommended on at least a yearly basis to identify the earliest HF [heart failure] stages and implement strategies to prevent transition to symptomatic HF.”
Test costs require targeting
But because of the relatively high current price for an NT-proBNP test, the cost-benefit ratio for widespread annual testing of all people with type 2 diabetes would be poor, some experts caution.
“Screening everyone may not be the right answer. Hundreds of millions of people worldwide” have type 2 diabetes. “You first need to target evaluation to people with symptoms,” advised Dr. Kosiborod.
He also warned that a low NT-proBNP level does not always rule out HFpEF, especially among people with type 2 diabetes who also have overweight or obesity, because NT-proBNP levels can be “artificially low” in people with obesity.
Other potential aids to diagnosis are assessment scores that researchers have developed, such as the H2FPEF score, which relies on variables that include age, obesity, and the presence of atrial fibrillation and hypertension.
However, this score also requires an echocardiography examination, another test that would have a questionable cost-benefit ratio if performed widely for patients with type 2 diabetes without targeting, Dr. Kosiborod said.
SGLT2 inhibitors benefit HFpEF regardless of glucose levels
A prespecified analysis of the DELIVER results that divided the study cohort on the basis of their glycemic status proved the efficacy of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin for patients with HFpEF regardless of whether or not they had type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, or were normoglycemic at entry into the study, Silvio E. Inzucchi, MD, reported at the EASD meeting.
Treatment with dapagliflozin cut the incidence of the trial’s primary outcome of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure by a significant 18% relative to placebo among all enrolled patients.
The new analysis reported by Dr. Inzucchi showed that treatment was associated with a 23% relative risk reduction among those with normoglycemia, a 13% reduction among those with prediabetes, and a 19% reduction among those with type 2 diabetes, with no signal of a significant difference among the three subgroups.
“There was no statistical interaction between categorical glycemic subgrouping and dapagliflozin’s treatment effect,” concluded Dr. Inzucchi, director of the Yale Medicine Diabetes Center, New Haven, Conn.
He also reported that, among the 6,259 people in the trial with HFpEF, 50% had diabetes, 31% had prediabetes, and a scant 19% had normoglycemia. The finding highlights once again the high prevalence of dysglycemia among people with HFpEF.
Previously, a prespecified secondary analysis of data from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial yielded similar findings for empagliflozin that showed the agent’s efficacy for people with HFpEF across the range of glucose levels.
The DELIVER trial was funded by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). The EMPEROR-Preserved trial was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, the companies that jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Lund has been a consultant to AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim and to numerous other companies, and he is a stockholder in AnaCardio. Dr. Sattar has been a consultant to and has received research support from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim, and he has been a consultant with numerous companies. Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant to and has received research funding from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim and has been a consultant to Eli Lilly and numerous other companies. Dr. Inzucchi has been a consultant to, given talks on behalf of, or served on trial committees for Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Esperion, Lexicon, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and vTv Therapetics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Recent study results confirm that two agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class can significantly cut the incidence of adverse cardiovascular events in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFpEF), a disease especially common in people with type 2 diabetes, obesity, or both.
And findings from secondary analyses of the studies – including one reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes – show that these SGLT2 inhibitors work as well for cutting incident adverse events (cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure) in patients with HFpEF and diabetes as they do for people with normal blood glucose levels.
But delivering treatment with these proven agents, dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and empagliflozin (Jardiance), first requires diagnosis of HFpEF, a task that clinicians have historically fallen short in accomplishing.
When in 2021, results from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial with empagliflozin and when in September 2022 results from the DELIVER trial with dapagliflozin established the efficacy of these two SGLT2 inhibitors as the first treatments proven to benefit patients with HFpEF, they also raised the stakes for clinicians to be much more diligent and systematic in evaluating people at high risk for developing HFpEF because of having type 2 diabetes or obesity, two of the most potent risk factors for this form of heart failure.
‘Vigilance ... needs to increase’
“Vigilance for HFpEF needs to increase because we can now help these patients,” declared Lars H. Lund, MD, PhD, speaking at the meeting. “Type 2 diabetes dramatically increases the incidence of HFpEF,” and the mechanisms by which it does this are “especially amenable to treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors,” said Dr. Lund, a cardiologist and heart failure specialist at the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm.
HFpEF has a history of going undetected in people with type 2 diabetes, an ironic situation given its high incidence as well as the elevated rate of adverse cardiovascular events when heart failure occurs in patients with type 2 diabetes compared with patients who do not have diabetes.
The key, say experts, is for clinicians to maintain a high index of suspicion for signs and symptoms of heart failure in people with type 2 diabetes and to regularly assess them, starting with just a few simple questions that probe for the presence of dyspnea, exertional fatigue, or both, an approach not widely employed up to now.
Clinicians who care for people with type 2 diabetes must become “alert to thinking about heart failure and alert to asking questions about signs and symptoms” that flag the presence of HFpEF, advised Naveed Sattar, MBChB, PhD, a professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow.
Soon, medical groups will issue guidelines for appropriate assessment for the presence of HFpEF in people with type 2 diabetes, Dr. Sattar predicted in an interview.
