User login
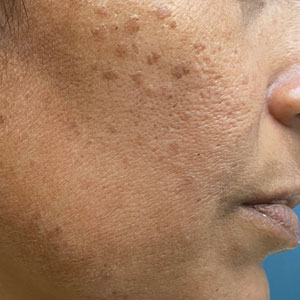
Pigmented Papules on the Face, Neck, and Chest
The Diagnosis: Syringoma
Syringomas are benign adnexal tumors with distinct histopathologic features, including the characteristic comma- or tadpole-shaped tail comprised of dilated cystic eccrine ducts. Clinically, syringomas typically present predominantly in the periorbital region in adolescent girls. They may present as solitary or multiple lesions, and sites such as the genital area, palms, scalp, and chest rarely can be involved.1 Eruptive syringoma is a clinical subtype of syringoma that is seen on the face, neck, chest, and axillae that predominantly occurs in females with skin of color in countries such as Asia and Africa before or during puberty.2,3 Lesions appear as small, flesh-colored or slightly pigmented, flat-topped papules.3 The condition can be cosmetically disfiguring and difficult to treat, especially in patients with darker skin.
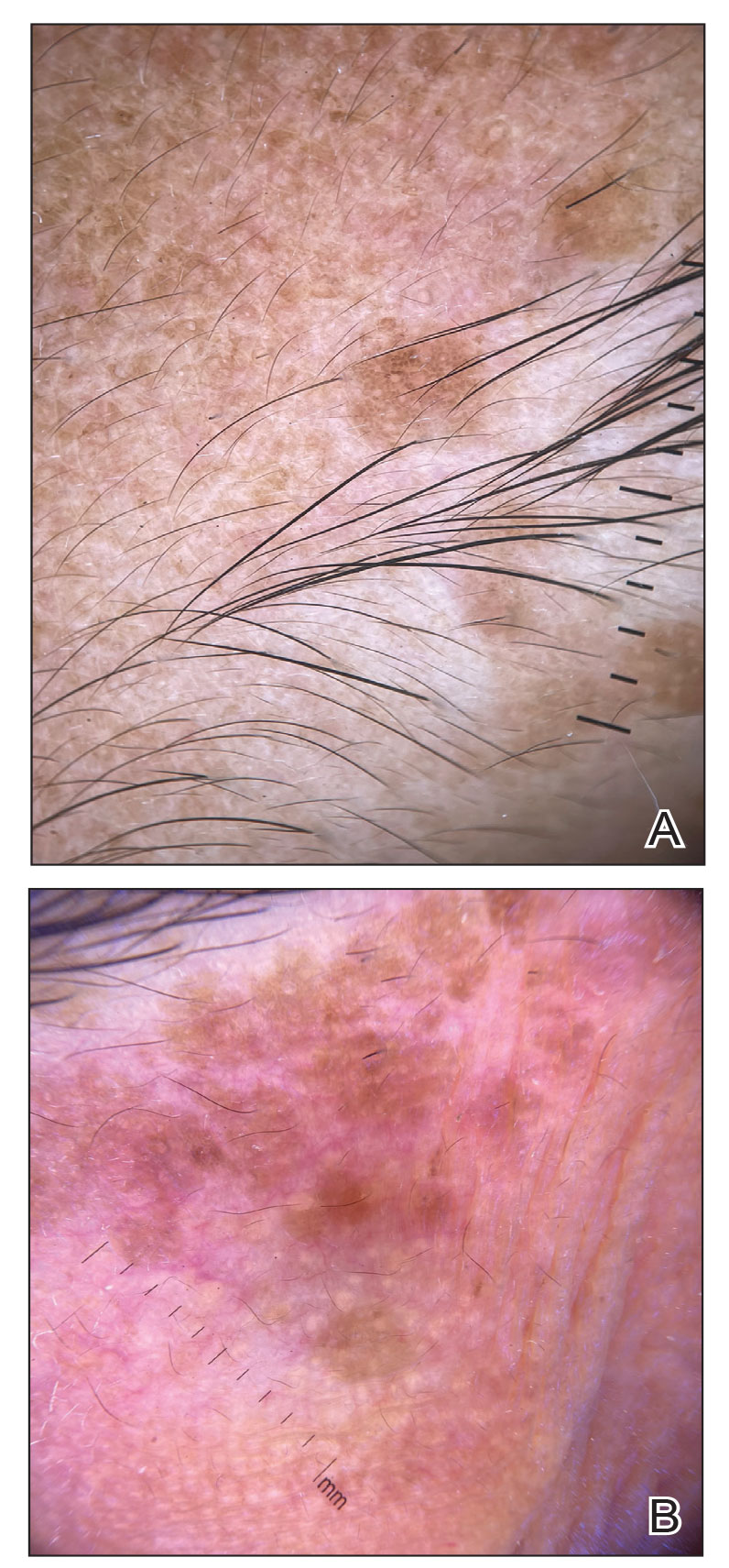
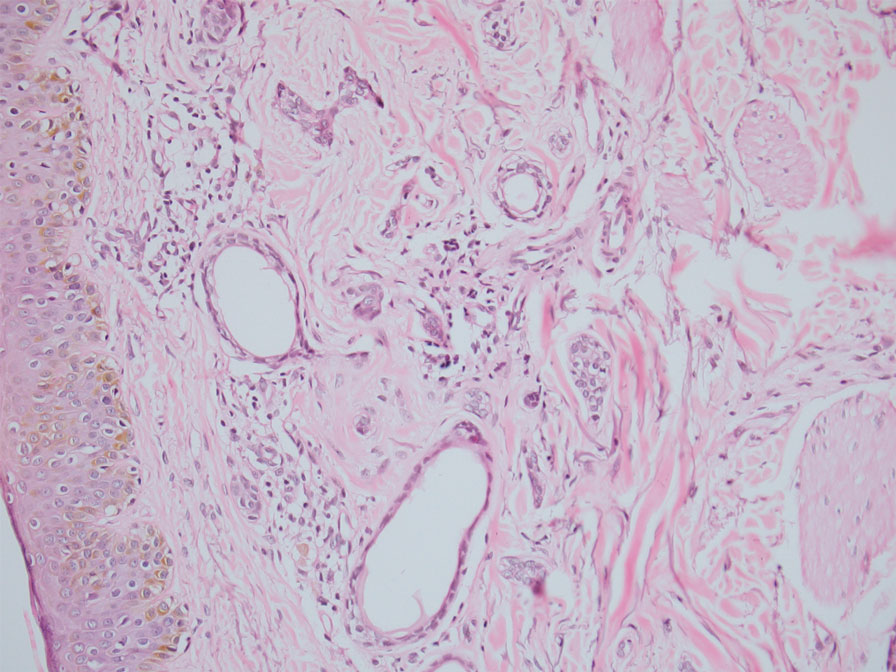
In our patient, dermoscopic evaluation revealed reticular light brown lines, structureless light brown areas, clustered brown dots, globules, and reticular vessels on a faint background (Figure 1A). Glittering yellow-whitish round structures over a fading pink-brown background also were seen at some sites (Figure 1B). Histologic examination of a neck lesion revealed an epidermis with focal acanthosis; the upper dermis had tumor islands and ducts with cells with round to vesicular nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm. A well-circumscribed tumor in the dermis composed of tubules of varying sizes lined by cuboidal cells was seen, consistent with syringoma (Figure 2).
Dermoscopic features of syringomas have not been widely studied. Hayashi et al4 reported the dermoscopic features of unilateral linear syringomas as a delicate and faint reticular pigmentation network and multiple hypopigmented areas. Sakiyama et al5 also defined an incomplete pigment network with faint erythema in 2 eruptive syringoma cases.
Treatment of this condition is for cosmetic reasons only, and there are no reports of long-term morbidity associated with the disease.6,7 Multiple therapeutic options are available but are associated with complications such as hyperpigmentation and sclerosis in patients with skin of color due to the dermal location of these syringomas. Management of syringomas includes topical and surgical methods, including topical retinoids such as tretinoin and atropine solution 1%; surgical methods include dermabrasion, excision, cryotherapy, electrocautery, electrofulguration, laser therapy, and chemical cautery. However, there is a substantial risk for recurrence with these treatment options. In a case series of 5 patients with periorbital syringomas, treatment using