User login
Depression in homeless patients: What can be done?
In a recent article published in JAMA Psychiatry, Joshua E. J. Buckman and coauthors described the results of a large research study which concludes that depression is harder to treat in those who are homeless or unemployed.
It is always good to get more data and this article adds to the literature about the social determinants of depression. A frustrating aspect is that this is no surprise at all, not least for anyone in the mental health field. We have known that intuitively for decades.
Again, data is always good to bolster intuition with science. But what are the actionable items to take from the paper?
However, there are a few policy and clinical points I would like to make, reflecting some of the chapters in a recently published book – edited by me and my colleague Maria D. Llorente – “Clinical Management of the Homeless Patient: Social Medical and Psychiatric Issues” (New York: Springer, May 2021).
The first is, if you really tackle homelessness, with a combination of federal, state, and local resources, you can make a difference. The Department of Veterans Affairs, under the leadership of former VA Secretary Eric Shinseki and others, has been markedly successful. Note, for instance, the Health Care for Homeless Veterans program , which conducts outreach to vulnerable veterans not currently receiving services and engages them in treatment and rehabilitative programs.
Secondly, there is a marked absence of shelters that can care for the homeless with medical problems. This leads to extended and extensive hospital stays. This is especially frustrating during the COVID era, when hospital beds are in such short supply. Having a safe place to discharge patients who still need wound or diabetes care would save money for the overall health care system and be best for the patient.
Third, it may be best to modify discharge regimens for those patients who are unhoused. For example, metformin, taken by mouth once a day, is more practical for unhoused patients with diabetes than insulin, which needs to be refrigerated and injected multiple times a day. While one can argue whether care for the homeless should differ from those who are housed, in practical terms, simplifying regimens is more likely to promote compliance.
My last take-home point is check the Feet. So many of our homeless patients who end up on hospital wards have been wearing ill-fitting or no shoes while they are out on the street. Their toenails may be long and thick. They may have cellulitis or ulcers. Or gangrene. Unfortunately, these medical issues can also cause surgical amputations of the lower extremities.
Back to the article by Buckman and colleagues. The data they provide is good to have. But we need more action to provide appropriate and compassionate care for those who are unhoused and ill – care that is good for them, good for the nation’s finances, and good for our moral standing in the world.
Dr. Ritchie is chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington (D.C.) Hospital Center. She is a member of the Clinical Psychiatry News editorial advisory board, and has no conflicts of interest.
In a recent article published in JAMA Psychiatry, Joshua E. J. Buckman and coauthors described the results of a large research study which concludes that depression is harder to treat in those who are homeless or unemployed.
It is always good to get more data and this article adds to the literature about the social determinants of depression. A frustrating aspect is that this is no surprise at all, not least for anyone in the mental health field. We have known that intuitively for decades.
Again, data is always good to bolster intuition with science. But what are the actionable items to take from the paper?
However, there are a few policy and clinical points I would like to make, reflecting some of the chapters in a recently published book – edited by me and my colleague Maria D. Llorente – “Clinical Management of the Homeless Patient: Social Medical and Psychiatric Issues” (New York: Springer, May 2021).
The first is, if you really tackle homelessness, with a combination of federal, state, and local resources, you can make a difference. The Department of Veterans Affairs, under the leadership of former VA Secretary Eric Shinseki and others, has been markedly successful. Note, for instance, the Health Care for Homeless Veterans program , which conducts outreach to vulnerable veterans not currently receiving services and engages them in treatment and rehabilitative programs.
Secondly, there is a marked absence of shelters that can care for the homeless with medical problems. This leads to extended and extensive hospital stays. This is especially frustrating during the COVID era, when hospital beds are in such short supply. Having a safe place to discharge patients who still need wound or diabetes care would save money for the overall health care system and be best for the patient.
Third, it may be best to modify discharge regimens for those patients who are unhoused. For example, metformin, taken by mouth once a day, is more practical for unhoused patients with diabetes than insulin, which needs to be refrigerated and injected multiple times a day. While one can argue whether care for the homeless should differ from those who are housed, in practical terms, simplifying regimens is more likely to promote compliance.
My last take-home point is check the Feet. So many of our homeless patients who end up on hospital wards have been wearing ill-fitting or no shoes while they are out on the street. Their toenails may be long and thick. They may have cellulitis or ulcers. Or gangrene. Unfortunately, these medical issues can also cause surgical amputations of the lower extremities.
Back to the article by Buckman and colleagues. The data they provide is good to have. But we need more action to provide appropriate and compassionate care for those who are unhoused and ill – care that is good for them, good for the nation’s finances, and good for our moral standing in the world.
Dr. Ritchie is chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington (D.C.) Hospital Center. She is a member of the Clinical Psychiatry News editorial advisory board, and has no conflicts of interest.
In a recent article published in JAMA Psychiatry, Joshua E. J. Buckman and coauthors described the results of a large research study which concludes that depression is harder to treat in those who are homeless or unemployed.
It is always good to get more data and this article adds to the literature about the social determinants of depression. A frustrating aspect is that this is no surprise at all, not least for anyone in the mental health field. We have known that intuitively for decades.
Again, data is always good to bolster intuition with science. But what are the actionable items to take from the paper?
However, there are a few policy and clinical points I would like to make, reflecting some of the chapters in a recently published book – edited by me and my colleague Maria D. Llorente – “Clinical Management of the Homeless Patient: Social Medical and Psychiatric Issues” (New York: Springer, May 2021).
The first is, if you really tackle homelessness, with a combination of federal, state, and local resources, you can make a difference. The Department of Veterans Affairs, under the leadership of former VA Secretary Eric Shinseki and others, has been markedly successful. Note, for instance, the Health Care for Homeless Veterans program , which conducts outreach to vulnerable veterans not currently receiving services and engages them in treatment and rehabilitative programs.
Secondly, there is a marked absence of shelters that can care for the homeless with medical problems. This leads to extended and extensive hospital stays. This is especially frustrating during the COVID era, when hospital beds are in such short supply. Having a safe place to discharge patients who still need wound or diabetes care would save money for the overall health care system and be best for the patient.
Third, it may be best to modify discharge regimens for those patients who are unhoused. For example, metformin, taken by mouth once a day, is more practical for unhoused patients with diabetes than insulin, which needs to be refrigerated and injected multiple times a day. While one can argue whether care for the homeless should differ from those who are housed, in practical terms, simplifying regimens is more likely to promote compliance.
My last take-home point is check the Feet. So many of our homeless patients who end up on hospital wards have been wearing ill-fitting or no shoes while they are out on the street. Their toenails may be long and thick. They may have cellulitis or ulcers. Or gangrene. Unfortunately, these medical issues can also cause surgical amputations of the lower extremities.
Back to the article by Buckman and colleagues. The data they provide is good to have. But we need more action to provide appropriate and compassionate care for those who are unhoused and ill – care that is good for them, good for the nation’s finances, and good for our moral standing in the world.
Dr. Ritchie is chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington (D.C.) Hospital Center. She is a member of the Clinical Psychiatry News editorial advisory board, and has no conflicts of interest.
Psilocybin ‘rewires’ the brain to alleviate depression
Led by investigators from the University of California, San Francisco, and Imperial College London’s Centre for Psychedelic Research, the findings come from a new analysis of brain scans of almost 60 patients with resistant depression treated with psilocybin.
“Not much is known about the changes in brain function after psychedelic experience. There has been much more research done on the acute brain action of psychedelics, but there is very little on the postacute or subacute changes in brain function,” study investigator Robin Carhart-Harris, PhD, former head of the Imperial Centre for Psychedelic Research and now director of the Neuroscape psychedelics division at UCSF, and senior author of the study, told this news organization.
“This research is a major advance because it is showing replication across two datasets with different designs. One in which the scanning is done 1 day after intervention and the other one when the posttreatment scanning is done 3 weeks after the second of two psilocybin therapy sessions,” Dr. Carhart-Harris added.
The study was published online in Nature Medicine.
A disruptor?
Psilocybin is one of a number of psychedelics under investigation as a potential therapy for psychiatric disorders. In the last 15 years, at least six separate clinical trials have reported impressive improvements in depressive symptoms with psilocybin therapy. Several studies have tested a synthesized a form of the drug to treat patients with depression and anxiety – with promising results.
However, the therapeutic action of psilocybin and other serotonergic psychedelics is still not completely understood, although it is known that they affect 5-HT2A receptors and are hypothesized to briefly disrupt these connections, allowing them to reform in new ways in the days and weeks following treatment.
This research assessed the subacute impact of psilocybin on brain function in two clinical trials of depression:
The first trial was an open-label trial of oral psilocybin in patients with treatment-resistant depression.
Patients had baseline clinical assessment and resting-state functional MRI, followed by fixed-order “low” (10 mg) and “high” (25 mg) psilocybin therapy dosing days separated by 1 week. Of the 19 patients recruited, 3 were excluded as a result of excessive fMRI head motion. The team confirmed an antidepressant effect of psilocybin in 16 patients via reduced questionnaire scores from baseline.
Brain network modularity was significantly reduced 1 day after psilocybin therapy in 10 of 16 participants (mean difference, –0.29; t15, 2.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.50; P = .012; d = 0.72). This result implies an increase in functional connectivity between the brain’s main intrinsic networks.
Pre- vs posttreatment change in modularity significantly correlated with change in Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) score at 6 months, relative to baseline (r14 = 0.54, 95% CI, 0.14-0.78, P = .033). Results imply that decreased brain modularity 1 day after psilocybin therapy relates to long-term improvements in symptom severity.
Effective antidepressant alternative?
The second trial was a double-blind, phase 2, randomized, controlled trial comparing psilocybin with escitalopram (Lexapro). Twenty-one patients were included in the escitalopram imaging sample and 22 patients were included in the psilocybin imaging sample.
Patients received either 2 x 25 mg oral psilocybin, 3 weeks apart, plus 6 weeks of daily placebo (psilocybin arm) or 2 x 1 mg oral psilocybin, 3 weeks apart, plus 6 weeks of daily escitalopram (10-20 mg) (escitalopram arm). Functional MRI was recorded at baseline and 3 weeks after the second psilocybin dose.
On average, BDI-measured reductions in depressive symptom severity were significantly greater under psilocybin than escitalopram, indicating superior efficacy of psilocybin therapy versus escitalopram.
Evidence indicated that the reduction in network modularity and its relationship to depression severity was specific to the psilocybin group. In the escitalopram group, network modularity did not change from baseline and there was no significant correlation between changes in modularity and changes in BDI scores.
Post–psilocybin therapy changes in network flexibility were correlated with changes in BDI score. After false discovery rate correction, increased executive network dynamic flexibility strongly correlated with greater symptom improvement at the 6-week primary endpoint for the psilocybin arm (r20, –0.76, 95% CI, −0.90 to –0.50, P = .001).
There were no significant correlations between changes in BDI scores and changes in dynamic flexibility in the escitalopram arm.
“These findings are important because for the first time we find that psilocybin works differently from conventional antidepressants, making the brain more flexible and fluid and less entrenched in the negative thinking patterns associated with depression. This supports our initial predictions and confirms psilocybin could be a real alternative approach to depression treatments,” study investigator David Nutt, DM, head of the Imperial Centre for Psychedelic Research, London, said in a release.
“In previous studies we had seen a similar effect in the brain when people were scanned whilst on a psychedelic, but here we’re seeing it weeks after treatment for depression, which suggests a carryover of the acute drug action,” said Dr. Carhart-Harris.
Durable effect?
“We don’t yet know how long the changes in brain activity seen with psilocybin therapy last, and we need to do more research to understand this,” said Dr. Carhart-Harris, who is a member of the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences. “If the changes don’t last, then is it related to relapse into a depressive episode? We need to do follow-up scans to see where people’s brains are at 3 months or even 6 months after treatment.
“We do know that some people relapse, and it may be that after a while their brains revert to the rigid patterns of activity we see in depression.
“One exciting implication of our findings is that we have discovered a fundamental mechanism via which psychedelic therapy works not just for depression but other mental illnesses, such as anorexia or addiction. We now need to test if this is the case, and if it is, then we have found something important,” added Dr. Carhart-Harris.
Successful phase 3, double-blind randomized, controlled trials will be required to achieve licensing for psilocybin therapy, but pragmatic trials may better address questions regarding treatment practicability, specificity, and optimization. Given the emerging research into psychedelic therapy, it is important for large-scale trials to establish the generalizability, reliability, and specificity of the drug’s antidepressant response.
So how close are we to full federal approval for psilocybin in the treatment of depression? Dr. Carhart-Harris estimated that within 4-5 years is realistic at the federal level. At the state level, in Oregon psilocybin therapy is on track for approval in 2023, including for patients currently undergoing treatment for depressive disorders. In addition, things are opening up in Canada, with some special-access opportunities.
The researchers cautioned that, while these findings are encouraging, trials assessing psilocybin for depression have taken place under controlled, clinical conditions, using a regulated dose formulated in a laboratory, and involved extensive psychological support by a mental health professional – before, during, and after dosing. Taking psychedelics in the absence of these combined safeguards may not have a positive outcome.
The research was supported by funding from the Alex Mosley Charitable Trust and founding donors of the Imperial Centre for Psychedelic Research. One coauthor was supported by the Imperial College London EPSRC Centre London for doctoral training in neurotechnology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Led by investigators from the University of California, San Francisco, and Imperial College London’s Centre for Psychedelic Research, the findings come from a new analysis of brain scans of almost 60 patients with resistant depression treated with psilocybin.
“Not much is known about the changes in brain function after psychedelic experience. There has been much more research done on the acute brain action of psychedelics, but there is very little on the postacute or subacute changes in brain function,” study investigator Robin Carhart-Harris, PhD, former head of the Imperial Centre for Psychedelic Research and now director of the Neuroscape psychedelics division at UCSF, and senior author of the study, told this news organization.
“This research is a major advance because it is showing replication across two datasets with different designs. One in which the scanning is done 1 day after intervention and the other one when the posttreatment scanning is done 3 weeks after the second of two psilocybin therapy sessions,” Dr. Carhart-Harris added.
The study was published online in Nature Medicine.
A disruptor?
Psilocybin is one of a number of psychedelics under investigation as a potential therapy for psychiatric disorders. In the last 15 years, at least six separate clinical trials have reported impressive improvements in depressive symptoms with psilocybin therapy. Several studies have tested a synthesized a form of the drug to treat patients with depression and anxiety – with promising results.
However, the therapeutic action of psilocybin and other serotonergic psychedelics is still not completely understood, although it is known that they affect 5-HT2A receptors and are hypothesized to briefly disrupt these connections, allowing them to reform in new ways in the days and weeks following treatment.
This research assessed the subacute impact of psilocybin on brain function in two clinical trials of depression:
The first trial was an open-label trial of oral psilocybin in patients with treatment-resistant depression.
Patients had baseline clinical assessment and resting-state functional MRI, followed by fixed-order “low” (10 mg) and “high” (25 mg) psilocybin therapy dosing days separated by 1 week. Of the 19 patients recruited, 3 were excluded as a result of excessive fMRI head motion. The team confirmed an antidepressant effect of psilocybin in 16 patients via reduced questionnaire scores from baseline.
Brain network modularity was significantly reduced 1 day after psilocybin therapy in 10 of 16 participants (mean difference, –0.29; t15, 2.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.50; P = .012; d = 0.72). This result implies an increase in functional connectivity between the brain’s main intrinsic networks.
Pre- vs posttreatment change in modularity significantly correlated with change in Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) score at 6 months, relative to baseline (r14 = 0.54, 95% CI, 0.14-0.78, P = .033). Results imply that decreased brain modularity 1 day after psilocybin therapy relates to long-term improvements in symptom severity.
Effective antidepressant alternative?
The second trial was a double-blind, phase 2, randomized, controlled trial comparing psilocybin with escitalopram (Lexapro). Twenty-one patients were included in the escitalopram imaging sample and 22 patients were included in the psilocybin imaging sample.
Patients received either 2 x 25 mg oral psilocybin, 3 weeks apart, plus 6 weeks of daily placebo (psilocybin arm) or 2 x 1 mg oral psilocybin, 3 weeks apart, plus 6 weeks of daily escitalopram (10-20 mg) (escitalopram arm). Functional MRI was recorded at baseline and 3 weeks after the second psilocybin dose.
On average, BDI-measured reductions in depressive symptom severity were significantly greater under psilocybin than escitalopram, indicating superior efficacy of psilocybin therapy versus escitalopram.
Evidence indicated that the reduction in network modularity and its relationship to depression severity was specific to the psilocybin group. In the escitalopram group, network modularity did not change from baseline and there was no significant correlation between changes in modularity and changes in BDI scores.
Post–psilocybin therapy changes in network flexibility were correlated with changes in BDI score. After false discovery rate correction, increased executive network dynamic flexibility strongly correlated with greater symptom improvement at the 6-week primary endpoint for the psilocybin arm (r20, –0.76, 95% CI, −0.90 to –0.50, P = .001).
There were no significant correlations between changes in BDI scores and changes in dynamic flexibility in the escitalopram arm.
“These findings are important because for the first time we find that psilocybin works differently from conventional antidepressants, making the brain more flexible and fluid and less entrenched in the negative thinking patterns associated with depression. This supports our initial predictions and confirms psilocybin could be a real alternative approach to depression treatments,” study investigator David Nutt, DM, head of the Imperial Centre for Psychedelic Research, London, said in a release.
“In previous studies we had seen a similar effect in the brain when people were scanned whilst on a psychedelic, but here we’re seeing it weeks after treatment for depression, which suggests a carryover of the acute drug action,” said Dr. Carhart-Harris.
Durable effect?
“We don’t yet know how long the changes in brain activity seen with psilocybin therapy last, and we need to do more research to understand this,” said Dr. Carhart-Harris, who is a member of the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences. “If the changes don’t last, then is it related to relapse into a depressive episode? We need to do follow-up scans to see where people’s brains are at 3 months or even 6 months after treatment.
“We do know that some people relapse, and it may be that after a while their brains revert to the rigid patterns of activity we see in depression.
“One exciting implication of our findings is that we have discovered a fundamental mechanism via which psychedelic therapy works not just for depression but other mental illnesses, such as anorexia or addiction. We now need to test if this is the case, and if it is, then we have found something important,” added Dr. Carhart-Harris.
Successful phase 3, double-blind randomized, controlled trials will be required to achieve licensing for psilocybin therapy, but pragmatic trials may better address questions regarding treatment practicability, specificity, and optimization. Given the emerging research into psychedelic therapy, it is important for large-scale trials to establish the generalizability, reliability, and specificity of the drug’s antidepressant response.