A need to probe
“You can’t simply ask patients with type 2 diabetes whether they have shortness of breath or exertional fatigue and stop there,” because often their first response will be no.
“Commonly, patients will initially say they have no dyspnea, but when you probe further, you find symptoms,” noted Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, codirector of Saint Luke’s Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence in Kansas City, Mo.
These people are often sedentary, so they frequently don’t experience shortness of breath at baseline, Dr. Kosiborod said in an interview. In some cases, they may limit their activity because of their exertional intolerance.
Once a person’s suggestive symptoms become known, the next step is to measure the serum level of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), a biomarker considered to be a generally reliable signal of existing heart failure when elevated.
Any value above 125 pg/mL is suggestive of prevalent heart failure and should lead to the next diagnostic step of echocardiography, Dr. Sattar said.
Elevated NT-proBNP has such good positive predictive value for identifying heart failure that it is tempting to use it broadly in people with type 2 diabetes. A 2022 consensus report from the American Diabetes Association says that “measurement of a natriuretic peptide [such as NT-proBNP] or high-sensitivity cardiac troponin is recommended on at least a yearly basis to identify the earliest HF [heart failure] stages and implement strategies to prevent transition to symptomatic HF.”
Test costs require targeting
But because of the relatively high current price for an NT-proBNP test, the cost-benefit ratio for widespread annual testing of all people with type 2 diabetes would be poor, some experts caution.
“Screening everyone may not be the right answer. Hundreds of millions of people worldwide” have type 2 diabetes. “You first need to target evaluation to people with symptoms,” advised Dr. Kosiborod.
He also warned that a low NT-proBNP level does not always rule out HFpEF, especially among people with type 2 diabetes who also have overweight or obesity, because NT-proBNP levels can be “artificially low” in people with obesity.
Other potential aids to diagnosis are assessment scores that researchers have developed, such as the H2FPEF score, which relies on variables that include age, obesity, and the presence of atrial fibrillation and hypertension.
However, this score also requires an echocardiography examination, another test that would have a questionable cost-benefit ratio if performed widely for patients with type 2 diabetes without targeting, Dr. Kosiborod said.
SGLT2 inhibitors benefit HFpEF regardless of glucose levels
A prespecified analysis of the DELIVER results that divided the study cohort on the basis of their glycemic status proved the efficacy of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin for patients with HFpEF regardless of whether or not they had type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, or were normoglycemic at entry into the study, Silvio E. Inzucchi, MD, reported at the EASD meeting.
Treatment with dapagliflozin cut the incidence of the trial’s primary outcome of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure by a significant 18% relative to placebo among all enrolled patients.
The new analysis reported by Dr. Inzucchi showed that treatment was associated with a 23% relative risk reduction among those with normoglycemia, a 13% reduction among those with prediabetes, and a 19% reduction among those with type 2 diabetes, with no signal of a significant difference among the three subgroups.
“There was no statistical interaction between categorical glycemic subgrouping and dapagliflozin’s treatment effect,” concluded Dr. Inzucchi, director of the Yale Medicine Diabetes Center, New Haven, Conn.
He also reported that, among the 6,259 people in the trial with HFpEF, 50% had diabetes, 31% had prediabetes, and a scant 19% had normoglycemia. The finding highlights once again the high prevalence of dysglycemia among people with HFpEF.
Previously, a prespecified secondary analysis of data from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial yielded similar findings for empagliflozin that showed the agent’s efficacy for people with HFpEF across the range of glucose levels.
The DELIVER trial was funded by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). The EMPEROR-Preserved trial was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, the companies that jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Lund has been a consultant to AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim and to numerous other companies, and he is a stockholder in AnaCardio. Dr. Sattar has been a consultant to and has received research support from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim, and he has been a consultant with numerous companies. Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant to and has received research funding from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim and has been a consultant to Eli Lilly and numerous other companies. Dr. Inzucchi has been a consultant to, given talks on behalf of, or served on trial committees for Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Esperion, Lexicon, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and vTv Therapetics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EASD 2022
The winding road that leads to optimal temperature management after cardiac arrest
In 2002, two landmark trials found that targeted temperature management (TTM) after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest led to improvements in neurologic outcomes. The larger of the two trials found a reduction in mortality. Such treatment benefits are hard to come by in critical care in general and in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in particular. With the therapeutic overconfidence typical of our profession, my institution embraced TTM quickly and completely soon after these trials were published. Remember, this was “back in the day” when sepsis management included drotrecogin alfa, Cortrosyn stim tests, tight glucose control (90-120 mg/dL), and horrible over-resuscitation via the early goal-directed therapy paradigm.
If you’ve been practicing critical care medicine for more than a few years, you already know where I’m going. Most of the interventions in the preceding paragraph were adopted but discarded before 2010. Hypothermia – temperature management with a goal of 32-36° C – has been struggling to stay relevant ever since the publication of the TTM randomized controlled trial (RCT) in 2013. Then came the HYPERION trial, which brought the 32-36° C target back from the dead (pun definitely intended) in 2019. This is critical care medicine: Today’s life-saving intervention proves harmful tomorrow, but withholding it may constitute malpractice a few months down the road.
