User login
Vacationing Doctors Intervene After Shark Attack
Ryan Forbess, MD: I live at the beach in Orange Beach, Alabama. I’ve lived in Hawaii, the Caymans, and other beach areas for years. I’ve seen a lot of sharks but never a shark attack. Not until now.
Mohammad Ali, MD: Ryan and I have been friends for 20 years. Every year, my family goes to 30A in Florida (a popular resort stretch of highway) to celebrate my wife’s birthday, and the Forbesses always meet us there. This year we had a group of about 18 people.
On Friday, it was beautiful, and we decided to make it a beach day. We had nine kids with us. So by the time we rounded them up and got there, it was noon, and there was nowhere to sit. We almost turned around and went to the pool. But my wife finally found a spot for an umbrella.
Dr. Forbess: We were in the water boogie boarding. I was with my 8-year-old son, and Mo was with his daughter who is the same age. Suddenly, we noticed a lot of commotion just to the left of us. My first thought was: Someone saw a shark, not an attack. They’re so rare. But seeing one would scare people.
We grabbed our kids and started running out of the water. As we got closer to the shore,
Dr. Ali: It was mass panic. People were screaming and running out of the water. Other people were running in and grabbing their kids. Everyone just looked frantic.
We saw two men dragging this poor girl out of the water. It was surreal. The majority of her right leg was severed, her femur bone visible and stark white; it didn’t look real. I kept telling myself I was in a dream and now I’d wake up.
A young EMT who was there had put an informal tourniquet on her leg, but she was still bleeding. So I compressed the femoral artery as hard as I could, something I’m very familiar with doing.
Dr. Forbess: People asked me later what we used for a tourniquet. I said, “Mo’s big hands.” I tease him because most doctors play golf or go fishing; Mo lives in the gym. He was just holding pressure.
The girl’s left hand was also severed off at the wrist. There were two nurses there, and they helped with holding tourniquets on her arm.
Lulu (the girl’s name) was 15 years old. She was in and out of consciousness. At one point, her face started getting really pale, so we tried to lift her extremities up to keep the blood flow to the heart. With such severe blood loss, I thought she might go into cardiovascular shock, and we would have to start compressions. But she had a pulse, and she was breathing.
Dr. Ali: The beach was very crowded, and a lot of people had gathered around. Everyone was emotional, shocked, really shaken up. But they gave us space to work.
Dr. Forbess: People were handing us things — towels, a ratchet strap to use as a tourniquet. There was even an anesthesiologist there who said, “If you need an airway, let me know.” It was like we had a trauma team.
Dr. Ali: Lulu’s mom had been having lunch with friends. When she saw all the commotion, she ran down to the beach to look for her daughter. It was heartbreaking to hear her screams when she saw Lulu. But I was able to tune it out because we had to just concentrate on decreasing the loss of blood.
Dr. Forbess: Another girl came over and said, “That’s my sister.” Lulu has a twin. So she sat there holding Lulu’s hand and being with her the whole time.
Waiting for the EMTs to get there, the seconds were like hours. It seemed like it took forever. Finally, they came, and we were able to get the real tourniquets on, get her boarded and off the beach.
After that, they closed the beach. We got all our stuff and got on the little trolley that would take us back to the house. The lady who was driving asked us, “Did y’all hear about the shark attack?” My wife said, “Yeah, we were there.” And she said, “No, there was one an hour and a half ago.”
Dr. Ali: What we didn’t know was there had been two other attacks that day. Around the same time, one of Lulu’s friends was bitten and got a flesh wound on her heel. And before that, about 4 miles away, there was a serious injury: A lady in her 40s lost her hand and forearm and was bitten in the pelvis.
Dr. Forbess: At that point, my wife leaned back to me and said, “You know we’re never going to the beach again, right? We’re never ever going to the beach.”
If we had known about those attacks, we definitely wouldn’t have been in the water.
Dr. Ali: My wife has never liked going in the water. The evening before, we had debated about taking our daughters in the ocean because she was worried about sharks. I had given her this condescending speech about waist-deep water and the statistical probabilities of ever witnessing a shark attack. I was in trouble.
Dr. Forbess: We didn’t know if Lulu would make it. I’ve done rural family medicine in Oklahoma, so I’ve seen my fair share of injuries — guys on oil rigs, this and that. But I had never seen anything like this kind of trauma and blood loss.
Later that day, I called my office manager to catch up with her and told her what happened. She was actually in Pensacola having dinner across the street from Sacred Heart Hospital where they had taken Lulu. She went over to the emergency room to try to find out Lulu’s status — she was alive.
My office manager was able to go upstairs and talk to Lulu’s mom. Then she called, and we talked to her mom on the phone. She just said, “Thank you for helping my daughter.” It was an emotional moment.
Dr. Ali: It was such a relief. We had no idea how things would turn out. Even if Lulu did survive, was she going to be neurologically sound? But thank God she was. We were so relieved to hear her mom say that it was looking good. We still didn’t know for sure. But at least she was alive and seemed to be functioning.
Dr. Forbess: A few days later, my wife and I went to go visit her at the hospital. Her mom and her grandma were there. They were giving us hugs. We FaceTimed Mo because he was back in Jackson. It was really amazing.
What are the odds? The chances of a shark attack are about one in 12 million. And to have two physicians trained in trauma, a trauma nurse, another nurse, and an anesthesiologist less than 20 yards away when it happened? It’s crazy to think about.
Dr. Ali: And we almost weren’t there. We could have turned away.
Dr. Forbess: Humans are on top of the food chain. Or we think we are. But water really isn’t our element. Against a 12-foot bull shark, we don’t stand a chance. Lulu is here though. It’s unbelievable.
Her mom told me that when Lulu woke up, she just said, “I made it!” That girl is meant to be here. She is a tough girl with a great personality. She has these new prosthetics now that she can move with her mind; it’s like Star Wars. She says she wants to be a physician someday. So she’ll probably cure cancer.
Dr. Forbess is a family medicine physician at Orange Beach Family Medicine in Orange Beach, Alabama. Dr. Ali is an interventional radiologist with Baptist Memorial Health in Jackson, Mississippi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ryan Forbess, MD: I live at the beach in Orange Beach, Alabama. I’ve lived in Hawaii, the Caymans, and other beach areas for years. I’ve seen a lot of sharks but never a shark attack. Not until now.
Mohammad Ali, MD: Ryan and I have been friends for 20 years. Every year, my family goes to 30A in Florida (a popular resort stretch of highway) to celebrate my wife’s birthday, and the Forbesses always meet us there. This year we had a group of about 18 people.
On Friday, it was beautiful, and we decided to make it a beach day. We had nine kids with us. So by the time we rounded them up and got there, it was noon, and there was nowhere to sit. We almost turned around and went to the pool. But my wife finally found a spot for an umbrella.
Dr. Forbess: We were in the water boogie boarding. I was with my 8-year-old son, and Mo was with his daughter who is the same age. Suddenly, we noticed a lot of commotion just to the left of us. My first thought was: Someone saw a shark, not an attack. They’re so rare. But seeing one would scare people.
We grabbed our kids and started running out of the water. As we got closer to the shore,
Dr. Ali: It was mass panic. People were screaming and running out of the water. Other people were running in and grabbing their kids. Everyone just looked frantic.
We saw two men dragging this poor girl out of the water. It was surreal. The majority of her right leg was severed, her femur bone visible and stark white; it didn’t look real. I kept telling myself I was in a dream and now I’d wake up.
A young EMT who was there had put an informal tourniquet on her leg, but she was still bleeding. So I compressed the femoral artery as hard as I could, something I’m very familiar with doing.
Dr. Forbess: People asked me later what we used for a tourniquet. I said, “Mo’s big hands.” I tease him because most doctors play golf or go fishing; Mo lives in the gym. He was just holding pressure.
The girl’s left hand was also severed off at the wrist. There were two nurses there, and they helped with holding tourniquets on her arm.
Lulu (the girl’s name) was 15 years old. She was in and out of consciousness. At one point, her face started getting really pale, so we tried to lift her extremities up to keep the blood flow to the heart. With such severe blood loss, I thought she might go into cardiovascular shock, and we would have to start compressions. But she had a pulse, and she was breathing.
Dr. Ali: The beach was very crowded, and a lot of people had gathered around. Everyone was emotional, shocked, really shaken up. But they gave us space to work.
Dr. Forbess: People were handing us things — towels, a ratchet strap to use as a tourniquet. There was even an anesthesiologist there who said, “If you need an airway, let me know.” It was like we had a trauma team.
Dr. Ali: Lulu’s mom had been having lunch with friends. When she saw all the commotion, she ran down to the beach to look for her daughter. It was heartbreaking to hear her screams when she saw Lulu. But I was able to tune it out because we had to just concentrate on decreasing the loss of blood.
Dr. Forbess: Another girl came over and said, “That’s my sister.” Lulu has a twin. So she sat there holding Lulu’s hand and being with her the whole time.
Waiting for the EMTs to get there, the seconds were like hours. It seemed like it took forever. Finally, they came, and we were able to get the real tourniquets on, get her boarded and off the beach.
After that, they closed the beach. We got all our stuff and got on the little trolley that would take us back to the house. The lady who was driving asked us, “Did y’all hear about the shark attack?” My wife said, “Yeah, we were there.” And she said, “No, there was one an hour and a half ago.”
Dr. Ali: What we didn’t know was there had been two other attacks that day. Around the same time, one of Lulu’s friends was bitten and got a flesh wound on her heel. And before that, about 4 miles away, there was a serious injury: A lady in her 40s lost her hand and forearm and was bitten in the pelvis.
Dr. Forbess: At that point, my wife leaned back to me and said, “You know we’re never going to the beach again, right? We’re never ever going to the beach.”
If we had known about those attacks, we definitely wouldn’t have been in the water.
Dr. Ali: My wife has never liked going in the water. The evening before, we had debated about taking our daughters in the ocean because she was worried about sharks. I had given her this condescending speech about waist-deep water and the statistical probabilities of ever witnessing a shark attack. I was in trouble.
Dr. Forbess: We didn’t know if Lulu would make it. I’ve done rural family medicine in Oklahoma, so I’ve seen my fair share of injuries — guys on oil rigs, this and that. But I had never seen anything like this kind of trauma and blood loss.
Later that day, I called my office manager to catch up with her and told her what happened. She was actually in Pensacola having dinner across the street from Sacred Heart Hospital where they had taken Lulu. She went over to the emergency room to try to find out Lulu’s status — she was alive.
My office manager was able to go upstairs and talk to Lulu’s mom. Then she called, and we talked to her mom on the phone. She just said, “Thank you for helping my daughter.” It was an emotional moment.
Dr. Ali: It was such a relief. We had no idea how things would turn out. Even if Lulu did survive, was she going to be neurologically sound? But thank God she was. We were so relieved to hear her mom say that it was looking good. We still didn’t know for sure. But at least she was alive and seemed to be functioning.
Dr. Forbess: A few days later, my wife and I went to go visit her at the hospital. Her mom and her grandma were there. They were giving us hugs. We FaceTimed Mo because he was back in Jackson. It was really amazing.
What are the odds? The chances of a shark attack are about one in 12 million. And to have two physicians trained in trauma, a trauma nurse, another nurse, and an anesthesiologist less than 20 yards away when it happened? It’s crazy to think about.
Dr. Ali: And we almost weren’t there. We could have turned away.
Dr. Forbess: Humans are on top of the food chain. Or we think we are. But water really isn’t our element. Against a 12-foot bull shark, we don’t stand a chance. Lulu is here though. It’s unbelievable.
Her mom told me that when Lulu woke up, she just said, “I made it!” That girl is meant to be here. She is a tough girl with a great personality. She has these new prosthetics now that she can move with her mind; it’s like Star Wars. She says she wants to be a physician someday. So she’ll probably cure cancer.
Dr. Forbess is a family medicine physician at Orange Beach Family Medicine in Orange Beach, Alabama. Dr. Ali is an interventional radiologist with Baptist Memorial Health in Jackson, Mississippi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ryan Forbess, MD: I live at the beach in Orange Beach, Alabama. I’ve lived in Hawaii, the Caymans, and other beach areas for years. I’ve seen a lot of sharks but never a shark attack. Not until now.
Mohammad Ali, MD: Ryan and I have been friends for 20 years. Every year, my family goes to 30A in Florida (a popular resort stretch of highway) to celebrate my wife’s birthday, and the Forbesses always meet us there. This year we had a group of about 18 people.
On Friday, it was beautiful, and we decided to make it a beach day. We had nine kids with us. So by the time we rounded them up and got there, it was noon, and there was nowhere to sit. We almost turned around and went to the pool. But my wife finally found a spot for an umbrella.
Dr. Forbess: We were in the water boogie boarding. I was with my 8-year-old son, and Mo was with his daughter who is the same age. Suddenly, we noticed a lot of commotion just to the left of us. My first thought was: Someone saw a shark, not an attack. They’re so rare. But seeing one would scare people.
We grabbed our kids and started running out of the water. As we got closer to the shore,
Dr. Ali: It was mass panic. People were screaming and running out of the water. Other people were running in and grabbing their kids. Everyone just looked frantic.
We saw two men dragging this poor girl out of the water. It was surreal. The majority of her right leg was severed, her femur bone visible and stark white; it didn’t look real. I kept telling myself I was in a dream and now I’d wake up.
A young EMT who was there had put an informal tourniquet on her leg, but she was still bleeding. So I compressed the femoral artery as hard as I could, something I’m very familiar with doing.
Dr. Forbess: People asked me later what we used for a tourniquet. I said, “Mo’s big hands.” I tease him because most doctors play golf or go fishing; Mo lives in the gym. He was just holding pressure.
The girl’s left hand was also severed off at the wrist. There were two nurses there, and they helped with holding tourniquets on her arm.
Lulu (the girl’s name) was 15 years old. She was in and out of consciousness. At one point, her face started getting really pale, so we tried to lift her extremities up to keep the blood flow to the heart. With such severe blood loss, I thought she might go into cardiovascular shock, and we would have to start compressions. But she had a pulse, and she was breathing.
Dr. Ali: The beach was very crowded, and a lot of people had gathered around. Everyone was emotional, shocked, really shaken up. But they gave us space to work.
Dr. Forbess: People were handing us things — towels, a ratchet strap to use as a tourniquet. There was even an anesthesiologist there who said, “If you need an airway, let me know.” It was like we had a trauma team.
Dr. Ali: Lulu’s mom had been having lunch with friends. When she saw all the commotion, she ran down to the beach to look for her daughter. It was heartbreaking to hear her screams when she saw Lulu. But I was able to tune it out because we had to just concentrate on decreasing the loss of blood.
Dr. Forbess: Another girl came over and said, “That’s my sister.” Lulu has a twin. So she sat there holding Lulu’s hand and being with her the whole time.
Waiting for the EMTs to get there, the seconds were like hours. It seemed like it took forever. Finally, they came, and we were able to get the real tourniquets on, get her boarded and off the beach.
After that, they closed the beach. We got all our stuff and got on the little trolley that would take us back to the house. The lady who was driving asked us, “Did y’all hear about the shark attack?” My wife said, “Yeah, we were there.” And she said, “No, there was one an hour and a half ago.”
Dr. Ali: What we didn’t know was there had been two other attacks that day. Around the same time, one of Lulu’s friends was bitten and got a flesh wound on her heel. And before that, about 4 miles away, there was a serious injury: A lady in her 40s lost her hand and forearm and was bitten in the pelvis.
Dr. Forbess: At that point, my wife leaned back to me and said, “You know we’re never going to the beach again, right? We’re never ever going to the beach.”
If we had known about those attacks, we definitely wouldn’t have been in the water.
Dr. Ali: My wife has never liked going in the water. The evening before, we had debated about taking our daughters in the ocean because she was worried about sharks. I had given her this condescending speech about waist-deep water and the statistical probabilities of ever witnessing a shark attack. I was in trouble.
Dr. Forbess: We didn’t know if Lulu would make it. I’ve done rural family medicine in Oklahoma, so I’ve seen my fair share of injuries — guys on oil rigs, this and that. But I had never seen anything like this kind of trauma and blood loss.
Later that day, I called my office manager to catch up with her and told her what happened. She was actually in Pensacola having dinner across the street from Sacred Heart Hospital where they had taken Lulu. She went over to the emergency room to try to find out Lulu’s status — she was alive.
My office manager was able to go upstairs and talk to Lulu’s mom. Then she called, and we talked to her mom on the phone. She just said, “Thank you for helping my daughter.” It was an emotional moment.
Dr. Ali: It was such a relief. We had no idea how things would turn out. Even if Lulu did survive, was she going to be neurologically sound? But thank God she was. We were so relieved to hear her mom say that it was looking good. We still didn’t know for sure. But at least she was alive and seemed to be functioning.
Dr. Forbess: A few days later, my wife and I went to go visit her at the hospital. Her mom and her grandma were there. They were giving us hugs. We FaceTimed Mo because he was back in Jackson. It was really amazing.
What are the odds? The chances of a shark attack are about one in 12 million. And to have two physicians trained in trauma, a trauma nurse, another nurse, and an anesthesiologist less than 20 yards away when it happened? It’s crazy to think about.
Dr. Ali: And we almost weren’t there. We could have turned away.
Dr. Forbess: Humans are on top of the food chain. Or we think we are. But water really isn’t our element. Against a 12-foot bull shark, we don’t stand a chance. Lulu is here though. It’s unbelievable.
Her mom told me that when Lulu woke up, she just said, “I made it!” That girl is meant to be here. She is a tough girl with a great personality. She has these new prosthetics now that she can move with her mind; it’s like Star Wars. She says she wants to be a physician someday. So she’ll probably cure cancer.
Dr. Forbess is a family medicine physician at Orange Beach Family Medicine in Orange Beach, Alabama. Dr. Ali is an interventional radiologist with Baptist Memorial Health in Jackson, Mississippi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Blood Everywhere’: Nurses Control In-Flight Crisis
My husband Scott and I were flying back to Washington state with our two kids, who were about 1 and 4. We had been in Florida for a family vacation, and we were near the end of the flight, with both kids passed out on top of me.
Suddenly, there was some scuffling and a lot of movement from the flight attendants. The announcement came: “Are there any healthcare providers on board?” My husband and I are both nurses. We looked at each other, and we looked at our sleeping kids. Should we say anything?
One of the stewardesses walked by looking very flustered. My husband was in the aisle seat, so he leaned out and told her that we were nurses. Her eyes got all big, and she said: “Oh yeah, come on up.”
She was looking at both of us. I said, “I think he’s got it.” I assumed it wasn’t that big of a deal. Plus — kids sleeping on top of me.
Scott went up to the front of the plane. But a few minutes later, the stewardess came back and said: “You need to help.” I was holding my 1-year-old son, so I handed her my kid. She sat down with him, and I boogied up to the front of the plane.
I got to the first-class stewards’ area where the restrooms are and the cabinets with all the food and drinks.
When I saw the bleeding, my first reaction was we need to apply pressure. I asked for a towel. There were no towels. A blanket? Anything to help absorb the blood? Nope. They had nothing. I was given a pair of gloves that were much too big and a fistful of cocktail napkins.
It was such a small space there wasn’t any way to be next to the man. So, I kind of squatted over the top of him to reach behind his head. I got a stack of napkins on there and held pressure as hard as I could with the tips of my fingers on one hand.
I’m a postanesthesia care unit nurse, so my next thought was to check his pupils and make sure he had a good airway by doing a jaw thrust and a chin lift. I noticed there was blood in his mouth. His breathing was in short gusts. I was trying to do all that with my free hand without crushing him with my body.
Scott had made some ice packs, so I applied those as well, which helped to constrict the bleeding. Then he checked the plane’s medical kit to try to get an intravenous (IV) started. It wasn’t easy. The IV start kit was very different from what you would normally use. And at the same time, the plane had started to descend for landing, so we were on an angle. But he tried.
We asked about what had happened. The steward team said the man had fallen and hit his head on one of the stainless steel cabinets. He seemed to be in his 70s or 80s, a tall, solid guy.
His wife was sitting nearby — pretty calm and stoic given the circumstances. We asked her about his medical history, trying to get a feel for why he might be unconscious. He was still totally out. She told us he had diabetes. He was on a blood pressure medication and also a blood thinner.
The plane kept going down. I was in a really awkward position, squatting and holding myself up against the cabinets. I just kept talking to the man, trying to get him to wake up. “Can you hear me? Everything’s okay. You hit your head.”
