User login
Readmission to non-index hospital following acute stroke linked to worse outcomes
ATLANTA – Following an acute stroke, optimizing stroke secondary prevention measures, medical complications, and transitions of care is essential to reducing 30-day readmissions and improving patient outcomes, a large analysis of national data showed.
“Care that is fragmented with readmissions to other hospitals results not only in more expensive care and longer length of stay but also increased mortality for our acute stroke patients,” lead study author Laura K. Stein, MD, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
In 2017, a study of the Nationwide Readmissions Database demonstrated that 12.1% of patients with acute ischemic stroke were readmitted within 30 days (Stroke 2017;48:1386-8). It cited that 89.6% were unplanned and 12.9% were preventable. “However, this study did not examine whether patients were admitted to the discharging hospital or a different hospital,” said Dr. Stein, a neurologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Furthermore, it did not include metrics such as cost, length of stay, and mortality with 30-day readmissions. Hospitals are increasingly held accountable and penalized for metrics such as length of stay and 30-day readmissions.”
In 2010, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services introduced the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program in an attempt to decrease readmissions following hospitalizations for acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, and pneumonia. “In 2012, CMS started reducing Medicare payments for hospitals with excess readmissions,” said Dr. Stein, who is a fellowship-trained stroke specialist. “While readmission to the same hospital has great implications for hospital systems, any readmission has great implications for patients.”
In what is believed to be the first study of its kind, Dr. Stein and her colleagues drew from the 2013 Nationwide Readmissions Database to examine in-hospital outcomes associated with 30-day readmission to a different hospital for acute ischemic stroke. They used ICD-9 codes to identify index stroke admissions and all-cause readmissions. Outcomes of interest were length of stay, total charges, and in-hospital mortality during the 30-day readmission. The main predictor was readmission to another hospital, compared with readmission to the same hospital as the index acute stroke admission. The researchers used linear regression for the outcomes of length of stay and charges, and logistic regression for in-hospital mortality. They adjusted for several variables during the index admission, including age, sex, vascular risk factors, hospital bed size, teaching hospital status, insurance status, discharge destination, National Center for Health Statistics urban-rural location classification, length of stay, and total charges.
Of 24,545 acute stroke patients readmitted within 30 days, 7,274 (30%) were readmitted to a different hospital. The top three reasons for readmission were acute cerebrovascular disease, septicemia, and renal failure. In fully adjusted models, readmission to a different hospital was associated with an increased length of stay of 0.97 days (P less than .0001) and a mean of $7,677.28 greater total charges, compared with readmission to the same hospital (P less than .0001). The fully adjusted odds ratio for in-hospital mortality during readmission was 1.17 for readmission to another hospital vs. readmission to the same hospital (P = .0079).
“While it is conceivable that cost and length of stay could be higher with readmission to a different hospital because of a need for additional testing with a lack of familiarity with the patient, it is concerning that mortality is higher,” Dr. Stein said. “These findings emphasize the importance of optimizing secondary stroke prevention and medical complications following acute stroke before discharge. Additionally, they emphasize the importance of good transitions of care from the inpatient to outpatient setting (whether that’s to a rehabilitation facility, skilled nursing facility, or home) and accessibility of the discharging stroke team after discharge.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including its reliance of administrative data, which could include misclassification of diagnoses and comorbidities based on ICD-9 codes. “However, we have chosen ICD-9 codes for stroke that have been previously validated in the literature,” Dr. Stein said. “For instance, the validated codes for stroke as the primary discharge diagnosis have a sensitivity of 74%, specificity of 95%, and positive predictive value of 88%. Second, we do not know stroke subtype or severity of stroke. Third, we do not know what the transitions of care plan were when the patients left the hospital following index acute ischemic stroke admission and why these patients ended up being readmitted to a different hospital rather than the one that treated them for their acute stroke.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Stein L et al. Ann Neurol. 2018;84[S22]:S149. Abstract M127.
ATLANTA – Following an acute stroke, optimizing stroke secondary prevention measures, medical complications, and transitions of care is essential to reducing 30-day readmissions and improving patient outcomes, a large analysis of national data showed.
“Care that is fragmented with readmissions to other hospitals results not only in more expensive care and longer length of stay but also increased mortality for our acute stroke patients,” lead study author Laura K. Stein, MD, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
In 2017, a study of the Nationwide Readmissions Database demonstrated that 12.1% of patients with acute ischemic stroke were readmitted within 30 days (Stroke 2017;48:1386-8). It cited that 89.6% were unplanned and 12.9% were preventable. “However, this study did not examine whether patients were admitted to the discharging hospital or a different hospital,” said Dr. Stein, a neurologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Furthermore, it did not include metrics such as cost, length of stay, and mortality with 30-day readmissions. Hospitals are increasingly held accountable and penalized for metrics such as length of stay and 30-day readmissions.”
In 2010, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services introduced the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program in an attempt to decrease readmissions following hospitalizations for acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, and pneumonia. “In 2012, CMS started reducing Medicare payments for hospitals with excess readmissions,” said Dr. Stein, who is a fellowship-trained stroke specialist. “While readmission to the same hospital has great implications for hospital systems, any readmission has great implications for patients.”
In what is believed to be the first study of its kind, Dr. Stein and her colleagues drew from the 2013 Nationwide Readmissions Database to examine in-hospital outcomes associated with 30-day readmission to a different hospital for acute ischemic stroke. They used ICD-9 codes to identify index stroke admissions and all-cause readmissions. Outcomes of interest were length of stay, total charges, and in-hospital mortality during the 30-day readmission. The main predictor was readmission to another hospital, compared with readmission to the same hospital as the index acute stroke admission. The researchers used linear regression for the outcomes of length of stay and charges, and logistic regression for in-hospital mortality. They adjusted for several variables during the index admission, including age, sex, vascular risk factors, hospital bed size, teaching hospital status, insurance status, discharge destination, National Center for Health Statistics urban-rural location classification, length of stay, and total charges.
Of 24,545 acute stroke patients readmitted within 30 days, 7,274 (30%) were readmitted to a different hospital. The top three reasons for readmission were acute cerebrovascular disease, septicemia, and renal failure. In fully adjusted models, readmission to a different hospital was associated with an increased length of stay of 0.97 days (P less than .0001) and a mean of $7,677.28 greater total charges, compared with readmission to the same hospital (P less than .0001). The fully adjusted odds ratio for in-hospital mortality during readmission was 1.17 for readmission to another hospital vs. readmission to the same hospital (P = .0079).
“While it is conceivable that cost and length of stay could be higher with readmission to a different hospital because of a need for additional testing with a lack of familiarity with the patient, it is concerning that mortality is higher,” Dr. Stein said. “These findings emphasize the importance of optimizing secondary stroke prevention and medical complications following acute stroke before discharge. Additionally, they emphasize the importance of good transitions of care from the inpatient to outpatient setting (whether that’s to a rehabilitation facility, skilled nursing facility, or home) and accessibility of the discharging stroke team after discharge.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including its reliance of administrative data, which could include misclassification of diagnoses and comorbidities based on ICD-9 codes. “However, we have chosen ICD-9 codes for stroke that have been previously validated in the literature,” Dr. Stein said. “For instance, the validated codes for stroke as the primary discharge diagnosis have a sensitivity of 74%, specificity of 95%, and positive predictive value of 88%. Second, we do not know stroke subtype or severity of stroke. Third, we do not know what the transitions of care plan were when the patients left the hospital following index acute ischemic stroke admission and why these patients ended up being readmitted to a different hospital rather than the one that treated them for their acute stroke.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Stein L et al. Ann Neurol. 2018;84[S22]:S149. Abstract M127.
ATLANTA – Following an acute stroke, optimizing stroke secondary prevention measures, medical complications, and transitions of care is essential to reducing 30-day readmissions and improving patient outcomes, a large analysis of national data showed.
“Care that is fragmented with readmissions to other hospitals results not only in more expensive care and longer length of stay but also increased mortality for our acute stroke patients,” lead study author Laura K. Stein, MD, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
In 2017, a study of the Nationwide Readmissions Database demonstrated that 12.1% of patients with acute ischemic stroke were readmitted within 30 days (Stroke 2017;48:1386-8). It cited that 89.6% were unplanned and 12.9% were preventable. “However, this study did not examine whether patients were admitted to the discharging hospital or a different hospital,” said Dr. Stein, a neurologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Furthermore, it did not include metrics such as cost, length of stay, and mortality with 30-day readmissions. Hospitals are increasingly held accountable and penalized for metrics such as length of stay and 30-day readmissions.”
In 2010, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services introduced the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program in an attempt to decrease readmissions following hospitalizations for acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, and pneumonia. “In 2012, CMS started reducing Medicare payments for hospitals with excess readmissions,” said Dr. Stein, who is a fellowship-trained stroke specialist. “While readmission to the same hospital has great implications for hospital systems, any readmission has great implications for patients.”
In what is believed to be the first study of its kind, Dr. Stein and her colleagues drew from the 2013 Nationwide Readmissions Database to examine in-hospital outcomes associated with 30-day readmission to a different hospital for acute ischemic stroke. They used ICD-9 codes to identify index stroke admissions and all-cause readmissions. Outcomes of interest were length of stay, total charges, and in-hospital mortality during the 30-day readmission. The main predictor was readmission to another hospital, compared with readmission to the same hospital as the index acute stroke admission. The researchers used linear regression for the outcomes of length of stay and charges, and logistic regression for in-hospital mortality. They adjusted for several variables during the index admission, including age, sex, vascular risk factors, hospital bed size, teaching hospital status, insurance status, discharge destination, National Center for Health Statistics urban-rural location classification, length of stay, and total charges.
Of 24,545 acute stroke patients readmitted within 30 days, 7,274 (30%) were readmitted to a different hospital. The top three reasons for readmission were acute cerebrovascular disease, septicemia, and renal failure. In fully adjusted models, readmission to a different hospital was associated with an increased length of stay of 0.97 days (P less than .0001) and a mean of $7,677.28 greater total charges, compared with readmission to the same hospital (P less than .0001). The fully adjusted odds ratio for in-hospital mortality during readmission was 1.17 for readmission to another hospital vs. readmission to the same hospital (P = .0079).
“While it is conceivable that cost and length of stay could be higher with readmission to a different hospital because of a need for additional testing with a lack of familiarity with the patient, it is concerning that mortality is higher,” Dr. Stein said. “These findings emphasize the importance of optimizing secondary stroke prevention and medical complications following acute stroke before discharge. Additionally, they emphasize the importance of good transitions of care from the inpatient to outpatient setting (whether that’s to a rehabilitation facility, skilled nursing facility, or home) and accessibility of the discharging stroke team after discharge.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including its reliance of administrative data, which could include misclassification of diagnoses and comorbidities based on ICD-9 codes. “However, we have chosen ICD-9 codes for stroke that have been previously validated in the literature,” Dr. Stein said. “For instance, the validated codes for stroke as the primary discharge diagnosis have a sensitivity of 74%, specificity of 95%, and positive predictive value of 88%. Second, we do not know stroke subtype or severity of stroke. Third, we do not know what the transitions of care plan were when the patients left the hospital following index acute ischemic stroke admission and why these patients ended up being readmitted to a different hospital rather than the one that treated them for their acute stroke.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Stein L et al. Ann Neurol. 2018;84[S22]:S149. Abstract M127.
REPORTING FROM ANA 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The adjusted odds ratio for in-hospital mortality during readmission was 1.17 for readmission to another hospital vs. readmission to the same hospital (P = .0079).
Study details: A review of 24,545 acute stroke patients 2013 from the Nationwide Readmissions Database.
Disclosures: The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Stein L et al. Ann Neurol. 2018;84[S22]:S149. Abstract M127.
Blood test may obviate need for head CTs in brain trauma evaluation
SAN DIEGO – A biomarker test based on the presence of two proteins in the blood appears to be suitable for ruling out significant intracranial injuries in patients with a history of mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) without the need for a CT head scan, according to data presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
according to Jeffrey J. Bazarian, MD, professor of emergency medicine, University of Rochester (New York).
In the ALERT-TBI study, which evaluated the biomarker test, 1,959 patients with suspected TBI at 22 participating EDs in the United States and Europe were enrolled and available for analysis. All had mild TBI as defined as a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of 13-15.
The treating ED physician’s decision to order a head CT scan was the major criterion for study entry. All enrolled patients had their blood drawn within 12 hours in order to quantify two biomarkers, C-terminal hydrolase-L1 (UCH-L1) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP).
The biomarker test for TBI was negative when the UCH-L1 value was less than 327 pg/mL and the GFAP was less than 22 pg/mL; the test was positive if either value was at this threshold or higher. To evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of this dual-biomarker test, results were correlated with head CT scans read by two neurologists blinded to the biomarker values.
The mean age of the study population was 48.8 years and slightly more than half were male. About half of the suspected TBI in these patients was attributed to falls and about one third to motor vehicle accidents.
Typical of TBI with GCS scores in the mild range, only 6% of the patients had a positive CT head scan. Of the 125 positive CT scans, the most common injury detected on CT scan was subarachnoid hemorrhage followed by subdural hematoma.
Of the 671 negative biomarker tests, 668 had normal head CT scans. Of the three false positives, one included a cavernous malformation that may have been present prior to the TBI. The others were a small subarachnoid hemorrhage and a small subdural hematoma. Overall the negative predictive value was 99.6% and the sensitivity was 97.6%.
Although the biomarker specificity was only 36% with an even-lower positive predictive value, the goal of the test was to rule out significant TBI to avoid the need for CT scan. On this basis, the biomarker test, which is being developed under the proprietary name Banyan BTI, appears to be promising. The data, according to Dr. Bazarian, have been submitted to the Food and Drug Administration.
