User login
Breathing enriched oxygen improves major depression
Maybe the hipsters patronizing trendy oxygen bars seeking elevation of mood back in the prepandemic era were actually onto something – because Israeli investigators have now shown in a pilot double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial that breathing enriched oxygen on a nightly basis resulted in clinically meaningful symptomatic improvement in mild to moderate major depression.
“We saw a highly significant effect of normobaric hyperoxia therapy in lowering Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression scores,” R. Haim Belmaker, MD, reported at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
In addition, the patients on enriched oxygen also showed statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements relative to sham-treated controls on the secondary endpoints of Clinical Global Impressions Scale, the World Health Organization–Five Well-Being Index, the Sheehan Disability Scale, and the Sense of Coherence Scale, added Dr. Belmaker, professor emeritus of psychiatry at the Ben Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheva, Israel.
Numerous PET imaging studies have documented diminished brain mitochondrial function in patients with depression or schizophrenia. And mitochondria need oxygen to do their work. Yet, the idea of administering enriched oxygen in an effort to boost mitochondrial energy metabolism has long been viewed with skepticism – even though it’s a simple and well-tolerated intervention – because of the fact that 90%-95% of the oxygen supply is carried bound to hemoglobin, and oxygen enrichment doesn’t further increase hemoglobin saturation in individuals with normal lung function. However, recently it has been shown that inspired enriched oxygen roughly doubles arterial oxygen tension, and while this doesn’t translate into anything close to a doubled oxygen supply to tissues, it may result in increased oxygen diffusion into brain tissue, the psychiatrist explained.
Normobaric hyperoxia therapy is not to be confused with hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which requires a special chamber to handle markedly increased atmospheric pressures and has some inherent dangers. Mobile bedside oxygen generator units for oxygen enrichment are commercially available over the counter. Those used in the Israeli study were about the size of a vacuum cleaner and weighed a little more than 40 lb. Much smaller, more convenient units are available as well, but are costlier.
Dr. Belmaker reported on 51 adults with mild or moderate symptoms of major depressive disorder and a mean 11-year disease history who were randomized double blind to breathe either 35% oxygen or normal air – that is, 21% oxygen – at 1 atm pressure delivered from an investigator-supplied oxygen generator through standard plastic nasal prongs at a flow rate of 5 L/min for 7 hours nightly for 1 month.
“Controls heard the same flow and felt the same feeling on the face but were receiving 21% oxygen,” he noted.
Oxygen generator units are capable of enriching air to more than 90% oxygen; however, the investigators wanted to be cautious in a pilot study of an untested therapy, and they found evidence from both animal and human studies that 40% oxygen is reassuringly safe. Study exclusion criteria included obesity, acute or chronic respiratory disease, psychosis, and suicidality.
The primary study endpoint was the change in Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression score at 1 month. From a mean baseline of 14.6, the score in the normobaric hyperoxia group dropped by more than 4 points while remaining unchanged in controls. In a subscale analysis, it was apparent that most of the improvement occurred in the anxiety and cognitive disturbance subscale domains, according to Dr. Belmaker.
Of note, all patients rated by blinded investigators as much improved or very much improved on the Clinical Global Impression scale came from the enriched oxygen group.
No treatment-related adverse events occurred in the study.
“We don’t know the mechanism of the benefit of oxygen on the brain. It’s complex. In stroke and acute MI we used to think oxygen was beneficial, but scientists now feel that it’s not,” the psychiatrist said. “This early data deserve replication with higher concentrations of oxygen, different time periods of application, and in different patient groups.”
He emphasized that, since individuals with physical illnesses – including sleep apnea and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease – were excluded from the study, it’s not possible to say whether normobaric hyperoxia therapy would have an antidepressant effect in such patients.
“I would be especially careful with the normobaric oxygen in any patients with any cardiovascular or hypertensive disease because the increased oxygen pressure can have the side effect of contracting cardiac capillaries as a reflex action. So I certainly cannot recommend applying this study in any patients with a physical disease at this point,” Dr. Belmaker emphasized.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by a grant from the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation.
SOURCE: Belmaker RH. ECNP 2020, Session S.12.
Maybe the hipsters patronizing trendy oxygen bars seeking elevation of mood back in the prepandemic era were actually onto something – because Israeli investigators have now shown in a pilot double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial that breathing enriched oxygen on a nightly basis resulted in clinically meaningful symptomatic improvement in mild to moderate major depression.
“We saw a highly significant effect of normobaric hyperoxia therapy in lowering Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression scores,” R. Haim Belmaker, MD, reported at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
In addition, the patients on enriched oxygen also showed statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements relative to sham-treated controls on the secondary endpoints of Clinical Global Impressions Scale, the World Health Organization–Five Well-Being Index, the Sheehan Disability Scale, and the Sense of Coherence Scale, added Dr. Belmaker, professor emeritus of psychiatry at the Ben Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheva, Israel.
Numerous PET imaging studies have documented diminished brain mitochondrial function in patients with depression or schizophrenia. And mitochondria need oxygen to do their work. Yet, the idea of administering enriched oxygen in an effort to boost mitochondrial energy metabolism has long been viewed with skepticism – even though it’s a simple and well-tolerated intervention – because of the fact that 90%-95% of the oxygen supply is carried bound to hemoglobin, and oxygen enrichment doesn’t further increase hemoglobin saturation in individuals with normal lung function. However, recently it has been shown that inspired enriched oxygen roughly doubles arterial oxygen tension, and while this doesn’t translate into anything close to a doubled oxygen supply to tissues, it may result in increased oxygen diffusion into brain tissue, the psychiatrist explained.
Normobaric hyperoxia therapy is not to be confused with hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which requires a special chamber to handle markedly increased atmospheric pressures and has some inherent dangers. Mobile bedside oxygen generator units for oxygen enrichment are commercially available over the counter. Those used in the Israeli study were about the size of a vacuum cleaner and weighed a little more than 40 lb. Much smaller, more convenient units are available as well, but are costlier.
Dr. Belmaker reported on 51 adults with mild or moderate symptoms of major depressive disorder and a mean 11-year disease history who were randomized double blind to breathe either 35% oxygen or normal air – that is, 21% oxygen – at 1 atm pressure delivered from an investigator-supplied oxygen generator through standard plastic nasal prongs at a flow rate of 5 L/min for 7 hours nightly for 1 month.
“Controls heard the same flow and felt the same feeling on the face but were receiving 21% oxygen,” he noted.
Oxygen generator units are capable of enriching air to more than 90% oxygen; however, the investigators wanted to be cautious in a pilot study of an untested therapy, and they found evidence from both animal and human studies that 40% oxygen is reassuringly safe. Study exclusion criteria included obesity, acute or chronic respiratory disease, psychosis, and suicidality.
The primary study endpoint was the change in Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression score at 1 month. From a mean baseline of 14.6, the score in the normobaric hyperoxia group dropped by more than 4 points while remaining unchanged in controls. In a subscale analysis, it was apparent that most of the improvement occurred in the anxiety and cognitive disturbance subscale domains, according to Dr. Belmaker.
Of note, all patients rated by blinded investigators as much improved or very much improved on the Clinical Global Impression scale came from the enriched oxygen group.
No treatment-related adverse events occurred in the study.
“We don’t know the mechanism of the benefit of oxygen on the brain. It’s complex. In stroke and acute MI we used to think oxygen was beneficial, but scientists now feel that it’s not,” the psychiatrist said. “This early data deserve replication with higher concentrations of oxygen, different time periods of application, and in different patient groups.”
He emphasized that, since individuals with physical illnesses – including sleep apnea and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease – were excluded from the study, it’s not possible to say whether normobaric hyperoxia therapy would have an antidepressant effect in such patients.
“I would be especially careful with the normobaric oxygen in any patients with any cardiovascular or hypertensive disease because the increased oxygen pressure can have the side effect of contracting cardiac capillaries as a reflex action. So I certainly cannot recommend applying this study in any patients with a physical disease at this point,” Dr. Belmaker emphasized.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by a grant from the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation.
SOURCE: Belmaker RH. ECNP 2020, Session S.12.
Maybe the hipsters patronizing trendy oxygen bars seeking elevation of mood back in the prepandemic era were actually onto something – because Israeli investigators have now shown in a pilot double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial that breathing enriched oxygen on a nightly basis resulted in clinically meaningful symptomatic improvement in mild to moderate major depression.
“We saw a highly significant effect of normobaric hyperoxia therapy in lowering Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression scores,” R. Haim Belmaker, MD, reported at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
In addition, the patients on enriched oxygen also showed statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements relative to sham-treated controls on the secondary endpoints of Clinical Global Impressions Scale, the World Health Organization–Five Well-Being Index, the Sheehan Disability Scale, and the Sense of Coherence Scale, added Dr. Belmaker, professor emeritus of psychiatry at the Ben Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheva, Israel.
Numerous PET imaging studies have documented diminished brain mitochondrial function in patients with depression or schizophrenia. And mitochondria need oxygen to do their work. Yet, the idea of administering enriched oxygen in an effort to boost mitochondrial energy metabolism has long been viewed with skepticism – even though it’s a simple and well-tolerated intervention – because of the fact that 90%-95% of the oxygen supply is carried bound to hemoglobin, and oxygen enrichment doesn’t further increase hemoglobin saturation in individuals with normal lung function. However, recently it has been shown that inspired enriched oxygen roughly doubles arterial oxygen tension, and while this doesn’t translate into anything close to a doubled oxygen supply to tissues, it may result in increased oxygen diffusion into brain tissue, the psychiatrist explained.
Normobaric hyperoxia therapy is not to be confused with hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which requires a special chamber to handle markedly increased atmospheric pressures and has some inherent dangers. Mobile bedside oxygen generator units for oxygen enrichment are commercially available over the counter. Those used in the Israeli study were about the size of a vacuum cleaner and weighed a little more than 40 lb. Much smaller, more convenient units are available as well, but are costlier.
Dr. Belmaker reported on 51 adults with mild or moderate symptoms of major depressive disorder and a mean 11-year disease history who were randomized double blind to breathe either 35% oxygen or normal air – that is, 21% oxygen – at 1 atm pressure delivered from an investigator-supplied oxygen generator through standard plastic nasal prongs at a flow rate of 5 L/min for 7 hours nightly for 1 month.
“Controls heard the same flow and felt the same feeling on the face but were receiving 21% oxygen,” he noted.
Oxygen generator units are capable of enriching air to more than 90% oxygen; however, the investigators wanted to be cautious in a pilot study of an untested therapy, and they found evidence from both animal and human studies that 40% oxygen is reassuringly safe. Study exclusion criteria included obesity, acute or chronic respiratory disease, psychosis, and suicidality.
The primary study endpoint was the change in Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression score at 1 month. From a mean baseline of 14.6, the score in the normobaric hyperoxia group dropped by more than 4 points while remaining unchanged in controls. In a subscale analysis, it was apparent that most of the improvement occurred in the anxiety and cognitive disturbance subscale domains, according to Dr. Belmaker.
Of note, all patients rated by blinded investigators as much improved or very much improved on the Clinical Global Impression scale came from the enriched oxygen group.
No treatment-related adverse events occurred in the study.
“We don’t know the mechanism of the benefit of oxygen on the brain. It’s complex. In stroke and acute MI we used to think oxygen was beneficial, but scientists now feel that it’s not,” the psychiatrist said. “This early data deserve replication with higher concentrations of oxygen, different time periods of application, and in different patient groups.”
He emphasized that, since individuals with physical illnesses – including sleep apnea and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease – were excluded from the study, it’s not possible to say whether normobaric hyperoxia therapy would have an antidepressant effect in such patients.
“I would be especially careful with the normobaric oxygen in any patients with any cardiovascular or hypertensive disease because the increased oxygen pressure can have the side effect of contracting cardiac capillaries as a reflex action. So I certainly cannot recommend applying this study in any patients with a physical disease at this point,” Dr. Belmaker emphasized.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by a grant from the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation.
SOURCE: Belmaker RH. ECNP 2020, Session S.12.
FROM ECNP 2020
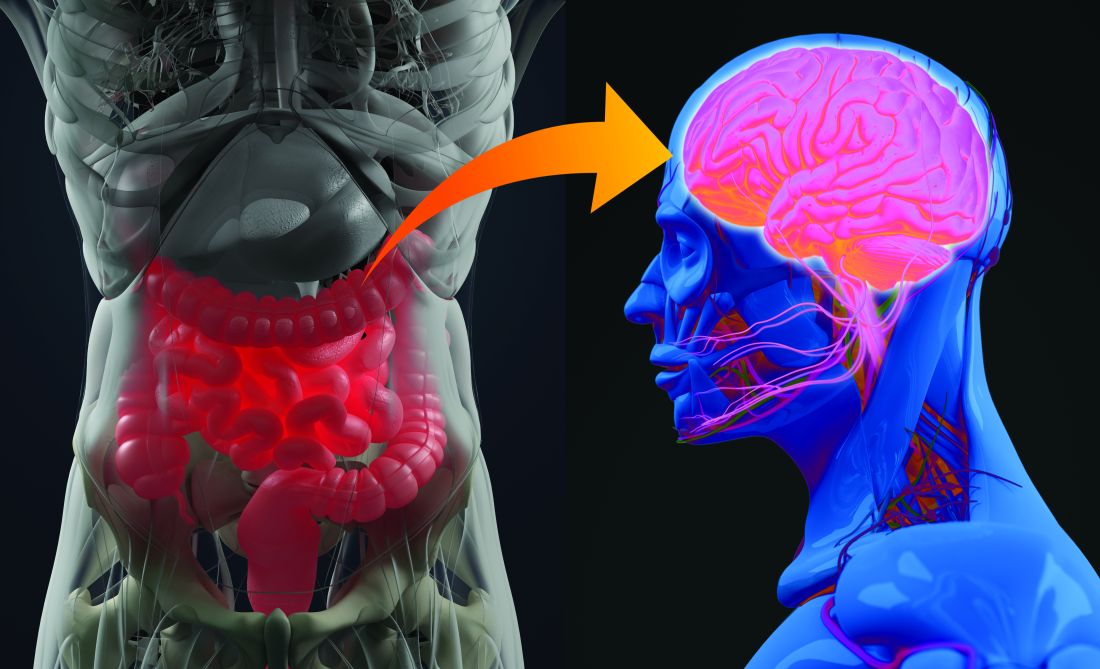
The gut a new therapeutic target for major depression?
The gut microbiota differs significantly between patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) and healthy individuals and may be modifiable with a probiotic diet to improve stress and depression scores, two new studies suggest.
In one study, investigators compared stool samples between patients with MDD and healthy controls. They found significant differences in bacterial profiles between the two groups, as well as between patients who responded vs those who were resistant to treatment.
“This finding further supports the relevance of an altered composition of the gut microbiota in the etiopathogenesis of MDD and suggests a role in response to antidepressants,” coinvestigator Andrea Fontana, MSc, Fondazione IRCCS Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza, San Giovanni Rotondo, Italy, said in an interview.
Results from the second study showed significant improvements in self-reported stress, anxiety, and depression scores in healthy individuals following a “psychobiotic” diet (using probiotics or prebiotics to manipulate the microbiota to improve mental health) that was rich in fruit, vegetables, and fermented foods vs. those who received dietary advice alone.
The investigators, led by Kirsten Berding, PhD, APC Microbiome Ireland, University College Cork, Ireland, now plan on testing their psychobiotic diet in patients with MDD and hope the findings could be helpful in “the development of adjuvant therapeutic opportunities” where pharmacologic treatment is not effective.
Both studies were presented at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A “hallmark” of major depression
Mr. Fontana and colleagues note that the mostly suboptimal response to pharmacologic treatments among patients with MDD is one of the factors that “contributes to the large socioeconomic burden” of the disease.
Previous research shows patients with MDD have gut dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the natural flora; that antidepressants have antimicrobial properties; and that probiotics have an antibiotic effect. However, the correlation between the composition of the gut microbiota and antidepressant response is poorly understood.
The investigators recruited 34 patients with MDD (aged 18-70 years) who were in a euthymic phase and who did not have comorbid conditions that could affect the gut microbiota.
Eight patients were treatment resistant, defined as a poor response to at least two adequate trials of different antidepressant classes, while 19 were treatment responsive and seven were treatment naive.
The researchers also recruited 20 healthy individuals via word of mouth to act as the control group. There were no significant differences between patients and the control group in terms of baseline characteristics.
Genomic sequencing of bacteria obtained from stool samples showed that it was possible to distinguish between patients with MDD and the healthy individuals, especially at the family, genus, and species levels.
In particular, there were significant differences in the Paenibacillaceae and Flavobacteriaceaea families, for the genus Fenollaria, and the species Flintibacter butyricus, Christensenella timonensis, and Eisenbergiella massiliensis, among others.
Results also showed that the phyla Proteobacteria, Tenericutes, and the family Peptostreptococcaceae were more common in patients with treatment-resistant MDD, whereas the phylum Actinobacteria was more abundant in treatment responders.
Moreover, several bacteria were found only in the microbiota of patients with treatment-resistant MDD, while others were seen only in treatment-responsive patients. This made it possible to discriminate not only between treatment-resistant and -responsive patients but also between those two patient groups and healthy controls.
“The results of our study confirm that gut dysbiosis is a hallmark of MDD, and suggests that the gut microbiota of patients with treatment-resistant MDD significantly differs from responders to antidepressants,” Mr. Fontana said.
Psychobiotic diet
For the second study, Dr. Berding and colleagues note that “psychobiotics” has previously achieved “promising results.”
In addition, diet is both “one of the most influential modifying factors” for the gut microbiota and an easily accessible strategy, they wrote. However, there is also a paucity of studies in this area, they added.
The researchers randomly assigned healthy volunteers with relatively poor dietary habits to either a 4-week psychobiotic diet group (n = 21) or a control group (n = 19).
Individuals in the psychobiotic group were told to eat a diet rich in prebiotics, such as fruit and vegetables, fiber including whole grains and legumes, and fermented foods. The control group was educated on Irish healthy-eating guidelines.
Stool and saliva samples were collected and the participants completed several self-reported mental health questionnaires, as well as a 7-day food diary. They also took the socially evaluated cold-pressor test (SECPT) to measure acute stress responses.
Results showed that total daily energy intake decreased significantly in both the diet and control groups over the study period (P = .04 for both) but did not differ significantly between the groups.
In contrast, dietary fiber intake increased significantly in the diet group (P < .001) and was significantly higher than in the control group at the end of the intervention (P = .03).
Individuals in the diet group showed significant decreases in scores on the Perceived Stress Scale (P = .002) and the Beck Depression Inventory (P = .007) during the study, an effect that was not found in the control group.
Dietary intervention
There were no significant effects of diet on the acute stress response, but both groups showed improvements in self-concept, or perceived ability to cope, on the Primary Appraisal, Secondary Appraisal index (P = .03 for the diet group, P = .04 for the control group).
The results show that a dietary intervention targeted at the microbiota “can improve subjective feelings of stress and depression in a healthy population,” the investigators wrote.
However, elucidating the “contribution of the microbiota-gut-brain axis on the signaling response to dietary interventions” will require further studies on microbiota sequencing and biological measures of stress, they added.
This will “contribute to the understanding of the benefits of a psychobiotic diet on stress and anxiety,” wrote the researchers.
Dr. Berding said in an interview that while the consumption of dietary fiber changed the most in the diet group, “it would not be the only nutrient” that had an impact on the results, with fermented foods a likely candidate.
She said the next step is to test the dietary intervention in patients with MDD; however, “doing nutritional interventions in diseased populations is always difficult.”
