User login
Does Ethnicity Affect Skin Cancer Risk?
Does Ethnicity Affect Skin Cancer Risk?
TOPLINE:
The incidence of skin cancer in England varied by ethnicity: White individuals had higher rates of melanoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma than Asian or Black individuals. In contrast, acral lentiginous melanoma was most common among Black individuals, whereas cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and Kaposi sarcoma were highest among those in the "Other" ethnic group.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analysed all cases of cutaneous melanoma (melanoma and acral lentiginous melanoma), basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and Kaposi sarcoma using data from the NHS National Disease Registration Service cancer registry between 2013 and 2020.
- Data collection incorporated ethnicity information from multiple health care datasets, including Clinical Outcomes and Services Dataset, Patient Administration System, Radiotherapy Dataset, Diagnostic Imaging Dataset, and Hospital Episode Statistics.
- A population analysis categorised patients into 7 standardised ethnic groups (on the basis of Office for National Statistics classifications): White, Asian, Chinese, Black, mixed, other, and unknown groups, with ethnicity data being self-reported by patients.
- Outcomes included European age-standardised rates calculated using the 2013 European Standard Population and reported per 100,000 person-years (PYs).
TAKEAWAY:
- White Individuals had 13-fold higher rates of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (61.75 per 100,000 PYs), 26-fold and 27-fold higher rates of basal cell carcinoma (153.69 per 100,000 PYs), and 33-fold and 16-fold higher rates of cutaneous melanoma (27.29 per 100,000 PYs) than Asian and Black individuals, respectively.
- Black individuals had the highest incidence of acral lentiginous melanoma (0.85 per 100,000 PYs), and those in the other ethnic group had the highest incidence of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (1.74 per 100,000 PYs) and Kaposi sarcoma (1.57 per 100,000 PYs).
- The presentation of early-stage melanoma was low among Asian (53.5%), Black (62.4%), mixed (62.5%), and other (76.4%) ethnic groups compared to that among White ethnicities (79.8%).
- Acral lentiginous melanomas were less likely to get urgent suspected cancer pathway referrals than overall melanoma (40.1% vs 44.6%; P < .001) and more likely to be diagnosed late than overall melanoma (stage I/II at diagnosis; 72% vs 80%; P < .0001).
IN PRACTICE:
"The findings emphasise the need for better, targeted ethnicity data collection strategies to address incidence, outcomes and health care equity for not just skin cancer but all health conditions in underserved populations," the authors wrote. "While projects like the Global Burden of Disease have improved global health care reporting, continuous audit and improvement of collected data are essential to provide better care across people of all ethnicities."
SOURCE:
This study was led by Shehnaz Ahmed, British Association of Dermatologists, London, England. It was published online on September 10, 2025, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Census data collection after every 10 years could have contributed to inaccurate population estimates and incidence rates. Small sample sizes in certain ethnic groups could have led to potential confounders, requiring a cautious interpretation of relative incidence. The NHS data included only self-reported ethnicity data with no available details of skin phototypes, skin tones, or racial ancestry. This study lacked granular ethnicity census data and stage data for basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous small cell carcinoma, and Kaposi sarcoma.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was supported through a partnership between the British Association of Dermatologists and NHS England's National Disease Registration Service. Two authors reported being employees of the British Association of Dermatologists.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The incidence of skin cancer in England varied by ethnicity: White individuals had higher rates of melanoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma than Asian or Black individuals. In contrast, acral lentiginous melanoma was most common among Black individuals, whereas cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and Kaposi sarcoma were highest among those in the "Other" ethnic group.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analysed all cases of cutaneous melanoma (melanoma and acral lentiginous melanoma), basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and Kaposi sarcoma using data from the NHS National Disease Registration Service cancer registry between 2013 and 2020.
- Data collection incorporated ethnicity information from multiple health care datasets, including Clinical Outcomes and Services Dataset, Patient Administration System, Radiotherapy Dataset, Diagnostic Imaging Dataset, and Hospital Episode Statistics.
- A population analysis categorised patients into 7 standardised ethnic groups (on the basis of Office for National Statistics classifications): White, Asian, Chinese, Black, mixed, other, and unknown groups, with ethnicity data being self-reported by patients.
- Outcomes included European age-standardised rates calculated using the 2013 European Standard Population and reported per 100,000 person-years (PYs).
TAKEAWAY:
- White Individuals had 13-fold higher rates of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (61.75 per 100,000 PYs), 26-fold and 27-fold higher rates of basal cell carcinoma (153.69 per 100,000 PYs), and 33-fold and 16-fold higher rates of cutaneous melanoma (27.29 per 100,000 PYs) than Asian and Black individuals, respectively.
- Black individuals had the highest incidence of acral lentiginous melanoma (0.85 per 100,000 PYs), and those in the other ethnic group had the highest incidence of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (1.74 per 100,000 PYs) and Kaposi sarcoma (1.57 per 100,000 PYs).
- The presentation of early-stage melanoma was low among Asian (53.5%), Black (62.4%), mixed (62.5%), and other (76.4%) ethnic groups compared to that among White ethnicities (79.8%).
- Acral lentiginous melanomas were less likely to get urgent suspected cancer pathway referrals than overall melanoma (40.1% vs 44.6%; P < .001) and more likely to be diagnosed late than overall melanoma (stage I/II at diagnosis; 72% vs 80%; P < .0001).
IN PRACTICE:
"The findings emphasise the need for better, targeted ethnicity data collection strategies to address incidence, outcomes and health care equity for not just skin cancer but all health conditions in underserved populations," the authors wrote. "While projects like the Global Burden of Disease have improved global health care reporting, continuous audit and improvement of collected data are essential to provide better care across people of all ethnicities."
SOURCE:
This study was led by Shehnaz Ahmed, British Association of Dermatologists, London, England. It was published online on September 10, 2025, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Census data collection after every 10 years could have contributed to inaccurate population estimates and incidence rates. Small sample sizes in certain ethnic groups could have led to potential confounders, requiring a cautious interpretation of relative incidence. The NHS data included only self-reported ethnicity data with no available details of skin phototypes, skin tones, or racial ancestry. This study lacked granular ethnicity census data and stage data for basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous small cell carcinoma, and Kaposi sarcoma.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was supported through a partnership between the British Association of Dermatologists and NHS England's National Disease Registration Service. Two authors reported being employees of the British Association of Dermatologists.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The incidence of skin cancer in England varied by ethnicity: White individuals had higher rates of melanoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma than Asian or Black individuals. In contrast, acral lentiginous melanoma was most common among Black individuals, whereas cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and Kaposi sarcoma were highest among those in the "Other" ethnic group.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analysed all cases of cutaneous melanoma (melanoma and acral lentiginous melanoma), basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and Kaposi sarcoma using data from the NHS National Disease Registration Service cancer registry between 2013 and 2020.
- Data collection incorporated ethnicity information from multiple health care datasets, including Clinical Outcomes and Services Dataset, Patient Administration System, Radiotherapy Dataset, Diagnostic Imaging Dataset, and Hospital Episode Statistics.
- A population analysis categorised patients into 7 standardised ethnic groups (on the basis of Office for National Statistics classifications): White, Asian, Chinese, Black, mixed, other, and unknown groups, with ethnicity data being self-reported by patients.
- Outcomes included European age-standardised rates calculated using the 2013 European Standard Population and reported per 100,000 person-years (PYs).
TAKEAWAY:
- White Individuals had 13-fold higher rates of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (61.75 per 100,000 PYs), 26-fold and 27-fold higher rates of basal cell carcinoma (153.69 per 100,000 PYs), and 33-fold and 16-fold higher rates of cutaneous melanoma (27.29 per 100,000 PYs) than Asian and Black individuals, respectively.
- Black individuals had the highest incidence of acral lentiginous melanoma (0.85 per 100,000 PYs), and those in the other ethnic group had the highest incidence of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (1.74 per 100,000 PYs) and Kaposi sarcoma (1.57 per 100,000 PYs).
- The presentation of early-stage melanoma was low among Asian (53.5%), Black (62.4%), mixed (62.5%), and other (76.4%) ethnic groups compared to that among White ethnicities (79.8%).
- Acral lentiginous melanomas were less likely to get urgent suspected cancer pathway referrals than overall melanoma (40.1% vs 44.6%; P < .001) and more likely to be diagnosed late than overall melanoma (stage I/II at diagnosis; 72% vs 80%; P < .0001).
IN PRACTICE:
"The findings emphasise the need for better, targeted ethnicity data collection strategies to address incidence, outcomes and health care equity for not just skin cancer but all health conditions in underserved populations," the authors wrote. "While projects like the Global Burden of Disease have improved global health care reporting, continuous audit and improvement of collected data are essential to provide better care across people of all ethnicities."
SOURCE:
This study was led by Shehnaz Ahmed, British Association of Dermatologists, London, England. It was published online on September 10, 2025, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Census data collection after every 10 years could have contributed to inaccurate population estimates and incidence rates. Small sample sizes in certain ethnic groups could have led to potential confounders, requiring a cautious interpretation of relative incidence. The NHS data included only self-reported ethnicity data with no available details of skin phototypes, skin tones, or racial ancestry. This study lacked granular ethnicity census data and stage data for basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous small cell carcinoma, and Kaposi sarcoma.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was supported through a partnership between the British Association of Dermatologists and NHS England's National Disease Registration Service. Two authors reported being employees of the British Association of Dermatologists.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does Ethnicity Affect Skin Cancer Risk?
Does Ethnicity Affect Skin Cancer Risk?
Consider Cultural Practices and Barriers to Care When Treating Alopecia Areata
Consider Cultural Practices and Barriers to Care When Treating Alopecia Areata
The Comparison
A. Alopecia areata in a young girl with a lighter skin tone. The fine white vellus hairs are signs of regrowth.
B. Alopecia areata in a 49-year-old man with tightly coiled hair and darker skin tone. Coiled white hairs are noted in the alopecia patches.
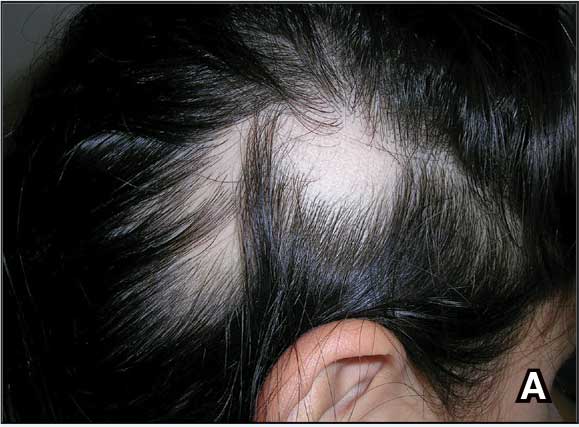
young girl with a lighter skin
tone. The fine white vellus
hairs are signs of regrowth. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.
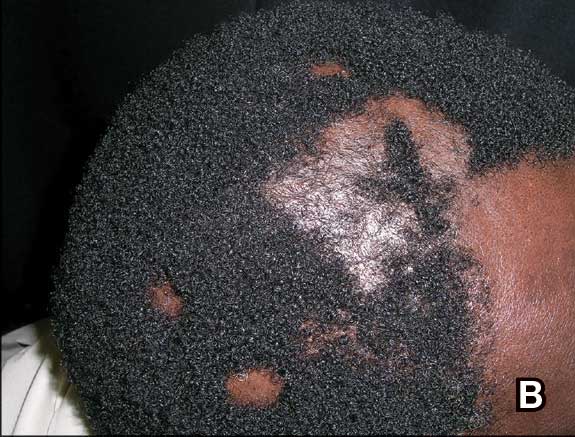

49-year-old man with tightly
coiled hair and darker skin
tone. Coiled white hairs
are noted in the alopecia
patches. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.
Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune condition characterized by hair loss resulting from a T cell–mediated attack on the hair follicles. It manifests as nonscarring patches of hair loss on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard area as well as more extensive complete loss of scalp and body hair. While AA may affect individuals of any age, most patients develop their first patch(es) of hair loss during childhood.1 The treatment landscape for AA has evolved considerably in recent years, but barriers to access to newer treatments persist.
Epidemiology
AA is most prevalent among pediatric and adult individuals of African, Asian, or Hispanic/Latino descent.2-4 In some studies, Black individuals had higher odds and Asian individuals had lower odds of developing AA, while other studies have reported the highest standardized prevalence among Asian individuals.5 In the United States, AA affects about 1.47% of adults and as many as 0.11% of children.6-8 In Black patients, AA often manifests early with a female predominance.5
AA frequently is associated with autoimmune comorbidities, the most common being thyroid disease.3,5 In Black patients, AA is associated with more atopic comorbidities, including asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis.5
Key Clinical Features
AA clinically manifests similarly across different skin tones; however, in patients with more tightly coiled or curly hair, the extent of scalp hair loss may be underestimated without a full examination. Culturally sensitive approaches to hair and scalp evaluation are essential, especially for Black women, whose hair care practices and scalp conditions may be overlooked or misunderstood during visits to evaluate hair loss. A thoughtful history and gentle examination of the hair and scalp that considers hair texture, cultural practices such as head coverings (eg, headwraps, turbans, hijabs), use of hair adornments (eg, clips, beads, bows), traditional braiding, and use of natural oils or herbal treatments, as well as styling methods including tight hairstyles, use of heat styling tools (eg, flat irons, curling irons), chemical application (eg, straighteners, hair color), and washing or styling frequency can improve diagnostic accuracy and help build trust in the patient-provider relationship.
Classic signs of AA visualized with dermoscopy include yellow and/or black dots on the scalp and exclamation point hairs. The appearance of fine white vellus hairs within the alopecic patches also may indicate early regrowth. On scalp trichoscopy, black dots are more prominent, and yellow dots are less prominent, in individuals with darker skin tones vs lighter skin tones.9
Worth Noting
In addition to a full examination of the scalp, documenting the extent of hair loss using validated severity scales, including the severity of alopecia tool (SALT), AA severity index (AASI), clinician-reported outcome assessment, and patient-reported outcome measures, can standardize disease severity assessment, facilitate timely insurance or medication approvals, and support objective tracking of treatment response, which may ultimately enhance access to care.10
Prompt treatment of AA is essential. Not surprisingly, patients given a diagnosis of AA may experience considerable emotional and psychological distress—regardless of the extent of the loss.11 Treatment options include mid- to high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids and newer and more targeted systemic options, including 3 Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors—baricitinib, ritlecitinib, and deuruxolitinib—for more extensive disease.12 Treatment with intralesional corticosteroids may cause transient hypopigmentation, which may be more noticeable in patients with darker skin tones. Delays in treatment with JAK inhibitors can lead to a less-than-optimal response. Of the 3 JAK inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for AA, only ritlecitinib is approved for children 12 years and older, leaving a therapeutic gap for younger patients that often leads to uncomfortable scalp injections, delayed or no treatment, off-label use of JAK inhibitors as well as the pairing of off-label dupilumab with oral minoxidil.12
Based on adult data, patients with severe disease and a shorter duration of hair loss (ie, < 4 years) tend to respond better to JAK inhibitors than those experiencing hair loss for longer periods. Also, those with more severe AA tend to have poorer outcomes than those with less severe disease.13 If treatment proves less than optimal, wigs and hair pieces may need to be considered. It is worth noting that some insurance companies will cover the cost of wigs for patients when prescribed as cranial prostheses.
Health Disparity Highlight
Health disparities in AA can be influenced by socioeconomic status and access to care. Patients from lower-income backgrounds often face barriers to accessing dermatologic care and treatments such as JAK inhibitors, which may remain inaccessible due to high costs and insurance limitations.14 These barriers can intersect with other factors such as age, sex, and race, potentially exacerbating disparities. Women with skin of color in underserved communities may experience delayed diagnosis, limited treatment options, and greater psychosocial distress from hair loss.14 Addressing these inequities requires advocacy, education for both patients and clinicians, and improved access to treatment to ensure comprehensive care for all patients.
- Kara T, Topkarcı Z. Interactions between posttraumatic stress disorder and alopecia areata in child with trauma exposure: two case reports. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:131-134. doi:10.4103/ijt.ijt_2_18
- Sy N, Mastacouris N, Strunk A, et al. Overall and racial and ethnic subgroup prevalences of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:419-423.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123.
- Lee HH, Gwillim E, Patel KR, et al. Epidemiology of alopecia areata, ophiasis, totalis, and universalis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:675-682.
- Mostaghimi A, Gao W, Ray M, et al. Trends in prevalence and incidence of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis among adults and children in a US employer-sponsored insured population. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:411-418.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1(suppl 1):12-23.
- Karampinis E, Toli O, Georgopoulou KE, et al. Exploring pediatric dermatology in skin of color: focus on dermoscopy. Life (Basel). 2024;14:1604.
- King BA, Senna MM, Ohyama M, et al. Defining severity in alopecia areata: current perspectives and a multidimensional framework. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:825-834.
- Toussi A, Barton VR, Le ST, et al. Psychosocial and psychiatric comorbidities and health-related quality of life in alopecia areata: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:162-175.
- Kalil L, Welch D, Heath CR, et al. Systemic therapies for pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1:36-42.
- King BA, Craiglow BG. Janus kinase inhibitors for alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:S29-S32.
- Klein EJ, Taiwò D, Kakpovbia E, et al. Disparities in Janus kinase inhibitor access for alopecia areata: a retrospective analysis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:E155.
- McKenzie PL, Maltenfort M, Bruckner AL, et al. Evaluation of the prevalence and incidence of pediatric alopecia areata using electronic health record data. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:547-551. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0351
The Comparison
A. Alopecia areata in a young girl with a lighter skin tone. The fine white vellus hairs are signs of regrowth.
B. Alopecia areata in a 49-year-old man with tightly coiled hair and darker skin tone. Coiled white hairs are noted in the alopecia patches.

young girl with a lighter skin
tone. The fine white vellus
hairs are signs of regrowth. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.

49-year-old man with tightly
coiled hair and darker skin
tone. Coiled white hairs
are noted in the alopecia
patches. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.
Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune condition characterized by hair loss resulting from a T cell–mediated attack on the hair follicles. It manifests as nonscarring patches of hair loss on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard area as well as more extensive complete loss of scalp and body hair. While AA may affect individuals of any age, most patients develop their first patch(es) of hair loss during childhood.1 The treatment landscape for AA has evolved considerably in recent years, but barriers to access to newer treatments persist.
Epidemiology
AA is most prevalent among pediatric and adult individuals of African, Asian, or Hispanic/Latino descent.2-4 In some studies, Black individuals had higher odds and Asian individuals had lower odds of developing AA, while other studies have reported the highest standardized prevalence among Asian individuals.5 In the United States, AA affects about 1.47% of adults and as many as 0.11% of children.6-8 In Black patients, AA often manifests early with a female predominance.5
AA frequently is associated with autoimmune comorbidities, the most common being thyroid disease.3,5 In Black patients, AA is associated with more atopic comorbidities, including asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis.5
Key Clinical Features
AA clinically manifests similarly across different skin tones; however, in patients with more tightly coiled or curly hair, the extent of scalp hair loss may be underestimated without a full examination. Culturally sensitive approaches to hair and scalp evaluation are essential, especially for Black women, whose hair care practices and scalp conditions may be overlooked or misunderstood during visits to evaluate hair loss. A thoughtful history and gentle examination of the hair and scalp that considers hair texture, cultural practices such as head coverings (eg, headwraps, turbans, hijabs), use of hair adornments (eg, clips, beads, bows), traditional braiding, and use of natural oils or herbal treatments, as well as styling methods including tight hairstyles, use of heat styling tools (eg, flat irons, curling irons), chemical application (eg, straighteners, hair color), and washing or styling frequency can improve diagnostic accuracy and help build trust in the patient-provider relationship.
Classic signs of AA visualized with dermoscopy include yellow and/or black dots on the scalp and exclamation point hairs. The appearance of fine white vellus hairs within the alopecic patches also may indicate early regrowth. On scalp trichoscopy, black dots are more prominent, and yellow dots are less prominent, in individuals with darker skin tones vs lighter skin tones.9
Worth Noting
In addition to a full examination of the scalp, documenting the extent of hair loss using validated severity scales, including the severity of alopecia tool (SALT), AA severity index (AASI), clinician-reported outcome assessment, and patient-reported outcome measures, can standardize disease severity assessment, facilitate timely insurance or medication approvals, and support objective tracking of treatment response, which may ultimately enhance access to care.10
Prompt treatment of AA is essential. Not surprisingly, patients given a diagnosis of AA may experience considerable emotional and psychological distress—regardless of the extent of the loss.11 Treatment options include mid- to high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids and newer and more targeted systemic options, including 3 Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors—baricitinib, ritlecitinib, and deuruxolitinib—for more extensive disease.12 Treatment with intralesional corticosteroids may cause transient hypopigmentation, which may be more noticeable in patients with darker skin tones. Delays in treatment with JAK inhibitors can lead to a less-than-optimal response. Of the 3 JAK inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for AA, only ritlecitinib is approved for children 12 years and older, leaving a therapeutic gap for younger patients that often leads to uncomfortable scalp injections, delayed or no treatment, off-label use of JAK inhibitors as well as the pairing of off-label dupilumab with oral minoxidil.12
Based on adult data, patients with severe disease and a shorter duration of hair loss (ie, < 4 years) tend to respond better to JAK inhibitors than those experiencing hair loss for longer periods. Also, those with more severe AA tend to have poorer outcomes than those with less severe disease.13 If treatment proves less than optimal, wigs and hair pieces may need to be considered. It is worth noting that some insurance companies will cover the cost of wigs for patients when prescribed as cranial prostheses.
Health Disparity Highlight
Health disparities in AA can be influenced by socioeconomic status and access to care. Patients from lower-income backgrounds often face barriers to accessing dermatologic care and treatments such as JAK inhibitors, which may remain inaccessible due to high costs and insurance limitations.14 These barriers can intersect with other factors such as age, sex, and race, potentially exacerbating disparities. Women with skin of color in underserved communities may experience delayed diagnosis, limited treatment options, and greater psychosocial distress from hair loss.14 Addressing these inequities requires advocacy, education for both patients and clinicians, and improved access to treatment to ensure comprehensive care for all patients.
The Comparison
A. Alopecia areata in a young girl with a lighter skin tone. The fine white vellus hairs are signs of regrowth.
B. Alopecia areata in a 49-year-old man with tightly coiled hair and darker skin tone. Coiled white hairs are noted in the alopecia patches.

young girl with a lighter skin
tone. The fine white vellus
hairs are signs of regrowth. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.

49-year-old man with tightly
coiled hair and darker skin
tone. Coiled white hairs
are noted in the alopecia
patches. Photographs courtesy of
Richard P. Usatine, MD.
Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune condition characterized by hair loss resulting from a T cell–mediated attack on the hair follicles. It manifests as nonscarring patches of hair loss on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard area as well as more extensive complete loss of scalp and body hair. While AA may affect individuals of any age, most patients develop their first patch(es) of hair loss during childhood.1 The treatment landscape for AA has evolved considerably in recent years, but barriers to access to newer treatments persist.
Epidemiology
AA is most prevalent among pediatric and adult individuals of African, Asian, or Hispanic/Latino descent.2-4 In some studies, Black individuals had higher odds and Asian individuals had lower odds of developing AA, while other studies have reported the highest standardized prevalence among Asian individuals.5 In the United States, AA affects about 1.47% of adults and as many as 0.11% of children.6-8 In Black patients, AA often manifests early with a female predominance.5
AA frequently is associated with autoimmune comorbidities, the most common being thyroid disease.3,5 In Black patients, AA is associated with more atopic comorbidities, including asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis.5
Key Clinical Features
AA clinically manifests similarly across different skin tones; however, in patients with more tightly coiled or curly hair, the extent of scalp hair loss may be underestimated without a full examination. Culturally sensitive approaches to hair and scalp evaluation are essential, especially for Black women, whose hair care practices and scalp conditions may be overlooked or misunderstood during visits to evaluate hair loss. A thoughtful history and gentle examination of the hair and scalp that considers hair texture, cultural practices such as head coverings (eg, headwraps, turbans, hijabs), use of hair adornments (eg, clips, beads, bows), traditional braiding, and use of natural oils or herbal treatments, as well as styling methods including tight hairstyles, use of heat styling tools (eg, flat irons, curling irons), chemical application (eg, straighteners, hair color), and washing or styling frequency can improve diagnostic accuracy and help build trust in the patient-provider relationship.
Classic signs of AA visualized with dermoscopy include yellow and/or black dots on the scalp and exclamation point hairs. The appearance of fine white vellus hairs within the alopecic patches also may indicate early regrowth. On scalp trichoscopy, black dots are more prominent, and yellow dots are less prominent, in individuals with darker skin tones vs lighter skin tones.9
Worth Noting
In addition to a full examination of the scalp, documenting the extent of hair loss using validated severity scales, including the severity of alopecia tool (SALT), AA severity index (AASI), clinician-reported outcome assessment, and patient-reported outcome measures, can standardize disease severity assessment, facilitate timely insurance or medication approvals, and support objective tracking of treatment response, which may ultimately enhance access to care.10
Prompt treatment of AA is essential. Not surprisingly, patients given a diagnosis of AA may experience considerable emotional and psychological distress—regardless of the extent of the loss.11 Treatment options include mid- to high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids and newer and more targeted systemic options, including 3 Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors—baricitinib, ritlecitinib, and deuruxolitinib—for more extensive disease.12 Treatment with intralesional corticosteroids may cause transient hypopigmentation, which may be more noticeable in patients with darker skin tones. Delays in treatment with JAK inhibitors can lead to a less-than-optimal response. Of the 3 JAK inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for AA, only ritlecitinib is approved for children 12 years and older, leaving a therapeutic gap for younger patients that often leads to uncomfortable scalp injections, delayed or no treatment, off-label use of JAK inhibitors as well as the pairing of off-label dupilumab with oral minoxidil.12
Based on adult data, patients with severe disease and a shorter duration of hair loss (ie, < 4 years) tend to respond better to JAK inhibitors than those experiencing hair loss for longer periods. Also, those with more severe AA tend to have poorer outcomes than those with less severe disease.13 If treatment proves less than optimal, wigs and hair pieces may need to be considered. It is worth noting that some insurance companies will cover the cost of wigs for patients when prescribed as cranial prostheses.
