User login
More than one in six patients with status epilepticus are readmitted after hospital discharge
PHILADELPHIA – according to research presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. It is possible to identify patients at high risk of readmission, which could allow neurologists to reduce their clinical and economic burden, said the investigators.
Status epilepticus is a major neurologic emergency. Patients often have significant disability and may represent a burden on their families and on the health care system. To identify independent predictors of 30-day hospital readmission among patients discharged after generalized convulsive status epilepticus, Mohamad Rahwan, MD, a neurologist at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and colleagues examined data from the 2014 Nationwide Readmission Database.
The investigators included adults with a primary discharge diagnosis of generalized convulsive status epilepticus, identified by the ICD-9-CM code 345.3, in their study. Patients who died during hospitalization, had missing information on the length of stay, or were discharged in December 2014 were excluded from analysis. Dr. Rahwan and colleagues calculated the overall 30-day readmission rate for the sample and compared prespecified groups by their 30-day readmission status. They performed multiple logistic regression analysis to identify independent predictors of 30-day readmission, adjusting for potential confounders.
In all, 14,562 adults were discharged with a diagnosis of generalized convulsive status epilepticus. Of this population, 2,520 patients (17.3%) were readmitted within 30 days. Multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that patients discharged against medical advice (odds ratio, 1.45), those discharged to short-term hospital (OR, 1.39), those with comorbid conditions (OR for Charlson Comorbidity Index of 1, 1.12; OR for Charlson Comorbidity Index of 2 or greater, 1.32), and those with a length of stay exceeding 6 days (OR, 1.42) had a greater risk of 30-day readmission. The researchers observed an inverse association for patients aged 45 years or older and for those in high-income households. “Greater attention to high-risk subgroups may identify opportunities to ameliorate the clinical and economic burden of early readmissions after generalized convulsive status epilepticus,” said the researchers.
The researchers had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Rahwan M et al. AAN 2019, Abstract S36.006.
PHILADELPHIA – according to research presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. It is possible to identify patients at high risk of readmission, which could allow neurologists to reduce their clinical and economic burden, said the investigators.
Status epilepticus is a major neurologic emergency. Patients often have significant disability and may represent a burden on their families and on the health care system. To identify independent predictors of 30-day hospital readmission among patients discharged after generalized convulsive status epilepticus, Mohamad Rahwan, MD, a neurologist at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and colleagues examined data from the 2014 Nationwide Readmission Database.
The investigators included adults with a primary discharge diagnosis of generalized convulsive status epilepticus, identified by the ICD-9-CM code 345.3, in their study. Patients who died during hospitalization, had missing information on the length of stay, or were discharged in December 2014 were excluded from analysis. Dr. Rahwan and colleagues calculated the overall 30-day readmission rate for the sample and compared prespecified groups by their 30-day readmission status. They performed multiple logistic regression analysis to identify independent predictors of 30-day readmission, adjusting for potential confounders.
In all, 14,562 adults were discharged with a diagnosis of generalized convulsive status epilepticus. Of this population, 2,520 patients (17.3%) were readmitted within 30 days. Multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that patients discharged against medical advice (odds ratio, 1.45), those discharged to short-term hospital (OR, 1.39), those with comorbid conditions (OR for Charlson Comorbidity Index of 1, 1.12; OR for Charlson Comorbidity Index of 2 or greater, 1.32), and those with a length of stay exceeding 6 days (OR, 1.42) had a greater risk of 30-day readmission. The researchers observed an inverse association for patients aged 45 years or older and for those in high-income households. “Greater attention to high-risk subgroups may identify opportunities to ameliorate the clinical and economic burden of early readmissions after generalized convulsive status epilepticus,” said the researchers.
The researchers had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Rahwan M et al. AAN 2019, Abstract S36.006.
PHILADELPHIA – according to research presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. It is possible to identify patients at high risk of readmission, which could allow neurologists to reduce their clinical and economic burden, said the investigators.
Status epilepticus is a major neurologic emergency. Patients often have significant disability and may represent a burden on their families and on the health care system. To identify independent predictors of 30-day hospital readmission among patients discharged after generalized convulsive status epilepticus, Mohamad Rahwan, MD, a neurologist at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and colleagues examined data from the 2014 Nationwide Readmission Database.
The investigators included adults with a primary discharge diagnosis of generalized convulsive status epilepticus, identified by the ICD-9-CM code 345.3, in their study. Patients who died during hospitalization, had missing information on the length of stay, or were discharged in December 2014 were excluded from analysis. Dr. Rahwan and colleagues calculated the overall 30-day readmission rate for the sample and compared prespecified groups by their 30-day readmission status. They performed multiple logistic regression analysis to identify independent predictors of 30-day readmission, adjusting for potential confounders.
In all, 14,562 adults were discharged with a diagnosis of generalized convulsive status epilepticus. Of this population, 2,520 patients (17.3%) were readmitted within 30 days. Multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that patients discharged against medical advice (odds ratio, 1.45), those discharged to short-term hospital (OR, 1.39), those with comorbid conditions (OR for Charlson Comorbidity Index of 1, 1.12; OR for Charlson Comorbidity Index of 2 or greater, 1.32), and those with a length of stay exceeding 6 days (OR, 1.42) had a greater risk of 30-day readmission. The researchers observed an inverse association for patients aged 45 years or older and for those in high-income households. “Greater attention to high-risk subgroups may identify opportunities to ameliorate the clinical and economic burden of early readmissions after generalized convulsive status epilepticus,” said the researchers.
The researchers had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Rahwan M et al. AAN 2019, Abstract S36.006.
REPORTING FROM AAN 2019
Changes in brain networks may predict MS worsening
PHILADELPHIA – (MS), according to a study described at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Neurologists do not have reliable biomarkers to predict disease evolution in the medium or long term for patients with MS. The ability to predict disease evolution accurately could aid in the choice of treatment.
Maria Assunta Rocca, MD, head of the Neuroimaging of CNS White Matter Unit, Department of Neurology, Institute of Experimental Neurology, Scientific Institute Ospedale, San Raffaele, Milan, Italy, and colleagues sought to evaluate structural and functional network MRI measures as predictors of clinical deterioration over 6.5 years. They obtained conventional, 3D, T1-weighted, diffusion-weighted MRI, and resting-state functional MRI images at baseline from 233 patients with MS and 77 healthy controls. Patients underwent a neurologic examination at baseline and after a median follow-up period of 6.5 years. At follow-up, the researchers classified patients as clinically stable or worsened, according to their change in Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score. They also evaluated conversion to secondary progressive MS among patients with relapsing remitting MS at baseline.
To identify the main large-scale resting state functional connectivity networks, Dr. Rocca and colleagues applied spatial independent component analysis to resting state functional MRI data. They applied the same technique to gray matter probability maps and fractional anisotropy maps to identify the corresponding structural gray matter and white matter networks.
At follow-up, 105 patients with MS (45%) had significant EDSS worsening. Of 157 patients with relapsing remitting MS, 26 (16%) converted to secondary progressive MS. The multivariable model, after adjustment for follow-up duration, identified baseline EDSS score (odds ratio, 1.59), normalized gray matter volume (OR, 0.99), and abnormally high baseline resting state functional connectivity of the left precentral gyrus in the sensorimotor network (OR, 1.67) as predictors of EDSS worsening. These variables remained significant after the researchers adjusted for treatment effect. Independent variables associated with conversion to secondary progressive MS included baseline EDSS score (OR, 2.8) and atrophy of gray matter networks associated with sensory (OR, 0.5) and motor (OR, 0.4) functions.
Dr. Rocca received personal compensation from Biogen Idec, Novartis, Genzyme, Sanofi-Aventis, Teva, Merck Serono, and Roche. Coauthors reported research support from Biogen, Merck Serono, Novartis, Teva, and Roche..
SOURCE: Filippi M et al. AAN 2019, Abstract S49.004.
PHILADELPHIA – (MS), according to a study described at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Neurologists do not have reliable biomarkers to predict disease evolution in the medium or long term for patients with MS. The ability to predict disease evolution accurately could aid in the choice of treatment.