radiofrequency and a CO2 laser was performed with favorable outcomes, highlighting the use of combination therapies for treatment.8 Seo et al9 reported a retrospective case series of 92 patients with periorbital syringomas in which they treated one group with CO2 laser and the other with botulinum toxin A injection; CO2 laser combined with botulinum toxin A showed a greater effect than laser treatment alone. The differential diagnosis includes pigmented plane warts, sebaceous hyperplasia, eruptive xanthomas, and hidrocystomas. Pigmented plane warts characteristically present as flat-topped papules with small hemorrhagic dots or tiny pinpoint vessels on dermoscopy. In sebaceous hyperplasia, yellowish umbilicated papular lesions are seen with crown vessels on dermoscopy. Eruptive xanthomas usually are erythematous to yellow, dome-shaped papules that appear mainly over the extensor aspects of the extremities. Hidrocystoma presents as a solitary translucent larger syringomalike lesion commonly seen in the periorbital region and/or on the cheeks.
We report a case of widespread syringomas with multiple close mimickers such as pigmented plane warts; however, dermoscopy of the lesions helped to arrive at the diagnosis. Dermatologists should be aware of this condition and its benign nature to ensure correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Williams K, Shinkai K. Evaluation and management of the patient with multiple syringomas: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1234.e9-1240.e9.
- Tsunemi Y, Ihn H, Saeki H, et al. Generalized eruptive syringoma. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:492-493.
- Singh S, Tewari R, Gupta S. An unusual case of generalised eruptive syringoma in an adult male. Med J Armed Forces India. 2014;70:389-391.
- Hayashi Y, Tanaka M, Nakajima S, et al. Unilateral linear syringoma in a Japanese female: dermoscopic differentiation from lichen lanus linearis. Dermatol Rep. 2011;3:E42.
- Sakiyama M, Maeda M, Fujimoto N, et al. Eruptive syringoma localized in intertriginous areas. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2014;12:72-73.
- Wang JI, Roenigk HH Jr. Treatment of multiple facial syringomas with the carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. Dermatol Surg. 1999;25:136-139.
- Tsunemi Y, Ihn H, Saeki H, et al. Generalized eruptive syringoma. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:492-493.
- Hasson A, Farias MM, Nicklas C, et al. Periorbital syringoma treated with radiofrequency and carbon dioxide (CO2) laser in 5 patients. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:879-880.
- Seo HM, Choi JY, Min J, et al. Carbon dioxide laser combined with botulinum toxin A for patients with periorbital syringomas [published online March 31, 2016]. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2016;18:149-153.
