User login
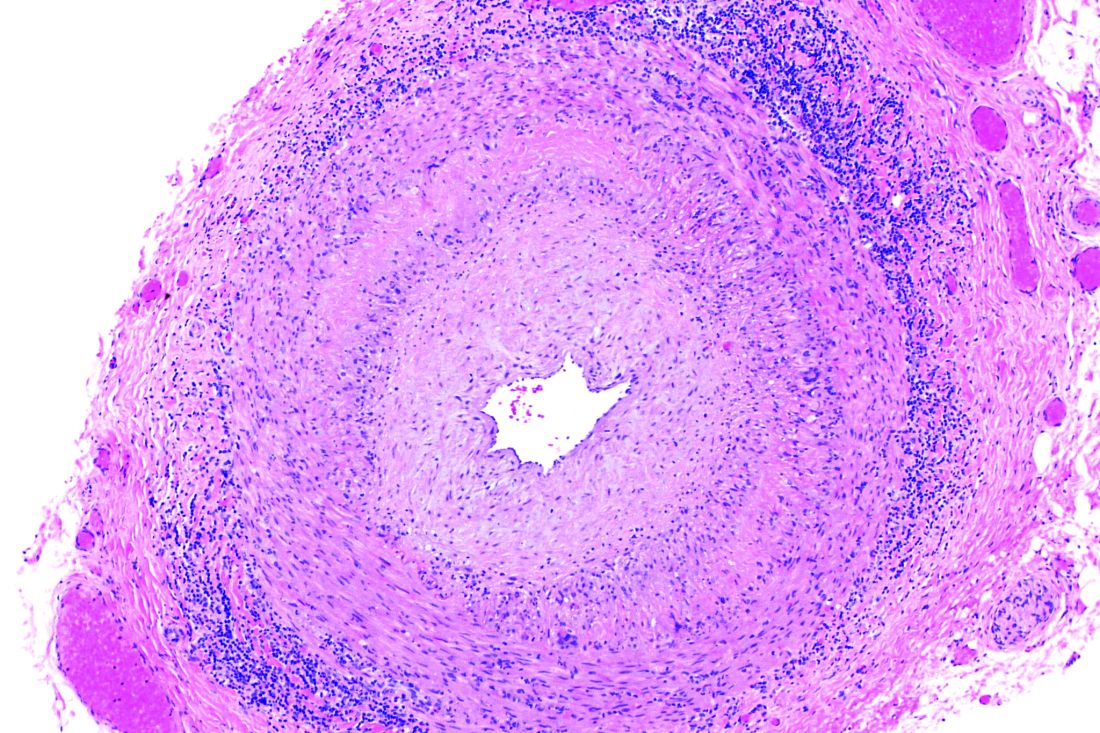
Frozen sections can guide biopsies for giant cell arteritis, but are they feasible?
Positive findings from frozen sections of a first temporal artery biopsy can effectively identify giant cell arteritis, ruling out in those cases the need to perform a second biopsy on the contralateral side and arguing against the use of simultaneous bilateral biopsies, according to results from a retrospective study of nearly 800 patients who underwent the procedure at the Mayo Clinic during 2010-2018.
Although temporal artery biopsy (TAB) remains the standard diagnostic test for giant cell arteritis (GCA), second TAB procedures are often performed in patients with a high level of suspicion for GCA, which may result in unnecessary treatments and complications, Devon A. Cohen, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues wrote. (Dr. Cohen is now a clinical fellow in ophthalmology at the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary.)
At the Mayo Clinic, TAB specimens are first examined with frozen sections at the time of the biopsy; this process, followed within days by formalin-fixed tissue permanent sections, is unique to Mayo. “A frozen section–guided sequential TAB is commonly performed, with the results of the first biopsy obtained within minutes, which determines the need for evaluation of the contralateral side,” the researchers said. However, the use of frozen sections to evaluate patients with GCA has not been well studied.
In a retrospective cohort study published in JAMA Ophthalmology, the researchers identified TAB patients aged 40 years and older who underwent TAB procedures between Jan. 1, 2010, and Dec. 1, 2018, at the Mayo Clinic. The average age of the patients was 72 years, and 41% were men.
Strong positive predictions from frozen sections
The researchers analyzed 1,162 TABs from 795 patients using frozen and permanent histologic sections.
Overall, 119 patients (15.0%) and 138 TABs had positive permanent section findings, and 103 (86.6%) of these patients also had positive frozen section findings, including 4 false positives and 20 false negatives. The frozen section specificity and sensitivity was 99.4% and 83.2%, respectively, for detecting inflammation suggestive of GCA, and the positive and negative predictive values were 96.1% and 96.6%, respectively. Positive and negative likelihood ratios for frozen section were 140.6 and 0.17, respectively.
In a multivariate analysis, the odds of a positive permanent section TAB significantly increased with age (odds ratio, 1.04), vision loss (OR, 2.72), diplopia (OR, 3.33), headache (OR, 2.32), weight loss (OR, 2.37), and anorexia (OR, 5.65).
A total of 60 patients underwent bilateral TABs, and 307 patients underwent bilateral frozen section–guided sequential TABs; the discordance rates based on permanent sections were 5.0% and 5.5%, respectively.
Those discordance rates are “an important result applying to everyone working with patients suspected for GCA,” Patricia Chévez-Barrios, MD, of Houston Methodist Hospital, wrote in an accompanying editorial. “This is on the low end of what was previously published (3%-40%) and supports the relative low need for bilateral synchronous TAB for the diagnosis of GCA.”
A key issue in GCA diagnosis is the need to confirm inflammation, Dr. Chévez-Barrios said. “The surgeon must obtain a significant portion of the artery, and the pathologist should review several sections and levels of the tissue to confidently say whether there is inflammation or no.”
Frozen sections can spare patients from second procedures
The findings suggest a role for frozen section to help to determine whether a unilateral or bilateral simultaneous TAB should be performed, the study authors noted.
“If the frozen section is positive on the first TAB, a contralateral TAB is deferred, given the very low false-positive rate (0.6%). However, if the frozen section does not align with the permanent section result, in particular if the frozen section is positive but permanent section is negative, the patient returns for a TAB on the contralateral side if the GCA suspicion remains high,” they said.
The use of frozen sections requires ideal conditions in order to be effective, Dr. Chévez-Barrios said. The Mayo Clinic approach “is only possible because of their appropriate hospital setting, the training of the histotechnologists, and the experience of the pathologists interpreting the stains and sections. For most pathology laboratories outside of the Mayo Clinic, frozen sections on arteries are the exception and are used only in specific scenarios.”
In addition, the American College of Rheumatology recommends that patients with a high suspicion of GCA should begin corticosteroids as soon as laboratory studies are obtained; “As a result, if a TAB is performed after treatment begins, the typical active pattern of inflammation in the artery changes,” Dr. Chévez-Barrios said. “This further challenges the diagnosis in a frozen section setting because of the need for immunohistochemistry.” Although frozen sections are feasible in specialized settings such as the Mayo Clinic, most patients receive adequate diagnosis and treatment based on permanent sections.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of data from patients at a single center and the unique setup of the Mayo Clinic to perform rapid processing of frozen sections, the researchers noted.
“Additionally, we acknowledge that there is controversy regarding the clinical interpretation of healed arteritis. At our institution, healed arteritis is interpreted in the context of patient clinical characteristics and radiographic findings, which may differ from other institutions and may impact the results of this study,” they said.
Overall, the results support the potential of frozen sections in guiding TAB, although “more studies with a comparative analysis of laboratory results, clinical symptoms, and patient demographic characteristics between positive and negative frozen and permanent TAB results are needed to confirm our findings,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. One author reported receiving grants from Eli Lilly and Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals as well as personal fees from Genentech-Roche and Sanofi. Dr. Chévez-Barrios had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Positive findings from frozen sections of a first temporal artery biopsy can effectively identify giant cell arteritis, ruling out in those cases the need to perform a second biopsy on the contralateral side and arguing against the use of simultaneous bilateral biopsies, according to results from a retrospective study of nearly 800 patients who underwent the procedure at the Mayo Clinic during 2010-2018.
Although temporal artery biopsy (TAB) remains the standard diagnostic test for giant cell arteritis (GCA), second TAB procedures are often performed in patients with a high level of suspicion for GCA, which may result in unnecessary treatments and complications, Devon A. Cohen, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues wrote. (Dr. Cohen is now a clinical fellow in ophthalmology at the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary.)
At the Mayo Clinic, TAB specimens are first examined with frozen sections at the time of the biopsy; this process, followed within days by formalin-fixed tissue permanent sections, is unique to Mayo. “A frozen section–guided sequential TAB is commonly performed, with the results of the first biopsy obtained within minutes, which determines the need for evaluation of the contralateral side,” the researchers said. However, the use of frozen sections to evaluate patients with GCA has not been well studied.
In a retrospective cohort study published in JAMA Ophthalmology, the researchers identified TAB patients aged 40 years and older who underwent TAB procedures between Jan. 1, 2010, and Dec. 1, 2018, at the Mayo Clinic. The average age of the patients was 72 years, and 41% were men.
Strong positive predictions from frozen sections
The researchers analyzed 1,162 TABs from 795 patients using frozen and permanent histologic sections.
Overall, 119 patients (15.0%) and 138 TABs had positive permanent section findings, and 103 (86.6%) of these patients also had positive frozen section findings, including 4 false positives and 20 false negatives. The frozen section specificity and sensitivity was 99.4% and 83.2%, respectively, for detecting inflammation suggestive of GCA, and the positive and negative predictive values were 96.1% and 96.6%, respectively. Positive and negative likelihood ratios for frozen section were 140.6 and 0.17, respectively.
In a multivariate analysis, the odds of a positive permanent section TAB significantly increased with age (odds ratio, 1.04), vision loss (OR, 2.72), diplopia (OR, 3.33), headache (OR, 2.32), weight loss (OR, 2.37), and anorexia (OR, 5.65).
A total of 60 patients underwent bilateral TABs, and 307 patients underwent bilateral frozen section–guided sequential TABs; the discordance rates based on permanent sections were 5.0% and 5.5%, respectively.
Those discordance rates are “an important result applying to everyone working with patients suspected for GCA,” Patricia Chévez-Barrios, MD, of Houston Methodist Hospital, wrote in an accompanying editorial. “This is on the low end of what was previously published (3%-40%) and supports the relative low need for bilateral synchronous TAB for the diagnosis of GCA.”
A key issue in GCA diagnosis is the need to confirm inflammation, Dr. Chévez-Barrios said. “The surgeon must obtain a significant portion of the artery, and the pathologist should review several sections and levels of the tissue to confidently say whether there is inflammation or no.”
Frozen sections can spare patients from second procedures
The findings suggest a role for frozen section to help to determine whether a unilateral or bilateral simultaneous TAB should be performed, the study authors noted.
“If the frozen section is positive on the first TAB, a contralateral TAB is deferred, given the very low false-positive rate (0.6%). However, if the frozen section does not align with the permanent section result, in particular if the frozen section is positive but permanent section is negative, the patient returns for a TAB on the contralateral side if the GCA suspicion remains high,” they said.
The use of frozen sections requires ideal conditions in order to be effective, Dr. Chévez-Barrios said. The Mayo Clinic approach “is only possible because of their appropriate hospital setting, the training of the histotechnologists, and the experience of the pathologists interpreting the stains and sections. For most pathology laboratories outside of the Mayo Clinic, frozen sections on arteries are the exception and are used only in specific scenarios.”
In addition, the American College of Rheumatology recommends that patients with a high suspicion of GCA should begin corticosteroids as soon as laboratory studies are obtained; “As a result, if a TAB is performed after treatment begins, the typical active pattern of inflammation in the artery changes,” Dr. Chévez-Barrios said. “This further challenges the diagnosis in a frozen section setting because of the need for immunohistochemistry.” Although frozen sections are feasible in specialized settings such as the Mayo Clinic, most patients receive adequate diagnosis and treatment based on permanent sections.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of data from patients at a single center and the unique setup of the Mayo Clinic to perform rapid processing of frozen sections, the researchers noted.
“Additionally, we acknowledge that there is controversy regarding the clinical interpretation of healed arteritis. At our institution, healed arteritis is interpreted in the context of patient clinical characteristics and radiographic findings, which may differ from other institutions and may impact the results of this study,” they said.
Overall, the results support the potential of frozen sections in guiding TAB, although “more studies with a comparative analysis of laboratory results, clinical symptoms, and patient demographic characteristics between positive and negative frozen and permanent TAB results are needed to confirm our findings,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. One author reported receiving grants from Eli Lilly and Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals as well as personal fees from Genentech-Roche and Sanofi. Dr. Chévez-Barrios had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Positive findings from frozen sections of a first temporal artery biopsy can effectively identify giant cell arteritis, ruling out in those cases the need to perform a second biopsy on the contralateral side and arguing against the use of simultaneous bilateral biopsies, according to results from a retrospective study of nearly 800 patients who underwent the procedure at the Mayo Clinic during 2010-2018.
Although temporal artery biopsy (TAB) remains the standard diagnostic test for giant cell arteritis (GCA), second TAB procedures are often performed in patients with a high level of suspicion for GCA, which may result in unnecessary treatments and complications, Devon A. Cohen, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues wrote. (Dr. Cohen is now a clinical fellow in ophthalmology at the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary.)
At the Mayo Clinic, TAB specimens are first examined with frozen sections at the time of the biopsy; this process, followed within days by formalin-fixed tissue permanent sections, is unique to Mayo. “A frozen section–guided sequential TAB is commonly performed, with the results of the first biopsy obtained within minutes, which determines the need for evaluation of the contralateral side,” the researchers said. However, the use of frozen sections to evaluate patients with GCA has not been well studied.
In a retrospective cohort study published in JAMA Ophthalmology, the researchers identified TAB patients aged 40 years and older who underwent TAB procedures between Jan. 1, 2010, and Dec. 1, 2018, at the Mayo Clinic. The average age of the patients was 72 years, and 41% were men.
Strong positive predictions from frozen sections
The researchers analyzed 1,162 TABs from 795 patients using frozen and permanent histologic sections.
Overall, 119 patients (15.0%) and 138 TABs had positive permanent section findings, and 103 (86.6%) of these patients also had positive frozen section findings, including 4 false positives and 20 false negatives. The frozen section specificity and sensitivity was 99.4% and 83.2%, respectively, for detecting inflammation suggestive of GCA, and the positive and negative predictive values were 96.1% and 96.6%, respectively. Positive and negative likelihood ratios for frozen section were 140.6 and 0.17, respectively.
In a multivariate analysis, the odds of a positive permanent section TAB significantly increased with age (odds ratio, 1.04), vision loss (OR, 2.72), diplopia (OR, 3.33), headache (OR, 2.32), weight loss (OR, 2.37), and anorexia (OR, 5.65).
A total of 60 patients underwent bilateral TABs, and 307 patients underwent bilateral frozen section–guided sequential TABs; the discordance rates based on permanent sections were 5.0% and 5.5%, respectively.
Those discordance rates are “an important result applying to everyone working with patients suspected for GCA,” Patricia Chévez-Barrios, MD, of Houston Methodist Hospital, wrote in an accompanying editorial. “This is on the low end of what was previously published (3%-40%) and supports the relative low need for bilateral synchronous TAB for the diagnosis of GCA.”
A key issue in GCA diagnosis is the need to confirm inflammation, Dr. Chévez-Barrios said. “The surgeon must obtain a significant portion of the artery, and the pathologist should review several sections and levels of the tissue to confidently say whether there is inflammation or no.”
Frozen sections can spare patients from second procedures
The findings suggest a role for frozen section to help to determine whether a unilateral or bilateral simultaneous TAB should be performed, the study authors noted.
“If the frozen section is positive on the first TAB, a contralateral TAB is deferred, given the very low false-positive rate (0.6%). However, if the frozen section does not align with the permanent section result, in particular if the frozen section is positive but permanent section is negative, the patient returns for a TAB on the contralateral side if the GCA suspicion remains high,” they said.
The use of frozen sections requires ideal conditions in order to be effective, Dr. Chévez-Barrios said. The Mayo Clinic approach “is only possible because of their appropriate hospital setting, the training of the histotechnologists, and the experience of the pathologists interpreting the stains and sections. For most pathology laboratories outside of the Mayo Clinic, frozen sections on arteries are the exception and are used only in specific scenarios.”
In addition, the American College of Rheumatology recommends that patients with a high suspicion of GCA should begin corticosteroids as soon as laboratory studies are obtained; “As a result, if a TAB is performed after treatment begins, the typical active pattern of inflammation in the artery changes,” Dr. Chévez-Barrios said. “This further challenges the diagnosis in a frozen section setting because of the need for immunohistochemistry.” Although frozen sections are feasible in specialized settings such as the Mayo Clinic, most patients receive adequate diagnosis and treatment based on permanent sections.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of data from patients at a single center and the unique setup of the Mayo Clinic to perform rapid processing of frozen sections, the researchers noted.
“Additionally, we acknowledge that there is controversy regarding the clinical interpretation of healed arteritis. At our institution, healed arteritis is interpreted in the context of patient clinical characteristics and radiographic findings, which may differ from other institutions and may impact the results of this study,” they said.
Overall, the results support the potential of frozen sections in guiding TAB, although “more studies with a comparative analysis of laboratory results, clinical symptoms, and patient demographic characteristics between positive and negative frozen and permanent TAB results are needed to confirm our findings,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. One author reported receiving grants from Eli Lilly and Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals as well as personal fees from Genentech-Roche and Sanofi. Dr. Chévez-Barrios had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA OPHTHALMOLOGY
Outcomes have improved for PAH in connective tissue disease
Survival rates for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue diseases have improved significantly in recent years, and there is growing evidence that treatments for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension can also benefit this group.