Health Disparity Highlight
Health disparities in AA can be influenced by socioeconomic status and access to care. Patients from lower-income backgrounds often face barriers to accessing dermatologic care and treatments such as JAK inhibitors, which may remain inaccessible due to high costs and insurance limitations.14 These barriers can intersect with other factors such as age, sex, and race, potentially exacerbating disparities. Women with skin of color in underserved communities may experience delayed diagnosis, limited treatment options, and greater psychosocial distress from hair loss.14 Addressing these inequities requires advocacy, education for both patients and clinicians, and improved access to treatment to ensure comprehensive care for all patients.
- Kara T, Topkarcı Z. Interactions between posttraumatic stress disorder and alopecia areata in child with trauma exposure: two case reports. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:131-134. doi:10.4103/ijt.ijt_2_18
- Sy N, Mastacouris N, Strunk A, et al. Overall and racial and ethnic subgroup prevalences of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:419-423.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123.
- Lee HH, Gwillim E, Patel KR, et al. Epidemiology of alopecia areata, ophiasis, totalis, and universalis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:675-682.
- Mostaghimi A, Gao W, Ray M, et al. Trends in prevalence and incidence of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis among adults and children in a US employer-sponsored insured population. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:411-418.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1(suppl 1):12-23.
- Karampinis E, Toli O, Georgopoulou KE, et al. Exploring pediatric dermatology in skin of color: focus on dermoscopy. Life (Basel). 2024;14:1604.
- King BA, Senna MM, Ohyama M, et al. Defining severity in alopecia areata: current perspectives and a multidimensional framework. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:825-834.
- Toussi A, Barton VR, Le ST, et al. Psychosocial and psychiatric comorbidities and health-related quality of life in alopecia areata: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:162-175.
- Kalil L, Welch D, Heath CR, et al. Systemic therapies for pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1:36-42.
- King BA, Craiglow BG. Janus kinase inhibitors for alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:S29-S32.
- Klein EJ, Taiwò D, Kakpovbia E, et al. Disparities in Janus kinase inhibitor access for alopecia areata: a retrospective analysis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:E155.
- McKenzie PL, Maltenfort M, Bruckner AL, et al. Evaluation of the prevalence and incidence of pediatric alopecia areata using electronic health record data. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:547-551. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0351
- Kara T, Topkarcı Z. Interactions between posttraumatic stress disorder and alopecia areata in child with trauma exposure: two case reports. Int J Trichology. 2018;10:131-134. doi:10.4103/ijt.ijt_2_18
- Sy N, Mastacouris N, Strunk A, et al. Overall and racial and ethnic subgroup prevalences of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:419-423.
- Lee H, Jung SJ, Patel AB, et al. Racial characteristics of alopecia areata in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1064-1070.
- Feaster B, McMichael AJ. Epidemiology of alopecia areata in Black patients: a retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1121-1123.
- Lee HH, Gwillim E, Patel KR, et al. Epidemiology of alopecia areata, ophiasis, totalis, and universalis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:675-682.
- Mostaghimi A, Gao W, Ray M, et al. Trends in prevalence and incidence of alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis among adults and children in a US employer-sponsored insured population. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:411-418.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1(suppl 1):12-23.
- Karampinis E, Toli O, Georgopoulou KE, et al. Exploring pediatric dermatology in skin of color: focus on dermoscopy. Life (Basel). 2024;14:1604.
- King BA, Senna MM, Ohyama M, et al. Defining severity in alopecia areata: current perspectives and a multidimensional framework. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:825-834.
- Toussi A, Barton VR, Le ST, et al. Psychosocial and psychiatric comorbidities and health-related quality of life in alopecia areata: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:162-175.
- Kalil L, Welch D, Heath CR, et al. Systemic therapies for pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42 suppl 1:36-42.
- King BA, Craiglow BG. Janus kinase inhibitors for alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:S29-S32.
- Klein EJ, Taiwò D, Kakpovbia E, et al. Disparities in Janus kinase inhibitor access for alopecia areata: a retrospective analysis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:E155.
- McKenzie PL, Maltenfort M, Bruckner AL, et al. Evaluation of the prevalence and incidence of pediatric alopecia areata using electronic health record data. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:547-551. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0351
Consider Cultural Practices and Barriers to Care When Treating Alopecia Areata
Consider Cultural Practices and Barriers to Care When Treating Alopecia Areata
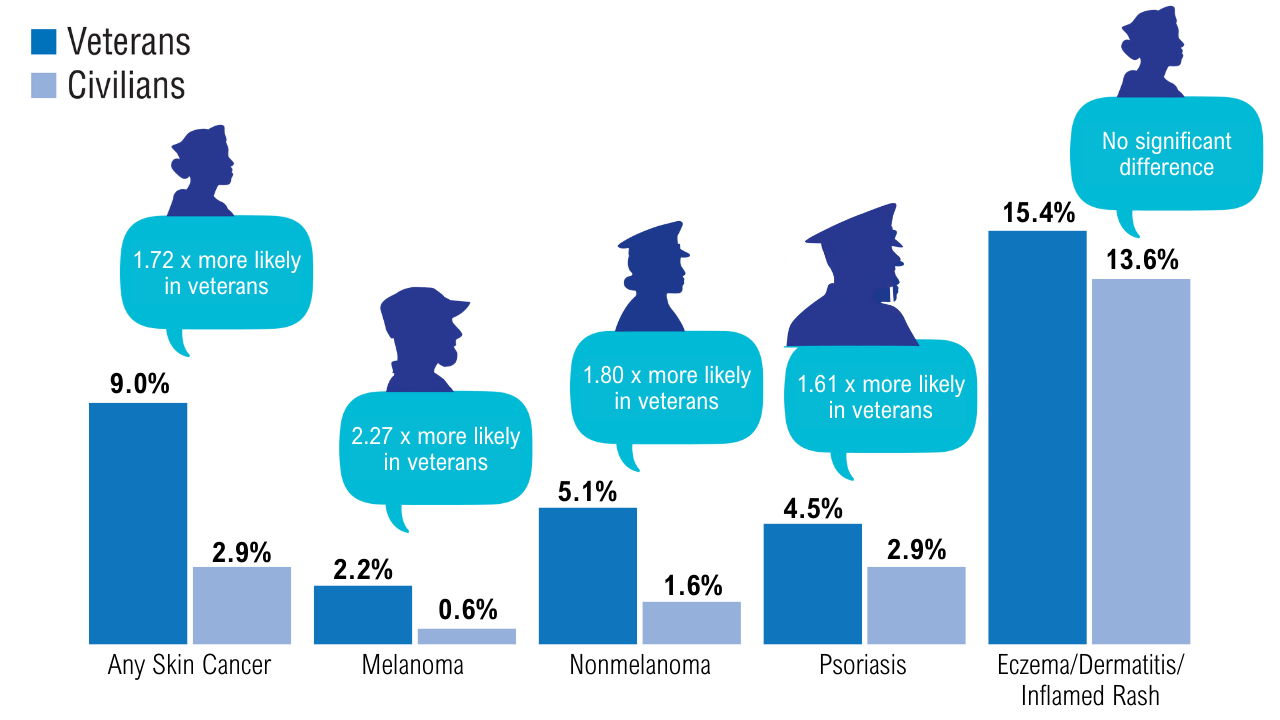
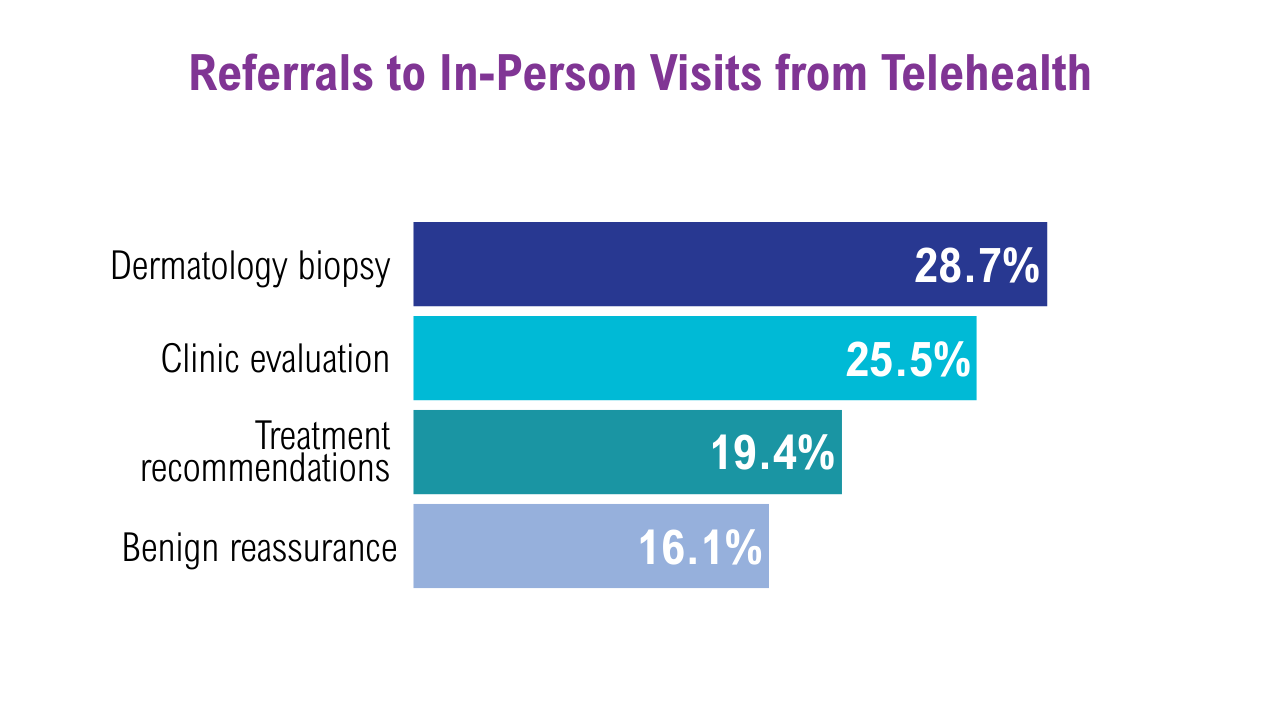
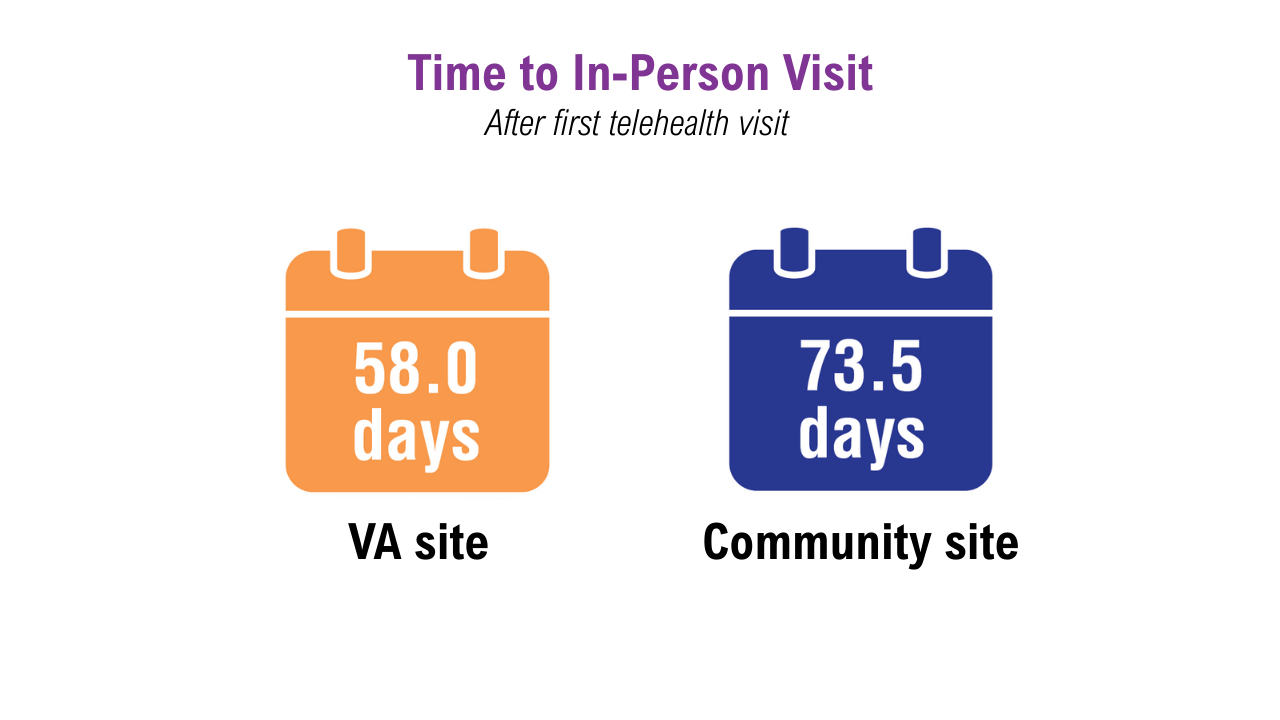
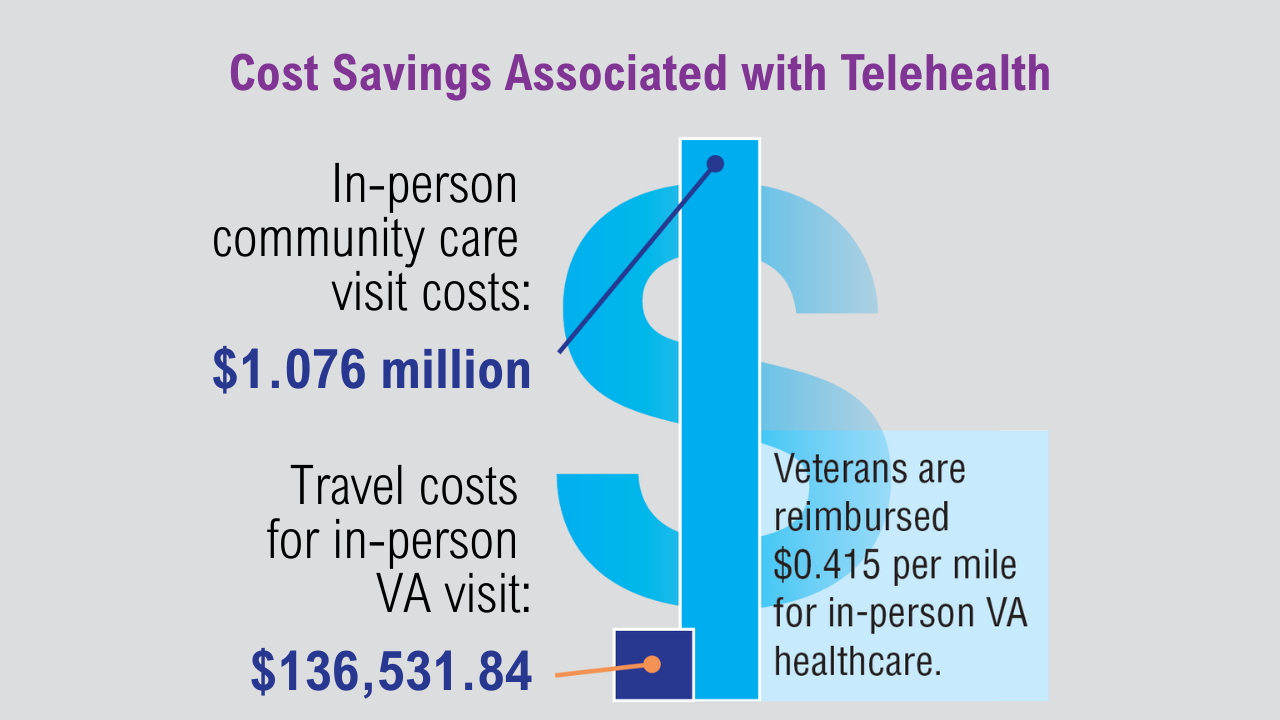
Data Trends 2025: Dermatology
Click here to view more from Federal Health Care Data Trends 2025.
- Rezaei SJ, et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160(10):1107-1111. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol. 2024.3043
- Singal A, Lipner SR. Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2267425. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2267425
- Reese R, et al. J Dermatolog Treat. 2024;35(1):2402912. doi:10.1080/09546634.2024.2402912
- Wallace MM, et al. Telemed J E Health. 2024;30(5):1411-1417. doi:10.1089/tmj.2022.0528
- Russell A, et al. Mil Med. 2024;189(11-12):e2374-e2381. doi:10.1093/milmed/usae139
Salahuddin T, et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37(7):e862-e864. doi:10.1111/jdv.18964
Click here to view more from Federal Health Care Data Trends 2025.
Click here to view more from Federal Health Care Data Trends 2025.
- Rezaei SJ, et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160(10):1107-1111. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol. 2024.3043
- Singal A, Lipner SR. Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2267425. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2267425
- Reese R, et al. J Dermatolog Treat. 2024;35(1):2402912. doi:10.1080/09546634.2024.2402912
- Wallace MM, et al. Telemed J E Health. 2024;30(5):1411-1417. doi:10.1089/tmj.2022.0528
- Russell A, et al. Mil Med. 2024;189(11-12):e2374-e2381. doi:10.1093/milmed/usae139
Salahuddin T, et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37(7):e862-e864. doi:10.1111/jdv.18964
- Rezaei SJ, et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160(10):1107-1111. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol. 2024.3043
- Singal A, Lipner SR. Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2267425. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2267425
- Reese R, et al. J Dermatolog Treat. 2024;35(1):2402912. doi:10.1080/09546634.2024.2402912
- Wallace MM, et al. Telemed J E Health. 2024;30(5):1411-1417. doi:10.1089/tmj.2022.0528
- Russell A, et al. Mil Med. 2024;189(11-12):e2374-e2381. doi:10.1093/milmed/usae139
Salahuddin T, et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37(7):e862-e864. doi:10.1111/jdv.18964
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
THE COMPARISON
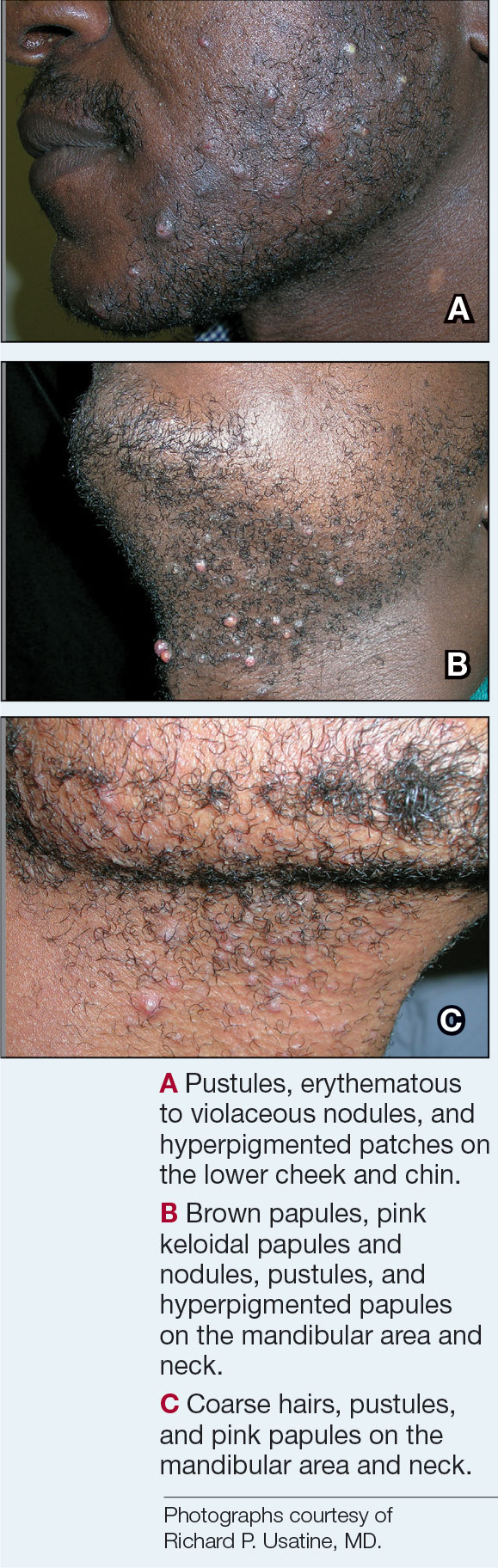
- A. Pustules, erythematous to violaceous nodules, and hyperpigmented patches on the lower cheek and chin.
- B. Brown papules, pink keloidal papules and nodules, pustules, and hyperpigmented papules on the mandibular area and neck.
- C. Coarse hairs, pustules, and pink papules on the mandibular area and neck.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), also known as razor bumps, is a common inflammatory condition characterized by papules and pustules that typically appear in the beard and cheek regions. It occurs when shaved hair regrows and penetrates the skin, leading to irritation and inflammation. While anyone who shaves can develop PFB, it is more prevalent and severe in individuals with naturally tightly coiled, coarse-textured hair.1,2 PFB is common in individuals who shave frequently due to personal choice or profession, such as members of the US military3,4 and firefighters, who are required to remain clean shaven for safety (eg, ensuring proper fit of a respirator mask).5 Early diagnosis and treatment of PFB are essential to prevent long-term complications such as scarring or hyperpigmentation, which may be more severe in those with darker skin tones.
Epidemiology
PFB is most common in Black men, affecting 45% to 83% of men of African ancestry.1,2 This condition also can affect individuals of various ethnicities with coarse or curly hair. The spiral shape of the hair increases the likelihood that it will regrow into the skin after shaving.6 Women with hirsutism who shave also can develop PFB.
Key Clinical Features
The papules and pustules seen in PFB may be flesh colored, erythematous, hyperpigmented, brown, or violaceous. Erythema may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones. Persistent and severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may occur, and hypertrophic or keloidal scars may develop in affected areas. Dermoscopy may reveal extrafollicular hair penetration as well as follicular or perifollicular pustules accompanied by hyperkeratosis.
Worth Noting
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving.1 If shaving is desired or necessary, it is recommended that patients apply lukewarm water to the affected area followed by a generous amount of shaving foam or gel to create a protective antifriction layer that allows the razor to glide more smoothly over the skin and reduces subsequent irritation.2 Using the right razor technology also may help alleviate symptoms. Research has shown that multiblade razors used in conjunction with preshave hair hydration and postshave moisturization do not worsen PFB.2 A recent study found that multiblade razor technology paired with use of a shave foam or gel actually improved skin appearance in patients with PFB.7
It is important to direct patients to shave in the direction of hair growth; however, this may not be possible for individuals with curly or coarse hair, as the hair may grow in many directions.8,9 Patients also should avoid pulling the skin taut while shaving, as doing so allows the hair to be clipped below the surface, where it can repenetrate the skin and cause further irritation. As an alternative to shaving with a razor, patients can use hair clippers to trim beard hair, which leaves behind stubble and interrupts the cycle of retracted hairs under the skin. Nd:YAG laser therapy has demonstrated efficacy in reduction of PFB papules and pustules.9-12 Greater mean improvement in inflammatory papules and reduction in hair density was noted in participants who received Nd:YAG laser plus eflornithine compared with those who received the laser or eflornithine alone.11 Patients should not pluck or dig into the skin to remove any ingrown hairs. If a tweezer is used, the patient should gently lift the tip of the ingrown hair with the tweezer to dislodge it from the skin and prevent plucking out the hair completely.
To help manage inflammation after shaving, topical treatments such as benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel can be used.3,13 A low-potency steroid such as topical hydrocortisone 2.5% applied once or twice daily for up to 2 to 3 days may be helpful.1,14 Adjunctive treatments including keratolytics (eg, topical retinoids, hydroxy acids) reduce perifollicular hyperkeratosis.14,15 Agents containing alpha hydroxy acids (eg, glycolic acid) also can decrease the curvature of the hair itself by reducing the sulfhydryl bonds.6 If secondary bacterial infections occur, oral antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) may be necessary.
Health Disparity Highlight
Individuals with darker skin tones are at higher risk for PFB and associated complications. Limited access to dermatology services may further exacerbate these challenges. Individuals with PFB may not seek medical treatment until the condition becomes severe. Clinicians also may underestimate the severity of PFB—particularly in those with darker skin tones—based on erythema alone because it may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones.16
While permanent hair reduction with laser therapy is a treatment option for PFB, it may be inaccessible to some patients because it can be expensive and is coded as a cosmetic procedure. Additionally, patients may not have access to specialists who are experienced in performing the procedure in those with darker skin tones.9 Some patients also may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.17
Pseudofolliculitis barbae also has been linked to professional disparities. One study found that members of the US Air Force who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver.18 Delays in promotion may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism, exclusion from high-profile duties, and concerns about career progression. While this delay was similar for individuals of all races, the majority of those in the waiver group were Black/African American. In 2021, 4 Black firefighters with PFB were unsuccessful in their bid to get a medical accommodation regarding a New York City Fire Department policy requiring them to be clean shaven where the oxygen mask seals against the skin.5 More research is needed on mask safety and efficiency relative to the length of facial hair. Accommodations or tailored masks for facial hair conditions also are necessary so individuals with PFB can meet job requirements while managing their condition.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):24-27.
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the U.S. military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57.
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302.
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Moran E, McMichael A, De Souza B, et al. New razor technology improves appearance and quality of life in men with pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2022;110:329-334.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin—challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):3-9.
- Ross EV. How would you treat this patient with lasers & EBDs? casebased panel. Presented at: Skin of Color Update; September 13, 2024; New York, NY.
- Ross EV, Cooke LM, Timko AL, et al. Treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed neodymium:yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:263-270.
- Shokeir H, Samy N, Taymour M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae treatment: efficacy of topical eflornithine, long-pulsed Nd-YAG laser versus their combination. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3517-3525.
- Amer A, Elsayed A, Gharib K. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of chemical peeling and long-pulse Nd:YAG laser in treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14859.
- Cook-Bolden FE, Barba A, Halder R, et al. Twice-daily applications of benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel versus vehicle in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2004;73(6 suppl):18-24.