So where are we now? Good question. I’ve had seasoned neurointensivists insist that 33° C remains the standard of care and others who’ve endorsed normothermia. So much for finding an answer via my more specialized colleagues.
Let’s go to the guidelines then. Prompted largely by HYPERION, a temperature target of 32-36° C was endorsed in 2020 and 2021. Then came publication of the TTM2 trial, the largest temperature management RCT to date, which found no benefit to targeting 33° C. A network meta-analysis published in 2021 reached a similar conclusion. A recently released update by the same international guideline group now recommends targeting normothermia (< 37.7° C) and avoiding fever, and it specifically says that there is insufficient evidence to support a 32-36° C target. Okay, everyone tracking all that?
Lest I sound overly catty and nihilistic, I see all this in a positive light. Huge credit goes to the critical care medicine academic community for putting together so many RCTs. The scientific reality is that it takes “a lotta” sample size to clarify the effects of an intervention. Throw in the inevitable bevy of confounders (in- vs. out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, resuscitation time, initial rhythm, and so on), and you get a feel for the work required to understand a treatment’s true effects.
Advances in guideline science and the hard, often unpaid work of panels are also important. The guideline panel I’ve been citing came out for aggressive temperature control (32-36° C) a few months before the TTM2 RCT was published. In the past, they updated their recommendations every 5 years, but this time, they were out with a new manuscript that incorporated TTM2 in less than a year. If you’ve been involved at any level with producing guidelines, you can appreciate this achievement. Assuming that aggressive hypothermia is truly harmful, waiting 5 years to incorporate TTM2 could have led to significant morbidity.
I do take issue with you early adopters, though. Given the litany of failed therapies that have shown initial promise, and the well-documented human tendency to underestimate the impact of sample size, your rapid implementation of major interventions is puzzling. One might think you’d learned your lessons after seeing drotrecogin alfa, Cortrosyn stim tests, tight glucose control, early goal-directed therapy, and aggressive TTM come and go. Your recent enthusiasm for vitamin C after publication of a single before-after study suggests that you haven’t.
Aaron B. Holley, MD, is an associate professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University and program director of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Md. He has received a research grant from Fisher-Paykel.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2002, two landmark trials found that targeted temperature management (TTM) after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest led to improvements in neurologic outcomes. The larger of the two trials found a reduction in mortality. Such treatment benefits are hard to come by in critical care in general and in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in particular. With the therapeutic overconfidence typical of our profession, my institution embraced TTM quickly and completely soon after these trials were published. Remember, this was “back in the day” when sepsis management included drotrecogin alfa, Cortrosyn stim tests, tight glucose control (90-120 mg/dL), and horrible over-resuscitation via the early goal-directed therapy paradigm.
If you’ve been practicing critical care medicine for more than a few years, you already know where I’m going. Most of the interventions in the preceding paragraph were adopted but discarded before 2010. Hypothermia – temperature management with a goal of 32-36° C – has been struggling to stay relevant ever since the publication of the TTM randomized controlled trial (RCT) in 2013. Then came the HYPERION trial, which brought the 32-36° C target back from the dead (pun definitely intended) in 2019. This is critical care medicine: Today’s life-saving intervention proves harmful tomorrow, but withholding it may constitute malpractice a few months down the road.
So where are we now? Good question. I’ve had seasoned neurointensivists insist that 33° C remains the standard of care and others who’ve endorsed normothermia. So much for finding an answer via my more specialized colleagues.
Let’s go to the guidelines then. Prompted largely by HYPERION, a temperature target of 32-36° C was endorsed in 2020 and 2021. Then came publication of the TTM2 trial, the largest temperature management RCT to date, which found no benefit to targeting 33° C. A network meta-analysis published in 2021 reached a similar conclusion. A recently released update by the same international guideline group now recommends targeting normothermia (< 37.7° C) and avoiding fever, and it specifically says that there is insufficient evidence to support a 32-36° C target. Okay, everyone tracking all that?
Lest I sound overly catty and nihilistic, I see all this in a positive light. Huge credit goes to the critical care medicine academic community for putting together so many RCTs. The scientific reality is that it takes “a lotta” sample size to clarify the effects of an intervention. Throw in the inevitable bevy of confounders (in- vs. out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, resuscitation time, initial rhythm, and so on), and you get a feel for the work required to understand a treatment’s true effects.
Advances in guideline science and the hard, often unpaid work of panels are also important. The guideline panel I’ve been citing came out for aggressive temperature control (32-36° C) a few months before the TTM2 RCT was published. In the past, they updated their recommendations every 5 years, but this time, they were out with a new manuscript that incorporated TTM2 in less than a year. If you’ve been involved at any level with producing guidelines, you can appreciate this achievement. Assuming that aggressive hypothermia is truly harmful, waiting 5 years to incorporate TTM2 could have led to significant morbidity.
I do take issue with you early adopters, though. Given the litany of failed therapies that have shown initial promise, and the well-documented human tendency to underestimate the impact of sample size, your rapid implementation of major interventions is puzzling. One might think you’d learned your lessons after seeing drotrecogin alfa, Cortrosyn stim tests, tight glucose control, early goal-directed therapy, and aggressive TTM come and go. Your recent enthusiasm for vitamin C after publication of a single before-after study suggests that you haven’t.