In an article published online Feb. 3, 2021, in Arthritis & Rheumatology, researchers report the outcomes of a meta-analysis to explore the effect of more modern pulmonary arterial hypertension treatments on patients with conditions such as systemic sclerosis.
First author Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc, of the division of rheumatology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview that connective tissue disease–associated pulmonary arterial hypertension (CTD-PAH) was a leading cause of death, but earlier clinical trials had found poor outcomes in patients with CTD, compared with those with idiopathic PAH.
“Recent clinical trial data show that aggressive, up-front PAH treatments have better outcomes in those with CTD-PAH, and we wanted to explore these observations carefully in a systematic review and meta-analysis,” Dr. Khanna said.
The analysis included 11 randomized, controlled trials, involving 4,329 patients with PAH (1,267 with CTD), and 19 registries with a total of 9,739 patients with PAH, including 4,008 with CTD. Trials were required to report long-term clinical outcomes with a median enrollment time of greater than 6 months, and outcomes measured between 3-6 months after the patients started treatment.
Patients with CTDs had an older mean age and a lower 6-minute walk distance than did those with idiopathic PAH.
Five randomized, controlled trials – involving 3,172 patients, 941 of whom had a CTD – found that additional PAH treatment was associated with a 36% reduction in the risk of morbidity or mortality events, compared with controls both in the overall PAH group and in those with CTD.
Additional therapy was also associated with a 34.6-meter increase in 6-minute walk distance in the general PAH population, and a 20.4-meter increase in those with CTD.
The authors commented that the smaller improvement in 6-minute walk distance among patients with CTD may be influenced by comorbidities such as musculoskeletal involvement that would be independent of their cardiopulmonary function.
Differential patient survival among PAH etiologies
“Our meta-analysis of RCTs demonstrated that patients with CTD-PAH derive a clinically significant benefit from currently available PAH therapies which, in many patients, comprised the addition of a drug targeting a second or third pathway involved in the pathophysiology of PAH,” the authors wrote.
When researchers analyzed data from nine registries that included a wide range of PAH etiologies, they found the overall survival rates were lower among patients with CTD, compared with the overall population. The analysis also suggested that patients with systemic sclerosis and PAH had lower survival rates than did those with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Dr. Khanna said this may relate to different pathophysiology of PAH in patients with CTDs, but could also be a reflection of other differences, such as older age and the involvement of other comorbidities, including lung fibrosis and heart involvement.
Data across all 19 registries also showed that survival rates among those with CTD were higher in registries where more than 50% of the registry study period was during or after 2010, compared with registries where 50% or more of the study period was before 2010.
The authors suggested the differences in survival rates may relate to increased screening for PAH, particularly among people with CTDs. They noted that increased screening leads to earlier diagnosis, which could introduce a lead-time bias such that later registries would have younger participants with less severe disease. However, their analysis found that the later registries had older patients but also with less severe disease, and they suggested that it wasn’t possible to determine if lead-time bias was playing a role in their results.
Improvements in treatment options could also account for differences in survival over time, although the authors commented that only six registries in the study included patients from 2015 or later, when currently available treatments came into use and early combination therapy was used more.
“These data also support the 2018 World Symposium on Pulmonary Hypertension recommendations to initiate up-front combination pulmonary arterial hypertension therapy in majority of cases with CTD-PAH,” Dr. Khanna said.
‘Still have to be aggressive at identifying the high-risk patients’
Commenting on the findings, Virginia Steen, MD, of the division of rheumatology at Georgetown University, Washington, said clinicians were finally seeing some significant changes over time in scleroderma-associated PAH.
“Although some of it may be just early diagnosis, I think that the combination of early diagnosis and more aggressive treatment with combination medication is definitely making a difference,” Dr. Steen said in an interview. “The bottom line is that we as rheumatologists still have to be aggressive at identifying the high-risk patients, making an early diagnosis, and working with our pulmonary hypertension colleagues and aggressively treating these patients so we can make a long-term difference.”
The authors of an accompanying editorial said the meta-analysis’ findings showed the positive impact of early combination therapy and early diagnosis through proactive screening.
“It is notable because the present analysis again confirms that outcomes are worse in CTD-PAH than in idiopathic or familial forms of PAH, the impact of treatments should no longer be regarded as insignificant,” the editorial’s authors wrote. “This is a practice changing observation, especially now that many of the drugs are available in generic formulations and so the cost of modern PAH treatment has fallen at the same time as its true value is convincingly demonstrated.”
They also argued there was strong evidence for the value of combination therapies, both for PAH-targeted drugs used in combination and concurrent use of immunosuppression and drugs specifically for PAH in some patients with CTD-PAH.
However, they pointed out that not all treatments for idiopathic PAH were suitable for patients with CTDs, highlighting the example of anticoagulation that can improve survival in the first but worsen it in the second.
The study was funded by Actelion. Six authors declared funding and grants from the pharmaceutical sector, including the study sponsor, and three authors were employees of Actelion.
Survival rates for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue diseases have improved significantly in recent years, and there is growing evidence that treatments for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension can also benefit this group.
In an article published online Feb. 3, 2021, in Arthritis & Rheumatology, researchers report the outcomes of a meta-analysis to explore the effect of more modern pulmonary arterial hypertension treatments on patients with conditions such as systemic sclerosis.
First author Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc, of the division of rheumatology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview that connective tissue disease–associated pulmonary arterial hypertension (CTD-PAH) was a leading cause of death, but earlier clinical trials had found poor outcomes in patients with CTD, compared with those with idiopathic PAH.
“Recent clinical trial data show that aggressive, up-front PAH treatments have better outcomes in those with CTD-PAH, and we wanted to explore these observations carefully in a systematic review and meta-analysis,” Dr. Khanna said.
The analysis included 11 randomized, controlled trials, involving 4,329 patients with PAH (1,267 with CTD), and 19 registries with a total of 9,739 patients with PAH, including 4,008 with CTD. Trials were required to report long-term clinical outcomes with a median enrollment time of greater than 6 months, and outcomes measured between 3-6 months after the patients started treatment.
Patients with CTDs had an older mean age and a lower 6-minute walk distance than did those with idiopathic PAH.
Five randomized, controlled trials – involving 3,172 patients, 941 of whom had a CTD – found that additional PAH treatment was associated with a 36% reduction in the risk of morbidity or mortality events, compared with controls both in the overall PAH group and in those with CTD.
Additional therapy was also associated with a 34.6-meter increase in 6-minute walk distance in the general PAH population, and a 20.4-meter increase in those with CTD.
The authors commented that the smaller improvement in 6-minute walk distance among patients with CTD may be influenced by comorbidities such as musculoskeletal involvement that would be independent of their cardiopulmonary function.
Differential patient survival among PAH etiologies
“Our meta-analysis of RCTs demonstrated that patients with CTD-PAH derive a clinically significant benefit from currently available PAH therapies which, in many patients, comprised the addition of a drug targeting a second or third pathway involved in the pathophysiology of PAH,” the authors wrote.
When researchers analyzed data from nine registries that included a wide range of PAH etiologies, they found the overall survival rates were lower among patients with CTD, compared with the overall population. The analysis also suggested that patients with systemic sclerosis and PAH had lower survival rates than did those with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Dr. Khanna said this may relate to different pathophysiology of PAH in patients with CTDs, but could also be a reflection of other differences, such as older age and the involvement of other comorbidities, including lung fibrosis and heart involvement.
Data across all 19 registries also showed that survival rates among those with CTD were higher in registries where more than 50% of the registry study period was during or after 2010, compared with registries where 50% or more of the study period was before 2010.
The authors suggested the differences in survival rates may relate to increased screening for PAH, particularly among people with CTDs. They noted that increased screening leads to earlier diagnosis, which could introduce a lead-time bias such that later registries would have younger participants with less severe disease. However, their analysis found that the later registries had older patients but also with less severe disease, and they suggested that it wasn’t possible to determine if lead-time bias was playing a role in their results.
Improvements in treatment options could also account for differences in survival over time, although the authors commented that only six registries in the study included patients from 2015 or later, when currently available treatments came into use and early combination therapy was used more.
“These data also support the 2018 World Symposium on Pulmonary Hypertension recommendations to initiate up-front combination pulmonary arterial hypertension therapy in majority of cases with CTD-PAH,” Dr. Khanna said.
‘Still have to be aggressive at identifying the high-risk patients’
Commenting on the findings, Virginia Steen, MD, of the division of rheumatology at Georgetown University, Washington, said clinicians were finally seeing some significant changes over time in scleroderma-associated PAH.
“Although some of it may be just early diagnosis, I think that the combination of early diagnosis and more aggressive treatment with combination medication is definitely making a difference,” Dr. Steen said in an interview. “The bottom line is that we as rheumatologists still have to be aggressive at identifying the high-risk patients, making an early diagnosis, and working with our pulmonary hypertension colleagues and aggressively treating these patients so we can make a long-term difference.”
The authors of an accompanying editorial said the meta-analysis’ findings showed the positive impact of early combination therapy and early diagnosis through proactive screening.
“It is notable because the present analysis again confirms that outcomes are worse in CTD-PAH than in idiopathic or familial forms of PAH, the impact of treatments should no longer be regarded as insignificant,” the editorial’s authors wrote. “This is a practice changing observation, especially now that many of the drugs are available in generic formulations and so the cost of modern PAH treatment has fallen at the same time as its true value is convincingly demonstrated.”
They also argued there was strong evidence for the value of combination therapies, both for PAH-targeted drugs used in combination and concurrent use of immunosuppression and drugs specifically for PAH in some patients with CTD-PAH.
However, they pointed out that not all treatments for idiopathic PAH were suitable for patients with CTDs, highlighting the example of anticoagulation that can improve survival in the first but worsen it in the second.
The study was funded by Actelion. Six authors declared funding and grants from the pharmaceutical sector, including the study sponsor, and three authors were employees of Actelion.
Survival rates for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue diseases have improved significantly in recent years, and there is growing evidence that treatments for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension can also benefit this group.
In an article published online Feb. 3, 2021, in Arthritis & Rheumatology, researchers report the outcomes of a meta-analysis to explore the effect of more modern pulmonary arterial hypertension treatments on patients with conditions such as systemic sclerosis.
First author Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc, of the division of rheumatology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview that connective tissue disease–associated pulmonary arterial hypertension (CTD-PAH) was a leading cause of death, but earlier clinical trials had found poor outcomes in patients with CTD, compared with those with idiopathic PAH.
“Recent clinical trial data show that aggressive, up-front PAH treatments have better outcomes in those with CTD-PAH, and we wanted to explore these observations carefully in a systematic review and meta-analysis,” Dr. Khanna said.
The analysis included 11 randomized, controlled trials, involving 4,329 patients with PAH (1,267 with CTD), and 19 registries with a total of 9,739 patients with PAH, including 4,008 with CTD. Trials were required to report long-term clinical outcomes with a median enrollment time of greater than 6 months, and outcomes measured between 3-6 months after the patients started treatment.
Patients with CTDs had an older mean age and a lower 6-minute walk distance than did those with idiopathic PAH.
Five randomized, controlled trials – involving 3,172 patients, 941 of whom had a CTD – found that additional PAH treatment was associated with a 36% reduction in the risk of morbidity or mortality events, compared with controls both in the overall PAH group and in those with CTD.
Additional therapy was also associated with a 34.6-meter increase in 6-minute walk distance in the general PAH population, and a 20.4-meter increase in those with CTD.
The authors commented that the smaller improvement in 6-minute walk distance among patients with CTD may be influenced by comorbidities such as musculoskeletal involvement that would be independent of their cardiopulmonary function.
Differential patient survival among PAH etiologies
“Our meta-analysis of RCTs demonstrated that patients with CTD-PAH derive a clinically significant benefit from currently available PAH therapies which, in many patients, comprised the addition of a drug targeting a second or third pathway involved in the pathophysiology of PAH,” the authors wrote.
When researchers analyzed data from nine registries that included a wide range of PAH etiologies, they found the overall survival rates were lower among patients with CTD, compared with the overall population. The analysis also suggested that patients with systemic sclerosis and PAH had lower survival rates than did those with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Dr. Khanna said this may relate to different pathophysiology of PAH in patients with CTDs, but could also be a reflection of other differences, such as older age and the involvement of other comorbidities, including lung fibrosis and heart involvement.
Data across all 19 registries also showed that survival rates among those with CTD were higher in registries where more than 50% of the registry study period was during or after 2010, compared with registries where 50% or more of the study period was before 2010.
The authors suggested the differences in survival rates may relate to increased screening for PAH, particularly among people with CTDs. They noted that increased screening leads to earlier diagnosis, which could introduce a lead-time bias such that later registries would have younger participants with less severe disease. However, their analysis found that the later registries had older patients but also with less severe disease, and they suggested that it wasn’t possible to determine if lead-time bias was playing a role in their results.
Improvements in treatment options could also account for differences in survival over time, although the authors commented that only six registries in the study included patients from 2015 or later, when currently available treatments came into use and early combination therapy was used more.
“These data also support the 2018 World Symposium on Pulmonary Hypertension recommendations to initiate up-front combination pulmonary arterial hypertension therapy in majority of cases with CTD-PAH,” Dr. Khanna said.
‘Still have to be aggressive at identifying the high-risk patients’
Commenting on the findings, Virginia Steen, MD, of the division of rheumatology at Georgetown University, Washington, said clinicians were finally seeing some significant changes over time in scleroderma-associated PAH.
“Although some of it may be just early diagnosis, I think that the combination of early diagnosis and more aggressive treatment with combination medication is definitely making a difference,” Dr. Steen said in an interview. “The bottom line is that we as rheumatologists still have to be aggressive at identifying the high-risk patients, making an early diagnosis, and working with our pulmonary hypertension colleagues and aggressively treating these patients so we can make a long-term difference.”
The authors of an accompanying editorial said the meta-analysis’ findings showed the positive impact of early combination therapy and early diagnosis through proactive screening.
“It is notable because the present analysis again confirms that outcomes are worse in CTD-PAH than in idiopathic or familial forms of PAH, the impact of treatments should no longer be regarded as insignificant,” the editorial’s authors wrote. “This is a practice changing observation, especially now that many of the drugs are available in generic formulations and so the cost of modern PAH treatment has fallen at the same time as its true value is convincingly demonstrated.”
They also argued there was strong evidence for the value of combination therapies, both for PAH-targeted drugs used in combination and concurrent use of immunosuppression and drugs specifically for PAH in some patients with CTD-PAH.
However, they pointed out that not all treatments for idiopathic PAH were suitable for patients with CTDs, highlighting the example of anticoagulation that can improve survival in the first but worsen it in the second.
The study was funded by Actelion. Six authors declared funding and grants from the pharmaceutical sector, including the study sponsor, and three authors were employees of Actelion.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Consider home subcutaneous immune globulin for refractory dermatomyositis
Home-based subcutaneous immune globulin therapy is a promising alternative to intravenous immune globulin therapy for patients with refractory dermatomyositis or polymyositis, Anna Postolova, MD, MPH, declared at the 2021 Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
“This is really exciting. I think in the years to come we may see a change to having our patients be able to do immune globulin therapy at home,” said Dr. Postolova, a rheumatologist and allergist/immunologist at Stanford (Calif.) Health Care.
“The technology is there. I think our patients might feel more comfortable getting immune globulin at home,” she said. “I would love to switch more patients from IVIg to SCIg [subcutaneous immune globulin] in my practice.”
A few caveats: SCIg remains off label for treatment of dermatomyositis (DM) or polymyositis (PM). Its approved indication is as replacement therapy in patients with primary or secondary immunodeficiency diseases. IVIg is approved for this indication, but is also approved for DM/PM refractory to high-dose corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. Yet SCIg is clearly effective for these autoimmune inflammatory diseases, albeit to date the supporting evidence comes chiefly from observational studies and anecdotal experience.
“I don’t know if insurers will cover it, but they should because it’s obviously a lot cheaper to do it at home,” she noted.
SCIg advantages
SCIg offers compelling advantages over IVIg in addition to its substantially lower cost. These include far fewer systemic side effects, shorter infusion time, greater bioavailability, and better quality of life. Patients self-administer SCIg at home, avoiding the inconvenience of IVIg therapy, which entails travel time for once-monthly hospitalization or long hours spent in an infusion center, she explained.
French investigators recently documented a previously unappreciated further advantage of home-based SCIg. They convened a focus group of patients with DM or PM experienced with both IVIg and home SCIg and determined that participants uniformly preferred home SCIg. The patients cited a new and welcome feeling of autonomy and control.
“All patients with experience of IVIg and SCIg expressed a clear preference for SCIg, which was described to be easy, less disruptive for daily life, well tolerated, and less time-consuming. Preference was mainly related to a restoration of autonomy. Home-based self-administration reinforced the feeling of independence,” according to the investigators.
Available products
Six preparations of SCIg are commercially available. Most are in 10% concentration, as are all IVIg products. However, a 20% formulation of SCIg known as Hizentra allows for a smaller infusion volume and quicker completion of a treatment session. And one SCIg product, HyQvia, uses recombinant human hyaluronidase-facilitated 10% immune globulin, allowing home infusion of large volumes of sustained-release immune globulin on a once-monthly basis.
The relatively recent introduction of home SCIg for treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases, including DM, PM, and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, has been pioneered mainly by European investigators. The treatment is often given by programmable mechanical pump once weekly. Italian investigators have reported efficacy in DM using 0.2 g/kg per week, which is about half the monthly total dose of IVIg employed. The infusion rate is 10-40 mL/hour, with a volume of around 35 mL per injection site.