So how close are we to full federal approval for psilocybin in the treatment of depression? Dr. Carhart-Harris estimated that within 4-5 years is realistic at the federal level. At the state level, in Oregon psilocybin therapy is on track for approval in 2023, including for patients currently undergoing treatment for depressive disorders. In addition, things are opening up in Canada, with some special-access opportunities.
The researchers cautioned that, while these findings are encouraging, trials assessing psilocybin for depression have taken place under controlled, clinical conditions, using a regulated dose formulated in a laboratory, and involved extensive psychological support by a mental health professional – before, during, and after dosing. Taking psychedelics in the absence of these combined safeguards may not have a positive outcome.
The research was supported by funding from the Alex Mosley Charitable Trust and founding donors of the Imperial Centre for Psychedelic Research. One coauthor was supported by the Imperial College London EPSRC Centre London for doctoral training in neurotechnology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Led by investigators from the University of California, San Francisco, and Imperial College London’s Centre for Psychedelic Research, the findings come from a new analysis of brain scans of almost 60 patients with resistant depression treated with psilocybin.
“Not much is known about the changes in brain function after psychedelic experience. There has been much more research done on the acute brain action of psychedelics, but there is very little on the postacute or subacute changes in brain function,” study investigator Robin Carhart-Harris, PhD, former head of the Imperial Centre for Psychedelic Research and now director of the Neuroscape psychedelics division at UCSF, and senior author of the study, told this news organization.
“This research is a major advance because it is showing replication across two datasets with different designs. One in which the scanning is done 1 day after intervention and the other one when the posttreatment scanning is done 3 weeks after the second of two psilocybin therapy sessions,” Dr. Carhart-Harris added.
The study was published online in Nature Medicine.
A disruptor?
Psilocybin is one of a number of psychedelics under investigation as a potential therapy for psychiatric disorders. In the last 15 years, at least six separate clinical trials have reported impressive improvements in depressive symptoms with psilocybin therapy. Several studies have tested a synthesized a form of the drug to treat patients with depression and anxiety – with promising results.
However, the therapeutic action of psilocybin and other serotonergic psychedelics is still not completely understood, although it is known that they affect 5-HT2A receptors and are hypothesized to briefly disrupt these connections, allowing them to reform in new ways in the days and weeks following treatment.
This research assessed the subacute impact of psilocybin on brain function in two clinical trials of depression:
The first trial was an open-label trial of oral psilocybin in patients with treatment-resistant depression.
Patients had baseline clinical assessment and resting-state functional MRI, followed by fixed-order “low” (10 mg) and “high” (25 mg) psilocybin therapy dosing days separated by 1 week. Of the 19 patients recruited, 3 were excluded as a result of excessive fMRI head motion. The team confirmed an antidepressant effect of psilocybin in 16 patients via reduced questionnaire scores from baseline.
Brain network modularity was significantly reduced 1 day after psilocybin therapy in 10 of 16 participants (mean difference, –0.29; t15, 2.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.50; P = .012; d = 0.72). This result implies an increase in functional connectivity between the brain’s main intrinsic networks.
Pre- vs posttreatment change in modularity significantly correlated with change in Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) score at 6 months, relative to baseline (r14 = 0.54, 95% CI, 0.14-0.78, P = .033). Results imply that decreased brain modularity 1 day after psilocybin therapy relates to long-term improvements in symptom severity.
Effective antidepressant alternative?
The second trial was a double-blind, phase 2, randomized, controlled trial comparing psilocybin with escitalopram (Lexapro). Twenty-one patients were included in the escitalopram imaging sample and 22 patients were included in the psilocybin imaging sample.
Patients received either 2 x 25 mg oral psilocybin, 3 weeks apart, plus 6 weeks of daily placebo (psilocybin arm) or 2 x 1 mg oral psilocybin, 3 weeks apart, plus 6 weeks of daily escitalopram (10-20 mg) (escitalopram arm). Functional MRI was recorded at baseline and 3 weeks after the second psilocybin dose.
On average, BDI-measured reductions in depressive symptom severity were significantly greater under psilocybin than escitalopram, indicating superior efficacy of psilocybin therapy versus escitalopram.
Evidence indicated that the reduction in network modularity and its relationship to depression severity was specific to the psilocybin group. In the escitalopram group, network modularity did not change from baseline and there was no significant correlation between changes in modularity and changes in BDI scores.
Post–psilocybin therapy changes in network flexibility were correlated with changes in BDI score. After false discovery rate correction, increased executive network dynamic flexibility strongly correlated with greater symptom improvement at the 6-week primary endpoint for the psilocybin arm (r20, –0.76, 95% CI, −0.90 to –0.50, P = .001).
There were no significant correlations between changes in BDI scores and changes in dynamic flexibility in the escitalopram arm.
“These findings are important because for the first time we find that psilocybin works differently from conventional antidepressants, making the brain more flexible and fluid and less entrenched in the negative thinking patterns associated with depression. This supports our initial predictions and confirms psilocybin could be a real alternative approach to depression treatments,” study investigator David Nutt, DM, head of the Imperial Centre for Psychedelic Research, London, said in a release.
“In previous studies we had seen a similar effect in the brain when people were scanned whilst on a psychedelic, but here we’re seeing it weeks after treatment for depression, which suggests a carryover of the acute drug action,” said Dr. Carhart-Harris.
Durable effect?
“We don’t yet know how long the changes in brain activity seen with psilocybin therapy last, and we need to do more research to understand this,” said Dr. Carhart-Harris, who is a member of the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences. “If the changes don’t last, then is it related to relapse into a depressive episode? We need to do follow-up scans to see where people’s brains are at 3 months or even 6 months after treatment.
“We do know that some people relapse, and it may be that after a while their brains revert to the rigid patterns of activity we see in depression.
“One exciting implication of our findings is that we have discovered a fundamental mechanism via which psychedelic therapy works not just for depression but other mental illnesses, such as anorexia or addiction. We now need to test if this is the case, and if it is, then we have found something important,” added Dr. Carhart-Harris.
Successful phase 3, double-blind randomized, controlled trials will be required to achieve licensing for psilocybin therapy, but pragmatic trials may better address questions regarding treatment practicability, specificity, and optimization. Given the emerging research into psychedelic therapy, it is important for large-scale trials to establish the generalizability, reliability, and specificity of the drug’s antidepressant response.
So how close are we to full federal approval for psilocybin in the treatment of depression? Dr. Carhart-Harris estimated that within 4-5 years is realistic at the federal level. At the state level, in Oregon psilocybin therapy is on track for approval in 2023, including for patients currently undergoing treatment for depressive disorders. In addition, things are opening up in Canada, with some special-access opportunities.
The researchers cautioned that, while these findings are encouraging, trials assessing psilocybin for depression have taken place under controlled, clinical conditions, using a regulated dose formulated in a laboratory, and involved extensive psychological support by a mental health professional – before, during, and after dosing. Taking psychedelics in the absence of these combined safeguards may not have a positive outcome.
The research was supported by funding from the Alex Mosley Charitable Trust and founding donors of the Imperial Centre for Psychedelic Research. One coauthor was supported by the Imperial College London EPSRC Centre London for doctoral training in neurotechnology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
Novel medication tied to better quality of life in major depression
DENVER –
In a phase 3 trial that included more than 500 adult patients with MDD, those who received zuranolone for 14 days showed greater improvement at day 15 across numerous QoL outcomes, compared with their counterparts in the placebo group.
In addition, combined analysis of four zuranolone clinical trials showed “mental well-being and functioning improved to near general population norm levels” for the active-treatment group, reported the researchers, led by Anita H. Clayton, MD, chair and professor of psychiatry, University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“Based on these integrated analyses, the benefit of treatment with zuranolone may extend beyond reduction in depressive symptoms to include potential improvement in quality of life and overall health, as perceived by patients,” they add.
The findings were presented as part of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America Anxiety & Depression conference.
First oral formulation
Zuranolone represents the second entry in the new class of neuroactive steroid drugs, which modulate GABA-A receptor activity – but it would be the first to have an oral formulation. Brexanolone, which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2019 for postpartum depression, is administered through continuous IV infusion over 60 hours.
As previously reported by this news organization, zuranolone improved depressive symptoms as early as day 3, achieving the primary endpoint of significantly greater reduction in scores on the 17-item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression from baseline to day 15 versus placebo (P = .014).
In the new analysis, patient-reported measures of functional health and well-being were assessed in the WATERFALL trial. It included 266 patients with MDD who were treated with zuranolone 50 mg daily for 2 weeks and 268 patients with MDD who were treated with placebo.
The study used the Short Form–36 (SF-36v2), which covers a wide range of patient-reported measures, including physical function, bodily pain, general health, vitality, social function, and “role-emotional” symptoms.
Results showed that although the treatment and placebo groups had similar baseline SF-36v2 scores, those receiving zuranolone reported significantly greater improvements at day 15 in almost all of the assessment’s domains, including physical function (treatment difference, 0.8), general health (1.0), vitality (3.1), social functioning (1.1), and role-emotional symptoms (1.5; for all comparisons, P < .05). The only exceptions were in role-physical symptoms and bodily pain.
In measures that included physical function, bodily pain, and general health, the patients achieved improvements at day 15 that were consistent with normal levels, with the improvement in vitality considered clinically meaningful versus placebo.
Integrated data
In further analysis of integrated data from four zuranolone clinical trials in the NEST and LANDSCAPE programs for patients with MDD and postpartum depression, results showed similar improvements at day 15 for zuranolone in QoL and overall health across all of the SF-36v2 functioning and well-being domains (P <.05), with the exceptions of physical measure and bodily pain.
By day 42, all of the domains showed significantly greater improvement with zuranolone versus placebo (all, P <.05).
Among the strongest score improvements in the integrated trials were measures in social functioning, which improved from baseline scores of 29.66 to 42.82 on day 15 and to 43.59 on day 42.
Emotional domain scores improved from 24.43 at baseline to 39.13 on day 15 and to 39.82 on day 42. For mental health, the integrated scores for the zuranolone group improved from 27.13 at baseline to 42.40 on day 15 and 42.62 on day 42.
Of note, the baseline scores for mental health represented just 54.3% of those in the normal population; with the increase at day 15, the level was 84.8% of the normal population.
“Across four completed placebo-controlled NEST and LANDSCAPE clinical trials, patient reports of functional health and well-being as assessed by the SF-36v2 indicated substantial impairment at baseline compared to the population norm,” the researchers reported.
The improvements are especially important in light of the fact that in some patients with MDD, functional improvement is a top priority.
“Patients have often prioritized returning to their usual level of functioning over reduction in depressive symptoms, and functional recovery has been associated with better prognosis of depression,” the investigators wrote.
Zuranolone trials have shown that treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occur among about 60% of patients, versus about 44% with placebo. The most common AEs are somnolence, dizziness, headache, sedation, and diarrhea, with no increases in suicidal ideation or withdrawal.
The rates of severe AEs are low, and they are observed in about 3% of patients, versus 1.1% with placebo, the researchers noted.
Further, as opposed to serotonergic antidepressants such as SNRIs and SSRIs, zuranolone does not appear to have the undesirable side effects of decreased libido and sexual dysfunction, they added.
Clinically meaningful?
Andrew J. Cutler, MD, clinical associate professor of psychiatry at State University of New York, Syracuse, said the data are “very significant” for a number of reasons.
“We need more options to treat depression, especially ones with novel mechanisms of action and faster onset of efficacy, such as zuranolone,” said Dr. Cutler, who was not involved in the current study. He has coauthored other studies on zuranolone.
Regarding the study’s QoL outcomes, “while improvement in depressive symptoms is very important, what really matters to patients is improvement in function and quality of life,” Dr. Cutler noted.
Also commenting on the study, Jonathan E. Alpert, MD, PhD, chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and professor of psychiatry, neuroscience, and pediatrics at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said the investigational drug could represent an important addition to the armamentarium for treating depression.
“Zuranolone has good oral bioavailability and would represent the first neuroactive steroid antidepressant available in oral form and, indeed, the first non–monoamine-based antidepressant available in oral form,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Alpert was not involved in the research and has no relationship with the drug’s development.
He noted that although there are modest differences between the patients who received zuranolone and those who received placebo in the trials, “this may have been related to high placebo response rates, which often complicate antidepressant trials.
“Further research is needed to determine whether differences between zuranolone and placebo are clinically meaningful, though the separation between drug and placebo on the primary endpoint, as well as some other measures, such as quality of life measures, is promising,” Dr. Alpert said.
However, he added that comparisons with other active antidepressants in terms of efficacy and tolerability remain to be seen.
“Given the large number of individuals with major depressive disorder who have incomplete response to or do not tolerate monoaminergic antidepressants, the development of agents that leverage novel nonmonoaminergic mechanisms is important,” Dr. Alpert concluded.
The study was funded by Sage Therapeutics and Biogen. Dr. Cutler has been involved in research of zuranolone for Sage Therapeutics. Dr. Alpert has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DENVER –
In a phase 3 trial that included more than 500 adult patients with MDD, those who received zuranolone for 14 days showed greater improvement at day 15 across numerous QoL outcomes, compared with their counterparts in the placebo group.
In addition, combined analysis of four zuranolone clinical trials showed “mental well-being and functioning improved to near general population norm levels” for the active-treatment group, reported the researchers, led by Anita H. Clayton, MD, chair and professor of psychiatry, University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“Based on these integrated analyses, the benefit of treatment with zuranolone may extend beyond reduction in depressive symptoms to include potential improvement in quality of life and overall health, as perceived by patients,” they add.
The findings were presented as part of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America Anxiety & Depression conference.
First oral formulation
Zuranolone represents the second entry in the new class of neuroactive steroid drugs, which modulate GABA-A receptor activity – but it would be the first to have an oral formulation. Brexanolone, which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2019 for postpartum depression, is administered through continuous IV infusion over 60 hours.
As previously reported by this news organization, zuranolone improved depressive symptoms as early as day 3, achieving the primary endpoint of significantly greater reduction in scores on the 17-item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression from baseline to day 15 versus placebo (P = .014).
In the new analysis, patient-reported measures of functional health and well-being were assessed in the WATERFALL trial. It included 266 patients with MDD who were treated with zuranolone 50 mg daily for 2 weeks and 268 patients with MDD who were treated with placebo.
The study used the Short Form–36 (SF-36v2), which covers a wide range of patient-reported measures, including physical function, bodily pain, general health, vitality, social function, and “role-emotional” symptoms.
Results showed that although the treatment and placebo groups had similar baseline SF-36v2 scores, those receiving zuranolone reported significantly greater improvements at day 15 in almost all of the assessment’s domains, including physical function (treatment difference, 0.8), general health (1.0), vitality (3.1), social functioning (1.1), and role-emotional symptoms (1.5; for all comparisons, P < .05). The only exceptions were in role-physical symptoms and bodily pain.
In measures that included physical function, bodily pain, and general health, the patients achieved improvements at day 15 that were consistent with normal levels, with the improvement in vitality considered clinically meaningful versus placebo.
Integrated data
In further analysis of integrated data from four zuranolone clinical trials in the NEST and LANDSCAPE programs for patients with MDD and postpartum depression, results showed similar improvements at day 15 for zuranolone in QoL and overall health across all of the SF-36v2 functioning and well-being domains (P <.05), with the exceptions of physical measure and bodily pain.
By day 42, all of the domains showed significantly greater improvement with zuranolone versus placebo (all, P <.05).
Among the strongest score improvements in the integrated trials were measures in social functioning, which improved from baseline scores of 29.66 to 42.82 on day 15 and to 43.59 on day 42.
Emotional domain scores improved from 24.43 at baseline to 39.13 on day 15 and to 39.82 on day 42. For mental health, the integrated scores for the zuranolone group improved from 27.13 at baseline to 42.40 on day 15 and 42.62 on day 42.
Of note, the baseline scores for mental health represented just 54.3% of those in the normal population; with the increase at day 15, the level was 84.8% of the normal population.
“Across four completed placebo-controlled NEST and LANDSCAPE clinical trials, patient reports of functional health and well-being as assessed by the SF-36v2 indicated substantial impairment at baseline compared to the population norm,” the researchers reported.
The improvements are especially important in light of the fact that in some patients with MDD, functional improvement is a top priority.
“Patients have often prioritized returning to their usual level of functioning over reduction in depressive symptoms, and functional recovery has been associated with better prognosis of depression,” the investigators wrote.
Zuranolone trials have shown that treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occur among about 60% of patients, versus about 44% with placebo. The most common AEs are somnolence, dizziness, headache, sedation, and diarrhea, with no increases in suicidal ideation or withdrawal.
The rates of severe AEs are low, and they are observed in about 3% of patients, versus 1.1% with placebo, the researchers noted.
Further, as opposed to serotonergic antidepressants such as SNRIs and SSRIs, zuranolone does not appear to have the undesirable side effects of decreased libido and sexual dysfunction, they added.
Clinically meaningful?
Andrew J. Cutler, MD, clinical associate professor of psychiatry at State University of New York, Syracuse, said the data are “very significant” for a number of reasons.
“We need more options to treat depression, especially ones with novel mechanisms of action and faster onset of efficacy, such as zuranolone,” said Dr. Cutler, who was not involved in the current study. He has coauthored other studies on zuranolone.
Regarding the study’s QoL outcomes, “while improvement in depressive symptoms is very important, what really matters to patients is improvement in function and quality of life,” Dr. Cutler noted.
Also commenting on the study, Jonathan E. Alpert, MD, PhD, chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and professor of psychiatry, neuroscience, and pediatrics at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said the investigational drug could represent an important addition to the armamentarium for treating depression.
“Zuranolone has good oral bioavailability and would represent the first neuroactive steroid antidepressant available in oral form and, indeed, the first non–monoamine-based antidepressant available in oral form,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Alpert was not involved in the research and has no relationship with the drug’s development.
He noted that although there are modest differences between the patients who received zuranolone and those who received placebo in the trials, “this may have been related to high placebo response rates, which often complicate antidepressant trials.
“Further research is needed to determine whether differences between zuranolone and placebo are clinically meaningful, though the separation between drug and placebo on the primary endpoint, as well as some other measures, such as quality of life measures, is promising,” Dr. Alpert said.
However, he added that comparisons with other active antidepressants in terms of efficacy and tolerability remain to be seen.
“Given the large number of individuals with major depressive disorder who have incomplete response to or do not tolerate monoaminergic antidepressants, the development of agents that leverage novel nonmonoaminergic mechanisms is important,” Dr. Alpert concluded.
The study was funded by Sage Therapeutics and Biogen. Dr. Cutler has been involved in research of zuranolone for Sage Therapeutics. Dr. Alpert has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DENVER –
In a phase 3 trial that included more than 500 adult patients with MDD, those who received zuranolone for 14 days showed greater improvement at day 15 across numerous QoL outcomes, compared with their counterparts in the placebo group.