The Diagnosis: Syringoma
Syringomas are benign adnexal tumors with distinct histopathologic features, including the characteristic comma- or tadpole-shaped tail comprised of dilated cystic eccrine ducts. Clinically, syringomas typically present predominantly in the periorbital region in adolescent girls. They may present as solitary or multiple lesions, and sites such as the genital area, palms, scalp, and chest rarely can be involved.1 Eruptive syringoma is a clinical subtype of syringoma that is seen on the face, neck, chest, and axillae that predominantly occurs in females with skin of color in countries such as Asia and Africa before or during puberty.2,3 Lesions appear as small, flesh-colored or slightly pigmented, flat-topped papules.3 The condition can be cosmetically disfiguring and difficult to treat, especially in patients with darker skin.

In our patient, dermoscopic evaluation revealed reticular light brown lines, structureless light brown areas, clustered brown dots, globules, and reticular vessels on a faint background (Figure 1A). Glittering yellow-whitish round structures over a fading pink-brown background also were seen at some sites (Figure 1B). Histologic examination of a neck lesion revealed an epidermis with focal acanthosis; the upper dermis had tumor islands and ducts with cells with round to vesicular nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm. A well-circumscribed tumor in the dermis composed of tubules of varying sizes lined by cuboidal cells was seen, consistent with syringoma (Figure 2).

Dermoscopic features of syringomas have not been widely studied. Hayashi et al4 reported the dermoscopic features of unilateral linear syringomas as a delicate and faint reticular pigmentation network and multiple hypopigmented areas. Sakiyama et al5 also defined an incomplete pigment network with faint erythema in 2 eruptive syringoma cases.
Treatment of this condition is for cosmetic reasons only, and there are no reports of long-term morbidity associated with the disease.6,7 Multiple therapeutic options are available but are associated with complications such as hyperpigmentation and sclerosis in patients with skin of color due to the dermal location of these syringomas. Management of syringomas includes topical and surgical methods, including topical retinoids such as tretinoin and atropine solution 1%; surgical methods include dermabrasion, excision, cryotherapy, electrocautery, electrofulguration, laser therapy, and chemical cautery. However, there is a substantial risk for recurrence with these treatment options. In a case series of 5 patients with periorbital syringomas, treatment using radiofrequency and a CO2 laser was performed with favorable outcomes, highlighting the use of combination therapies for treatment.8 Seo et al9 reported a retrospective case series of 92 patients with periorbital syringomas in which they treated one group with CO2 laser and the other with botulinum toxin A injection; CO2 laser combined with botulinum toxin A showed a greater effect than laser treatment alone. The differential diagnosis includes pigmented plane warts, sebaceous hyperplasia, eruptive xanthomas, and hidrocystomas. Pigmented plane warts characteristically present as flat-topped papules with small hemorrhagic dots or tiny pinpoint vessels on dermoscopy. In sebaceous hyperplasia, yellowish umbilicated papular lesions are seen with crown vessels on dermoscopy. Eruptive xanthomas usually are erythematous to yellow, dome-shaped papules that appear mainly over the extensor aspects of the extremities. Hidrocystoma presents as a solitary translucent larger syringomalike lesion commonly seen in the periorbital region and/or on the cheeks.
We report a case of widespread syringomas with multiple close mimickers such as pigmented plane warts; however, dermoscopy of the lesions helped to arrive at the diagnosis. Dermatologists should be aware of this condition and its benign nature to ensure correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The Diagnosis: Syringoma
Syringomas are benign adnexal tumors with distinct histopathologic features, including the characteristic comma- or tadpole-shaped tail comprised of dilated cystic eccrine ducts. Clinically, syringomas typically present predominantly in the periorbital region in adolescent girls. They may present as solitary or multiple lesions, and sites such as the genital area, palms, scalp, and chest rarely can be involved.1 Eruptive syringoma is a clinical subtype of syringoma that is seen on the face, neck, chest, and axillae that predominantly occurs in females with skin of color in countries such as Asia and Africa before or during puberty.2,3 Lesions appear as small, flesh-colored or slightly pigmented, flat-topped papules.3 The condition can be cosmetically disfiguring and difficult to treat, especially in patients with darker skin.

In our patient, dermoscopic evaluation revealed reticular light brown lines, structureless light brown areas, clustered brown dots, globules, and reticular vessels on a faint background (Figure 1A). Glittering yellow-whitish round structures over a fading pink-brown background also were seen at some sites (Figure 1B). Histologic examination of a neck lesion revealed an epidermis with focal acanthosis; the upper dermis had tumor islands and ducts with cells with round to vesicular nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm. A well-circumscribed tumor in the dermis composed of tubules of varying sizes lined by cuboidal cells was seen, consistent with syringoma (Figure 2).

Dermoscopic features of syringomas have not been widely studied. Hayashi et al4 reported the dermoscopic features of unilateral linear syringomas as a delicate and faint reticular pigmentation network and multiple hypopigmented areas. Sakiyama et al5 also defined an incomplete pigment network with faint erythema in 2 eruptive syringoma cases.
