User login
Children and COVID: New cases climb slowly but steadily
The current sustained increase in COVID-19 has brought the total number of cases in children to over 13 million since the start of the pandemic, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, when cases dropped to their lowest point since last summer. The cumulative number of cases in children is 13,052,988, which accounts for 19.0% of all cases reported in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.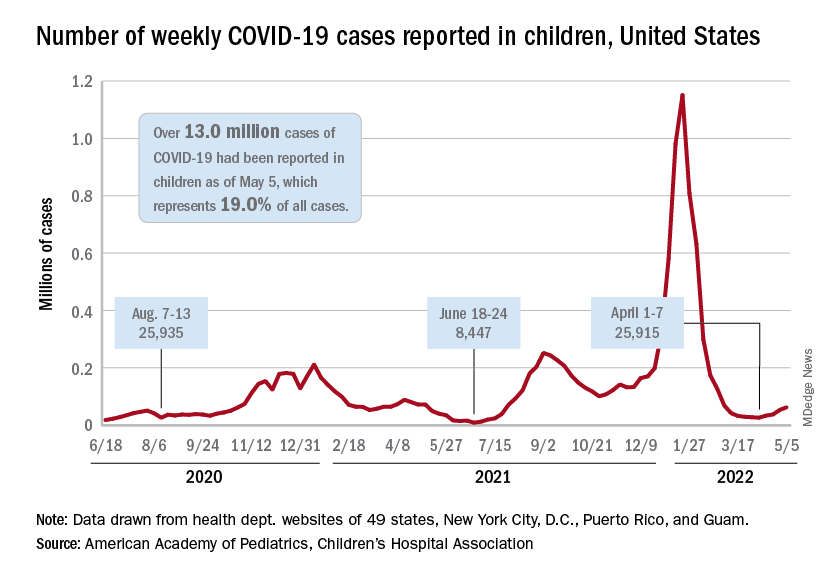
Other measures of incidence show the same steady rise. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID-19, which had dipped as low as 0.13 per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.19 per 100,000 on May 6, and the 7-day average for total admissions was 136 per day for May 1-7, compared with 118 for the last week of April, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
At the state level, new admission rates for May 6 show wide variation, even regionally. Rhode Island came in with a 0.00 per 100,000 on that day, while Vermont recorded 0.88 admissions per 100,000, the highest of any state and lower only than the District of Columbia’s 1.23 per 100,000. Connecticut (0.45) and Massachusetts (0.33) also were in the highest group (see map), while Maine was in the lowest, CDC data show.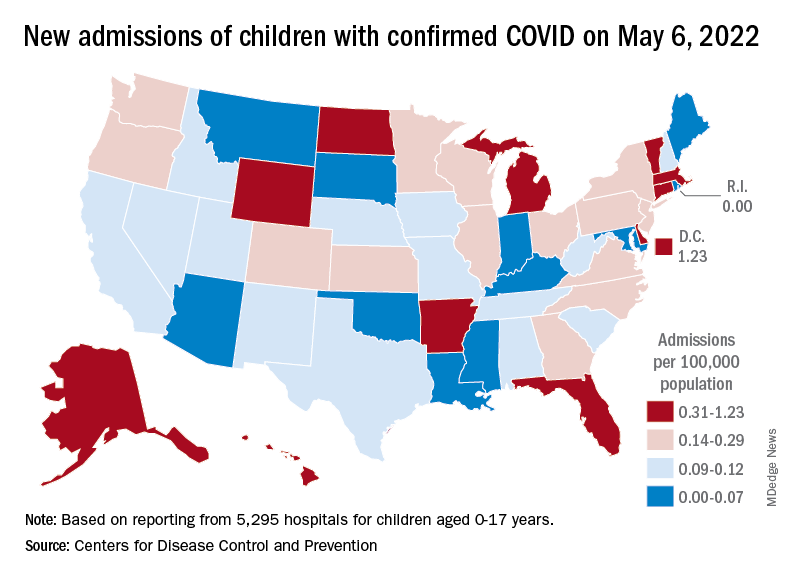
Nationally, emergency department visits also have been rising over the last month or so. Children aged 0-11 years, who were down to a 7-day average of 0.5% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID-19 in early April, saw that number rise to 1.4% on May 5. Children aged 12-15 years went from a rate of 0.3% in late March to the current 1.2%, as did 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccination effort, meanwhile, continues to lose steam, at least among children who are currently eligible. Initial vaccinations in those aged 5-11 slipped to their lowest-ever 1-week total, 47,000 for April 28 to May 4, while children aged 16-17 continued a long-term slide that has the weekly count down to just 29,000, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
Here’s how those latest recipients changed the populations of vaccinated children in the last week: 35.4% of all 5- to 11-year-olds had received at least one dose as of May 4, compared with 35.3% on April 27, with increases from 67.4% to 67.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 72.7% to 72.8% among those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
The current sustained increase in COVID-19 has brought the total number of cases in children to over 13 million since the start of the pandemic, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, when cases dropped to their lowest point since last summer. The cumulative number of cases in children is 13,052,988, which accounts for 19.0% of all cases reported in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Other measures of incidence show the same steady rise. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID-19, which had dipped as low as 0.13 per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.19 per 100,000 on May 6, and the 7-day average for total admissions was 136 per day for May 1-7, compared with 118 for the last week of April, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
At the state level, new admission rates for May 6 show wide variation, even regionally. Rhode Island came in with a 0.00 per 100,000 on that day, while Vermont recorded 0.88 admissions per 100,000, the highest of any state and lower only than the District of Columbia’s 1.23 per 100,000. Connecticut (0.45) and Massachusetts (0.33) also were in the highest group (see map), while Maine was in the lowest, CDC data show.
Nationally, emergency department visits also have been rising over the last month or so. Children aged 0-11 years, who were down to a 7-day average of 0.5% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID-19 in early April, saw that number rise to 1.4% on May 5. Children aged 12-15 years went from a rate of 0.3% in late March to the current 1.2%, as did 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccination effort, meanwhile, continues to lose steam, at least among children who are currently eligible. Initial vaccinations in those aged 5-11 slipped to their lowest-ever 1-week total, 47,000 for April 28 to May 4, while children aged 16-17 continued a long-term slide that has the weekly count down to just 29,000, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
Here’s how those latest recipients changed the populations of vaccinated children in the last week: 35.4% of all 5- to 11-year-olds had received at least one dose as of May 4, compared with 35.3% on April 27, with increases from 67.4% to 67.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 72.7% to 72.8% among those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
The current sustained increase in COVID-19 has brought the total number of cases in children to over 13 million since the start of the pandemic, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, when cases dropped to their lowest point since last summer. The cumulative number of cases in children is 13,052,988, which accounts for 19.0% of all cases reported in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Other measures of incidence show the same steady rise. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID-19, which had dipped as low as 0.13 per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.19 per 100,000 on May 6, and the 7-day average for total admissions was 136 per day for May 1-7, compared with 118 for the last week of April, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
At the state level, new admission rates for May 6 show wide variation, even regionally. Rhode Island came in with a 0.00 per 100,000 on that day, while Vermont recorded 0.88 admissions per 100,000, the highest of any state and lower only than the District of Columbia’s 1.23 per 100,000. Connecticut (0.45) and Massachusetts (0.33) also were in the highest group (see map), while Maine was in the lowest, CDC data show.
Nationally, emergency department visits also have been rising over the last month or so. Children aged 0-11 years, who were down to a 7-day average of 0.5% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID-19 in early April, saw that number rise to 1.4% on May 5. Children aged 12-15 years went from a rate of 0.3% in late March to the current 1.2%, as did 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccination effort, meanwhile, continues to lose steam, at least among children who are currently eligible. Initial vaccinations in those aged 5-11 slipped to their lowest-ever 1-week total, 47,000 for April 28 to May 4, while children aged 16-17 continued a long-term slide that has the weekly count down to just 29,000, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
Here’s how those latest recipients changed the populations of vaccinated children in the last week: 35.4% of all 5- to 11-year-olds had received at least one dose as of May 4, compared with 35.3% on April 27, with increases from 67.4% to 67.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 72.7% to 72.8% among those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
My choice? Unvaccinated pose outsize risk to vaccinated
according to a mathematical modeling study.
The study, which simulated patterns of infection among vaccinated and unvaccinated populations, showed that, as the populations mixed less, attack rates decreased among vaccinated people (from 15% to 10%) and increased among unvaccinated people (from 62% to 79%). The unvaccinated increasingly became the source of infection, however.
“When the vaccinated and unvaccinated mix, indirect protection is conferred upon the unvaccinated by the buffering effect of vaccinated individuals, and by contrast, risk in the vaccinated goes up,” lead author David Fisman, MD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, told this news organization.
As the groups mix less and less, the size of the epidemic increases among the unvaccinated and decreases among the vaccinated. “But the impact of the unvaccinated on risk in the vaccinated is disproportionate to the numbers of contacts between the two groups,” said Dr. Fisman.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Relative contributions to risk
The researchers used a model of a respiratory viral disease “similar to SARS-CoV-2 infection with Delta variant.” They included reproduction values to capture the dynamics of the Omicron variant, which was emerging at the time. In the study, vaccines ranged in effectiveness from 40% to 80%. The study incorporated various levels of mixing between a partially vaccinated and an unvaccinated population. The mixing ranged from random mixing to like-with-like mixing (“assortativity”). There were three possible “compartments” of people in the model: those considered susceptible to infection, those considered infected and infectious, and those considered immune because of recovery.
The model showed that, as mixing between the vaccinated and the unvaccinated populations increased, case numbers rose, “with cases in the unvaccinated subpopulation accounting for a substantial proportion of infections.” However, as mixing between the populations decreased, the final attack rate decreased among vaccinated people, but the relative “contribution of risk to vaccinated people caused by infection acquired from contact with unvaccinated people ... increased.”
When the vaccination rate was increased in the model, case numbers among the vaccinated declined “as expected, owing to indirect protective effects,” the researchers noted. But this also “further increased the relative contribution to risk in vaccinated people by those who were unvaccinated.”
Self-regarding risk?
The findings show that “choices made by people who forgo vaccination contribute disproportionately to risk among those who do get vaccinated,” the researchers wrote. “Although risk associated with avoiding vaccination during a virulent pandemic accrues chiefly to those who are unvaccinated, the choice of some individuals to refuse vaccination is likely to affect the health and safety of vaccinated people in a manner disproportionate to the fraction of unvaccinated people in the population.”
The fact that like-with-like mixing cannot mitigate the risk to vaccinated people “undermines the assertion that vaccine choice is best left to the individual and supports strong public actions aimed at enhancing vaccine uptake and limiting access to public spaces for unvaccinated people,” they wrote.
Mandates and passports
“Our model provides support for vaccine mandates and passports during epidemics, such that vaccination is required for people to take part in nonessential activities,” said Dr. Fisman. The choice to not be vaccinated against COVID-19 should not be considered “self-regarding,” he added. “Risk is self-regarding when it only impacts the person engaging in the activity. Something like smoking cigarettes (alone, without others around) creates a lot of risk over time, but if nobody is breathing your secondhand smoke, you’re only creating risk for yourself. By contrast, we regulate, in Ontario, your right to smoke in public indoor spaces such as restaurants, because once other people are around, the risk isn’t self-regarding anymore. You’re creating risk for others.”
The authors also noted that the risks created by the unvaccinated extend beyond those of infection by “creating a risk that those around them may not be able to obtain the care they need.” They recommended that considerations of equity and justice for people who do choose to be vaccinated, as well as those who choose not to be, need to be included in formulating vaccination policy.
Illuminating the discussion
Asked to comment on the study, Matthew Oughton, MD, assistant professor of medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said: “It is easy to dismiss a mathematical model as a series of assumptions that leads to an implausible conclusion. ... However, they can serve to illustrate and, to an extent, quantify the results of complex interactions, and this study does just that.” Dr. Oughton was not involved in the research.
During the past 2 years, the scientific press and the general press have often discussed the individual and collective effects of disease-prevention methods, including nonpharmaceutical interventions. “Models like this can help illuminate those discussions by highlighting important consequences of preventive measures,” said Dr. Oughton, who also works in the division of infectious diseases at the Jewish General Hospital, Montreal.