“Head CT scans are the current standard for evaluating intracranial injuries after TBI, but they are overused, based on the high proportion that do not show an injury,” said Dr. Bazarian. Although he does not know the disposition of the FDA application, he said, based on these data, “I would definitely be using this test if it were available.”
SAN DIEGO – A biomarker test based on the presence of two proteins in the blood appears to be suitable for ruling out significant intracranial injuries in patients with a history of mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) without the need for a CT head scan, according to data presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
according to Jeffrey J. Bazarian, MD, professor of emergency medicine, University of Rochester (New York).
In the ALERT-TBI study, which evaluated the biomarker test, 1,959 patients with suspected TBI at 22 participating EDs in the United States and Europe were enrolled and available for analysis. All had mild TBI as defined as a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of 13-15.
The treating ED physician’s decision to order a head CT scan was the major criterion for study entry. All enrolled patients had their blood drawn within 12 hours in order to quantify two biomarkers, C-terminal hydrolase-L1 (UCH-L1) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP).
The biomarker test for TBI was negative when the UCH-L1 value was less than 327 pg/mL and the GFAP was less than 22 pg/mL; the test was positive if either value was at this threshold or higher. To evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of this dual-biomarker test, results were correlated with head CT scans read by two neurologists blinded to the biomarker values.
The mean age of the study population was 48.8 years and slightly more than half were male. About half of the suspected TBI in these patients was attributed to falls and about one third to motor vehicle accidents.
Typical of TBI with GCS scores in the mild range, only 6% of the patients had a positive CT head scan. Of the 125 positive CT scans, the most common injury detected on CT scan was subarachnoid hemorrhage followed by subdural hematoma.
Of the 671 negative biomarker tests, 668 had normal head CT scans. Of the three false positives, one included a cavernous malformation that may have been present prior to the TBI. The others were a small subarachnoid hemorrhage and a small subdural hematoma. Overall the negative predictive value was 99.6% and the sensitivity was 97.6%.
Although the biomarker specificity was only 36% with an even-lower positive predictive value, the goal of the test was to rule out significant TBI to avoid the need for CT scan. On this basis, the biomarker test, which is being developed under the proprietary name Banyan BTI, appears to be promising. The data, according to Dr. Bazarian, have been submitted to the Food and Drug Administration.
“Head CT scans are the current standard for evaluating intracranial injuries after TBI, but they are overused, based on the high proportion that do not show an injury,” said Dr. Bazarian. Although he does not know the disposition of the FDA application, he said, based on these data, “I would definitely be using this test if it were available.”
SAN DIEGO – A biomarker test based on the presence of two proteins in the blood appears to be suitable for ruling out significant intracranial injuries in patients with a history of mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) without the need for a CT head scan, according to data presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
according to Jeffrey J. Bazarian, MD, professor of emergency medicine, University of Rochester (New York).
In the ALERT-TBI study, which evaluated the biomarker test, 1,959 patients with suspected TBI at 22 participating EDs in the United States and Europe were enrolled and available for analysis. All had mild TBI as defined as a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of 13-15.
The treating ED physician’s decision to order a head CT scan was the major criterion for study entry. All enrolled patients had their blood drawn within 12 hours in order to quantify two biomarkers, C-terminal hydrolase-L1 (UCH-L1) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP).
The biomarker test for TBI was negative when the UCH-L1 value was less than 327 pg/mL and the GFAP was less than 22 pg/mL; the test was positive if either value was at this threshold or higher. To evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of this dual-biomarker test, results were correlated with head CT scans read by two neurologists blinded to the biomarker values.
The mean age of the study population was 48.8 years and slightly more than half were male. About half of the suspected TBI in these patients was attributed to falls and about one third to motor vehicle accidents.
Typical of TBI with GCS scores in the mild range, only 6% of the patients had a positive CT head scan. Of the 125 positive CT scans, the most common injury detected on CT scan was subarachnoid hemorrhage followed by subdural hematoma.
Of the 671 negative biomarker tests, 668 had normal head CT scans. Of the three false positives, one included a cavernous malformation that may have been present prior to the TBI. The others were a small subarachnoid hemorrhage and a small subdural hematoma. Overall the negative predictive value was 99.6% and the sensitivity was 97.6%.
Although the biomarker specificity was only 36% with an even-lower positive predictive value, the goal of the test was to rule out significant TBI to avoid the need for CT scan. On this basis, the biomarker test, which is being developed under the proprietary name Banyan BTI, appears to be promising. The data, according to Dr. Bazarian, have been submitted to the Food and Drug Administration.
“Head CT scans are the current standard for evaluating intracranial injuries after TBI, but they are overused, based on the high proportion that do not show an injury,” said Dr. Bazarian. Although he does not know the disposition of the FDA application, he said, based on these data, “I would definitely be using this test if it were available.”
FROM ACEP 2018
Key clinical point: In patients with mild head trauma, a simple blood test may eliminate need and cost for routine CT scans.
Major finding: In patients a history of head trauma, the biomarker test had a 99.6% negative predictive value in ruling out injury.
Study details: Prospective, controlled registration study.
Disclosures: Dr. Bazarian reported no financial relationships relevant to this study, which was in part funded by Banyan Biomarkers.
Sensory feedback modalities tackle gait, balance problems in PD
NEW YORK – Sending sensory feedback upstream to patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) may offer a low-risk, nonpharmaceutical method to retain and improve motor function. These interventions may be especially helpful in the subpopulation of patients who are intolerant to exercise, with a growing body of evidence showing sustained benefit for newer sensory stimulation techniques.
“In a healthy person, movement is the seamless integration of sensory and motor systems,” said Ben Weinstock, DPT, speaking at the International Conference on Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders, pointing out that movement stimulates the senses, and sensory stimulation improves movement.
By contrast, patients with PD experience more than just problems with motor function. Patients with PD and sensory or autonomic dysfunction may find these disturbances contributing to motor dysfunction, said Dr. Weinstock, who treats patients with PD and a variety of complex medical conditions in his private practice.
Some of the hallmark features of PD are movement related: the cogwheel rigidity, bradykinesia, and freezing all contribute to poor balance and a fear of falling. Commonly, PD patients also experience fatigue and alterations in cognition and mood.
However, afferent small-fiber neuropathies and centrally mediated mechanisms in PD can also disturb sensory input: Vestibular function, equilibrium, proprioception, and light and deep touch may all be affected, Dr. Weinstock said.
Autonomic dysfunction can be an underappreciated feature of PD, but such manifestations as orthostatic hypotension and poor thermal regulation can have significant negative impact on quality of life for an individual with PD.
Perhaps the gravest variant of autonomic dysregulation, however, is the cardiac denervation that frequently accompanies PD, said Dr. Weinstock. “Although there is a belief that intensive exercise helps people with PD, many individuals are actually exercise intolerant because of loss of cardiac norepinephrine,” he said (J Neurochem. 2014;131[2]:219-228). “A person with PD who is exercise intolerant is at risk” of syncope, falls, and even serious cardiac events during exercise, he noted.
Cardiovascular dysautonomia in PD has been documented in serial 18F-dopamine PET scans, showing progressive reduction in uptake over the course of several years in individual patients (Neurobiol Dis. 2012 June;46[3]:572-80). Similarly, studies have shown lower cardiac radiotracer uptake in patients with PD, compared with normal controls, he said (NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2017. doi: 10.1038/S41531-017-0017-1).
It’s not easy to determine what level of nonmotor dysfunction a given patient has at a particular point in disease progression, said Dr. Weinstock.
“There is no correlation between motor and nonmotor deterioration,” he said. “Somebody might be newly diagnosed with just a mild tremor and still have significant cardiac denervation.”
Weighing how to help an exercise-intolerant patient with PD means taking into consideration the known risks and side effect profile of PD medications, Dr. Weinstock pointed out. Increasing medications, or beginning a new drug therapy, can mean increased risk for unwanted psychiatric side effects and ototoxicity, among other potential ill effects.
Similarly, the decision to implant deep brain stimulation is not to be taken lightly, since depression can begin or worsen, and any surgical procedure carries risks.
For Dr. Weinstock, using strategies to improve sensory input are “a valid option for people with PD.” Such a strategy is safe, and even brief bouts of stimulation “can have significant, beneficial effects,” he said. “The overall goal is to avoid sedentary behavior,” with its accompanying ills, he said.
Dr. Weinstock noted that he uses different strategies to stimulate the various senses, including bright light therapy, which can help regulate circadian rhythms and promote appropriate melatonin secretion, improving sleep and upping daytime wakefulness.
Another visual strategy when working on gait is to use surface lines, a checkerboard pattern, or other targets that provide a visual goal for step length, which typically shortens with PD progression. Though more high-tech options exist, Dr. Weinstock suggested patients begin with just laying lines of masking tape along the floor to mark the target gait length. “Usually the cheap technique is a good test to see if it’s going to work,” he said.
An auditory strategy to improve the gait cycle is use of a metronome or other rhythmic auditory stimulation; music can be helpful in this regard and as a general cognitive and emotional stimulus, said Dr. Weinstock.
“Loss of smell is an early sign of Parkinson’s,” said Dr. Weinstock, and taste also can be dulled. Though offering tasty meals could help reduce risk of malnutrition in PD patients, “It remains to be seen if aromatherapy can lead to neural plasticity and reverse smell loss in PD.”
Vestibular rehabilitation techniques can help not just with balance, but also with helping to lift mood and improve functional activities, according to one study (Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2009;67[2-A]:219-23).
Other ways to provide proprioceptive feedback include the use of orthotics and textured insoles and the use of a weighted vest. Dr. Weinstock also gives consideration to skin taping, which may give patients useful feedback about their bodies’ position in space, he said.
Intriguing results have been seen with acupuncture, acupressure, and electroacupuncture for PD patients, said Dr. Weinstock. In particular, a technique called automated mechanical pressure stimulation uses a bootlike device to provide mechanical stimulation to points at the head of the great toe and on the ball of the foot at the head of the first metatarsal bone.
One functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study showed acutely increased resting state functional connectivity after such stimulation, in comparison with a sham procedure that also applied pressure, but over a broader area, he said.
After the stimulation procedure used in the study, the patients who received actual stimulation also saw improved ability to initiate voluntary movements, less tremor and rigidity, and less gait freezing (PLoS One. 2015 Oct 15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137977).
Other studies of the mechanical stimulation device showed similar results, with some showing that repeated sessions helped maintain these and other benefits, such as improved walking velocity, stride length, and Timed Up and Go results – an assessment of fall risk (Int J Rehabil Res. 2015 Sep;38[3]:238-45). Treatment with the device, dubbed Gondola, is most widely available in Italy, where clinical trials are ongoing.
Stimulation to an acupuncture point located on the proximal lateral leg, near the head of the fibula, showed improvements in gait parameters and in fMRI-assessed brain connectivity as well, noted Dr. Weinstock (CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Sep;18[9]:781-90).
“There’s a growing amount of evidence that various types of sensory stimulation can have significant benefits for people with Parkinson’s Disease, especially for those who are exercise intolerant,” said Dr. Weinstock.
Dr. Weinstock reported no relevant disclosures.
[email protected]
NEW YORK – Sending sensory feedback upstream to patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) may offer a low-risk, nonpharmaceutical method to retain and improve motor function. These interventions may be especially helpful in the subpopulation of patients who are intolerant to exercise, with a growing body of evidence showing sustained benefit for newer sensory stimulation techniques.
“In a healthy person, movement is the seamless integration of sensory and motor systems,” said Ben Weinstock, DPT, speaking at the International Conference on Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders, pointing out that movement stimulates the senses, and sensory stimulation improves movement.
By contrast, patients with PD experience more than just problems with motor function. Patients with PD and sensory or autonomic dysfunction may find these disturbances contributing to motor dysfunction, said Dr. Weinstock, who treats patients with PD and a variety of complex medical conditions in his private practice.
Some of the hallmark features of PD are movement related: the cogwheel rigidity, bradykinesia, and freezing all contribute to poor balance and a fear of falling. Commonly, PD patients also experience fatigue and alterations in cognition and mood.
However, afferent small-fiber neuropathies and centrally mediated mechanisms in PD can also disturb sensory input: Vestibular function, equilibrium, proprioception, and light and deep touch may all be affected, Dr. Weinstock said.
Autonomic dysfunction can be an underappreciated feature of PD, but such manifestations as orthostatic hypotension and poor thermal regulation can have significant negative impact on quality of life for an individual with PD.
Perhaps the gravest variant of autonomic dysregulation, however, is the cardiac denervation that frequently accompanies PD, said Dr. Weinstock. “Although there is a belief that intensive exercise helps people with PD, many individuals are actually exercise intolerant because of loss of cardiac norepinephrine,” he said (J Neurochem. 2014;131[2]:219-228). “A person with PD who is exercise intolerant is at risk” of syncope, falls, and even serious cardiac events during exercise, he noted.
Cardiovascular dysautonomia in PD has been documented in serial 18F-dopamine PET scans, showing progressive reduction in uptake over the course of several years in individual patients (Neurobiol Dis. 2012 June;46[3]:572-80). Similarly, studies have shown lower cardiac radiotracer uptake in patients with PD, compared with normal controls, he said (NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2017. doi: 10.1038/S41531-017-0017-1).
It’s not easy to determine what level of nonmotor dysfunction a given patient has at a particular point in disease progression, said Dr. Weinstock.
“There is no correlation between motor and nonmotor deterioration,” he said. “Somebody might be newly diagnosed with just a mild tremor and still have significant cardiac denervation.”
Weighing how to help an exercise-intolerant patient with PD means taking into consideration the known risks and side effect profile of PD medications, Dr. Weinstock pointed out. Increasing medications, or beginning a new drug therapy, can mean increased risk for unwanted psychiatric side effects and ototoxicity, among other potential ill effects.