Aaron B. Holley, MD, is an associate professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University and program director of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Md. He has received a research grant from Fisher-Paykel.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2002, two landmark trials found that targeted temperature management (TTM) after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest led to improvements in neurologic outcomes. The larger of the two trials found a reduction in mortality. Such treatment benefits are hard to come by in critical care in general and in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in particular. With the therapeutic overconfidence typical of our profession, my institution embraced TTM quickly and completely soon after these trials were published. Remember, this was “back in the day” when sepsis management included drotrecogin alfa, Cortrosyn stim tests, tight glucose control (90-120 mg/dL), and horrible over-resuscitation via the early goal-directed therapy paradigm.
If you’ve been practicing critical care medicine for more than a few years, you already know where I’m going. Most of the interventions in the preceding paragraph were adopted but discarded before 2010. Hypothermia – temperature management with a goal of 32-36° C – has been struggling to stay relevant ever since the publication of the TTM randomized controlled trial (RCT) in 2013. Then came the HYPERION trial, which brought the 32-36° C target back from the dead (pun definitely intended) in 2019. This is critical care medicine: Today’s life-saving intervention proves harmful tomorrow, but withholding it may constitute malpractice a few months down the road.
So where are we now? Good question. I’ve had seasoned neurointensivists insist that 33° C remains the standard of care and others who’ve endorsed normothermia. So much for finding an answer via my more specialized colleagues.
Let’s go to the guidelines then. Prompted largely by HYPERION, a temperature target of 32-36° C was endorsed in 2020 and 2021. Then came publication of the TTM2 trial, the largest temperature management RCT to date, which found no benefit to targeting 33° C. A network meta-analysis published in 2021 reached a similar conclusion. A recently released update by the same international guideline group now recommends targeting normothermia (< 37.7° C) and avoiding fever, and it specifically says that there is insufficient evidence to support a 32-36° C target. Okay, everyone tracking all that?
Lest I sound overly catty and nihilistic, I see all this in a positive light. Huge credit goes to the critical care medicine academic community for putting together so many RCTs. The scientific reality is that it takes “a lotta” sample size to clarify the effects of an intervention. Throw in the inevitable bevy of confounders (in- vs. out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, resuscitation time, initial rhythm, and so on), and you get a feel for the work required to understand a treatment’s true effects.
Advances in guideline science and the hard, often unpaid work of panels are also important. The guideline panel I’ve been citing came out for aggressive temperature control (32-36° C) a few months before the TTM2 RCT was published. In the past, they updated their recommendations every 5 years, but this time, they were out with a new manuscript that incorporated TTM2 in less than a year. If you’ve been involved at any level with producing guidelines, you can appreciate this achievement. Assuming that aggressive hypothermia is truly harmful, waiting 5 years to incorporate TTM2 could have led to significant morbidity.
I do take issue with you early adopters, though. Given the litany of failed therapies that have shown initial promise, and the well-documented human tendency to underestimate the impact of sample size, your rapid implementation of major interventions is puzzling. One might think you’d learned your lessons after seeing drotrecogin alfa, Cortrosyn stim tests, tight glucose control, early goal-directed therapy, and aggressive TTM come and go. Your recent enthusiasm for vitamin C after publication of a single before-after study suggests that you haven’t.
Aaron B. Holley, MD, is an associate professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University and program director of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Md. He has received a research grant from Fisher-Paykel.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Aspirin primary prevention benefit in those with raised Lp(a)?
Aspirin may be of specific benefit for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in individuals with raised Lp(a) levels, a new study has suggested.
The study analyzed data from the ASPREE (ASPirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly) trial, which randomized 19,000 individuals aged 70 years or older without a history of cardiovascular disease to aspirin (100 mg/day) or placebo. While the main results, reported previously, showed no net benefit of aspirin in the overall population, the current analysis suggests there may be a benefit in individuals with raised Lp(a) levels.
The current analysis was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Our study provides evidence that aspirin may specifically benefit older individuals with genotypes for elevated plasma Lp(a) in the setting of high-risk primary prevention of cardiovascular events and that overall benefit may outweigh harm related to major bleeding,” the authors, led by Paul Lacaze, PhD, Monash University, Melbourne, conclude.
They also point out that similar observations have been previously seen in another large aspirin primary prevention study conducted in younger women, the Women’s Health Study, and the current analysis provides validation of those findings.
“Our results provide new evidence to support the potential use of aspirin to target individuals with elevated Lp(a) for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events,” the researchers say.
They acknowledge that these results would be strengthened by the use of directly measured plasma Lp(a) levels, in addition to Lp(a) genotypes.
But they add: “Nonetheless, given the lack of any currently approved therapies for targeting elevated Lp(a), our findings may have widespread clinical implications, adding evidence to the rationale that aspirin may be a viable option for reducing Lp(a)-mediated cardiovascular risk.”
Dr. Lacaze and colleagues explain that elevated plasma Lp(a) levels confer up to fourfold increased risk of cardiovascular disease, with around 20%-30% of the general population affected. Despite the high burden and prevalence of elevated plasma Lp(a), there are currently no approved pharmacologic therapies targeting this lipoprotein. Although promising candidates are in development for the secondary prevention of Lp(a)-mediated cardiovascular disease, it will be many years before these candidates are assessed for primary prevention.