Dr. Berding suggested that the best approach would be to study inpatients in a clinic, as “we would be able to provide every meal and only provide foods that are part of the dietary intervention.”
Although another option would be to conduct the study in outpatients, she noted that assessing inpatients “would give us the best control over compliance.”
“Brilliant ideas”
Commenting on the findings, Sergueï Fetissov, MD, PhD, professor of physiology at Rouen University, Mont-Saint-Aignan, France, said that although both studies bring attention to a possible role for the gut microbiota in MDD, neither “provide any experimental evidence of a causative nature.”
Dr. Fetissov, who was not involved in either study, noted that this topic has been the subject of clinical nutritional research for many years.
However, “we still need some strong evidence to prove that some bacteria can influence the regulation of mood and anxiety and stress,” he said.
In addition, researchers currently do not know what actually causes MDD. “How we can say the gut bacteria regulates something if we don’t know what really causes the altered mood?” said Dr. Fetissov.
He noted that over the last 50 years, there have been great advances in the development of drugs that alleviate depression and anxiety by regulating dopamine, serotonin, and other neurotransmitters. However, it is still unknown whether these reflect primary or secondary aspects of mood disorders.
Furthermore, it is not clear “how probiotics to bacteria can influence these neuronal pathways,” he said.
The research by Dr. Berding and colleagues is funded by a postdoctoral fellowship grant from the Irish Research Council. The study authors and Dr. Fetissov have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The gut microbiota differs significantly between patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) and healthy individuals and may be modifiable with a probiotic diet to improve stress and depression scores, two new studies suggest.
In one study, investigators compared stool samples between patients with MDD and healthy controls. They found significant differences in bacterial profiles between the two groups, as well as between patients who responded vs those who were resistant to treatment.
“This finding further supports the relevance of an altered composition of the gut microbiota in the etiopathogenesis of MDD and suggests a role in response to antidepressants,” coinvestigator Andrea Fontana, MSc, Fondazione IRCCS Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza, San Giovanni Rotondo, Italy, said in an interview.
Results from the second study showed significant improvements in self-reported stress, anxiety, and depression scores in healthy individuals following a “psychobiotic” diet (using probiotics or prebiotics to manipulate the microbiota to improve mental health) that was rich in fruit, vegetables, and fermented foods vs. those who received dietary advice alone.
The investigators, led by Kirsten Berding, PhD, APC Microbiome Ireland, University College Cork, Ireland, now plan on testing their psychobiotic diet in patients with MDD and hope the findings could be helpful in “the development of adjuvant therapeutic opportunities” where pharmacologic treatment is not effective.
Both studies were presented at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A “hallmark” of major depression
Mr. Fontana and colleagues note that the mostly suboptimal response to pharmacologic treatments among patients with MDD is one of the factors that “contributes to the large socioeconomic burden” of the disease.
Previous research shows patients with MDD have gut dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the natural flora; that antidepressants have antimicrobial properties; and that probiotics have an antibiotic effect. However, the correlation between the composition of the gut microbiota and antidepressant response is poorly understood.
The investigators recruited 34 patients with MDD (aged 18-70 years) who were in a euthymic phase and who did not have comorbid conditions that could affect the gut microbiota.
Eight patients were treatment resistant, defined as a poor response to at least two adequate trials of different antidepressant classes, while 19 were treatment responsive and seven were treatment naive.
The researchers also recruited 20 healthy individuals via word of mouth to act as the control group. There were no significant differences between patients and the control group in terms of baseline characteristics.
Genomic sequencing of bacteria obtained from stool samples showed that it was possible to distinguish between patients with MDD and the healthy individuals, especially at the family, genus, and species levels.
In particular, there were significant differences in the Paenibacillaceae and Flavobacteriaceaea families, for the genus Fenollaria, and the species Flintibacter butyricus, Christensenella timonensis, and Eisenbergiella massiliensis, among others.
Results also showed that the phyla Proteobacteria, Tenericutes, and the family Peptostreptococcaceae were more common in patients with treatment-resistant MDD, whereas the phylum Actinobacteria was more abundant in treatment responders.
Moreover, several bacteria were found only in the microbiota of patients with treatment-resistant MDD, while others were seen only in treatment-responsive patients. This made it possible to discriminate not only between treatment-resistant and -responsive patients but also between those two patient groups and healthy controls.
“The results of our study confirm that gut dysbiosis is a hallmark of MDD, and suggests that the gut microbiota of patients with treatment-resistant MDD significantly differs from responders to antidepressants,” Mr. Fontana said.
Psychobiotic diet
For the second study, Dr. Berding and colleagues note that “psychobiotics” has previously achieved “promising results.”
In addition, diet is both “one of the most influential modifying factors” for the gut microbiota and an easily accessible strategy, they wrote. However, there is also a paucity of studies in this area, they added.
The researchers randomly assigned healthy volunteers with relatively poor dietary habits to either a 4-week psychobiotic diet group (n = 21) or a control group (n = 19).
Individuals in the psychobiotic group were told to eat a diet rich in prebiotics, such as fruit and vegetables, fiber including whole grains and legumes, and fermented foods. The control group was educated on Irish healthy-eating guidelines.
Stool and saliva samples were collected and the participants completed several self-reported mental health questionnaires, as well as a 7-day food diary. They also took the socially evaluated cold-pressor test (SECPT) to measure acute stress responses.
Results showed that total daily energy intake decreased significantly in both the diet and control groups over the study period (P = .04 for both) but did not differ significantly between the groups.
In contrast, dietary fiber intake increased significantly in the diet group (P < .001) and was significantly higher than in the control group at the end of the intervention (P = .03).
Individuals in the diet group showed significant decreases in scores on the Perceived Stress Scale (P = .002) and the Beck Depression Inventory (P = .007) during the study, an effect that was not found in the control group.
Dietary intervention
There were no significant effects of diet on the acute stress response, but both groups showed improvements in self-concept, or perceived ability to cope, on the Primary Appraisal, Secondary Appraisal index (P = .03 for the diet group, P = .04 for the control group).
The results show that a dietary intervention targeted at the microbiota “can improve subjective feelings of stress and depression in a healthy population,” the investigators wrote.
However, elucidating the “contribution of the microbiota-gut-brain axis on the signaling response to dietary interventions” will require further studies on microbiota sequencing and biological measures of stress, they added.
This will “contribute to the understanding of the benefits of a psychobiotic diet on stress and anxiety,” wrote the researchers.
Dr. Berding said in an interview that while the consumption of dietary fiber changed the most in the diet group, “it would not be the only nutrient” that had an impact on the results, with fermented foods a likely candidate.
She said the next step is to test the dietary intervention in patients with MDD; however, “doing nutritional interventions in diseased populations is always difficult.”
Dr. Berding suggested that the best approach would be to study inpatients in a clinic, as “we would be able to provide every meal and only provide foods that are part of the dietary intervention.”
Although another option would be to conduct the study in outpatients, she noted that assessing inpatients “would give us the best control over compliance.”
“Brilliant ideas”
Commenting on the findings, Sergueï Fetissov, MD, PhD, professor of physiology at Rouen University, Mont-Saint-Aignan, France, said that although both studies bring attention to a possible role for the gut microbiota in MDD, neither “provide any experimental evidence of a causative nature.”
Dr. Fetissov, who was not involved in either study, noted that this topic has been the subject of clinical nutritional research for many years.
However, “we still need some strong evidence to prove that some bacteria can influence the regulation of mood and anxiety and stress,” he said.
In addition, researchers currently do not know what actually causes MDD. “How we can say the gut bacteria regulates something if we don’t know what really causes the altered mood?” said Dr. Fetissov.
He noted that over the last 50 years, there have been great advances in the development of drugs that alleviate depression and anxiety by regulating dopamine, serotonin, and other neurotransmitters. However, it is still unknown whether these reflect primary or secondary aspects of mood disorders.
Furthermore, it is not clear “how probiotics to bacteria can influence these neuronal pathways,” he said.
The research by Dr. Berding and colleagues is funded by a postdoctoral fellowship grant from the Irish Research Council. The study authors and Dr. Fetissov have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The gut microbiota differs significantly between patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) and healthy individuals and may be modifiable with a probiotic diet to improve stress and depression scores, two new studies suggest.
In one study, investigators compared stool samples between patients with MDD and healthy controls. They found significant differences in bacterial profiles between the two groups, as well as between patients who responded vs those who were resistant to treatment.
“This finding further supports the relevance of an altered composition of the gut microbiota in the etiopathogenesis of MDD and suggests a role in response to antidepressants,” coinvestigator Andrea Fontana, MSc, Fondazione IRCCS Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza, San Giovanni Rotondo, Italy, said in an interview.
Results from the second study showed significant improvements in self-reported stress, anxiety, and depression scores in healthy individuals following a “psychobiotic” diet (using probiotics or prebiotics to manipulate the microbiota to improve mental health) that was rich in fruit, vegetables, and fermented foods vs. those who received dietary advice alone.
The investigators, led by Kirsten Berding, PhD, APC Microbiome Ireland, University College Cork, Ireland, now plan on testing their psychobiotic diet in patients with MDD and hope the findings could be helpful in “the development of adjuvant therapeutic opportunities” where pharmacologic treatment is not effective.
Both studies were presented at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A “hallmark” of major depression
Mr. Fontana and colleagues note that the mostly suboptimal response to pharmacologic treatments among patients with MDD is one of the factors that “contributes to the large socioeconomic burden” of the disease.
Previous research shows patients with MDD have gut dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the natural flora; that antidepressants have antimicrobial properties; and that probiotics have an antibiotic effect. However, the correlation between the composition of the gut microbiota and antidepressant response is poorly understood.
The investigators recruited 34 patients with MDD (aged 18-70 years) who were in a euthymic phase and who did not have comorbid conditions that could affect the gut microbiota.
Eight patients were treatment resistant, defined as a poor response to at least two adequate trials of different antidepressant classes, while 19 were treatment responsive and seven were treatment naive.
The researchers also recruited 20 healthy individuals via word of mouth to act as the control group. There were no significant differences between patients and the control group in terms of baseline characteristics.
Genomic sequencing of bacteria obtained from stool samples showed that it was possible to distinguish between patients with MDD and the healthy individuals, especially at the family, genus, and species levels.
In particular, there were significant differences in the Paenibacillaceae and Flavobacteriaceaea families, for the genus Fenollaria, and the species Flintibacter butyricus, Christensenella timonensis, and Eisenbergiella massiliensis, among others.
Results also showed that the phyla Proteobacteria, Tenericutes, and the family Peptostreptococcaceae were more common in patients with treatment-resistant MDD, whereas the phylum Actinobacteria was more abundant in treatment responders.
Moreover, several bacteria were found only in the microbiota of patients with treatment-resistant MDD, while others were seen only in treatment-responsive patients. This made it possible to discriminate not only between treatment-resistant and -responsive patients but also between those two patient groups and healthy controls.
“The results of our study confirm that gut dysbiosis is a hallmark of MDD, and suggests that the gut microbiota of patients with treatment-resistant MDD significantly differs from responders to antidepressants,” Mr. Fontana said.
Psychobiotic diet
For the second study, Dr. Berding and colleagues note that “psychobiotics” has previously achieved “promising results.”
In addition, diet is both “one of the most influential modifying factors” for the gut microbiota and an easily accessible strategy, they wrote. However, there is also a paucity of studies in this area, they added.
The researchers randomly assigned healthy volunteers with relatively poor dietary habits to either a 4-week psychobiotic diet group (n = 21) or a control group (n = 19).
Individuals in the psychobiotic group were told to eat a diet rich in prebiotics, such as fruit and vegetables, fiber including whole grains and legumes, and fermented foods. The control group was educated on Irish healthy-eating guidelines.
Stool and saliva samples were collected and the participants completed several self-reported mental health questionnaires, as well as a 7-day food diary. They also took the socially evaluated cold-pressor test (SECPT) to measure acute stress responses.
Results showed that total daily energy intake decreased significantly in both the diet and control groups over the study period (P = .04 for both) but did not differ significantly between the groups.
In contrast, dietary fiber intake increased significantly in the diet group (P < .001) and was significantly higher than in the control group at the end of the intervention (P = .03).
Individuals in the diet group showed significant decreases in scores on the Perceived Stress Scale (P = .002) and the Beck Depression Inventory (P = .007) during the study, an effect that was not found in the control group.
Dietary intervention
There were no significant effects of diet on the acute stress response, but both groups showed improvements in self-concept, or perceived ability to cope, on the Primary Appraisal, Secondary Appraisal index (P = .03 for the diet group, P = .04 for the control group).
The results show that a dietary intervention targeted at the microbiota “can improve subjective feelings of stress and depression in a healthy population,” the investigators wrote.
However, elucidating the “contribution of the microbiota-gut-brain axis on the signaling response to dietary interventions” will require further studies on microbiota sequencing and biological measures of stress, they added.
This will “contribute to the understanding of the benefits of a psychobiotic diet on stress and anxiety,” wrote the researchers.
Dr. Berding said in an interview that while the consumption of dietary fiber changed the most in the diet group, “it would not be the only nutrient” that had an impact on the results, with fermented foods a likely candidate.
She said the next step is to test the dietary intervention in patients with MDD; however, “doing nutritional interventions in diseased populations is always difficult.”
Dr. Berding suggested that the best approach would be to study inpatients in a clinic, as “we would be able to provide every meal and only provide foods that are part of the dietary intervention.”
Although another option would be to conduct the study in outpatients, she noted that assessing inpatients “would give us the best control over compliance.”
“Brilliant ideas”
Commenting on the findings, Sergueï Fetissov, MD, PhD, professor of physiology at Rouen University, Mont-Saint-Aignan, France, said that although both studies bring attention to a possible role for the gut microbiota in MDD, neither “provide any experimental evidence of a causative nature.”
Dr. Fetissov, who was not involved in either study, noted that this topic has been the subject of clinical nutritional research for many years.
However, “we still need some strong evidence to prove that some bacteria can influence the regulation of mood and anxiety and stress,” he said.
In addition, researchers currently do not know what actually causes MDD. “How we can say the gut bacteria regulates something if we don’t know what really causes the altered mood?” said Dr. Fetissov.
He noted that over the last 50 years, there have been great advances in the development of drugs that alleviate depression and anxiety by regulating dopamine, serotonin, and other neurotransmitters. However, it is still unknown whether these reflect primary or secondary aspects of mood disorders.
Furthermore, it is not clear “how probiotics to bacteria can influence these neuronal pathways,” he said.
The research by Dr. Berding and colleagues is funded by a postdoctoral fellowship grant from the Irish Research Council. The study authors and Dr. Fetissov have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Counterintuitive findings for domestic violence during COVID-19
Intimate partner violence (IPV) has not increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, at least during the early stages of the pandemic, new research suggests.
In April 2020, investigators surveyed over 1,750 individuals in intimate partner relationships. The survey was drawn from social media and email distribution lists. The researchers found that, of the roughly one-fifth who screened positive for IPV, half stated that the degree of victimization had remained the same since the COVID-19 outbreak; 17% reported that it had worsened; and one third reported that it had gotten better.
Those who reported worsening victimization said that sexual and physical violence, in particular, were exacerbated early in the pandemic’s course.
“I was surprised by this finding, and we certainly were not expecting it – in fact, I expected that the vast majority of victims would report that victimization got worse during stay-at-home policies, but that wasn’t the case,” lead author Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of epidemiology, human genetics, and environmental sciences, University of Texas Health Science Center, Dallas, said in an interview.
“I think the biggest take-home message is that some victims got better, but the vast majority stayed the same. These victims, men and women, were isolated with their perpetrator during COVID-19, so she added.
The study was published online Sept. 1 in Injury Prevention.
‘Shadow pandemic?’
The World Health Organization called upon health care organizations to be prepared to curb a potential IPV “shadow pandemic” during the COVID-19 pandemic.
However, no study has specifically evaluated whether self-reported victimization, particularly with regard to the severity and type of abuse, changed during the early period after COVID-19 social distancing polices were mandated.
“We scrambled right away when the pandemic hit because it was a unique opportunity to examine how behaviors change due to early stay-at-home policies; and, as a violence and injury epidemiologist, I am always curious about IPV, and this was a small subanalysis of that larger question,” Dr. Jetelina said.
The researchers recruited participants through their university and private social media accounts as well as professional distribution lists. Of those who completed the survey, 1,759 (mean age, 42 years) reported that they currently had an intimate partner. These participants were included in the study.
IPV was determined using the five-item Extended Hurt, Insulted, Threatened, and Scream (E-HITS) construct. Respondents were asked how often their partner physically hurt them, insulted them, threatened them with harm, screamed or cursed at them, or forced them to engage in sexual activities.
Each item was answered using a 5-point Likert scale. Scores ranged from 1, indicating never, to 5, indicating frequently. Participants who scored ≥7 were considered IPV positive.
Participants were also asked whether IPV severity had gotten much/somewhat better, had remained the same, or had gotten somewhat/much worse.
First peek
Of the total sample, 18% screened positive for IPV. Of these, 54% reported that the victimization had remained the same, 17% reported that it had worsened, and 30% said it had improved.
The majority of IPV victims experienced being insulted (97%) or being screamed at (86%).
Among those who reported worsening of IPV, the risk for physical violence was 4.38 times higher than the risk for nonphysical victimization. The risk for sexual victimization was 2.31 times higher than the risk for nonsexual victimization.
Among those who reported that IPV had gotten better, the improvement was 3.47 times higher with regard to physical victimization, compared with nonphysical victimization. Dr. Jetelina acknowledged that the findings cannot be generalized to the broader population.
“This was a convenience sample, but it is the first peek into what is happening behind closed doors and a first step to hearing collecting data from the victims themselves to better understand this ‘shadow pandemic’ and inform creative efforts to create better services for them while they are in isolation,” she said.
Lethality indicators
Commenting on the study, Peter Cronholm, MD, MSCE, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, questioned the use of a score of 7 on the E-HITS screen to determine the presence of IPV.
“I think there are other thresholds that might be important, and even low levels of sexual violence may be different than higher levels of emotional violence,” said Dr. Cronholm, who was not involved with the study.
“Someone may have been sexually assaulted frequently but not cross the threshold, so I think it would have been helpful for the researchers to look at different types of violence,” he said.
Also commenting on the study, Jessica Palardy, LSW, program supervisor at STOP Intimate Partner Violence, Philadelphia, said, the findings “solidify a trend we sensed was happening but couldn’t confirm.”
She said her agency’s clients “have had a wide variety of experiences, in terms of increases or decreases in victimization.”
Some clients were able to use the quarantine as an excuse to stay with family or friends and so could avoid seeing their partners. “Others indicated that because their partners were distracted by figuring out a new method of work, the tension shifted away from the victim,” said Ms. Palardy, who was not involved in the research.
“For those who saw an increase in victimization, we noticed that this increase also came with an increase in lethality indicators, such as strangulation, physical violence, use of weapons and substances, etc,” she said.
She emphasized that it is critical to screen people for IPV to ensure their safety.
“The goal is to connect people with resources before they are in a more lethal situation so that they can increase their safety and know their options,” Ms. Palardy said.
The National Domestic Violence Hotline and the Crisis Text Line are two sources of support for IPV victims.
Dr. Jetelina and coauthors, Dr. Cronholm, and Ms. Palardy reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Intimate partner violence (IPV) has not increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, at least during the early stages of the pandemic, new research suggests.
In April 2020, investigators surveyed over 1,750 individuals in intimate partner relationships. The survey was drawn from social media and email distribution lists. The researchers found that, of the roughly one-fifth who screened positive for IPV, half stated that the degree of victimization had remained the same since the COVID-19 outbreak; 17% reported that it had worsened; and one third reported that it had gotten better.