- Nussbaum D, Friedman A. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: a review of current treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:246-250.
- Quarles FN, Brody H, Johnson BA, et al. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2007;20:133-136.
- McMichael AJ, Frey C. Challenging the tools used to measure cutaneous lupus severity in patients of all skin types. JAMA Dermatol. 2025;161:9-10.
- Okonkwo E, Neal B, Harper HL. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military and the need for social awareness. Mil Med. 2021;186:143-144.
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247.
THE COMPARISON
- A. Pustules, erythematous to violaceous nodules, and hyperpigmented patches on the lower cheek and chin.
- B. Brown papules, pink keloidal papules and nodules, pustules, and hyperpigmented papules on the mandibular area and neck.
- C. Coarse hairs, pustules, and pink papules on the mandibular area and neck.

Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), also known as razor bumps, is a common inflammatory condition characterized by papules and pustules that typically appear in the beard and cheek regions. It occurs when shaved hair regrows and penetrates the skin, leading to irritation and inflammation. While anyone who shaves can develop PFB, it is more prevalent and severe in individuals with naturally tightly coiled, coarse-textured hair.1,2 PFB is common in individuals who shave frequently due to personal choice or profession, such as members of the US military3,4 and firefighters, who are required to remain clean shaven for safety (eg, ensuring proper fit of a respirator mask).5 Early diagnosis and treatment of PFB are essential to prevent long-term complications such as scarring or hyperpigmentation, which may be more severe in those with darker skin tones.
Epidemiology
PFB is most common in Black men, affecting 45% to 83% of men of African ancestry.1,2 This condition also can affect individuals of various ethnicities with coarse or curly hair. The spiral shape of the hair increases the likelihood that it will regrow into the skin after shaving.6 Women with hirsutism who shave also can develop PFB.
Key Clinical Features
The papules and pustules seen in PFB may be flesh colored, erythematous, hyperpigmented, brown, or violaceous. Erythema may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones. Persistent and severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may occur, and hypertrophic or keloidal scars may develop in affected areas. Dermoscopy may reveal extrafollicular hair penetration as well as follicular or perifollicular pustules accompanied by hyperkeratosis.
Worth Noting
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving.1 If shaving is desired or necessary, it is recommended that patients apply lukewarm water to the affected area followed by a generous amount of shaving foam or gel to create a protective antifriction layer that allows the razor to glide more smoothly over the skin and reduces subsequent irritation.2 Using the right razor technology also may help alleviate symptoms. Research has shown that multiblade razors used in conjunction with preshave hair hydration and postshave moisturization do not worsen PFB.2 A recent study found that multiblade razor technology paired with use of a shave foam or gel actually improved skin appearance in patients with PFB.7
It is important to direct patients to shave in the direction of hair growth; however, this may not be possible for individuals with curly or coarse hair, as the hair may grow in many directions.8,9 Patients also should avoid pulling the skin taut while shaving, as doing so allows the hair to be clipped below the surface, where it can repenetrate the skin and cause further irritation. As an alternative to shaving with a razor, patients can use hair clippers to trim beard hair, which leaves behind stubble and interrupts the cycle of retracted hairs under the skin. Nd:YAG laser therapy has demonstrated efficacy in reduction of PFB papules and pustules.9-12 Greater mean improvement in inflammatory papules and reduction in hair density was noted in participants who received Nd:YAG laser plus eflornithine compared with those who received the laser or eflornithine alone.11 Patients should not pluck or dig into the skin to remove any ingrown hairs. If a tweezer is used, the patient should gently lift the tip of the ingrown hair with the tweezer to dislodge it from the skin and prevent plucking out the hair completely.
To help manage inflammation after shaving, topical treatments such as benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel can be used.3,13 A low-potency steroid such as topical hydrocortisone 2.5% applied once or twice daily for up to 2 to 3 days may be helpful.1,14 Adjunctive treatments including keratolytics (eg, topical retinoids, hydroxy acids) reduce perifollicular hyperkeratosis.14,15 Agents containing alpha hydroxy acids (eg, glycolic acid) also can decrease the curvature of the hair itself by reducing the sulfhydryl bonds.6 If secondary bacterial infections occur, oral antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) may be necessary.
Health Disparity Highlight
Individuals with darker skin tones are at higher risk for PFB and associated complications. Limited access to dermatology services may further exacerbate these challenges. Individuals with PFB may not seek medical treatment until the condition becomes severe. Clinicians also may underestimate the severity of PFB—particularly in those with darker skin tones—based on erythema alone because it may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones.16
While permanent hair reduction with laser therapy is a treatment option for PFB, it may be inaccessible to some patients because it can be expensive and is coded as a cosmetic procedure. Additionally, patients may not have access to specialists who are experienced in performing the procedure in those with darker skin tones.9 Some patients also may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.17
Pseudofolliculitis barbae also has been linked to professional disparities. One study found that members of the US Air Force who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver.18 Delays in promotion may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism, exclusion from high-profile duties, and concerns about career progression. While this delay was similar for individuals of all races, the majority of those in the waiver group were Black/African American. In 2021, 4 Black firefighters with PFB were unsuccessful in their bid to get a medical accommodation regarding a New York City Fire Department policy requiring them to be clean shaven where the oxygen mask seals against the skin.5 More research is needed on mask safety and efficiency relative to the length of facial hair. Accommodations or tailored masks for facial hair conditions also are necessary so individuals with PFB can meet job requirements while managing their condition.
THE COMPARISON
- A. Pustules, erythematous to violaceous nodules, and hyperpigmented patches on the lower cheek and chin.
- B. Brown papules, pink keloidal papules and nodules, pustules, and hyperpigmented papules on the mandibular area and neck.
- C. Coarse hairs, pustules, and pink papules on the mandibular area and neck.

Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), also known as razor bumps, is a common inflammatory condition characterized by papules and pustules that typically appear in the beard and cheek regions. It occurs when shaved hair regrows and penetrates the skin, leading to irritation and inflammation. While anyone who shaves can develop PFB, it is more prevalent and severe in individuals with naturally tightly coiled, coarse-textured hair.1,2 PFB is common in individuals who shave frequently due to personal choice or profession, such as members of the US military3,4 and firefighters, who are required to remain clean shaven for safety (eg, ensuring proper fit of a respirator mask).5 Early diagnosis and treatment of PFB are essential to prevent long-term complications such as scarring or hyperpigmentation, which may be more severe in those with darker skin tones.
Epidemiology
PFB is most common in Black men, affecting 45% to 83% of men of African ancestry.1,2 This condition also can affect individuals of various ethnicities with coarse or curly hair. The spiral shape of the hair increases the likelihood that it will regrow into the skin after shaving.6 Women with hirsutism who shave also can develop PFB.
Key Clinical Features
The papules and pustules seen in PFB may be flesh colored, erythematous, hyperpigmented, brown, or violaceous. Erythema may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones. Persistent and severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may occur, and hypertrophic or keloidal scars may develop in affected areas. Dermoscopy may reveal extrafollicular hair penetration as well as follicular or perifollicular pustules accompanied by hyperkeratosis.
Worth Noting
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving.1 If shaving is desired or necessary, it is recommended that patients apply lukewarm water to the affected area followed by a generous amount of shaving foam or gel to create a protective antifriction layer that allows the razor to glide more smoothly over the skin and reduces subsequent irritation.2 Using the right razor technology also may help alleviate symptoms. Research has shown that multiblade razors used in conjunction with preshave hair hydration and postshave moisturization do not worsen PFB.2 A recent study found that multiblade razor technology paired with use of a shave foam or gel actually improved skin appearance in patients with PFB.7
It is important to direct patients to shave in the direction of hair growth; however, this may not be possible for individuals with curly or coarse hair, as the hair may grow in many directions.8,9 Patients also should avoid pulling the skin taut while shaving, as doing so allows the hair to be clipped below the surface, where it can repenetrate the skin and cause further irritation. As an alternative to shaving with a razor, patients can use hair clippers to trim beard hair, which leaves behind stubble and interrupts the cycle of retracted hairs under the skin. Nd:YAG laser therapy has demonstrated efficacy in reduction of PFB papules and pustules.9-12 Greater mean improvement in inflammatory papules and reduction in hair density was noted in participants who received Nd:YAG laser plus eflornithine compared with those who received the laser or eflornithine alone.11 Patients should not pluck or dig into the skin to remove any ingrown hairs. If a tweezer is used, the patient should gently lift the tip of the ingrown hair with the tweezer to dislodge it from the skin and prevent plucking out the hair completely.
To help manage inflammation after shaving, topical treatments such as benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel can be used.3,13 A low-potency steroid such as topical hydrocortisone 2.5% applied once or twice daily for up to 2 to 3 days may be helpful.1,14 Adjunctive treatments including keratolytics (eg, topical retinoids, hydroxy acids) reduce perifollicular hyperkeratosis.14,15 Agents containing alpha hydroxy acids (eg, glycolic acid) also can decrease the curvature of the hair itself by reducing the sulfhydryl bonds.6 If secondary bacterial infections occur, oral antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) may be necessary.
Health Disparity Highlight
Individuals with darker skin tones are at higher risk for PFB and associated complications. Limited access to dermatology services may further exacerbate these challenges. Individuals with PFB may not seek medical treatment until the condition becomes severe. Clinicians also may underestimate the severity of PFB—particularly in those with darker skin tones—based on erythema alone because it may be less pronounced in darker vs lighter skin tones.16
While permanent hair reduction with laser therapy is a treatment option for PFB, it may be inaccessible to some patients because it can be expensive and is coded as a cosmetic procedure. Additionally, patients may not have access to specialists who are experienced in performing the procedure in those with darker skin tones.9 Some patients also may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.17
Pseudofolliculitis barbae also has been linked to professional disparities. One study found that members of the US Air Force who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver.18 Delays in promotion may be linked to perceptions of unprofessionalism, exclusion from high-profile duties, and concerns about career progression. While this delay was similar for individuals of all races, the majority of those in the waiver group were Black/African American. In 2021, 4 Black firefighters with PFB were unsuccessful in their bid to get a medical accommodation regarding a New York City Fire Department policy requiring them to be clean shaven where the oxygen mask seals against the skin.5 More research is needed on mask safety and efficiency relative to the length of facial hair. Accommodations or tailored masks for facial hair conditions also are necessary so individuals with PFB can meet job requirements while managing their condition.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):24-27.
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the U.S. military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57.
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302.
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Moran E, McMichael A, De Souza B, et al. New razor technology improves appearance and quality of life in men with pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2022;110:329-334.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin—challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):3-9.
- Ross EV. How would you treat this patient with lasers & EBDs? casebased panel. Presented at: Skin of Color Update; September 13, 2024; New York, NY.
- Ross EV, Cooke LM, Timko AL, et al. Treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed neodymium:yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:263-270.
- Shokeir H, Samy N, Taymour M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae treatment: efficacy of topical eflornithine, long-pulsed Nd-YAG laser versus their combination. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3517-3525.
- Amer A, Elsayed A, Gharib K. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of chemical peeling and long-pulse Nd:YAG laser in treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14859.
- Cook-Bolden FE, Barba A, Halder R, et al. Twice-daily applications of benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel versus vehicle in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2004;73(6 suppl):18-24.
- Nussbaum D, Friedman A. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: a review of current treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:246-250.
- Quarles FN, Brody H, Johnson BA, et al. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2007;20:133-136.
- McMichael AJ, Frey C. Challenging the tools used to measure cutaneous lupus severity in patients of all skin types. JAMA Dermatol. 2025;161:9-10.
- Okonkwo E, Neal B, Harper HL. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military and the need for social awareness. Mil Med. 2021;186:143-144.
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):24-27.
- Tshudy MT, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the U.S. military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186:E52-E57.
- Jung I, Lannan FM, Weiss A, et al. Treatment and current policies on pseudofolliculitis barbae in the US military. Cutis. 2023;112:299-302.
- Jiang YR. Reasonable accommodation and disparate impact: clean shave policy discrimination in today’s workplace. J Law Med Ethics. 2023;51:185-195.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Moran E, McMichael A, De Souza B, et al. New razor technology improves appearance and quality of life in men with pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2022;110:329-334.
- Maurer M, Rietzler M, Burghardt R, et al. The male beard hair and facial skin—challenges for shaving. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38 (suppl 1):3-9.
- Ross EV. How would you treat this patient with lasers & EBDs? casebased panel. Presented at: Skin of Color Update; September 13, 2024; New York, NY.
- Ross EV, Cooke LM, Timko AL, et al. Treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed neodymium:yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:263-270.
- Shokeir H, Samy N, Taymour M. Pseudofolliculitis barbae treatment: efficacy of topical eflornithine, long-pulsed Nd-YAG laser versus their combination. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3517-3525.
- Amer A, Elsayed A, Gharib K. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of chemical peeling and long-pulse Nd:YAG laser in treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14859.
- Cook-Bolden FE, Barba A, Halder R, et al. Twice-daily applications of benzoyl peroxide 5%/clindamycin 1% gel versus vehicle in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae. Cutis. 2004;73(6 suppl):18-24.
- Nussbaum D, Friedman A. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: a review of current treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:246-250.
- Quarles FN, Brody H, Johnson BA, et al. Pseudofolliculitis barbae. Dermatol Ther. 2007;20:133-136.
- McMichael AJ, Frey C. Challenging the tools used to measure cutaneous lupus severity in patients of all skin types. JAMA Dermatol. 2025;161:9-10.
- Okonkwo E, Neal B, Harper HL. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the military and the need for social awareness. Mil Med. 2021;186:143-144.
- Ritchie S, Park J, Banta J, et al. Shaving waivers in the United States Air Force and their impact on promotions of Black/African-American members. Mil Med. 2023;188:E242-E247.
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
Beyond the Razor: Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae in Skin of Color
End of Medical Exemptions for Grooming Impacts Black Soldiers
End of Medical Exemptions for Grooming Impacts Black Soldiers
The US military has revised its grooming standards to remove medical exemptions for male facial hair, a policy change that may put careers at risk for thousands of service members. According to the updated guidelines, all soldiers must be clean-shaven on duty when in uniform or civilian clothes, with temporary exemptions for medical reasons and permanent exemptions for religious accommodations.
The Army is the latest service branch to update its guidelines about beards: Soldiers with skin conditions will no longer be granted permanent medical waivers that allow them to avoid shaving. The Air Force and Space Force updated their guidance on grooming waivers in January, as did the Marine Corps in March.
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth, who ordered the guideline review, focused on grooming and appearance. In a Feb. 7 townhall with troops and department employees, he said, “It starts with the basic stuff, right? It’s grooming standards and uniform standards and training standards, fitness standards, all of that matters.”
Hegseth compared not enforcing grooming standards to the “broken windows” theory of policing: “I’m not saying if you violate grooming standards, you’re a criminal. The analogy is incomplete. But if you violate the small stuff and you allow it to happen, it creates a culture where the big stuff, you’re not held accountable for.”
The policy changes are particularly significant for soldiers who grow beards because they suffer from pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), an often-painful genetic condition that causes ingrown hairs. PFB produces flesh-colored or red follicular papules, which can be itchy, tender, and may bleed when shaved. Even if they heal, the lesions may lead to postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, scarring (including keloid scarring), and abscess.
Although the updated standards affect all service members with beards, they draw ire from those who claim the rules disproportionately affect men of African descent. Up to 60% of Black men have PFB, according to the American Osteopathic College of Dermatology. According to the US Department of Defense (DoD) 2023 Demographics: Profile of the Military Community, service members who self-identify as Black or African American make up 17% of the total DoD military force (N = 2,034,426). Of 1,273,382 active-duty members, 18% are Black. Of 1,038,909 active-duty enlisted members, 20% are Black, and 9% of 234,473 active-duty officers are Black.
“Almost 65% of the US Air Force shaving waivers are held by Black men. And PFB is one of the most common reasons,” DanTasia Welch, MS, told Federal Practitioner. She, along with Richard P. Usatine, MD, and Candrice R. Heath, MD, wrote a recent review of the impact of PFB that was published in Federal Practitioner.
“It is almost exclusively found in men of African descent,” Usatine said. “That just means if you have a policy that affects people with this condition, you are basically aiming that policy directly at Black men.”
“Pseudofolliculitis barbae, a lot of that just has to do with your shaving technique is what we’ve determined,” Steve Warren, an Army spokesman, told reporters in early July. “A vast majority of minority soldiers, African American soldiers, are within the standards all the time.”
Usatine disagreed: “[PFB] is genetic, and whether you shave with or against the direction of the hairs, the problem is still there, and you can't just shave it away by ‘shaving correctly.’ They're going after one racial/ethnic group who has this problem, because almost everyone that has the problem is of African descent.”
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving. Grooming techniques and topical medications can be effective in treating mild-to-moderate cases of PFB, but more severe cases respond best to laser therapy. The Army, Navy, and Marine Corps advise laser therapy as a treatment option, but it has drawbacks. It is expensive and coded as a cosmetic procedure, and patients also may not have access to specialists experienced in performing the procedure in people with darker skin tones. Some patients may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.
A survey of Air Force members with 10,383 responses suggested that the men who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver. Most in the waiver group were Black or African American.
The branches have handled the rule change in different ways. The Air Force, for example, which began tightening its standards on uniform and shaving waivers in January 2025, grants long-term shaving waivers only to airmen or guardians who have severe cases of PFB following consultation with medical practitioners. Air Force Surgeon General Lt. Gen. John DeGoes said in a video that the department’s 2020 (now expired) policy allowing 5-year shaving waivers did not give clinicians enough clarity on diagnosis by not differentiating between PFB and shaving irritation.
“They are 2 different things,” DeGoes said. “Ensuring a standardized approach to managing PFB is essential. And it is crucial that we provide consistent and effective care to our service members, enabling them to meet grooming standards while managing their condition.”
The new grooming policies leave many service members in an uncomfortable quandary: Keep the beard, run the risk of getting kicked out; keep shaving and put your skin and health at risk for complications; or receive laser treatment and have to deal with lack of beard hair after leaving the military.
Simply changing the rules isn’t enough. Candrice Heath, MD, told Federal Practitioner, “You need to always strike a balance. One of those points that’s always raised is about the facial equipment that's needed to protect during times of war.”
Heath called for more research funding to develop equipment, so people can have some facial hair if needed. “There is an opportunity to not just say, hey, this is an issue, but there's an opportunity for innovation here, to really think about it this problem in a different way, so that we are solution-focused.”
The US military has revised its grooming standards to remove medical exemptions for male facial hair, a policy change that may put careers at risk for thousands of service members. According to the updated guidelines, all soldiers must be clean-shaven on duty when in uniform or civilian clothes, with temporary exemptions for medical reasons and permanent exemptions for religious accommodations.
The Army is the latest service branch to update its guidelines about beards: Soldiers with skin conditions will no longer be granted permanent medical waivers that allow them to avoid shaving. The Air Force and Space Force updated their guidance on grooming waivers in January, as did the Marine Corps in March.
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth, who ordered the guideline review, focused on grooming and appearance. In a Feb. 7 townhall with troops and department employees, he said, “It starts with the basic stuff, right? It’s grooming standards and uniform standards and training standards, fitness standards, all of that matters.”
Hegseth compared not enforcing grooming standards to the “broken windows” theory of policing: “I’m not saying if you violate grooming standards, you’re a criminal. The analogy is incomplete. But if you violate the small stuff and you allow it to happen, it creates a culture where the big stuff, you’re not held accountable for.”
The policy changes are particularly significant for soldiers who grow beards because they suffer from pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), an often-painful genetic condition that causes ingrown hairs. PFB produces flesh-colored or red follicular papules, which can be itchy, tender, and may bleed when shaved. Even if they heal, the lesions may lead to postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, scarring (including keloid scarring), and abscess.
Although the updated standards affect all service members with beards, they draw ire from those who claim the rules disproportionately affect men of African descent. Up to 60% of Black men have PFB, according to the American Osteopathic College of Dermatology. According to the US Department of Defense (DoD) 2023 Demographics: Profile of the Military Community, service members who self-identify as Black or African American make up 17% of the total DoD military force (N = 2,034,426). Of 1,273,382 active-duty members, 18% are Black. Of 1,038,909 active-duty enlisted members, 20% are Black, and 9% of 234,473 active-duty officers are Black.
“Almost 65% of the US Air Force shaving waivers are held by Black men. And PFB is one of the most common reasons,” DanTasia Welch, MS, told Federal Practitioner. She, along with Richard P. Usatine, MD, and Candrice R. Heath, MD, wrote a recent review of the impact of PFB that was published in Federal Practitioner.
“It is almost exclusively found in men of African descent,” Usatine said. “That just means if you have a policy that affects people with this condition, you are basically aiming that policy directly at Black men.”
“Pseudofolliculitis barbae, a lot of that just has to do with your shaving technique is what we’ve determined,” Steve Warren, an Army spokesman, told reporters in early July. “A vast majority of minority soldiers, African American soldiers, are within the standards all the time.”
Usatine disagreed: “[PFB] is genetic, and whether you shave with or against the direction of the hairs, the problem is still there, and you can't just shave it away by ‘shaving correctly.’ They're going after one racial/ethnic group who has this problem, because almost everyone that has the problem is of African descent.”
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving. Grooming techniques and topical medications can be effective in treating mild-to-moderate cases of PFB, but more severe cases respond best to laser therapy. The Army, Navy, and Marine Corps advise laser therapy as a treatment option, but it has drawbacks. It is expensive and coded as a cosmetic procedure, and patients also may not have access to specialists experienced in performing the procedure in people with darker skin tones. Some patients may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.
A survey of Air Force members with 10,383 responses suggested that the men who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver. Most in the waiver group were Black or African American.
The branches have handled the rule change in different ways. The Air Force, for example, which began tightening its standards on uniform and shaving waivers in January 2025, grants long-term shaving waivers only to airmen or guardians who have severe cases of PFB following consultation with medical practitioners. Air Force Surgeon General Lt. Gen. John DeGoes said in a video that the department’s 2020 (now expired) policy allowing 5-year shaving waivers did not give clinicians enough clarity on diagnosis by not differentiating between PFB and shaving irritation.
“They are 2 different things,” DeGoes said. “Ensuring a standardized approach to managing PFB is essential. And it is crucial that we provide consistent and effective care to our service members, enabling them to meet grooming standards while managing their condition.”
The new grooming policies leave many service members in an uncomfortable quandary: Keep the beard, run the risk of getting kicked out; keep shaving and put your skin and health at risk for complications; or receive laser treatment and have to deal with lack of beard hair after leaving the military.
Simply changing the rules isn’t enough. Candrice Heath, MD, told Federal Practitioner, “You need to always strike a balance. One of those points that’s always raised is about the facial equipment that's needed to protect during times of war.”
Heath called for more research funding to develop equipment, so people can have some facial hair if needed. “There is an opportunity to not just say, hey, this is an issue, but there's an opportunity for innovation here, to really think about it this problem in a different way, so that we are solution-focused.”
The US military has revised its grooming standards to remove medical exemptions for male facial hair, a policy change that may put careers at risk for thousands of service members. According to the updated guidelines, all soldiers must be clean-shaven on duty when in uniform or civilian clothes, with temporary exemptions for medical reasons and permanent exemptions for religious accommodations.
The Army is the latest service branch to update its guidelines about beards: Soldiers with skin conditions will no longer be granted permanent medical waivers that allow them to avoid shaving. The Air Force and Space Force updated their guidance on grooming waivers in January, as did the Marine Corps in March.
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth, who ordered the guideline review, focused on grooming and appearance. In a Feb. 7 townhall with troops and department employees, he said, “It starts with the basic stuff, right? It’s grooming standards and uniform standards and training standards, fitness standards, all of that matters.”
Hegseth compared not enforcing grooming standards to the “broken windows” theory of policing: “I’m not saying if you violate grooming standards, you’re a criminal. The analogy is incomplete. But if you violate the small stuff and you allow it to happen, it creates a culture where the big stuff, you’re not held accountable for.”
The policy changes are particularly significant for soldiers who grow beards because they suffer from pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB), an often-painful genetic condition that causes ingrown hairs. PFB produces flesh-colored or red follicular papules, which can be itchy, tender, and may bleed when shaved. Even if they heal, the lesions may lead to postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, scarring (including keloid scarring), and abscess.
Although the updated standards affect all service members with beards, they draw ire from those who claim the rules disproportionately affect men of African descent. Up to 60% of Black men have PFB, according to the American Osteopathic College of Dermatology. According to the US Department of Defense (DoD) 2023 Demographics: Profile of the Military Community, service members who self-identify as Black or African American make up 17% of the total DoD military force (N = 2,034,426). Of 1,273,382 active-duty members, 18% are Black. Of 1,038,909 active-duty enlisted members, 20% are Black, and 9% of 234,473 active-duty officers are Black.
“Almost 65% of the US Air Force shaving waivers are held by Black men. And PFB is one of the most common reasons,” DanTasia Welch, MS, told Federal Practitioner. She, along with Richard P. Usatine, MD, and Candrice R. Heath, MD, wrote a recent review of the impact of PFB that was published in Federal Practitioner.
“It is almost exclusively found in men of African descent,” Usatine said. “That just means if you have a policy that affects people with this condition, you are basically aiming that policy directly at Black men.”
“Pseudofolliculitis barbae, a lot of that just has to do with your shaving technique is what we’ve determined,” Steve Warren, an Army spokesman, told reporters in early July. “A vast majority of minority soldiers, African American soldiers, are within the standards all the time.”
Usatine disagreed: “[PFB] is genetic, and whether you shave with or against the direction of the hairs, the problem is still there, and you can't just shave it away by ‘shaving correctly.’ They're going after one racial/ethnic group who has this problem, because almost everyone that has the problem is of African descent.”
The most effective management for PFB is to discontinue shaving. Grooming techniques and topical medications can be effective in treating mild-to-moderate cases of PFB, but more severe cases respond best to laser therapy. The Army, Navy, and Marine Corps advise laser therapy as a treatment option, but it has drawbacks. It is expensive and coded as a cosmetic procedure, and patients also may not have access to specialists experienced in performing the procedure in people with darker skin tones. Some patients may not want to permanently reduce the amount of hair that grows in the beard area for personal or religious reasons.