Alternatively, SCIg can be delivered by rapid push infusions of smaller volumes with a syringe two or three times per week; that’s the regimen that was used at 2 g/kg over the course of a month by patients in the French focus group study, who didn’t mind the more frequent dosing.
“As they have had severe long-lasting symptoms, SCIg was perceived as a curative rather than a preventive therapy,” according to the French investigators.
More than 40% of patients experience adverse reactions to IVIg. These often involve headaches, nausea, back or abdominal pain, arthralgias, and/or difficulty breathing. Thromboembolic events and acute renal failure occur occasionally. For this reason, many physicians give a prophylactic dose of corticosteroids an hour before a patient’s first dose of IVIg. These systemic side effects are so rare with SCIg that Dr. Postolova has never pretreated with steroids, even though the main reason she resorts to the home therapy is a patient’s track record of poor tolerance of IVIg. The lower abdomen and thigh are the most commonly used subcutaneous infusion sites. Mild local infusion site reactions are fairly common.
Formulating IVIg and SCIg is a complex process that entails plasma procurement and pooling, fractionation, and purification. It takes 10,000-60,000 plasma donations to make one lot of IVIg. Donations are accepted only from repeated donors. Samples are held for 6 months and tested for infectious agents. However, efforts are underway to develop bioengineered recombinant immune globulin products that don’t require donated plasma. These products are being designed to capture and enhance the most important mechanisms of benefit of plasma-derived immunoglobulins using Fc fragments that target key receptors, rather than relying on full-length immune globulin. The goal is enhanced efficacy at much lower doses than with IVIg or SCIg.
Dr. Postolova reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
Home-based subcutaneous immune globulin therapy is a promising alternative to intravenous immune globulin therapy for patients with refractory dermatomyositis or polymyositis, Anna Postolova, MD, MPH, declared at the 2021 Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
“This is really exciting. I think in the years to come we may see a change to having our patients be able to do immune globulin therapy at home,” said Dr. Postolova, a rheumatologist and allergist/immunologist at Stanford (Calif.) Health Care.
“The technology is there. I think our patients might feel more comfortable getting immune globulin at home,” she said. “I would love to switch more patients from IVIg to SCIg [subcutaneous immune globulin] in my practice.”
A few caveats: SCIg remains off label for treatment of dermatomyositis (DM) or polymyositis (PM). Its approved indication is as replacement therapy in patients with primary or secondary immunodeficiency diseases. IVIg is approved for this indication, but is also approved for DM/PM refractory to high-dose corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. Yet SCIg is clearly effective for these autoimmune inflammatory diseases, albeit to date the supporting evidence comes chiefly from observational studies and anecdotal experience.
“I don’t know if insurers will cover it, but they should because it’s obviously a lot cheaper to do it at home,” she noted.
SCIg advantages
SCIg offers compelling advantages over IVIg in addition to its substantially lower cost. These include far fewer systemic side effects, shorter infusion time, greater bioavailability, and better quality of life. Patients self-administer SCIg at home, avoiding the inconvenience of IVIg therapy, which entails travel time for once-monthly hospitalization or long hours spent in an infusion center, she explained.
French investigators recently documented a previously unappreciated further advantage of home-based SCIg. They convened a focus group of patients with DM or PM experienced with both IVIg and home SCIg and determined that participants uniformly preferred home SCIg. The patients cited a new and welcome feeling of autonomy and control.
“All patients with experience of IVIg and SCIg expressed a clear preference for SCIg, which was described to be easy, less disruptive for daily life, well tolerated, and less time-consuming. Preference was mainly related to a restoration of autonomy. Home-based self-administration reinforced the feeling of independence,” according to the investigators.
Available products
Six preparations of SCIg are commercially available. Most are in 10% concentration, as are all IVIg products. However, a 20% formulation of SCIg known as Hizentra allows for a smaller infusion volume and quicker completion of a treatment session. And one SCIg product, HyQvia, uses recombinant human hyaluronidase-facilitated 10% immune globulin, allowing home infusion of large volumes of sustained-release immune globulin on a once-monthly basis.
The relatively recent introduction of home SCIg for treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases, including DM, PM, and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, has been pioneered mainly by European investigators. The treatment is often given by programmable mechanical pump once weekly. Italian investigators have reported efficacy in DM using 0.2 g/kg per week, which is about half the monthly total dose of IVIg employed. The infusion rate is 10-40 mL/hour, with a volume of around 35 mL per injection site.
Alternatively, SCIg can be delivered by rapid push infusions of smaller volumes with a syringe two or three times per week; that’s the regimen that was used at 2 g/kg over the course of a month by patients in the French focus group study, who didn’t mind the more frequent dosing.
“As they have had severe long-lasting symptoms, SCIg was perceived as a curative rather than a preventive therapy,” according to the French investigators.
More than 40% of patients experience adverse reactions to IVIg. These often involve headaches, nausea, back or abdominal pain, arthralgias, and/or difficulty breathing. Thromboembolic events and acute renal failure occur occasionally. For this reason, many physicians give a prophylactic dose of corticosteroids an hour before a patient’s first dose of IVIg. These systemic side effects are so rare with SCIg that Dr. Postolova has never pretreated with steroids, even though the main reason she resorts to the home therapy is a patient’s track record of poor tolerance of IVIg. The lower abdomen and thigh are the most commonly used subcutaneous infusion sites. Mild local infusion site reactions are fairly common.
Formulating IVIg and SCIg is a complex process that entails plasma procurement and pooling, fractionation, and purification. It takes 10,000-60,000 plasma donations to make one lot of IVIg. Donations are accepted only from repeated donors. Samples are held for 6 months and tested for infectious agents. However, efforts are underway to develop bioengineered recombinant immune globulin products that don’t require donated plasma. These products are being designed to capture and enhance the most important mechanisms of benefit of plasma-derived immunoglobulins using Fc fragments that target key receptors, rather than relying on full-length immune globulin. The goal is enhanced efficacy at much lower doses than with IVIg or SCIg.
Dr. Postolova reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
Home-based subcutaneous immune globulin therapy is a promising alternative to intravenous immune globulin therapy for patients with refractory dermatomyositis or polymyositis, Anna Postolova, MD, MPH, declared at the 2021 Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
“This is really exciting. I think in the years to come we may see a change to having our patients be able to do immune globulin therapy at home,” said Dr. Postolova, a rheumatologist and allergist/immunologist at Stanford (Calif.) Health Care.
“The technology is there. I think our patients might feel more comfortable getting immune globulin at home,” she said. “I would love to switch more patients from IVIg to SCIg [subcutaneous immune globulin] in my practice.”
A few caveats: SCIg remains off label for treatment of dermatomyositis (DM) or polymyositis (PM). Its approved indication is as replacement therapy in patients with primary or secondary immunodeficiency diseases. IVIg is approved for this indication, but is also approved for DM/PM refractory to high-dose corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. Yet SCIg is clearly effective for these autoimmune inflammatory diseases, albeit to date the supporting evidence comes chiefly from observational studies and anecdotal experience.
“I don’t know if insurers will cover it, but they should because it’s obviously a lot cheaper to do it at home,” she noted.
SCIg advantages
SCIg offers compelling advantages over IVIg in addition to its substantially lower cost. These include far fewer systemic side effects, shorter infusion time, greater bioavailability, and better quality of life. Patients self-administer SCIg at home, avoiding the inconvenience of IVIg therapy, which entails travel time for once-monthly hospitalization or long hours spent in an infusion center, she explained.
French investigators recently documented a previously unappreciated further advantage of home-based SCIg. They convened a focus group of patients with DM or PM experienced with both IVIg and home SCIg and determined that participants uniformly preferred home SCIg. The patients cited a new and welcome feeling of autonomy and control.
“All patients with experience of IVIg and SCIg expressed a clear preference for SCIg, which was described to be easy, less disruptive for daily life, well tolerated, and less time-consuming. Preference was mainly related to a restoration of autonomy. Home-based self-administration reinforced the feeling of independence,” according to the investigators.
Available products
Six preparations of SCIg are commercially available. Most are in 10% concentration, as are all IVIg products. However, a 20% formulation of SCIg known as Hizentra allows for a smaller infusion volume and quicker completion of a treatment session. And one SCIg product, HyQvia, uses recombinant human hyaluronidase-facilitated 10% immune globulin, allowing home infusion of large volumes of sustained-release immune globulin on a once-monthly basis.
The relatively recent introduction of home SCIg for treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases, including DM, PM, and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, has been pioneered mainly by European investigators. The treatment is often given by programmable mechanical pump once weekly. Italian investigators have reported efficacy in DM using 0.2 g/kg per week, which is about half the monthly total dose of IVIg employed. The infusion rate is 10-40 mL/hour, with a volume of around 35 mL per injection site.
Alternatively, SCIg can be delivered by rapid push infusions of smaller volumes with a syringe two or three times per week; that’s the regimen that was used at 2 g/kg over the course of a month by patients in the French focus group study, who didn’t mind the more frequent dosing.
“As they have had severe long-lasting symptoms, SCIg was perceived as a curative rather than a preventive therapy,” according to the French investigators.
More than 40% of patients experience adverse reactions to IVIg. These often involve headaches, nausea, back or abdominal pain, arthralgias, and/or difficulty breathing. Thromboembolic events and acute renal failure occur occasionally. For this reason, many physicians give a prophylactic dose of corticosteroids an hour before a patient’s first dose of IVIg. These systemic side effects are so rare with SCIg that Dr. Postolova has never pretreated with steroids, even though the main reason she resorts to the home therapy is a patient’s track record of poor tolerance of IVIg. The lower abdomen and thigh are the most commonly used subcutaneous infusion sites. Mild local infusion site reactions are fairly common.
Formulating IVIg and SCIg is a complex process that entails plasma procurement and pooling, fractionation, and purification. It takes 10,000-60,000 plasma donations to make one lot of IVIg. Donations are accepted only from repeated donors. Samples are held for 6 months and tested for infectious agents. However, efforts are underway to develop bioengineered recombinant immune globulin products that don’t require donated plasma. These products are being designed to capture and enhance the most important mechanisms of benefit of plasma-derived immunoglobulins using Fc fragments that target key receptors, rather than relying on full-length immune globulin. The goal is enhanced efficacy at much lower doses than with IVIg or SCIg.
Dr. Postolova reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
FROM RWCS 2021
Tocilizumab may improve lung function in early systemic sclerosis
Treatment with tocilizumab (Actemra) could stabilize or improve lung function in people with early interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD), a new study has found.
A paper published online Feb. 3 in Arthritis & Rheumatology presents the results of a post hoc analysis of data from a phase 3, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of subcutaneous tocilizumab in patients with SSc and progressive skin disease, which included high-resolution chest CT to assess lung involvement and fibrosis.
Tocilizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets interleukin-6 and is currently approved for the treatment of immune-mediated diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, giant cell arteritis, cytokine release syndrome, and systemic and polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
Two previous studies of tocilizumab in patients with early, diffuse cutaneous SSc had also found that the treatment was associated with preservation of lung function but did not characterize that effect using radiography.
Of the 210 participants in the trial, called focuSSced, 136 were found to have interstitial lung disease at baseline and were randomized to 162 mg tocilizumab weekly or placebo for 48 weeks.
At baseline, around three-quarters of those with interstitial lung disease had moderate to severe lung involvement, defined as ground glass opacities, honeycombing, and fibrotic reticulation across at least 20% of the whole lung.
Those in the tocilizumab group showed a 0.1% mean decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) over the 48-week study, while those in the placebo group had a mean decline of 6.3%.
When stratified by severity of lung involvement, those with mild lung disease group treated with tocilizumab had a 4.1% decline in FVC, compared with a 10% decline in the placebo group; those with moderate disease in the treatment group had an 0.7% mean increase in FVC, compared with a 5.7% decrease in the placebo group, and those with severe lung involvement in the treatment arm had a 2.1% increase in FVC, compared with a 6.7% decrease in the placebo arm.
Those treated with tocilizumab also showed a statistically significant 1.8% improvement in the amount of lung involvement, which was largely seen in those with more extensive lung involvement at baseline. Those with more than 20% of the lung affected had a significant 4.9% reduction in lung area affected, while those in the placebo arm showed a significant increase in fibrosis.
First author David Roofeh, MD, of the University of Michigan Scleroderma Program, and colleagues wrote that most patients with SSc will develop interstitial lung disease – particularly those with early, diffuse cutaneous SSc and elevated markers such as C-reactive protein.
“Patients with these high-risk features, especially those with disease in the initial phase of development, represent an important target for early intervention as ILD is largely irreversible in SSc,” the authors wrote.
Findings from a specific patient population may not be generalizable
Commenting on the findings, Lorinda Chung, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview that the study demonstrated that tocilizumab could prevent radiographic progression of ILD in early diffuse SSc patients with mild to severe lung disease and evidence of active skin disease, as well as elevated inflammatory markers.
“This was a very specific patient population who was studied in the focuSSced clinical trial, and this paper only evaluated a subset of these patients,” Dr. Chung said. “The results may not be generalizable to all SSc-ILD patients and further studies are needed.”
The authors suggested that the patients with progressive skin disease and elevated acute phase reactants may represent a group in the immunoinflammatory phase of the disease rather than the advanced fibrotic stage, and that this might be a “window of therapeutic opportunity to preserve lung function.”
Dr. Chung noted that the radiographic improvement induced by tocilizumab treatment was greatest in those with the most radiographic disease at baseline.
“This may reflect tocilizumab’s impact on decreasing inflammation, but we are not provided the data on the effects of tocilizumab on the individual components of the QILD [quantitative ILD: summation of ground glass opacities, honeycombing, and fibrotic reticulation],” she said.
The study’s authors also made a point about the utility of screening patients with high-resolution chest CT to detect early signs of ILD.
“Our data demonstrate the value of obtaining HRCT at the time of diagnosis: PFTs [pulmonary function tests] are not sensitive enough to accurately assess the presence of ILD and delays in treatment initiation may lead to irreversible disease,” they wrote.
Describing the results as ‘hypothesis-generating’ owing to the post hoc nature of the analysis, the authors said that FVC was an indirect measure of the flow-resistive properties of the lung, and that other aspects of SSc – such as hide-bound chest thickness – could cause thoracic restriction.
Two authors were funded by the National Institutes of Health. Six authors declared grants, funding, and other support from the pharmaceutical sector, including Roche, which sponsored the original focuSSced trial.
Treatment with tocilizumab (Actemra) could stabilize or improve lung function in people with early interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD), a new study has found.
A paper published online Feb. 3 in Arthritis & Rheumatology presents the results of a post hoc analysis of data from a phase 3, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of subcutaneous tocilizumab in patients with SSc and progressive skin disease, which included high-resolution chest CT to assess lung involvement and fibrosis.
Tocilizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets interleukin-6 and is currently approved for the treatment of immune-mediated diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, giant cell arteritis, cytokine release syndrome, and systemic and polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
Two previous studies of tocilizumab in patients with early, diffuse cutaneous SSc had also found that the treatment was associated with preservation of lung function but did not characterize that effect using radiography.
Of the 210 participants in the trial, called focuSSced, 136 were found to have interstitial lung disease at baseline and were randomized to 162 mg tocilizumab weekly or placebo for 48 weeks.
At baseline, around three-quarters of those with interstitial lung disease had moderate to severe lung involvement, defined as ground glass opacities, honeycombing, and fibrotic reticulation across at least 20% of the whole lung.
Those in the tocilizumab group showed a 0.1% mean decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) over the 48-week study, while those in the placebo group had a mean decline of 6.3%.
When stratified by severity of lung involvement, those with mild lung disease group treated with tocilizumab had a 4.1% decline in FVC, compared with a 10% decline in the placebo group; those with moderate disease in the treatment group had an 0.7% mean increase in FVC, compared with a 5.7% decrease in the placebo group, and those with severe lung involvement in the treatment arm had a 2.1% increase in FVC, compared with a 6.7% decrease in the placebo arm.
Those treated with tocilizumab also showed a statistically significant 1.8% improvement in the amount of lung involvement, which was largely seen in those with more extensive lung involvement at baseline. Those with more than 20% of the lung affected had a significant 4.9% reduction in lung area affected, while those in the placebo arm showed a significant increase in fibrosis.
First author David Roofeh, MD, of the University of Michigan Scleroderma Program, and colleagues wrote that most patients with SSc will develop interstitial lung disease – particularly those with early, diffuse cutaneous SSc and elevated markers such as C-reactive protein.
“Patients with these high-risk features, especially those with disease in the initial phase of development, represent an important target for early intervention as ILD is largely irreversible in SSc,” the authors wrote.
Findings from a specific patient population may not be generalizable
Commenting on the findings, Lorinda Chung, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview that the study demonstrated that tocilizumab could prevent radiographic progression of ILD in early diffuse SSc patients with mild to severe lung disease and evidence of active skin disease, as well as elevated inflammatory markers.
“This was a very specific patient population who was studied in the focuSSced clinical trial, and this paper only evaluated a subset of these patients,” Dr. Chung said. “The results may not be generalizable to all SSc-ILD patients and further studies are needed.”
The authors suggested that the patients with progressive skin disease and elevated acute phase reactants may represent a group in the immunoinflammatory phase of the disease rather than the advanced fibrotic stage, and that this might be a “window of therapeutic opportunity to preserve lung function.”
Dr. Chung noted that the radiographic improvement induced by tocilizumab treatment was greatest in those with the most radiographic disease at baseline.
“This may reflect tocilizumab’s impact on decreasing inflammation, but we are not provided the data on the effects of tocilizumab on the individual components of the QILD [quantitative ILD: summation of ground glass opacities, honeycombing, and fibrotic reticulation],” she said.