Maria Assunta Rocca, MD, head of the Neuroimaging of CNS White Matter Unit, Department of Neurology, Institute of Experimental Neurology, Scientific Institute Ospedale, San Raffaele, Milan, Italy, and colleagues sought to evaluate structural and functional network MRI measures as predictors of clinical deterioration over 6.5 years. They obtained conventional, 3D, T1-weighted, diffusion-weighted MRI, and resting-state functional MRI images at baseline from 233 patients with MS and 77 healthy controls. Patients underwent a neurologic examination at baseline and after a median follow-up period of 6.5 years. At follow-up, the researchers classified patients as clinically stable or worsened, according to their change in Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score. They also evaluated conversion to secondary progressive MS among patients with relapsing remitting MS at baseline.
To identify the main large-scale resting state functional connectivity networks, Dr. Rocca and colleagues applied spatial independent component analysis to resting state functional MRI data. They applied the same technique to gray matter probability maps and fractional anisotropy maps to identify the corresponding structural gray matter and white matter networks.
At follow-up, 105 patients with MS (45%) had significant EDSS worsening. Of 157 patients with relapsing remitting MS, 26 (16%) converted to secondary progressive MS. The multivariable model, after adjustment for follow-up duration, identified baseline EDSS score (odds ratio, 1.59), normalized gray matter volume (OR, 0.99), and abnormally high baseline resting state functional connectivity of the left precentral gyrus in the sensorimotor network (OR, 1.67) as predictors of EDSS worsening. These variables remained significant after the researchers adjusted for treatment effect. Independent variables associated with conversion to secondary progressive MS included baseline EDSS score (OR, 2.8) and atrophy of gray matter networks associated with sensory (OR, 0.5) and motor (OR, 0.4) functions.
Dr. Rocca received personal compensation from Biogen Idec, Novartis, Genzyme, Sanofi-Aventis, Teva, Merck Serono, and Roche. Coauthors reported research support from Biogen, Merck Serono, Novartis, Teva, and Roche..
SOURCE: Filippi M et al. AAN 2019, Abstract S49.004.
PHILADELPHIA – (MS), according to a study described at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Neurologists do not have reliable biomarkers to predict disease evolution in the medium or long term for patients with MS. The ability to predict disease evolution accurately could aid in the choice of treatment.
Maria Assunta Rocca, MD, head of the Neuroimaging of CNS White Matter Unit, Department of Neurology, Institute of Experimental Neurology, Scientific Institute Ospedale, San Raffaele, Milan, Italy, and colleagues sought to evaluate structural and functional network MRI measures as predictors of clinical deterioration over 6.5 years. They obtained conventional, 3D, T1-weighted, diffusion-weighted MRI, and resting-state functional MRI images at baseline from 233 patients with MS and 77 healthy controls. Patients underwent a neurologic examination at baseline and after a median follow-up period of 6.5 years. At follow-up, the researchers classified patients as clinically stable or worsened, according to their change in Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score. They also evaluated conversion to secondary progressive MS among patients with relapsing remitting MS at baseline.
To identify the main large-scale resting state functional connectivity networks, Dr. Rocca and colleagues applied spatial independent component analysis to resting state functional MRI data. They applied the same technique to gray matter probability maps and fractional anisotropy maps to identify the corresponding structural gray matter and white matter networks.
At follow-up, 105 patients with MS (45%) had significant EDSS worsening. Of 157 patients with relapsing remitting MS, 26 (16%) converted to secondary progressive MS. The multivariable model, after adjustment for follow-up duration, identified baseline EDSS score (odds ratio, 1.59), normalized gray matter volume (OR, 0.99), and abnormally high baseline resting state functional connectivity of the left precentral gyrus in the sensorimotor network (OR, 1.67) as predictors of EDSS worsening. These variables remained significant after the researchers adjusted for treatment effect. Independent variables associated with conversion to secondary progressive MS included baseline EDSS score (OR, 2.8) and atrophy of gray matter networks associated with sensory (OR, 0.5) and motor (OR, 0.4) functions.
Dr. Rocca received personal compensation from Biogen Idec, Novartis, Genzyme, Sanofi-Aventis, Teva, Merck Serono, and Roche. Coauthors reported research support from Biogen, Merck Serono, Novartis, Teva, and Roche..
SOURCE: Filippi M et al. AAN 2019, Abstract S49.004.
REPORTING FROM AAN 2019
Key clinical point: Structural and functional network MRI measures predict long-term worsening in multiple sclerosis.
Major finding: The odds ratio of worsening for patients with abnormally high baseline resting state functional connectivity is 1.67.
Study details: A prospective imaging study of 233 patients with multiple sclerosis and 77 healthy controls.
Disclosures: Dr. Rocca received personal compensation from Biogen Idec, Novartis, Genzyme, Sanofi-Aventis, Teva, Merck Serono, and Roche. Coauthors reported research support from Biogen, Merck Serono, Novartis, Teva, and Roche.
Source: Filippi M et al. AAN 2019, Abstract S49.004.
Ibudilast’s efficacy differs in primary and secondary progressive MS
PHILADELPHIA – researchers reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The difference may be related to faster atrophy rates among patients with primary progressive MS who received placebo, compared with those with secondary progressive MS who received placebo.
The finding was surprising, said Andrew Goodman, MD, professor of neurology, chief of the neuroimmunology unit, and director of the multiple sclerosis center at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). “Going into the trial, it was my bias and expectation that both primary and secondary progressive MS would behave more similarly than different.”
The trial, SPRINT-MS, included more than 250 patients with progressive MS at 28 sites. Patients were aged 18-65 years and were followed for 96 weeks. Patients had primary progressive MS (n = 134) or secondary progressive MS (n = 121) and were randomized 1:1 to ibudilast or placebo.
Ibudilast is an orally administered small molecule that has been used in Japan for approximately 30 years for asthma and other indications, Dr. Goodman said. Preclinical models suggested that the drug may have neuroprotective effects.
The trial’s primary result – a 48% slowing in the rate of whole brain atrophy as measured by brain parenchymal fraction with ibudilast – was reported last year (N Engl J Med. 2018 Aug 30;379[9]:846-55).
The present study examined whether the treatment effect of ibudilast was similar by progressive disease type using a linear mixed model analytic approach.
The group with primary progressive MS included a smaller percentage of women. Patients with secondary progressive MS had longer disease duration and more brain atrophy at baseline.
“The overall benefit which we previously reported appears to be driven by subjects with primary progressive rather than secondary progressive MS,” Dr. Goodman said. Accounting for baseline covariates did not affect this result.
Among patients who received placebo, brain atrophy in those with secondary progressive MS was 57% slower than in those with primary progressive MS. The rate of atrophy for untreated patients with primary progressive MS “was roughly twice as fast as that in the secondary progressive MS group, which we think may explain in part the differential in efficacy,” Dr. Goodman said. “These findings may impact future trial design for progressive MS.”
The SPRINT-MS trial was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. The National Multiple Sclerosis Society and MediciNova also supported the study. Dr. Goodman reported receiving research support from pharmaceutical companies, as well as personal compensation from companies for consulting, serving on a scientific advisory board, and speaking.
SOURCE: Goodman A et al. AAN 2019, Abstract S12.007.
PHILADELPHIA – researchers reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The difference may be related to faster atrophy rates among patients with primary progressive MS who received placebo, compared with those with secondary progressive MS who received placebo.
The finding was surprising, said Andrew Goodman, MD, professor of neurology, chief of the neuroimmunology unit, and director of the multiple sclerosis center at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). “Going into the trial, it was my bias and expectation that both primary and secondary progressive MS would behave more similarly than different.”
The trial, SPRINT-MS, included more than 250 patients with progressive MS at 28 sites. Patients were aged 18-65 years and were followed for 96 weeks. Patients had primary progressive MS (n = 134) or secondary progressive MS (n = 121) and were randomized 1:1 to ibudilast or placebo.
Ibudilast is an orally administered small molecule that has been used in Japan for approximately 30 years for asthma and other indications, Dr. Goodman said. Preclinical models suggested that the drug may have neuroprotective effects.
The trial’s primary result – a 48% slowing in the rate of whole brain atrophy as measured by brain parenchymal fraction with ibudilast – was reported last year (N Engl J Med. 2018 Aug 30;379[9]:846-55).
The present study examined whether the treatment effect of ibudilast was similar by progressive disease type using a linear mixed model analytic approach.
The group with primary progressive MS included a smaller percentage of women. Patients with secondary progressive MS had longer disease duration and more brain atrophy at baseline.