It’s worth noting that the authors modeled vaccine effectiveness against all infection, “rather than the generally greater and more durable effects we have seen for vaccines in prevention of severe infection,” said Dr. Oughton. He added that the authors did not include the effect of vaccination in reducing forward transmission. “Inclusion of this effect would presumably have reduced overall infectious burden in mixed populations and increased the difference between groups at lower levels of mixing between populations.”
The research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Fisman has served on advisory boards related to influenza and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for Seqirus, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Sanofi-Pasteur Vaccines and has served as a legal expert on issues related to COVID-19 epidemiology for the Elementary Teachers Federation of Ontario and the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario. Dr. Oughton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a mathematical modeling study.
The study, which simulated patterns of infection among vaccinated and unvaccinated populations, showed that, as the populations mixed less, attack rates decreased among vaccinated people (from 15% to 10%) and increased among unvaccinated people (from 62% to 79%). The unvaccinated increasingly became the source of infection, however.
“When the vaccinated and unvaccinated mix, indirect protection is conferred upon the unvaccinated by the buffering effect of vaccinated individuals, and by contrast, risk in the vaccinated goes up,” lead author David Fisman, MD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, told this news organization.
As the groups mix less and less, the size of the epidemic increases among the unvaccinated and decreases among the vaccinated. “But the impact of the unvaccinated on risk in the vaccinated is disproportionate to the numbers of contacts between the two groups,” said Dr. Fisman.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Relative contributions to risk
The researchers used a model of a respiratory viral disease “similar to SARS-CoV-2 infection with Delta variant.” They included reproduction values to capture the dynamics of the Omicron variant, which was emerging at the time. In the study, vaccines ranged in effectiveness from 40% to 80%. The study incorporated various levels of mixing between a partially vaccinated and an unvaccinated population. The mixing ranged from random mixing to like-with-like mixing (“assortativity”). There were three possible “compartments” of people in the model: those considered susceptible to infection, those considered infected and infectious, and those considered immune because of recovery.
The model showed that, as mixing between the vaccinated and the unvaccinated populations increased, case numbers rose, “with cases in the unvaccinated subpopulation accounting for a substantial proportion of infections.” However, as mixing between the populations decreased, the final attack rate decreased among vaccinated people, but the relative “contribution of risk to vaccinated people caused by infection acquired from contact with unvaccinated people ... increased.”
When the vaccination rate was increased in the model, case numbers among the vaccinated declined “as expected, owing to indirect protective effects,” the researchers noted. But this also “further increased the relative contribution to risk in vaccinated people by those who were unvaccinated.”
Self-regarding risk?
The findings show that “choices made by people who forgo vaccination contribute disproportionately to risk among those who do get vaccinated,” the researchers wrote. “Although risk associated with avoiding vaccination during a virulent pandemic accrues chiefly to those who are unvaccinated, the choice of some individuals to refuse vaccination is likely to affect the health and safety of vaccinated people in a manner disproportionate to the fraction of unvaccinated people in the population.”
The fact that like-with-like mixing cannot mitigate the risk to vaccinated people “undermines the assertion that vaccine choice is best left to the individual and supports strong public actions aimed at enhancing vaccine uptake and limiting access to public spaces for unvaccinated people,” they wrote.
Mandates and passports
“Our model provides support for vaccine mandates and passports during epidemics, such that vaccination is required for people to take part in nonessential activities,” said Dr. Fisman. The choice to not be vaccinated against COVID-19 should not be considered “self-regarding,” he added. “Risk is self-regarding when it only impacts the person engaging in the activity. Something like smoking cigarettes (alone, without others around) creates a lot of risk over time, but if nobody is breathing your secondhand smoke, you’re only creating risk for yourself. By contrast, we regulate, in Ontario, your right to smoke in public indoor spaces such as restaurants, because once other people are around, the risk isn’t self-regarding anymore. You’re creating risk for others.”
The authors also noted that the risks created by the unvaccinated extend beyond those of infection by “creating a risk that those around them may not be able to obtain the care they need.” They recommended that considerations of equity and justice for people who do choose to be vaccinated, as well as those who choose not to be, need to be included in formulating vaccination policy.
Illuminating the discussion
Asked to comment on the study, Matthew Oughton, MD, assistant professor of medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said: “It is easy to dismiss a mathematical model as a series of assumptions that leads to an implausible conclusion. ... However, they can serve to illustrate and, to an extent, quantify the results of complex interactions, and this study does just that.” Dr. Oughton was not involved in the research.
During the past 2 years, the scientific press and the general press have often discussed the individual and collective effects of disease-prevention methods, including nonpharmaceutical interventions. “Models like this can help illuminate those discussions by highlighting important consequences of preventive measures,” said Dr. Oughton, who also works in the division of infectious diseases at the Jewish General Hospital, Montreal.
It’s worth noting that the authors modeled vaccine effectiveness against all infection, “rather than the generally greater and more durable effects we have seen for vaccines in prevention of severe infection,” said Dr. Oughton. He added that the authors did not include the effect of vaccination in reducing forward transmission. “Inclusion of this effect would presumably have reduced overall infectious burden in mixed populations and increased the difference between groups at lower levels of mixing between populations.”
The research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Fisman has served on advisory boards related to influenza and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for Seqirus, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Sanofi-Pasteur Vaccines and has served as a legal expert on issues related to COVID-19 epidemiology for the Elementary Teachers Federation of Ontario and the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario. Dr. Oughton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a mathematical modeling study.
The study, which simulated patterns of infection among vaccinated and unvaccinated populations, showed that, as the populations mixed less, attack rates decreased among vaccinated people (from 15% to 10%) and increased among unvaccinated people (from 62% to 79%). The unvaccinated increasingly became the source of infection, however.
“When the vaccinated and unvaccinated mix, indirect protection is conferred upon the unvaccinated by the buffering effect of vaccinated individuals, and by contrast, risk in the vaccinated goes up,” lead author David Fisman, MD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, told this news organization.
As the groups mix less and less, the size of the epidemic increases among the unvaccinated and decreases among the vaccinated. “But the impact of the unvaccinated on risk in the vaccinated is disproportionate to the numbers of contacts between the two groups,” said Dr. Fisman.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Relative contributions to risk
The researchers used a model of a respiratory viral disease “similar to SARS-CoV-2 infection with Delta variant.” They included reproduction values to capture the dynamics of the Omicron variant, which was emerging at the time. In the study, vaccines ranged in effectiveness from 40% to 80%. The study incorporated various levels of mixing between a partially vaccinated and an unvaccinated population. The mixing ranged from random mixing to like-with-like mixing (“assortativity”). There were three possible “compartments” of people in the model: those considered susceptible to infection, those considered infected and infectious, and those considered immune because of recovery.
The model showed that, as mixing between the vaccinated and the unvaccinated populations increased, case numbers rose, “with cases in the unvaccinated subpopulation accounting for a substantial proportion of infections.” However, as mixing between the populations decreased, the final attack rate decreased among vaccinated people, but the relative “contribution of risk to vaccinated people caused by infection acquired from contact with unvaccinated people ... increased.”
When the vaccination rate was increased in the model, case numbers among the vaccinated declined “as expected, owing to indirect protective effects,” the researchers noted. But this also “further increased the relative contribution to risk in vaccinated people by those who were unvaccinated.”
Self-regarding risk?
The findings show that “choices made by people who forgo vaccination contribute disproportionately to risk among those who do get vaccinated,” the researchers wrote. “Although risk associated with avoiding vaccination during a virulent pandemic accrues chiefly to those who are unvaccinated, the choice of some individuals to refuse vaccination is likely to affect the health and safety of vaccinated people in a manner disproportionate to the fraction of unvaccinated people in the population.”
The fact that like-with-like mixing cannot mitigate the risk to vaccinated people “undermines the assertion that vaccine choice is best left to the individual and supports strong public actions aimed at enhancing vaccine uptake and limiting access to public spaces for unvaccinated people,” they wrote.
Mandates and passports
“Our model provides support for vaccine mandates and passports during epidemics, such that vaccination is required for people to take part in nonessential activities,” said Dr. Fisman. The choice to not be vaccinated against COVID-19 should not be considered “self-regarding,” he added. “Risk is self-regarding when it only impacts the person engaging in the activity. Something like smoking cigarettes (alone, without others around) creates a lot of risk over time, but if nobody is breathing your secondhand smoke, you’re only creating risk for yourself. By contrast, we regulate, in Ontario, your right to smoke in public indoor spaces such as restaurants, because once other people are around, the risk isn’t self-regarding anymore. You’re creating risk for others.”
The authors also noted that the risks created by the unvaccinated extend beyond those of infection by “creating a risk that those around them may not be able to obtain the care they need.” They recommended that considerations of equity and justice for people who do choose to be vaccinated, as well as those who choose not to be, need to be included in formulating vaccination policy.
Illuminating the discussion
Asked to comment on the study, Matthew Oughton, MD, assistant professor of medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said: “It is easy to dismiss a mathematical model as a series of assumptions that leads to an implausible conclusion. ... However, they can serve to illustrate and, to an extent, quantify the results of complex interactions, and this study does just that.” Dr. Oughton was not involved in the research.
During the past 2 years, the scientific press and the general press have often discussed the individual and collective effects of disease-prevention methods, including nonpharmaceutical interventions. “Models like this can help illuminate those discussions by highlighting important consequences of preventive measures,” said Dr. Oughton, who also works in the division of infectious diseases at the Jewish General Hospital, Montreal.
It’s worth noting that the authors modeled vaccine effectiveness against all infection, “rather than the generally greater and more durable effects we have seen for vaccines in prevention of severe infection,” said Dr. Oughton. He added that the authors did not include the effect of vaccination in reducing forward transmission. “Inclusion of this effect would presumably have reduced overall infectious burden in mixed populations and increased the difference between groups at lower levels of mixing between populations.”
The research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Fisman has served on advisory boards related to influenza and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for Seqirus, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Sanofi-Pasteur Vaccines and has served as a legal expert on issues related to COVID-19 epidemiology for the Elementary Teachers Federation of Ontario and the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario. Dr. Oughton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION JOURNAL
COVID fallout: ‘Alarming’ dip in routine vax for pregnant women
The percentage of low-income pregnant mothers who received influenza and Tdap vaccinations fell sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic, especially in Black and Hispanic patients, a new study finds.
The percentage of patients who received the influenza vaccines at two Medicaid clinics in Houston dropped from 78% before the pandemic to 61% during it (adjusted odds ratio, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.26-0.53; P < .01), researchers reported at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The percentage receiving the Tdap vaccine dipped from 85% to 76% (aOR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.40-0.79; P < .01).
New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center pediatrician Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, who’s familiar with the study findings, called them “alarming” and said in an interview that they should be “a call to action for providers.”
“Continuing the status quo in our routine preventative health care and clinic operations means that we are losing ground in reduction and elimination of vaccine-preventable diseases,” Dr. Permar said in an interview.
According to corresponding author Bani Ratan, MD, an ob.gyn. with the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, there’s been little if any previous research into routine, non-COVID vaccination in pregnant women during the pandemic.
For the study, researchers retrospectively analyzed the records of 939 pregnant women who entered prenatal care before 20 weeks (462 from May–November 2019, and 477 from May–November 2020) and delivered at full term.
Among ethnic groups, non-Hispanic Blacks saw the largest decline in influenza vaccines. Among them, the percentage who got them fell from 64% (73/114) to 35% (35/101; aOR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.17-0.52; P < .01). Only Hispanics had a statistically significant decline in Tdap vaccination (OR, 0.52, 95% CI, 0.34-0.80; P < .01, percentages not provided).
Another study presented at ACOG examined vaccination rates during the pandemic and found that Tdap vaccination rates dipped among pregnant women in a Philadelphia-area health care system.
Possible causes for the decline in routine vaccination include hesitancy linked to the COVID-19 vaccines and fewer office visits because of telemedicine, said Dr. Batan in an interview.
Dr. Permar blamed the role of vaccine misinformation during the pandemic and the mistrust caused by the exclusion of pregnant women from early vaccine trials. She added that “challenges in health care staffing and issues of health care provider burnout that worsened during the pandemic likely contributed to a fraying of the focus on preventive health maintenance simply due to bandwidth of health professionals.”
