User login
Support for Laser Treatment to Reduce NMSC Risk is Increasing
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — and a key 2017 publication laid the groundwork for current approaches, according to Elizabeth Tanzi, MD.
In the article, which was published in Molecules, Mike Kemp, PhD, and Jeffrey Bryant Travers, MD, PhD, at Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio, and Dan F. Spandau, PhD, at Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, demonstrated that geriatric skin responds to ultraviolet B (UVB) differently than young skin because of differences in insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels produced by dermal fibroblasts.
“As we age, our fibroblasts become senescent, inactive,” Dr. Tanzi, associate clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery symposium. “They don’t make as many growth factors, particularly IGF-1, and therefore we don’t stimulate the responses. We need more of our growth factors.”
In later, separate work, Dr. Travers, Dr. Spandau, and colleagues found that using dermabrasion or fractionated laser resurfacing to wound the skin can result in increased dermal IGF-1 levels and normalization of the abnormal pro-carcinogenic UV response associated with geriatric skin — a treatment that has the potential to prevent NMSC. That study “was the epiphany” for fostering interest among researchers in the field of lasers and medicine, Dr. Tanzi said.
In a retrospective cohort study, Mathew Avram, MD, JD, and colleagues reviewed patients with a history of facial keratinocyte carcinoma (KC) who were treated at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston between 2005 and 2021. The study population included 43 patients treated with either the 1927- or the 1550-nm nonablative fractional laser (NAFL) and 52 matched controls. The rate of subsequent facial KC development was 20.9% in NAFL-treated patients and 40.4% in controls (relative risk, 0.52, P = .049).
During a separate presentation at the meeting, Dr. Avram, director of lasers and cosmetics at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said that, when he and his colleagues controlled for age, gender, and skin type, controls were 2.65 times more likely to develop new facial KC, compared with those treated with NAFL (P = .0169). “This enhanced effect was seen with the 1550-nm device, compared with the 1927-nm device. The study shows us that 1550-nm/1927-nm NAFL may have a protective effect for patients with a history of KC, but the role of each wavelength is to be determined. We also need a prospective, controlled study to verify the results.”
In an ongoing study first presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, Dr. Tanzi and colleagues enrolled 15 patients aged ≥ 55 years to evaluate the restoration of physiologic features and biomarkers in skin treated with 25% trichloroacetic acid (TCA), plus the 1550-nm or 1927-nm NAFL. Four sites on the back were treated and biopsies were taken at baseline and at 3 months post treatment. The protocol involved TCA 25% to speckled frost, with the 1550-nm device set to level 6 at 70 mJ and the 1927-nm device set to level 8 at 20 mJ. Immunohistochemical stains are still pending; however, physiologic changes were noted.
Three months after a single treatment, the 1927-nm treated areas showed statistically significant elongation of fibroblasts (consistent with younger fibroblasts) on histology. “Although not a large study, it supports the growing body of research that demonstrates we are improving the health of our patients’ skin with certain types of laser treatments, not just beautifying it,” Dr. Tanzi said.
Dr. Tanzi disclosed being a member of the advisory board for AbbVie/Allergan and Sciton, and is a consultant for Alastin/Galderma, Candesant Biomedical, Cytrellis, Revance, and Solta Medical. Dr. Avram disclosed that he receives intellectual property royalties from and holds stock options in Cytrellis, and is a consultant to Allergan and holds stock options in BAI Biosciences, Sofwave, and La Jolla NanoMedical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — and a key 2017 publication laid the groundwork for current approaches, according to Elizabeth Tanzi, MD.
In the article, which was published in Molecules, Mike Kemp, PhD, and Jeffrey Bryant Travers, MD, PhD, at Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio, and Dan F. Spandau, PhD, at Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, demonstrated that geriatric skin responds to ultraviolet B (UVB) differently than young skin because of differences in insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels produced by dermal fibroblasts.
“As we age, our fibroblasts become senescent, inactive,” Dr. Tanzi, associate clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery symposium. “They don’t make as many growth factors, particularly IGF-1, and therefore we don’t stimulate the responses. We need more of our growth factors.”
In later, separate work, Dr. Travers, Dr. Spandau, and colleagues found that using dermabrasion or fractionated laser resurfacing to wound the skin can result in increased dermal IGF-1 levels and normalization of the abnormal pro-carcinogenic UV response associated with geriatric skin — a treatment that has the potential to prevent NMSC. That study “was the epiphany” for fostering interest among researchers in the field of lasers and medicine, Dr. Tanzi said.
In a retrospective cohort study, Mathew Avram, MD, JD, and colleagues reviewed patients with a history of facial keratinocyte carcinoma (KC) who were treated at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston between 2005 and 2021. The study population included 43 patients treated with either the 1927- or the 1550-nm nonablative fractional laser (NAFL) and 52 matched controls. The rate of subsequent facial KC development was 20.9% in NAFL-treated patients and 40.4% in controls (relative risk, 0.52, P = .049).
During a separate presentation at the meeting, Dr. Avram, director of lasers and cosmetics at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said that, when he and his colleagues controlled for age, gender, and skin type, controls were 2.65 times more likely to develop new facial KC, compared with those treated with NAFL (P = .0169). “This enhanced effect was seen with the 1550-nm device, compared with the 1927-nm device. The study shows us that 1550-nm/1927-nm NAFL may have a protective effect for patients with a history of KC, but the role of each wavelength is to be determined. We also need a prospective, controlled study to verify the results.”
In an ongoing study first presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, Dr. Tanzi and colleagues enrolled 15 patients aged ≥ 55 years to evaluate the restoration of physiologic features and biomarkers in skin treated with 25% trichloroacetic acid (TCA), plus the 1550-nm or 1927-nm NAFL. Four sites on the back were treated and biopsies were taken at baseline and at 3 months post treatment. The protocol involved TCA 25% to speckled frost, with the 1550-nm device set to level 6 at 70 mJ and the 1927-nm device set to level 8 at 20 mJ. Immunohistochemical stains are still pending; however, physiologic changes were noted.
Three months after a single treatment, the 1927-nm treated areas showed statistically significant elongation of fibroblasts (consistent with younger fibroblasts) on histology. “Although not a large study, it supports the growing body of research that demonstrates we are improving the health of our patients’ skin with certain types of laser treatments, not just beautifying it,” Dr. Tanzi said.
Dr. Tanzi disclosed being a member of the advisory board for AbbVie/Allergan and Sciton, and is a consultant for Alastin/Galderma, Candesant Biomedical, Cytrellis, Revance, and Solta Medical. Dr. Avram disclosed that he receives intellectual property royalties from and holds stock options in Cytrellis, and is a consultant to Allergan and holds stock options in BAI Biosciences, Sofwave, and La Jolla NanoMedical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — and a key 2017 publication laid the groundwork for current approaches, according to Elizabeth Tanzi, MD.
In the article, which was published in Molecules, Mike Kemp, PhD, and Jeffrey Bryant Travers, MD, PhD, at Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio, and Dan F. Spandau, PhD, at Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, demonstrated that geriatric skin responds to ultraviolet B (UVB) differently than young skin because of differences in insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels produced by dermal fibroblasts.
“As we age, our fibroblasts become senescent, inactive,” Dr. Tanzi, associate clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery symposium. “They don’t make as many growth factors, particularly IGF-1, and therefore we don’t stimulate the responses. We need more of our growth factors.”
In later, separate work, Dr. Travers, Dr. Spandau, and colleagues found that using dermabrasion or fractionated laser resurfacing to wound the skin can result in increased dermal IGF-1 levels and normalization of the abnormal pro-carcinogenic UV response associated with geriatric skin — a treatment that has the potential to prevent NMSC. That study “was the epiphany” for fostering interest among researchers in the field of lasers and medicine, Dr. Tanzi said.