Someone brought us an oxygen tank. I looked for the mask. And realized it wasn’t a mask. It was a plastic bag. I set it on the patient’s face, and it felt like I was suffocating him. So, I tried to do it blowby to just increase the oxygen in the air near his face.
At one point, his breathing was agonal for a few minutes, which really concerned me. My fear was that he was going to stop breathing. I rubbed his chest and kind of said: “Hey, let’s not do that!”
I would have felt a lot better about resuscitating him with an actual oxygen mask rather than a plastic bag.
The amount of blood definitely looked alarming. I couldn’t tell how much he was actively bleeding. But it was a lot. He wasn’t turning gray though, so that was a good sign.
Finally, he started coming to and opening his eyes. I introduced myself and asked him: “Do you know where you are? Do you know what’s going on?” Trying to see if he was oriented at all.
Eventually, he was able to talk to me, so I kept asking questions: “Are you guys on vacation? Where are you headed? Where are you staying?”
He told me they were going to visit his granddaughter, and he was able to talk about that. He didn’t try to get up, which I was glad about, because that would’ve been really challenging to navigate.
I could tell he was embarrassed about what had happened. I’ve helped a lot of older gentlemen after falling down, and their egos are often bruised. They don’t want to be in a position of needing help.
Finally, the plane landed. There was blood absolutely everywhere. The ice packs had melted, and the water had mixed with the pool of blood. It was such a mess.
The pilots had called the airport ahead to let them know we needed medical services. So, the first responding team came on right away. They stabilized the man with a board, put the neck brace on him, and did all the stuff you do for a patient after a fall.
I gave them a report — that’s just my style. But it didn’t seem like they needed a lot of information at that point.
I was finally able to talk to the man’s wife who was clearly terrified. I gave her a hug and told her he would be all right. She thanked us.
The emergency team didn’t seem to have anything to help staunch the bleeding either because the rolling gurney left puddles of blood all down the gangway, causing a significant biohazard problem.
They let one person leave who had a connecting flight, but everyone else had to get off from the rear of the plane and walk across the tarmac.
When we finally got back to our seats, the stewardess was still sitting with our kids. They were both totally chill, watching some show, apparently very well behaved. Our daughter asked us what was going on, and I said: “Oh, somebody got hurt at the front of the plane.” She’s so used to hearing that we work with sick people that it didn’t faze her at all.
As we left, we got a lot of thank-yous from people who had been sitting up front and saw what happened.
When we got home, there was still blood on my shoes. I remember looking at them and thinking: Disinfect or throw away? I disinfected them. They were still a good pair of shoes.
A few days later, we got an email from the airline with a voucher, expressing their gratitude for our help. That was nice and unexpected.
I responded with a suggestion: How about having some protocols for medical events on airplanes? Pilots go through checklists for almost everything they do. Why wouldn’t they have something like that for medical responses?
I also asked how the man and his wife were doing. But they couldn’t disclose that information.
It was certainly strange being out of my element, helping a patient in that tiny little space; I’m used to working in a recovery room where you have literally everything you need within arm’s reach — the Ambu bag, suction, and bandages. And with airway management, there’s usually more than one person in the room to assist. If there’s a problem, a whole bunch of people show up around the bed so fast.
I’m definitely thinking about field medicine a lot more. Wondering what I would do in certain situations. While debriefing with my mom (an advanced registered nurse practitioner), she pointed out that we should have asked passengers for sanitary pads or diapers to stabilize the bleeding instead of the cocktail napkins. Brilliant idea! I didn’t think of it in the moment. But I’m keeping that little tip tucked in my back pocket for any future bleeding-in-the-wild scenarios.
Audra Podruzny, MSN, RN, CPAN, lives in Washington state and is currently attending the Washington State University Doctor of Nursing Practice Family Nurse Practitioner program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
My husband Scott and I were flying back to Washington state with our two kids, who were about 1 and 4. We had been in Florida for a family vacation, and we were near the end of the flight, with both kids passed out on top of me.
Suddenly, there was some scuffling and a lot of movement from the flight attendants. The announcement came: “Are there any healthcare providers on board?” My husband and I are both nurses. We looked at each other, and we looked at our sleeping kids. Should we say anything?
One of the stewardesses walked by looking very flustered. My husband was in the aisle seat, so he leaned out and told her that we were nurses. Her eyes got all big, and she said: “Oh yeah, come on up.”
She was looking at both of us. I said, “I think he’s got it.” I assumed it wasn’t that big of a deal. Plus — kids sleeping on top of me.
Scott went up to the front of the plane. But a few minutes later, the stewardess came back and said: “You need to help.” I was holding my 1-year-old son, so I handed her my kid. She sat down with him, and I boogied up to the front of the plane.
I got to the first-class stewards’ area where the restrooms are and the cabinets with all the food and drinks.
When I saw the bleeding, my first reaction was we need to apply pressure. I asked for a towel. There were no towels. A blanket? Anything to help absorb the blood? Nope. They had nothing. I was given a pair of gloves that were much too big and a fistful of cocktail napkins.
It was such a small space there wasn’t any way to be next to the man. So, I kind of squatted over the top of him to reach behind his head. I got a stack of napkins on there and held pressure as hard as I could with the tips of my fingers on one hand.
I’m a postanesthesia care unit nurse, so my next thought was to check his pupils and make sure he had a good airway by doing a jaw thrust and a chin lift. I noticed there was blood in his mouth. His breathing was in short gusts. I was trying to do all that with my free hand without crushing him with my body.
Scott had made some ice packs, so I applied those as well, which helped to constrict the bleeding. Then he checked the plane’s medical kit to try to get an intravenous (IV) started. It wasn’t easy. The IV start kit was very different from what you would normally use. And at the same time, the plane had started to descend for landing, so we were on an angle. But he tried.
We asked about what had happened. The steward team said the man had fallen and hit his head on one of the stainless steel cabinets. He seemed to be in his 70s or 80s, a tall, solid guy.
His wife was sitting nearby — pretty calm and stoic given the circumstances. We asked her about his medical history, trying to get a feel for why he might be unconscious. He was still totally out. She told us he had diabetes. He was on a blood pressure medication and also a blood thinner.
The plane kept going down. I was in a really awkward position, squatting and holding myself up against the cabinets. I just kept talking to the man, trying to get him to wake up. “Can you hear me? Everything’s okay. You hit your head.”
Someone brought us an oxygen tank. I looked for the mask. And realized it wasn’t a mask. It was a plastic bag. I set it on the patient’s face, and it felt like I was suffocating him. So, I tried to do it blowby to just increase the oxygen in the air near his face.
At one point, his breathing was agonal for a few minutes, which really concerned me. My fear was that he was going to stop breathing. I rubbed his chest and kind of said: “Hey, let’s not do that!”
I would have felt a lot better about resuscitating him with an actual oxygen mask rather than a plastic bag.
The amount of blood definitely looked alarming. I couldn’t tell how much he was actively bleeding. But it was a lot. He wasn’t turning gray though, so that was a good sign.
Finally, he started coming to and opening his eyes. I introduced myself and asked him: “Do you know where you are? Do you know what’s going on?” Trying to see if he was oriented at all.
Eventually, he was able to talk to me, so I kept asking questions: “Are you guys on vacation? Where are you headed? Where are you staying?”
He told me they were going to visit his granddaughter, and he was able to talk about that. He didn’t try to get up, which I was glad about, because that would’ve been really challenging to navigate.
I could tell he was embarrassed about what had happened. I’ve helped a lot of older gentlemen after falling down, and their egos are often bruised. They don’t want to be in a position of needing help.
Finally, the plane landed. There was blood absolutely everywhere. The ice packs had melted, and the water had mixed with the pool of blood. It was such a mess.
The pilots had called the airport ahead to let them know we needed medical services. So, the first responding team came on right away. They stabilized the man with a board, put the neck brace on him, and did all the stuff you do for a patient after a fall.
I gave them a report — that’s just my style. But it didn’t seem like they needed a lot of information at that point.
I was finally able to talk to the man’s wife who was clearly terrified. I gave her a hug and told her he would be all right. She thanked us.
The emergency team didn’t seem to have anything to help staunch the bleeding either because the rolling gurney left puddles of blood all down the gangway, causing a significant biohazard problem.
They let one person leave who had a connecting flight, but everyone else had to get off from the rear of the plane and walk across the tarmac.
When we finally got back to our seats, the stewardess was still sitting with our kids. They were both totally chill, watching some show, apparently very well behaved. Our daughter asked us what was going on, and I said: “Oh, somebody got hurt at the front of the plane.” She’s so used to hearing that we work with sick people that it didn’t faze her at all.
As we left, we got a lot of thank-yous from people who had been sitting up front and saw what happened.
When we got home, there was still blood on my shoes. I remember looking at them and thinking: Disinfect or throw away? I disinfected them. They were still a good pair of shoes.
A few days later, we got an email from the airline with a voucher, expressing their gratitude for our help. That was nice and unexpected.
I responded with a suggestion: How about having some protocols for medical events on airplanes? Pilots go through checklists for almost everything they do. Why wouldn’t they have something like that for medical responses?
I also asked how the man and his wife were doing. But they couldn’t disclose that information.
It was certainly strange being out of my element, helping a patient in that tiny little space; I’m used to working in a recovery room where you have literally everything you need within arm’s reach — the Ambu bag, suction, and bandages. And with airway management, there’s usually more than one person in the room to assist. If there’s a problem, a whole bunch of people show up around the bed so fast.
I’m definitely thinking about field medicine a lot more. Wondering what I would do in certain situations. While debriefing with my mom (an advanced registered nurse practitioner), she pointed out that we should have asked passengers for sanitary pads or diapers to stabilize the bleeding instead of the cocktail napkins. Brilliant idea! I didn’t think of it in the moment. But I’m keeping that little tip tucked in my back pocket for any future bleeding-in-the-wild scenarios.
Audra Podruzny, MSN, RN, CPAN, lives in Washington state and is currently attending the Washington State University Doctor of Nursing Practice Family Nurse Practitioner program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
My husband Scott and I were flying back to Washington state with our two kids, who were about 1 and 4. We had been in Florida for a family vacation, and we were near the end of the flight, with both kids passed out on top of me.
Suddenly, there was some scuffling and a lot of movement from the flight attendants. The announcement came: “Are there any healthcare providers on board?” My husband and I are both nurses. We looked at each other, and we looked at our sleeping kids. Should we say anything?
One of the stewardesses walked by looking very flustered. My husband was in the aisle seat, so he leaned out and told her that we were nurses. Her eyes got all big, and she said: “Oh yeah, come on up.”
She was looking at both of us. I said, “I think he’s got it.” I assumed it wasn’t that big of a deal. Plus — kids sleeping on top of me.
Scott went up to the front of the plane. But a few minutes later, the stewardess came back and said: “You need to help.” I was holding my 1-year-old son, so I handed her my kid. She sat down with him, and I boogied up to the front of the plane.
I got to the first-class stewards’ area where the restrooms are and the cabinets with all the food and drinks.
When I saw the bleeding, my first reaction was we need to apply pressure. I asked for a towel. There were no towels. A blanket? Anything to help absorb the blood? Nope. They had nothing. I was given a pair of gloves that were much too big and a fistful of cocktail napkins.
It was such a small space there wasn’t any way to be next to the man. So, I kind of squatted over the top of him to reach behind his head. I got a stack of napkins on there and held pressure as hard as I could with the tips of my fingers on one hand.
I’m a postanesthesia care unit nurse, so my next thought was to check his pupils and make sure he had a good airway by doing a jaw thrust and a chin lift. I noticed there was blood in his mouth. His breathing was in short gusts. I was trying to do all that with my free hand without crushing him with my body.
Scott had made some ice packs, so I applied those as well, which helped to constrict the bleeding. Then he checked the plane’s medical kit to try to get an intravenous (IV) started. It wasn’t easy. The IV start kit was very different from what you would normally use. And at the same time, the plane had started to descend for landing, so we were on an angle. But he tried.
We asked about what had happened. The steward team said the man had fallen and hit his head on one of the stainless steel cabinets. He seemed to be in his 70s or 80s, a tall, solid guy.
His wife was sitting nearby — pretty calm and stoic given the circumstances. We asked her about his medical history, trying to get a feel for why he might be unconscious. He was still totally out. She told us he had diabetes. He was on a blood pressure medication and also a blood thinner.
The plane kept going down. I was in a really awkward position, squatting and holding myself up against the cabinets. I just kept talking to the man, trying to get him to wake up. “Can you hear me? Everything’s okay. You hit your head.”
Someone brought us an oxygen tank. I looked for the mask. And realized it wasn’t a mask. It was a plastic bag. I set it on the patient’s face, and it felt like I was suffocating him. So, I tried to do it blowby to just increase the oxygen in the air near his face.
At one point, his breathing was agonal for a few minutes, which really concerned me. My fear was that he was going to stop breathing. I rubbed his chest and kind of said: “Hey, let’s not do that!”
I would have felt a lot better about resuscitating him with an actual oxygen mask rather than a plastic bag.
The amount of blood definitely looked alarming. I couldn’t tell how much he was actively bleeding. But it was a lot. He wasn’t turning gray though, so that was a good sign.
Finally, he started coming to and opening his eyes. I introduced myself and asked him: “Do you know where you are? Do you know what’s going on?” Trying to see if he was oriented at all.
Eventually, he was able to talk to me, so I kept asking questions: “Are you guys on vacation? Where are you headed? Where are you staying?”
He told me they were going to visit his granddaughter, and he was able to talk about that. He didn’t try to get up, which I was glad about, because that would’ve been really challenging to navigate.
I could tell he was embarrassed about what had happened. I’ve helped a lot of older gentlemen after falling down, and their egos are often bruised. They don’t want to be in a position of needing help.
Finally, the plane landed. There was blood absolutely everywhere. The ice packs had melted, and the water had mixed with the pool of blood. It was such a mess.
The pilots had called the airport ahead to let them know we needed medical services. So, the first responding team came on right away. They stabilized the man with a board, put the neck brace on him, and did all the stuff you do for a patient after a fall.
I gave them a report — that’s just my style. But it didn’t seem like they needed a lot of information at that point.
I was finally able to talk to the man’s wife who was clearly terrified. I gave her a hug and told her he would be all right. She thanked us.
The emergency team didn’t seem to have anything to help staunch the bleeding either because the rolling gurney left puddles of blood all down the gangway, causing a significant biohazard problem.
They let one person leave who had a connecting flight, but everyone else had to get off from the rear of the plane and walk across the tarmac.
When we finally got back to our seats, the stewardess was still sitting with our kids. They were both totally chill, watching some show, apparently very well behaved. Our daughter asked us what was going on, and I said: “Oh, somebody got hurt at the front of the plane.” She’s so used to hearing that we work with sick people that it didn’t faze her at all.
As we left, we got a lot of thank-yous from people who had been sitting up front and saw what happened.
When we got home, there was still blood on my shoes. I remember looking at them and thinking: Disinfect or throw away? I disinfected them. They were still a good pair of shoes.
A few days later, we got an email from the airline with a voucher, expressing their gratitude for our help. That was nice and unexpected.
I responded with a suggestion: How about having some protocols for medical events on airplanes? Pilots go through checklists for almost everything they do. Why wouldn’t they have something like that for medical responses?
I also asked how the man and his wife were doing. But they couldn’t disclose that information.
It was certainly strange being out of my element, helping a patient in that tiny little space; I’m used to working in a recovery room where you have literally everything you need within arm’s reach — the Ambu bag, suction, and bandages. And with airway management, there’s usually more than one person in the room to assist. If there’s a problem, a whole bunch of people show up around the bed so fast.
I’m definitely thinking about field medicine a lot more. Wondering what I would do in certain situations. While debriefing with my mom (an advanced registered nurse practitioner), she pointed out that we should have asked passengers for sanitary pads or diapers to stabilize the bleeding instead of the cocktail napkins. Brilliant idea! I didn’t think of it in the moment. But I’m keeping that little tip tucked in my back pocket for any future bleeding-in-the-wild scenarios.
Audra Podruzny, MSN, RN, CPAN, lives in Washington state and is currently attending the Washington State University Doctor of Nursing Practice Family Nurse Practitioner program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How Drones Are Reducing Emergency Response Times
The drones are coming.
Starting in September, if someone in Clemmons, North Carolina, calls 911 to report a cardiac arrest, the first responder on the scene may be a drone carrying an automated external defibrillator, or AED.
“The idea is for the drone to get there several minutes before first responders,” such as an emergency medical technician or an ambulance, said Daniel Crews, a spokesperson for the sheriff’s office in Forsyth County, where Clemmons is located. The sheriff’s office is partnering on the project with local emergency services, the Clinical Research Institute at Duke University, and the drone consulting firm Hovecon. “The ultimate goal is to save lives and improve life expectancy for someone experiencing a cardiac episode,” Mr. Crews said.
The Forsyth County program is one of a growing number of efforts by public safety and healthcare organizations across the country to use drones to speed up lifesaving treatment in situations in which every second counts.
More than 356,000 people have a cardiac arrest outside of a hospital setting every year in the United States, according to the American Heart Association. Most people are at home when it happens, and about 90% die because they don’t get immediate help from first responders or bystanders. Every minute that passes without medical intervention decreases the odds of survival by 10%.
“We’ve never been able to move the needle for cardiac arrest in private settings, and this technology could meet that need,” said Monique Anderson Starks, MD, a cardiologist and associate professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Starks is leading pilot studies in Forsyth County and James City County, Virginia, to test whether drone AED delivery can improve treatment response times. The work is funded by a 4-year grant from the American Heart Association.
Dr. Starks said she believes the drone-delivered AEDs in the pilot study could reduce the time to treatment by 4 minutes compared with first responders.
Unlike a heart attack, which occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, a cardiac arrest happens when a heart malfunction causes it to stop beating, typically because of an arrhythmia or an electrical problem. Eighty percent of cardiac arrests start as heart attacks. The only way to get the heart restarted is with CPR and a defibrillator.
In Forsyth County, a drone pilot from the sheriff’s department will listen in on 911 calls. If there’s a suspected cardiac arrest, the pilot can dispatch the drone even before emergency medical services are contacted. The drone, which weighs 22 pounds and can travel 60 mph, will fly to the location and hover 125 feet in the air before lowering an AED to the ground on a winch. The AED provides simple verbal instructions; the 911 dispatcher on the phone can also help a bystander use the AED.
Eventually there will be six drone bases in Forsyth and James City counties, Dr. Starks said.
While the technology is promising and research has often found that drones arrive faster than first responders, there’s little conclusive evidence that drones improve health outcomes.
A Swedish study published in The Lancet in 2023 compared the response times between drones and ambulances for suspected cardiac arrest in 58 deployments in an area of about 200,000 people. It found that drones beat the ambulance to the scene two thirds of the time, by a median of 3 minutes and 14 seconds.
In the United States, most programs are just getting started, and they are exploring the use of drones to also provide remedies for drug overdoses and major trauma or potential drowning rescues.
In Florida, Tampa General Hospital, Manatee County, and Archer First Response Systems, or AFRS, began a program in May to deliver AEDs, a tourniquet, and Narcan, a nasal spray that can reverse an opioid overdose. The program initially covers a 7-square-mile area, and EMS dispatchers deploy the drones, which are monitored by drone pilots.
There were nearly 108,000 drug overdose deaths in the United States in 2022, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
As of early July, the Tampa program hadn’t yet deployed any drones, said Gordon Folkes, the founder and chief executive of AFRS, which develops and deploys emergency drone logistics systems. One request in June to send a drone to an overdose couldn’t be fulfilled because of a violent thunderstorm, Mr. Folkes said. In the testing area, which covers about 7,000 residents, Mr. Folkes estimates that 10-15 drones might be deployed each year.
“The bread and butter for these systems is suburban areas” like Manatee County that are well-populated and where the drones have the advantage of being able to avoid traffic congestion, Mr. Folkes said.
There are other uses for drones in medical emergencies. The New York Police Department plans to drop emergency flotation devices to struggling swimmers at local beaches. In Chula Vista, California, a police drone was able to pinpoint the location of a burning car, and then officers pulled the driver out, said Sgt. Tony Molina.
Rescue personnel have used drones to locate people who wander away from nursing homes, said James Augustine, a spokesperson for the American College of Emergency Physicians who is the medical director for the International Association of Fire Chiefs.
In the United States, one hurdle for drone programs is that the Federal Aviation Administration typically requires that drones be operated within the operators’ visual line of sight. In May, when Congress passed the FAA reauthorization bill, it gave the FAA 4 months to issue a notice of proposed rule-making on drone operations beyond the visual line of sight.