For the current study, researchers analyzed data from 12,815 ASPREE participants who had undergone genotyping and compared outcomes with aspirin versus placebo in those with and without genotypes associated with elevated Lp(a) levels.
Results showed that individuals with elevated Lp(a)-associated genotypes, defined in two different ways, showed a reduction in ischemic events with aspirin versus placebo, and this benefit was not outweighed by an increased bleeding risk.
Specifically, in the placebo group, individuals who carried the rs3798220-C allele, which is known to be associated with raised Lp(a) levels, making up 3.2% of the genotyped population in the study, had an almost twofold increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events than those not carrying this genotype. However, the risk was attenuated in the aspirin group, with carriers of the rs3798220-C allele actually having a lower rate of cardiovascular events than noncarriers.
In addition, rs3798220-C carrier status was not significantly associated with increased risk of clinically significant bleeding events in the aspirin group.
Similar results were seen with the second way of identifying patients with a high risk of elevated Lp(a) levels using a 43-variant genetic risk score (LPA-GRS).
In the whole study population, aspirin reduced major adverse cardiovascular events by 1.7 events per 1,000 person-years and increased clinically significant bleeding events by 1.7 events per 1,000 person-years, suggesting parity between overall benefit versus harm.
However, in the rs3798220-C subgroup, aspirin reduced major adverse cardiovascular events by 11.4 events per 1,000 person-years (a more than sixfold higher magnitude of cardiovascular disease risk reduction than in the overall cohort), with a bleeding risk of 3.3 events per 1,000 person-years, the researchers report.
“Hence in rs3798220-C carriers, aspirin appeared to have a net benefit of 8.1 events per 1,000 person-years,” they state.
In the highest LPA-GRS quintile, aspirin reduced major adverse cardiovascular events by 3.3 events per 1,000 person-years (approximately twofold higher magnitude of risk reduction, compared with the overall cohort), with an increase in bleeding risk of 1.6 events per 1,000 person-years (almost identical bleeding risk to the overall cohort). This shifted the benefit versus harm balance in the highest LPA-GRS quintile to a net benefit of 1.7 events per 1,000 person-years.
Similar findings in the Women’s Health Study
Dr. Lacaze and colleagues point out that similar results have also been seen in another large aspirin primary prevention study – the Women’s Health Study (WHS).
The WHS compared aspirin 100 mg every other day with placebo in initially healthy younger women. Previously reported results showed that women carrying the rs3798220-C variant, associated with highly elevated Lp(a) levels, had a twofold higher risk of cardiovascular events than noncarrier women in the placebo group, but this risk was reduced in the aspirin group. And there was no increased risk of bleeding in women with elevated Lp(a).
“These results, in the absence of any other randomized controlled trial evidence or approved therapy for treating Lp(a)-associated risk, have been used by some physicians as justification for prescribing aspirin in patients with elevated Lp(a),” Dr. Lacaze and colleagues note.
“In the present study of the ASPREE trial population, our results were consistent with the WHS analysis, despite randomizing older individuals (both men and women),” they add.
They say this validation of the WHS result provides evidence that a very high-risk subgroup of individuals with highly elevated Lp(a) – those carrying the rs3798220-C allele – may benefit from low-dose aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events. Further, the benefits in this subgroup specifically may outweigh any bleeding risk.
But they point out that rs3798220-C carriers comprise only a small portion of all individuals with elevated Lp(a) in the general population, while the polygenic LPA-GRS explains about 60% of the variation in directly measured plasma Lp(a) levels and has the potential advantage of being able to identify a larger group of individuals at increased risk.
The researchers note, however, that it is not clear to what extent the LPA-GRS results add further evidence to suggest that individuals with elevated Lp(a), beyond rs3798220-C carriers, may be more likely to benefit from aspirin.
“If the benefit of aspirin extends beyond very high-risk rs3798220-C carriers alone, to the broader 20%-30% of individuals with elevated Lp(a), the potential utility of aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events would increase substantially,” they say.
‘Very high clinical relevance’
In an accompanying editorial, Ana Devesa, MD, Borja Ibanez, MD, PhD, and Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, The National Center for Cardiovascular Research, Madrid, say that: “[Dr.] Lacaze et al. are to be congratulated for a study of very high clinical relevance that represents a first indication for primary prevention for patients at high cardiovascular risk.”
They explain that the pathogenic mechanism of Lp(a) is believed to be a combination of prothrombotic and proatherogenic effects, and the current findings support the hypothesis that the prothrombotic mechanism of Lp(a) is mediated by platelet aggregation.
This would explain the occurrence of thrombotic events in the presence of atherosclerosis in that elevated Lp(a) levels may induce platelet adhesion and aggregation to the activated atherosclerotic plaque, thus enhancing the atherothrombotic process. Moreover, activated platelets release several mediators that result in cell adhesion and attraction of chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines, driving an inflammatory response and mediating atherosclerosis progression, they add.