“The overall benefit which we previously reported appears to be driven by subjects with primary progressive rather than secondary progressive MS,” Dr. Goodman said. Accounting for baseline covariates did not affect this result.
Among patients who received placebo, brain atrophy in those with secondary progressive MS was 57% slower than in those with primary progressive MS. The rate of atrophy for untreated patients with primary progressive MS “was roughly twice as fast as that in the secondary progressive MS group, which we think may explain in part the differential in efficacy,” Dr. Goodman said. “These findings may impact future trial design for progressive MS.”
The SPRINT-MS trial was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. The National Multiple Sclerosis Society and MediciNova also supported the study. Dr. Goodman reported receiving research support from pharmaceutical companies, as well as personal compensation from companies for consulting, serving on a scientific advisory board, and speaking.
SOURCE: Goodman A et al. AAN 2019, Abstract S12.007.
PHILADELPHIA – researchers reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The difference may be related to faster atrophy rates among patients with primary progressive MS who received placebo, compared with those with secondary progressive MS who received placebo.
The finding was surprising, said Andrew Goodman, MD, professor of neurology, chief of the neuroimmunology unit, and director of the multiple sclerosis center at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). “Going into the trial, it was my bias and expectation that both primary and secondary progressive MS would behave more similarly than different.”
The trial, SPRINT-MS, included more than 250 patients with progressive MS at 28 sites. Patients were aged 18-65 years and were followed for 96 weeks. Patients had primary progressive MS (n = 134) or secondary progressive MS (n = 121) and were randomized 1:1 to ibudilast or placebo.
Ibudilast is an orally administered small molecule that has been used in Japan for approximately 30 years for asthma and other indications, Dr. Goodman said. Preclinical models suggested that the drug may have neuroprotective effects.
The trial’s primary result – a 48% slowing in the rate of whole brain atrophy as measured by brain parenchymal fraction with ibudilast – was reported last year (N Engl J Med. 2018 Aug 30;379[9]:846-55).
The present study examined whether the treatment effect of ibudilast was similar by progressive disease type using a linear mixed model analytic approach.
The group with primary progressive MS included a smaller percentage of women. Patients with secondary progressive MS had longer disease duration and more brain atrophy at baseline.
“The overall benefit which we previously reported appears to be driven by subjects with primary progressive rather than secondary progressive MS,” Dr. Goodman said. Accounting for baseline covariates did not affect this result.
Among patients who received placebo, brain atrophy in those with secondary progressive MS was 57% slower than in those with primary progressive MS. The rate of atrophy for untreated patients with primary progressive MS “was roughly twice as fast as that in the secondary progressive MS group, which we think may explain in part the differential in efficacy,” Dr. Goodman said. “These findings may impact future trial design for progressive MS.”
The SPRINT-MS trial was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. The National Multiple Sclerosis Society and MediciNova also supported the study. Dr. Goodman reported receiving research support from pharmaceutical companies, as well as personal compensation from companies for consulting, serving on a scientific advisory board, and speaking.
SOURCE: Goodman A et al. AAN 2019, Abstract S12.007.
REPORTING FROM AAN 2019
Rimegepant dissolving tablets treat acute migraine in phase 3 trial
PHILADELPHIA – according to phase 3 trial results presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. The treatment’s efficacy is sustained for 2-48 hours, researchers reported.
Rimegepant is a small molecule calcitonin gene–related peptide receptor antagonist. A 75-mg oral tablet formulation was effective in phase 3 trials. The present study evaluated a novel, orally dissolving tablet formulation that is intended to speed the drug’s onset. The tablet’s time to peak concentration is 1.50 hours, compared with 1.99 hours for the oral tablet.
Formulation preferences
“People with migraine prefer orally dissolving tablets to oral tablets, mainly for their convenience, onset of action, and ability to be taken without drinking liquids,” said first author Richard B. Lipton, MD, of Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and colleagues.
To assess the formulation’s efficacy and safety, the investigators conducted a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Participants were aged at least 18 years and had migraine for at least 1 year. They had 2-8 moderate or severe migraine attacks and fewer than 15 headache days per month during the 3 months before the trial. Their preventive migraine medication doses, if any, had been stable for at least 3 months.
Coprimary efficacy endpoints were pain freedom 2 hours post dose and freedom from the most bothersome symptom at 2 hours post dose. The efficacy analyses included randomized subjects who had a qualifying migraine attack, took the study medication, and provided at least one postbaseline efficacy data point.
The investigators included 1,351 patients in their efficacy analysis – 669 who received rimegepant and 682 who received placebo. About 85% were female, and patients’ mean age was 40.2 years. They averaged 4.6 migraine attacks per month, and their most bothersome symptoms included photophobia (57%), nausea (23.5%), and phonophobia (19.3%). About 14% used preventive treatment.
Within 45 days of randomization, patients treated a migraine attack of moderate to severe intensity and completed an electronic diary predose to 48 hours post dose.
Less use of rescue medication
At 2 hours post dose, patients who received 75 mg rimegepant were more likely than patients who received placebo to achieve pain freedom (21.2% vs. 10.9%) and freedom from the most bothersome symptom (35.1% vs. 26.8%).
Numerical differences in the likelihood of pain relief between group began 15 minutes post dose, and the difference was statistically significant at 60 minutes (36.8% vs. 31.2%).
Various secondary endpoints, including ability to function normally at 2 hours post dose (38.1% vs. 25.8%), sustained pain relief from 2-48 hours (42.2% vs. 25.2%), and use of rescue medications within 24 hours (14.2% vs. 29.2%), also were statistically significant.
In the safety analysis, the most common adverse events were nausea (1.6% in the rimegepant group and 0.4% in the placebo group) and urinary tract infection (1.5% in the rimegepant group and 0.6% in the placebo group). There were no serious adverse events. “Safety and tolerability were similar to placebo,” Dr. Lipton and colleagues said.
Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, the developer of the drug, sponsored the study. Dr. Lipton has received honoraria and research support from Biohaven and holds stock in the company. Coauthors are employees of Biohaven.
PHILADELPHIA – according to phase 3 trial results presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. The treatment’s efficacy is sustained for 2-48 hours, researchers reported.
Rimegepant is a small molecule calcitonin gene–related peptide receptor antagonist. A 75-mg oral tablet formulation was effective in phase 3 trials. The present study evaluated a novel, orally dissolving tablet formulation that is intended to speed the drug’s onset. The tablet’s time to peak concentration is 1.50 hours, compared with 1.99 hours for the oral tablet.
Formulation preferences
“People with migraine prefer orally dissolving tablets to oral tablets, mainly for their convenience, onset of action, and ability to be taken without drinking liquids,” said first author Richard B. Lipton, MD, of Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and colleagues.
To assess the formulation’s efficacy and safety, the investigators conducted a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Participants were aged at least 18 years and had migraine for at least 1 year. They had 2-8 moderate or severe migraine attacks and fewer than 15 headache days per month during the 3 months before the trial. Their preventive migraine medication doses, if any, had been stable for at least 3 months.
Coprimary efficacy endpoints were pain freedom 2 hours post dose and freedom from the most bothersome symptom at 2 hours post dose. The efficacy analyses included randomized subjects who had a qualifying migraine attack, took the study medication, and provided at least one postbaseline efficacy data point.
The investigators included 1,351 patients in their efficacy analysis – 669 who received rimegepant and 682 who received placebo. About 85% were female, and patients’ mean age was 40.2 years. They averaged 4.6 migraine attacks per month, and their most bothersome symptoms included photophobia (57%), nausea (23.5%), and phonophobia (19.3%). About 14% used preventive treatment.
Within 45 days of randomization, patients treated a migraine attack of moderate to severe intensity and completed an electronic diary predose to 48 hours post dose.
Less use of rescue medication
At 2 hours post dose, patients who received 75 mg rimegepant were more likely than patients who received placebo to achieve pain freedom (21.2% vs. 10.9%) and freedom from the most bothersome symptom (35.1% vs. 26.8%).
Numerical differences in the likelihood of pain relief between group began 15 minutes post dose, and the difference was statistically significant at 60 minutes (36.8% vs. 31.2%).
Various secondary endpoints, including ability to function normally at 2 hours post dose (38.1% vs. 25.8%), sustained pain relief from 2-48 hours (42.2% vs. 25.2%), and use of rescue medications within 24 hours (14.2% vs. 29.2%), also were statistically significant.