“The FAA is focused on developing standard rules to make [Beyond Visual Line of Sight] operations routine, scalable, and economically viable,” said Rick Breitenfeldt, an FAA spokesperson.
Some civil liberties groups are concerned that the FAA’s new rules may not provide enough protection from drone cameras for people on the ground.
Jay Stanley, a senior policy analyst at the American Civil Liberties Union, acknowledged the benefits of using drones in emergency situations but said there are issues that need to be addressed.
“The concern is that the FAA is going to significantly loosen the reins of drones without any significant privacy protections,” he said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF — the independent source for health policy research, polling, and journalism.
The drones are coming.
Starting in September, if someone in Clemmons, North Carolina, calls 911 to report a cardiac arrest, the first responder on the scene may be a drone carrying an automated external defibrillator, or AED.
“The idea is for the drone to get there several minutes before first responders,” such as an emergency medical technician or an ambulance, said Daniel Crews, a spokesperson for the sheriff’s office in Forsyth County, where Clemmons is located. The sheriff’s office is partnering on the project with local emergency services, the Clinical Research Institute at Duke University, and the drone consulting firm Hovecon. “The ultimate goal is to save lives and improve life expectancy for someone experiencing a cardiac episode,” Mr. Crews said.
The Forsyth County program is one of a growing number of efforts by public safety and healthcare organizations across the country to use drones to speed up lifesaving treatment in situations in which every second counts.
More than 356,000 people have a cardiac arrest outside of a hospital setting every year in the United States, according to the American Heart Association. Most people are at home when it happens, and about 90% die because they don’t get immediate help from first responders or bystanders. Every minute that passes without medical intervention decreases the odds of survival by 10%.
“We’ve never been able to move the needle for cardiac arrest in private settings, and this technology could meet that need,” said Monique Anderson Starks, MD, a cardiologist and associate professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Starks is leading pilot studies in Forsyth County and James City County, Virginia, to test whether drone AED delivery can improve treatment response times. The work is funded by a 4-year grant from the American Heart Association.
Dr. Starks said she believes the drone-delivered AEDs in the pilot study could reduce the time to treatment by 4 minutes compared with first responders.
Unlike a heart attack, which occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, a cardiac arrest happens when a heart malfunction causes it to stop beating, typically because of an arrhythmia or an electrical problem. Eighty percent of cardiac arrests start as heart attacks. The only way to get the heart restarted is with CPR and a defibrillator.
In Forsyth County, a drone pilot from the sheriff’s department will listen in on 911 calls. If there’s a suspected cardiac arrest, the pilot can dispatch the drone even before emergency medical services are contacted. The drone, which weighs 22 pounds and can travel 60 mph, will fly to the location and hover 125 feet in the air before lowering an AED to the ground on a winch. The AED provides simple verbal instructions; the 911 dispatcher on the phone can also help a bystander use the AED.
Eventually there will be six drone bases in Forsyth and James City counties, Dr. Starks said.
While the technology is promising and research has often found that drones arrive faster than first responders, there’s little conclusive evidence that drones improve health outcomes.
A Swedish study published in The Lancet in 2023 compared the response times between drones and ambulances for suspected cardiac arrest in 58 deployments in an area of about 200,000 people. It found that drones beat the ambulance to the scene two thirds of the time, by a median of 3 minutes and 14 seconds.
In the United States, most programs are just getting started, and they are exploring the use of drones to also provide remedies for drug overdoses and major trauma or potential drowning rescues.
In Florida, Tampa General Hospital, Manatee County, and Archer First Response Systems, or AFRS, began a program in May to deliver AEDs, a tourniquet, and Narcan, a nasal spray that can reverse an opioid overdose. The program initially covers a 7-square-mile area, and EMS dispatchers deploy the drones, which are monitored by drone pilots.
There were nearly 108,000 drug overdose deaths in the United States in 2022, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
As of early July, the Tampa program hadn’t yet deployed any drones, said Gordon Folkes, the founder and chief executive of AFRS, which develops and deploys emergency drone logistics systems. One request in June to send a drone to an overdose couldn’t be fulfilled because of a violent thunderstorm, Mr. Folkes said. In the testing area, which covers about 7,000 residents, Mr. Folkes estimates that 10-15 drones might be deployed each year.
“The bread and butter for these systems is suburban areas” like Manatee County that are well-populated and where the drones have the advantage of being able to avoid traffic congestion, Mr. Folkes said.
There are other uses for drones in medical emergencies. The New York Police Department plans to drop emergency flotation devices to struggling swimmers at local beaches. In Chula Vista, California, a police drone was able to pinpoint the location of a burning car, and then officers pulled the driver out, said Sgt. Tony Molina.
Rescue personnel have used drones to locate people who wander away from nursing homes, said James Augustine, a spokesperson for the American College of Emergency Physicians who is the medical director for the International Association of Fire Chiefs.
In the United States, one hurdle for drone programs is that the Federal Aviation Administration typically requires that drones be operated within the operators’ visual line of sight. In May, when Congress passed the FAA reauthorization bill, it gave the FAA 4 months to issue a notice of proposed rule-making on drone operations beyond the visual line of sight.
“The FAA is focused on developing standard rules to make [Beyond Visual Line of Sight] operations routine, scalable, and economically viable,” said Rick Breitenfeldt, an FAA spokesperson.
Some civil liberties groups are concerned that the FAA’s new rules may not provide enough protection from drone cameras for people on the ground.
Jay Stanley, a senior policy analyst at the American Civil Liberties Union, acknowledged the benefits of using drones in emergency situations but said there are issues that need to be addressed.
“The concern is that the FAA is going to significantly loosen the reins of drones without any significant privacy protections,” he said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF — the independent source for health policy research, polling, and journalism.
The drones are coming.
Starting in September, if someone in Clemmons, North Carolina, calls 911 to report a cardiac arrest, the first responder on the scene may be a drone carrying an automated external defibrillator, or AED.
“The idea is for the drone to get there several minutes before first responders,” such as an emergency medical technician or an ambulance, said Daniel Crews, a spokesperson for the sheriff’s office in Forsyth County, where Clemmons is located. The sheriff’s office is partnering on the project with local emergency services, the Clinical Research Institute at Duke University, and the drone consulting firm Hovecon. “The ultimate goal is to save lives and improve life expectancy for someone experiencing a cardiac episode,” Mr. Crews said.
The Forsyth County program is one of a growing number of efforts by public safety and healthcare organizations across the country to use drones to speed up lifesaving treatment in situations in which every second counts.
More than 356,000 people have a cardiac arrest outside of a hospital setting every year in the United States, according to the American Heart Association. Most people are at home when it happens, and about 90% die because they don’t get immediate help from first responders or bystanders. Every minute that passes without medical intervention decreases the odds of survival by 10%.
“We’ve never been able to move the needle for cardiac arrest in private settings, and this technology could meet that need,” said Monique Anderson Starks, MD, a cardiologist and associate professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Starks is leading pilot studies in Forsyth County and James City County, Virginia, to test whether drone AED delivery can improve treatment response times. The work is funded by a 4-year grant from the American Heart Association.
Dr. Starks said she believes the drone-delivered AEDs in the pilot study could reduce the time to treatment by 4 minutes compared with first responders.
Unlike a heart attack, which occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, a cardiac arrest happens when a heart malfunction causes it to stop beating, typically because of an arrhythmia or an electrical problem. Eighty percent of cardiac arrests start as heart attacks. The only way to get the heart restarted is with CPR and a defibrillator.
In Forsyth County, a drone pilot from the sheriff’s department will listen in on 911 calls. If there’s a suspected cardiac arrest, the pilot can dispatch the drone even before emergency medical services are contacted. The drone, which weighs 22 pounds and can travel 60 mph, will fly to the location and hover 125 feet in the air before lowering an AED to the ground on a winch. The AED provides simple verbal instructions; the 911 dispatcher on the phone can also help a bystander use the AED.
Eventually there will be six drone bases in Forsyth and James City counties, Dr. Starks said.
While the technology is promising and research has often found that drones arrive faster than first responders, there’s little conclusive evidence that drones improve health outcomes.
A Swedish study published in The Lancet in 2023 compared the response times between drones and ambulances for suspected cardiac arrest in 58 deployments in an area of about 200,000 people. It found that drones beat the ambulance to the scene two thirds of the time, by a median of 3 minutes and 14 seconds.
In the United States, most programs are just getting started, and they are exploring the use of drones to also provide remedies for drug overdoses and major trauma or potential drowning rescues.
In Florida, Tampa General Hospital, Manatee County, and Archer First Response Systems, or AFRS, began a program in May to deliver AEDs, a tourniquet, and Narcan, a nasal spray that can reverse an opioid overdose. The program initially covers a 7-square-mile area, and EMS dispatchers deploy the drones, which are monitored by drone pilots.
There were nearly 108,000 drug overdose deaths in the United States in 2022, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
As of early July, the Tampa program hadn’t yet deployed any drones, said Gordon Folkes, the founder and chief executive of AFRS, which develops and deploys emergency drone logistics systems. One request in June to send a drone to an overdose couldn’t be fulfilled because of a violent thunderstorm, Mr. Folkes said. In the testing area, which covers about 7,000 residents, Mr. Folkes estimates that 10-15 drones might be deployed each year.
“The bread and butter for these systems is suburban areas” like Manatee County that are well-populated and where the drones have the advantage of being able to avoid traffic congestion, Mr. Folkes said.
There are other uses for drones in medical emergencies. The New York Police Department plans to drop emergency flotation devices to struggling swimmers at local beaches. In Chula Vista, California, a police drone was able to pinpoint the location of a burning car, and then officers pulled the driver out, said Sgt. Tony Molina.
Rescue personnel have used drones to locate people who wander away from nursing homes, said James Augustine, a spokesperson for the American College of Emergency Physicians who is the medical director for the International Association of Fire Chiefs.
In the United States, one hurdle for drone programs is that the Federal Aviation Administration typically requires that drones be operated within the operators’ visual line of sight. In May, when Congress passed the FAA reauthorization bill, it gave the FAA 4 months to issue a notice of proposed rule-making on drone operations beyond the visual line of sight.
“The FAA is focused on developing standard rules to make [Beyond Visual Line of Sight] operations routine, scalable, and economically viable,” said Rick Breitenfeldt, an FAA spokesperson.
Some civil liberties groups are concerned that the FAA’s new rules may not provide enough protection from drone cameras for people on the ground.
Jay Stanley, a senior policy analyst at the American Civil Liberties Union, acknowledged the benefits of using drones in emergency situations but said there are issues that need to be addressed.
“The concern is that the FAA is going to significantly loosen the reins of drones without any significant privacy protections,” he said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF — the independent source for health policy research, polling, and journalism.
US 911 System Is Nearing Its Own Emergency
Just after lunchtime on June 18, Massachusetts’ leaders discovered that the statewide 911 system was down.
A scramble to handle the crisis was on.
Police texted out administrative numbers that callers could use, Boston Mayor Michelle Wu gave outage updates at a press conference outlining plans for the Celtics’ championship parade, and local officials urged people to summon help by pulling red fire alarm boxes.
About 7 million people went roughly 2 hours with no 911 service. Such crashes have become more of a feature than a bug in the nation’s fragmented emergency response system.
While some states, cities, and counties have already modernized their systems or have made plans to upgrade, many others are lagging.
911 is typically supported by fees tacked on to phone bills, but state and local governments also tap general funds or other resources.
“Now there are haves and have-nots,” said Jonathan Gilad, vice president of government affairs at the National Emergency Number Association (NENA), which represents 911 first responders. “Next-generation 911 shouldn’t be for people who happen to have an emergency in a good location.”
Meanwhile, federal legislation that could steer billions of dollars into modernizing the patchwork 911 system remains waylaid in Congress.
“This is a national security imperative,” said George Kelemen, executive director of the Industry Council for Emergency Response Technologies, a trade association that represents companies that provide hardware and software to the emergency response industry.
“In a crisis — a school shooting or a house fire or, God forbid, a terrorist attack — people call 911 first,” he said. “The system can’t go down.”
The United States debuted a single, universal 911 emergency number in February 1968 to simplify crisis response. But instead of a seamless national program, the 911 response network has evolved into a massive puzzle of many interlocking pieces. There are more than 6,000 911 call centers to handle an estimated 240 million emergency calls each year, according to federal data. More than three-quarters of call centers experienced outages in the prior 12 months, according to a survey in February by NENA, which sets standards and advocates for 911, and Carbyne, a provider of public safety technology solutions.
In April, widespread 911 outages affected millions in Nebraska, Nevada, South Dakota, and Texas. The shutdown was blamed on workers’ severing a fiber line while installing a light pole.
In February, tens of thousands of people in areas of California, Georgia, Illinois, Texas, and other states lost cellphone service, including some 911 services, from an outage.
And in June, Verizon agreed to pay a $1.05 million fine to settle a Federal Communications Commission (FCC) probe into a December 2022 outage that affected 911 calls in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Tennessee.
The fires that raced across the Hawaiian island of Maui in August 2023 highlighted the critical importance of 911 systems. Dispatchers there fielded more than 4,500 contacts, meaning calls and texts, on Aug. 8, the day the fires broke out, compared with about 400 on a typical day, said Davlynn Racadio, emergency services dispatch coordinator in Maui County.
“We’re dying out here,” one caller told 911 operators.
But some cell towers faltered because of widespread service outages, according to county officials. Maui County in May filed a lawsuit against four telecommunications companies, saying they failed to inform dispatchers about the outages.
“If 911 calls came in with no voice, we would send text messages,” Ms. Racadio said. “The state is looking at upgrading our system. Next-generation 911 would take us even further into the future.”
Florida, Illinois, Montana, and Oklahoma passed legislation in 2023 to advance or fund modernized 911 systems, according to the National Conference of State Legislatures. The upgrades include replacing analog 911 infrastructure with digital, Internet-based systems.
Instead of just fielding calls, next-generation systems can pinpoint a caller’s location, accept texts, and enable residents in a crisis to send videos and images to dispatchers. While outages can still occur, modernized systems often include more redundancy to minimize the odds of a shutdown, Mr. Gilad said.
Lawmakers have looked at modernizing 911 systems by tapping revenue the FCC gets from auctioning off the rights to transmit signals over specific bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
But the U.S. Senate, in March 2023, for the first time allowed a lapse of the FCC’s authority to auction spectrum bands.
Legislation that would allocate almost $15 billion in grants from auction proceeds to speed deployment of next-generation 911 in every state unanimously passed the House Energy and Commerce Committee in May 2023. The bill, HR 3565, sponsored by Rep. Cathy McMorris Rodgers (R-Wash.), would also extend the FCC’s auction authority.
Other bills have been introduced by various lawmakers, including one in March from Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas) and legislation from Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-Wash.) to extend the auction authority. For now, neither effort has advanced. Nine former FCC chairs wrote lawmakers in February, urging them to make 911 upgrades a national priority. They suggested Congress tap unspent federal COVID-19 money.
“Whatever the funding source, the need is urgent and the time to act is now,” they wrote.
Ajit Pai, who served as chair of the FCC from 2017 to 2021, said outages often occur in older, legacy systems.
“The fact that the FCC doesn’t have authority to auction spectrum is a real hindrance now,” Mr. Pai said in an interview. “You may never need to call 911, but it can make the difference between life and death. We need more of an organized effort at the federal level because 911 is so decentralized.”
Meanwhile, some safety leaders are making backup plans for 911 outages or conducting investigations into their causes. In Massachusetts, a firewall designed to prevent hacking led to the recent 2-hour outage, according to the state 911 department.
“Outages bring to everyone’s attention that we rely on 911 and we don’t think about how we really rely on it until something happens,” said April Heinze, chief of 911 operations at NENA.
Mass General Brigham, a health system in the Boston area, sent out emergency alerts when the outage happened letting clinics and smaller practices know how to find their 10-digit emergency numbers. In the wake of the outage, it plans to keep the backup numbers next to phones at those facilities.
“Two hours can be a long time,” said Paul Biddinger, chief preparedness and continuity officer at the health system.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Just after lunchtime on June 18, Massachusetts’ leaders discovered that the statewide 911 system was down.
A scramble to handle the crisis was on.
Police texted out administrative numbers that callers could use, Boston Mayor Michelle Wu gave outage updates at a press conference outlining plans for the Celtics’ championship parade, and local officials urged people to summon help by pulling red fire alarm boxes.
About 7 million people went roughly 2 hours with no 911 service. Such crashes have become more of a feature than a bug in the nation’s fragmented emergency response system.
While some states, cities, and counties have already modernized their systems or have made plans to upgrade, many others are lagging.
911 is typically supported by fees tacked on to phone bills, but state and local governments also tap general funds or other resources.
“Now there are haves and have-nots,” said Jonathan Gilad, vice president of government affairs at the National Emergency Number Association (NENA), which represents 911 first responders. “Next-generation 911 shouldn’t be for people who happen to have an emergency in a good location.”
Meanwhile, federal legislation that could steer billions of dollars into modernizing the patchwork 911 system remains waylaid in Congress.
“This is a national security imperative,” said George Kelemen, executive director of the Industry Council for Emergency Response Technologies, a trade association that represents companies that provide hardware and software to the emergency response industry.
“In a crisis — a school shooting or a house fire or, God forbid, a terrorist attack — people call 911 first,” he said. “The system can’t go down.”
The United States debuted a single, universal 911 emergency number in February 1968 to simplify crisis response. But instead of a seamless national program, the 911 response network has evolved into a massive puzzle of many interlocking pieces. There are more than 6,000 911 call centers to handle an estimated 240 million emergency calls each year, according to federal data. More than three-quarters of call centers experienced outages in the prior 12 months, according to a survey in February by NENA, which sets standards and advocates for 911, and Carbyne, a provider of public safety technology solutions.
In April, widespread 911 outages affected millions in Nebraska, Nevada, South Dakota, and Texas. The shutdown was blamed on workers’ severing a fiber line while installing a light pole.
In February, tens of thousands of people in areas of California, Georgia, Illinois, Texas, and other states lost cellphone service, including some 911 services, from an outage.
And in June, Verizon agreed to pay a $1.05 million fine to settle a Federal Communications Commission (FCC) probe into a December 2022 outage that affected 911 calls in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Tennessee.
The fires that raced across the Hawaiian island of Maui in August 2023 highlighted the critical importance of 911 systems. Dispatchers there fielded more than 4,500 contacts, meaning calls and texts, on Aug. 8, the day the fires broke out, compared with about 400 on a typical day, said Davlynn Racadio, emergency services dispatch coordinator in Maui County.
“We’re dying out here,” one caller told 911 operators.
But some cell towers faltered because of widespread service outages, according to county officials. Maui County in May filed a lawsuit against four telecommunications companies, saying they failed to inform dispatchers about the outages.
“If 911 calls came in with no voice, we would send text messages,” Ms. Racadio said. “The state is looking at upgrading our system. Next-generation 911 would take us even further into the future.”
Florida, Illinois, Montana, and Oklahoma passed legislation in 2023 to advance or fund modernized 911 systems, according to the National Conference of State Legislatures. The upgrades include replacing analog 911 infrastructure with digital, Internet-based systems.
Instead of just fielding calls, next-generation systems can pinpoint a caller’s location, accept texts, and enable residents in a crisis to send videos and images to dispatchers. While outages can still occur, modernized systems often include more redundancy to minimize the odds of a shutdown, Mr. Gilad said.
Lawmakers have looked at modernizing 911 systems by tapping revenue the FCC gets from auctioning off the rights to transmit signals over specific bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
But the U.S. Senate, in March 2023, for the first time allowed a lapse of the FCC’s authority to auction spectrum bands.
Legislation that would allocate almost $15 billion in grants from auction proceeds to speed deployment of next-generation 911 in every state unanimously passed the House Energy and Commerce Committee in May 2023. The bill, HR 3565, sponsored by Rep. Cathy McMorris Rodgers (R-Wash.), would also extend the FCC’s auction authority.
Other bills have been introduced by various lawmakers, including one in March from Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas) and legislation from Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-Wash.) to extend the auction authority. For now, neither effort has advanced. Nine former FCC chairs wrote lawmakers in February, urging them to make 911 upgrades a national priority. They suggested Congress tap unspent federal COVID-19 money.
“Whatever the funding source, the need is urgent and the time to act is now,” they wrote.
Ajit Pai, who served as chair of the FCC from 2017 to 2021, said outages often occur in older, legacy systems.
“The fact that the FCC doesn’t have authority to auction spectrum is a real hindrance now,” Mr. Pai said in an interview. “You may never need to call 911, but it can make the difference between life and death. We need more of an organized effort at the federal level because 911 is so decentralized.”