In addition, combined analysis of four zuranolone clinical trials showed “mental well-being and functioning improved to near general population norm levels” for the active-treatment group, reported the researchers, led by Anita H. Clayton, MD, chair and professor of psychiatry, University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“Based on these integrated analyses, the benefit of treatment with zuranolone may extend beyond reduction in depressive symptoms to include potential improvement in quality of life and overall health, as perceived by patients,” they add.
The findings were presented as part of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America Anxiety & Depression conference.
First oral formulation
Zuranolone represents the second entry in the new class of neuroactive steroid drugs, which modulate GABA-A receptor activity – but it would be the first to have an oral formulation. Brexanolone, which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2019 for postpartum depression, is administered through continuous IV infusion over 60 hours.
As previously reported by this news organization, zuranolone improved depressive symptoms as early as day 3, achieving the primary endpoint of significantly greater reduction in scores on the 17-item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression from baseline to day 15 versus placebo (P = .014).
In the new analysis, patient-reported measures of functional health and well-being were assessed in the WATERFALL trial. It included 266 patients with MDD who were treated with zuranolone 50 mg daily for 2 weeks and 268 patients with MDD who were treated with placebo.
The study used the Short Form–36 (SF-36v2), which covers a wide range of patient-reported measures, including physical function, bodily pain, general health, vitality, social function, and “role-emotional” symptoms.
Results showed that although the treatment and placebo groups had similar baseline SF-36v2 scores, those receiving zuranolone reported significantly greater improvements at day 15 in almost all of the assessment’s domains, including physical function (treatment difference, 0.8), general health (1.0), vitality (3.1), social functioning (1.1), and role-emotional symptoms (1.5; for all comparisons, P < .05). The only exceptions were in role-physical symptoms and bodily pain.
In measures that included physical function, bodily pain, and general health, the patients achieved improvements at day 15 that were consistent with normal levels, with the improvement in vitality considered clinically meaningful versus placebo.
Integrated data
In further analysis of integrated data from four zuranolone clinical trials in the NEST and LANDSCAPE programs for patients with MDD and postpartum depression, results showed similar improvements at day 15 for zuranolone in QoL and overall health across all of the SF-36v2 functioning and well-being domains (P <.05), with the exceptions of physical measure and bodily pain.
By day 42, all of the domains showed significantly greater improvement with zuranolone versus placebo (all, P <.05).
Among the strongest score improvements in the integrated trials were measures in social functioning, which improved from baseline scores of 29.66 to 42.82 on day 15 and to 43.59 on day 42.
Emotional domain scores improved from 24.43 at baseline to 39.13 on day 15 and to 39.82 on day 42. For mental health, the integrated scores for the zuranolone group improved from 27.13 at baseline to 42.40 on day 15 and 42.62 on day 42.
Of note, the baseline scores for mental health represented just 54.3% of those in the normal population; with the increase at day 15, the level was 84.8% of the normal population.
“Across four completed placebo-controlled NEST and LANDSCAPE clinical trials, patient reports of functional health and well-being as assessed by the SF-36v2 indicated substantial impairment at baseline compared to the population norm,” the researchers reported.
The improvements are especially important in light of the fact that in some patients with MDD, functional improvement is a top priority.
“Patients have often prioritized returning to their usual level of functioning over reduction in depressive symptoms, and functional recovery has been associated with better prognosis of depression,” the investigators wrote.
Zuranolone trials have shown that treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occur among about 60% of patients, versus about 44% with placebo. The most common AEs are somnolence, dizziness, headache, sedation, and diarrhea, with no increases in suicidal ideation or withdrawal.
The rates of severe AEs are low, and they are observed in about 3% of patients, versus 1.1% with placebo, the researchers noted.
Further, as opposed to serotonergic antidepressants such as SNRIs and SSRIs, zuranolone does not appear to have the undesirable side effects of decreased libido and sexual dysfunction, they added.
Clinically meaningful?
Andrew J. Cutler, MD, clinical associate professor of psychiatry at State University of New York, Syracuse, said the data are “very significant” for a number of reasons.
“We need more options to treat depression, especially ones with novel mechanisms of action and faster onset of efficacy, such as zuranolone,” said Dr. Cutler, who was not involved in the current study. He has coauthored other studies on zuranolone.
Regarding the study’s QoL outcomes, “while improvement in depressive symptoms is very important, what really matters to patients is improvement in function and quality of life,” Dr. Cutler noted.
Also commenting on the study, Jonathan E. Alpert, MD, PhD, chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and professor of psychiatry, neuroscience, and pediatrics at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said the investigational drug could represent an important addition to the armamentarium for treating depression.
“Zuranolone has good oral bioavailability and would represent the first neuroactive steroid antidepressant available in oral form and, indeed, the first non–monoamine-based antidepressant available in oral form,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Alpert was not involved in the research and has no relationship with the drug’s development.
He noted that although there are modest differences between the patients who received zuranolone and those who received placebo in the trials, “this may have been related to high placebo response rates, which often complicate antidepressant trials.
“Further research is needed to determine whether differences between zuranolone and placebo are clinically meaningful, though the separation between drug and placebo on the primary endpoint, as well as some other measures, such as quality of life measures, is promising,” Dr. Alpert said.
However, he added that comparisons with other active antidepressants in terms of efficacy and tolerability remain to be seen.
“Given the large number of individuals with major depressive disorder who have incomplete response to or do not tolerate monoaminergic antidepressants, the development of agents that leverage novel nonmonoaminergic mechanisms is important,” Dr. Alpert concluded.
The study was funded by Sage Therapeutics and Biogen. Dr. Cutler has been involved in research of zuranolone for Sage Therapeutics. Dr. Alpert has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ADAA 2022
The importance of treating insomnia in psychiatric illness
Data suggests this symptom, defined as chronic sleep onset and/or sleep continuity problems associated with impaired daytime functioning, is common in psychiatric illnesses, and can worsen their course.2
The incidence of psychiatric illness in patients with insomnia is estimated at near 50%, with the highest rates found in mood disorders such as depression and bipolar disorder, as well as anxiety disorders.3 In patients with diagnosed major depressive disorder, insomnia rates can approach 90%.4-6
Insomnia has been identified as a risk factor for development of mental illness, including doubling the risk of major depressive disorder and tripling the risk of any depressive or anxiety disorder.7,8 It can also significantly increase the risk of alcohol abuse and psychosis.8
Sleep disturbances can worsen symptoms of diagnosed mental illness, including substance abuse, mood and psychotic disorders.9-10 In one study, nearly 75% of patients with a diagnosis of schizophrenia or bipolar spectrum disorder had at least one type of sleep disturbance (insomnia, hypersomnia, or delayed sleep phase).10 This was almost twice the rate in healthy controls. Importantly, compared with well-rested subjects with mental illness in this study, sleep-disordered participants had higher rates of negative and depressive symptoms on the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale, as well as significantly lower function via the global assessment of functioning.11,12
Additional data suggests simply being awake during the night (00:00-05:59) elevates risk of suicide. The mean incident rate of completed suicide in one study was a striking four times the rate noted during daytime hours (06:00-23:59 ) (P < .001).13
Although insomnia symptoms can resolve after relief from a particular life stressor, as many as half of patients with more severe symptoms develop a chronic course.14 This then leads to an extended use of many types of sedative-hypnotics designed and studied primarily for short-term use.15 In a survey reviewing national use of prescription drugs for insomnia, as many as 20% of individuals use a medication to target insomnia in a given month.16
Fortunately, despite the many challenges posed by COVID-19, particularly for those with psychiatric illness and limited access to care, telehealth has become more readily available. Additionally, digital versions of evidence-based treatments specifically for sleep problems, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), are regularly being developed.
The benefits of CBT-I have been demonstrated repeatedly and it is recommended as the first line treatment for insomnia by the Clinical Guidelines of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the National Institutes of Health.17-21 Studies suggest benefits persist long-term, even after completing the therapy sessions, which differ in durability from medication choices.18
One group that may be particularly suited for treatment with CBT-I is women with insomnia during pregnancy or the postpartum period. In these women, options for treatment may be limited by risk of medication during breastfeeding, as well as difficulty traveling to a physician’s or therapist’s office to receive psychotherapy. However, two recent studies evaluated the use of digital CBT-I to treat insomnia during pregnancy and in the postpartum period, respectively.22-23
In both studies,the same group of women with insomnia diagnosed during pregnancy were given six weekly 20-minute sessions of digital CBT-I or standard treatment for insomnia, including medication and psychotherapy per their usual provider.
By study end, the pregnant women receiving the CBT-I intervention not only had significantly improved severity of insomnia, they also experienced improved depression and anxiety symptoms, and a decrease in the use of prescription or over-the-counter sleep aides, compared with the standard treatment group, lowering the fetal exposure to medication during pregnancy.22
In the more recent study, the same group was followed for 6 months post partum.23 Results were again notable, with the women who received CBT-I reporting significantly less insomnia, as well as significantly lower rates of probable major depression at 3 and 6 months (18% vs. 4%, 10% vs. 0%, respectively.) They also exhibited lower rates of moderate to severe anxiety (17% vs. 4%) at 3 months, compared with those receiving standard care. With as many as one in seven women suffering from postpartum depression, these findings represent a substantial public health benefit.
In summary, insomnia is a critical area of focus for any provider diagnosing and treating psychiatric illness. Attempts to optimize sleep, whether through CBT-I or other psychotherapy approaches, or evidence-based medications dosed for appropriate lengths and at safe doses, should be a part of most, if not all, clinical encounters.
Dr. Reid is a board-certified psychiatrist and award-winning medical educator with a private practice in Philadelphia, as well as a clinical faculty role at the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia. She attended medical school at Columbia University, New York, and completed her psychiatry residency at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Reid is a regular contributor to Psychology Today with her blog, “Think Like a Shrink,” and writes and podcasts as The Reflective Doc.
References
1. Voitsidis P et al. Psychiatry Res. 2020 Jul;289:113076. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113076.
2. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Arlington, Va.: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013.
3. Ford DE and Kamerow DB. JAMA. 1989;262(11):1479-84. doi: 10.1001/jama.1989.03430110069030.
4. Ohayon MM and Roth T. J Psychiatr Res. Jan-Feb 2003;37(1):9-15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3956(02)00052-3.
5. Seow LSE et al. J Ment Health. 2016 Dec;25(6):492-9. doi: 10.3109/09638237.2015.1124390.
6. Thase ME. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999;60 Suppl 17:28-31; discussion 46-8.
7. Baglioni C et al. J Affect Disord. 2011 Dec;135(1-3):10-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.01.011.
8. Hertenstein E et al. Sleep Med Rev. 2019 Feb;43:96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2018.10.006.
9. Brower KJ et al. Medical Hypotheses. 2010;74(5):928-33. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2009.10.020.
10. Laskemoen JF et al. Compr Psychiatry. 2019 May;91:6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2019.02.006.
11. Kay SR et al. Schizophr Bull. 1987;13(2):261-76. doi: 10.1093/schbul/13.2.261.
12. Hall R. Psychosomatics. May-Jun 1995;36(3):267-75. doi: 10.1016/S0033-3182(95)71666-8.
13. Perlis ML et al. J Clin Psychiatry. 2016 Jun;77(6):e726-33. doi: 10.4088/JCP.15m10131.
14. Morin CM et al. Arch Intern Med. 2009 Mar 9. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2008.610.
15. Cheung J et al. Sleep Med Clin. 2019 Jun;14(2):253-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jsmc.2019.01.006.
16. Bertisch SM et al. Sleep. 2014 Feb 1. doi: 10.5665/sleep.3410.
17. Okajima I et al. Sleep Biol Rhythms. 2010 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-8425.2010.00481.x.
18. Trauer JM et al. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Aug 4. doi: 10.7326/M14-2841.
19. Edinger J et al. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021 Feb 1. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.8986.
20. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/sleep/for-clinicians.html.
21. National Institutes of Health. Sleep Health. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/education-and-awareness/sleep-health.
22. Felder JN et al. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77(5):484-92. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.4491.
23. Felder JN et al. Sleep. 2022 Feb 14. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab280.
Data suggests this symptom, defined as chronic sleep onset and/or sleep continuity problems associated with impaired daytime functioning, is common in psychiatric illnesses, and can worsen their course.2
The incidence of psychiatric illness in patients with insomnia is estimated at near 50%, with the highest rates found in mood disorders such as depression and bipolar disorder, as well as anxiety disorders.3 In patients with diagnosed major depressive disorder, insomnia rates can approach 90%.4-6
Insomnia has been identified as a risk factor for development of mental illness, including doubling the risk of major depressive disorder and tripling the risk of any depressive or anxiety disorder.7,8 It can also significantly increase the risk of alcohol abuse and psychosis.8
Sleep disturbances can worsen symptoms of diagnosed mental illness, including substance abuse, mood and psychotic disorders.9-10 In one study, nearly 75% of patients with a diagnosis of schizophrenia or bipolar spectrum disorder had at least one type of sleep disturbance (insomnia, hypersomnia, or delayed sleep phase).10 This was almost twice the rate in healthy controls. Importantly, compared with well-rested subjects with mental illness in this study, sleep-disordered participants had higher rates of negative and depressive symptoms on the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale, as well as significantly lower function via the global assessment of functioning.11,12
Additional data suggests simply being awake during the night (00:00-05:59) elevates risk of suicide. The mean incident rate of completed suicide in one study was a striking four times the rate noted during daytime hours (06:00-23:59 ) (P < .001).13
Although insomnia symptoms can resolve after relief from a particular life stressor, as many as half of patients with more severe symptoms develop a chronic course.14 This then leads to an extended use of many types of sedative-hypnotics designed and studied primarily for short-term use.15 In a survey reviewing national use of prescription drugs for insomnia, as many as 20% of individuals use a medication to target insomnia in a given month.16
Fortunately, despite the many challenges posed by COVID-19, particularly for those with psychiatric illness and limited access to care, telehealth has become more readily available. Additionally, digital versions of evidence-based treatments specifically for sleep problems, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), are regularly being developed.
The benefits of CBT-I have been demonstrated repeatedly and it is recommended as the first line treatment for insomnia by the Clinical Guidelines of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the National Institutes of Health.17-21 Studies suggest benefits persist long-term, even after completing the therapy sessions, which differ in durability from medication choices.18
One group that may be particularly suited for treatment with CBT-I is women with insomnia during pregnancy or the postpartum period. In these women, options for treatment may be limited by risk of medication during breastfeeding, as well as difficulty traveling to a physician’s or therapist’s office to receive psychotherapy. However, two recent studies evaluated the use of digital CBT-I to treat insomnia during pregnancy and in the postpartum period, respectively.22-23
In both studies,the same group of women with insomnia diagnosed during pregnancy were given six weekly 20-minute sessions of digital CBT-I or standard treatment for insomnia, including medication and psychotherapy per their usual provider.
By study end, the pregnant women receiving the CBT-I intervention not only had significantly improved severity of insomnia, they also experienced improved depression and anxiety symptoms, and a decrease in the use of prescription or over-the-counter sleep aides, compared with the standard treatment group, lowering the fetal exposure to medication during pregnancy.22
In the more recent study, the same group was followed for 6 months post partum.23 Results were again notable, with the women who received CBT-I reporting significantly less insomnia, as well as significantly lower rates of probable major depression at 3 and 6 months (18% vs. 4%, 10% vs. 0%, respectively.) They also exhibited lower rates of moderate to severe anxiety (17% vs. 4%) at 3 months, compared with those receiving standard care. With as many as one in seven women suffering from postpartum depression, these findings represent a substantial public health benefit.
In summary, insomnia is a critical area of focus for any provider diagnosing and treating psychiatric illness. Attempts to optimize sleep, whether through CBT-I or other psychotherapy approaches, or evidence-based medications dosed for appropriate lengths and at safe doses, should be a part of most, if not all, clinical encounters.
Dr. Reid is a board-certified psychiatrist and award-winning medical educator with a private practice in Philadelphia, as well as a clinical faculty role at the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia. She attended medical school at Columbia University, New York, and completed her psychiatry residency at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Reid is a regular contributor to Psychology Today with her blog, “Think Like a Shrink,” and writes and podcasts as The Reflective Doc.
References
1. Voitsidis P et al. Psychiatry Res. 2020 Jul;289:113076. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113076.
2. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Arlington, Va.: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013.
3. Ford DE and Kamerow DB. JAMA. 1989;262(11):1479-84. doi: 10.1001/jama.1989.03430110069030.
4. Ohayon MM and Roth T. J Psychiatr Res. Jan-Feb 2003;37(1):9-15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3956(02)00052-3.
5. Seow LSE et al. J Ment Health. 2016 Dec;25(6):492-9. doi: 10.3109/09638237.2015.1124390.
6. Thase ME. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999;60 Suppl 17:28-31; discussion 46-8.
7. Baglioni C et al. J Affect Disord. 2011 Dec;135(1-3):10-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.01.011.
8. Hertenstein E et al. Sleep Med Rev. 2019 Feb;43:96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2018.10.006.
9. Brower KJ et al. Medical Hypotheses. 2010;74(5):928-33. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2009.10.020.
10. Laskemoen JF et al. Compr Psychiatry. 2019 May;91:6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2019.02.006.
11. Kay SR et al. Schizophr Bull. 1987;13(2):261-76. doi: 10.1093/schbul/13.2.261.
12. Hall R. Psychosomatics. May-Jun 1995;36(3):267-75. doi: 10.1016/S0033-3182(95)71666-8.
13. Perlis ML et al. J Clin Psychiatry. 2016 Jun;77(6):e726-33. doi: 10.4088/JCP.15m10131.
14. Morin CM et al. Arch Intern Med. 2009 Mar 9. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2008.610.
15. Cheung J et al. Sleep Med Clin. 2019 Jun;14(2):253-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jsmc.2019.01.006.
16. Bertisch SM et al. Sleep. 2014 Feb 1. doi: 10.5665/sleep.3410.
17. Okajima I et al. Sleep Biol Rhythms. 2010 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-8425.2010.00481.x.
18. Trauer JM et al. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Aug 4. doi: 10.7326/M14-2841.
19. Edinger J et al. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021 Feb 1. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.8986.
20. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/sleep/for-clinicians.html.
21. National Institutes of Health. Sleep Health. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/education-and-awareness/sleep-health.
22. Felder JN et al. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77(5):484-92. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.4491.