Treatment of this condition is for cosmetic reasons only, and there are no reports of long-term morbidity associated with the disease.6,7 Multiple therapeutic options are available but are associated with complications such as hyperpigmentation and sclerosis in patients with skin of color due to the dermal location of these syringomas. Management of syringomas includes topical and surgical methods, including topical retinoids such as tretinoin and atropine solution 1%; surgical methods include dermabrasion, excision, cryotherapy, electrocautery, electrofulguration, laser therapy, and chemical cautery. However, there is a substantial risk for recurrence with these treatment options. In a case series of 5 patients with periorbital syringomas, treatment using radiofrequency and a CO2 laser was performed with favorable outcomes, highlighting the use of combination therapies for treatment.8 Seo et al9 reported a retrospective case series of 92 patients with periorbital syringomas in which they treated one group with CO2 laser and the other with botulinum toxin A injection; CO2 laser combined with botulinum toxin A showed a greater effect than laser treatment alone. The differential diagnosis includes pigmented plane warts, sebaceous hyperplasia, eruptive xanthomas, and hidrocystomas. Pigmented plane warts characteristically present as flat-topped papules with small hemorrhagic dots or tiny pinpoint vessels on dermoscopy. In sebaceous hyperplasia, yellowish umbilicated papular lesions are seen with crown vessels on dermoscopy. Eruptive xanthomas usually are erythematous to yellow, dome-shaped papules that appear mainly over the extensor aspects of the extremities. Hidrocystoma presents as a solitary translucent larger syringomalike lesion commonly seen in the periorbital region and/or on the cheeks.
We report a case of widespread syringomas with multiple close mimickers such as pigmented plane warts; however, dermoscopy of the lesions helped to arrive at the diagnosis. Dermatologists should be aware of this condition and its benign nature to ensure correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Williams K, Shinkai K. Evaluation and management of the patient with multiple syringomas: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1234.e9-1240.e9.
- Tsunemi Y, Ihn H, Saeki H, et al. Generalized eruptive syringoma. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:492-493.
- Singh S, Tewari R, Gupta S. An unusual case of generalised eruptive syringoma in an adult male. Med J Armed Forces India. 2014;70:389-391.
- Hayashi Y, Tanaka M, Nakajima S, et al. Unilateral linear syringoma in a Japanese female: dermoscopic differentiation from lichen lanus linearis. Dermatol Rep. 2011;3:E42.
- Sakiyama M, Maeda M, Fujimoto N, et al. Eruptive syringoma localized in intertriginous areas. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2014;12:72-73.
- Wang JI, Roenigk HH Jr. Treatment of multiple facial syringomas with the carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. Dermatol Surg. 1999;25:136-139.
- Tsunemi Y, Ihn H, Saeki H, et al. Generalized eruptive syringoma. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:492-493.
- Hasson A, Farias MM, Nicklas C, et al. Periorbital syringoma treated with radiofrequency and carbon dioxide (CO2) laser in 5 patients. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:879-880.
- Seo HM, Choi JY, Min J, et al. Carbon dioxide laser combined with botulinum toxin A for patients with periorbital syringomas [published online March 31, 2016]. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2016;18:149-153.
- Williams K, Shinkai K. Evaluation and management of the patient with multiple syringomas: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1234.e9-1240.e9.
- Tsunemi Y, Ihn H, Saeki H, et al. Generalized eruptive syringoma. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:492-493.
- Singh S, Tewari R, Gupta S. An unusual case of generalised eruptive syringoma in an adult male. Med J Armed Forces India. 2014;70:389-391.
- Hayashi Y, Tanaka M, Nakajima S, et al. Unilateral linear syringoma in a Japanese female: dermoscopic differentiation from lichen lanus linearis. Dermatol Rep. 2011;3:E42.
- Sakiyama M, Maeda M, Fujimoto N, et al. Eruptive syringoma localized in intertriginous areas. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2014;12:72-73.
- Wang JI, Roenigk HH Jr. Treatment of multiple facial syringomas with the carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. Dermatol Surg. 1999;25:136-139.
- Tsunemi Y, Ihn H, Saeki H, et al. Generalized eruptive syringoma. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:492-493.
- Hasson A, Farias MM, Nicklas C, et al. Periorbital syringoma treated with radiofrequency and carbon dioxide (CO2) laser in 5 patients. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:879-880.
- Seo HM, Choi JY, Min J, et al. Carbon dioxide laser combined with botulinum toxin A for patients with periorbital syringomas [published online March 31, 2016]. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2016;18:149-153.