In the safety analysis, the most common adverse events were nausea (1.6% in the rimegepant group and 0.4% in the placebo group) and urinary tract infection (1.5% in the rimegepant group and 0.6% in the placebo group). There were no serious adverse events. “Safety and tolerability were similar to placebo,” Dr. Lipton and colleagues said.
Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, the developer of the drug, sponsored the study. Dr. Lipton has received honoraria and research support from Biohaven and holds stock in the company. Coauthors are employees of Biohaven.
PHILADELPHIA – according to phase 3 trial results presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. The treatment’s efficacy is sustained for 2-48 hours, researchers reported.
Rimegepant is a small molecule calcitonin gene–related peptide receptor antagonist. A 75-mg oral tablet formulation was effective in phase 3 trials. The present study evaluated a novel, orally dissolving tablet formulation that is intended to speed the drug’s onset. The tablet’s time to peak concentration is 1.50 hours, compared with 1.99 hours for the oral tablet.
Formulation preferences
“People with migraine prefer orally dissolving tablets to oral tablets, mainly for their convenience, onset of action, and ability to be taken without drinking liquids,” said first author Richard B. Lipton, MD, of Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and colleagues.
To assess the formulation’s efficacy and safety, the investigators conducted a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Participants were aged at least 18 years and had migraine for at least 1 year. They had 2-8 moderate or severe migraine attacks and fewer than 15 headache days per month during the 3 months before the trial. Their preventive migraine medication doses, if any, had been stable for at least 3 months.
Coprimary efficacy endpoints were pain freedom 2 hours post dose and freedom from the most bothersome symptom at 2 hours post dose. The efficacy analyses included randomized subjects who had a qualifying migraine attack, took the study medication, and provided at least one postbaseline efficacy data point.
The investigators included 1,351 patients in their efficacy analysis – 669 who received rimegepant and 682 who received placebo. About 85% were female, and patients’ mean age was 40.2 years. They averaged 4.6 migraine attacks per month, and their most bothersome symptoms included photophobia (57%), nausea (23.5%), and phonophobia (19.3%). About 14% used preventive treatment.
Within 45 days of randomization, patients treated a migraine attack of moderate to severe intensity and completed an electronic diary predose to 48 hours post dose.
Less use of rescue medication
At 2 hours post dose, patients who received 75 mg rimegepant were more likely than patients who received placebo to achieve pain freedom (21.2% vs. 10.9%) and freedom from the most bothersome symptom (35.1% vs. 26.8%).
Numerical differences in the likelihood of pain relief between group began 15 minutes post dose, and the difference was statistically significant at 60 minutes (36.8% vs. 31.2%).
Various secondary endpoints, including ability to function normally at 2 hours post dose (38.1% vs. 25.8%), sustained pain relief from 2-48 hours (42.2% vs. 25.2%), and use of rescue medications within 24 hours (14.2% vs. 29.2%), also were statistically significant.
In the safety analysis, the most common adverse events were nausea (1.6% in the rimegepant group and 0.4% in the placebo group) and urinary tract infection (1.5% in the rimegepant group and 0.6% in the placebo group). There were no serious adverse events. “Safety and tolerability were similar to placebo,” Dr. Lipton and colleagues said.
Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, the developer of the drug, sponsored the study. Dr. Lipton has received honoraria and research support from Biohaven and holds stock in the company. Coauthors are employees of Biohaven.
REPORTING FROM AAN 2019
QI boosts adherence to protocol-based care for elevated blood lead levels
according to current guidelines, reported Courtney M. Brown, MD, and associates at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and the University of Cincinnati.
The study protocol, undertaken at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center’s pediatric primary care center, consisted of ordering multivitamins with iron and follow-up lead testing, educating families about identifying and reducing sources of lead exposure, and referring to a specialty environmental health clinic when indicated. Quality improvement and a real-time decision support program called Epic SmartPhrase was used to increase provider adherence. Results from patients aged 9-27 months who were seen at the hospital from February 2016 to June 2018 were included, according to the researchers. Their findings were published in Pediatrics.
Over the study period, 634 elevated blood lead levels (BLLs) were recorded. Between February 2016 – when the protocol was distributed – and May 2017 – when Epic SmartPhrase was introduced – a mean of 5% of cases received protocol-based care. After introduction of Epic Smartphase, the rate of adherence to protocol increased to 90%, which was maintained for the rest of the study.
“A reliable system for responding to BLLs is critical for optimizing outcomes for individuals, as well as activating public health systems to reduce environmental lead sources. Using tools within the EHR, we increased provider adherence with published guidelines. Our Epic SmartPhrase could be easily reproduced by other practices using EHRs. Similar strategies could be applied for standardizing the response to other laboratory tests,” the investigators wrote. “This type of intervention could ensure that screenings of all kinds trigger meaningful interventions.”
The study was supported by the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center through the All Children Thrive community health initiative; the study authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Brown CM et al. Pediatrics. 2019 May 9. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-3085.
according to current guidelines, reported Courtney M. Brown, MD, and associates at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and the University of Cincinnati.
The study protocol, undertaken at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center’s pediatric primary care center, consisted of ordering multivitamins with iron and follow-up lead testing, educating families about identifying and reducing sources of lead exposure, and referring to a specialty environmental health clinic when indicated. Quality improvement and a real-time decision support program called Epic SmartPhrase was used to increase provider adherence. Results from patients aged 9-27 months who were seen at the hospital from February 2016 to June 2018 were included, according to the researchers. Their findings were published in Pediatrics.
Over the study period, 634 elevated blood lead levels (BLLs) were recorded. Between February 2016 – when the protocol was distributed – and May 2017 – when Epic SmartPhrase was introduced – a mean of 5% of cases received protocol-based care. After introduction of Epic Smartphase, the rate of adherence to protocol increased to 90%, which was maintained for the rest of the study.
“A reliable system for responding to BLLs is critical for optimizing outcomes for individuals, as well as activating public health systems to reduce environmental lead sources. Using tools within the EHR, we increased provider adherence with published guidelines. Our Epic SmartPhrase could be easily reproduced by other practices using EHRs. Similar strategies could be applied for standardizing the response to other laboratory tests,” the investigators wrote. “This type of intervention could ensure that screenings of all kinds trigger meaningful interventions.”
The study was supported by the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center through the All Children Thrive community health initiative; the study authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Brown CM et al. Pediatrics. 2019 May 9. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-3085.
according to current guidelines, reported Courtney M. Brown, MD, and associates at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and the University of Cincinnati.
The study protocol, undertaken at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center’s pediatric primary care center, consisted of ordering multivitamins with iron and follow-up lead testing, educating families about identifying and reducing sources of lead exposure, and referring to a specialty environmental health clinic when indicated. Quality improvement and a real-time decision support program called Epic SmartPhrase was used to increase provider adherence. Results from patients aged 9-27 months who were seen at the hospital from February 2016 to June 2018 were included, according to the researchers. Their findings were published in Pediatrics.
Over the study period, 634 elevated blood lead levels (BLLs) were recorded. Between February 2016 – when the protocol was distributed – and May 2017 – when Epic SmartPhrase was introduced – a mean of 5% of cases received protocol-based care. After introduction of Epic Smartphase, the rate of adherence to protocol increased to 90%, which was maintained for the rest of the study.
“A reliable system for responding to BLLs is critical for optimizing outcomes for individuals, as well as activating public health systems to reduce environmental lead sources. Using tools within the EHR, we increased provider adherence with published guidelines. Our Epic SmartPhrase could be easily reproduced by other practices using EHRs. Similar strategies could be applied for standardizing the response to other laboratory tests,” the investigators wrote. “This type of intervention could ensure that screenings of all kinds trigger meaningful interventions.”
The study was supported by the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center through the All Children Thrive community health initiative; the study authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Brown CM et al. Pediatrics. 2019 May 9. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-3085.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Experts discuss what’s new in migraine treatment
PHILADELPHIA – At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, sat down with Stewart J. Tepper, MD, professor of neurology at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., to discuss in a video some of the new data presented at the meeting regarding the CGRP monoclonal antibodies, the small molecule receptor antagonists (gepants), and what Dr. Tepper described as “a real shift in paradigm and a watershed moment in migraine.”