In a retrospective cohort study, Mathew Avram, MD, JD, and colleagues reviewed patients with a history of facial keratinocyte carcinoma (KC) who were treated at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston between 2005 and 2021. The study population included 43 patients treated with either the 1927- or the 1550-nm nonablative fractional laser (NAFL) and 52 matched controls. The rate of subsequent facial KC development was 20.9% in NAFL-treated patients and 40.4% in controls (relative risk, 0.52, P = .049).
During a separate presentation at the meeting, Dr. Avram, director of lasers and cosmetics at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said that, when he and his colleagues controlled for age, gender, and skin type, controls were 2.65 times more likely to develop new facial KC, compared with those treated with NAFL (P = .0169). “This enhanced effect was seen with the 1550-nm device, compared with the 1927-nm device. The study shows us that 1550-nm/1927-nm NAFL may have a protective effect for patients with a history of KC, but the role of each wavelength is to be determined. We also need a prospective, controlled study to verify the results.”
In an ongoing study first presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, Dr. Tanzi and colleagues enrolled 15 patients aged ≥ 55 years to evaluate the restoration of physiologic features and biomarkers in skin treated with 25% trichloroacetic acid (TCA), plus the 1550-nm or 1927-nm NAFL. Four sites on the back were treated and biopsies were taken at baseline and at 3 months post treatment. The protocol involved TCA 25% to speckled frost, with the 1550-nm device set to level 6 at 70 mJ and the 1927-nm device set to level 8 at 20 mJ. Immunohistochemical stains are still pending; however, physiologic changes were noted.
Three months after a single treatment, the 1927-nm treated areas showed statistically significant elongation of fibroblasts (consistent with younger fibroblasts) on histology. “Although not a large study, it supports the growing body of research that demonstrates we are improving the health of our patients’ skin with certain types of laser treatments, not just beautifying it,” Dr. Tanzi said.
Dr. Tanzi disclosed being a member of the advisory board for AbbVie/Allergan and Sciton, and is a consultant for Alastin/Galderma, Candesant Biomedical, Cytrellis, Revance, and Solta Medical. Dr. Avram disclosed that he receives intellectual property royalties from and holds stock options in Cytrellis, and is a consultant to Allergan and holds stock options in BAI Biosciences, Sofwave, and La Jolla NanoMedical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Risk Reduced After Patients Quit Smoking
TOPLINE:
, with this reduction becoming evident 3-4 years after cessation, in a cohort study from Korea.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database.
- A total of 6,230,189 participants in South Korea who underwent two consecutive biennial health examinations from 2004 to 2005 and 2006 to 2007 were included.
- Participants were categorized into six groups on the basis of their smoking status at both checkups: Sustained smokers, relapsed smokers, new smokers, smoking quitters, sustained ex-smokers, and never smokers.
- The primary outcome was the development of HS.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 3761 HS cases were detected during the 84,457,025 person-years of observation.
- Smoking quitters (adjusted hazard ratio [AHR], 0.68; 95% CI, 0.56-0.83), sustained ex-smokers (AHR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.57-0.77), and never smokers (AHR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.52-0.63) exhibited a reduced risk of developing HS compared with sustained smokers.
- The risk of developing HS varied over time, with smoking quitters showing no significant risk reduction compared with sustained smokers in the first 3 years. After 3 years, a statistically significant decrease in HS risk was observed among quitters, which persisted over time.
- At 3-6 years, the risk reduction in sustained quitters was comparable with that of never smokers (AHR, 0.58 and 0.63, respectively).
IN PRACTICE:
“Smoking cessation and maintaining a smoke-free lifestyle may be important preventive measures against the development of HS,” the authors concluded. In an accompanying editorial, Alexandra Charrow, MD, and Leandra A. Barnes, MD, of the departments of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Stanford University, Palo Alto, California, respectively, wrote that while the study “importantly contributes to the understanding of the association of smoking tobacco and HS onset, prospective cohort studies in large, diverse cohorts of patients with HS may help dermatologists better understand the causal relationship between smoking and the onset or exacerbation of HS.” For now, they added, “dermatologists must continue to use comprehensive HS treatment strategies, including lifestyle modifications that promote overall health like smoking cessation, to improve the lives of those enduring HS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Seong Rae Kim, MD, Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea, and was published online, along with the editorial, on August 21 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study limitations include the potential for unexamined confounding factors like hereditary background, reliance on self-reported smoking status, and the exclusion of electronic cigarette use and nicotine replacement therapy. The predominantly male smoker population may limit generalizability, and delayed diagnosis of HS may not reflect the actual time of onset.
DISCLOSURES:
The study funding source was not disclosed. One study author reported various financial ties with pharmaceutical companies outside this work; other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Charrow’s disclosures included receiving personal fees from several pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, with this reduction becoming evident 3-4 years after cessation, in a cohort study from Korea.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database.
- A total of 6,230,189 participants in South Korea who underwent two consecutive biennial health examinations from 2004 to 2005 and 2006 to 2007 were included.
- Participants were categorized into six groups on the basis of their smoking status at both checkups: Sustained smokers, relapsed smokers, new smokers, smoking quitters, sustained ex-smokers, and never smokers.
- The primary outcome was the development of HS.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 3761 HS cases were detected during the 84,457,025 person-years of observation.
- Smoking quitters (adjusted hazard ratio [AHR], 0.68; 95% CI, 0.56-0.83), sustained ex-smokers (AHR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.57-0.77), and never smokers (AHR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.52-0.63) exhibited a reduced risk of developing HS compared with sustained smokers.
- The risk of developing HS varied over time, with smoking quitters showing no significant risk reduction compared with sustained smokers in the first 3 years. After 3 years, a statistically significant decrease in HS risk was observed among quitters, which persisted over time.
- At 3-6 years, the risk reduction in sustained quitters was comparable with that of never smokers (AHR, 0.58 and 0.63, respectively).
IN PRACTICE:
“Smoking cessation and maintaining a smoke-free lifestyle may be important preventive measures against the development of HS,” the authors concluded. In an accompanying editorial, Alexandra Charrow, MD, and Leandra A. Barnes, MD, of the departments of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Stanford University, Palo Alto, California, respectively, wrote that while the study “importantly contributes to the understanding of the association of smoking tobacco and HS onset, prospective cohort studies in large, diverse cohorts of patients with HS may help dermatologists better understand the causal relationship between smoking and the onset or exacerbation of HS.” For now, they added, “dermatologists must continue to use comprehensive HS treatment strategies, including lifestyle modifications that promote overall health like smoking cessation, to improve the lives of those enduring HS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Seong Rae Kim, MD, Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea, and was published online, along with the editorial, on August 21 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study limitations include the potential for unexamined confounding factors like hereditary background, reliance on self-reported smoking status, and the exclusion of electronic cigarette use and nicotine replacement therapy. The predominantly male smoker population may limit generalizability, and delayed diagnosis of HS may not reflect the actual time of onset.
DISCLOSURES:
The study funding source was not disclosed. One study author reported various financial ties with pharmaceutical companies outside this work; other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Charrow’s disclosures included receiving personal fees from several pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, with this reduction becoming evident 3-4 years after cessation, in a cohort study from Korea.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database.
- A total of 6,230,189 participants in South Korea who underwent two consecutive biennial health examinations from 2004 to 2005 and 2006 to 2007 were included.
- Participants were categorized into six groups on the basis of their smoking status at both checkups: Sustained smokers, relapsed smokers, new smokers, smoking quitters, sustained ex-smokers, and never smokers.
- The primary outcome was the development of HS.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 3761 HS cases were detected during the 84,457,025 person-years of observation.
- Smoking quitters (adjusted hazard ratio [AHR], 0.68; 95% CI, 0.56-0.83), sustained ex-smokers (AHR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.57-0.77), and never smokers (AHR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.52-0.63) exhibited a reduced risk of developing HS compared with sustained smokers.