Those who reported worsening victimization said that sexual and physical violence, in particular, were exacerbated early in the pandemic’s course.
“I was surprised by this finding, and we certainly were not expecting it – in fact, I expected that the vast majority of victims would report that victimization got worse during stay-at-home policies, but that wasn’t the case,” lead author Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of epidemiology, human genetics, and environmental sciences, University of Texas Health Science Center, Dallas, said in an interview.
“I think the biggest take-home message is that some victims got better, but the vast majority stayed the same. These victims, men and women, were isolated with their perpetrator during COVID-19, so she added.
The study was published online Sept. 1 in Injury Prevention.
‘Shadow pandemic?’
The World Health Organization called upon health care organizations to be prepared to curb a potential IPV “shadow pandemic” during the COVID-19 pandemic.
However, no study has specifically evaluated whether self-reported victimization, particularly with regard to the severity and type of abuse, changed during the early period after COVID-19 social distancing polices were mandated.
“We scrambled right away when the pandemic hit because it was a unique opportunity to examine how behaviors change due to early stay-at-home policies; and, as a violence and injury epidemiologist, I am always curious about IPV, and this was a small subanalysis of that larger question,” Dr. Jetelina said.
The researchers recruited participants through their university and private social media accounts as well as professional distribution lists. Of those who completed the survey, 1,759 (mean age, 42 years) reported that they currently had an intimate partner. These participants were included in the study.
IPV was determined using the five-item Extended Hurt, Insulted, Threatened, and Scream (E-HITS) construct. Respondents were asked how often their partner physically hurt them, insulted them, threatened them with harm, screamed or cursed at them, or forced them to engage in sexual activities.
Each item was answered using a 5-point Likert scale. Scores ranged from 1, indicating never, to 5, indicating frequently. Participants who scored ≥7 were considered IPV positive.
Participants were also asked whether IPV severity had gotten much/somewhat better, had remained the same, or had gotten somewhat/much worse.
First peek
Of the total sample, 18% screened positive for IPV. Of these, 54% reported that the victimization had remained the same, 17% reported that it had worsened, and 30% said it had improved.
The majority of IPV victims experienced being insulted (97%) or being screamed at (86%).
Among those who reported worsening of IPV, the risk for physical violence was 4.38 times higher than the risk for nonphysical victimization. The risk for sexual victimization was 2.31 times higher than the risk for nonsexual victimization.
Among those who reported that IPV had gotten better, the improvement was 3.47 times higher with regard to physical victimization, compared with nonphysical victimization. Dr. Jetelina acknowledged that the findings cannot be generalized to the broader population.
“This was a convenience sample, but it is the first peek into what is happening behind closed doors and a first step to hearing collecting data from the victims themselves to better understand this ‘shadow pandemic’ and inform creative efforts to create better services for them while they are in isolation,” she said.
Lethality indicators
Commenting on the study, Peter Cronholm, MD, MSCE, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, questioned the use of a score of 7 on the E-HITS screen to determine the presence of IPV.
“I think there are other thresholds that might be important, and even low levels of sexual violence may be different than higher levels of emotional violence,” said Dr. Cronholm, who was not involved with the study.
“Someone may have been sexually assaulted frequently but not cross the threshold, so I think it would have been helpful for the researchers to look at different types of violence,” he said.
Also commenting on the study, Jessica Palardy, LSW, program supervisor at STOP Intimate Partner Violence, Philadelphia, said, the findings “solidify a trend we sensed was happening but couldn’t confirm.”
She said her agency’s clients “have had a wide variety of experiences, in terms of increases or decreases in victimization.”
Some clients were able to use the quarantine as an excuse to stay with family or friends and so could avoid seeing their partners. “Others indicated that because their partners were distracted by figuring out a new method of work, the tension shifted away from the victim,” said Ms. Palardy, who was not involved in the research.
“For those who saw an increase in victimization, we noticed that this increase also came with an increase in lethality indicators, such as strangulation, physical violence, use of weapons and substances, etc,” she said.
She emphasized that it is critical to screen people for IPV to ensure their safety.
“The goal is to connect people with resources before they are in a more lethal situation so that they can increase their safety and know their options,” Ms. Palardy said.
The National Domestic Violence Hotline and the Crisis Text Line are two sources of support for IPV victims.
Dr. Jetelina and coauthors, Dr. Cronholm, and Ms. Palardy reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Intimate partner violence (IPV) has not increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, at least during the early stages of the pandemic, new research suggests.
In April 2020, investigators surveyed over 1,750 individuals in intimate partner relationships. The survey was drawn from social media and email distribution lists. The researchers found that, of the roughly one-fifth who screened positive for IPV, half stated that the degree of victimization had remained the same since the COVID-19 outbreak; 17% reported that it had worsened; and one third reported that it had gotten better.
Those who reported worsening victimization said that sexual and physical violence, in particular, were exacerbated early in the pandemic’s course.
“I was surprised by this finding, and we certainly were not expecting it – in fact, I expected that the vast majority of victims would report that victimization got worse during stay-at-home policies, but that wasn’t the case,” lead author Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of epidemiology, human genetics, and environmental sciences, University of Texas Health Science Center, Dallas, said in an interview.
“I think the biggest take-home message is that some victims got better, but the vast majority stayed the same. These victims, men and women, were isolated with their perpetrator during COVID-19, so she added.
The study was published online Sept. 1 in Injury Prevention.
‘Shadow pandemic?’
The World Health Organization called upon health care organizations to be prepared to curb a potential IPV “shadow pandemic” during the COVID-19 pandemic.
However, no study has specifically evaluated whether self-reported victimization, particularly with regard to the severity and type of abuse, changed during the early period after COVID-19 social distancing polices were mandated.
“We scrambled right away when the pandemic hit because it was a unique opportunity to examine how behaviors change due to early stay-at-home policies; and, as a violence and injury epidemiologist, I am always curious about IPV, and this was a small subanalysis of that larger question,” Dr. Jetelina said.
The researchers recruited participants through their university and private social media accounts as well as professional distribution lists. Of those who completed the survey, 1,759 (mean age, 42 years) reported that they currently had an intimate partner. These participants were included in the study.
IPV was determined using the five-item Extended Hurt, Insulted, Threatened, and Scream (E-HITS) construct. Respondents were asked how often their partner physically hurt them, insulted them, threatened them with harm, screamed or cursed at them, or forced them to engage in sexual activities.
Each item was answered using a 5-point Likert scale. Scores ranged from 1, indicating never, to 5, indicating frequently. Participants who scored ≥7 were considered IPV positive.
Participants were also asked whether IPV severity had gotten much/somewhat better, had remained the same, or had gotten somewhat/much worse.
First peek
Of the total sample, 18% screened positive for IPV. Of these, 54% reported that the victimization had remained the same, 17% reported that it had worsened, and 30% said it had improved.
The majority of IPV victims experienced being insulted (97%) or being screamed at (86%).
Among those who reported worsening of IPV, the risk for physical violence was 4.38 times higher than the risk for nonphysical victimization. The risk for sexual victimization was 2.31 times higher than the risk for nonsexual victimization.
Among those who reported that IPV had gotten better, the improvement was 3.47 times higher with regard to physical victimization, compared with nonphysical victimization. Dr. Jetelina acknowledged that the findings cannot be generalized to the broader population.
“This was a convenience sample, but it is the first peek into what is happening behind closed doors and a first step to hearing collecting data from the victims themselves to better understand this ‘shadow pandemic’ and inform creative efforts to create better services for them while they are in isolation,” she said.
Lethality indicators
Commenting on the study, Peter Cronholm, MD, MSCE, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, questioned the use of a score of 7 on the E-HITS screen to determine the presence of IPV.
“I think there are other thresholds that might be important, and even low levels of sexual violence may be different than higher levels of emotional violence,” said Dr. Cronholm, who was not involved with the study.
“Someone may have been sexually assaulted frequently but not cross the threshold, so I think it would have been helpful for the researchers to look at different types of violence,” he said.
Also commenting on the study, Jessica Palardy, LSW, program supervisor at STOP Intimate Partner Violence, Philadelphia, said, the findings “solidify a trend we sensed was happening but couldn’t confirm.”
She said her agency’s clients “have had a wide variety of experiences, in terms of increases or decreases in victimization.”
Some clients were able to use the quarantine as an excuse to stay with family or friends and so could avoid seeing their partners. “Others indicated that because their partners were distracted by figuring out a new method of work, the tension shifted away from the victim,” said Ms. Palardy, who was not involved in the research.
“For those who saw an increase in victimization, we noticed that this increase also came with an increase in lethality indicators, such as strangulation, physical violence, use of weapons and substances, etc,” she said.
She emphasized that it is critical to screen people for IPV to ensure their safety.
“The goal is to connect people with resources before they are in a more lethal situation so that they can increase their safety and know their options,” Ms. Palardy said.
The National Domestic Violence Hotline and the Crisis Text Line are two sources of support for IPV victims.
Dr. Jetelina and coauthors, Dr. Cronholm, and Ms. Palardy reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Evaluate, manage the stress response in susceptible individuals affected by COVID-19
Steroid therapy should be explored for quarantined mental health patients
Psychological First Aid is an innovative program launched by the American Red Cross with the goal of addressing issues of concern such as those stemming from COVID-19–related stress. According to Red Cross mental health volunteer representative Deb Butman-Perkins, the program provides “a general overview of what does stress look like, how do we feel it, how do we recognize it in our bodies ... physical, emotional, spiritual, physiological, where does all that stress occur?”1
The program brings a spotlight to the interdisciplinary nature of the stress response, especially with respect to the importance of developing the necessary coping skills during an ongoing crisis. However, to effectively evaluate and manage the overall stress response for psychiatric patients during quarantine conditions, as well as those who are formally diagnosed with COVID-19, clinicians also will need to revisit what we’ve learned about the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
We know that the stress response – which varies somewhat across the spectrum – is necessary to ensure homeostatic regulation. A feedback loop is initiated at the receptor level, involving a myriad of hormones and chemical signals that bring forth the body’s “flight-or-fight” response. Hormones such as epinephrine/norepinephrine and cortisol are secreted by the HPA axis in reaction to the stress response, resulting in a spike in heart rate, blood pressure, and transient hyperglycemia, respectively. In particular, hyperglycemia provides immediate energy to muscles during a perceived crisis.2
In addition, prolonged exposure to living in quarantine can lead to feelings of isolation and estrangement – and excessive anxiety. Combined, those conditions may exert an indelible effect on the HPA axis – leading to a warped pattern of cortisol secretion with respect to baseline.3 (It has been noted in the literature that serum cortisol plays a protective role in thwarting off the effects of PTSD development. Consistent with this line of thinking, military personnel have been preemptively treated with high-dose cortisol during acute exposure.)
Prolonged exposure to psychosocial stressors also increases the overall risk of developing medical comorbidities. Patients who adopt maladaptive responses to traumatic events, for example, may experience dysregulation in eating behaviors and/or disordered sleep.4
In light of those realities, clinicians should explore the role of steroid therapy as a means of treating mental health patients experiencing psychological stress formation tied to ongoing quarantine conditions.
Challenges of neuroendocrine medications for COVID-19
COVID-19, caused by exposure to SARS-CoV-2, adeptly leverages the ACE2 receptor of the lungs as an entry point to evade the host’s defenses. It should be noted that the ACE2 protein is expressed on the cells of multiple organs of the body, including the adrenals, which are largely responsible for coordinating the stress response of the HPA axis.
Postmortem analysis from severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV is also from the Coronaviridae family) patients indicates the presence of necrotic adrenal cells, further solidifying the association of the HPA axis to the COVID-19 disease state and pathophysiological course.5 Molecular mimicry of the adrenocorticotropic hormone allows SARS-CoV the ability to infiltrate the host’s defenses, in particular, the ability to mount a clinically apt cortisol stress response (e.g., hypocortisolism).As for those who survived the 2003 SARS outbreak, less than half of the patients have been observed to develop symptoms of frank hypocortisolism within a few months after exposure.
and an ongoing clinical trial is evaluating the safety and efficacy parameters of corticosteroids in COVID-19–exposed patients.
In addition, there is reason to believe that application of prophylactic steroids might affect the overall clinical course of COVID-19, thereby reducing mortality and morbidity rates in patients with severe presentation, such as septic shock. The rationale for this line of thought is based on the ability of glucocorticoids to suppress an ensuing cytokine storm by the virus in question.5,6 In clinical practice, steroids have been used to treat a host of viral diseases, including influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus.
Aside from the selective use of corticosteroids, the medication regimen may incorporate ACE inhibitors and/or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) because of COVID-19’s ability to activate the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system with respect to the physiological stress response.
The interplay of the HPA axis with the sympathoadrenal system is responsible for adaptive behaviors in the individual. Disrupted feedback loops from prolonged activation are associated with numerous stress-based conditions in mental illness, namely, PTSD, anxiety, and mood disorders. We are concerned about frontline health care workers, who are particularly prone to chronic stress and burnout because of the cumbersome patient load and equipment shortage that have characterized the coronavirus crisis.
Timely administration of corticosteroids on a case-by-case basis would keep the cytokines at bay by precluding their undue activation of the HPA axis and corresponding cascade stress response. Steroids are also known to restore disrupted feedback loops at the level of the immune cells. However, because of conflicting reports concerning viral clearance in some SARS and COVID-19 studies, treatment with steroids may be limited to select patient populations with the necessary dose adjustments. Ongoing clinical trials will further elucidate upon the applicability of steroids as well as the role of other neuroendocrine agents, such as ACE inhibitors or ARBs, in the treatment of COVID-19.
Behavioral manifestations and psychosocial health
As far as the stress response is concerned, an analysis performed by researchers in China after the COVID-19 outbreak found gender disparities in symptom expression. In the study (n = 1,210) the researchers found in female citizens a greater frequency of behavioral manifestations, including acute stress reaction, and symptoms of anxiety and mood disorders – namely, depression.7 Patient perception and awareness of the perils of coronavirus typically varied across the spectrum; some individuals reportedly undermined and devalued their risk of contracting COVID-19 – these patients may benefit from therapeutic modalities, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), as a means of challenging their firmly entrenched cognitive distortions. CBT is an effective tool in addressing maladaptive coping responses, because these strategies tend to correspond with poor prognosis with respect to overall mental health. Aside from CBT, the clinician may advise other behavioral techniques, such as relaxation training, with the aim of controlling the symptoms of mood and anxiety disorders.
We often take for granted general pandemic safety precautions, such as maintaining physical distancing coupled with engaging in regular hand hygiene and wearing masks, but these actions also are known to alleviate mental anguish. Access to accurate and easy-to-consume health information regarding COVID-19 is also associated with psychological well-being during the quarantine.8
An intriguing “phenomenon” has emerged in the form of “panic buying.”However, researchers reported in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Human Behaviour that this pattern of behaviors is not typical for those under distress and represents an overstated misnomer of sorts. According to Jay J. Van Bavel, PhD, and associates, prevailing reports from news outlets have skewed the features of a panic. “News stories that employ the language of panic often create the very phenomena that they purport to condemn,” Dr. Van Bavel and associates wrote. “They can foster the very individualism and competitiveness that turn sensible preparations into dysfunctional stockpiling and undermine the sense of collective purpose which facilitates people supporting one another during an emergency.”9
The researchers proceeded to highlight the scope of effective crisis leadership with respect to establishing a sense of communal “self-efficacy and hope.” The influence of organized leadership serves to solidify the structure of the community as a whole, allowing group members the opportunity to address the stressors of interest. Such leadership may mitigate the stress response by fostering a necessary, healthy set for stress management.
Strategies aimed at supporting mental health
Coping and stress management strategies may include the process of building virtual networks (e.g., social media platforms) because physical distancing may contribute toward further isolation and social estrangement. However, it should be noted that ideally social media consumption should be centered upon interactive enrichment activities that provide a suitable substitute for the absence of physical support systems. The goal is to facilitate meaningful relationships and enduring communications that produce healthy and resilient mindsets.
In particular, individuals who possess adaptive mindsets with a realistic view of ongoing psychosocial stressors, be it from the impact of the pandemic or other influential events, are more likely to benefit when moving forward with life. In other words, the individual in question leverages these experiences as a means of “stress-related growth,” thereby enhancing the overall quality of relationships. Tentative studies in stress management have yielded promising support for interventions that aim to modulate mindsets (as a function of the stress response) by proper appraisal of the stress stimuli, according to Dr. Van Bavel and associates.
Employing assessment scales
To mitigate the stress response, clinicians need to use the relevant stress scales for assessing the full impact of distress brought on by COVID-19 and optimizing therapeutic modalities for those who need them most. Again, the stress response would vary, depending on the patient, and may include paranoia, xenophobia, compulsive ritualistic behavior, as well as full-fledged symptoms of acute stress disorder/PTSD.Steven Taylor, PhD, RPsych, and associates, part of a research team funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Regina (Sask.), formulated their proprietary COVID Stress Scales (CSS) based on 36 items pertaining to individual anxiety and/or stress responses.10
As general purpose pandemic scales, the assessment tools will be transferable to similar outbreaks, and have been examined for validity and reliability. Additional validation scales include the Patient Health Questionnaire–4 for anxiety and depression, the Short Health Anxiety Inventory for anxiety (irrespective of physical condition), and the Marlowe-Crowne Social Desirability Scale–Short Form for psychological well-being based on the presence (or the lack thereof) of desirable characteristics.10 As a composite scale and predictive tool (especially with respect to future pandemics), the CSS allows clinicians a means of identifying the people who are most compliant with safety procedures, social distancing, hygiene expectations, and vaccine protocols – when applicable – reported Dr. Taylor and associates.
Moving forward: The next step in COVID-19 preparedness
As clinicians continue to develop guidelines that are befitting of COVID-19’s “new normal,” a holistic psychosocial framework will need to integrate the various psychometrics gathered from assessment scales, as well as understanding trauma, especially with respect to the HPA axis.
For starters, there is a certain element of “anticipatory anxiety” for those experiencing distress from COVID-19. A highly uncertain future with no immediate cure in the future, isolation and social estrangement, as well as financial setbacks, compound the situation. Moreover, the DSM fails to acknowledge other sources of traumatic experiences that are systemic in nature, such as discriminatory practices, injustice, and/or persecution.
It has also been noted that some distressed individuals experience a hypervigilant state that is comparable with PTSD.11 There may be a push to incorporate machine learning and other modalities to better identify those at risk (for example, health care professionals who perform their duties with limited resources, thereby inducing sleep dysregulation, anxiety, and hopelessness) for mental health deterioration. Interventions may need to be coordinated in a timely manner to disrupt the progression of acute stress disorder to PTSD. Peer support programs and resiliency training – successful therapeutic approaches for PTSD – may prove to have considerable utility for mitigating the overall stress response of COVID-19.12
References
1. “Red Cross offering online course to manage crisis-related stress.” ABC 6 News. kaaltv.com, 2020 Aug 29.
2. Islam FA, Choudhry C. J Psychiatry Psychiatric Disord 2017;1(5): 290-3.
3. Faravelli C et al. World J Psychiatry. 2012 Feb 22;2(1):13-25.
4. Carmassi C et al. Psychiatry Res. 2015 Jan 30;225(1-2):64-9.
5. Pal R. Endocrine. 2020 Apr 28. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02325-1.
6. Steenblock C et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2020 May. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0758-9.