The three gepants that are farthest along in clinical trials are ubrogepant, rimegepant, and atogepant. “Reassuring data” was presented, Dr. Tepper said, regarding liver toxicity, which has been a concern with earlier generations of the gepants. The Food and Drug Administration had mandated a close look at liver function with the use of these drugs, which are metabolized in the liver, and, to date, no safety signals have emerged.
The three CGRP monoclonal antibodies that are currently on the market are erenumab (Aimovig), fremanezumab (Ajovy), and galcanezumab (Emgality). Data from numerous open-label extension studies were presented. In general, it seems that “the monoclonal antibodies accumulate greater efficacy over time,” Dr. Tepper said. No safety concerns have emerged from 5 years of clinical trial data. With 250,000 patients on these drugs worldwide, that is “very reassuring,” Dr. Tepper said.
New data also show that the majority of patients with chronic migraine who are taking monoclonal antibodies convert from chronic migraine to episodic migraine. Additionally, new data show that use of monoclonal antibodies “dramatically reduce all migraine medication use,” Dr. Tepper said.
PHILADELPHIA – At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, sat down with Stewart J. Tepper, MD, professor of neurology at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., to discuss in a video some of the new data presented at the meeting regarding the CGRP monoclonal antibodies, the small molecule receptor antagonists (gepants), and what Dr. Tepper described as “a real shift in paradigm and a watershed moment in migraine.”
The three gepants that are farthest along in clinical trials are ubrogepant, rimegepant, and atogepant. “Reassuring data” was presented, Dr. Tepper said, regarding liver toxicity, which has been a concern with earlier generations of the gepants. The Food and Drug Administration had mandated a close look at liver function with the use of these drugs, which are metabolized in the liver, and, to date, no safety signals have emerged.
The three CGRP monoclonal antibodies that are currently on the market are erenumab (Aimovig), fremanezumab (Ajovy), and galcanezumab (Emgality). Data from numerous open-label extension studies were presented. In general, it seems that “the monoclonal antibodies accumulate greater efficacy over time,” Dr. Tepper said. No safety concerns have emerged from 5 years of clinical trial data. With 250,000 patients on these drugs worldwide, that is “very reassuring,” Dr. Tepper said.
New data also show that the majority of patients with chronic migraine who are taking monoclonal antibodies convert from chronic migraine to episodic migraine. Additionally, new data show that use of monoclonal antibodies “dramatically reduce all migraine medication use,” Dr. Tepper said.
PHILADELPHIA – At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, sat down with Stewart J. Tepper, MD, professor of neurology at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., to discuss in a video some of the new data presented at the meeting regarding the CGRP monoclonal antibodies, the small molecule receptor antagonists (gepants), and what Dr. Tepper described as “a real shift in paradigm and a watershed moment in migraine.”
The three gepants that are farthest along in clinical trials are ubrogepant, rimegepant, and atogepant. “Reassuring data” was presented, Dr. Tepper said, regarding liver toxicity, which has been a concern with earlier generations of the gepants. The Food and Drug Administration had mandated a close look at liver function with the use of these drugs, which are metabolized in the liver, and, to date, no safety signals have emerged.
The three CGRP monoclonal antibodies that are currently on the market are erenumab (Aimovig), fremanezumab (Ajovy), and galcanezumab (Emgality). Data from numerous open-label extension studies were presented. In general, it seems that “the monoclonal antibodies accumulate greater efficacy over time,” Dr. Tepper said. No safety concerns have emerged from 5 years of clinical trial data. With 250,000 patients on these drugs worldwide, that is “very reassuring,” Dr. Tepper said.
New data also show that the majority of patients with chronic migraine who are taking monoclonal antibodies convert from chronic migraine to episodic migraine. Additionally, new data show that use of monoclonal antibodies “dramatically reduce all migraine medication use,” Dr. Tepper said.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AAN 2019
Appendectomy linked to increased risk of subsequent Parkinson’s
.
“One of the factors that’s seen in the brains of patients with Parkinson’s disease is accumulation of an abnormal protein known as alpha-synuclein,” one of the study authors, Gregory S. Cooper, MD, said during a media briefing in advance of the annual Digestive Disease Week. “It’s released by damaged nerve cells in the brain. Not only is alpha-synuclein found in the brain of patients with Parkinson’s disease; it’s also found in the GI tract. It’s thought that its accumulation in the GI tract occurs prior to the development of its accumulation in the brain.”
This has prompted scientists around the world to evaluate the GI tract, including the appendix, for evidence about the pathophysiology and onset of Parkinson’s disease, said Dr. Cooper, professor of medicine, oncology, and population and quantitative health sciences at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland. “It’s thought that, potentially, in the presence of inflammation, [molecules] of this protein are released from damaged nerves in the gut and then are transported to the brain, where they accumulate,” he said. “Or, it could be that the appendix is a storage place for this protein and gets released at the time of appendectomy.”
To investigate if appendectomy increases the risk of Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Cooper and colleagues drew from the Explorys database, which contains EHRs from 26 integrated U.S. health care systems. They limited their search to patients who underwent appendectomies and those who were diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease based on Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine–Clinical Terms. The researchers chose a washout period of 6 months to the development of Parkinson’s disease after appendectomy, and compared the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in the general population to those with appendectomies.
Of the 62,218,050 records in the database, Dr. Cooper and colleagues identified 488,190 patients who underwent appendectomies. In all, 4,470 cases of Parkinson’s disease were observed in patients with appendectomies, and 177,230 cases of Parkinson’s disease in patients without appendectomies. The overall relative risk of developing Parkinson’s disease in patients after appendectomies was 3.19 (95% confidence interval, 3.10-3.28; P less than .0001), compared with those who did not undergo the procedure. The relative risk was higher in patients aged 18-64 years (RR, 4.27; 95% CI, 3.99-4.57; P less than .0001), compared with those 65 years and older (RR, 2.20; 95% CI, 2.13-2.27; P less than .0001). “We know that Parkinson’s disease is more common in the elderly,” Dr. Cooper said. “But at virtually all ages, the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease was higher in patients who had an appendectomy, compared to those without an appendectomy.”
The overall relative risk of developing Parkinson’s disease in patients after appendectomies was slightly higher in females (RR, 3.86; 95% CI, 3.71-4.02; P less than .0001), compared with males (RR, 2.67; 95% CI, 2.56-2.79; P less than .0001). The researchers also observed a similar effect of appendectomy by race. The overall relative risk of developing Parkinson’s disease in patients after appendectomy was slightly higher in African Americans (RR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.69-3.58; P less than .0001), compared with Asians (RR, 2.73; 95% CI, 2.19-3.41; P less than .0001), and whites (RR, 2.55; 95% CI, 2.48-2.63; P less than .0001).
“If these data get borne out, it may question the role of doing a discretionary appendectomy in a patient who’s having surgery for another reason,” Dr. Cooper said. “Our research does show a clear relationship between appendectomy and Parkinson’s disease. However, at this point, it’s only an association. As a next step, we’d like to conduct additional research to confirm this connection and better understand the mechanisms involved.”
He pointed out that, because of the nature of the Explorys database, he and his colleagues were unable to determine the length of time following appendectomy to the development of Parkinson’s disease.
The study’s lead author was Mohammed Z. Sheriff, MD, also of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Sheriff MZ et al. DDW 2019, Abstract 739.
.
“One of the factors that’s seen in the brains of patients with Parkinson’s disease is accumulation of an abnormal protein known as alpha-synuclein,” one of the study authors, Gregory S. Cooper, MD, said during a media briefing in advance of the annual Digestive Disease Week. “It’s released by damaged nerve cells in the brain. Not only is alpha-synuclein found in the brain of patients with Parkinson’s disease; it’s also found in the GI tract. It’s thought that its accumulation in the GI tract occurs prior to the development of its accumulation in the brain.”
This has prompted scientists around the world to evaluate the GI tract, including the appendix, for evidence about the pathophysiology and onset of Parkinson’s disease, said Dr. Cooper, professor of medicine, oncology, and population and quantitative health sciences at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland. “It’s thought that, potentially, in the presence of inflammation, [molecules] of this protein are released from damaged nerves in the gut and then are transported to the brain, where they accumulate,” he said. “Or, it could be that the appendix is a storage place for this protein and gets released at the time of appendectomy.”