- The risk of developing HS varied over time, with smoking quitters showing no significant risk reduction compared with sustained smokers in the first 3 years. After 3 years, a statistically significant decrease in HS risk was observed among quitters, which persisted over time.
- At 3-6 years, the risk reduction in sustained quitters was comparable with that of never smokers (AHR, 0.58 and 0.63, respectively).
IN PRACTICE:
“Smoking cessation and maintaining a smoke-free lifestyle may be important preventive measures against the development of HS,” the authors concluded. In an accompanying editorial, Alexandra Charrow, MD, and Leandra A. Barnes, MD, of the departments of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Stanford University, Palo Alto, California, respectively, wrote that while the study “importantly contributes to the understanding of the association of smoking tobacco and HS onset, prospective cohort studies in large, diverse cohorts of patients with HS may help dermatologists better understand the causal relationship between smoking and the onset or exacerbation of HS.” For now, they added, “dermatologists must continue to use comprehensive HS treatment strategies, including lifestyle modifications that promote overall health like smoking cessation, to improve the lives of those enduring HS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Seong Rae Kim, MD, Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea, and was published online, along with the editorial, on August 21 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study limitations include the potential for unexamined confounding factors like hereditary background, reliance on self-reported smoking status, and the exclusion of electronic cigarette use and nicotine replacement therapy. The predominantly male smoker population may limit generalizability, and delayed diagnosis of HS may not reflect the actual time of onset.
DISCLOSURES:
The study funding source was not disclosed. One study author reported various financial ties with pharmaceutical companies outside this work; other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Charrow’s disclosures included receiving personal fees from several pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TYK2 Inhibitor Effective for Psoriasis in Phase 2 Study
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers performed a phase 2b, randomized, double-blind trial to assess the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of different doses of zasocitinib in adults with moderate to severe psoriasis (mean age, 47 years; 32% women) at 47 centers in the United States and eight centers in Canada. Most (83%) were White, 7% were Black, and 8% were Asian.
- A total of 287 patients were randomly assigned to receive one of the four oral doses of zasocitinib (2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, or 30 mg, once daily) or a matched placebo for 12 weeks, followed by a 4-week safety monitoring period.
- The primary outcome was the proportion of patients achieving a ≥ 75% improvement in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75) from baseline at week 12.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, PASI 75 was achieved by 18%, 44%, 68%, and 67% of patients receiving zasocitinib at doses of 2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, and 30 mg, respectively, vs 6% of patients receiving placebo.
- PASI 90 was achieved in 8%, 21%, 45%, and 46% of patients receiving zasocitinib at 2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, and 30 mg, respectively, and in no patients in the placebo group.
- At week 12, 10%, 27%, 49%, and 52% of patients receiving zasocitinib at 2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, and 30 mg, respectively, had no or mild disease (a score of 0 or 1) according to the Physician Global Assessment tool vs 4% in the placebo group.
- Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 53%-62% of patients in the zasocitinib groups compared with 44% in the placebo group. The most common were COVID-19, acne/acneiform dermatitis, and diarrhea. There were no reports of major adverse cardiovascular events, thromboembolic events, or opportunistic infections.
IN PRACTICE:
“Zasocitinib, an advanced, potent, and highly selective oral TYK2 inhibitor bioengineered to optimize target coverage and functional selectivity, achieved biologic-level efficacy with complete skin clearance observed after only a 12-week treatment period in up to one third of patients, with a low incidence of known tolerability issues and absence of serious toxic effects that are characteristic of [Janus kinase] 1-3 inhibition,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, University of California, Los Angeles, and was published online on August 21, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by a relatively small sample size and a short duration. In addition, the inclusion of predominantly White patients may limit the generalizability of findings to a diverse population.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Nimbus Discovery, which includes Nimbus Therapeutics and Nimbus Lakshmi. Dr. Armstrong’s disclosures included receiving grants and/or personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies, including Nimbus Therapeutics and Nimbus. Three authors were employees of and reported holding equity, stocks, or shares in Nimbus. Several authors had disclosures related to pharmaceutical companies, including Nimbus.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers performed a phase 2b, randomized, double-blind trial to assess the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of different doses of zasocitinib in adults with moderate to severe psoriasis (mean age, 47 years; 32% women) at 47 centers in the United States and eight centers in Canada. Most (83%) were White, 7% were Black, and 8% were Asian.
- A total of 287 patients were randomly assigned to receive one of the four oral doses of zasocitinib (2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, or 30 mg, once daily) or a matched placebo for 12 weeks, followed by a 4-week safety monitoring period.
- The primary outcome was the proportion of patients achieving a ≥ 75% improvement in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75) from baseline at week 12.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, PASI 75 was achieved by 18%, 44%, 68%, and 67% of patients receiving zasocitinib at doses of 2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, and 30 mg, respectively, vs 6% of patients receiving placebo.
- PASI 90 was achieved in 8%, 21%, 45%, and 46% of patients receiving zasocitinib at 2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, and 30 mg, respectively, and in no patients in the placebo group.
- At week 12, 10%, 27%, 49%, and 52% of patients receiving zasocitinib at 2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, and 30 mg, respectively, had no or mild disease (a score of 0 or 1) according to the Physician Global Assessment tool vs 4% in the placebo group.
- Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 53%-62% of patients in the zasocitinib groups compared with 44% in the placebo group. The most common were COVID-19, acne/acneiform dermatitis, and diarrhea. There were no reports of major adverse cardiovascular events, thromboembolic events, or opportunistic infections.
IN PRACTICE:
“Zasocitinib, an advanced, potent, and highly selective oral TYK2 inhibitor bioengineered to optimize target coverage and functional selectivity, achieved biologic-level efficacy with complete skin clearance observed after only a 12-week treatment period in up to one third of patients, with a low incidence of known tolerability issues and absence of serious toxic effects that are characteristic of [Janus kinase] 1-3 inhibition,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, University of California, Los Angeles, and was published online on August 21, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by a relatively small sample size and a short duration. In addition, the inclusion of predominantly White patients may limit the generalizability of findings to a diverse population.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Nimbus Discovery, which includes Nimbus Therapeutics and Nimbus Lakshmi. Dr. Armstrong’s disclosures included receiving grants and/or personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies, including Nimbus Therapeutics and Nimbus. Three authors were employees of and reported holding equity, stocks, or shares in Nimbus. Several authors had disclosures related to pharmaceutical companies, including Nimbus.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers performed a phase 2b, randomized, double-blind trial to assess the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of different doses of zasocitinib in adults with moderate to severe psoriasis (mean age, 47 years; 32% women) at 47 centers in the United States and eight centers in Canada. Most (83%) were White, 7% were Black, and 8% were Asian.
- A total of 287 patients were randomly assigned to receive one of the four oral doses of zasocitinib (2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, or 30 mg, once daily) or a matched placebo for 12 weeks, followed by a 4-week safety monitoring period.
- The primary outcome was the proportion of patients achieving a ≥ 75% improvement in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75) from baseline at week 12.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, PASI 75 was achieved by 18%, 44%, 68%, and 67% of patients receiving zasocitinib at doses of 2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, and 30 mg, respectively, vs 6% of patients receiving placebo.
- PASI 90 was achieved in 8%, 21%, 45%, and 46% of patients receiving zasocitinib at 2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, and 30 mg, respectively, and in no patients in the placebo group.
- At week 12, 10%, 27%, 49%, and 52% of patients receiving zasocitinib at 2 mg, 5 mg, 15 mg, and 30 mg, respectively, had no or mild disease (a score of 0 or 1) according to the Physician Global Assessment tool vs 4% in the placebo group.
- Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 53%-62% of patients in the zasocitinib groups compared with 44% in the placebo group. The most common were COVID-19, acne/acneiform dermatitis, and diarrhea. There were no reports of major adverse cardiovascular events, thromboembolic events, or opportunistic infections.
IN PRACTICE:
“Zasocitinib, an advanced, potent, and highly selective oral TYK2 inhibitor bioengineered to optimize target coverage and functional selectivity, achieved biologic-level efficacy with complete skin clearance observed after only a 12-week treatment period in up to one third of patients, with a low incidence of known tolerability issues and absence of serious toxic effects that are characteristic of [Janus kinase] 1-3 inhibition,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, University of California, Los Angeles, and was published online on August 21, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by a relatively small sample size and a short duration. In addition, the inclusion of predominantly White patients may limit the generalizability of findings to a diverse population.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Nimbus Discovery, which includes Nimbus Therapeutics and Nimbus Lakshmi. Dr. Armstrong’s disclosures included receiving grants and/or personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies, including Nimbus Therapeutics and Nimbus. Three authors were employees of and reported holding equity, stocks, or shares in Nimbus. Several authors had disclosures related to pharmaceutical companies, including Nimbus.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Timing of iPLEDGE Updates Unclear
iPLEDGE, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–required Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program launched in 2010, aims to manage the risks for the teratogenic acne drug isotretinoin and prevent fetal exposure. But it’s been dogged by issues and controversy, causing difficulties for patients and prescribers.
Late in 2023, there seemed to be a reason for optimism that improvements were coming. On November 30, 2023, the FDA informed isotretinoin manufacturers — known as the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturing Group (IPMG) — that they had 6 months to make five changes to the existing iPLEDGE REMS, addressing the controversies and potentially reducing glitches in the program and minimizing the burden of the program on patients, prescribers, and pharmacies — while maintaining safe use of the drug — and to submit their proposal by May 30, 2024.
The timeline for when an improved program might be in place remains unclear.
An FDA spokesperson, without confirming that the submission was submitted on time, recently said the review timeline once such a submission is received is generally 6 months.
‘Radio Silence’
No official FDA announcement has been made about the timeline, nor has information been forthcoming from the IPMG, and the silence has been frustrating for John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts. He chairs the American Academy of Dermatology Association’s IPLEDGE Work Group, which works with both the FDA and IPMG.
He began writing about issues with iPLEDGE about 4 years ago, when he and colleagues suggested, among other changes, simplifying the iPLEDGE contraception requirements in a paper published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In an interview, Dr. Barbieri expressed frustration about the lack of information on the status of the iPLEDGE changes. “We’ve been given no timeline [beyond the FDA’s May 30 deadline for the IPMG to respond] of what might happen when. We’ve asked what was submitted. No one will share it with us or tell us anything about it. It’s just radio silence.”
Dr. Barbieri is also frustrated at the lack of response from IPMG. Despite repeated requests to the group to include the dermatologists in the discussions, IPMG has repeatedly declined the help, he said.
IPMG appears to have no dedicated website. No response had been received to an email sent to an address attributed to the group asking if it would share the submission to the FDA.
Currently, isotretinoin, originally marketed as Accutane, is marketed under such brand names as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane.
Asked for specific information on the proposed changes, an FDA spokesperson said in an August 19 email that “the submission to the FDA from the isotretinoin manufacturers will be a major modification, and the review timeline is generally 6 months. Once approved, the isotretinoin manufacturers will need additional time to implement the changes.”
The spokesperson declined to provide additional information on the status of the IPMG proposal, to share the proposal itself, or to estimate the implementation period.
Reason for Hope?
In response to the comment that the review generally takes 6 months, Dr. Barbieri said it doesn’t give him much hope, adding that “any delay of implementing these reforms is a missed opportunity to improve the care of patients with acne.” He is also hopeful that the FDA will invite some public comment during the review period “so that stakeholders can share their feedback about the proposal to help guide FDA decision-making and ensure effective implementation.”
From Meeting to Mandate
The FDA order for the changes followed a joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee in March 2023 about the program requirements. It included feedback from patients and dermatologists and recommendations for changes, with a goal of reducing the burden of the program on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers without compromising patient safety.
The Five Requested Changes
In the November 30 letter, the FDA requested the following from the IPMG:
- Remove the requirement that pregnancy tests be performed in a specially certified lab (such as a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments lab). This would enable the tests to be done in a clinic setting rather than sending patients to a separate lab.
- Allow prescribers the option of letting patients use home pregnancy tests during and after treatment, with steps in place to minimize falsification.
- Remove the waiting period requirement, known as the “19-day lockout,” for patients if they don’t obtain the isotretinoin from the pharmacy within the first 7-day prescription window. Before initiation of isotretinoin, a repeat confirmatory test must be done in a medical setting without any required waiting period.
- Revise the pregnancy registry requirement, removing the objective to document the outcome and associated collection of data for each pregnancy.
- Revise the requirement for prescribers to document patient counseling for those who can’t become pregnant from monthly counseling to counseling at enrollment only. Before each prescription is dispensed, the authorization must verify patient enrollment and prescriber certification. (In December 2021, a new, gender-neutral approach, approved by the FDA, was launched. It places potential patients into two risk categories — those who can become pregnant and those who cannot. Previously, there were three such categories: Females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males.)
Perspective on the Requested Changes
Of the requested changes, “really the most important is eliminating the request for monthly counseling for patients who cannot become pregnant,” Dr. Barbieri said. Because of that requirement, all patients need to have monthly visits with a dermatologist to get the medication refills, “and that creates a logistical barrier,” plus reducing time available for dermatologists to care for other patients with other dermatologic issues.
As for missing the 7-day prescription window, Dr. Barbieri said, in his experience, “it’s almost never the patient’s fault; it’s almost always an insurance problem.”
Dr. Barbieri reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
iPLEDGE, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–required Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program launched in 2010, aims to manage the risks for the teratogenic acne drug isotretinoin and prevent fetal exposure. But it’s been dogged by issues and controversy, causing difficulties for patients and prescribers.
Late in 2023, there seemed to be a reason for optimism that improvements were coming. On November 30, 2023, the FDA informed isotretinoin manufacturers — known as the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturing Group (IPMG) — that they had 6 months to make five changes to the existing iPLEDGE REMS, addressing the controversies and potentially reducing glitches in the program and minimizing the burden of the program on patients, prescribers, and pharmacies — while maintaining safe use of the drug — and to submit their proposal by May 30, 2024.
The timeline for when an improved program might be in place remains unclear.
An FDA spokesperson, without confirming that the submission was submitted on time, recently said the review timeline once such a submission is received is generally 6 months.
‘Radio Silence’
No official FDA announcement has been made about the timeline, nor has information been forthcoming from the IPMG, and the silence has been frustrating for John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts. He chairs the American Academy of Dermatology Association’s IPLEDGE Work Group, which works with both the FDA and IPMG.
He began writing about issues with iPLEDGE about 4 years ago, when he and colleagues suggested, among other changes, simplifying the iPLEDGE contraception requirements in a paper published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In an interview, Dr. Barbieri expressed frustration about the lack of information on the status of the iPLEDGE changes. “We’ve been given no timeline [beyond the FDA’s May 30 deadline for the IPMG to respond] of what might happen when. We’ve asked what was submitted. No one will share it with us or tell us anything about it. It’s just radio silence.”
Dr. Barbieri is also frustrated at the lack of response from IPMG. Despite repeated requests to the group to include the dermatologists in the discussions, IPMG has repeatedly declined the help, he said.
IPMG appears to have no dedicated website. No response had been received to an email sent to an address attributed to the group asking if it would share the submission to the FDA.
Currently, isotretinoin, originally marketed as Accutane, is marketed under such brand names as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane.