In a separate study presented at ACOG, researchers at the State University of New York, Syracuse, reported on a survey of 157 pregnant women of whom just 38.2% were vaccinated against COVID-19. Among the unvaccinated, who were more likely to have less education, 66% reported that lack of data about vaccination was their primary concern.
No funding or disclosures are reported by study authors. Dr. Permar reported consulting for Merck, Moderna, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Dynavax, and Hookipa on cytomegalovirus vaccine programs.
*This story was updated on 5/11/2022.
The percentage of low-income pregnant mothers who received influenza and Tdap vaccinations fell sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic, especially in Black and Hispanic patients, a new study finds.
The percentage of patients who received the influenza vaccines at two Medicaid clinics in Houston dropped from 78% before the pandemic to 61% during it (adjusted odds ratio, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.26-0.53; P < .01), researchers reported at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The percentage receiving the Tdap vaccine dipped from 85% to 76% (aOR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.40-0.79; P < .01).
New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center pediatrician Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, who’s familiar with the study findings, called them “alarming” and said in an interview that they should be “a call to action for providers.”
“Continuing the status quo in our routine preventative health care and clinic operations means that we are losing ground in reduction and elimination of vaccine-preventable diseases,” Dr. Permar said in an interview.
According to corresponding author Bani Ratan, MD, an ob.gyn. with the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, there’s been little if any previous research into routine, non-COVID vaccination in pregnant women during the pandemic.
For the study, researchers retrospectively analyzed the records of 939 pregnant women who entered prenatal care before 20 weeks (462 from May–November 2019, and 477 from May–November 2020) and delivered at full term.
Among ethnic groups, non-Hispanic Blacks saw the largest decline in influenza vaccines. Among them, the percentage who got them fell from 64% (73/114) to 35% (35/101; aOR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.17-0.52; P < .01). Only Hispanics had a statistically significant decline in Tdap vaccination (OR, 0.52, 95% CI, 0.34-0.80; P < .01, percentages not provided).
Another study presented at ACOG examined vaccination rates during the pandemic and found that Tdap vaccination rates dipped among pregnant women in a Philadelphia-area health care system.
Possible causes for the decline in routine vaccination include hesitancy linked to the COVID-19 vaccines and fewer office visits because of telemedicine, said Dr. Batan in an interview.
Dr. Permar blamed the role of vaccine misinformation during the pandemic and the mistrust caused by the exclusion of pregnant women from early vaccine trials. She added that “challenges in health care staffing and issues of health care provider burnout that worsened during the pandemic likely contributed to a fraying of the focus on preventive health maintenance simply due to bandwidth of health professionals.”
In a separate study presented at ACOG, researchers at the State University of New York, Syracuse, reported on a survey of 157 pregnant women of whom just 38.2% were vaccinated against COVID-19. Among the unvaccinated, who were more likely to have less education, 66% reported that lack of data about vaccination was their primary concern.
No funding or disclosures are reported by study authors. Dr. Permar reported consulting for Merck, Moderna, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Dynavax, and Hookipa on cytomegalovirus vaccine programs.
*This story was updated on 5/11/2022.
The percentage of low-income pregnant mothers who received influenza and Tdap vaccinations fell sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic, especially in Black and Hispanic patients, a new study finds.
The percentage of patients who received the influenza vaccines at two Medicaid clinics in Houston dropped from 78% before the pandemic to 61% during it (adjusted odds ratio, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.26-0.53; P < .01), researchers reported at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The percentage receiving the Tdap vaccine dipped from 85% to 76% (aOR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.40-0.79; P < .01).
New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center pediatrician Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, who’s familiar with the study findings, called them “alarming” and said in an interview that they should be “a call to action for providers.”
“Continuing the status quo in our routine preventative health care and clinic operations means that we are losing ground in reduction and elimination of vaccine-preventable diseases,” Dr. Permar said in an interview.
According to corresponding author Bani Ratan, MD, an ob.gyn. with the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, there’s been little if any previous research into routine, non-COVID vaccination in pregnant women during the pandemic.
For the study, researchers retrospectively analyzed the records of 939 pregnant women who entered prenatal care before 20 weeks (462 from May–November 2019, and 477 from May–November 2020) and delivered at full term.
Among ethnic groups, non-Hispanic Blacks saw the largest decline in influenza vaccines. Among them, the percentage who got them fell from 64% (73/114) to 35% (35/101; aOR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.17-0.52; P < .01). Only Hispanics had a statistically significant decline in Tdap vaccination (OR, 0.52, 95% CI, 0.34-0.80; P < .01, percentages not provided).
Another study presented at ACOG examined vaccination rates during the pandemic and found that Tdap vaccination rates dipped among pregnant women in a Philadelphia-area health care system.
Possible causes for the decline in routine vaccination include hesitancy linked to the COVID-19 vaccines and fewer office visits because of telemedicine, said Dr. Batan in an interview.
Dr. Permar blamed the role of vaccine misinformation during the pandemic and the mistrust caused by the exclusion of pregnant women from early vaccine trials. She added that “challenges in health care staffing and issues of health care provider burnout that worsened during the pandemic likely contributed to a fraying of the focus on preventive health maintenance simply due to bandwidth of health professionals.”
In a separate study presented at ACOG, researchers at the State University of New York, Syracuse, reported on a survey of 157 pregnant women of whom just 38.2% were vaccinated against COVID-19. Among the unvaccinated, who were more likely to have less education, 66% reported that lack of data about vaccination was their primary concern.
No funding or disclosures are reported by study authors. Dr. Permar reported consulting for Merck, Moderna, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Dynavax, and Hookipa on cytomegalovirus vaccine programs.
*This story was updated on 5/11/2022.
FROM ACOG 2022
CDC predicts a rise in COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths in coming weeks
, according to a national forecast used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national model also predicts that about 5,000 deaths will occur over the next two weeks, with Ohio, New Jersey, and New York projected to see the largest totals of daily deaths in upcoming weeks.
The numbers follow several weeks of steady increases in infections across the country. More than 67,000 new cases are being reported daily, according to the data tracker from The New York Times, marking a 59% increase in the past two weeks.
In the Northeast, infection rates have risen by nearly 65%. In the New York and New Jersey region, infection rates are up about 55% in the past two weeks.
Hospitalizations have already begun to climb as well, with about 19,000 COVID-19 patients hospitalized nationwide and 1,725 in intensive care, according to the latest data from the Department of Health and Human Services. In the last week, hospital admissions have jumped by 20%, and emergency department visits are up by 18%.
The CDC forecast shows that 42 states and territories will see increases in hospital admissions during the next two weeks. Florida, Minnesota, New York, and Wisconsin will see some of the largest increases.
On average, more than 2,200 COVID-19 patients are entering the hospital each day, which has increased about 20% in the last week, according to ABC News. This also marks the highest number of COVID-19 patients needing hospital care since mid-March.
Public health officials have cited several factors for the increase in cases, such as states lifting mask mandates and other safety restrictions, ABC News reported. Highly contagious Omicron subvariants, such as BA.2 and BA.2.12.1, continue to spread in the United States and escape immunity from previous infections.
The BA.2 subvariant accounts for 62% of new national cases, according to the latest CDC data. The BA.2.12.1 subvariant makes up about 36% of new cases across the United States but 62% in the New York area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a national forecast used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national model also predicts that about 5,000 deaths will occur over the next two weeks, with Ohio, New Jersey, and New York projected to see the largest totals of daily deaths in upcoming weeks.
The numbers follow several weeks of steady increases in infections across the country. More than 67,000 new cases are being reported daily, according to the data tracker from The New York Times, marking a 59% increase in the past two weeks.
In the Northeast, infection rates have risen by nearly 65%. In the New York and New Jersey region, infection rates are up about 55% in the past two weeks.
Hospitalizations have already begun to climb as well, with about 19,000 COVID-19 patients hospitalized nationwide and 1,725 in intensive care, according to the latest data from the Department of Health and Human Services. In the last week, hospital admissions have jumped by 20%, and emergency department visits are up by 18%.
The CDC forecast shows that 42 states and territories will see increases in hospital admissions during the next two weeks. Florida, Minnesota, New York, and Wisconsin will see some of the largest increases.
On average, more than 2,200 COVID-19 patients are entering the hospital each day, which has increased about 20% in the last week, according to ABC News. This also marks the highest number of COVID-19 patients needing hospital care since mid-March.
Public health officials have cited several factors for the increase in cases, such as states lifting mask mandates and other safety restrictions, ABC News reported. Highly contagious Omicron subvariants, such as BA.2 and BA.2.12.1, continue to spread in the United States and escape immunity from previous infections.
The BA.2 subvariant accounts for 62% of new national cases, according to the latest CDC data. The BA.2.12.1 subvariant makes up about 36% of new cases across the United States but 62% in the New York area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a national forecast used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national model also predicts that about 5,000 deaths will occur over the next two weeks, with Ohio, New Jersey, and New York projected to see the largest totals of daily deaths in upcoming weeks.
The numbers follow several weeks of steady increases in infections across the country. More than 67,000 new cases are being reported daily, according to the data tracker from The New York Times, marking a 59% increase in the past two weeks.
In the Northeast, infection rates have risen by nearly 65%. In the New York and New Jersey region, infection rates are up about 55% in the past two weeks.
Hospitalizations have already begun to climb as well, with about 19,000 COVID-19 patients hospitalized nationwide and 1,725 in intensive care, according to the latest data from the Department of Health and Human Services. In the last week, hospital admissions have jumped by 20%, and emergency department visits are up by 18%.
The CDC forecast shows that 42 states and territories will see increases in hospital admissions during the next two weeks. Florida, Minnesota, New York, and Wisconsin will see some of the largest increases.
On average, more than 2,200 COVID-19 patients are entering the hospital each day, which has increased about 20% in the last week, according to ABC News. This also marks the highest number of COVID-19 patients needing hospital care since mid-March.
Public health officials have cited several factors for the increase in cases, such as states lifting mask mandates and other safety restrictions, ABC News reported. Highly contagious Omicron subvariants, such as BA.2 and BA.2.12.1, continue to spread in the United States and escape immunity from previous infections.
The BA.2 subvariant accounts for 62% of new national cases, according to the latest CDC data. The BA.2.12.1 subvariant makes up about 36% of new cases across the United States but 62% in the New York area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA limits use of J&J COVID vaccine over blood clot risk
In a statement issued May 5, the FDA said the J&J vaccine should only be given to people 18 and older who don’t have access to other vaccines or for whom other vaccines are not clinically appropriate. People 18 and older can also get the J&J vaccine if they choose to because they wouldn’t otherwise receive any vaccine, the FDA said.
The FDA statement was similar to the recommendation made in December by a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention committee of experts.
The FDA said the decision was made after more information was shared about the occurrence of a rare blood clotting condition, thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS), 1 or 2 weeks after people received the J&J vaccine. The finding “warrants limiting the authorized use of the vaccine,” the FDA said.
“We recognize that the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine still has a role in the current pandemic response in the United States and across the global community,” Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the statement.
“Our action reflects our updated analysis of the risk of TTS following administration of this vaccine and limits the use of the vaccine to certain individuals.”
The CDC says 16.9 million people are fully vaccinated with the J&J vaccine, compared with 76.5 million with Moderna and 126.3 million with Pfizer.
Through March 18, the CDC and FDA have detected 60 confirmed cases of TTS, including 9 fatal cases, ABC News reported.
The J&J vaccine was granted emergency authorization in February 2021. Health authorities hoped it would help spread vaccines across the nation because it only required one initial dose and didn’t need to be stored at extremely cold temperatures, unlike the two-dose Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
But 2 months after authorization, the government paused its use for 10 days because of reports of TTS. In December 2021, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices said the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines were preferred over J&J because J&J carried the rare risk of blood clots and bleeding in the brain.
The FDA said the cause of the blood clotting is not known. But the “known and potential benefits of the vaccine” outweigh the risks for those people now allowed to receive it, the FDA said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In a statement issued May 5, the FDA said the J&J vaccine should only be given to people 18 and older who don’t have access to other vaccines or for whom other vaccines are not clinically appropriate. People 18 and older can also get the J&J vaccine if they choose to because they wouldn’t otherwise receive any vaccine, the FDA said.
The FDA statement was similar to the recommendation made in December by a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention committee of experts.
The FDA said the decision was made after more information was shared about the occurrence of a rare blood clotting condition, thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS), 1 or 2 weeks after people received the J&J vaccine. The finding “warrants limiting the authorized use of the vaccine,” the FDA said.