7. Wang C et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan;17(5):1729.
8. Ho CS et al. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2020 Mar 16;49(3):155-60.
9. Van Bavel JJ et al. Nat Hum Behav. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1038/s41562-020-0884-z.
10. Taylor S et al. J Anxiety Disord. 2020 May 4;72:102232.
11. Horesh D, Brown AD. Psychol Trauma. 2020 May;12(4):331-5.
12. Clark H et al. National Health Library and Knowledge Service/Evidence Team. Summary of Evidence: COVID-19, 2020 May 22. Version 2.0.
Dr. Faisal A. Islam is a medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Mohammed S. Islam is a research physician and extern at Interfaith Medical Center, New York. Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation. Dr. Jolayemi is an attending psychiatrist at Interfaith Medical Center. No disclosures were reported.
Steroid therapy should be explored for quarantined mental health patients
Steroid therapy should be explored for quarantined mental health patients
Psychological First Aid is an innovative program launched by the American Red Cross with the goal of addressing issues of concern such as those stemming from COVID-19–related stress. According to Red Cross mental health volunteer representative Deb Butman-Perkins, the program provides “a general overview of what does stress look like, how do we feel it, how do we recognize it in our bodies ... physical, emotional, spiritual, physiological, where does all that stress occur?”1
The program brings a spotlight to the interdisciplinary nature of the stress response, especially with respect to the importance of developing the necessary coping skills during an ongoing crisis. However, to effectively evaluate and manage the overall stress response for psychiatric patients during quarantine conditions, as well as those who are formally diagnosed with COVID-19, clinicians also will need to revisit what we’ve learned about the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
We know that the stress response – which varies somewhat across the spectrum – is necessary to ensure homeostatic regulation. A feedback loop is initiated at the receptor level, involving a myriad of hormones and chemical signals that bring forth the body’s “flight-or-fight” response. Hormones such as epinephrine/norepinephrine and cortisol are secreted by the HPA axis in reaction to the stress response, resulting in a spike in heart rate, blood pressure, and transient hyperglycemia, respectively. In particular, hyperglycemia provides immediate energy to muscles during a perceived crisis.2
In addition, prolonged exposure to living in quarantine can lead to feelings of isolation and estrangement – and excessive anxiety. Combined, those conditions may exert an indelible effect on the HPA axis – leading to a warped pattern of cortisol secretion with respect to baseline.3 (It has been noted in the literature that serum cortisol plays a protective role in thwarting off the effects of PTSD development. Consistent with this line of thinking, military personnel have been preemptively treated with high-dose cortisol during acute exposure.)
Prolonged exposure to psychosocial stressors also increases the overall risk of developing medical comorbidities. Patients who adopt maladaptive responses to traumatic events, for example, may experience dysregulation in eating behaviors and/or disordered sleep.4
In light of those realities, clinicians should explore the role of steroid therapy as a means of treating mental health patients experiencing psychological stress formation tied to ongoing quarantine conditions.
Challenges of neuroendocrine medications for COVID-19
COVID-19, caused by exposure to SARS-CoV-2, adeptly leverages the ACE2 receptor of the lungs as an entry point to evade the host’s defenses. It should be noted that the ACE2 protein is expressed on the cells of multiple organs of the body, including the adrenals, which are largely responsible for coordinating the stress response of the HPA axis.
Postmortem analysis from severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV is also from the Coronaviridae family) patients indicates the presence of necrotic adrenal cells, further solidifying the association of the HPA axis to the COVID-19 disease state and pathophysiological course.5 Molecular mimicry of the adrenocorticotropic hormone allows SARS-CoV the ability to infiltrate the host’s defenses, in particular, the ability to mount a clinically apt cortisol stress response (e.g., hypocortisolism).As for those who survived the 2003 SARS outbreak, less than half of the patients have been observed to develop symptoms of frank hypocortisolism within a few months after exposure.
and an ongoing clinical trial is evaluating the safety and efficacy parameters of corticosteroids in COVID-19–exposed patients.
In addition, there is reason to believe that application of prophylactic steroids might affect the overall clinical course of COVID-19, thereby reducing mortality and morbidity rates in patients with severe presentation, such as septic shock. The rationale for this line of thought is based on the ability of glucocorticoids to suppress an ensuing cytokine storm by the virus in question.5,6 In clinical practice, steroids have been used to treat a host of viral diseases, including influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus.
Aside from the selective use of corticosteroids, the medication regimen may incorporate ACE inhibitors and/or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) because of COVID-19’s ability to activate the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system with respect to the physiological stress response.
The interplay of the HPA axis with the sympathoadrenal system is responsible for adaptive behaviors in the individual. Disrupted feedback loops from prolonged activation are associated with numerous stress-based conditions in mental illness, namely, PTSD, anxiety, and mood disorders. We are concerned about frontline health care workers, who are particularly prone to chronic stress and burnout because of the cumbersome patient load and equipment shortage that have characterized the coronavirus crisis.
Timely administration of corticosteroids on a case-by-case basis would keep the cytokines at bay by precluding their undue activation of the HPA axis and corresponding cascade stress response. Steroids are also known to restore disrupted feedback loops at the level of the immune cells. However, because of conflicting reports concerning viral clearance in some SARS and COVID-19 studies, treatment with steroids may be limited to select patient populations with the necessary dose adjustments. Ongoing clinical trials will further elucidate upon the applicability of steroids as well as the role of other neuroendocrine agents, such as ACE inhibitors or ARBs, in the treatment of COVID-19.
Behavioral manifestations and psychosocial health
As far as the stress response is concerned, an analysis performed by researchers in China after the COVID-19 outbreak found gender disparities in symptom expression. In the study (n = 1,210) the researchers found in female citizens a greater frequency of behavioral manifestations, including acute stress reaction, and symptoms of anxiety and mood disorders – namely, depression.7 Patient perception and awareness of the perils of coronavirus typically varied across the spectrum; some individuals reportedly undermined and devalued their risk of contracting COVID-19 – these patients may benefit from therapeutic modalities, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), as a means of challenging their firmly entrenched cognitive distortions. CBT is an effective tool in addressing maladaptive coping responses, because these strategies tend to correspond with poor prognosis with respect to overall mental health. Aside from CBT, the clinician may advise other behavioral techniques, such as relaxation training, with the aim of controlling the symptoms of mood and anxiety disorders.
We often take for granted general pandemic safety precautions, such as maintaining physical distancing coupled with engaging in regular hand hygiene and wearing masks, but these actions also are known to alleviate mental anguish. Access to accurate and easy-to-consume health information regarding COVID-19 is also associated with psychological well-being during the quarantine.8
An intriguing “phenomenon” has emerged in the form of “panic buying.”However, researchers reported in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Human Behaviour that this pattern of behaviors is not typical for those under distress and represents an overstated misnomer of sorts. According to Jay J. Van Bavel, PhD, and associates, prevailing reports from news outlets have skewed the features of a panic. “News stories that employ the language of panic often create the very phenomena that they purport to condemn,” Dr. Van Bavel and associates wrote. “They can foster the very individualism and competitiveness that turn sensible preparations into dysfunctional stockpiling and undermine the sense of collective purpose which facilitates people supporting one another during an emergency.”9
The researchers proceeded to highlight the scope of effective crisis leadership with respect to establishing a sense of communal “self-efficacy and hope.” The influence of organized leadership serves to solidify the structure of the community as a whole, allowing group members the opportunity to address the stressors of interest. Such leadership may mitigate the stress response by fostering a necessary, healthy set for stress management.
Strategies aimed at supporting mental health
Coping and stress management strategies may include the process of building virtual networks (e.g., social media platforms) because physical distancing may contribute toward further isolation and social estrangement. However, it should be noted that ideally social media consumption should be centered upon interactive enrichment activities that provide a suitable substitute for the absence of physical support systems. The goal is to facilitate meaningful relationships and enduring communications that produce healthy and resilient mindsets.
In particular, individuals who possess adaptive mindsets with a realistic view of ongoing psychosocial stressors, be it from the impact of the pandemic or other influential events, are more likely to benefit when moving forward with life. In other words, the individual in question leverages these experiences as a means of “stress-related growth,” thereby enhancing the overall quality of relationships. Tentative studies in stress management have yielded promising support for interventions that aim to modulate mindsets (as a function of the stress response) by proper appraisal of the stress stimuli, according to Dr. Van Bavel and associates.
Employing assessment scales
To mitigate the stress response, clinicians need to use the relevant stress scales for assessing the full impact of distress brought on by COVID-19 and optimizing therapeutic modalities for those who need them most. Again, the stress response would vary, depending on the patient, and may include paranoia, xenophobia, compulsive ritualistic behavior, as well as full-fledged symptoms of acute stress disorder/PTSD.Steven Taylor, PhD, RPsych, and associates, part of a research team funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Regina (Sask.), formulated their proprietary COVID Stress Scales (CSS) based on 36 items pertaining to individual anxiety and/or stress responses.10
As general purpose pandemic scales, the assessment tools will be transferable to similar outbreaks, and have been examined for validity and reliability. Additional validation scales include the Patient Health Questionnaire–4 for anxiety and depression, the Short Health Anxiety Inventory for anxiety (irrespective of physical condition), and the Marlowe-Crowne Social Desirability Scale–Short Form for psychological well-being based on the presence (or the lack thereof) of desirable characteristics.10 As a composite scale and predictive tool (especially with respect to future pandemics), the CSS allows clinicians a means of identifying the people who are most compliant with safety procedures, social distancing, hygiene expectations, and vaccine protocols – when applicable – reported Dr. Taylor and associates.
Moving forward: The next step in COVID-19 preparedness
As clinicians continue to develop guidelines that are befitting of COVID-19’s “new normal,” a holistic psychosocial framework will need to integrate the various psychometrics gathered from assessment scales, as well as understanding trauma, especially with respect to the HPA axis.
For starters, there is a certain element of “anticipatory anxiety” for those experiencing distress from COVID-19. A highly uncertain future with no immediate cure in the future, isolation and social estrangement, as well as financial setbacks, compound the situation. Moreover, the DSM fails to acknowledge other sources of traumatic experiences that are systemic in nature, such as discriminatory practices, injustice, and/or persecution.
It has also been noted that some distressed individuals experience a hypervigilant state that is comparable with PTSD.11 There may be a push to incorporate machine learning and other modalities to better identify those at risk (for example, health care professionals who perform their duties with limited resources, thereby inducing sleep dysregulation, anxiety, and hopelessness) for mental health deterioration. Interventions may need to be coordinated in a timely manner to disrupt the progression of acute stress disorder to PTSD. Peer support programs and resiliency training – successful therapeutic approaches for PTSD – may prove to have considerable utility for mitigating the overall stress response of COVID-19.12
References
1. “Red Cross offering online course to manage crisis-related stress.” ABC 6 News. kaaltv.com, 2020 Aug 29.
2. Islam FA, Choudhry C. J Psychiatry Psychiatric Disord 2017;1(5): 290-3.
3. Faravelli C et al. World J Psychiatry. 2012 Feb 22;2(1):13-25.
4. Carmassi C et al. Psychiatry Res. 2015 Jan 30;225(1-2):64-9.
5. Pal R. Endocrine. 2020 Apr 28. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02325-1.
6. Steenblock C et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2020 May. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0758-9.
7. Wang C et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan;17(5):1729.
8. Ho CS et al. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2020 Mar 16;49(3):155-60.
9. Van Bavel JJ et al. Nat Hum Behav. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1038/s41562-020-0884-z.
10. Taylor S et al. J Anxiety Disord. 2020 May 4;72:102232.
11. Horesh D, Brown AD. Psychol Trauma. 2020 May;12(4):331-5.
12. Clark H et al. National Health Library and Knowledge Service/Evidence Team. Summary of Evidence: COVID-19, 2020 May 22. Version 2.0.
Dr. Faisal A. Islam is a medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Mohammed S. Islam is a research physician and extern at Interfaith Medical Center, New York. Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation. Dr. Jolayemi is an attending psychiatrist at Interfaith Medical Center. No disclosures were reported.
Psychological First Aid is an innovative program launched by the American Red Cross with the goal of addressing issues of concern such as those stemming from COVID-19–related stress. According to Red Cross mental health volunteer representative Deb Butman-Perkins, the program provides “a general overview of what does stress look like, how do we feel it, how do we recognize it in our bodies ... physical, emotional, spiritual, physiological, where does all that stress occur?”1
The program brings a spotlight to the interdisciplinary nature of the stress response, especially with respect to the importance of developing the necessary coping skills during an ongoing crisis. However, to effectively evaluate and manage the overall stress response for psychiatric patients during quarantine conditions, as well as those who are formally diagnosed with COVID-19, clinicians also will need to revisit what we’ve learned about the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
We know that the stress response – which varies somewhat across the spectrum – is necessary to ensure homeostatic regulation. A feedback loop is initiated at the receptor level, involving a myriad of hormones and chemical signals that bring forth the body’s “flight-or-fight” response. Hormones such as epinephrine/norepinephrine and cortisol are secreted by the HPA axis in reaction to the stress response, resulting in a spike in heart rate, blood pressure, and transient hyperglycemia, respectively. In particular, hyperglycemia provides immediate energy to muscles during a perceived crisis.2
In addition, prolonged exposure to living in quarantine can lead to feelings of isolation and estrangement – and excessive anxiety. Combined, those conditions may exert an indelible effect on the HPA axis – leading to a warped pattern of cortisol secretion with respect to baseline.3 (It has been noted in the literature that serum cortisol plays a protective role in thwarting off the effects of PTSD development. Consistent with this line of thinking, military personnel have been preemptively treated with high-dose cortisol during acute exposure.)
Prolonged exposure to psychosocial stressors also increases the overall risk of developing medical comorbidities. Patients who adopt maladaptive responses to traumatic events, for example, may experience dysregulation in eating behaviors and/or disordered sleep.4
In light of those realities, clinicians should explore the role of steroid therapy as a means of treating mental health patients experiencing psychological stress formation tied to ongoing quarantine conditions.
Challenges of neuroendocrine medications for COVID-19
COVID-19, caused by exposure to SARS-CoV-2, adeptly leverages the ACE2 receptor of the lungs as an entry point to evade the host’s defenses. It should be noted that the ACE2 protein is expressed on the cells of multiple organs of the body, including the adrenals, which are largely responsible for coordinating the stress response of the HPA axis.
Postmortem analysis from severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV is also from the Coronaviridae family) patients indicates the presence of necrotic adrenal cells, further solidifying the association of the HPA axis to the COVID-19 disease state and pathophysiological course.5 Molecular mimicry of the adrenocorticotropic hormone allows SARS-CoV the ability to infiltrate the host’s defenses, in particular, the ability to mount a clinically apt cortisol stress response (e.g., hypocortisolism).As for those who survived the 2003 SARS outbreak, less than half of the patients have been observed to develop symptoms of frank hypocortisolism within a few months after exposure.
and an ongoing clinical trial is evaluating the safety and efficacy parameters of corticosteroids in COVID-19–exposed patients.
In addition, there is reason to believe that application of prophylactic steroids might affect the overall clinical course of COVID-19, thereby reducing mortality and morbidity rates in patients with severe presentation, such as septic shock. The rationale for this line of thought is based on the ability of glucocorticoids to suppress an ensuing cytokine storm by the virus in question.5,6 In clinical practice, steroids have been used to treat a host of viral diseases, including influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus.
Aside from the selective use of corticosteroids, the medication regimen may incorporate ACE inhibitors and/or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) because of COVID-19’s ability to activate the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system with respect to the physiological stress response.
The interplay of the HPA axis with the sympathoadrenal system is responsible for adaptive behaviors in the individual. Disrupted feedback loops from prolonged activation are associated with numerous stress-based conditions in mental illness, namely, PTSD, anxiety, and mood disorders. We are concerned about frontline health care workers, who are particularly prone to chronic stress and burnout because of the cumbersome patient load and equipment shortage that have characterized the coronavirus crisis.
Timely administration of corticosteroids on a case-by-case basis would keep the cytokines at bay by precluding their undue activation of the HPA axis and corresponding cascade stress response. Steroids are also known to restore disrupted feedback loops at the level of the immune cells. However, because of conflicting reports concerning viral clearance in some SARS and COVID-19 studies, treatment with steroids may be limited to select patient populations with the necessary dose adjustments. Ongoing clinical trials will further elucidate upon the applicability of steroids as well as the role of other neuroendocrine agents, such as ACE inhibitors or ARBs, in the treatment of COVID-19.
Behavioral manifestations and psychosocial health
As far as the stress response is concerned, an analysis performed by researchers in China after the COVID-19 outbreak found gender disparities in symptom expression. In the study (n = 1,210) the researchers found in female citizens a greater frequency of behavioral manifestations, including acute stress reaction, and symptoms of anxiety and mood disorders – namely, depression.7 Patient perception and awareness of the perils of coronavirus typically varied across the spectrum; some individuals reportedly undermined and devalued their risk of contracting COVID-19 – these patients may benefit from therapeutic modalities, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), as a means of challenging their firmly entrenched cognitive distortions. CBT is an effective tool in addressing maladaptive coping responses, because these strategies tend to correspond with poor prognosis with respect to overall mental health. Aside from CBT, the clinician may advise other behavioral techniques, such as relaxation training, with the aim of controlling the symptoms of mood and anxiety disorders.
We often take for granted general pandemic safety precautions, such as maintaining physical distancing coupled with engaging in regular hand hygiene and wearing masks, but these actions also are known to alleviate mental anguish. Access to accurate and easy-to-consume health information regarding COVID-19 is also associated with psychological well-being during the quarantine.8
An intriguing “phenomenon” has emerged in the form of “panic buying.”However, researchers reported in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Human Behaviour that this pattern of behaviors is not typical for those under distress and represents an overstated misnomer of sorts. According to Jay J. Van Bavel, PhD, and associates, prevailing reports from news outlets have skewed the features of a panic. “News stories that employ the language of panic often create the very phenomena that they purport to condemn,” Dr. Van Bavel and associates wrote. “They can foster the very individualism and competitiveness that turn sensible preparations into dysfunctional stockpiling and undermine the sense of collective purpose which facilitates people supporting one another during an emergency.”9
The researchers proceeded to highlight the scope of effective crisis leadership with respect to establishing a sense of communal “self-efficacy and hope.” The influence of organized leadership serves to solidify the structure of the community as a whole, allowing group members the opportunity to address the stressors of interest. Such leadership may mitigate the stress response by fostering a necessary, healthy set for stress management.
Strategies aimed at supporting mental health
Coping and stress management strategies may include the process of building virtual networks (e.g., social media platforms) because physical distancing may contribute toward further isolation and social estrangement. However, it should be noted that ideally social media consumption should be centered upon interactive enrichment activities that provide a suitable substitute for the absence of physical support systems. The goal is to facilitate meaningful relationships and enduring communications that produce healthy and resilient mindsets.
In particular, individuals who possess adaptive mindsets with a realistic view of ongoing psychosocial stressors, be it from the impact of the pandemic or other influential events, are more likely to benefit when moving forward with life. In other words, the individual in question leverages these experiences as a means of “stress-related growth,” thereby enhancing the overall quality of relationships. Tentative studies in stress management have yielded promising support for interventions that aim to modulate mindsets (as a function of the stress response) by proper appraisal of the stress stimuli, according to Dr. Van Bavel and associates.