The study’s authors also made a point about the utility of screening patients with high-resolution chest CT to detect early signs of ILD.
“Our data demonstrate the value of obtaining HRCT at the time of diagnosis: PFTs [pulmonary function tests] are not sensitive enough to accurately assess the presence of ILD and delays in treatment initiation may lead to irreversible disease,” they wrote.
Describing the results as ‘hypothesis-generating’ owing to the post hoc nature of the analysis, the authors said that FVC was an indirect measure of the flow-resistive properties of the lung, and that other aspects of SSc – such as hide-bound chest thickness – could cause thoracic restriction.
Two authors were funded by the National Institutes of Health. Six authors declared grants, funding, and other support from the pharmaceutical sector, including Roche, which sponsored the original focuSSced trial.
Treatment with tocilizumab (Actemra) could stabilize or improve lung function in people with early interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD), a new study has found.
A paper published online Feb. 3 in Arthritis & Rheumatology presents the results of a post hoc analysis of data from a phase 3, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of subcutaneous tocilizumab in patients with SSc and progressive skin disease, which included high-resolution chest CT to assess lung involvement and fibrosis.
Tocilizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets interleukin-6 and is currently approved for the treatment of immune-mediated diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, giant cell arteritis, cytokine release syndrome, and systemic and polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
Two previous studies of tocilizumab in patients with early, diffuse cutaneous SSc had also found that the treatment was associated with preservation of lung function but did not characterize that effect using radiography.
Of the 210 participants in the trial, called focuSSced, 136 were found to have interstitial lung disease at baseline and were randomized to 162 mg tocilizumab weekly or placebo for 48 weeks.
At baseline, around three-quarters of those with interstitial lung disease had moderate to severe lung involvement, defined as ground glass opacities, honeycombing, and fibrotic reticulation across at least 20% of the whole lung.
Those in the tocilizumab group showed a 0.1% mean decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) over the 48-week study, while those in the placebo group had a mean decline of 6.3%.
When stratified by severity of lung involvement, those with mild lung disease group treated with tocilizumab had a 4.1% decline in FVC, compared with a 10% decline in the placebo group; those with moderate disease in the treatment group had an 0.7% mean increase in FVC, compared with a 5.7% decrease in the placebo group, and those with severe lung involvement in the treatment arm had a 2.1% increase in FVC, compared with a 6.7% decrease in the placebo arm.
Those treated with tocilizumab also showed a statistically significant 1.8% improvement in the amount of lung involvement, which was largely seen in those with more extensive lung involvement at baseline. Those with more than 20% of the lung affected had a significant 4.9% reduction in lung area affected, while those in the placebo arm showed a significant increase in fibrosis.
First author David Roofeh, MD, of the University of Michigan Scleroderma Program, and colleagues wrote that most patients with SSc will develop interstitial lung disease – particularly those with early, diffuse cutaneous SSc and elevated markers such as C-reactive protein.
“Patients with these high-risk features, especially those with disease in the initial phase of development, represent an important target for early intervention as ILD is largely irreversible in SSc,” the authors wrote.
Findings from a specific patient population may not be generalizable
Commenting on the findings, Lorinda Chung, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview that the study demonstrated that tocilizumab could prevent radiographic progression of ILD in early diffuse SSc patients with mild to severe lung disease and evidence of active skin disease, as well as elevated inflammatory markers.
“This was a very specific patient population who was studied in the focuSSced clinical trial, and this paper only evaluated a subset of these patients,” Dr. Chung said. “The results may not be generalizable to all SSc-ILD patients and further studies are needed.”
The authors suggested that the patients with progressive skin disease and elevated acute phase reactants may represent a group in the immunoinflammatory phase of the disease rather than the advanced fibrotic stage, and that this might be a “window of therapeutic opportunity to preserve lung function.”
Dr. Chung noted that the radiographic improvement induced by tocilizumab treatment was greatest in those with the most radiographic disease at baseline.
“This may reflect tocilizumab’s impact on decreasing inflammation, but we are not provided the data on the effects of tocilizumab on the individual components of the QILD [quantitative ILD: summation of ground glass opacities, honeycombing, and fibrotic reticulation],” she said.
The study’s authors also made a point about the utility of screening patients with high-resolution chest CT to detect early signs of ILD.
“Our data demonstrate the value of obtaining HRCT at the time of diagnosis: PFTs [pulmonary function tests] are not sensitive enough to accurately assess the presence of ILD and delays in treatment initiation may lead to irreversible disease,” they wrote.
Describing the results as ‘hypothesis-generating’ owing to the post hoc nature of the analysis, the authors said that FVC was an indirect measure of the flow-resistive properties of the lung, and that other aspects of SSc – such as hide-bound chest thickness – could cause thoracic restriction.
Two authors were funded by the National Institutes of Health. Six authors declared grants, funding, and other support from the pharmaceutical sector, including Roche, which sponsored the original focuSSced trial.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Checkpoint inhibitors’ ‘big picture’ safety shown with preexisting autoimmune diseases
Patients with advanced melanoma and preexisting autoimmune diseases (AIDs) who were treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) responded well and did not suffer more grade 3 or higher immune-related adverse events than patients without an AID, a new study finds, although some concerns were raised regarding patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to bridge this knowledge gap by presenting ‘real-world’ data on the safety and efficacy of ICI on a national scale,” wrote Monique K. van der Kooij, MD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center and coauthors. The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
To investigate ICI use and response among this specific subset of melanoma patients, the researchers launched a nationwide cohort study set in the Netherlands. Data were gathered via the Dutch Melanoma Treatment Registry (DMTR), in which 4,367 patients with advanced melanoma were enrolled between July 2013 and July 2018.
Within that cohort, 415 (9.5%) had preexisting AIDs. Nearly 55% had rheumatologic AIDs (n = 227) – which included RA, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, sarcoidosis, and vasculitis – with the next most frequent being endocrine AID (n = 143) and IBD (n = 55). Patients with AID were older than patients without (67 vs. 63 years) and were more likely to be female (53% vs. 41%).
The ICIs used in the study included anti-CTLA4 (ipilimumab), anti–programmed death 1 (PD-1) (nivolumab or pembrolizumab), or a combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab. Of the patients with AID, 55% (n = 228) were treated with ICI, compared with 58% of patients without AID. A total of 87 AID patients were treated with anti-CTLA4, 187 received anti-PD-1, and 34 received the combination. The combination was not readily available in the Netherlands until 2017, the authors stated, acknowledging that it may be wise to revisit its effects in the coming years.
Incidence of immune-related adverse events
The incidence of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) grade 3 and above for patients with and without AID who were given anti-CTLA4 was 30%. The incidence rate of irAEs was also similar for patients with (17%; 95% confidence interval, 12%-23%) and without (13%; 95% CI, 12%-15%) AID on anti-PD-1. Patients with AIDs who took anti-PD-1 therapy discontinued it more often because of toxicity than did the patients without AIDs.
The combination group had irAE incidence rates of 44% (95% CI, 27%-62%) for patients with AID, compared with 48% (95% CI, 43%-53%) for patients without AIDs. Overall, no patients with AIDs on ICIs died of toxicity, compared with three deaths among patients without AID on anti-CTLA4, five deaths among patients on anti-PD-1, and one patient on the combination.
Patients with IBD had a notably higher risk of anti-PD-1–induced colitis (19%; 95% CI, 7%-37%), compared with patients with other AIDs (3%; 95% CI, 0%-6%) and patients without AIDs (2%; 95% CI, 2%-3%). IBD patients were also more likely than all other groups on ICIs to stop treatment because of toxicity, leading the researchers to note that “close monitoring in patients with IBD is advised.”
Overall survival after diagnosis was similar in patients with AIDs (median, 13 months; 95% CI, 10-16 months) and without (median, 14 months; 95% CI, 13-15 months), as was the objective response rate to anti-CTLA4 treatment (10% vs. 16%), anti-PD-1 treatment (40% vs. 44%), and combination therapy (39% vs. 43%).
Study largely bypasses the effects of checkpoint inhibitors on RA patients
“For detail, you can’t look to this study,” Anne R. Bass, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “But for a big-picture look at ‘how safe are checkpoint inhibitors,’ I think it’s an important one.”
Dr. Bass noted that the investigators lumped certain elements together and bypassed others, including their focus on grade 3 or higher adverse events. That was a decision the authors themselves recognized as a potential limitation of their research.
“Understandably, they were worried about life-threatening adverse events, and that’s fine,” she said. But for patients with arthritis who flare, their events are usually grade 2 or even grade 1 and therefore not captured or analyzed in the study. “This does not really address the risk of flare in an RA patient.”
She also questioned their grouping of AIDs, with a bevy of rheumatic diseases categorized as one cluster and the “other” group being particularly broad in its inclusion of “all AIDs not listed” – though only eight patients were placed into that group.
That said, the researchers relied on an oncology database, not one aimed at AID or adverse events. “The numbers are so much bigger than any other study in this area that’s been done,” she said. “It’s both a strength and a weakness of this kind of database.”
Indeed, the authors considered their use of nationwide, population-based data from the DMTR a benefit, calling it “a strength of our approach.”
The DMTR was funded by a grant from the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development and sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Roche Nederland, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pierre Fabre via the Dutch Institute for Clinical Auditing.
Patients with advanced melanoma and preexisting autoimmune diseases (AIDs) who were treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) responded well and did not suffer more grade 3 or higher immune-related adverse events than patients without an AID, a new study finds, although some concerns were raised regarding patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to bridge this knowledge gap by presenting ‘real-world’ data on the safety and efficacy of ICI on a national scale,” wrote Monique K. van der Kooij, MD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center and coauthors. The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
To investigate ICI use and response among this specific subset of melanoma patients, the researchers launched a nationwide cohort study set in the Netherlands. Data were gathered via the Dutch Melanoma Treatment Registry (DMTR), in which 4,367 patients with advanced melanoma were enrolled between July 2013 and July 2018.
Within that cohort, 415 (9.5%) had preexisting AIDs. Nearly 55% had rheumatologic AIDs (n = 227) – which included RA, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, sarcoidosis, and vasculitis – with the next most frequent being endocrine AID (n = 143) and IBD (n = 55). Patients with AID were older than patients without (67 vs. 63 years) and were more likely to be female (53% vs. 41%).
The ICIs used in the study included anti-CTLA4 (ipilimumab), anti–programmed death 1 (PD-1) (nivolumab or pembrolizumab), or a combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab. Of the patients with AID, 55% (n = 228) were treated with ICI, compared with 58% of patients without AID. A total of 87 AID patients were treated with anti-CTLA4, 187 received anti-PD-1, and 34 received the combination. The combination was not readily available in the Netherlands until 2017, the authors stated, acknowledging that it may be wise to revisit its effects in the coming years.
Incidence of immune-related adverse events
The incidence of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) grade 3 and above for patients with and without AID who were given anti-CTLA4 was 30%. The incidence rate of irAEs was also similar for patients with (17%; 95% confidence interval, 12%-23%) and without (13%; 95% CI, 12%-15%) AID on anti-PD-1. Patients with AIDs who took anti-PD-1 therapy discontinued it more often because of toxicity than did the patients without AIDs.
The combination group had irAE incidence rates of 44% (95% CI, 27%-62%) for patients with AID, compared with 48% (95% CI, 43%-53%) for patients without AIDs. Overall, no patients with AIDs on ICIs died of toxicity, compared with three deaths among patients without AID on anti-CTLA4, five deaths among patients on anti-PD-1, and one patient on the combination.
Patients with IBD had a notably higher risk of anti-PD-1–induced colitis (19%; 95% CI, 7%-37%), compared with patients with other AIDs (3%; 95% CI, 0%-6%) and patients without AIDs (2%; 95% CI, 2%-3%). IBD patients were also more likely than all other groups on ICIs to stop treatment because of toxicity, leading the researchers to note that “close monitoring in patients with IBD is advised.”
Overall survival after diagnosis was similar in patients with AIDs (median, 13 months; 95% CI, 10-16 months) and without (median, 14 months; 95% CI, 13-15 months), as was the objective response rate to anti-CTLA4 treatment (10% vs. 16%), anti-PD-1 treatment (40% vs. 44%), and combination therapy (39% vs. 43%).
Study largely bypasses the effects of checkpoint inhibitors on RA patients
“For detail, you can’t look to this study,” Anne R. Bass, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “But for a big-picture look at ‘how safe are checkpoint inhibitors,’ I think it’s an important one.”
Dr. Bass noted that the investigators lumped certain elements together and bypassed others, including their focus on grade 3 or higher adverse events. That was a decision the authors themselves recognized as a potential limitation of their research.
“Understandably, they were worried about life-threatening adverse events, and that’s fine,” she said. But for patients with arthritis who flare, their events are usually grade 2 or even grade 1 and therefore not captured or analyzed in the study. “This does not really address the risk of flare in an RA patient.”
She also questioned their grouping of AIDs, with a bevy of rheumatic diseases categorized as one cluster and the “other” group being particularly broad in its inclusion of “all AIDs not listed” – though only eight patients were placed into that group.
That said, the researchers relied on an oncology database, not one aimed at AID or adverse events. “The numbers are so much bigger than any other study in this area that’s been done,” she said. “It’s both a strength and a weakness of this kind of database.”
Indeed, the authors considered their use of nationwide, population-based data from the DMTR a benefit, calling it “a strength of our approach.”
The DMTR was funded by a grant from the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development and sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Roche Nederland, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pierre Fabre via the Dutch Institute for Clinical Auditing.
Patients with advanced melanoma and preexisting autoimmune diseases (AIDs) who were treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) responded well and did not suffer more grade 3 or higher immune-related adverse events than patients without an AID, a new study finds, although some concerns were raised regarding patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to bridge this knowledge gap by presenting ‘real-world’ data on the safety and efficacy of ICI on a national scale,” wrote Monique K. van der Kooij, MD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center and coauthors. The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
To investigate ICI use and response among this specific subset of melanoma patients, the researchers launched a nationwide cohort study set in the Netherlands. Data were gathered via the Dutch Melanoma Treatment Registry (DMTR), in which 4,367 patients with advanced melanoma were enrolled between July 2013 and July 2018.
Within that cohort, 415 (9.5%) had preexisting AIDs. Nearly 55% had rheumatologic AIDs (n = 227) – which included RA, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, sarcoidosis, and vasculitis – with the next most frequent being endocrine AID (n = 143) and IBD (n = 55). Patients with AID were older than patients without (67 vs. 63 years) and were more likely to be female (53% vs. 41%).
The ICIs used in the study included anti-CTLA4 (ipilimumab), anti–programmed death 1 (PD-1) (nivolumab or pembrolizumab), or a combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab. Of the patients with AID, 55% (n = 228) were treated with ICI, compared with 58% of patients without AID. A total of 87 AID patients were treated with anti-CTLA4, 187 received anti-PD-1, and 34 received the combination. The combination was not readily available in the Netherlands until 2017, the authors stated, acknowledging that it may be wise to revisit its effects in the coming years.
Incidence of immune-related adverse events
The incidence of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) grade 3 and above for patients with and without AID who were given anti-CTLA4 was 30%. The incidence rate of irAEs was also similar for patients with (17%; 95% confidence interval, 12%-23%) and without (13%; 95% CI, 12%-15%) AID on anti-PD-1. Patients with AIDs who took anti-PD-1 therapy discontinued it more often because of toxicity than did the patients without AIDs.
The combination group had irAE incidence rates of 44% (95% CI, 27%-62%) for patients with AID, compared with 48% (95% CI, 43%-53%) for patients without AIDs. Overall, no patients with AIDs on ICIs died of toxicity, compared with three deaths among patients without AID on anti-CTLA4, five deaths among patients on anti-PD-1, and one patient on the combination.
Patients with IBD had a notably higher risk of anti-PD-1–induced colitis (19%; 95% CI, 7%-37%), compared with patients with other AIDs (3%; 95% CI, 0%-6%) and patients without AIDs (2%; 95% CI, 2%-3%). IBD patients were also more likely than all other groups on ICIs to stop treatment because of toxicity, leading the researchers to note that “close monitoring in patients with IBD is advised.”
Overall survival after diagnosis was similar in patients with AIDs (median, 13 months; 95% CI, 10-16 months) and without (median, 14 months; 95% CI, 13-15 months), as was the objective response rate to anti-CTLA4 treatment (10% vs. 16%), anti-PD-1 treatment (40% vs. 44%), and combination therapy (39% vs. 43%).
Study largely bypasses the effects of checkpoint inhibitors on RA patients
“For detail, you can’t look to this study,” Anne R. Bass, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “But for a big-picture look at ‘how safe are checkpoint inhibitors,’ I think it’s an important one.”
Dr. Bass noted that the investigators lumped certain elements together and bypassed others, including their focus on grade 3 or higher adverse events. That was a decision the authors themselves recognized as a potential limitation of their research.
“Understandably, they were worried about life-threatening adverse events, and that’s fine,” she said. But for patients with arthritis who flare, their events are usually grade 2 or even grade 1 and therefore not captured or analyzed in the study. “This does not really address the risk of flare in an RA patient.”
She also questioned their grouping of AIDs, with a bevy of rheumatic diseases categorized as one cluster and the “other” group being particularly broad in its inclusion of “all AIDs not listed” – though only eight patients were placed into that group.
That said, the researchers relied on an oncology database, not one aimed at AID or adverse events. “The numbers are so much bigger than any other study in this area that’s been done,” she said. “It’s both a strength and a weakness of this kind of database.”
Indeed, the authors considered their use of nationwide, population-based data from the DMTR a benefit, calling it “a strength of our approach.”