To investigate if appendectomy increases the risk of Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Cooper and colleagues drew from the Explorys database, which contains EHRs from 26 integrated U.S. health care systems. They limited their search to patients who underwent appendectomies and those who were diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease based on Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine–Clinical Terms. The researchers chose a washout period of 6 months to the development of Parkinson’s disease after appendectomy, and compared the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in the general population to those with appendectomies.
Of the 62,218,050 records in the database, Dr. Cooper and colleagues identified 488,190 patients who underwent appendectomies. In all, 4,470 cases of Parkinson’s disease were observed in patients with appendectomies, and 177,230 cases of Parkinson’s disease in patients without appendectomies. The overall relative risk of developing Parkinson’s disease in patients after appendectomies was 3.19 (95% confidence interval, 3.10-3.28; P less than .0001), compared with those who did not undergo the procedure. The relative risk was higher in patients aged 18-64 years (RR, 4.27; 95% CI, 3.99-4.57; P less than .0001), compared with those 65 years and older (RR, 2.20; 95% CI, 2.13-2.27; P less than .0001). “We know that Parkinson’s disease is more common in the elderly,” Dr. Cooper said. “But at virtually all ages, the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease was higher in patients who had an appendectomy, compared to those without an appendectomy.”
The overall relative risk of developing Parkinson’s disease in patients after appendectomies was slightly higher in females (RR, 3.86; 95% CI, 3.71-4.02; P less than .0001), compared with males (RR, 2.67; 95% CI, 2.56-2.79; P less than .0001). The researchers also observed a similar effect of appendectomy by race. The overall relative risk of developing Parkinson’s disease in patients after appendectomy was slightly higher in African Americans (RR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.69-3.58; P less than .0001), compared with Asians (RR, 2.73; 95% CI, 2.19-3.41; P less than .0001), and whites (RR, 2.55; 95% CI, 2.48-2.63; P less than .0001).
“If these data get borne out, it may question the role of doing a discretionary appendectomy in a patient who’s having surgery for another reason,” Dr. Cooper said. “Our research does show a clear relationship between appendectomy and Parkinson’s disease. However, at this point, it’s only an association. As a next step, we’d like to conduct additional research to confirm this connection and better understand the mechanisms involved.”
He pointed out that, because of the nature of the Explorys database, he and his colleagues were unable to determine the length of time following appendectomy to the development of Parkinson’s disease.
The study’s lead author was Mohammed Z. Sheriff, MD, also of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Sheriff MZ et al. DDW 2019, Abstract 739.
.
“One of the factors that’s seen in the brains of patients with Parkinson’s disease is accumulation of an abnormal protein known as alpha-synuclein,” one of the study authors, Gregory S. Cooper, MD, said during a media briefing in advance of the annual Digestive Disease Week. “It’s released by damaged nerve cells in the brain. Not only is alpha-synuclein found in the brain of patients with Parkinson’s disease; it’s also found in the GI tract. It’s thought that its accumulation in the GI tract occurs prior to the development of its accumulation in the brain.”
This has prompted scientists around the world to evaluate the GI tract, including the appendix, for evidence about the pathophysiology and onset of Parkinson’s disease, said Dr. Cooper, professor of medicine, oncology, and population and quantitative health sciences at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland. “It’s thought that, potentially, in the presence of inflammation, [molecules] of this protein are released from damaged nerves in the gut and then are transported to the brain, where they accumulate,” he said. “Or, it could be that the appendix is a storage place for this protein and gets released at the time of appendectomy.”
To investigate if appendectomy increases the risk of Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Cooper and colleagues drew from the Explorys database, which contains EHRs from 26 integrated U.S. health care systems. They limited their search to patients who underwent appendectomies and those who were diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease based on Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine–Clinical Terms. The researchers chose a washout period of 6 months to the development of Parkinson’s disease after appendectomy, and compared the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in the general population to those with appendectomies.
Of the 62,218,050 records in the database, Dr. Cooper and colleagues identified 488,190 patients who underwent appendectomies. In all, 4,470 cases of Parkinson’s disease were observed in patients with appendectomies, and 177,230 cases of Parkinson’s disease in patients without appendectomies. The overall relative risk of developing Parkinson’s disease in patients after appendectomies was 3.19 (95% confidence interval, 3.10-3.28; P less than .0001), compared with those who did not undergo the procedure. The relative risk was higher in patients aged 18-64 years (RR, 4.27; 95% CI, 3.99-4.57; P less than .0001), compared with those 65 years and older (RR, 2.20; 95% CI, 2.13-2.27; P less than .0001). “We know that Parkinson’s disease is more common in the elderly,” Dr. Cooper said. “But at virtually all ages, the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease was higher in patients who had an appendectomy, compared to those without an appendectomy.”
The overall relative risk of developing Parkinson’s disease in patients after appendectomies was slightly higher in females (RR, 3.86; 95% CI, 3.71-4.02; P less than .0001), compared with males (RR, 2.67; 95% CI, 2.56-2.79; P less than .0001). The researchers also observed a similar effect of appendectomy by race. The overall relative risk of developing Parkinson’s disease in patients after appendectomy was slightly higher in African Americans (RR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.69-3.58; P less than .0001), compared with Asians (RR, 2.73; 95% CI, 2.19-3.41; P less than .0001), and whites (RR, 2.55; 95% CI, 2.48-2.63; P less than .0001).
“If these data get borne out, it may question the role of doing a discretionary appendectomy in a patient who’s having surgery for another reason,” Dr. Cooper said. “Our research does show a clear relationship between appendectomy and Parkinson’s disease. However, at this point, it’s only an association. As a next step, we’d like to conduct additional research to confirm this connection and better understand the mechanisms involved.”
He pointed out that, because of the nature of the Explorys database, he and his colleagues were unable to determine the length of time following appendectomy to the development of Parkinson’s disease.
The study’s lead author was Mohammed Z. Sheriff, MD, also of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Sheriff MZ et al. DDW 2019, Abstract 739.
REPORTING FROM DDW 2019
Key clinical point: Appendectomy appears to increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.
Major finding: The overall relative risk of developing Parkinson’s disease in patients after appendectomy was 3.19 (95% CI, 3.10-3.28; P less than .0001), compared with those who did not undergo the procedure.
Study details: A population-based study of more than 62 million medical records from a national database.
Disclosures: The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Sheriff MZ et al. DDW 2019, Abstract 739.
Galcanezumab reduces cluster headache attack frequency
PHILADELPHIA – according to study results presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. The treatment has a similar safety profile in this patient population as it has among people with episodic or chronic migraine, said the researchers.
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) has an important role in the pathogenesis of cluster headache. Galcanezumab (Emgality)is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to CGRP. Eli Lilly & Co. developed the molecule as a treatment for migraine. Cluster headache is characterized by recurrent unilateral headache attacks accompanied by autonomic symptoms. The most common acute treatments for cluster headache are sumatriptan (Imitrex) and high-flow oxygen, but some patients do not respond to these therapies.
David W. Dodick, MD, director of the headache, sports neurology, and concussion programs at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, and colleagues conducted a trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of galcanezumab in patients with episodic cluster headache.
After screening, participants underwent a prospective baseline diary phase for 7 consecutive days. The investigators subsequently randomized patients in equal groups to galcanezumab (300 mg subcutaneously) or placebo. Treatment was administered subcutaneously once monthly. The double-blind treatment period lasted for 8 weeks, and a washout period followed. The trial’s primary endpoint was the overall mean change from baseline in weekly cluster headache attack frequency during weeks 1-3, as recorded in patient diaries. The main secondary endpoint was the proportion of patients who had a reduction in weekly cluster headache attack frequency of 50% or more at week 3.
In all, 49 patients were randomized to galcanezumab, and 57 were randomized to placebo. Mean age was 45-47 years. Between 82% and 84% of patients were male. The mean number of weekly cluster headache attacks at baseline was approximately 17.5 in both groups.
During weeks 1-3, the mean change in weekly attack frequency was −8.7 in the galcanezumab group and −5.2 for controls. The difference between groups was statistically significant. The percentage of participants with a reduction in weekly attack frequency of at least 50% at week 3 was 76% for galcanezumab versus 57% for placebo. The between-group differences in these endpoints were statistically significant.