Meanwhile, some safety leaders are making backup plans for 911 outages or conducting investigations into their causes. In Massachusetts, a firewall designed to prevent hacking led to the recent 2-hour outage, according to the state 911 department.
“Outages bring to everyone’s attention that we rely on 911 and we don’t think about how we really rely on it until something happens,” said April Heinze, chief of 911 operations at NENA.
Mass General Brigham, a health system in the Boston area, sent out emergency alerts when the outage happened letting clinics and smaller practices know how to find their 10-digit emergency numbers. In the wake of the outage, it plans to keep the backup numbers next to phones at those facilities.
“Two hours can be a long time,” said Paul Biddinger, chief preparedness and continuity officer at the health system.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Just after lunchtime on June 18, Massachusetts’ leaders discovered that the statewide 911 system was down.
A scramble to handle the crisis was on.
Police texted out administrative numbers that callers could use, Boston Mayor Michelle Wu gave outage updates at a press conference outlining plans for the Celtics’ championship parade, and local officials urged people to summon help by pulling red fire alarm boxes.
About 7 million people went roughly 2 hours with no 911 service. Such crashes have become more of a feature than a bug in the nation’s fragmented emergency response system.
While some states, cities, and counties have already modernized their systems or have made plans to upgrade, many others are lagging.
911 is typically supported by fees tacked on to phone bills, but state and local governments also tap general funds or other resources.
“Now there are haves and have-nots,” said Jonathan Gilad, vice president of government affairs at the National Emergency Number Association (NENA), which represents 911 first responders. “Next-generation 911 shouldn’t be for people who happen to have an emergency in a good location.”
Meanwhile, federal legislation that could steer billions of dollars into modernizing the patchwork 911 system remains waylaid in Congress.
“This is a national security imperative,” said George Kelemen, executive director of the Industry Council for Emergency Response Technologies, a trade association that represents companies that provide hardware and software to the emergency response industry.
“In a crisis — a school shooting or a house fire or, God forbid, a terrorist attack — people call 911 first,” he said. “The system can’t go down.”
The United States debuted a single, universal 911 emergency number in February 1968 to simplify crisis response. But instead of a seamless national program, the 911 response network has evolved into a massive puzzle of many interlocking pieces. There are more than 6,000 911 call centers to handle an estimated 240 million emergency calls each year, according to federal data. More than three-quarters of call centers experienced outages in the prior 12 months, according to a survey in February by NENA, which sets standards and advocates for 911, and Carbyne, a provider of public safety technology solutions.
In April, widespread 911 outages affected millions in Nebraska, Nevada, South Dakota, and Texas. The shutdown was blamed on workers’ severing a fiber line while installing a light pole.
In February, tens of thousands of people in areas of California, Georgia, Illinois, Texas, and other states lost cellphone service, including some 911 services, from an outage.
And in June, Verizon agreed to pay a $1.05 million fine to settle a Federal Communications Commission (FCC) probe into a December 2022 outage that affected 911 calls in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Tennessee.
The fires that raced across the Hawaiian island of Maui in August 2023 highlighted the critical importance of 911 systems. Dispatchers there fielded more than 4,500 contacts, meaning calls and texts, on Aug. 8, the day the fires broke out, compared with about 400 on a typical day, said Davlynn Racadio, emergency services dispatch coordinator in Maui County.
“We’re dying out here,” one caller told 911 operators.
But some cell towers faltered because of widespread service outages, according to county officials. Maui County in May filed a lawsuit against four telecommunications companies, saying they failed to inform dispatchers about the outages.
“If 911 calls came in with no voice, we would send text messages,” Ms. Racadio said. “The state is looking at upgrading our system. Next-generation 911 would take us even further into the future.”
Florida, Illinois, Montana, and Oklahoma passed legislation in 2023 to advance or fund modernized 911 systems, according to the National Conference of State Legislatures. The upgrades include replacing analog 911 infrastructure with digital, Internet-based systems.
Instead of just fielding calls, next-generation systems can pinpoint a caller’s location, accept texts, and enable residents in a crisis to send videos and images to dispatchers. While outages can still occur, modernized systems often include more redundancy to minimize the odds of a shutdown, Mr. Gilad said.
Lawmakers have looked at modernizing 911 systems by tapping revenue the FCC gets from auctioning off the rights to transmit signals over specific bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
But the U.S. Senate, in March 2023, for the first time allowed a lapse of the FCC’s authority to auction spectrum bands.
Legislation that would allocate almost $15 billion in grants from auction proceeds to speed deployment of next-generation 911 in every state unanimously passed the House Energy and Commerce Committee in May 2023. The bill, HR 3565, sponsored by Rep. Cathy McMorris Rodgers (R-Wash.), would also extend the FCC’s auction authority.
Other bills have been introduced by various lawmakers, including one in March from Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas) and legislation from Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-Wash.) to extend the auction authority. For now, neither effort has advanced. Nine former FCC chairs wrote lawmakers in February, urging them to make 911 upgrades a national priority. They suggested Congress tap unspent federal COVID-19 money.
“Whatever the funding source, the need is urgent and the time to act is now,” they wrote.
Ajit Pai, who served as chair of the FCC from 2017 to 2021, said outages often occur in older, legacy systems.
“The fact that the FCC doesn’t have authority to auction spectrum is a real hindrance now,” Mr. Pai said in an interview. “You may never need to call 911, but it can make the difference between life and death. We need more of an organized effort at the federal level because 911 is so decentralized.”
Meanwhile, some safety leaders are making backup plans for 911 outages or conducting investigations into their causes. In Massachusetts, a firewall designed to prevent hacking led to the recent 2-hour outage, according to the state 911 department.
“Outages bring to everyone’s attention that we rely on 911 and we don’t think about how we really rely on it until something happens,” said April Heinze, chief of 911 operations at NENA.
Mass General Brigham, a health system in the Boston area, sent out emergency alerts when the outage happened letting clinics and smaller practices know how to find their 10-digit emergency numbers. In the wake of the outage, it plans to keep the backup numbers next to phones at those facilities.
“Two hours can be a long time,” said Paul Biddinger, chief preparedness and continuity officer at the health system.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
‘Just Be Prepared’: MD Finds Overdose Victim in an Alley
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime, and sometimes, medical professionals find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. Is There a Doctor in the House? is a Medscape Medical News series telling these stories.
I had worked a normal 7:00 a.m. to 3:00 p.m. shift in our emergency department. It was a nice day out, so I put my headphones in and started walking home through the Capitol Hill neighborhood in Denver. I passed a couple of buildings and reached an alleyway. At that moment, I glanced over.
Two guys were standing over a third person who was down on the ground. One of the people standing was on the phone. I paused for a second and thought, that doesn’t look right.
The guy on the ground was clearly out. And the other two were looking concerned like they didn’t know what to do.
I walked up the alley and asked, “What’s going on? Can I help?” One of the guys explained that they had just found this man lying here and had already called 911. They sounded a little bit out of their element. They certainly weren’t medically trained.
I leaned down next to the man on the ground. He was probably in his mid-to-late 40s. Unconscious. I always start with, “Hello? Can you hear me?” No response.
I felt for a pulse and he had one, but he didn’t appear to be breathing. I thought, I know what this is. I said, “Sir, I’m going to open your eyes.” I opened his eyes, and his pupils were tiny. It was almost certainly an opioid overdose.
And I had naloxone in my bag.
I got it out and started to assemble it. I didn’t have Narcan, which is the easy one. I had to put this kit together, draw up the medication, and put on the little nasal atomizer.
The two other guys were standing there watching. Then the one on the phone walked down to the end of the alley to where the ambulance was probably going to arrive so he could wave them down.
I gave the man the 4 mg of naloxone, two in each nostril.
He still wasn’t breathing. I did a basic maneuver where you lift his jaw a little bit to help open up the airway.
Suddenly, he started breathing again. I couldn’t do any meaningful measurements of his oxygen saturation or anything like that. I just kind of looked at him and thought, Okay, he has a pulse. He’s breathing now. That’s good.
Luckily, the cavalry arrived soon after that. Our Denver Health paramedics pulled up into the alley, and one of them recognized me from the ER. I explained that I had already given the guy naloxone. They did their assessment, and he still wasn’t breathing well, so they gave him some breaths with a mask and a bag.
We got him onto the gurney and into the back of the ambulance. They started an IV. He seemed to be breathing okay by then, and his numbers looked okay. But he wasn’t awake yet by any means.
I handed off care to them and disposed of my sharp in the ambulance. Then they took him into the ER that I had just left moments ago.
The two other guys had already disappeared. I think they saw the ambulance and thought, our job is done. So, I didn’t end up talking to them at all.
So, just like that ... I started walking home again.
I like to think of myself as a cool, calm, collected person working in the ER. But my heart was definitely going fast at that point. I called my wife to tell her about the crazy thing that just happened, and she could hear in my voice how amped up I was.
In the ER, it’s very common to see patients who need naloxone, have opioid toxicity, or have received Narcan in the community. Luckily, this man was found right away. He had likely overdosed only a few minutes earlier. Those scenarios can go bad very quickly. If there’s no one there, people often die.
That’s why I started carrying naloxone.
Now, I encourage all my friends to have some, and I suggest all medical professionals to keep some with them. Just be prepared. Put it in your backpack, your purse, keep it in the house, in the car, wherever. The nasal autoinjectors are incredibly easy. Like, stick it up the nose, push the big red button. Done.
When we train lay people to administer Narcan, we try to keep it simple. If you see someone, and they’re not responsive, not breathing, just give it. It’s not that there’s no possible harm if you’re wrong. But the benefits so vastly outweigh the risks that we are very aggressive to say, go ahead and give it.
I think we all have a responsibility to care for our communities. Obviously, that can take a lot of different forms. I had the privilege of being in the right place at the right time with the right tool to potentially save a life. That was the form it took for me that day.
Later, I followed up with a friend who took care of the man in the ER. He went through our standard procedure, being monitored to make sure the opioids didn’t outlast the naloxone. We have a lot of resources and next steps for people that have opioid use disorder. He was made aware of those. And then he walked out. I never saw him again.
It’s not the sexy part of our job in emergency medicine, not the super high–intensity adrenaline rush–type work, but a lot of what we do is talk to people like this guy. We counsel them. We think about their longer-term health and not just the overdose. This is an incredibly high-risk population in terms of their mortality risk from the opioid use disorder. It’s astronomical.
I obviously believed in this work before, but that day changed something for me. It added a layer of urgency. Now, when I have a moment in the emergency room to connect with someone, I know the reality — this person sitting in front of me could die in an alley. Maybe not today, but next week or next month.
I have the naloxone in my bag. Just in case.
Patrick Joynt, MD, is an emergency medicine physician with Denver Health in Denver.
Are you a medical professional with a dramatic story outside the clinic? Medscape Medical News would love to consider your story for Is There a Doctor in the House? Please email your contact information and a short summary to [email protected].
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime, and sometimes, medical professionals find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. Is There a Doctor in the House? is a Medscape Medical News series telling these stories.
I had worked a normal 7:00 a.m. to 3:00 p.m. shift in our emergency department. It was a nice day out, so I put my headphones in and started walking home through the Capitol Hill neighborhood in Denver. I passed a couple of buildings and reached an alleyway. At that moment, I glanced over.
Two guys were standing over a third person who was down on the ground. One of the people standing was on the phone. I paused for a second and thought, that doesn’t look right.
The guy on the ground was clearly out. And the other two were looking concerned like they didn’t know what to do.
I walked up the alley and asked, “What’s going on? Can I help?” One of the guys explained that they had just found this man lying here and had already called 911. They sounded a little bit out of their element. They certainly weren’t medically trained.
I leaned down next to the man on the ground. He was probably in his mid-to-late 40s. Unconscious. I always start with, “Hello? Can you hear me?” No response.
I felt for a pulse and he had one, but he didn’t appear to be breathing. I thought, I know what this is. I said, “Sir, I’m going to open your eyes.” I opened his eyes, and his pupils were tiny. It was almost certainly an opioid overdose.
And I had naloxone in my bag.
I got it out and started to assemble it. I didn’t have Narcan, which is the easy one. I had to put this kit together, draw up the medication, and put on the little nasal atomizer.
The two other guys were standing there watching. Then the one on the phone walked down to the end of the alley to where the ambulance was probably going to arrive so he could wave them down.
I gave the man the 4 mg of naloxone, two in each nostril.
He still wasn’t breathing. I did a basic maneuver where you lift his jaw a little bit to help open up the airway.
Suddenly, he started breathing again. I couldn’t do any meaningful measurements of his oxygen saturation or anything like that. I just kind of looked at him and thought, Okay, he has a pulse. He’s breathing now. That’s good.
Luckily, the cavalry arrived soon after that. Our Denver Health paramedics pulled up into the alley, and one of them recognized me from the ER. I explained that I had already given the guy naloxone. They did their assessment, and he still wasn’t breathing well, so they gave him some breaths with a mask and a bag.
We got him onto the gurney and into the back of the ambulance. They started an IV. He seemed to be breathing okay by then, and his numbers looked okay. But he wasn’t awake yet by any means.
I handed off care to them and disposed of my sharp in the ambulance. Then they took him into the ER that I had just left moments ago.
The two other guys had already disappeared. I think they saw the ambulance and thought, our job is done. So, I didn’t end up talking to them at all.
So, just like that ... I started walking home again.
I like to think of myself as a cool, calm, collected person working in the ER. But my heart was definitely going fast at that point. I called my wife to tell her about the crazy thing that just happened, and she could hear in my voice how amped up I was.
In the ER, it’s very common to see patients who need naloxone, have opioid toxicity, or have received Narcan in the community. Luckily, this man was found right away. He had likely overdosed only a few minutes earlier. Those scenarios can go bad very quickly. If there’s no one there, people often die.
That’s why I started carrying naloxone.
Now, I encourage all my friends to have some, and I suggest all medical professionals to keep some with them. Just be prepared. Put it in your backpack, your purse, keep it in the house, in the car, wherever. The nasal autoinjectors are incredibly easy. Like, stick it up the nose, push the big red button. Done.
When we train lay people to administer Narcan, we try to keep it simple. If you see someone, and they’re not responsive, not breathing, just give it. It’s not that there’s no possible harm if you’re wrong. But the benefits so vastly outweigh the risks that we are very aggressive to say, go ahead and give it.
I think we all have a responsibility to care for our communities. Obviously, that can take a lot of different forms. I had the privilege of being in the right place at the right time with the right tool to potentially save a life. That was the form it took for me that day.
Later, I followed up with a friend who took care of the man in the ER. He went through our standard procedure, being monitored to make sure the opioids didn’t outlast the naloxone. We have a lot of resources and next steps for people that have opioid use disorder. He was made aware of those. And then he walked out. I never saw him again.
It’s not the sexy part of our job in emergency medicine, not the super high–intensity adrenaline rush–type work, but a lot of what we do is talk to people like this guy. We counsel them. We think about their longer-term health and not just the overdose. This is an incredibly high-risk population in terms of their mortality risk from the opioid use disorder. It’s astronomical.
I obviously believed in this work before, but that day changed something for me. It added a layer of urgency. Now, when I have a moment in the emergency room to connect with someone, I know the reality — this person sitting in front of me could die in an alley. Maybe not today, but next week or next month.
I have the naloxone in my bag. Just in case.
Patrick Joynt, MD, is an emergency medicine physician with Denver Health in Denver.
Are you a medical professional with a dramatic story outside the clinic? Medscape Medical News would love to consider your story for Is There a Doctor in the House? Please email your contact information and a short summary to [email protected].
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime, and sometimes, medical professionals find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. Is There a Doctor in the House? is a Medscape Medical News series telling these stories.
I had worked a normal 7:00 a.m. to 3:00 p.m. shift in our emergency department. It was a nice day out, so I put my headphones in and started walking home through the Capitol Hill neighborhood in Denver. I passed a couple of buildings and reached an alleyway. At that moment, I glanced over.
Two guys were standing over a third person who was down on the ground. One of the people standing was on the phone. I paused for a second and thought, that doesn’t look right.
The guy on the ground was clearly out. And the other two were looking concerned like they didn’t know what to do.
I walked up the alley and asked, “What’s going on? Can I help?” One of the guys explained that they had just found this man lying here and had already called 911. They sounded a little bit out of their element. They certainly weren’t medically trained.
I leaned down next to the man on the ground. He was probably in his mid-to-late 40s. Unconscious. I always start with, “Hello? Can you hear me?” No response.
I felt for a pulse and he had one, but he didn’t appear to be breathing. I thought, I know what this is. I said, “Sir, I’m going to open your eyes.” I opened his eyes, and his pupils were tiny. It was almost certainly an opioid overdose.
And I had naloxone in my bag.
I got it out and started to assemble it. I didn’t have Narcan, which is the easy one. I had to put this kit together, draw up the medication, and put on the little nasal atomizer.
The two other guys were standing there watching. Then the one on the phone walked down to the end of the alley to where the ambulance was probably going to arrive so he could wave them down.
I gave the man the 4 mg of naloxone, two in each nostril.
He still wasn’t breathing. I did a basic maneuver where you lift his jaw a little bit to help open up the airway.
Suddenly, he started breathing again. I couldn’t do any meaningful measurements of his oxygen saturation or anything like that. I just kind of looked at him and thought, Okay, he has a pulse. He’s breathing now. That’s good.
Luckily, the cavalry arrived soon after that. Our Denver Health paramedics pulled up into the alley, and one of them recognized me from the ER. I explained that I had already given the guy naloxone. They did their assessment, and he still wasn’t breathing well, so they gave him some breaths with a mask and a bag.
We got him onto the gurney and into the back of the ambulance. They started an IV. He seemed to be breathing okay by then, and his numbers looked okay. But he wasn’t awake yet by any means.
I handed off care to them and disposed of my sharp in the ambulance. Then they took him into the ER that I had just left moments ago.
The two other guys had already disappeared. I think they saw the ambulance and thought, our job is done. So, I didn’t end up talking to them at all.
So, just like that ... I started walking home again.
I like to think of myself as a cool, calm, collected person working in the ER. But my heart was definitely going fast at that point. I called my wife to tell her about the crazy thing that just happened, and she could hear in my voice how amped up I was.
In the ER, it’s very common to see patients who need naloxone, have opioid toxicity, or have received Narcan in the community. Luckily, this man was found right away. He had likely overdosed only a few minutes earlier. Those scenarios can go bad very quickly. If there’s no one there, people often die.
That’s why I started carrying naloxone.
Now, I encourage all my friends to have some, and I suggest all medical professionals to keep some with them. Just be prepared. Put it in your backpack, your purse, keep it in the house, in the car, wherever. The nasal autoinjectors are incredibly easy. Like, stick it up the nose, push the big red button. Done.
When we train lay people to administer Narcan, we try to keep it simple. If you see someone, and they’re not responsive, not breathing, just give it. It’s not that there’s no possible harm if you’re wrong. But the benefits so vastly outweigh the risks that we are very aggressive to say, go ahead and give it.
I think we all have a responsibility to care for our communities. Obviously, that can take a lot of different forms. I had the privilege of being in the right place at the right time with the right tool to potentially save a life. That was the form it took for me that day.
Later, I followed up with a friend who took care of the man in the ER. He went through our standard procedure, being monitored to make sure the opioids didn’t outlast the naloxone. We have a lot of resources and next steps for people that have opioid use disorder. He was made aware of those. And then he walked out. I never saw him again.
It’s not the sexy part of our job in emergency medicine, not the super high–intensity adrenaline rush–type work, but a lot of what we do is talk to people like this guy. We counsel them. We think about their longer-term health and not just the overdose. This is an incredibly high-risk population in terms of their mortality risk from the opioid use disorder. It’s astronomical.
I obviously believed in this work before, but that day changed something for me. It added a layer of urgency. Now, when I have a moment in the emergency room to connect with someone, I know the reality — this person sitting in front of me could die in an alley. Maybe not today, but next week or next month.
I have the naloxone in my bag. Just in case.
Patrick Joynt, MD, is an emergency medicine physician with Denver Health in Denver.
Are you a medical professional with a dramatic story outside the clinic? Medscape Medical News would love to consider your story for Is There a Doctor in the House? Please email your contact information and a short summary to [email protected].
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
New Blood Test for Large Vessel Stroke Could Be a ‘Game Changer’
When combined with clinical scores, a “game-changing” blood test can expedite the diagnosis and treatment of large vessel occlusion (LVO) stroke, potentially saving many lives, new data suggested.