Similarly, the decision to implant deep brain stimulation is not to be taken lightly, since depression can begin or worsen, and any surgical procedure carries risks.
For Dr. Weinstock, using strategies to improve sensory input are “a valid option for people with PD.” Such a strategy is safe, and even brief bouts of stimulation “can have significant, beneficial effects,” he said. “The overall goal is to avoid sedentary behavior,” with its accompanying ills, he said.
Dr. Weinstock noted that he uses different strategies to stimulate the various senses, including bright light therapy, which can help regulate circadian rhythms and promote appropriate melatonin secretion, improving sleep and upping daytime wakefulness.
Another visual strategy when working on gait is to use surface lines, a checkerboard pattern, or other targets that provide a visual goal for step length, which typically shortens with PD progression. Though more high-tech options exist, Dr. Weinstock suggested patients begin with just laying lines of masking tape along the floor to mark the target gait length. “Usually the cheap technique is a good test to see if it’s going to work,” he said.
An auditory strategy to improve the gait cycle is use of a metronome or other rhythmic auditory stimulation; music can be helpful in this regard and as a general cognitive and emotional stimulus, said Dr. Weinstock.
“Loss of smell is an early sign of Parkinson’s,” said Dr. Weinstock, and taste also can be dulled. Though offering tasty meals could help reduce risk of malnutrition in PD patients, “It remains to be seen if aromatherapy can lead to neural plasticity and reverse smell loss in PD.”
Vestibular rehabilitation techniques can help not just with balance, but also with helping to lift mood and improve functional activities, according to one study (Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2009;67[2-A]:219-23).
Other ways to provide proprioceptive feedback include the use of orthotics and textured insoles and the use of a weighted vest. Dr. Weinstock also gives consideration to skin taping, which may give patients useful feedback about their bodies’ position in space, he said.
Intriguing results have been seen with acupuncture, acupressure, and electroacupuncture for PD patients, said Dr. Weinstock. In particular, a technique called automated mechanical pressure stimulation uses a bootlike device to provide mechanical stimulation to points at the head of the great toe and on the ball of the foot at the head of the first metatarsal bone.
One functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study showed acutely increased resting state functional connectivity after such stimulation, in comparison with a sham procedure that also applied pressure, but over a broader area, he said.
After the stimulation procedure used in the study, the patients who received actual stimulation also saw improved ability to initiate voluntary movements, less tremor and rigidity, and less gait freezing (PLoS One. 2015 Oct 15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137977).
Other studies of the mechanical stimulation device showed similar results, with some showing that repeated sessions helped maintain these and other benefits, such as improved walking velocity, stride length, and Timed Up and Go results – an assessment of fall risk (Int J Rehabil Res. 2015 Sep;38[3]:238-45). Treatment with the device, dubbed Gondola, is most widely available in Italy, where clinical trials are ongoing.
Stimulation to an acupuncture point located on the proximal lateral leg, near the head of the fibula, showed improvements in gait parameters and in fMRI-assessed brain connectivity as well, noted Dr. Weinstock (CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Sep;18[9]:781-90).
“There’s a growing amount of evidence that various types of sensory stimulation can have significant benefits for people with Parkinson’s Disease, especially for those who are exercise intolerant,” said Dr. Weinstock.
Dr. Weinstock reported no relevant disclosures.
[email protected]
NEW YORK – Sending sensory feedback upstream to patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) may offer a low-risk, nonpharmaceutical method to retain and improve motor function. These interventions may be especially helpful in the subpopulation of patients who are intolerant to exercise, with a growing body of evidence showing sustained benefit for newer sensory stimulation techniques.
“In a healthy person, movement is the seamless integration of sensory and motor systems,” said Ben Weinstock, DPT, speaking at the International Conference on Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders, pointing out that movement stimulates the senses, and sensory stimulation improves movement.
By contrast, patients with PD experience more than just problems with motor function. Patients with PD and sensory or autonomic dysfunction may find these disturbances contributing to motor dysfunction, said Dr. Weinstock, who treats patients with PD and a variety of complex medical conditions in his private practice.
Some of the hallmark features of PD are movement related: the cogwheel rigidity, bradykinesia, and freezing all contribute to poor balance and a fear of falling. Commonly, PD patients also experience fatigue and alterations in cognition and mood.
However, afferent small-fiber neuropathies and centrally mediated mechanisms in PD can also disturb sensory input: Vestibular function, equilibrium, proprioception, and light and deep touch may all be affected, Dr. Weinstock said.
Autonomic dysfunction can be an underappreciated feature of PD, but such manifestations as orthostatic hypotension and poor thermal regulation can have significant negative impact on quality of life for an individual with PD.
Perhaps the gravest variant of autonomic dysregulation, however, is the cardiac denervation that frequently accompanies PD, said Dr. Weinstock. “Although there is a belief that intensive exercise helps people with PD, many individuals are actually exercise intolerant because of loss of cardiac norepinephrine,” he said (J Neurochem. 2014;131[2]:219-228). “A person with PD who is exercise intolerant is at risk” of syncope, falls, and even serious cardiac events during exercise, he noted.
Cardiovascular dysautonomia in PD has been documented in serial 18F-dopamine PET scans, showing progressive reduction in uptake over the course of several years in individual patients (Neurobiol Dis. 2012 June;46[3]:572-80). Similarly, studies have shown lower cardiac radiotracer uptake in patients with PD, compared with normal controls, he said (NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2017. doi: 10.1038/S41531-017-0017-1).
It’s not easy to determine what level of nonmotor dysfunction a given patient has at a particular point in disease progression, said Dr. Weinstock.
“There is no correlation between motor and nonmotor deterioration,” he said. “Somebody might be newly diagnosed with just a mild tremor and still have significant cardiac denervation.”
Weighing how to help an exercise-intolerant patient with PD means taking into consideration the known risks and side effect profile of PD medications, Dr. Weinstock pointed out. Increasing medications, or beginning a new drug therapy, can mean increased risk for unwanted psychiatric side effects and ototoxicity, among other potential ill effects.
Similarly, the decision to implant deep brain stimulation is not to be taken lightly, since depression can begin or worsen, and any surgical procedure carries risks.
For Dr. Weinstock, using strategies to improve sensory input are “a valid option for people with PD.” Such a strategy is safe, and even brief bouts of stimulation “can have significant, beneficial effects,” he said. “The overall goal is to avoid sedentary behavior,” with its accompanying ills, he said.
Dr. Weinstock noted that he uses different strategies to stimulate the various senses, including bright light therapy, which can help regulate circadian rhythms and promote appropriate melatonin secretion, improving sleep and upping daytime wakefulness.
Another visual strategy when working on gait is to use surface lines, a checkerboard pattern, or other targets that provide a visual goal for step length, which typically shortens with PD progression. Though more high-tech options exist, Dr. Weinstock suggested patients begin with just laying lines of masking tape along the floor to mark the target gait length. “Usually the cheap technique is a good test to see if it’s going to work,” he said.
An auditory strategy to improve the gait cycle is use of a metronome or other rhythmic auditory stimulation; music can be helpful in this regard and as a general cognitive and emotional stimulus, said Dr. Weinstock.
“Loss of smell is an early sign of Parkinson’s,” said Dr. Weinstock, and taste also can be dulled. Though offering tasty meals could help reduce risk of malnutrition in PD patients, “It remains to be seen if aromatherapy can lead to neural plasticity and reverse smell loss in PD.”
Vestibular rehabilitation techniques can help not just with balance, but also with helping to lift mood and improve functional activities, according to one study (Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2009;67[2-A]:219-23).
Other ways to provide proprioceptive feedback include the use of orthotics and textured insoles and the use of a weighted vest. Dr. Weinstock also gives consideration to skin taping, which may give patients useful feedback about their bodies’ position in space, he said.
Intriguing results have been seen with acupuncture, acupressure, and electroacupuncture for PD patients, said Dr. Weinstock. In particular, a technique called automated mechanical pressure stimulation uses a bootlike device to provide mechanical stimulation to points at the head of the great toe and on the ball of the foot at the head of the first metatarsal bone.
One functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study showed acutely increased resting state functional connectivity after such stimulation, in comparison with a sham procedure that also applied pressure, but over a broader area, he said.
After the stimulation procedure used in the study, the patients who received actual stimulation also saw improved ability to initiate voluntary movements, less tremor and rigidity, and less gait freezing (PLoS One. 2015 Oct 15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137977).
Other studies of the mechanical stimulation device showed similar results, with some showing that repeated sessions helped maintain these and other benefits, such as improved walking velocity, stride length, and Timed Up and Go results – an assessment of fall risk (Int J Rehabil Res. 2015 Sep;38[3]:238-45). Treatment with the device, dubbed Gondola, is most widely available in Italy, where clinical trials are ongoing.
Stimulation to an acupuncture point located on the proximal lateral leg, near the head of the fibula, showed improvements in gait parameters and in fMRI-assessed brain connectivity as well, noted Dr. Weinstock (CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Sep;18[9]:781-90).
“There’s a growing amount of evidence that various types of sensory stimulation can have significant benefits for people with Parkinson’s Disease, especially for those who are exercise intolerant,” said Dr. Weinstock.
Dr. Weinstock reported no relevant disclosures.
[email protected]
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ICPDMD 2018
DAPT’s benefit after stroke or TIA clusters in first 21 days
MONTREAL – The optimal length for dual antiplatelet therapy in patients who have just had a mild stroke or transient ischemic attack is 21 days, a duration of combined treatment that maximized protection against major ischemic events while minimizing the extra risk for a major hemorrhage, according to a prespecified analysis of data from the POINT trial.
The POINT (Platelet-Oriented Inhibition in New TIA and Minor Ischemic Stroke) trial randomized 4,881 patients with a very recent mild stroke or transient ischemic attack and without atrial fibrillation to treatment with either clopidogrel plus aspirin or aspirin alone for 90 days. Compared with aspirin alone, dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) cut the incidence of a major ischemic event by a relative 25% but also more than doubled the rate of major hemorrhage (New Engl J Med. 2018 Jul 19;377[3]:215-25).
The new, prespecified analysis looked at outcomes on a week-by-week basis over the course of 90 days of treatment, and showed that during the first 21 days the rate of major ischemic events was 5.6% among patients on aspirin only and 3.6% among those on DAPT, a statistically significant 35% relative cut in these adverse outcomes by using DAPT, Jordan J. Elm, PhD, reported at the World Stroke Congress. During the subsequent 69 days on treatment, the incidence of major ischemic events was roughly 1% in both arms of the study, showing that after 3 weeks the incremental benefit from DAPT disappeared, said Dr. Elm, a biostatistician at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
In contrast, the doubled rate of major hemorrhages (mostly reversible gastrointestinal bleeds) with DAPT, compared with aspirin alone, occurred at a relatively uniform rate throughout the 90 days of treatment, meaning that limiting DAPT to just 21 days could prevent many of the excess hemorrhages.
“These results suggest that limiting clopidogrel plus aspirin use to 21 days may maximize benefit and reduce risk,” Dr. Elm said, especially in light of the findings confirming the efficacy of 21 days of DAPT following a minor stroke or TIA that had been reported several years ago in the CHANCE (Clopidogrel in High-Risk Patients with Acute Nondisabling Cerebrovascular Events) trial (New Engl J Med. 2013 Jul 4;369[1]:11-9).
Although the new finding from the POINT results came in a secondary analysis, it’s statistically legitimate and should be taken into account when writing treatment guidelines, she said, emphasizing that “this is a very important analysis that is not just hypothesis generating.”
Another finding from the new analysis was that a large number of major ischemic events, and hence a large number of the events prevented by DAPT, occurred in the first 2 days following the index event, a finding made possible because the POINT investigators enrolled patients and started treatment within 12 hours of the qualifying events.
“It’s better to start treatment early,” Dr. Elm noted, but she also highlighted that major ischemic events continued to accumulate during days 3-21, suggesting that patients could still benefit from DAPT even if treatment did not start until 24 or 48 hours after their index event.
POINT received no commercial funding aside from study drugs supplied by Sanofi. Dr. Elm reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Elm JJ et al. World Stroke Congress, Late-breaking session.
The new model using data from the POINT trial confirms what had been previously shown in the CHANCE trial – that 21 days is a sensible cutoff for dual antiplatelet treatment for patients immediately following a mild stroke or transient ischemic attack. Treatment with dual antiplatelet therapy for 21 days provides the same added benefit as 90 days of treatment but with less excess bleeding. The new findings confirm that the CHANCE results were not specific to a Chinese population.

For the time being, clopidogrel is the evidence-based antiplatelet drug to pair with aspirin for this indication. Clopidogrel has the advantages of being generic, cheap, available, and familiar. It’s possible that another P2Y12 inhibitor, such as ticagrelor (Brilinta), might work even better, but that needs to be proven to justify the added expense of a brand-name antiplatelet drug.
Mike Sharma, MD , is a stroke neurologist at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. He has been an advisor to Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer. He made these comments in an interview.
The new model using data from the POINT trial confirms what had been previously shown in the CHANCE trial – that 21 days is a sensible cutoff for dual antiplatelet treatment for patients immediately following a mild stroke or transient ischemic attack. Treatment with dual antiplatelet therapy for 21 days provides the same added benefit as 90 days of treatment but with less excess bleeding. The new findings confirm that the CHANCE results were not specific to a Chinese population.

For the time being, clopidogrel is the evidence-based antiplatelet drug to pair with aspirin for this indication. Clopidogrel has the advantages of being generic, cheap, available, and familiar. It’s possible that another P2Y12 inhibitor, such as ticagrelor (Brilinta), might work even better, but that needs to be proven to justify the added expense of a brand-name antiplatelet drug.