The discontinuation rate was 8% (4 participants) in the galcanezumab group and 21% (12 participants) in the placebo group. Eight participants (14%) in the placebo group discontinued treatment because of lack of efficacy, compared with one participant (2%) in the galcanezumab group. The researchers observed no clinically meaningful differences between treatment groups on tolerability or safety parameters except for a greater incidence of injection-site pain with galcanezumab versus placebo (8.2% vs. 0%).
Eli Lilly and Co. sponsored the study. Dr. Dodick has a consulting relationship with the company.
SOURCE: Bardos JN et al. AAN 2019, Abstract 02.004.
PHILADELPHIA – according to study results presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. The treatment has a similar safety profile in this patient population as it has among people with episodic or chronic migraine, said the researchers.
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) has an important role in the pathogenesis of cluster headache. Galcanezumab (Emgality)is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to CGRP. Eli Lilly & Co. developed the molecule as a treatment for migraine. Cluster headache is characterized by recurrent unilateral headache attacks accompanied by autonomic symptoms. The most common acute treatments for cluster headache are sumatriptan (Imitrex) and high-flow oxygen, but some patients do not respond to these therapies.
David W. Dodick, MD, director of the headache, sports neurology, and concussion programs at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, and colleagues conducted a trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of galcanezumab in patients with episodic cluster headache.
After screening, participants underwent a prospective baseline diary phase for 7 consecutive days. The investigators subsequently randomized patients in equal groups to galcanezumab (300 mg subcutaneously) or placebo. Treatment was administered subcutaneously once monthly. The double-blind treatment period lasted for 8 weeks, and a washout period followed. The trial’s primary endpoint was the overall mean change from baseline in weekly cluster headache attack frequency during weeks 1-3, as recorded in patient diaries. The main secondary endpoint was the proportion of patients who had a reduction in weekly cluster headache attack frequency of 50% or more at week 3.
In all, 49 patients were randomized to galcanezumab, and 57 were randomized to placebo. Mean age was 45-47 years. Between 82% and 84% of patients were male. The mean number of weekly cluster headache attacks at baseline was approximately 17.5 in both groups.
During weeks 1-3, the mean change in weekly attack frequency was −8.7 in the galcanezumab group and −5.2 for controls. The difference between groups was statistically significant. The percentage of participants with a reduction in weekly attack frequency of at least 50% at week 3 was 76% for galcanezumab versus 57% for placebo. The between-group differences in these endpoints were statistically significant.
The discontinuation rate was 8% (4 participants) in the galcanezumab group and 21% (12 participants) in the placebo group. Eight participants (14%) in the placebo group discontinued treatment because of lack of efficacy, compared with one participant (2%) in the galcanezumab group. The researchers observed no clinically meaningful differences between treatment groups on tolerability or safety parameters except for a greater incidence of injection-site pain with galcanezumab versus placebo (8.2% vs. 0%).
Eli Lilly and Co. sponsored the study. Dr. Dodick has a consulting relationship with the company.
SOURCE: Bardos JN et al. AAN 2019, Abstract 02.004.
PHILADELPHIA – according to study results presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. The treatment has a similar safety profile in this patient population as it has among people with episodic or chronic migraine, said the researchers.
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) has an important role in the pathogenesis of cluster headache. Galcanezumab (Emgality)is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to CGRP. Eli Lilly & Co. developed the molecule as a treatment for migraine. Cluster headache is characterized by recurrent unilateral headache attacks accompanied by autonomic symptoms. The most common acute treatments for cluster headache are sumatriptan (Imitrex) and high-flow oxygen, but some patients do not respond to these therapies.
David W. Dodick, MD, director of the headache, sports neurology, and concussion programs at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, and colleagues conducted a trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of galcanezumab in patients with episodic cluster headache.
After screening, participants underwent a prospective baseline diary phase for 7 consecutive days. The investigators subsequently randomized patients in equal groups to galcanezumab (300 mg subcutaneously) or placebo. Treatment was administered subcutaneously once monthly. The double-blind treatment period lasted for 8 weeks, and a washout period followed. The trial’s primary endpoint was the overall mean change from baseline in weekly cluster headache attack frequency during weeks 1-3, as recorded in patient diaries. The main secondary endpoint was the proportion of patients who had a reduction in weekly cluster headache attack frequency of 50% or more at week 3.
In all, 49 patients were randomized to galcanezumab, and 57 were randomized to placebo. Mean age was 45-47 years. Between 82% and 84% of patients were male. The mean number of weekly cluster headache attacks at baseline was approximately 17.5 in both groups.
During weeks 1-3, the mean change in weekly attack frequency was −8.7 in the galcanezumab group and −5.2 for controls. The difference between groups was statistically significant. The percentage of participants with a reduction in weekly attack frequency of at least 50% at week 3 was 76% for galcanezumab versus 57% for placebo. The between-group differences in these endpoints were statistically significant.
The discontinuation rate was 8% (4 participants) in the galcanezumab group and 21% (12 participants) in the placebo group. Eight participants (14%) in the placebo group discontinued treatment because of lack of efficacy, compared with one participant (2%) in the galcanezumab group. The researchers observed no clinically meaningful differences between treatment groups on tolerability or safety parameters except for a greater incidence of injection-site pain with galcanezumab versus placebo (8.2% vs. 0%).
Eli Lilly and Co. sponsored the study. Dr. Dodick has a consulting relationship with the company.
SOURCE: Bardos JN et al. AAN 2019, Abstract 02.004.
REPORTING FROM AAN 2019
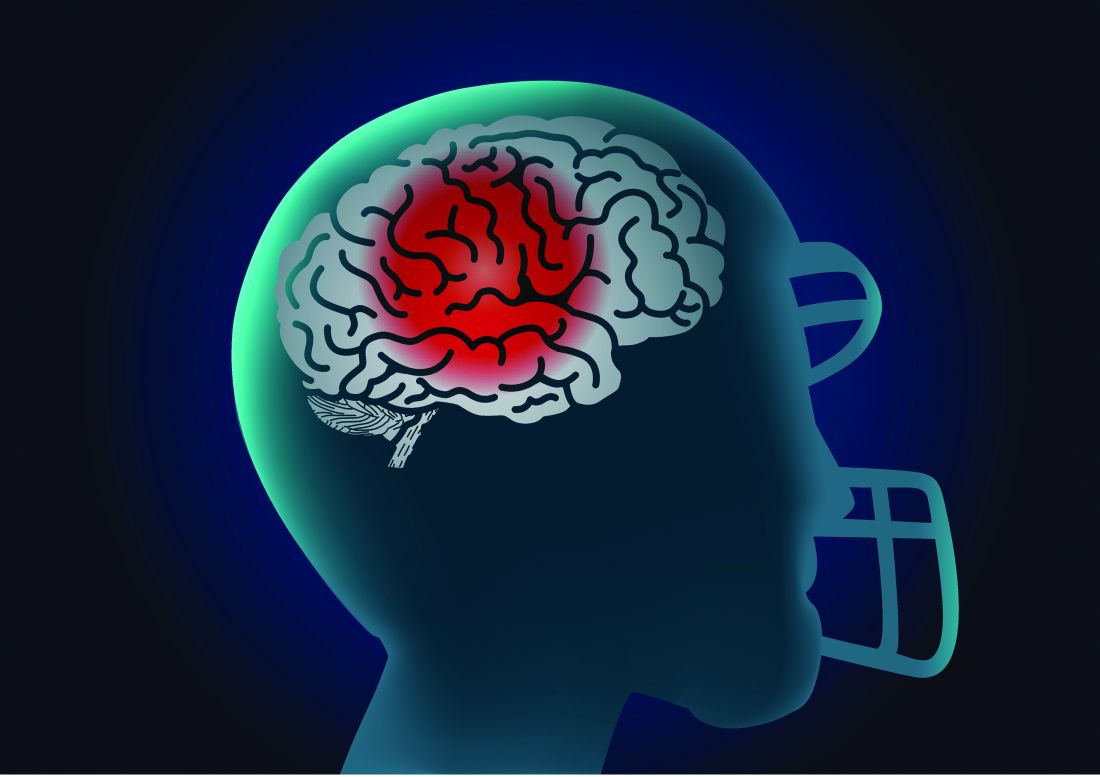
Biomarkers support impact of concussions on cognitive function
Former athletes with a history of concussion averaged higher levels of total tau in their cerebrospinal fluid than did healthy controls, and those with the highest levels showed signs of reduced cognitive function in a case-control study.