Using cutoff levels of two blood biomarkers, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; 213 pg/mL) and D-dimer (600 ng/mL), and the field assessment stroke triage for emergency destination (FAST-ED) (score, > 2), investigators were able to detect LVOs with 81% sensitivity and 93% specificity less than 6 hours from the onset of symptoms.
GFAP has previously been linked to brain bleeds and traumatic brain injury.
The test also ruled out all patients with brain bleeds, and investigators noted that it could also be used to detect intracerebral hemorrhage.
“We have developed a game-changing, accessible tool that could help ensure that more people suffering from stroke are in the right place at the right time to receive critical, life-restoring care,” senior author Joshua Bernstock, MD, PhD, MPH, a clinical fellow in the department of neurosurgery at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in a press release.
The findings were published online on May 17 in Stroke: Vascular and Interventional Neurology.
Early Identification Crucial
Acute LVO stroke is one of the most treatable stroke types because of the availability of endovascular thrombectomy (EVT). However, EVT requires specialized equipment and teams that represent a small subset of accredited stroke centers and an even smaller subset of emergency medical facilities, so early identification of LVO is crucial, the investigators noted.
Dr. Bernstock and his team developed the TIME trial to assess the sensitivity and specificity of the blood biomarkers and scale cutoff values for identifying LVO vs non-LVO stroke.
As part of the observational prospective cohort trial, investigators included consecutive patients admitted to the Brandon Regional Hospital Emergency Department in Brandon, Florida, between May 2021 and August 2022 if they were referred for a suspected stroke and the time from symptom onset was under 18 hours.
Patients were excluded if they received thrombolytic therapy before blood was collected or if it was anticipated that blood collection would be difficult.
Investigators gathered information on patients’ clinical data, hematology results, time since last known well, and imaging findings to construct a clinical diagnosis (LVO, non-LVO, ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, or transient ischemic attack [TIA]).
In addition to the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, patients were assessed with the FAST-ED, the Rapid Arterial oCclusion Evaluation (RACE), the Cincinnati Stroke Triage Assessment Tool, and the Emergency Medical Stroke Assessment.
Of 323 patients in the final study sample, 29 (9%) had LVO ischemic stroke, and 48 (15%) had non-LVO ischemic stroke. Another 13 (4%) had hemorrhagic stroke, 12 had TIA (3.7%), and the largest proportion of patients had stroke mimic (n = 220; 68%), which included encephalopathy, hyperglycemia, hypertensive emergency, migraine, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, and undetermined.
The Case for Biomarkers
When investigators looked at those with LVO ischemic stroke, they found the concentration of plasma D-dimer was significantly higher than that in patients with non-LVO suspected stroke (LVO suspected stroke, 1213 ng/mL; interquartile range [IQR], 733-1609 vs non-LVO suspected stroke, 617 ng/mL; IQR, 377-1345; P < .001).
In addition, GFAP was significantly increased in the plasma of patients with hemorrhagic stroke vs all other patients with suspected stroke (hemorrhagic stroke, 1464 pg/mL; IQR, 292-2580 vs nonhemorrhagic suspected stroke, 48 pg/mL; IQR, 12-98; P < .005).
Combinations of the blood biomarkers with the scales FAST-ED or RACE showed the best performance for LVO detection, with a specificity of 94% (for either scale combination) and a sensitivity of 71% for both scales.
When investigators analyzed data for just those patients identified within 6 hours of symptom onset, the combination of biomarkers plus FAST-ED resulted in a specificity of 93% and a sensitivity of 81%.
Given that clinical stroke scales in patients with hemorrhagic stroke frequently suggest LVO and that these patients are not candidates for EVT, a tool capable of ruling out hemorrhage and identifying only nonhemorrhagic ischemic LVO is essential, the investigators noted.
“In stroke care, time is brain,” Dr. Bernstock said. “The sooner a patient is put on the right care pathway, the better they are going to do. Whether that means ruling out bleeds or ruling in something that needs an intervention, being able to do this in a prehospital setting with the technology that we built is going to be truly transformative.”
The study was funded by the Innovate UK grant and private funding. Dr. Bernstock has positions and equity in Pockit Diagnostics Ltd. and Treovir Inc. and is on the boards of Centile Bio and NeuroX1. Other disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When combined with clinical scores, a “game-changing” blood test can expedite the diagnosis and treatment of large vessel occlusion (LVO) stroke, potentially saving many lives, new data suggested.
Using cutoff levels of two blood biomarkers, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; 213 pg/mL) and D-dimer (600 ng/mL), and the field assessment stroke triage for emergency destination (FAST-ED) (score, > 2), investigators were able to detect LVOs with 81% sensitivity and 93% specificity less than 6 hours from the onset of symptoms.
GFAP has previously been linked to brain bleeds and traumatic brain injury.
The test also ruled out all patients with brain bleeds, and investigators noted that it could also be used to detect intracerebral hemorrhage.
“We have developed a game-changing, accessible tool that could help ensure that more people suffering from stroke are in the right place at the right time to receive critical, life-restoring care,” senior author Joshua Bernstock, MD, PhD, MPH, a clinical fellow in the department of neurosurgery at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in a press release.
The findings were published online on May 17 in Stroke: Vascular and Interventional Neurology.
Early Identification Crucial
Acute LVO stroke is one of the most treatable stroke types because of the availability of endovascular thrombectomy (EVT). However, EVT requires specialized equipment and teams that represent a small subset of accredited stroke centers and an even smaller subset of emergency medical facilities, so early identification of LVO is crucial, the investigators noted.
Dr. Bernstock and his team developed the TIME trial to assess the sensitivity and specificity of the blood biomarkers and scale cutoff values for identifying LVO vs non-LVO stroke.
As part of the observational prospective cohort trial, investigators included consecutive patients admitted to the Brandon Regional Hospital Emergency Department in Brandon, Florida, between May 2021 and August 2022 if they were referred for a suspected stroke and the time from symptom onset was under 18 hours.
Patients were excluded if they received thrombolytic therapy before blood was collected or if it was anticipated that blood collection would be difficult.
Investigators gathered information on patients’ clinical data, hematology results, time since last known well, and imaging findings to construct a clinical diagnosis (LVO, non-LVO, ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, or transient ischemic attack [TIA]).
In addition to the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, patients were assessed with the FAST-ED, the Rapid Arterial oCclusion Evaluation (RACE), the Cincinnati Stroke Triage Assessment Tool, and the Emergency Medical Stroke Assessment.
Of 323 patients in the final study sample, 29 (9%) had LVO ischemic stroke, and 48 (15%) had non-LVO ischemic stroke. Another 13 (4%) had hemorrhagic stroke, 12 had TIA (3.7%), and the largest proportion of patients had stroke mimic (n = 220; 68%), which included encephalopathy, hyperglycemia, hypertensive emergency, migraine, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, and undetermined.
The Case for Biomarkers
When investigators looked at those with LVO ischemic stroke, they found the concentration of plasma D-dimer was significantly higher than that in patients with non-LVO suspected stroke (LVO suspected stroke, 1213 ng/mL; interquartile range [IQR], 733-1609 vs non-LVO suspected stroke, 617 ng/mL; IQR, 377-1345; P < .001).
In addition, GFAP was significantly increased in the plasma of patients with hemorrhagic stroke vs all other patients with suspected stroke (hemorrhagic stroke, 1464 pg/mL; IQR, 292-2580 vs nonhemorrhagic suspected stroke, 48 pg/mL; IQR, 12-98; P < .005).
Combinations of the blood biomarkers with the scales FAST-ED or RACE showed the best performance for LVO detection, with a specificity of 94% (for either scale combination) and a sensitivity of 71% for both scales.
When investigators analyzed data for just those patients identified within 6 hours of symptom onset, the combination of biomarkers plus FAST-ED resulted in a specificity of 93% and a sensitivity of 81%.
Given that clinical stroke scales in patients with hemorrhagic stroke frequently suggest LVO and that these patients are not candidates for EVT, a tool capable of ruling out hemorrhage and identifying only nonhemorrhagic ischemic LVO is essential, the investigators noted.
“In stroke care, time is brain,” Dr. Bernstock said. “The sooner a patient is put on the right care pathway, the better they are going to do. Whether that means ruling out bleeds or ruling in something that needs an intervention, being able to do this in a prehospital setting with the technology that we built is going to be truly transformative.”
The study was funded by the Innovate UK grant and private funding. Dr. Bernstock has positions and equity in Pockit Diagnostics Ltd. and Treovir Inc. and is on the boards of Centile Bio and NeuroX1. Other disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When combined with clinical scores, a “game-changing” blood test can expedite the diagnosis and treatment of large vessel occlusion (LVO) stroke, potentially saving many lives, new data suggested.
Using cutoff levels of two blood biomarkers, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; 213 pg/mL) and D-dimer (600 ng/mL), and the field assessment stroke triage for emergency destination (FAST-ED) (score, > 2), investigators were able to detect LVOs with 81% sensitivity and 93% specificity less than 6 hours from the onset of symptoms.
GFAP has previously been linked to brain bleeds and traumatic brain injury.
The test also ruled out all patients with brain bleeds, and investigators noted that it could also be used to detect intracerebral hemorrhage.
“We have developed a game-changing, accessible tool that could help ensure that more people suffering from stroke are in the right place at the right time to receive critical, life-restoring care,” senior author Joshua Bernstock, MD, PhD, MPH, a clinical fellow in the department of neurosurgery at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in a press release.
The findings were published online on May 17 in Stroke: Vascular and Interventional Neurology.
Early Identification Crucial
Acute LVO stroke is one of the most treatable stroke types because of the availability of endovascular thrombectomy (EVT). However, EVT requires specialized equipment and teams that represent a small subset of accredited stroke centers and an even smaller subset of emergency medical facilities, so early identification of LVO is crucial, the investigators noted.
Dr. Bernstock and his team developed the TIME trial to assess the sensitivity and specificity of the blood biomarkers and scale cutoff values for identifying LVO vs non-LVO stroke.
As part of the observational prospective cohort trial, investigators included consecutive patients admitted to the Brandon Regional Hospital Emergency Department in Brandon, Florida, between May 2021 and August 2022 if they were referred for a suspected stroke and the time from symptom onset was under 18 hours.
Patients were excluded if they received thrombolytic therapy before blood was collected or if it was anticipated that blood collection would be difficult.
Investigators gathered information on patients’ clinical data, hematology results, time since last known well, and imaging findings to construct a clinical diagnosis (LVO, non-LVO, ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, or transient ischemic attack [TIA]).
In addition to the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, patients were assessed with the FAST-ED, the Rapid Arterial oCclusion Evaluation (RACE), the Cincinnati Stroke Triage Assessment Tool, and the Emergency Medical Stroke Assessment.
Of 323 patients in the final study sample, 29 (9%) had LVO ischemic stroke, and 48 (15%) had non-LVO ischemic stroke. Another 13 (4%) had hemorrhagic stroke, 12 had TIA (3.7%), and the largest proportion of patients had stroke mimic (n = 220; 68%), which included encephalopathy, hyperglycemia, hypertensive emergency, migraine, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, and undetermined.
The Case for Biomarkers
When investigators looked at those with LVO ischemic stroke, they found the concentration of plasma D-dimer was significantly higher than that in patients with non-LVO suspected stroke (LVO suspected stroke, 1213 ng/mL; interquartile range [IQR], 733-1609 vs non-LVO suspected stroke, 617 ng/mL; IQR, 377-1345; P < .001).
In addition, GFAP was significantly increased in the plasma of patients with hemorrhagic stroke vs all other patients with suspected stroke (hemorrhagic stroke, 1464 pg/mL; IQR, 292-2580 vs nonhemorrhagic suspected stroke, 48 pg/mL; IQR, 12-98; P < .005).
Combinations of the blood biomarkers with the scales FAST-ED or RACE showed the best performance for LVO detection, with a specificity of 94% (for either scale combination) and a sensitivity of 71% for both scales.
When investigators analyzed data for just those patients identified within 6 hours of symptom onset, the combination of biomarkers plus FAST-ED resulted in a specificity of 93% and a sensitivity of 81%.
Given that clinical stroke scales in patients with hemorrhagic stroke frequently suggest LVO and that these patients are not candidates for EVT, a tool capable of ruling out hemorrhage and identifying only nonhemorrhagic ischemic LVO is essential, the investigators noted.
“In stroke care, time is brain,” Dr. Bernstock said. “The sooner a patient is put on the right care pathway, the better they are going to do. Whether that means ruling out bleeds or ruling in something that needs an intervention, being able to do this in a prehospital setting with the technology that we built is going to be truly transformative.”
The study was funded by the Innovate UK grant and private funding. Dr. Bernstock has positions and equity in Pockit Diagnostics Ltd. and Treovir Inc. and is on the boards of Centile Bio and NeuroX1. Other disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM STROKE: VASCULAR AND INTERVENTIONAL NEUROLOGY
In the Future, a Robot Intensivist May Save Your Life
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
They call it the “golden hour”: 60 minutes, give or take, when the chance to save the life of a trauma victim is at its greatest. If the patient can be resuscitated and stabilized in that time window, they stand a good chance of surviving. If not, well, they don’t.
But resuscitation is complicated. It requires blood products, fluids, vasopressors — all given in precise doses in response to rapidly changing hemodynamics. To do it right takes specialized training, advanced life support (ALS). If the patient is in a remote area or an area without ALS-certified emergency medical services, or is far from the nearest trauma center, that golden hour is lost. And the patient may be as well.
But we live in the future. We have robots in factories, self-driving cars, autonomous drones. Why not an autonomous trauma doctor? If you are in a life-threatening accident, would you want to be treated ... by a robot?
Enter “resuscitation based on functional hemodynamic monitoring,” or “ReFit,” introduced in this article appearing in the journal Intensive Care Medicine Experimental.
The idea behind ReFit is straightforward. Resuscitation after trauma should be based on hitting key hemodynamic targets using the tools we have available in the field: blood, fluids, pressors. The researchers wanted to develop a closed-loop system, something that could be used by minimally trained personnel. The input to the system? Hemodynamic data, provided through a single measurement device, an arterial catheter. The output: blood, fluids, and pressors, delivered intravenously.
The body (a prototype) of the system looks like this. You can see various pumps labeled with various fluids, electronic controllers, and so forth.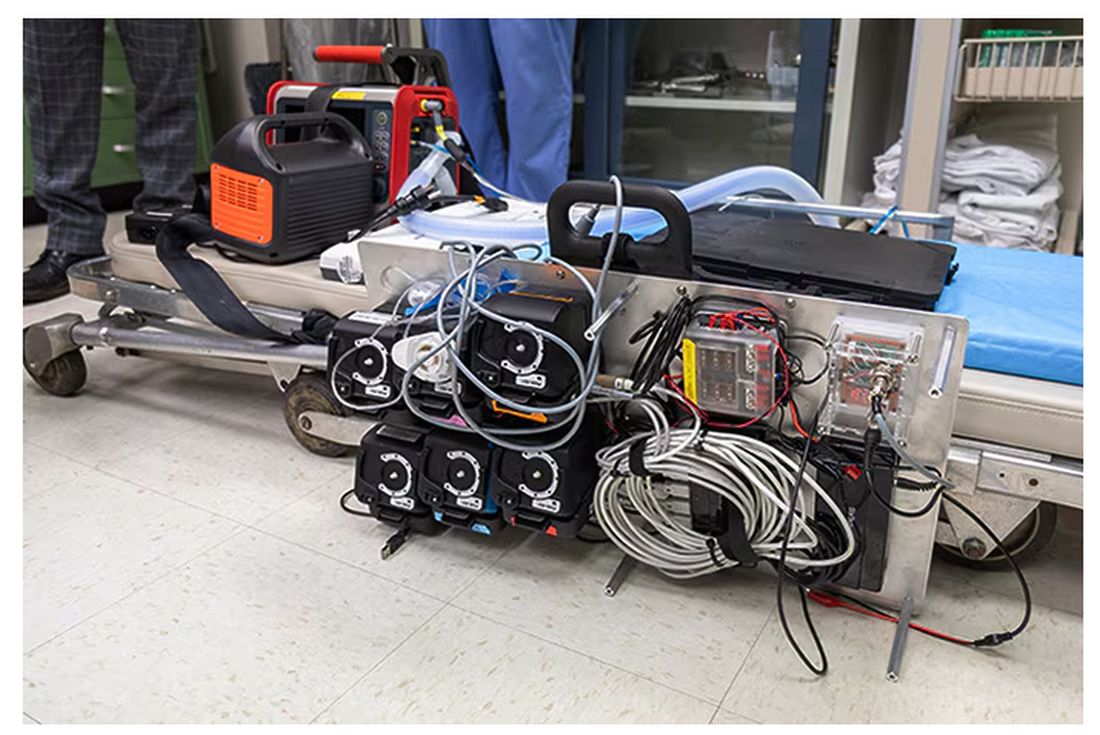
If that’s the body, then this is the brain – a ruggedized laptop interpreting a readout of that arterial catheter.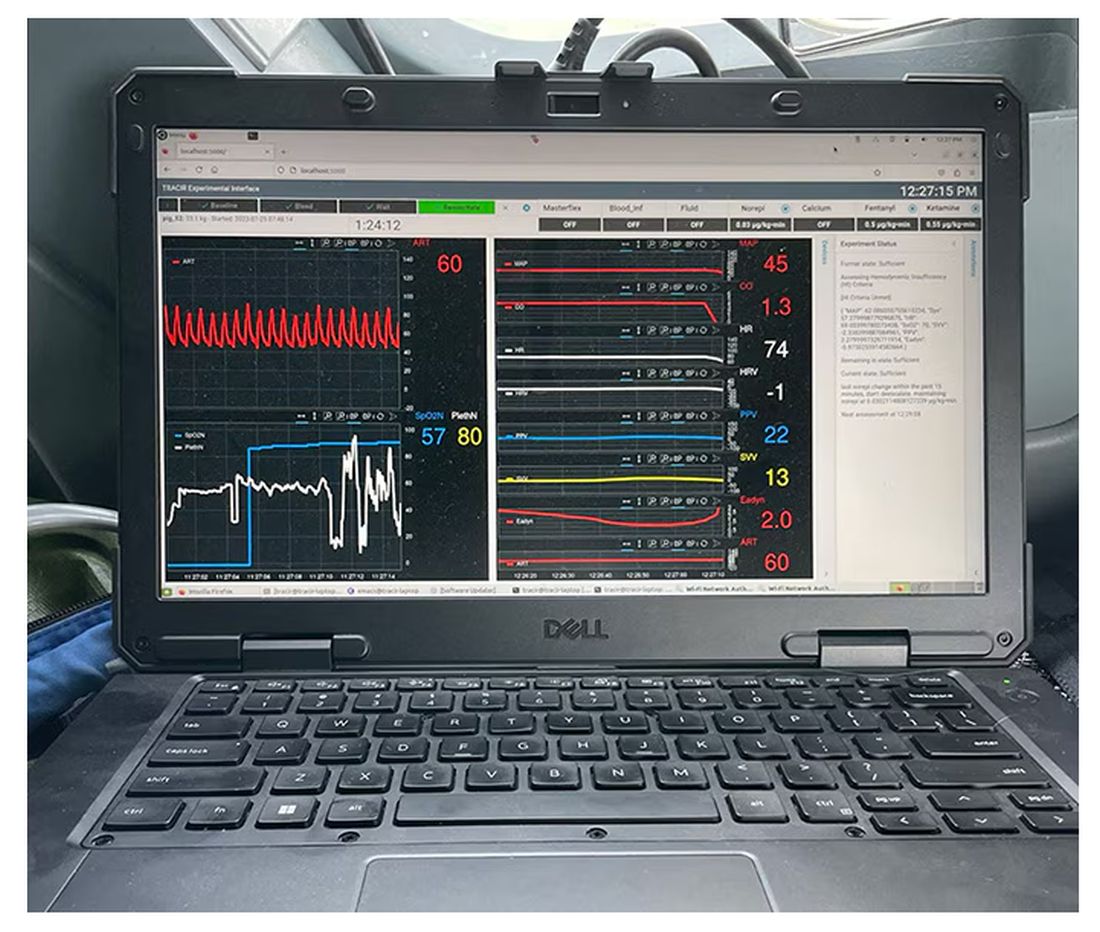
If that’s the brain, then the ReFit algorithm is the mind. The algorithm does its best to leverage all the data it can, so I want to walk through it in a bit of detail.
First, check to see whether the patient is stable, defined as a heart rate < 110 beats/min and a mean arterial pressure > 60 mm Hg. If not, you’re off to the races, starting with a bolus of whole blood.