Mike Sharma, MD , is a stroke neurologist at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. He has been an advisor to Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer. He made these comments in an interview.
The new model using data from the POINT trial confirms what had been previously shown in the CHANCE trial – that 21 days is a sensible cutoff for dual antiplatelet treatment for patients immediately following a mild stroke or transient ischemic attack. Treatment with dual antiplatelet therapy for 21 days provides the same added benefit as 90 days of treatment but with less excess bleeding. The new findings confirm that the CHANCE results were not specific to a Chinese population.

For the time being, clopidogrel is the evidence-based antiplatelet drug to pair with aspirin for this indication. Clopidogrel has the advantages of being generic, cheap, available, and familiar. It’s possible that another P2Y12 inhibitor, such as ticagrelor (Brilinta), might work even better, but that needs to be proven to justify the added expense of a brand-name antiplatelet drug.
Mike Sharma, MD , is a stroke neurologist at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. He has been an advisor to Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer. He made these comments in an interview.
MONTREAL – The optimal length for dual antiplatelet therapy in patients who have just had a mild stroke or transient ischemic attack is 21 days, a duration of combined treatment that maximized protection against major ischemic events while minimizing the extra risk for a major hemorrhage, according to a prespecified analysis of data from the POINT trial.
The POINT (Platelet-Oriented Inhibition in New TIA and Minor Ischemic Stroke) trial randomized 4,881 patients with a very recent mild stroke or transient ischemic attack and without atrial fibrillation to treatment with either clopidogrel plus aspirin or aspirin alone for 90 days. Compared with aspirin alone, dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) cut the incidence of a major ischemic event by a relative 25% but also more than doubled the rate of major hemorrhage (New Engl J Med. 2018 Jul 19;377[3]:215-25).
The new, prespecified analysis looked at outcomes on a week-by-week basis over the course of 90 days of treatment, and showed that during the first 21 days the rate of major ischemic events was 5.6% among patients on aspirin only and 3.6% among those on DAPT, a statistically significant 35% relative cut in these adverse outcomes by using DAPT, Jordan J. Elm, PhD, reported at the World Stroke Congress. During the subsequent 69 days on treatment, the incidence of major ischemic events was roughly 1% in both arms of the study, showing that after 3 weeks the incremental benefit from DAPT disappeared, said Dr. Elm, a biostatistician at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
In contrast, the doubled rate of major hemorrhages (mostly reversible gastrointestinal bleeds) with DAPT, compared with aspirin alone, occurred at a relatively uniform rate throughout the 90 days of treatment, meaning that limiting DAPT to just 21 days could prevent many of the excess hemorrhages.
“These results suggest that limiting clopidogrel plus aspirin use to 21 days may maximize benefit and reduce risk,” Dr. Elm said, especially in light of the findings confirming the efficacy of 21 days of DAPT following a minor stroke or TIA that had been reported several years ago in the CHANCE (Clopidogrel in High-Risk Patients with Acute Nondisabling Cerebrovascular Events) trial (New Engl J Med. 2013 Jul 4;369[1]:11-9).
Although the new finding from the POINT results came in a secondary analysis, it’s statistically legitimate and should be taken into account when writing treatment guidelines, she said, emphasizing that “this is a very important analysis that is not just hypothesis generating.”
Another finding from the new analysis was that a large number of major ischemic events, and hence a large number of the events prevented by DAPT, occurred in the first 2 days following the index event, a finding made possible because the POINT investigators enrolled patients and started treatment within 12 hours of the qualifying events.
“It’s better to start treatment early,” Dr. Elm noted, but she also highlighted that major ischemic events continued to accumulate during days 3-21, suggesting that patients could still benefit from DAPT even if treatment did not start until 24 or 48 hours after their index event.
POINT received no commercial funding aside from study drugs supplied by Sanofi. Dr. Elm reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Elm JJ et al. World Stroke Congress, Late-breaking session.
MONTREAL – The optimal length for dual antiplatelet therapy in patients who have just had a mild stroke or transient ischemic attack is 21 days, a duration of combined treatment that maximized protection against major ischemic events while minimizing the extra risk for a major hemorrhage, according to a prespecified analysis of data from the POINT trial.
The POINT (Platelet-Oriented Inhibition in New TIA and Minor Ischemic Stroke) trial randomized 4,881 patients with a very recent mild stroke or transient ischemic attack and without atrial fibrillation to treatment with either clopidogrel plus aspirin or aspirin alone for 90 days. Compared with aspirin alone, dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) cut the incidence of a major ischemic event by a relative 25% but also more than doubled the rate of major hemorrhage (New Engl J Med. 2018 Jul 19;377[3]:215-25).
The new, prespecified analysis looked at outcomes on a week-by-week basis over the course of 90 days of treatment, and showed that during the first 21 days the rate of major ischemic events was 5.6% among patients on aspirin only and 3.6% among those on DAPT, a statistically significant 35% relative cut in these adverse outcomes by using DAPT, Jordan J. Elm, PhD, reported at the World Stroke Congress. During the subsequent 69 days on treatment, the incidence of major ischemic events was roughly 1% in both arms of the study, showing that after 3 weeks the incremental benefit from DAPT disappeared, said Dr. Elm, a biostatistician at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
In contrast, the doubled rate of major hemorrhages (mostly reversible gastrointestinal bleeds) with DAPT, compared with aspirin alone, occurred at a relatively uniform rate throughout the 90 days of treatment, meaning that limiting DAPT to just 21 days could prevent many of the excess hemorrhages.
“These results suggest that limiting clopidogrel plus aspirin use to 21 days may maximize benefit and reduce risk,” Dr. Elm said, especially in light of the findings confirming the efficacy of 21 days of DAPT following a minor stroke or TIA that had been reported several years ago in the CHANCE (Clopidogrel in High-Risk Patients with Acute Nondisabling Cerebrovascular Events) trial (New Engl J Med. 2013 Jul 4;369[1]:11-9).
Although the new finding from the POINT results came in a secondary analysis, it’s statistically legitimate and should be taken into account when writing treatment guidelines, she said, emphasizing that “this is a very important analysis that is not just hypothesis generating.”
Another finding from the new analysis was that a large number of major ischemic events, and hence a large number of the events prevented by DAPT, occurred in the first 2 days following the index event, a finding made possible because the POINT investigators enrolled patients and started treatment within 12 hours of the qualifying events.
“It’s better to start treatment early,” Dr. Elm noted, but she also highlighted that major ischemic events continued to accumulate during days 3-21, suggesting that patients could still benefit from DAPT even if treatment did not start until 24 or 48 hours after their index event.
POINT received no commercial funding aside from study drugs supplied by Sanofi. Dr. Elm reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Elm JJ et al. World Stroke Congress, Late-breaking session.
REPORTING FROM THE WORLD STROKE CONGRESS
Key clinical point: All of DAPT’s extra benefit over aspirin alone in recent stroke or transient ischemic attack patients happened during the first 21 days.
Major finding: During the first 21 days, DAPT cut major ischemic events by 35%, compared with aspirin only.
Study details: A prespecified, secondary analysis from POINT, a multicenter, randomized trial with 4,881 patients.
Disclosures: POINT received no commercial funding aside from study drugs supplied by Sanofi. Dr. Elm had no disclosures.
Source: Elm JJ et al. World Stroke Congress, Late-breaking session.
Smartphone device beat Holter for post-stroke AF detection
MONTREAL – A smartphone-based method for quick and inexpensive monitoring for atrial fibrillation in patients hospitalized for a recent acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack identified three times more patients with the arrhythmia than did 24-hour Holter monitoring of the same patients after their hospital discharge.
This high level of atrial fibrillation (AF) detection using a relatively cheap and noninvasive device suggests that this method is a good “complement” to conventional monitoring by a 24-hour Holter recording or an implanted loop recorder in recent stroke patients, as called for in current guidelines of the world’s cardiology societies.
In the study, 294 of 1,079 patients hospitalized for an acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) underwent Holter monitoring, which identified 8 patients (3%) with AF, compared with 25 of these 294 patients (9%) identified with AF while they were hospitalized using serial, 30-second monitoring with the AliveCor device for smartphone assessment of ECG measurement, Bernard Yan, MD, said at the World Stroke Congress. Seven of the eight patients identified with AF by Holter monitoring were also found to have AF by the AliveCor device.
Dr. Yan, an interventional neurologist at the Comprehensive Stroke Center at the Royal Melbourne Hospital, attributed the higher pick-up rate for AF by monitoring during hospitalization to the timing of screening, which was within days of the stroke or TIA, rather than waiting to run a Holter sometime after the patient left the hospital.
“I suspect the difference in timing explains the difference” in detection, he said in an interview. “The difference may be because we monitored patients [with the AliveCor device] much earlier, during their ‘hot’ period, right after their stroke.”
The SPOT-AF trial ran at several centers in Australia, China, and Hong Kong, and enrolled 1,079 patients hospitalized for acute ischemic stroke or TIA who all underwent AliveCor monitoring during their median 4-day stay in the hospital. Patients performed a 30-second heart rhythm check every time a nurse saw them for a routine vital-sign examination, usually three or four times a day. The current analysis focused on the 294 patients (27% of the 1,079 patients) who also underwent 24-hour Holter monitoring following hospital discharge when ordered by their personal physician. This 27% incidence of postdischarge Holter monitoring despite guidelines that call for AF screening in all recent ischemic stroke and TIA patients was consistent with a 2016 review of more than 17,000 stroke or TIA patients in Canada that showed 31% underwent 24-hour Holter monitoring for AF during the 30 days following their index event (Stroke. 2016 Aug;47[8]:1982-9).
Although AF screening with a smartphone-based device is inexpensive and easy, Dr. Yan stopped short of suggesting that it is time for this approach to replace a Holter monitor or an implanted loop recorder because that is what current guidelines call for. “To change the guidelines, we need a different study that compares these approaches head to head.”
SPOT-AF received partial funding from Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Yan has been a speaker on behalf of Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, and Stryker.
MONTREAL – A smartphone-based method for quick and inexpensive monitoring for atrial fibrillation in patients hospitalized for a recent acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack identified three times more patients with the arrhythmia than did 24-hour Holter monitoring of the same patients after their hospital discharge.
This high level of atrial fibrillation (AF) detection using a relatively cheap and noninvasive device suggests that this method is a good “complement” to conventional monitoring by a 24-hour Holter recording or an implanted loop recorder in recent stroke patients, as called for in current guidelines of the world’s cardiology societies.
In the study, 294 of 1,079 patients hospitalized for an acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) underwent Holter monitoring, which identified 8 patients (3%) with AF, compared with 25 of these 294 patients (9%) identified with AF while they were hospitalized using serial, 30-second monitoring with the AliveCor device for smartphone assessment of ECG measurement, Bernard Yan, MD, said at the World Stroke Congress. Seven of the eight patients identified with AF by Holter monitoring were also found to have AF by the AliveCor device.
Dr. Yan, an interventional neurologist at the Comprehensive Stroke Center at the Royal Melbourne Hospital, attributed the higher pick-up rate for AF by monitoring during hospitalization to the timing of screening, which was within days of the stroke or TIA, rather than waiting to run a Holter sometime after the patient left the hospital.
“I suspect the difference in timing explains the difference” in detection, he said in an interview. “The difference may be because we monitored patients [with the AliveCor device] much earlier, during their ‘hot’ period, right after their stroke.”
The SPOT-AF trial ran at several centers in Australia, China, and Hong Kong, and enrolled 1,079 patients hospitalized for acute ischemic stroke or TIA who all underwent AliveCor monitoring during their median 4-day stay in the hospital. Patients performed a 30-second heart rhythm check every time a nurse saw them for a routine vital-sign examination, usually three or four times a day. The current analysis focused on the 294 patients (27% of the 1,079 patients) who also underwent 24-hour Holter monitoring following hospital discharge when ordered by their personal physician. This 27% incidence of postdischarge Holter monitoring despite guidelines that call for AF screening in all recent ischemic stroke and TIA patients was consistent with a 2016 review of more than 17,000 stroke or TIA patients in Canada that showed 31% underwent 24-hour Holter monitoring for AF during the 30 days following their index event (Stroke. 2016 Aug;47[8]:1982-9).
Although AF screening with a smartphone-based device is inexpensive and easy, Dr. Yan stopped short of suggesting that it is time for this approach to replace a Holter monitor or an implanted loop recorder because that is what current guidelines call for. “To change the guidelines, we need a different study that compares these approaches head to head.”
SPOT-AF received partial funding from Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Yan has been a speaker on behalf of Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, and Stryker.
MONTREAL – A smartphone-based method for quick and inexpensive monitoring for atrial fibrillation in patients hospitalized for a recent acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack identified three times more patients with the arrhythmia than did 24-hour Holter monitoring of the same patients after their hospital discharge.
This high level of atrial fibrillation (AF) detection using a relatively cheap and noninvasive device suggests that this method is a good “complement” to conventional monitoring by a 24-hour Holter recording or an implanted loop recorder in recent stroke patients, as called for in current guidelines of the world’s cardiology societies.
In the study, 294 of 1,079 patients hospitalized for an acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) underwent Holter monitoring, which identified 8 patients (3%) with AF, compared with 25 of these 294 patients (9%) identified with AF while they were hospitalized using serial, 30-second monitoring with the AliveCor device for smartphone assessment of ECG measurement, Bernard Yan, MD, said at the World Stroke Congress. Seven of the eight patients identified with AF by Holter monitoring were also found to have AF by the AliveCor device.
Dr. Yan, an interventional neurologist at the Comprehensive Stroke Center at the Royal Melbourne Hospital, attributed the higher pick-up rate for AF by monitoring during hospitalization to the timing of screening, which was within days of the stroke or TIA, rather than waiting to run a Holter sometime after the patient left the hospital.