Employing assessment scales
To mitigate the stress response, clinicians need to use the relevant stress scales for assessing the full impact of distress brought on by COVID-19 and optimizing therapeutic modalities for those who need them most. Again, the stress response would vary, depending on the patient, and may include paranoia, xenophobia, compulsive ritualistic behavior, as well as full-fledged symptoms of acute stress disorder/PTSD.Steven Taylor, PhD, RPsych, and associates, part of a research team funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Regina (Sask.), formulated their proprietary COVID Stress Scales (CSS) based on 36 items pertaining to individual anxiety and/or stress responses.10
As general purpose pandemic scales, the assessment tools will be transferable to similar outbreaks, and have been examined for validity and reliability. Additional validation scales include the Patient Health Questionnaire–4 for anxiety and depression, the Short Health Anxiety Inventory for anxiety (irrespective of physical condition), and the Marlowe-Crowne Social Desirability Scale–Short Form for psychological well-being based on the presence (or the lack thereof) of desirable characteristics.10 As a composite scale and predictive tool (especially with respect to future pandemics), the CSS allows clinicians a means of identifying the people who are most compliant with safety procedures, social distancing, hygiene expectations, and vaccine protocols – when applicable – reported Dr. Taylor and associates.
Moving forward: The next step in COVID-19 preparedness
As clinicians continue to develop guidelines that are befitting of COVID-19’s “new normal,” a holistic psychosocial framework will need to integrate the various psychometrics gathered from assessment scales, as well as understanding trauma, especially with respect to the HPA axis.
For starters, there is a certain element of “anticipatory anxiety” for those experiencing distress from COVID-19. A highly uncertain future with no immediate cure in the future, isolation and social estrangement, as well as financial setbacks, compound the situation. Moreover, the DSM fails to acknowledge other sources of traumatic experiences that are systemic in nature, such as discriminatory practices, injustice, and/or persecution.
It has also been noted that some distressed individuals experience a hypervigilant state that is comparable with PTSD.11 There may be a push to incorporate machine learning and other modalities to better identify those at risk (for example, health care professionals who perform their duties with limited resources, thereby inducing sleep dysregulation, anxiety, and hopelessness) for mental health deterioration. Interventions may need to be coordinated in a timely manner to disrupt the progression of acute stress disorder to PTSD. Peer support programs and resiliency training – successful therapeutic approaches for PTSD – may prove to have considerable utility for mitigating the overall stress response of COVID-19.12
References
1. “Red Cross offering online course to manage crisis-related stress.” ABC 6 News. kaaltv.com, 2020 Aug 29.
2. Islam FA, Choudhry C. J Psychiatry Psychiatric Disord 2017;1(5): 290-3.
3. Faravelli C et al. World J Psychiatry. 2012 Feb 22;2(1):13-25.
4. Carmassi C et al. Psychiatry Res. 2015 Jan 30;225(1-2):64-9.
5. Pal R. Endocrine. 2020 Apr 28. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02325-1.
6. Steenblock C et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2020 May. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0758-9.
7. Wang C et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan;17(5):1729.
8. Ho CS et al. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2020 Mar 16;49(3):155-60.
9. Van Bavel JJ et al. Nat Hum Behav. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1038/s41562-020-0884-z.
10. Taylor S et al. J Anxiety Disord. 2020 May 4;72:102232.
11. Horesh D, Brown AD. Psychol Trauma. 2020 May;12(4):331-5.
12. Clark H et al. National Health Library and Knowledge Service/Evidence Team. Summary of Evidence: COVID-19, 2020 May 22. Version 2.0.
Dr. Faisal A. Islam is a medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Mohammed S. Islam is a research physician and extern at Interfaith Medical Center, New York. Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation. Dr. Jolayemi is an attending psychiatrist at Interfaith Medical Center. No disclosures were reported.
ECT reduces all-cause mortality in Danish study
The two top developments of the year in the field of neurostimulation involve the oldest form of the therapy: electroconvulsive therapy, Alexander Sartorius, MD, said at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
One of these studies shot down the longstanding notion that ECT causes brain damage. The other, a Danish national registry study, demonstrated that ECT is associated with lower all-cause mortality than in patients with similarly severe depression who don’t undergo ECT.
“The take-home messages are that ECT does not lead to brain damage but rather to a profound gray matter increase. And secondly, ECT lowers all-cause mortality in patients with depression,” said Dr. Sartorius, a psychiatrist at the Central Institute of Mental Health in Mannheim, Germany.
The year has been less fruitful in terms of research involving deep brain stimulation using implantable electrodes, he continued.
“Basically, one can state that there is no breaking news in the field of deep brain stimulation. DBS remains a highly experimental form of therapy,” Dr. Sartorius said.
ECT-induced brain changes
Investigators participating in the international multicenter Global ECT-MRI Research Collaboration (GEMRIC) reported on the longitudinal effects of ECT on gray matter, white matter, and ventricular volumes in 328 patients who underwent imaging before and after ECT for a major depressive episode, as well as in 95 nondepressed controls.
The key finding was that ECT induced a widespread, nonspecific global increase in gray matter volume. Indeed, the volumetric increase was documented in 79 of 84 gray matter regions of interest. Subcortical gray matter volume increased by a mean of 1.47% in ECT-treated patients, and total cortical volume rose by 1.04%. Total white matter volume remained unchanged.
“The gray matter increase induced by ECT looks quite similar to the gray matter increase seen with physical activity,” Dr. Sartorius noted.
The size of the gray matter volume increase rose with the number of ECT sessions. However, gray matter enlargement in response to ECT showed no relationship with clinical response, indicating that this finding on brain imaging doesn’t have a promising future as a potential biomarker of treatment effectiveness (Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Mar 1;87[5]:451-61).
“The good news from this study is there is no gray matter decrease,” Dr. Sartorius said. “This study enhances the existing evidence falsifying the old idea or dogma that ECT induces brain damage. I would claim that the opposite is clearly the case.”
ECT and mortality
The same group of investigators at the University of Copenhagen who several years ago harnessed Danish national patient registries data to report that ECT was associated with an unadjusted 32% and adjusted 23% reduction in the risk of developing dementia in patients aged 70 years and older (Lancet Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;5[4]:348-56) have recently concluded that ECT was also associated with a 19% reduction in all-cause mortality, compared with that of patients hospitalized for major depression who didn’t receive ECT.
The national registries study included 5,004 patients who were treated with ECT and nearly 88,000 others who were hospitalized for major depression during 2005-2016 but didn’t receive ECT. During up to 11.3 years of follow-up, the risk of all-cause mortality was 8% lower with ECT than with no ECT in patients categorized as having mild depression, 17% lower with a history of ECT for moderate depression, 4% less with severe depression without psychotic features, and 30% less with ECT than no ECT for severe depression with psychotic features (J Psychopharmacol. 2020 Mar;34[3]:273-9).
ECT was associated with an adjusted 6.99-fold increased risk of suicide in patients with mild depression. At first look that’s unsettling, Dr. Sartorius said, but he pointed out that the size of the ECT-associated suicide risk lessened with increasing severity of depression, and in fact, there was no increased suicide risk with ECT in severely depressed patients with psychotic features. ECT was also associated with significantly higher rates of psychiatric rehospitalization, emergency department visits, and suicidal behavior in patients classified as having mild or moderate depression. Dr. Sartorius suspects these findings reflect diagnostic uncertainty surrounding the milder forms of depression, coupled with the reality that ECT is generally reserved for the most unstable, treatment-resistant patients.
Deep transcranial magnetic stimulation
A Taiwanese meta-analysis has helped clarify the role of deep transcranial magnetic stimulation (dTMS) for treatment-resistant depression. The meta-analysis included 198 patients with treatment-resistant depression who underwent dTMS and 219 who received sham treatment in a total of 15 studies, only three of which were randomized controlled trials.
Active treatment was associated with a 2.06-fold increased likelihood of remission of depressive symptoms; however, the effect was statistically significant only in the subgroup of patients on concurrent antidepressant medication. Moreover, the therapeutic benefit of dTMS was significantly greater in the nonrandomized studies, where the odds ratio for remission was 3.8-fold greater than with sham therapy. In contrast, the odds ratio for remission with dTMS dropped to 1.37 in the randomized trials (Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 20;99:109850. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109850). “dTMS has quite a bit of antidepressant potential in treatment-resistant depression, but as an augmentation strategy. More randomized trials are needed, with a particular focus on which classes of antidepressants might be most effective as concurrent therapy,” Dr. Sartorius concluded.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
SOURCE: Sartorius A. ECNP 2020, Session TP.03.
The two top developments of the year in the field of neurostimulation involve the oldest form of the therapy: electroconvulsive therapy, Alexander Sartorius, MD, said at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
One of these studies shot down the longstanding notion that ECT causes brain damage. The other, a Danish national registry study, demonstrated that ECT is associated with lower all-cause mortality than in patients with similarly severe depression who don’t undergo ECT.
“The take-home messages are that ECT does not lead to brain damage but rather to a profound gray matter increase. And secondly, ECT lowers all-cause mortality in patients with depression,” said Dr. Sartorius, a psychiatrist at the Central Institute of Mental Health in Mannheim, Germany.
The year has been less fruitful in terms of research involving deep brain stimulation using implantable electrodes, he continued.
“Basically, one can state that there is no breaking news in the field of deep brain stimulation. DBS remains a highly experimental form of therapy,” Dr. Sartorius said.
ECT-induced brain changes
Investigators participating in the international multicenter Global ECT-MRI Research Collaboration (GEMRIC) reported on the longitudinal effects of ECT on gray matter, white matter, and ventricular volumes in 328 patients who underwent imaging before and after ECT for a major depressive episode, as well as in 95 nondepressed controls.
The key finding was that ECT induced a widespread, nonspecific global increase in gray matter volume. Indeed, the volumetric increase was documented in 79 of 84 gray matter regions of interest. Subcortical gray matter volume increased by a mean of 1.47% in ECT-treated patients, and total cortical volume rose by 1.04%. Total white matter volume remained unchanged.
“The gray matter increase induced by ECT looks quite similar to the gray matter increase seen with physical activity,” Dr. Sartorius noted.
The size of the gray matter volume increase rose with the number of ECT sessions. However, gray matter enlargement in response to ECT showed no relationship with clinical response, indicating that this finding on brain imaging doesn’t have a promising future as a potential biomarker of treatment effectiveness (Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Mar 1;87[5]:451-61).
“The good news from this study is there is no gray matter decrease,” Dr. Sartorius said. “This study enhances the existing evidence falsifying the old idea or dogma that ECT induces brain damage. I would claim that the opposite is clearly the case.”
ECT and mortality
The same group of investigators at the University of Copenhagen who several years ago harnessed Danish national patient registries data to report that ECT was associated with an unadjusted 32% and adjusted 23% reduction in the risk of developing dementia in patients aged 70 years and older (Lancet Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;5[4]:348-56) have recently concluded that ECT was also associated with a 19% reduction in all-cause mortality, compared with that of patients hospitalized for major depression who didn’t receive ECT.
The national registries study included 5,004 patients who were treated with ECT and nearly 88,000 others who were hospitalized for major depression during 2005-2016 but didn’t receive ECT. During up to 11.3 years of follow-up, the risk of all-cause mortality was 8% lower with ECT than with no ECT in patients categorized as having mild depression, 17% lower with a history of ECT for moderate depression, 4% less with severe depression without psychotic features, and 30% less with ECT than no ECT for severe depression with psychotic features (J Psychopharmacol. 2020 Mar;34[3]:273-9).
ECT was associated with an adjusted 6.99-fold increased risk of suicide in patients with mild depression. At first look that’s unsettling, Dr. Sartorius said, but he pointed out that the size of the ECT-associated suicide risk lessened with increasing severity of depression, and in fact, there was no increased suicide risk with ECT in severely depressed patients with psychotic features. ECT was also associated with significantly higher rates of psychiatric rehospitalization, emergency department visits, and suicidal behavior in patients classified as having mild or moderate depression. Dr. Sartorius suspects these findings reflect diagnostic uncertainty surrounding the milder forms of depression, coupled with the reality that ECT is generally reserved for the most unstable, treatment-resistant patients.
Deep transcranial magnetic stimulation
A Taiwanese meta-analysis has helped clarify the role of deep transcranial magnetic stimulation (dTMS) for treatment-resistant depression. The meta-analysis included 198 patients with treatment-resistant depression who underwent dTMS and 219 who received sham treatment in a total of 15 studies, only three of which were randomized controlled trials.
Active treatment was associated with a 2.06-fold increased likelihood of remission of depressive symptoms; however, the effect was statistically significant only in the subgroup of patients on concurrent antidepressant medication. Moreover, the therapeutic benefit of dTMS was significantly greater in the nonrandomized studies, where the odds ratio for remission was 3.8-fold greater than with sham therapy. In contrast, the odds ratio for remission with dTMS dropped to 1.37 in the randomized trials (Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 20;99:109850. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109850). “dTMS has quite a bit of antidepressant potential in treatment-resistant depression, but as an augmentation strategy. More randomized trials are needed, with a particular focus on which classes of antidepressants might be most effective as concurrent therapy,” Dr. Sartorius concluded.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
SOURCE: Sartorius A. ECNP 2020, Session TP.03.
The two top developments of the year in the field of neurostimulation involve the oldest form of the therapy: electroconvulsive therapy, Alexander Sartorius, MD, said at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
One of these studies shot down the longstanding notion that ECT causes brain damage. The other, a Danish national registry study, demonstrated that ECT is associated with lower all-cause mortality than in patients with similarly severe depression who don’t undergo ECT.
“The take-home messages are that ECT does not lead to brain damage but rather to a profound gray matter increase. And secondly, ECT lowers all-cause mortality in patients with depression,” said Dr. Sartorius, a psychiatrist at the Central Institute of Mental Health in Mannheim, Germany.
The year has been less fruitful in terms of research involving deep brain stimulation using implantable electrodes, he continued.
“Basically, one can state that there is no breaking news in the field of deep brain stimulation. DBS remains a highly experimental form of therapy,” Dr. Sartorius said.
ECT-induced brain changes
Investigators participating in the international multicenter Global ECT-MRI Research Collaboration (GEMRIC) reported on the longitudinal effects of ECT on gray matter, white matter, and ventricular volumes in 328 patients who underwent imaging before and after ECT for a major depressive episode, as well as in 95 nondepressed controls.
The key finding was that ECT induced a widespread, nonspecific global increase in gray matter volume. Indeed, the volumetric increase was documented in 79 of 84 gray matter regions of interest. Subcortical gray matter volume increased by a mean of 1.47% in ECT-treated patients, and total cortical volume rose by 1.04%. Total white matter volume remained unchanged.
“The gray matter increase induced by ECT looks quite similar to the gray matter increase seen with physical activity,” Dr. Sartorius noted.
The size of the gray matter volume increase rose with the number of ECT sessions. However, gray matter enlargement in response to ECT showed no relationship with clinical response, indicating that this finding on brain imaging doesn’t have a promising future as a potential biomarker of treatment effectiveness (Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Mar 1;87[5]:451-61).
“The good news from this study is there is no gray matter decrease,” Dr. Sartorius said. “This study enhances the existing evidence falsifying the old idea or dogma that ECT induces brain damage. I would claim that the opposite is clearly the case.”
ECT and mortality
The same group of investigators at the University of Copenhagen who several years ago harnessed Danish national patient registries data to report that ECT was associated with an unadjusted 32% and adjusted 23% reduction in the risk of developing dementia in patients aged 70 years and older (Lancet Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;5[4]:348-56) have recently concluded that ECT was also associated with a 19% reduction in all-cause mortality, compared with that of patients hospitalized for major depression who didn’t receive ECT.
The national registries study included 5,004 patients who were treated with ECT and nearly 88,000 others who were hospitalized for major depression during 2005-2016 but didn’t receive ECT. During up to 11.3 years of follow-up, the risk of all-cause mortality was 8% lower with ECT than with no ECT in patients categorized as having mild depression, 17% lower with a history of ECT for moderate depression, 4% less with severe depression without psychotic features, and 30% less with ECT than no ECT for severe depression with psychotic features (J Psychopharmacol. 2020 Mar;34[3]:273-9).
ECT was associated with an adjusted 6.99-fold increased risk of suicide in patients with mild depression. At first look that’s unsettling, Dr. Sartorius said, but he pointed out that the size of the ECT-associated suicide risk lessened with increasing severity of depression, and in fact, there was no increased suicide risk with ECT in severely depressed patients with psychotic features. ECT was also associated with significantly higher rates of psychiatric rehospitalization, emergency department visits, and suicidal behavior in patients classified as having mild or moderate depression. Dr. Sartorius suspects these findings reflect diagnostic uncertainty surrounding the milder forms of depression, coupled with the reality that ECT is generally reserved for the most unstable, treatment-resistant patients.
Deep transcranial magnetic stimulation
A Taiwanese meta-analysis has helped clarify the role of deep transcranial magnetic stimulation (dTMS) for treatment-resistant depression. The meta-analysis included 198 patients with treatment-resistant depression who underwent dTMS and 219 who received sham treatment in a total of 15 studies, only three of which were randomized controlled trials.
Active treatment was associated with a 2.06-fold increased likelihood of remission of depressive symptoms; however, the effect was statistically significant only in the subgroup of patients on concurrent antidepressant medication. Moreover, the therapeutic benefit of dTMS was significantly greater in the nonrandomized studies, where the odds ratio for remission was 3.8-fold greater than with sham therapy. In contrast, the odds ratio for remission with dTMS dropped to 1.37 in the randomized trials (Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 20;99:109850. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109850). “dTMS has quite a bit of antidepressant potential in treatment-resistant depression, but as an augmentation strategy. More randomized trials are needed, with a particular focus on which classes of antidepressants might be most effective as concurrent therapy,” Dr. Sartorius concluded.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
SOURCE: Sartorius A. ECNP 2020, Session TP.03.
FROM ECNP 2020
Watch for nonsuicidal self-injury in girls with ADHD, comorbidities
Recent studies constitute a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen adolescents with ADHD for nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI) and its risk factors, Judit Balazs, MD, PhD, said at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
She was lead author of one of these studies, which drew a remarkable and disturbing conclusion: “We found – and it’s a very alarming result – that more than 70% of those people who had ADHD and [nonsuicidal self-injury] were girls. The girls with ADHD seem to be a high-risk population,” observed Dr. Balazs, professor and chair of the department of developmental psychology at Eotvos Lorand University, Budapest.
NSSI first became a specific diagnosis in the DSM-5. It is defined as deliberate, nonculturally sanctioned, nonsuicidal self-injury on at least five occasions within the past year and carried out with the aim of improving one’s emotional state as a result. The prevalence of NSSI among the general population of adolescents is high, with various investigators reporting rates of 15%-45%. Among adolescents with mental disorders, the reported prevalence climbs to 40%-80%. even though it’s now clear that many cases of pediatric-onset ADHD continue on well into adulthood, albeit often undiagnosed.
Whether NSSI and suicidal behavior are actually the same entity is currently a topic of intense research, according to Dr. Balazs, who is both a child and adolescent psychiatrist, as well as an adult psychiatrist.
She presented highlights of her cross-sectional study of 202 adolescent inpatients, 51% of them female, at the Vadaskert Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Hospital, a tertiary care center in Budapest. Using the structured diagnostic Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview for Children and Adolescents (MINI Kid) and the self-rated Deliberate Self-Harm Inventory, Dr. Balazs and her coinvestigators determined that 52 of the adolescents, including 23 boys and 29 girls, met full diagnostic criteria for ADHD and another 77 demonstrated more than five subthreshold ADHD symptoms.
Strikingly, 35 of the 52 teens diagnosed with ADHD, or 67%, had current NSSI. Only 10 of these patients were boys. The other 25, or 71% of the total, were girls.
Psychiatric comorbidities proved to be the rule rather than the exception in the adolescent inpatients with ADHD plus NSSI. Among these inpatients, 94% had a history of suicidal behavior. In addition, 66% carried the diagnosis of oppositional defiant disorder, 63% generalized anxiety disorder, 60% had a psychotic disorder, and 51% had experienced a manic episode. Among them, 49% were diagnosed with social anxiety disorder, 46% with obsessive-compulsive disorder, 31% with panic disorder, 23% with conduct disorder, and an equal percentage with agoraphobia. Furthermore, 43% had a major depressive disorder and 34%, dysthymia. Alcohol abuse or dependence was present in 20%, and an equal percentage had psychoactive substance use disorder.