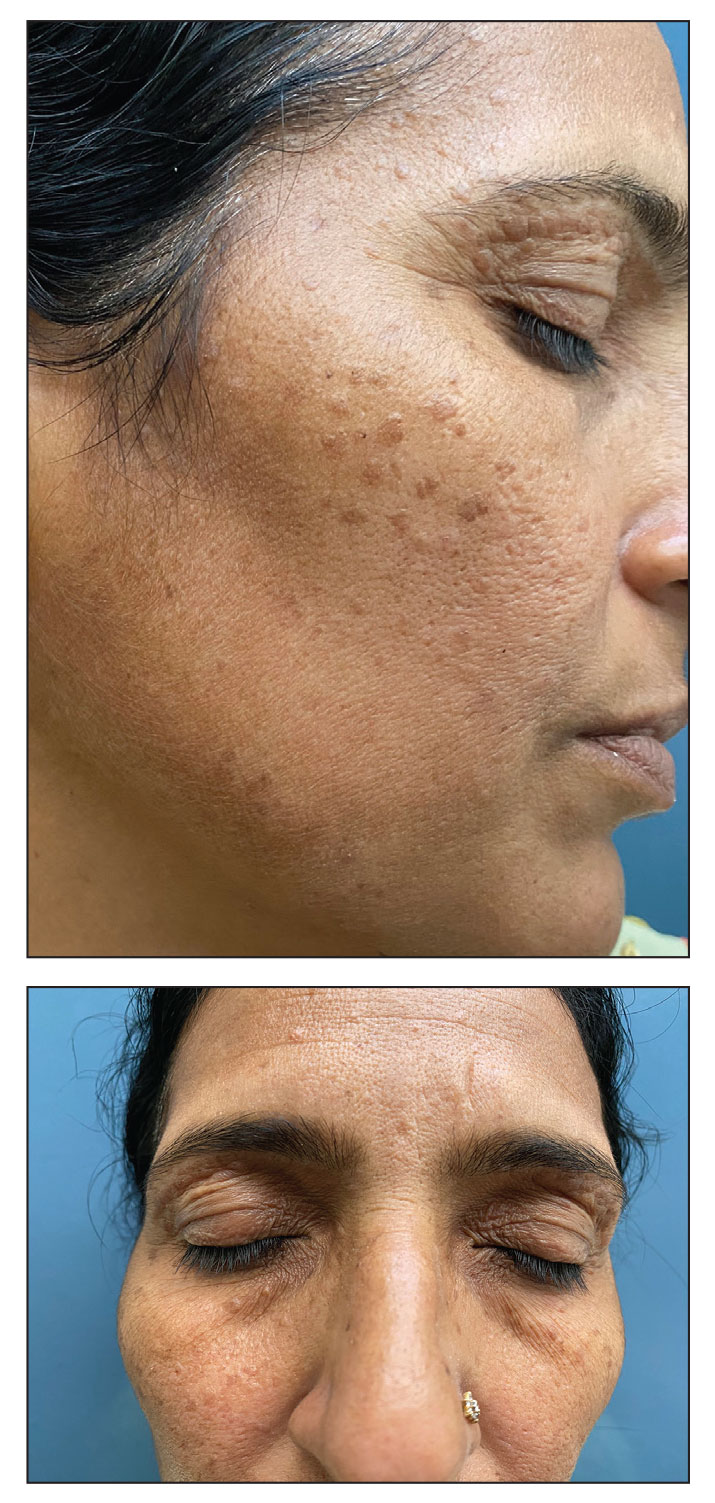
A 46-year-old woman presented with multiple asymptomatic, flesh-colored, hyperpigmented papules on the face of 5 to 6 months’ duration that were progressively increasing in number. The lesions first appeared near the eyebrows and cheeks (top) and subsequently spread to involve the neck. She had no notable medical history. Cutaneous examination revealed multiple tan to brown papules over the periorbital, malar, and neck regions ranging in size from 1 to 5 mm. The lesions over the periorbital region were arranged in a linear pattern (bottom). Similar lesions also were present on the chest and arms. No other sites were involved, and systemic examination was normal.
FDA approves topical ruxolitinib for nonsegmental vitiligo
The on July 18. The treatment, which was approved for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in September 2021, is a cream formulation of ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase 1 (JAK1)/JAK2 inhibitor.
Previously, no treatment was approved to repigment patients with vitiligo, says David Rosmarin, MD, vice chair for research and education in the department of dermatology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston. “It’s important to have options that we can give to patients that are both safe and effective to get them the desired results,” Dr. Rosmarin, the lead investigator of the phase 3 clinical trials of topical ruxolitinib, said in an interview. Vitiligo is “a disease that can really affect quality of life. Some people [with vitiligo] feel as if they’re being stared at or they’re being bullied; they don’t feel confident. It can affect relationships and intimacy.”
Approval was based on the results of two phase 3 trials (TruE-V1 and TruE-V2) in 674 patients with nonsegmental vitiligo aged 12 years or older. At 24 weeks, about 30% of the patients on treatment, applied twice a day, achieved at least a 75% improvement in the facial Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI75), compared with about 8% and 13% among those in the vehicle groups in the two trials.
At 52 weeks, about 50% of the patients treated with topical ruxolitinib achieved F-VASI75.
Also, using self-reporting as measured by the Vitiligo Noticeability Scale, about 30%-40% of patients described their vitiligo as being “a lot less noticeable” or “no longer noticeable” at week 52. Dr. Rosmarin reported the 52-week results at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The trial group used 1.5% ruxolitinib cream twice daily for the full year. The vehicle group began using ruxolitinib halfway through the trial. In this group, 26.8% and 29.6% achieved F-VASI 75 at 52 weeks in the two trials.
For treating vitiligo, patients are advised to apply a thin layer of topical ruxolitinib to affected areas twice a day, “up to 10% body surface area,” according to the prescribing information, which adds: “Satisfactory patient response may require treatment … for more than 24 weeks. If the patient does not find the repigmentation meaningful by 24 weeks, the patient should be reevaluated by the health care provider.”
The most common side effects during the vehicle-controlled part of the trials were development of acne and pruritus at the application site, headache, urinary tract infections, erythema at the application site, and pyrexia, according to the company.
The approved label for topical ruxolitinib includes a boxed warning about serious infections, mortality, cancer, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis – which, the warning notes, is based on reports in patients treated with oral JAK inhibitors for inflammatory conditions.
Dr. Rosmarin believes that using this drug with other therapies, like light treatment, might yield even better responses. The available data are in patients treated with ruxolitinib as monotherapy, without complementary therapies.