“We recognize that the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine still has a role in the current pandemic response in the United States and across the global community,” Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the statement.
“Our action reflects our updated analysis of the risk of TTS following administration of this vaccine and limits the use of the vaccine to certain individuals.”
The CDC says 16.9 million people are fully vaccinated with the J&J vaccine, compared with 76.5 million with Moderna and 126.3 million with Pfizer.
Through March 18, the CDC and FDA have detected 60 confirmed cases of TTS, including 9 fatal cases, ABC News reported.
The J&J vaccine was granted emergency authorization in February 2021. Health authorities hoped it would help spread vaccines across the nation because it only required one initial dose and didn’t need to be stored at extremely cold temperatures, unlike the two-dose Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
But 2 months after authorization, the government paused its use for 10 days because of reports of TTS. In December 2021, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices said the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines were preferred over J&J because J&J carried the rare risk of blood clots and bleeding in the brain.
The FDA said the cause of the blood clotting is not known. But the “known and potential benefits of the vaccine” outweigh the risks for those people now allowed to receive it, the FDA said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In a statement issued May 5, the FDA said the J&J vaccine should only be given to people 18 and older who don’t have access to other vaccines or for whom other vaccines are not clinically appropriate. People 18 and older can also get the J&J vaccine if they choose to because they wouldn’t otherwise receive any vaccine, the FDA said.
The FDA statement was similar to the recommendation made in December by a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention committee of experts.
The FDA said the decision was made after more information was shared about the occurrence of a rare blood clotting condition, thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS), 1 or 2 weeks after people received the J&J vaccine. The finding “warrants limiting the authorized use of the vaccine,” the FDA said.
“We recognize that the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine still has a role in the current pandemic response in the United States and across the global community,” Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the statement.
“Our action reflects our updated analysis of the risk of TTS following administration of this vaccine and limits the use of the vaccine to certain individuals.”
The CDC says 16.9 million people are fully vaccinated with the J&J vaccine, compared with 76.5 million with Moderna and 126.3 million with Pfizer.
Through March 18, the CDC and FDA have detected 60 confirmed cases of TTS, including 9 fatal cases, ABC News reported.
The J&J vaccine was granted emergency authorization in February 2021. Health authorities hoped it would help spread vaccines across the nation because it only required one initial dose and didn’t need to be stored at extremely cold temperatures, unlike the two-dose Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
But 2 months after authorization, the government paused its use for 10 days because of reports of TTS. In December 2021, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices said the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines were preferred over J&J because J&J carried the rare risk of blood clots and bleeding in the brain.
The FDA said the cause of the blood clotting is not known. But the “known and potential benefits of the vaccine” outweigh the risks for those people now allowed to receive it, the FDA said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Second COVID booster: Who should receive it and when?
The more boosters the better? Data from Israel show that immune protection in elderly people is strengthened even further after a fourth dose. Karl Lauterbach, MD, German minister of health, recently pleaded for a second booster for those aged 18 years and older, and he pushed for a European Union–wide recommendation. He has not been able to implement this yet.
Just as before, Germany’s Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) is only recommending the second booster for people aged 70 years and older, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is recommending the fourth vaccination for everyone aged 80 years and older, and the United States has set the general age limit at 50 years.
Specialists remain skeptical about expanding the availability of the second booster. “From an immunologic perspective, people under the age of 70 with a healthy immune system do not need this fourth vaccination,” said Christiane Falk, PhD, head of the Institute for Transplantation Immunology of the Hannover Medical School (Germany) and member of the German Federal Government COVID Expert Panel, at a Science Media Center press briefing.
After the second vaccination, young healthy people are sufficiently protected against a severe course of the disease. Dr. Falk sees the STIKO recommendation as feasible, since it can be worked with. People in nursing facilities or those with additional underlying conditions would be considered for a fourth vaccination, explained Dr. Falk.
Complete protection unrealistic
Achieving complete protection against infection through multiple boosters is not realistic, said Christoph Neumann-Haefelin, MD, head of the Working Group for Translational Virus Immunology at the Clinic for Internal Medicine II, University Hospital Freiburg, Germany. Therefore, this should not be pursued when discussing boosters. “The aim of the booster vaccination should be to protect different groups of people against severe courses of the disease,” said Dr. Neumann-Haefelin.
Neutralizing antibodies that are only present in high concentrations for a few weeks after infection or vaccination are sometimes able to prevent the infection on their own. The immunologic memory of B cells and T cells, which ensures long-lasting protection against severe courses of the disease, is at a high level after two doses, and a third dose increases the protection more.
While people with a weak immune system need significantly more vaccinations in a shorter period to receive the same protection, too many booster vaccinations against SARS-CoV-2 are not sensible for young healthy people.
Immune saturation effect
A recent study in macaques showed that an adjusted Omicron booster did not lead to higher antibody titers, compared with a usual booster. In January 2022, the EMA warned against frequent consecutive boosters that may no longer produce the desired immune response.
If someone receives a booster too early, a saturation effect can occur, warned Andreas Radbruch, PhD, scientific director of the German Rheumatism Research Center Berlin. “We know this from lots of experimental studies but also from lots of other vaccinations. For example, you cannot be vaccinated against tetanus twice at 3- or 4-week intervals. Nothing at all will happen the second time,” explained Dr. Radbruch.
If the same antigen is applied again and again at the same dose, the immune system is made so active that the antigen is directly intercepted and cannot have any new effect on the immune system. This mechanism has been known for a long time, said Dr. Radbruch.
‘Original antigenic sin’
Premature boosting could even be a handicap in the competition between immune response and virus, said Dr. Radbruch. This is due to the principle of “original antigenic sin.” If the immune system has already come into contact with a virus, contact with a new virus variant will cause it to form antibodies predominantly against those epitopes that were already present in the original virus. As a result of this, too many boosters can weaken protection against different variants.
“We have not actually observed this with SARS-CoV-2, however,” said Dr. Radbruch. “Immunity is always extremely broad. With a double or triple vaccination, all previously existing variants are covered by an affinity-matured immune system.”
Dr. Neumann-Haefelin confirmed this and added that all virus mutations, including Omicron, have different epitopes that affect the antibody response, but the T-cell response does not differ.
Dr. Radbruch said that the vaccine protection probably lasts for decades. Following an infection or vaccination, the antibody concentration in the bone marrow is similar to that achieved after a measles or tetanus vaccination. “The vaccination is already extremely efficient. You have protection at the same magnitude as for other infectious diseases or vaccinations, which is expected to last decades,” said Dr. Radbruch.
He clarified that the decrease in antibodies after vaccination and infection is normal and does not indicate a drop in protection. “Quantity and quality must not be confused here. There is simply less mass, but the grade of remaining antibody increases.”
In the competition around the virus antigens (referred to as affinity maturation), antibodies develop that bind 10 to 100 times better and are particularly protective against the virus. The immune system is thereby sustainably effective.
For whom and when?
Since the immune response is age dependent, it makes more sense to administer an additional booster to elderly people than to young people. Also included in this group, however, are people whose immune system still does not provide the same level of protection after the second or even third vaccination as that of younger, healthy people.
Dr. Radbruch noted that 4% of people older than 70 years exhibited autoantibodies against interferons. The effects are huge. “That is 20% of patients in an intensive care unit – and they all have a very poor prognosis,” said Dr. Radbruch. These people are extremely threatened by the virus. Multiple vaccinations are sensible for them.
Even people with a weak immune response benefit from multiple vaccinations, confirmed Dr. Neumann-Haefelin. “We are not seeing the antibody responses here that we see in young people with healthy immune systems until the third or fourth vaccination sometimes.”
Although for young healthy people, it is particularly important to ensure a sufficient period between vaccinations so that the affinity maturation is not impaired, those with a weak immune response can be vaccinated again as soon as after 3 months.
The “optimum minimum period of time” for people with healthy immune systems is 6 months, according to Dr. Neumann-Haefelin. “This is true for everyone in whom a proper response is expected.” The vaccine protection probably lasts significantly longer, and therefore, frequent boosting may not be necessary in the future, he said. The time separation also applies for medical personnel, for whom the Robert Koch Institute also recommends a second booster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The more boosters the better? Data from Israel show that immune protection in elderly people is strengthened even further after a fourth dose. Karl Lauterbach, MD, German minister of health, recently pleaded for a second booster for those aged 18 years and older, and he pushed for a European Union–wide recommendation. He has not been able to implement this yet.
Just as before, Germany’s Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) is only recommending the second booster for people aged 70 years and older, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is recommending the fourth vaccination for everyone aged 80 years and older, and the United States has set the general age limit at 50 years.
Specialists remain skeptical about expanding the availability of the second booster. “From an immunologic perspective, people under the age of 70 with a healthy immune system do not need this fourth vaccination,” said Christiane Falk, PhD, head of the Institute for Transplantation Immunology of the Hannover Medical School (Germany) and member of the German Federal Government COVID Expert Panel, at a Science Media Center press briefing.
After the second vaccination, young healthy people are sufficiently protected against a severe course of the disease. Dr. Falk sees the STIKO recommendation as feasible, since it can be worked with. People in nursing facilities or those with additional underlying conditions would be considered for a fourth vaccination, explained Dr. Falk.
Complete protection unrealistic
Achieving complete protection against infection through multiple boosters is not realistic, said Christoph Neumann-Haefelin, MD, head of the Working Group for Translational Virus Immunology at the Clinic for Internal Medicine II, University Hospital Freiburg, Germany. Therefore, this should not be pursued when discussing boosters. “The aim of the booster vaccination should be to protect different groups of people against severe courses of the disease,” said Dr. Neumann-Haefelin.
Neutralizing antibodies that are only present in high concentrations for a few weeks after infection or vaccination are sometimes able to prevent the infection on their own. The immunologic memory of B cells and T cells, which ensures long-lasting protection against severe courses of the disease, is at a high level after two doses, and a third dose increases the protection more.
While people with a weak immune system need significantly more vaccinations in a shorter period to receive the same protection, too many booster vaccinations against SARS-CoV-2 are not sensible for young healthy people.
Immune saturation effect
A recent study in macaques showed that an adjusted Omicron booster did not lead to higher antibody titers, compared with a usual booster. In January 2022, the EMA warned against frequent consecutive boosters that may no longer produce the desired immune response.
If someone receives a booster too early, a saturation effect can occur, warned Andreas Radbruch, PhD, scientific director of the German Rheumatism Research Center Berlin. “We know this from lots of experimental studies but also from lots of other vaccinations. For example, you cannot be vaccinated against tetanus twice at 3- or 4-week intervals. Nothing at all will happen the second time,” explained Dr. Radbruch.
If the same antigen is applied again and again at the same dose, the immune system is made so active that the antigen is directly intercepted and cannot have any new effect on the immune system. This mechanism has been known for a long time, said Dr. Radbruch.
‘Original antigenic sin’
Premature boosting could even be a handicap in the competition between immune response and virus, said Dr. Radbruch. This is due to the principle of “original antigenic sin.” If the immune system has already come into contact with a virus, contact with a new virus variant will cause it to form antibodies predominantly against those epitopes that were already present in the original virus. As a result of this, too many boosters can weaken protection against different variants.
“We have not actually observed this with SARS-CoV-2, however,” said Dr. Radbruch. “Immunity is always extremely broad. With a double or triple vaccination, all previously existing variants are covered by an affinity-matured immune system.”
Dr. Neumann-Haefelin confirmed this and added that all virus mutations, including Omicron, have different epitopes that affect the antibody response, but the T-cell response does not differ.
Dr. Radbruch said that the vaccine protection probably lasts for decades. Following an infection or vaccination, the antibody concentration in the bone marrow is similar to that achieved after a measles or tetanus vaccination. “The vaccination is already extremely efficient. You have protection at the same magnitude as for other infectious diseases or vaccinations, which is expected to last decades,” said Dr. Radbruch.
He clarified that the decrease in antibodies after vaccination and infection is normal and does not indicate a drop in protection. “Quantity and quality must not be confused here. There is simply less mass, but the grade of remaining antibody increases.”
In the competition around the virus antigens (referred to as affinity maturation), antibodies develop that bind 10 to 100 times better and are particularly protective against the virus. The immune system is thereby sustainably effective.