Dr. Balazs said she and her coinvestigators were surprised by the high prevalence of symptoms of comorbid psychotic disorder in conjunction with NSSI and ADHD. One possible explanation, she opined, is that as inpatients the study participants were at the more severe end of the disease spectrum, and some patients may have been admitted not solely because of the severity of their comorbidities. Another possibility is that, in some cases, what was labeled psychotic disorder may actually have been prodromal unipolar depression.
A key finding in Dr. Balazs’s study was that, according to a regression analysis, the relationship between ADHD and NSSI was mediated entirely by the symptoms of the ADHD comorbidities. Specifically, the significant risk factors for NSSI in patients with ADHD were affective disorders, suicidality, and psychotic disorders in both sexes, with the addition of comorbid alcohol abuse or dependence in girls only. There was no evidence of a direct causal relationship between ADHD, per se, and NSSI.
‘Findings warrant further investigation’
The study, which looks at the association between NSSI and adolescents is interesting, yet preliminary, said David Fassler, MD, in an interview.
“The authors conclude that girls with ADHD are at particularly high risk of NSSI,” said Dr. Fassler, clinical professor of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington. Dr. Fassler was not involved with the study.
“It is limited by sample size, acuity, and the incidence of comorbidities,” said Dr. Fassler, who had no conflicts of interest. “Nonetheless, the findings are intriguing and warrant further investigation with larger samples in diverse clinical settings.”
The study was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund. In addition, Dr. Balazs received funding from the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. The full details of the study have been published (BMC Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 6;18[1]:34).
SOURCE: Balazs J et al. ECNP 2020, Abstract EDU.02.
Recent studies constitute a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen adolescents with ADHD for nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI) and its risk factors, Judit Balazs, MD, PhD, said at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
She was lead author of one of these studies, which drew a remarkable and disturbing conclusion: “We found – and it’s a very alarming result – that more than 70% of those people who had ADHD and [nonsuicidal self-injury] were girls. The girls with ADHD seem to be a high-risk population,” observed Dr. Balazs, professor and chair of the department of developmental psychology at Eotvos Lorand University, Budapest.
NSSI first became a specific diagnosis in the DSM-5. It is defined as deliberate, nonculturally sanctioned, nonsuicidal self-injury on at least five occasions within the past year and carried out with the aim of improving one’s emotional state as a result. The prevalence of NSSI among the general population of adolescents is high, with various investigators reporting rates of 15%-45%. Among adolescents with mental disorders, the reported prevalence climbs to 40%-80%. even though it’s now clear that many cases of pediatric-onset ADHD continue on well into adulthood, albeit often undiagnosed.
Whether NSSI and suicidal behavior are actually the same entity is currently a topic of intense research, according to Dr. Balazs, who is both a child and adolescent psychiatrist, as well as an adult psychiatrist.
She presented highlights of her cross-sectional study of 202 adolescent inpatients, 51% of them female, at the Vadaskert Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Hospital, a tertiary care center in Budapest. Using the structured diagnostic Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview for Children and Adolescents (MINI Kid) and the self-rated Deliberate Self-Harm Inventory, Dr. Balazs and her coinvestigators determined that 52 of the adolescents, including 23 boys and 29 girls, met full diagnostic criteria for ADHD and another 77 demonstrated more than five subthreshold ADHD symptoms.
Strikingly, 35 of the 52 teens diagnosed with ADHD, or 67%, had current NSSI. Only 10 of these patients were boys. The other 25, or 71% of the total, were girls.
Psychiatric comorbidities proved to be the rule rather than the exception in the adolescent inpatients with ADHD plus NSSI. Among these inpatients, 94% had a history of suicidal behavior. In addition, 66% carried the diagnosis of oppositional defiant disorder, 63% generalized anxiety disorder, 60% had a psychotic disorder, and 51% had experienced a manic episode. Among them, 49% were diagnosed with social anxiety disorder, 46% with obsessive-compulsive disorder, 31% with panic disorder, 23% with conduct disorder, and an equal percentage with agoraphobia. Furthermore, 43% had a major depressive disorder and 34%, dysthymia. Alcohol abuse or dependence was present in 20%, and an equal percentage had psychoactive substance use disorder.
Dr. Balazs said she and her coinvestigators were surprised by the high prevalence of symptoms of comorbid psychotic disorder in conjunction with NSSI and ADHD. One possible explanation, she opined, is that as inpatients the study participants were at the more severe end of the disease spectrum, and some patients may have been admitted not solely because of the severity of their comorbidities. Another possibility is that, in some cases, what was labeled psychotic disorder may actually have been prodromal unipolar depression.
A key finding in Dr. Balazs’s study was that, according to a regression analysis, the relationship between ADHD and NSSI was mediated entirely by the symptoms of the ADHD comorbidities. Specifically, the significant risk factors for NSSI in patients with ADHD were affective disorders, suicidality, and psychotic disorders in both sexes, with the addition of comorbid alcohol abuse or dependence in girls only. There was no evidence of a direct causal relationship between ADHD, per se, and NSSI.
‘Findings warrant further investigation’
The study, which looks at the association between NSSI and adolescents is interesting, yet preliminary, said David Fassler, MD, in an interview.
“The authors conclude that girls with ADHD are at particularly high risk of NSSI,” said Dr. Fassler, clinical professor of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington. Dr. Fassler was not involved with the study.
“It is limited by sample size, acuity, and the incidence of comorbidities,” said Dr. Fassler, who had no conflicts of interest. “Nonetheless, the findings are intriguing and warrant further investigation with larger samples in diverse clinical settings.”
The study was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund. In addition, Dr. Balazs received funding from the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. The full details of the study have been published (BMC Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 6;18[1]:34).
SOURCE: Balazs J et al. ECNP 2020, Abstract EDU.02.
Recent studies constitute a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen adolescents with ADHD for nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI) and its risk factors, Judit Balazs, MD, PhD, said at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
She was lead author of one of these studies, which drew a remarkable and disturbing conclusion: “We found – and it’s a very alarming result – that more than 70% of those people who had ADHD and [nonsuicidal self-injury] were girls. The girls with ADHD seem to be a high-risk population,” observed Dr. Balazs, professor and chair of the department of developmental psychology at Eotvos Lorand University, Budapest.
NSSI first became a specific diagnosis in the DSM-5. It is defined as deliberate, nonculturally sanctioned, nonsuicidal self-injury on at least five occasions within the past year and carried out with the aim of improving one’s emotional state as a result. The prevalence of NSSI among the general population of adolescents is high, with various investigators reporting rates of 15%-45%. Among adolescents with mental disorders, the reported prevalence climbs to 40%-80%. even though it’s now clear that many cases of pediatric-onset ADHD continue on well into adulthood, albeit often undiagnosed.
Whether NSSI and suicidal behavior are actually the same entity is currently a topic of intense research, according to Dr. Balazs, who is both a child and adolescent psychiatrist, as well as an adult psychiatrist.
She presented highlights of her cross-sectional study of 202 adolescent inpatients, 51% of them female, at the Vadaskert Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Hospital, a tertiary care center in Budapest. Using the structured diagnostic Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview for Children and Adolescents (MINI Kid) and the self-rated Deliberate Self-Harm Inventory, Dr. Balazs and her coinvestigators determined that 52 of the adolescents, including 23 boys and 29 girls, met full diagnostic criteria for ADHD and another 77 demonstrated more than five subthreshold ADHD symptoms.
Strikingly, 35 of the 52 teens diagnosed with ADHD, or 67%, had current NSSI. Only 10 of these patients were boys. The other 25, or 71% of the total, were girls.
Psychiatric comorbidities proved to be the rule rather than the exception in the adolescent inpatients with ADHD plus NSSI. Among these inpatients, 94% had a history of suicidal behavior. In addition, 66% carried the diagnosis of oppositional defiant disorder, 63% generalized anxiety disorder, 60% had a psychotic disorder, and 51% had experienced a manic episode. Among them, 49% were diagnosed with social anxiety disorder, 46% with obsessive-compulsive disorder, 31% with panic disorder, 23% with conduct disorder, and an equal percentage with agoraphobia. Furthermore, 43% had a major depressive disorder and 34%, dysthymia. Alcohol abuse or dependence was present in 20%, and an equal percentage had psychoactive substance use disorder.
Dr. Balazs said she and her coinvestigators were surprised by the high prevalence of symptoms of comorbid psychotic disorder in conjunction with NSSI and ADHD. One possible explanation, she opined, is that as inpatients the study participants were at the more severe end of the disease spectrum, and some patients may have been admitted not solely because of the severity of their comorbidities. Another possibility is that, in some cases, what was labeled psychotic disorder may actually have been prodromal unipolar depression.
A key finding in Dr. Balazs’s study was that, according to a regression analysis, the relationship between ADHD and NSSI was mediated entirely by the symptoms of the ADHD comorbidities. Specifically, the significant risk factors for NSSI in patients with ADHD were affective disorders, suicidality, and psychotic disorders in both sexes, with the addition of comorbid alcohol abuse or dependence in girls only. There was no evidence of a direct causal relationship between ADHD, per se, and NSSI.
‘Findings warrant further investigation’
The study, which looks at the association between NSSI and adolescents is interesting, yet preliminary, said David Fassler, MD, in an interview.
“The authors conclude that girls with ADHD are at particularly high risk of NSSI,” said Dr. Fassler, clinical professor of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington. Dr. Fassler was not involved with the study.
“It is limited by sample size, acuity, and the incidence of comorbidities,” said Dr. Fassler, who had no conflicts of interest. “Nonetheless, the findings are intriguing and warrant further investigation with larger samples in diverse clinical settings.”
The study was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund. In addition, Dr. Balazs received funding from the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. The full details of the study have been published (BMC Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 6;18[1]:34).
SOURCE: Balazs J et al. ECNP 2020, Abstract EDU.02.
FROM ECNP 2020
Can experiencing bigotry and racism lead to PTSD?
I have been studying, writing about, and treating posttraumatic stress disorder for many years. Over this time, I have seen PTSD expand to more and more areas of life, including my own view of a “subthreshold” version, which occurs in vulnerable people who experience a job loss, divorce, financial setbacks, or any number of painful life events.
As I noted in my recent book, “Find Freedom Fast,” for some people, PTSD can be triggered in the wake of events that are not life-threatening yet catastrophic for them and not tied to manmade or natural disasters, torture, assault, or war zone experiences.
The expansion of PTSD has led to the disorder being recognized in ICU patients during and after recovery (Crit Care Med. 2015 May;43[5]:1121-9), as well as in people diagnosed with cancer (Lancet Psychiatry. 2017 Apr;4[4]:330-8) and other illnesses that may cause emotional trauma – where one feels that one’s life is threatened. In some instances, the person’s life might indeed be in danger, not unlike what can happen in disasters, wars, torture, and even in some encounters with law enforcement.
This leads me to yet another circumstance that in some, may be tied to PTSD – and that is racial, religious, ethnic, and gender-related bigotry. In these cases, individuals feel threatened just for who they are in a society. Being on the receiving end of a circumstance that threatens a person’s very existence would seem to me to place a person as a potential survivor of PTSD, as well as any number of disorders, including anxiety, depression, or even paranoia.
Yes, discrimination and prejudice have been with us for a long time, and what concerns me is the psychological effect it has on children as well as adults. Friends of Irish descent remind me of hearing stories from parents and grandparents about employment signs reading, “Irish need not apply.” Certainly, those of Italian ancestry will easily recall the prejudice focused against them. And members of the Jewish community also can easily remember the bigotry and exclusion they have been subject to in certain neighborhoods and organizations, in addition to the horrors of the Holocaust during World War II, and the anti-Semitic chants in Charlottesville, Va., from just 3 years ago – with gun-carrying militants doing the chanting.
Obviously, in certain circles, we still have private clubs, plus neighborhoods and residential buildings that exclude people for a variety of reasons.
Coming from a medical family, years ago I heard stories that, if you were Roman Catholic, it would be hard to get into certain medical schools – which might explain the establishment of Catholic medical schools that often were open to people of other faiths. Then we had medical school discrimination toward Jewish students, which was followed by the establishment of medical schools focused on admitting more Jewish students. The African American community also responded to discrimination by establishing medical schools, such as the school at Howard University in Washington.
Furthermore, we cannot forget the discrimination that women faced in institutions of higher learning. My father had two women in his medical school class, I was told. In my era, I would say at least 30% were women, and today, in the United States, medical school classes are more equally balanced with men and women. Some schools have more women than men.
The question I ask, is: How did all those women feel for so many years knowing that, for reasons beyond their control, they were prevented from achieving their chosen goals? Some might have felt badly, and others might have internalized the rejection. Others might have developed PTSD based on feelings of rejection.
However, the question here mainly is: Can PTSD result when exclusion and prejudice induce fear and terror in those on the receiving end – especially innocent children? Children separated from their parents at the U.S.-Mexico border and those who witness their parents being shot immediately come to mind. This trauma can last well beyond childhood.
and make us realize the extent to which the African American community has been traumatized. Perhaps we should not be surprised by a study that found that the prevalence of PTSD among African Americans is 9.1%, compared with 6.8% for Whites (J Anxiety Dis. 2009 Jun;23[5]:573-90). Speaking with Black colleagues, friends, and patients, reading books such “The Warmth of Other Suns,” and watching films such as “Green Book,” give us a sense of how dangerous it was for Black families to travel in certain parts of the country in the recent past. I recall as a child hearing that, in Miami Beach, people of color could not stay overnight. (Even as a child I was surprised – having never heard anything like that. After all, I went to school with people of many religions and backgrounds. My parents thought those practices were terrible, and were appalled when they learned that some hotels were closed to Jews and others closed to Catholics.)
DSM-5, ICD-10 fall short
The DSM-5 describes trauma using a more or less one-dimensional set of guidelines as the focus. Those guidelines include exposure to direct violence, manmade or natural disasters, war, or torture, as well as exposure to a disaster or a life-threatening situation affecting a loved one. The ICD-10 is less restrictive about trauma but still has some limitations.
While considering potential PTSD, I try to use a less rigid diagnostic multidimensional approach, where I assess individual differences and experiences that play a role in those experiences as well as the patient’s vulnerability to the causation of PTSD – which also has to include any exposure to trauma (Curr Opin Psychol. 2017 Apr;14:29-34) before age 11 or 12. The data suggest that such early exposure leaves people more vulnerable to PTSD as adults (Soc Sci Med. 2018 Feb;199:230-40).
In my view, if individuals are frightened because of who they are – be it tied to their religion, race, sexual identity, or ethnicity – and what harm may come to them, and if they live in fear and avoidance of these potential traumatic situations that affect their mental stability and the way they live their lives, they might fit the PTSD model.
If we clinicians focus on what’s currently being brought vividly into the public eye today regarding the African American community, we would see that some of the ongoing fears of racism – whether tied to residential or workplace discrimination, unfair treatment by figures of authority, harassment, health inequities, or microaggressions – may give rise to PTSD. I know we can do better. We should broaden our definition and awareness of this very serious disorder – and be prepared to treat it.
Dr. London has been a practicing psychiatrist for 4 decades and a newspaper columnist for almost as long. He has a private practice in New York and is author of “Find Freedom Fast: Short-Term Therapy That Works” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). Dr. London has no conflicts of interest.
I have been studying, writing about, and treating posttraumatic stress disorder for many years. Over this time, I have seen PTSD expand to more and more areas of life, including my own view of a “subthreshold” version, which occurs in vulnerable people who experience a job loss, divorce, financial setbacks, or any number of painful life events.
As I noted in my recent book, “Find Freedom Fast,” for some people, PTSD can be triggered in the wake of events that are not life-threatening yet catastrophic for them and not tied to manmade or natural disasters, torture, assault, or war zone experiences.
The expansion of PTSD has led to the disorder being recognized in ICU patients during and after recovery (Crit Care Med. 2015 May;43[5]:1121-9), as well as in people diagnosed with cancer (Lancet Psychiatry. 2017 Apr;4[4]:330-8) and other illnesses that may cause emotional trauma – where one feels that one’s life is threatened. In some instances, the person’s life might indeed be in danger, not unlike what can happen in disasters, wars, torture, and even in some encounters with law enforcement.
This leads me to yet another circumstance that in some, may be tied to PTSD – and that is racial, religious, ethnic, and gender-related bigotry. In these cases, individuals feel threatened just for who they are in a society. Being on the receiving end of a circumstance that threatens a person’s very existence would seem to me to place a person as a potential survivor of PTSD, as well as any number of disorders, including anxiety, depression, or even paranoia.
Yes, discrimination and prejudice have been with us for a long time, and what concerns me is the psychological effect it has on children as well as adults. Friends of Irish descent remind me of hearing stories from parents and grandparents about employment signs reading, “Irish need not apply.” Certainly, those of Italian ancestry will easily recall the prejudice focused against them. And members of the Jewish community also can easily remember the bigotry and exclusion they have been subject to in certain neighborhoods and organizations, in addition to the horrors of the Holocaust during World War II, and the anti-Semitic chants in Charlottesville, Va., from just 3 years ago – with gun-carrying militants doing the chanting.
Obviously, in certain circles, we still have private clubs, plus neighborhoods and residential buildings that exclude people for a variety of reasons.
Coming from a medical family, years ago I heard stories that, if you were Roman Catholic, it would be hard to get into certain medical schools – which might explain the establishment of Catholic medical schools that often were open to people of other faiths. Then we had medical school discrimination toward Jewish students, which was followed by the establishment of medical schools focused on admitting more Jewish students. The African American community also responded to discrimination by establishing medical schools, such as the school at Howard University in Washington.
Furthermore, we cannot forget the discrimination that women faced in institutions of higher learning. My father had two women in his medical school class, I was told. In my era, I would say at least 30% were women, and today, in the United States, medical school classes are more equally balanced with men and women. Some schools have more women than men.
The question I ask, is: How did all those women feel for so many years knowing that, for reasons beyond their control, they were prevented from achieving their chosen goals? Some might have felt badly, and others might have internalized the rejection. Others might have developed PTSD based on feelings of rejection.
However, the question here mainly is: Can PTSD result when exclusion and prejudice induce fear and terror in those on the receiving end – especially innocent children? Children separated from their parents at the U.S.-Mexico border and those who witness their parents being shot immediately come to mind. This trauma can last well beyond childhood.
and make us realize the extent to which the African American community has been traumatized. Perhaps we should not be surprised by a study that found that the prevalence of PTSD among African Americans is 9.1%, compared with 6.8% for Whites (J Anxiety Dis. 2009 Jun;23[5]:573-90). Speaking with Black colleagues, friends, and patients, reading books such “The Warmth of Other Suns,” and watching films such as “Green Book,” give us a sense of how dangerous it was for Black families to travel in certain parts of the country in the recent past. I recall as a child hearing that, in Miami Beach, people of color could not stay overnight. (Even as a child I was surprised – having never heard anything like that. After all, I went to school with people of many religions and backgrounds. My parents thought those practices were terrible, and were appalled when they learned that some hotels were closed to Jews and others closed to Catholics.)
DSM-5, ICD-10 fall short
The DSM-5 describes trauma using a more or less one-dimensional set of guidelines as the focus. Those guidelines include exposure to direct violence, manmade or natural disasters, war, or torture, as well as exposure to a disaster or a life-threatening situation affecting a loved one. The ICD-10 is less restrictive about trauma but still has some limitations.