The editorialists highlight the limitations of the study already acknowledged by the authors: The analysis used genotypes rather than elevated Lp(a) levels and included only those of European ancestry, meaning the results are difficult to extrapolate to other populations.
“The next steps in clinical practice should be defined, and there are still questions to be answered,” they conclude. “Will every patient benefit from antithrombotic therapies? Should all patients who have elevated Lp(a) levels be treated with aspirin?”
The ASPREE Biobank is supported by grants from the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Monash University, Menzies Research Institute, Australian National University, University of Melbourne, National Institutes of Health, National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, and the Victorian Cancer Agency. Dr. Lacaze is supported by a National Heart Foundation Future Leader Fellowship.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Aspirin may be of specific benefit for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in individuals with raised Lp(a) levels, a new study has suggested.
The study analyzed data from the ASPREE (ASPirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly) trial, which randomized 19,000 individuals aged 70 years or older without a history of cardiovascular disease to aspirin (100 mg/day) or placebo. While the main results, reported previously, showed no net benefit of aspirin in the overall population, the current analysis suggests there may be a benefit in individuals with raised Lp(a) levels.
The current analysis was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Our study provides evidence that aspirin may specifically benefit older individuals with genotypes for elevated plasma Lp(a) in the setting of high-risk primary prevention of cardiovascular events and that overall benefit may outweigh harm related to major bleeding,” the authors, led by Paul Lacaze, PhD, Monash University, Melbourne, conclude.
They also point out that similar observations have been previously seen in another large aspirin primary prevention study conducted in younger women, the Women’s Health Study, and the current analysis provides validation of those findings.
“Our results provide new evidence to support the potential use of aspirin to target individuals with elevated Lp(a) for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events,” the researchers say.
They acknowledge that these results would be strengthened by the use of directly measured plasma Lp(a) levels, in addition to Lp(a) genotypes.
But they add: “Nonetheless, given the lack of any currently approved therapies for targeting elevated Lp(a), our findings may have widespread clinical implications, adding evidence to the rationale that aspirin may be a viable option for reducing Lp(a)-mediated cardiovascular risk.”
Dr. Lacaze and colleagues explain that elevated plasma Lp(a) levels confer up to fourfold increased risk of cardiovascular disease, with around 20%-30% of the general population affected. Despite the high burden and prevalence of elevated plasma Lp(a), there are currently no approved pharmacologic therapies targeting this lipoprotein. Although promising candidates are in development for the secondary prevention of Lp(a)-mediated cardiovascular disease, it will be many years before these candidates are assessed for primary prevention.
For the current study, researchers analyzed data from 12,815 ASPREE participants who had undergone genotyping and compared outcomes with aspirin versus placebo in those with and without genotypes associated with elevated Lp(a) levels.
Results showed that individuals with elevated Lp(a)-associated genotypes, defined in two different ways, showed a reduction in ischemic events with aspirin versus placebo, and this benefit was not outweighed by an increased bleeding risk.
Specifically, in the placebo group, individuals who carried the rs3798220-C allele, which is known to be associated with raised Lp(a) levels, making up 3.2% of the genotyped population in the study, had an almost twofold increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events than those not carrying this genotype. However, the risk was attenuated in the aspirin group, with carriers of the rs3798220-C allele actually having a lower rate of cardiovascular events than noncarriers.
In addition, rs3798220-C carrier status was not significantly associated with increased risk of clinically significant bleeding events in the aspirin group.
Similar results were seen with the second way of identifying patients with a high risk of elevated Lp(a) levels using a 43-variant genetic risk score (LPA-GRS).
In the whole study population, aspirin reduced major adverse cardiovascular events by 1.7 events per 1,000 person-years and increased clinically significant bleeding events by 1.7 events per 1,000 person-years, suggesting parity between overall benefit versus harm.
However, in the rs3798220-C subgroup, aspirin reduced major adverse cardiovascular events by 11.4 events per 1,000 person-years (a more than sixfold higher magnitude of cardiovascular disease risk reduction than in the overall cohort), with a bleeding risk of 3.3 events per 1,000 person-years, the researchers report.
“Hence in rs3798220-C carriers, aspirin appeared to have a net benefit of 8.1 events per 1,000 person-years,” they state.
In the highest LPA-GRS quintile, aspirin reduced major adverse cardiovascular events by 3.3 events per 1,000 person-years (approximately twofold higher magnitude of risk reduction, compared with the overall cohort), with an increase in bleeding risk of 1.6 events per 1,000 person-years (almost identical bleeding risk to the overall cohort). This shifted the benefit versus harm balance in the highest LPA-GRS quintile to a net benefit of 1.7 events per 1,000 person-years.
Similar findings in the Women’s Health Study
Dr. Lacaze and colleagues point out that similar results have also been seen in another large aspirin primary prevention study – the Women’s Health Study (WHS).
The WHS compared aspirin 100 mg every other day with placebo in initially healthy younger women. Previously reported results showed that women carrying the rs3798220-C variant, associated with highly elevated Lp(a) levels, had a twofold higher risk of cardiovascular events than noncarrier women in the placebo group, but this risk was reduced in the aspirin group. And there was no increased risk of bleeding in women with elevated Lp(a).