23. Felder JN et al. Sleep. 2022 Feb 14. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab280.
Data suggests this symptom, defined as chronic sleep onset and/or sleep continuity problems associated with impaired daytime functioning, is common in psychiatric illnesses, and can worsen their course.2
The incidence of psychiatric illness in patients with insomnia is estimated at near 50%, with the highest rates found in mood disorders such as depression and bipolar disorder, as well as anxiety disorders.3 In patients with diagnosed major depressive disorder, insomnia rates can approach 90%.4-6
Insomnia has been identified as a risk factor for development of mental illness, including doubling the risk of major depressive disorder and tripling the risk of any depressive or anxiety disorder.7,8 It can also significantly increase the risk of alcohol abuse and psychosis.8
Sleep disturbances can worsen symptoms of diagnosed mental illness, including substance abuse, mood and psychotic disorders.9-10 In one study, nearly 75% of patients with a diagnosis of schizophrenia or bipolar spectrum disorder had at least one type of sleep disturbance (insomnia, hypersomnia, or delayed sleep phase).10 This was almost twice the rate in healthy controls. Importantly, compared with well-rested subjects with mental illness in this study, sleep-disordered participants had higher rates of negative and depressive symptoms on the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale, as well as significantly lower function via the global assessment of functioning.11,12
Additional data suggests simply being awake during the night (00:00-05:59) elevates risk of suicide. The mean incident rate of completed suicide in one study was a striking four times the rate noted during daytime hours (06:00-23:59 ) (P < .001).13
Although insomnia symptoms can resolve after relief from a particular life stressor, as many as half of patients with more severe symptoms develop a chronic course.14 This then leads to an extended use of many types of sedative-hypnotics designed and studied primarily for short-term use.15 In a survey reviewing national use of prescription drugs for insomnia, as many as 20% of individuals use a medication to target insomnia in a given month.16
Fortunately, despite the many challenges posed by COVID-19, particularly for those with psychiatric illness and limited access to care, telehealth has become more readily available. Additionally, digital versions of evidence-based treatments specifically for sleep problems, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), are regularly being developed.
The benefits of CBT-I have been demonstrated repeatedly and it is recommended as the first line treatment for insomnia by the Clinical Guidelines of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the National Institutes of Health.17-21 Studies suggest benefits persist long-term, even after completing the therapy sessions, which differ in durability from medication choices.18
One group that may be particularly suited for treatment with CBT-I is women with insomnia during pregnancy or the postpartum period. In these women, options for treatment may be limited by risk of medication during breastfeeding, as well as difficulty traveling to a physician’s or therapist’s office to receive psychotherapy. However, two recent studies evaluated the use of digital CBT-I to treat insomnia during pregnancy and in the postpartum period, respectively.22-23
In both studies,the same group of women with insomnia diagnosed during pregnancy were given six weekly 20-minute sessions of digital CBT-I or standard treatment for insomnia, including medication and psychotherapy per their usual provider.
By study end, the pregnant women receiving the CBT-I intervention not only had significantly improved severity of insomnia, they also experienced improved depression and anxiety symptoms, and a decrease in the use of prescription or over-the-counter sleep aides, compared with the standard treatment group, lowering the fetal exposure to medication during pregnancy.22
In the more recent study, the same group was followed for 6 months post partum.23 Results were again notable, with the women who received CBT-I reporting significantly less insomnia, as well as significantly lower rates of probable major depression at 3 and 6 months (18% vs. 4%, 10% vs. 0%, respectively.) They also exhibited lower rates of moderate to severe anxiety (17% vs. 4%) at 3 months, compared with those receiving standard care. With as many as one in seven women suffering from postpartum depression, these findings represent a substantial public health benefit.
In summary, insomnia is a critical area of focus for any provider diagnosing and treating psychiatric illness. Attempts to optimize sleep, whether through CBT-I or other psychotherapy approaches, or evidence-based medications dosed for appropriate lengths and at safe doses, should be a part of most, if not all, clinical encounters.
Dr. Reid is a board-certified psychiatrist and award-winning medical educator with a private practice in Philadelphia, as well as a clinical faculty role at the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia. She attended medical school at Columbia University, New York, and completed her psychiatry residency at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Reid is a regular contributor to Psychology Today with her blog, “Think Like a Shrink,” and writes and podcasts as The Reflective Doc.
References
1. Voitsidis P et al. Psychiatry Res. 2020 Jul;289:113076. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113076.
2. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Arlington, Va.: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013.
3. Ford DE and Kamerow DB. JAMA. 1989;262(11):1479-84. doi: 10.1001/jama.1989.03430110069030.
4. Ohayon MM and Roth T. J Psychiatr Res. Jan-Feb 2003;37(1):9-15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3956(02)00052-3.
5. Seow LSE et al. J Ment Health. 2016 Dec;25(6):492-9. doi: 10.3109/09638237.2015.1124390.
6. Thase ME. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999;60 Suppl 17:28-31; discussion 46-8.
7. Baglioni C et al. J Affect Disord. 2011 Dec;135(1-3):10-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.01.011.
8. Hertenstein E et al. Sleep Med Rev. 2019 Feb;43:96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2018.10.006.
9. Brower KJ et al. Medical Hypotheses. 2010;74(5):928-33. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2009.10.020.
10. Laskemoen JF et al. Compr Psychiatry. 2019 May;91:6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2019.02.006.
11. Kay SR et al. Schizophr Bull. 1987;13(2):261-76. doi: 10.1093/schbul/13.2.261.
12. Hall R. Psychosomatics. May-Jun 1995;36(3):267-75. doi: 10.1016/S0033-3182(95)71666-8.
13. Perlis ML et al. J Clin Psychiatry. 2016 Jun;77(6):e726-33. doi: 10.4088/JCP.15m10131.
14. Morin CM et al. Arch Intern Med. 2009 Mar 9. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2008.610.
15. Cheung J et al. Sleep Med Clin. 2019 Jun;14(2):253-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jsmc.2019.01.006.
16. Bertisch SM et al. Sleep. 2014 Feb 1. doi: 10.5665/sleep.3410.
17. Okajima I et al. Sleep Biol Rhythms. 2010 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-8425.2010.00481.x.
18. Trauer JM et al. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Aug 4. doi: 10.7326/M14-2841.
19. Edinger J et al. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021 Feb 1. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.8986.
20. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/sleep/for-clinicians.html.
21. National Institutes of Health. Sleep Health. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/education-and-awareness/sleep-health.
22. Felder JN et al. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77(5):484-92. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.4491.
23. Felder JN et al. Sleep. 2022 Feb 14. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab280.
Microdosing psychedelics: Untapped potential in psychiatry?
In her month-long memoir, A Really Good Day: How Microdosing Made a Mega Difference in My Mood, My Marriage, and My Life (Knopf, 2017), author Ayelet Waldman turns herself into a one-woman experiment.
Over a single month she takes one-tenth of a recreational dose of LSD every third day. She plots her emotions, her productivity, and her pain along the way. Ms. Waldman obtains the LSD in a single vial, enough for 10 doses, from a researcher, who is retiring. What she’s looking for, she tells the reader, is a really good day – something that has been elusive in her turbulent life.
Although psychedelics remain illegal for both recreational and therapeutic use, they are increasingly being studied at academic centers, and there is hope that they will offer something that our traditional medications might not. However, these are not “micro” doses, but full doses of psychedelic agents that induce clinically-monitored “trips” in order to treat conditions such as depression, anorexia nervosa, or for smoking cessation, to name just a few.
Yet
Because these drugs are illegal under most circumstances, many of the studies involve surveys of users in their natural environments who are already microdosing in an uncontrolled manner. In a 2019 study published in PLOS One, Vince Polito and Richard Stevenson, from Macquarie University, Sydney, gave daily surveys of psychological functioning to 98 microdosers over 6 weeks. Several participants were excluded for using doses that were too high or for concurrent use of other illicit substances.
Whereas the authors found that many people claimed to have positive experiences, there was an increase in neuroticism in some of the subjects. There was no control group and no uniformity to what the subject claimed to be ingesting with regard to dose, frequency, substance, or verification of the chemical content.
University of Chicago neuroscientist Harriet De Wit, PhD, leads one of the few laboratories that conducts controlled, double-blind studies looking at microdosing LSD.
“With microdosing there are expectations, and we don’t know if it’s the expectation or the agent that is making a difference,” she explained. And when asked who in her experience is experimenting with microdosing psychedelics, she expounded “Everybody under the sun!”
Dr. De Wit notes that people microdose to increase their creativity, productivity, focus, and energy, to heighten their spiritual awareness, improve empathy and social relational skills, and to improve their mood – all purported benefits of low-dose psychedelics.
Her group published a study in Addiction Biology, in which 39 subjects were administered low doses of LSD four times over 2 weeks. To address the issues of expectation, the subjects were not told they were participating in a study of hallucinogens specifically but were instead given a list of pharmaceuticals in different classes that they might be given. Microdoses of LSD did not improve either mood or performance, but they did appear to be safe, and they produced no adverse effects.
To date, studies on microdosing have looked at their effects on healthy populations, and the practice has been associated with “Silicon Valley techies” looking for performance enhancement. Ms. Waldman, however, is different.
She is open about her diagnosis of bipolar disorder, and her long history with therapy and medications. As she describes herself in the beginning of her book, she is emotionally uncomfortable, and both irritable and reactive to the point that her life is propelled by interpersonal chaos. In her uncontrolled ‘study,’ she is an N of 1, and she is pleased with the results. Microdosing, she believes, helped her become less irritable, more resilient, and in fact, have some very good days.
By the end of her memoir, she was looking for a way to continue microdosing but was unsure how to safely obtain more LSD and be certain of its purity. Her experience does raise the possibility that microdoses may have therapeutic benefits in people with certain psychiatric conditions, but this has yet to be studied.
J. Raymond DePaulo Jr., MD, is the chair of the National Network of Depression Centers and a distinguished service professor at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore. “Microdosing of psychedelics is very problematic for two equally serious reasons,” he cautioned. “There is no control over what it is that people are actually taking, it is completely unstudied scientifically, and there is no agreement on what a ‘micro’ dose is.”
He noted that one of his patients thought he was taking psilocybin. A chemical analysis was done that revealed the agent to contain a combination of THC, a stimulant, morphine, and fluoxetine. There wasn’t a trace of psilocybin. “Mislabeling is the rule, not the exception,” Dr. DePaulo has concluded.
He also believes the placebo effect has a powerful role with microdosing. “It’s not working because of what is in the pill, more likely it is working because of what is advertised to be in it.”
Ms. De Wit noted that when she started her study, she tried to find people who were elevated on measures of depression or anxiety, but she was not looking for a specific clinical population of patients with these clinical diagnoses. “We found a handful of people, and they improved, but so did those in the placebo group; they all got better.”
Psychedelic agents interact with antidepressants, so subjects in controlled studies need to go off their medications before enrolling – this is a limiting factor in studies of both macro- and microdosing. Ms. De Wit also notes that there are logistical and practical obstacles – it is difficult to get approval to use these agents, and the patients have to remain in the lab and be observed for several hours after they are administered, just as with standard doses.
As might be expected, data collection and anecdotal microdosing experiences are rampant on the internet. The social media forum Reddit alone boasts 192,000 members in its microdosing group, while Imperial College London invites microdosers to take part in surveys intended to add to the body of knowledge. But despite its popularity, there is little in the way of prospective, agent-verified, placebo-controlled research exploring whether or not microdosing is truly beneficial beyond just anecdotal evidence.
Perhaps microdosing is a fad, or perhaps it offers some benefits to some people. Given the current interest in the therapeutic uses of psychedelics, it would be useful to have controlled studies of lower doses that don’t carry the risk of “bad trips.”
Certainly, psychiatry could use more agents to address mental health issues, and society might benefit from the use of agents that are proven to be evidence-based options for improving creativity and productivity. Anything that has potential to reduce psychiatric suffering seems worthy of further study to delineate which populations could be helped or harmed.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In her month-long memoir, A Really Good Day: How Microdosing Made a Mega Difference in My Mood, My Marriage, and My Life (Knopf, 2017), author Ayelet Waldman turns herself into a one-woman experiment.
Over a single month she takes one-tenth of a recreational dose of LSD every third day. She plots her emotions, her productivity, and her pain along the way. Ms. Waldman obtains the LSD in a single vial, enough for 10 doses, from a researcher, who is retiring. What she’s looking for, she tells the reader, is a really good day – something that has been elusive in her turbulent life.
Although psychedelics remain illegal for both recreational and therapeutic use, they are increasingly being studied at academic centers, and there is hope that they will offer something that our traditional medications might not. However, these are not “micro” doses, but full doses of psychedelic agents that induce clinically-monitored “trips” in order to treat conditions such as depression, anorexia nervosa, or for smoking cessation, to name just a few.
Yet
Because these drugs are illegal under most circumstances, many of the studies involve surveys of users in their natural environments who are already microdosing in an uncontrolled manner. In a 2019 study published in PLOS One, Vince Polito and Richard Stevenson, from Macquarie University, Sydney, gave daily surveys of psychological functioning to 98 microdosers over 6 weeks. Several participants were excluded for using doses that were too high or for concurrent use of other illicit substances.
Whereas the authors found that many people claimed to have positive experiences, there was an increase in neuroticism in some of the subjects. There was no control group and no uniformity to what the subject claimed to be ingesting with regard to dose, frequency, substance, or verification of the chemical content.
University of Chicago neuroscientist Harriet De Wit, PhD, leads one of the few laboratories that conducts controlled, double-blind studies looking at microdosing LSD.
“With microdosing there are expectations, and we don’t know if it’s the expectation or the agent that is making a difference,” she explained. And when asked who in her experience is experimenting with microdosing psychedelics, she expounded “Everybody under the sun!”
Dr. De Wit notes that people microdose to increase their creativity, productivity, focus, and energy, to heighten their spiritual awareness, improve empathy and social relational skills, and to improve their mood – all purported benefits of low-dose psychedelics.
Her group published a study in Addiction Biology, in which 39 subjects were administered low doses of LSD four times over 2 weeks. To address the issues of expectation, the subjects were not told they were participating in a study of hallucinogens specifically but were instead given a list of pharmaceuticals in different classes that they might be given. Microdoses of LSD did not improve either mood or performance, but they did appear to be safe, and they produced no adverse effects.
To date, studies on microdosing have looked at their effects on healthy populations, and the practice has been associated with “Silicon Valley techies” looking for performance enhancement. Ms. Waldman, however, is different.
She is open about her diagnosis of bipolar disorder, and her long history with therapy and medications. As she describes herself in the beginning of her book, she is emotionally uncomfortable, and both irritable and reactive to the point that her life is propelled by interpersonal chaos. In her uncontrolled ‘study,’ she is an N of 1, and she is pleased with the results. Microdosing, she believes, helped her become less irritable, more resilient, and in fact, have some very good days.
By the end of her memoir, she was looking for a way to continue microdosing but was unsure how to safely obtain more LSD and be certain of its purity. Her experience does raise the possibility that microdoses may have therapeutic benefits in people with certain psychiatric conditions, but this has yet to be studied.
J. Raymond DePaulo Jr., MD, is the chair of the National Network of Depression Centers and a distinguished service professor at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore. “Microdosing of psychedelics is very problematic for two equally serious reasons,” he cautioned. “There is no control over what it is that people are actually taking, it is completely unstudied scientifically, and there is no agreement on what a ‘micro’ dose is.”
He noted that one of his patients thought he was taking psilocybin. A chemical analysis was done that revealed the agent to contain a combination of THC, a stimulant, morphine, and fluoxetine. There wasn’t a trace of psilocybin. “Mislabeling is the rule, not the exception,” Dr. DePaulo has concluded.
He also believes the placebo effect has a powerful role with microdosing. “It’s not working because of what is in the pill, more likely it is working because of what is advertised to be in it.”
Ms. De Wit noted that when she started her study, she tried to find people who were elevated on measures of depression or anxiety, but she was not looking for a specific clinical population of patients with these clinical diagnoses. “We found a handful of people, and they improved, but so did those in the placebo group; they all got better.”
Psychedelic agents interact with antidepressants, so subjects in controlled studies need to go off their medications before enrolling – this is a limiting factor in studies of both macro- and microdosing. Ms. De Wit also notes that there are logistical and practical obstacles – it is difficult to get approval to use these agents, and the patients have to remain in the lab and be observed for several hours after they are administered, just as with standard doses.
As might be expected, data collection and anecdotal microdosing experiences are rampant on the internet. The social media forum Reddit alone boasts 192,000 members in its microdosing group, while Imperial College London invites microdosers to take part in surveys intended to add to the body of knowledge. But despite its popularity, there is little in the way of prospective, agent-verified, placebo-controlled research exploring whether or not microdosing is truly beneficial beyond just anecdotal evidence.
Perhaps microdosing is a fad, or perhaps it offers some benefits to some people. Given the current interest in the therapeutic uses of psychedelics, it would be useful to have controlled studies of lower doses that don’t carry the risk of “bad trips.”
Certainly, psychiatry could use more agents to address mental health issues, and society might benefit from the use of agents that are proven to be evidence-based options for improving creativity and productivity. Anything that has potential to reduce psychiatric suffering seems worthy of further study to delineate which populations could be helped or harmed.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In her month-long memoir, A Really Good Day: How Microdosing Made a Mega Difference in My Mood, My Marriage, and My Life (Knopf, 2017), author Ayelet Waldman turns herself into a one-woman experiment.
Over a single month she takes one-tenth of a recreational dose of LSD every third day. She plots her emotions, her productivity, and her pain along the way. Ms. Waldman obtains the LSD in a single vial, enough for 10 doses, from a researcher, who is retiring. What she’s looking for, she tells the reader, is a really good day – something that has been elusive in her turbulent life.
Although psychedelics remain illegal for both recreational and therapeutic use, they are increasingly being studied at academic centers, and there is hope that they will offer something that our traditional medications might not. However, these are not “micro” doses, but full doses of psychedelic agents that induce clinically-monitored “trips” in order to treat conditions such as depression, anorexia nervosa, or for smoking cessation, to name just a few.
Yet
Because these drugs are illegal under most circumstances, many of the studies involve surveys of users in their natural environments who are already microdosing in an uncontrolled manner. In a 2019 study published in PLOS One, Vince Polito and Richard Stevenson, from Macquarie University, Sydney, gave daily surveys of psychological functioning to 98 microdosers over 6 weeks. Several participants were excluded for using doses that were too high or for concurrent use of other illicit substances.
Whereas the authors found that many people claimed to have positive experiences, there was an increase in neuroticism in some of the subjects. There was no control group and no uniformity to what the subject claimed to be ingesting with regard to dose, frequency, substance, or verification of the chemical content.
University of Chicago neuroscientist Harriet De Wit, PhD, leads one of the few laboratories that conducts controlled, double-blind studies looking at microdosing LSD.