Next, the algorithm gets really interesting. If the patient is still unstable, the computer assesses fluid responsiveness by giving a test dose of fluid and measuring the pulse pressure variation. Greater pulse pressure variation means more fluid responsiveness and the algorithm gives more fluid. Less pulse pressure variation leads the algorithm to uptitrate pressors — in this case, norepinephrine.
This cycle of evaluation and response keeps repeating. The computer titrates fluids and pressors up and down entirely on its own, in theory freeing the human team members to do other things, like getting the patient to a trauma center for definitive care.
So, how do you test whether something like this works? Clearly, you don’t want the trial run of a system like this to be used on a real human suffering from a real traumatic injury.
Once again, we have animals to thank for research advances — in this case, pigs. Fifteen pigs are described in the study. To simulate a severe, hemorrhagic trauma, they were anesthetized and the liver was lacerated. They were then observed passively until the mean arterial pressure had dropped to below 40 mm Hg.
This is a pretty severe injury. Three unfortunate animals served as controls, two of which died within the 3-hour time window of the study. Eight animals were plugged into the ReFit system.
For a window into what happens during this process, let’s take a look at the mean arterial pressure and heart rate readouts for one of the animals. You see that the blood pressure starts to fall precipitously after the liver laceration. The heart rate quickly picks up to compensate, raising the mean arterial pressure a bit, but this would be unsustainable with ongoing bleeding.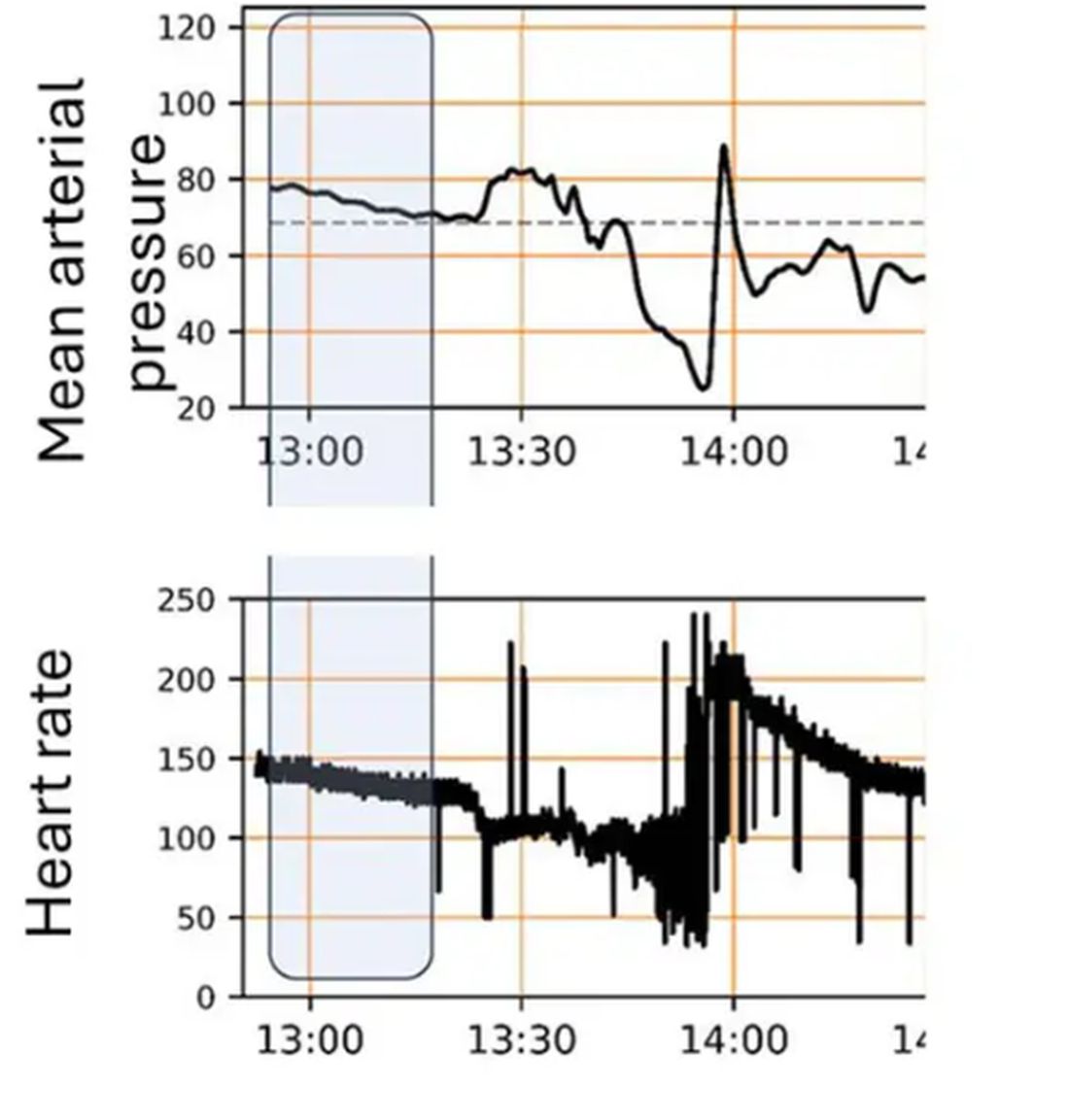
Here, the ReFit system takes over. Autonomously, the system administers two units of blood, followed by fluids, and then norepinephrine or further fluids per the protocol I described earlier. 
The practical upshot of all of this is stabilization, despite an as-yet untreated liver laceration.
Could an experienced ALS provider do this? Of course. But, as I mentioned before, you aren’t always near an experienced ALS provider.
This is all well and good in the lab, but in the real world, you actually need to transport a trauma patient. The researchers tried this also. To prove feasibility, four pigs were taken from the lab to the top of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, flown to Allegheny County Airport and back. Total time before liver laceration repair? Three hours. And all four survived.
It won’t surprise you to hear that this work was funded by the Department of Defense. You can see how a system like this, made a bit more rugged, a bit smaller, and a bit more self-contained could have real uses in the battlefield. But trauma is not unique to war, and something that can extend the time you have to safely transport a patient to definitive care — well, that’s worth its weight in golden hours.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
They call it the “golden hour”: 60 minutes, give or take, when the chance to save the life of a trauma victim is at its greatest. If the patient can be resuscitated and stabilized in that time window, they stand a good chance of surviving. If not, well, they don’t.
But resuscitation is complicated. It requires blood products, fluids, vasopressors — all given in precise doses in response to rapidly changing hemodynamics. To do it right takes specialized training, advanced life support (ALS). If the patient is in a remote area or an area without ALS-certified emergency medical services, or is far from the nearest trauma center, that golden hour is lost. And the patient may be as well.
But we live in the future. We have robots in factories, self-driving cars, autonomous drones. Why not an autonomous trauma doctor? If you are in a life-threatening accident, would you want to be treated ... by a robot?
Enter “resuscitation based on functional hemodynamic monitoring,” or “ReFit,” introduced in this article appearing in the journal Intensive Care Medicine Experimental.
The idea behind ReFit is straightforward. Resuscitation after trauma should be based on hitting key hemodynamic targets using the tools we have available in the field: blood, fluids, pressors. The researchers wanted to develop a closed-loop system, something that could be used by minimally trained personnel. The input to the system? Hemodynamic data, provided through a single measurement device, an arterial catheter. The output: blood, fluids, and pressors, delivered intravenously.
The body (a prototype) of the system looks like this. You can see various pumps labeled with various fluids, electronic controllers, and so forth.
If that’s the body, then this is the brain – a ruggedized laptop interpreting a readout of that arterial catheter.
If that’s the brain, then the ReFit algorithm is the mind. The algorithm does its best to leverage all the data it can, so I want to walk through it in a bit of detail.
First, check to see whether the patient is stable, defined as a heart rate < 110 beats/min and a mean arterial pressure > 60 mm Hg. If not, you’re off to the races, starting with a bolus of whole blood.
Next, the algorithm gets really interesting. If the patient is still unstable, the computer assesses fluid responsiveness by giving a test dose of fluid and measuring the pulse pressure variation. Greater pulse pressure variation means more fluid responsiveness and the algorithm gives more fluid. Less pulse pressure variation leads the algorithm to uptitrate pressors — in this case, norepinephrine.
This cycle of evaluation and response keeps repeating. The computer titrates fluids and pressors up and down entirely on its own, in theory freeing the human team members to do other things, like getting the patient to a trauma center for definitive care.
So, how do you test whether something like this works? Clearly, you don’t want the trial run of a system like this to be used on a real human suffering from a real traumatic injury.
Once again, we have animals to thank for research advances — in this case, pigs. Fifteen pigs are described in the study. To simulate a severe, hemorrhagic trauma, they were anesthetized and the liver was lacerated. They were then observed passively until the mean arterial pressure had dropped to below 40 mm Hg.
This is a pretty severe injury. Three unfortunate animals served as controls, two of which died within the 3-hour time window of the study. Eight animals were plugged into the ReFit system.
For a window into what happens during this process, let’s take a look at the mean arterial pressure and heart rate readouts for one of the animals. You see that the blood pressure starts to fall precipitously after the liver laceration. The heart rate quickly picks up to compensate, raising the mean arterial pressure a bit, but this would be unsustainable with ongoing bleeding.
Here, the ReFit system takes over. Autonomously, the system administers two units of blood, followed by fluids, and then norepinephrine or further fluids per the protocol I described earlier. 
The practical upshot of all of this is stabilization, despite an as-yet untreated liver laceration.
Could an experienced ALS provider do this? Of course. But, as I mentioned before, you aren’t always near an experienced ALS provider.
This is all well and good in the lab, but in the real world, you actually need to transport a trauma patient. The researchers tried this also. To prove feasibility, four pigs were taken from the lab to the top of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, flown to Allegheny County Airport and back. Total time before liver laceration repair? Three hours. And all four survived.
It won’t surprise you to hear that this work was funded by the Department of Defense. You can see how a system like this, made a bit more rugged, a bit smaller, and a bit more self-contained could have real uses in the battlefield. But trauma is not unique to war, and something that can extend the time you have to safely transport a patient to definitive care — well, that’s worth its weight in golden hours.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
They call it the “golden hour”: 60 minutes, give or take, when the chance to save the life of a trauma victim is at its greatest. If the patient can be resuscitated and stabilized in that time window, they stand a good chance of surviving. If not, well, they don’t.
But resuscitation is complicated. It requires blood products, fluids, vasopressors — all given in precise doses in response to rapidly changing hemodynamics. To do it right takes specialized training, advanced life support (ALS). If the patient is in a remote area or an area without ALS-certified emergency medical services, or is far from the nearest trauma center, that golden hour is lost. And the patient may be as well.
But we live in the future. We have robots in factories, self-driving cars, autonomous drones. Why not an autonomous trauma doctor? If you are in a life-threatening accident, would you want to be treated ... by a robot?
Enter “resuscitation based on functional hemodynamic monitoring,” or “ReFit,” introduced in this article appearing in the journal Intensive Care Medicine Experimental.
The idea behind ReFit is straightforward. Resuscitation after trauma should be based on hitting key hemodynamic targets using the tools we have available in the field: blood, fluids, pressors. The researchers wanted to develop a closed-loop system, something that could be used by minimally trained personnel. The input to the system? Hemodynamic data, provided through a single measurement device, an arterial catheter. The output: blood, fluids, and pressors, delivered intravenously.
The body (a prototype) of the system looks like this. You can see various pumps labeled with various fluids, electronic controllers, and so forth.
If that’s the body, then this is the brain – a ruggedized laptop interpreting a readout of that arterial catheter.
If that’s the brain, then the ReFit algorithm is the mind. The algorithm does its best to leverage all the data it can, so I want to walk through it in a bit of detail.
First, check to see whether the patient is stable, defined as a heart rate < 110 beats/min and a mean arterial pressure > 60 mm Hg. If not, you’re off to the races, starting with a bolus of whole blood.
Next, the algorithm gets really interesting. If the patient is still unstable, the computer assesses fluid responsiveness by giving a test dose of fluid and measuring the pulse pressure variation. Greater pulse pressure variation means more fluid responsiveness and the algorithm gives more fluid. Less pulse pressure variation leads the algorithm to uptitrate pressors — in this case, norepinephrine.
This cycle of evaluation and response keeps repeating. The computer titrates fluids and pressors up and down entirely on its own, in theory freeing the human team members to do other things, like getting the patient to a trauma center for definitive care.
So, how do you test whether something like this works? Clearly, you don’t want the trial run of a system like this to be used on a real human suffering from a real traumatic injury.
Once again, we have animals to thank for research advances — in this case, pigs. Fifteen pigs are described in the study. To simulate a severe, hemorrhagic trauma, they were anesthetized and the liver was lacerated. They were then observed passively until the mean arterial pressure had dropped to below 40 mm Hg.
This is a pretty severe injury. Three unfortunate animals served as controls, two of which died within the 3-hour time window of the study. Eight animals were plugged into the ReFit system.
For a window into what happens during this process, let’s take a look at the mean arterial pressure and heart rate readouts for one of the animals. You see that the blood pressure starts to fall precipitously after the liver laceration. The heart rate quickly picks up to compensate, raising the mean arterial pressure a bit, but this would be unsustainable with ongoing bleeding.
Here, the ReFit system takes over. Autonomously, the system administers two units of blood, followed by fluids, and then norepinephrine or further fluids per the protocol I described earlier. 
The practical upshot of all of this is stabilization, despite an as-yet untreated liver laceration.
Could an experienced ALS provider do this? Of course. But, as I mentioned before, you aren’t always near an experienced ALS provider.
This is all well and good in the lab, but in the real world, you actually need to transport a trauma patient. The researchers tried this also. To prove feasibility, four pigs were taken from the lab to the top of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, flown to Allegheny County Airport and back. Total time before liver laceration repair? Three hours. And all four survived.
It won’t surprise you to hear that this work was funded by the Department of Defense. You can see how a system like this, made a bit more rugged, a bit smaller, and a bit more self-contained could have real uses in the battlefield. But trauma is not unique to war, and something that can extend the time you have to safely transport a patient to definitive care — well, that’s worth its weight in golden hours.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
‘No Pulse’: An MD’s First Night Off in 2 Weeks Turns Grave
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime, and sometimes, medical professionals find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. Is There a Doctor in the House? is a series by this news organization that tells these stories.
It was my first night off after 12 days. It was a Friday night, and I went to a bar in Naples to get a beer with some friends. As it turned out, it wasn’t a night off after all.
As soon as we got inside, we heard over the speaker that they needed medical personnel and to please go to the left side of the bar. I thought it would be syncope or something like that.
I went over there and saw a woman holding up a man. He was basically leaning all over her. The light was low, and the music was pounding. I started to assess him and tried to get him to answer me. No response. I checked for pulses — nothing.
The woman helped me lower him to the floor. I checked again for a pulse. Still nothing. I said, “Call 911,” and started compressions.
The difficult part was the place was completely dark. I knew where his body was on the floor. I could see his chest. But I couldn’t see his face at all.
It was also extremely loud with the music thumping. After a while, they finally shut it off.
Pretty soon, the security personnel from the bar brought me an automated external defibrillator, and it showed the man was having V-fib arrest. I shocked him. Still no pulse. I continued with cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
I hadn’t noticed, but lots of people were crowding around us. Somebody came up and said, “He’s my friend. He has a 9-year-old daughter. He can’t die. Let me help with the compressions.” I was like, “Go for it.”
The guy started kind of pushing on the man’s abdomen. He had no idea how to do compressions. I said, “Okay, let me take over again.”
Out of the crowd, nobody else volunteered to help. No one asked me, “Hey, what can I do?” Meanwhile, I found out later that someone was filming the whole thing on their phone.
But what the guy said about the man’s young daughter stayed in my brain. I thought, we need to keep going.
I did more compressions and shocked him again. Still no pulse. At that point, the police and emergency medical services showed up. They checked, nothing had changed, so they got him into the ambulance.
I asked one of the paramedics, “Where are you taking him? I can call ahead.”
But he said, “That’s HIPAA. We can’t tell you.” They also wouldn’t let me go with him in the ambulance.
“I have an active Florida license, and I work in the ICU [intensive care unit],” I said.
“No, we need to follow our protocol,” he replied.
I understood that, but I just wanted to help.
It was around 10:30 PM by then, and I was drenched in sweat. I had to go home. The first thing I did after taking a shower was open the computer and check my system. I needed to find out what happened to the guy.
I was looking for admissions, and I didn’t see him. I called the main hospital downtown and the one in North Naples. I couldn’t find him anywhere. I stayed up until almost 1:00 AM checking for his name. At that point I thought, okay, maybe he died.
The next night, Saturday, I was home and got a call from one of my colleagues. “Hey, were you in a bar yesterday? Did you do CPR on somebody?”
“How did you know?” I said.
He said the paramedics had described me — “a tall doctor with glasses who was a nice guy.” It was funny that he knew that was me.
He told me, “The guy’s alive. He’s sick and needs to be put on dialysis, but he’s alive.”
Apparently, the guy had gone to the emergency department at North Naples, and the doctors in the emergency room (ER) worked on him for over an hour. They did continuous CPR and shocked him for close to 40 minutes. They finally got his pulse back, and after that, he was transferred to the main hospital ICU. They didn’t admit him at the ER, which was why I couldn’t find his name.
On Sunday, I was checking my patients’ charts for the ICU that coming week. And there he was. I saw his name and the documentation by the ED that CPR was provided by a critical care doctor in the field. He was still alive. That gave me so much joy.
So, the man I had helped became my patient. When I saw him on Monday, he was intubated and needed dialysis. I finally saw his face and thought, Oh, so that’s what you look like. I hadn’t realized he was only 39 years old.
When he was awake, I explained to him I was the doctor that provided CPR at the bar. He was very grateful, but of course, he didn’t remember anything.
Eventually, I met his daughter, and she just said, “Thank you for allowing me to have my dad.”
The funny part is that he broke his leg. Well, that’s not funny, but no one had any idea how it happened. That was his only complaint. He was asking me, “Doctor, how did you break my leg?”
“Hey, I have no idea how you broke your leg,” I replied. “I was trying to save your life.”
He was in the hospital for almost a month but made a full recovery. The amazing part: After all the evaluations, he has no neurological deficits. He’s back to a normal life now.
They never found a cause for the cardiac arrest. I mean, he had an ejection fraction of 10%. All my money was on something drug related, but that wasn’t the case. They’d done a cardiac cut, and there was no obstruction. They couldn’t find a reason.
We’ve become friends. He still works as a DJ at the bar. He changed his name to “DJ the Survivor” or something like that.
Sometimes, he’ll text me: “Doctor, what are you doing? You want to come down to the bar?”
I’m like, “No. I don’t.”
It’s been more than a year, but I remember every detail. When you go into medicine, you dream that one day you’ll be able to say, “I saved somebody.”
He texted me a year later and told me he’s celebrating two birthdays now. He said, “I’m turning 1 year old today!”
I think about the value of life. How we can take it for granted. We think, I’m young, nothing is going to happen to me. But this guy was 39. He went to work and died that night.
I was able to help bring him back. That makes me thankful for every day.
Jose Valle Giler, MD, is a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine physician at NCH Healthcare System in Naples, Florida.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime, and sometimes, medical professionals find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. Is There a Doctor in the House? is a series by this news organization that tells these stories.
It was my first night off after 12 days. It was a Friday night, and I went to a bar in Naples to get a beer with some friends. As it turned out, it wasn’t a night off after all.
As soon as we got inside, we heard over the speaker that they needed medical personnel and to please go to the left side of the bar. I thought it would be syncope or something like that.
I went over there and saw a woman holding up a man. He was basically leaning all over her. The light was low, and the music was pounding. I started to assess him and tried to get him to answer me. No response. I checked for pulses — nothing.
The woman helped me lower him to the floor. I checked again for a pulse. Still nothing. I said, “Call 911,” and started compressions.
The difficult part was the place was completely dark. I knew where his body was on the floor. I could see his chest. But I couldn’t see his face at all.
It was also extremely loud with the music thumping. After a while, they finally shut it off.
Pretty soon, the security personnel from the bar brought me an automated external defibrillator, and it showed the man was having V-fib arrest. I shocked him. Still no pulse. I continued with cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
I hadn’t noticed, but lots of people were crowding around us. Somebody came up and said, “He’s my friend. He has a 9-year-old daughter. He can’t die. Let me help with the compressions.” I was like, “Go for it.”
The guy started kind of pushing on the man’s abdomen. He had no idea how to do compressions. I said, “Okay, let me take over again.”