Asked for specific information on the proposed changes, an FDA spokesperson said in an August 19 email that “the submission to the FDA from the isotretinoin manufacturers will be a major modification, and the review timeline is generally 6 months. Once approved, the isotretinoin manufacturers will need additional time to implement the changes.”
The spokesperson declined to provide additional information on the status of the IPMG proposal, to share the proposal itself, or to estimate the implementation period.
Reason for Hope?
In response to the comment that the review generally takes 6 months, Dr. Barbieri said it doesn’t give him much hope, adding that “any delay of implementing these reforms is a missed opportunity to improve the care of patients with acne.” He is also hopeful that the FDA will invite some public comment during the review period “so that stakeholders can share their feedback about the proposal to help guide FDA decision-making and ensure effective implementation.”
From Meeting to Mandate
The FDA order for the changes followed a joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee in March 2023 about the program requirements. It included feedback from patients and dermatologists and recommendations for changes, with a goal of reducing the burden of the program on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers without compromising patient safety.
The Five Requested Changes
In the November 30 letter, the FDA requested the following from the IPMG:
- Remove the requirement that pregnancy tests be performed in a specially certified lab (such as a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments lab). This would enable the tests to be done in a clinic setting rather than sending patients to a separate lab.
- Allow prescribers the option of letting patients use home pregnancy tests during and after treatment, with steps in place to minimize falsification.
- Remove the waiting period requirement, known as the “19-day lockout,” for patients if they don’t obtain the isotretinoin from the pharmacy within the first 7-day prescription window. Before initiation of isotretinoin, a repeat confirmatory test must be done in a medical setting without any required waiting period.
- Revise the pregnancy registry requirement, removing the objective to document the outcome and associated collection of data for each pregnancy.
- Revise the requirement for prescribers to document patient counseling for those who can’t become pregnant from monthly counseling to counseling at enrollment only. Before each prescription is dispensed, the authorization must verify patient enrollment and prescriber certification. (In December 2021, a new, gender-neutral approach, approved by the FDA, was launched. It places potential patients into two risk categories — those who can become pregnant and those who cannot. Previously, there were three such categories: Females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males.)
Perspective on the Requested Changes
Of the requested changes, “really the most important is eliminating the request for monthly counseling for patients who cannot become pregnant,” Dr. Barbieri said. Because of that requirement, all patients need to have monthly visits with a dermatologist to get the medication refills, “and that creates a logistical barrier,” plus reducing time available for dermatologists to care for other patients with other dermatologic issues.
As for missing the 7-day prescription window, Dr. Barbieri said, in his experience, “it’s almost never the patient’s fault; it’s almost always an insurance problem.”
Dr. Barbieri reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
iPLEDGE, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–required Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program launched in 2010, aims to manage the risks for the teratogenic acne drug isotretinoin and prevent fetal exposure. But it’s been dogged by issues and controversy, causing difficulties for patients and prescribers.
Late in 2023, there seemed to be a reason for optimism that improvements were coming. On November 30, 2023, the FDA informed isotretinoin manufacturers — known as the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturing Group (IPMG) — that they had 6 months to make five changes to the existing iPLEDGE REMS, addressing the controversies and potentially reducing glitches in the program and minimizing the burden of the program on patients, prescribers, and pharmacies — while maintaining safe use of the drug — and to submit their proposal by May 30, 2024.
The timeline for when an improved program might be in place remains unclear.
An FDA spokesperson, without confirming that the submission was submitted on time, recently said the review timeline once such a submission is received is generally 6 months.
‘Radio Silence’
No official FDA announcement has been made about the timeline, nor has information been forthcoming from the IPMG, and the silence has been frustrating for John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts. He chairs the American Academy of Dermatology Association’s IPLEDGE Work Group, which works with both the FDA and IPMG.
He began writing about issues with iPLEDGE about 4 years ago, when he and colleagues suggested, among other changes, simplifying the iPLEDGE contraception requirements in a paper published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In an interview, Dr. Barbieri expressed frustration about the lack of information on the status of the iPLEDGE changes. “We’ve been given no timeline [beyond the FDA’s May 30 deadline for the IPMG to respond] of what might happen when. We’ve asked what was submitted. No one will share it with us or tell us anything about it. It’s just radio silence.”
Dr. Barbieri is also frustrated at the lack of response from IPMG. Despite repeated requests to the group to include the dermatologists in the discussions, IPMG has repeatedly declined the help, he said.
IPMG appears to have no dedicated website. No response had been received to an email sent to an address attributed to the group asking if it would share the submission to the FDA.
Currently, isotretinoin, originally marketed as Accutane, is marketed under such brand names as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane.
Asked for specific information on the proposed changes, an FDA spokesperson said in an August 19 email that “the submission to the FDA from the isotretinoin manufacturers will be a major modification, and the review timeline is generally 6 months. Once approved, the isotretinoin manufacturers will need additional time to implement the changes.”
The spokesperson declined to provide additional information on the status of the IPMG proposal, to share the proposal itself, or to estimate the implementation period.
Reason for Hope?
In response to the comment that the review generally takes 6 months, Dr. Barbieri said it doesn’t give him much hope, adding that “any delay of implementing these reforms is a missed opportunity to improve the care of patients with acne.” He is also hopeful that the FDA will invite some public comment during the review period “so that stakeholders can share their feedback about the proposal to help guide FDA decision-making and ensure effective implementation.”
From Meeting to Mandate
The FDA order for the changes followed a joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee in March 2023 about the program requirements. It included feedback from patients and dermatologists and recommendations for changes, with a goal of reducing the burden of the program on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers without compromising patient safety.
The Five Requested Changes
In the November 30 letter, the FDA requested the following from the IPMG:
- Remove the requirement that pregnancy tests be performed in a specially certified lab (such as a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments lab). This would enable the tests to be done in a clinic setting rather than sending patients to a separate lab.
- Allow prescribers the option of letting patients use home pregnancy tests during and after treatment, with steps in place to minimize falsification.
- Remove the waiting period requirement, known as the “19-day lockout,” for patients if they don’t obtain the isotretinoin from the pharmacy within the first 7-day prescription window. Before initiation of isotretinoin, a repeat confirmatory test must be done in a medical setting without any required waiting period.
- Revise the pregnancy registry requirement, removing the objective to document the outcome and associated collection of data for each pregnancy.
- Revise the requirement for prescribers to document patient counseling for those who can’t become pregnant from monthly counseling to counseling at enrollment only. Before each prescription is dispensed, the authorization must verify patient enrollment and prescriber certification. (In December 2021, a new, gender-neutral approach, approved by the FDA, was launched. It places potential patients into two risk categories — those who can become pregnant and those who cannot. Previously, there were three such categories: Females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males.)
Perspective on the Requested Changes
Of the requested changes, “really the most important is eliminating the request for monthly counseling for patients who cannot become pregnant,” Dr. Barbieri said. Because of that requirement, all patients need to have monthly visits with a dermatologist to get the medication refills, “and that creates a logistical barrier,” plus reducing time available for dermatologists to care for other patients with other dermatologic issues.
As for missing the 7-day prescription window, Dr. Barbieri said, in his experience, “it’s almost never the patient’s fault; it’s almost always an insurance problem.”
Dr. Barbieri reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients With Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases, Type 2 Diabetes Reap GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Benefits, Too
TOPLINE:
Compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs reduce the risk for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and stroke in patients with diabetes. However, previous trials have excluded those with IMIDs, leaving a gap in understanding the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs in this population.
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study to assess if patients with an IMID derive greater benefits from GLP-1 RAs than DPP-4 inhibitors.
- They used administrative health data from British Columbia, Canada, to include 10,855 patients with IMIDs (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic disease, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, or systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease) and T2D who initiated either GLP-1 RA (n = 3570) or DPP-4 inhibitor (n = 7285).