William Damsky, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and dermatopathology at Yale University, New Haven, who was not involved in the trials, said what is most exciting about this drug is its novelty. Although some topical steroids are used off-label to treat vitiligo, their efficacy is far from what’s been observed in these trials of topical ruxolitinib, he told this news organization. “It’s huge for a number of reasons. … One very big reason is it just provides some hope” for the many patients with vitiligo who, over the years, have been told “that there’s nothing that could be done for their disease, and this really changes that.”
Dr. Rosmarin reports financial relationships with over 20 pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Damsky disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The on July 18. The treatment, which was approved for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in September 2021, is a cream formulation of ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase 1 (JAK1)/JAK2 inhibitor.
Previously, no treatment was approved to repigment patients with vitiligo, says David Rosmarin, MD, vice chair for research and education in the department of dermatology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston. “It’s important to have options that we can give to patients that are both safe and effective to get them the desired results,” Dr. Rosmarin, the lead investigator of the phase 3 clinical trials of topical ruxolitinib, said in an interview. Vitiligo is “a disease that can really affect quality of life. Some people [with vitiligo] feel as if they’re being stared at or they’re being bullied; they don’t feel confident. It can affect relationships and intimacy.”
Approval was based on the results of two phase 3 trials (TruE-V1 and TruE-V2) in 674 patients with nonsegmental vitiligo aged 12 years or older. At 24 weeks, about 30% of the patients on treatment, applied twice a day, achieved at least a 75% improvement in the facial Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI75), compared with about 8% and 13% among those in the vehicle groups in the two trials.
At 52 weeks, about 50% of the patients treated with topical ruxolitinib achieved F-VASI75.
Also, using self-reporting as measured by the Vitiligo Noticeability Scale, about 30%-40% of patients described their vitiligo as being “a lot less noticeable” or “no longer noticeable” at week 52. Dr. Rosmarin reported the 52-week results at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The trial group used 1.5% ruxolitinib cream twice daily for the full year. The vehicle group began using ruxolitinib halfway through the trial. In this group, 26.8% and 29.6% achieved F-VASI 75 at 52 weeks in the two trials.
For treating vitiligo, patients are advised to apply a thin layer of topical ruxolitinib to affected areas twice a day, “up to 10% body surface area,” according to the prescribing information, which adds: “Satisfactory patient response may require treatment … for more than 24 weeks. If the patient does not find the repigmentation meaningful by 24 weeks, the patient should be reevaluated by the health care provider.”
The most common side effects during the vehicle-controlled part of the trials were development of acne and pruritus at the application site, headache, urinary tract infections, erythema at the application site, and pyrexia, according to the company.
The approved label for topical ruxolitinib includes a boxed warning about serious infections, mortality, cancer, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis – which, the warning notes, is based on reports in patients treated with oral JAK inhibitors for inflammatory conditions.
Dr. Rosmarin believes that using this drug with other therapies, like light treatment, might yield even better responses. The available data are in patients treated with ruxolitinib as monotherapy, without complementary therapies.
William Damsky, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and dermatopathology at Yale University, New Haven, who was not involved in the trials, said what is most exciting about this drug is its novelty. Although some topical steroids are used off-label to treat vitiligo, their efficacy is far from what’s been observed in these trials of topical ruxolitinib, he told this news organization. “It’s huge for a number of reasons. … One very big reason is it just provides some hope” for the many patients with vitiligo who, over the years, have been told “that there’s nothing that could be done for their disease, and this really changes that.”
Dr. Rosmarin reports financial relationships with over 20 pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Damsky disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The on July 18. The treatment, which was approved for treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in September 2021, is a cream formulation of ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase 1 (JAK1)/JAK2 inhibitor.
Previously, no treatment was approved to repigment patients with vitiligo, says David Rosmarin, MD, vice chair for research and education in the department of dermatology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston. “It’s important to have options that we can give to patients that are both safe and effective to get them the desired results,” Dr. Rosmarin, the lead investigator of the phase 3 clinical trials of topical ruxolitinib, said in an interview. Vitiligo is “a disease that can really affect quality of life. Some people [with vitiligo] feel as if they’re being stared at or they’re being bullied; they don’t feel confident. It can affect relationships and intimacy.”
Approval was based on the results of two phase 3 trials (TruE-V1 and TruE-V2) in 674 patients with nonsegmental vitiligo aged 12 years or older. At 24 weeks, about 30% of the patients on treatment, applied twice a day, achieved at least a 75% improvement in the facial Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI75), compared with about 8% and 13% among those in the vehicle groups in the two trials.
At 52 weeks, about 50% of the patients treated with topical ruxolitinib achieved F-VASI75.
Also, using self-reporting as measured by the Vitiligo Noticeability Scale, about 30%-40% of patients described their vitiligo as being “a lot less noticeable” or “no longer noticeable” at week 52. Dr. Rosmarin reported the 52-week results at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The trial group used 1.5% ruxolitinib cream twice daily for the full year. The vehicle group began using ruxolitinib halfway through the trial. In this group, 26.8% and 29.6% achieved F-VASI 75 at 52 weeks in the two trials.
For treating vitiligo, patients are advised to apply a thin layer of topical ruxolitinib to affected areas twice a day, “up to 10% body surface area,” according to the prescribing information, which adds: “Satisfactory patient response may require treatment … for more than 24 weeks. If the patient does not find the repigmentation meaningful by 24 weeks, the patient should be reevaluated by the health care provider.”
The most common side effects during the vehicle-controlled part of the trials were development of acne and pruritus at the application site, headache, urinary tract infections, erythema at the application site, and pyrexia, according to the company.