“I suspect the difference in timing explains the difference” in detection, he said in an interview. “The difference may be because we monitored patients [with the AliveCor device] much earlier, during their ‘hot’ period, right after their stroke.”
The SPOT-AF trial ran at several centers in Australia, China, and Hong Kong, and enrolled 1,079 patients hospitalized for acute ischemic stroke or TIA who all underwent AliveCor monitoring during their median 4-day stay in the hospital. Patients performed a 30-second heart rhythm check every time a nurse saw them for a routine vital-sign examination, usually three or four times a day. The current analysis focused on the 294 patients (27% of the 1,079 patients) who also underwent 24-hour Holter monitoring following hospital discharge when ordered by their personal physician. This 27% incidence of postdischarge Holter monitoring despite guidelines that call for AF screening in all recent ischemic stroke and TIA patients was consistent with a 2016 review of more than 17,000 stroke or TIA patients in Canada that showed 31% underwent 24-hour Holter monitoring for AF during the 30 days following their index event (Stroke. 2016 Aug;47[8]:1982-9).
Although AF screening with a smartphone-based device is inexpensive and easy, Dr. Yan stopped short of suggesting that it is time for this approach to replace a Holter monitor or an implanted loop recorder because that is what current guidelines call for. “To change the guidelines, we need a different study that compares these approaches head to head.”
SPOT-AF received partial funding from Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Yan has been a speaker on behalf of Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, and Stryker.
REPORTING FROM THE WORLD STROKE CONGRESS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Holter monitoring detected atrial fibrillation in 8 of 294 patients, while smartphone monitoring identified 25 with the arrhythmia.
Study details: SPOT-AF, a multicenter study with 1,079 total patients, including 294 who underwent Holter monitoring.
Disclosures: SPOT-AF received partial funding from Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Yan has been a speaker on behalf of Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, and Stryker.
Anti-inflammatory Drug Could Help Prevent MS Brain Tissue Loss
Findings from a recent study of ibudilast, an anti-inflammatory drug, “provide a glimmer of hope” for people with progressive multiple sclerosis, according to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke researchers.
Ibudilast is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor with bronchodilator, vasodilator, and neuroprotective effects, mainly used in the treatment of asthma and stroke.
In the placebo-controlled study, 255 participants were assigned to take up to 10 capsules of ibudilast or placebo per day for 96 weeks. Every 6 months, they had magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain scans. The researchers observed a difference in brain shrinkage of about 2.5 mL of brain tissue per year between the 2 groups. (The human brain has a volume of about 1,350 mL.) It is unknown whether the difference had an effect on symptoms or loss of function.
Reported adverse events were similar in both groups. The most common with ibudilast were gastrointestinal, headaches, and depression.
Findings from a recent study of ibudilast, an anti-inflammatory drug, “provide a glimmer of hope” for people with progressive multiple sclerosis, according to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke researchers.
Ibudilast is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor with bronchodilator, vasodilator, and neuroprotective effects, mainly used in the treatment of asthma and stroke.
In the placebo-controlled study, 255 participants were assigned to take up to 10 capsules of ibudilast or placebo per day for 96 weeks. Every 6 months, they had magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain scans. The researchers observed a difference in brain shrinkage of about 2.5 mL of brain tissue per year between the 2 groups. (The human brain has a volume of about 1,350 mL.) It is unknown whether the difference had an effect on symptoms or loss of function.
Reported adverse events were similar in both groups. The most common with ibudilast were gastrointestinal, headaches, and depression.
Findings from a recent study of ibudilast, an anti-inflammatory drug, “provide a glimmer of hope” for people with progressive multiple sclerosis, according to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke researchers.
Ibudilast is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor with bronchodilator, vasodilator, and neuroprotective effects, mainly used in the treatment of asthma and stroke.
In the placebo-controlled study, 255 participants were assigned to take up to 10 capsules of ibudilast or placebo per day for 96 weeks. Every 6 months, they had magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain scans. The researchers observed a difference in brain shrinkage of about 2.5 mL of brain tissue per year between the 2 groups. (The human brain has a volume of about 1,350 mL.) It is unknown whether the difference had an effect on symptoms or loss of function.
Reported adverse events were similar in both groups. The most common with ibudilast were gastrointestinal, headaches, and depression.
Mysterious polio-like illness baffles medical experts while frightening parents
A spike in the number of children with a rare neurological disease that causes polio-like symptoms has health officials across the country scrambling to understand the illness. Yet, more than 4 years after health officials first recorded the most recent uptick in cases, much about the national outbreak remains a mystery.
Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) affects the gray matter in the spinal cord, causing sudden muscle weakness and a loss of reflexes. The illness can lead to serious complications – including paralysis or respiratory failure – and requires immediate medical attention.
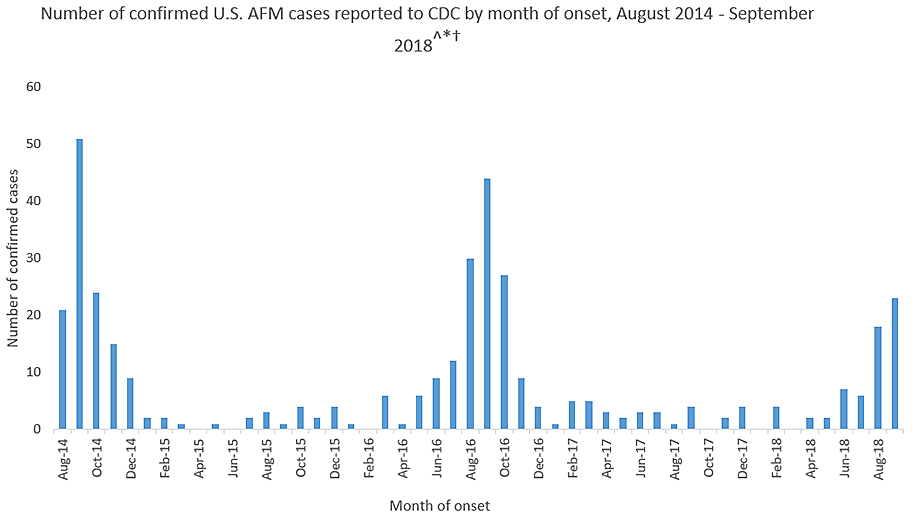
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is investigating 127 cases of possible AFM, including 62 that have been confirmed in 22 states this year. At least 90% of the cases are among patients 18 years old and younger. The average age of a patient is 4 years old.
AFM remains extremely rare, even with the recent increase. The CDC estimates fewer than 1 in a million Americans will get the disease. Officials advised parents not to panic but remain vigilant for any sudden onset of symptoms. They also suggested that children stay up to date with their vaccines and practice good hand washing habits.
This year’s outbreak marks the third spike of AFM in 4 years. From August 2014 to September 2018, 386 cases have been confirmed. Yet, experts still do not understand crucial aspects of the disease, including its origins and who is most at risk.
“There is a lot we don’t know about AFM,” said Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. Here’s what puzzles health officials about AFM:
The cause is still unknown
Acute flaccid myelitis can be caused by viruses, such as polio or West Nile. But federal officials said that those viruses have not been linked to the U.S. outbreak over the past 4 years. They have not isolated the cause of these cases.
Despite symptoms reminiscent of polio, no AFM cases have tested positive for that virus, according to the CDC. Investigators have also ruled out a variety of germs. Environmental agents, viruses, and other pathogens are still being considered.
The 2014 outbreak of AFM coincided with a surge of another virus that caused severe respiratory problems, called EV-D68. However, the CDC could not establish a causal link between AFM and the virus. Since then, no large outbreaks of the virus have occurred, according to the CDC.
Carlos Pardo-Villamizar, MD, a neurologist and director of the Johns Hopkins Transverse Myelitis Center, said that the mystery lies in whether the damage seen in AFM is caused by an external agent or the body’s own defenses.
“At this moment, we don’t know if it’s a virus that is coming and producing direct damage of the gray matter in the spinal cord,” he said, “or if a virus is triggering immunological responses that produce a secondary damage in the spinal cord.”
It’s not clear who is at risk
Although the disease appears to target a certain age group, federal disease experts do not know who is likely to get acute flaccid myelitis.
Dr. Pardo-Villamizar said identifying vulnerable populations is “a work in progress.”
Mary Anne Jackson, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist and interim dean of the school of medicine at the University of Missouri–Kansas City, said many of the patients she saw were healthy children before falling ill with the disease. She suspects that a host of factors play a role in the likelihood of getting AFM, but more cases must be reviewed in order to find an answer.
The long-term effects are unknown
The CDC said it doesn’t know how long symptoms of the disease will last for patients. However, experts say that initial indications from a small number of cases suggest a grim outlook.
A study published last year found six of eight children in Colorado with acute flaccid myelitis still struggled with motor skills 1 year after their diagnosis. Nonetheless, the researchers found that the patients and families “demonstrated a high degree of resilience and recovery.”
“The majority of these patients are left with extensive problems,” said Dr. Pardo-Villamizar, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Jackson, who also saw persistent muscle weakness in her patients, said she believes the CDC may be hesitant to specify the long-term effects of the disease because existing studies have included only small numbers of patients. More studies that include a larger proportion of confirmed cases are needed to better understand long-term outcomes, she said.
KHN’s coverage of children’s health care issues is supported in part by the Heising-Simons Foundation. Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
A spike in the number of children with a rare neurological disease that causes polio-like symptoms has health officials across the country scrambling to understand the illness. Yet, more than 4 years after health officials first recorded the most recent uptick in cases, much about the national outbreak remains a mystery.

Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) affects the gray matter in the spinal cord, causing sudden muscle weakness and a loss of reflexes. The illness can lead to serious complications – including paralysis or respiratory failure – and requires immediate medical attention.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is investigating 127 cases of possible AFM, including 62 that have been confirmed in 22 states this year. At least 90% of the cases are among patients 18 years old and younger. The average age of a patient is 4 years old.
AFM remains extremely rare, even with the recent increase. The CDC estimates fewer than 1 in a million Americans will get the disease. Officials advised parents not to panic but remain vigilant for any sudden onset of symptoms. They also suggested that children stay up to date with their vaccines and practice good hand washing habits.
This year’s outbreak marks the third spike of AFM in 4 years. From August 2014 to September 2018, 386 cases have been confirmed. Yet, experts still do not understand crucial aspects of the disease, including its origins and who is most at risk.
“There is a lot we don’t know about AFM,” said Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. Here’s what puzzles health officials about AFM:
The cause is still unknown
Acute flaccid myelitis can be caused by viruses, such as polio or West Nile. But federal officials said that those viruses have not been linked to the U.S. outbreak over the past 4 years. They have not isolated the cause of these cases.
Despite symptoms reminiscent of polio, no AFM cases have tested positive for that virus, according to the CDC. Investigators have also ruled out a variety of germs. Environmental agents, viruses, and other pathogens are still being considered.
The 2014 outbreak of AFM coincided with a surge of another virus that caused severe respiratory problems, called EV-D68. However, the CDC could not establish a causal link between AFM and the virus. Since then, no large outbreaks of the virus have occurred, according to the CDC.
Carlos Pardo-Villamizar, MD, a neurologist and director of the Johns Hopkins Transverse Myelitis Center, said that the mystery lies in whether the damage seen in AFM is caused by an external agent or the body’s own defenses.
“At this moment, we don’t know if it’s a virus that is coming and producing direct damage of the gray matter in the spinal cord,” he said, “or if a virus is triggering immunological responses that produce a secondary damage in the spinal cord.”
It’s not clear who is at risk
Although the disease appears to target a certain age group, federal disease experts do not know who is likely to get acute flaccid myelitis.
Dr. Pardo-Villamizar said identifying vulnerable populations is “a work in progress.”
Mary Anne Jackson, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist and interim dean of the school of medicine at the University of Missouri–Kansas City, said many of the patients she saw were healthy children before falling ill with the disease. She suspects that a host of factors play a role in the likelihood of getting AFM, but more cases must be reviewed in order to find an answer.
The long-term effects are unknown
The CDC said it doesn’t know how long symptoms of the disease will last for patients. However, experts say that initial indications from a small number of cases suggest a grim outlook.
A study published last year found six of eight children in Colorado with acute flaccid myelitis still struggled with motor skills 1 year after their diagnosis. Nonetheless, the researchers found that the patients and families “demonstrated a high degree of resilience and recovery.”
“The majority of these patients are left with extensive problems,” said Dr. Pardo-Villamizar, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Jackson, who also saw persistent muscle weakness in her patients, said she believes the CDC may be hesitant to specify the long-term effects of the disease because existing studies have included only small numbers of patients. More studies that include a larger proportion of confirmed cases are needed to better understand long-term outcomes, she said.
KHN’s coverage of children’s health care issues is supported in part by the Heising-Simons Foundation. Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
A spike in the number of children with a rare neurological disease that causes polio-like symptoms has health officials across the country scrambling to understand the illness. Yet, more than 4 years after health officials first recorded the most recent uptick in cases, much about the national outbreak remains a mystery.

Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) affects the gray matter in the spinal cord, causing sudden muscle weakness and a loss of reflexes. The illness can lead to serious complications – including paralysis or respiratory failure – and requires immediate medical attention.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is investigating 127 cases of possible AFM, including 62 that have been confirmed in 22 states this year. At least 90% of the cases are among patients 18 years old and younger. The average age of a patient is 4 years old.
AFM remains extremely rare, even with the recent increase. The CDC estimates fewer than 1 in a million Americans will get the disease. Officials advised parents not to panic but remain vigilant for any sudden onset of symptoms. They also suggested that children stay up to date with their vaccines and practice good hand washing habits.
This year’s outbreak marks the third spike of AFM in 4 years. From August 2014 to September 2018, 386 cases have been confirmed. Yet, experts still do not understand crucial aspects of the disease, including its origins and who is most at risk.