- The mean follow-up was 1.46 and 1.88 years in the GLP-1 RA and DPP-4 inhibitor cohorts, respectively.
- The primary outcome was all-cause mortality, and the secondary outcome was MACE, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and ischemic stroke.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for all-cause mortality was 52% lower in patients who initiated GLP-1 RAs than in those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors (weighted hazard ratio [HR], 0.48; 95% CI, 0.31-0.75).
- Additionally, patients initiating DPP-4 inhibitors.
- In the subgroup of patients with GLP-1 RAs had a significantly lower risk for MACE (weighted HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.50-0.88), particularly myocardial infarction (weighted HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40-0.96), than those initiating rheumatoid arthritis and T2D, those who initiated GLP-1 RAs had a 55% lower risk for all-cause mortality and 61% lower risk for MACE than those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“This corresponds to nine fewer deaths and 11 fewer MACE per 1000 person-years, respectively, supporting the hypothesis that these agents have a cardioprotective effect in this high-risk population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Derin Karacabeyli, MD, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, and was published online on August 8, 2024, in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s dependence on administrative health data might have resulted in incomplete capture of comorbidities, particularly obesity. The mean follow-up period was relatively short, which might have limited the long-term applicability of these findings. The accuracy of the case definitions for IMIDs and T2D, according to International Classification of Diseases codes, could not be fully ascertained.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Two authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, or participating in advisory boards outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs reduce the risk for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and stroke in patients with diabetes. However, previous trials have excluded those with IMIDs, leaving a gap in understanding the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs in this population.
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study to assess if patients with an IMID derive greater benefits from GLP-1 RAs than DPP-4 inhibitors.
- They used administrative health data from British Columbia, Canada, to include 10,855 patients with IMIDs (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic disease, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, or systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease) and T2D who initiated either GLP-1 RA (n = 3570) or DPP-4 inhibitor (n = 7285).
- The mean follow-up was 1.46 and 1.88 years in the GLP-1 RA and DPP-4 inhibitor cohorts, respectively.
- The primary outcome was all-cause mortality, and the secondary outcome was MACE, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and ischemic stroke.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for all-cause mortality was 52% lower in patients who initiated GLP-1 RAs than in those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors (weighted hazard ratio [HR], 0.48; 95% CI, 0.31-0.75).
- Additionally, patients initiating DPP-4 inhibitors.
- In the subgroup of patients with GLP-1 RAs had a significantly lower risk for MACE (weighted HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.50-0.88), particularly myocardial infarction (weighted HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40-0.96), than those initiating rheumatoid arthritis and T2D, those who initiated GLP-1 RAs had a 55% lower risk for all-cause mortality and 61% lower risk for MACE than those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“This corresponds to nine fewer deaths and 11 fewer MACE per 1000 person-years, respectively, supporting the hypothesis that these agents have a cardioprotective effect in this high-risk population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Derin Karacabeyli, MD, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, and was published online on August 8, 2024, in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s dependence on administrative health data might have resulted in incomplete capture of comorbidities, particularly obesity. The mean follow-up period was relatively short, which might have limited the long-term applicability of these findings. The accuracy of the case definitions for IMIDs and T2D, according to International Classification of Diseases codes, could not be fully ascertained.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Two authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, or participating in advisory boards outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- GLP-1 RAs reduce the risk for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and stroke in patients with diabetes. However, previous trials have excluded those with IMIDs, leaving a gap in understanding the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs in this population.
- Researchers conducted a population-based cohort study to assess if patients with an IMID derive greater benefits from GLP-1 RAs than DPP-4 inhibitors.
- They used administrative health data from British Columbia, Canada, to include 10,855 patients with IMIDs (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic disease, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, or systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease) and T2D who initiated either GLP-1 RA (n = 3570) or DPP-4 inhibitor (n = 7285).
- The mean follow-up was 1.46 and 1.88 years in the GLP-1 RA and DPP-4 inhibitor cohorts, respectively.
- The primary outcome was all-cause mortality, and the secondary outcome was MACE, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and ischemic stroke.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for all-cause mortality was 52% lower in patients who initiated GLP-1 RAs than in those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors (weighted hazard ratio [HR], 0.48; 95% CI, 0.31-0.75).
- Additionally, patients initiating DPP-4 inhibitors.
- In the subgroup of patients with GLP-1 RAs had a significantly lower risk for MACE (weighted HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.50-0.88), particularly myocardial infarction (weighted HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40-0.96), than those initiating rheumatoid arthritis and T2D, those who initiated GLP-1 RAs had a 55% lower risk for all-cause mortality and 61% lower risk for MACE than those who initiated DPP-4 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“This corresponds to nine fewer deaths and 11 fewer MACE per 1000 person-years, respectively, supporting the hypothesis that these agents have a cardioprotective effect in this high-risk population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Derin Karacabeyli, MD, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, and was published online on August 8, 2024, in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s dependence on administrative health data might have resulted in incomplete capture of comorbidities, particularly obesity. The mean follow-up period was relatively short, which might have limited the long-term applicability of these findings. The accuracy of the case definitions for IMIDs and T2D, according to International Classification of Diseases codes, could not be fully ascertained.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Two authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, or participating in advisory boards outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Do You Have Patients With JAKne — JAK Inhibitor–Associated Acne? Here’s What to Know
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
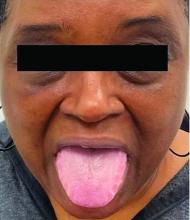
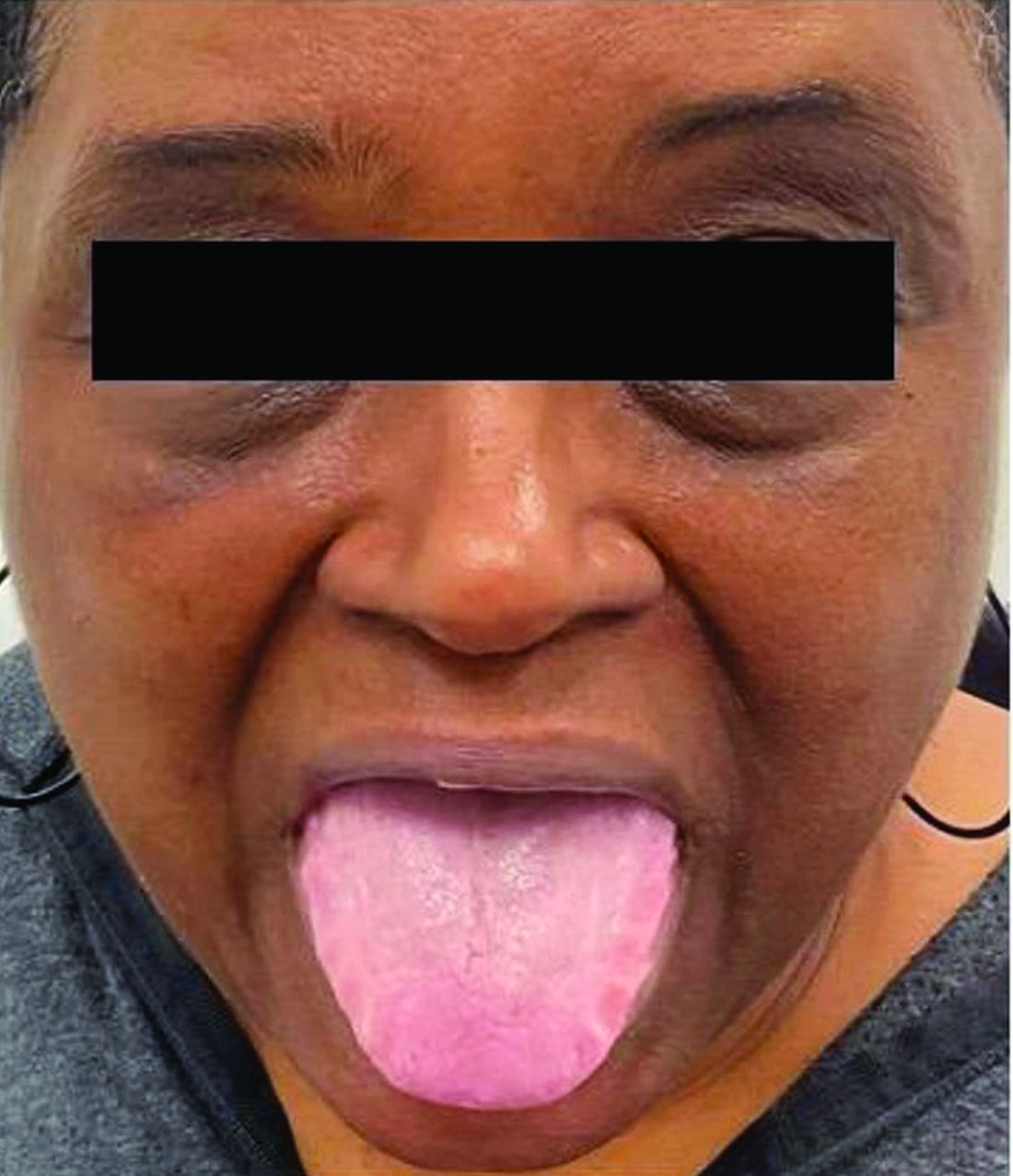
A 62-year-old Black female presented with an epidermal inclusion cyst on her left upper back
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
Diagnosing, Treating Rashes In Patients on Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ELDERDERM 2024
Second Treatment for Prurigo Nodularis Approved by FDA
On August 13, 2024, the
A first-in-class monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL)–31 signaling, nemolizumab, will be available in a prefilled pen for subcutaneous injection and will be marketed as Nemluvio. It is currently under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis in adolescents and adults.