While considering potential PTSD, I try to use a less rigid diagnostic multidimensional approach, where I assess individual differences and experiences that play a role in those experiences as well as the patient’s vulnerability to the causation of PTSD – which also has to include any exposure to trauma (Curr Opin Psychol. 2017 Apr;14:29-34) before age 11 or 12. The data suggest that such early exposure leaves people more vulnerable to PTSD as adults (Soc Sci Med. 2018 Feb;199:230-40).
In my view, if individuals are frightened because of who they are – be it tied to their religion, race, sexual identity, or ethnicity – and what harm may come to them, and if they live in fear and avoidance of these potential traumatic situations that affect their mental stability and the way they live their lives, they might fit the PTSD model.
If we clinicians focus on what’s currently being brought vividly into the public eye today regarding the African American community, we would see that some of the ongoing fears of racism – whether tied to residential or workplace discrimination, unfair treatment by figures of authority, harassment, health inequities, or microaggressions – may give rise to PTSD. I know we can do better. We should broaden our definition and awareness of this very serious disorder – and be prepared to treat it.
Dr. London has been a practicing psychiatrist for 4 decades and a newspaper columnist for almost as long. He has a private practice in New York and is author of “Find Freedom Fast: Short-Term Therapy That Works” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). Dr. London has no conflicts of interest.
I have been studying, writing about, and treating posttraumatic stress disorder for many years. Over this time, I have seen PTSD expand to more and more areas of life, including my own view of a “subthreshold” version, which occurs in vulnerable people who experience a job loss, divorce, financial setbacks, or any number of painful life events.
As I noted in my recent book, “Find Freedom Fast,” for some people, PTSD can be triggered in the wake of events that are not life-threatening yet catastrophic for them and not tied to manmade or natural disasters, torture, assault, or war zone experiences.
The expansion of PTSD has led to the disorder being recognized in ICU patients during and after recovery (Crit Care Med. 2015 May;43[5]:1121-9), as well as in people diagnosed with cancer (Lancet Psychiatry. 2017 Apr;4[4]:330-8) and other illnesses that may cause emotional trauma – where one feels that one’s life is threatened. In some instances, the person’s life might indeed be in danger, not unlike what can happen in disasters, wars, torture, and even in some encounters with law enforcement.
This leads me to yet another circumstance that in some, may be tied to PTSD – and that is racial, religious, ethnic, and gender-related bigotry. In these cases, individuals feel threatened just for who they are in a society. Being on the receiving end of a circumstance that threatens a person’s very existence would seem to me to place a person as a potential survivor of PTSD, as well as any number of disorders, including anxiety, depression, or even paranoia.
Yes, discrimination and prejudice have been with us for a long time, and what concerns me is the psychological effect it has on children as well as adults. Friends of Irish descent remind me of hearing stories from parents and grandparents about employment signs reading, “Irish need not apply.” Certainly, those of Italian ancestry will easily recall the prejudice focused against them. And members of the Jewish community also can easily remember the bigotry and exclusion they have been subject to in certain neighborhoods and organizations, in addition to the horrors of the Holocaust during World War II, and the anti-Semitic chants in Charlottesville, Va., from just 3 years ago – with gun-carrying militants doing the chanting.
Obviously, in certain circles, we still have private clubs, plus neighborhoods and residential buildings that exclude people for a variety of reasons.
Coming from a medical family, years ago I heard stories that, if you were Roman Catholic, it would be hard to get into certain medical schools – which might explain the establishment of Catholic medical schools that often were open to people of other faiths. Then we had medical school discrimination toward Jewish students, which was followed by the establishment of medical schools focused on admitting more Jewish students. The African American community also responded to discrimination by establishing medical schools, such as the school at Howard University in Washington.
Furthermore, we cannot forget the discrimination that women faced in institutions of higher learning. My father had two women in his medical school class, I was told. In my era, I would say at least 30% were women, and today, in the United States, medical school classes are more equally balanced with men and women. Some schools have more women than men.
The question I ask, is: How did all those women feel for so many years knowing that, for reasons beyond their control, they were prevented from achieving their chosen goals? Some might have felt badly, and others might have internalized the rejection. Others might have developed PTSD based on feelings of rejection.
However, the question here mainly is: Can PTSD result when exclusion and prejudice induce fear and terror in those on the receiving end – especially innocent children? Children separated from their parents at the U.S.-Mexico border and those who witness their parents being shot immediately come to mind. This trauma can last well beyond childhood.
and make us realize the extent to which the African American community has been traumatized. Perhaps we should not be surprised by a study that found that the prevalence of PTSD among African Americans is 9.1%, compared with 6.8% for Whites (J Anxiety Dis. 2009 Jun;23[5]:573-90). Speaking with Black colleagues, friends, and patients, reading books such “The Warmth of Other Suns,” and watching films such as “Green Book,” give us a sense of how dangerous it was for Black families to travel in certain parts of the country in the recent past. I recall as a child hearing that, in Miami Beach, people of color could not stay overnight. (Even as a child I was surprised – having never heard anything like that. After all, I went to school with people of many religions and backgrounds. My parents thought those practices were terrible, and were appalled when they learned that some hotels were closed to Jews and others closed to Catholics.)
DSM-5, ICD-10 fall short
The DSM-5 describes trauma using a more or less one-dimensional set of guidelines as the focus. Those guidelines include exposure to direct violence, manmade or natural disasters, war, or torture, as well as exposure to a disaster or a life-threatening situation affecting a loved one. The ICD-10 is less restrictive about trauma but still has some limitations.
While considering potential PTSD, I try to use a less rigid diagnostic multidimensional approach, where I assess individual differences and experiences that play a role in those experiences as well as the patient’s vulnerability to the causation of PTSD – which also has to include any exposure to trauma (Curr Opin Psychol. 2017 Apr;14:29-34) before age 11 or 12. The data suggest that such early exposure leaves people more vulnerable to PTSD as adults (Soc Sci Med. 2018 Feb;199:230-40).
In my view, if individuals are frightened because of who they are – be it tied to their religion, race, sexual identity, or ethnicity – and what harm may come to them, and if they live in fear and avoidance of these potential traumatic situations that affect their mental stability and the way they live their lives, they might fit the PTSD model.
If we clinicians focus on what’s currently being brought vividly into the public eye today regarding the African American community, we would see that some of the ongoing fears of racism – whether tied to residential or workplace discrimination, unfair treatment by figures of authority, harassment, health inequities, or microaggressions – may give rise to PTSD. I know we can do better. We should broaden our definition and awareness of this very serious disorder – and be prepared to treat it.
Dr. London has been a practicing psychiatrist for 4 decades and a newspaper columnist for almost as long. He has a private practice in New York and is author of “Find Freedom Fast: Short-Term Therapy That Works” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). Dr. London has no conflicts of interest.
Sleep EEG may predict later antidepressant response
A change in rapid eye movement sleeping pattern as measured by quantitative EEG in patients with major depressive disorder after just a single week on a first-line antidepressant predicts eventual clinical response or nonresponse to the medication weeks later, Thorsten Mikoteit, MD, reported at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
This finding from a small, randomized, controlled trial opens the door to a novel biomarker-based treatment strategy: namely, an immediate switch to a different antidepressant in predicted nonresponders to the first agent. The goal is to improve the final treatment response rate while collapsing the time required to get there, explained Dr. Mikoteit, a psychiatrist affiliated with the University of Basel (Switzerland).
“In real terms, it means that patients, often in the depths of despair, might not need to wait weeks to see if their therapy is working before modifying their treatment,” he observed.
There is a huge unmet need for a biomarker predictive of response to antidepressant medication in patients with major depression, the psychiatrist added. At present, the treatment response rate is unsatisfactory. Moreover, clinical improvement takes a long time to achieve, often requiring several rounds of therapeutic trials during which patients are exposed to weeks of unpleasant side effects of drugs that are ultimately switched out for lack of efficacy or poor tolerance.
The quantitative EEG biomarker under investigation is prefrontal theta cordance (PTC) during REM sleep. It is computed from the absolute and relative theta power in tonic REM sleep. PTC has been shown to correlate with frontocingulate brain activity and cerebral blood perfusion. In an earlier pilot study, Dr. Mikoteit and coinvestigators demonstrated in 33 patients who were experiencing a depressive episode that an increase in PTC after their first week on an antidepressant was associated a significantly increased treatment response rate at the end of the fourth week on the drug, while nonresponders failed to show such increase (J Psychiatr Res. 2017 Sep;92:64-73).
At ECNP 2020, Dr. Mikoteit presented preliminary results from an ongoing randomized, controlled trial including 37 patients hospitalized for major depressive disorder. All underwent baseline evaluation using the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD) and were placed on the first-line antidepressant of their psychiatrist’s choice. After 1 week of therapy, participants underwent polysomnography with PTC measurement during tonic REM sleep.
Twenty-two patients were randomized to the intervention arm, in which investigators informed treating psychiatrists of the PTC results. The clinicians were instructed to change to another antidepressant if the biomarker predicted nonresponse or stay the course if the PTC results were favorable. Polysomnography was repeated 1 week later in the intervention arm, and the second-line antidepressant was either continued or switched out depending on the PTC findings. In the control arm, psychiatrists weren’t informed of the PTC results and patients continued on their initial antidepressant. The intervention and control groups were comparable in terms of age, sex, and severity of depression, with an average baseline HAMD score of 22.
A treatment response was defined as at least a 50% reduction in HAMD score from baseline to week 5. About 86% of patients who switched antidepressants based upon their 1-week quantitative EEG findings were categorized as treatment responders at week 5, compared with 20% of controls.
The overall 5-week response rate in the intervention group was 73%, compared with 60% in the control arm. This favorable trend didn’t achieve statistical significance, presumably because of the study’s sample size; however, the study is continuing to enroll participants in order to achieve a definitive result.
Dr. Mikoteit noted that the cost and inconvenience of spending a night in a sleep laboratory would be worthwhile if it resulted in the ability to give effective treatment much sooner. This would be particularly advantageous in patients at increased risk for suicide.
he said.
Study could have “enormous implications”
Of note, in the landmark National Institute of Mental Health–sponsored Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression (STAR*D) study, slightly less than half of patients with major depressive disorder achieved a treatment response to their first-line antidepressant, and it took an average of 6 weeks of therapy to do. About one in four nonresponders who chose to switch to a different antidepressant got better.
“The STAR*D trial is still the gold standard for understanding antidepressant response, and so being able to see if an antidepressant works within 1 week would be a real breakthrough,” Catherine Harmer, DPhil, said in an interview.
“Most of the time, patients need to wait for around 4 weeks before they can tell if they are responding to a particular antidepressant or not. This is a hugely disabling and lengthy process, and often a different treatment then needs to be started,” added Dr. Harmer, professor of cognitive neuroscience and director of the Psychopharmacology and Emotional Research Lab at the University of Oxford (England).
“If the study results presented by Dr. Mikoteit are replicated in a larger blinded study, then it would have enormous implications for the future treatment of individuals with depression,” according to Dr. Harmer, who was not involved in the study and has no conflicts of interest related to it.
Dr. Mikoteit reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by the Psychiatric University Hospital of Basel.
SOURCE: Mikoteit T et al. ECNP 2020, Abstract P.733.
A change in rapid eye movement sleeping pattern as measured by quantitative EEG in patients with major depressive disorder after just a single week on a first-line antidepressant predicts eventual clinical response or nonresponse to the medication weeks later, Thorsten Mikoteit, MD, reported at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
This finding from a small, randomized, controlled trial opens the door to a novel biomarker-based treatment strategy: namely, an immediate switch to a different antidepressant in predicted nonresponders to the first agent. The goal is to improve the final treatment response rate while collapsing the time required to get there, explained Dr. Mikoteit, a psychiatrist affiliated with the University of Basel (Switzerland).
“In real terms, it means that patients, often in the depths of despair, might not need to wait weeks to see if their therapy is working before modifying their treatment,” he observed.
There is a huge unmet need for a biomarker predictive of response to antidepressant medication in patients with major depression, the psychiatrist added. At present, the treatment response rate is unsatisfactory. Moreover, clinical improvement takes a long time to achieve, often requiring several rounds of therapeutic trials during which patients are exposed to weeks of unpleasant side effects of drugs that are ultimately switched out for lack of efficacy or poor tolerance.
The quantitative EEG biomarker under investigation is prefrontal theta cordance (PTC) during REM sleep. It is computed from the absolute and relative theta power in tonic REM sleep. PTC has been shown to correlate with frontocingulate brain activity and cerebral blood perfusion. In an earlier pilot study, Dr. Mikoteit and coinvestigators demonstrated in 33 patients who were experiencing a depressive episode that an increase in PTC after their first week on an antidepressant was associated a significantly increased treatment response rate at the end of the fourth week on the drug, while nonresponders failed to show such increase (J Psychiatr Res. 2017 Sep;92:64-73).
At ECNP 2020, Dr. Mikoteit presented preliminary results from an ongoing randomized, controlled trial including 37 patients hospitalized for major depressive disorder. All underwent baseline evaluation using the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD) and were placed on the first-line antidepressant of their psychiatrist’s choice. After 1 week of therapy, participants underwent polysomnography with PTC measurement during tonic REM sleep.
Twenty-two patients were randomized to the intervention arm, in which investigators informed treating psychiatrists of the PTC results. The clinicians were instructed to change to another antidepressant if the biomarker predicted nonresponse or stay the course if the PTC results were favorable. Polysomnography was repeated 1 week later in the intervention arm, and the second-line antidepressant was either continued or switched out depending on the PTC findings. In the control arm, psychiatrists weren’t informed of the PTC results and patients continued on their initial antidepressant. The intervention and control groups were comparable in terms of age, sex, and severity of depression, with an average baseline HAMD score of 22.
A treatment response was defined as at least a 50% reduction in HAMD score from baseline to week 5. About 86% of patients who switched antidepressants based upon their 1-week quantitative EEG findings were categorized as treatment responders at week 5, compared with 20% of controls.
The overall 5-week response rate in the intervention group was 73%, compared with 60% in the control arm. This favorable trend didn’t achieve statistical significance, presumably because of the study’s sample size; however, the study is continuing to enroll participants in order to achieve a definitive result.
Dr. Mikoteit noted that the cost and inconvenience of spending a night in a sleep laboratory would be worthwhile if it resulted in the ability to give effective treatment much sooner. This would be particularly advantageous in patients at increased risk for suicide.
he said.
Study could have “enormous implications”
Of note, in the landmark National Institute of Mental Health–sponsored Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression (STAR*D) study, slightly less than half of patients with major depressive disorder achieved a treatment response to their first-line antidepressant, and it took an average of 6 weeks of therapy to do. About one in four nonresponders who chose to switch to a different antidepressant got better.
“The STAR*D trial is still the gold standard for understanding antidepressant response, and so being able to see if an antidepressant works within 1 week would be a real breakthrough,” Catherine Harmer, DPhil, said in an interview.
“Most of the time, patients need to wait for around 4 weeks before they can tell if they are responding to a particular antidepressant or not. This is a hugely disabling and lengthy process, and often a different treatment then needs to be started,” added Dr. Harmer, professor of cognitive neuroscience and director of the Psychopharmacology and Emotional Research Lab at the University of Oxford (England).
“If the study results presented by Dr. Mikoteit are replicated in a larger blinded study, then it would have enormous implications for the future treatment of individuals with depression,” according to Dr. Harmer, who was not involved in the study and has no conflicts of interest related to it.
Dr. Mikoteit reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by the Psychiatric University Hospital of Basel.
SOURCE: Mikoteit T et al. ECNP 2020, Abstract P.733.
A change in rapid eye movement sleeping pattern as measured by quantitative EEG in patients with major depressive disorder after just a single week on a first-line antidepressant predicts eventual clinical response or nonresponse to the medication weeks later, Thorsten Mikoteit, MD, reported at the virtual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
This finding from a small, randomized, controlled trial opens the door to a novel biomarker-based treatment strategy: namely, an immediate switch to a different antidepressant in predicted nonresponders to the first agent. The goal is to improve the final treatment response rate while collapsing the time required to get there, explained Dr. Mikoteit, a psychiatrist affiliated with the University of Basel (Switzerland).
“In real terms, it means that patients, often in the depths of despair, might not need to wait weeks to see if their therapy is working before modifying their treatment,” he observed.
There is a huge unmet need for a biomarker predictive of response to antidepressant medication in patients with major depression, the psychiatrist added. At present, the treatment response rate is unsatisfactory. Moreover, clinical improvement takes a long time to achieve, often requiring several rounds of therapeutic trials during which patients are exposed to weeks of unpleasant side effects of drugs that are ultimately switched out for lack of efficacy or poor tolerance.
The quantitative EEG biomarker under investigation is prefrontal theta cordance (PTC) during REM sleep. It is computed from the absolute and relative theta power in tonic REM sleep. PTC has been shown to correlate with frontocingulate brain activity and cerebral blood perfusion. In an earlier pilot study, Dr. Mikoteit and coinvestigators demonstrated in 33 patients who were experiencing a depressive episode that an increase in PTC after their first week on an antidepressant was associated a significantly increased treatment response rate at the end of the fourth week on the drug, while nonresponders failed to show such increase (J Psychiatr Res. 2017 Sep;92:64-73).
At ECNP 2020, Dr. Mikoteit presented preliminary results from an ongoing randomized, controlled trial including 37 patients hospitalized for major depressive disorder. All underwent baseline evaluation using the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD) and were placed on the first-line antidepressant of their psychiatrist’s choice. After 1 week of therapy, participants underwent polysomnography with PTC measurement during tonic REM sleep.
Twenty-two patients were randomized to the intervention arm, in which investigators informed treating psychiatrists of the PTC results. The clinicians were instructed to change to another antidepressant if the biomarker predicted nonresponse or stay the course if the PTC results were favorable. Polysomnography was repeated 1 week later in the intervention arm, and the second-line antidepressant was either continued or switched out depending on the PTC findings. In the control arm, psychiatrists weren’t informed of the PTC results and patients continued on their initial antidepressant. The intervention and control groups were comparable in terms of age, sex, and severity of depression, with an average baseline HAMD score of 22.
A treatment response was defined as at least a 50% reduction in HAMD score from baseline to week 5. About 86% of patients who switched antidepressants based upon their 1-week quantitative EEG findings were categorized as treatment responders at week 5, compared with 20% of controls.
The overall 5-week response rate in the intervention group was 73%, compared with 60% in the control arm. This favorable trend didn’t achieve statistical significance, presumably because of the study’s sample size; however, the study is continuing to enroll participants in order to achieve a definitive result.
Dr. Mikoteit noted that the cost and inconvenience of spending a night in a sleep laboratory would be worthwhile if it resulted in the ability to give effective treatment much sooner. This would be particularly advantageous in patients at increased risk for suicide.
he said.
Study could have “enormous implications”
Of note, in the landmark National Institute of Mental Health–sponsored Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression (STAR*D) study, slightly less than half of patients with major depressive disorder achieved a treatment response to their first-line antidepressant, and it took an average of 6 weeks of therapy to do. About one in four nonresponders who chose to switch to a different antidepressant got better.
“The STAR*D trial is still the gold standard for understanding antidepressant response, and so being able to see if an antidepressant works within 1 week would be a real breakthrough,” Catherine Harmer, DPhil, said in an interview.
“Most of the time, patients need to wait for around 4 weeks before they can tell if they are responding to a particular antidepressant or not. This is a hugely disabling and lengthy process, and often a different treatment then needs to be started,” added Dr. Harmer, professor of cognitive neuroscience and director of the Psychopharmacology and Emotional Research Lab at the University of Oxford (England).