“There is a lot we don’t know about AFM,” said Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. Here’s what puzzles health officials about AFM:
The cause is still unknown
Acute flaccid myelitis can be caused by viruses, such as polio or West Nile. But federal officials said that those viruses have not been linked to the U.S. outbreak over the past 4 years. They have not isolated the cause of these cases.
Despite symptoms reminiscent of polio, no AFM cases have tested positive for that virus, according to the CDC. Investigators have also ruled out a variety of germs. Environmental agents, viruses, and other pathogens are still being considered.
The 2014 outbreak of AFM coincided with a surge of another virus that caused severe respiratory problems, called EV-D68. However, the CDC could not establish a causal link between AFM and the virus. Since then, no large outbreaks of the virus have occurred, according to the CDC.
Carlos Pardo-Villamizar, MD, a neurologist and director of the Johns Hopkins Transverse Myelitis Center, said that the mystery lies in whether the damage seen in AFM is caused by an external agent or the body’s own defenses.
“At this moment, we don’t know if it’s a virus that is coming and producing direct damage of the gray matter in the spinal cord,” he said, “or if a virus is triggering immunological responses that produce a secondary damage in the spinal cord.”
It’s not clear who is at risk
Although the disease appears to target a certain age group, federal disease experts do not know who is likely to get acute flaccid myelitis.
Dr. Pardo-Villamizar said identifying vulnerable populations is “a work in progress.”
Mary Anne Jackson, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist and interim dean of the school of medicine at the University of Missouri–Kansas City, said many of the patients she saw were healthy children before falling ill with the disease. She suspects that a host of factors play a role in the likelihood of getting AFM, but more cases must be reviewed in order to find an answer.
The long-term effects are unknown
The CDC said it doesn’t know how long symptoms of the disease will last for patients. However, experts say that initial indications from a small number of cases suggest a grim outlook.
A study published last year found six of eight children in Colorado with acute flaccid myelitis still struggled with motor skills 1 year after their diagnosis. Nonetheless, the researchers found that the patients and families “demonstrated a high degree of resilience and recovery.”
“The majority of these patients are left with extensive problems,” said Dr. Pardo-Villamizar, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Jackson, who also saw persistent muscle weakness in her patients, said she believes the CDC may be hesitant to specify the long-term effects of the disease because existing studies have included only small numbers of patients. More studies that include a larger proportion of confirmed cases are needed to better understand long-term outcomes, she said.
KHN’s coverage of children’s health care issues is supported in part by the Heising-Simons Foundation. Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Higher rate of loss seen in unplanned pregnancies for women with epilepsy
when compared against women with epilepsy who planned their pregnancy, according to recent results from a retrospective study published in JAMA Neurology.
“This analysis adds the finding that unplanned pregnancy may increase the risk of [spontaneous fetal loss] in women with epilepsy and identifies pregnancy planning, maternal age, and interpregnancy interval as significant modifiable variables,” Andrew G. Herzog, MD, of the Harvard Neuroendocrine Unit at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Wellesley, Mass., and colleagues wrote in their study.
The researchers examined results from a web-based survey completed by 1,144 women in the Epilepsy Birth Control Registry (EBCR) between 2010 and 2014 with data on contraception use, pregnancy history, and antiepileptic drug (AED) treatment. Patients were aged 18-47 years (mean 28.5 years) with 8.7% of the cohort consisting of minority women and 39.8% having household incomes of $25,000 or less.
Pregnancy history data included number of pregnancies, number of planned or unplanned pregnancies, AED type used during pregnancies, pregnancy outcomes such as live birth, induced abortion, and spontaneous fetal loss (SFL), while AED data included categorizing patients into no therapy, monotherapy, and polytherapy groups. AED use was further subdivided into no AED, enzyme-inducing AED, non–enzyme-inducing AED, enzyme-inhibiting AED, glucuronidated AED, and mixed category groups.
Of 794 pregnancies, 530 pregnancies (66.8%) were unplanned and 264 (33.2%) were planned, with 473 live births (59.6%), 141 induced abortions (17.8%), and 180 SFL (22.7%). Among patients who did not have an induced abortion, SFL risk was higher if the pregnancy was unplanned (137 patients, 35.0%), compared with those who planned (43 patients, 16.4%) their pregnancy (risk ratio = 2.14; 95% confidence interval, 1.59-2.90; P less than .001). According to a regression analysis, SFL risk was higher for patients where “planning was entered alone” in unplanned pregnancies (odds ratio = 2.75; 95% CI, 1.87-4.05; P less than .001) as well as when adjusted for AED category, maternal age, and interpregnancy interval (OR = 3.57; 95% CI, 1.54-8.78; P = .003).
There was an association between maternal age (OR = 0.957; 95% CI, 0.928-0.986; P = .02) and risk of SFL, with lower risk seen in the 18- to 27-year-old group (118 patients, 29.5%; RR = 0.57; 95% CI, 0.39-0.84; P less than .004) and 28- to 37-year-old group (44 patients, 20.8%; RR = 0.40; 95% CI, 0.26-0.62; P less than .001), compared with the under-18 group (15 patients, 51.7%). There was also a higher risk of SFL with regard to interpregnancy interval (OR = 2.878; 95% CI, 1.8094-4.5801; P = .008), with a greater risk seen if the interpregnancy interval was under 1 year (56 patients, 45.9%), compared with 1 year (56 patients, 22.8%) or higher (RR = 2.02; 95% CI, 1.49-2.72; P less than .001).
“In view of the finding of increased risk for SFL in unplanned pregnancies in women with epilepsy, and because a history of SFL in women with epilepsy may increase the risk that subsequent live-born offspring will develop epilepsy, the finding warrants prospective investigation with medical record verification of pregnancy outcomes,” Dr. Herzog and his colleagues wrote.
The Epilepsy Foundation and Lundbeck funded the study. Dr. Herzog reports support by grants, and two coauthors received salary support from grants, from the two organizations.
SOURCE: Herzog AG et al. JAMA Neurol. 2018 Oct 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.3089.
when compared against women with epilepsy who planned their pregnancy, according to recent results from a retrospective study published in JAMA Neurology.
“This analysis adds the finding that unplanned pregnancy may increase the risk of [spontaneous fetal loss] in women with epilepsy and identifies pregnancy planning, maternal age, and interpregnancy interval as significant modifiable variables,” Andrew G. Herzog, MD, of the Harvard Neuroendocrine Unit at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Wellesley, Mass., and colleagues wrote in their study.
The researchers examined results from a web-based survey completed by 1,144 women in the Epilepsy Birth Control Registry (EBCR) between 2010 and 2014 with data on contraception use, pregnancy history, and antiepileptic drug (AED) treatment. Patients were aged 18-47 years (mean 28.5 years) with 8.7% of the cohort consisting of minority women and 39.8% having household incomes of $25,000 or less.
Pregnancy history data included number of pregnancies, number of planned or unplanned pregnancies, AED type used during pregnancies, pregnancy outcomes such as live birth, induced abortion, and spontaneous fetal loss (SFL), while AED data included categorizing patients into no therapy, monotherapy, and polytherapy groups. AED use was further subdivided into no AED, enzyme-inducing AED, non–enzyme-inducing AED, enzyme-inhibiting AED, glucuronidated AED, and mixed category groups.
Of 794 pregnancies, 530 pregnancies (66.8%) were unplanned and 264 (33.2%) were planned, with 473 live births (59.6%), 141 induced abortions (17.8%), and 180 SFL (22.7%). Among patients who did not have an induced abortion, SFL risk was higher if the pregnancy was unplanned (137 patients, 35.0%), compared with those who planned (43 patients, 16.4%) their pregnancy (risk ratio = 2.14; 95% confidence interval, 1.59-2.90; P less than .001). According to a regression analysis, SFL risk was higher for patients where “planning was entered alone” in unplanned pregnancies (odds ratio = 2.75; 95% CI, 1.87-4.05; P less than .001) as well as when adjusted for AED category, maternal age, and interpregnancy interval (OR = 3.57; 95% CI, 1.54-8.78; P = .003).
There was an association between maternal age (OR = 0.957; 95% CI, 0.928-0.986; P = .02) and risk of SFL, with lower risk seen in the 18- to 27-year-old group (118 patients, 29.5%; RR = 0.57; 95% CI, 0.39-0.84; P less than .004) and 28- to 37-year-old group (44 patients, 20.8%; RR = 0.40; 95% CI, 0.26-0.62; P less than .001), compared with the under-18 group (15 patients, 51.7%). There was also a higher risk of SFL with regard to interpregnancy interval (OR = 2.878; 95% CI, 1.8094-4.5801; P = .008), with a greater risk seen if the interpregnancy interval was under 1 year (56 patients, 45.9%), compared with 1 year (56 patients, 22.8%) or higher (RR = 2.02; 95% CI, 1.49-2.72; P less than .001).
“In view of the finding of increased risk for SFL in unplanned pregnancies in women with epilepsy, and because a history of SFL in women with epilepsy may increase the risk that subsequent live-born offspring will develop epilepsy, the finding warrants prospective investigation with medical record verification of pregnancy outcomes,” Dr. Herzog and his colleagues wrote.
The Epilepsy Foundation and Lundbeck funded the study. Dr. Herzog reports support by grants, and two coauthors received salary support from grants, from the two organizations.
SOURCE: Herzog AG et al. JAMA Neurol. 2018 Oct 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.3089.
when compared against women with epilepsy who planned their pregnancy, according to recent results from a retrospective study published in JAMA Neurology.
“This analysis adds the finding that unplanned pregnancy may increase the risk of [spontaneous fetal loss] in women with epilepsy and identifies pregnancy planning, maternal age, and interpregnancy interval as significant modifiable variables,” Andrew G. Herzog, MD, of the Harvard Neuroendocrine Unit at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Wellesley, Mass., and colleagues wrote in their study.
The researchers examined results from a web-based survey completed by 1,144 women in the Epilepsy Birth Control Registry (EBCR) between 2010 and 2014 with data on contraception use, pregnancy history, and antiepileptic drug (AED) treatment. Patients were aged 18-47 years (mean 28.5 years) with 8.7% of the cohort consisting of minority women and 39.8% having household incomes of $25,000 or less.
Pregnancy history data included number of pregnancies, number of planned or unplanned pregnancies, AED type used during pregnancies, pregnancy outcomes such as live birth, induced abortion, and spontaneous fetal loss (SFL), while AED data included categorizing patients into no therapy, monotherapy, and polytherapy groups. AED use was further subdivided into no AED, enzyme-inducing AED, non–enzyme-inducing AED, enzyme-inhibiting AED, glucuronidated AED, and mixed category groups.
Of 794 pregnancies, 530 pregnancies (66.8%) were unplanned and 264 (33.2%) were planned, with 473 live births (59.6%), 141 induced abortions (17.8%), and 180 SFL (22.7%). Among patients who did not have an induced abortion, SFL risk was higher if the pregnancy was unplanned (137 patients, 35.0%), compared with those who planned (43 patients, 16.4%) their pregnancy (risk ratio = 2.14; 95% confidence interval, 1.59-2.90; P less than .001). According to a regression analysis, SFL risk was higher for patients where “planning was entered alone” in unplanned pregnancies (odds ratio = 2.75; 95% CI, 1.87-4.05; P less than .001) as well as when adjusted for AED category, maternal age, and interpregnancy interval (OR = 3.57; 95% CI, 1.54-8.78; P = .003).
There was an association between maternal age (OR = 0.957; 95% CI, 0.928-0.986; P = .02) and risk of SFL, with lower risk seen in the 18- to 27-year-old group (118 patients, 29.5%; RR = 0.57; 95% CI, 0.39-0.84; P less than .004) and 28- to 37-year-old group (44 patients, 20.8%; RR = 0.40; 95% CI, 0.26-0.62; P less than .001), compared with the under-18 group (15 patients, 51.7%). There was also a higher risk of SFL with regard to interpregnancy interval (OR = 2.878; 95% CI, 1.8094-4.5801; P = .008), with a greater risk seen if the interpregnancy interval was under 1 year (56 patients, 45.9%), compared with 1 year (56 patients, 22.8%) or higher (RR = 2.02; 95% CI, 1.49-2.72; P less than .001).
“In view of the finding of increased risk for SFL in unplanned pregnancies in women with epilepsy, and because a history of SFL in women with epilepsy may increase the risk that subsequent live-born offspring will develop epilepsy, the finding warrants prospective investigation with medical record verification of pregnancy outcomes,” Dr. Herzog and his colleagues wrote.
The Epilepsy Foundation and Lundbeck funded the study. Dr. Herzog reports support by grants, and two coauthors received salary support from grants, from the two organizations.
SOURCE: Herzog AG et al. JAMA Neurol. 2018 Oct 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.3089.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Key clinical point: Women with epilepsy who experience unplanned pregnancies have a higher rate of spontaneous fetal loss, compared with those with epilepsy who plan their pregnancies.
Major finding: Thirty-five percent of women with unplanned pregnancies experienced spontaneous fetal loss, compared with 16.4% of women in the planned pregnancy group.
Study details: A retrospective analysis of results from a web-based survey of 1,144 women from the Epilepsy Birth Control Registry.
Disclosures: The Epilepsy Foundation and Lundbeck funded the study. Dr. Herzog reports support by grants, and two coauthors received salary support from grants, from the two organizations.
Source: Herzog AG et al. JAMA Neurol. 2018 Oct 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.3089.
MS cognitive decline buffered by early high vitamin D levels
BERLIN – , according to a recent study.
“Higher vitamin D in the first years after [clinically isolated syndrome] was associated with better cognitive function and lower neuronal injury at year 11,” said Marianna Cortese, MD, presenting her findings during a late-breaking abstracts session at the annual congress of the European Society for Education and Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis.