Approval for PN is based on data from the phase 3 OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in 560 patients with PN, according to a press release from Galderma, the manufacturer.
According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and OLYMPIA 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a 4-point reduction in itch intensity at week 16 as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale, compared with 16% in both placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the Investigator Global Assessment score at week 16, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
According to the company press release, the most common side effects of nemolizumab are headache and rashes in the form of eczema, atopic dermatitis, and nummular eczema.
“By inhibiting the signaling of IL-31, Nemluvio addresses a key driver of prurigo nodularis, safely and effectively improving itch as well as skin nodules,” Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and lead investigator of the OLYMPIA program, stated in the press release.
The regulatory submission of nemolizumab in atopic dermatitis is based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. A decision on approval for this indication from the FDA is expected in December 2024.
In September 2022, dupilumab became the first FDA-approved treatment for PN in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On August 13, 2024, the
A first-in-class monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL)–31 signaling, nemolizumab, will be available in a prefilled pen for subcutaneous injection and will be marketed as Nemluvio. It is currently under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis in adolescents and adults.
Approval for PN is based on data from the phase 3 OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in 560 patients with PN, according to a press release from Galderma, the manufacturer.
According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and OLYMPIA 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a 4-point reduction in itch intensity at week 16 as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale, compared with 16% in both placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the Investigator Global Assessment score at week 16, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
According to the company press release, the most common side effects of nemolizumab are headache and rashes in the form of eczema, atopic dermatitis, and nummular eczema.
“By inhibiting the signaling of IL-31, Nemluvio addresses a key driver of prurigo nodularis, safely and effectively improving itch as well as skin nodules,” Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and lead investigator of the OLYMPIA program, stated in the press release.
The regulatory submission of nemolizumab in atopic dermatitis is based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. A decision on approval for this indication from the FDA is expected in December 2024.
In September 2022, dupilumab became the first FDA-approved treatment for PN in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On August 13, 2024, the
A first-in-class monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL)–31 signaling, nemolizumab, will be available in a prefilled pen for subcutaneous injection and will be marketed as Nemluvio. It is currently under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis in adolescents and adults.
Approval for PN is based on data from the phase 3 OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in 560 patients with PN, according to a press release from Galderma, the manufacturer.
According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and OLYMPIA 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a 4-point reduction in itch intensity at week 16 as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale, compared with 16% in both placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the Investigator Global Assessment score at week 16, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
According to the company press release, the most common side effects of nemolizumab are headache and rashes in the form of eczema, atopic dermatitis, and nummular eczema.
“By inhibiting the signaling of IL-31, Nemluvio addresses a key driver of prurigo nodularis, safely and effectively improving itch as well as skin nodules,” Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and lead investigator of the OLYMPIA program, stated in the press release.
The regulatory submission of nemolizumab in atopic dermatitis is based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. A decision on approval for this indication from the FDA is expected in December 2024.
In September 2022, dupilumab became the first FDA-approved treatment for PN in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Storybooks Can Help Children Deal with Skin Conditions
TORONTO —
So far, “the study demonstrates that these books have value to patients and families,” one of the study authors, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“There are tools to help kids cope with their skin conditions, but we’re underutilizing them,” she added. “And part of the reason we’re underutilizing storybooks is that we just don’t know what’s out there.” For the study, the researchers received funding to purchase 18 “creative and thoughtful” storybooks related to pediatric skin conditions, reviewed by at least two pediatric dermatologists before being selected, which are just a sample of related books that are available.
The study results were presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Children with visible skin conditions, which can include port-wine stains, capillary malformations, and congenital moles, may be subjected to teasing or bullying at school, and the conditions can also affect their quality of life.
Beauty and the Birthmark
The books include one titled “Beauty with a Birthmark” and another, “My Hair Went on Vacation.” An illustrated book, “Just Ask: Be Different, Be Brave, Be You,” by US Supreme Court Justice Sonia Sotomayor, offers tips on how to answer common questions about someone’s appearance.
Dr. Havele said that Justice Sotomayor’s book “empowers kids, their siblings, their classmates ... to ask questions, and it teaches patients not to be afraid of those questions, and to really lean into educating their peers, and their family members.”
“Kids are really just curious,” she added. “They’ll make comments like: ‘Hey, what’s that spot on your face?’ Or, they’ll ask about vitiligo because they’ve never seen somebody with it before.”
To evaluate the psychosocial impact of these types of books for children with visible skin conditions, Dr. Havele and colleagues designed a study that includes patients aged 2-12 years dealing with issues related to self-esteem, acceptance, coping, or bullying. Parents are provided with a relevant storybook to read at home with their child in a “safe and comfortable space” and “at their own pace and their own time,” said Dr. Havele.
Inside the book is a QR code to access the validated Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI). Families complete the survey at baseline and provide feedback after reading the book. Researchers collect information about demographics, age, gender, and skin conditions, which included atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, hemangioma, and port-wine stain.
The response rate so far is 34%, and close to 80 parents have completed the survey with their child, Dr. Havele said.
At baseline, many of the children were either moderately or severely affected in terms of their quality of life (45% scored ≥ 6 on the CDLQI).
After reading the book, about 80% of parents reported it had a positive impact, and about 20% said it had a somewhat positive impact on their child’s self-image or confidence. Almost 80% agreed, and the remainder somewhat agreed it encouraged their child to embrace differences.
Most respondents also said the book helped the parent and child cope with the child’s condition. “So really, it was overall a positive response,” said Dr. Havele. “We are able to demonstrate that these books have value in a more scientific or objective way.”
This may not be surprising. Dr. Havele referred to more formal bibliotherapy (book therapy), which has been studied in other pediatric populations, including patients with cancer and those who have experienced trauma.
Awesome Space
Pediatric dermatologists are perfectly positioned to play a role in improving the lives of their patients with skin issues. “We see the impact of visible skin disease on children all the time,” said Dr. Havele. “The dermatology visit is an awesome space and opportunity to introduce these books to families and potentially help them talk about the skin condition with their child.”
In addition to prescribing therapies, “we’re also with these kids through an emotional journey, and I think giving them tools for that emotional journey is very helpful,” she added.
Such books would have been a great help to Dr. Havele herself. Growing up, she had severe atopic dermatitis covering much of her body. “Having such a resource would have helped me better cope with my reality of being different than everyone else.”
She hopes a database will be established to house these resources so other providers can refer patients to the list of books. Other books include “The Itchy-saurus: The Dino with an itch that can’t be scratched,” “Hair in My Brush,” and “I am Unique!”
Dr. Havele had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TORONTO —
So far, “the study demonstrates that these books have value to patients and families,” one of the study authors, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“There are tools to help kids cope with their skin conditions, but we’re underutilizing them,” she added. “And part of the reason we’re underutilizing storybooks is that we just don’t know what’s out there.” For the study, the researchers received funding to purchase 18 “creative and thoughtful” storybooks related to pediatric skin conditions, reviewed by at least two pediatric dermatologists before being selected, which are just a sample of related books that are available.
The study results were presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Children with visible skin conditions, which can include port-wine stains, capillary malformations, and congenital moles, may be subjected to teasing or bullying at school, and the conditions can also affect their quality of life.
Beauty and the Birthmark
The books include one titled “Beauty with a Birthmark” and another, “My Hair Went on Vacation.” An illustrated book, “Just Ask: Be Different, Be Brave, Be You,” by US Supreme Court Justice Sonia Sotomayor, offers tips on how to answer common questions about someone’s appearance.
Dr. Havele said that Justice Sotomayor’s book “empowers kids, their siblings, their classmates ... to ask questions, and it teaches patients not to be afraid of those questions, and to really lean into educating their peers, and their family members.”
“Kids are really just curious,” she added. “They’ll make comments like: ‘Hey, what’s that spot on your face?’ Or, they’ll ask about vitiligo because they’ve never seen somebody with it before.”
To evaluate the psychosocial impact of these types of books for children with visible skin conditions, Dr. Havele and colleagues designed a study that includes patients aged 2-12 years dealing with issues related to self-esteem, acceptance, coping, or bullying. Parents are provided with a relevant storybook to read at home with their child in a “safe and comfortable space” and “at their own pace and their own time,” said Dr. Havele.
Inside the book is a QR code to access the validated Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI). Families complete the survey at baseline and provide feedback after reading the book. Researchers collect information about demographics, age, gender, and skin conditions, which included atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, hemangioma, and port-wine stain.
The response rate so far is 34%, and close to 80 parents have completed the survey with their child, Dr. Havele said.
At baseline, many of the children were either moderately or severely affected in terms of their quality of life (45% scored ≥ 6 on the CDLQI).
After reading the book, about 80% of parents reported it had a positive impact, and about 20% said it had a somewhat positive impact on their child’s self-image or confidence. Almost 80% agreed, and the remainder somewhat agreed it encouraged their child to embrace differences.
Most respondents also said the book helped the parent and child cope with the child’s condition. “So really, it was overall a positive response,” said Dr. Havele. “We are able to demonstrate that these books have value in a more scientific or objective way.”
This may not be surprising. Dr. Havele referred to more formal bibliotherapy (book therapy), which has been studied in other pediatric populations, including patients with cancer and those who have experienced trauma.
Awesome Space
Pediatric dermatologists are perfectly positioned to play a role in improving the lives of their patients with skin issues. “We see the impact of visible skin disease on children all the time,” said Dr. Havele. “The dermatology visit is an awesome space and opportunity to introduce these books to families and potentially help them talk about the skin condition with their child.”
In addition to prescribing therapies, “we’re also with these kids through an emotional journey, and I think giving them tools for that emotional journey is very helpful,” she added.
Such books would have been a great help to Dr. Havele herself. Growing up, she had severe atopic dermatitis covering much of her body. “Having such a resource would have helped me better cope with my reality of being different than everyone else.”
She hopes a database will be established to house these resources so other providers can refer patients to the list of books. Other books include “The Itchy-saurus: The Dino with an itch that can’t be scratched,” “Hair in My Brush,” and “I am Unique!”
Dr. Havele had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TORONTO —
So far, “the study demonstrates that these books have value to patients and families,” one of the study authors, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“There are tools to help kids cope with their skin conditions, but we’re underutilizing them,” she added. “And part of the reason we’re underutilizing storybooks is that we just don’t know what’s out there.” For the study, the researchers received funding to purchase 18 “creative and thoughtful” storybooks related to pediatric skin conditions, reviewed by at least two pediatric dermatologists before being selected, which are just a sample of related books that are available.
The study results were presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Children with visible skin conditions, which can include port-wine stains, capillary malformations, and congenital moles, may be subjected to teasing or bullying at school, and the conditions can also affect their quality of life.
Beauty and the Birthmark
The books include one titled “Beauty with a Birthmark” and another, “My Hair Went on Vacation.” An illustrated book, “Just Ask: Be Different, Be Brave, Be You,” by US Supreme Court Justice Sonia Sotomayor, offers tips on how to answer common questions about someone’s appearance.
Dr. Havele said that Justice Sotomayor’s book “empowers kids, their siblings, their classmates ... to ask questions, and it teaches patients not to be afraid of those questions, and to really lean into educating their peers, and their family members.”
“Kids are really just curious,” she added. “They’ll make comments like: ‘Hey, what’s that spot on your face?’ Or, they’ll ask about vitiligo because they’ve never seen somebody with it before.”
To evaluate the psychosocial impact of these types of books for children with visible skin conditions, Dr. Havele and colleagues designed a study that includes patients aged 2-12 years dealing with issues related to self-esteem, acceptance, coping, or bullying. Parents are provided with a relevant storybook to read at home with their child in a “safe and comfortable space” and “at their own pace and their own time,” said Dr. Havele.
Inside the book is a QR code to access the validated Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI). Families complete the survey at baseline and provide feedback after reading the book. Researchers collect information about demographics, age, gender, and skin conditions, which included atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, hemangioma, and port-wine stain.
The response rate so far is 34%, and close to 80 parents have completed the survey with their child, Dr. Havele said.
At baseline, many of the children were either moderately or severely affected in terms of their quality of life (45% scored ≥ 6 on the CDLQI).
After reading the book, about 80% of parents reported it had a positive impact, and about 20% said it had a somewhat positive impact on their child’s self-image or confidence. Almost 80% agreed, and the remainder somewhat agreed it encouraged their child to embrace differences.
Most respondents also said the book helped the parent and child cope with the child’s condition. “So really, it was overall a positive response,” said Dr. Havele. “We are able to demonstrate that these books have value in a more scientific or objective way.”
This may not be surprising. Dr. Havele referred to more formal bibliotherapy (book therapy), which has been studied in other pediatric populations, including patients with cancer and those who have experienced trauma.
Awesome Space
Pediatric dermatologists are perfectly positioned to play a role in improving the lives of their patients with skin issues. “We see the impact of visible skin disease on children all the time,” said Dr. Havele. “The dermatology visit is an awesome space and opportunity to introduce these books to families and potentially help them talk about the skin condition with their child.”
In addition to prescribing therapies, “we’re also with these kids through an emotional journey, and I think giving them tools for that emotional journey is very helpful,” she added.
Such books would have been a great help to Dr. Havele herself. Growing up, she had severe atopic dermatitis covering much of her body. “Having such a resource would have helped me better cope with my reality of being different than everyone else.”
She hopes a database will be established to house these resources so other providers can refer patients to the list of books. Other books include “The Itchy-saurus: The Dino with an itch that can’t be scratched,” “Hair in My Brush,” and “I am Unique!”
Dr. Havele had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SPD 2024