“With microdosing there are expectations, and we don’t know if it’s the expectation or the agent that is making a difference,” she explained. And when asked who in her experience is experimenting with microdosing psychedelics, she expounded “Everybody under the sun!”
Dr. De Wit notes that people microdose to increase their creativity, productivity, focus, and energy, to heighten their spiritual awareness, improve empathy and social relational skills, and to improve their mood – all purported benefits of low-dose psychedelics.
Her group published a study in Addiction Biology, in which 39 subjects were administered low doses of LSD four times over 2 weeks. To address the issues of expectation, the subjects were not told they were participating in a study of hallucinogens specifically but were instead given a list of pharmaceuticals in different classes that they might be given. Microdoses of LSD did not improve either mood or performance, but they did appear to be safe, and they produced no adverse effects.
To date, studies on microdosing have looked at their effects on healthy populations, and the practice has been associated with “Silicon Valley techies” looking for performance enhancement. Ms. Waldman, however, is different.
She is open about her diagnosis of bipolar disorder, and her long history with therapy and medications. As she describes herself in the beginning of her book, she is emotionally uncomfortable, and both irritable and reactive to the point that her life is propelled by interpersonal chaos. In her uncontrolled ‘study,’ she is an N of 1, and she is pleased with the results. Microdosing, she believes, helped her become less irritable, more resilient, and in fact, have some very good days.
By the end of her memoir, she was looking for a way to continue microdosing but was unsure how to safely obtain more LSD and be certain of its purity. Her experience does raise the possibility that microdoses may have therapeutic benefits in people with certain psychiatric conditions, but this has yet to be studied.
J. Raymond DePaulo Jr., MD, is the chair of the National Network of Depression Centers and a distinguished service professor at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore. “Microdosing of psychedelics is very problematic for two equally serious reasons,” he cautioned. “There is no control over what it is that people are actually taking, it is completely unstudied scientifically, and there is no agreement on what a ‘micro’ dose is.”
He noted that one of his patients thought he was taking psilocybin. A chemical analysis was done that revealed the agent to contain a combination of THC, a stimulant, morphine, and fluoxetine. There wasn’t a trace of psilocybin. “Mislabeling is the rule, not the exception,” Dr. DePaulo has concluded.
He also believes the placebo effect has a powerful role with microdosing. “It’s not working because of what is in the pill, more likely it is working because of what is advertised to be in it.”
Ms. De Wit noted that when she started her study, she tried to find people who were elevated on measures of depression or anxiety, but she was not looking for a specific clinical population of patients with these clinical diagnoses. “We found a handful of people, and they improved, but so did those in the placebo group; they all got better.”
Psychedelic agents interact with antidepressants, so subjects in controlled studies need to go off their medications before enrolling – this is a limiting factor in studies of both macro- and microdosing. Ms. De Wit also notes that there are logistical and practical obstacles – it is difficult to get approval to use these agents, and the patients have to remain in the lab and be observed for several hours after they are administered, just as with standard doses.
As might be expected, data collection and anecdotal microdosing experiences are rampant on the internet. The social media forum Reddit alone boasts 192,000 members in its microdosing group, while Imperial College London invites microdosers to take part in surveys intended to add to the body of knowledge. But despite its popularity, there is little in the way of prospective, agent-verified, placebo-controlled research exploring whether or not microdosing is truly beneficial beyond just anecdotal evidence.
Perhaps microdosing is a fad, or perhaps it offers some benefits to some people. Given the current interest in the therapeutic uses of psychedelics, it would be useful to have controlled studies of lower doses that don’t carry the risk of “bad trips.”
Certainly, psychiatry could use more agents to address mental health issues, and society might benefit from the use of agents that are proven to be evidence-based options for improving creativity and productivity. Anything that has potential to reduce psychiatric suffering seems worthy of further study to delineate which populations could be helped or harmed.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Pre-death grief’ is a real, but overlooked, syndrome
When an individual develops a terminal illness, those closest to them often start to grieve long before the person dies. Although a common syndrome, it often goes unrecognized and unaddressed.
A new review proposes a way of defining this specific type of grief in the hope that better, more precise descriptive categories will inform therapeutic interventions to help those facing a life-changing loss.
, lead author Jonathan Singer, PhD, visiting assistant professor of clinical psychology, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, told this news organization.
“We proposed the overarching term ‘pre-death grief,’ with the two separate constructs under pre-death grief – anticipatory grief [AG] and illness-related grief [IRG],” he said. “These definitions provide the field with uniform constructs to advance the study of grief before the death of an individual with a life-limiting illness.
“Research examining grief experienced by family members prior to an individual’s death to a life-limiting illness revealed wide variation in the terminology used and characterization of such grief across studies,”
The study was published online Feb. 23 in Palliative Medicine.
‘Typical’ versus ‘impairing’ grief
“Most deaths worldwide are attributed to a chronic or life-limiting Illness,” the authors write. The experience of grief before the loss of a family member “has been studied frequently, but there have been conceptualization issues, which is problematic, as it hinders the potential advancement of the field in differentiating typical grief from more impairing grief before the death,” Dr. Singer said. “Further complicating the picture is the sheer number of terms used to describe grief before death.”
Dr. Singer said that when he started conducting research in this field, he “realized someone had to combine the articles that have been published in order to create definitions that will advance the field, so risk and protective factors could be identified and interventions could be tested.”
For the current study, the investigators searched six databases to find research that “evaluated family members’ or friends’ grief related to an individual currently living with a life-limiting illness.” They excluded studies that evaluated grief after death.
Of 9,568 records reviewed, the researchers selected 134 full-text articles that met inclusion criteria. Most studies (57.46%) were quantitative; 23.88% were qualitative, and 17.91% used mixed methods. Most studies were retrospective, although 14.93% were prospective, and 3% included both prospective and retrospective analyses.
Most participants reported that the family member/friend was diagnosed either with “late-stage dementia” or “advanced cancer.” The majority (58%) were adult children of the individual with the illness, followed by spouses/partners (28.1%) and other relatives/friends (13.9%) in studies that reported the relationship to the participant and the person with the illness.
Various scales were used in the studies to measure grief, particularly the Marwit-Meuser-Caregiver Grief Inventory (n = 28), the Anticipatory Grief Scale (n = 18), and the Prolonged Grief–12 (n = 13).
A new name
Owing to the large number of articles included in the review, the researchers limited the analysis to those in which a given term was used in ≥ 1 articles.
The researchers found 18 different terms used by family members/friends of individuals with life-limiting illness to describe grief, including AG (used in the most studies, n = 54); pre-death grief (n = 18), grief (n = 12), pre-loss grief (n = 6), caregiver grief (n = 5), and anticipatory mourning (n = 4). These 18 terms were associated with greater than or equal to 30 different definitions across all of the various studies.
“Definitions of these terms differed drastically,” and many studies used the term AG without defining it.
Nineteen studies used multiple terms within a single article, and the terms were “used interchangeably, with the same definition applied,” the researchers report.
For example, one study defined AG as “the process associated with grieving the eventual loss of a family member in advance of their inevitable death,” while another defined AG as “a series of losses based on a loved one’s progression of cognitive and physical decline.”
On the basis of this analysis, the researchers chose the term “pre-death grief,” which encompasses IRG and AG.
Dr. Singer explained that IRG is “present-oriented” and involves the “longing and yearning for the family member to be as they were before the illness.” AG is “future oriented” and is defined as “family members’ grief experience while the person with the life-limiting illness is alive but that is focused on feared or anticipated losses that will occur after the person’s death.”
The study was intended “to advance the field and provide the knowledge and definitions in order to create and test an evidence-based intervention,” Dr. Singer said.
He pointed to interventions (for example: behavioral activation, meaning-centered grief therapy) that could be tested to reduce pre-death grief or specific interventions that focus on addressing IRG or AG. “For example, cognitive behavior therapy might be used to challenge worry about life without the person, which would be classified as AG.”
Dr. Singer feels it is “vital” to reduce pre-death grief, insofar as numerous studies have shown that high rates of pre-death grief “result in higher rates of prolonged grief disorder.”
‘Paradoxical reality’
Francesca Falzarano, PhD, a postdoctoral associate in medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, called the article a “timely piece drawing much-needed attention to an all-too-often overlooked experience lived by those affected by terminal illnesses.”
Dr. Falzarano, who was not involved in the review, said that “from her own experience” as both a caregiver and behavioral scientist conducting research in this area, the concept of pre-death grief is a paradoxical reality – “how do we grieve someone we haven’t lost yet?”
The experience of pre-death grief is “quite distinct from grief after bereavement” because there is no end date. Rather, the person “cycles back and forth between preparing themselves for an impending death while also attending to whatever is happening in the current moment.” It’s also “unique in that both patients and caregivers individually and collectively grieve losses over the course of the illness,” she noted.
“We as researchers absolutely need to focus our attention on achieving consensus on an appropriate definition for pre-death grief that adequately encompasses its complexity and multidimensionality,” she said.
The authors and Dr. Falzarano report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When an individual develops a terminal illness, those closest to them often start to grieve long before the person dies. Although a common syndrome, it often goes unrecognized and unaddressed.
A new review proposes a way of defining this specific type of grief in the hope that better, more precise descriptive categories will inform therapeutic interventions to help those facing a life-changing loss.
, lead author Jonathan Singer, PhD, visiting assistant professor of clinical psychology, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, told this news organization.
“We proposed the overarching term ‘pre-death grief,’ with the two separate constructs under pre-death grief – anticipatory grief [AG] and illness-related grief [IRG],” he said. “These definitions provide the field with uniform constructs to advance the study of grief before the death of an individual with a life-limiting illness.
“Research examining grief experienced by family members prior to an individual’s death to a life-limiting illness revealed wide variation in the terminology used and characterization of such grief across studies,”
The study was published online Feb. 23 in Palliative Medicine.
‘Typical’ versus ‘impairing’ grief
“Most deaths worldwide are attributed to a chronic or life-limiting Illness,” the authors write. The experience of grief before the loss of a family member “has been studied frequently, but there have been conceptualization issues, which is problematic, as it hinders the potential advancement of the field in differentiating typical grief from more impairing grief before the death,” Dr. Singer said. “Further complicating the picture is the sheer number of terms used to describe grief before death.”
Dr. Singer said that when he started conducting research in this field, he “realized someone had to combine the articles that have been published in order to create definitions that will advance the field, so risk and protective factors could be identified and interventions could be tested.”
For the current study, the investigators searched six databases to find research that “evaluated family members’ or friends’ grief related to an individual currently living with a life-limiting illness.” They excluded studies that evaluated grief after death.
Of 9,568 records reviewed, the researchers selected 134 full-text articles that met inclusion criteria. Most studies (57.46%) were quantitative; 23.88% were qualitative, and 17.91% used mixed methods. Most studies were retrospective, although 14.93% were prospective, and 3% included both prospective and retrospective analyses.
Most participants reported that the family member/friend was diagnosed either with “late-stage dementia” or “advanced cancer.” The majority (58%) were adult children of the individual with the illness, followed by spouses/partners (28.1%) and other relatives/friends (13.9%) in studies that reported the relationship to the participant and the person with the illness.
Various scales were used in the studies to measure grief, particularly the Marwit-Meuser-Caregiver Grief Inventory (n = 28), the Anticipatory Grief Scale (n = 18), and the Prolonged Grief–12 (n = 13).
A new name
Owing to the large number of articles included in the review, the researchers limited the analysis to those in which a given term was used in ≥ 1 articles.
The researchers found 18 different terms used by family members/friends of individuals with life-limiting illness to describe grief, including AG (used in the most studies, n = 54); pre-death grief (n = 18), grief (n = 12), pre-loss grief (n = 6), caregiver grief (n = 5), and anticipatory mourning (n = 4). These 18 terms were associated with greater than or equal to 30 different definitions across all of the various studies.
“Definitions of these terms differed drastically,” and many studies used the term AG without defining it.
Nineteen studies used multiple terms within a single article, and the terms were “used interchangeably, with the same definition applied,” the researchers report.
For example, one study defined AG as “the process associated with grieving the eventual loss of a family member in advance of their inevitable death,” while another defined AG as “a series of losses based on a loved one’s progression of cognitive and physical decline.”
On the basis of this analysis, the researchers chose the term “pre-death grief,” which encompasses IRG and AG.
Dr. Singer explained that IRG is “present-oriented” and involves the “longing and yearning for the family member to be as they were before the illness.” AG is “future oriented” and is defined as “family members’ grief experience while the person with the life-limiting illness is alive but that is focused on feared or anticipated losses that will occur after the person’s death.”
The study was intended “to advance the field and provide the knowledge and definitions in order to create and test an evidence-based intervention,” Dr. Singer said.
He pointed to interventions (for example: behavioral activation, meaning-centered grief therapy) that could be tested to reduce pre-death grief or specific interventions that focus on addressing IRG or AG. “For example, cognitive behavior therapy might be used to challenge worry about life without the person, which would be classified as AG.”
Dr. Singer feels it is “vital” to reduce pre-death grief, insofar as numerous studies have shown that high rates of pre-death grief “result in higher rates of prolonged grief disorder.”
‘Paradoxical reality’
Francesca Falzarano, PhD, a postdoctoral associate in medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, called the article a “timely piece drawing much-needed attention to an all-too-often overlooked experience lived by those affected by terminal illnesses.”
Dr. Falzarano, who was not involved in the review, said that “from her own experience” as both a caregiver and behavioral scientist conducting research in this area, the concept of pre-death grief is a paradoxical reality – “how do we grieve someone we haven’t lost yet?”
The experience of pre-death grief is “quite distinct from grief after bereavement” because there is no end date. Rather, the person “cycles back and forth between preparing themselves for an impending death while also attending to whatever is happening in the current moment.” It’s also “unique in that both patients and caregivers individually and collectively grieve losses over the course of the illness,” she noted.
“We as researchers absolutely need to focus our attention on achieving consensus on an appropriate definition for pre-death grief that adequately encompasses its complexity and multidimensionality,” she said.
The authors and Dr. Falzarano report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When an individual develops a terminal illness, those closest to them often start to grieve long before the person dies. Although a common syndrome, it often goes unrecognized and unaddressed.
A new review proposes a way of defining this specific type of grief in the hope that better, more precise descriptive categories will inform therapeutic interventions to help those facing a life-changing loss.
, lead author Jonathan Singer, PhD, visiting assistant professor of clinical psychology, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, told this news organization.
“We proposed the overarching term ‘pre-death grief,’ with the two separate constructs under pre-death grief – anticipatory grief [AG] and illness-related grief [IRG],” he said. “These definitions provide the field with uniform constructs to advance the study of grief before the death of an individual with a life-limiting illness.
“Research examining grief experienced by family members prior to an individual’s death to a life-limiting illness revealed wide variation in the terminology used and characterization of such grief across studies,”
The study was published online Feb. 23 in Palliative Medicine.
‘Typical’ versus ‘impairing’ grief
“Most deaths worldwide are attributed to a chronic or life-limiting Illness,” the authors write. The experience of grief before the loss of a family member “has been studied frequently, but there have been conceptualization issues, which is problematic, as it hinders the potential advancement of the field in differentiating typical grief from more impairing grief before the death,” Dr. Singer said. “Further complicating the picture is the sheer number of terms used to describe grief before death.”
Dr. Singer said that when he started conducting research in this field, he “realized someone had to combine the articles that have been published in order to create definitions that will advance the field, so risk and protective factors could be identified and interventions could be tested.”
For the current study, the investigators searched six databases to find research that “evaluated family members’ or friends’ grief related to an individual currently living with a life-limiting illness.” They excluded studies that evaluated grief after death.
Of 9,568 records reviewed, the researchers selected 134 full-text articles that met inclusion criteria. Most studies (57.46%) were quantitative; 23.88% were qualitative, and 17.91% used mixed methods. Most studies were retrospective, although 14.93% were prospective, and 3% included both prospective and retrospective analyses.
Most participants reported that the family member/friend was diagnosed either with “late-stage dementia” or “advanced cancer.” The majority (58%) were adult children of the individual with the illness, followed by spouses/partners (28.1%) and other relatives/friends (13.9%) in studies that reported the relationship to the participant and the person with the illness.
Various scales were used in the studies to measure grief, particularly the Marwit-Meuser-Caregiver Grief Inventory (n = 28), the Anticipatory Grief Scale (n = 18), and the Prolonged Grief–12 (n = 13).
A new name
Owing to the large number of articles included in the review, the researchers limited the analysis to those in which a given term was used in ≥ 1 articles.
The researchers found 18 different terms used by family members/friends of individuals with life-limiting illness to describe grief, including AG (used in the most studies, n = 54); pre-death grief (n = 18), grief (n = 12), pre-loss grief (n = 6), caregiver grief (n = 5), and anticipatory mourning (n = 4). These 18 terms were associated with greater than or equal to 30 different definitions across all of the various studies.
“Definitions of these terms differed drastically,” and many studies used the term AG without defining it.
Nineteen studies used multiple terms within a single article, and the terms were “used interchangeably, with the same definition applied,” the researchers report.
For example, one study defined AG as “the process associated with grieving the eventual loss of a family member in advance of their inevitable death,” while another defined AG as “a series of losses based on a loved one’s progression of cognitive and physical decline.”
On the basis of this analysis, the researchers chose the term “pre-death grief,” which encompasses IRG and AG.
Dr. Singer explained that IRG is “present-oriented” and involves the “longing and yearning for the family member to be as they were before the illness.” AG is “future oriented” and is defined as “family members’ grief experience while the person with the life-limiting illness is alive but that is focused on feared or anticipated losses that will occur after the person’s death.”
The study was intended “to advance the field and provide the knowledge and definitions in order to create and test an evidence-based intervention,” Dr. Singer said.
He pointed to interventions (for example: behavioral activation, meaning-centered grief therapy) that could be tested to reduce pre-death grief or specific interventions that focus on addressing IRG or AG. “For example, cognitive behavior therapy might be used to challenge worry about life without the person, which would be classified as AG.”
Dr. Singer feels it is “vital” to reduce pre-death grief, insofar as numerous studies have shown that high rates of pre-death grief “result in higher rates of prolonged grief disorder.”
‘Paradoxical reality’
Francesca Falzarano, PhD, a postdoctoral associate in medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, called the article a “timely piece drawing much-needed attention to an all-too-often overlooked experience lived by those affected by terminal illnesses.”
Dr. Falzarano, who was not involved in the review, said that “from her own experience” as both a caregiver and behavioral scientist conducting research in this area, the concept of pre-death grief is a paradoxical reality – “how do we grieve someone we haven’t lost yet?”