A survey of Air Force members with 10,383 responses suggested that the men who had medical shaving waivers experienced longer times to promotion than those with no waiver. Most in the waiver group were Black or African American.
The branches have handled the rule change in different ways. The Air Force, for example, which began tightening its standards on uniform and shaving waivers in January 2025, grants long-term shaving waivers only to airmen or guardians who have severe cases of PFB following consultation with medical practitioners. Air Force Surgeon General Lt. Gen. John DeGoes said in a video that the department’s 2020 (now expired) policy allowing 5-year shaving waivers did not give clinicians enough clarity on diagnosis by not differentiating between PFB and shaving irritation.
“They are 2 different things,” DeGoes said. “Ensuring a standardized approach to managing PFB is essential. And it is crucial that we provide consistent and effective care to our service members, enabling them to meet grooming standards while managing their condition.”
The new grooming policies leave many service members in an uncomfortable quandary: Keep the beard, run the risk of getting kicked out; keep shaving and put your skin and health at risk for complications; or receive laser treatment and have to deal with lack of beard hair after leaving the military.
Simply changing the rules isn’t enough. Candrice Heath, MD, told Federal Practitioner, “You need to always strike a balance. One of those points that’s always raised is about the facial equipment that's needed to protect during times of war.”
Heath called for more research funding to develop equipment, so people can have some facial hair if needed. “There is an opportunity to not just say, hey, this is an issue, but there's an opportunity for innovation here, to really think about it this problem in a different way, so that we are solution-focused.”
End of Medical Exemptions for Grooming Impacts Black Soldiers
End of Medical Exemptions for Grooming Impacts Black Soldiers
Successful Treatment of Tinea Versicolor With Salicylic Acid 30% Peel
Successful Treatment of Tinea Versicolor With Salicylic Acid 30% Peel
Tinea versicolor (TV) is a common, chronic, and recurrent superficial fungal infection caused by Malassezia species, most commonly Malassezia furfur (M. furfur)—a dimorphic fungus that is a part of the normal skin flora and resides in the stratum corneum.1 TV manifests as hypopigmented, hyperpigmented, or erythematous macules and patches with scaling, typically found on the trunk and proximal upper extremities. The condition is most common among young to middle-aged individuals exposed to high temperatures and humidity.1
While many cases respond to topical antifungal treatment, application can be cumbersome, particularly in large areas that are difficult to reach. An efficient and cost effective in-office treatment option could alleviate patient burden and improve satisfaction. This article presents a case of TV successfully treated with an in-office salicylic acid (SA) 30% peel, an uncommon application of this medication.
Case Presentation
An 18-year-old female active-duty US Army service member with a history of acne vulgaris presented to a dermatology clinic with a mildly pruritic rash that had been present for several weeks. An examination revealed hyperpigmented macules and patches with overlying fine scales across the patient’s back and bilateral arms (Figures 1 and 2). She reported no history of similar lesions. The patient had recently completed a military basic training course during which she wore a uniform jacket and trousers daily in hot and humid conditions. A skin scraping was obtained. Microscopic examination with potassium hydroxide preparation revealed hyphae and spores, consistent with TV.
The diagnosis of TV and treatment options (topical ketoconazole 2% shampoo, topical terbinafine, or oral fluconazole) were discussed with the patient. Due to military training-related constraints, residence in the barracks, and personal preference, the patient felt unable to regularly apply topical medications to the entirety of the affected area and preferred to avoid oral medication. The decision was made to pursue in-clinic treatment with a SA 30% peel. The affected areas (back and bilateral arms) were thoroughly cleansed and prepped with alcohol. SA 30% in hydroethanolic solution was applied evenly to the affected area. The patient was observed for pseudofrosting, a precipitation of SA crystals that indicates peel completion (Figure 3). The peel was left in place, as it is self-neutralizing, and the patient was instructed to shower that same day with a gentle cleanser. This procedure was repeated 10 days later. Both treatments were well tolerated, with only a transient burning sensation reported during the application. At 3-week follow-up, the patient presented with complete resolution of her arm lesions and significant improvement of the back lesions (Figures 4 and 5). She also reported improvement in the acne vulgaris on her back.
Discussion
SA 30% is a lipid-soluble hydroxybenzoic acid with comedolytic and desmolytic qualities. This results in the disruption of epidermal cell cohesion and promotes exfoliation.2 Lipophilic properties allow SA to penetrate sebaceous glands and disrupt sebum production, making it particularly effective in seborrheic conditions such as acne. This mechanism may have increased therapeutic effect in this case.3 Additionally, as a salicylate, SA possesses anti-inflammatory properties, though this effect is most pronounced at lower concentrations. SA 30% is considered a superficial peel, as the depth of chemexfoliation is limited to the epidermis.3 A modified SA preparation is a safe and effective treatment for moderate-to-severe acne vulgaris. The apparent pseudofrost during application is due to precipitated SA, rather than the precipitation of dermal proteins seen in deeper peels, such as trichloroacetic acid.2 Unlike glycolic or pyruvic acid peels, SA does not require neutralization.
SA is cost-effective and has been used safely in all skin types to treat various epidermal conditions, including acne vulgaris, melasma, photodamage, freckles, lentigines and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).2 Mild adverse effects occur in about 15% to 30% of patients and include prolonged erythema, intense exfoliation, dryness, crusting, and pigmentary dyschromias. Rare adverse effects include systemic toxicity (salicylism) and hypoglycemia. Contraindications to SA 30% peels include history of allergy to salicylates, active bacterial or viral infection, dermatitis in the treatment area, pregnancy, and skin malignancy.2
Chemical peels are typically used with caution in patients with skin of color due to a higher risk of PIH. However, SA 30% has been shown to be safe and effective in these populations.4 A study by Grimes found that 88% of patients with Fitzpatrick skin types V and VI experienced significant improvement in PIH, melasma, or enlarged pores with minimal to no adverse effects.4 Subsequent larger studies have reinforced these findings. In a study involving 250 patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV and V, no patients experienced PIH, confirming the safety of SA in darker skin tones. This is likely due to the superficial nature of the peel, which does not affect the basal layer of the epidermis where melanocytes reside, reducing the risk of pigmentary complications. Additionally, SA peels are self-neutralizing, unlike glycolic or trichloroacetic acid peels, which require manual neutralization and carry a higher risk of PIH if not neutralized properly.5
SA has been as shown to be a moderately successful treatment for PIH. The Grimes study found that 4 of 5 patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV and V saw a 75% improvement in PIH after SA peels.4 Davis et al found a nonsignificant trend toward skin lightening in Korean adults treated for acne and PIH, with significant decreases in erythema and improvements in greasiness, dryness, and scaliness.6 Importantly, the risk of PIH following TV is higher in patients with skin of color.7 SA may be effective in treating TV and PIH, offering a multifactorial approach by addressing both conditions while posing a low risk for causing PIH.8
TV and other Malassezia spp infections are common concerns in dermatology and primary care, with Malassezia-associated superficial mycoses (eg, dandruff, pityriasis versicolor, and folliculitis) affecting up to 50% of the population worldwide.9 Despite this, there has been little recent advancement in antifungal treatments. Ketoconazole, terbinafine, and fluconazole have been in use since the 1980s and 1990s.8 Most antifungal drugs target ergosterol, a component of the fungal cell wall.10 Additionally, Malassezia spp have been increasingly reported to cause invasive infections in immunocompromised patients.11 Given the rise in antifungal resistance, the judicious use of antifungals and implementation of novel treatment strategies is essential.
While SA lacks intrinsic antifungal properties, different combinations (Whitfield ointment consisting of 3% SA and 6% benzoic acid; 2% sulfur and 2% SA) have been effective in the treatment of TV.1 It is theorized that the effectiveness of SA against TV is due to its ability to exfoliate and acidify the stratum corneum, the natural habitat of M. furfur.
SA also reduces sebum production by downregulating sebocyte lipogenesis via the sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 pathway and suppressing the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway, a key pathway in inflammation.12 These mechanisms make SA an effective acne treatment. Additionally, M. furfur is a lipid-dependent yeast, thus the decreased lipogenesis by sebocytes may be beneficial in treating TV as well.12 A study of 25 patients with TV in India found that 88% achieved clinical and microbiological cure after 4 once-weekly treatments of a SA 30% peel.8
In a study of deployed military personnel, fungal infections affected about 11% of participants.13 Contributing factors to the development of fungal infections included excessive sweating, humid conditions, and limited access to hygiene facilities. In such settings, traditional antifungal therapies may be less effective or challenging to adhere to, making alternative treatments more desirable. SA peels could offer a practical solution in these circumstances, as they are easily applied in the clinic, require no neutralization or downtime, and do not require the patient to apply medications between visits.
In this case, the patient demonstrated significant improvement with 2 SA peels, with noted improvement in her acne. SA 30% peel was highlighted as a useful treatment option for patients with TV who struggle with topical medication adherence; furthermore, it may be particularly beneficial for patients with concomitant acne.
Conclusions
This case demonstrates the successful use of in-office SA 30% peel as a treatment for TV. The rapid improvement and resolution of lesions with minimal adverse effects suggest that SA peel may serve as a valuable alternative for patients with extensive disease in difficult-to-reach affected areas, or those who are dissatisfied with traditional therapies. Additionally, the concurrent improvement of the patient’s back acne underscores the dual therapeutic potential of this treatment. Given the ease of application, cost effectiveness, and favorable safety profile, SA 30% peel is a viable option in the management of TV, especially in cases where topical or oral antifungals are impractical. Further studies could help establish standardized protocols and assess long-term outcomes of this treatment modality.
- Leung AK, Barankin B, Lam JM, et al. Tinea versicolor: an updated review. Drugs Context. 2022;11:2022-9-2. doi:10.7573/dic.2022-9-2
- Arif T. Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: a comprehensive review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:455-461. doi:10.2147/CCID.S84765
- Shao X, Chen Y, Zhang L, et al. Effect of 30% supramolecular salicylic acid peel on skin microbiota and inflammation in patients with moderate-to-severe acne vulgaris. Dermatol Ther. 2022;13(1):155-168. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00844-5
- Grimes PE. The safety and efficacy of salicylic acid chemical peels in darker racial-ethnic groups. Dermatol Surg Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg Al. 1999;25(1). doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.1999.08145.x
- Kang HY, Choi Y, Cho HJ. Salicylic acid peels for the treatment of acne vulgaris in Fitzpatrick skin types IV-V: a multicenter study. Dermatol Surg. Published online 2006. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2006.32146.x.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. J Clin Aesthetic Dermatol. 2010;3(7):20-31.
- Kallini JR, Riaz F, Khachemoune A. Tinea versicolor in dark-skinned individuals. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53(2):137- 141. doi:10.1111/ijd.12345
- Saoji V, Madke B. Efficacy of salicylic acid peel in dermatophytosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021;87(5). doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_853_18
- Arce M, Gutiérrez-Mendoza D. Pityriasis versicolor: treatment update. Curr Fungal Infect Rep 2018;12(11):195–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12281-018-0328-7
- Leong C, Kit JCW, Lee SM, et al. Azole resistance mechanisms in pathogenic M. furfur. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021;65(5):e01975-20. doi:10.1128/AAC.01975-20
- Chang HJ, Miller HL, Watkins N, et al. An epidemic of Malassezia pachydermatis in an intensive care nursery associated with colonization of health care workers’ pet dogs. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(11):706-711. doi:10.1056/NEJM199803123381102
- Lu J, Cong T, Wen X, et al. Salicylic acid treats acne vulgaris by suppressing AMPK/SREBP1 pathway in sebocytes. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28(7):786-794. doi:10.1111/exd.13934
- Singal A, Lipner SR. A review of skin disease in military soldiers: challenges and potential solutions. Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2267425. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2267425
Tinea versicolor (TV) is a common, chronic, and recurrent superficial fungal infection caused by Malassezia species, most commonly Malassezia furfur (M. furfur)—a dimorphic fungus that is a part of the normal skin flora and resides in the stratum corneum.1 TV manifests as hypopigmented, hyperpigmented, or erythematous macules and patches with scaling, typically found on the trunk and proximal upper extremities. The condition is most common among young to middle-aged individuals exposed to high temperatures and humidity.1
While many cases respond to topical antifungal treatment, application can be cumbersome, particularly in large areas that are difficult to reach. An efficient and cost effective in-office treatment option could alleviate patient burden and improve satisfaction. This article presents a case of TV successfully treated with an in-office salicylic acid (SA) 30% peel, an uncommon application of this medication.
Case Presentation
An 18-year-old female active-duty US Army service member with a history of acne vulgaris presented to a dermatology clinic with a mildly pruritic rash that had been present for several weeks. An examination revealed hyperpigmented macules and patches with overlying fine scales across the patient’s back and bilateral arms (Figures 1 and 2). She reported no history of similar lesions. The patient had recently completed a military basic training course during which she wore a uniform jacket and trousers daily in hot and humid conditions. A skin scraping was obtained. Microscopic examination with potassium hydroxide preparation revealed hyphae and spores, consistent with TV.


The diagnosis of TV and treatment options (topical ketoconazole 2% shampoo, topical terbinafine, or oral fluconazole) were discussed with the patient. Due to military training-related constraints, residence in the barracks, and personal preference, the patient felt unable to regularly apply topical medications to the entirety of the affected area and preferred to avoid oral medication. The decision was made to pursue in-clinic treatment with a SA 30% peel. The affected areas (back and bilateral arms) were thoroughly cleansed and prepped with alcohol. SA 30% in hydroethanolic solution was applied evenly to the affected area. The patient was observed for pseudofrosting, a precipitation of SA crystals that indicates peel completion (Figure 3). The peel was left in place, as it is self-neutralizing, and the patient was instructed to shower that same day with a gentle cleanser. This procedure was repeated 10 days later. Both treatments were well tolerated, with only a transient burning sensation reported during the application. At 3-week follow-up, the patient presented with complete resolution of her arm lesions and significant improvement of the back lesions (Figures 4 and 5). She also reported improvement in the acne vulgaris on her back.



Discussion
SA 30% is a lipid-soluble hydroxybenzoic acid with comedolytic and desmolytic qualities. This results in the disruption of epidermal cell cohesion and promotes exfoliation.2 Lipophilic properties allow SA to penetrate sebaceous glands and disrupt sebum production, making it particularly effective in seborrheic conditions such as acne. This mechanism may have increased therapeutic effect in this case.3 Additionally, as a salicylate, SA possesses anti-inflammatory properties, though this effect is most pronounced at lower concentrations. SA 30% is considered a superficial peel, as the depth of chemexfoliation is limited to the epidermis.3 A modified SA preparation is a safe and effective treatment for moderate-to-severe acne vulgaris. The apparent pseudofrost during application is due to precipitated SA, rather than the precipitation of dermal proteins seen in deeper peels, such as trichloroacetic acid.2 Unlike glycolic or pyruvic acid peels, SA does not require neutralization.
SA is cost-effective and has been used safely in all skin types to treat various epidermal conditions, including acne vulgaris, melasma, photodamage, freckles, lentigines and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).2 Mild adverse effects occur in about 15% to 30% of patients and include prolonged erythema, intense exfoliation, dryness, crusting, and pigmentary dyschromias. Rare adverse effects include systemic toxicity (salicylism) and hypoglycemia. Contraindications to SA 30% peels include history of allergy to salicylates, active bacterial or viral infection, dermatitis in the treatment area, pregnancy, and skin malignancy.2
Chemical peels are typically used with caution in patients with skin of color due to a higher risk of PIH. However, SA 30% has been shown to be safe and effective in these populations.4 A study by Grimes found that 88% of patients with Fitzpatrick skin types V and VI experienced significant improvement in PIH, melasma, or enlarged pores with minimal to no adverse effects.4 Subsequent larger studies have reinforced these findings. In a study involving 250 patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV and V, no patients experienced PIH, confirming the safety of SA in darker skin tones. This is likely due to the superficial nature of the peel, which does not affect the basal layer of the epidermis where melanocytes reside, reducing the risk of pigmentary complications. Additionally, SA peels are self-neutralizing, unlike glycolic or trichloroacetic acid peels, which require manual neutralization and carry a higher risk of PIH if not neutralized properly.5
SA has been as shown to be a moderately successful treatment for PIH. The Grimes study found that 4 of 5 patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV and V saw a 75% improvement in PIH after SA peels.4 Davis et al found a nonsignificant trend toward skin lightening in Korean adults treated for acne and PIH, with significant decreases in erythema and improvements in greasiness, dryness, and scaliness.6 Importantly, the risk of PIH following TV is higher in patients with skin of color.7 SA may be effective in treating TV and PIH, offering a multifactorial approach by addressing both conditions while posing a low risk for causing PIH.8
TV and other Malassezia spp infections are common concerns in dermatology and primary care, with Malassezia-associated superficial mycoses (eg, dandruff, pityriasis versicolor, and folliculitis) affecting up to 50% of the population worldwide.9 Despite this, there has been little recent advancement in antifungal treatments. Ketoconazole, terbinafine, and fluconazole have been in use since the 1980s and 1990s.8 Most antifungal drugs target ergosterol, a component of the fungal cell wall.10 Additionally, Malassezia spp have been increasingly reported to cause invasive infections in immunocompromised patients.11 Given the rise in antifungal resistance, the judicious use of antifungals and implementation of novel treatment strategies is essential.
While SA lacks intrinsic antifungal properties, different combinations (Whitfield ointment consisting of 3% SA and 6% benzoic acid; 2% sulfur and 2% SA) have been effective in the treatment of TV.1 It is theorized that the effectiveness of SA against TV is due to its ability to exfoliate and acidify the stratum corneum, the natural habitat of M. furfur.
SA also reduces sebum production by downregulating sebocyte lipogenesis via the sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 pathway and suppressing the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway, a key pathway in inflammation.12 These mechanisms make SA an effective acne treatment. Additionally, M. furfur is a lipid-dependent yeast, thus the decreased lipogenesis by sebocytes may be beneficial in treating TV as well.12 A study of 25 patients with TV in India found that 88% achieved clinical and microbiological cure after 4 once-weekly treatments of a SA 30% peel.8
In a study of deployed military personnel, fungal infections affected about 11% of participants.13 Contributing factors to the development of fungal infections included excessive sweating, humid conditions, and limited access to hygiene facilities. In such settings, traditional antifungal therapies may be less effective or challenging to adhere to, making alternative treatments more desirable. SA peels could offer a practical solution in these circumstances, as they are easily applied in the clinic, require no neutralization or downtime, and do not require the patient to apply medications between visits.
In this case, the patient demonstrated significant improvement with 2 SA peels, with noted improvement in her acne. SA 30% peel was highlighted as a useful treatment option for patients with TV who struggle with topical medication adherence; furthermore, it may be particularly beneficial for patients with concomitant acne.
Conclusions
This case demonstrates the successful use of in-office SA 30% peel as a treatment for TV. The rapid improvement and resolution of lesions with minimal adverse effects suggest that SA peel may serve as a valuable alternative for patients with extensive disease in difficult-to-reach affected areas, or those who are dissatisfied with traditional therapies. Additionally, the concurrent improvement of the patient’s back acne underscores the dual therapeutic potential of this treatment. Given the ease of application, cost effectiveness, and favorable safety profile, SA 30% peel is a viable option in the management of TV, especially in cases where topical or oral antifungals are impractical. Further studies could help establish standardized protocols and assess long-term outcomes of this treatment modality.
Tinea versicolor (TV) is a common, chronic, and recurrent superficial fungal infection caused by Malassezia species, most commonly Malassezia furfur (M. furfur)—a dimorphic fungus that is a part of the normal skin flora and resides in the stratum corneum.1 TV manifests as hypopigmented, hyperpigmented, or erythematous macules and patches with scaling, typically found on the trunk and proximal upper extremities. The condition is most common among young to middle-aged individuals exposed to high temperatures and humidity.1
While many cases respond to topical antifungal treatment, application can be cumbersome, particularly in large areas that are difficult to reach. An efficient and cost effective in-office treatment option could alleviate patient burden and improve satisfaction. This article presents a case of TV successfully treated with an in-office salicylic acid (SA) 30% peel, an uncommon application of this medication.
Case Presentation
An 18-year-old female active-duty US Army service member with a history of acne vulgaris presented to a dermatology clinic with a mildly pruritic rash that had been present for several weeks. An examination revealed hyperpigmented macules and patches with overlying fine scales across the patient’s back and bilateral arms (Figures 1 and 2). She reported no history of similar lesions. The patient had recently completed a military basic training course during which she wore a uniform jacket and trousers daily in hot and humid conditions. A skin scraping was obtained. Microscopic examination with potassium hydroxide preparation revealed hyphae and spores, consistent with TV.


The diagnosis of TV and treatment options (topical ketoconazole 2% shampoo, topical terbinafine, or oral fluconazole) were discussed with the patient. Due to military training-related constraints, residence in the barracks, and personal preference, the patient felt unable to regularly apply topical medications to the entirety of the affected area and preferred to avoid oral medication. The decision was made to pursue in-clinic treatment with a SA 30% peel. The affected areas (back and bilateral arms) were thoroughly cleansed and prepped with alcohol. SA 30% in hydroethanolic solution was applied evenly to the affected area. The patient was observed for pseudofrosting, a precipitation of SA crystals that indicates peel completion (Figure 3). The peel was left in place, as it is self-neutralizing, and the patient was instructed to shower that same day with a gentle cleanser. This procedure was repeated 10 days later. Both treatments were well tolerated, with only a transient burning sensation reported during the application. At 3-week follow-up, the patient presented with complete resolution of her arm lesions and significant improvement of the back lesions (Figures 4 and 5). She also reported improvement in the acne vulgaris on her back.



Discussion
SA 30% is a lipid-soluble hydroxybenzoic acid with comedolytic and desmolytic qualities. This results in the disruption of epidermal cell cohesion and promotes exfoliation.2 Lipophilic properties allow SA to penetrate sebaceous glands and disrupt sebum production, making it particularly effective in seborrheic conditions such as acne. This mechanism may have increased therapeutic effect in this case.3 Additionally, as a salicylate, SA possesses anti-inflammatory properties, though this effect is most pronounced at lower concentrations. SA 30% is considered a superficial peel, as the depth of chemexfoliation is limited to the epidermis.3 A modified SA preparation is a safe and effective treatment for moderate-to-severe acne vulgaris. The apparent pseudofrost during application is due to precipitated SA, rather than the precipitation of dermal proteins seen in deeper peels, such as trichloroacetic acid.2 Unlike glycolic or pyruvic acid peels, SA does not require neutralization.
SA is cost-effective and has been used safely in all skin types to treat various epidermal conditions, including acne vulgaris, melasma, photodamage, freckles, lentigines and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).2 Mild adverse effects occur in about 15% to 30% of patients and include prolonged erythema, intense exfoliation, dryness, crusting, and pigmentary dyschromias. Rare adverse effects include systemic toxicity (salicylism) and hypoglycemia. Contraindications to SA 30% peels include history of allergy to salicylates, active bacterial or viral infection, dermatitis in the treatment area, pregnancy, and skin malignancy.2
Chemical peels are typically used with caution in patients with skin of color due to a higher risk of PIH. However, SA 30% has been shown to be safe and effective in these populations.4 A study by Grimes found that 88% of patients with Fitzpatrick skin types V and VI experienced significant improvement in PIH, melasma, or enlarged pores with minimal to no adverse effects.4 Subsequent larger studies have reinforced these findings. In a study involving 250 patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV and V, no patients experienced PIH, confirming the safety of SA in darker skin tones. This is likely due to the superficial nature of the peel, which does not affect the basal layer of the epidermis where melanocytes reside, reducing the risk of pigmentary complications. Additionally, SA peels are self-neutralizing, unlike glycolic or trichloroacetic acid peels, which require manual neutralization and carry a higher risk of PIH if not neutralized properly.5
SA has been as shown to be a moderately successful treatment for PIH. The Grimes study found that 4 of 5 patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV and V saw a 75% improvement in PIH after SA peels.4 Davis et al found a nonsignificant trend toward skin lightening in Korean adults treated for acne and PIH, with significant decreases in erythema and improvements in greasiness, dryness, and scaliness.6 Importantly, the risk of PIH following TV is higher in patients with skin of color.7 SA may be effective in treating TV and PIH, offering a multifactorial approach by addressing both conditions while posing a low risk for causing PIH.8
TV and other Malassezia spp infections are common concerns in dermatology and primary care, with Malassezia-associated superficial mycoses (eg, dandruff, pityriasis versicolor, and folliculitis) affecting up to 50% of the population worldwide.9 Despite this, there has been little recent advancement in antifungal treatments. Ketoconazole, terbinafine, and fluconazole have been in use since the 1980s and 1990s.8 Most antifungal drugs target ergosterol, a component of the fungal cell wall.10 Additionally, Malassezia spp have been increasingly reported to cause invasive infections in immunocompromised patients.11 Given the rise in antifungal resistance, the judicious use of antifungals and implementation of novel treatment strategies is essential.
While SA lacks intrinsic antifungal properties, different combinations (Whitfield ointment consisting of 3% SA and 6% benzoic acid; 2% sulfur and 2% SA) have been effective in the treatment of TV.1 It is theorized that the effectiveness of SA against TV is due to its ability to exfoliate and acidify the stratum corneum, the natural habitat of M. furfur.
SA also reduces sebum production by downregulating sebocyte lipogenesis via the sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 pathway and suppressing the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway, a key pathway in inflammation.12 These mechanisms make SA an effective acne treatment. Additionally, M. furfur is a lipid-dependent yeast, thus the decreased lipogenesis by sebocytes may be beneficial in treating TV as well.12 A study of 25 patients with TV in India found that 88% achieved clinical and microbiological cure after 4 once-weekly treatments of a SA 30% peel.8
In a study of deployed military personnel, fungal infections affected about 11% of participants.13 Contributing factors to the development of fungal infections included excessive sweating, humid conditions, and limited access to hygiene facilities. In such settings, traditional antifungal therapies may be less effective or challenging to adhere to, making alternative treatments more desirable. SA peels could offer a practical solution in these circumstances, as they are easily applied in the clinic, require no neutralization or downtime, and do not require the patient to apply medications between visits.