For whom and when?
Since the immune response is age dependent, it makes more sense to administer an additional booster to elderly people than to young people. Also included in this group, however, are people whose immune system still does not provide the same level of protection after the second or even third vaccination as that of younger, healthy people.
Dr. Radbruch noted that 4% of people older than 70 years exhibited autoantibodies against interferons. The effects are huge. “That is 20% of patients in an intensive care unit – and they all have a very poor prognosis,” said Dr. Radbruch. These people are extremely threatened by the virus. Multiple vaccinations are sensible for them.
Even people with a weak immune response benefit from multiple vaccinations, confirmed Dr. Neumann-Haefelin. “We are not seeing the antibody responses here that we see in young people with healthy immune systems until the third or fourth vaccination sometimes.”
Although for young healthy people, it is particularly important to ensure a sufficient period between vaccinations so that the affinity maturation is not impaired, those with a weak immune response can be vaccinated again as soon as after 3 months.
The “optimum minimum period of time” for people with healthy immune systems is 6 months, according to Dr. Neumann-Haefelin. “This is true for everyone in whom a proper response is expected.” The vaccine protection probably lasts significantly longer, and therefore, frequent boosting may not be necessary in the future, he said. The time separation also applies for medical personnel, for whom the Robert Koch Institute also recommends a second booster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The more boosters the better? Data from Israel show that immune protection in elderly people is strengthened even further after a fourth dose. Karl Lauterbach, MD, German minister of health, recently pleaded for a second booster for those aged 18 years and older, and he pushed for a European Union–wide recommendation. He has not been able to implement this yet.
Just as before, Germany’s Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) is only recommending the second booster for people aged 70 years and older, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is recommending the fourth vaccination for everyone aged 80 years and older, and the United States has set the general age limit at 50 years.
Specialists remain skeptical about expanding the availability of the second booster. “From an immunologic perspective, people under the age of 70 with a healthy immune system do not need this fourth vaccination,” said Christiane Falk, PhD, head of the Institute for Transplantation Immunology of the Hannover Medical School (Germany) and member of the German Federal Government COVID Expert Panel, at a Science Media Center press briefing.
After the second vaccination, young healthy people are sufficiently protected against a severe course of the disease. Dr. Falk sees the STIKO recommendation as feasible, since it can be worked with. People in nursing facilities or those with additional underlying conditions would be considered for a fourth vaccination, explained Dr. Falk.
Complete protection unrealistic
Achieving complete protection against infection through multiple boosters is not realistic, said Christoph Neumann-Haefelin, MD, head of the Working Group for Translational Virus Immunology at the Clinic for Internal Medicine II, University Hospital Freiburg, Germany. Therefore, this should not be pursued when discussing boosters. “The aim of the booster vaccination should be to protect different groups of people against severe courses of the disease,” said Dr. Neumann-Haefelin.
Neutralizing antibodies that are only present in high concentrations for a few weeks after infection or vaccination are sometimes able to prevent the infection on their own. The immunologic memory of B cells and T cells, which ensures long-lasting protection against severe courses of the disease, is at a high level after two doses, and a third dose increases the protection more.
While people with a weak immune system need significantly more vaccinations in a shorter period to receive the same protection, too many booster vaccinations against SARS-CoV-2 are not sensible for young healthy people.
Immune saturation effect
A recent study in macaques showed that an adjusted Omicron booster did not lead to higher antibody titers, compared with a usual booster. In January 2022, the EMA warned against frequent consecutive boosters that may no longer produce the desired immune response.
If someone receives a booster too early, a saturation effect can occur, warned Andreas Radbruch, PhD, scientific director of the German Rheumatism Research Center Berlin. “We know this from lots of experimental studies but also from lots of other vaccinations. For example, you cannot be vaccinated against tetanus twice at 3- or 4-week intervals. Nothing at all will happen the second time,” explained Dr. Radbruch.
If the same antigen is applied again and again at the same dose, the immune system is made so active that the antigen is directly intercepted and cannot have any new effect on the immune system. This mechanism has been known for a long time, said Dr. Radbruch.
‘Original antigenic sin’
Premature boosting could even be a handicap in the competition between immune response and virus, said Dr. Radbruch. This is due to the principle of “original antigenic sin.” If the immune system has already come into contact with a virus, contact with a new virus variant will cause it to form antibodies predominantly against those epitopes that were already present in the original virus. As a result of this, too many boosters can weaken protection against different variants.
“We have not actually observed this with SARS-CoV-2, however,” said Dr. Radbruch. “Immunity is always extremely broad. With a double or triple vaccination, all previously existing variants are covered by an affinity-matured immune system.”
Dr. Neumann-Haefelin confirmed this and added that all virus mutations, including Omicron, have different epitopes that affect the antibody response, but the T-cell response does not differ.
Dr. Radbruch said that the vaccine protection probably lasts for decades. Following an infection or vaccination, the antibody concentration in the bone marrow is similar to that achieved after a measles or tetanus vaccination. “The vaccination is already extremely efficient. You have protection at the same magnitude as for other infectious diseases or vaccinations, which is expected to last decades,” said Dr. Radbruch.
He clarified that the decrease in antibodies after vaccination and infection is normal and does not indicate a drop in protection. “Quantity and quality must not be confused here. There is simply less mass, but the grade of remaining antibody increases.”
In the competition around the virus antigens (referred to as affinity maturation), antibodies develop that bind 10 to 100 times better and are particularly protective against the virus. The immune system is thereby sustainably effective.
For whom and when?
Since the immune response is age dependent, it makes more sense to administer an additional booster to elderly people than to young people. Also included in this group, however, are people whose immune system still does not provide the same level of protection after the second or even third vaccination as that of younger, healthy people.
Dr. Radbruch noted that 4% of people older than 70 years exhibited autoantibodies against interferons. The effects are huge. “That is 20% of patients in an intensive care unit – and they all have a very poor prognosis,” said Dr. Radbruch. These people are extremely threatened by the virus. Multiple vaccinations are sensible for them.
Even people with a weak immune response benefit from multiple vaccinations, confirmed Dr. Neumann-Haefelin. “We are not seeing the antibody responses here that we see in young people with healthy immune systems until the third or fourth vaccination sometimes.”
Although for young healthy people, it is particularly important to ensure a sufficient period between vaccinations so that the affinity maturation is not impaired, those with a weak immune response can be vaccinated again as soon as after 3 months.
The “optimum minimum period of time” for people with healthy immune systems is 6 months, according to Dr. Neumann-Haefelin. “This is true for everyone in whom a proper response is expected.” The vaccine protection probably lasts significantly longer, and therefore, frequent boosting may not be necessary in the future, he said. The time separation also applies for medical personnel, for whom the Robert Koch Institute also recommends a second booster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Omicron sublineages evade immunity from past infection
A South African study based on blood samples found that the BA.4 and BA.5 sublineages of Omicron were more likely to evade antibodies produced by previous Omicron infections than the immunity provided by vaccinations.
Scientists took blood samples from 39 people infected with Omicron, with 24 people not vaccinated and 15 vaccinated with the Pfizer or the Johnson & Johnson vaccines, Reuters reported.
“The vaccinated group showed about a fivefold higher neutralization capacity ... and should be better protected,” the investigators found, according to Reuters.
There was an eightfold decrease in antibody protection in unvaccinated blood samples when exposed to the subvariants compared to a threefold decrease in the blood samples from vaccinated people.
“Based on neutralization escape, BA.4 and BA.5 have potential to result in a new infection wave,” the investigators found.
The finding is important because health authorities say cases caused by the sublineages are increasing in South Africa to a degree that the nation may be entering a fifth wave of COVID, Reuters said.
Health Minister Joe Phaahla said recently that hospitalizations were increasing but that ICU admissions had not greatly gone up yet.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A South African study based on blood samples found that the BA.4 and BA.5 sublineages of Omicron were more likely to evade antibodies produced by previous Omicron infections than the immunity provided by vaccinations.
Scientists took blood samples from 39 people infected with Omicron, with 24 people not vaccinated and 15 vaccinated with the Pfizer or the Johnson & Johnson vaccines, Reuters reported.
“The vaccinated group showed about a fivefold higher neutralization capacity ... and should be better protected,” the investigators found, according to Reuters.
There was an eightfold decrease in antibody protection in unvaccinated blood samples when exposed to the subvariants compared to a threefold decrease in the blood samples from vaccinated people.
“Based on neutralization escape, BA.4 and BA.5 have potential to result in a new infection wave,” the investigators found.
The finding is important because health authorities say cases caused by the sublineages are increasing in South Africa to a degree that the nation may be entering a fifth wave of COVID, Reuters said.
Health Minister Joe Phaahla said recently that hospitalizations were increasing but that ICU admissions had not greatly gone up yet.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A South African study based on blood samples found that the BA.4 and BA.5 sublineages of Omicron were more likely to evade antibodies produced by previous Omicron infections than the immunity provided by vaccinations.
Scientists took blood samples from 39 people infected with Omicron, with 24 people not vaccinated and 15 vaccinated with the Pfizer or the Johnson & Johnson vaccines, Reuters reported.
“The vaccinated group showed about a fivefold higher neutralization capacity ... and should be better protected,” the investigators found, according to Reuters.
There was an eightfold decrease in antibody protection in unvaccinated blood samples when exposed to the subvariants compared to a threefold decrease in the blood samples from vaccinated people.
“Based on neutralization escape, BA.4 and BA.5 have potential to result in a new infection wave,” the investigators found.
The finding is important because health authorities say cases caused by the sublineages are increasing in South Africa to a degree that the nation may be entering a fifth wave of COVID, Reuters said.
Health Minister Joe Phaahla said recently that hospitalizations were increasing but that ICU admissions had not greatly gone up yet.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Newly defined liver disorder associated with COVID mortality
People with metabolic dysfunction–associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) – a newly defined condition – may be more likely to die from COVID-19, researchers say.
A cohort of people hospitalized for COVID-19 in Central Military Hospital, Mexico City, who met the criteria for MAFLD died at a higher rate than a control group without fatty liver disease, said Martín Uriel Vázquez-Medina, MSc, a researcher in the National Polytechnic Institute in Mexico City.
Patients who met only the criteria for the traditional classification, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also died of COVID-19 at a higher rate than the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant.
“It is important to screen for MAFLD,” Mr. Vázquez-Medina told this news organization. “It’s a new definition, but it has really helped us to identify which patients are going to get worse by COVID-19.”
The study was published in Hepatology Communications.
More evidence for clinical relevance of MAFLD
The finding lends support to an initiative to use MAFLD instead of NAFLD to identify patients whose liver steatosis poses a threat to their health, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said.
NAFLD affects as much as a quarter of the world’s population. No drugs have been approved to treat it. Some researchers have reasoned that the imprecision of the definition of NAFLD could be one reason for the lack of progress in treatment.
“NAFLD is something that doesn’t have positive criteria to be diagnosed,” said Mr. Vázquez-Medina. “You only say NAFLD when you don’t find hepatitis or another disease.”
In an article published in Gastroenterology, an international consensus panel proposed MAFLD as an alternative, arguing that a focus on metabolic dysfunction could more accurately reflect the pathogenesis of the disease and help stratify patients.
Previous research has suggested that patients with MAFLD have a higher risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and that the prevalence of colorectal adenomas is a higher in these patients, compared with patients with NAFLD.
The high prevalence of MAFLD in Mexico – about 30% – could help explain the country’s high rate of mortality from COVID-19, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said. Almost 6% of people diagnosed with COVID in Mexico have died from it, according to the Johns Hopkins University and Medical Center Coronavirus Resource Center.
Sorting COVID outcomes by liver steatosis
To understand the interaction of MAFLD, NAFLD, liver fibrosis, and COVID-19, Mr. Vázquez-Medina and his colleagues analyzed the records of all patients admitted to the Central Military Hospital with COVID-19 from April 4, 2020, to June 24, 2020.
They excluded patients for whom complete data were lacking or for whom a liver function test was not conducted in the first 24 hours of hospitalization. Also excluded were patients with significant consumption of alcohol (> 30 g/day for men and > 20 g/day for women) and those with a history of autoimmune liver disease, liver cancer, decompensated cirrhosis, platelet disorders, or myopathies.
The remaining patients were divided into three groups – 220 who met the criteria for MAFLD, 79 who met the criteria for NAFLD but not MAFLD, and 60 other patients as a control group.