The experience of pre-death grief is “quite distinct from grief after bereavement” because there is no end date. Rather, the person “cycles back and forth between preparing themselves for an impending death while also attending to whatever is happening in the current moment.” It’s also “unique in that both patients and caregivers individually and collectively grieve losses over the course of the illness,” she noted.
“We as researchers absolutely need to focus our attention on achieving consensus on an appropriate definition for pre-death grief that adequately encompasses its complexity and multidimensionality,” she said.
The authors and Dr. Falzarano report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Progressive muscle relaxation outperforms mindfulness in reducing grief severity
DENVER –
“Both progressive muscle relaxation and mindfulness training were shown to improve grief severity, yearning, depression symptoms, and stress, [but] the results from this study suggest that progressive muscle relaxation is most effective, compared to a wait-list control condition for improving grief,” study investigator Lindsey Knowles, PhD, senior fellow, MS Center of Excellence, Veterans Affairs Puget Sound Health Care System, and University of Washington, Seattle, told this news organization.
“With replication, progressive muscle relaxation could be a standalone intervention for nondisordered grief or a component of treatment for disordered grief,” Dr. Knowles said.
The findings were presented as part of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America Anxiety & Depression conference.
Disordered grief
Approximately 10% of individuals grappling with loss “get stuck” in their grief and develop disordered grief, which is distinguished by repetitive thought processes of yearning and grief rumination, the investigators noted.
The researchers hypothesized that mindfulness training, which has been shown to reduce maladaptive repetitive thought, could be an effective intervention to prevent disordered grief.
To investigate, they enrolled 94 widows and widowers (mean age, 67.5 years) who were experiencing bereavement-related grief and were between 6 months and 4 years post loss.
The researchers compared a 6-week mindfulness intervention (n = 37) with a 6-week progressive muscle relaxation intervention (n = 35), Dr. Knowles said, because there has been speculation that benefits from mindfulness training may be related more to the relaxation response than to the actual mindfulness component.
Both study groups received the intervention in similar settings with matched instructors.
The mindfulness intervention sessions included 10-25 minutes of meditation and mindfulness practices. It also included instructions for home practice.
Participants in the progressive muscle relaxation group were trained to tense and relax the body’s various muscle groups with an end goal of learning to relax four key muscle groups without initial tensing.
A third group of patients were placed on a wait list with no intervention (n = 22).
Measures taken throughout the study interventions and at 1 month postintervention showed reductions in the study’s two primary outcomes of grief severity and yearning for both interventions versus baseline (P = < .003).
However, only the progressive muscle relaxation group had a significantly greater reduction in grief severity vs the wait-list control group (P = .020).
The muscle relaxation group also showed lower grief severity at 1month follow-up versus the wait-list group (P = .049) – with a value at that time falling below an established cutoff for complicated grief, based on the Revised Inventory of Complicated Grief.
All three treatment groups showed a drop in the third primary outcome of grief rumination (P < .001).
Secondary outcomes of depression and stress were reduced in both active study groups versus the wait-list group (P = .028). Sleep quality also improved in both active intervention groups.
Simple technique
Dr. Knowles said the study’s findings were unexpected.
“We had hypothesized that mindfulness training would outperform progressive muscle relaxation and wait-list for improving grief outcomes,” she said.
Mindfulness experts underscore that a state of global relaxation is considered integral to the benefits of mindfulness, which could explain the benefits of progressive muscle relaxation, Dr. Knowles noted.
Importantly, progressive muscle relaxation has a key advantage: It is quickly and easily learned, which may partially explain the study’s findings, she added.
“Progressive muscle relaxation is a relatively simple technique, so it is also likely that participants were able to master [the technique] over the 6-week intervention,” Dr. Knowles said. “On the other hand, the mindfulness intervention was an introduction to mindfulness, and mastery was not expected or likely over the 6-week intervention.”
Either way, the results shed important light on a potentially beneficial grief intervention.
“Although mindfulness training and progressive muscle relaxation practices may both be perceived as relaxing, mastering progressive muscle relaxation may in fact enable people to maintain better focus in the present moment and generalize nonreactive awareness to both positively and negatively balanced phenomena,” Dr. Knowles said.
However, “more research is necessary to clarify how progressive muscle relaxation improves grief outcomes in widows and widowers.”
CNS benefits?
Zoe Donaldson, PhD, assistant professor in behavioral neuroscience, department of psychology and neuroscience, University of Colorado, Boulder, said the study is important for ongoing efforts in finding effective therapies for grief.
“We often struggle to try to help those experiencing the pain of loss and this study suggests a discrete set of exercises that may help,” said Dr. Donaldson, who was not involved with the research.
She also described the study results as surprising, and speculated that a combination of factors could explain the findings.
“First, mindfulness is hard to achieve, so the moderate beneficial effects might increase with more substantial mindfulness training. Secondly, it is not clear why progressive muscle relaxation had an effect, but the focus and attention to detail may engage the central nervous system in a beneficial way that we don’t fully understand,” Dr. Donaldson said.
Importantly, it’s key to remember that grief is an individual condition when investigating therapies, Dr. Donaldson noted.
“We likely need to develop multiple interventions to help those who are grieving. Incorporating loss can take many forms,” she said.
The investigators and Dr. Donaldson reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DENVER –
“Both progressive muscle relaxation and mindfulness training were shown to improve grief severity, yearning, depression symptoms, and stress, [but] the results from this study suggest that progressive muscle relaxation is most effective, compared to a wait-list control condition for improving grief,” study investigator Lindsey Knowles, PhD, senior fellow, MS Center of Excellence, Veterans Affairs Puget Sound Health Care System, and University of Washington, Seattle, told this news organization.
“With replication, progressive muscle relaxation could be a standalone intervention for nondisordered grief or a component of treatment for disordered grief,” Dr. Knowles said.
The findings were presented as part of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America Anxiety & Depression conference.
Disordered grief
Approximately 10% of individuals grappling with loss “get stuck” in their grief and develop disordered grief, which is distinguished by repetitive thought processes of yearning and grief rumination, the investigators noted.
The researchers hypothesized that mindfulness training, which has been shown to reduce maladaptive repetitive thought, could be an effective intervention to prevent disordered grief.
To investigate, they enrolled 94 widows and widowers (mean age, 67.5 years) who were experiencing bereavement-related grief and were between 6 months and 4 years post loss.
The researchers compared a 6-week mindfulness intervention (n = 37) with a 6-week progressive muscle relaxation intervention (n = 35), Dr. Knowles said, because there has been speculation that benefits from mindfulness training may be related more to the relaxation response than to the actual mindfulness component.
Both study groups received the intervention in similar settings with matched instructors.
The mindfulness intervention sessions included 10-25 minutes of meditation and mindfulness practices. It also included instructions for home practice.
Participants in the progressive muscle relaxation group were trained to tense and relax the body’s various muscle groups with an end goal of learning to relax four key muscle groups without initial tensing.
A third group of patients were placed on a wait list with no intervention (n = 22).
Measures taken throughout the study interventions and at 1 month postintervention showed reductions in the study’s two primary outcomes of grief severity and yearning for both interventions versus baseline (P = < .003).
However, only the progressive muscle relaxation group had a significantly greater reduction in grief severity vs the wait-list control group (P = .020).
The muscle relaxation group also showed lower grief severity at 1month follow-up versus the wait-list group (P = .049) – with a value at that time falling below an established cutoff for complicated grief, based on the Revised Inventory of Complicated Grief.
All three treatment groups showed a drop in the third primary outcome of grief rumination (P < .001).
Secondary outcomes of depression and stress were reduced in both active study groups versus the wait-list group (P = .028). Sleep quality also improved in both active intervention groups.
Simple technique
Dr. Knowles said the study’s findings were unexpected.
“We had hypothesized that mindfulness training would outperform progressive muscle relaxation and wait-list for improving grief outcomes,” she said.
Mindfulness experts underscore that a state of global relaxation is considered integral to the benefits of mindfulness, which could explain the benefits of progressive muscle relaxation, Dr. Knowles noted.
Importantly, progressive muscle relaxation has a key advantage: It is quickly and easily learned, which may partially explain the study’s findings, she added.
“Progressive muscle relaxation is a relatively simple technique, so it is also likely that participants were able to master [the technique] over the 6-week intervention,” Dr. Knowles said. “On the other hand, the mindfulness intervention was an introduction to mindfulness, and mastery was not expected or likely over the 6-week intervention.”
Either way, the results shed important light on a potentially beneficial grief intervention.
“Although mindfulness training and progressive muscle relaxation practices may both be perceived as relaxing, mastering progressive muscle relaxation may in fact enable people to maintain better focus in the present moment and generalize nonreactive awareness to both positively and negatively balanced phenomena,” Dr. Knowles said.
However, “more research is necessary to clarify how progressive muscle relaxation improves grief outcomes in widows and widowers.”
CNS benefits?
Zoe Donaldson, PhD, assistant professor in behavioral neuroscience, department of psychology and neuroscience, University of Colorado, Boulder, said the study is important for ongoing efforts in finding effective therapies for grief.
“We often struggle to try to help those experiencing the pain of loss and this study suggests a discrete set of exercises that may help,” said Dr. Donaldson, who was not involved with the research.
She also described the study results as surprising, and speculated that a combination of factors could explain the findings.
“First, mindfulness is hard to achieve, so the moderate beneficial effects might increase with more substantial mindfulness training. Secondly, it is not clear why progressive muscle relaxation had an effect, but the focus and attention to detail may engage the central nervous system in a beneficial way that we don’t fully understand,” Dr. Donaldson said.
Importantly, it’s key to remember that grief is an individual condition when investigating therapies, Dr. Donaldson noted.
“We likely need to develop multiple interventions to help those who are grieving. Incorporating loss can take many forms,” she said.
The investigators and Dr. Donaldson reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DENVER –
“Both progressive muscle relaxation and mindfulness training were shown to improve grief severity, yearning, depression symptoms, and stress, [but] the results from this study suggest that progressive muscle relaxation is most effective, compared to a wait-list control condition for improving grief,” study investigator Lindsey Knowles, PhD, senior fellow, MS Center of Excellence, Veterans Affairs Puget Sound Health Care System, and University of Washington, Seattle, told this news organization.
“With replication, progressive muscle relaxation could be a standalone intervention for nondisordered grief or a component of treatment for disordered grief,” Dr. Knowles said.
The findings were presented as part of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America Anxiety & Depression conference.
Disordered grief
Approximately 10% of individuals grappling with loss “get stuck” in their grief and develop disordered grief, which is distinguished by repetitive thought processes of yearning and grief rumination, the investigators noted.
The researchers hypothesized that mindfulness training, which has been shown to reduce maladaptive repetitive thought, could be an effective intervention to prevent disordered grief.
To investigate, they enrolled 94 widows and widowers (mean age, 67.5 years) who were experiencing bereavement-related grief and were between 6 months and 4 years post loss.
The researchers compared a 6-week mindfulness intervention (n = 37) with a 6-week progressive muscle relaxation intervention (n = 35), Dr. Knowles said, because there has been speculation that benefits from mindfulness training may be related more to the relaxation response than to the actual mindfulness component.
Both study groups received the intervention in similar settings with matched instructors.
The mindfulness intervention sessions included 10-25 minutes of meditation and mindfulness practices. It also included instructions for home practice.
Participants in the progressive muscle relaxation group were trained to tense and relax the body’s various muscle groups with an end goal of learning to relax four key muscle groups without initial tensing.
A third group of patients were placed on a wait list with no intervention (n = 22).
Measures taken throughout the study interventions and at 1 month postintervention showed reductions in the study’s two primary outcomes of grief severity and yearning for both interventions versus baseline (P = < .003).
However, only the progressive muscle relaxation group had a significantly greater reduction in grief severity vs the wait-list control group (P = .020).
The muscle relaxation group also showed lower grief severity at 1month follow-up versus the wait-list group (P = .049) – with a value at that time falling below an established cutoff for complicated grief, based on the Revised Inventory of Complicated Grief.
All three treatment groups showed a drop in the third primary outcome of grief rumination (P < .001).
Secondary outcomes of depression and stress were reduced in both active study groups versus the wait-list group (P = .028). Sleep quality also improved in both active intervention groups.
Simple technique
Dr. Knowles said the study’s findings were unexpected.
“We had hypothesized that mindfulness training would outperform progressive muscle relaxation and wait-list for improving grief outcomes,” she said.
Mindfulness experts underscore that a state of global relaxation is considered integral to the benefits of mindfulness, which could explain the benefits of progressive muscle relaxation, Dr. Knowles noted.
Importantly, progressive muscle relaxation has a key advantage: It is quickly and easily learned, which may partially explain the study’s findings, she added.
“Progressive muscle relaxation is a relatively simple technique, so it is also likely that participants were able to master [the technique] over the 6-week intervention,” Dr. Knowles said. “On the other hand, the mindfulness intervention was an introduction to mindfulness, and mastery was not expected or likely over the 6-week intervention.”
Either way, the results shed important light on a potentially beneficial grief intervention.
“Although mindfulness training and progressive muscle relaxation practices may both be perceived as relaxing, mastering progressive muscle relaxation may in fact enable people to maintain better focus in the present moment and generalize nonreactive awareness to both positively and negatively balanced phenomena,” Dr. Knowles said.
However, “more research is necessary to clarify how progressive muscle relaxation improves grief outcomes in widows and widowers.”
CNS benefits?
Zoe Donaldson, PhD, assistant professor in behavioral neuroscience, department of psychology and neuroscience, University of Colorado, Boulder, said the study is important for ongoing efforts in finding effective therapies for grief.
“We often struggle to try to help those experiencing the pain of loss and this study suggests a discrete set of exercises that may help,” said Dr. Donaldson, who was not involved with the research.
She also described the study results as surprising, and speculated that a combination of factors could explain the findings.
“First, mindfulness is hard to achieve, so the moderate beneficial effects might increase with more substantial mindfulness training. Secondly, it is not clear why progressive muscle relaxation had an effect, but the focus and attention to detail may engage the central nervous system in a beneficial way that we don’t fully understand,” Dr. Donaldson said.
Importantly, it’s key to remember that grief is an individual condition when investigating therapies, Dr. Donaldson noted.
“We likely need to develop multiple interventions to help those who are grieving. Incorporating loss can take many forms,” she said.
The investigators and Dr. Donaldson reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ADAA 2022
Suicide attempts in kids ages 10-12 quadrupled over 20 years
Suicide attempts spurring calls to poison control centers more than quadrupled among U.S. children aged 10-12 years from 2000 to 2020, according to research published in JAMA Pediatrics.
The reasons for the increase in suicide attempts isn’t clear from the new study, but the researchers note that popular social media networks launched during the 20-year period, and other studies have linked spending time on social media with depression in adolescence. The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in the last year the researchers looked at, also disrupted normal life and routines for children.
For all children older than age 9, the proportion of incidents in which kids ate or drank something harmful that were deemed suicide attempts increased, while those classified as misuse or abuse of potentially poisonous substances declined. Children aged 6-9 did not have an increase in suicide attempts, the study found.
“It’s a huge problem we’re seeing in [ERs]. It’s exponentially blowing up numbers across the nation,” says David Sheridan, MD, an ER pediatric doctor at the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, who led the study.
Adolescents or preteens who have attempted suicide can sit in ERs “for days or weeks” as they wait to be moved elsewhere in the hospital or to an outpatient facility for treatment, Dr. Sheridan says. The delays are not only unpleasant for the children, he says, but they also strain hospitals by leaving less space available for other patients coming to the ER.
“It’s really tough on the entire health care system, and most importantly, it’s really rough on the families who are going through a crisis,” Dr. Sheridan says. He noted that young people often attempt suicide by taking excessive quantities of common over-the-counter products found in many medicine cabinets – acetaminophen, ibuprofen, diphenhydramine – not items marked “poison.”
Twenty-year trend
The researchers examined phone calls to poison control centers about kids age 6 and up taking in potentially harmful substances from 2000-2020 recorded in the National Poison Data System, which is maintained by the American Association of Poison Control Centers.
Of more than 1.2 million total calls, 854,000 involved girls. A poison control data analyst determined if the call involved attempted suicide or the deliberate misuse or abuse of a potentially poisonous substance.
The researchers identified 1,005 deaths. About 70% of the total cases had either no effect or a minor effect on the child’s health.
Over the 20-year period, more than 90% of the calls involved children aged at least 13 years, with approximately 72,000 (5.7%) about children aged 10-12. Most calls for children 13 and older were for suicide attempts.
Suspected suicide attempts accounted for about 50% of the total calls to poison control centers among children aged 10-12 in 2000 – a figure that ballooned to 80% in 2020, the researchers found.
Both the number of calls and the proportion related to suicide attempts increased among children aged 10-12, Dr. Sheridan says. By 2020, the researchers found, poison control centers were fielding 4.5 times as many suicide-related calls among kids of this age group as they had in 2000. This jump was the largest such increase for any age group in the study, he says.
The reasons for such a large increase of suicide-related calls among preadolescents are unclear, the researchers note.
The increase became apparent around 2013, at the time many popular social media networks launched. Dr. Sheridan and his colleagues cite studies showing an association between spending more time on social media or watching television and depression in adolescence but said further research is needed to understand the root causes of this increase.
The latest study did not look specifically at the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on suicide among young people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention earlier reported a sharp rise in suicide attempts among youth during the early months of the pandemic, especially among girls aged 12-17 years. By February 2021, suicide attempts within this group had climbed by 50%, compared with 2 years earlier.
Although suicide attempts are concerning enough, deaths by suicide are even more worrisome, experts said.
The researchers’ findings are consistent with overall recent trends in youth suicide deaths, says Jeff Bridge, PhD, an epidemiologist at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus. From 2010-2020, suicide rates increased by 50% among 13- to 18-year-olds, Dr. Bridge said, and more than doubled in children aged 10-12.
The latest study captured only calls to poison control centers, so it did not count suicide attempts that did not result in a call for help. Another limitation of the study is that poison control data are not categorized by race or ethnicity, prompting Dr. Bridge to urge researchers to look specifically at the effect of race and ethnicity on these trends.
“This study supports screening for suicide risk as young as 10 years old,” Dr. Bridge says.
Dr. Sheridan agrees that prevention is essential: “The ER is where kids come when they’re in crisis. Trying to be more preventative by diagnosing or picking up on this earlier, I think, is really important.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Suicide attempts spurring calls to poison control centers more than quadrupled among U.S. children aged 10-12 years from 2000 to 2020, according to research published in JAMA Pediatrics.
The reasons for the increase in suicide attempts isn’t clear from the new study, but the researchers note that popular social media networks launched during the 20-year period, and other studies have linked spending time on social media with depression in adolescence. The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in the last year the researchers looked at, also disrupted normal life and routines for children.