Out of the crowd, nobody else volunteered to help. No one asked me, “Hey, what can I do?” Meanwhile, I found out later that someone was filming the whole thing on their phone.
But what the guy said about the man’s young daughter stayed in my brain. I thought, we need to keep going.
I did more compressions and shocked him again. Still no pulse. At that point, the police and emergency medical services showed up. They checked, nothing had changed, so they got him into the ambulance.
I asked one of the paramedics, “Where are you taking him? I can call ahead.”
But he said, “That’s HIPAA. We can’t tell you.” They also wouldn’t let me go with him in the ambulance.
“I have an active Florida license, and I work in the ICU [intensive care unit],” I said.
“No, we need to follow our protocol,” he replied.
I understood that, but I just wanted to help.
It was around 10:30 PM by then, and I was drenched in sweat. I had to go home. The first thing I did after taking a shower was open the computer and check my system. I needed to find out what happened to the guy.
I was looking for admissions, and I didn’t see him. I called the main hospital downtown and the one in North Naples. I couldn’t find him anywhere. I stayed up until almost 1:00 AM checking for his name. At that point I thought, okay, maybe he died.
The next night, Saturday, I was home and got a call from one of my colleagues. “Hey, were you in a bar yesterday? Did you do CPR on somebody?”
“How did you know?” I said.
He said the paramedics had described me — “a tall doctor with glasses who was a nice guy.” It was funny that he knew that was me.
He told me, “The guy’s alive. He’s sick and needs to be put on dialysis, but he’s alive.”
Apparently, the guy had gone to the emergency department at North Naples, and the doctors in the emergency room (ER) worked on him for over an hour. They did continuous CPR and shocked him for close to 40 minutes. They finally got his pulse back, and after that, he was transferred to the main hospital ICU. They didn’t admit him at the ER, which was why I couldn’t find his name.
On Sunday, I was checking my patients’ charts for the ICU that coming week. And there he was. I saw his name and the documentation by the ED that CPR was provided by a critical care doctor in the field. He was still alive. That gave me so much joy.
So, the man I had helped became my patient. When I saw him on Monday, he was intubated and needed dialysis. I finally saw his face and thought, Oh, so that’s what you look like. I hadn’t realized he was only 39 years old.
When he was awake, I explained to him I was the doctor that provided CPR at the bar. He was very grateful, but of course, he didn’t remember anything.
Eventually, I met his daughter, and she just said, “Thank you for allowing me to have my dad.”
The funny part is that he broke his leg. Well, that’s not funny, but no one had any idea how it happened. That was his only complaint. He was asking me, “Doctor, how did you break my leg?”
“Hey, I have no idea how you broke your leg,” I replied. “I was trying to save your life.”
He was in the hospital for almost a month but made a full recovery. The amazing part: After all the evaluations, he has no neurological deficits. He’s back to a normal life now.
They never found a cause for the cardiac arrest. I mean, he had an ejection fraction of 10%. All my money was on something drug related, but that wasn’t the case. They’d done a cardiac cut, and there was no obstruction. They couldn’t find a reason.
We’ve become friends. He still works as a DJ at the bar. He changed his name to “DJ the Survivor” or something like that.
Sometimes, he’ll text me: “Doctor, what are you doing? You want to come down to the bar?”
I’m like, “No. I don’t.”
It’s been more than a year, but I remember every detail. When you go into medicine, you dream that one day you’ll be able to say, “I saved somebody.”
He texted me a year later and told me he’s celebrating two birthdays now. He said, “I’m turning 1 year old today!”
I think about the value of life. How we can take it for granted. We think, I’m young, nothing is going to happen to me. But this guy was 39. He went to work and died that night.
I was able to help bring him back. That makes me thankful for every day.
Jose Valle Giler, MD, is a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine physician at NCH Healthcare System in Naples, Florida.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime, and sometimes, medical professionals find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. Is There a Doctor in the House? is a series by this news organization that tells these stories.
It was my first night off after 12 days. It was a Friday night, and I went to a bar in Naples to get a beer with some friends. As it turned out, it wasn’t a night off after all.
As soon as we got inside, we heard over the speaker that they needed medical personnel and to please go to the left side of the bar. I thought it would be syncope or something like that.
I went over there and saw a woman holding up a man. He was basically leaning all over her. The light was low, and the music was pounding. I started to assess him and tried to get him to answer me. No response. I checked for pulses — nothing.
The woman helped me lower him to the floor. I checked again for a pulse. Still nothing. I said, “Call 911,” and started compressions.
The difficult part was the place was completely dark. I knew where his body was on the floor. I could see his chest. But I couldn’t see his face at all.
It was also extremely loud with the music thumping. After a while, they finally shut it off.
Pretty soon, the security personnel from the bar brought me an automated external defibrillator, and it showed the man was having V-fib arrest. I shocked him. Still no pulse. I continued with cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
I hadn’t noticed, but lots of people were crowding around us. Somebody came up and said, “He’s my friend. He has a 9-year-old daughter. He can’t die. Let me help with the compressions.” I was like, “Go for it.”
The guy started kind of pushing on the man’s abdomen. He had no idea how to do compressions. I said, “Okay, let me take over again.”
Out of the crowd, nobody else volunteered to help. No one asked me, “Hey, what can I do?” Meanwhile, I found out later that someone was filming the whole thing on their phone.
But what the guy said about the man’s young daughter stayed in my brain. I thought, we need to keep going.
I did more compressions and shocked him again. Still no pulse. At that point, the police and emergency medical services showed up. They checked, nothing had changed, so they got him into the ambulance.
I asked one of the paramedics, “Where are you taking him? I can call ahead.”
But he said, “That’s HIPAA. We can’t tell you.” They also wouldn’t let me go with him in the ambulance.
“I have an active Florida license, and I work in the ICU [intensive care unit],” I said.
“No, we need to follow our protocol,” he replied.
I understood that, but I just wanted to help.
It was around 10:30 PM by then, and I was drenched in sweat. I had to go home. The first thing I did after taking a shower was open the computer and check my system. I needed to find out what happened to the guy.
I was looking for admissions, and I didn’t see him. I called the main hospital downtown and the one in North Naples. I couldn’t find him anywhere. I stayed up until almost 1:00 AM checking for his name. At that point I thought, okay, maybe he died.
The next night, Saturday, I was home and got a call from one of my colleagues. “Hey, were you in a bar yesterday? Did you do CPR on somebody?”
“How did you know?” I said.
He said the paramedics had described me — “a tall doctor with glasses who was a nice guy.” It was funny that he knew that was me.
He told me, “The guy’s alive. He’s sick and needs to be put on dialysis, but he’s alive.”
Apparently, the guy had gone to the emergency department at North Naples, and the doctors in the emergency room (ER) worked on him for over an hour. They did continuous CPR and shocked him for close to 40 minutes. They finally got his pulse back, and after that, he was transferred to the main hospital ICU. They didn’t admit him at the ER, which was why I couldn’t find his name.
On Sunday, I was checking my patients’ charts for the ICU that coming week. And there he was. I saw his name and the documentation by the ED that CPR was provided by a critical care doctor in the field. He was still alive. That gave me so much joy.
So, the man I had helped became my patient. When I saw him on Monday, he was intubated and needed dialysis. I finally saw his face and thought, Oh, so that’s what you look like. I hadn’t realized he was only 39 years old.
When he was awake, I explained to him I was the doctor that provided CPR at the bar. He was very grateful, but of course, he didn’t remember anything.
Eventually, I met his daughter, and she just said, “Thank you for allowing me to have my dad.”
The funny part is that he broke his leg. Well, that’s not funny, but no one had any idea how it happened. That was his only complaint. He was asking me, “Doctor, how did you break my leg?”
“Hey, I have no idea how you broke your leg,” I replied. “I was trying to save your life.”
He was in the hospital for almost a month but made a full recovery. The amazing part: After all the evaluations, he has no neurological deficits. He’s back to a normal life now.
They never found a cause for the cardiac arrest. I mean, he had an ejection fraction of 10%. All my money was on something drug related, but that wasn’t the case. They’d done a cardiac cut, and there was no obstruction. They couldn’t find a reason.
We’ve become friends. He still works as a DJ at the bar. He changed his name to “DJ the Survivor” or something like that.
Sometimes, he’ll text me: “Doctor, what are you doing? You want to come down to the bar?”
I’m like, “No. I don’t.”
It’s been more than a year, but I remember every detail. When you go into medicine, you dream that one day you’ll be able to say, “I saved somebody.”
He texted me a year later and told me he’s celebrating two birthdays now. He said, “I’m turning 1 year old today!”
I think about the value of life. How we can take it for granted. We think, I’m young, nothing is going to happen to me. But this guy was 39. He went to work and died that night.
I was able to help bring him back. That makes me thankful for every day.
Jose Valle Giler, MD, is a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine physician at NCH Healthcare System in Naples, Florida.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Why Everyone Needs Their Own Emergency Medicine Doctor
How emerging models come close to making this reality
As emergency medicine doctors, we regularly give medical advice to family and close friends when they get sick or are injured and don’t know what to do. In a matter of moments, we triage, diagnose, and assemble a logical plan, whatever the issue may be. This skill comes from our training and years of experience in treating emergencies and also routine medical matters. The value proposition is clear.
Frankly, it’s a service everyone should have. Think about the potential time and money saved if this option for medical care and triage was broadly available. Overtriage would plummet. That’s when people run to the emergency department (ED) and wait endless hours, only to be reassured or receive limited treatment. Undertriage would also decline. That’s when people should go to the ED but, unwisely, wait. For example, this may occur when symptoms of dizziness end up being a stroke.
Why doesn’t everyone have an ED doctor they can call? The primary reason is that the current system mostly doesn’t support it. The most common scenario is that insurance companies pay us to see patients in an expensive box called the ED. Most EDs are situated within an even more expensive box, called a hospital.
Here’s the good news: Better access to emergency care and people who are formally trained in emergency medicine and routine matters of urgent care is increasing.
One example is telemedicine, where a remote doctor — either your own or a doctor through an app — conducts a visit. Telemedicine is more common since the pandemic, now that insurance pays for it. In emergency situations, it’s rare that your own doctor can see you immediately by telemedicine. By contrast, direct-to-consumer telemedicine (eg, Teladoc, Doctor On Demand, and others) connects you with a random doctor.
In many apps, it’s unclear not only who the doctor is, but more importantly, what their specific medical specialty or training is. It may be an ED doctor evaluating your child’s fever, or it may be a retired general surgeon or an adult rheumatology specialist in the midst of their fellowship, making an extra buck, who may have no pediatric training.
Training Matters
Clinical training and whether the doctor knows you matters. A recent JAMA study from Ontario, Canada, found that patients with virtual visits who saw outside family physicians (whom they had never met) compared with their own family physicians were 66% more likely to visit an ED within 7 days after the visit. This illustrates the importance of understanding your personal history in assessing acute symptoms.
Some healthcare systems do use ED physicians for on-demand telehealth services, such as Thomas Jefferson’s JeffConnect. Amazon Clinic recently entered this space, providing condition-specific acute or chronic care to adults aged 18-64 years for a fee that is, notably, not covered by insurance.
A second innovative approach, albeit not specifically in the realm of a personal emergency medicine doctor, is artificial intelligence (AI)–powered kiosks. A concierge medicine company known as Forward recently unveiled an innovative concept known as CarePods that are now available in Sacramento, California; Chandler, Arizona; and Chicago. For a membership fee, you swipe into what looks like an oversize, space-age porta-potty. You sit in a chair and run through a series of health apps, which includes a biometric body scan along with mental health screenings. It even takes your blood (without a needle) and sequences your DNA. Results are reviewed by a doctor (not yours) who talks to you by video. They advertise that AI helps make the diagnosis. Although diagnostic AI is emerging and exciting, its benefit is not clear in emergency conditions. Yet, one clear value in a kiosk over telemedicine is the ability to obtain vital signs and lab results, which are useful for diagnosis.
Another approach is the telehealth offerings used in integrated systems of care, such as Kaiser Permanente. Kaiser is both an insurance company and a deliverer of healthcare services. Kaiser maintains a nurse call center and can handle urgent e-visits. Integrated systems not only help triage patients’ acute issues but also have access to their personal health histories. They can also provide a definitive plan for in-person treatment or a specific referral. A downside of integrated care is that it often limits your choice of provider.
Insurance companies also maintain call-in lines such as HumanaFirst, which is also staffed by nurses. We have not seen data on the calls such services receive, but we doubt people that want to call their insurance company when sick or injured, knowing that the insurer benefits when you receive less care. Additionally, studies have found that nurse-only triage is not as effective as physician triage and results in higher ED referral rates.
The Concierge Option
Probably the closest thing to having your own personal emergency medicine doctor is concierge medicine, which combines personalized care and accessibility. Concierge doctors come in many forms, but they usually charge a fixed fee for 24/7 availability and same-day appointments. A downside of concierge medicine is its expense ($2000–$3500 per year), and that many don’t take insurance. Concierge medicine is also criticized because, as doctors gravitate toward it, people in the community often lose their physician if they can’t afford the fees.
Ultimately, remote medical advice for emergency care is clearly evolving in new ways. The inability of traditional care models to achieve this goal will lead to innovation to improve the available options that have led us to think outside of the proverbial “box” we refer to as the ED-in-the-case.
At this time, will any option come close to having a personal emergency medicine physician willing to answer your questions, real-time, as with family and close friends? We think not.
But the future certainly holds promise for alternatives that will hopefully make payers and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services take notice. Innovations in personalized care that reduce costs will be critical in our current healthcare landscape.
Dr. Pines is clinical professor of emergency medicine at George Washington University in Washington, DC, and chief of clinical innovation at US Acute Care Solutions in Canton, Ohio. He disclosed ties with CSL Behring and Abbott Point-of-Care. Dr. Glatter is assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. He is a medical advisor for Medscape and hosts the Hot Topics in EM series. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How emerging models come close to making this reality
How emerging models come close to making this reality
As emergency medicine doctors, we regularly give medical advice to family and close friends when they get sick or are injured and don’t know what to do. In a matter of moments, we triage, diagnose, and assemble a logical plan, whatever the issue may be. This skill comes from our training and years of experience in treating emergencies and also routine medical matters. The value proposition is clear.
Frankly, it’s a service everyone should have. Think about the potential time and money saved if this option for medical care and triage was broadly available. Overtriage would plummet. That’s when people run to the emergency department (ED) and wait endless hours, only to be reassured or receive limited treatment. Undertriage would also decline. That’s when people should go to the ED but, unwisely, wait. For example, this may occur when symptoms of dizziness end up being a stroke.
Why doesn’t everyone have an ED doctor they can call? The primary reason is that the current system mostly doesn’t support it. The most common scenario is that insurance companies pay us to see patients in an expensive box called the ED. Most EDs are situated within an even more expensive box, called a hospital.
Here’s the good news: Better access to emergency care and people who are formally trained in emergency medicine and routine matters of urgent care is increasing.
One example is telemedicine, where a remote doctor — either your own or a doctor through an app — conducts a visit. Telemedicine is more common since the pandemic, now that insurance pays for it. In emergency situations, it’s rare that your own doctor can see you immediately by telemedicine. By contrast, direct-to-consumer telemedicine (eg, Teladoc, Doctor On Demand, and others) connects you with a random doctor.
In many apps, it’s unclear not only who the doctor is, but more importantly, what their specific medical specialty or training is. It may be an ED doctor evaluating your child’s fever, or it may be a retired general surgeon or an adult rheumatology specialist in the midst of their fellowship, making an extra buck, who may have no pediatric training.
Training Matters
Clinical training and whether the doctor knows you matters. A recent JAMA study from Ontario, Canada, found that patients with virtual visits who saw outside family physicians (whom they had never met) compared with their own family physicians were 66% more likely to visit an ED within 7 days after the visit. This illustrates the importance of understanding your personal history in assessing acute symptoms.
Some healthcare systems do use ED physicians for on-demand telehealth services, such as Thomas Jefferson’s JeffConnect. Amazon Clinic recently entered this space, providing condition-specific acute or chronic care to adults aged 18-64 years for a fee that is, notably, not covered by insurance.
A second innovative approach, albeit not specifically in the realm of a personal emergency medicine doctor, is artificial intelligence (AI)–powered kiosks. A concierge medicine company known as Forward recently unveiled an innovative concept known as CarePods that are now available in Sacramento, California; Chandler, Arizona; and Chicago. For a membership fee, you swipe into what looks like an oversize, space-age porta-potty. You sit in a chair and run through a series of health apps, which includes a biometric body scan along with mental health screenings. It even takes your blood (without a needle) and sequences your DNA. Results are reviewed by a doctor (not yours) who talks to you by video. They advertise that AI helps make the diagnosis. Although diagnostic AI is emerging and exciting, its benefit is not clear in emergency conditions. Yet, one clear value in a kiosk over telemedicine is the ability to obtain vital signs and lab results, which are useful for diagnosis.
Another approach is the telehealth offerings used in integrated systems of care, such as Kaiser Permanente. Kaiser is both an insurance company and a deliverer of healthcare services. Kaiser maintains a nurse call center and can handle urgent e-visits. Integrated systems not only help triage patients’ acute issues but also have access to their personal health histories. They can also provide a definitive plan for in-person treatment or a specific referral. A downside of integrated care is that it often limits your choice of provider.
Insurance companies also maintain call-in lines such as HumanaFirst, which is also staffed by nurses. We have not seen data on the calls such services receive, but we doubt people that want to call their insurance company when sick or injured, knowing that the insurer benefits when you receive less care. Additionally, studies have found that nurse-only triage is not as effective as physician triage and results in higher ED referral rates.
The Concierge Option
Probably the closest thing to having your own personal emergency medicine doctor is concierge medicine, which combines personalized care and accessibility. Concierge doctors come in many forms, but they usually charge a fixed fee for 24/7 availability and same-day appointments. A downside of concierge medicine is its expense ($2000–$3500 per year), and that many don’t take insurance. Concierge medicine is also criticized because, as doctors gravitate toward it, people in the community often lose their physician if they can’t afford the fees.
Ultimately, remote medical advice for emergency care is clearly evolving in new ways. The inability of traditional care models to achieve this goal will lead to innovation to improve the available options that have led us to think outside of the proverbial “box” we refer to as the ED-in-the-case.
At this time, will any option come close to having a personal emergency medicine physician willing to answer your questions, real-time, as with family and close friends? We think not.
But the future certainly holds promise for alternatives that will hopefully make payers and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services take notice. Innovations in personalized care that reduce costs will be critical in our current healthcare landscape.
Dr. Pines is clinical professor of emergency medicine at George Washington University in Washington, DC, and chief of clinical innovation at US Acute Care Solutions in Canton, Ohio. He disclosed ties with CSL Behring and Abbott Point-of-Care. Dr. Glatter is assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. He is a medical advisor for Medscape and hosts the Hot Topics in EM series. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As emergency medicine doctors, we regularly give medical advice to family and close friends when they get sick or are injured and don’t know what to do. In a matter of moments, we triage, diagnose, and assemble a logical plan, whatever the issue may be. This skill comes from our training and years of experience in treating emergencies and also routine medical matters. The value proposition is clear.
Frankly, it’s a service everyone should have. Think about the potential time and money saved if this option for medical care and triage was broadly available. Overtriage would plummet. That’s when people run to the emergency department (ED) and wait endless hours, only to be reassured or receive limited treatment. Undertriage would also decline. That’s when people should go to the ED but, unwisely, wait. For example, this may occur when symptoms of dizziness end up being a stroke.
Why doesn’t everyone have an ED doctor they can call? The primary reason is that the current system mostly doesn’t support it. The most common scenario is that insurance companies pay us to see patients in an expensive box called the ED. Most EDs are situated within an even more expensive box, called a hospital.
Here’s the good news: Better access to emergency care and people who are formally trained in emergency medicine and routine matters of urgent care is increasing.
One example is telemedicine, where a remote doctor — either your own or a doctor through an app — conducts a visit. Telemedicine is more common since the pandemic, now that insurance pays for it. In emergency situations, it’s rare that your own doctor can see you immediately by telemedicine. By contrast, direct-to-consumer telemedicine (eg, Teladoc, Doctor On Demand, and others) connects you with a random doctor.
In many apps, it’s unclear not only who the doctor is, but more importantly, what their specific medical specialty or training is. It may be an ED doctor evaluating your child’s fever, or it may be a retired general surgeon or an adult rheumatology specialist in the midst of their fellowship, making an extra buck, who may have no pediatric training.