“If the study results presented by Dr. Mikoteit are replicated in a larger blinded study, then it would have enormous implications for the future treatment of individuals with depression,” according to Dr. Harmer, who was not involved in the study and has no conflicts of interest related to it.
Dr. Mikoteit reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by the Psychiatric University Hospital of Basel.
SOURCE: Mikoteit T et al. ECNP 2020, Abstract P.733.
FROM ECNP 2020
COVID-19: New guidance to stem mental health crisis in frontline HCPs
A new review offers fresh guidance to help stem the mental health toll of the COVID-19 pandemic on frontline clinicians.
Investigators gathered practice guidelines and resources from a wide range of health care organizations and professional societies to develop a conceptual framework of mental health support for health care professionals (HCPs) caring for COVID-19 patients.
“Support needs to be deployed in multiple dimensions – including individual, organizational, and societal levels – and include training in resilience, stress reduction, emotional awareness, and self-care strategies,” lead author Rachel Schwartz, PhD, health services researcher, Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview.
The review was published Aug. 21 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
An opportune moment
Coauthor Rebecca Margolis, DO, director of well-being in the division of medical education and faculty development, Children’s Hospital of Los Angeles, said that this is “an opportune moment to look at how we treat frontline providers in this country.”
Studies of previous pandemics have shown heightened distress in HCPs, even years after the pandemic, and the unique challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic surpass those of previous pandemics, Dr. Margolis said in an interview.
Dr. Schwartz, Dr. Margolis, and coauthors Uma Anand, PhD, LP, and Jina Sinskey, MD, met through the Collaborative for Healing and Renewal in Medicine network, a group of medical educators, leaders in academic medicine, experts in burnout research and interventions, and trainees working together to promote well-being among trainees and practicing physicians.
“We were brought together on a conference call in March, when things were particularly bad in New York, and started looking to see what resources we could get to frontline providers who were suffering. It was great to lean on each other and stand on the shoulders of colleagues in New York, who were the ones we learned from on these calls,” said Dr. Margolis.
The authors recommended addressing clinicians’ basic practical needs, including ensuring essentials like meals and transportation, establishing a “well-being area” within hospitals for staff to rest, and providing well-stocked living quarters so clinicians can safely quarantine from family, as well as personal protective equipment and child care.
Clinicians are often asked to “assume new professional roles to meet evolving needs” during a pandemic, which can increase stress. The authors recommended targeted training, assessment of clinician skills before redeployment to a new clinical role, and clear communication practices around redeployment.
Recognition from hospital and government leaders improves morale and supports clinicians’ ability to continue delivering care. Leadership should “leverage communication strategies to provide clinicians with up-to-date information and reassurance,” they wrote.
‘Uniquely isolated’
Dr. Margolis noted that
“My colleagues feel a sense of moral injury, putting their lives on the line at work, performing the most perilous job, and their kids can’t hang out with other kids, which just puts salt on the wound,” she said.
Additional sources of moral injury are deciding which patients should receive life support in the event of inadequate resources and bearing witness to, or enforcing, policies that lead to patients dying alone.
Leaders should encourage clinicians to “seek informal support from colleagues, managers, or chaplains” and to “provide rapid access to professional help,” the authors noted.
Furthermore, they contended that leaders should “proactively and routinely monitor the psychological well-being of their teams,” since guilt and shame often prevent clinicians from disclosing feelings of moral injury.
“Being provided with routine mental health support should be normalized and it should be part of the job – not only during COVID-19 but in general,” Dr. Schwartz said.
‘Battle buddies’
Dr. Margolis recommended the “battle buddy” model for mutual peer support.
Dr. Anand, a mental health clinician at Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., elaborated.
“We connect residents with each other, and they form pairs to support each other and watch for warning signs such as withdrawal from colleagues, being frequently tearful, not showing up at work or showing up late, missing assignments, making mistakes at work, increased use of alcohol, or verbalizing serious concerns,” Dr. Anand said.
If the buddy shows any of these warning signs, he or she can be directed to appropriate resources to get help.
Since the pandemic has interfered with the ability to connect with colleagues and family members, attention should be paid to addressing the social support needs of clinicians.
Dr. Anand suggested that clinicians maintain contact with counselors, friends, and family, even if they cannot be together in person and must connect “virtually.”
Resilience and strength training are “key” components of reducing clinician distress, but trainings as well as processing groups and support workshops should be offered during protected time, Dr. Margolis advised, since it can be burdensome for clinicians to wake up early or stay late to attend these sessions.
Leaders and administrators should “model self-care and well-being,” she noted. For example, sending emails to clinicians late at night or on weekends creates an expectation of a rapid reply, which leads to additional pressure for the clinician.
“This is of the most powerful unspoken curricula we can develop,” Dr. Margolis emphasized.
Self-care critical
Marcus S. Shaker, MD, MSc, associate professor of pediatrics, medicine, and community and family medicine, Children’s Hospital at Dartmouth-Hitchcock in Lebanon, N.H., and Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., said the study was “a much appreciated, timely reminder of the importance of clinician wellness.”
Moreover, “without self-care, our ability to help our patients withers. This article provides a useful conceptual framework for individuals and organizations to provide the right care at the right time in these unprecedented times,” said Dr. Shaker, who was not involved with the study.
The authors agreed, stating that clinicians “require proactive psychological protection specifically because they are a population known for putting others’ needs before their own.”
They recommended several resources for HCPs, including the Physician Support Line; Headspace, a mindfulness Web-based app for reducing stress and anxiety; the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline; and the Crisis Text Line.
The authors and Dr. Shaker disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A new review offers fresh guidance to help stem the mental health toll of the COVID-19 pandemic on frontline clinicians.
Investigators gathered practice guidelines and resources from a wide range of health care organizations and professional societies to develop a conceptual framework of mental health support for health care professionals (HCPs) caring for COVID-19 patients.
“Support needs to be deployed in multiple dimensions – including individual, organizational, and societal levels – and include training in resilience, stress reduction, emotional awareness, and self-care strategies,” lead author Rachel Schwartz, PhD, health services researcher, Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview.
The review was published Aug. 21 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
An opportune moment
Coauthor Rebecca Margolis, DO, director of well-being in the division of medical education and faculty development, Children’s Hospital of Los Angeles, said that this is “an opportune moment to look at how we treat frontline providers in this country.”
Studies of previous pandemics have shown heightened distress in HCPs, even years after the pandemic, and the unique challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic surpass those of previous pandemics, Dr. Margolis said in an interview.
Dr. Schwartz, Dr. Margolis, and coauthors Uma Anand, PhD, LP, and Jina Sinskey, MD, met through the Collaborative for Healing and Renewal in Medicine network, a group of medical educators, leaders in academic medicine, experts in burnout research and interventions, and trainees working together to promote well-being among trainees and practicing physicians.
“We were brought together on a conference call in March, when things were particularly bad in New York, and started looking to see what resources we could get to frontline providers who were suffering. It was great to lean on each other and stand on the shoulders of colleagues in New York, who were the ones we learned from on these calls,” said Dr. Margolis.
The authors recommended addressing clinicians’ basic practical needs, including ensuring essentials like meals and transportation, establishing a “well-being area” within hospitals for staff to rest, and providing well-stocked living quarters so clinicians can safely quarantine from family, as well as personal protective equipment and child care.
Clinicians are often asked to “assume new professional roles to meet evolving needs” during a pandemic, which can increase stress. The authors recommended targeted training, assessment of clinician skills before redeployment to a new clinical role, and clear communication practices around redeployment.
Recognition from hospital and government leaders improves morale and supports clinicians’ ability to continue delivering care. Leadership should “leverage communication strategies to provide clinicians with up-to-date information and reassurance,” they wrote.
‘Uniquely isolated’
Dr. Margolis noted that
“My colleagues feel a sense of moral injury, putting their lives on the line at work, performing the most perilous job, and their kids can’t hang out with other kids, which just puts salt on the wound,” she said.
Additional sources of moral injury are deciding which patients should receive life support in the event of inadequate resources and bearing witness to, or enforcing, policies that lead to patients dying alone.
Leaders should encourage clinicians to “seek informal support from colleagues, managers, or chaplains” and to “provide rapid access to professional help,” the authors noted.
Furthermore, they contended that leaders should “proactively and routinely monitor the psychological well-being of their teams,” since guilt and shame often prevent clinicians from disclosing feelings of moral injury.
“Being provided with routine mental health support should be normalized and it should be part of the job – not only during COVID-19 but in general,” Dr. Schwartz said.
‘Battle buddies’
Dr. Margolis recommended the “battle buddy” model for mutual peer support.
Dr. Anand, a mental health clinician at Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., elaborated.
“We connect residents with each other, and they form pairs to support each other and watch for warning signs such as withdrawal from colleagues, being frequently tearful, not showing up at work or showing up late, missing assignments, making mistakes at work, increased use of alcohol, or verbalizing serious concerns,” Dr. Anand said.
If the buddy shows any of these warning signs, he or she can be directed to appropriate resources to get help.
Since the pandemic has interfered with the ability to connect with colleagues and family members, attention should be paid to addressing the social support needs of clinicians.
Dr. Anand suggested that clinicians maintain contact with counselors, friends, and family, even if they cannot be together in person and must connect “virtually.”
Resilience and strength training are “key” components of reducing clinician distress, but trainings as well as processing groups and support workshops should be offered during protected time, Dr. Margolis advised, since it can be burdensome for clinicians to wake up early or stay late to attend these sessions.
Leaders and administrators should “model self-care and well-being,” she noted. For example, sending emails to clinicians late at night or on weekends creates an expectation of a rapid reply, which leads to additional pressure for the clinician.
“This is of the most powerful unspoken curricula we can develop,” Dr. Margolis emphasized.
Self-care critical
Marcus S. Shaker, MD, MSc, associate professor of pediatrics, medicine, and community and family medicine, Children’s Hospital at Dartmouth-Hitchcock in Lebanon, N.H., and Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., said the study was “a much appreciated, timely reminder of the importance of clinician wellness.”
Moreover, “without self-care, our ability to help our patients withers. This article provides a useful conceptual framework for individuals and organizations to provide the right care at the right time in these unprecedented times,” said Dr. Shaker, who was not involved with the study.
The authors agreed, stating that clinicians “require proactive psychological protection specifically because they are a population known for putting others’ needs before their own.”
They recommended several resources for HCPs, including the Physician Support Line; Headspace, a mindfulness Web-based app for reducing stress and anxiety; the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline; and the Crisis Text Line.
The authors and Dr. Shaker disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A new review offers fresh guidance to help stem the mental health toll of the COVID-19 pandemic on frontline clinicians.
Investigators gathered practice guidelines and resources from a wide range of health care organizations and professional societies to develop a conceptual framework of mental health support for health care professionals (HCPs) caring for COVID-19 patients.
“Support needs to be deployed in multiple dimensions – including individual, organizational, and societal levels – and include training in resilience, stress reduction, emotional awareness, and self-care strategies,” lead author Rachel Schwartz, PhD, health services researcher, Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview.
The review was published Aug. 21 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
An opportune moment
Coauthor Rebecca Margolis, DO, director of well-being in the division of medical education and faculty development, Children’s Hospital of Los Angeles, said that this is “an opportune moment to look at how we treat frontline providers in this country.”
Studies of previous pandemics have shown heightened distress in HCPs, even years after the pandemic, and the unique challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic surpass those of previous pandemics, Dr. Margolis said in an interview.
Dr. Schwartz, Dr. Margolis, and coauthors Uma Anand, PhD, LP, and Jina Sinskey, MD, met through the Collaborative for Healing and Renewal in Medicine network, a group of medical educators, leaders in academic medicine, experts in burnout research and interventions, and trainees working together to promote well-being among trainees and practicing physicians.
“We were brought together on a conference call in March, when things were particularly bad in New York, and started looking to see what resources we could get to frontline providers who were suffering. It was great to lean on each other and stand on the shoulders of colleagues in New York, who were the ones we learned from on these calls,” said Dr. Margolis.
The authors recommended addressing clinicians’ basic practical needs, including ensuring essentials like meals and transportation, establishing a “well-being area” within hospitals for staff to rest, and providing well-stocked living quarters so clinicians can safely quarantine from family, as well as personal protective equipment and child care.
Clinicians are often asked to “assume new professional roles to meet evolving needs” during a pandemic, which can increase stress. The authors recommended targeted training, assessment of clinician skills before redeployment to a new clinical role, and clear communication practices around redeployment.
Recognition from hospital and government leaders improves morale and supports clinicians’ ability to continue delivering care. Leadership should “leverage communication strategies to provide clinicians with up-to-date information and reassurance,” they wrote.
‘Uniquely isolated’
Dr. Margolis noted that
“My colleagues feel a sense of moral injury, putting their lives on the line at work, performing the most perilous job, and their kids can’t hang out with other kids, which just puts salt on the wound,” she said.
Additional sources of moral injury are deciding which patients should receive life support in the event of inadequate resources and bearing witness to, or enforcing, policies that lead to patients dying alone.
Leaders should encourage clinicians to “seek informal support from colleagues, managers, or chaplains” and to “provide rapid access to professional help,” the authors noted.
Furthermore, they contended that leaders should “proactively and routinely monitor the psychological well-being of their teams,” since guilt and shame often prevent clinicians from disclosing feelings of moral injury.
“Being provided with routine mental health support should be normalized and it should be part of the job – not only during COVID-19 but in general,” Dr. Schwartz said.
‘Battle buddies’
Dr. Margolis recommended the “battle buddy” model for mutual peer support.
Dr. Anand, a mental health clinician at Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., elaborated.
“We connect residents with each other, and they form pairs to support each other and watch for warning signs such as withdrawal from colleagues, being frequently tearful, not showing up at work or showing up late, missing assignments, making mistakes at work, increased use of alcohol, or verbalizing serious concerns,” Dr. Anand said.
If the buddy shows any of these warning signs, he or she can be directed to appropriate resources to get help.
Since the pandemic has interfered with the ability to connect with colleagues and family members, attention should be paid to addressing the social support needs of clinicians.
Dr. Anand suggested that clinicians maintain contact with counselors, friends, and family, even if they cannot be together in person and must connect “virtually.”
Resilience and strength training are “key” components of reducing clinician distress, but trainings as well as processing groups and support workshops should be offered during protected time, Dr. Margolis advised, since it can be burdensome for clinicians to wake up early or stay late to attend these sessions.
Leaders and administrators should “model self-care and well-being,” she noted. For example, sending emails to clinicians late at night or on weekends creates an expectation of a rapid reply, which leads to additional pressure for the clinician.
“This is of the most powerful unspoken curricula we can develop,” Dr. Margolis emphasized.
Self-care critical
Marcus S. Shaker, MD, MSc, associate professor of pediatrics, medicine, and community and family medicine, Children’s Hospital at Dartmouth-Hitchcock in Lebanon, N.H., and Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., said the study was “a much appreciated, timely reminder of the importance of clinician wellness.”
Moreover, “without self-care, our ability to help our patients withers. This article provides a useful conceptual framework for individuals and organizations to provide the right care at the right time in these unprecedented times,” said Dr. Shaker, who was not involved with the study.
The authors agreed, stating that clinicians “require proactive psychological protection specifically because they are a population known for putting others’ needs before their own.”
They recommended several resources for HCPs, including the Physician Support Line; Headspace, a mindfulness Web-based app for reducing stress and anxiety; the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline; and the Crisis Text Line.
The authors and Dr. Shaker disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Antidepressant use shows gender, racial disparities
Women are more than twice as likely as men to use antidepressants, and use among White women is at least double that of other races/ethnicities, according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.
Here are the actual numbers: 17.7% of women and 8.4% of men used an antidepressant in the 30 days before being interviewed for the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Put them together, and it works out to 13.2% of all adults over the 4-year period from 2015 to 2018, Debra J. Brody, MPH, and Qiuping Gu, MD, PhD, said Sept. 4 in an NCHS data brief.
Non-Hispanic White women had a past-30-day prevalence of 22.3%, compared with 10.0% for non-Hispanic Black women, 3.4% for non-Hispanic Asian women, and 8.9% for Hispanic women, based on the NHANES data.
The order was the same for men, but the numbers are lower. Non-Hispanic Whites had the highest antidepressant use at 10.5%, followed by non-Hispanic Blacks (5.0%), non-Hispanic Asians (2.1%), and Hispanics (4.0%). All of the differences between Whites and non-Whites were significant for both women and men, the researchers noted.
A look at trends over time shows that the gap between men and women has widened in the last 10 years. Past-30-day use among women went from 13.8% in 2009-2010 to 18.6% in 2017-2018, with a corresponding increase from 7.1% to 8.7% in men. For women, that change was significant; for men, it was not, Ms. Brody and Dr. Gu said.
The sample size averaged just over 6,000 for each of the five 2-year NHANES cycles included in the analysis. The survey includes a household interview and a physical examination at a mobile exam center.
Women are more than twice as likely as men to use antidepressants, and use among White women is at least double that of other races/ethnicities, according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.

Here are the actual numbers: 17.7% of women and 8.4% of men used an antidepressant in the 30 days before being interviewed for the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Put them together, and it works out to 13.2% of all adults over the 4-year period from 2015 to 2018, Debra J. Brody, MPH, and Qiuping Gu, MD, PhD, said Sept. 4 in an NCHS data brief.
Non-Hispanic White women had a past-30-day prevalence of 22.3%, compared with 10.0% for non-Hispanic Black women, 3.4% for non-Hispanic Asian women, and 8.9% for Hispanic women, based on the NHANES data.
The order was the same for men, but the numbers are lower. Non-Hispanic Whites had the highest antidepressant use at 10.5%, followed by non-Hispanic Blacks (5.0%), non-Hispanic Asians (2.1%), and Hispanics (4.0%). All of the differences between Whites and non-Whites were significant for both women and men, the researchers noted.
A look at trends over time shows that the gap between men and women has widened in the last 10 years. Past-30-day use among women went from 13.8% in 2009-2010 to 18.6% in 2017-2018, with a corresponding increase from 7.1% to 8.7% in men. For women, that change was significant; for men, it was not, Ms. Brody and Dr. Gu said.
The sample size averaged just over 6,000 for each of the five 2-year NHANES cycles included in the analysis. The survey includes a household interview and a physical examination at a mobile exam center.
Women are more than twice as likely as men to use antidepressants, and use among White women is at least double that of other races/ethnicities, according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.

Here are the actual numbers: 17.7% of women and 8.4% of men used an antidepressant in the 30 days before being interviewed for the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Put them together, and it works out to 13.2% of all adults over the 4-year period from 2015 to 2018, Debra J. Brody, MPH, and Qiuping Gu, MD, PhD, said Sept. 4 in an NCHS data brief.
Non-Hispanic White women had a past-30-day prevalence of 22.3%, compared with 10.0% for non-Hispanic Black women, 3.4% for non-Hispanic Asian women, and 8.9% for Hispanic women, based on the NHANES data.
The order was the same for men, but the numbers are lower. Non-Hispanic Whites had the highest antidepressant use at 10.5%, followed by non-Hispanic Blacks (5.0%), non-Hispanic Asians (2.1%), and Hispanics (4.0%). All of the differences between Whites and non-Whites were significant for both women and men, the researchers noted.
A look at trends over time shows that the gap between men and women has widened in the last 10 years. Past-30-day use among women went from 13.8% in 2009-2010 to 18.6% in 2017-2018, with a corresponding increase from 7.1% to 8.7% in men. For women, that change was significant; for men, it was not, Ms. Brody and Dr. Gu said.
The sample size averaged just over 6,000 for each of the five 2-year NHANES cycles included in the analysis. The survey includes a household interview and a physical examination at a mobile exam center.