In this case, the patient demonstrated significant improvement with 2 SA peels, with noted improvement in her acne. SA 30% peel was highlighted as a useful treatment option for patients with TV who struggle with topical medication adherence; furthermore, it may be particularly beneficial for patients with concomitant acne.
Conclusions
This case demonstrates the successful use of in-office SA 30% peel as a treatment for TV. The rapid improvement and resolution of lesions with minimal adverse effects suggest that SA peel may serve as a valuable alternative for patients with extensive disease in difficult-to-reach affected areas, or those who are dissatisfied with traditional therapies. Additionally, the concurrent improvement of the patient’s back acne underscores the dual therapeutic potential of this treatment. Given the ease of application, cost effectiveness, and favorable safety profile, SA 30% peel is a viable option in the management of TV, especially in cases where topical or oral antifungals are impractical. Further studies could help establish standardized protocols and assess long-term outcomes of this treatment modality.
- Leung AK, Barankin B, Lam JM, et al. Tinea versicolor: an updated review. Drugs Context. 2022;11:2022-9-2. doi:10.7573/dic.2022-9-2
- Arif T. Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: a comprehensive review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:455-461. doi:10.2147/CCID.S84765
- Shao X, Chen Y, Zhang L, et al. Effect of 30% supramolecular salicylic acid peel on skin microbiota and inflammation in patients with moderate-to-severe acne vulgaris. Dermatol Ther. 2022;13(1):155-168. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00844-5
- Grimes PE. The safety and efficacy of salicylic acid chemical peels in darker racial-ethnic groups. Dermatol Surg Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg Al. 1999;25(1). doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.1999.08145.x
- Kang HY, Choi Y, Cho HJ. Salicylic acid peels for the treatment of acne vulgaris in Fitzpatrick skin types IV-V: a multicenter study. Dermatol Surg. Published online 2006. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2006.32146.x.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. J Clin Aesthetic Dermatol. 2010;3(7):20-31.
- Kallini JR, Riaz F, Khachemoune A. Tinea versicolor in dark-skinned individuals. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53(2):137- 141. doi:10.1111/ijd.12345
- Saoji V, Madke B. Efficacy of salicylic acid peel in dermatophytosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021;87(5). doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_853_18
- Arce M, Gutiérrez-Mendoza D. Pityriasis versicolor: treatment update. Curr Fungal Infect Rep 2018;12(11):195–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12281-018-0328-7
- Leong C, Kit JCW, Lee SM, et al. Azole resistance mechanisms in pathogenic M. furfur. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021;65(5):e01975-20. doi:10.1128/AAC.01975-20
- Chang HJ, Miller HL, Watkins N, et al. An epidemic of Malassezia pachydermatis in an intensive care nursery associated with colonization of health care workers’ pet dogs. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(11):706-711. doi:10.1056/NEJM199803123381102
- Lu J, Cong T, Wen X, et al. Salicylic acid treats acne vulgaris by suppressing AMPK/SREBP1 pathway in sebocytes. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28(7):786-794. doi:10.1111/exd.13934
- Singal A, Lipner SR. A review of skin disease in military soldiers: challenges and potential solutions. Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2267425. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2267425
- Leung AK, Barankin B, Lam JM, et al. Tinea versicolor: an updated review. Drugs Context. 2022;11:2022-9-2. doi:10.7573/dic.2022-9-2
- Arif T. Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: a comprehensive review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:455-461. doi:10.2147/CCID.S84765
- Shao X, Chen Y, Zhang L, et al. Effect of 30% supramolecular salicylic acid peel on skin microbiota and inflammation in patients with moderate-to-severe acne vulgaris. Dermatol Ther. 2022;13(1):155-168. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00844-5
- Grimes PE. The safety and efficacy of salicylic acid chemical peels in darker racial-ethnic groups. Dermatol Surg Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg Al. 1999;25(1). doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.1999.08145.x
- Kang HY, Choi Y, Cho HJ. Salicylic acid peels for the treatment of acne vulgaris in Fitzpatrick skin types IV-V: a multicenter study. Dermatol Surg. Published online 2006. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2006.32146.x.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. J Clin Aesthetic Dermatol. 2010;3(7):20-31.
- Kallini JR, Riaz F, Khachemoune A. Tinea versicolor in dark-skinned individuals. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53(2):137- 141. doi:10.1111/ijd.12345
- Saoji V, Madke B. Efficacy of salicylic acid peel in dermatophytosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021;87(5). doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_853_18
- Arce M, Gutiérrez-Mendoza D. Pityriasis versicolor: treatment update. Curr Fungal Infect Rep 2018;12(11):195–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12281-018-0328-7
- Leong C, Kit JCW, Lee SM, et al. Azole resistance mechanisms in pathogenic M. furfur. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021;65(5):e01975-20. doi:10.1128/AAC.01975-20
- Chang HJ, Miller HL, Watkins N, et al. An epidemic of Malassezia pachydermatis in an intensive care nursery associated with colonization of health care workers’ pet dogs. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(11):706-711. doi:10.1056/NEJM199803123381102
- Lu J, Cong T, Wen X, et al. Salicylic acid treats acne vulgaris by suppressing AMPK/SREBP1 pathway in sebocytes. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28(7):786-794. doi:10.1111/exd.13934
- Singal A, Lipner SR. A review of skin disease in military soldiers: challenges and potential solutions. Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2267425. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2267425
Successful Treatment of Tinea Versicolor With Salicylic Acid 30% Peel
Successful Treatment of Tinea Versicolor With Salicylic Acid 30% Peel
Blue Subcutaneous Nodules in a Young Service Member
Blue Subcutaneous Nodules in a Young Service Member
DISCUSSION
A diagnosis of familial glomangiomatosis was made based on the clinical history and histopathologic findings from the punch biopsy. Glomus tumors are comprised of glomus cells, or undifferentiated smooth muscle cells responsible for thermoregulation.1 Glomus tumors are classified into 3 categories: solid (predominantly glomus cells), glomangiomas (predominantly blood vessels), and glomangiomyomas (predominantly smooth muscle cells).2 Glomangiomas, which comprise up to 20% of glomus tumors, typically present as bluish-purple, papular or nodular, hyperkeratotic lesions that are 2 to 10 mm in diameter.1 These lesions are tender to palpation and pain may worsen with exposure to cold. Glomangiomas are associated with a classic triad of symptoms that include hypersensitivity, intermittent pain, and pinpoint pain, but patients rarely present with all 3.3
Glomangiomas tend to occur in areas rich with glomus bodies—the distal extremities—specifically the palms, wrists, forearms, feet, and subungual regions; visceral organ involvement including the GI tract is very rare.1,4,5 About 38% to 68% of these lesions are hereditary or can be sporadic. If these lesions are hereditary, a patient is said to have familial glomangiomatosis. In familial glomangiomatosis, the glomulin gene is mutated in an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern with incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity. Inherited glomangiomas may present at birth or puberty similar to other vascular anomalies.4
Histopathology of glomangiomas shows rows of glomus cells (modified smooth muscle cells) surrounding distorted venous channels.6,7 These lesions stain positive for CD34, vimentin, calponin, and α-smooth muscle actin, but are negative for desmin, S-100, and von Willebrand factor.1,8 Although the patient’s medical history and physical examination are important in establishing the diagnosis, histopathology is confirmatory.
While the punch biopsy results were pending, a complete blood count (CBC) and fecal occult blood test (FOBT) were ordered due to concerns for blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome (BRBNS), a rare disorder with about 200 reported cases. Patients present with multiple blue to violaceous compressible nodules that feel rubbery in consistency and may be painful with compression. Lesions may be up to 5 cm in diameter and with time, the GI tract may also become involved.9 In the GI tract, the small bowel is the most common site of involvement and patients may present with severe iron deficiency anemia due to hemorrhage.10 Histopathologic features are nonspecific and have features of venous malformations but may include large, tortuous, dilated vessels with a single endothelial lining with possible smooth muscle in vessel walls or calcifications.11 Due to concerns of BRBNS, laboratory studies (CBC and FOBT) were obtained but did not indicate the patient was experiencing a GI hemorrhage.
The differential diagnosis included Maffucci syndrome, also known as dyschondrodysplasia with hemangiomas, enchondromatosis with cavernous hemangiomas, or hemangiomatosis chondrodystrophic. Patients with Maffucci syndrome present with multiple enchondromas, soft tissue hemangiomas or lymphangiomas, and gliomas. These lesions tend to undergo malignant transformation from enchondromas to chondrosarcomas and hemangiomas to vascular sarcomas.12 This diagnosis was less likely in the patient in this case as there were no concerns of skeletal involvement upon history and physical examination.
Lastly, Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome can be associated with similar cutaneous vascular manifestations.13,14 This syndrome occurs due to somatic mutations altering angiogenesis during embryological development. This results in varicosities of superficial and deep venous systems, persistent embryonic veins, and valvular incompetence. However, these patients typically have capillary manifestations such as a flat, red, or purple port-wine stain present at birth and associated limb hypertrophy predominantly affecting a single lower limb.15,16 The patient reported not having the lesions present at birth and because bilateral upper/lower extremity and trunk involvement is rare in this syndrome, a Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome diagnosis was unlikely even in the absence of biopsy results.
Treatment
Based on pathology results, the patient was diagnosed with familial glomangiomatosis and a discussion of treatment options ensued. Asymptomatic lesions can be periodically managed. In addition, there are several treatments for symptomatic lesions. Symptomatic lesions may be tender to palpation and or hypersensitive to temperature change (cold). Though they exhibit slow growth, they can invade surrounding tissues including nerve sheaths which can worsen pain.
Surgical resection, sclerotherapy, laser therapy, and electron beam radiation have been used on patients with symptomatic lesions.8,17 Sclerotherapy involves introducing sterile solutions into a blood vessel’s lumen or into the vascular lesion itself to induce permanent endofibrosis and ablation.17 Hypertonic saline, sodium tetradecyl sulfate (STS), and absolute alcohol have been used to treat vascular anomalies as well as glomangiomas.17 Though case reports have noticed significant improvement in symptomatic lesions, sclerotherapy has been shown to be more effective in treating venous malformations than glomangiomas.18,19
A long-pulsed 1064-nm neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) laser has also been effective in treating larger glomangiomas that would otherwise be difficult to excise.20 The Nd:YAG laser has successfully treated lesions in patients with familial glomangiomatosis.21,22
Our patient opted for sclerotherapy with STS on symptomatic lesions of the bilateral upper extremities and trunk. The patient reported moderate improvement of some lesions at a 4-week follow-up appointment and sclerotherapy with STS was repeated.
It is important to note that if a glomangioma is fully excised, the prognosis is favorable; however, recurrence after surgical excision is seen in 10% to 33% of cases.23,24 Our patient had symptomatic lesions excised on the face, but they recurred. Glomangiomas confer a low risk of malignancy but some risk factors include lesions > 2 cm in size, deep lesions, muscle and/or bone invasion, and high mitotic activity.17,25 If left untreated, high-risk glomangiomas can potentially be life-threatening due to growth, bleeding, or vital organ obstruction.26
Primary Care Role
This patient was referred by his PCP assuming that these were symptomatic vascular lesions or telangiectasias (spider veins). Glomus cell tumors are classified as neurovascular neoplasms which may appear similar to vascular malformations or hemangiomas. 27 PCPs serve an important role in performing cutaneous biopsies to increase patient access to dermatologic care, increase patient awareness of skin conditions including skin cancer, and to potentially diagnose a malignant lesion.28 However, the PCP ultimately referred the patient to dermatology due to the number of growing, painful lesions. If the patient had a single lesion, it may have been appropriate to biopsy for diagnostic clarity.
A retrospective review found that the clinical diagnosis of glomus tumor showed concordance with histopathological diagnosis in 45.4% of cases. The most common alternate histopathological diagnoses were vascular tumors (25.9%) followed by other skin or soft tissue tumors like neuromas, leiomyomas, lipomas, or nevi.29 Even if the PCP performed an initial biopsy with high clinical suspicion of a vascular malformation, some glomus cell tumors may be vascular tumors and vice versa.
Though the patient’s history was consistent with the classic triad of glomangiomas including hypersensitivity, intermittent pain, and pinpoint pain, histopathology was necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Given that these appeared to be similar to telangiectasias to the PCP, a rare condition like BRBNS was likely not considered upon initial presentation. Furthermore, the patient had a negative review of systems to include GI symptoms like melena or hematochezia. The PCP had no concern of GI hemorrhage as these lesions can involve the GI tract. If the patient were to endorse additional symptoms, a CBC to evaluate for anemia as well as a GI referral would be warranted.
CONCLUSIONS
This case exhibits the importance of differentiating glomus cell tumors from other more common vascular anomalies via a patient’s history and histopathological findings. Diagnosis and treatment may be difficult depending on the extent of lesions.
- Brouillard P, Boon LM, Mulliken JB, et al. Mutations in a novel factor, glomulin, are responsible for glomuvenous malformations (“glomangiomas”). Am J Hum Genet. 2002;70(4):866- 874. doi:10.1086/339492
- Chatterjee JS, Youssef AH, Brown RM, Nishikawa H. Congenital nodular multiple glomangioma: a case report. J Clin Pathol. 2005;58(1):102-103. doi:10.1136/jcp.2003.014324
- Larsen DK, Madsen PV. Ugeskr Laeger. 2018;180(30):V10170807.
- Boon LM, Brouillard P, Irrthum A, et al. A gene for inherited cutaneous venous anomalies (“glomangiomas”) localizes to chromosome 1p21-22. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;65(1):125-133. doi:10.1086/302450
- Tewattanarat N, Srinakarin J, Wongwiwatchai J, et al. Imaging of a glomus tumor of the liver in a child. Radiol Case Rep. 2020;15(4):311-315. doi:10.1016/j.radcr.2019.12.014
- Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2024.
- Elston D, Ferringer T, Ko CJ, Peckham S, High WA, DiCaudo DJ. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Leger M, Patel U, Mandal R, et al. Glomangioma. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16(11):11.
- Jin XL, Wang ZH, Xiao XB, Huang LS, Zhao XY. Blue rub ber bleb nevus syndrome: a case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(45):17254-17259. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17254
- Aravindan U, Ganesan R, Thamarai Kannan M. Surgery for blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome-a case report. Indian J Surg. 2018;80(3):272-274. doi:10.1007/s12262-017-1715-y
- Dobru D, Seuchea N, Dorin M, Careianu V. Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome: case report and literature review. Rom J Gastroenterol. 2004;13(3):237-240.
- Prokopchuk O, Andres S, Becker K, Holzapfel K, Hartmann D, Friess H. Maffucci syndrome and neoplasms: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9:126. doi:10.1186/s13104-016-1913-x
- Wang SK, Drucker NA, Gupta AK, Marshalleck FE, Dalsing MC. Diagnosis and management of the venous malformations of Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2017;5(4):587-595. doi:10.1016/j.jvsv.2016.10.084
- Yamaki T, Konoeda H, Fujisawa D, et al. Prevalence of various congenital vascular malformations in patients with Klippel- Trenaunay syndrome. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2013;1(2):187-193. doi:10.1016/j.jvsv.2012.07.010
- Alwalid O, Makamure J, Cheng QG, et al. Radiological aspect of Klippel-Trénaunay Syndrome: a case series with review of literature. Curr Med Sci. 2018;38(5):925-931. doi:10.1007/s11596-018-1964-4
- Sung HM, Chung HY, Lee SJ, et al. Clinical experience of the Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome. Arch Plast Surg. Sep 2015;42(5):552-558. doi:10.5999/aps.2015.42.5.552
- Jha A, Khunger N, Malarvizhi K, Ramesh V, Singh A. Familial disseminated cutaneous glomuvenous malformation: treatment with polidocanol sclerotherapy. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2016;9(4):266-269. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.197083
- Enjolras O, Ciabrini D, Mazoyer E, Laurian C, Herbreteau D. Extensive pure venous malformations in the upper or lower limb: a review of 27 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36(2 Pt 1):219-225. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70284-6
- Berenguer B, Burrows PE, Zurakowski D, Mulliken JB. Sclerotherapy of craniofacial venous malformations: complications and results. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999;104(1):1-15.
- Rivers JK, Rivers CA, Li MK, Martinka M. Laser therapy for an acquired glomuvenous malformation (glomus tumour): a nonsurgical approach. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20(1):80-183. doi:10.1177/1203475415596121
- Phillips CB, Guerrero C, Theos A. Nd:YAG laser offers promising treatment option for familial glomuvenous malformation. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21(4).
- Jha A, Ramesh V, Singh A. Disseminated cutaneous glomuvenous malformation. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014;80(6):556-558. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.144200
- Gonçalves R, Lopes A, Júlio C, Durão C, de Mello RA. Knee glomangioma: a rare location for a glomus tumor. Rare Tumors. 2014;6(4):5588. doi:10.4081/rt.2014.5588
- Cabral CR, Oliveira Filho J, Matsumoto JL, Cignachi S, Tebet AC, Nasser KaR. Type 2 segmental glomangioma- -Case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90(3 Suppl 1):97-100. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20152483
- Tony G, Hauxwell S, Nair N, Harrison DA, Richards PJ. Large plaque-like glomangioma in a patient with multiple glomus tumours: review of imaging and histology. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38(7):693-700. doi:10.1111/ced.12122
- Boon LM, Mulliken JB, Enjolras O, Vikkula M. Glomuvenous malformation (glomangioma) and venous malformation: distinct clinicopathologic and genetic entities. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140(8):971-976. doi:10.1001/archderm.140.8.971
- Honsawek S, Kitidumrongsook P, Luangjarmekorn P, Pataradool K, Thanakit V, Patradul A. Glomus tumors of the fingers: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. World J Orthop. 2016;7(12):843-846. doi:10.5312/wjo.v7.i12.843
- Jones TP, Boiko PE, Piepkorn MW. Skin biopsy indications in primary care practice: a population-based study. J Am Board Fam Pract. 1996;9(6):397-404.
- Mravic M, LaChaud G, Nguyen A, Scott MA, Dry SM, James AW. Clinical and histopathological diagnosis of glomus tumor: an institutional experience of 138 cases. Int J Surg Pathol. 2015;23(3):181-188. doi:10.1177/1066896914567330
DISCUSSION
A diagnosis of familial glomangiomatosis was made based on the clinical history and histopathologic findings from the punch biopsy. Glomus tumors are comprised of glomus cells, or undifferentiated smooth muscle cells responsible for thermoregulation.1 Glomus tumors are classified into 3 categories: solid (predominantly glomus cells), glomangiomas (predominantly blood vessels), and glomangiomyomas (predominantly smooth muscle cells).2 Glomangiomas, which comprise up to 20% of glomus tumors, typically present as bluish-purple, papular or nodular, hyperkeratotic lesions that are 2 to 10 mm in diameter.1 These lesions are tender to palpation and pain may worsen with exposure to cold. Glomangiomas are associated with a classic triad of symptoms that include hypersensitivity, intermittent pain, and pinpoint pain, but patients rarely present with all 3.3
Glomangiomas tend to occur in areas rich with glomus bodies—the distal extremities—specifically the palms, wrists, forearms, feet, and subungual regions; visceral organ involvement including the GI tract is very rare.1,4,5 About 38% to 68% of these lesions are hereditary or can be sporadic. If these lesions are hereditary, a patient is said to have familial glomangiomatosis. In familial glomangiomatosis, the glomulin gene is mutated in an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern with incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity. Inherited glomangiomas may present at birth or puberty similar to other vascular anomalies.4
Histopathology of glomangiomas shows rows of glomus cells (modified smooth muscle cells) surrounding distorted venous channels.6,7 These lesions stain positive for CD34, vimentin, calponin, and α-smooth muscle actin, but are negative for desmin, S-100, and von Willebrand factor.1,8 Although the patient’s medical history and physical examination are important in establishing the diagnosis, histopathology is confirmatory.
While the punch biopsy results were pending, a complete blood count (CBC) and fecal occult blood test (FOBT) were ordered due to concerns for blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome (BRBNS), a rare disorder with about 200 reported cases. Patients present with multiple blue to violaceous compressible nodules that feel rubbery in consistency and may be painful with compression. Lesions may be up to 5 cm in diameter and with time, the GI tract may also become involved.9 In the GI tract, the small bowel is the most common site of involvement and patients may present with severe iron deficiency anemia due to hemorrhage.10 Histopathologic features are nonspecific and have features of venous malformations but may include large, tortuous, dilated vessels with a single endothelial lining with possible smooth muscle in vessel walls or calcifications.11 Due to concerns of BRBNS, laboratory studies (CBC and FOBT) were obtained but did not indicate the patient was experiencing a GI hemorrhage.
The differential diagnosis included Maffucci syndrome, also known as dyschondrodysplasia with hemangiomas, enchondromatosis with cavernous hemangiomas, or hemangiomatosis chondrodystrophic. Patients with Maffucci syndrome present with multiple enchondromas, soft tissue hemangiomas or lymphangiomas, and gliomas. These lesions tend to undergo malignant transformation from enchondromas to chondrosarcomas and hemangiomas to vascular sarcomas.12 This diagnosis was less likely in the patient in this case as there were no concerns of skeletal involvement upon history and physical examination.
Lastly, Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome can be associated with similar cutaneous vascular manifestations.13,14 This syndrome occurs due to somatic mutations altering angiogenesis during embryological development. This results in varicosities of superficial and deep venous systems, persistent embryonic veins, and valvular incompetence. However, these patients typically have capillary manifestations such as a flat, red, or purple port-wine stain present at birth and associated limb hypertrophy predominantly affecting a single lower limb.15,16 The patient reported not having the lesions present at birth and because bilateral upper/lower extremity and trunk involvement is rare in this syndrome, a Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome diagnosis was unlikely even in the absence of biopsy results.
Treatment
Based on pathology results, the patient was diagnosed with familial glomangiomatosis and a discussion of treatment options ensued. Asymptomatic lesions can be periodically managed. In addition, there are several treatments for symptomatic lesions. Symptomatic lesions may be tender to palpation and or hypersensitive to temperature change (cold). Though they exhibit slow growth, they can invade surrounding tissues including nerve sheaths which can worsen pain.
Surgical resection, sclerotherapy, laser therapy, and electron beam radiation have been used on patients with symptomatic lesions.8,17 Sclerotherapy involves introducing sterile solutions into a blood vessel’s lumen or into the vascular lesion itself to induce permanent endofibrosis and ablation.17 Hypertonic saline, sodium tetradecyl sulfate (STS), and absolute alcohol have been used to treat vascular anomalies as well as glomangiomas.17 Though case reports have noticed significant improvement in symptomatic lesions, sclerotherapy has been shown to be more effective in treating venous malformations than glomangiomas.18,19
A long-pulsed 1064-nm neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) laser has also been effective in treating larger glomangiomas that would otherwise be difficult to excise.20 The Nd:YAG laser has successfully treated lesions in patients with familial glomangiomatosis.21,22
Our patient opted for sclerotherapy with STS on symptomatic lesions of the bilateral upper extremities and trunk. The patient reported moderate improvement of some lesions at a 4-week follow-up appointment and sclerotherapy with STS was repeated.
It is important to note that if a glomangioma is fully excised, the prognosis is favorable; however, recurrence after surgical excision is seen in 10% to 33% of cases.23,24 Our patient had symptomatic lesions excised on the face, but they recurred. Glomangiomas confer a low risk of malignancy but some risk factors include lesions > 2 cm in size, deep lesions, muscle and/or bone invasion, and high mitotic activity.17,25 If left untreated, high-risk glomangiomas can potentially be life-threatening due to growth, bleeding, or vital organ obstruction.26
Primary Care Role
This patient was referred by his PCP assuming that these were symptomatic vascular lesions or telangiectasias (spider veins). Glomus cell tumors are classified as neurovascular neoplasms which may appear similar to vascular malformations or hemangiomas. 27 PCPs serve an important role in performing cutaneous biopsies to increase patient access to dermatologic care, increase patient awareness of skin conditions including skin cancer, and to potentially diagnose a malignant lesion.28 However, the PCP ultimately referred the patient to dermatology due to the number of growing, painful lesions. If the patient had a single lesion, it may have been appropriate to biopsy for diagnostic clarity.
A retrospective review found that the clinical diagnosis of glomus tumor showed concordance with histopathological diagnosis in 45.4% of cases. The most common alternate histopathological diagnoses were vascular tumors (25.9%) followed by other skin or soft tissue tumors like neuromas, leiomyomas, lipomas, or nevi.29 Even if the PCP performed an initial biopsy with high clinical suspicion of a vascular malformation, some glomus cell tumors may be vascular tumors and vice versa.
Though the patient’s history was consistent with the classic triad of glomangiomas including hypersensitivity, intermittent pain, and pinpoint pain, histopathology was necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Given that these appeared to be similar to telangiectasias to the PCP, a rare condition like BRBNS was likely not considered upon initial presentation. Furthermore, the patient had a negative review of systems to include GI symptoms like melena or hematochezia. The PCP had no concern of GI hemorrhage as these lesions can involve the GI tract. If the patient were to endorse additional symptoms, a CBC to evaluate for anemia as well as a GI referral would be warranted.
CONCLUSIONS
This case exhibits the importance of differentiating glomus cell tumors from other more common vascular anomalies via a patient’s history and histopathological findings. Diagnosis and treatment may be difficult depending on the extent of lesions.
DISCUSSION
A diagnosis of familial glomangiomatosis was made based on the clinical history and histopathologic findings from the punch biopsy. Glomus tumors are comprised of glomus cells, or undifferentiated smooth muscle cells responsible for thermoregulation.1 Glomus tumors are classified into 3 categories: solid (predominantly glomus cells), glomangiomas (predominantly blood vessels), and glomangiomyomas (predominantly smooth muscle cells).2 Glomangiomas, which comprise up to 20% of glomus tumors, typically present as bluish-purple, papular or nodular, hyperkeratotic lesions that are 2 to 10 mm in diameter.1 These lesions are tender to palpation and pain may worsen with exposure to cold. Glomangiomas are associated with a classic triad of symptoms that include hypersensitivity, intermittent pain, and pinpoint pain, but patients rarely present with all 3.3
Glomangiomas tend to occur in areas rich with glomus bodies—the distal extremities—specifically the palms, wrists, forearms, feet, and subungual regions; visceral organ involvement including the GI tract is very rare.1,4,5 About 38% to 68% of these lesions are hereditary or can be sporadic. If these lesions are hereditary, a patient is said to have familial glomangiomatosis. In familial glomangiomatosis, the glomulin gene is mutated in an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern with incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity. Inherited glomangiomas may present at birth or puberty similar to other vascular anomalies.4
Histopathology of glomangiomas shows rows of glomus cells (modified smooth muscle cells) surrounding distorted venous channels.6,7 These lesions stain positive for CD34, vimentin, calponin, and α-smooth muscle actin, but are negative for desmin, S-100, and von Willebrand factor.1,8 Although the patient’s medical history and physical examination are important in establishing the diagnosis, histopathology is confirmatory.