The DMTR was funded by a grant from the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development and sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Roche Nederland, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pierre Fabre via the Dutch Institute for Clinical Auditing.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Women increasingly turn to CBD, with or without doc’s blessing
When 42-year-old Danielle Simone Brand started having hormonal migraines, she first turned to cannabidiol (CBD) oil, eventually adding an occasional pull on a prefilled tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) vape for nighttime use. She was careful to avoid THC during work hours. A parenting and cannabis writer, Ms. Brand had more than a cursory background in cannabinoid medicine and had spent time at her local California dispensary discussing various cannabinoid components that might help alleviate her pain.
A self-professed “do-it-yourselfer,” Ms. Brand continues to use cannabinoids for her monthly headaches, forgoing any other pain medication. “There are times for conventional medicine in partnership with your doctor, but when it comes to health and wellness, women should be empowered to make decisions and self-experiment,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Brand is not alone. Significant numbers of women are replacing or supplementing prescription medications with cannabinoids, often without consulting their primary care physician, ob.gyn., or other specialist. At times, women have tried to have these conversations, only to be met with silence or worse.
Take Linda Fuller, a 58-year-old yoga instructor from Long Island who says that she uses CBD and THC for chronic sacroiliac pain after a car accident and to alleviate stress-triggered eczema flares. “I’ve had doctors turn their backs on me; I’ve had nurse practitioners walk out on me in the middle of a sentence,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Fuller said her conversion to cannabinoid medicine is relatively new; she never used cannabis recreationally before her accident but now considers it a gift. She doesn’t keep aspirin in the house and refused pain medication immediately after she injured her back.
Diana Krach, a 34-year-old writer from Maryland, says she’s encountered roadblocks about her decision to use cannabinoids for endometriosis and for pain from Crohn’s disease. When she tried to discuss her CBD use with a gastroenterologist, he interrupted her: “Whatever pot you’re smoking isn’t going to work, you’re going on biologics.”
Ms. Krach had not been smoking anything but had turned to a CBD tincture for symptom relief after prescription pain medications failed to help.
Ms. Brand, Ms. Fuller, and Ms. Krach are the tip of the iceberg when it comes to women seeking symptom relief outside the medicine cabinet. A recent survey in the Journal of Women’s Health of almost 1,000 women show that 90% (most between the ages of 35 and 44) had used cannabis and would consider using it to treat gynecologic pain. Roughly 80% said they would consider using it for procedure-related pain or other conditions. Additionally, women have reported using cannabinoids for PTSD, sleep disturbances or insomnia, anxiety, and migraine headaches.
Observational survey data have likewise shown that 80% of women with advanced or recurrent gynecologic malignancies who were prescribed cannabis reported that it was equivalent or superior to other medications for relieving pain, neuropathy, nausea, insomnia, decreased appetite, and anxiety.
In another survey, almost half (45%) of women with gynecologic malignancies who used nonprescribed cannabis for the same symptoms reported that they had reduced their use of prescription narcotics after initiating use of cannabis.
The gray zone
There has been a surge in self-reported cannabis use among pregnant women in particular. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health findings for the periods 2002-2003 and 2016-2017 highlight increases in adjusted prevalence rates from 3.4% to 7% in past-month use among pregnant women overall and from 5.7% to 12.1% during the first trimester alone.
“The more that you talk to pregnant women, the more that you realize that a lot are using cannabinoids for something that is basically medicinal, for sleep, for anxiety, or for nausea,” Katrina Mark, MD, an ob.gyn. and associate professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, College Park, said in an interview. “I’m not saying it’s fine to use drugs in pregnancy, but it is a grayer conversation than a lot of colleagues want to believe. Telling women to quit seems foolish since the alternative is to be anxious, don’t sleep, don’t eat, or use a medication that also has risks to it.”
One observational study shows that pregnant women themselves are conflicted. Although the majority believe that cannabis is “natural” and “safe,” compared with prescription drugs, they aren’t entirely in the dark about potential risks. They often express frustration with practitioners’ responses when these topics are broached during office visits. An observational survey among women and practitioners published in 2020 highlights that only half of doctors openly discouraged perinatal cannabis use and that others opted out of the discussion entirely.
This is the experience of many of the women that this news organization spoke with. Ms. Krach pointed out that “there’s a big deficit in listening; the doctor is supposed to be working for our behalf, especially when it comes to reproductive health.”
Dr. Mark believed that a lot of the conversation has been clouded by the illegality of the substance but that cannabinoids deserve as much of a fair chance for discussion and consideration as other medicines, which also carry risks in pregnancy. “There’s literally no evidence that it will work in pregnancy [for these symptoms], but there’s no evidence that it doesn’t, either,” she said in an interview. “When I have this conversation with colleagues who do not share my views, I try to encourage them to look at the actual risks versus the benefits versus the alternatives.”
The ‘entourage effect’
Data supporting cannabinoids have been mostly laboratory based, case based, or observational. However, several well-designed (albeit small) trials have demonstrated efficacy for chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic and headache pain, as well as in Crohn’s disease. Most investigators have concluded that dosage is important and that there is a synergistic interaction between compounds (known as the “entourage effect”) that relates to cannabinoid efficacy or lack thereof, as well as possible adverse effects.
In addition to legality issues, the entourage effect is one of the most important factors related to the medical use of cannabinoids. “There are literally thousands of cultivars of cannabis, each with their own phytocannabinoid and terpenic profiles that may produce distinct therapeutic effects, [so] it is misguided to speak of cannabis in monolithic terms. It is like making broad claims about soup,” wrote coauthor Samoon Ahmad, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook.
Additionally, the role that reproductive hormones play is not entirely understood. Reproductive-aged women appear to be more susceptible to a “telescoping” (gender-related progression to dependence) effect in comparison with men. Ziva Cooper, PhD, director of the Cannabis Research Initiative at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. She explained that research has shown that factors such as the degree of exposure, frequency of use, and menses confound this susceptibility.
It’s the data
Frustration over cannabinoid therapeutics abound, especially when it comes to data, legal issues, and lack of training. “The feedback that I hear from providers is that there isn’t enough information; we just don’t know enough about it,” Dr. Mark said, “but there is information that we do have, and ignoring it is not beneficial.”
Dr. Cooper concurred. Although she readily acknowledges that data from randomized, placebo-controlled trials are mostly lacking, she says, “There are signals in the literature providing evidence for the utility of cannabis and cannabinoids for pain and some other effects.”
Other practitioners said in an interview that some patients admit to using cannabinoids but that they lack the ample information to guide these patients. By and large, many women equate “natural” with “safe,” and some will experiment on their own to see what works.
Those experiments are not without risk, which is why “it’s just as important for physicians to talk to their patients about cannabis use as it is for patients to be forthcoming about that use,” said Dr. Cooper. “It could have implications on their overall health as well as interactions with other drugs that they’re using.”
That balance from a clinical perspective on cannabis is crucial, wrote coauthor Kenneth Hill, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook. “Without it,” he wrote, “the window of opportunity for a patient to accept treatment that she needs may not be open very long.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When 42-year-old Danielle Simone Brand started having hormonal migraines, she first turned to cannabidiol (CBD) oil, eventually adding an occasional pull on a prefilled tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) vape for nighttime use. She was careful to avoid THC during work hours. A parenting and cannabis writer, Ms. Brand had more than a cursory background in cannabinoid medicine and had spent time at her local California dispensary discussing various cannabinoid components that might help alleviate her pain.
A self-professed “do-it-yourselfer,” Ms. Brand continues to use cannabinoids for her monthly headaches, forgoing any other pain medication. “There are times for conventional medicine in partnership with your doctor, but when it comes to health and wellness, women should be empowered to make decisions and self-experiment,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Brand is not alone. Significant numbers of women are replacing or supplementing prescription medications with cannabinoids, often without consulting their primary care physician, ob.gyn., or other specialist. At times, women have tried to have these conversations, only to be met with silence or worse.
Take Linda Fuller, a 58-year-old yoga instructor from Long Island who says that she uses CBD and THC for chronic sacroiliac pain after a car accident and to alleviate stress-triggered eczema flares. “I’ve had doctors turn their backs on me; I’ve had nurse practitioners walk out on me in the middle of a sentence,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Fuller said her conversion to cannabinoid medicine is relatively new; she never used cannabis recreationally before her accident but now considers it a gift. She doesn’t keep aspirin in the house and refused pain medication immediately after she injured her back.
Diana Krach, a 34-year-old writer from Maryland, says she’s encountered roadblocks about her decision to use cannabinoids for endometriosis and for pain from Crohn’s disease. When she tried to discuss her CBD use with a gastroenterologist, he interrupted her: “Whatever pot you’re smoking isn’t going to work, you’re going on biologics.”
Ms. Krach had not been smoking anything but had turned to a CBD tincture for symptom relief after prescription pain medications failed to help.
Ms. Brand, Ms. Fuller, and Ms. Krach are the tip of the iceberg when it comes to women seeking symptom relief outside the medicine cabinet. A recent survey in the Journal of Women’s Health of almost 1,000 women show that 90% (most between the ages of 35 and 44) had used cannabis and would consider using it to treat gynecologic pain. Roughly 80% said they would consider using it for procedure-related pain or other conditions. Additionally, women have reported using cannabinoids for PTSD, sleep disturbances or insomnia, anxiety, and migraine headaches.
Observational survey data have likewise shown that 80% of women with advanced or recurrent gynecologic malignancies who were prescribed cannabis reported that it was equivalent or superior to other medications for relieving pain, neuropathy, nausea, insomnia, decreased appetite, and anxiety.
In another survey, almost half (45%) of women with gynecologic malignancies who used nonprescribed cannabis for the same symptoms reported that they had reduced their use of prescription narcotics after initiating use of cannabis.
The gray zone
There has been a surge in self-reported cannabis use among pregnant women in particular. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health findings for the periods 2002-2003 and 2016-2017 highlight increases in adjusted prevalence rates from 3.4% to 7% in past-month use among pregnant women overall and from 5.7% to 12.1% during the first trimester alone.
“The more that you talk to pregnant women, the more that you realize that a lot are using cannabinoids for something that is basically medicinal, for sleep, for anxiety, or for nausea,” Katrina Mark, MD, an ob.gyn. and associate professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, College Park, said in an interview. “I’m not saying it’s fine to use drugs in pregnancy, but it is a grayer conversation than a lot of colleagues want to believe. Telling women to quit seems foolish since the alternative is to be anxious, don’t sleep, don’t eat, or use a medication that also has risks to it.”
One observational study shows that pregnant women themselves are conflicted. Although the majority believe that cannabis is “natural” and “safe,” compared with prescription drugs, they aren’t entirely in the dark about potential risks. They often express frustration with practitioners’ responses when these topics are broached during office visits. An observational survey among women and practitioners published in 2020 highlights that only half of doctors openly discouraged perinatal cannabis use and that others opted out of the discussion entirely.
This is the experience of many of the women that this news organization spoke with. Ms. Krach pointed out that “there’s a big deficit in listening; the doctor is supposed to be working for our behalf, especially when it comes to reproductive health.”
Dr. Mark believed that a lot of the conversation has been clouded by the illegality of the substance but that cannabinoids deserve as much of a fair chance for discussion and consideration as other medicines, which also carry risks in pregnancy. “There’s literally no evidence that it will work in pregnancy [for these symptoms], but there’s no evidence that it doesn’t, either,” she said in an interview. “When I have this conversation with colleagues who do not share my views, I try to encourage them to look at the actual risks versus the benefits versus the alternatives.”
The ‘entourage effect’
Data supporting cannabinoids have been mostly laboratory based, case based, or observational. However, several well-designed (albeit small) trials have demonstrated efficacy for chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic and headache pain, as well as in Crohn’s disease. Most investigators have concluded that dosage is important and that there is a synergistic interaction between compounds (known as the “entourage effect”) that relates to cannabinoid efficacy or lack thereof, as well as possible adverse effects.
In addition to legality issues, the entourage effect is one of the most important factors related to the medical use of cannabinoids. “There are literally thousands of cultivars of cannabis, each with their own phytocannabinoid and terpenic profiles that may produce distinct therapeutic effects, [so] it is misguided to speak of cannabis in monolithic terms. It is like making broad claims about soup,” wrote coauthor Samoon Ahmad, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook.
Additionally, the role that reproductive hormones play is not entirely understood. Reproductive-aged women appear to be more susceptible to a “telescoping” (gender-related progression to dependence) effect in comparison with men. Ziva Cooper, PhD, director of the Cannabis Research Initiative at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. She explained that research has shown that factors such as the degree of exposure, frequency of use, and menses confound this susceptibility.
It’s the data
Frustration over cannabinoid therapeutics abound, especially when it comes to data, legal issues, and lack of training. “The feedback that I hear from providers is that there isn’t enough information; we just don’t know enough about it,” Dr. Mark said, “but there is information that we do have, and ignoring it is not beneficial.”
Dr. Cooper concurred. Although she readily acknowledges that data from randomized, placebo-controlled trials are mostly lacking, she says, “There are signals in the literature providing evidence for the utility of cannabis and cannabinoids for pain and some other effects.”
Other practitioners said in an interview that some patients admit to using cannabinoids but that they lack the ample information to guide these patients. By and large, many women equate “natural” with “safe,” and some will experiment on their own to see what works.
Those experiments are not without risk, which is why “it’s just as important for physicians to talk to their patients about cannabis use as it is for patients to be forthcoming about that use,” said Dr. Cooper. “It could have implications on their overall health as well as interactions with other drugs that they’re using.”
That balance from a clinical perspective on cannabis is crucial, wrote coauthor Kenneth Hill, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook. “Without it,” he wrote, “the window of opportunity for a patient to accept treatment that she needs may not be open very long.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When 42-year-old Danielle Simone Brand started having hormonal migraines, she first turned to cannabidiol (CBD) oil, eventually adding an occasional pull on a prefilled tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) vape for nighttime use. She was careful to avoid THC during work hours. A parenting and cannabis writer, Ms. Brand had more than a cursory background in cannabinoid medicine and had spent time at her local California dispensary discussing various cannabinoid components that might help alleviate her pain.
A self-professed “do-it-yourselfer,” Ms. Brand continues to use cannabinoids for her monthly headaches, forgoing any other pain medication. “There are times for conventional medicine in partnership with your doctor, but when it comes to health and wellness, women should be empowered to make decisions and self-experiment,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Brand is not alone. Significant numbers of women are replacing or supplementing prescription medications with cannabinoids, often without consulting their primary care physician, ob.gyn., or other specialist. At times, women have tried to have these conversations, only to be met with silence or worse.
Take Linda Fuller, a 58-year-old yoga instructor from Long Island who says that she uses CBD and THC for chronic sacroiliac pain after a car accident and to alleviate stress-triggered eczema flares. “I’ve had doctors turn their backs on me; I’ve had nurse practitioners walk out on me in the middle of a sentence,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Fuller said her conversion to cannabinoid medicine is relatively new; she never used cannabis recreationally before her accident but now considers it a gift. She doesn’t keep aspirin in the house and refused pain medication immediately after she injured her back.
Diana Krach, a 34-year-old writer from Maryland, says she’s encountered roadblocks about her decision to use cannabinoids for endometriosis and for pain from Crohn’s disease. When she tried to discuss her CBD use with a gastroenterologist, he interrupted her: “Whatever pot you’re smoking isn’t going to work, you’re going on biologics.”
Ms. Krach had not been smoking anything but had turned to a CBD tincture for symptom relief after prescription pain medications failed to help.
Ms. Brand, Ms. Fuller, and Ms. Krach are the tip of the iceberg when it comes to women seeking symptom relief outside the medicine cabinet. A recent survey in the Journal of Women’s Health of almost 1,000 women show that 90% (most between the ages of 35 and 44) had used cannabis and would consider using it to treat gynecologic pain. Roughly 80% said they would consider using it for procedure-related pain or other conditions. Additionally, women have reported using cannabinoids for PTSD, sleep disturbances or insomnia, anxiety, and migraine headaches.
Observational survey data have likewise shown that 80% of women with advanced or recurrent gynecologic malignancies who were prescribed cannabis reported that it was equivalent or superior to other medications for relieving pain, neuropathy, nausea, insomnia, decreased appetite, and anxiety.
In another survey, almost half (45%) of women with gynecologic malignancies who used nonprescribed cannabis for the same symptoms reported that they had reduced their use of prescription narcotics after initiating use of cannabis.
The gray zone
There has been a surge in self-reported cannabis use among pregnant women in particular. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health findings for the periods 2002-2003 and 2016-2017 highlight increases in adjusted prevalence rates from 3.4% to 7% in past-month use among pregnant women overall and from 5.7% to 12.1% during the first trimester alone.
“The more that you talk to pregnant women, the more that you realize that a lot are using cannabinoids for something that is basically medicinal, for sleep, for anxiety, or for nausea,” Katrina Mark, MD, an ob.gyn. and associate professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, College Park, said in an interview. “I’m not saying it’s fine to use drugs in pregnancy, but it is a grayer conversation than a lot of colleagues want to believe. Telling women to quit seems foolish since the alternative is to be anxious, don’t sleep, don’t eat, or use a medication that also has risks to it.”
One observational study shows that pregnant women themselves are conflicted. Although the majority believe that cannabis is “natural” and “safe,” compared with prescription drugs, they aren’t entirely in the dark about potential risks. They often express frustration with practitioners’ responses when these topics are broached during office visits. An observational survey among women and practitioners published in 2020 highlights that only half of doctors openly discouraged perinatal cannabis use and that others opted out of the discussion entirely.
This is the experience of many of the women that this news organization spoke with. Ms. Krach pointed out that “there’s a big deficit in listening; the doctor is supposed to be working for our behalf, especially when it comes to reproductive health.”