The researchers defined MAFLD as the presence of liver steatosis detected with a noninvasive method and one of the following: overweight (body mass index, 25-29.9 kg/m2), type 2 diabetes, or the presence of two metabolic abnormalities (blood pressure > 140/90 mm Hg, plasma triglycerides > 150 mg/dL, plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol < 40 mg/dL in men and < 50 mg/dL in women, and prediabetes).
They defined NAFLD as the presence of liver steatosis without the other criteria for MAFLD.
The patients with MAFLD were the most likely to be intubated and were the most likely to die (intubation, 44.09%; mortality, 55%), followed by those with NAFLD (intubation, 40.51%; mortality, 51.9%) and those in the control group (intubation, 20%; mortality, 38.33%).
The difference in mortality between the MAFLD group and the control group was statistically significant (P = .02). The mortality difference between the NAFLD and the control group fell just short of statistical significance (P = .07).
For intubation, the difference between the MAFLD and the control group was highly statistically significant (P = .001), and the difference between the NAFLD and the control group was also statistically significant (P = .01)
Patients with advanced fibrosis and either MAFLD or NAFLD were also more likely to die than patients in the control group with advanced fibrosis.
That’s why screening for MAFLD is important, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said.
Next steps and new questions
Future research should examine whether patients with MAFLD have elevated levels of biomarkers for inflammation, such as interleukin 6, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said. A “chronic low proinflammatory state” may be the key to understanding the vulnerability of patients to MAFLD to COVID-19, he speculated.
The metabolic traits associated with MAFLD could explain the higher mortality and intubation rates with COVID, said Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc, a professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology at the University of California, San Diego, who was not involved in the study.
“Hypertension, diabetes, and obesity increase the risk of complications from COVID in all patients, whether they have been diagnosed with NAFLD or not,” he told this news organization in an email.
Mr. Vasquez-Medina pointed out that the patients with MAFLD had a higher risk of mortality even after adjusting for age, sex, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, overweight, and obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2). MAFLD also was more strongly associated with a poor outcome than either hypertension alone or obesity alone. Only age emerged as a significant independent covariate in the study.
Dr. Loomba also questioned whether the regression model used in this study for liver steatosis was “fully reflective of NAFLD.”
The researchers identified liver steatosis with a diagnostic formula that used noninvasive clinical BMI and laboratory tests (alanine aminotransferase), citing a study that found the regression formula was better at diagnosing NAFLD than FibroScan.
Mr. Vázquez-Medina reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Loomba serves as a consultant to Aardvark Therapeutics, Altimmune, Anylam/Regeneron, Amgen, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CohBar, Eli Lilly, Galmed, Gilead, Glympse Bio, Hightide, Inipharma, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, Janssen, Madrigal, Metacrine, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Pfizer, Sagimet, Theratechnologies, 89bio, Terns Pharmaceuticals, and Viking Therapeutics. He is co-founder of LipoNexus.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with metabolic dysfunction–associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) – a newly defined condition – may be more likely to die from COVID-19, researchers say.
A cohort of people hospitalized for COVID-19 in Central Military Hospital, Mexico City, who met the criteria for MAFLD died at a higher rate than a control group without fatty liver disease, said Martín Uriel Vázquez-Medina, MSc, a researcher in the National Polytechnic Institute in Mexico City.
Patients who met only the criteria for the traditional classification, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also died of COVID-19 at a higher rate than the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant.
“It is important to screen for MAFLD,” Mr. Vázquez-Medina told this news organization. “It’s a new definition, but it has really helped us to identify which patients are going to get worse by COVID-19.”
The study was published in Hepatology Communications.
More evidence for clinical relevance of MAFLD
The finding lends support to an initiative to use MAFLD instead of NAFLD to identify patients whose liver steatosis poses a threat to their health, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said.
NAFLD affects as much as a quarter of the world’s population. No drugs have been approved to treat it. Some researchers have reasoned that the imprecision of the definition of NAFLD could be one reason for the lack of progress in treatment.
“NAFLD is something that doesn’t have positive criteria to be diagnosed,” said Mr. Vázquez-Medina. “You only say NAFLD when you don’t find hepatitis or another disease.”
In an article published in Gastroenterology, an international consensus panel proposed MAFLD as an alternative, arguing that a focus on metabolic dysfunction could more accurately reflect the pathogenesis of the disease and help stratify patients.
Previous research has suggested that patients with MAFLD have a higher risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and that the prevalence of colorectal adenomas is a higher in these patients, compared with patients with NAFLD.
The high prevalence of MAFLD in Mexico – about 30% – could help explain the country’s high rate of mortality from COVID-19, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said. Almost 6% of people diagnosed with COVID in Mexico have died from it, according to the Johns Hopkins University and Medical Center Coronavirus Resource Center.
Sorting COVID outcomes by liver steatosis
To understand the interaction of MAFLD, NAFLD, liver fibrosis, and COVID-19, Mr. Vázquez-Medina and his colleagues analyzed the records of all patients admitted to the Central Military Hospital with COVID-19 from April 4, 2020, to June 24, 2020.
They excluded patients for whom complete data were lacking or for whom a liver function test was not conducted in the first 24 hours of hospitalization. Also excluded were patients with significant consumption of alcohol (> 30 g/day for men and > 20 g/day for women) and those with a history of autoimmune liver disease, liver cancer, decompensated cirrhosis, platelet disorders, or myopathies.
The remaining patients were divided into three groups – 220 who met the criteria for MAFLD, 79 who met the criteria for NAFLD but not MAFLD, and 60 other patients as a control group.
The researchers defined MAFLD as the presence of liver steatosis detected with a noninvasive method and one of the following: overweight (body mass index, 25-29.9 kg/m2), type 2 diabetes, or the presence of two metabolic abnormalities (blood pressure > 140/90 mm Hg, plasma triglycerides > 150 mg/dL, plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol < 40 mg/dL in men and < 50 mg/dL in women, and prediabetes).
They defined NAFLD as the presence of liver steatosis without the other criteria for MAFLD.
The patients with MAFLD were the most likely to be intubated and were the most likely to die (intubation, 44.09%; mortality, 55%), followed by those with NAFLD (intubation, 40.51%; mortality, 51.9%) and those in the control group (intubation, 20%; mortality, 38.33%).
The difference in mortality between the MAFLD group and the control group was statistically significant (P = .02). The mortality difference between the NAFLD and the control group fell just short of statistical significance (P = .07).
For intubation, the difference between the MAFLD and the control group was highly statistically significant (P = .001), and the difference between the NAFLD and the control group was also statistically significant (P = .01)
Patients with advanced fibrosis and either MAFLD or NAFLD were also more likely to die than patients in the control group with advanced fibrosis.
That’s why screening for MAFLD is important, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said.
Next steps and new questions
Future research should examine whether patients with MAFLD have elevated levels of biomarkers for inflammation, such as interleukin 6, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said. A “chronic low proinflammatory state” may be the key to understanding the vulnerability of patients to MAFLD to COVID-19, he speculated.
The metabolic traits associated with MAFLD could explain the higher mortality and intubation rates with COVID, said Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc, a professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology at the University of California, San Diego, who was not involved in the study.
“Hypertension, diabetes, and obesity increase the risk of complications from COVID in all patients, whether they have been diagnosed with NAFLD or not,” he told this news organization in an email.
Mr. Vasquez-Medina pointed out that the patients with MAFLD had a higher risk of mortality even after adjusting for age, sex, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, overweight, and obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2). MAFLD also was more strongly associated with a poor outcome than either hypertension alone or obesity alone. Only age emerged as a significant independent covariate in the study.
Dr. Loomba also questioned whether the regression model used in this study for liver steatosis was “fully reflective of NAFLD.”
The researchers identified liver steatosis with a diagnostic formula that used noninvasive clinical BMI and laboratory tests (alanine aminotransferase), citing a study that found the regression formula was better at diagnosing NAFLD than FibroScan.
Mr. Vázquez-Medina reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Loomba serves as a consultant to Aardvark Therapeutics, Altimmune, Anylam/Regeneron, Amgen, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CohBar, Eli Lilly, Galmed, Gilead, Glympse Bio, Hightide, Inipharma, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, Janssen, Madrigal, Metacrine, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Pfizer, Sagimet, Theratechnologies, 89bio, Terns Pharmaceuticals, and Viking Therapeutics. He is co-founder of LipoNexus.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with metabolic dysfunction–associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) – a newly defined condition – may be more likely to die from COVID-19, researchers say.
A cohort of people hospitalized for COVID-19 in Central Military Hospital, Mexico City, who met the criteria for MAFLD died at a higher rate than a control group without fatty liver disease, said Martín Uriel Vázquez-Medina, MSc, a researcher in the National Polytechnic Institute in Mexico City.
Patients who met only the criteria for the traditional classification, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also died of COVID-19 at a higher rate than the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant.
“It is important to screen for MAFLD,” Mr. Vázquez-Medina told this news organization. “It’s a new definition, but it has really helped us to identify which patients are going to get worse by COVID-19.”
The study was published in Hepatology Communications.
More evidence for clinical relevance of MAFLD
The finding lends support to an initiative to use MAFLD instead of NAFLD to identify patients whose liver steatosis poses a threat to their health, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said.
NAFLD affects as much as a quarter of the world’s population. No drugs have been approved to treat it. Some researchers have reasoned that the imprecision of the definition of NAFLD could be one reason for the lack of progress in treatment.
“NAFLD is something that doesn’t have positive criteria to be diagnosed,” said Mr. Vázquez-Medina. “You only say NAFLD when you don’t find hepatitis or another disease.”
In an article published in Gastroenterology, an international consensus panel proposed MAFLD as an alternative, arguing that a focus on metabolic dysfunction could more accurately reflect the pathogenesis of the disease and help stratify patients.
Previous research has suggested that patients with MAFLD have a higher risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and that the prevalence of colorectal adenomas is a higher in these patients, compared with patients with NAFLD.
The high prevalence of MAFLD in Mexico – about 30% – could help explain the country’s high rate of mortality from COVID-19, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said. Almost 6% of people diagnosed with COVID in Mexico have died from it, according to the Johns Hopkins University and Medical Center Coronavirus Resource Center.
Sorting COVID outcomes by liver steatosis
To understand the interaction of MAFLD, NAFLD, liver fibrosis, and COVID-19, Mr. Vázquez-Medina and his colleagues analyzed the records of all patients admitted to the Central Military Hospital with COVID-19 from April 4, 2020, to June 24, 2020.
They excluded patients for whom complete data were lacking or for whom a liver function test was not conducted in the first 24 hours of hospitalization. Also excluded were patients with significant consumption of alcohol (> 30 g/day for men and > 20 g/day for women) and those with a history of autoimmune liver disease, liver cancer, decompensated cirrhosis, platelet disorders, or myopathies.
The remaining patients were divided into three groups – 220 who met the criteria for MAFLD, 79 who met the criteria for NAFLD but not MAFLD, and 60 other patients as a control group.
The researchers defined MAFLD as the presence of liver steatosis detected with a noninvasive method and one of the following: overweight (body mass index, 25-29.9 kg/m2), type 2 diabetes, or the presence of two metabolic abnormalities (blood pressure > 140/90 mm Hg, plasma triglycerides > 150 mg/dL, plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol < 40 mg/dL in men and < 50 mg/dL in women, and prediabetes).
They defined NAFLD as the presence of liver steatosis without the other criteria for MAFLD.
The patients with MAFLD were the most likely to be intubated and were the most likely to die (intubation, 44.09%; mortality, 55%), followed by those with NAFLD (intubation, 40.51%; mortality, 51.9%) and those in the control group (intubation, 20%; mortality, 38.33%).
The difference in mortality between the MAFLD group and the control group was statistically significant (P = .02). The mortality difference between the NAFLD and the control group fell just short of statistical significance (P = .07).
For intubation, the difference between the MAFLD and the control group was highly statistically significant (P = .001), and the difference between the NAFLD and the control group was also statistically significant (P = .01)
Patients with advanced fibrosis and either MAFLD or NAFLD were also more likely to die than patients in the control group with advanced fibrosis.
That’s why screening for MAFLD is important, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said.