The approved label for topical ruxolitinib includes a boxed warning about serious infections, mortality, cancer, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis – which, the warning notes, is based on reports in patients treated with oral JAK inhibitors for inflammatory conditions.
Dr. Rosmarin believes that using this drug with other therapies, like light treatment, might yield even better responses. The available data are in patients treated with ruxolitinib as monotherapy, without complementary therapies.
William Damsky, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and dermatopathology at Yale University, New Haven, who was not involved in the trials, said what is most exciting about this drug is its novelty. Although some topical steroids are used off-label to treat vitiligo, their efficacy is far from what’s been observed in these trials of topical ruxolitinib, he told this news organization. “It’s huge for a number of reasons. … One very big reason is it just provides some hope” for the many patients with vitiligo who, over the years, have been told “that there’s nothing that could be done for their disease, and this really changes that.”
Dr. Rosmarin reports financial relationships with over 20 pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Damsky disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ruxolitinib found to benefit adolescents with vitiligo up to one year
INDIANAPOLIS – and a higher proportion responded at week 52, results from a pooled analysis of phase 3 data showed.
Currently, there is no treatment approved by the Food and Drug Administration to repigment patients with vitiligo, but the cream formulation of the Janus kinase inhibitor ruxolitinib was shown to be effective and have a favorable safety profile in patients aged 12 years and up in the phase 3 clinical trials, TRuE-V1 and TruE-V2. “We know that about half of patients will develop vitiligo by the age of 20, so there is a significant need to have treatments available for the pediatric population,” lead study author David Rosmarin, MD, told this news organization in advance of the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In September 2021, topical ruxolitinib (Opzelura) was approved by the FDA for treating atopic dermatitis in nonimmunocompromised patients aged 12 years and older. The manufacturer, Incyte, has submitted an application for approval to the agency for treating vitiligo in patients ages 12 years and older based on 24-week results; the FDA is expected to make a decision by July 18.
For the current study, presented during a poster session at the meeting, Dr. Rosmarin, of the department of dermatology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, and colleagues pooled efficacy and safety data for adolescent patients aged 12-17 years from the TRuE-V studies, which enrolled patients 12 years of age and older diagnosed with nonsegmental vitiligo with depigmentation covering up to 10% of total body surface area (BSA), including facial and total Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI/T-VASI) scores of ≥ 0.5/≥ 3. Investigators randomized patients 2:1 to twice-daily 1.5% ruxolitinib cream or vehicle for 24 weeks, after which all patients could apply 1.5% ruxolitinib cream through week 52. Efficacy endpoints included the proportions of patients who achieved at least 75%, 50%, and 90% improvement from baseline in F-VASI scores (F-VASI75, F-VASI50, F-VASI90); the proportion of patients who achieved at least a 50% improvement from baseline in T-VASI (T-VASI50); the proportion of patients who achieved a Vitiligo Noticeability Scale (VNS) rating of 4 or 5; and percentage change from baseline in facial BSA (F-BSA). Safety and tolerability were also assessed.
For the pooled analysis, Dr. Rosmarin and colleagues reported results on 72 adolescents: 55 who received ruxolitinib cream and 17 who received vehicle. At week 24, 32.1% of adolescents treated with ruxolitinib cream achieved F-VASI75, compared with none of those in the vehicle group. Further, response rates at week 52 for patients who applied ruxolitinib cream from day 1 were as follows: F-VASI75, 48.0%; F-VASI50, 70.0%; F-VASI90, 24.0%; T-VASI50, 60.0%; VNS score of 4/5, 56.0%; and F-BSA mean percentage change from baseline, –41.9%.
Efficacy at week 52 among crossover patients (after 28 weeks of ruxolitinib cream) was consistent with week 24 data in patients who applied ruxolitinib cream from day 1.
“As we know that repigmentation takes time, about half of the patients achieved the F-VASI75 at the 52-week endpoint,” said Dr. Rosmarin, who is also vice-chair for research and education at Tufts Medical Center, Boston. “Particularly remarkable is that 60% of adolescents achieved a T-VASI50 [50% or more repigmentation of the whole body at the year mark] and over half the patients described their vitiligo as a lot less noticeable or no longer noticeable at the year mark.”
In terms of safety, treatment-related adverse events occurred in 12.9% of patients treated with ruxolitinib (no information was available on the specific events). Serious adverse events occurred in 1.4% of patients; none were considered related to treatment.
“Overall, these results are quite impressive,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “While it can be very challenging to repigment patients with vitiligo, ruxolitinib cream provides an effective option which can help many of my patients.” He acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including the fact that the TRuE-V studies were conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, “which may have contributed to patients being lost to follow-up. Also, the majority of the patients had skin phototypes 1-3.”
Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that patients with vitiligo need treatment options that are well-studied and covered by insurance. “This study is a great step forward in developing medications for this underserved patient population,” said Dr. Coughlin, who directs the section of pediatric dermatology at Washington University/St. Louis Children’s Hospital.
However, she continued, “the authors mention approximately 13% of patients had a treatment-related adverse reaction, but the abstract does not delineate these reactions.” In addition, the study was limited to children who had less than or equal to 10% body surface area involvement of vitiligo, she noted, adding that “more work is needed to learn about safety of application to larger surface areas.”
Going forward, “it will be important to learn the durability of response,” said Dr. Coughlin, who is also assistant professor of dermatology at Washington University in St. Louis. “Does the vitiligo return if patients stop applying the ruxolitinib cream?”