For all children older than age 9, the proportion of incidents in which kids ate or drank something harmful that were deemed suicide attempts increased, while those classified as misuse or abuse of potentially poisonous substances declined. Children aged 6-9 did not have an increase in suicide attempts, the study found.
“It’s a huge problem we’re seeing in [ERs]. It’s exponentially blowing up numbers across the nation,” says David Sheridan, MD, an ER pediatric doctor at the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, who led the study.
Adolescents or preteens who have attempted suicide can sit in ERs “for days or weeks” as they wait to be moved elsewhere in the hospital or to an outpatient facility for treatment, Dr. Sheridan says. The delays are not only unpleasant for the children, he says, but they also strain hospitals by leaving less space available for other patients coming to the ER.
“It’s really tough on the entire health care system, and most importantly, it’s really rough on the families who are going through a crisis,” Dr. Sheridan says. He noted that young people often attempt suicide by taking excessive quantities of common over-the-counter products found in many medicine cabinets – acetaminophen, ibuprofen, diphenhydramine – not items marked “poison.”
Twenty-year trend
The researchers examined phone calls to poison control centers about kids age 6 and up taking in potentially harmful substances from 2000-2020 recorded in the National Poison Data System, which is maintained by the American Association of Poison Control Centers.
Of more than 1.2 million total calls, 854,000 involved girls. A poison control data analyst determined if the call involved attempted suicide or the deliberate misuse or abuse of a potentially poisonous substance.
The researchers identified 1,005 deaths. About 70% of the total cases had either no effect or a minor effect on the child’s health.
Over the 20-year period, more than 90% of the calls involved children aged at least 13 years, with approximately 72,000 (5.7%) about children aged 10-12. Most calls for children 13 and older were for suicide attempts.
Suspected suicide attempts accounted for about 50% of the total calls to poison control centers among children aged 10-12 in 2000 – a figure that ballooned to 80% in 2020, the researchers found.
Both the number of calls and the proportion related to suicide attempts increased among children aged 10-12, Dr. Sheridan says. By 2020, the researchers found, poison control centers were fielding 4.5 times as many suicide-related calls among kids of this age group as they had in 2000. This jump was the largest such increase for any age group in the study, he says.
The reasons for such a large increase of suicide-related calls among preadolescents are unclear, the researchers note.
The increase became apparent around 2013, at the time many popular social media networks launched. Dr. Sheridan and his colleagues cite studies showing an association between spending more time on social media or watching television and depression in adolescence but said further research is needed to understand the root causes of this increase.
The latest study did not look specifically at the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on suicide among young people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention earlier reported a sharp rise in suicide attempts among youth during the early months of the pandemic, especially among girls aged 12-17 years. By February 2021, suicide attempts within this group had climbed by 50%, compared with 2 years earlier.
Although suicide attempts are concerning enough, deaths by suicide are even more worrisome, experts said.
The researchers’ findings are consistent with overall recent trends in youth suicide deaths, says Jeff Bridge, PhD, an epidemiologist at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus. From 2010-2020, suicide rates increased by 50% among 13- to 18-year-olds, Dr. Bridge said, and more than doubled in children aged 10-12.
The latest study captured only calls to poison control centers, so it did not count suicide attempts that did not result in a call for help. Another limitation of the study is that poison control data are not categorized by race or ethnicity, prompting Dr. Bridge to urge researchers to look specifically at the effect of race and ethnicity on these trends.
“This study supports screening for suicide risk as young as 10 years old,” Dr. Bridge says.
Dr. Sheridan agrees that prevention is essential: “The ER is where kids come when they’re in crisis. Trying to be more preventative by diagnosing or picking up on this earlier, I think, is really important.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Suicide attempts spurring calls to poison control centers more than quadrupled among U.S. children aged 10-12 years from 2000 to 2020, according to research published in JAMA Pediatrics.
The reasons for the increase in suicide attempts isn’t clear from the new study, but the researchers note that popular social media networks launched during the 20-year period, and other studies have linked spending time on social media with depression in adolescence. The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in the last year the researchers looked at, also disrupted normal life and routines for children.
For all children older than age 9, the proportion of incidents in which kids ate or drank something harmful that were deemed suicide attempts increased, while those classified as misuse or abuse of potentially poisonous substances declined. Children aged 6-9 did not have an increase in suicide attempts, the study found.
“It’s a huge problem we’re seeing in [ERs]. It’s exponentially blowing up numbers across the nation,” says David Sheridan, MD, an ER pediatric doctor at the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, who led the study.
Adolescents or preteens who have attempted suicide can sit in ERs “for days or weeks” as they wait to be moved elsewhere in the hospital or to an outpatient facility for treatment, Dr. Sheridan says. The delays are not only unpleasant for the children, he says, but they also strain hospitals by leaving less space available for other patients coming to the ER.
“It’s really tough on the entire health care system, and most importantly, it’s really rough on the families who are going through a crisis,” Dr. Sheridan says. He noted that young people often attempt suicide by taking excessive quantities of common over-the-counter products found in many medicine cabinets – acetaminophen, ibuprofen, diphenhydramine – not items marked “poison.”
Twenty-year trend
The researchers examined phone calls to poison control centers about kids age 6 and up taking in potentially harmful substances from 2000-2020 recorded in the National Poison Data System, which is maintained by the American Association of Poison Control Centers.
Of more than 1.2 million total calls, 854,000 involved girls. A poison control data analyst determined if the call involved attempted suicide or the deliberate misuse or abuse of a potentially poisonous substance.
The researchers identified 1,005 deaths. About 70% of the total cases had either no effect or a minor effect on the child’s health.
Over the 20-year period, more than 90% of the calls involved children aged at least 13 years, with approximately 72,000 (5.7%) about children aged 10-12. Most calls for children 13 and older were for suicide attempts.
Suspected suicide attempts accounted for about 50% of the total calls to poison control centers among children aged 10-12 in 2000 – a figure that ballooned to 80% in 2020, the researchers found.
Both the number of calls and the proportion related to suicide attempts increased among children aged 10-12, Dr. Sheridan says. By 2020, the researchers found, poison control centers were fielding 4.5 times as many suicide-related calls among kids of this age group as they had in 2000. This jump was the largest such increase for any age group in the study, he says.
The reasons for such a large increase of suicide-related calls among preadolescents are unclear, the researchers note.
The increase became apparent around 2013, at the time many popular social media networks launched. Dr. Sheridan and his colleagues cite studies showing an association between spending more time on social media or watching television and depression in adolescence but said further research is needed to understand the root causes of this increase.
The latest study did not look specifically at the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on suicide among young people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention earlier reported a sharp rise in suicide attempts among youth during the early months of the pandemic, especially among girls aged 12-17 years. By February 2021, suicide attempts within this group had climbed by 50%, compared with 2 years earlier.
Although suicide attempts are concerning enough, deaths by suicide are even more worrisome, experts said.
The researchers’ findings are consistent with overall recent trends in youth suicide deaths, says Jeff Bridge, PhD, an epidemiologist at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus. From 2010-2020, suicide rates increased by 50% among 13- to 18-year-olds, Dr. Bridge said, and more than doubled in children aged 10-12.
The latest study captured only calls to poison control centers, so it did not count suicide attempts that did not result in a call for help. Another limitation of the study is that poison control data are not categorized by race or ethnicity, prompting Dr. Bridge to urge researchers to look specifically at the effect of race and ethnicity on these trends.
“This study supports screening for suicide risk as young as 10 years old,” Dr. Bridge says.
Dr. Sheridan agrees that prevention is essential: “The ER is where kids come when they’re in crisis. Trying to be more preventative by diagnosing or picking up on this earlier, I think, is really important.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Psychedelics’ interaction with psych meds: More questions than answers
“Despite prolific psychedelic research and public interest, I was surprised to see little clinical research on how psilocybin and common psychiatric treatments interact,” study investigator Aryan Sarparast, MD, department of psychiatry, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, told this news organization.
The review was published online March 7, 2022, in Psychopharmacology.
Need for RCTs
The Food and Drug Administration recently granted breakthrough therapy designation to psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for major depression and treatment-resistant depression and to MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD.
The investigators assessed the volume of available research on interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications, such as antidepressants.
They found 40 studies dating back to 1958, including 26 randomized controlled trials, 11 case reports, and 3 epidemiologic studies.
Only one randomized clinical trial evaluated the interaction between psilocybin and the most common psychiatric treatment, SSRIs, said Dr. Sarparast.
However, this study is “reassuring and overlaps with our hypothesis that there is a low risk of psilocybin and most psychiatric drugs causing harm when combined,” he noted.
Yet all of the clinical trials exclusively included young healthy adults, who were often recruited from university campuses. “We don’t have data on what happens when a depressed person on an SSRI takes psilocybin,” said Dr. Sarparast.
He added that he is concerned that the lack of evidence on drug-drug interactions will lead some providers to require patients to be tapered off existing traditional psychiatric medications before initiation of psilocybin therapy.
This may force vulnerable patients to choose between their existing therapy and psilocybin.
In addition, patients who opt for the “DIY method” of tapering risk mental health relapse and medication withdrawal effects. “That’s a very, very tough place to be,” Dr. Sarparast said.
Ideally, Dr. Sarparast would like to see a study in which depressed patients who have been receiving long-term antidepressant treatment are randomly assigned to received low, medium, and high doses of psilocybin. “This would clarify a lot of question marks.”
Evidence gap
In a comment, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, said: “The point in this article is very well taken. Indeed, more research is needed” on potential interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications.
“Before we embark on completing research and development for psychedelics – or, for that matter, any psychoactive substance – we should endeavor to identify what the potential safety and toxicity concerns are when they are coprescribed with other prescribed medications, over-the-counter medications, and other substances (e.g., marijuana) that people take,” Dr. McIntyre said.
A case in point – a 2017 study conducted by McIntyre and colleagues revealed “significant drug-drug interactions with cannabis, which never receives that much attention.”
Also weighing in, Albert Garcia-Romeu, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, confirmed that there is “an evidence gap” on psilocybin’s and other psychedelic drugs’ interactions with other medications.
“This has not been formally studied for a number of reasons, but mainly because psilocybin has primarily been considered a drug of abuse. Psilocybin has only recently started to be looked at as a potential medication, and as such, research on drug-drug interactions is still limited, but growing,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu told this news organization.
He noted that studies are underway to better understand potential interactions between psilocybin and other medications.
“This will allow us to better understand how psilocybin should be used medically and what types of interactions could occur with other drugs or medications,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sarparast, Dr. McIntyre, and Dr. Garcia-Romeu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Despite prolific psychedelic research and public interest, I was surprised to see little clinical research on how psilocybin and common psychiatric treatments interact,” study investigator Aryan Sarparast, MD, department of psychiatry, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, told this news organization.
The review was published online March 7, 2022, in Psychopharmacology.
Need for RCTs
The Food and Drug Administration recently granted breakthrough therapy designation to psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for major depression and treatment-resistant depression and to MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD.
The investigators assessed the volume of available research on interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications, such as antidepressants.
They found 40 studies dating back to 1958, including 26 randomized controlled trials, 11 case reports, and 3 epidemiologic studies.
Only one randomized clinical trial evaluated the interaction between psilocybin and the most common psychiatric treatment, SSRIs, said Dr. Sarparast.
However, this study is “reassuring and overlaps with our hypothesis that there is a low risk of psilocybin and most psychiatric drugs causing harm when combined,” he noted.
Yet all of the clinical trials exclusively included young healthy adults, who were often recruited from university campuses. “We don’t have data on what happens when a depressed person on an SSRI takes psilocybin,” said Dr. Sarparast.
He added that he is concerned that the lack of evidence on drug-drug interactions will lead some providers to require patients to be tapered off existing traditional psychiatric medications before initiation of psilocybin therapy.
This may force vulnerable patients to choose between their existing therapy and psilocybin.
In addition, patients who opt for the “DIY method” of tapering risk mental health relapse and medication withdrawal effects. “That’s a very, very tough place to be,” Dr. Sarparast said.
Ideally, Dr. Sarparast would like to see a study in which depressed patients who have been receiving long-term antidepressant treatment are randomly assigned to received low, medium, and high doses of psilocybin. “This would clarify a lot of question marks.”
Evidence gap
In a comment, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, said: “The point in this article is very well taken. Indeed, more research is needed” on potential interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications.
“Before we embark on completing research and development for psychedelics – or, for that matter, any psychoactive substance – we should endeavor to identify what the potential safety and toxicity concerns are when they are coprescribed with other prescribed medications, over-the-counter medications, and other substances (e.g., marijuana) that people take,” Dr. McIntyre said.
A case in point – a 2017 study conducted by McIntyre and colleagues revealed “significant drug-drug interactions with cannabis, which never receives that much attention.”
Also weighing in, Albert Garcia-Romeu, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, confirmed that there is “an evidence gap” on psilocybin’s and other psychedelic drugs’ interactions with other medications.
“This has not been formally studied for a number of reasons, but mainly because psilocybin has primarily been considered a drug of abuse. Psilocybin has only recently started to be looked at as a potential medication, and as such, research on drug-drug interactions is still limited, but growing,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu told this news organization.
He noted that studies are underway to better understand potential interactions between psilocybin and other medications.
“This will allow us to better understand how psilocybin should be used medically and what types of interactions could occur with other drugs or medications,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sarparast, Dr. McIntyre, and Dr. Garcia-Romeu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Despite prolific psychedelic research and public interest, I was surprised to see little clinical research on how psilocybin and common psychiatric treatments interact,” study investigator Aryan Sarparast, MD, department of psychiatry, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, told this news organization.
The review was published online March 7, 2022, in Psychopharmacology.
Need for RCTs
The Food and Drug Administration recently granted breakthrough therapy designation to psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for major depression and treatment-resistant depression and to MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD.
The investigators assessed the volume of available research on interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications, such as antidepressants.
They found 40 studies dating back to 1958, including 26 randomized controlled trials, 11 case reports, and 3 epidemiologic studies.
Only one randomized clinical trial evaluated the interaction between psilocybin and the most common psychiatric treatment, SSRIs, said Dr. Sarparast.
However, this study is “reassuring and overlaps with our hypothesis that there is a low risk of psilocybin and most psychiatric drugs causing harm when combined,” he noted.
Yet all of the clinical trials exclusively included young healthy adults, who were often recruited from university campuses. “We don’t have data on what happens when a depressed person on an SSRI takes psilocybin,” said Dr. Sarparast.
He added that he is concerned that the lack of evidence on drug-drug interactions will lead some providers to require patients to be tapered off existing traditional psychiatric medications before initiation of psilocybin therapy.
This may force vulnerable patients to choose between their existing therapy and psilocybin.
In addition, patients who opt for the “DIY method” of tapering risk mental health relapse and medication withdrawal effects. “That’s a very, very tough place to be,” Dr. Sarparast said.
Ideally, Dr. Sarparast would like to see a study in which depressed patients who have been receiving long-term antidepressant treatment are randomly assigned to received low, medium, and high doses of psilocybin. “This would clarify a lot of question marks.”
Evidence gap
In a comment, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, said: “The point in this article is very well taken. Indeed, more research is needed” on potential interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications.
“Before we embark on completing research and development for psychedelics – or, for that matter, any psychoactive substance – we should endeavor to identify what the potential safety and toxicity concerns are when they are coprescribed with other prescribed medications, over-the-counter medications, and other substances (e.g., marijuana) that people take,” Dr. McIntyre said.
A case in point – a 2017 study conducted by McIntyre and colleagues revealed “significant drug-drug interactions with cannabis, which never receives that much attention.”
Also weighing in, Albert Garcia-Romeu, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, confirmed that there is “an evidence gap” on psilocybin’s and other psychedelic drugs’ interactions with other medications.
“This has not been formally studied for a number of reasons, but mainly because psilocybin has primarily been considered a drug of abuse. Psilocybin has only recently started to be looked at as a potential medication, and as such, research on drug-drug interactions is still limited, but growing,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu told this news organization.
He noted that studies are underway to better understand potential interactions between psilocybin and other medications.
“This will allow us to better understand how psilocybin should be used medically and what types of interactions could occur with other drugs or medications,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sarparast, Dr. McIntyre, and Dr. Garcia-Romeu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY
‘Alarming’ worldwide decline in mental health
The Mental Health Million project of Sapien Labs issued its second report, published online March 15, encompassing 34 countries and over 220,000 Internet-enabled adults. It found a continued decline in mental health in all age groups and genders, with English-speaking countries having the lowest mental well-being.
The decline was significantly correlated with the stringency of COVID-19 lockdown measures in each country and was directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
The youngest age group (18-24 years) reported the poorest mental well-being, with better mental health scores rising in every successively older age group.
“Some of our findings, especially regarding mental health in young adults, are alarming,” Tara Thiagarajan, PhD, Sapien Labs founder and chief scientist, told this news organization.
“Our data, which are continually updated in real time, are freely available for nonprofit, noncommercial use and research, and we hope that researchers will get involved in an interdisciplinary way that spans sociology, economics, psychiatry, and other fields,” she said.
Pioneering research
Dr. Thiagarajan and her team pioneered the Mental Health Million project, an ongoing research initiative utilizing a “free and anonymous assessment tool,” the Mental Health Quotient (MHQ), which “encompasses a comprehensive view of our emotional, social, and cognitive function and capability.”
The MHQ consists of 47 “elements of mental well-being,” with scores ranging from –100 to +200. (Negative scores indicate poorer mental well-being.) The MHQ categorizes respondents as “clinical, at-risk, enduring, managing, succeeding, and thriving” and computes scores on the basis of six broad dimensions of mental health: core cognition, complex cognition, mood and outlook, drive and motivation, social self, and mind-body connection.
As reported by this news organization, Sapien Lab’s first Mental Health State of the World report (n = 49,000 adults) was conducted in eight English-speaking countries in 2020. Participants were compared to a smaller sample of people from the same countries polled in 2019.
In this year’s report, “we expanded quite substantially,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. The project added Spanish, French, and Arabic and recruited participants from 34 countries on six continents (n = 223,087) via advertising on Google and Facebook.