Next steps and new questions
Future research should examine whether patients with MAFLD have elevated levels of biomarkers for inflammation, such as interleukin 6, Mr. Vázquez-Medina said. A “chronic low proinflammatory state” may be the key to understanding the vulnerability of patients to MAFLD to COVID-19, he speculated.
The metabolic traits associated with MAFLD could explain the higher mortality and intubation rates with COVID, said Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc, a professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology at the University of California, San Diego, who was not involved in the study.
“Hypertension, diabetes, and obesity increase the risk of complications from COVID in all patients, whether they have been diagnosed with NAFLD or not,” he told this news organization in an email.
Mr. Vasquez-Medina pointed out that the patients with MAFLD had a higher risk of mortality even after adjusting for age, sex, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, overweight, and obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2). MAFLD also was more strongly associated with a poor outcome than either hypertension alone or obesity alone. Only age emerged as a significant independent covariate in the study.
Dr. Loomba also questioned whether the regression model used in this study for liver steatosis was “fully reflective of NAFLD.”
The researchers identified liver steatosis with a diagnostic formula that used noninvasive clinical BMI and laboratory tests (alanine aminotransferase), citing a study that found the regression formula was better at diagnosing NAFLD than FibroScan.
Mr. Vázquez-Medina reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Loomba serves as a consultant to Aardvark Therapeutics, Altimmune, Anylam/Regeneron, Amgen, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CohBar, Eli Lilly, Galmed, Gilead, Glympse Bio, Hightide, Inipharma, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, Janssen, Madrigal, Metacrine, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Pfizer, Sagimet, Theratechnologies, 89bio, Terns Pharmaceuticals, and Viking Therapeutics. He is co-founder of LipoNexus.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HEPATOLOGY COMMUNICATIONS
Severe COVID-19 adds 20 years of cognitive aging: Study
adding that the impairment is “equivalent to losing 10 IQ points.”
In their study, published in eClinicalMedicine, a team of scientists from the University of Cambridge and Imperial College London said there is growing evidence that COVID-19 can cause lasting cognitive and mental health problems. Patients report fatigue, “brain fog,” problems recalling words, sleep disturbances, anxiety, and even posttraumatic stress disorder months after infection.
The researchers analyzed data from 46 individuals who received critical care for COVID-19 at Addenbrooke’s Hospital between March and July 2020 (27 females, 19 males, mean age 51 years, 16 of whom had mechanical ventilation) and were recruited to the NIHR COVID-19 BioResource project.
At an average of 6 months after acute COVID-19 illness, the study participants underwent detailed computerized cognitive tests via the Cognitron platform, comprising eight tasks deployed on an iPad measuring mental function such as memory, attention, and reasoning. Also assessed were anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder via standard mood, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress scales – specifically the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7 (GAD-7), the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9), and the PTSD Checklist for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 (PCL-5). Their data were compared against 460 controls – matched for age, sex, education, and first language – and the pattern of deficits across tasks was qualitatively compared with normal age-related decline and early-stage dementia.
Less accurate and slower response times
The authors highlighted how this was the first time a “rigorous assessment and comparison” had been carried out in relation to the after-effects of severe COVID-19.
“Cognitive impairment is common to a wide range of neurological disorders, including dementia, and even routine aging, but the patterns we saw – the cognitive ‘fingerprint’ of COVID-19 – was distinct from all of these,” said David Menon, MD, division of anesthesia at the University of Cambridge, England, and the study’s senior author.
The scientists found that COVID-19 survivors were less accurate and had slower response times than the control population, and added that survivors scored particularly poorly on verbal analogical reasoning and showed slower processing speeds.
Critically, the scale of the cognitive deficits correlated with acute illness severity, but not fatigue or mental health status at the time of cognitive assessment, said the authors.
Recovery ‘at best gradual’
The effects were strongest for those with more severe acute illness, and who required mechanical ventilation, said the authors, who found that acute illness severity was “better at predicting the cognitive deficits.”
The authors pointed out how these deficits were still detectable when patients were followed up 6 months later, and that, although patients’ scores and reaction times began to improve over time, any recovery was “at best gradual” and likely to be influenced by factors such as illness severity and its neurological or psychological impacts.
“We followed some patients up as late as 10 months after their acute infection, so were able to see a very slow improvement,” Dr. Menon said. He explained how, while this improvement was not statistically significant, it was “at least heading in the right direction.”
However, he warned it is very possible that some of these individuals “will never fully recover.”
The cognitive deficits observed may be due to several factors in combination, said the authors, including inadequate oxygen or blood supply to the brain, blockage of large or small blood vessels due to clotting, and microscopic bleeds. They highlighted how the most important mechanism, however, may be “damage caused by the body’s own inflammatory response and immune system.”
Adam Hampshire, PhD, of the department of brain sciences at Imperial College London, one of the study’s authors, described how around 40,000 people have been through intensive care with COVID-19 in England alone, with many more despite having been very sick not admitted to hospital. This means there is a “large number of people out there still experiencing problems with cognition many months later,” he said. “We urgently need to look at what can be done to help these people.”
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.
adding that the impairment is “equivalent to losing 10 IQ points.”
In their study, published in eClinicalMedicine, a team of scientists from the University of Cambridge and Imperial College London said there is growing evidence that COVID-19 can cause lasting cognitive and mental health problems. Patients report fatigue, “brain fog,” problems recalling words, sleep disturbances, anxiety, and even posttraumatic stress disorder months after infection.
The researchers analyzed data from 46 individuals who received critical care for COVID-19 at Addenbrooke’s Hospital between March and July 2020 (27 females, 19 males, mean age 51 years, 16 of whom had mechanical ventilation) and were recruited to the NIHR COVID-19 BioResource project.
At an average of 6 months after acute COVID-19 illness, the study participants underwent detailed computerized cognitive tests via the Cognitron platform, comprising eight tasks deployed on an iPad measuring mental function such as memory, attention, and reasoning. Also assessed were anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder via standard mood, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress scales – specifically the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7 (GAD-7), the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9), and the PTSD Checklist for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 (PCL-5). Their data were compared against 460 controls – matched for age, sex, education, and first language – and the pattern of deficits across tasks was qualitatively compared with normal age-related decline and early-stage dementia.
Less accurate and slower response times
The authors highlighted how this was the first time a “rigorous assessment and comparison” had been carried out in relation to the after-effects of severe COVID-19.
“Cognitive impairment is common to a wide range of neurological disorders, including dementia, and even routine aging, but the patterns we saw – the cognitive ‘fingerprint’ of COVID-19 – was distinct from all of these,” said David Menon, MD, division of anesthesia at the University of Cambridge, England, and the study’s senior author.
The scientists found that COVID-19 survivors were less accurate and had slower response times than the control population, and added that survivors scored particularly poorly on verbal analogical reasoning and showed slower processing speeds.
Critically, the scale of the cognitive deficits correlated with acute illness severity, but not fatigue or mental health status at the time of cognitive assessment, said the authors.
Recovery ‘at best gradual’
The effects were strongest for those with more severe acute illness, and who required mechanical ventilation, said the authors, who found that acute illness severity was “better at predicting the cognitive deficits.”
The authors pointed out how these deficits were still detectable when patients were followed up 6 months later, and that, although patients’ scores and reaction times began to improve over time, any recovery was “at best gradual” and likely to be influenced by factors such as illness severity and its neurological or psychological impacts.
“We followed some patients up as late as 10 months after their acute infection, so were able to see a very slow improvement,” Dr. Menon said. He explained how, while this improvement was not statistically significant, it was “at least heading in the right direction.”
However, he warned it is very possible that some of these individuals “will never fully recover.”
The cognitive deficits observed may be due to several factors in combination, said the authors, including inadequate oxygen or blood supply to the brain, blockage of large or small blood vessels due to clotting, and microscopic bleeds. They highlighted how the most important mechanism, however, may be “damage caused by the body’s own inflammatory response and immune system.”
Adam Hampshire, PhD, of the department of brain sciences at Imperial College London, one of the study’s authors, described how around 40,000 people have been through intensive care with COVID-19 in England alone, with many more despite having been very sick not admitted to hospital. This means there is a “large number of people out there still experiencing problems with cognition many months later,” he said. “We urgently need to look at what can be done to help these people.”
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.
adding that the impairment is “equivalent to losing 10 IQ points.”
In their study, published in eClinicalMedicine, a team of scientists from the University of Cambridge and Imperial College London said there is growing evidence that COVID-19 can cause lasting cognitive and mental health problems. Patients report fatigue, “brain fog,” problems recalling words, sleep disturbances, anxiety, and even posttraumatic stress disorder months after infection.
The researchers analyzed data from 46 individuals who received critical care for COVID-19 at Addenbrooke’s Hospital between March and July 2020 (27 females, 19 males, mean age 51 years, 16 of whom had mechanical ventilation) and were recruited to the NIHR COVID-19 BioResource project.
At an average of 6 months after acute COVID-19 illness, the study participants underwent detailed computerized cognitive tests via the Cognitron platform, comprising eight tasks deployed on an iPad measuring mental function such as memory, attention, and reasoning. Also assessed were anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder via standard mood, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress scales – specifically the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7 (GAD-7), the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9), and the PTSD Checklist for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 (PCL-5). Their data were compared against 460 controls – matched for age, sex, education, and first language – and the pattern of deficits across tasks was qualitatively compared with normal age-related decline and early-stage dementia.
Less accurate and slower response times
The authors highlighted how this was the first time a “rigorous assessment and comparison” had been carried out in relation to the after-effects of severe COVID-19.
“Cognitive impairment is common to a wide range of neurological disorders, including dementia, and even routine aging, but the patterns we saw – the cognitive ‘fingerprint’ of COVID-19 – was distinct from all of these,” said David Menon, MD, division of anesthesia at the University of Cambridge, England, and the study’s senior author.
The scientists found that COVID-19 survivors were less accurate and had slower response times than the control population, and added that survivors scored particularly poorly on verbal analogical reasoning and showed slower processing speeds.
Critically, the scale of the cognitive deficits correlated with acute illness severity, but not fatigue or mental health status at the time of cognitive assessment, said the authors.
Recovery ‘at best gradual’
The effects were strongest for those with more severe acute illness, and who required mechanical ventilation, said the authors, who found that acute illness severity was “better at predicting the cognitive deficits.”
The authors pointed out how these deficits were still detectable when patients were followed up 6 months later, and that, although patients’ scores and reaction times began to improve over time, any recovery was “at best gradual” and likely to be influenced by factors such as illness severity and its neurological or psychological impacts.
“We followed some patients up as late as 10 months after their acute infection, so were able to see a very slow improvement,” Dr. Menon said. He explained how, while this improvement was not statistically significant, it was “at least heading in the right direction.”
However, he warned it is very possible that some of these individuals “will never fully recover.”
The cognitive deficits observed may be due to several factors in combination, said the authors, including inadequate oxygen or blood supply to the brain, blockage of large or small blood vessels due to clotting, and microscopic bleeds. They highlighted how the most important mechanism, however, may be “damage caused by the body’s own inflammatory response and immune system.”
Adam Hampshire, PhD, of the department of brain sciences at Imperial College London, one of the study’s authors, described how around 40,000 people have been through intensive care with COVID-19 in England alone, with many more despite having been very sick not admitted to hospital. This means there is a “large number of people out there still experiencing problems with cognition many months later,” he said. “We urgently need to look at what can be done to help these people.”
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.
FROM ECLINICAL MEDICINE
When it’s not long, but medium COVID?
Symptom timelines surrounding COVID infection tend to center on either the immediate 5-day quarantine protocols for acute infection or the long-COVID symptoms that can last a month or potentially far longer.
People may return to work or daily routines, but something is off: What had been simple exercise regimens become onerous. Everyday tasks take more effort.
Does this ill-defined subset point to a “medium COVID?”
Farha Ikramuddin, MD, MHA, a physiatrist and rehabilitation specialist at the University of Minnesota and M Health Fairview in Minneapolis, points out there is no definition or diagnostic code or shared official understanding of a middle category for COVID.
“But am I seeing that? Absolutely,” she said in an interview.
“I have seen patients who are younger, healthier, [and] with not so many comorbidities have either persistence of symptoms or reappearance after the initial infection is done,” she said.