Dr. Mark believed that a lot of the conversation has been clouded by the illegality of the substance but that cannabinoids deserve as much of a fair chance for discussion and consideration as other medicines, which also carry risks in pregnancy. “There’s literally no evidence that it will work in pregnancy [for these symptoms], but there’s no evidence that it doesn’t, either,” she said in an interview. “When I have this conversation with colleagues who do not share my views, I try to encourage them to look at the actual risks versus the benefits versus the alternatives.”
The ‘entourage effect’
Data supporting cannabinoids have been mostly laboratory based, case based, or observational. However, several well-designed (albeit small) trials have demonstrated efficacy for chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic and headache pain, as well as in Crohn’s disease. Most investigators have concluded that dosage is important and that there is a synergistic interaction between compounds (known as the “entourage effect”) that relates to cannabinoid efficacy or lack thereof, as well as possible adverse effects.
In addition to legality issues, the entourage effect is one of the most important factors related to the medical use of cannabinoids. “There are literally thousands of cultivars of cannabis, each with their own phytocannabinoid and terpenic profiles that may produce distinct therapeutic effects, [so] it is misguided to speak of cannabis in monolithic terms. It is like making broad claims about soup,” wrote coauthor Samoon Ahmad, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook.
Additionally, the role that reproductive hormones play is not entirely understood. Reproductive-aged women appear to be more susceptible to a “telescoping” (gender-related progression to dependence) effect in comparison with men. Ziva Cooper, PhD, director of the Cannabis Research Initiative at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. She explained that research has shown that factors such as the degree of exposure, frequency of use, and menses confound this susceptibility.
It’s the data
Frustration over cannabinoid therapeutics abound, especially when it comes to data, legal issues, and lack of training. “The feedback that I hear from providers is that there isn’t enough information; we just don’t know enough about it,” Dr. Mark said, “but there is information that we do have, and ignoring it is not beneficial.”
Dr. Cooper concurred. Although she readily acknowledges that data from randomized, placebo-controlled trials are mostly lacking, she says, “There are signals in the literature providing evidence for the utility of cannabis and cannabinoids for pain and some other effects.”
Other practitioners said in an interview that some patients admit to using cannabinoids but that they lack the ample information to guide these patients. By and large, many women equate “natural” with “safe,” and some will experiment on their own to see what works.
Those experiments are not without risk, which is why “it’s just as important for physicians to talk to their patients about cannabis use as it is for patients to be forthcoming about that use,” said Dr. Cooper. “It could have implications on their overall health as well as interactions with other drugs that they’re using.”
That balance from a clinical perspective on cannabis is crucial, wrote coauthor Kenneth Hill, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook. “Without it,” he wrote, “the window of opportunity for a patient to accept treatment that she needs may not be open very long.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rheumatologic disease activity an important influencer of COVID-19 death risk
People with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) who contract the SARS-CoV-2 virus appear more likely to die from COVID-19 if their rheumatologic condition is not being well controlled at the time of their infection.
New data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance (GRA) physician registry reported in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases have found that the odds of dying from COVID-19 were 87% higher in individuals recorded as having moderate to high disease activity versus those reported to be in remission or having low disease activity.
“I think this really highlights the importance of continuing to appropriately, and actively, treat our patients, and the importance of controlling their disease,” Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Machado, an associate professor in rheumatology and muscle diseases at University College London and a consultant rheumatologist at several U.K. hospitals, has been involved in the GRA physician registry from the start, and sits on the GRA steering committee.
Alongside higher disease activity, several other important factors were found to be associated with increased odds of dying from COVID-19 – older age, male gender, and the presence of one or more comorbidities, such as hypertension combined with cardiovascular disease or chronic lung disease.
These demographic and disease-based factors have been linked to an increased risk for COVID-19–related hospitalization before, both in people with RMDs and in the general population, but the latest GRA physician registry data now take that a step further, and link them also to an increased risk for death, together with several other factors more specific to RMDs.
Logging COVID-19 rheumatologic cases
Since the start of the global pandemic, the potential effects that SARS-CoV-2 infection might have on people with RMDs in particular has concerned the rheumatology community. The main worries being that, either because of the underlying RMD itself or to its treatment, there may be immunoregulatory deficits or other risk factors that would make individuals more susceptible to not only infection but also to developing more severe COVID-19 than the general population.
These concerns led to the rapid formation of the GRA and the COVID-19 GRA physician registry in March 2020 to collect and analyze data on adults with rheumatic disease and confirmed or presumptive COVID-19. Entries into the registry are made by or under the direction of rheumatologists, and this is a voluntary process.
“This population cannot ever be entirely representative of the population of patients with rheumatic diseases,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. There will be selection and other biases that affect the reported data. That said, it’s the largest database of reported COVID-19 cases in adult rheumatology patients across the world, with more than 9,000 cases so far included from multiple registries, including those based in Europe and North and South America. Data from one of these – the French RMD cohort – have also recently been published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, showing much the same findings but on a national level.
Hospitalization was the focus of a previous report because “you need large sample sizes” to look at endpoints that occur less frequently. When the first analysis was done, there were around 600 cases from 40 countries in the registry with sufficient data that could be used. Now, with a greater number of recorded cases, factors influencing the risk for death could be examined.
Death rate and risk factors found
Data on 3,729 COVID-19 cases in people with RMDs were included in the current analysis, all recorded in the first few months of the registry being open and up until July 1, 2020. In all, 390 (10.5%) of people died. While this is “clearly higher” than reported in the general population in most countries, the analysis was not designed to calculate a precise estimate.
“It should not be taken as an estimate of the overall death rate among patients with rheumatic diseases and COVID-19,” Dr. Machado and coauthors have been keen to point out.
“Age is always the biggest risk factor,” Dr. Machado explained. “There’s always a gradient: the older the patient, the worse the outcome.”
Indeed, there was a threefold increased risk for death among those aged 66-75 years versus those who were 65 years or younger (odds ratio, 3.00), and a sixfold increased risk for patients older than 75, compared with the younger age group (OR, 6.18).
Having both hypertension and cardiovascular disease was associated with an OR of 1.89, and coexisting chronic lung disease also significantly increased the chances of dying from COVID-19 (OR, 1.68).
Being of male sex was associated with a 46% increased risk for death from COVID-19 versus being of female sex.
The risk for COVID-19 death also rose with the use of corticosteroids. Compared with no steroid use, there was a 69% increased risk for with death at doses of 10 mg or more prednisolone equivalent per day.
“The finding about moderate to high doses of steroids being associated with a worse outcome is consistent with the first report; it was the same for hospitalization,” Dr. Machado observed.
The general consensus on steroid use in the COVID-19 setting is that they should be continued as needed, but at the lowest possible dose, as outlined in provisional recommendations set out by the recently renamed European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology.
The GRA physician registry findings provide further support for this, suggesting that disease control should be optimized with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, ideally without increasing the dose of steroids.
Surprise over sulfasalazine risk
“Taking all medications into account – such as methotrexate, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, [tumor necrosis factor] blockers, interleukin-6 blockers, and [Janus kinase] inhibitors – it is quite reassuring because we did not see an association with worse outcome with those drugs overall,” Dr. Machado said.
However, treatment with rituximab (OR, 4.0), sulfasalazine (OR, 3.6), and immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, mycophenolate, or tacrolimus (OR, 2.2), were associated with higher odds of dying from COVID-19 when compared with treatment with methotrexate alone.
The findings for rituximab and immunosuppressant use were perhaps not unexpected, but the possible association between sulfasalazine and COVID-19 death was “a bit intriguing,” Dr. Machado observed. “Sulfasalazine is believed to have low immunosuppressive effect.”
This warrants further investigation, but there are likely a range of confounding factors at play. One could be that people considered to be at higher risk may have been more often prescribed sulfasalazine because it was thought to be less immunosuppressive. Another might be because people taking sulfasalazine were more likely to be smokers, and they were also not advised to protect themselves from exposure to the virus (shielding) during the first wave of the pandemic, at least not in the United Kingdom.
Rituximab caution and vaccination
“Rituximab is a concern,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. “It is a concern that rheumatologists are now aware of and they are addressing, but then it’s a concern for a very specific subgroup of patients.”
While rheumatologists are, and will continue to prescribe it, there will be even more careful consideration over when, in whom, and how to use it during, and possibly even after, the pandemic.
“COVID is here to stay, it will become endemic, and it’s going to be part of our lives like the flu virus is,” Dr. Machado predicted.
Then there is the issue on vaccinating people against COVID-19, should those on rituximab still receive it? The answer is a yes, but, as with other vaccinations it’s all about the timing of when the vaccination is given.
Societies such as the British Society for Rheumatology have already begun to include guidance on this, recommending one of the available COVID-19 vaccines is given at least a month before the next or first dose of rituximab is due. As rituximab is given every few months, with doses sometimes spaced as much as 9 months or even a year apart, this should not be too much of a problem, but it is “better to have the vaccine first,” Dr. Machado said.
Has COVID-19 care improved in RMDs?
In separate research published in The Lancet Rheumatology, April Jorge, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and associates found that the risks of severe COVID-19 outcomes have improved over time, although they still “remain substantial.”
Dr. Jorge and colleagues looked at temporal trends in COVID-19 outcomes in patients with RMDs over the course of the first 6 months of the pandemic in 2020, using data from a large, multicenter, electronic health record network (TriNetX).
They formed two patient cohorts – a late (diagnosed from April 20 to July 20) and an early (diagnosed from January 20 to April 20) cohort – to see if outcomes had improved and discovered lower relative risks among patients in the late cohort for hospitalization (0.67), admission to the ICU (0.56), mechanical ventilation (0.39), acute kidney injury (0.66), renal replacement (0.53), and death (0.39).
“These results are encouraging,” but it’s difficult to match these different populations of patients, Dr. Machado said. “There are always factors that you cannot match for” and were not included in the U.S. analysis.
While there are important caveats in how the analysis was performed and thus in interpreting these data, they do “suggest that one of the reasons why outcomes have improved is because we have become better at treating these patients,” Dr. Machado added.
“Our treatment has improved, and our capacity to treat the complications has improved. We understand better how the disease behaves – we know that they can have thromboembolic complications that we can manage, and we are now able to manage ventilation issues better.”
Moreover, Dr. Machado said that, not only were clinicians more aware of what they should or should not do, there were treatments that were being used routinely or in some cases based on recent clinical trial results. “I think we are indeed treating these patients better.”
The COVID-19 GRA physician registry is financially supported by the American College of Rheumatology and EULAR. Dr. Machado had no relevant conflicts of interest.
People with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) who contract the SARS-CoV-2 virus appear more likely to die from COVID-19 if their rheumatologic condition is not being well controlled at the time of their infection.
New data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance (GRA) physician registry reported in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases have found that the odds of dying from COVID-19 were 87% higher in individuals recorded as having moderate to high disease activity versus those reported to be in remission or having low disease activity.
“I think this really highlights the importance of continuing to appropriately, and actively, treat our patients, and the importance of controlling their disease,” Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Machado, an associate professor in rheumatology and muscle diseases at University College London and a consultant rheumatologist at several U.K. hospitals, has been involved in the GRA physician registry from the start, and sits on the GRA steering committee.
Alongside higher disease activity, several other important factors were found to be associated with increased odds of dying from COVID-19 – older age, male gender, and the presence of one or more comorbidities, such as hypertension combined with cardiovascular disease or chronic lung disease.
These demographic and disease-based factors have been linked to an increased risk for COVID-19–related hospitalization before, both in people with RMDs and in the general population, but the latest GRA physician registry data now take that a step further, and link them also to an increased risk for death, together with several other factors more specific to RMDs.
Logging COVID-19 rheumatologic cases
Since the start of the global pandemic, the potential effects that SARS-CoV-2 infection might have on people with RMDs in particular has concerned the rheumatology community. The main worries being that, either because of the underlying RMD itself or to its treatment, there may be immunoregulatory deficits or other risk factors that would make individuals more susceptible to not only infection but also to developing more severe COVID-19 than the general population.
These concerns led to the rapid formation of the GRA and the COVID-19 GRA physician registry in March 2020 to collect and analyze data on adults with rheumatic disease and confirmed or presumptive COVID-19. Entries into the registry are made by or under the direction of rheumatologists, and this is a voluntary process.
“This population cannot ever be entirely representative of the population of patients with rheumatic diseases,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. There will be selection and other biases that affect the reported data. That said, it’s the largest database of reported COVID-19 cases in adult rheumatology patients across the world, with more than 9,000 cases so far included from multiple registries, including those based in Europe and North and South America. Data from one of these – the French RMD cohort – have also recently been published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, showing much the same findings but on a national level.
Hospitalization was the focus of a previous report because “you need large sample sizes” to look at endpoints that occur less frequently. When the first analysis was done, there were around 600 cases from 40 countries in the registry with sufficient data that could be used. Now, with a greater number of recorded cases, factors influencing the risk for death could be examined.
Death rate and risk factors found
Data on 3,729 COVID-19 cases in people with RMDs were included in the current analysis, all recorded in the first few months of the registry being open and up until July 1, 2020. In all, 390 (10.5%) of people died. While this is “clearly higher” than reported in the general population in most countries, the analysis was not designed to calculate a precise estimate.
“It should not be taken as an estimate of the overall death rate among patients with rheumatic diseases and COVID-19,” Dr. Machado and coauthors have been keen to point out.
“Age is always the biggest risk factor,” Dr. Machado explained. “There’s always a gradient: the older the patient, the worse the outcome.”
Indeed, there was a threefold increased risk for death among those aged 66-75 years versus those who were 65 years or younger (odds ratio, 3.00), and a sixfold increased risk for patients older than 75, compared with the younger age group (OR, 6.18).
Having both hypertension and cardiovascular disease was associated with an OR of 1.89, and coexisting chronic lung disease also significantly increased the chances of dying from COVID-19 (OR, 1.68).
Being of male sex was associated with a 46% increased risk for death from COVID-19 versus being of female sex.
The risk for COVID-19 death also rose with the use of corticosteroids. Compared with no steroid use, there was a 69% increased risk for with death at doses of 10 mg or more prednisolone equivalent per day.
“The finding about moderate to high doses of steroids being associated with a worse outcome is consistent with the first report; it was the same for hospitalization,” Dr. Machado observed.
The general consensus on steroid use in the COVID-19 setting is that they should be continued as needed, but at the lowest possible dose, as outlined in provisional recommendations set out by the recently renamed European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology.
The GRA physician registry findings provide further support for this, suggesting that disease control should be optimized with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, ideally without increasing the dose of steroids.
Surprise over sulfasalazine risk
“Taking all medications into account – such as methotrexate, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, [tumor necrosis factor] blockers, interleukin-6 blockers, and [Janus kinase] inhibitors – it is quite reassuring because we did not see an association with worse outcome with those drugs overall,” Dr. Machado said.
However, treatment with rituximab (OR, 4.0), sulfasalazine (OR, 3.6), and immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, mycophenolate, or tacrolimus (OR, 2.2), were associated with higher odds of dying from COVID-19 when compared with treatment with methotrexate alone.
The findings for rituximab and immunosuppressant use were perhaps not unexpected, but the possible association between sulfasalazine and COVID-19 death was “a bit intriguing,” Dr. Machado observed. “Sulfasalazine is believed to have low immunosuppressive effect.”
This warrants further investigation, but there are likely a range of confounding factors at play. One could be that people considered to be at higher risk may have been more often prescribed sulfasalazine because it was thought to be less immunosuppressive. Another might be because people taking sulfasalazine were more likely to be smokers, and they were also not advised to protect themselves from exposure to the virus (shielding) during the first wave of the pandemic, at least not in the United Kingdom.
Rituximab caution and vaccination
“Rituximab is a concern,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. “It is a concern that rheumatologists are now aware of and they are addressing, but then it’s a concern for a very specific subgroup of patients.”
While rheumatologists are, and will continue to prescribe it, there will be even more careful consideration over when, in whom, and how to use it during, and possibly even after, the pandemic.
“COVID is here to stay, it will become endemic, and it’s going to be part of our lives like the flu virus is,” Dr. Machado predicted.
Then there is the issue on vaccinating people against COVID-19, should those on rituximab still receive it? The answer is a yes, but, as with other vaccinations it’s all about the timing of when the vaccination is given.
Societies such as the British Society for Rheumatology have already begun to include guidance on this, recommending one of the available COVID-19 vaccines is given at least a month before the next or first dose of rituximab is due. As rituximab is given every few months, with doses sometimes spaced as much as 9 months or even a year apart, this should not be too much of a problem, but it is “better to have the vaccine first,” Dr. Machado said.
Has COVID-19 care improved in RMDs?
In separate research published in The Lancet Rheumatology, April Jorge, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and associates found that the risks of severe COVID-19 outcomes have improved over time, although they still “remain substantial.”
Dr. Jorge and colleagues looked at temporal trends in COVID-19 outcomes in patients with RMDs over the course of the first 6 months of the pandemic in 2020, using data from a large, multicenter, electronic health record network (TriNetX).
They formed two patient cohorts – a late (diagnosed from April 20 to July 20) and an early (diagnosed from January 20 to April 20) cohort – to see if outcomes had improved and discovered lower relative risks among patients in the late cohort for hospitalization (0.67), admission to the ICU (0.56), mechanical ventilation (0.39), acute kidney injury (0.66), renal replacement (0.53), and death (0.39).
“These results are encouraging,” but it’s difficult to match these different populations of patients, Dr. Machado said. “There are always factors that you cannot match for” and were not included in the U.S. analysis.
While there are important caveats in how the analysis was performed and thus in interpreting these data, they do “suggest that one of the reasons why outcomes have improved is because we have become better at treating these patients,” Dr. Machado added.