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) remains a postmortem diagnosis, but “the potential for treating postconcussion degeneration such as CTE depends on being able to detect the in vivo pathology at an early stage to intervene before the disease progresses to an irreversible stage,” wrote Foad Taghdiri, MD, of the University of Toronto and colleagues.
In a study published in Neurology, the researchers measured concentrations of phosphorylated tau181, total tau (t-tau), and beta-amyloid in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of three groups: 22 former professional athletes who had suffered multiple concussions, 5 healthy controls, and 12 individuals diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The average ages of the groups were 56 years, 57 years, and 60 years, respectively. All the athletes were male, and their sports included snowboarding, hockey, and football.
The average t-tau level in the CSF of the athletes was significantly higher than that of controls (349.3 pg/mL vs. 188.8 pg/mL) and significantly lower than that of AD patients (857.0 pg/mL).
Normal CSF t-tau was defined as 300 pg/mL, and 12 former athletes (45%) had high t-tau levels, with an average of 499.3 pg/mL. In this group of high t-tau former athletes, the average score on the Trail Making Test (TMT) Part B was significantly lower than the average score among the 10 former athletes with normal CSF t-tau levels (t scores 45.6 vs. 62.3; P = .017).
In addition, results from MRI scans showed that fractional anisotropy values across all the tracts were significantly lower for those with high CSF t-tau levels, compared with those who had normal CSF t-tau levels (P = .036).
The findings were limited by several factors, including the small sample size, lack of female athletes, and limited ability to compare white matter integrity between high and normal CSF t-tau groups, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that “multiple concussive or subconcussive events may trigger neurodegeneration to a greater degree than expected on the basis of age alone,” they said. Although the study did not allow for diagnosing the participants with CTE, “we are engaged in longitudinal studies to track neurologic and neuropsychological function, CSF biomarkers, and structural brain changes over time to further assess the delayed effects of multiple concussions on the brain,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the Toronto General and Western Hospital Foundation, PSI Foundation, and the Canadian Institute of Health Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Taghdiri F et al. Neurology. 2019 May 8. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007608
Former athletes with a history of concussion averaged higher levels of total tau in their cerebrospinal fluid than did healthy controls, and those with the highest levels showed signs of reduced cognitive function in a case-control study.
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) remains a postmortem diagnosis, but “the potential for treating postconcussion degeneration such as CTE depends on being able to detect the in vivo pathology at an early stage to intervene before the disease progresses to an irreversible stage,” wrote Foad Taghdiri, MD, of the University of Toronto and colleagues.
In a study published in Neurology, the researchers measured concentrations of phosphorylated tau181, total tau (t-tau), and beta-amyloid in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of three groups: 22 former professional athletes who had suffered multiple concussions, 5 healthy controls, and 12 individuals diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The average ages of the groups were 56 years, 57 years, and 60 years, respectively. All the athletes were male, and their sports included snowboarding, hockey, and football.
The average t-tau level in the CSF of the athletes was significantly higher than that of controls (349.3 pg/mL vs. 188.8 pg/mL) and significantly lower than that of AD patients (857.0 pg/mL).
Normal CSF t-tau was defined as 300 pg/mL, and 12 former athletes (45%) had high t-tau levels, with an average of 499.3 pg/mL. In this group of high t-tau former athletes, the average score on the Trail Making Test (TMT) Part B was significantly lower than the average score among the 10 former athletes with normal CSF t-tau levels (t scores 45.6 vs. 62.3; P = .017).
In addition, results from MRI scans showed that fractional anisotropy values across all the tracts were significantly lower for those with high CSF t-tau levels, compared with those who had normal CSF t-tau levels (P = .036).
The findings were limited by several factors, including the small sample size, lack of female athletes, and limited ability to compare white matter integrity between high and normal CSF t-tau groups, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that “multiple concussive or subconcussive events may trigger neurodegeneration to a greater degree than expected on the basis of age alone,” they said. Although the study did not allow for diagnosing the participants with CTE, “we are engaged in longitudinal studies to track neurologic and neuropsychological function, CSF biomarkers, and structural brain changes over time to further assess the delayed effects of multiple concussions on the brain,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the Toronto General and Western Hospital Foundation, PSI Foundation, and the Canadian Institute of Health Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Taghdiri F et al. Neurology. 2019 May 8. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007608
Former athletes with a history of concussion averaged higher levels of total tau in their cerebrospinal fluid than did healthy controls, and those with the highest levels showed signs of reduced cognitive function in a case-control study.
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) remains a postmortem diagnosis, but “the potential for treating postconcussion degeneration such as CTE depends on being able to detect the in vivo pathology at an early stage to intervene before the disease progresses to an irreversible stage,” wrote Foad Taghdiri, MD, of the University of Toronto and colleagues.
In a study published in Neurology, the researchers measured concentrations of phosphorylated tau181, total tau (t-tau), and beta-amyloid in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of three groups: 22 former professional athletes who had suffered multiple concussions, 5 healthy controls, and 12 individuals diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The average ages of the groups were 56 years, 57 years, and 60 years, respectively. All the athletes were male, and their sports included snowboarding, hockey, and football.
The average t-tau level in the CSF of the athletes was significantly higher than that of controls (349.3 pg/mL vs. 188.8 pg/mL) and significantly lower than that of AD patients (857.0 pg/mL).
Normal CSF t-tau was defined as 300 pg/mL, and 12 former athletes (45%) had high t-tau levels, with an average of 499.3 pg/mL. In this group of high t-tau former athletes, the average score on the Trail Making Test (TMT) Part B was significantly lower than the average score among the 10 former athletes with normal CSF t-tau levels (t scores 45.6 vs. 62.3; P = .017).
In addition, results from MRI scans showed that fractional anisotropy values across all the tracts were significantly lower for those with high CSF t-tau levels, compared with those who had normal CSF t-tau levels (P = .036).
The findings were limited by several factors, including the small sample size, lack of female athletes, and limited ability to compare white matter integrity between high and normal CSF t-tau groups, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that “multiple concussive or subconcussive events may trigger neurodegeneration to a greater degree than expected on the basis of age alone,” they said. Although the study did not allow for diagnosing the participants with CTE, “we are engaged in longitudinal studies to track neurologic and neuropsychological function, CSF biomarkers, and structural brain changes over time to further assess the delayed effects of multiple concussions on the brain,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the Toronto General and Western Hospital Foundation, PSI Foundation, and the Canadian Institute of Health Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Taghdiri F et al. Neurology. 2019 May 8. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007608
FROM NEUROLOGY
Insomnia meds get boxed warning from FDA
The Food and Drug Administration will now require that certain
Complex sleep behaviors have been seen with these medications in patients with and without a history of them, at low doses, and even after one dose of the medication. They’ve also been observed with and without concomitant use of alcohol or other CNS depressants.
Health care professionals should advise patients about these risks, even though they are rare. Patients should contact health care professionals if they either experience a complex sleep behavior while not fully awake on one of these medicines or have performed activities they don’t remember while taking the medicine.
More information about these risks and the safety warnings can be found in the FDA’s safety announcement. Other information is also available in a press announcement from the agency.
The Food and Drug Administration will now require that certain
Complex sleep behaviors have been seen with these medications in patients with and without a history of them, at low doses, and even after one dose of the medication. They’ve also been observed with and without concomitant use of alcohol or other CNS depressants.
Health care professionals should advise patients about these risks, even though they are rare. Patients should contact health care professionals if they either experience a complex sleep behavior while not fully awake on one of these medicines or have performed activities they don’t remember while taking the medicine.
More information about these risks and the safety warnings can be found in the FDA’s safety announcement. Other information is also available in a press announcement from the agency.
The Food and Drug Administration will now require that certain
Complex sleep behaviors have been seen with these medications in patients with and without a history of them, at low doses, and even after one dose of the medication. They’ve also been observed with and without concomitant use of alcohol or other CNS depressants.
Health care professionals should advise patients about these risks, even though they are rare. Patients should contact health care professionals if they either experience a complex sleep behavior while not fully awake on one of these medicines or have performed activities they don’t remember while taking the medicine.
More information about these risks and the safety warnings can be found in the FDA’s safety announcement. Other information is also available in a press announcement from the agency.