Some patients report they had very low infection or were nonsymptomatic and returned to their normal health fairly quickly after infection. Then a week later they began experiencing fatigue, lost appetite, loss of smell, and feeling full after a few bites, Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Part of the trouble in categorizing the space between returning to normal after a week and having symptoms for months is that organizations can’t agree on a timeline for when symptoms warrant a “long-COVID” label.
For instance, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines it as 4 or more weeks after infection. The World Health Organization defines it as starting 3 months after COVID-19 symptom onset.
“I’m seeing ‘medium COVID’ – as one would call it – in younger and healthier patients. I’m also noticing that these symptoms are not severe enough to warrant stopping their job or changing their job schedules,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
They go back to work, she said, but start noticing something is off.
“I am seeing that.”
“I discharge at least two patients a week from my clinic because they have moved on and no longer have symptoms,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
In a story from Kaiser Health News published last month, WHYY health reporter Nina Feldman writes: “What I’ve come to think of as my ‘medium COVID’ affected my life. I couldn’t socialize much, drink, or stay up past 9:30 p.m. It took me 10 weeks to go for my first run – I’d been too afraid to try.”
She described a dinner with a friend after ending initial isolation protocols: “One glass of wine left me feeling like I’d had a whole bottle. I was bone-achingly exhausted but couldn’t sleep.”
Medical mystery
Dr. Ikramuddin notes the mechanism behind prolonged COVID-19 symptoms is still a medical mystery.
“In one scenario,” she said, “the question is being asked about whether the virus is staying dormant, similar to herpes zoster or HIV.”
“Right now, instead of getting more answers, we’re getting more questions,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Mouhib Naddour, MD, a pulmonary specialist with Sharp HealthCare in San Diego, said he’s seeing that it’s taking some patients who have had COVID longer to recover than it would for other viral infections.
Some patients fall between those recovering within 2-3 weeks and patients having long COVID. Those patients in the gap could be lumped into a middle-range COVID, he told this news organization.
“We try to put things into tables and boxes but it is hard with this disease,” Dr. Naddour said.
He agrees there’s no medical definition for “medium” COVID, but he said the idea should bring hope for patients to know that, if their symptoms are persisting they don’t necessarily have long COVID – and their symptoms may still disappear.
“This is an illness that may take longer to completely recover from,” he said. “The majority of patients we’re seeing in this group could be healthy young patients who get COVID, then 2-3 weeks after they test negative, still have lingering symptoms.”
Common symptoms
Some commonly reported symptoms of those with enduring illness, which often overlap with other stages of COVID, are difficulty breathing, chest tightness, dry cough, chest pain, muscle and joint pain, fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and mood swings, Dr. Naddour said.
“We need to do an extensive assessment to make sure there’s no other problem causing these symptoms,” he said.
Still, there is no set timeline for the medium-COVID range, he noted, so checking in with a primary care physician is important for people experiencing symptoms.
It’s a continuum, not a category
Fernando Carnavali, MD, coordinator for Mount Sinai’s Center for Post-COVID Care in New York, said he is not ready to recognize a separate category for a “medium” COVID.
He noted that science can’t even agree on a name for lasting post-COVID symptoms, whether it’s “long COVID” or “long-haul COVID,” “post-COVID syndrome” or “post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC ).” There’s no agreed-upon pathophysiology or biomarker.
“That creates these gaps of understanding on where we are,” Dr. Carnavali said in an interview.
He said he understands people’s need to categorize symptoms, but rather than a middle ground he sees a continuum.
It doesn’t mean what others may call COVID’s middle ground doesn’t exist, Dr. Carnavali said: “We are in the infancy of defining this. Trying to classify them may create more anxiety.”
The clinicians interviewed for this story report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Symptom timelines surrounding COVID infection tend to center on either the immediate 5-day quarantine protocols for acute infection or the long-COVID symptoms that can last a month or potentially far longer.
People may return to work or daily routines, but something is off: What had been simple exercise regimens become onerous. Everyday tasks take more effort.
Does this ill-defined subset point to a “medium COVID?”
Farha Ikramuddin, MD, MHA, a physiatrist and rehabilitation specialist at the University of Minnesota and M Health Fairview in Minneapolis, points out there is no definition or diagnostic code or shared official understanding of a middle category for COVID.
“But am I seeing that? Absolutely,” she said in an interview.
“I have seen patients who are younger, healthier, [and] with not so many comorbidities have either persistence of symptoms or reappearance after the initial infection is done,” she said.
Some patients report they had very low infection or were nonsymptomatic and returned to their normal health fairly quickly after infection. Then a week later they began experiencing fatigue, lost appetite, loss of smell, and feeling full after a few bites, Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Part of the trouble in categorizing the space between returning to normal after a week and having symptoms for months is that organizations can’t agree on a timeline for when symptoms warrant a “long-COVID” label.
For instance, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines it as 4 or more weeks after infection. The World Health Organization defines it as starting 3 months after COVID-19 symptom onset.
“I’m seeing ‘medium COVID’ – as one would call it – in younger and healthier patients. I’m also noticing that these symptoms are not severe enough to warrant stopping their job or changing their job schedules,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
They go back to work, she said, but start noticing something is off.
“I am seeing that.”
“I discharge at least two patients a week from my clinic because they have moved on and no longer have symptoms,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
In a story from Kaiser Health News published last month, WHYY health reporter Nina Feldman writes: “What I’ve come to think of as my ‘medium COVID’ affected my life. I couldn’t socialize much, drink, or stay up past 9:30 p.m. It took me 10 weeks to go for my first run – I’d been too afraid to try.”
She described a dinner with a friend after ending initial isolation protocols: “One glass of wine left me feeling like I’d had a whole bottle. I was bone-achingly exhausted but couldn’t sleep.”
Medical mystery
Dr. Ikramuddin notes the mechanism behind prolonged COVID-19 symptoms is still a medical mystery.
“In one scenario,” she said, “the question is being asked about whether the virus is staying dormant, similar to herpes zoster or HIV.”
“Right now, instead of getting more answers, we’re getting more questions,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Mouhib Naddour, MD, a pulmonary specialist with Sharp HealthCare in San Diego, said he’s seeing that it’s taking some patients who have had COVID longer to recover than it would for other viral infections.
Some patients fall between those recovering within 2-3 weeks and patients having long COVID. Those patients in the gap could be lumped into a middle-range COVID, he told this news organization.
“We try to put things into tables and boxes but it is hard with this disease,” Dr. Naddour said.
He agrees there’s no medical definition for “medium” COVID, but he said the idea should bring hope for patients to know that, if their symptoms are persisting they don’t necessarily have long COVID – and their symptoms may still disappear.
“This is an illness that may take longer to completely recover from,” he said. “The majority of patients we’re seeing in this group could be healthy young patients who get COVID, then 2-3 weeks after they test negative, still have lingering symptoms.”
Common symptoms
Some commonly reported symptoms of those with enduring illness, which often overlap with other stages of COVID, are difficulty breathing, chest tightness, dry cough, chest pain, muscle and joint pain, fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and mood swings, Dr. Naddour said.
“We need to do an extensive assessment to make sure there’s no other problem causing these symptoms,” he said.
Still, there is no set timeline for the medium-COVID range, he noted, so checking in with a primary care physician is important for people experiencing symptoms.
It’s a continuum, not a category
Fernando Carnavali, MD, coordinator for Mount Sinai’s Center for Post-COVID Care in New York, said he is not ready to recognize a separate category for a “medium” COVID.
He noted that science can’t even agree on a name for lasting post-COVID symptoms, whether it’s “long COVID” or “long-haul COVID,” “post-COVID syndrome” or “post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC ).” There’s no agreed-upon pathophysiology or biomarker.
“That creates these gaps of understanding on where we are,” Dr. Carnavali said in an interview.
He said he understands people’s need to categorize symptoms, but rather than a middle ground he sees a continuum.
It doesn’t mean what others may call COVID’s middle ground doesn’t exist, Dr. Carnavali said: “We are in the infancy of defining this. Trying to classify them may create more anxiety.”
The clinicians interviewed for this story report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Symptom timelines surrounding COVID infection tend to center on either the immediate 5-day quarantine protocols for acute infection or the long-COVID symptoms that can last a month or potentially far longer.
People may return to work or daily routines, but something is off: What had been simple exercise regimens become onerous. Everyday tasks take more effort.
Does this ill-defined subset point to a “medium COVID?”
Farha Ikramuddin, MD, MHA, a physiatrist and rehabilitation specialist at the University of Minnesota and M Health Fairview in Minneapolis, points out there is no definition or diagnostic code or shared official understanding of a middle category for COVID.
“But am I seeing that? Absolutely,” she said in an interview.
“I have seen patients who are younger, healthier, [and] with not so many comorbidities have either persistence of symptoms or reappearance after the initial infection is done,” she said.
Some patients report they had very low infection or were nonsymptomatic and returned to their normal health fairly quickly after infection. Then a week later they began experiencing fatigue, lost appetite, loss of smell, and feeling full after a few bites, Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Part of the trouble in categorizing the space between returning to normal after a week and having symptoms for months is that organizations can’t agree on a timeline for when symptoms warrant a “long-COVID” label.
For instance, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines it as 4 or more weeks after infection. The World Health Organization defines it as starting 3 months after COVID-19 symptom onset.
“I’m seeing ‘medium COVID’ – as one would call it – in younger and healthier patients. I’m also noticing that these symptoms are not severe enough to warrant stopping their job or changing their job schedules,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
They go back to work, she said, but start noticing something is off.
“I am seeing that.”
“I discharge at least two patients a week from my clinic because they have moved on and no longer have symptoms,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
In a story from Kaiser Health News published last month, WHYY health reporter Nina Feldman writes: “What I’ve come to think of as my ‘medium COVID’ affected my life. I couldn’t socialize much, drink, or stay up past 9:30 p.m. It took me 10 weeks to go for my first run – I’d been too afraid to try.”
She described a dinner with a friend after ending initial isolation protocols: “One glass of wine left me feeling like I’d had a whole bottle. I was bone-achingly exhausted but couldn’t sleep.”
Medical mystery
Dr. Ikramuddin notes the mechanism behind prolonged COVID-19 symptoms is still a medical mystery.
“In one scenario,” she said, “the question is being asked about whether the virus is staying dormant, similar to herpes zoster or HIV.”
“Right now, instead of getting more answers, we’re getting more questions,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Mouhib Naddour, MD, a pulmonary specialist with Sharp HealthCare in San Diego, said he’s seeing that it’s taking some patients who have had COVID longer to recover than it would for other viral infections.
Some patients fall between those recovering within 2-3 weeks and patients having long COVID. Those patients in the gap could be lumped into a middle-range COVID, he told this news organization.
“We try to put things into tables and boxes but it is hard with this disease,” Dr. Naddour said.
He agrees there’s no medical definition for “medium” COVID, but he said the idea should bring hope for patients to know that, if their symptoms are persisting they don’t necessarily have long COVID – and their symptoms may still disappear.
“This is an illness that may take longer to completely recover from,” he said. “The majority of patients we’re seeing in this group could be healthy young patients who get COVID, then 2-3 weeks after they test negative, still have lingering symptoms.”
Common symptoms
Some commonly reported symptoms of those with enduring illness, which often overlap with other stages of COVID, are difficulty breathing, chest tightness, dry cough, chest pain, muscle and joint pain, fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and mood swings, Dr. Naddour said.
“We need to do an extensive assessment to make sure there’s no other problem causing these symptoms,” he said.
Still, there is no set timeline for the medium-COVID range, he noted, so checking in with a primary care physician is important for people experiencing symptoms.
It’s a continuum, not a category
Fernando Carnavali, MD, coordinator for Mount Sinai’s Center for Post-COVID Care in New York, said he is not ready to recognize a separate category for a “medium” COVID.
He noted that science can’t even agree on a name for lasting post-COVID symptoms, whether it’s “long COVID” or “long-haul COVID,” “post-COVID syndrome” or “post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC ).” There’s no agreed-upon pathophysiology or biomarker.
“That creates these gaps of understanding on where we are,” Dr. Carnavali said in an interview.
He said he understands people’s need to categorize symptoms, but rather than a middle ground he sees a continuum.
It doesn’t mean what others may call COVID’s middle ground doesn’t exist, Dr. Carnavali said: “We are in the infancy of defining this. Trying to classify them may create more anxiety.”
The clinicians interviewed for this story report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.