“These results, in the absence of any other randomized controlled trial evidence or approved therapy for treating Lp(a)-associated risk, have been used by some physicians as justification for prescribing aspirin in patients with elevated Lp(a),” Dr. Lacaze and colleagues note.
“In the present study of the ASPREE trial population, our results were consistent with the WHS analysis, despite randomizing older individuals (both men and women),” they add.
They say this validation of the WHS result provides evidence that a very high-risk subgroup of individuals with highly elevated Lp(a) – those carrying the rs3798220-C allele – may benefit from low-dose aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events. Further, the benefits in this subgroup specifically may outweigh any bleeding risk.
But they point out that rs3798220-C carriers comprise only a small portion of all individuals with elevated Lp(a) in the general population, while the polygenic LPA-GRS explains about 60% of the variation in directly measured plasma Lp(a) levels and has the potential advantage of being able to identify a larger group of individuals at increased risk.
The researchers note, however, that it is not clear to what extent the LPA-GRS results add further evidence to suggest that individuals with elevated Lp(a), beyond rs3798220-C carriers, may be more likely to benefit from aspirin.
“If the benefit of aspirin extends beyond very high-risk rs3798220-C carriers alone, to the broader 20%-30% of individuals with elevated Lp(a), the potential utility of aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events would increase substantially,” they say.
‘Very high clinical relevance’
In an accompanying editorial, Ana Devesa, MD, Borja Ibanez, MD, PhD, and Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, The National Center for Cardiovascular Research, Madrid, say that: “[Dr.] Lacaze et al. are to be congratulated for a study of very high clinical relevance that represents a first indication for primary prevention for patients at high cardiovascular risk.”
They explain that the pathogenic mechanism of Lp(a) is believed to be a combination of prothrombotic and proatherogenic effects, and the current findings support the hypothesis that the prothrombotic mechanism of Lp(a) is mediated by platelet aggregation.
This would explain the occurrence of thrombotic events in the presence of atherosclerosis in that elevated Lp(a) levels may induce platelet adhesion and aggregation to the activated atherosclerotic plaque, thus enhancing the atherothrombotic process. Moreover, activated platelets release several mediators that result in cell adhesion and attraction of chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines, driving an inflammatory response and mediating atherosclerosis progression, they add.
The editorialists highlight the limitations of the study already acknowledged by the authors: The analysis used genotypes rather than elevated Lp(a) levels and included only those of European ancestry, meaning the results are difficult to extrapolate to other populations.
“The next steps in clinical practice should be defined, and there are still questions to be answered,” they conclude. “Will every patient benefit from antithrombotic therapies? Should all patients who have elevated Lp(a) levels be treated with aspirin?”
The ASPREE Biobank is supported by grants from the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Monash University, Menzies Research Institute, Australian National University, University of Melbourne, National Institutes of Health, National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, and the Victorian Cancer Agency. Dr. Lacaze is supported by a National Heart Foundation Future Leader Fellowship.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Aspirin may be of specific benefit for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in individuals with raised Lp(a) levels, a new study has suggested.
The study analyzed data from the ASPREE (ASPirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly) trial, which randomized 19,000 individuals aged 70 years or older without a history of cardiovascular disease to aspirin (100 mg/day) or placebo. While the main results, reported previously, showed no net benefit of aspirin in the overall population, the current analysis suggests there may be a benefit in individuals with raised Lp(a) levels.
The current analysis was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Our study provides evidence that aspirin may specifically benefit older individuals with genotypes for elevated plasma Lp(a) in the setting of high-risk primary prevention of cardiovascular events and that overall benefit may outweigh harm related to major bleeding,” the authors, led by Paul Lacaze, PhD, Monash University, Melbourne, conclude.
They also point out that similar observations have been previously seen in another large aspirin primary prevention study conducted in younger women, the Women’s Health Study, and the current analysis provides validation of those findings.
“Our results provide new evidence to support the potential use of aspirin to target individuals with elevated Lp(a) for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events,” the researchers say.
They acknowledge that these results would be strengthened by the use of directly measured plasma Lp(a) levels, in addition to Lp(a) genotypes.
But they add: “Nonetheless, given the lack of any currently approved therapies for targeting elevated Lp(a), our findings may have widespread clinical implications, adding evidence to the rationale that aspirin may be a viable option for reducing Lp(a)-mediated cardiovascular risk.”
Dr. Lacaze and colleagues explain that elevated plasma Lp(a) levels confer up to fourfold increased risk of cardiovascular disease, with around 20%-30% of the general population affected. Despite the high burden and prevalence of elevated plasma Lp(a), there are currently no approved pharmacologic therapies targeting this lipoprotein. Although promising candidates are in development for the secondary prevention of Lp(a)-mediated cardiovascular disease, it will be many years before these candidates are assessed for primary prevention.
For the current study, researchers analyzed data from 12,815 ASPREE participants who had undergone genotyping and compared outcomes with aspirin versus placebo in those with and without genotypes associated with elevated Lp(a) levels.
Results showed that individuals with elevated Lp(a)-associated genotypes, defined in two different ways, showed a reduction in ischemic events with aspirin versus placebo, and this benefit was not outweighed by an increased bleeding risk.