Training Matters
Clinical training and whether the doctor knows you matters. A recent JAMA study from Ontario, Canada, found that patients with virtual visits who saw outside family physicians (whom they had never met) compared with their own family physicians were 66% more likely to visit an ED within 7 days after the visit. This illustrates the importance of understanding your personal history in assessing acute symptoms.
Some healthcare systems do use ED physicians for on-demand telehealth services, such as Thomas Jefferson’s JeffConnect. Amazon Clinic recently entered this space, providing condition-specific acute or chronic care to adults aged 18-64 years for a fee that is, notably, not covered by insurance.
A second innovative approach, albeit not specifically in the realm of a personal emergency medicine doctor, is artificial intelligence (AI)–powered kiosks. A concierge medicine company known as Forward recently unveiled an innovative concept known as CarePods that are now available in Sacramento, California; Chandler, Arizona; and Chicago. For a membership fee, you swipe into what looks like an oversize, space-age porta-potty. You sit in a chair and run through a series of health apps, which includes a biometric body scan along with mental health screenings. It even takes your blood (without a needle) and sequences your DNA. Results are reviewed by a doctor (not yours) who talks to you by video. They advertise that AI helps make the diagnosis. Although diagnostic AI is emerging and exciting, its benefit is not clear in emergency conditions. Yet, one clear value in a kiosk over telemedicine is the ability to obtain vital signs and lab results, which are useful for diagnosis.
Another approach is the telehealth offerings used in integrated systems of care, such as Kaiser Permanente. Kaiser is both an insurance company and a deliverer of healthcare services. Kaiser maintains a nurse call center and can handle urgent e-visits. Integrated systems not only help triage patients’ acute issues but also have access to their personal health histories. They can also provide a definitive plan for in-person treatment or a specific referral. A downside of integrated care is that it often limits your choice of provider.
Insurance companies also maintain call-in lines such as HumanaFirst, which is also staffed by nurses. We have not seen data on the calls such services receive, but we doubt people that want to call their insurance company when sick or injured, knowing that the insurer benefits when you receive less care. Additionally, studies have found that nurse-only triage is not as effective as physician triage and results in higher ED referral rates.
The Concierge Option
Probably the closest thing to having your own personal emergency medicine doctor is concierge medicine, which combines personalized care and accessibility. Concierge doctors come in many forms, but they usually charge a fixed fee for 24/7 availability and same-day appointments. A downside of concierge medicine is its expense ($2000–$3500 per year), and that many don’t take insurance. Concierge medicine is also criticized because, as doctors gravitate toward it, people in the community often lose their physician if they can’t afford the fees.
Ultimately, remote medical advice for emergency care is clearly evolving in new ways. The inability of traditional care models to achieve this goal will lead to innovation to improve the available options that have led us to think outside of the proverbial “box” we refer to as the ED-in-the-case.
At this time, will any option come close to having a personal emergency medicine physician willing to answer your questions, real-time, as with family and close friends? We think not.
But the future certainly holds promise for alternatives that will hopefully make payers and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services take notice. Innovations in personalized care that reduce costs will be critical in our current healthcare landscape.
Dr. Pines is clinical professor of emergency medicine at George Washington University in Washington, DC, and chief of clinical innovation at US Acute Care Solutions in Canton, Ohio. He disclosed ties with CSL Behring and Abbott Point-of-Care. Dr. Glatter is assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. He is a medical advisor for Medscape and hosts the Hot Topics in EM series. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Why is buprenorphine use flatlining?
Opioid overdose deaths are at a record high in the United States, and many of these deaths can be prevented with medications such as buprenorphine, said lead author Kao-Ping Chua, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, in an interview. “However, buprenorphine cannot prevent opioid overdose deaths if patients are never started on the medication or only stay on the medication for a short time. For that reason, rates of buprenorphine initiation and retention are critical metrics for measuring how well the U.S. health care system is responding to the opioid epidemic,” he said.
“At the time we started our study, several other research groups had evaluated U.S. rates of buprenorphine initiation and retention using data through 2020. However, more recent national data were lacking,” Dr. Chua told this news organization. “We felt that this was an important knowledge gap given the many changes in society that have occurred since 2020,” he noted. “For example, it was possible that the relaxation of social distancing measures during 2021 and 2022 might have reduced barriers to health care visits, thereby increasing opportunities to initiate treatment for opioid addiction with buprenorphine,” he said.
Dr. Chua and colleagues used data from the IQVIA Longitudinal Prescription Database, which reports 92% of prescriptions dispensed from retail pharmacies in the United States. “Buprenorphine products included immediate-release and extended-release formulations approved for opioid use disorder but not formulations primarily used to treat pain,” they write.
Monthly buprenorphine initiation was defined as the number of patients initiating therapy per 100,000 individuals. For retention, the researchers used a National Quality Forum-endorsed quality measure that defined retention as continuous use of buprenorphine for at least 180 days.
A total of 3,006,629 patients began buprenorphine therapy during the study period; approximately 43% were female.
During the first years of the study period, from January 2016 through September 2018, the monthly buprenorphine initiation rate increased from 12.5 per 100,000 to 15.9 per 100,000, with a statistically significant monthly percentage change of 0.62% (P < .001).
However, from October 2018 through October 2022, the monthly percentage remained essentially the same (P = .62) with a monthly percentage change of −0.03%.
From March 2020 through December 2020, the median monthly buprenorphine initiation rate was 14.4 per 100,000, only slightly lower than the rates from January 2019 through February 2020 and from January 2021 through October 2022 (15.5 per 100,000 and 15.0 per 100,000, respectively).
Over the entire study period from January 2016 through October 2022, the median monthly retention rate for buprenorphine use was 22.2%. This rate increased minimally, with no significant changes in slope and a monthly percentage change of 0.08% (P = .04).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including a lack of data on race and ethnicity, in-clinic administration of buprenorphine, and buprenorphine dispensing through methadone outpatient programs, the researchers note. Also, data did not indicate whether some patients began buprenorphine to treat pain, they say. The timing of the flattening of buprenorphine use also suggests the influence of factors beyond the COVID-19 pandemic, they write.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and suggest that efforts to date to increase buprenorphine use have been unsuccessful, the researchers write. “A comprehensive approach is needed to eliminate barriers to buprenorphine initiation and retention, such as stigma and uneven access to prescribers,” they conclude.
Study highlights underuse of buprenorphine option
“Our study shows that buprenorphine initiation rates have been flat since the end of 2018 and that rates of 180-day retention in buprenorphine therapy have remained low throughout 2016-2022,” Dr. Chua told this news organization. “Neither of these findings are particularly surprising, but they are disappointing,” he said. “There were a lot of policy and clinical efforts to maintain and expand access to buprenorphine during the COVID-19 pandemic, such as allowing buprenorphine to be prescribed via telehealth without an in-person visit and eliminating training requirements for the waiver that previously was required to prescribe buprenorphine.
“The fact that buprenorphine initiation and retention did not rise after these efforts were implemented suggests that they were insufficient to meet the rising need for this medication,” he said.
The current study “adds to a growing body of research suggesting that clinicians are not maximizing opportunities to initiate buprenorphine treatment among patients with opioid addiction,” Dr. Chua said. He cited another of his recent studies in which 1 in 12 patients were prescribed buprenorphine within 30 days of an emergency department visit for opioid overdose from August 2019 to April 2021, but half of patients with emergency department visits with anaphylaxis were prescribed anepinephrine auto-injector.
“My hope is that our new study will further underscore to clinicians how much the health care system is underusing a critical tool to prevent opioid overdose deaths,” he said.
The federal government’s recent elimination of the waiver needed to prescribe buprenorphine may move the needle, but to what degree remains to be seen, Dr. Chua added. “It is possible this intervention will be insufficient to overcome the many other barriers to buprenorphine initiation and retention, such as stigma about the drug among clinicians, patients, and pharmacists,” he said.
Lack of education remains a barrier to buprenorphine use
The current study is important to determine whether attempts to increase buprenorphine initiation and treatment retention are working, said Reuben J. Strayer, MD, director of addiction medicine in the emergency medicine department at Maimonides Medical Center, New York, in an interview.
Dr. Strayer was not involved in the current study, but said he was surprised that initiation of buprenorphine didn’t decrease more dramatically during the pandemic, given the significant barriers to accessing care during that time.
However, “efforts to increase buprenorphine initiation and retention have not been sufficiently effective,” Dr. Strayer said. “The rise of fentanyl as a primary street opioid, replacing heroin, has dissuaded both patients and providers from initiating buprenorphine for fear of precipitated withdrawal.”
The elimination of the DATA 2000 (X) waiver was the removal of a potential barrier to increased buprenorphine use, said Dr. Strayer. “Now that the DATA 2000 (X) waiver has been eliminated, the focus of buprenorphine access is educating primary care and inpatient providers on its use, so that patients with OUD [opioid use disorder] can be treated, regardless of the venue at which they seek care,” he said.
Looking ahead, “The priority in buprenorphine research is determining the most effective way to initiate buprenorphine without the risk of precipitated withdrawal,” Dr. Strayer added.
The study was supported in part by the Benter Foundation, the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services, and the Susan B. Meister Child Health Evaluation and Research Center in the department of pediatrics at the University of Michigan. Dr. Chua was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Strayer has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid overdose deaths are at a record high in the United States, and many of these deaths can be prevented with medications such as buprenorphine, said lead author Kao-Ping Chua, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, in an interview. “However, buprenorphine cannot prevent opioid overdose deaths if patients are never started on the medication or only stay on the medication for a short time. For that reason, rates of buprenorphine initiation and retention are critical metrics for measuring how well the U.S. health care system is responding to the opioid epidemic,” he said.
“At the time we started our study, several other research groups had evaluated U.S. rates of buprenorphine initiation and retention using data through 2020. However, more recent national data were lacking,” Dr. Chua told this news organization. “We felt that this was an important knowledge gap given the many changes in society that have occurred since 2020,” he noted. “For example, it was possible that the relaxation of social distancing measures during 2021 and 2022 might have reduced barriers to health care visits, thereby increasing opportunities to initiate treatment for opioid addiction with buprenorphine,” he said.
Dr. Chua and colleagues used data from the IQVIA Longitudinal Prescription Database, which reports 92% of prescriptions dispensed from retail pharmacies in the United States. “Buprenorphine products included immediate-release and extended-release formulations approved for opioid use disorder but not formulations primarily used to treat pain,” they write.
Monthly buprenorphine initiation was defined as the number of patients initiating therapy per 100,000 individuals. For retention, the researchers used a National Quality Forum-endorsed quality measure that defined retention as continuous use of buprenorphine for at least 180 days.
A total of 3,006,629 patients began buprenorphine therapy during the study period; approximately 43% were female.
During the first years of the study period, from January 2016 through September 2018, the monthly buprenorphine initiation rate increased from 12.5 per 100,000 to 15.9 per 100,000, with a statistically significant monthly percentage change of 0.62% (P < .001).
However, from October 2018 through October 2022, the monthly percentage remained essentially the same (P = .62) with a monthly percentage change of −0.03%.
From March 2020 through December 2020, the median monthly buprenorphine initiation rate was 14.4 per 100,000, only slightly lower than the rates from January 2019 through February 2020 and from January 2021 through October 2022 (15.5 per 100,000 and 15.0 per 100,000, respectively).
Over the entire study period from January 2016 through October 2022, the median monthly retention rate for buprenorphine use was 22.2%. This rate increased minimally, with no significant changes in slope and a monthly percentage change of 0.08% (P = .04).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including a lack of data on race and ethnicity, in-clinic administration of buprenorphine, and buprenorphine dispensing through methadone outpatient programs, the researchers note. Also, data did not indicate whether some patients began buprenorphine to treat pain, they say. The timing of the flattening of buprenorphine use also suggests the influence of factors beyond the COVID-19 pandemic, they write.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and suggest that efforts to date to increase buprenorphine use have been unsuccessful, the researchers write. “A comprehensive approach is needed to eliminate barriers to buprenorphine initiation and retention, such as stigma and uneven access to prescribers,” they conclude.
Study highlights underuse of buprenorphine option
“Our study shows that buprenorphine initiation rates have been flat since the end of 2018 and that rates of 180-day retention in buprenorphine therapy have remained low throughout 2016-2022,” Dr. Chua told this news organization. “Neither of these findings are particularly surprising, but they are disappointing,” he said. “There were a lot of policy and clinical efforts to maintain and expand access to buprenorphine during the COVID-19 pandemic, such as allowing buprenorphine to be prescribed via telehealth without an in-person visit and eliminating training requirements for the waiver that previously was required to prescribe buprenorphine.
“The fact that buprenorphine initiation and retention did not rise after these efforts were implemented suggests that they were insufficient to meet the rising need for this medication,” he said.
The current study “adds to a growing body of research suggesting that clinicians are not maximizing opportunities to initiate buprenorphine treatment among patients with opioid addiction,” Dr. Chua said. He cited another of his recent studies in which 1 in 12 patients were prescribed buprenorphine within 30 days of an emergency department visit for opioid overdose from August 2019 to April 2021, but half of patients with emergency department visits with anaphylaxis were prescribed anepinephrine auto-injector.
“My hope is that our new study will further underscore to clinicians how much the health care system is underusing a critical tool to prevent opioid overdose deaths,” he said.
The federal government’s recent elimination of the waiver needed to prescribe buprenorphine may move the needle, but to what degree remains to be seen, Dr. Chua added. “It is possible this intervention will be insufficient to overcome the many other barriers to buprenorphine initiation and retention, such as stigma about the drug among clinicians, patients, and pharmacists,” he said.
Lack of education remains a barrier to buprenorphine use
The current study is important to determine whether attempts to increase buprenorphine initiation and treatment retention are working, said Reuben J. Strayer, MD, director of addiction medicine in the emergency medicine department at Maimonides Medical Center, New York, in an interview.
Dr. Strayer was not involved in the current study, but said he was surprised that initiation of buprenorphine didn’t decrease more dramatically during the pandemic, given the significant barriers to accessing care during that time.
However, “efforts to increase buprenorphine initiation and retention have not been sufficiently effective,” Dr. Strayer said. “The rise of fentanyl as a primary street opioid, replacing heroin, has dissuaded both patients and providers from initiating buprenorphine for fear of precipitated withdrawal.”
The elimination of the DATA 2000 (X) waiver was the removal of a potential barrier to increased buprenorphine use, said Dr. Strayer. “Now that the DATA 2000 (X) waiver has been eliminated, the focus of buprenorphine access is educating primary care and inpatient providers on its use, so that patients with OUD [opioid use disorder] can be treated, regardless of the venue at which they seek care,” he said.
Looking ahead, “The priority in buprenorphine research is determining the most effective way to initiate buprenorphine without the risk of precipitated withdrawal,” Dr. Strayer added.
The study was supported in part by the Benter Foundation, the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services, and the Susan B. Meister Child Health Evaluation and Research Center in the department of pediatrics at the University of Michigan. Dr. Chua was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Strayer has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid overdose deaths are at a record high in the United States, and many of these deaths can be prevented with medications such as buprenorphine, said lead author Kao-Ping Chua, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, in an interview. “However, buprenorphine cannot prevent opioid overdose deaths if patients are never started on the medication or only stay on the medication for a short time. For that reason, rates of buprenorphine initiation and retention are critical metrics for measuring how well the U.S. health care system is responding to the opioid epidemic,” he said.
“At the time we started our study, several other research groups had evaluated U.S. rates of buprenorphine initiation and retention using data through 2020. However, more recent national data were lacking,” Dr. Chua told this news organization. “We felt that this was an important knowledge gap given the many changes in society that have occurred since 2020,” he noted. “For example, it was possible that the relaxation of social distancing measures during 2021 and 2022 might have reduced barriers to health care visits, thereby increasing opportunities to initiate treatment for opioid addiction with buprenorphine,” he said.
Dr. Chua and colleagues used data from the IQVIA Longitudinal Prescription Database, which reports 92% of prescriptions dispensed from retail pharmacies in the United States. “Buprenorphine products included immediate-release and extended-release formulations approved for opioid use disorder but not formulations primarily used to treat pain,” they write.
Monthly buprenorphine initiation was defined as the number of patients initiating therapy per 100,000 individuals. For retention, the researchers used a National Quality Forum-endorsed quality measure that defined retention as continuous use of buprenorphine for at least 180 days.
A total of 3,006,629 patients began buprenorphine therapy during the study period; approximately 43% were female.
During the first years of the study period, from January 2016 through September 2018, the monthly buprenorphine initiation rate increased from 12.5 per 100,000 to 15.9 per 100,000, with a statistically significant monthly percentage change of 0.62% (P < .001).
However, from October 2018 through October 2022, the monthly percentage remained essentially the same (P = .62) with a monthly percentage change of −0.03%.
From March 2020 through December 2020, the median monthly buprenorphine initiation rate was 14.4 per 100,000, only slightly lower than the rates from January 2019 through February 2020 and from January 2021 through October 2022 (15.5 per 100,000 and 15.0 per 100,000, respectively).
Over the entire study period from January 2016 through October 2022, the median monthly retention rate for buprenorphine use was 22.2%. This rate increased minimally, with no significant changes in slope and a monthly percentage change of 0.08% (P = .04).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including a lack of data on race and ethnicity, in-clinic administration of buprenorphine, and buprenorphine dispensing through methadone outpatient programs, the researchers note. Also, data did not indicate whether some patients began buprenorphine to treat pain, they say. The timing of the flattening of buprenorphine use also suggests the influence of factors beyond the COVID-19 pandemic, they write.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and suggest that efforts to date to increase buprenorphine use have been unsuccessful, the researchers write. “A comprehensive approach is needed to eliminate barriers to buprenorphine initiation and retention, such as stigma and uneven access to prescribers,” they conclude.
Study highlights underuse of buprenorphine option
“Our study shows that buprenorphine initiation rates have been flat since the end of 2018 and that rates of 180-day retention in buprenorphine therapy have remained low throughout 2016-2022,” Dr. Chua told this news organization. “Neither of these findings are particularly surprising, but they are disappointing,” he said. “There were a lot of policy and clinical efforts to maintain and expand access to buprenorphine during the COVID-19 pandemic, such as allowing buprenorphine to be prescribed via telehealth without an in-person visit and eliminating training requirements for the waiver that previously was required to prescribe buprenorphine.
“The fact that buprenorphine initiation and retention did not rise after these efforts were implemented suggests that they were insufficient to meet the rising need for this medication,” he said.
The current study “adds to a growing body of research suggesting that clinicians are not maximizing opportunities to initiate buprenorphine treatment among patients with opioid addiction,” Dr. Chua said. He cited another of his recent studies in which 1 in 12 patients were prescribed buprenorphine within 30 days of an emergency department visit for opioid overdose from August 2019 to April 2021, but half of patients with emergency department visits with anaphylaxis were prescribed anepinephrine auto-injector.
“My hope is that our new study will further underscore to clinicians how much the health care system is underusing a critical tool to prevent opioid overdose deaths,” he said.
The federal government’s recent elimination of the waiver needed to prescribe buprenorphine may move the needle, but to what degree remains to be seen, Dr. Chua added. “It is possible this intervention will be insufficient to overcome the many other barriers to buprenorphine initiation and retention, such as stigma about the drug among clinicians, patients, and pharmacists,” he said.
Lack of education remains a barrier to buprenorphine use
The current study is important to determine whether attempts to increase buprenorphine initiation and treatment retention are working, said Reuben J. Strayer, MD, director of addiction medicine in the emergency medicine department at Maimonides Medical Center, New York, in an interview.
Dr. Strayer was not involved in the current study, but said he was surprised that initiation of buprenorphine didn’t decrease more dramatically during the pandemic, given the significant barriers to accessing care during that time.
However, “efforts to increase buprenorphine initiation and retention have not been sufficiently effective,” Dr. Strayer said. “The rise of fentanyl as a primary street opioid, replacing heroin, has dissuaded both patients and providers from initiating buprenorphine for fear of precipitated withdrawal.”
The elimination of the DATA 2000 (X) waiver was the removal of a potential barrier to increased buprenorphine use, said Dr. Strayer. “Now that the DATA 2000 (X) waiver has been eliminated, the focus of buprenorphine access is educating primary care and inpatient providers on its use, so that patients with OUD [opioid use disorder] can be treated, regardless of the venue at which they seek care,” he said.
Looking ahead, “The priority in buprenorphine research is determining the most effective way to initiate buprenorphine without the risk of precipitated withdrawal,” Dr. Strayer added.
The study was supported in part by the Benter Foundation, the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services, and the Susan B. Meister Child Health Evaluation and Research Center in the department of pediatrics at the University of Michigan. Dr. Chua was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Strayer has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA