User login
Eating fish tied to fewer CVD events in high-risk people
People with cardiovascular disease who regularly ate fish had significantly fewer major CVD events and there were fewer total deaths, compared with similar individuals who didn’t eat fish, but there was no beneficial link from eating fish among the general population in prospective data collected from more than 191,000 people from 58 countries.
Despite the neutral finding among people without CVD, the finding that eating fish was associated with significant benefit for those with CVD or who were at high risk for CVD confirms the public health importance of regular fish or fish oil consumption, said one expert.
A little over a quarter of those included in the new study had a history of CVD or were at high risk for CVD. In this subgroup of more than 51,000 people, those who consumed on average at least two servings of fish weekly (at least 175 g, or about 6.2 ounces per week) had a significant 16% lower rate of major CVD events during a median follow-up of about 7.5 years.
The rate of all-cause death was a significant 18% lower among people who ate two or more fish portions weekly, compared with those who didn’t, Deepa Mohan, PhD, and associates wrote in their report in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The researchers saw no additional benefit when people regularly ate greater amounts of fish.
“There is a significant protective benefit of fish consumption in people with cardiovascular disease,” said Andrew Mente, PhD, a senior investigator on the study and an epidemiologist at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont..
“This study has important implications for guidelines on fish intake globally. It indicates that increasing fish consumption and particularly oily fish in vascular patients may produce a modest cardiovascular benefit,” he said in a statement released by McMaster.
‘A large body of evidence’ for CVD benefit
The neutral finding of no significant benefit (as well as no harm) regarding either CVD events or total mortality among people without CVD “does not alter the large body of prior observational evidence supporting the cardiac benefits of fish intake in general populations,” noted Dariush Mozaffarian, MD, DrPH, in a commentary that accompanies the report by Dr. Mohan and colleagues.
Although the new analysis failed to show a significant association between regular fish consumption and fewer CVD events for people without established CVD or CVD risk, “based on the cumulative evidence from prospective observational studies, randomized clinical trials, and mechanistic and experimental studies, modest fish consumption appears to have some cardiac benefits,” he added.
“Adults should aim to consume about two servings of fish per week, and larger benefits may accrue from nonfried oily (dark meat) fish,” wrote Dr. Mozaffarian, a professor of medicine and nutrition at Tufts University, Boston.
Oily, dark fishes include salmon, tuna steak, mackerel, herring, and sardines. Species such as these contain the highest levels of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid, and docosapentaenoic acid; these nutrients likely underlie the CVD benefits from fish, Dr. Mozaffarian said in an interview with JAMA Internal Medicine that accompanied his commentary. (Dr. Mente also participated.)
“Fish oil lowers heart rate, blood pressure, and triglycerides (at high dosages), increases adiponectin, improves endothelial function, and in some studies improves oxygen consumption in myocardium. If there is benefit from fish it’s from the omega 3s, and all in all the evidence supports this,” but because the evidence is primarily observational, it can only show linkage and cannot prove causation, he explained.
Given the potential benefit and limited risk, “I think everyone should aim to eat two servings of fish each week, preferentially oily fish. That’s very solid,” said Dr. Mozaffarian, who is also a cardiologist and dean of the Tufts Friedman School of Nutrition Science.
The investigators did not have adequate data to compare the associations between outcomes and a diet with oily fish versus less oily fish.
OTC fish oil capsules are ‘very reasonable’
For people who either can’t consume two fish meals a week or want to ensure their omega 3 intake is adequate, “it’s very reasonable for the average person to take one OTC [over-the-counter] fish oil capsule a day,” Dr. Mozaffarian added.
He acknowledged that several studies of fish oil supplements failed to show benefit, but several others have. “It’s a confusing field, but the evidence supports benefit from omega 3s,” he concluded.
He discounted the new finding that only people with established CVD or who are at high-risk benefit. “I’m not sure we should make too much of this, because many prior studies showed a lower CVD risk in fish-eating people without prevalent CVD,” he said. The new study “provides important information given its worldwide breadth.”
The new report used data regarding 191,558 people enrolled prospectively in any of four studies. The average age of the participants was 54 years, and 52% were women.
During follow-up, death from any cause occurred in 6% of those without CVD or CVD risk and in 13% of those with these factors. Major CVD events occurred in 5% and 17% of these two subgroups, respectively. To calculate the relative risks between those who ate fish and those who did not, the investigators used standard multivariate adjustment for potential confounders and adjusted for several dietary variables, Dr. Mente said.
Dr. Mohan and Dr. Mente disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mozaffarian has received personal fees from Acasti Pharma, Amarin, America’s Test Kitchen, Barilla, Danone, GEOD, and Motif Food Works, and he has been an adviser to numerous companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with cardiovascular disease who regularly ate fish had significantly fewer major CVD events and there were fewer total deaths, compared with similar individuals who didn’t eat fish, but there was no beneficial link from eating fish among the general population in prospective data collected from more than 191,000 people from 58 countries.
Despite the neutral finding among people without CVD, the finding that eating fish was associated with significant benefit for those with CVD or who were at high risk for CVD confirms the public health importance of regular fish or fish oil consumption, said one expert.
A little over a quarter of those included in the new study had a history of CVD or were at high risk for CVD. In this subgroup of more than 51,000 people, those who consumed on average at least two servings of fish weekly (at least 175 g, or about 6.2 ounces per week) had a significant 16% lower rate of major CVD events during a median follow-up of about 7.5 years.
The rate of all-cause death was a significant 18% lower among people who ate two or more fish portions weekly, compared with those who didn’t, Deepa Mohan, PhD, and associates wrote in their report in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The researchers saw no additional benefit when people regularly ate greater amounts of fish.
“There is a significant protective benefit of fish consumption in people with cardiovascular disease,” said Andrew Mente, PhD, a senior investigator on the study and an epidemiologist at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont..
“This study has important implications for guidelines on fish intake globally. It indicates that increasing fish consumption and particularly oily fish in vascular patients may produce a modest cardiovascular benefit,” he said in a statement released by McMaster.
‘A large body of evidence’ for CVD benefit
The neutral finding of no significant benefit (as well as no harm) regarding either CVD events or total mortality among people without CVD “does not alter the large body of prior observational evidence supporting the cardiac benefits of fish intake in general populations,” noted Dariush Mozaffarian, MD, DrPH, in a commentary that accompanies the report by Dr. Mohan and colleagues.
Although the new analysis failed to show a significant association between regular fish consumption and fewer CVD events for people without established CVD or CVD risk, “based on the cumulative evidence from prospective observational studies, randomized clinical trials, and mechanistic and experimental studies, modest fish consumption appears to have some cardiac benefits,” he added.
“Adults should aim to consume about two servings of fish per week, and larger benefits may accrue from nonfried oily (dark meat) fish,” wrote Dr. Mozaffarian, a professor of medicine and nutrition at Tufts University, Boston.
Oily, dark fishes include salmon, tuna steak, mackerel, herring, and sardines. Species such as these contain the highest levels of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid, and docosapentaenoic acid; these nutrients likely underlie the CVD benefits from fish, Dr. Mozaffarian said in an interview with JAMA Internal Medicine that accompanied his commentary. (Dr. Mente also participated.)
“Fish oil lowers heart rate, blood pressure, and triglycerides (at high dosages), increases adiponectin, improves endothelial function, and in some studies improves oxygen consumption in myocardium. If there is benefit from fish it’s from the omega 3s, and all in all the evidence supports this,” but because the evidence is primarily observational, it can only show linkage and cannot prove causation, he explained.
Given the potential benefit and limited risk, “I think everyone should aim to eat two servings of fish each week, preferentially oily fish. That’s very solid,” said Dr. Mozaffarian, who is also a cardiologist and dean of the Tufts Friedman School of Nutrition Science.
The investigators did not have adequate data to compare the associations between outcomes and a diet with oily fish versus less oily fish.
OTC fish oil capsules are ‘very reasonable’
For people who either can’t consume two fish meals a week or want to ensure their omega 3 intake is adequate, “it’s very reasonable for the average person to take one OTC [over-the-counter] fish oil capsule a day,” Dr. Mozaffarian added.
He acknowledged that several studies of fish oil supplements failed to show benefit, but several others have. “It’s a confusing field, but the evidence supports benefit from omega 3s,” he concluded.
He discounted the new finding that only people with established CVD or who are at high-risk benefit. “I’m not sure we should make too much of this, because many prior studies showed a lower CVD risk in fish-eating people without prevalent CVD,” he said. The new study “provides important information given its worldwide breadth.”
The new report used data regarding 191,558 people enrolled prospectively in any of four studies. The average age of the participants was 54 years, and 52% were women.
During follow-up, death from any cause occurred in 6% of those without CVD or CVD risk and in 13% of those with these factors. Major CVD events occurred in 5% and 17% of these two subgroups, respectively. To calculate the relative risks between those who ate fish and those who did not, the investigators used standard multivariate adjustment for potential confounders and adjusted for several dietary variables, Dr. Mente said.
Dr. Mohan and Dr. Mente disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mozaffarian has received personal fees from Acasti Pharma, Amarin, America’s Test Kitchen, Barilla, Danone, GEOD, and Motif Food Works, and he has been an adviser to numerous companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with cardiovascular disease who regularly ate fish had significantly fewer major CVD events and there were fewer total deaths, compared with similar individuals who didn’t eat fish, but there was no beneficial link from eating fish among the general population in prospective data collected from more than 191,000 people from 58 countries.
Despite the neutral finding among people without CVD, the finding that eating fish was associated with significant benefit for those with CVD or who were at high risk for CVD confirms the public health importance of regular fish or fish oil consumption, said one expert.
A little over a quarter of those included in the new study had a history of CVD or were at high risk for CVD. In this subgroup of more than 51,000 people, those who consumed on average at least two servings of fish weekly (at least 175 g, or about 6.2 ounces per week) had a significant 16% lower rate of major CVD events during a median follow-up of about 7.5 years.
The rate of all-cause death was a significant 18% lower among people who ate two or more fish portions weekly, compared with those who didn’t, Deepa Mohan, PhD, and associates wrote in their report in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The researchers saw no additional benefit when people regularly ate greater amounts of fish.
“There is a significant protective benefit of fish consumption in people with cardiovascular disease,” said Andrew Mente, PhD, a senior investigator on the study and an epidemiologist at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont..
“This study has important implications for guidelines on fish intake globally. It indicates that increasing fish consumption and particularly oily fish in vascular patients may produce a modest cardiovascular benefit,” he said in a statement released by McMaster.
‘A large body of evidence’ for CVD benefit
The neutral finding of no significant benefit (as well as no harm) regarding either CVD events or total mortality among people without CVD “does not alter the large body of prior observational evidence supporting the cardiac benefits of fish intake in general populations,” noted Dariush Mozaffarian, MD, DrPH, in a commentary that accompanies the report by Dr. Mohan and colleagues.
Although the new analysis failed to show a significant association between regular fish consumption and fewer CVD events for people without established CVD or CVD risk, “based on the cumulative evidence from prospective observational studies, randomized clinical trials, and mechanistic and experimental studies, modest fish consumption appears to have some cardiac benefits,” he added.
“Adults should aim to consume about two servings of fish per week, and larger benefits may accrue from nonfried oily (dark meat) fish,” wrote Dr. Mozaffarian, a professor of medicine and nutrition at Tufts University, Boston.
Oily, dark fishes include salmon, tuna steak, mackerel, herring, and sardines. Species such as these contain the highest levels of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid, and docosapentaenoic acid; these nutrients likely underlie the CVD benefits from fish, Dr. Mozaffarian said in an interview with JAMA Internal Medicine that accompanied his commentary. (Dr. Mente also participated.)
“Fish oil lowers heart rate, blood pressure, and triglycerides (at high dosages), increases adiponectin, improves endothelial function, and in some studies improves oxygen consumption in myocardium. If there is benefit from fish it’s from the omega 3s, and all in all the evidence supports this,” but because the evidence is primarily observational, it can only show linkage and cannot prove causation, he explained.
Given the potential benefit and limited risk, “I think everyone should aim to eat two servings of fish each week, preferentially oily fish. That’s very solid,” said Dr. Mozaffarian, who is also a cardiologist and dean of the Tufts Friedman School of Nutrition Science.
The investigators did not have adequate data to compare the associations between outcomes and a diet with oily fish versus less oily fish.
OTC fish oil capsules are ‘very reasonable’
For people who either can’t consume two fish meals a week or want to ensure their omega 3 intake is adequate, “it’s very reasonable for the average person to take one OTC [over-the-counter] fish oil capsule a day,” Dr. Mozaffarian added.
He acknowledged that several studies of fish oil supplements failed to show benefit, but several others have. “It’s a confusing field, but the evidence supports benefit from omega 3s,” he concluded.
He discounted the new finding that only people with established CVD or who are at high-risk benefit. “I’m not sure we should make too much of this, because many prior studies showed a lower CVD risk in fish-eating people without prevalent CVD,” he said. The new study “provides important information given its worldwide breadth.”
The new report used data regarding 191,558 people enrolled prospectively in any of four studies. The average age of the participants was 54 years, and 52% were women.
During follow-up, death from any cause occurred in 6% of those without CVD or CVD risk and in 13% of those with these factors. Major CVD events occurred in 5% and 17% of these two subgroups, respectively. To calculate the relative risks between those who ate fish and those who did not, the investigators used standard multivariate adjustment for potential confounders and adjusted for several dietary variables, Dr. Mente said.
Dr. Mohan and Dr. Mente disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mozaffarian has received personal fees from Acasti Pharma, Amarin, America’s Test Kitchen, Barilla, Danone, GEOD, and Motif Food Works, and he has been an adviser to numerous companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Obesity: A ‘double hit’ in pregnant women with heart disease
Being obese and pregnant raises the risk for cardiac complications in women with preexisting heart disease, new research suggests, highlighting the need for earlier interventions in this high-risk population.
The analysis of 790 pregnancies revealed that 23% of women with obesity, defined as body mass index greater than 30 kg/m2, had a cardiac event during pregnancy versus 14% of women with normal body weight (P = .006).
The difference was driven largely by an increase in heart failure (8% vs. 3%; P = .02), although arrhythmias also trended higher in obese women (14% vs. 10%; P = .19).
Nearly half of the women with obesity and a cardiac event presented in the postpartum period (47%).
In multivariate analysis, both obesity and Canadian Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy Study (CARPREG) II risk score were independent predictors of cardiac events (odds ratios for both, 1.7), the investigators, led by Birgit Pfaller, MD, University of Toronto, reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Although obesity has been linked to worse pregnancy outcomes and higher cardiovascular risk after delivery in the general population, the authors noted that this is the first study to examine its effect on outcomes in women with heart disease.
“We wanted to look at this high-risk group of women that had preexisting heart disease, but in addition had obesity, to try and find out if there was a kind of double hit for these women – and that, in the end, is what we found. It’s not just simply having heart disease, not simply having obesity, but the combination that’s problematic,” senior author and cardiologist Candice Silversides, MD, University of Toronto, said in an interview.
The findings are concerning given the rising prevalence of obesity worldwide. National data from 2018 show that slightly more than half of women who gave birth in the United States were significantly overweight or obese before becoming pregnant.
Similarly, in the present analysis of 600 women in the CARPREG study who gave birth from 2004 to 2014, nearly 1 in 5 pregnancies (19%) occurred in women with obesity and 25% were in overweight women.
Obese women were significantly more likely than those without obesity to have coronary artery disease (6% vs. 2%), cardiomyopathies (19% vs. 8%) and left ventricular dysfunction (19% vs. 12%) and to be hypertensive or have a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (13% vs. 3%).
Preeclampsia developed in 32 women during the index pregnancy and 69% of these women were obese or overweight. Cardiac event rates were similar in women with or without preeclampsia but trended higher in women with preeclampsia with versus without obesity (36% vs. 14%; P = .20).
The ill effects of obesity were also reflected in fetal and neonatal events. Overall, 43% of women with obesity and 33% of normal-weight women had at least one fetal event (P = .02), with higher rates of preterm birth (19% vs. 10%; P = .005) and respiratory distress syndrome (8% vs. 3%; P = .02) in women with obesity. Congenital cardiac malformations were present in 6% of women in both groups.
Taken together, the composite of cardiac events, preeclampsia, or fetal events was significantly more common in women with obesity than in normal-weight women (56% vs. 41%; P = .002).
“We’ve spent the last number of years trying to research and understand what the drivers of these adverse outcomes are in this high-risk pregnant cohort, but on a bigger picture the real issue is how do we start intervening in a meaningful way,” Dr. Silversides said.
Like many in the burgeoning field of cardio-obstetrics, the team proposed a multidisciplinary approach that stresses preconception counseling, educating pregnant women with heart disease and obesity about their risks, ensuring that dietary advice, weight-gain recommendations, and comorbidities are addressed as part of routine care, and providing postpartum surveillance.
Preconception screening “has been the recommendation for a long, long time; it’s just that it doesn’t always happen in reality,” she said. “Many pregnancies aren’t planned and not all women are filtered into preconception counseling. So sometimes you’ll do it at the first antenatal visit and try to ensure women are educated but optimally you want to do it well in advance of pregnancy.”
Part of that preconception counseling “should also include giving them appropriate advice for contraception, if what they want to do is avoid pregnancy,” added Dr. Silversides.
Garima Sharma, MD, Ciccarone Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial that the adverse events observed in this high-risk cohort have “important implications for cardio-obstetricians and should be incorporated in routine prepregnancy and antenatal counseling, monitoring, and risk stratification for women with existing cardiovascular disease.”
They pointed to a paucity of data incorporating maternal prepregnancy obesity and gestational weight gain in risk prediction and called for larger population-based studies on the additive impact of obesity severity on predicting adverse cardiac events in women with existing cardiovascular disease.
Randomized trials are also urgently needed to evaluate the effect of nutritional and behavioral interventions in pregnancy on short- and long-term outcomes in mother and child.
“As the obesity epidemic continues to grow and public health interventions promoting lifestyle changes for obesity management remain a major challenge, maternal obesity may prove to be the ‘Achilles’ heel’ of sustainable national efforts to reduce maternal mortality and improve health equity. This is a call to action,” Dr. Sharma and colleagues concluded.
The investigators noted that the study was conducted at a single center and used self-reported pregnancy weight collected at the first antenatal visit, which may have underestimated obesity rates. Other limitations are that weight changes over the course of pregnancy were not studied and there was a limited number of women with a body mass index of 40 or higher.
The study was supported by a grant from the Allan E. Tiffin Trust, Toronto General and Western Hospital Foundation, and by a donation from Mrs. Josephine Rogers, Toronto General Hospital. Dr. Silversides is supported by the Miles Nadal Chair in Pregnancy and Heart Disease. Dr. Sharma and colleagues disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Being obese and pregnant raises the risk for cardiac complications in women with preexisting heart disease, new research suggests, highlighting the need for earlier interventions in this high-risk population.
The analysis of 790 pregnancies revealed that 23% of women with obesity, defined as body mass index greater than 30 kg/m2, had a cardiac event during pregnancy versus 14% of women with normal body weight (P = .006).
The difference was driven largely by an increase in heart failure (8% vs. 3%; P = .02), although arrhythmias also trended higher in obese women (14% vs. 10%; P = .19).
Nearly half of the women with obesity and a cardiac event presented in the postpartum period (47%).
In multivariate analysis, both obesity and Canadian Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy Study (CARPREG) II risk score were independent predictors of cardiac events (odds ratios for both, 1.7), the investigators, led by Birgit Pfaller, MD, University of Toronto, reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Although obesity has been linked to worse pregnancy outcomes and higher cardiovascular risk after delivery in the general population, the authors noted that this is the first study to examine its effect on outcomes in women with heart disease.
“We wanted to look at this high-risk group of women that had preexisting heart disease, but in addition had obesity, to try and find out if there was a kind of double hit for these women – and that, in the end, is what we found. It’s not just simply having heart disease, not simply having obesity, but the combination that’s problematic,” senior author and cardiologist Candice Silversides, MD, University of Toronto, said in an interview.
The findings are concerning given the rising prevalence of obesity worldwide. National data from 2018 show that slightly more than half of women who gave birth in the United States were significantly overweight or obese before becoming pregnant.
Similarly, in the present analysis of 600 women in the CARPREG study who gave birth from 2004 to 2014, nearly 1 in 5 pregnancies (19%) occurred in women with obesity and 25% were in overweight women.
Obese women were significantly more likely than those without obesity to have coronary artery disease (6% vs. 2%), cardiomyopathies (19% vs. 8%) and left ventricular dysfunction (19% vs. 12%) and to be hypertensive or have a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (13% vs. 3%).
Preeclampsia developed in 32 women during the index pregnancy and 69% of these women were obese or overweight. Cardiac event rates were similar in women with or without preeclampsia but trended higher in women with preeclampsia with versus without obesity (36% vs. 14%; P = .20).
The ill effects of obesity were also reflected in fetal and neonatal events. Overall, 43% of women with obesity and 33% of normal-weight women had at least one fetal event (P = .02), with higher rates of preterm birth (19% vs. 10%; P = .005) and respiratory distress syndrome (8% vs. 3%; P = .02) in women with obesity. Congenital cardiac malformations were present in 6% of women in both groups.
Taken together, the composite of cardiac events, preeclampsia, or fetal events was significantly more common in women with obesity than in normal-weight women (56% vs. 41%; P = .002).
“We’ve spent the last number of years trying to research and understand what the drivers of these adverse outcomes are in this high-risk pregnant cohort, but on a bigger picture the real issue is how do we start intervening in a meaningful way,” Dr. Silversides said.
Like many in the burgeoning field of cardio-obstetrics, the team proposed a multidisciplinary approach that stresses preconception counseling, educating pregnant women with heart disease and obesity about their risks, ensuring that dietary advice, weight-gain recommendations, and comorbidities are addressed as part of routine care, and providing postpartum surveillance.
Preconception screening “has been the recommendation for a long, long time; it’s just that it doesn’t always happen in reality,” she said. “Many pregnancies aren’t planned and not all women are filtered into preconception counseling. So sometimes you’ll do it at the first antenatal visit and try to ensure women are educated but optimally you want to do it well in advance of pregnancy.”
Part of that preconception counseling “should also include giving them appropriate advice for contraception, if what they want to do is avoid pregnancy,” added Dr. Silversides.
Garima Sharma, MD, Ciccarone Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial that the adverse events observed in this high-risk cohort have “important implications for cardio-obstetricians and should be incorporated in routine prepregnancy and antenatal counseling, monitoring, and risk stratification for women with existing cardiovascular disease.”
They pointed to a paucity of data incorporating maternal prepregnancy obesity and gestational weight gain in risk prediction and called for larger population-based studies on the additive impact of obesity severity on predicting adverse cardiac events in women with existing cardiovascular disease.
Randomized trials are also urgently needed to evaluate the effect of nutritional and behavioral interventions in pregnancy on short- and long-term outcomes in mother and child.
“As the obesity epidemic continues to grow and public health interventions promoting lifestyle changes for obesity management remain a major challenge, maternal obesity may prove to be the ‘Achilles’ heel’ of sustainable national efforts to reduce maternal mortality and improve health equity. This is a call to action,” Dr. Sharma and colleagues concluded.
The investigators noted that the study was conducted at a single center and used self-reported pregnancy weight collected at the first antenatal visit, which may have underestimated obesity rates. Other limitations are that weight changes over the course of pregnancy were not studied and there was a limited number of women with a body mass index of 40 or higher.
The study was supported by a grant from the Allan E. Tiffin Trust, Toronto General and Western Hospital Foundation, and by a donation from Mrs. Josephine Rogers, Toronto General Hospital. Dr. Silversides is supported by the Miles Nadal Chair in Pregnancy and Heart Disease. Dr. Sharma and colleagues disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Being obese and pregnant raises the risk for cardiac complications in women with preexisting heart disease, new research suggests, highlighting the need for earlier interventions in this high-risk population.
The analysis of 790 pregnancies revealed that 23% of women with obesity, defined as body mass index greater than 30 kg/m2, had a cardiac event during pregnancy versus 14% of women with normal body weight (P = .006).
The difference was driven largely by an increase in heart failure (8% vs. 3%; P = .02), although arrhythmias also trended higher in obese women (14% vs. 10%; P = .19).
Nearly half of the women with obesity and a cardiac event presented in the postpartum period (47%).
In multivariate analysis, both obesity and Canadian Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy Study (CARPREG) II risk score were independent predictors of cardiac events (odds ratios for both, 1.7), the investigators, led by Birgit Pfaller, MD, University of Toronto, reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Although obesity has been linked to worse pregnancy outcomes and higher cardiovascular risk after delivery in the general population, the authors noted that this is the first study to examine its effect on outcomes in women with heart disease.
“We wanted to look at this high-risk group of women that had preexisting heart disease, but in addition had obesity, to try and find out if there was a kind of double hit for these women – and that, in the end, is what we found. It’s not just simply having heart disease, not simply having obesity, but the combination that’s problematic,” senior author and cardiologist Candice Silversides, MD, University of Toronto, said in an interview.
The findings are concerning given the rising prevalence of obesity worldwide. National data from 2018 show that slightly more than half of women who gave birth in the United States were significantly overweight or obese before becoming pregnant.
Similarly, in the present analysis of 600 women in the CARPREG study who gave birth from 2004 to 2014, nearly 1 in 5 pregnancies (19%) occurred in women with obesity and 25% were in overweight women.
Obese women were significantly more likely than those without obesity to have coronary artery disease (6% vs. 2%), cardiomyopathies (19% vs. 8%) and left ventricular dysfunction (19% vs. 12%) and to be hypertensive or have a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (13% vs. 3%).
Preeclampsia developed in 32 women during the index pregnancy and 69% of these women were obese or overweight. Cardiac event rates were similar in women with or without preeclampsia but trended higher in women with preeclampsia with versus without obesity (36% vs. 14%; P = .20).
The ill effects of obesity were also reflected in fetal and neonatal events. Overall, 43% of women with obesity and 33% of normal-weight women had at least one fetal event (P = .02), with higher rates of preterm birth (19% vs. 10%; P = .005) and respiratory distress syndrome (8% vs. 3%; P = .02) in women with obesity. Congenital cardiac malformations were present in 6% of women in both groups.
Taken together, the composite of cardiac events, preeclampsia, or fetal events was significantly more common in women with obesity than in normal-weight women (56% vs. 41%; P = .002).
“We’ve spent the last number of years trying to research and understand what the drivers of these adverse outcomes are in this high-risk pregnant cohort, but on a bigger picture the real issue is how do we start intervening in a meaningful way,” Dr. Silversides said.
Like many in the burgeoning field of cardio-obstetrics, the team proposed a multidisciplinary approach that stresses preconception counseling, educating pregnant women with heart disease and obesity about their risks, ensuring that dietary advice, weight-gain recommendations, and comorbidities are addressed as part of routine care, and providing postpartum surveillance.
Preconception screening “has been the recommendation for a long, long time; it’s just that it doesn’t always happen in reality,” she said. “Many pregnancies aren’t planned and not all women are filtered into preconception counseling. So sometimes you’ll do it at the first antenatal visit and try to ensure women are educated but optimally you want to do it well in advance of pregnancy.”
Part of that preconception counseling “should also include giving them appropriate advice for contraception, if what they want to do is avoid pregnancy,” added Dr. Silversides.
Garima Sharma, MD, Ciccarone Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial that the adverse events observed in this high-risk cohort have “important implications for cardio-obstetricians and should be incorporated in routine prepregnancy and antenatal counseling, monitoring, and risk stratification for women with existing cardiovascular disease.”
They pointed to a paucity of data incorporating maternal prepregnancy obesity and gestational weight gain in risk prediction and called for larger population-based studies on the additive impact of obesity severity on predicting adverse cardiac events in women with existing cardiovascular disease.
Randomized trials are also urgently needed to evaluate the effect of nutritional and behavioral interventions in pregnancy on short- and long-term outcomes in mother and child.
“As the obesity epidemic continues to grow and public health interventions promoting lifestyle changes for obesity management remain a major challenge, maternal obesity may prove to be the ‘Achilles’ heel’ of sustainable national efforts to reduce maternal mortality and improve health equity. This is a call to action,” Dr. Sharma and colleagues concluded.
The investigators noted that the study was conducted at a single center and used self-reported pregnancy weight collected at the first antenatal visit, which may have underestimated obesity rates. Other limitations are that weight changes over the course of pregnancy were not studied and there was a limited number of women with a body mass index of 40 or higher.
The study was supported by a grant from the Allan E. Tiffin Trust, Toronto General and Western Hospital Foundation, and by a donation from Mrs. Josephine Rogers, Toronto General Hospital. Dr. Silversides is supported by the Miles Nadal Chair in Pregnancy and Heart Disease. Dr. Sharma and colleagues disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide for meaningful weight loss in obesity and diabetes?
A 2.4-mg weekly injection of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist semaglutide led to a clinically meaningful 5% loss in weight for roughly two-thirds of patients with both overweight/obesity and type 2 diabetes, researchers report.
These findings from the Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People With Obesity 2 (STEP 2) trial, one of four phase 3 trials of this drug, which is currently under regulatory review for weight loss, were published March 2 in The Lancet.
More than 1,000 patients (mean initial weight, 100 kg [220 pounds]) were randomly assigned to receive a lifestyle intervention plus a weekly injection of semaglutide 2.4 mg or semaglutide 1.0 mg or placebo. At 68 weeks, they had lost a mean of 9.6%, 7.0%, and 3.4%, respectively, of their starting weight.
In addition, 69% of patients who had received semaglutide 2.4 mg experienced a clinically meaningful 5% loss of weight, compared with 57% of patients who had received the lower dose and 29% of patients who had received placebo.
The higher dose of semaglutide was associated with a greater improvement in cardiometabolic risk factors. The safety profile was similar to that seen with other drugs in this class.
“By far the best results with any weight loss medicine in diabetes”
Importantly, “more than a quarter of participants lost over 15% of their body weight,” senior author Ildiko Lingvay, MD, stressed. This “is by far the best result we had with any weight loss medicine in patients with diabetes,” Dr. Lingvay, of the University of Texas, Dallas, said in a statement from the university.
“The drug works by suppressing appetite centers in the brain to reduce caloric intake,” she explained. “The medication continually tells the body that you just ate, you’re full.”
Similarly, lead author Melanie J. Davies, MD, said that the STEP 2 results “are exciting and represent a new era in weight management in people with type 2 diabetes.
“They mark a real paradigm shift in our ability to treat obesity,” with results closer to those achieved with bariatric surgery, Dr. Davies, of the University of Leicester, England, said in a statement from her institution.
“It is really encouraging,” she continued, “that along with the weight loss we saw real improvements in general health, with significant improvement in physical functioning scores, blood pressure, and blood glucose control.”
Dr. Lingvay noted that on average, patients in the four STEP clinical trials lost 10%-17% of their body weight, “which is a huge step forward compared with all other medications currently available to treat obesity.” She stressed that these results are comparable to the 20%-30% weight loss seen with bariatric surgery.
One of four trials under review
More than 90% of people with type 2 diabetes are overweight or have obesity, and more than 20% of people with obesity have diabetes, wrote Dr. Davies and colleagues.
Semaglutide (Ozempic), administered subcutaneously at a dose of 0.5 mg to 1 mg weekly, is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Dosing studies indicated that it is associated with weight loss.
As previously reported, four trials of the use of semaglutide for weight loss (STEP 1, 2, 3, and 4) have been completed. The combined data were submitted to the FDA on Dec. 4, 2020 (a decision is expected within 6 months) and to the European Medicines Agency on Dec. 18, 2020.
The STEP 1 and STEP 3 trials of semaglutide 2.4 mg vs. placebo were recently published. The STEP 1 trial involved 1,961 adults with obesity or overweight; the STEP 3 trial, 611 adults with obesity or overweight. In each of the trials, some patients also underwent an intensive lifestyle intervention, and some did not. In both trials, patients with type 2 diabetes were excluded.
Topline results from STEP 2 were reported in June 2020.
STEP 2 enrolled patients with type 2 diabetes
STEP 2 involved 1,210 adults in 149 outpatient clinics in 12 countries in Europe, North America, South America, the Middle East, South Africa, and Asia. All participants had type 2 diabetes.
For all patients, the body mass index was ≥27 kg/m2, and the A1c concentration was 7%-10%. The mean BMI was 35.7 kg/m2, and the mean A1c was 8.1%.
The mean age of the patients was 55 years, and 51% were women; 62% were White, 26% were Asian, 13% were Hispanic, 8% were Black, and 4% were of other ethnicity.
Participants were managed with diet and exercise alone or underwent treatment with a stable dose of up to three oral glucose-lowering agents (metformin, sulfonylureas, SGLT2 inhibitors, or thiazolidinediones) for at least 90 days. They were then randomly assigned in 1:1:1 ratio to receive semaglutide 2.4 mg, semaglutide 1.0 mg, or placebo.
The starting dose of semaglutide was 0.25 mg/wk; the dose was escalated every 4 weeks to reach the target dose.
All patients received monthly counseling from a dietitian about calories (the goal was a 500-calorie/day deficit) and activity (the goal was 150 minutes of walking or stair climbing per week).
The mean A1c dropped by 1.6% and 1.5% in the semaglutide groups and by 0.4% in the placebo group.
Adverse events were more frequent among the patients who received semaglutide (88% and 82%) than in the placebo group (77%).
Gastrointestinal events that were mainly mild to moderate in severity were reported by 64% of patients in the 2.4-mg semaglutide group, 58% in the 1.0-mg semaglutide group, and 34% in the placebo group.
Semaglutide (Rybelsus) is approved in the United States as a once-daily oral agent for use in type 2 diabetes in doses of 7 mg and 14 mg to improve glycemic control along with diet and exercise. It is the first GLP-1 agonist available in tablet form.
The study was supported by Novo Nordisk. The authors’ relevant financial relationships are listed in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 2.4-mg weekly injection of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist semaglutide led to a clinically meaningful 5% loss in weight for roughly two-thirds of patients with both overweight/obesity and type 2 diabetes, researchers report.
These findings from the Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People With Obesity 2 (STEP 2) trial, one of four phase 3 trials of this drug, which is currently under regulatory review for weight loss, were published March 2 in The Lancet.
More than 1,000 patients (mean initial weight, 100 kg [220 pounds]) were randomly assigned to receive a lifestyle intervention plus a weekly injection of semaglutide 2.4 mg or semaglutide 1.0 mg or placebo. At 68 weeks, they had lost a mean of 9.6%, 7.0%, and 3.4%, respectively, of their starting weight.
In addition, 69% of patients who had received semaglutide 2.4 mg experienced a clinically meaningful 5% loss of weight, compared with 57% of patients who had received the lower dose and 29% of patients who had received placebo.
The higher dose of semaglutide was associated with a greater improvement in cardiometabolic risk factors. The safety profile was similar to that seen with other drugs in this class.
“By far the best results with any weight loss medicine in diabetes”
Importantly, “more than a quarter of participants lost over 15% of their body weight,” senior author Ildiko Lingvay, MD, stressed. This “is by far the best result we had with any weight loss medicine in patients with diabetes,” Dr. Lingvay, of the University of Texas, Dallas, said in a statement from the university.
“The drug works by suppressing appetite centers in the brain to reduce caloric intake,” she explained. “The medication continually tells the body that you just ate, you’re full.”
Similarly, lead author Melanie J. Davies, MD, said that the STEP 2 results “are exciting and represent a new era in weight management in people with type 2 diabetes.
“They mark a real paradigm shift in our ability to treat obesity,” with results closer to those achieved with bariatric surgery, Dr. Davies, of the University of Leicester, England, said in a statement from her institution.
“It is really encouraging,” she continued, “that along with the weight loss we saw real improvements in general health, with significant improvement in physical functioning scores, blood pressure, and blood glucose control.”
Dr. Lingvay noted that on average, patients in the four STEP clinical trials lost 10%-17% of their body weight, “which is a huge step forward compared with all other medications currently available to treat obesity.” She stressed that these results are comparable to the 20%-30% weight loss seen with bariatric surgery.
One of four trials under review
More than 90% of people with type 2 diabetes are overweight or have obesity, and more than 20% of people with obesity have diabetes, wrote Dr. Davies and colleagues.
Semaglutide (Ozempic), administered subcutaneously at a dose of 0.5 mg to 1 mg weekly, is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Dosing studies indicated that it is associated with weight loss.
As previously reported, four trials of the use of semaglutide for weight loss (STEP 1, 2, 3, and 4) have been completed. The combined data were submitted to the FDA on Dec. 4, 2020 (a decision is expected within 6 months) and to the European Medicines Agency on Dec. 18, 2020.
The STEP 1 and STEP 3 trials of semaglutide 2.4 mg vs. placebo were recently published. The STEP 1 trial involved 1,961 adults with obesity or overweight; the STEP 3 trial, 611 adults with obesity or overweight. In each of the trials, some patients also underwent an intensive lifestyle intervention, and some did not. In both trials, patients with type 2 diabetes were excluded.
Topline results from STEP 2 were reported in June 2020.
STEP 2 enrolled patients with type 2 diabetes
STEP 2 involved 1,210 adults in 149 outpatient clinics in 12 countries in Europe, North America, South America, the Middle East, South Africa, and Asia. All participants had type 2 diabetes.
For all patients, the body mass index was ≥27 kg/m2, and the A1c concentration was 7%-10%. The mean BMI was 35.7 kg/m2, and the mean A1c was 8.1%.
The mean age of the patients was 55 years, and 51% were women; 62% were White, 26% were Asian, 13% were Hispanic, 8% were Black, and 4% were of other ethnicity.
Participants were managed with diet and exercise alone or underwent treatment with a stable dose of up to three oral glucose-lowering agents (metformin, sulfonylureas, SGLT2 inhibitors, or thiazolidinediones) for at least 90 days. They were then randomly assigned in 1:1:1 ratio to receive semaglutide 2.4 mg, semaglutide 1.0 mg, or placebo.
The starting dose of semaglutide was 0.25 mg/wk; the dose was escalated every 4 weeks to reach the target dose.
All patients received monthly counseling from a dietitian about calories (the goal was a 500-calorie/day deficit) and activity (the goal was 150 minutes of walking or stair climbing per week).
The mean A1c dropped by 1.6% and 1.5% in the semaglutide groups and by 0.4% in the placebo group.
Adverse events were more frequent among the patients who received semaglutide (88% and 82%) than in the placebo group (77%).
Gastrointestinal events that were mainly mild to moderate in severity were reported by 64% of patients in the 2.4-mg semaglutide group, 58% in the 1.0-mg semaglutide group, and 34% in the placebo group.
Semaglutide (Rybelsus) is approved in the United States as a once-daily oral agent for use in type 2 diabetes in doses of 7 mg and 14 mg to improve glycemic control along with diet and exercise. It is the first GLP-1 agonist available in tablet form.
The study was supported by Novo Nordisk. The authors’ relevant financial relationships are listed in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 2.4-mg weekly injection of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist semaglutide led to a clinically meaningful 5% loss in weight for roughly two-thirds of patients with both overweight/obesity and type 2 diabetes, researchers report.
These findings from the Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People With Obesity 2 (STEP 2) trial, one of four phase 3 trials of this drug, which is currently under regulatory review for weight loss, were published March 2 in The Lancet.
More than 1,000 patients (mean initial weight, 100 kg [220 pounds]) were randomly assigned to receive a lifestyle intervention plus a weekly injection of semaglutide 2.4 mg or semaglutide 1.0 mg or placebo. At 68 weeks, they had lost a mean of 9.6%, 7.0%, and 3.4%, respectively, of their starting weight.
In addition, 69% of patients who had received semaglutide 2.4 mg experienced a clinically meaningful 5% loss of weight, compared with 57% of patients who had received the lower dose and 29% of patients who had received placebo.
The higher dose of semaglutide was associated with a greater improvement in cardiometabolic risk factors. The safety profile was similar to that seen with other drugs in this class.
“By far the best results with any weight loss medicine in diabetes”
Importantly, “more than a quarter of participants lost over 15% of their body weight,” senior author Ildiko Lingvay, MD, stressed. This “is by far the best result we had with any weight loss medicine in patients with diabetes,” Dr. Lingvay, of the University of Texas, Dallas, said in a statement from the university.
“The drug works by suppressing appetite centers in the brain to reduce caloric intake,” she explained. “The medication continually tells the body that you just ate, you’re full.”
Similarly, lead author Melanie J. Davies, MD, said that the STEP 2 results “are exciting and represent a new era in weight management in people with type 2 diabetes.
“They mark a real paradigm shift in our ability to treat obesity,” with results closer to those achieved with bariatric surgery, Dr. Davies, of the University of Leicester, England, said in a statement from her institution.
“It is really encouraging,” she continued, “that along with the weight loss we saw real improvements in general health, with significant improvement in physical functioning scores, blood pressure, and blood glucose control.”
Dr. Lingvay noted that on average, patients in the four STEP clinical trials lost 10%-17% of their body weight, “which is a huge step forward compared with all other medications currently available to treat obesity.” She stressed that these results are comparable to the 20%-30% weight loss seen with bariatric surgery.
One of four trials under review
More than 90% of people with type 2 diabetes are overweight or have obesity, and more than 20% of people with obesity have diabetes, wrote Dr. Davies and colleagues.
Semaglutide (Ozempic), administered subcutaneously at a dose of 0.5 mg to 1 mg weekly, is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Dosing studies indicated that it is associated with weight loss.
As previously reported, four trials of the use of semaglutide for weight loss (STEP 1, 2, 3, and 4) have been completed. The combined data were submitted to the FDA on Dec. 4, 2020 (a decision is expected within 6 months) and to the European Medicines Agency on Dec. 18, 2020.
The STEP 1 and STEP 3 trials of semaglutide 2.4 mg vs. placebo were recently published. The STEP 1 trial involved 1,961 adults with obesity or overweight; the STEP 3 trial, 611 adults with obesity or overweight. In each of the trials, some patients also underwent an intensive lifestyle intervention, and some did not. In both trials, patients with type 2 diabetes were excluded.
Topline results from STEP 2 were reported in June 2020.
STEP 2 enrolled patients with type 2 diabetes
STEP 2 involved 1,210 adults in 149 outpatient clinics in 12 countries in Europe, North America, South America, the Middle East, South Africa, and Asia. All participants had type 2 diabetes.
For all patients, the body mass index was ≥27 kg/m2, and the A1c concentration was 7%-10%. The mean BMI was 35.7 kg/m2, and the mean A1c was 8.1%.
The mean age of the patients was 55 years, and 51% were women; 62% were White, 26% were Asian, 13% were Hispanic, 8% were Black, and 4% were of other ethnicity.
Participants were managed with diet and exercise alone or underwent treatment with a stable dose of up to three oral glucose-lowering agents (metformin, sulfonylureas, SGLT2 inhibitors, or thiazolidinediones) for at least 90 days. They were then randomly assigned in 1:1:1 ratio to receive semaglutide 2.4 mg, semaglutide 1.0 mg, or placebo.
The starting dose of semaglutide was 0.25 mg/wk; the dose was escalated every 4 weeks to reach the target dose.
All patients received monthly counseling from a dietitian about calories (the goal was a 500-calorie/day deficit) and activity (the goal was 150 minutes of walking or stair climbing per week).
The mean A1c dropped by 1.6% and 1.5% in the semaglutide groups and by 0.4% in the placebo group.
Adverse events were more frequent among the patients who received semaglutide (88% and 82%) than in the placebo group (77%).
Gastrointestinal events that were mainly mild to moderate in severity were reported by 64% of patients in the 2.4-mg semaglutide group, 58% in the 1.0-mg semaglutide group, and 34% in the placebo group.
Semaglutide (Rybelsus) is approved in the United States as a once-daily oral agent for use in type 2 diabetes in doses of 7 mg and 14 mg to improve glycemic control along with diet and exercise. It is the first GLP-1 agonist available in tablet form.
The study was supported by Novo Nordisk. The authors’ relevant financial relationships are listed in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How to convince patients muscle pain isn’t a statin Achilles heel: StatinWISE
Another randomized trial, on the heels of the recently published SAMSON, has concluded – many would say confirmed – that .
Affected patients who sorely doubt that conclusion might possibly embrace statins, researchers say, if the new trial’s creative methodology could somehow be applied to them in clinical practice.
The recent SAMSON trial made waves in November 2020 by concluding, with some caveats, that about 90% of the burden of muscle symptoms reported by patients on statins may be attributable to a nocebo effect; that is, they are attributed to the drugs – perhaps because of negative expectations – but not actually caused by them.
The new trial, StatinWISE (Statin Web-based Investigation of Side Effects), triple the size but similar in design and conducted parallel to SAMSON, similarly saw no important differences in patient-reported muscle symptom prevalence or severity during administration of atorvastatin 20 mg/day or placebo, in withdrawal from the study because of such symptoms, or in patient quality of life.
The findings also support years of observational evidence that argues against a statin effect on muscle symptoms except in rare cases of confirmed myopathy, as well as results from randomized trials like ODYSSEY ALTERNATIVE and GAUSS-3, in which significant muscle symptoms in “statin-intolerant” patients were unusual, note StatinWISE investigators in their report, published online Feb. 24 in BMJ, with lead author Emily Herrett, MSc, PhD, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
“I’m hoping it can change minds a bit and reassure people. That was part of the reason we did it, to inform this debate about harms and benefits of statins,” principal investigator Liam Smeeth, MBChB, MSc, PhD, from the same institution, said during a virtual press conference on the trial conducted by the U.K. nonprofit Science Media Centre.
“In thinking through whether to take a statin or not, people can be reassured that these muscle symptoms are rare; they aren’t common. Aches and pains are common, but are not caused by statins,” said Dr. Smeeth, who is senior author on the trial publication.
Another goal of the 200-patient study, he said, was to explore whether patients who had experienced muscle symptoms on a statin but were willing to explore whether the statin was to blame could be convinced – depending on what they learned in the trial – to stay on the drugs.
It seemed to work; two-thirds of the participants who finished the study “decided that they would actually want to try starting statins again, which was quite amazing.”
But there was a “slight caveat,” Dr. Smeeth observed. “To join our trial, yes, you had to have had a bad experience with statins, but you probably had to be a little bit open to the idea of trying them again. So, I can’t claim that that two-thirds would apply to everybody in the population.”
Because StatinWISE entered only patients who had reported severe muscle symptoms on a statin but hadn’t showed significant enzymatic evidence of myopathy, all had either taken themselves off the statin or were “considering” it. And the study had excluded anyone with “persistent, generalized, unexplained muscle pain” regardless of any statin therapy.
“This was very deliberately a select group of people who had serious problems taking statins. This was not a random sample by any means,” Dr. Smeeth said.
“The patients in the study were willing to participate and take statins again,” suggesting they “may not be completely representative of all those who believe they experience side effects with statins, as anyone who refused to take statins ever again would not have been recruited,” observed Tim Chico, MBChB, MD, University of Sheffield (England) in a Science Media Centre press release on StatinWISE.
Still, even among this “supersaturated group of people” selected for having had muscle symptoms on statins, Dr. Smeeth said at the briefing, “in almost all cases, their pains and aches were no worse on statins than they were on placebo. We’re not saying that anyone is making up their aches and pains. These are real aches and pains. What we’re showing very clearly is that those aches and pains are no worse on statins than they are on placebo.”
Rechallenge is possible
Some people are more likely than others to experience adverse reactions to any drug, “and that’s true of statins,” Neil J. Stone, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, told this news organization. But StatinWISE underscores that many patients with muscle symptoms on the drugs can be convinced to continue with them rather than stop them entirely.
“The study didn’t say that everybody who has symptoms on a statin is having a nocebo effect,” said Dr. Stone, vice chair for the multisociety 2018 Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol, who was not involved with StatinWISE.
“It simply said,” allowing for some caveats, “that a significant number of patients may have symptoms that don’t preclude them from being rechallenged with a statin again, once they understand what this nocebo effect is.”
And, Dr. Stone said, “it amplifies the 2018 guidelines, with their emphasis on the clinician-patient discussion before starting therapy,” by showing that statin-associated muscle pain isn’t necessarily caused by the drugs and isn’t a reason to stop them.
“That there is a second study confirming SAMSON is helpful, and the results are helpful because they say many of these patients, once they are shown the results, can be rechallenged and will then tolerate statins,” Steven E. Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“They were able to get two-thirds of those completing the trial into long-term treatment, which I think is obviously very admirable and very important,” said Dr. Nissen, who was GAUSS-3 principal investigator but not associated with StatinWISE.
“I think it is important, however, that we not completely dismiss patients who complain of adverse effects. Because, in fact, there probably are some people who do have muscle-related symptoms,” he said. “But you know, to really call somebody statin intolerant, they really should fail three statins, which would be a very good standard.”
In his experience, said Patrick M. Moriarty, MD, who directs the Atherosclerosis & Lipoprotein-Apheresis Center at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, perhaps 80%-90% of patients who believe they are statin intolerant because of muscle symptoms are actually not statin intolerant at all.
“I think a massive amount of it is supratentorial,” Dr. Moriarty, who was not part of StatinWISE, told this news organization. It comes directly from “what they heard, what they read, or what they were told – and at their age, they’re going to have aches and pains.”
Value of the n-of-1 trial
Dr. Smeeth and colleagues framed StatinWISE in part as a test of a strategy for overcoming nocebo-based aversion to statins. One goal was to see whether these methods might be helpful in practice for convincing patients who want to reject statins because of muscle symptoms to give the drugs another chance.
In StatinWISE, patients were individually assigned to take atorvastatin or placebo in randomized order with multiple blinding during each of six successive 2-month periods, so that they were on one or the other agent half the time. They rated their symptoms at the end of each period.
So the trial in composite was, as the publication states, “a series of randomized, placebo-controlled n-of-1 trials.” SAMSON followed a similar scheme, except – as previously reported – it had specified 4 months of atorvastatin, 4 months of placebo, and 4 months with patients on neither statin nor placebo.
StatinWISE “provides a useful approach (the n = 1 study) that could be used in real life to help patients understand the cause of their own possible side effects, which could also be applied to medications other than statins,” Dr. Chico added in the Science Media Centre release.
“I often encounter people who have a firmly held view that statins cause muscle pains, even when they haven’t taken these medications themselves, and I hope that this study may help change this view and make them willing to try such an ‘experiment,’ ” he said.
Others aren’t sure an experiment resembling an n-of-1 trial would be practical or effective when conducted in routine practice.
More efficient and useful, Dr. Moriarty noted, would be for physicians to nurture a close relationship with patients, one that could help transform their negative feelings about statins into a willingness to accept the drugs. “This is a trust you have to build; these are human beings.”
He said getting the patient’s confidence is critical. “You have to explain the pluses and minuses of getting treatment, of the 30% reduction in cardiovascular events that occur with the statin. You don’t go ‘testing this and that.’ I think it’s more about getting them on board.”
No statin effect on muscle symptoms
Patients in StatinWISE were recruited from 50 primary care practices in England and Wales from December 2016 to April 2018, the report notes; their mean age was 69 years, and 58% were men. Of the 200 patients, 151 recorded muscle-symptom scores for at least one statin period and one placebo period, and so were included in the primary-endpoint assessment.
The mean muscle symptom score was lower on statin therapy than on placebo (1.68 vs. 2.57), but there was no significant difference in adjusted analysis (mean difference, –0.11 (95% confidence interval, –0.36 to 0.14; P = .40).
Statins showed no significant effect on development of muscle symptoms overall, it was reported, with an odds ratio of 1.11 (99% confidence interval, 0.62-1.99). Nor was there an effect on “muscle symptoms that could not be attributed to another cause,” (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.77-1.94).
Of the 80 withdrawals during the study for any reason, 43% occurred when the patient was on the statin, 49% when the patient was on placebo, and 9% after randomization but before either statin or placebo had been initiated. Of those, 33 were because of “intolerable muscle symptoms,” says the report. But withdrawal occurred about as often on statin therapy as off the drug – 9% and 7%, respectively – throughout the 1-year study.
“This study provides further evidence through the lived experience of individuals that muscle pains often attributed to statins are not due to the drug,” said Sir Nilesh J. Samani, MBChB, MD, medical director for the British Heart Foundation, as quoted in the Science Media Centre press release.
“The use of each patient as their own control in the trial provides a powerful way of distinguishing the effect of a statin from that of taking a pill,” he said. “The findings should give confidence to patients who may be concerned about taking statins.”
StatinWISE was funded by the National Institute for Health Research-Health Technology Program and sponsored by the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. The authors declare that they have “no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.” Dr. Smeeth reports receiving grants from GlaxoSmithKline, and personal fees for advisory work from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Stone reports no industry relationships or other disclosures. Dr. Nissen reports that his center has received funding for clinical trials from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Cerenis, Eli Lilly, Esperion, Medtronic, MyoKardia, Novartis, Orexigen, Pfizer, Takeda, The Medicines Company, and Silence Therapeutics; that he is involved in these trials but receives no personal remuneration; and that he consults for many pharmaceutical companies but requires them to donate all honoraria or fees directly to charity so that he receives neither income nor a tax deduction. Dr. Chico had no conflicts. Dr. Moriarty declared no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Samani had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Another randomized trial, on the heels of the recently published SAMSON, has concluded – many would say confirmed – that .
Affected patients who sorely doubt that conclusion might possibly embrace statins, researchers say, if the new trial’s creative methodology could somehow be applied to them in clinical practice.
The recent SAMSON trial made waves in November 2020 by concluding, with some caveats, that about 90% of the burden of muscle symptoms reported by patients on statins may be attributable to a nocebo effect; that is, they are attributed to the drugs – perhaps because of negative expectations – but not actually caused by them.
The new trial, StatinWISE (Statin Web-based Investigation of Side Effects), triple the size but similar in design and conducted parallel to SAMSON, similarly saw no important differences in patient-reported muscle symptom prevalence or severity during administration of atorvastatin 20 mg/day or placebo, in withdrawal from the study because of such symptoms, or in patient quality of life.
The findings also support years of observational evidence that argues against a statin effect on muscle symptoms except in rare cases of confirmed myopathy, as well as results from randomized trials like ODYSSEY ALTERNATIVE and GAUSS-3, in which significant muscle symptoms in “statin-intolerant” patients were unusual, note StatinWISE investigators in their report, published online Feb. 24 in BMJ, with lead author Emily Herrett, MSc, PhD, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
“I’m hoping it can change minds a bit and reassure people. That was part of the reason we did it, to inform this debate about harms and benefits of statins,” principal investigator Liam Smeeth, MBChB, MSc, PhD, from the same institution, said during a virtual press conference on the trial conducted by the U.K. nonprofit Science Media Centre.
“In thinking through whether to take a statin or not, people can be reassured that these muscle symptoms are rare; they aren’t common. Aches and pains are common, but are not caused by statins,” said Dr. Smeeth, who is senior author on the trial publication.
Another goal of the 200-patient study, he said, was to explore whether patients who had experienced muscle symptoms on a statin but were willing to explore whether the statin was to blame could be convinced – depending on what they learned in the trial – to stay on the drugs.
It seemed to work; two-thirds of the participants who finished the study “decided that they would actually want to try starting statins again, which was quite amazing.”
But there was a “slight caveat,” Dr. Smeeth observed. “To join our trial, yes, you had to have had a bad experience with statins, but you probably had to be a little bit open to the idea of trying them again. So, I can’t claim that that two-thirds would apply to everybody in the population.”
Because StatinWISE entered only patients who had reported severe muscle symptoms on a statin but hadn’t showed significant enzymatic evidence of myopathy, all had either taken themselves off the statin or were “considering” it. And the study had excluded anyone with “persistent, generalized, unexplained muscle pain” regardless of any statin therapy.
“This was very deliberately a select group of people who had serious problems taking statins. This was not a random sample by any means,” Dr. Smeeth said.
“The patients in the study were willing to participate and take statins again,” suggesting they “may not be completely representative of all those who believe they experience side effects with statins, as anyone who refused to take statins ever again would not have been recruited,” observed Tim Chico, MBChB, MD, University of Sheffield (England) in a Science Media Centre press release on StatinWISE.
Still, even among this “supersaturated group of people” selected for having had muscle symptoms on statins, Dr. Smeeth said at the briefing, “in almost all cases, their pains and aches were no worse on statins than they were on placebo. We’re not saying that anyone is making up their aches and pains. These are real aches and pains. What we’re showing very clearly is that those aches and pains are no worse on statins than they are on placebo.”
Rechallenge is possible
Some people are more likely than others to experience adverse reactions to any drug, “and that’s true of statins,” Neil J. Stone, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, told this news organization. But StatinWISE underscores that many patients with muscle symptoms on the drugs can be convinced to continue with them rather than stop them entirely.
“The study didn’t say that everybody who has symptoms on a statin is having a nocebo effect,” said Dr. Stone, vice chair for the multisociety 2018 Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol, who was not involved with StatinWISE.
“It simply said,” allowing for some caveats, “that a significant number of patients may have symptoms that don’t preclude them from being rechallenged with a statin again, once they understand what this nocebo effect is.”
And, Dr. Stone said, “it amplifies the 2018 guidelines, with their emphasis on the clinician-patient discussion before starting therapy,” by showing that statin-associated muscle pain isn’t necessarily caused by the drugs and isn’t a reason to stop them.
“That there is a second study confirming SAMSON is helpful, and the results are helpful because they say many of these patients, once they are shown the results, can be rechallenged and will then tolerate statins,” Steven E. Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“They were able to get two-thirds of those completing the trial into long-term treatment, which I think is obviously very admirable and very important,” said Dr. Nissen, who was GAUSS-3 principal investigator but not associated with StatinWISE.
“I think it is important, however, that we not completely dismiss patients who complain of adverse effects. Because, in fact, there probably are some people who do have muscle-related symptoms,” he said. “But you know, to really call somebody statin intolerant, they really should fail three statins, which would be a very good standard.”
In his experience, said Patrick M. Moriarty, MD, who directs the Atherosclerosis & Lipoprotein-Apheresis Center at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, perhaps 80%-90% of patients who believe they are statin intolerant because of muscle symptoms are actually not statin intolerant at all.
“I think a massive amount of it is supratentorial,” Dr. Moriarty, who was not part of StatinWISE, told this news organization. It comes directly from “what they heard, what they read, or what they were told – and at their age, they’re going to have aches and pains.”
Value of the n-of-1 trial
Dr. Smeeth and colleagues framed StatinWISE in part as a test of a strategy for overcoming nocebo-based aversion to statins. One goal was to see whether these methods might be helpful in practice for convincing patients who want to reject statins because of muscle symptoms to give the drugs another chance.
In StatinWISE, patients were individually assigned to take atorvastatin or placebo in randomized order with multiple blinding during each of six successive 2-month periods, so that they were on one or the other agent half the time. They rated their symptoms at the end of each period.
So the trial in composite was, as the publication states, “a series of randomized, placebo-controlled n-of-1 trials.” SAMSON followed a similar scheme, except – as previously reported – it had specified 4 months of atorvastatin, 4 months of placebo, and 4 months with patients on neither statin nor placebo.
StatinWISE “provides a useful approach (the n = 1 study) that could be used in real life to help patients understand the cause of their own possible side effects, which could also be applied to medications other than statins,” Dr. Chico added in the Science Media Centre release.
“I often encounter people who have a firmly held view that statins cause muscle pains, even when they haven’t taken these medications themselves, and I hope that this study may help change this view and make them willing to try such an ‘experiment,’ ” he said.
Others aren’t sure an experiment resembling an n-of-1 trial would be practical or effective when conducted in routine practice.
More efficient and useful, Dr. Moriarty noted, would be for physicians to nurture a close relationship with patients, one that could help transform their negative feelings about statins into a willingness to accept the drugs. “This is a trust you have to build; these are human beings.”
He said getting the patient’s confidence is critical. “You have to explain the pluses and minuses of getting treatment, of the 30% reduction in cardiovascular events that occur with the statin. You don’t go ‘testing this and that.’ I think it’s more about getting them on board.”
No statin effect on muscle symptoms
Patients in StatinWISE were recruited from 50 primary care practices in England and Wales from December 2016 to April 2018, the report notes; their mean age was 69 years, and 58% were men. Of the 200 patients, 151 recorded muscle-symptom scores for at least one statin period and one placebo period, and so were included in the primary-endpoint assessment.
The mean muscle symptom score was lower on statin therapy than on placebo (1.68 vs. 2.57), but there was no significant difference in adjusted analysis (mean difference, –0.11 (95% confidence interval, –0.36 to 0.14; P = .40).
Statins showed no significant effect on development of muscle symptoms overall, it was reported, with an odds ratio of 1.11 (99% confidence interval, 0.62-1.99). Nor was there an effect on “muscle symptoms that could not be attributed to another cause,” (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.77-1.94).
Of the 80 withdrawals during the study for any reason, 43% occurred when the patient was on the statin, 49% when the patient was on placebo, and 9% after randomization but before either statin or placebo had been initiated. Of those, 33 were because of “intolerable muscle symptoms,” says the report. But withdrawal occurred about as often on statin therapy as off the drug – 9% and 7%, respectively – throughout the 1-year study.
“This study provides further evidence through the lived experience of individuals that muscle pains often attributed to statins are not due to the drug,” said Sir Nilesh J. Samani, MBChB, MD, medical director for the British Heart Foundation, as quoted in the Science Media Centre press release.
“The use of each patient as their own control in the trial provides a powerful way of distinguishing the effect of a statin from that of taking a pill,” he said. “The findings should give confidence to patients who may be concerned about taking statins.”
StatinWISE was funded by the National Institute for Health Research-Health Technology Program and sponsored by the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. The authors declare that they have “no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.” Dr. Smeeth reports receiving grants from GlaxoSmithKline, and personal fees for advisory work from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Stone reports no industry relationships or other disclosures. Dr. Nissen reports that his center has received funding for clinical trials from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Cerenis, Eli Lilly, Esperion, Medtronic, MyoKardia, Novartis, Orexigen, Pfizer, Takeda, The Medicines Company, and Silence Therapeutics; that he is involved in these trials but receives no personal remuneration; and that he consults for many pharmaceutical companies but requires them to donate all honoraria or fees directly to charity so that he receives neither income nor a tax deduction. Dr. Chico had no conflicts. Dr. Moriarty declared no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Samani had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Another randomized trial, on the heels of the recently published SAMSON, has concluded – many would say confirmed – that .
Affected patients who sorely doubt that conclusion might possibly embrace statins, researchers say, if the new trial’s creative methodology could somehow be applied to them in clinical practice.
The recent SAMSON trial made waves in November 2020 by concluding, with some caveats, that about 90% of the burden of muscle symptoms reported by patients on statins may be attributable to a nocebo effect; that is, they are attributed to the drugs – perhaps because of negative expectations – but not actually caused by them.
The new trial, StatinWISE (Statin Web-based Investigation of Side Effects), triple the size but similar in design and conducted parallel to SAMSON, similarly saw no important differences in patient-reported muscle symptom prevalence or severity during administration of atorvastatin 20 mg/day or placebo, in withdrawal from the study because of such symptoms, or in patient quality of life.
The findings also support years of observational evidence that argues against a statin effect on muscle symptoms except in rare cases of confirmed myopathy, as well as results from randomized trials like ODYSSEY ALTERNATIVE and GAUSS-3, in which significant muscle symptoms in “statin-intolerant” patients were unusual, note StatinWISE investigators in their report, published online Feb. 24 in BMJ, with lead author Emily Herrett, MSc, PhD, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
“I’m hoping it can change minds a bit and reassure people. That was part of the reason we did it, to inform this debate about harms and benefits of statins,” principal investigator Liam Smeeth, MBChB, MSc, PhD, from the same institution, said during a virtual press conference on the trial conducted by the U.K. nonprofit Science Media Centre.
“In thinking through whether to take a statin or not, people can be reassured that these muscle symptoms are rare; they aren’t common. Aches and pains are common, but are not caused by statins,” said Dr. Smeeth, who is senior author on the trial publication.
Another goal of the 200-patient study, he said, was to explore whether patients who had experienced muscle symptoms on a statin but were willing to explore whether the statin was to blame could be convinced – depending on what they learned in the trial – to stay on the drugs.
It seemed to work; two-thirds of the participants who finished the study “decided that they would actually want to try starting statins again, which was quite amazing.”
But there was a “slight caveat,” Dr. Smeeth observed. “To join our trial, yes, you had to have had a bad experience with statins, but you probably had to be a little bit open to the idea of trying them again. So, I can’t claim that that two-thirds would apply to everybody in the population.”
Because StatinWISE entered only patients who had reported severe muscle symptoms on a statin but hadn’t showed significant enzymatic evidence of myopathy, all had either taken themselves off the statin or were “considering” it. And the study had excluded anyone with “persistent, generalized, unexplained muscle pain” regardless of any statin therapy.
“This was very deliberately a select group of people who had serious problems taking statins. This was not a random sample by any means,” Dr. Smeeth said.
“The patients in the study were willing to participate and take statins again,” suggesting they “may not be completely representative of all those who believe they experience side effects with statins, as anyone who refused to take statins ever again would not have been recruited,” observed Tim Chico, MBChB, MD, University of Sheffield (England) in a Science Media Centre press release on StatinWISE.
Still, even among this “supersaturated group of people” selected for having had muscle symptoms on statins, Dr. Smeeth said at the briefing, “in almost all cases, their pains and aches were no worse on statins than they were on placebo. We’re not saying that anyone is making up their aches and pains. These are real aches and pains. What we’re showing very clearly is that those aches and pains are no worse on statins than they are on placebo.”
Rechallenge is possible
Some people are more likely than others to experience adverse reactions to any drug, “and that’s true of statins,” Neil J. Stone, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, told this news organization. But StatinWISE underscores that many patients with muscle symptoms on the drugs can be convinced to continue with them rather than stop them entirely.
“The study didn’t say that everybody who has symptoms on a statin is having a nocebo effect,” said Dr. Stone, vice chair for the multisociety 2018 Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol, who was not involved with StatinWISE.
“It simply said,” allowing for some caveats, “that a significant number of patients may have symptoms that don’t preclude them from being rechallenged with a statin again, once they understand what this nocebo effect is.”
And, Dr. Stone said, “it amplifies the 2018 guidelines, with their emphasis on the clinician-patient discussion before starting therapy,” by showing that statin-associated muscle pain isn’t necessarily caused by the drugs and isn’t a reason to stop them.
“That there is a second study confirming SAMSON is helpful, and the results are helpful because they say many of these patients, once they are shown the results, can be rechallenged and will then tolerate statins,” Steven E. Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“They were able to get two-thirds of those completing the trial into long-term treatment, which I think is obviously very admirable and very important,” said Dr. Nissen, who was GAUSS-3 principal investigator but not associated with StatinWISE.
“I think it is important, however, that we not completely dismiss patients who complain of adverse effects. Because, in fact, there probably are some people who do have muscle-related symptoms,” he said. “But you know, to really call somebody statin intolerant, they really should fail three statins, which would be a very good standard.”
In his experience, said Patrick M. Moriarty, MD, who directs the Atherosclerosis & Lipoprotein-Apheresis Center at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, perhaps 80%-90% of patients who believe they are statin intolerant because of muscle symptoms are actually not statin intolerant at all.
“I think a massive amount of it is supratentorial,” Dr. Moriarty, who was not part of StatinWISE, told this news organization. It comes directly from “what they heard, what they read, or what they were told – and at their age, they’re going to have aches and pains.”
Value of the n-of-1 trial
Dr. Smeeth and colleagues framed StatinWISE in part as a test of a strategy for overcoming nocebo-based aversion to statins. One goal was to see whether these methods might be helpful in practice for convincing patients who want to reject statins because of muscle symptoms to give the drugs another chance.
In StatinWISE, patients were individually assigned to take atorvastatin or placebo in randomized order with multiple blinding during each of six successive 2-month periods, so that they were on one or the other agent half the time. They rated their symptoms at the end of each period.
So the trial in composite was, as the publication states, “a series of randomized, placebo-controlled n-of-1 trials.” SAMSON followed a similar scheme, except – as previously reported – it had specified 4 months of atorvastatin, 4 months of placebo, and 4 months with patients on neither statin nor placebo.
StatinWISE “provides a useful approach (the n = 1 study) that could be used in real life to help patients understand the cause of their own possible side effects, which could also be applied to medications other than statins,” Dr. Chico added in the Science Media Centre release.
“I often encounter people who have a firmly held view that statins cause muscle pains, even when they haven’t taken these medications themselves, and I hope that this study may help change this view and make them willing to try such an ‘experiment,’ ” he said.
Others aren’t sure an experiment resembling an n-of-1 trial would be practical or effective when conducted in routine practice.
More efficient and useful, Dr. Moriarty noted, would be for physicians to nurture a close relationship with patients, one that could help transform their negative feelings about statins into a willingness to accept the drugs. “This is a trust you have to build; these are human beings.”
He said getting the patient’s confidence is critical. “You have to explain the pluses and minuses of getting treatment, of the 30% reduction in cardiovascular events that occur with the statin. You don’t go ‘testing this and that.’ I think it’s more about getting them on board.”
No statin effect on muscle symptoms
Patients in StatinWISE were recruited from 50 primary care practices in England and Wales from December 2016 to April 2018, the report notes; their mean age was 69 years, and 58% were men. Of the 200 patients, 151 recorded muscle-symptom scores for at least one statin period and one placebo period, and so were included in the primary-endpoint assessment.
The mean muscle symptom score was lower on statin therapy than on placebo (1.68 vs. 2.57), but there was no significant difference in adjusted analysis (mean difference, –0.11 (95% confidence interval, –0.36 to 0.14; P = .40).
Statins showed no significant effect on development of muscle symptoms overall, it was reported, with an odds ratio of 1.11 (99% confidence interval, 0.62-1.99). Nor was there an effect on “muscle symptoms that could not be attributed to another cause,” (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.77-1.94).
Of the 80 withdrawals during the study for any reason, 43% occurred when the patient was on the statin, 49% when the patient was on placebo, and 9% after randomization but before either statin or placebo had been initiated. Of those, 33 were because of “intolerable muscle symptoms,” says the report. But withdrawal occurred about as often on statin therapy as off the drug – 9% and 7%, respectively – throughout the 1-year study.
“This study provides further evidence through the lived experience of individuals that muscle pains often attributed to statins are not due to the drug,” said Sir Nilesh J. Samani, MBChB, MD, medical director for the British Heart Foundation, as quoted in the Science Media Centre press release.
“The use of each patient as their own control in the trial provides a powerful way of distinguishing the effect of a statin from that of taking a pill,” he said. “The findings should give confidence to patients who may be concerned about taking statins.”
StatinWISE was funded by the National Institute for Health Research-Health Technology Program and sponsored by the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. The authors declare that they have “no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.” Dr. Smeeth reports receiving grants from GlaxoSmithKline, and personal fees for advisory work from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Stone reports no industry relationships or other disclosures. Dr. Nissen reports that his center has received funding for clinical trials from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Cerenis, Eli Lilly, Esperion, Medtronic, MyoKardia, Novartis, Orexigen, Pfizer, Takeda, The Medicines Company, and Silence Therapeutics; that he is involved in these trials but receives no personal remuneration; and that he consults for many pharmaceutical companies but requires them to donate all honoraria or fees directly to charity so that he receives neither income nor a tax deduction. Dr. Chico had no conflicts. Dr. Moriarty declared no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Samani had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide for weight loss? A good first STEP, with caveats
The phase 3a STEP 1 trial that investigated the use of semaglutide (Novo Nordisk), a glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonist, for weight loss is aptly named, some say.
“In sum, we have a long way to go to control the obesity epidemic ... but on the face of it, the STEP 1 trial (like its name) is a good beginning,” wrote coeditorialists Julie R. Ingelfinger, MD, from Harvard Medical School, Boston, and a deputy editor of the New England Journal of Medicine, and Clifford J. Rosen, MD, from Tufts University School of Medicine, also in Boston.
The trial findings by John P.H. Wilding, DM, University of Liverpool (England), and colleagues and an accompanying editorial were published online Feb. 10, 2021, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The results are encouraging, with significantly more patients in the semaglutide group having clinically important weight loss,” Dr. Ingelfinger and Dr. Rosen stressed.
However, they also cautioned that “despite the positive results of this trial, the present study has some important limitations” and “there are concerns, including adverse events (mostly gastrointestinal – nausea, sometimes vomiting, and diarrhea) related primarily to the class of the agent.”
Two U.K. experts drew similar takeaways, speaking to the U.K. Science Media Centre.
“This was a well-designed study with unequivocal findings,” which showed that semaglutide “is indeed likely to be a game-changer in the fight against obesity,” according to Baptiste Leurent, PhD, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
However, if the drug is approved at this dose for this use, patients would need close monitoring for gastrointestinal disorders, and “we also need to better understand what is happening once the treatment is stopped, and whether it could be taken for a shorter period of time.”
Sir Stephen O’Rahilly, MD, MRC Metabolic Diseases Unit, University of Cambridge (England), pointed out that “GLP-1 is made by cells in the intestine and levels increase in the blood after a meal, providing some of the signal to the brain that tells us we are ‘full,’ ” so GLP-1 agonists have been studied as appetite suppressants, in addition to their approved use to treat type 2 diabetes.
Only about 4.5% of participants in STEP 1 stopped taking semaglutide because of gastrointestinal issues, he noted, although more participants in that group reported problems with gallstones, which can follow rapid weight loss.
And “unlike some previous appetite suppressant drugs which caused significant psychological and psychiatric side effects, there is no evidence that semaglutide has any adverse effects of that nature,” Dr. O’Rahilly noted.
In sum, he said, “this is the start of a new era for obesity drug development with the future direction being to achieve levels of weight loss comparable to semaglutide, while having fewer side effects.”
‘Pressing need’ to address obesity; semaglutide filed for obesity
There is a “pressing need” to address the worldwide increase in obesity and weight-related coexisting conditions, Dr. Ingelfinger and Dr. Rosen noted.
Sustained long-term weight loss with diet and exercise is challenging; behavioral weight-loss strategies “fail more often than not,” bariatric surgery is invasive and often followed by eventual weight regain, they wrote.
In addition, said Dr. Wilding and colleagues, the “use of available [weight-loss] medications remains limited by modest efficacy, safety concerns, and cost.”
Subcutaneous semaglutide, approved for treating type 2 diabetes (as Ozempic) in adults at doses of up to 1 mg/week, induced weight loss at higher doses. The current study is part of the global Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People With Obesity program of four trials (STEP 1, 2, 3, and 4) that aimed to test the safety and efficacy of subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week for weight loss.
Topline results from STEP 1 were presented June 4, 2020.
And as reported earlier, results from STEP 3 – a 68-week trial of semaglutide versus placebo in 611 participants who all received very intensive diet and exercise counseling – were presented at the virtual ObesityWeek 2020 meeting.
The four trials of semaglutide for weight loss have been completed and the data were submitted to the Food and Drug Administration on Dec. 4, 2020 (with a decision expected within 6 months) and to the European Medicines Agency on Dec. 18, 2020.
Most patients had 5% weight loss with semaglutide
The STEP 1 trial enrolled 1,961 adults with a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2 or at least 27 with at least one weight-related coexisting condition, but without type 2 diabetes, at 129 sites in 16 countries in Asia, Europe, North America, and South America.
Participants were a mean age of 47 and three-quarters were women. Most participants were White (76%), followed by Asian (13%), Black or African American (6%), or other (5%).
On average, they had a BMI of 38 and weighed 105 kg. Three-quarters had one or more coexisting conditions.
Participants were randomized to receive semaglutide (1,306 patients) or placebo (655 patients), added to lifestyle intervention.
Everyone received 17 monthly individual counseling sessions during which they learned about adhering to a diet with a 500-calorie/day deficit, were encouraged to build up to walking 150 minutes each week, and recorded their daily diet and exercise (in a diary or using an app).
Semaglutide was administered with a prefilled pen injector at a dose of 0.25 mg/week for the first 4 weeks, escalated to 2.4 mg/week by week 16 (or lower if the patient had unacceptable side effects).
At 68 weeks, participants in the semaglutide versus placebo group had greater mean weight loss (14.9% vs. 2.4%, or 15.3 kg vs. 2.6 kg).
Participants in the semaglutide versus placebo group were much more likely to have lost at least 5% of their initial weight (86% vs. 31.5%) or at least 10% of their initial weight (69.1% vs. 12.0%), or at least 15% of their initial weight (50.5% vs. 4.9%; P < .001 for all three comparisons).
About 80% of participants adhered to the study treatment. A third of participants in the semaglutide group who completed the study lost at least 20% of their initial weight, which approaches the 20%-30% reported weight loss 1-3 years after sleeve gastrectomy, the researchers noted.
Participants in the semaglutide group also had greater improvements in waist circumference and levels of hemoglobin A1c, C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation), and fasting lipids, as well as in physical function scores on SF-36 and IWQOL-Lite-CT questionnaires.
In their editorial, Dr. Ingelfinger and Dr. Rosen noted that “daily oral semaglutide [already approved in 7-mg and 14-mg doses for the treatment of type 2 diabetes as Rybelsus] might be more appealing to many people,” as a weight-loss medication than a once-weekly subcutaneous dose. Semaglutide is the first GLP-1 agonist available as an oral agent.
The ongoing Semaglutide Effects on Heart Disease and Stroke in Patients With Overweight or Obesity (SELECT) trial (with expected completion in 2023) will shed light on cardiovascular outcomes after 2.5-5 years.
GI disorders and ‘important limitations’
More participants in the semaglutide than the placebo group reported gastrointestinal disorders (typically nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation; 74.2% vs. 47.9%), which were mostly transient and mild to moderate in severity, but also led to more treatment discontinuation (7.0% vs. 3.1%).
More patients in the semaglutide versus placebo group had a gall bladder–related disorder (2.6% vs. 1.2%, mostly cholelithiasis) and mild acute pancreatitis (3 vs. 0 participants), but there were no between-group differences in neoplasms.
Dr. Wilding and colleagues acknowledge the limitations of the study, including the fact that it enrolled mainly women, mainly non-White participants, was relatively short, and excluded patients with type 2 diabetes.
Mean placebo-corrected weight loss with 2.4 mg/weekly subcutaneous semaglutide was greater than with 3.0 mg once-daily subcutaneous liraglutide (Saxenda, Novo Nordisk) – the only GLP-1 agonist approved for weight management – in the 56-week SCALE trial (12.4% vs. 4.5%); however, the two studies had different populations.
The study was supported by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Ingelfinger is a deputy editor and Dr. Rosen is an associate editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Dr. Ingelfinger, Dr. Rosen, and Dr. Leurent have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. O’Rahilly has a current research collaboration with Novo Nordisk scientists in an unrelated area and has been a consultant for the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The phase 3a STEP 1 trial that investigated the use of semaglutide (Novo Nordisk), a glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonist, for weight loss is aptly named, some say.
“In sum, we have a long way to go to control the obesity epidemic ... but on the face of it, the STEP 1 trial (like its name) is a good beginning,” wrote coeditorialists Julie R. Ingelfinger, MD, from Harvard Medical School, Boston, and a deputy editor of the New England Journal of Medicine, and Clifford J. Rosen, MD, from Tufts University School of Medicine, also in Boston.
The trial findings by John P.H. Wilding, DM, University of Liverpool (England), and colleagues and an accompanying editorial were published online Feb. 10, 2021, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The results are encouraging, with significantly more patients in the semaglutide group having clinically important weight loss,” Dr. Ingelfinger and Dr. Rosen stressed.
However, they also cautioned that “despite the positive results of this trial, the present study has some important limitations” and “there are concerns, including adverse events (mostly gastrointestinal – nausea, sometimes vomiting, and diarrhea) related primarily to the class of the agent.”
Two U.K. experts drew similar takeaways, speaking to the U.K. Science Media Centre.
“This was a well-designed study with unequivocal findings,” which showed that semaglutide “is indeed likely to be a game-changer in the fight against obesity,” according to Baptiste Leurent, PhD, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
However, if the drug is approved at this dose for this use, patients would need close monitoring for gastrointestinal disorders, and “we also need to better understand what is happening once the treatment is stopped, and whether it could be taken for a shorter period of time.”
Sir Stephen O’Rahilly, MD, MRC Metabolic Diseases Unit, University of Cambridge (England), pointed out that “GLP-1 is made by cells in the intestine and levels increase in the blood after a meal, providing some of the signal to the brain that tells us we are ‘full,’ ” so GLP-1 agonists have been studied as appetite suppressants, in addition to their approved use to treat type 2 diabetes.
Only about 4.5% of participants in STEP 1 stopped taking semaglutide because of gastrointestinal issues, he noted, although more participants in that group reported problems with gallstones, which can follow rapid weight loss.
And “unlike some previous appetite suppressant drugs which caused significant psychological and psychiatric side effects, there is no evidence that semaglutide has any adverse effects of that nature,” Dr. O’Rahilly noted.
In sum, he said, “this is the start of a new era for obesity drug development with the future direction being to achieve levels of weight loss comparable to semaglutide, while having fewer side effects.”
‘Pressing need’ to address obesity; semaglutide filed for obesity
There is a “pressing need” to address the worldwide increase in obesity and weight-related coexisting conditions, Dr. Ingelfinger and Dr. Rosen noted.
Sustained long-term weight loss with diet and exercise is challenging; behavioral weight-loss strategies “fail more often than not,” bariatric surgery is invasive and often followed by eventual weight regain, they wrote.
In addition, said Dr. Wilding and colleagues, the “use of available [weight-loss] medications remains limited by modest efficacy, safety concerns, and cost.”
Subcutaneous semaglutide, approved for treating type 2 diabetes (as Ozempic) in adults at doses of up to 1 mg/week, induced weight loss at higher doses. The current study is part of the global Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People With Obesity program of four trials (STEP 1, 2, 3, and 4) that aimed to test the safety and efficacy of subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week for weight loss.
Topline results from STEP 1 were presented June 4, 2020.
And as reported earlier, results from STEP 3 – a 68-week trial of semaglutide versus placebo in 611 participants who all received very intensive diet and exercise counseling – were presented at the virtual ObesityWeek 2020 meeting.
The four trials of semaglutide for weight loss have been completed and the data were submitted to the Food and Drug Administration on Dec. 4, 2020 (with a decision expected within 6 months) and to the European Medicines Agency on Dec. 18, 2020.
Most patients had 5% weight loss with semaglutide
The STEP 1 trial enrolled 1,961 adults with a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2 or at least 27 with at least one weight-related coexisting condition, but without type 2 diabetes, at 129 sites in 16 countries in Asia, Europe, North America, and South America.
Participants were a mean age of 47 and three-quarters were women. Most participants were White (76%), followed by Asian (13%), Black or African American (6%), or other (5%).
On average, they had a BMI of 38 and weighed 105 kg. Three-quarters had one or more coexisting conditions.
Participants were randomized to receive semaglutide (1,306 patients) or placebo (655 patients), added to lifestyle intervention.
Everyone received 17 monthly individual counseling sessions during which they learned about adhering to a diet with a 500-calorie/day deficit, were encouraged to build up to walking 150 minutes each week, and recorded their daily diet and exercise (in a diary or using an app).
Semaglutide was administered with a prefilled pen injector at a dose of 0.25 mg/week for the first 4 weeks, escalated to 2.4 mg/week by week 16 (or lower if the patient had unacceptable side effects).
At 68 weeks, participants in the semaglutide versus placebo group had greater mean weight loss (14.9% vs. 2.4%, or 15.3 kg vs. 2.6 kg).
Participants in the semaglutide versus placebo group were much more likely to have lost at least 5% of their initial weight (86% vs. 31.5%) or at least 10% of their initial weight (69.1% vs. 12.0%), or at least 15% of their initial weight (50.5% vs. 4.9%; P < .001 for all three comparisons).
About 80% of participants adhered to the study treatment. A third of participants in the semaglutide group who completed the study lost at least 20% of their initial weight, which approaches the 20%-30% reported weight loss 1-3 years after sleeve gastrectomy, the researchers noted.
Participants in the semaglutide group also had greater improvements in waist circumference and levels of hemoglobin A1c, C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation), and fasting lipids, as well as in physical function scores on SF-36 and IWQOL-Lite-CT questionnaires.
In their editorial, Dr. Ingelfinger and Dr. Rosen noted that “daily oral semaglutide [already approved in 7-mg and 14-mg doses for the treatment of type 2 diabetes as Rybelsus] might be more appealing to many people,” as a weight-loss medication than a once-weekly subcutaneous dose. Semaglutide is the first GLP-1 agonist available as an oral agent.
The ongoing Semaglutide Effects on Heart Disease and Stroke in Patients With Overweight or Obesity (SELECT) trial (with expected completion in 2023) will shed light on cardiovascular outcomes after 2.5-5 years.
GI disorders and ‘important limitations’
More participants in the semaglutide than the placebo group reported gastrointestinal disorders (typically nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation; 74.2% vs. 47.9%), which were mostly transient and mild to moderate in severity, but also led to more treatment discontinuation (7.0% vs. 3.1%).
More patients in the semaglutide versus placebo group had a gall bladder–related disorder (2.6% vs. 1.2%, mostly cholelithiasis) and mild acute pancreatitis (3 vs. 0 participants), but there were no between-group differences in neoplasms.
Dr. Wilding and colleagues acknowledge the limitations of the study, including the fact that it enrolled mainly women, mainly non-White participants, was relatively short, and excluded patients with type 2 diabetes.
Mean placebo-corrected weight loss with 2.4 mg/weekly subcutaneous semaglutide was greater than with 3.0 mg once-daily subcutaneous liraglutide (Saxenda, Novo Nordisk) – the only GLP-1 agonist approved for weight management – in the 56-week SCALE trial (12.4% vs. 4.5%); however, the two studies had different populations.
The study was supported by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Ingelfinger is a deputy editor and Dr. Rosen is an associate editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Dr. Ingelfinger, Dr. Rosen, and Dr. Leurent have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. O’Rahilly has a current research collaboration with Novo Nordisk scientists in an unrelated area and has been a consultant for the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The phase 3a STEP 1 trial that investigated the use of semaglutide (Novo Nordisk), a glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonist, for weight loss is aptly named, some say.
“In sum, we have a long way to go to control the obesity epidemic ... but on the face of it, the STEP 1 trial (like its name) is a good beginning,” wrote coeditorialists Julie R. Ingelfinger, MD, from Harvard Medical School, Boston, and a deputy editor of the New England Journal of Medicine, and Clifford J. Rosen, MD, from Tufts University School of Medicine, also in Boston.
The trial findings by John P.H. Wilding, DM, University of Liverpool (England), and colleagues and an accompanying editorial were published online Feb. 10, 2021, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The results are encouraging, with significantly more patients in the semaglutide group having clinically important weight loss,” Dr. Ingelfinger and Dr. Rosen stressed.
However, they also cautioned that “despite the positive results of this trial, the present study has some important limitations” and “there are concerns, including adverse events (mostly gastrointestinal – nausea, sometimes vomiting, and diarrhea) related primarily to the class of the agent.”
Two U.K. experts drew similar takeaways, speaking to the U.K. Science Media Centre.
“This was a well-designed study with unequivocal findings,” which showed that semaglutide “is indeed likely to be a game-changer in the fight against obesity,” according to Baptiste Leurent, PhD, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
However, if the drug is approved at this dose for this use, patients would need close monitoring for gastrointestinal disorders, and “we also need to better understand what is happening once the treatment is stopped, and whether it could be taken for a shorter period of time.”
Sir Stephen O’Rahilly, MD, MRC Metabolic Diseases Unit, University of Cambridge (England), pointed out that “GLP-1 is made by cells in the intestine and levels increase in the blood after a meal, providing some of the signal to the brain that tells us we are ‘full,’ ” so GLP-1 agonists have been studied as appetite suppressants, in addition to their approved use to treat type 2 diabetes.
Only about 4.5% of participants in STEP 1 stopped taking semaglutide because of gastrointestinal issues, he noted, although more participants in that group reported problems with gallstones, which can follow rapid weight loss.
And “unlike some previous appetite suppressant drugs which caused significant psychological and psychiatric side effects, there is no evidence that semaglutide has any adverse effects of that nature,” Dr. O’Rahilly noted.
In sum, he said, “this is the start of a new era for obesity drug development with the future direction being to achieve levels of weight loss comparable to semaglutide, while having fewer side effects.”
‘Pressing need’ to address obesity; semaglutide filed for obesity
There is a “pressing need” to address the worldwide increase in obesity and weight-related coexisting conditions, Dr. Ingelfinger and Dr. Rosen noted.
Sustained long-term weight loss with diet and exercise is challenging; behavioral weight-loss strategies “fail more often than not,” bariatric surgery is invasive and often followed by eventual weight regain, they wrote.
In addition, said Dr. Wilding and colleagues, the “use of available [weight-loss] medications remains limited by modest efficacy, safety concerns, and cost.”
Subcutaneous semaglutide, approved for treating type 2 diabetes (as Ozempic) in adults at doses of up to 1 mg/week, induced weight loss at higher doses. The current study is part of the global Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People With Obesity program of four trials (STEP 1, 2, 3, and 4) that aimed to test the safety and efficacy of subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg/week for weight loss.
Topline results from STEP 1 were presented June 4, 2020.
And as reported earlier, results from STEP 3 – a 68-week trial of semaglutide versus placebo in 611 participants who all received very intensive diet and exercise counseling – were presented at the virtual ObesityWeek 2020 meeting.
The four trials of semaglutide for weight loss have been completed and the data were submitted to the Food and Drug Administration on Dec. 4, 2020 (with a decision expected within 6 months) and to the European Medicines Agency on Dec. 18, 2020.
Most patients had 5% weight loss with semaglutide
The STEP 1 trial enrolled 1,961 adults with a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2 or at least 27 with at least one weight-related coexisting condition, but without type 2 diabetes, at 129 sites in 16 countries in Asia, Europe, North America, and South America.
Participants were a mean age of 47 and three-quarters were women. Most participants were White (76%), followed by Asian (13%), Black or African American (6%), or other (5%).
On average, they had a BMI of 38 and weighed 105 kg. Three-quarters had one or more coexisting conditions.
Participants were randomized to receive semaglutide (1,306 patients) or placebo (655 patients), added to lifestyle intervention.
Everyone received 17 monthly individual counseling sessions during which they learned about adhering to a diet with a 500-calorie/day deficit, were encouraged to build up to walking 150 minutes each week, and recorded their daily diet and exercise (in a diary or using an app).
Semaglutide was administered with a prefilled pen injector at a dose of 0.25 mg/week for the first 4 weeks, escalated to 2.4 mg/week by week 16 (or lower if the patient had unacceptable side effects).
At 68 weeks, participants in the semaglutide versus placebo group had greater mean weight loss (14.9% vs. 2.4%, or 15.3 kg vs. 2.6 kg).
Participants in the semaglutide versus placebo group were much more likely to have lost at least 5% of their initial weight (86% vs. 31.5%) or at least 10% of their initial weight (69.1% vs. 12.0%), or at least 15% of their initial weight (50.5% vs. 4.9%; P < .001 for all three comparisons).
About 80% of participants adhered to the study treatment. A third of participants in the semaglutide group who completed the study lost at least 20% of their initial weight, which approaches the 20%-30% reported weight loss 1-3 years after sleeve gastrectomy, the researchers noted.
Participants in the semaglutide group also had greater improvements in waist circumference and levels of hemoglobin A1c, C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation), and fasting lipids, as well as in physical function scores on SF-36 and IWQOL-Lite-CT questionnaires.
In their editorial, Dr. Ingelfinger and Dr. Rosen noted that “daily oral semaglutide [already approved in 7-mg and 14-mg doses for the treatment of type 2 diabetes as Rybelsus] might be more appealing to many people,” as a weight-loss medication than a once-weekly subcutaneous dose. Semaglutide is the first GLP-1 agonist available as an oral agent.
The ongoing Semaglutide Effects on Heart Disease and Stroke in Patients With Overweight or Obesity (SELECT) trial (with expected completion in 2023) will shed light on cardiovascular outcomes after 2.5-5 years.
GI disorders and ‘important limitations’
More participants in the semaglutide than the placebo group reported gastrointestinal disorders (typically nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation; 74.2% vs. 47.9%), which were mostly transient and mild to moderate in severity, but also led to more treatment discontinuation (7.0% vs. 3.1%).
More patients in the semaglutide versus placebo group had a gall bladder–related disorder (2.6% vs. 1.2%, mostly cholelithiasis) and mild acute pancreatitis (3 vs. 0 participants), but there were no between-group differences in neoplasms.
Dr. Wilding and colleagues acknowledge the limitations of the study, including the fact that it enrolled mainly women, mainly non-White participants, was relatively short, and excluded patients with type 2 diabetes.
Mean placebo-corrected weight loss with 2.4 mg/weekly subcutaneous semaglutide was greater than with 3.0 mg once-daily subcutaneous liraglutide (Saxenda, Novo Nordisk) – the only GLP-1 agonist approved for weight management – in the 56-week SCALE trial (12.4% vs. 4.5%); however, the two studies had different populations.
The study was supported by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Ingelfinger is a deputy editor and Dr. Rosen is an associate editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Dr. Ingelfinger, Dr. Rosen, and Dr. Leurent have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. O’Rahilly has a current research collaboration with Novo Nordisk scientists in an unrelated area and has been a consultant for the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves orphan drug evinacumab-dgnb for homozygous FH
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the fully human monoclonal antibody evinacumab-dgnb (Evkeeza, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals) for use on top of other cholesterol-modifying medication in patients aged 12 years and older with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH), the agency and Regeneron have announced.
Evinacumab had received orphan drug designation and underwent priority regulatory review based primarily on the phase 3 ELIPSE trial, presented at a meeting in March 2020 and published in August 2020 in the New England Journal of Medicine (doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2004215).
In the trial with 65 patients with HoFH on guideline-based lipid-modifying therapy, those who also received evinacumab 15 mg/kg intravenously every 4 weeks showed a nearly 50% drop in LDL cholesterol levels after 24 weeks, compared with patients given a placebo. Only 2% of patients in both groups discontinued therapy because of adverse reactions.
The drug blocks angiopoietin-like 3, itself an inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase and endothelial lipase. It therefore lowers LDL cholesterol levels by mechanisms that don’t directly involve the LDL receptor.
Regeneron estimates that about 1300 people in the United States have the homozygous genetic disorder, which can lead to LDL cholesterol levels of a 1,000 mg/dL or higher, advanced premature atherosclerosis, and extreme risk for cardiovascular events.
The drug’s average wholesale acquisition cost per patient in the United States is expected to be about $450,000 per year, the company said, adding that it has a financial support program to help qualified patients with out-of-pocket costs.
Regeneron’s announcement included a comment from dyslipidemia-therapy expert Daniel J. Rader, MD, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who called evinacumab “a potentially transformational new treatment for people with HoFH.”
The drug is currently under regulatory review for the same indication in Europe, the company said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the fully human monoclonal antibody evinacumab-dgnb (Evkeeza, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals) for use on top of other cholesterol-modifying medication in patients aged 12 years and older with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH), the agency and Regeneron have announced.
Evinacumab had received orphan drug designation and underwent priority regulatory review based primarily on the phase 3 ELIPSE trial, presented at a meeting in March 2020 and published in August 2020 in the New England Journal of Medicine (doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2004215).
In the trial with 65 patients with HoFH on guideline-based lipid-modifying therapy, those who also received evinacumab 15 mg/kg intravenously every 4 weeks showed a nearly 50% drop in LDL cholesterol levels after 24 weeks, compared with patients given a placebo. Only 2% of patients in both groups discontinued therapy because of adverse reactions.
The drug blocks angiopoietin-like 3, itself an inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase and endothelial lipase. It therefore lowers LDL cholesterol levels by mechanisms that don’t directly involve the LDL receptor.
Regeneron estimates that about 1300 people in the United States have the homozygous genetic disorder, which can lead to LDL cholesterol levels of a 1,000 mg/dL or higher, advanced premature atherosclerosis, and extreme risk for cardiovascular events.
The drug’s average wholesale acquisition cost per patient in the United States is expected to be about $450,000 per year, the company said, adding that it has a financial support program to help qualified patients with out-of-pocket costs.
Regeneron’s announcement included a comment from dyslipidemia-therapy expert Daniel J. Rader, MD, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who called evinacumab “a potentially transformational new treatment for people with HoFH.”
The drug is currently under regulatory review for the same indication in Europe, the company said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the fully human monoclonal antibody evinacumab-dgnb (Evkeeza, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals) for use on top of other cholesterol-modifying medication in patients aged 12 years and older with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH), the agency and Regeneron have announced.
Evinacumab had received orphan drug designation and underwent priority regulatory review based primarily on the phase 3 ELIPSE trial, presented at a meeting in March 2020 and published in August 2020 in the New England Journal of Medicine (doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2004215).
In the trial with 65 patients with HoFH on guideline-based lipid-modifying therapy, those who also received evinacumab 15 mg/kg intravenously every 4 weeks showed a nearly 50% drop in LDL cholesterol levels after 24 weeks, compared with patients given a placebo. Only 2% of patients in both groups discontinued therapy because of adverse reactions.
The drug blocks angiopoietin-like 3, itself an inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase and endothelial lipase. It therefore lowers LDL cholesterol levels by mechanisms that don’t directly involve the LDL receptor.
Regeneron estimates that about 1300 people in the United States have the homozygous genetic disorder, which can lead to LDL cholesterol levels of a 1,000 mg/dL or higher, advanced premature atherosclerosis, and extreme risk for cardiovascular events.
The drug’s average wholesale acquisition cost per patient in the United States is expected to be about $450,000 per year, the company said, adding that it has a financial support program to help qualified patients with out-of-pocket costs.
Regeneron’s announcement included a comment from dyslipidemia-therapy expert Daniel J. Rader, MD, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who called evinacumab “a potentially transformational new treatment for people with HoFH.”
The drug is currently under regulatory review for the same indication in Europe, the company said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ColCORONA: More questions than answers for colchicine in COVID-19
Science by press release and preprint has cooled clinician enthusiasm for the use of colchicine in nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, despite a pressing need for early treatments.
As previously reported by this news organization, a Jan. 22 press release announced that the massive ColCORONA study missed its primary endpoint of hospitalization or death among 4,488 newly diagnosed patients at increased risk for hospitalization.
But it also touted that use of the anti-inflammatory drug significantly reduced the primary endpoint in 4,159 of those patients with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID and led to reductions of 25%, 50%, and 44%, respectively, for hospitalizations, ventilations, and death.
Lead investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, director of the Montreal Heart Institute Research Centre, deemed the findings a “medical breakthrough.”
When the preprint released a few days later, however, newly revealed confidence intervals showed colchicine did not meaningfully reduce the need for mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-1.07) or death alone (OR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.19-1.66).
Further, the significant benefit on the primary outcome came at the cost of a fivefold increase in pulmonary embolism (11 vs. 2; P = .01), which was not mentioned in the press release.
“Whether this represents a real phenomenon or simply the play of chance is not known,” Dr. Tardif and colleagues noted later in the preprint.
“I read the preprint on colchicine and I have so many questions,” Aaron E. Glatt, MD, spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases, Mount Sinai South Nassau, Hewlett, N.Y., said in an interview. “I’ve been burned too many times with COVID and prefer to see better data.
“People sometimes say if you wait for perfect data, people are going to die,” he said. “Yeah, but we have no idea if people are going to die from getting this drug more than not getting it. That’s what concerns me. How many pulmonary emboli are going to be fatal versus the slight benefit that the study showed?”
The pushback to the non–peer-reviewed data on social media and via emails was so strong that Dr. Tardif posted a nearly 2,000-word letter responding to the many questions at play.
Chief among them was why the trial, originally planned for 6,000 patients, was stopped early by the investigators without consultation with the data safety monitoring board (DSMB).
The explanation in the letter that logistical issues like running the study call center, budget constraints, and a perceived need to quickly communicate the results left some calling foul that the study wasn’t allowed to finish and come to a more definitive conclusion.
“I can be a little bit sympathetic to their cause but at the same time the DSMB should have said no,” said David Boulware, MD, MPH, who led a recent hydroxychloroquine trial in COVID-19. “The problem is we’re sort of left in limbo, where some people kind of believe it and some say it’s not really a thing. So it’s not really moving the needle, as far as guidelines go.”
Indeed, a Twitter poll by cardiologist James Januzzi Jr., MD, captured the uncertainty, with 28% of respondents saying the trial was “neutral,” 58% saying “maybe but meh,” and 14% saying “colchicine for all.”
Another poll cheekily asked whether ColCORONA was the Gamestop/Reddit equivalent of COVID.
“The press release really didn’t help things because it very much oversold the effect. That, I think, poisoned the well,” said Dr. Boulware, professor of medicine in infectious diseases at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“The question I’m left with is not whether colchicine works, but who does it work in,” he said. “That’s really the fundamental question because it does seem that there are probably high-risk groups in their trial and others where they benefit, whereas other groups don’t benefit. In the subgroup analysis, there was absolutely no beneficial effect in women.”
According to the authors, the number needed to treat to prevent one death or hospitalization was 71 overall, but 29 for patients with diabetes, 31 for those aged 70 years and older, 53 for patients with respiratory disease, and 25 for those with coronary disease or heart failure.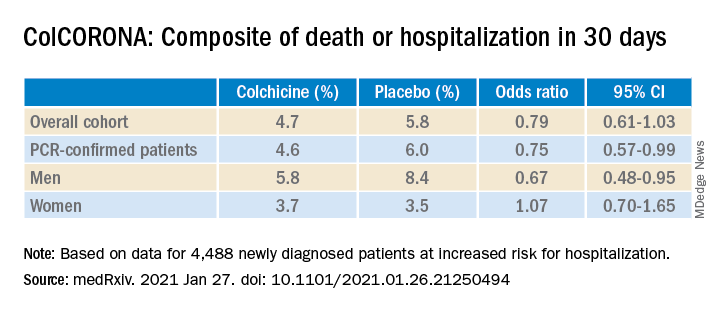
Men are at higher risk overall for poor outcomes. But “the authors didn’t present a multivariable analysis, so it is unclear if another factor, such as a differential prevalence of smoking or cardiovascular risk factors, contributed to the differential benefit,” Rachel Bender Ignacio, MD, MPH, infectious disease specialist, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Importantly, in this pragmatic study, duration and severity of symptoms were not reported, observed Dr. Bender Ignacio, who is also a STOP-COVID-2 investigator. “We don’t yet have data as to whether colchicine shortens duration or severity of symptoms or prevents long COVID, so we need more data on that.”
The overall risk for serious adverse events was lower in the colchicine group, but the difference in pulmonary embolism (PE) was striking, she said. This could be caused by a real biologic effect, or it’s possible that persons with shortness of breath and hypoxia, without evident viral pneumonia on chest x-ray after a positive COVID-19 test, were more likely to receive a CT-PE study.
The press release also failed to include information, later noted in the preprint, that the MHI has submitted two patents related to colchicine: “Methods of treating a coronavirus infection using colchicine” and “Early administration of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction.”
Reached for clarification, MHI communications adviser Camille Turbide said in an interview that the first patent “simply refers to the novel concept of preventing complications of COVID-19, such as admission to the hospital, with colchicine as tested in the ColCORONA study.”
The second patent, she said, refers to the “novel concept that administering colchicine early after a major adverse cardiovascular event is better than waiting several days,” as supported by the COLCOT study, which Dr. Tardif also led.
The patents are being reviewed by authorities and “Dr. Tardif has waived his rights in these patents and does not stand to benefit financially at all if colchicine becomes used as a treatment for COVID-19,” Ms. Turbide said.
Dr. Tardif did not respond to interview requests for this story. Dr. Glatt said conflicts of interest must be assessed and are “something that is of great concern in any scientific study.”
Cardiologist Steve Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic said in an interview that, “despite the negative results, the study does suggest that colchicine might have a benefit and should be studied in future trials. These findings are not sufficient evidence to suggest use of the drug in patients infected with COVID-19.”
He noted that adverse effects like diarrhea were expected but that the excess PE was unexpected and needs greater clarification.
“Stopping the trial for administrative reasons is puzzling and undermined the ability of the trial to give a reliable answer,” Dr. Nissen said. “This is a reasonable pilot study that should be viewed as hypothesis generating but inconclusive.”
Several sources said a new trial is unlikely, particularly given the cost and 28 trials already evaluating colchicine. Among these are RECOVERY and COLCOVID, testing whether colchicine can reduce the duration of hospitalization or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Because there are so many trials ongoing right now, including for antivirals and other immunomodulators, it’s important that, if colchicine comes to routine clinical use, it provides access to treatment for those not able or willing to access clinical trials, rather than impeding clinical trial enrollment, Dr. Bender Ignacio suggested.
“We have already learned the lesson in the pandemic that early adoption of potentially promising therapies can negatively impact our ability to study and develop other promising treatments,” she said.
The trial was coordinated by the Montreal Heart Institute and funded by the government of Quebec; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; Montreal philanthropist Sophie Desmarais, and the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator launched by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and Mastercard. CGI, Dacima, and Pharmascience of Montreal were also collaborators. Dr. Glatt reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Boulware reported receiving $18 in food and beverages from Gilead Sciences in 2018.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Science by press release and preprint has cooled clinician enthusiasm for the use of colchicine in nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, despite a pressing need for early treatments.
As previously reported by this news organization, a Jan. 22 press release announced that the massive ColCORONA study missed its primary endpoint of hospitalization or death among 4,488 newly diagnosed patients at increased risk for hospitalization.
But it also touted that use of the anti-inflammatory drug significantly reduced the primary endpoint in 4,159 of those patients with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID and led to reductions of 25%, 50%, and 44%, respectively, for hospitalizations, ventilations, and death.
Lead investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, director of the Montreal Heart Institute Research Centre, deemed the findings a “medical breakthrough.”
When the preprint released a few days later, however, newly revealed confidence intervals showed colchicine did not meaningfully reduce the need for mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-1.07) or death alone (OR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.19-1.66).
Further, the significant benefit on the primary outcome came at the cost of a fivefold increase in pulmonary embolism (11 vs. 2; P = .01), which was not mentioned in the press release.
“Whether this represents a real phenomenon or simply the play of chance is not known,” Dr. Tardif and colleagues noted later in the preprint.
“I read the preprint on colchicine and I have so many questions,” Aaron E. Glatt, MD, spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases, Mount Sinai South Nassau, Hewlett, N.Y., said in an interview. “I’ve been burned too many times with COVID and prefer to see better data.
“People sometimes say if you wait for perfect data, people are going to die,” he said. “Yeah, but we have no idea if people are going to die from getting this drug more than not getting it. That’s what concerns me. How many pulmonary emboli are going to be fatal versus the slight benefit that the study showed?”
The pushback to the non–peer-reviewed data on social media and via emails was so strong that Dr. Tardif posted a nearly 2,000-word letter responding to the many questions at play.
Chief among them was why the trial, originally planned for 6,000 patients, was stopped early by the investigators without consultation with the data safety monitoring board (DSMB).
The explanation in the letter that logistical issues like running the study call center, budget constraints, and a perceived need to quickly communicate the results left some calling foul that the study wasn’t allowed to finish and come to a more definitive conclusion.
“I can be a little bit sympathetic to their cause but at the same time the DSMB should have said no,” said David Boulware, MD, MPH, who led a recent hydroxychloroquine trial in COVID-19. “The problem is we’re sort of left in limbo, where some people kind of believe it and some say it’s not really a thing. So it’s not really moving the needle, as far as guidelines go.”
Indeed, a Twitter poll by cardiologist James Januzzi Jr., MD, captured the uncertainty, with 28% of respondents saying the trial was “neutral,” 58% saying “maybe but meh,” and 14% saying “colchicine for all.”
Another poll cheekily asked whether ColCORONA was the Gamestop/Reddit equivalent of COVID.
“The press release really didn’t help things because it very much oversold the effect. That, I think, poisoned the well,” said Dr. Boulware, professor of medicine in infectious diseases at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“The question I’m left with is not whether colchicine works, but who does it work in,” he said. “That’s really the fundamental question because it does seem that there are probably high-risk groups in their trial and others where they benefit, whereas other groups don’t benefit. In the subgroup analysis, there was absolutely no beneficial effect in women.”
According to the authors, the number needed to treat to prevent one death or hospitalization was 71 overall, but 29 for patients with diabetes, 31 for those aged 70 years and older, 53 for patients with respiratory disease, and 25 for those with coronary disease or heart failure.
Men are at higher risk overall for poor outcomes. But “the authors didn’t present a multivariable analysis, so it is unclear if another factor, such as a differential prevalence of smoking or cardiovascular risk factors, contributed to the differential benefit,” Rachel Bender Ignacio, MD, MPH, infectious disease specialist, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Importantly, in this pragmatic study, duration and severity of symptoms were not reported, observed Dr. Bender Ignacio, who is also a STOP-COVID-2 investigator. “We don’t yet have data as to whether colchicine shortens duration or severity of symptoms or prevents long COVID, so we need more data on that.”
The overall risk for serious adverse events was lower in the colchicine group, but the difference in pulmonary embolism (PE) was striking, she said. This could be caused by a real biologic effect, or it’s possible that persons with shortness of breath and hypoxia, without evident viral pneumonia on chest x-ray after a positive COVID-19 test, were more likely to receive a CT-PE study.
The press release also failed to include information, later noted in the preprint, that the MHI has submitted two patents related to colchicine: “Methods of treating a coronavirus infection using colchicine” and “Early administration of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction.”
Reached for clarification, MHI communications adviser Camille Turbide said in an interview that the first patent “simply refers to the novel concept of preventing complications of COVID-19, such as admission to the hospital, with colchicine as tested in the ColCORONA study.”
The second patent, she said, refers to the “novel concept that administering colchicine early after a major adverse cardiovascular event is better than waiting several days,” as supported by the COLCOT study, which Dr. Tardif also led.
The patents are being reviewed by authorities and “Dr. Tardif has waived his rights in these patents and does not stand to benefit financially at all if colchicine becomes used as a treatment for COVID-19,” Ms. Turbide said.
Dr. Tardif did not respond to interview requests for this story. Dr. Glatt said conflicts of interest must be assessed and are “something that is of great concern in any scientific study.”
Cardiologist Steve Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic said in an interview that, “despite the negative results, the study does suggest that colchicine might have a benefit and should be studied in future trials. These findings are not sufficient evidence to suggest use of the drug in patients infected with COVID-19.”
He noted that adverse effects like diarrhea were expected but that the excess PE was unexpected and needs greater clarification.
“Stopping the trial for administrative reasons is puzzling and undermined the ability of the trial to give a reliable answer,” Dr. Nissen said. “This is a reasonable pilot study that should be viewed as hypothesis generating but inconclusive.”
Several sources said a new trial is unlikely, particularly given the cost and 28 trials already evaluating colchicine. Among these are RECOVERY and COLCOVID, testing whether colchicine can reduce the duration of hospitalization or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Because there are so many trials ongoing right now, including for antivirals and other immunomodulators, it’s important that, if colchicine comes to routine clinical use, it provides access to treatment for those not able or willing to access clinical trials, rather than impeding clinical trial enrollment, Dr. Bender Ignacio suggested.
“We have already learned the lesson in the pandemic that early adoption of potentially promising therapies can negatively impact our ability to study and develop other promising treatments,” she said.
The trial was coordinated by the Montreal Heart Institute and funded by the government of Quebec; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; Montreal philanthropist Sophie Desmarais, and the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator launched by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and Mastercard. CGI, Dacima, and Pharmascience of Montreal were also collaborators. Dr. Glatt reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Boulware reported receiving $18 in food and beverages from Gilead Sciences in 2018.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Science by press release and preprint has cooled clinician enthusiasm for the use of colchicine in nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, despite a pressing need for early treatments.
As previously reported by this news organization, a Jan. 22 press release announced that the massive ColCORONA study missed its primary endpoint of hospitalization or death among 4,488 newly diagnosed patients at increased risk for hospitalization.
But it also touted that use of the anti-inflammatory drug significantly reduced the primary endpoint in 4,159 of those patients with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID and led to reductions of 25%, 50%, and 44%, respectively, for hospitalizations, ventilations, and death.
Lead investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, director of the Montreal Heart Institute Research Centre, deemed the findings a “medical breakthrough.”
When the preprint released a few days later, however, newly revealed confidence intervals showed colchicine did not meaningfully reduce the need for mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-1.07) or death alone (OR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.19-1.66).
Further, the significant benefit on the primary outcome came at the cost of a fivefold increase in pulmonary embolism (11 vs. 2; P = .01), which was not mentioned in the press release.
“Whether this represents a real phenomenon or simply the play of chance is not known,” Dr. Tardif and colleagues noted later in the preprint.
“I read the preprint on colchicine and I have so many questions,” Aaron E. Glatt, MD, spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases, Mount Sinai South Nassau, Hewlett, N.Y., said in an interview. “I’ve been burned too many times with COVID and prefer to see better data.
“People sometimes say if you wait for perfect data, people are going to die,” he said. “Yeah, but we have no idea if people are going to die from getting this drug more than not getting it. That’s what concerns me. How many pulmonary emboli are going to be fatal versus the slight benefit that the study showed?”
The pushback to the non–peer-reviewed data on social media and via emails was so strong that Dr. Tardif posted a nearly 2,000-word letter responding to the many questions at play.
Chief among them was why the trial, originally planned for 6,000 patients, was stopped early by the investigators without consultation with the data safety monitoring board (DSMB).
The explanation in the letter that logistical issues like running the study call center, budget constraints, and a perceived need to quickly communicate the results left some calling foul that the study wasn’t allowed to finish and come to a more definitive conclusion.
“I can be a little bit sympathetic to their cause but at the same time the DSMB should have said no,” said David Boulware, MD, MPH, who led a recent hydroxychloroquine trial in COVID-19. “The problem is we’re sort of left in limbo, where some people kind of believe it and some say it’s not really a thing. So it’s not really moving the needle, as far as guidelines go.”
Indeed, a Twitter poll by cardiologist James Januzzi Jr., MD, captured the uncertainty, with 28% of respondents saying the trial was “neutral,” 58% saying “maybe but meh,” and 14% saying “colchicine for all.”
Another poll cheekily asked whether ColCORONA was the Gamestop/Reddit equivalent of COVID.
“The press release really didn’t help things because it very much oversold the effect. That, I think, poisoned the well,” said Dr. Boulware, professor of medicine in infectious diseases at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“The question I’m left with is not whether colchicine works, but who does it work in,” he said. “That’s really the fundamental question because it does seem that there are probably high-risk groups in their trial and others where they benefit, whereas other groups don’t benefit. In the subgroup analysis, there was absolutely no beneficial effect in women.”
According to the authors, the number needed to treat to prevent one death or hospitalization was 71 overall, but 29 for patients with diabetes, 31 for those aged 70 years and older, 53 for patients with respiratory disease, and 25 for those with coronary disease or heart failure.
Men are at higher risk overall for poor outcomes. But “the authors didn’t present a multivariable analysis, so it is unclear if another factor, such as a differential prevalence of smoking or cardiovascular risk factors, contributed to the differential benefit,” Rachel Bender Ignacio, MD, MPH, infectious disease specialist, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Importantly, in this pragmatic study, duration and severity of symptoms were not reported, observed Dr. Bender Ignacio, who is also a STOP-COVID-2 investigator. “We don’t yet have data as to whether colchicine shortens duration or severity of symptoms or prevents long COVID, so we need more data on that.”
The overall risk for serious adverse events was lower in the colchicine group, but the difference in pulmonary embolism (PE) was striking, she said. This could be caused by a real biologic effect, or it’s possible that persons with shortness of breath and hypoxia, without evident viral pneumonia on chest x-ray after a positive COVID-19 test, were more likely to receive a CT-PE study.
The press release also failed to include information, later noted in the preprint, that the MHI has submitted two patents related to colchicine: “Methods of treating a coronavirus infection using colchicine” and “Early administration of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction.”
Reached for clarification, MHI communications adviser Camille Turbide said in an interview that the first patent “simply refers to the novel concept of preventing complications of COVID-19, such as admission to the hospital, with colchicine as tested in the ColCORONA study.”
The second patent, she said, refers to the “novel concept that administering colchicine early after a major adverse cardiovascular event is better than waiting several days,” as supported by the COLCOT study, which Dr. Tardif also led.
The patents are being reviewed by authorities and “Dr. Tardif has waived his rights in these patents and does not stand to benefit financially at all if colchicine becomes used as a treatment for COVID-19,” Ms. Turbide said.
Dr. Tardif did not respond to interview requests for this story. Dr. Glatt said conflicts of interest must be assessed and are “something that is of great concern in any scientific study.”
Cardiologist Steve Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic said in an interview that, “despite the negative results, the study does suggest that colchicine might have a benefit and should be studied in future trials. These findings are not sufficient evidence to suggest use of the drug in patients infected with COVID-19.”
He noted that adverse effects like diarrhea were expected but that the excess PE was unexpected and needs greater clarification.
“Stopping the trial for administrative reasons is puzzling and undermined the ability of the trial to give a reliable answer,” Dr. Nissen said. “This is a reasonable pilot study that should be viewed as hypothesis generating but inconclusive.”
Several sources said a new trial is unlikely, particularly given the cost and 28 trials already evaluating colchicine. Among these are RECOVERY and COLCOVID, testing whether colchicine can reduce the duration of hospitalization or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Because there are so many trials ongoing right now, including for antivirals and other immunomodulators, it’s important that, if colchicine comes to routine clinical use, it provides access to treatment for those not able or willing to access clinical trials, rather than impeding clinical trial enrollment, Dr. Bender Ignacio suggested.
“We have already learned the lesson in the pandemic that early adoption of potentially promising therapies can negatively impact our ability to study and develop other promising treatments,” she said.
The trial was coordinated by the Montreal Heart Institute and funded by the government of Quebec; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; Montreal philanthropist Sophie Desmarais, and the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator launched by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and Mastercard. CGI, Dacima, and Pharmascience of Montreal were also collaborators. Dr. Glatt reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Boulware reported receiving $18 in food and beverages from Gilead Sciences in 2018.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oily fish linked to lower risk of diabetes in largest study to date
People who report regularly eating oily fish had a significantly reduced risk for developing type 2 diabetes in a prospective, observational study of nearly 400,000 UK residents.
The results also show a significant, but weaker, positive link between regular use of fish oil supplements and a drop in the incidence of type 2 diabetes, Qibin Qi, PhD, and colleagues wrote in a report published in Diabetes Care. Their analysis failed to show a significant link between consumption of non-oily fish and type 2 diabetes onset.
The study is notable for being “the largest so far” to examine the link between fish consumption and type 2 diabetes incidence, and the first to establish a clear, significant association between regularly eating oily fish and a drop in the incidence of diabetes, said Dr. Qi, an epidemiologist at Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York.
“At present, it is prudent to recommend fresh oily fish as a part of a healthy dietary pattern instead of fish oil supplements for diabetes prevention,” said Dr. Qi and coauthors.
The study included just over 392,000 adults without type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease at baseline enrolled in the UK Biobank. Median follow-up was just over 10 years, during which 7,262 participants developed diabetes.
Participants who ate either one, or two or more, servings of oily fish weekly each had a significant 22% lower rate of incident type 2 diabetes than that of those who ate no oily fish, after adjustment for multiple confounders. Those who reported regularly taking a fish oil supplement had a significant 9% lower incidence of type 2 diabetes than that of those who didn’t.
Evidence growing to add oily fish to diet to prevent type 2 diabetes
“Many current dietary guidelines recommend consumption of two servings of fish, preferably oily, per week, primarily based on cardiovascular benefits,” Dr. Qi said in an interview.
“No prior statements recommended oily fish for prevention of type 2 diabetes,” he explained, adding: “Our findings support future recommendations, but the evidence is not strong enough to make a [formal] recommendation now. We need evidence from clinical trials.”
Jason Wu, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of New South Wales in Sydney, Australia, who specializes in this field but was not involved with the current study, said it “is a very well-conducted study, and certainly generates important new evidence supporting the potential benefits of regular consumption of oily fish.”
But he agrees that the evidence remains too preliminary for any official recommendations on eating oily fish for preventing the development of type 2 diabetes, including targeting advice to high-risk subgroups such as those with prediabetes or people who are obese.
Before any groups make recommendations, “we need to thoroughly review all the literature in this space to appraise the overall body of evidence,” Dr. Wu noted in an interview.
Oily fish: Solid evidence for prevention of CVD events
In contrast, the case for including oily fish in the diet to prevent CVD events seems settled. In 2018, a panel assembled by the American Heart Association to address the issue released a statement that concluded: “Current scientific evidence strongly supports the recommendation that seafood be an integral component of a heart-healthy dietary pattern.” It added that “a large body of evidence supports the recommendation to consume nonfried seafood, especially species higher in long-chain n-3 fatty acids, one to two times per week for cardiovascular benefits, including reduced risk of cardiac death, coronary heart disease, and ischemic stroke.”
The statement highlighted that “cold-water oily fish such as salmon, anchovies, herring, mackerel (Atlantic and Pacific), tuna (bluefin and albacore), and sardines have the highest levels” of long-chain n-3 fatty acids, notably eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, also collectively known as omega-3 fatty acids.
These fish types were among the oily fishes tallied in the UK Biobank data used by Dr. Qi and colleagues.
The case for fish oil supplements for preventing CVD events is much rockier, as summarized in a 2019 editorial, with some studies reporting no discernible effect while others indicate efficacy.
A second commentary from December 2020 highlighted how results from the REDUCE-IT trial showed clear benefit for preventing CVD using a highly purified form of fish oil, icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin). However, findings from two other recent reports, the STRENGTH and OMENI studies, failed to show CVD benefits from more conventional fish oil formulations.
Composite CVD and diabetes prevention effects?
The new findings by Dr. Qi and colleagues “highlight the need to specifically test the effect of fish oil supplements on glucose metabolism in people who cannot or choose not to regularly eat oily fish,” said Dr. Wu, a researcher at the George Institute for Global Health in Newtown, Australia.
“If eventually there is really strong evidence that fish, fish oil, or both have independent effects on both CVD and type 2 diabetes” it would be reasonable to integrate both outcomes into a single, composite, efficacy endpoint for the purpose of future studies, he added.
Dr. Qi agreed on both points. “A randomized, controlled trial of fish oil on type 2 diabetes as a primary outcome is needed. Most existing data are based on secondary analyses in the randomized trials for CVD,” he explained.
But, he added, “our results suggest a potential beneficial effect from fish oil supplements,” which implies that these may be “better than nothing” for people who can’t add oily fish to their regular diet.
The means by which fish and fish oil might slow or stop progression to type 2 diabetes remains uncertain.
The mechanisms for preventing both diabetes and CVD events may overlap, Dr. Qi noted, such as anti-inflammatory effects and improved insulin sensitivity, both of which have been observed in animal studies.
Evidence is “still lacking from human studies,” he explained, but if such mechanisms were at play, Dr. Wu said that would “add biologic plausibility” to a possible causal link between oily fish consumption and diabetes prevention.
“But we can’t assume that omega-3 fatty acids alone will have the same effect as oily fish, which obviously contains many other components.”
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Qi and Dr. Wu have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who report regularly eating oily fish had a significantly reduced risk for developing type 2 diabetes in a prospective, observational study of nearly 400,000 UK residents.
The results also show a significant, but weaker, positive link between regular use of fish oil supplements and a drop in the incidence of type 2 diabetes, Qibin Qi, PhD, and colleagues wrote in a report published in Diabetes Care. Their analysis failed to show a significant link between consumption of non-oily fish and type 2 diabetes onset.
The study is notable for being “the largest so far” to examine the link between fish consumption and type 2 diabetes incidence, and the first to establish a clear, significant association between regularly eating oily fish and a drop in the incidence of diabetes, said Dr. Qi, an epidemiologist at Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York.
“At present, it is prudent to recommend fresh oily fish as a part of a healthy dietary pattern instead of fish oil supplements for diabetes prevention,” said Dr. Qi and coauthors.
The study included just over 392,000 adults without type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease at baseline enrolled in the UK Biobank. Median follow-up was just over 10 years, during which 7,262 participants developed diabetes.
Participants who ate either one, or two or more, servings of oily fish weekly each had a significant 22% lower rate of incident type 2 diabetes than that of those who ate no oily fish, after adjustment for multiple confounders. Those who reported regularly taking a fish oil supplement had a significant 9% lower incidence of type 2 diabetes than that of those who didn’t.
Evidence growing to add oily fish to diet to prevent type 2 diabetes
“Many current dietary guidelines recommend consumption of two servings of fish, preferably oily, per week, primarily based on cardiovascular benefits,” Dr. Qi said in an interview.
“No prior statements recommended oily fish for prevention of type 2 diabetes,” he explained, adding: “Our findings support future recommendations, but the evidence is not strong enough to make a [formal] recommendation now. We need evidence from clinical trials.”
Jason Wu, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of New South Wales in Sydney, Australia, who specializes in this field but was not involved with the current study, said it “is a very well-conducted study, and certainly generates important new evidence supporting the potential benefits of regular consumption of oily fish.”
But he agrees that the evidence remains too preliminary for any official recommendations on eating oily fish for preventing the development of type 2 diabetes, including targeting advice to high-risk subgroups such as those with prediabetes or people who are obese.
Before any groups make recommendations, “we need to thoroughly review all the literature in this space to appraise the overall body of evidence,” Dr. Wu noted in an interview.
Oily fish: Solid evidence for prevention of CVD events
In contrast, the case for including oily fish in the diet to prevent CVD events seems settled. In 2018, a panel assembled by the American Heart Association to address the issue released a statement that concluded: “Current scientific evidence strongly supports the recommendation that seafood be an integral component of a heart-healthy dietary pattern.” It added that “a large body of evidence supports the recommendation to consume nonfried seafood, especially species higher in long-chain n-3 fatty acids, one to two times per week for cardiovascular benefits, including reduced risk of cardiac death, coronary heart disease, and ischemic stroke.”
The statement highlighted that “cold-water oily fish such as salmon, anchovies, herring, mackerel (Atlantic and Pacific), tuna (bluefin and albacore), and sardines have the highest levels” of long-chain n-3 fatty acids, notably eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, also collectively known as omega-3 fatty acids.
These fish types were among the oily fishes tallied in the UK Biobank data used by Dr. Qi and colleagues.
The case for fish oil supplements for preventing CVD events is much rockier, as summarized in a 2019 editorial, with some studies reporting no discernible effect while others indicate efficacy.
A second commentary from December 2020 highlighted how results from the REDUCE-IT trial showed clear benefit for preventing CVD using a highly purified form of fish oil, icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin). However, findings from two other recent reports, the STRENGTH and OMENI studies, failed to show CVD benefits from more conventional fish oil formulations.
Composite CVD and diabetes prevention effects?
The new findings by Dr. Qi and colleagues “highlight the need to specifically test the effect of fish oil supplements on glucose metabolism in people who cannot or choose not to regularly eat oily fish,” said Dr. Wu, a researcher at the George Institute for Global Health in Newtown, Australia.
“If eventually there is really strong evidence that fish, fish oil, or both have independent effects on both CVD and type 2 diabetes” it would be reasonable to integrate both outcomes into a single, composite, efficacy endpoint for the purpose of future studies, he added.
Dr. Qi agreed on both points. “A randomized, controlled trial of fish oil on type 2 diabetes as a primary outcome is needed. Most existing data are based on secondary analyses in the randomized trials for CVD,” he explained.
But, he added, “our results suggest a potential beneficial effect from fish oil supplements,” which implies that these may be “better than nothing” for people who can’t add oily fish to their regular diet.
The means by which fish and fish oil might slow or stop progression to type 2 diabetes remains uncertain.
The mechanisms for preventing both diabetes and CVD events may overlap, Dr. Qi noted, such as anti-inflammatory effects and improved insulin sensitivity, both of which have been observed in animal studies.
Evidence is “still lacking from human studies,” he explained, but if such mechanisms were at play, Dr. Wu said that would “add biologic plausibility” to a possible causal link between oily fish consumption and diabetes prevention.
“But we can’t assume that omega-3 fatty acids alone will have the same effect as oily fish, which obviously contains many other components.”
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Qi and Dr. Wu have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who report regularly eating oily fish had a significantly reduced risk for developing type 2 diabetes in a prospective, observational study of nearly 400,000 UK residents.
The results also show a significant, but weaker, positive link between regular use of fish oil supplements and a drop in the incidence of type 2 diabetes, Qibin Qi, PhD, and colleagues wrote in a report published in Diabetes Care. Their analysis failed to show a significant link between consumption of non-oily fish and type 2 diabetes onset.
The study is notable for being “the largest so far” to examine the link between fish consumption and type 2 diabetes incidence, and the first to establish a clear, significant association between regularly eating oily fish and a drop in the incidence of diabetes, said Dr. Qi, an epidemiologist at Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York.
“At present, it is prudent to recommend fresh oily fish as a part of a healthy dietary pattern instead of fish oil supplements for diabetes prevention,” said Dr. Qi and coauthors.
The study included just over 392,000 adults without type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease at baseline enrolled in the UK Biobank. Median follow-up was just over 10 years, during which 7,262 participants developed diabetes.
Participants who ate either one, or two or more, servings of oily fish weekly each had a significant 22% lower rate of incident type 2 diabetes than that of those who ate no oily fish, after adjustment for multiple confounders. Those who reported regularly taking a fish oil supplement had a significant 9% lower incidence of type 2 diabetes than that of those who didn’t.
Evidence growing to add oily fish to diet to prevent type 2 diabetes
“Many current dietary guidelines recommend consumption of two servings of fish, preferably oily, per week, primarily based on cardiovascular benefits,” Dr. Qi said in an interview.
“No prior statements recommended oily fish for prevention of type 2 diabetes,” he explained, adding: “Our findings support future recommendations, but the evidence is not strong enough to make a [formal] recommendation now. We need evidence from clinical trials.”
Jason Wu, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of New South Wales in Sydney, Australia, who specializes in this field but was not involved with the current study, said it “is a very well-conducted study, and certainly generates important new evidence supporting the potential benefits of regular consumption of oily fish.”
But he agrees that the evidence remains too preliminary for any official recommendations on eating oily fish for preventing the development of type 2 diabetes, including targeting advice to high-risk subgroups such as those with prediabetes or people who are obese.
Before any groups make recommendations, “we need to thoroughly review all the literature in this space to appraise the overall body of evidence,” Dr. Wu noted in an interview.
Oily fish: Solid evidence for prevention of CVD events
In contrast, the case for including oily fish in the diet to prevent CVD events seems settled. In 2018, a panel assembled by the American Heart Association to address the issue released a statement that concluded: “Current scientific evidence strongly supports the recommendation that seafood be an integral component of a heart-healthy dietary pattern.” It added that “a large body of evidence supports the recommendation to consume nonfried seafood, especially species higher in long-chain n-3 fatty acids, one to two times per week for cardiovascular benefits, including reduced risk of cardiac death, coronary heart disease, and ischemic stroke.”
The statement highlighted that “cold-water oily fish such as salmon, anchovies, herring, mackerel (Atlantic and Pacific), tuna (bluefin and albacore), and sardines have the highest levels” of long-chain n-3 fatty acids, notably eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, also collectively known as omega-3 fatty acids.
These fish types were among the oily fishes tallied in the UK Biobank data used by Dr. Qi and colleagues.
The case for fish oil supplements for preventing CVD events is much rockier, as summarized in a 2019 editorial, with some studies reporting no discernible effect while others indicate efficacy.
A second commentary from December 2020 highlighted how results from the REDUCE-IT trial showed clear benefit for preventing CVD using a highly purified form of fish oil, icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin). However, findings from two other recent reports, the STRENGTH and OMENI studies, failed to show CVD benefits from more conventional fish oil formulations.
Composite CVD and diabetes prevention effects?
The new findings by Dr. Qi and colleagues “highlight the need to specifically test the effect of fish oil supplements on glucose metabolism in people who cannot or choose not to regularly eat oily fish,” said Dr. Wu, a researcher at the George Institute for Global Health in Newtown, Australia.
“If eventually there is really strong evidence that fish, fish oil, or both have independent effects on both CVD and type 2 diabetes” it would be reasonable to integrate both outcomes into a single, composite, efficacy endpoint for the purpose of future studies, he added.
Dr. Qi agreed on both points. “A randomized, controlled trial of fish oil on type 2 diabetes as a primary outcome is needed. Most existing data are based on secondary analyses in the randomized trials for CVD,” he explained.
But, he added, “our results suggest a potential beneficial effect from fish oil supplements,” which implies that these may be “better than nothing” for people who can’t add oily fish to their regular diet.
The means by which fish and fish oil might slow or stop progression to type 2 diabetes remains uncertain.
The mechanisms for preventing both diabetes and CVD events may overlap, Dr. Qi noted, such as anti-inflammatory effects and improved insulin sensitivity, both of which have been observed in animal studies.
Evidence is “still lacking from human studies,” he explained, but if such mechanisms were at play, Dr. Wu said that would “add biologic plausibility” to a possible causal link between oily fish consumption and diabetes prevention.
“But we can’t assume that omega-3 fatty acids alone will have the same effect as oily fish, which obviously contains many other components.”
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Qi and Dr. Wu have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study flags cardiovascular disease in men with breast cancer
.
Among 24 male breast cancer patients evaluated over a decade in the Washington area, 88% were obese or overweight, 58% had hypertension, and 54% had hyperlipidemia.
Tachyarrhythmia existed in 8% of the men before cancer treatment and developed in 13% during treatment.
Two patients had preexisting heart failure, two patients developed the disease after treatment, and another two patients experienced a decline in left ventricular ejection fraction during the course of their cancer treatment.
“Our hope is that treating male breast cancer patients becomes a multidisciplinary approach where oncologists recruit their cardio-oncologist counterparts to mitigate cardiovascular risk factors, so patients live a long and healthy life after cancer treatment,” said Michael Ibrahim, one of the study authors and a 4th-year medical student at Georgetown University in Washington.
The data were presented Jan. 25 as part of the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient virtual course, which is hosting live sessions Feb. 5-6.
Although the association between cardiovascular disease and breast cancer is well documented in female breast cancer patients, there is little evidence in their male counterparts, especially African Americans, Mr. Ibrahim noted.
To provide some context, Mr. Ibrahim highlighted a 2018 report in nearly 3,500 female breast cancer patients, ages 40-79, in whom 52% were obese/overweight, 35% had hypertension, and 28% had hyperlipidemia.
Diabetes was present in 7.5% of the women, which was roughly equivalent to the 8% found among the men, Mr. Ibrahim said. The men were of similar age (38-79 years), with 42% being African American, 29% White, 4% Hispanic, and 25% another ethnicity.
Importantly, half of the men had a family history of breast cancer, and two were positive for a mutation in the BRCA gene.
A 2017 in-depth review of male breast cancer cites advancing age, hormonal imbalance, radiation exposure, and family history of breast cancer as key risk factors for the development of the disease, but the “most relevant risk factor” is a mutation in the BRCA2 gene.
Male breast cancer accounts for less than 1% of all breast cancers, but the incidence is rising and, in some patient groups, reaching 15% over their lifetimes, the paper notes. Additionally, these patients are at special risk for developing a second cancer.
Remarkably, 25% of men in the D.C. cohort were diagnosed with a second primary malignancy, 13% a third primary cancer, and 4% a fourth primary cancer, Mr. Ibrahim reported. “This goes to show that male breast cancer patients should routinely undergo cancer screening,” he said.
The initial diagnosis was invasive ductal carcinoma in 79% of the men, with the remaining ductal carcinoma in situ. All patients underwent mastectomy, 17% had anthracycline chemotherapy, 8% received HER2-targeted therapy, 16% had radiation, and 71% received hormone therapy.
In terms of cardiovascular management, statins were the most prescribed medication (46%), followed by antiplatelet therapy (42%) and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin-receptor blockers (38%).
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator/pacemaker was the most common intervention (16%), followed by bypass surgery in 8% and coronary angioplasty in 4%.
Mr. Ibrahim noted that the study was limited by the small sample size and that further research is needed to understand the risk of preexisting cardiovascular disease on long-term outcomes as well as the cardiotoxic effects of chemoradiation in male breast cancer patients.
In a statement, Mr. Ibrahim reiterated the need for a multidisciplinary cancer care team to evaluate patients’ cardiovascular risk prior to and through cancer treatment.
“On a more personal level, cancer patients are already surprised by their cancer diagnosis,” he added. “Similar to the pretreatment consultation with radiation oncology, breast surgery, and medical oncology, an upfront cardiovascular risk assessment provides greater comfort and further minimizes psychological surprise with cardiovascular complications going into cancer treatment.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
Among 24 male breast cancer patients evaluated over a decade in the Washington area, 88% were obese or overweight, 58% had hypertension, and 54% had hyperlipidemia.
Tachyarrhythmia existed in 8% of the men before cancer treatment and developed in 13% during treatment.
Two patients had preexisting heart failure, two patients developed the disease after treatment, and another two patients experienced a decline in left ventricular ejection fraction during the course of their cancer treatment.
“Our hope is that treating male breast cancer patients becomes a multidisciplinary approach where oncologists recruit their cardio-oncologist counterparts to mitigate cardiovascular risk factors, so patients live a long and healthy life after cancer treatment,” said Michael Ibrahim, one of the study authors and a 4th-year medical student at Georgetown University in Washington.
The data were presented Jan. 25 as part of the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient virtual course, which is hosting live sessions Feb. 5-6.
Although the association between cardiovascular disease and breast cancer is well documented in female breast cancer patients, there is little evidence in their male counterparts, especially African Americans, Mr. Ibrahim noted.
To provide some context, Mr. Ibrahim highlighted a 2018 report in nearly 3,500 female breast cancer patients, ages 40-79, in whom 52% were obese/overweight, 35% had hypertension, and 28% had hyperlipidemia.
Diabetes was present in 7.5% of the women, which was roughly equivalent to the 8% found among the men, Mr. Ibrahim said. The men were of similar age (38-79 years), with 42% being African American, 29% White, 4% Hispanic, and 25% another ethnicity.
Importantly, half of the men had a family history of breast cancer, and two were positive for a mutation in the BRCA gene.
A 2017 in-depth review of male breast cancer cites advancing age, hormonal imbalance, radiation exposure, and family history of breast cancer as key risk factors for the development of the disease, but the “most relevant risk factor” is a mutation in the BRCA2 gene.
Male breast cancer accounts for less than 1% of all breast cancers, but the incidence is rising and, in some patient groups, reaching 15% over their lifetimes, the paper notes. Additionally, these patients are at special risk for developing a second cancer.
Remarkably, 25% of men in the D.C. cohort were diagnosed with a second primary malignancy, 13% a third primary cancer, and 4% a fourth primary cancer, Mr. Ibrahim reported. “This goes to show that male breast cancer patients should routinely undergo cancer screening,” he said.
The initial diagnosis was invasive ductal carcinoma in 79% of the men, with the remaining ductal carcinoma in situ. All patients underwent mastectomy, 17% had anthracycline chemotherapy, 8% received HER2-targeted therapy, 16% had radiation, and 71% received hormone therapy.
In terms of cardiovascular management, statins were the most prescribed medication (46%), followed by antiplatelet therapy (42%) and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin-receptor blockers (38%).
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator/pacemaker was the most common intervention (16%), followed by bypass surgery in 8% and coronary angioplasty in 4%.
Mr. Ibrahim noted that the study was limited by the small sample size and that further research is needed to understand the risk of preexisting cardiovascular disease on long-term outcomes as well as the cardiotoxic effects of chemoradiation in male breast cancer patients.
In a statement, Mr. Ibrahim reiterated the need for a multidisciplinary cancer care team to evaluate patients’ cardiovascular risk prior to and through cancer treatment.
“On a more personal level, cancer patients are already surprised by their cancer diagnosis,” he added. “Similar to the pretreatment consultation with radiation oncology, breast surgery, and medical oncology, an upfront cardiovascular risk assessment provides greater comfort and further minimizes psychological surprise with cardiovascular complications going into cancer treatment.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
Among 24 male breast cancer patients evaluated over a decade in the Washington area, 88% were obese or overweight, 58% had hypertension, and 54% had hyperlipidemia.
Tachyarrhythmia existed in 8% of the men before cancer treatment and developed in 13% during treatment.
Two patients had preexisting heart failure, two patients developed the disease after treatment, and another two patients experienced a decline in left ventricular ejection fraction during the course of their cancer treatment.
“Our hope is that treating male breast cancer patients becomes a multidisciplinary approach where oncologists recruit their cardio-oncologist counterparts to mitigate cardiovascular risk factors, so patients live a long and healthy life after cancer treatment,” said Michael Ibrahim, one of the study authors and a 4th-year medical student at Georgetown University in Washington.
The data were presented Jan. 25 as part of the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient virtual course, which is hosting live sessions Feb. 5-6.
Although the association between cardiovascular disease and breast cancer is well documented in female breast cancer patients, there is little evidence in their male counterparts, especially African Americans, Mr. Ibrahim noted.
To provide some context, Mr. Ibrahim highlighted a 2018 report in nearly 3,500 female breast cancer patients, ages 40-79, in whom 52% were obese/overweight, 35% had hypertension, and 28% had hyperlipidemia.
Diabetes was present in 7.5% of the women, which was roughly equivalent to the 8% found among the men, Mr. Ibrahim said. The men were of similar age (38-79 years), with 42% being African American, 29% White, 4% Hispanic, and 25% another ethnicity.
Importantly, half of the men had a family history of breast cancer, and two were positive for a mutation in the BRCA gene.
A 2017 in-depth review of male breast cancer cites advancing age, hormonal imbalance, radiation exposure, and family history of breast cancer as key risk factors for the development of the disease, but the “most relevant risk factor” is a mutation in the BRCA2 gene.
Male breast cancer accounts for less than 1% of all breast cancers, but the incidence is rising and, in some patient groups, reaching 15% over their lifetimes, the paper notes. Additionally, these patients are at special risk for developing a second cancer.
Remarkably, 25% of men in the D.C. cohort were diagnosed with a second primary malignancy, 13% a third primary cancer, and 4% a fourth primary cancer, Mr. Ibrahim reported. “This goes to show that male breast cancer patients should routinely undergo cancer screening,” he said.
The initial diagnosis was invasive ductal carcinoma in 79% of the men, with the remaining ductal carcinoma in situ. All patients underwent mastectomy, 17% had anthracycline chemotherapy, 8% received HER2-targeted therapy, 16% had radiation, and 71% received hormone therapy.
In terms of cardiovascular management, statins were the most prescribed medication (46%), followed by antiplatelet therapy (42%) and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin-receptor blockers (38%).
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator/pacemaker was the most common intervention (16%), followed by bypass surgery in 8% and coronary angioplasty in 4%.
Mr. Ibrahim noted that the study was limited by the small sample size and that further research is needed to understand the risk of preexisting cardiovascular disease on long-term outcomes as well as the cardiotoxic effects of chemoradiation in male breast cancer patients.
In a statement, Mr. Ibrahim reiterated the need for a multidisciplinary cancer care team to evaluate patients’ cardiovascular risk prior to and through cancer treatment.
“On a more personal level, cancer patients are already surprised by their cancer diagnosis,” he added. “Similar to the pretreatment consultation with radiation oncology, breast surgery, and medical oncology, an upfront cardiovascular risk assessment provides greater comfort and further minimizes psychological surprise with cardiovascular complications going into cancer treatment.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Large study weighs in on ‘fat but fit’ paradox
Physical activity mitigated the impact of high body mass index (BMI) on cardiovascular risk factors, but not overall cardiovascular disease risk, according to an observational study of half a million individuals.
Despite the historically high rates of overweight and obesity worldwide, some evidence suggests that cardiorespiratory fitness could reduce the effects of excess weight on cardiovascular disease risk, wrote Pedro L. Valenzuela, PhD, of the University of Alcalá, Madrid, and colleagues.
“To clarify the existence of the ‘fat-but-fit’ [or ‘elevated BMI but active’] paradox, in this observational study, we assessed the joint association between different BMI categories and physical activity levels, respectively, and the prevalence of major CVD risk factors,” they said.
In a population-based cohort study published in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, the researchers identified 527,662 adults aged 18-64 years who were insured by an occupational risk–prevention company and underwent annual medical exams as part of their coverage. The average age of the participants was 42 years, 32% were women, and the average BMI was 26.2 kg/m2.
The participants were categorized as normal weight (42%), overweight (41%), and obese (18%), and their activity levels were categorized as inactive (64%), insufficiently active (12%), and regularly active (24%). In addition, 30% had hypercholesterolemia, 15% had hypertension, and 3% had diabetes.
Overall, compared with inactivity, insufficient activity or regular activity reduced CVD risk factors within each BMI category, and subgroups. “However, regular/insufficient PA did not compensate for the negative effects of overweight/obesity, as individuals with overweight/obesity were at greater CVD risk than their peers with normal weight, irrespective of PA levels,” the researchers said. Compared with active normal-weight men, the odds ratios for hypertension in active overweight men and active obese men were 1.98 and 4.93, respectively; the odds ratios for hypercholesterolemia were 1.61 and 2.03, respectively, and the odds ratios for diabetes were 1.33 and 3.62, respectively (P < .001 for all). Trends were similar for women.
The study results were limited by the cross-sectional design; inability to control for participants’ diet, and the reliance of self-reports of leisure-time physical activity. However, the findings were strengthened by the large sample size and “refute the notion that a physically active lifestyle can completely negate the deleterious effects of overweight/obesity,” the researchers said.
Although increasing physical activity should remain a priority for health policies, “weight loss per se should remain a primary target for health policies aimed at reducing CVD risk in people with overweight/obesity,” they concluded.
Interpret findings with caution
“With the ever-increasing public health problem of overweight and obesity, it is useful to assess any measure or measures that can have a favorable or adverse effect on cardiometabolic risk factors and the risk of CVD” Prakash Deedwania, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
Dr. Deedwania said he was not entirely surprised by the study findings. “The investigators have correlated only the self-reported level of physical activity (which is not always reliable) to the presence of three cardiac risk factors: hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes.”
The study “is not comparable to prior reports that had shown a favorable impact of carefully assessed cardiorespiratory fitness with the risk of CVD,” Dr. Deedwania noted. “However, this is one of the largest population-wide surveillance studies of more than a half million active workers across Spain, and it does show that, despite self-reported physical activity, overweight and obesity are associated with higher risks of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia,” he explained.
“The main message of these findings is that, although physical activity does have a dose-dependent favorable impact on CV risk, the main public health intervention to reduce the risk of CV risk should focus on weight loss in overweight and obese individuals,” Dr. Deedwania emphasized.
“Future studies should focus on comparing various levels of daily activities and routine exercise such as walking, bicycling, etc., with the beneficial impact on cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight and obese individuals,” he said.
Dr. Valenzuela disclosed support from the University of Alcalá. Research by corresponding author Dr. Lucia was funded by grants from Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation and Fondos FEDER. Dr. Deedwania had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Physical activity mitigated the impact of high body mass index (BMI) on cardiovascular risk factors, but not overall cardiovascular disease risk, according to an observational study of half a million individuals.
Despite the historically high rates of overweight and obesity worldwide, some evidence suggests that cardiorespiratory fitness could reduce the effects of excess weight on cardiovascular disease risk, wrote Pedro L. Valenzuela, PhD, of the University of Alcalá, Madrid, and colleagues.
“To clarify the existence of the ‘fat-but-fit’ [or ‘elevated BMI but active’] paradox, in this observational study, we assessed the joint association between different BMI categories and physical activity levels, respectively, and the prevalence of major CVD risk factors,” they said.
In a population-based cohort study published in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, the researchers identified 527,662 adults aged 18-64 years who were insured by an occupational risk–prevention company and underwent annual medical exams as part of their coverage. The average age of the participants was 42 years, 32% were women, and the average BMI was 26.2 kg/m2.
The participants were categorized as normal weight (42%), overweight (41%), and obese (18%), and their activity levels were categorized as inactive (64%), insufficiently active (12%), and regularly active (24%). In addition, 30% had hypercholesterolemia, 15% had hypertension, and 3% had diabetes.
Overall, compared with inactivity, insufficient activity or regular activity reduced CVD risk factors within each BMI category, and subgroups. “However, regular/insufficient PA did not compensate for the negative effects of overweight/obesity, as individuals with overweight/obesity were at greater CVD risk than their peers with normal weight, irrespective of PA levels,” the researchers said. Compared with active normal-weight men, the odds ratios for hypertension in active overweight men and active obese men were 1.98 and 4.93, respectively; the odds ratios for hypercholesterolemia were 1.61 and 2.03, respectively, and the odds ratios for diabetes were 1.33 and 3.62, respectively (P < .001 for all). Trends were similar for women.
The study results were limited by the cross-sectional design; inability to control for participants’ diet, and the reliance of self-reports of leisure-time physical activity. However, the findings were strengthened by the large sample size and “refute the notion that a physically active lifestyle can completely negate the deleterious effects of overweight/obesity,” the researchers said.
Although increasing physical activity should remain a priority for health policies, “weight loss per se should remain a primary target for health policies aimed at reducing CVD risk in people with overweight/obesity,” they concluded.
Interpret findings with caution
“With the ever-increasing public health problem of overweight and obesity, it is useful to assess any measure or measures that can have a favorable or adverse effect on cardiometabolic risk factors and the risk of CVD” Prakash Deedwania, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
Dr. Deedwania said he was not entirely surprised by the study findings. “The investigators have correlated only the self-reported level of physical activity (which is not always reliable) to the presence of three cardiac risk factors: hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes.”
The study “is not comparable to prior reports that had shown a favorable impact of carefully assessed cardiorespiratory fitness with the risk of CVD,” Dr. Deedwania noted. “However, this is one of the largest population-wide surveillance studies of more than a half million active workers across Spain, and it does show that, despite self-reported physical activity, overweight and obesity are associated with higher risks of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia,” he explained.
“The main message of these findings is that, although physical activity does have a dose-dependent favorable impact on CV risk, the main public health intervention to reduce the risk of CV risk should focus on weight loss in overweight and obese individuals,” Dr. Deedwania emphasized.
“Future studies should focus on comparing various levels of daily activities and routine exercise such as walking, bicycling, etc., with the beneficial impact on cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight and obese individuals,” he said.
Dr. Valenzuela disclosed support from the University of Alcalá. Research by corresponding author Dr. Lucia was funded by grants from Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation and Fondos FEDER. Dr. Deedwania had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Physical activity mitigated the impact of high body mass index (BMI) on cardiovascular risk factors, but not overall cardiovascular disease risk, according to an observational study of half a million individuals.
Despite the historically high rates of overweight and obesity worldwide, some evidence suggests that cardiorespiratory fitness could reduce the effects of excess weight on cardiovascular disease risk, wrote Pedro L. Valenzuela, PhD, of the University of Alcalá, Madrid, and colleagues.
“To clarify the existence of the ‘fat-but-fit’ [or ‘elevated BMI but active’] paradox, in this observational study, we assessed the joint association between different BMI categories and physical activity levels, respectively, and the prevalence of major CVD risk factors,” they said.
In a population-based cohort study published in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, the researchers identified 527,662 adults aged 18-64 years who were insured by an occupational risk–prevention company and underwent annual medical exams as part of their coverage. The average age of the participants was 42 years, 32% were women, and the average BMI was 26.2 kg/m2.
The participants were categorized as normal weight (42%), overweight (41%), and obese (18%), and their activity levels were categorized as inactive (64%), insufficiently active (12%), and regularly active (24%). In addition, 30% had hypercholesterolemia, 15% had hypertension, and 3% had diabetes.
Overall, compared with inactivity, insufficient activity or regular activity reduced CVD risk factors within each BMI category, and subgroups. “However, regular/insufficient PA did not compensate for the negative effects of overweight/obesity, as individuals with overweight/obesity were at greater CVD risk than their peers with normal weight, irrespective of PA levels,” the researchers said. Compared with active normal-weight men, the odds ratios for hypertension in active overweight men and active obese men were 1.98 and 4.93, respectively; the odds ratios for hypercholesterolemia were 1.61 and 2.03, respectively, and the odds ratios for diabetes were 1.33 and 3.62, respectively (P < .001 for all). Trends were similar for women.
The study results were limited by the cross-sectional design; inability to control for participants’ diet, and the reliance of self-reports of leisure-time physical activity. However, the findings were strengthened by the large sample size and “refute the notion that a physically active lifestyle can completely negate the deleterious effects of overweight/obesity,” the researchers said.
Although increasing physical activity should remain a priority for health policies, “weight loss per se should remain a primary target for health policies aimed at reducing CVD risk in people with overweight/obesity,” they concluded.
Interpret findings with caution
“With the ever-increasing public health problem of overweight and obesity, it is useful to assess any measure or measures that can have a favorable or adverse effect on cardiometabolic risk factors and the risk of CVD” Prakash Deedwania, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
Dr. Deedwania said he was not entirely surprised by the study findings. “The investigators have correlated only the self-reported level of physical activity (which is not always reliable) to the presence of three cardiac risk factors: hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes.”
The study “is not comparable to prior reports that had shown a favorable impact of carefully assessed cardiorespiratory fitness with the risk of CVD,” Dr. Deedwania noted. “However, this is one of the largest population-wide surveillance studies of more than a half million active workers across Spain, and it does show that, despite self-reported physical activity, overweight and obesity are associated with higher risks of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia,” he explained.
“The main message of these findings is that, although physical activity does have a dose-dependent favorable impact on CV risk, the main public health intervention to reduce the risk of CV risk should focus on weight loss in overweight and obese individuals,” Dr. Deedwania emphasized.
“Future studies should focus on comparing various levels of daily activities and routine exercise such as walking, bicycling, etc., with the beneficial impact on cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight and obese individuals,” he said.
Dr. Valenzuela disclosed support from the University of Alcalá. Research by corresponding author Dr. Lucia was funded by grants from Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation and Fondos FEDER. Dr. Deedwania had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PREVENTIVE CARDIOLOGY