“Vitamin D supplementation during the early years with the disease might be neuroprotective,” she said.
According to Dr. Cortese, 40%-70% of patients with MS will experience cognitive decline across their disease course; there is no currently known specific treatment for cognitive decline.
Smoking, low levels of vitamin D [as 25(OH)D], and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) seropositivity are known risk factors for MS, and have been associated with more active MS and progressive disease, but whether these factors predict cognitive status had not been known, said Dr. Cortese of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Accordingly, she said, investigators in the BENEFIT-11 trial sought to determine whether low vitamin D levels, smoking status, and EBV seropositivity detected early after the first disease manifestation in MS would affect later cognitive function.
The study is an observational study that followed 278 participants with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) in the original BENEFIT trial, which was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of interferon beta-1b for early treatment of clinically isolated syndrome. The primary goal of BENEFIT-11, said Dr. Cortese, was to assess the effects of early treatment on long-term outcomes.
“To minimize reverse causation, we used exposure status in the first 2 years after CIS to predict progression outcomes at year 11,” explained Dr. Cortese. The investigators obtained biomarkers at baseline, and at study months 6, 12, and 24. Cotinine was used as a biomarker for current or recent nicotine exposure. Serum 25(OH)D levels were used to determine vitamin D levels, and immunoglobulin G levels for EBV antigen-1 were used for EBV seropositivity.
In terms of outcome measurements, the cognitive performance measure used in the study was the Paced Auditory Serial Addition Test, a validated test of processing speed, attention, and working memory, said Dr. Cortese. This test was performed at enrollment, and at study years 1, 2, 5, and 11. At study year 11, neuroaxonal injury was measured using serum neurofilament light chain levels.
In multivariable analysis, the study design adjusted for baseline age and sex, treatment allocation at baseline, unifocal versus multifocal disease seen on baseline magnetic resonance imaging, body mass index, and whether the patient was treated with steroids during the initial CIS.
“Higher quintiles of mean vitamin D levels during the first 2 years were associated with lower odds of scoring worse on the PASAT at year 11,” said Dr. Cortese (P-trend = .028). The significant trend across the quintiles “suggests a dose-response relationship,” she said.* For vitamin D levels over the first 5 years, the P-trend was .049. Dr. Cortese explained that “scoring worse” meant scoring below the median.
Looking at the effect of early vitamin D levels another way, incremental increases of 50 nmol/L of mean 25(OH)D in study months 6-24 predicted 65% lower odds of having a PASAT score below the median at year 11 (P = .027). “Within-person increases in vitamin D during the study were also significantly associated with a better PASAT score when we used the repeated measurement in a linear mixed model,” said Dr. Cortese.
Turning to the effect of smoking on cognitive function at year 11, Dr. Cortese explained that cotinine levels obtained during the first 2 years were all used to determine smoking status. If all levels were below 10 ng/mL, the participant was designated a nonsmoker (N = 125). If any levels were above 25 ng/mL, that patient was classified as a smoker. The investigators also looked at the small number of patients (N = 9) who were very heavy smokers, with cotinine levels over 191 ng/mL.
“Smokers – compared to nonsmokers – had a significantly lower standardized PASAT score at year 11,” said Dr. Cortese (P trend = .042 in age- and sex-adjusted analysis; P-trend = .056 in full multivariable analysis). “Actually, smokers had an up to 0.6-standard deviation-lower PASAT score at year 11 when we looked at heavy smokers. ...This difference corresponds to about 5 points of the PASAT, so I would say [the score is] clinically meaningful.”
Dr. Cortese pointed out that early smoking, again, showed a dose-response relationship with later cognitive status. “It continues to be important to encourage smoking cessation for patients.”
Epstein-Barr antibodies were not associated with cognitive function at year 11, according to the analysis (P-trend = .93).
“The findings of neuroaxonal injury at year 11 using serum neurofilament light-chain measures corroborated the main findings on cognitive function at year 11,” said Dr. Cortese.
For a 50-nmol higher vitamin D level within the first 5 years, neurofilament light chain levels at year 11 were 20% lower, said Dr. Cortese. Conversely, patients who had cotinine levels higher than 25 ng/mL during the first 5 years had neurofilament light chain levels 20% higher than other participants: “So they did worse. They had more neuroaxonal loss,” said Dr. Cortese. No association was seen between neurofilament light chain levels at year 11 and early EBV status, she said.
Though just cognitive function data from BENEFIT-11 were reported by Dr. Cortese, she said that radiologic and other clinical data are also being studied and will be reported in the future.
Dr. Cortese reported that she had no conflicts of interest. Several coauthors reported financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies. The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, with clinical support from Bayer HealthCare.
SOURCE: Cortese M et al. ECTRIMS 2018, Late breaking abstracts session.
*Correction, 10/25/18: An earlier version of this article mischaracterized the relationship between vitamin D scores during the first 2 years and PASAT scores at year 11.
BERLIN – , according to a recent study.
“Higher vitamin D in the first years after [clinically isolated syndrome] was associated with better cognitive function and lower neuronal injury at year 11,” said Marianna Cortese, MD, presenting her findings during a late-breaking abstracts session at the annual congress of the European Society for Education and Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis.
“Vitamin D supplementation during the early years with the disease might be neuroprotective,” she said.
According to Dr. Cortese, 40%-70% of patients with MS will experience cognitive decline across their disease course; there is no currently known specific treatment for cognitive decline.
Smoking, low levels of vitamin D [as 25(OH)D], and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) seropositivity are known risk factors for MS, and have been associated with more active MS and progressive disease, but whether these factors predict cognitive status had not been known, said Dr. Cortese of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Accordingly, she said, investigators in the BENEFIT-11 trial sought to determine whether low vitamin D levels, smoking status, and EBV seropositivity detected early after the first disease manifestation in MS would affect later cognitive function.
The study is an observational study that followed 278 participants with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) in the original BENEFIT trial, which was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of interferon beta-1b for early treatment of clinically isolated syndrome. The primary goal of BENEFIT-11, said Dr. Cortese, was to assess the effects of early treatment on long-term outcomes.
“To minimize reverse causation, we used exposure status in the first 2 years after CIS to predict progression outcomes at year 11,” explained Dr. Cortese. The investigators obtained biomarkers at baseline, and at study months 6, 12, and 24. Cotinine was used as a biomarker for current or recent nicotine exposure. Serum 25(OH)D levels were used to determine vitamin D levels, and immunoglobulin G levels for EBV antigen-1 were used for EBV seropositivity.
In terms of outcome measurements, the cognitive performance measure used in the study was the Paced Auditory Serial Addition Test, a validated test of processing speed, attention, and working memory, said Dr. Cortese. This test was performed at enrollment, and at study years 1, 2, 5, and 11. At study year 11, neuroaxonal injury was measured using serum neurofilament light chain levels.
In multivariable analysis, the study design adjusted for baseline age and sex, treatment allocation at baseline, unifocal versus multifocal disease seen on baseline magnetic resonance imaging, body mass index, and whether the patient was treated with steroids during the initial CIS.
“Higher quintiles of mean vitamin D levels during the first 2 years were associated with lower odds of scoring worse on the PASAT at year 11,” said Dr. Cortese (P-trend = .028). The significant trend across the quintiles “suggests a dose-response relationship,” she said.* For vitamin D levels over the first 5 years, the P-trend was .049. Dr. Cortese explained that “scoring worse” meant scoring below the median.
Looking at the effect of early vitamin D levels another way, incremental increases of 50 nmol/L of mean 25(OH)D in study months 6-24 predicted 65% lower odds of having a PASAT score below the median at year 11 (P = .027). “Within-person increases in vitamin D during the study were also significantly associated with a better PASAT score when we used the repeated measurement in a linear mixed model,” said Dr. Cortese.
Turning to the effect of smoking on cognitive function at year 11, Dr. Cortese explained that cotinine levels obtained during the first 2 years were all used to determine smoking status. If all levels were below 10 ng/mL, the participant was designated a nonsmoker (N = 125). If any levels were above 25 ng/mL, that patient was classified as a smoker. The investigators also looked at the small number of patients (N = 9) who were very heavy smokers, with cotinine levels over 191 ng/mL.
“Smokers – compared to nonsmokers – had a significantly lower standardized PASAT score at year 11,” said Dr. Cortese (P trend = .042 in age- and sex-adjusted analysis; P-trend = .056 in full multivariable analysis). “Actually, smokers had an up to 0.6-standard deviation-lower PASAT score at year 11 when we looked at heavy smokers. ...This difference corresponds to about 5 points of the PASAT, so I would say [the score is] clinically meaningful.”
Dr. Cortese pointed out that early smoking, again, showed a dose-response relationship with later cognitive status. “It continues to be important to encourage smoking cessation for patients.”
Epstein-Barr antibodies were not associated with cognitive function at year 11, according to the analysis (P-trend = .93).
“The findings of neuroaxonal injury at year 11 using serum neurofilament light-chain measures corroborated the main findings on cognitive function at year 11,” said Dr. Cortese.
For a 50-nmol higher vitamin D level within the first 5 years, neurofilament light chain levels at year 11 were 20% lower, said Dr. Cortese. Conversely, patients who had cotinine levels higher than 25 ng/mL during the first 5 years had neurofilament light chain levels 20% higher than other participants: “So they did worse. They had more neuroaxonal loss,” said Dr. Cortese. No association was seen between neurofilament light chain levels at year 11 and early EBV status, she said.
Though just cognitive function data from BENEFIT-11 were reported by Dr. Cortese, she said that radiologic and other clinical data are also being studied and will be reported in the future.
Dr. Cortese reported that she had no conflicts of interest. Several coauthors reported financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies. The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, with clinical support from Bayer HealthCare.
SOURCE: Cortese M et al. ECTRIMS 2018, Late breaking abstracts session.
*Correction, 10/25/18: An earlier version of this article mischaracterized the relationship between vitamin D scores during the first 2 years and PASAT scores at year 11.
BERLIN – , according to a recent study.
“Higher vitamin D in the first years after [clinically isolated syndrome] was associated with better cognitive function and lower neuronal injury at year 11,” said Marianna Cortese, MD, presenting her findings during a late-breaking abstracts session at the annual congress of the European Society for Education and Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis.
“Vitamin D supplementation during the early years with the disease might be neuroprotective,” she said.
According to Dr. Cortese, 40%-70% of patients with MS will experience cognitive decline across their disease course; there is no currently known specific treatment for cognitive decline.
Smoking, low levels of vitamin D [as 25(OH)D], and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) seropositivity are known risk factors for MS, and have been associated with more active MS and progressive disease, but whether these factors predict cognitive status had not been known, said Dr. Cortese of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Accordingly, she said, investigators in the BENEFIT-11 trial sought to determine whether low vitamin D levels, smoking status, and EBV seropositivity detected early after the first disease manifestation in MS would affect later cognitive function.
The study is an observational study that followed 278 participants with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) in the original BENEFIT trial, which was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of interferon beta-1b for early treatment of clinically isolated syndrome. The primary goal of BENEFIT-11, said Dr. Cortese, was to assess the effects of early treatment on long-term outcomes.
“To minimize reverse causation, we used exposure status in the first 2 years after CIS to predict progression outcomes at year 11,” explained Dr. Cortese. The investigators obtained biomarkers at baseline, and at study months 6, 12, and 24. Cotinine was used as a biomarker for current or recent nicotine exposure. Serum 25(OH)D levels were used to determine vitamin D levels, and immunoglobulin G levels for EBV antigen-1 were used for EBV seropositivity.
In terms of outcome measurements, the cognitive performance measure used in the study was the Paced Auditory Serial Addition Test, a validated test of processing speed, attention, and working memory, said Dr. Cortese. This test was performed at enrollment, and at study years 1, 2, 5, and 11. At study year 11, neuroaxonal injury was measured using serum neurofilament light chain levels.
In multivariable analysis, the study design adjusted for baseline age and sex, treatment allocation at baseline, unifocal versus multifocal disease seen on baseline magnetic resonance imaging, body mass index, and whether the patient was treated with steroids during the initial CIS.
“Higher quintiles of mean vitamin D levels during the first 2 years were associated with lower odds of scoring worse on the PASAT at year 11,” said Dr. Cortese (P-trend = .028). The significant trend across the quintiles “suggests a dose-response relationship,” she said.* For vitamin D levels over the first 5 years, the P-trend was .049. Dr. Cortese explained that “scoring worse” meant scoring below the median.
Looking at the effect of early vitamin D levels another way, incremental increases of 50 nmol/L of mean 25(OH)D in study months 6-24 predicted 65% lower odds of having a PASAT score below the median at year 11 (P = .027). “Within-person increases in vitamin D during the study were also significantly associated with a better PASAT score when we used the repeated measurement in a linear mixed model,” said Dr. Cortese.
Turning to the effect of smoking on cognitive function at year 11, Dr. Cortese explained that cotinine levels obtained during the first 2 years were all used to determine smoking status. If all levels were below 10 ng/mL, the participant was designated a nonsmoker (N = 125). If any levels were above 25 ng/mL, that patient was classified as a smoker. The investigators also looked at the small number of patients (N = 9) who were very heavy smokers, with cotinine levels over 191 ng/mL.
“Smokers – compared to nonsmokers – had a significantly lower standardized PASAT score at year 11,” said Dr. Cortese (P trend = .042 in age- and sex-adjusted analysis; P-trend = .056 in full multivariable analysis). “Actually, smokers had an up to 0.6-standard deviation-lower PASAT score at year 11 when we looked at heavy smokers. ...This difference corresponds to about 5 points of the PASAT, so I would say [the score is] clinically meaningful.”
Dr. Cortese pointed out that early smoking, again, showed a dose-response relationship with later cognitive status. “It continues to be important to encourage smoking cessation for patients.”