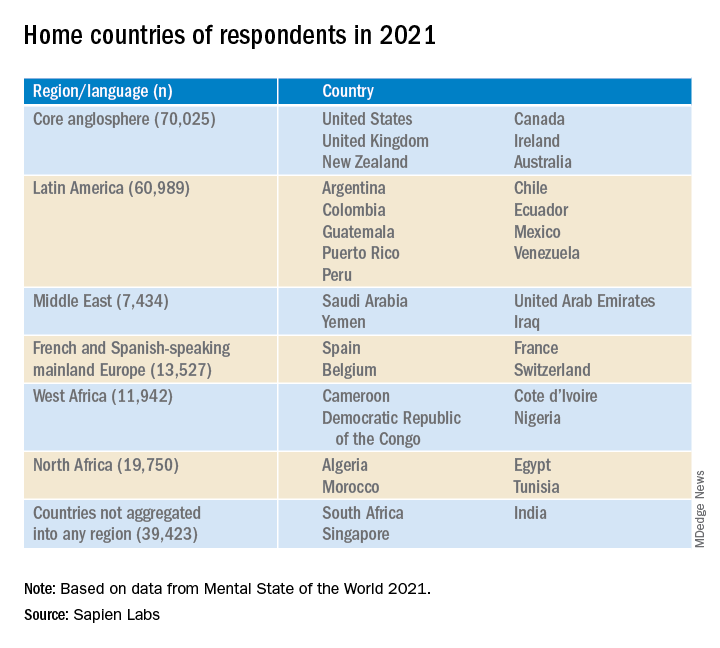
Economic prosperity not protective
Across the eight English-speaking countries, there was a decline in mental well-being of 3% from 2020 to 2021, which was smaller than the 8% decline from 2019 to 2020. The percentage of people who were “distressed or struggling” increased from 26% to 30% in 2021.
“Now that a lot of pandemic issue seems to be easing up, I hope we’ll see mental well-being coming back up, but at least it’s a smaller decline than we saw between 2019 and 2020,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
The decline across countries from 2019 to 2021 was significantly correlated with the stringency of governmental COVID-19-related measures (based on the Oxford COVID-19 Government Response Tracker, 2022; r = .54) and directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
In total, 30% of respondents in English-speaking countries had mental well-being scores in the “distressed” or “struggling” range – higher than the Middle Eastern countries, North Africa, Latin America, and Europe (23%, 23%, 24%, and 18%, respectively).
Only 36% of participants in the English-speaking countries, the Middle East, and North Africa reported “thriving or succeeding,” vs. 45% and 46% in Latin America and Europe, respectively. Venezuela topped the list with an average MHQ of 91, while the United Kingdom and South Africa had the lowest scores, at 46 each.
Mental well-being was slightly higher in males than in females but was dramatically lower in nonbinary/third-gender respondents. In fact, those identifying as nonbinary/third gender had the lowest mental well-being of any group.
Across all countries and languages, higher education was associated with better mental well-being. Employment was also associated with superior mental well-being, compared with being unemployed – particularly in core English-speaking countries.
However, “country indicators of economic prosperity were negatively correlated with mental well-being, particularly for young adults and males, belying the commonly held belief that national economic prosperity translates into greater mental well-being,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
‘Stark’ contrast
The most dramatic finding was the difference in mental well-being between younger and older adults, which was two- to threefold larger than differences in other dimensions (for example, age, gender, employment). Even the maximum difference between countries overall (15%) was still smaller than the generational gap within any region.
While only 7% (6%- 9%) of participants aged ≥65 years were “distressed and struggling” with their mental well-being to a “clinical” extent, 44% (38%-50%) of those aged 18-24 years reported mental well-being scores in the “distressed or struggling” range – representing a “growing gap between generations that, while present prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has since been exacerbated,” the authors state.
With every successive decrement in age group, mental well-being “plummeted,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. She noted that research conducted prior to 2010 in several regions of the world showed that young adults typically had the highest well-being. “Our findings stand in stark contrast to these previous patterns.”
The relationship between lockdown stringency and poorer mental health could play a role. “The impact of social isolation may be most strongly felt in younger people,” she said.
Internet a culprit?
“Within almost every region, scores for cognition and drive and motivation were highest while mood and outlook and social self were the lowest,” the authors report.
The aggregate percentage of respondents who reported being “distressed or struggling” in the various MHQ dimensions is shown in the following table.
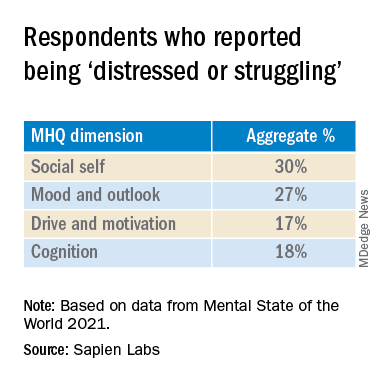
In particular, English-speaking countries scored lowest on the social self scale.
The sense of social self is “how you see yourself with respect to others, how you relate to others and the ability to form strong, stable relationships and maintain them with other people,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
Internet use might account for the “massive” difference between the youngest and the oldest generations, she suggested. “Following 2010, mobile phone penetration picked up and rose rapidly. ... Mobile phones took over the world.”
Time spent on the Internet – an estimated 7-10 hours per day – “eats into the time people in older generations used in building the social self. Kids who grow up on the Internet are losing thousands of hours in social interactions, which is challenging their ability to form relationships, how they see themselves, and how they fit into the social fabric,” Dr. Thiagarajan added
Sedentary time
Commenting for this news organization, Bernardo Ng, MD, a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on International Psychiatry and Global Health and medical director of Sun Valley Research Center, Imperial, Calif., called the report “interesting, with an impressive sample size” and an “impressive geographic distribution.”
Dr. Ng, who was not involved in the report, said, “I did not think the impact of Internet use on mental health was as dramatic before looking at this report.
“On the other hand, I have personally been interested in the impact of sedentarism in mental health – not only emotionally but also biologically. Sedentarism, which is directly related to screen use time, produces inflammation that worsens brain function.”
Also commenting, Ken Duckworth, MD, chief medical officer of the National Alliance of Mental Illness, called the survey “extremely well timed and creative, although it looked only at Internet-enabled populations, so one cannot make too many overall pronouncements, because a lot of people don’t have access to the Internet.”
The data regarding young people are particularly powerful. “The idea that young people are having a decrease in their experience of mental health across the world is something I haven’t seen before.”
Dr. Duckworth suggested the reason might “have to do with the impact of the COVID lockdown on normal development that young people go through, while older people don’t struggle with these developmental challenges in the same way.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Mental Health Million project of Sapien Labs issued its second report, published online March 15, encompassing 34 countries and over 220,000 Internet-enabled adults. It found a continued decline in mental health in all age groups and genders, with English-speaking countries having the lowest mental well-being.
The decline was significantly correlated with the stringency of COVID-19 lockdown measures in each country and was directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
The youngest age group (18-24 years) reported the poorest mental well-being, with better mental health scores rising in every successively older age group.
“Some of our findings, especially regarding mental health in young adults, are alarming,” Tara Thiagarajan, PhD, Sapien Labs founder and chief scientist, told this news organization.
“Our data, which are continually updated in real time, are freely available for nonprofit, noncommercial use and research, and we hope that researchers will get involved in an interdisciplinary way that spans sociology, economics, psychiatry, and other fields,” she said.
Pioneering research
Dr. Thiagarajan and her team pioneered the Mental Health Million project, an ongoing research initiative utilizing a “free and anonymous assessment tool,” the Mental Health Quotient (MHQ), which “encompasses a comprehensive view of our emotional, social, and cognitive function and capability.”
The MHQ consists of 47 “elements of mental well-being,” with scores ranging from –100 to +200. (Negative scores indicate poorer mental well-being.) The MHQ categorizes respondents as “clinical, at-risk, enduring, managing, succeeding, and thriving” and computes scores on the basis of six broad dimensions of mental health: core cognition, complex cognition, mood and outlook, drive and motivation, social self, and mind-body connection.
As reported by this news organization, Sapien Lab’s first Mental Health State of the World report (n = 49,000 adults) was conducted in eight English-speaking countries in 2020. Participants were compared to a smaller sample of people from the same countries polled in 2019.
In this year’s report, “we expanded quite substantially,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. The project added Spanish, French, and Arabic and recruited participants from 34 countries on six continents (n = 223,087) via advertising on Google and Facebook.

Economic prosperity not protective
Across the eight English-speaking countries, there was a decline in mental well-being of 3% from 2020 to 2021, which was smaller than the 8% decline from 2019 to 2020. The percentage of people who were “distressed or struggling” increased from 26% to 30% in 2021.
“Now that a lot of pandemic issue seems to be easing up, I hope we’ll see mental well-being coming back up, but at least it’s a smaller decline than we saw between 2019 and 2020,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
The decline across countries from 2019 to 2021 was significantly correlated with the stringency of governmental COVID-19-related measures (based on the Oxford COVID-19 Government Response Tracker, 2022; r = .54) and directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
In total, 30% of respondents in English-speaking countries had mental well-being scores in the “distressed” or “struggling” range – higher than the Middle Eastern countries, North Africa, Latin America, and Europe (23%, 23%, 24%, and 18%, respectively).
Only 36% of participants in the English-speaking countries, the Middle East, and North Africa reported “thriving or succeeding,” vs. 45% and 46% in Latin America and Europe, respectively. Venezuela topped the list with an average MHQ of 91, while the United Kingdom and South Africa had the lowest scores, at 46 each.
Mental well-being was slightly higher in males than in females but was dramatically lower in nonbinary/third-gender respondents. In fact, those identifying as nonbinary/third gender had the lowest mental well-being of any group.
Across all countries and languages, higher education was associated with better mental well-being. Employment was also associated with superior mental well-being, compared with being unemployed – particularly in core English-speaking countries.
However, “country indicators of economic prosperity were negatively correlated with mental well-being, particularly for young adults and males, belying the commonly held belief that national economic prosperity translates into greater mental well-being,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
‘Stark’ contrast
The most dramatic finding was the difference in mental well-being between younger and older adults, which was two- to threefold larger than differences in other dimensions (for example, age, gender, employment). Even the maximum difference between countries overall (15%) was still smaller than the generational gap within any region.
While only 7% (6%- 9%) of participants aged ≥65 years were “distressed and struggling” with their mental well-being to a “clinical” extent, 44% (38%-50%) of those aged 18-24 years reported mental well-being scores in the “distressed or struggling” range – representing a “growing gap between generations that, while present prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has since been exacerbated,” the authors state.
With every successive decrement in age group, mental well-being “plummeted,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. She noted that research conducted prior to 2010 in several regions of the world showed that young adults typically had the highest well-being. “Our findings stand in stark contrast to these previous patterns.”
The relationship between lockdown stringency and poorer mental health could play a role. “The impact of social isolation may be most strongly felt in younger people,” she said.
Internet a culprit?
“Within almost every region, scores for cognition and drive and motivation were highest while mood and outlook and social self were the lowest,” the authors report.
The aggregate percentage of respondents who reported being “distressed or struggling” in the various MHQ dimensions is shown in the following table.

In particular, English-speaking countries scored lowest on the social self scale.
The sense of social self is “how you see yourself with respect to others, how you relate to others and the ability to form strong, stable relationships and maintain them with other people,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
Internet use might account for the “massive” difference between the youngest and the oldest generations, she suggested. “Following 2010, mobile phone penetration picked up and rose rapidly. ... Mobile phones took over the world.”
Time spent on the Internet – an estimated 7-10 hours per day – “eats into the time people in older generations used in building the social self. Kids who grow up on the Internet are losing thousands of hours in social interactions, which is challenging their ability to form relationships, how they see themselves, and how they fit into the social fabric,” Dr. Thiagarajan added
Sedentary time
Commenting for this news organization, Bernardo Ng, MD, a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on International Psychiatry and Global Health and medical director of Sun Valley Research Center, Imperial, Calif., called the report “interesting, with an impressive sample size” and an “impressive geographic distribution.”
Dr. Ng, who was not involved in the report, said, “I did not think the impact of Internet use on mental health was as dramatic before looking at this report.
“On the other hand, I have personally been interested in the impact of sedentarism in mental health – not only emotionally but also biologically. Sedentarism, which is directly related to screen use time, produces inflammation that worsens brain function.”
Also commenting, Ken Duckworth, MD, chief medical officer of the National Alliance of Mental Illness, called the survey “extremely well timed and creative, although it looked only at Internet-enabled populations, so one cannot make too many overall pronouncements, because a lot of people don’t have access to the Internet.”
The data regarding young people are particularly powerful. “The idea that young people are having a decrease in their experience of mental health across the world is something I haven’t seen before.”
Dr. Duckworth suggested the reason might “have to do with the impact of the COVID lockdown on normal development that young people go through, while older people don’t struggle with these developmental challenges in the same way.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Mental Health Million project of Sapien Labs issued its second report, published online March 15, encompassing 34 countries and over 220,000 Internet-enabled adults. It found a continued decline in mental health in all age groups and genders, with English-speaking countries having the lowest mental well-being.
The decline was significantly correlated with the stringency of COVID-19 lockdown measures in each country and was directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
The youngest age group (18-24 years) reported the poorest mental well-being, with better mental health scores rising in every successively older age group.
“Some of our findings, especially regarding mental health in young adults, are alarming,” Tara Thiagarajan, PhD, Sapien Labs founder and chief scientist, told this news organization.
“Our data, which are continually updated in real time, are freely available for nonprofit, noncommercial use and research, and we hope that researchers will get involved in an interdisciplinary way that spans sociology, economics, psychiatry, and other fields,” she said.
Pioneering research
Dr. Thiagarajan and her team pioneered the Mental Health Million project, an ongoing research initiative utilizing a “free and anonymous assessment tool,” the Mental Health Quotient (MHQ), which “encompasses a comprehensive view of our emotional, social, and cognitive function and capability.”
The MHQ consists of 47 “elements of mental well-being,” with scores ranging from –100 to +200. (Negative scores indicate poorer mental well-being.) The MHQ categorizes respondents as “clinical, at-risk, enduring, managing, succeeding, and thriving” and computes scores on the basis of six broad dimensions of mental health: core cognition, complex cognition, mood and outlook, drive and motivation, social self, and mind-body connection.
As reported by this news organization, Sapien Lab’s first Mental Health State of the World report (n = 49,000 adults) was conducted in eight English-speaking countries in 2020. Participants were compared to a smaller sample of people from the same countries polled in 2019.
In this year’s report, “we expanded quite substantially,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. The project added Spanish, French, and Arabic and recruited participants from 34 countries on six continents (n = 223,087) via advertising on Google and Facebook.

Economic prosperity not protective
Across the eight English-speaking countries, there was a decline in mental well-being of 3% from 2020 to 2021, which was smaller than the 8% decline from 2019 to 2020. The percentage of people who were “distressed or struggling” increased from 26% to 30% in 2021.
“Now that a lot of pandemic issue seems to be easing up, I hope we’ll see mental well-being coming back up, but at least it’s a smaller decline than we saw between 2019 and 2020,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
The decline across countries from 2019 to 2021 was significantly correlated with the stringency of governmental COVID-19-related measures (based on the Oxford COVID-19 Government Response Tracker, 2022; r = .54) and directionally correlated to the cases and deaths per million.
In total, 30% of respondents in English-speaking countries had mental well-being scores in the “distressed” or “struggling” range – higher than the Middle Eastern countries, North Africa, Latin America, and Europe (23%, 23%, 24%, and 18%, respectively).
Only 36% of participants in the English-speaking countries, the Middle East, and North Africa reported “thriving or succeeding,” vs. 45% and 46% in Latin America and Europe, respectively. Venezuela topped the list with an average MHQ of 91, while the United Kingdom and South Africa had the lowest scores, at 46 each.
Mental well-being was slightly higher in males than in females but was dramatically lower in nonbinary/third-gender respondents. In fact, those identifying as nonbinary/third gender had the lowest mental well-being of any group.
Across all countries and languages, higher education was associated with better mental well-being. Employment was also associated with superior mental well-being, compared with being unemployed – particularly in core English-speaking countries.
However, “country indicators of economic prosperity were negatively correlated with mental well-being, particularly for young adults and males, belying the commonly held belief that national economic prosperity translates into greater mental well-being,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
‘Stark’ contrast
The most dramatic finding was the difference in mental well-being between younger and older adults, which was two- to threefold larger than differences in other dimensions (for example, age, gender, employment). Even the maximum difference between countries overall (15%) was still smaller than the generational gap within any region.
While only 7% (6%- 9%) of participants aged ≥65 years were “distressed and struggling” with their mental well-being to a “clinical” extent, 44% (38%-50%) of those aged 18-24 years reported mental well-being scores in the “distressed or struggling” range – representing a “growing gap between generations that, while present prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has since been exacerbated,” the authors state.
With every successive decrement in age group, mental well-being “plummeted,” Dr. Thiagarajan said. She noted that research conducted prior to 2010 in several regions of the world showed that young adults typically had the highest well-being. “Our findings stand in stark contrast to these previous patterns.”
The relationship between lockdown stringency and poorer mental health could play a role. “The impact of social isolation may be most strongly felt in younger people,” she said.
Internet a culprit?
“Within almost every region, scores for cognition and drive and motivation were highest while mood and outlook and social self were the lowest,” the authors report.
The aggregate percentage of respondents who reported being “distressed or struggling” in the various MHQ dimensions is shown in the following table.

In particular, English-speaking countries scored lowest on the social self scale.
The sense of social self is “how you see yourself with respect to others, how you relate to others and the ability to form strong, stable relationships and maintain them with other people,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
Internet use might account for the “massive” difference between the youngest and the oldest generations, she suggested. “Following 2010, mobile phone penetration picked up and rose rapidly. ... Mobile phones took over the world.”
Time spent on the Internet – an estimated 7-10 hours per day – “eats into the time people in older generations used in building the social self. Kids who grow up on the Internet are losing thousands of hours in social interactions, which is challenging their ability to form relationships, how they see themselves, and how they fit into the social fabric,” Dr. Thiagarajan added
Sedentary time
Commenting for this news organization, Bernardo Ng, MD, a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on International Psychiatry and Global Health and medical director of Sun Valley Research Center, Imperial, Calif., called the report “interesting, with an impressive sample size” and an “impressive geographic distribution.”
Dr. Ng, who was not involved in the report, said, “I did not think the impact of Internet use on mental health was as dramatic before looking at this report.
“On the other hand, I have personally been interested in the impact of sedentarism in mental health – not only emotionally but also biologically. Sedentarism, which is directly related to screen use time, produces inflammation that worsens brain function.”
Also commenting, Ken Duckworth, MD, chief medical officer of the National Alliance of Mental Illness, called the survey “extremely well timed and creative, although it looked only at Internet-enabled populations, so one cannot make too many overall pronouncements, because a lot of people don’t have access to the Internet.”
The data regarding young people are particularly powerful. “The idea that young people are having a decrease in their experience of mental health across the world is something I haven’t seen before.”
Dr. Duckworth suggested the reason might “have to do with the impact of the COVID lockdown on normal development that young people go through, while older people don’t struggle with these developmental challenges in the same way.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.



