“Our treatment has improved, and our capacity to treat the complications has improved. We understand better how the disease behaves – we know that they can have thromboembolic complications that we can manage, and we are now able to manage ventilation issues better.”
Moreover, Dr. Machado said that, not only were clinicians more aware of what they should or should not do, there were treatments that were being used routinely or in some cases based on recent clinical trial results. “I think we are indeed treating these patients better.”
The COVID-19 GRA physician registry is financially supported by the American College of Rheumatology and EULAR. Dr. Machado had no relevant conflicts of interest.
People with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) who contract the SARS-CoV-2 virus appear more likely to die from COVID-19 if their rheumatologic condition is not being well controlled at the time of their infection.
New data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance (GRA) physician registry reported in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases have found that the odds of dying from COVID-19 were 87% higher in individuals recorded as having moderate to high disease activity versus those reported to be in remission or having low disease activity.
“I think this really highlights the importance of continuing to appropriately, and actively, treat our patients, and the importance of controlling their disease,” Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Machado, an associate professor in rheumatology and muscle diseases at University College London and a consultant rheumatologist at several U.K. hospitals, has been involved in the GRA physician registry from the start, and sits on the GRA steering committee.
Alongside higher disease activity, several other important factors were found to be associated with increased odds of dying from COVID-19 – older age, male gender, and the presence of one or more comorbidities, such as hypertension combined with cardiovascular disease or chronic lung disease.
These demographic and disease-based factors have been linked to an increased risk for COVID-19–related hospitalization before, both in people with RMDs and in the general population, but the latest GRA physician registry data now take that a step further, and link them also to an increased risk for death, together with several other factors more specific to RMDs.
Logging COVID-19 rheumatologic cases
Since the start of the global pandemic, the potential effects that SARS-CoV-2 infection might have on people with RMDs in particular has concerned the rheumatology community. The main worries being that, either because of the underlying RMD itself or to its treatment, there may be immunoregulatory deficits or other risk factors that would make individuals more susceptible to not only infection but also to developing more severe COVID-19 than the general population.
These concerns led to the rapid formation of the GRA and the COVID-19 GRA physician registry in March 2020 to collect and analyze data on adults with rheumatic disease and confirmed or presumptive COVID-19. Entries into the registry are made by or under the direction of rheumatologists, and this is a voluntary process.
“This population cannot ever be entirely representative of the population of patients with rheumatic diseases,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. There will be selection and other biases that affect the reported data. That said, it’s the largest database of reported COVID-19 cases in adult rheumatology patients across the world, with more than 9,000 cases so far included from multiple registries, including those based in Europe and North and South America. Data from one of these – the French RMD cohort – have also recently been published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, showing much the same findings but on a national level.
Hospitalization was the focus of a previous report because “you need large sample sizes” to look at endpoints that occur less frequently. When the first analysis was done, there were around 600 cases from 40 countries in the registry with sufficient data that could be used. Now, with a greater number of recorded cases, factors influencing the risk for death could be examined.
Death rate and risk factors found
Data on 3,729 COVID-19 cases in people with RMDs were included in the current analysis, all recorded in the first few months of the registry being open and up until July 1, 2020. In all, 390 (10.5%) of people died. While this is “clearly higher” than reported in the general population in most countries, the analysis was not designed to calculate a precise estimate.
“It should not be taken as an estimate of the overall death rate among patients with rheumatic diseases and COVID-19,” Dr. Machado and coauthors have been keen to point out.
“Age is always the biggest risk factor,” Dr. Machado explained. “There’s always a gradient: the older the patient, the worse the outcome.”
Indeed, there was a threefold increased risk for death among those aged 66-75 years versus those who were 65 years or younger (odds ratio, 3.00), and a sixfold increased risk for patients older than 75, compared with the younger age group (OR, 6.18).
Having both hypertension and cardiovascular disease was associated with an OR of 1.89, and coexisting chronic lung disease also significantly increased the chances of dying from COVID-19 (OR, 1.68).
Being of male sex was associated with a 46% increased risk for death from COVID-19 versus being of female sex.
The risk for COVID-19 death also rose with the use of corticosteroids. Compared with no steroid use, there was a 69% increased risk for with death at doses of 10 mg or more prednisolone equivalent per day.
“The finding about moderate to high doses of steroids being associated with a worse outcome is consistent with the first report; it was the same for hospitalization,” Dr. Machado observed.
The general consensus on steroid use in the COVID-19 setting is that they should be continued as needed, but at the lowest possible dose, as outlined in provisional recommendations set out by the recently renamed European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology.
The GRA physician registry findings provide further support for this, suggesting that disease control should be optimized with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, ideally without increasing the dose of steroids.
Surprise over sulfasalazine risk
“Taking all medications into account – such as methotrexate, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, [tumor necrosis factor] blockers, interleukin-6 blockers, and [Janus kinase] inhibitors – it is quite reassuring because we did not see an association with worse outcome with those drugs overall,” Dr. Machado said.
However, treatment with rituximab (OR, 4.0), sulfasalazine (OR, 3.6), and immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, mycophenolate, or tacrolimus (OR, 2.2), were associated with higher odds of dying from COVID-19 when compared with treatment with methotrexate alone.
The findings for rituximab and immunosuppressant use were perhaps not unexpected, but the possible association between sulfasalazine and COVID-19 death was “a bit intriguing,” Dr. Machado observed. “Sulfasalazine is believed to have low immunosuppressive effect.”
This warrants further investigation, but there are likely a range of confounding factors at play. One could be that people considered to be at higher risk may have been more often prescribed sulfasalazine because it was thought to be less immunosuppressive. Another might be because people taking sulfasalazine were more likely to be smokers, and they were also not advised to protect themselves from exposure to the virus (shielding) during the first wave of the pandemic, at least not in the United Kingdom.
Rituximab caution and vaccination
“Rituximab is a concern,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. “It is a concern that rheumatologists are now aware of and they are addressing, but then it’s a concern for a very specific subgroup of patients.”
While rheumatologists are, and will continue to prescribe it, there will be even more careful consideration over when, in whom, and how to use it during, and possibly even after, the pandemic.
“COVID is here to stay, it will become endemic, and it’s going to be part of our lives like the flu virus is,” Dr. Machado predicted.
Then there is the issue on vaccinating people against COVID-19, should those on rituximab still receive it? The answer is a yes, but, as with other vaccinations it’s all about the timing of when the vaccination is given.
Societies such as the British Society for Rheumatology have already begun to include guidance on this, recommending one of the available COVID-19 vaccines is given at least a month before the next or first dose of rituximab is due. As rituximab is given every few months, with doses sometimes spaced as much as 9 months or even a year apart, this should not be too much of a problem, but it is “better to have the vaccine first,” Dr. Machado said.
Has COVID-19 care improved in RMDs?
In separate research published in The Lancet Rheumatology, April Jorge, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and associates found that the risks of severe COVID-19 outcomes have improved over time, although they still “remain substantial.”
Dr. Jorge and colleagues looked at temporal trends in COVID-19 outcomes in patients with RMDs over the course of the first 6 months of the pandemic in 2020, using data from a large, multicenter, electronic health record network (TriNetX).
They formed two patient cohorts – a late (diagnosed from April 20 to July 20) and an early (diagnosed from January 20 to April 20) cohort – to see if outcomes had improved and discovered lower relative risks among patients in the late cohort for hospitalization (0.67), admission to the ICU (0.56), mechanical ventilation (0.39), acute kidney injury (0.66), renal replacement (0.53), and death (0.39).
“These results are encouraging,” but it’s difficult to match these different populations of patients, Dr. Machado said. “There are always factors that you cannot match for” and were not included in the U.S. analysis.
While there are important caveats in how the analysis was performed and thus in interpreting these data, they do “suggest that one of the reasons why outcomes have improved is because we have become better at treating these patients,” Dr. Machado added.
“Our treatment has improved, and our capacity to treat the complications has improved. We understand better how the disease behaves – we know that they can have thromboembolic complications that we can manage, and we are now able to manage ventilation issues better.”
Moreover, Dr. Machado said that, not only were clinicians more aware of what they should or should not do, there were treatments that were being used routinely or in some cases based on recent clinical trial results. “I think we are indeed treating these patients better.”
The COVID-19 GRA physician registry is financially supported by the American College of Rheumatology and EULAR. Dr. Machado had no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
Meta-analysis finds much less lupus than expected
The prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) appears to be much lower than previously believed and may pose “a potential risk to research funding for the disease,” according to results of a meta-analysis involving a network of population-based registries.
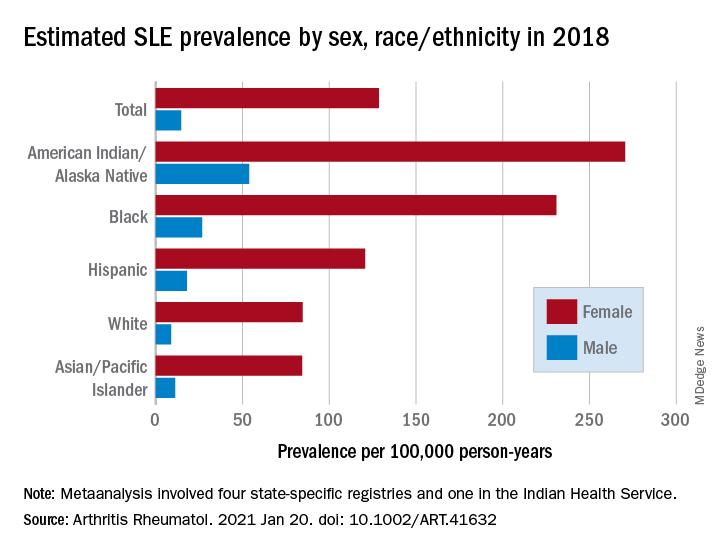
“When we started this study, a widely cited lupus statistic was that approximately 1.5 million Americans were affected. Our meta-analysis found the actual prevalence to be slightly more than 200,000: a number that approaches the [Food and Drug Administration’s] definition of a rare disease,” Emily Somers, PhD, ScM, senior author and associate professor of rheumatology and environmental health sciences at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in a written statement.
Their estimates, published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology, put the overall SLE prevalence in the United States at 72.8 per 100,000 person-years in 2018, with nearly nine times more females affected (128.7 cases per 100,000) than males (14.6 per 100,000). Race and ethnicity also play a role, as prevalence was highest among American Indian/Alaska Native and Black females, with Hispanic females lower but still higher than White and Asian/Pacific Islander females, Peter M. Izmirly, MD, MSc, of New York University, the lead author, and associates said.
SLE prevalence was distributed similarly in men, although there was a greater relative margin between American Indians/Alaska Natives (53.8 cases per 100,000 person-years) and Blacks (26.7 per 100,000), and Asians/Pacific Islanders were higher than Whites (11.2 vs. 8.9), the investigators reported.
The meta-analysis leveraged data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s national lupus registries, which include four state-specific SLE registries and a fifth in the Indian Health Service. All cases of SLE occurred in 2002-2009, and the data were age adjusted to the 2000 U.S. population and separately extrapolated to the 2018 U.S. Census population, they explained.
The analysis was funded by cooperative agreements between the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene and New York University, and the CDC and National Institute of Health.
The prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) appears to be much lower than previously believed and may pose “a potential risk to research funding for the disease,” according to results of a meta-analysis involving a network of population-based registries.

“When we started this study, a widely cited lupus statistic was that approximately 1.5 million Americans were affected. Our meta-analysis found the actual prevalence to be slightly more than 200,000: a number that approaches the [Food and Drug Administration’s] definition of a rare disease,” Emily Somers, PhD, ScM, senior author and associate professor of rheumatology and environmental health sciences at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in a written statement.
Their estimates, published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology, put the overall SLE prevalence in the United States at 72.8 per 100,000 person-years in 2018, with nearly nine times more females affected (128.7 cases per 100,000) than males (14.6 per 100,000). Race and ethnicity also play a role, as prevalence was highest among American Indian/Alaska Native and Black females, with Hispanic females lower but still higher than White and Asian/Pacific Islander females, Peter M. Izmirly, MD, MSc, of New York University, the lead author, and associates said.
SLE prevalence was distributed similarly in men, although there was a greater relative margin between American Indians/Alaska Natives (53.8 cases per 100,000 person-years) and Blacks (26.7 per 100,000), and Asians/Pacific Islanders were higher than Whites (11.2 vs. 8.9), the investigators reported.
The meta-analysis leveraged data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s national lupus registries, which include four state-specific SLE registries and a fifth in the Indian Health Service. All cases of SLE occurred in 2002-2009, and the data were age adjusted to the 2000 U.S. population and separately extrapolated to the 2018 U.S. Census population, they explained.
The analysis was funded by cooperative agreements between the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene and New York University, and the CDC and National Institute of Health.
The prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) appears to be much lower than previously believed and may pose “a potential risk to research funding for the disease,” according to results of a meta-analysis involving a network of population-based registries.

“When we started this study, a widely cited lupus statistic was that approximately 1.5 million Americans were affected. Our meta-analysis found the actual prevalence to be slightly more than 200,000: a number that approaches the [Food and Drug Administration’s] definition of a rare disease,” Emily Somers, PhD, ScM, senior author and associate professor of rheumatology and environmental health sciences at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in a written statement.
Their estimates, published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology, put the overall SLE prevalence in the United States at 72.8 per 100,000 person-years in 2018, with nearly nine times more females affected (128.7 cases per 100,000) than males (14.6 per 100,000). Race and ethnicity also play a role, as prevalence was highest among American Indian/Alaska Native and Black females, with Hispanic females lower but still higher than White and Asian/Pacific Islander females, Peter M. Izmirly, MD, MSc, of New York University, the lead author, and associates said.
SLE prevalence was distributed similarly in men, although there was a greater relative margin between American Indians/Alaska Natives (53.8 cases per 100,000 person-years) and Blacks (26.7 per 100,000), and Asians/Pacific Islanders were higher than Whites (11.2 vs. 8.9), the investigators reported.
The meta-analysis leveraged data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s national lupus registries, which include four state-specific SLE registries and a fifth in the Indian Health Service. All cases of SLE occurred in 2002-2009, and the data were age adjusted to the 2000 U.S. population and separately extrapolated to the 2018 U.S. Census population, they explained.
The analysis was funded by cooperative agreements between the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene and New York University, and the CDC and National Institute of Health.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Palliative care underused in pulmonary arterial hypertension
of more than 30,000 hospital admissions has found.
“Specialty palliative care services (PCS) are present in the vast majority of hospitals with more than 300 beds, and PCS use for patients who are facing serious illness with potentially life-limiting prognoses increasingly is becoming the standard of care,” wrote Vidhu Anand, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues. But despite experts recommending PCS in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), data on the use of palliative care referrals for PAH patients are limited, they added.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers used the National (Nationwide) Inpatient Sample to identify 30,495 admissions with a primary diagnosis of PAH between 2001 through 2017. The primary outcome was the use of PCS in these patients.
Overall, inpatient use of PCS was 2.2%, but that figure increased from 0.5% in 2001 to 7.6% in 2017, representing a fivefold increase over the study period, with a significant increase after 2009. The reason for this notable increase remains unclear; however, “it may be related to recognition of palliative care and hospice as a medical subspecialty with board certification in 2008 or identification of palliative care by the National Priorities Partnership as one of six priority areas in 2008,” the researchers said.
Incorporating palliative care in a treatment strategy
The perception of PCS as an element of treatment plans for patients with severe lung disease, and not only as end-of-life care, has certainly increased in recent years, Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP, said in an interview.
Dr. Gupta is a pulmonologist practicing in the San Francisco Bay area, and he did not take part in the study. He recommended early integration of PCS treating patients with PAH. “I have frequently asked PCS to aid early on during inpatient admission with PAH patients for pain management, as well as for aiding in POLST [Physician Orders for Life-Sustaining Treatment] paperwork to be completed. Increased age and comorbidities are certainly risk factors themselves for a longer hospital course and worse outcomes; in addition, in center-based PAH care there are more means available by which to give a patient with right heart failure that ‘one last shot’ – an opportunity for a longer life. I truly think it is a relationship with the patient, built from the outpatient pulmonary hypertension clinic, that allows the treating physician to have a better sense of a patient’s quality of life longitudinally, and to have the candid conversation when things begin to decline.”
Which patients receive PCS?
The study found that socioeconomic factors, and the severity of illness, are the drivers of PCS referrals. In a multivariate analysis, independent predictors of PCS use included white race, private insurance, and higher socioeconomic status. Additional independent predictors of PCS use included increased comorbidities, admission to an urban hospital, admission to a small hospital, presence of heart failure and cardiogenic shock, acute noncardiac organ failure, and use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and noninvasive mechanical ventilation, the researchers noted.
Patients who received PCS consultation were significantly more likely than those not receiving PCS to have DNR status (46.2% vs. 1.8%), longer length of hospital stay (12.9 days vs. 7.2 days), higher hospitalization costs $130,434 vs. $56,499), and higher in-hospital mortality (52.8% vs. 6.4%; P < .001 for all).
Some patients refuse PCS and others are not offered PCS. Dr. Gupta noted that it should be no surprise that not all patients are comfortable with the idea of a PCS referral. “Fear, misunderstanding, and cultural beliefs may be individually or together at the root of resistance to PCS. Their reluctance may be due to a ‘false narrative’ of the purpose of palliative care. The conception of PCS being for end-of-life care may be the result of personal experiences or experience with loved ones. Occasionally, a patient equates PCS with access to narcotics (‘knock me out’), which they may or may not want. I try to reassure patients that there will be no coercion for anything they do not want, and at the end of the day, the medical team is the main driver of their care, not the palliative service.”