While the punch biopsy results were pending, a complete blood count (CBC) and fecal occult blood test (FOBT) were ordered due to concerns for blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome (BRBNS), a rare disorder with about 200 reported cases. Patients present with multiple blue to violaceous compressible nodules that feel rubbery in consistency and may be painful with compression. Lesions may be up to 5 cm in diameter and with time, the GI tract may also become involved.9 In the GI tract, the small bowel is the most common site of involvement and patients may present with severe iron deficiency anemia due to hemorrhage.10 Histopathologic features are nonspecific and have features of venous malformations but may include large, tortuous, dilated vessels with a single endothelial lining with possible smooth muscle in vessel walls or calcifications.11 Due to concerns of BRBNS, laboratory studies (CBC and FOBT) were obtained but did not indicate the patient was experiencing a GI hemorrhage.
The differential diagnosis included Maffucci syndrome, also known as dyschondrodysplasia with hemangiomas, enchondromatosis with cavernous hemangiomas, or hemangiomatosis chondrodystrophic. Patients with Maffucci syndrome present with multiple enchondromas, soft tissue hemangiomas or lymphangiomas, and gliomas. These lesions tend to undergo malignant transformation from enchondromas to chondrosarcomas and hemangiomas to vascular sarcomas.12 This diagnosis was less likely in the patient in this case as there were no concerns of skeletal involvement upon history and physical examination.
Lastly, Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome can be associated with similar cutaneous vascular manifestations.13,14 This syndrome occurs due to somatic mutations altering angiogenesis during embryological development. This results in varicosities of superficial and deep venous systems, persistent embryonic veins, and valvular incompetence. However, these patients typically have capillary manifestations such as a flat, red, or purple port-wine stain present at birth and associated limb hypertrophy predominantly affecting a single lower limb.15,16 The patient reported not having the lesions present at birth and because bilateral upper/lower extremity and trunk involvement is rare in this syndrome, a Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome diagnosis was unlikely even in the absence of biopsy results.
Treatment
Based on pathology results, the patient was diagnosed with familial glomangiomatosis and a discussion of treatment options ensued. Asymptomatic lesions can be periodically managed. In addition, there are several treatments for symptomatic lesions. Symptomatic lesions may be tender to palpation and or hypersensitive to temperature change (cold). Though they exhibit slow growth, they can invade surrounding tissues including nerve sheaths which can worsen pain.
Surgical resection, sclerotherapy, laser therapy, and electron beam radiation have been used on patients with symptomatic lesions.8,17 Sclerotherapy involves introducing sterile solutions into a blood vessel’s lumen or into the vascular lesion itself to induce permanent endofibrosis and ablation.17 Hypertonic saline, sodium tetradecyl sulfate (STS), and absolute alcohol have been used to treat vascular anomalies as well as glomangiomas.17 Though case reports have noticed significant improvement in symptomatic lesions, sclerotherapy has been shown to be more effective in treating venous malformations than glomangiomas.18,19
A long-pulsed 1064-nm neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) laser has also been effective in treating larger glomangiomas that would otherwise be difficult to excise.20 The Nd:YAG laser has successfully treated lesions in patients with familial glomangiomatosis.21,22
Our patient opted for sclerotherapy with STS on symptomatic lesions of the bilateral upper extremities and trunk. The patient reported moderate improvement of some lesions at a 4-week follow-up appointment and sclerotherapy with STS was repeated.
It is important to note that if a glomangioma is fully excised, the prognosis is favorable; however, recurrence after surgical excision is seen in 10% to 33% of cases.23,24 Our patient had symptomatic lesions excised on the face, but they recurred. Glomangiomas confer a low risk of malignancy but some risk factors include lesions > 2 cm in size, deep lesions, muscle and/or bone invasion, and high mitotic activity.17,25 If left untreated, high-risk glomangiomas can potentially be life-threatening due to growth, bleeding, or vital organ obstruction.26
Primary Care Role
This patient was referred by his PCP assuming that these were symptomatic vascular lesions or telangiectasias (spider veins). Glomus cell tumors are classified as neurovascular neoplasms which may appear similar to vascular malformations or hemangiomas. 27 PCPs serve an important role in performing cutaneous biopsies to increase patient access to dermatologic care, increase patient awareness of skin conditions including skin cancer, and to potentially diagnose a malignant lesion.28 However, the PCP ultimately referred the patient to dermatology due to the number of growing, painful lesions. If the patient had a single lesion, it may have been appropriate to biopsy for diagnostic clarity.
A retrospective review found that the clinical diagnosis of glomus tumor showed concordance with histopathological diagnosis in 45.4% of cases. The most common alternate histopathological diagnoses were vascular tumors (25.9%) followed by other skin or soft tissue tumors like neuromas, leiomyomas, lipomas, or nevi.29 Even if the PCP performed an initial biopsy with high clinical suspicion of a vascular malformation, some glomus cell tumors may be vascular tumors and vice versa.
Though the patient’s history was consistent with the classic triad of glomangiomas including hypersensitivity, intermittent pain, and pinpoint pain, histopathology was necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Given that these appeared to be similar to telangiectasias to the PCP, a rare condition like BRBNS was likely not considered upon initial presentation. Furthermore, the patient had a negative review of systems to include GI symptoms like melena or hematochezia. The PCP had no concern of GI hemorrhage as these lesions can involve the GI tract. If the patient were to endorse additional symptoms, a CBC to evaluate for anemia as well as a GI referral would be warranted.
CONCLUSIONS
This case exhibits the importance of differentiating glomus cell tumors from other more common vascular anomalies via a patient’s history and histopathological findings. Diagnosis and treatment may be difficult depending on the extent of lesions.
- Brouillard P, Boon LM, Mulliken JB, et al. Mutations in a novel factor, glomulin, are responsible for glomuvenous malformations (“glomangiomas”). Am J Hum Genet. 2002;70(4):866- 874. doi:10.1086/339492
- Chatterjee JS, Youssef AH, Brown RM, Nishikawa H. Congenital nodular multiple glomangioma: a case report. J Clin Pathol. 2005;58(1):102-103. doi:10.1136/jcp.2003.014324
- Larsen DK, Madsen PV. Ugeskr Laeger. 2018;180(30):V10170807.
- Boon LM, Brouillard P, Irrthum A, et al. A gene for inherited cutaneous venous anomalies (“glomangiomas”) localizes to chromosome 1p21-22. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;65(1):125-133. doi:10.1086/302450
- Tewattanarat N, Srinakarin J, Wongwiwatchai J, et al. Imaging of a glomus tumor of the liver in a child. Radiol Case Rep. 2020;15(4):311-315. doi:10.1016/j.radcr.2019.12.014
- Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2024.
- Elston D, Ferringer T, Ko CJ, Peckham S, High WA, DiCaudo DJ. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Leger M, Patel U, Mandal R, et al. Glomangioma. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16(11):11.
- Jin XL, Wang ZH, Xiao XB, Huang LS, Zhao XY. Blue rub ber bleb nevus syndrome: a case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(45):17254-17259. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17254
- Aravindan U, Ganesan R, Thamarai Kannan M. Surgery for blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome-a case report. Indian J Surg. 2018;80(3):272-274. doi:10.1007/s12262-017-1715-y
- Dobru D, Seuchea N, Dorin M, Careianu V. Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome: case report and literature review. Rom J Gastroenterol. 2004;13(3):237-240.
- Prokopchuk O, Andres S, Becker K, Holzapfel K, Hartmann D, Friess H. Maffucci syndrome and neoplasms: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9:126. doi:10.1186/s13104-016-1913-x
- Wang SK, Drucker NA, Gupta AK, Marshalleck FE, Dalsing MC. Diagnosis and management of the venous malformations of Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2017;5(4):587-595. doi:10.1016/j.jvsv.2016.10.084
- Yamaki T, Konoeda H, Fujisawa D, et al. Prevalence of various congenital vascular malformations in patients with Klippel- Trenaunay syndrome. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2013;1(2):187-193. doi:10.1016/j.jvsv.2012.07.010
- Alwalid O, Makamure J, Cheng QG, et al. Radiological aspect of Klippel-Trénaunay Syndrome: a case series with review of literature. Curr Med Sci. 2018;38(5):925-931. doi:10.1007/s11596-018-1964-4
- Sung HM, Chung HY, Lee SJ, et al. Clinical experience of the Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome. Arch Plast Surg. Sep 2015;42(5):552-558. doi:10.5999/aps.2015.42.5.552
- Jha A, Khunger N, Malarvizhi K, Ramesh V, Singh A. Familial disseminated cutaneous glomuvenous malformation: treatment with polidocanol sclerotherapy. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2016;9(4):266-269. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.197083
- Enjolras O, Ciabrini D, Mazoyer E, Laurian C, Herbreteau D. Extensive pure venous malformations in the upper or lower limb: a review of 27 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36(2 Pt 1):219-225. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70284-6
- Berenguer B, Burrows PE, Zurakowski D, Mulliken JB. Sclerotherapy of craniofacial venous malformations: complications and results. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999;104(1):1-15.
- Rivers JK, Rivers CA, Li MK, Martinka M. Laser therapy for an acquired glomuvenous malformation (glomus tumour): a nonsurgical approach. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20(1):80-183. doi:10.1177/1203475415596121
- Phillips CB, Guerrero C, Theos A. Nd:YAG laser offers promising treatment option for familial glomuvenous malformation. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21(4).
- Jha A, Ramesh V, Singh A. Disseminated cutaneous glomuvenous malformation. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014;80(6):556-558. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.144200
- Gonçalves R, Lopes A, Júlio C, Durão C, de Mello RA. Knee glomangioma: a rare location for a glomus tumor. Rare Tumors. 2014;6(4):5588. doi:10.4081/rt.2014.5588
- Cabral CR, Oliveira Filho J, Matsumoto JL, Cignachi S, Tebet AC, Nasser KaR. Type 2 segmental glomangioma- -Case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90(3 Suppl 1):97-100. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20152483
- Tony G, Hauxwell S, Nair N, Harrison DA, Richards PJ. Large plaque-like glomangioma in a patient with multiple glomus tumours: review of imaging and histology. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38(7):693-700. doi:10.1111/ced.12122
- Boon LM, Mulliken JB, Enjolras O, Vikkula M. Glomuvenous malformation (glomangioma) and venous malformation: distinct clinicopathologic and genetic entities. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140(8):971-976. doi:10.1001/archderm.140.8.971
- Honsawek S, Kitidumrongsook P, Luangjarmekorn P, Pataradool K, Thanakit V, Patradul A. Glomus tumors of the fingers: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. World J Orthop. 2016;7(12):843-846. doi:10.5312/wjo.v7.i12.843
- Jones TP, Boiko PE, Piepkorn MW. Skin biopsy indications in primary care practice: a population-based study. J Am Board Fam Pract. 1996;9(6):397-404.
- Mravic M, LaChaud G, Nguyen A, Scott MA, Dry SM, James AW. Clinical and histopathological diagnosis of glomus tumor: an institutional experience of 138 cases. Int J Surg Pathol. 2015;23(3):181-188. doi:10.1177/1066896914567330
- Brouillard P, Boon LM, Mulliken JB, et al. Mutations in a novel factor, glomulin, are responsible for glomuvenous malformations (“glomangiomas”). Am J Hum Genet. 2002;70(4):866- 874. doi:10.1086/339492
- Chatterjee JS, Youssef AH, Brown RM, Nishikawa H. Congenital nodular multiple glomangioma: a case report. J Clin Pathol. 2005;58(1):102-103. doi:10.1136/jcp.2003.014324
- Larsen DK, Madsen PV. Ugeskr Laeger. 2018;180(30):V10170807.
- Boon LM, Brouillard P, Irrthum A, et al. A gene for inherited cutaneous venous anomalies (“glomangiomas”) localizes to chromosome 1p21-22. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;65(1):125-133. doi:10.1086/302450
- Tewattanarat N, Srinakarin J, Wongwiwatchai J, et al. Imaging of a glomus tumor of the liver in a child. Radiol Case Rep. 2020;15(4):311-315. doi:10.1016/j.radcr.2019.12.014
- Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2024.
- Elston D, Ferringer T, Ko CJ, Peckham S, High WA, DiCaudo DJ. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Leger M, Patel U, Mandal R, et al. Glomangioma. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16(11):11.
- Jin XL, Wang ZH, Xiao XB, Huang LS, Zhao XY. Blue rub ber bleb nevus syndrome: a case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(45):17254-17259. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17254
- Aravindan U, Ganesan R, Thamarai Kannan M. Surgery for blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome-a case report. Indian J Surg. 2018;80(3):272-274. doi:10.1007/s12262-017-1715-y
- Dobru D, Seuchea N, Dorin M, Careianu V. Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome: case report and literature review. Rom J Gastroenterol. 2004;13(3):237-240.
- Prokopchuk O, Andres S, Becker K, Holzapfel K, Hartmann D, Friess H. Maffucci syndrome and neoplasms: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9:126. doi:10.1186/s13104-016-1913-x
- Wang SK, Drucker NA, Gupta AK, Marshalleck FE, Dalsing MC. Diagnosis and management of the venous malformations of Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2017;5(4):587-595. doi:10.1016/j.jvsv.2016.10.084
- Yamaki T, Konoeda H, Fujisawa D, et al. Prevalence of various congenital vascular malformations in patients with Klippel- Trenaunay syndrome. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2013;1(2):187-193. doi:10.1016/j.jvsv.2012.07.010
- Alwalid O, Makamure J, Cheng QG, et al. Radiological aspect of Klippel-Trénaunay Syndrome: a case series with review of literature. Curr Med Sci. 2018;38(5):925-931. doi:10.1007/s11596-018-1964-4
- Sung HM, Chung HY, Lee SJ, et al. Clinical experience of the Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome. Arch Plast Surg. Sep 2015;42(5):552-558. doi:10.5999/aps.2015.42.5.552
- Jha A, Khunger N, Malarvizhi K, Ramesh V, Singh A. Familial disseminated cutaneous glomuvenous malformation: treatment with polidocanol sclerotherapy. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2016;9(4):266-269. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.197083
- Enjolras O, Ciabrini D, Mazoyer E, Laurian C, Herbreteau D. Extensive pure venous malformations in the upper or lower limb: a review of 27 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36(2 Pt 1):219-225. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70284-6
- Berenguer B, Burrows PE, Zurakowski D, Mulliken JB. Sclerotherapy of craniofacial venous malformations: complications and results. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999;104(1):1-15.
- Rivers JK, Rivers CA, Li MK, Martinka M. Laser therapy for an acquired glomuvenous malformation (glomus tumour): a nonsurgical approach. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20(1):80-183. doi:10.1177/1203475415596121
- Phillips CB, Guerrero C, Theos A. Nd:YAG laser offers promising treatment option for familial glomuvenous malformation. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21(4).
- Jha A, Ramesh V, Singh A. Disseminated cutaneous glomuvenous malformation. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014;80(6):556-558. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.144200
- Gonçalves R, Lopes A, Júlio C, Durão C, de Mello RA. Knee glomangioma: a rare location for a glomus tumor. Rare Tumors. 2014;6(4):5588. doi:10.4081/rt.2014.5588
- Cabral CR, Oliveira Filho J, Matsumoto JL, Cignachi S, Tebet AC, Nasser KaR. Type 2 segmental glomangioma- -Case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90(3 Suppl 1):97-100. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20152483
- Tony G, Hauxwell S, Nair N, Harrison DA, Richards PJ. Large plaque-like glomangioma in a patient with multiple glomus tumours: review of imaging and histology. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38(7):693-700. doi:10.1111/ced.12122
- Boon LM, Mulliken JB, Enjolras O, Vikkula M. Glomuvenous malformation (glomangioma) and venous malformation: distinct clinicopathologic and genetic entities. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140(8):971-976. doi:10.1001/archderm.140.8.971
- Honsawek S, Kitidumrongsook P, Luangjarmekorn P, Pataradool K, Thanakit V, Patradul A. Glomus tumors of the fingers: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. World J Orthop. 2016;7(12):843-846. doi:10.5312/wjo.v7.i12.843
- Jones TP, Boiko PE, Piepkorn MW. Skin biopsy indications in primary care practice: a population-based study. J Am Board Fam Pract. 1996;9(6):397-404.
- Mravic M, LaChaud G, Nguyen A, Scott MA, Dry SM, James AW. Clinical and histopathological diagnosis of glomus tumor: an institutional experience of 138 cases. Int J Surg Pathol. 2015;23(3):181-188. doi:10.1177/1066896914567330
Blue Subcutaneous Nodules in a Young Service Member
Blue Subcutaneous Nodules in a Young Service Member
A 26-year-old male with Fitzpatrick skin type II presented for evaluation in the dermatology clinic after being referred by his primary care practitioner (PCP) with a complaint of spider veins. The patient reported a lifelong history of blue subcutaneous nodules that initially appeared on his face during childhood but have since involved his trunk and upper and lower extremities. The patient reported that some of the nodules were painful and increased in size with exercise. His medical history was unremarkable with no other chronic conditions or daily medication use. The patient reported no gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms, melena, or hematochezia. The patient’s mother had similar nodules but his 7 siblings did not.
Upon physical examination, numerous blue subcutaneous nodules, 2 to 8 mm in size, were scattered across his trunk, and proximal and distal extremities were present (Figure 1). The physical examination was otherwise unremarkable. Upon discussing differential diagnosis of these lesions with the patient, he was amenable to a punch biopsy for further diagnostic clarity (Figure 2).
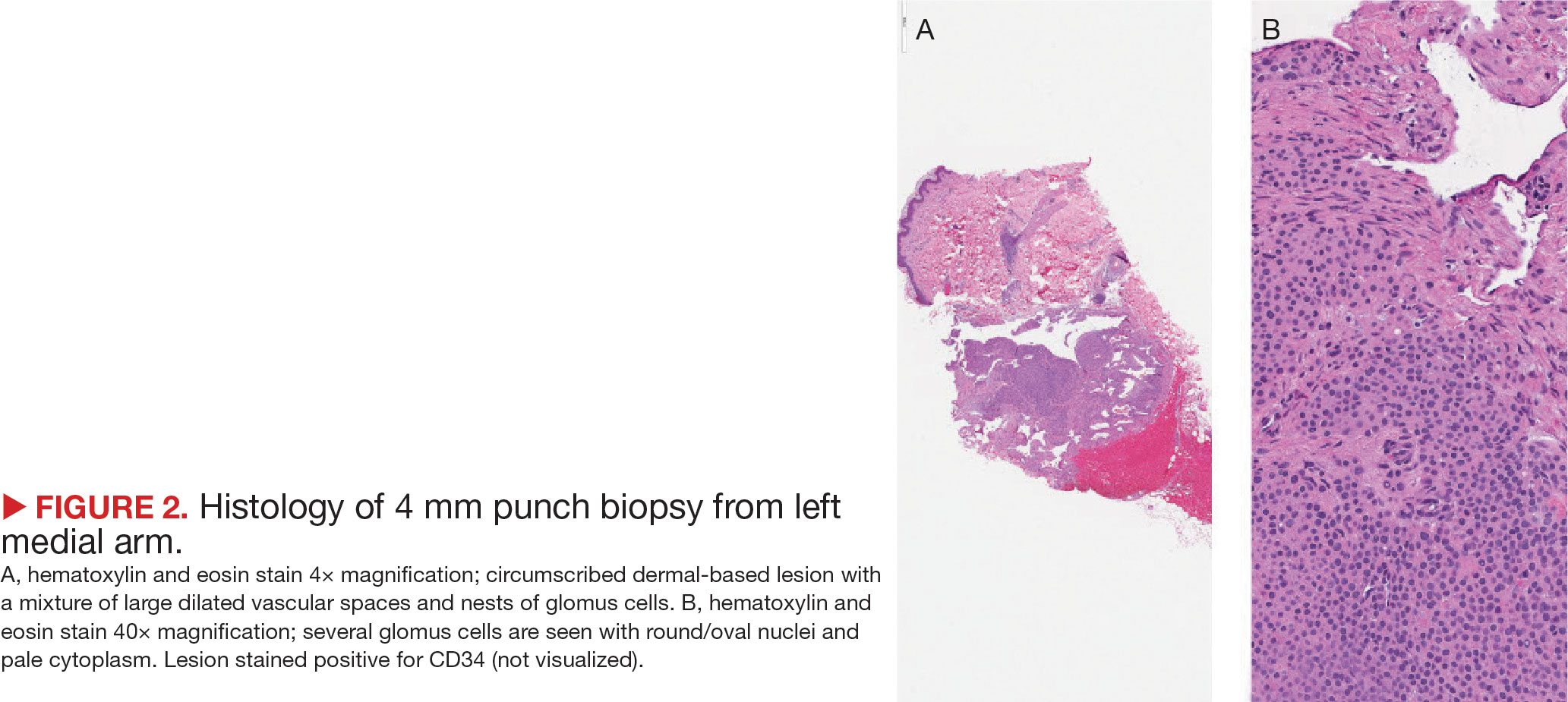
Violaceous Papules on Face
Violaceous Papules on Face
Discussion
The patient’s violaceous papule on the nose with an apple jelly appearance is consistent with lupus pernio—a cutaneous form of sarcoidosis associated with respiratory involvement. Lupus pernio disproportionately affects African Americans, which further supports this diagnosis.1 Lupus pernio is characterized by violaceous, indurated plaques predominantly on the face. It has a strong association with systemic sarcoidosis and often involves the lungs and other organs, as seen in this case. The laboratory results support this diagnosis. Hypercalcemia is a common systemic manifestation of sarcoidosis due to increased production of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D by activated macrophages with granulomas.2 Elevated chitotriosidase, an enzyme produced by macrophages, is another biomarker of sarcoidosis reflecting granuloma burden.3
The differential diagnoses included Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH), discoid lupus erythematosus, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and granuloma annulare. However, these diagnoses did not fully align with the entirety of the patient’s clinical presentation and laboratory findings. LCH is a rare neoplastic disorder characterized by the abnormal proliferation and accumulation of Langerhans cells, a type of dendritic cell involved in immune response, in various tissues such as the skin and bone. Dermatologic findings in LCH include brown/purple papules and an erythematous papular rash rather than the violaceous plaques/papules in lupus pernio. LCH can have lung involvement; it typically presents with nodular or cystic changes in the upper lobes as opposed to the bibasilar opacities seen in this case.
Discoid lupus erythematosus presents with characteristic round, erythematous, scaly plaques on the cheeks, scalp, and ears. This is different from the apple jelly appearance seen in this case and does not present with systemic granulomatous involvement.
Typical manifestations of granulomatosis with polyangiitis, formerly known as Wegener’s granulomatosis, include renal disease, upper and lower respiratory tract involvement, or necrotizing vasculitis. Cutaneous manifestions of granulomatosis with polyangiitis typically include purpura or ulcers rather than the violaceous plaques seen in lupus pernio. Patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis would also present with nonspecific systemic symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and malaise, which are not depicted in this case.4
Granuloma annulare is a benign condition that often presents with annular plaques that are skin-colored rather than violaceous. These plaques are often found on the hands and feet rather than the face. This condition also lacks the systemic manifestations seen in this case.
In primary care, encountering violaceous papule and plaques on the face, especially on the nasal alae or ear, should be concerning for possible lupus pernio, particularly in high-risk populations such as young African Americans. These lesions generally have a more indurated “deep” and “doughy” appearance and can result in scarring, distinguishing them from other types of cutaneous sarcoidosis. An apple jelly appearance seen on diascopy with a glass slide can further support the diagnosis. While the lesions are typically asymptomatic, patients may be concerned about potential cosmetic disfigurement. Given the potential for scarring and the association with systemic sarcoidosis, a dermatology referral is recommended for further evaluation and management.
A detailed patient history, physical examination, and laboratory exams are essential to accurately diagnose lupus pernio. Biopsy of a skin lesion, serum markers, and imaging studies were utilized to help assess systemic involvement and further confirm diagnosis in this patient. Following the diagnosis, the patient was started on his current regimen of prednisone, methotrexate, and hydroxychloroquine, which are standard therapies for managing both cutaneous and systemic sarcoidosis.
This case shows the importance of recognizing lupus pernio, a distinct form of cutaneous sarcoidosis, in patients presenting with characteristic skin lesions and systemic involvement. It is essential to differentiate it from other granulomatous and inflammatory skin conditions to ensure appropriate management and prevent complications.
Federal Practitioner thanks the Association of Military Dermatologists (militaryderm.org) for their assistance in developing the Image Challenge. Submissions based on photographs, radiography, or any other visual medium are welcomed.