Specifically, in the placebo group, individuals who carried the rs3798220-C allele, which is known to be associated with raised Lp(a) levels, making up 3.2% of the genotyped population in the study, had an almost twofold increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events than those not carrying this genotype. However, the risk was attenuated in the aspirin group, with carriers of the rs3798220-C allele actually having a lower rate of cardiovascular events than noncarriers.
In addition, rs3798220-C carrier status was not significantly associated with increased risk of clinically significant bleeding events in the aspirin group.
Similar results were seen with the second way of identifying patients with a high risk of elevated Lp(a) levels using a 43-variant genetic risk score (LPA-GRS).
In the whole study population, aspirin reduced major adverse cardiovascular events by 1.7 events per 1,000 person-years and increased clinically significant bleeding events by 1.7 events per 1,000 person-years, suggesting parity between overall benefit versus harm.
However, in the rs3798220-C subgroup, aspirin reduced major adverse cardiovascular events by 11.4 events per 1,000 person-years (a more than sixfold higher magnitude of cardiovascular disease risk reduction than in the overall cohort), with a bleeding risk of 3.3 events per 1,000 person-years, the researchers report.
“Hence in rs3798220-C carriers, aspirin appeared to have a net benefit of 8.1 events per 1,000 person-years,” they state.
In the highest LPA-GRS quintile, aspirin reduced major adverse cardiovascular events by 3.3 events per 1,000 person-years (approximately twofold higher magnitude of risk reduction, compared with the overall cohort), with an increase in bleeding risk of 1.6 events per 1,000 person-years (almost identical bleeding risk to the overall cohort). This shifted the benefit versus harm balance in the highest LPA-GRS quintile to a net benefit of 1.7 events per 1,000 person-years.
Similar findings in the Women’s Health Study
Dr. Lacaze and colleagues point out that similar results have also been seen in another large aspirin primary prevention study – the Women’s Health Study (WHS).
The WHS compared aspirin 100 mg every other day with placebo in initially healthy younger women. Previously reported results showed that women carrying the rs3798220-C variant, associated with highly elevated Lp(a) levels, had a twofold higher risk of cardiovascular events than noncarrier women in the placebo group, but this risk was reduced in the aspirin group. And there was no increased risk of bleeding in women with elevated Lp(a).
“These results, in the absence of any other randomized controlled trial evidence or approved therapy for treating Lp(a)-associated risk, have been used by some physicians as justification for prescribing aspirin in patients with elevated Lp(a),” Dr. Lacaze and colleagues note.
“In the present study of the ASPREE trial population, our results were consistent with the WHS analysis, despite randomizing older individuals (both men and women),” they add.
They say this validation of the WHS result provides evidence that a very high-risk subgroup of individuals with highly elevated Lp(a) – those carrying the rs3798220-C allele – may benefit from low-dose aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events. Further, the benefits in this subgroup specifically may outweigh any bleeding risk.
But they point out that rs3798220-C carriers comprise only a small portion of all individuals with elevated Lp(a) in the general population, while the polygenic LPA-GRS explains about 60% of the variation in directly measured plasma Lp(a) levels and has the potential advantage of being able to identify a larger group of individuals at increased risk.
The researchers note, however, that it is not clear to what extent the LPA-GRS results add further evidence to suggest that individuals with elevated Lp(a), beyond rs3798220-C carriers, may be more likely to benefit from aspirin.
“If the benefit of aspirin extends beyond very high-risk rs3798220-C carriers alone, to the broader 20%-30% of individuals with elevated Lp(a), the potential utility of aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events would increase substantially,” they say.
‘Very high clinical relevance’
In an accompanying editorial, Ana Devesa, MD, Borja Ibanez, MD, PhD, and Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, The National Center for Cardiovascular Research, Madrid, say that: “[Dr.] Lacaze et al. are to be congratulated for a study of very high clinical relevance that represents a first indication for primary prevention for patients at high cardiovascular risk.”
They explain that the pathogenic mechanism of Lp(a) is believed to be a combination of prothrombotic and proatherogenic effects, and the current findings support the hypothesis that the prothrombotic mechanism of Lp(a) is mediated by platelet aggregation.
This would explain the occurrence of thrombotic events in the presence of atherosclerosis in that elevated Lp(a) levels may induce platelet adhesion and aggregation to the activated atherosclerotic plaque, thus enhancing the atherothrombotic process. Moreover, activated platelets release several mediators that result in cell adhesion and attraction of chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines, driving an inflammatory response and mediating atherosclerosis progression, they add.
The editorialists highlight the limitations of the study already acknowledged by the authors: The analysis used genotypes rather than elevated Lp(a) levels and included only those of European ancestry, meaning the results are difficult to extrapolate to other populations.
“The next steps in clinical practice should be defined, and there are still questions to be answered,” they conclude. “Will every patient benefit from antithrombotic therapies? Should all patients who have elevated Lp(a) levels be treated with aspirin?”
The ASPREE Biobank is supported by grants from the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Monash University, Menzies Research Institute, Australian National University, University of Melbourne, National Institutes of Health, National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, and the Victorian Cancer Agency. Dr. Lacaze is supported by a National Heart Foundation Future Leader Fellowship.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.