Actively drug-abusing PAH patients are a particular challenge, said Dr. Gupta. These patients often refuse palliative care referral both as inpatients and outpatients. “Such patients are an enigma for many PAH-treating physicians as they may survive to discharge, despite a terrible prognosis predicted by their testing.”
In addition, patients in whom organ transplantation is being pursued may not receive timely PCS, he said. “It can be an absolute challenge to bring such patients to the finish line (transplantation), and the timing of PCS referral is often deferred. Arguably, for better or worse, such patients refuse, or more often are not offered, PCS as inpatients while there is still a chance organ transplantation is a viable option for them.”
The use of PCS in less than 10% of PAH admissions is similar to previous studies showing low use of PCS for patients with acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, and COPD, the researchers noted. However, “Given the high morbidity and mortality associated with PAH even after hospitalization, hospital admissions without PCS use represent a missed opportunity,” the investigators wrote.
Early warning on the need for PCS
Increasing PCS referrals for PAH patients requires clinicians to be proactive, Dr. Gupta stressed. “Pulmonologists, especially those managing pulmonary hypertension outpatients without the aid of a PAH center, should remain vigilant at all routine visits to calculate a patient’s risk score (i.e. REVEAL 2.0 risk calculator) to stratify their risk of 1-year mortality. Based on this assessment, shared decision making can help guide next steps including early outpatient PCS involvement for those at high risk. I also calculate a patient’s risk score, based on the data I have, when PAH patients are admitted to the hospital. Occasionally, a patient who I initially think is moderate risk turns out to be high risk when I calculate their risk score. In such high-risk patients, PCS consultation should certainly be considered early on.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possible coding errors associated with use of discharge diagnosis, lack of data on medication and the cause of PAH, and lack of information on the reasons for PCS referrals, the researchers noted. However, the results “addressed an important knowledge gap highlighting the national use of PCS in PAH,” they said. Further research is needed to address disparities and the integration of PCS into PAH care protocols, they added.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study received no outside funding; one coauthor disclosed support from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences Clinical and Translational Science.
of more than 30,000 hospital admissions has found.
“Specialty palliative care services (PCS) are present in the vast majority of hospitals with more than 300 beds, and PCS use for patients who are facing serious illness with potentially life-limiting prognoses increasingly is becoming the standard of care,” wrote Vidhu Anand, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues. But despite experts recommending PCS in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), data on the use of palliative care referrals for PAH patients are limited, they added.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers used the National (Nationwide) Inpatient Sample to identify 30,495 admissions with a primary diagnosis of PAH between 2001 through 2017. The primary outcome was the use of PCS in these patients.
Overall, inpatient use of PCS was 2.2%, but that figure increased from 0.5% in 2001 to 7.6% in 2017, representing a fivefold increase over the study period, with a significant increase after 2009. The reason for this notable increase remains unclear; however, “it may be related to recognition of palliative care and hospice as a medical subspecialty with board certification in 2008 or identification of palliative care by the National Priorities Partnership as one of six priority areas in 2008,” the researchers said.
Incorporating palliative care in a treatment strategy
The perception of PCS as an element of treatment plans for patients with severe lung disease, and not only as end-of-life care, has certainly increased in recent years, Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP, said in an interview.
Dr. Gupta is a pulmonologist practicing in the San Francisco Bay area, and he did not take part in the study. He recommended early integration of PCS treating patients with PAH. “I have frequently asked PCS to aid early on during inpatient admission with PAH patients for pain management, as well as for aiding in POLST [Physician Orders for Life-Sustaining Treatment] paperwork to be completed. Increased age and comorbidities are certainly risk factors themselves for a longer hospital course and worse outcomes; in addition, in center-based PAH care there are more means available by which to give a patient with right heart failure that ‘one last shot’ – an opportunity for a longer life. I truly think it is a relationship with the patient, built from the outpatient pulmonary hypertension clinic, that allows the treating physician to have a better sense of a patient’s quality of life longitudinally, and to have the candid conversation when things begin to decline.”
Which patients receive PCS?
The study found that socioeconomic factors, and the severity of illness, are the drivers of PCS referrals. In a multivariate analysis, independent predictors of PCS use included white race, private insurance, and higher socioeconomic status. Additional independent predictors of PCS use included increased comorbidities, admission to an urban hospital, admission to a small hospital, presence of heart failure and cardiogenic shock, acute noncardiac organ failure, and use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and noninvasive mechanical ventilation, the researchers noted.
Patients who received PCS consultation were significantly more likely than those not receiving PCS to have DNR status (46.2% vs. 1.8%), longer length of hospital stay (12.9 days vs. 7.2 days), higher hospitalization costs $130,434 vs. $56,499), and higher in-hospital mortality (52.8% vs. 6.4%; P < .001 for all).
Some patients refuse PCS and others are not offered PCS. Dr. Gupta noted that it should be no surprise that not all patients are comfortable with the idea of a PCS referral. “Fear, misunderstanding, and cultural beliefs may be individually or together at the root of resistance to PCS. Their reluctance may be due to a ‘false narrative’ of the purpose of palliative care. The conception of PCS being for end-of-life care may be the result of personal experiences or experience with loved ones. Occasionally, a patient equates PCS with access to narcotics (‘knock me out’), which they may or may not want. I try to reassure patients that there will be no coercion for anything they do not want, and at the end of the day, the medical team is the main driver of their care, not the palliative service.”
Actively drug-abusing PAH patients are a particular challenge, said Dr. Gupta. These patients often refuse palliative care referral both as inpatients and outpatients. “Such patients are an enigma for many PAH-treating physicians as they may survive to discharge, despite a terrible prognosis predicted by their testing.”
In addition, patients in whom organ transplantation is being pursued may not receive timely PCS, he said. “It can be an absolute challenge to bring such patients to the finish line (transplantation), and the timing of PCS referral is often deferred. Arguably, for better or worse, such patients refuse, or more often are not offered, PCS as inpatients while there is still a chance organ transplantation is a viable option for them.”
The use of PCS in less than 10% of PAH admissions is similar to previous studies showing low use of PCS for patients with acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, and COPD, the researchers noted. However, “Given the high morbidity and mortality associated with PAH even after hospitalization, hospital admissions without PCS use represent a missed opportunity,” the investigators wrote.
Early warning on the need for PCS
Increasing PCS referrals for PAH patients requires clinicians to be proactive, Dr. Gupta stressed. “Pulmonologists, especially those managing pulmonary hypertension outpatients without the aid of a PAH center, should remain vigilant at all routine visits to calculate a patient’s risk score (i.e. REVEAL 2.0 risk calculator) to stratify their risk of 1-year mortality. Based on this assessment, shared decision making can help guide next steps including early outpatient PCS involvement for those at high risk. I also calculate a patient’s risk score, based on the data I have, when PAH patients are admitted to the hospital. Occasionally, a patient who I initially think is moderate risk turns out to be high risk when I calculate their risk score. In such high-risk patients, PCS consultation should certainly be considered early on.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possible coding errors associated with use of discharge diagnosis, lack of data on medication and the cause of PAH, and lack of information on the reasons for PCS referrals, the researchers noted. However, the results “addressed an important knowledge gap highlighting the national use of PCS in PAH,” they said. Further research is needed to address disparities and the integration of PCS into PAH care protocols, they added.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study received no outside funding; one coauthor disclosed support from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences Clinical and Translational Science.
of more than 30,000 hospital admissions has found.
“Specialty palliative care services (PCS) are present in the vast majority of hospitals with more than 300 beds, and PCS use for patients who are facing serious illness with potentially life-limiting prognoses increasingly is becoming the standard of care,” wrote Vidhu Anand, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues. But despite experts recommending PCS in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), data on the use of palliative care referrals for PAH patients are limited, they added.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers used the National (Nationwide) Inpatient Sample to identify 30,495 admissions with a primary diagnosis of PAH between 2001 through 2017. The primary outcome was the use of PCS in these patients.
Overall, inpatient use of PCS was 2.2%, but that figure increased from 0.5% in 2001 to 7.6% in 2017, representing a fivefold increase over the study period, with a significant increase after 2009. The reason for this notable increase remains unclear; however, “it may be related to recognition of palliative care and hospice as a medical subspecialty with board certification in 2008 or identification of palliative care by the National Priorities Partnership as one of six priority areas in 2008,” the researchers said.
Incorporating palliative care in a treatment strategy
The perception of PCS as an element of treatment plans for patients with severe lung disease, and not only as end-of-life care, has certainly increased in recent years, Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP, said in an interview.
Dr. Gupta is a pulmonologist practicing in the San Francisco Bay area, and he did not take part in the study. He recommended early integration of PCS treating patients with PAH. “I have frequently asked PCS to aid early on during inpatient admission with PAH patients for pain management, as well as for aiding in POLST [Physician Orders for Life-Sustaining Treatment] paperwork to be completed. Increased age and comorbidities are certainly risk factors themselves for a longer hospital course and worse outcomes; in addition, in center-based PAH care there are more means available by which to give a patient with right heart failure that ‘one last shot’ – an opportunity for a longer life. I truly think it is a relationship with the patient, built from the outpatient pulmonary hypertension clinic, that allows the treating physician to have a better sense of a patient’s quality of life longitudinally, and to have the candid conversation when things begin to decline.”
Which patients receive PCS?
The study found that socioeconomic factors, and the severity of illness, are the drivers of PCS referrals. In a multivariate analysis, independent predictors of PCS use included white race, private insurance, and higher socioeconomic status. Additional independent predictors of PCS use included increased comorbidities, admission to an urban hospital, admission to a small hospital, presence of heart failure and cardiogenic shock, acute noncardiac organ failure, and use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and noninvasive mechanical ventilation, the researchers noted.
Patients who received PCS consultation were significantly more likely than those not receiving PCS to have DNR status (46.2% vs. 1.8%), longer length of hospital stay (12.9 days vs. 7.2 days), higher hospitalization costs $130,434 vs. $56,499), and higher in-hospital mortality (52.8% vs. 6.4%; P < .001 for all).
Some patients refuse PCS and others are not offered PCS. Dr. Gupta noted that it should be no surprise that not all patients are comfortable with the idea of a PCS referral. “Fear, misunderstanding, and cultural beliefs may be individually or together at the root of resistance to PCS. Their reluctance may be due to a ‘false narrative’ of the purpose of palliative care. The conception of PCS being for end-of-life care may be the result of personal experiences or experience with loved ones. Occasionally, a patient equates PCS with access to narcotics (‘knock me out’), which they may or may not want. I try to reassure patients that there will be no coercion for anything they do not want, and at the end of the day, the medical team is the main driver of their care, not the palliative service.”
Actively drug-abusing PAH patients are a particular challenge, said Dr. Gupta. These patients often refuse palliative care referral both as inpatients and outpatients. “Such patients are an enigma for many PAH-treating physicians as they may survive to discharge, despite a terrible prognosis predicted by their testing.”
In addition, patients in whom organ transplantation is being pursued may not receive timely PCS, he said. “It can be an absolute challenge to bring such patients to the finish line (transplantation), and the timing of PCS referral is often deferred. Arguably, for better or worse, such patients refuse, or more often are not offered, PCS as inpatients while there is still a chance organ transplantation is a viable option for them.”
The use of PCS in less than 10% of PAH admissions is similar to previous studies showing low use of PCS for patients with acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, and COPD, the researchers noted. However, “Given the high morbidity and mortality associated with PAH even after hospitalization, hospital admissions without PCS use represent a missed opportunity,” the investigators wrote.
Early warning on the need for PCS
Increasing PCS referrals for PAH patients requires clinicians to be proactive, Dr. Gupta stressed. “Pulmonologists, especially those managing pulmonary hypertension outpatients without the aid of a PAH center, should remain vigilant at all routine visits to calculate a patient’s risk score (i.e. REVEAL 2.0 risk calculator) to stratify their risk of 1-year mortality. Based on this assessment, shared decision making can help guide next steps including early outpatient PCS involvement for those at high risk. I also calculate a patient’s risk score, based on the data I have, when PAH patients are admitted to the hospital. Occasionally, a patient who I initially think is moderate risk turns out to be high risk when I calculate their risk score. In such high-risk patients, PCS consultation should certainly be considered early on.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possible coding errors associated with use of discharge diagnosis, lack of data on medication and the cause of PAH, and lack of information on the reasons for PCS referrals, the researchers noted. However, the results “addressed an important knowledge gap highlighting the national use of PCS in PAH,” they said. Further research is needed to address disparities and the integration of PCS into PAH care protocols, they added.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study received no outside funding; one coauthor disclosed support from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences Clinical and Translational Science.
FROM CHEST
FDA approves voclosporin for lupus nephritis
The Food and Drug Administration has approved voclosporin (Lupkynis) for the treatment of lupus nephritis, according to a Jan. 22 press release from manufacturer Aurinia Pharmaceuticals.
Lupkynis is a calcineurin-inhibitor immunosuppressant, and is the first oral medication to show effectiveness in lupus nephritis, according to the company. The drug is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active lupus nephritis in combination with a background immunosuppressive therapy regimen, according to the drug label, which also has a boxed warning describing the increased risk of infections and malignancies, including lymphoma.
The approval of voclosporin was based on data from two studies, the AURORA phase 3 study and the AURA-LV phase 2 study. The studies included 533 adults with lupus nephritis who were randomized to 23.7 mg or placebo of voclosporin twice daily in the form of oral capsules, or placebo capsules, in addition to standard of care (mycophenolate mofetil plus low-dose glucocorticoids).
In the AURORA phase 3 study of 357 patients, close to twice as many patients in the treatment group showed a complete renal response, compared with the placebo group after 1 year (40.8% vs. 22.5%). In addition, patients treated with voclosporin more quickly achieved a significant reduction in urine protein to creatinine ratio, compared with the placebo patients (169 days vs. 372 days).
Severe adverse events were similar between the groups, including the most common complication of infection (10.1% and 11.2% for voclosporin and control groups, respectively). Other adverse reactions reported in at least 3% of the study participants included a decrease in glomerular filtration rate, hypertension, diarrhea, headache, anemia, cough, urinary tract infection, upper abdominal pain, dyspepsia, alopecia, renal impairment, abdominal pain, mouth ulceration, fatigue, tremor, acute kidney injury, and decreased appetite, according to the company press release.
Full clinical trial information for the AURORA study is available here.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved voclosporin (Lupkynis) for the treatment of lupus nephritis, according to a Jan. 22 press release from manufacturer Aurinia Pharmaceuticals.
Lupkynis is a calcineurin-inhibitor immunosuppressant, and is the first oral medication to show effectiveness in lupus nephritis, according to the company. The drug is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active lupus nephritis in combination with a background immunosuppressive therapy regimen, according to the drug label, which also has a boxed warning describing the increased risk of infections and malignancies, including lymphoma.
The approval of voclosporin was based on data from two studies, the AURORA phase 3 study and the AURA-LV phase 2 study. The studies included 533 adults with lupus nephritis who were randomized to 23.7 mg or placebo of voclosporin twice daily in the form of oral capsules, or placebo capsules, in addition to standard of care (mycophenolate mofetil plus low-dose glucocorticoids).
In the AURORA phase 3 study of 357 patients, close to twice as many patients in the treatment group showed a complete renal response, compared with the placebo group after 1 year (40.8% vs. 22.5%). In addition, patients treated with voclosporin more quickly achieved a significant reduction in urine protein to creatinine ratio, compared with the placebo patients (169 days vs. 372 days).
Severe adverse events were similar between the groups, including the most common complication of infection (10.1% and 11.2% for voclosporin and control groups, respectively). Other adverse reactions reported in at least 3% of the study participants included a decrease in glomerular filtration rate, hypertension, diarrhea, headache, anemia, cough, urinary tract infection, upper abdominal pain, dyspepsia, alopecia, renal impairment, abdominal pain, mouth ulceration, fatigue, tremor, acute kidney injury, and decreased appetite, according to the company press release.
Full clinical trial information for the AURORA study is available here.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved voclosporin (Lupkynis) for the treatment of lupus nephritis, according to a Jan. 22 press release from manufacturer Aurinia Pharmaceuticals.
Lupkynis is a calcineurin-inhibitor immunosuppressant, and is the first oral medication to show effectiveness in lupus nephritis, according to the company. The drug is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active lupus nephritis in combination with a background immunosuppressive therapy regimen, according to the drug label, which also has a boxed warning describing the increased risk of infections and malignancies, including lymphoma.
The approval of voclosporin was based on data from two studies, the AURORA phase 3 study and the AURA-LV phase 2 study. The studies included 533 adults with lupus nephritis who were randomized to 23.7 mg or placebo of voclosporin twice daily in the form of oral capsules, or placebo capsules, in addition to standard of care (mycophenolate mofetil plus low-dose glucocorticoids).
In the AURORA phase 3 study of 357 patients, close to twice as many patients in the treatment group showed a complete renal response, compared with the placebo group after 1 year (40.8% vs. 22.5%). In addition, patients treated with voclosporin more quickly achieved a significant reduction in urine protein to creatinine ratio, compared with the placebo patients (169 days vs. 372 days).
Severe adverse events were similar between the groups, including the most common complication of infection (10.1% and 11.2% for voclosporin and control groups, respectively). Other adverse reactions reported in at least 3% of the study participants included a decrease in glomerular filtration rate, hypertension, diarrhea, headache, anemia, cough, urinary tract infection, upper abdominal pain, dyspepsia, alopecia, renal impairment, abdominal pain, mouth ulceration, fatigue, tremor, acute kidney injury, and decreased appetite, according to the company press release.
Full clinical trial information for the AURORA study is available here.