- Lai J, Almazan E, Le T, Taylor MT, Alhariri J, Kwatra SG. Demographics, cutaneous manifestations, and comorbidities associated with progressive cutaneous sarcoidosis: a retrospective cohort study. Medicines (Basel). 2023;10(10):57. doi:10.3390/medicines10100057
- Burke RR, Rybicki BA, Rao DS. Calcium and vitamin D in sarcoidosis: how to assess and manage. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31(4):474-484. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1262215
- Bargagli E, Maggiorelli C, Rottoli P. Human chitotriosidase: a potential new marker of sarcoidosis severity. Respiration. 2008;76(2):234-238. doi:10.1159/000134009
- Kubaisi B, Abu Samra K, Foster CS. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s disease): An updated review of ocular disease manifestations. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2016;5(2):61-69. doi:10.5582/irdr.2016.01014
Discussion
The patient’s violaceous papule on the nose with an apple jelly appearance is consistent with lupus pernio—a cutaneous form of sarcoidosis associated with respiratory involvement. Lupus pernio disproportionately affects African Americans, which further supports this diagnosis.1 Lupus pernio is characterized by violaceous, indurated plaques predominantly on the face. It has a strong association with systemic sarcoidosis and often involves the lungs and other organs, as seen in this case. The laboratory results support this diagnosis. Hypercalcemia is a common systemic manifestation of sarcoidosis due to increased production of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D by activated macrophages with granulomas.2 Elevated chitotriosidase, an enzyme produced by macrophages, is another biomarker of sarcoidosis reflecting granuloma burden.3
The differential diagnoses included Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH), discoid lupus erythematosus, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and granuloma annulare. However, these diagnoses did not fully align with the entirety of the patient’s clinical presentation and laboratory findings. LCH is a rare neoplastic disorder characterized by the abnormal proliferation and accumulation of Langerhans cells, a type of dendritic cell involved in immune response, in various tissues such as the skin and bone. Dermatologic findings in LCH include brown/purple papules and an erythematous papular rash rather than the violaceous plaques/papules in lupus pernio. LCH can have lung involvement; it typically presents with nodular or cystic changes in the upper lobes as opposed to the bibasilar opacities seen in this case.
Discoid lupus erythematosus presents with characteristic round, erythematous, scaly plaques on the cheeks, scalp, and ears. This is different from the apple jelly appearance seen in this case and does not present with systemic granulomatous involvement.
Typical manifestations of granulomatosis with polyangiitis, formerly known as Wegener’s granulomatosis, include renal disease, upper and lower respiratory tract involvement, or necrotizing vasculitis. Cutaneous manifestions of granulomatosis with polyangiitis typically include purpura or ulcers rather than the violaceous plaques seen in lupus pernio. Patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis would also present with nonspecific systemic symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and malaise, which are not depicted in this case.4
Granuloma annulare is a benign condition that often presents with annular plaques that are skin-colored rather than violaceous. These plaques are often found on the hands and feet rather than the face. This condition also lacks the systemic manifestations seen in this case.
In primary care, encountering violaceous papule and plaques on the face, especially on the nasal alae or ear, should be concerning for possible lupus pernio, particularly in high-risk populations such as young African Americans. These lesions generally have a more indurated “deep” and “doughy” appearance and can result in scarring, distinguishing them from other types of cutaneous sarcoidosis. An apple jelly appearance seen on diascopy with a glass slide can further support the diagnosis. While the lesions are typically asymptomatic, patients may be concerned about potential cosmetic disfigurement. Given the potential for scarring and the association with systemic sarcoidosis, a dermatology referral is recommended for further evaluation and management.
A detailed patient history, physical examination, and laboratory exams are essential to accurately diagnose lupus pernio. Biopsy of a skin lesion, serum markers, and imaging studies were utilized to help assess systemic involvement and further confirm diagnosis in this patient. Following the diagnosis, the patient was started on his current regimen of prednisone, methotrexate, and hydroxychloroquine, which are standard therapies for managing both cutaneous and systemic sarcoidosis.
This case shows the importance of recognizing lupus pernio, a distinct form of cutaneous sarcoidosis, in patients presenting with characteristic skin lesions and systemic involvement. It is essential to differentiate it from other granulomatous and inflammatory skin conditions to ensure appropriate management and prevent complications.
Federal Practitioner thanks the Association of Military Dermatologists (militaryderm.org) for their assistance in developing the Image Challenge. Submissions based on photographs, radiography, or any other visual medium are welcomed.
Discussion
The patient’s violaceous papule on the nose with an apple jelly appearance is consistent with lupus pernio—a cutaneous form of sarcoidosis associated with respiratory involvement. Lupus pernio disproportionately affects African Americans, which further supports this diagnosis.1 Lupus pernio is characterized by violaceous, indurated plaques predominantly on the face. It has a strong association with systemic sarcoidosis and often involves the lungs and other organs, as seen in this case. The laboratory results support this diagnosis. Hypercalcemia is a common systemic manifestation of sarcoidosis due to increased production of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D by activated macrophages with granulomas.2 Elevated chitotriosidase, an enzyme produced by macrophages, is another biomarker of sarcoidosis reflecting granuloma burden.3
The differential diagnoses included Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH), discoid lupus erythematosus, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and granuloma annulare. However, these diagnoses did not fully align with the entirety of the patient’s clinical presentation and laboratory findings. LCH is a rare neoplastic disorder characterized by the abnormal proliferation and accumulation of Langerhans cells, a type of dendritic cell involved in immune response, in various tissues such as the skin and bone. Dermatologic findings in LCH include brown/purple papules and an erythematous papular rash rather than the violaceous plaques/papules in lupus pernio. LCH can have lung involvement; it typically presents with nodular or cystic changes in the upper lobes as opposed to the bibasilar opacities seen in this case.
Discoid lupus erythematosus presents with characteristic round, erythematous, scaly plaques on the cheeks, scalp, and ears. This is different from the apple jelly appearance seen in this case and does not present with systemic granulomatous involvement.
Typical manifestations of granulomatosis with polyangiitis, formerly known as Wegener’s granulomatosis, include renal disease, upper and lower respiratory tract involvement, or necrotizing vasculitis. Cutaneous manifestions of granulomatosis with polyangiitis typically include purpura or ulcers rather than the violaceous plaques seen in lupus pernio. Patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis would also present with nonspecific systemic symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and malaise, which are not depicted in this case.4
Granuloma annulare is a benign condition that often presents with annular plaques that are skin-colored rather than violaceous. These plaques are often found on the hands and feet rather than the face. This condition also lacks the systemic manifestations seen in this case.
In primary care, encountering violaceous papule and plaques on the face, especially on the nasal alae or ear, should be concerning for possible lupus pernio, particularly in high-risk populations such as young African Americans. These lesions generally have a more indurated “deep” and “doughy” appearance and can result in scarring, distinguishing them from other types of cutaneous sarcoidosis. An apple jelly appearance seen on diascopy with a glass slide can further support the diagnosis. While the lesions are typically asymptomatic, patients may be concerned about potential cosmetic disfigurement. Given the potential for scarring and the association with systemic sarcoidosis, a dermatology referral is recommended for further evaluation and management.
A detailed patient history, physical examination, and laboratory exams are essential to accurately diagnose lupus pernio. Biopsy of a skin lesion, serum markers, and imaging studies were utilized to help assess systemic involvement and further confirm diagnosis in this patient. Following the diagnosis, the patient was started on his current regimen of prednisone, methotrexate, and hydroxychloroquine, which are standard therapies for managing both cutaneous and systemic sarcoidosis.
This case shows the importance of recognizing lupus pernio, a distinct form of cutaneous sarcoidosis, in patients presenting with characteristic skin lesions and systemic involvement. It is essential to differentiate it from other granulomatous and inflammatory skin conditions to ensure appropriate management and prevent complications.
Federal Practitioner thanks the Association of Military Dermatologists (militaryderm.org) for their assistance in developing the Image Challenge. Submissions based on photographs, radiography, or any other visual medium are welcomed.
- Lai J, Almazan E, Le T, Taylor MT, Alhariri J, Kwatra SG. Demographics, cutaneous manifestations, and comorbidities associated with progressive cutaneous sarcoidosis: a retrospective cohort study. Medicines (Basel). 2023;10(10):57. doi:10.3390/medicines10100057
- Burke RR, Rybicki BA, Rao DS. Calcium and vitamin D in sarcoidosis: how to assess and manage. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31(4):474-484. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1262215
- Bargagli E, Maggiorelli C, Rottoli P. Human chitotriosidase: a potential new marker of sarcoidosis severity. Respiration. 2008;76(2):234-238. doi:10.1159/000134009
- Kubaisi B, Abu Samra K, Foster CS. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s disease): An updated review of ocular disease manifestations. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2016;5(2):61-69. doi:10.5582/irdr.2016.01014
- Lai J, Almazan E, Le T, Taylor MT, Alhariri J, Kwatra SG. Demographics, cutaneous manifestations, and comorbidities associated with progressive cutaneous sarcoidosis: a retrospective cohort study. Medicines (Basel). 2023;10(10):57. doi:10.3390/medicines10100057
- Burke RR, Rybicki BA, Rao DS. Calcium and vitamin D in sarcoidosis: how to assess and manage. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31(4):474-484. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1262215
- Bargagli E, Maggiorelli C, Rottoli P. Human chitotriosidase: a potential new marker of sarcoidosis severity. Respiration. 2008;76(2):234-238. doi:10.1159/000134009
- Kubaisi B, Abu Samra K, Foster CS. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s disease): An updated review of ocular disease manifestations. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2016;5(2):61-69. doi:10.5582/irdr.2016.01014
Violaceous Papules on Face
Violaceous Papules on Face
A 40-year-old man with no significant medical history or comorbidities presented with a violaceous papule involving his nasal tip and scaly, violaceous plaques with associated alopecia involving his beard (Figure). Skin biopsy confirmed granulomatous dermatitis. Additional workup was notable for hypercalcemia (10.5 mg/dL; reference range, 8.4-10.2 mg/dL), elevated chitotriosidase (317 nmol/h/mL; reference range, < 150 nmol/h/mL), and bibasilar opacities with left perihilar consolidation on chest X-ray. The patient had a prolonged PR interval (207 ms; reference range, 120-200 ms) on electrocardiogram. A cardiac positron emission tomography revealed low level fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the left ventricle. No ocular involvement was noted on evaluation by ophthalmology. The patient’s pharmacotherapy included prednisone 10 mg daily, methotrexate 7.5 mg weekly, and hydroxychloroquine 200 mg daily.
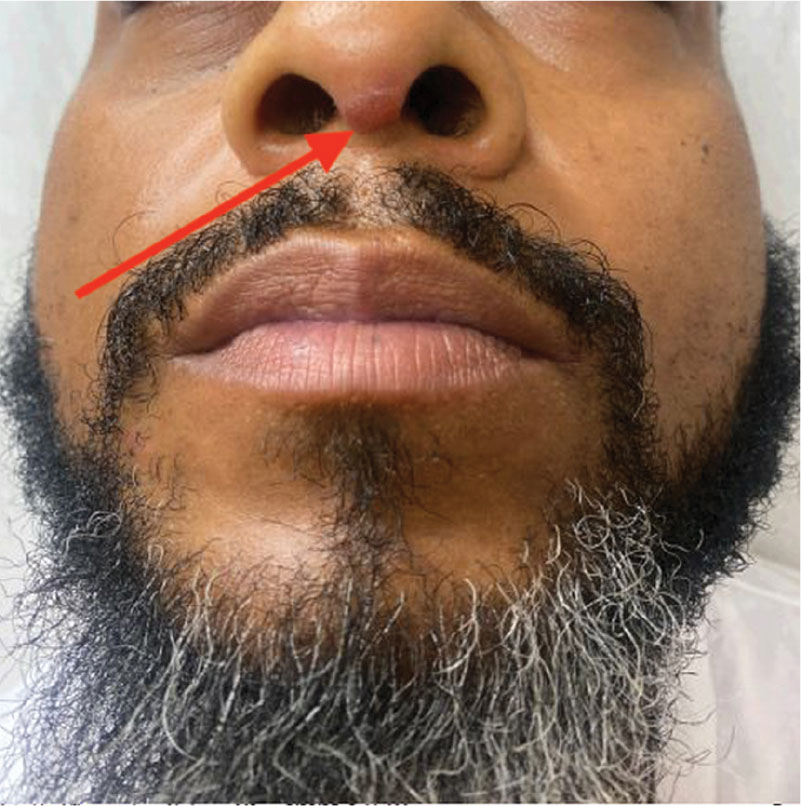
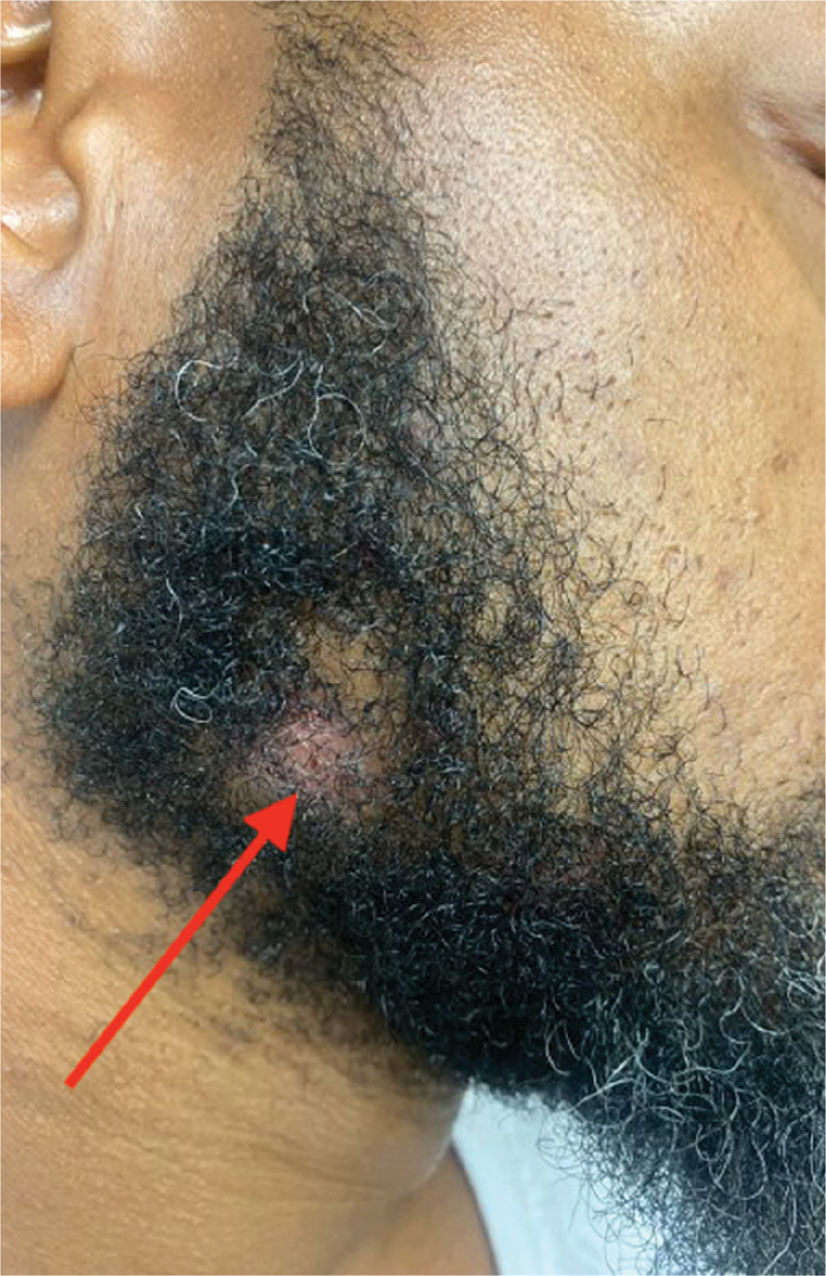
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN), a subvariant of seborrheic keratosis (SK), is characterized by benign pigmented epidermal neoplasms that typically manifest on the face, neck, and trunk in individuals with darker skin tones (Figure).1,2 While DPN meets the diagnostic criteria for SK, certain characteristics can help distinguish these lesions from other SK types. Treatment of DPN in patients with skin of color requires caution, particularly regarding the use of abrasive methods as well as cryotherapy, which generally should be avoided.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The incidence of SKs increases with age.3,4 Although it can occur in patients of all skin tones, SK is more common in lighter skin tones, while DPN predominantly is diagnosed in darker skin types.1,4 The prevalence of DPN in Black patients ranges from 10% to 30%, and Black women are twice as likely to be diagnosed with DPN as men.2 One study reported a first-degree relative with DPN in 84% (42/50) of patients.5 The number and size of DPN papules increase with age.1
KEY CLINICAL FEATURES
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK have distinctive morphologies: DPN typically manifests as raised, round or filiform, sessile, brown to black, 1- to 5-mm papules. 2 Seborrheic keratoses tend to be larger with a “stuck on” appearance and manifest as well-demarcated, pink to black papules or plaques that can range in size from millimeters to a few centimeters. 3,4 In DPN, the lesions usually are asymptomatic but may be tender, pruritic, dry, or scaly and may become irritated.1,2 They develop symmetrically in sun-exposed areas, and the most common sites are the malar face, temporal region, neck, and trunk.1,2,6,7 Seborrheic keratoses can appear throughout the body, including in sun-exposed areas, but have varying textures (eg, greasy, waxy, verrucous).3,4
WORTH NOTING
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK can resemble each other histologically: DPN demonstrates a fibrous stroma, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, and acanthosis at the intraepidermal layer, which are diagnostic criteria for SK.2,4,8 However, other histologic features characteristic of SK that are not seen in DPN include pseudohorn cysts, spindle tumor cells, and basaloid cell nests.8
Dermoscopy can be useful in ruling out malignant skin cancers when evaluating pigmented lesions. The most common dermoscopic features of SK are cerebriform patterns such as fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and pigmented fingerprintlike structures.3,4 To a lesser degree, milialike cysts, sharp demarcation, and hairpin-shaped vascular structures also may be present.4 The dermoscopic findings of DPN have not been well evaluated, but one study revealed that DPN had similar dermoscopic features to SK with some predominant features.6 Ridges and fissures were seen in 59% of patients diagnosed with DPN followed by comedolike openings seen in 27% of patients. The coexistence of a cerebriform pattern with comedolike openings was infrequent, and milialike cysts were rare.6
While DPN and SK are benign, patients often seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. Factors to consider when choosing a treatment modality include location of the lesions, the patient’s skin tone, and postprocedural outcomes (eg, depigmentation, wound healing). In general, treatments for SK include cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and topical therapeutics such as hydrogen peroxide 40%, topical vitamin D3, and nitric-zinc 30%-50% solutions. 4,8 Well-established treatment options for DPN include electrodesiccation, laser therapies, scissor excision, and cryotherapy, but topical options such as tazarotene also have been reported.1,9 Of the treatments for DPN, electrodesiccation and laser therapy routinely are used.10
The efficacy of electrodessication and potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser were assessed in a randomized, investigatorblinded split-face study.11 Both modalities received high improvement ratings, with the results favoring the KTP laser. The patients (most of whom were Black) reported that KTP laser was more effective but more painful than electrodessication (P =.002).11 In another randomized study, patients received 3 treatments—electrodessication, pulsed dye laser, and curettage—for select DPN papules.10 There was no difference in the degree of clearance, cosmetic outcome, or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation between the 3 modalities, but patients found the laser to be the most painful.
It is important to exercise caution when using abrasive methods (eg, laser therapy, electrodesiccation, curettage) in patients with darker skin tones because of the increased risk for postinflammatory pigment alteration.1,2,12 Adverse effects of treatment are a top concern in the management of DPN.5,13 While cryotherapy is a preferred treatment of SK in lighter skin tones, it generally is avoided for DPN in darker skin types because melanocyte destruction can lead to cosmetically unsatisfactory and easily visible depigmentation.9
To mitigate postprocedural adverse effects, proper aftercare can promote wound healing and minimize postinflammatory pigment alteration. In one split-face study of Black patients, 2 DPN papules were removed from each side of the face using fine-curved surgical scissors.14 Next, a petrolatum-based ointment and an antibiotic ointment with polymyxin B sulfate/bacitracin zinc was applied twice daily for 21 days to opposite sides of the face. Patients did not develop infection, tolerated both treatments well, and demonstrated improved general wound appearance according to investigator- rated clinical assessment.14 Other reported postprocedural approaches include using topical agents with ingredients shown to improve hyperpigmentation (eg, niacinamide, azelaic acid) as well as photoprotection.12
HEALTH DISPARITY HIGHLIGHT
While DPN is benign, it can have adverse psychosocial effects on patients. A study in Senegal revealed that 60% (19/30) of patients with DPN experienced anxiety related to their condition, while others noted that DPN hindered their social relationships.13 In one US study of 50 Black patients with DPN, there was a moderate effect on quality of life, and 36% (18/50) of patients had the lesions removed. However, of the treated patients, 67% (12/18) reported few—if any—symptoms prior to removal.5 Although treatment of DPN is widely considered a cosmetic procedure, therapeutic management can address— and may improve—mental health in patients with skin of color.1,5,13 Despite the high prevalence of DPN in patients with darker skin tones, data on treatment frequency and insurance coverage are not widely available, thus limiting our understanding of treatment accessibility and economic burden.
- Frazier WT, Proddutur S, Swope K. Common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2023;107:26-34.
- Metin SA, Lee BW, Lambert WC, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a clinically and histopathologically distinct entity. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:491-496.
- Braun RP, Ludwig S, Marghoob AA. Differential diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis: clinical and dermoscopic features. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:835-842.
- Sun MD, Halpern AC. Advances in the etiology, detection, and clinical management of seborrheic keratoses. Dermatology. 2022;238:205-217.
- Uwakwe LN, De Souza B, Subash J, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a quality of life survey study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:17-19.
- Bhat RM, Patrao N, Monteiro R, et al. A clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathological study of dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN)—an Indian perspective. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:957-960.
- Karampinis E, Georgopoulou KE, Kampra E, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic patterns of basal cell carcinoma and its mimickers in skin of color: a practical summary. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60:1386.
- Gorai S, Ahmad S, Raza SSM, et al. Update of pathophysiology and treatment options of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15934.
- Jain S, Caire H, Haas CJ. Management of dermatosis papulosa nigra: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. Published online October 4, 2024.
- Garcia MS, Azari R, Eisen DB. Treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra in 10 patients: a comparison trial of electrodesiccation, pulsed dye laser, and curettage. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1968-1972.
- Kundu RV, Joshi SS, Suh KY, et al. Comparison of electrodesiccation and potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser for treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:1079-1083.
- Markiewicz E, Karaman-Jurukovska N, Mammone T, et al. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in dark skin: molecular mechanism and skincare implications. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:2555-2565.
- Niang SO, Kane A, Diallo M, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra in Dakar, Senegal. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46(suppl 1):45-47.
- Taylor SC, Averyhart AN, Heath CR. Postprocedural wound-healing efficacy following removal of dermatosis papulosa nigra lesions in an African American population: a comparison of a skin protectant ointment and a topical antibiotic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64(suppl 3):S30-S35.
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN), a subvariant of seborrheic keratosis (SK), is characterized by benign pigmented epidermal neoplasms that typically manifest on the face, neck, and trunk in individuals with darker skin tones (Figure).1,2 While DPN meets the diagnostic criteria for SK, certain characteristics can help distinguish these lesions from other SK types. Treatment of DPN in patients with skin of color requires caution, particularly regarding the use of abrasive methods as well as cryotherapy, which generally should be avoided.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The incidence of SKs increases with age.3,4 Although it can occur in patients of all skin tones, SK is more common in lighter skin tones, while DPN predominantly is diagnosed in darker skin types.1,4 The prevalence of DPN in Black patients ranges from 10% to 30%, and Black women are twice as likely to be diagnosed with DPN as men.2 One study reported a first-degree relative with DPN in 84% (42/50) of patients.5 The number and size of DPN papules increase with age.1
KEY CLINICAL FEATURES
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK have distinctive morphologies: DPN typically manifests as raised, round or filiform, sessile, brown to black, 1- to 5-mm papules. 2 Seborrheic keratoses tend to be larger with a “stuck on” appearance and manifest as well-demarcated, pink to black papules or plaques that can range in size from millimeters to a few centimeters. 3,4 In DPN, the lesions usually are asymptomatic but may be tender, pruritic, dry, or scaly and may become irritated.1,2 They develop symmetrically in sun-exposed areas, and the most common sites are the malar face, temporal region, neck, and trunk.1,2,6,7 Seborrheic keratoses can appear throughout the body, including in sun-exposed areas, but have varying textures (eg, greasy, waxy, verrucous).3,4
WORTH NOTING
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK can resemble each other histologically: DPN demonstrates a fibrous stroma, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, and acanthosis at the intraepidermal layer, which are diagnostic criteria for SK.2,4,8 However, other histologic features characteristic of SK that are not seen in DPN include pseudohorn cysts, spindle tumor cells, and basaloid cell nests.8
Dermoscopy can be useful in ruling out malignant skin cancers when evaluating pigmented lesions. The most common dermoscopic features of SK are cerebriform patterns such as fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and pigmented fingerprintlike structures.3,4 To a lesser degree, milialike cysts, sharp demarcation, and hairpin-shaped vascular structures also may be present.4 The dermoscopic findings of DPN have not been well evaluated, but one study revealed that DPN had similar dermoscopic features to SK with some predominant features.6 Ridges and fissures were seen in 59% of patients diagnosed with DPN followed by comedolike openings seen in 27% of patients. The coexistence of a cerebriform pattern with comedolike openings was infrequent, and milialike cysts were rare.6
While DPN and SK are benign, patients often seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. Factors to consider when choosing a treatment modality include location of the lesions, the patient’s skin tone, and postprocedural outcomes (eg, depigmentation, wound healing). In general, treatments for SK include cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and topical therapeutics such as hydrogen peroxide 40%, topical vitamin D3, and nitric-zinc 30%-50% solutions. 4,8 Well-established treatment options for DPN include electrodesiccation, laser therapies, scissor excision, and cryotherapy, but topical options such as tazarotene also have been reported.1,9 Of the treatments for DPN, electrodesiccation and laser therapy routinely are used.10
The efficacy of electrodessication and potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser were assessed in a randomized, investigatorblinded split-face study.11 Both modalities received high improvement ratings, with the results favoring the KTP laser. The patients (most of whom were Black) reported that KTP laser was more effective but more painful than electrodessication (P =.002).11 In another randomized study, patients received 3 treatments—electrodessication, pulsed dye laser, and curettage—for select DPN papules.10 There was no difference in the degree of clearance, cosmetic outcome, or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation between the 3 modalities, but patients found the laser to be the most painful.