Epstein-Barr antibodies were not associated with cognitive function at year 11, according to the analysis (P-trend = .93).
“The findings of neuroaxonal injury at year 11 using serum neurofilament light-chain measures corroborated the main findings on cognitive function at year 11,” said Dr. Cortese.
For a 50-nmol higher vitamin D level within the first 5 years, neurofilament light chain levels at year 11 were 20% lower, said Dr. Cortese. Conversely, patients who had cotinine levels higher than 25 ng/mL during the first 5 years had neurofilament light chain levels 20% higher than other participants: “So they did worse. They had more neuroaxonal loss,” said Dr. Cortese. No association was seen between neurofilament light chain levels at year 11 and early EBV status, she said.
Though just cognitive function data from BENEFIT-11 were reported by Dr. Cortese, she said that radiologic and other clinical data are also being studied and will be reported in the future.
Dr. Cortese reported that she had no conflicts of interest. Several coauthors reported financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies. The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, with clinical support from Bayer HealthCare.
SOURCE: Cortese M et al. ECTRIMS 2018, Late breaking abstracts session.
*Correction, 10/25/18: An earlier version of this article mischaracterized the relationship between vitamin D scores during the first 2 years and PASAT scores at year 11.
REPORTING FROM ECTRIMS 2018
Key clinical point: Higher early levels of vitamin D were associated with better later cognitive status in MS.
Major finding: Higher quintiles of baseline 25(OH)D were associated with higher PASAT scores (P-trend = .028).
Study details: Longitudinal observational study of 278 BENEFIT participants with CIS.
Disclosures: Dr. Cortese reported that she had no conflicts of interest. Several coauthors reported financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies. The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, with clinical support from Bayer HealthCare.
Source: Cortese M et al. ECTRIMS 2018, Late breaking abstracts session.
Low spinal cord volume linked to higher MS disability
BERLIN – Spinal cord volume deficits in patients with multiple sclerosis may contribute to clinical disability that appears out of proportion to lesion load on brain imaging, according to new research.
In a pool of 362 patients with mild to moderate MS-related disability but identical white matter lesion load identified by MRI, those with higher disability had significantly lower spinal cord volumes when compared against those with disability scores in the mild range (P less than .001).
Though brain MRI is a key tool used to track disease severity and progression in MS, some patients have relatively high disability but a low burden of white matter intracerebral lesions on MRI. Little is known about spinal cord volume in MS patients with pronounced dissociation between intracerebral lesion load and disability, Michaela Andelova, MD, said in an interview during a poster session at the annual congress of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
Dr. Andelova, of Charles University, Prague, said that she and her colleagues hypothesized that spinal cord volume would differ between patients who had varying levels of disability, despite identical white matter lesion load.
To test this, she and her colleagues looked at records of 1,245 patients with relapsing-remitting MS. They divided them into three groups by severity of clinical disability, and also by extent of cerebral T2 hyperintense lesion load. The investigators identified a group of patients (n = 53) whose total volume of T2-weighted hyperintense lesions was less than 3 mL, but whose Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores were at least 3.5; this was the low lesion load/high disability (LLHD) group.
Dr. Andelova and her colleagues then identified another group of patients (n = 71) who had a volume of T2-weighted hyperintensities that was greater than 9 mL, but whose EDSS score was less than 1.5. This was the high lesion load/low disability (HLLD) group.
The remaining patients (n = 1,121), who did not have these paradoxical associations, were analyzed separately.
For all patients, mean upper cervical cord area (MUCCA) was also measured. Using images acquired by a 3 T MRI scanner, MUCCA was calculated as the mean sum of spinal cord area in 21 slices centered at the C3/4 intervertebral disk, using an in-house, semiautomated method.
“Despite higher disability, LLHD patients demonstrated significantly higher normalized total brain volume, higher normalized volumes of thalamus and callosum, and smaller lateral ventricles than [the] HLLD group,” wrote Dr. Andelova and her collaborators.
However, the LLHD patients had MUCCA values that were significantly lower than the other groups: The nonparadoxical group’s mean MUCCA was 84.02 mm2, while the HLLD group had a mean MUCCA of 85.75 mm2. This difference was not statistically significant. By contrast, the LLHD group’s mean MUCCA was significantly smaller, at 80.40 mm2 (P = .023 versus nonparadoxical patients, and P = .007 versus HLLD patients).
Looking at the data another way, Dr. Andelova and her colleagues compared 362 evenly divided patients with moderate disability (EDSS 3.5-6.5) with matched patients who had mild MS-related disability (EDSS less than 3) and identical cerebral lesion loads. They found that MUCCA was significantly smaller in the moderate disability group (78.86 versus 84.44 mm2; P less than .001).
In addition to having identical lesions loads, the mild and moderate disability groups didn’t differ significantly in normalized total brain volume or regional brain volumes. The group with moderate disability did have slightly less white matter volume (P = .039), Dr. Andelova pointed out.
All differences found between groups retained statistical significance even after adjustment for such potential confounders as age, sex, and duration of disease, Dr. Andelova said.
“Reduced spinal cord volume may explain part of the clinical-radiological paradox in patients who have high disability despite low intracranial lesion load,” Dr. Andelova and her collaborators wrote. “In line with this finding, relatively preserved spinal cord volume may be associated with functional reserve and less physical disability in patients with low disability despite high cerebral lesion load.”
Further work looking more precisely at cerebral lesion distribution and quantitative MRI investigation of lesion distribution is in the works for Dr. Andelova and her collaborators. They are hoping to see some association between various distribution patterns and accelerated spinal atrophy.
The research was supported by the Czech government. Dr. Andelova and several of her collaborators reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Andelova M et al. Mult Scler. 2018;24(Suppl 2):211, Abstract P477.
BERLIN – Spinal cord volume deficits in patients with multiple sclerosis may contribute to clinical disability that appears out of proportion to lesion load on brain imaging, according to new research.
In a pool of 362 patients with mild to moderate MS-related disability but identical white matter lesion load identified by MRI, those with higher disability had significantly lower spinal cord volumes when compared against those with disability scores in the mild range (P less than .001).
Though brain MRI is a key tool used to track disease severity and progression in MS, some patients have relatively high disability but a low burden of white matter intracerebral lesions on MRI. Little is known about spinal cord volume in MS patients with pronounced dissociation between intracerebral lesion load and disability, Michaela Andelova, MD, said in an interview during a poster session at the annual congress of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
Dr. Andelova, of Charles University, Prague, said that she and her colleagues hypothesized that spinal cord volume would differ between patients who had varying levels of disability, despite identical white matter lesion load.
To test this, she and her colleagues looked at records of 1,245 patients with relapsing-remitting MS. They divided them into three groups by severity of clinical disability, and also by extent of cerebral T2 hyperintense lesion load. The investigators identified a group of patients (n = 53) whose total volume of T2-weighted hyperintense lesions was less than 3 mL, but whose Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores were at least 3.5; this was the low lesion load/high disability (LLHD) group.
Dr. Andelova and her colleagues then identified another group of patients (n = 71) who had a volume of T2-weighted hyperintensities that was greater than 9 mL, but whose EDSS score was less than 1.5. This was the high lesion load/low disability (HLLD) group.
The remaining patients (n = 1,121), who did not have these paradoxical associations, were analyzed separately.
For all patients, mean upper cervical cord area (MUCCA) was also measured. Using images acquired by a 3 T MRI scanner, MUCCA was calculated as the mean sum of spinal cord area in 21 slices centered at the C3/4 intervertebral disk, using an in-house, semiautomated method.
“Despite higher disability, LLHD patients demonstrated significantly higher normalized total brain volume, higher normalized volumes of thalamus and callosum, and smaller lateral ventricles than [the] HLLD group,” wrote Dr. Andelova and her collaborators.
However, the LLHD patients had MUCCA values that were significantly lower than the other groups: The nonparadoxical group’s mean MUCCA was 84.02 mm2, while the HLLD group had a mean MUCCA of 85.75 mm2. This difference was not statistically significant. By contrast, the LLHD group’s mean MUCCA was significantly smaller, at 80.40 mm2 (P = .023 versus nonparadoxical patients, and P = .007 versus HLLD patients).
Looking at the data another way, Dr. Andelova and her colleagues compared 362 evenly divided patients with moderate disability (EDSS 3.5-6.5) with matched patients who had mild MS-related disability (EDSS less than 3) and identical cerebral lesion loads. They found that MUCCA was significantly smaller in the moderate disability group (78.86 versus 84.44 mm2; P less than .001).
In addition to having identical lesions loads, the mild and moderate disability groups didn’t differ significantly in normalized total brain volume or regional brain volumes. The group with moderate disability did have slightly less white matter volume (P = .039), Dr. Andelova pointed out.
All differences found between groups retained statistical significance even after adjustment for such potential confounders as age, sex, and duration of disease, Dr. Andelova said.
“Reduced spinal cord volume may explain part of the clinical-radiological paradox in patients who have high disability despite low intracranial lesion load,” Dr. Andelova and her collaborators wrote. “In line with this finding, relatively preserved spinal cord volume may be associated with functional reserve and less physical disability in patients with low disability despite high cerebral lesion load.”
Further work looking more precisely at cerebral lesion distribution and quantitative MRI investigation of lesion distribution is in the works for Dr. Andelova and her collaborators. They are hoping to see some association between various distribution patterns and accelerated spinal atrophy.
The research was supported by the Czech government. Dr. Andelova and several of her collaborators reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Andelova M et al. Mult Scler. 2018;24(Suppl 2):211, Abstract P477.
BERLIN – Spinal cord volume deficits in patients with multiple sclerosis may contribute to clinical disability that appears out of proportion to lesion load on brain imaging, according to new research.
In a pool of 362 patients with mild to moderate MS-related disability but identical white matter lesion load identified by MRI, those with higher disability had significantly lower spinal cord volumes when compared against those with disability scores in the mild range (P less than .001).
Though brain MRI is a key tool used to track disease severity and progression in MS, some patients have relatively high disability but a low burden of white matter intracerebral lesions on MRI. Little is known about spinal cord volume in MS patients with pronounced dissociation between intracerebral lesion load and disability, Michaela Andelova, MD, said in an interview during a poster session at the annual congress of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
Dr. Andelova, of Charles University, Prague, said that she and her colleagues hypothesized that spinal cord volume would differ between patients who had varying levels of disability, despite identical white matter lesion load.
To test this, she and her colleagues looked at records of 1,245 patients with relapsing-remitting MS. They divided them into three groups by severity of clinical disability, and also by extent of cerebral T2 hyperintense lesion load. The investigators identified a group of patients (n = 53) whose total volume of T2-weighted hyperintense lesions was less than 3 mL, but whose Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores were at least 3.5; this was the low lesion load/high disability (LLHD) group.
Dr. Andelova and her colleagues then identified another group of patients (n = 71) who had a volume of T2-weighted hyperintensities that was greater than 9 mL, but whose EDSS score was less than 1.5. This was the high lesion load/low disability (HLLD) group.
The remaining patients (n = 1,121), who did not have these paradoxical associations, were analyzed separately.
For all patients, mean upper cervical cord area (MUCCA) was also measured. Using images acquired by a 3 T MRI scanner, MUCCA was calculated as the mean sum of spinal cord area in 21 slices centered at the C3/4 intervertebral disk, using an in-house, semiautomated method.
“Despite higher disability, LLHD patients demonstrated significantly higher normalized total brain volume, higher normalized volumes of thalamus and callosum, and smaller lateral ventricles than [the] HLLD group,” wrote Dr. Andelova and her collaborators.
However, the LLHD patients had MUCCA values that were significantly lower than the other groups: The nonparadoxical group’s mean MUCCA was 84.02 mm2, while the HLLD group had a mean MUCCA of 85.75 mm2. This difference was not statistically significant. By contrast, the LLHD group’s mean MUCCA was significantly smaller, at 80.40 mm2 (P = .023 versus nonparadoxical patients, and P = .007 versus HLLD patients).
Looking at the data another way, Dr. Andelova and her colleagues compared 362 evenly divided patients with moderate disability (EDSS 3.5-6.5) with matched patients who had mild MS-related disability (EDSS less than 3) and identical cerebral lesion loads. They found that MUCCA was significantly smaller in the moderate disability group (78.86 versus 84.44 mm2; P less than .001).
In addition to having identical lesions loads, the mild and moderate disability groups didn’t differ significantly in normalized total brain volume or regional brain volumes. The group with moderate disability did have slightly less white matter volume (P = .039), Dr. Andelova pointed out.
All differences found between groups retained statistical significance even after adjustment for such potential confounders as age, sex, and duration of disease, Dr. Andelova said.
“Reduced spinal cord volume may explain part of the clinical-radiological paradox in patients who have high disability despite low intracranial lesion load,” Dr. Andelova and her collaborators wrote. “In line with this finding, relatively preserved spinal cord volume may be associated with functional reserve and less physical disability in patients with low disability despite high cerebral lesion load.”
Further work looking more precisely at cerebral lesion distribution and quantitative MRI investigation of lesion distribution is in the works for Dr. Andelova and her collaborators. They are hoping to see some association between various distribution patterns and accelerated spinal atrophy.
The research was supported by the Czech government. Dr. Andelova and several of her collaborators reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Andelova M et al. Mult Scler. 2018;24(Suppl 2):211, Abstract P477.
REPORTING FROM ECTRIMS 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Moderate disability patients had lower spinal cord volumes than did those with mild disability but a similar intracerebral lesion load.
Study details: Retrospective study of 1,245 patients with relapsing-remitting MS.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by a grant from the Czech government. Several authors, including Dr. Andelova, reported multiple financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Andelova M et al. Mult Scler. 2018;24(Suppl 2):211, Abstract P477.