It is important to exercise caution when using abrasive methods (eg, laser therapy, electrodesiccation, curettage) in patients with darker skin tones because of the increased risk for postinflammatory pigment alteration.1,2,12 Adverse effects of treatment are a top concern in the management of DPN.5,13 While cryotherapy is a preferred treatment of SK in lighter skin tones, it generally is avoided for DPN in darker skin types because melanocyte destruction can lead to cosmetically unsatisfactory and easily visible depigmentation.9
To mitigate postprocedural adverse effects, proper aftercare can promote wound healing and minimize postinflammatory pigment alteration. In one split-face study of Black patients, 2 DPN papules were removed from each side of the face using fine-curved surgical scissors.14 Next, a petrolatum-based ointment and an antibiotic ointment with polymyxin B sulfate/bacitracin zinc was applied twice daily for 21 days to opposite sides of the face. Patients did not develop infection, tolerated both treatments well, and demonstrated improved general wound appearance according to investigator- rated clinical assessment.14 Other reported postprocedural approaches include using topical agents with ingredients shown to improve hyperpigmentation (eg, niacinamide, azelaic acid) as well as photoprotection.12
HEALTH DISPARITY HIGHLIGHT
While DPN is benign, it can have adverse psychosocial effects on patients. A study in Senegal revealed that 60% (19/30) of patients with DPN experienced anxiety related to their condition, while others noted that DPN hindered their social relationships.13 In one US study of 50 Black patients with DPN, there was a moderate effect on quality of life, and 36% (18/50) of patients had the lesions removed. However, of the treated patients, 67% (12/18) reported few—if any—symptoms prior to removal.5 Although treatment of DPN is widely considered a cosmetic procedure, therapeutic management can address— and may improve—mental health in patients with skin of color.1,5,13 Despite the high prevalence of DPN in patients with darker skin tones, data on treatment frequency and insurance coverage are not widely available, thus limiting our understanding of treatment accessibility and economic burden.
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN), a subvariant of seborrheic keratosis (SK), is characterized by benign pigmented epidermal neoplasms that typically manifest on the face, neck, and trunk in individuals with darker skin tones (Figure).1,2 While DPN meets the diagnostic criteria for SK, certain characteristics can help distinguish these lesions from other SK types. Treatment of DPN in patients with skin of color requires caution, particularly regarding the use of abrasive methods as well as cryotherapy, which generally should be avoided.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The incidence of SKs increases with age.3,4 Although it can occur in patients of all skin tones, SK is more common in lighter skin tones, while DPN predominantly is diagnosed in darker skin types.1,4 The prevalence of DPN in Black patients ranges from 10% to 30%, and Black women are twice as likely to be diagnosed with DPN as men.2 One study reported a first-degree relative with DPN in 84% (42/50) of patients.5 The number and size of DPN papules increase with age.1
KEY CLINICAL FEATURES
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK have distinctive morphologies: DPN typically manifests as raised, round or filiform, sessile, brown to black, 1- to 5-mm papules. 2 Seborrheic keratoses tend to be larger with a “stuck on” appearance and manifest as well-demarcated, pink to black papules or plaques that can range in size from millimeters to a few centimeters. 3,4 In DPN, the lesions usually are asymptomatic but may be tender, pruritic, dry, or scaly and may become irritated.1,2 They develop symmetrically in sun-exposed areas, and the most common sites are the malar face, temporal region, neck, and trunk.1,2,6,7 Seborrheic keratoses can appear throughout the body, including in sun-exposed areas, but have varying textures (eg, greasy, waxy, verrucous).3,4
WORTH NOTING
Dermatosis papulosa nigra and SK can resemble each other histologically: DPN demonstrates a fibrous stroma, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, and acanthosis at the intraepidermal layer, which are diagnostic criteria for SK.2,4,8 However, other histologic features characteristic of SK that are not seen in DPN include pseudohorn cysts, spindle tumor cells, and basaloid cell nests.8
Dermoscopy can be useful in ruling out malignant skin cancers when evaluating pigmented lesions. The most common dermoscopic features of SK are cerebriform patterns such as fissures and ridges, comedolike openings, and pigmented fingerprintlike structures.3,4 To a lesser degree, milialike cysts, sharp demarcation, and hairpin-shaped vascular structures also may be present.4 The dermoscopic findings of DPN have not been well evaluated, but one study revealed that DPN had similar dermoscopic features to SK with some predominant features.6 Ridges and fissures were seen in 59% of patients diagnosed with DPN followed by comedolike openings seen in 27% of patients. The coexistence of a cerebriform pattern with comedolike openings was infrequent, and milialike cysts were rare.6
While DPN and SK are benign, patients often seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. Factors to consider when choosing a treatment modality include location of the lesions, the patient’s skin tone, and postprocedural outcomes (eg, depigmentation, wound healing). In general, treatments for SK include cryotherapy, electrodesiccation and curettage, and topical therapeutics such as hydrogen peroxide 40%, topical vitamin D3, and nitric-zinc 30%-50% solutions. 4,8 Well-established treatment options for DPN include electrodesiccation, laser therapies, scissor excision, and cryotherapy, but topical options such as tazarotene also have been reported.1,9 Of the treatments for DPN, electrodesiccation and laser therapy routinely are used.10
The efficacy of electrodessication and potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser were assessed in a randomized, investigatorblinded split-face study.11 Both modalities received high improvement ratings, with the results favoring the KTP laser. The patients (most of whom were Black) reported that KTP laser was more effective but more painful than electrodessication (P =.002).11 In another randomized study, patients received 3 treatments—electrodessication, pulsed dye laser, and curettage—for select DPN papules.10 There was no difference in the degree of clearance, cosmetic outcome, or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation between the 3 modalities, but patients found the laser to be the most painful.
It is important to exercise caution when using abrasive methods (eg, laser therapy, electrodesiccation, curettage) in patients with darker skin tones because of the increased risk for postinflammatory pigment alteration.1,2,12 Adverse effects of treatment are a top concern in the management of DPN.5,13 While cryotherapy is a preferred treatment of SK in lighter skin tones, it generally is avoided for DPN in darker skin types because melanocyte destruction can lead to cosmetically unsatisfactory and easily visible depigmentation.9
To mitigate postprocedural adverse effects, proper aftercare can promote wound healing and minimize postinflammatory pigment alteration. In one split-face study of Black patients, 2 DPN papules were removed from each side of the face using fine-curved surgical scissors.14 Next, a petrolatum-based ointment and an antibiotic ointment with polymyxin B sulfate/bacitracin zinc was applied twice daily for 21 days to opposite sides of the face. Patients did not develop infection, tolerated both treatments well, and demonstrated improved general wound appearance according to investigator- rated clinical assessment.14 Other reported postprocedural approaches include using topical agents with ingredients shown to improve hyperpigmentation (eg, niacinamide, azelaic acid) as well as photoprotection.12
HEALTH DISPARITY HIGHLIGHT
While DPN is benign, it can have adverse psychosocial effects on patients. A study in Senegal revealed that 60% (19/30) of patients with DPN experienced anxiety related to their condition, while others noted that DPN hindered their social relationships.13 In one US study of 50 Black patients with DPN, there was a moderate effect on quality of life, and 36% (18/50) of patients had the lesions removed. However, of the treated patients, 67% (12/18) reported few—if any—symptoms prior to removal.5 Although treatment of DPN is widely considered a cosmetic procedure, therapeutic management can address— and may improve—mental health in patients with skin of color.1,5,13 Despite the high prevalence of DPN in patients with darker skin tones, data on treatment frequency and insurance coverage are not widely available, thus limiting our understanding of treatment accessibility and economic burden.
- Frazier WT, Proddutur S, Swope K. Common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2023;107:26-34.
- Metin SA, Lee BW, Lambert WC, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a clinically and histopathologically distinct entity. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:491-496.
- Braun RP, Ludwig S, Marghoob AA. Differential diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis: clinical and dermoscopic features. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:835-842.
- Sun MD, Halpern AC. Advances in the etiology, detection, and clinical management of seborrheic keratoses. Dermatology. 2022;238:205-217.
- Uwakwe LN, De Souza B, Subash J, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a quality of life survey study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:17-19.
- Bhat RM, Patrao N, Monteiro R, et al. A clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathological study of dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN)—an Indian perspective. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:957-960.
- Karampinis E, Georgopoulou KE, Kampra E, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic patterns of basal cell carcinoma and its mimickers in skin of color: a practical summary. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60:1386.
- Gorai S, Ahmad S, Raza SSM, et al. Update of pathophysiology and treatment options of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15934.
- Jain S, Caire H, Haas CJ. Management of dermatosis papulosa nigra: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. Published online October 4, 2024.
- Garcia MS, Azari R, Eisen DB. Treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra in 10 patients: a comparison trial of electrodesiccation, pulsed dye laser, and curettage. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1968-1972.
- Kundu RV, Joshi SS, Suh KY, et al. Comparison of electrodesiccation and potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser for treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:1079-1083.
- Markiewicz E, Karaman-Jurukovska N, Mammone T, et al. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in dark skin: molecular mechanism and skincare implications. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:2555-2565.
- Niang SO, Kane A, Diallo M, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra in Dakar, Senegal. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46(suppl 1):45-47.
- Taylor SC, Averyhart AN, Heath CR. Postprocedural wound-healing efficacy following removal of dermatosis papulosa nigra lesions in an African American population: a comparison of a skin protectant ointment and a topical antibiotic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64(suppl 3):S30-S35.
- Frazier WT, Proddutur S, Swope K. Common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2023;107:26-34.
- Metin SA, Lee BW, Lambert WC, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a clinically and histopathologically distinct entity. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:491-496.
- Braun RP, Ludwig S, Marghoob AA. Differential diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis: clinical and dermoscopic features. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:835-842.
- Sun MD, Halpern AC. Advances in the etiology, detection, and clinical management of seborrheic keratoses. Dermatology. 2022;238:205-217.
- Uwakwe LN, De Souza B, Subash J, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a quality of life survey study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:17-19.
- Bhat RM, Patrao N, Monteiro R, et al. A clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathological study of dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN)—an Indian perspective. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:957-960.
- Karampinis E, Georgopoulou KE, Kampra E, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic patterns of basal cell carcinoma and its mimickers in skin of color: a practical summary. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60:1386.
- Gorai S, Ahmad S, Raza SSM, et al. Update of pathophysiology and treatment options of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15934.
- Jain S, Caire H, Haas CJ. Management of dermatosis papulosa nigra: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. Published online October 4, 2024.
- Garcia MS, Azari R, Eisen DB. Treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra in 10 patients: a comparison trial of electrodesiccation, pulsed dye laser, and curettage. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1968-1972.
- Kundu RV, Joshi SS, Suh KY, et al. Comparison of electrodesiccation and potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser for treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:1079-1083.
- Markiewicz E, Karaman-Jurukovska N, Mammone T, et al. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in dark skin: molecular mechanism and skincare implications. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:2555-2565.
- Niang SO, Kane A, Diallo M, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra in Dakar, Senegal. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46(suppl 1):45-47.
- Taylor SC, Averyhart AN, Heath CR. Postprocedural wound-healing efficacy following removal of dermatosis papulosa nigra lesions in an African American population: a comparison of a skin protectant ointment and a topical antibiotic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64(suppl 3):S30-S35.
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis
Key Features of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra vs Seborrheic Keratosis
Atopic Dermatitis and Sleep Disturbances
Recently one of my keep-up-to-date apps alerted me to a study in Pediatric Dermatology on sleep and atopic dermatitis. When I chased down the abstract it was a shoulder-shrugging-so-what encounter. The authors reported that having a child with atopic dermatitis decreased the odds of a parent getting 7 hours of sleep a night and increased the odds that the parent was also taking sleep-aiding medications. The authors felt their data was meaningful enough to publish based on the size and the cross-sectional nature of their sample. However, anyone who has worked with families with atopic dermatitis shouldn’t be surprised at their findings.
Curious about what other investigators had discovered about the anecdotally obvious relationship between sleep and atopic dermatitis, I dug until I found a rather thorough discussion of the literature published in The Journal of Clinical Immunology Practice. These authors from the University of Rochester Medical School in New York begin by pointing out that, although 47%-80% of children with atopic dermatitis and 33%-90% of adults with atopic dermatitis have disturbed sleep, “literature on this topic remains sparse with most studies evaluating sleep as a secondary outcome using subjective measures.” They further note that sleep is one of the three most problematic symptoms for children with atopic dermatitis and their families.
Characterizing the Sleep Loss
Difficulty falling asleep, frequent and long waking, and excessive daytime sleepiness are the most common symptoms reported. In the few sleep laboratory studies that have been done there has been no significant decrease in sleep duration, which is a bit of a surprise. However, as expected, sleep-onset latency, more wake time after sleep onset, sleep fragmentation, and decreased sleep efficiency have been observed in the atopic dermatitis patients. In other studies of younger children, female gender and lower socioeconomic status seem to be associated with poor sleep quality.
Most studies found that in general the prevalence and severity of sleep disturbances increases with the severity of the disease. As the disease flares, increased bedtime resistance, nocturnal wakings and daytime sleepiness become more likely. These parentally reported associations have also been confirmed by sleep laboratory observations.
The sleep disturbances quickly become a family affair with 60% of siblings and parents reporting disturbed sleep. When the child with atopic dermatitis is having a flareup, nearly 90% of their parents report losing up to 2.5 hours of sleep. Not surprisingly sleep disturbances have been associated with behavioral and emotional problems including decreased happiness, poor cognitive performance, hyperactivity, and inattention. Mothers seem to bear the brunt of the problem and interpersonal conflicts and exhaustion are unfortunately not uncommon.
Probing the Causes
So why are atopic dermatitis patients and their families so prone to the ill effects of disturbed sleep? Although you might think it should be obvious, this review of the “sparse” literature doesn’t provide a satisfying answer. However, the authors provide three possible explanations.
The one with the least supporting evidence is circadian variations in the products of inflammation such as cytokines and their effect on melatonin production. The explanation which I think most of us have already considered is that pruritus disrupts sleep. This is the often-quoted itch-scratch feedback cycle which can release inflammatory mediators (“pruritogens”). However, the investigators have found that many studies report “conflicting results or only weak correlations.”
The third alternative posed by the authors is by far the most appealing and hinges on the assumption that, as with many other chronic conditions, atopic dermatitis renders the patient vulnerable to insomnia. “Nocturnal scratching disrupts sleep and sets the stage for cognitive and behavioral factors that reinforce insomnia as a conditioned response.” In other words, even after the “co-concurring condition” resolves insomnia related sleep behaviors continue. The investigators point to a study supporting this explanation which found that, even after a child’s skin cleared, his/her sleep arousals failed to return to normal suggesting that learned behavior patterns might be playing a role.
It may be a stretch to suggest that poor sleep hygiene might in and of itself cause atopic dermatitis, but it can’t be ruled out. At a minimum the current research suggests that there is a bidirectional relationship between sleep disturbances and atopic dermatitis.
Next Steps
The authors of this study urge that we be more creative in using already-existing portable and relatively low-cost sleep monitoring technology to better define this relationship. While that is a worthwhile avenue for research, I think we who see children (both primary care providers and dermatologists) now have enough evidence to move managing the sleep hygiene of our atopic dermatitis patients to the front burner, along with moisturizers and topical medications, without needing to do costly and time-consuming studies.
This means taking a thorough sleep history. If, in the rare cases where the child’s sleep habits are normal, the parents should be warned that falling off the sleep wagon is likely to exacerbate the child’s skin. If the history reveals an inefficient and dysfunctional bedtime routine or other symptoms of insomnia, advise the parents on how it can be improved. Then follow up at each visit if there has been no improvement. Sleep management can be time-consuming as well but it should be part of every primary care pediatrician’s toolbox. For the dermatologist who doesn’t feel comfortable managing sleep problems, a consultation with a pediatrician or a sleep specialist is in order.
The adult with atopic dermatitis is a somewhat different animal and a formal sleep study may be indicated. Cognitive-behavioral therapy might be helpful for adult population but the investigators could find no trials of its use in patients with atopic dermatitis.
Convincing the parents of an atopic dermatitis patient that their family’s disturbed sleep may not only be the result of his/her itchy skin but may be a preexisting compounding problem may not be an easy sell. I hope if you can be open to the strong possibility that disordered sleep is not just the effect but in some ways may be a likely contributor to your patients’ atopic dermatitis, you may become more effective in managing the disease.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Recently one of my keep-up-to-date apps alerted me to a study in Pediatric Dermatology on sleep and atopic dermatitis. When I chased down the abstract it was a shoulder-shrugging-so-what encounter. The authors reported that having a child with atopic dermatitis decreased the odds of a parent getting 7 hours of sleep a night and increased the odds that the parent was also taking sleep-aiding medications. The authors felt their data was meaningful enough to publish based on the size and the cross-sectional nature of their sample. However, anyone who has worked with families with atopic dermatitis shouldn’t be surprised at their findings.
Curious about what other investigators had discovered about the anecdotally obvious relationship between sleep and atopic dermatitis, I dug until I found a rather thorough discussion of the literature published in The Journal of Clinical Immunology Practice. These authors from the University of Rochester Medical School in New York begin by pointing out that, although 47%-80% of children with atopic dermatitis and 33%-90% of adults with atopic dermatitis have disturbed sleep, “literature on this topic remains sparse with most studies evaluating sleep as a secondary outcome using subjective measures.” They further note that sleep is one of the three most problematic symptoms for children with atopic dermatitis and their families.
Characterizing the Sleep Loss
Difficulty falling asleep, frequent and long waking, and excessive daytime sleepiness are the most common symptoms reported. In the few sleep laboratory studies that have been done there has been no significant decrease in sleep duration, which is a bit of a surprise. However, as expected, sleep-onset latency, more wake time after sleep onset, sleep fragmentation, and decreased sleep efficiency have been observed in the atopic dermatitis patients. In other studies of younger children, female gender and lower socioeconomic status seem to be associated with poor sleep quality.
Most studies found that in general the prevalence and severity of sleep disturbances increases with the severity of the disease. As the disease flares, increased bedtime resistance, nocturnal wakings and daytime sleepiness become more likely. These parentally reported associations have also been confirmed by sleep laboratory observations.
The sleep disturbances quickly become a family affair with 60% of siblings and parents reporting disturbed sleep. When the child with atopic dermatitis is having a flareup, nearly 90% of their parents report losing up to 2.5 hours of sleep. Not surprisingly sleep disturbances have been associated with behavioral and emotional problems including decreased happiness, poor cognitive performance, hyperactivity, and inattention. Mothers seem to bear the brunt of the problem and interpersonal conflicts and exhaustion are unfortunately not uncommon.
Probing the Causes
So why are atopic dermatitis patients and their families so prone to the ill effects of disturbed sleep? Although you might think it should be obvious, this review of the “sparse” literature doesn’t provide a satisfying answer. However, the authors provide three possible explanations.
The one with the least supporting evidence is circadian variations in the products of inflammation such as cytokines and their effect on melatonin production. The explanation which I think most of us have already considered is that pruritus disrupts sleep. This is the often-quoted itch-scratch feedback cycle which can release inflammatory mediators (“pruritogens”). However, the investigators have found that many studies report “conflicting results or only weak correlations.”
The third alternative posed by the authors is by far the most appealing and hinges on the assumption that, as with many other chronic conditions, atopic dermatitis renders the patient vulnerable to insomnia. “Nocturnal scratching disrupts sleep and sets the stage for cognitive and behavioral factors that reinforce insomnia as a conditioned response.” In other words, even after the “co-concurring condition” resolves insomnia related sleep behaviors continue. The investigators point to a study supporting this explanation which found that, even after a child’s skin cleared, his/her sleep arousals failed to return to normal suggesting that learned behavior patterns might be playing a role.
It may be a stretch to suggest that poor sleep hygiene might in and of itself cause atopic dermatitis, but it can’t be ruled out. At a minimum the current research suggests that there is a bidirectional relationship between sleep disturbances and atopic dermatitis.
Next Steps
The authors of this study urge that we be more creative in using already-existing portable and relatively low-cost sleep monitoring technology to better define this relationship. While that is a worthwhile avenue for research, I think we who see children (both primary care providers and dermatologists) now have enough evidence to move managing the sleep hygiene of our atopic dermatitis patients to the front burner, along with moisturizers and topical medications, without needing to do costly and time-consuming studies.
This means taking a thorough sleep history. If, in the rare cases where the child’s sleep habits are normal, the parents should be warned that falling off the sleep wagon is likely to exacerbate the child’s skin. If the history reveals an inefficient and dysfunctional bedtime routine or other symptoms of insomnia, advise the parents on how it can be improved. Then follow up at each visit if there has been no improvement. Sleep management can be time-consuming as well but it should be part of every primary care pediatrician’s toolbox. For the dermatologist who doesn’t feel comfortable managing sleep problems, a consultation with a pediatrician or a sleep specialist is in order.
The adult with atopic dermatitis is a somewhat different animal and a formal sleep study may be indicated. Cognitive-behavioral therapy might be helpful for adult population but the investigators could find no trials of its use in patients with atopic dermatitis.
Convincing the parents of an atopic dermatitis patient that their family’s disturbed sleep may not only be the result of his/her itchy skin but may be a preexisting compounding problem may not be an easy sell. I hope if you can be open to the strong possibility that disordered sleep is not just the effect but in some ways may be a likely contributor to your patients’ atopic dermatitis, you may become more effective in managing the disease.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Recently one of my keep-up-to-date apps alerted me to a study in Pediatric Dermatology on sleep and atopic dermatitis. When I chased down the abstract it was a shoulder-shrugging-so-what encounter. The authors reported that having a child with atopic dermatitis decreased the odds of a parent getting 7 hours of sleep a night and increased the odds that the parent was also taking sleep-aiding medications. The authors felt their data was meaningful enough to publish based on the size and the cross-sectional nature of their sample. However, anyone who has worked with families with atopic dermatitis shouldn’t be surprised at their findings.
Curious about what other investigators had discovered about the anecdotally obvious relationship between sleep and atopic dermatitis, I dug until I found a rather thorough discussion of the literature published in The Journal of Clinical Immunology Practice. These authors from the University of Rochester Medical School in New York begin by pointing out that, although 47%-80% of children with atopic dermatitis and 33%-90% of adults with atopic dermatitis have disturbed sleep, “literature on this topic remains sparse with most studies evaluating sleep as a secondary outcome using subjective measures.” They further note that sleep is one of the three most problematic symptoms for children with atopic dermatitis and their families.
Characterizing the Sleep Loss
Difficulty falling asleep, frequent and long waking, and excessive daytime sleepiness are the most common symptoms reported. In the few sleep laboratory studies that have been done there has been no significant decrease in sleep duration, which is a bit of a surprise. However, as expected, sleep-onset latency, more wake time after sleep onset, sleep fragmentation, and decreased sleep efficiency have been observed in the atopic dermatitis patients. In other studies of younger children, female gender and lower socioeconomic status seem to be associated with poor sleep quality.
Most studies found that in general the prevalence and severity of sleep disturbances increases with the severity of the disease. As the disease flares, increased bedtime resistance, nocturnal wakings and daytime sleepiness become more likely. These parentally reported associations have also been confirmed by sleep laboratory observations.
The sleep disturbances quickly become a family affair with 60% of siblings and parents reporting disturbed sleep. When the child with atopic dermatitis is having a flareup, nearly 90% of their parents report losing up to 2.5 hours of sleep. Not surprisingly sleep disturbances have been associated with behavioral and emotional problems including decreased happiness, poor cognitive performance, hyperactivity, and inattention. Mothers seem to bear the brunt of the problem and interpersonal conflicts and exhaustion are unfortunately not uncommon.
Probing the Causes
So why are atopic dermatitis patients and their families so prone to the ill effects of disturbed sleep? Although you might think it should be obvious, this review of the “sparse” literature doesn’t provide a satisfying answer. However, the authors provide three possible explanations.
The one with the least supporting evidence is circadian variations in the products of inflammation such as cytokines and their effect on melatonin production. The explanation which I think most of us have already considered is that pruritus disrupts sleep. This is the often-quoted itch-scratch feedback cycle which can release inflammatory mediators (“pruritogens”). However, the investigators have found that many studies report “conflicting results or only weak correlations.”
The third alternative posed by the authors is by far the most appealing and hinges on the assumption that, as with many other chronic conditions, atopic dermatitis renders the patient vulnerable to insomnia. “Nocturnal scratching disrupts sleep and sets the stage for cognitive and behavioral factors that reinforce insomnia as a conditioned response.” In other words, even after the “co-concurring condition” resolves insomnia related sleep behaviors continue. The investigators point to a study supporting this explanation which found that, even after a child’s skin cleared, his/her sleep arousals failed to return to normal suggesting that learned behavior patterns might be playing a role.
It may be a stretch to suggest that poor sleep hygiene might in and of itself cause atopic dermatitis, but it can’t be ruled out. At a minimum the current research suggests that there is a bidirectional relationship between sleep disturbances and atopic dermatitis.
Next Steps
The authors of this study urge that we be more creative in using already-existing portable and relatively low-cost sleep monitoring technology to better define this relationship. While that is a worthwhile avenue for research, I think we who see children (both primary care providers and dermatologists) now have enough evidence to move managing the sleep hygiene of our atopic dermatitis patients to the front burner, along with moisturizers and topical medications, without needing to do costly and time-consuming studies.
This means taking a thorough sleep history. If, in the rare cases where the child’s sleep habits are normal, the parents should be warned that falling off the sleep wagon is likely to exacerbate the child’s skin. If the history reveals an inefficient and dysfunctional bedtime routine or other symptoms of insomnia, advise the parents on how it can be improved. Then follow up at each visit if there has been no improvement. Sleep management can be time-consuming as well but it should be part of every primary care pediatrician’s toolbox. For the dermatologist who doesn’t feel comfortable managing sleep problems, a consultation with a pediatrician or a sleep specialist is in order.
The adult with atopic dermatitis is a somewhat different animal and a formal sleep study may be indicated. Cognitive-behavioral therapy might be helpful for adult population but the investigators could find no trials of its use in patients with atopic dermatitis.
Convincing the parents of an atopic dermatitis patient that their family’s disturbed sleep may not only be the result of his/her itchy skin but may be a preexisting compounding problem may not be an easy sell. I hope if you can be open to the strong possibility that disordered sleep is not just the effect but in some ways may be a likely contributor to your patients’ atopic dermatitis, you may become more effective in managing the disease.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].