Dr. Rosmarin disclosed that he has received honoraria as a consultant for Incyte, AbbVie, Abcuro, AltruBio, Arena, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Celgene, Concert, CSL Behring, Dermavant, Dermira, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Revolo Biotherapeutics, Sanofi, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and VielaBio. He has also received research support from Incyte, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Dermira, Galderma, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Regeneron; and has served as a paid speaker for Incyte, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Incyte, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Coughlin is on the board of the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance and the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative.
INDIANAPOLIS – and a higher proportion responded at week 52, results from a pooled analysis of phase 3 data showed.
Currently, there is no treatment approved by the Food and Drug Administration to repigment patients with vitiligo, but the cream formulation of the Janus kinase inhibitor ruxolitinib was shown to be effective and have a favorable safety profile in patients aged 12 years and up in the phase 3 clinical trials, TRuE-V1 and TruE-V2. “We know that about half of patients will develop vitiligo by the age of 20, so there is a significant need to have treatments available for the pediatric population,” lead study author David Rosmarin, MD, told this news organization in advance of the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In September 2021, topical ruxolitinib (Opzelura) was approved by the FDA for treating atopic dermatitis in nonimmunocompromised patients aged 12 years and older. The manufacturer, Incyte, has submitted an application for approval to the agency for treating vitiligo in patients ages 12 years and older based on 24-week results; the FDA is expected to make a decision by July 18.
For the current study, presented during a poster session at the meeting, Dr. Rosmarin, of the department of dermatology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, and colleagues pooled efficacy and safety data for adolescent patients aged 12-17 years from the TRuE-V studies, which enrolled patients 12 years of age and older diagnosed with nonsegmental vitiligo with depigmentation covering up to 10% of total body surface area (BSA), including facial and total Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI/T-VASI) scores of ≥ 0.5/≥ 3. Investigators randomized patients 2:1 to twice-daily 1.5% ruxolitinib cream or vehicle for 24 weeks, after which all patients could apply 1.5% ruxolitinib cream through week 52. Efficacy endpoints included the proportions of patients who achieved at least 75%, 50%, and 90% improvement from baseline in F-VASI scores (F-VASI75, F-VASI50, F-VASI90); the proportion of patients who achieved at least a 50% improvement from baseline in T-VASI (T-VASI50); the proportion of patients who achieved a Vitiligo Noticeability Scale (VNS) rating of 4 or 5; and percentage change from baseline in facial BSA (F-BSA). Safety and tolerability were also assessed.
For the pooled analysis, Dr. Rosmarin and colleagues reported results on 72 adolescents: 55 who received ruxolitinib cream and 17 who received vehicle. At week 24, 32.1% of adolescents treated with ruxolitinib cream achieved F-VASI75, compared with none of those in the vehicle group. Further, response rates at week 52 for patients who applied ruxolitinib cream from day 1 were as follows: F-VASI75, 48.0%; F-VASI50, 70.0%; F-VASI90, 24.0%; T-VASI50, 60.0%; VNS score of 4/5, 56.0%; and F-BSA mean percentage change from baseline, –41.9%.
Efficacy at week 52 among crossover patients (after 28 weeks of ruxolitinib cream) was consistent with week 24 data in patients who applied ruxolitinib cream from day 1.
“As we know that repigmentation takes time, about half of the patients achieved the F-VASI75 at the 52-week endpoint,” said Dr. Rosmarin, who is also vice-chair for research and education at Tufts Medical Center, Boston. “Particularly remarkable is that 60% of adolescents achieved a T-VASI50 [50% or more repigmentation of the whole body at the year mark] and over half the patients described their vitiligo as a lot less noticeable or no longer noticeable at the year mark.”
In terms of safety, treatment-related adverse events occurred in 12.9% of patients treated with ruxolitinib (no information was available on the specific events). Serious adverse events occurred in 1.4% of patients; none were considered related to treatment.
“Overall, these results are quite impressive,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “While it can be very challenging to repigment patients with vitiligo, ruxolitinib cream provides an effective option which can help many of my patients.” He acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including the fact that the TRuE-V studies were conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, “which may have contributed to patients being lost to follow-up. Also, the majority of the patients had skin phototypes 1-3.”
Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that patients with vitiligo need treatment options that are well-studied and covered by insurance. “This study is a great step forward in developing medications for this underserved patient population,” said Dr. Coughlin, who directs the section of pediatric dermatology at Washington University/St. Louis Children’s Hospital.
However, she continued, “the authors mention approximately 13% of patients had a treatment-related adverse reaction, but the abstract does not delineate these reactions.” In addition, the study was limited to children who had less than or equal to 10% body surface area involvement of vitiligo, she noted, adding that “more work is needed to learn about safety of application to larger surface areas.”
Going forward, “it will be important to learn the durability of response,” said Dr. Coughlin, who is also assistant professor of dermatology at Washington University in St. Louis. “Does the vitiligo return if patients stop applying the ruxolitinib cream?”
Dr. Rosmarin disclosed that he has received honoraria as a consultant for Incyte, AbbVie, Abcuro, AltruBio, Arena, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Celgene, Concert, CSL Behring, Dermavant, Dermira, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Revolo Biotherapeutics, Sanofi, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and VielaBio. He has also received research support from Incyte, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Dermira, Galderma, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Regeneron; and has served as a paid speaker for Incyte, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Incyte, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Coughlin is on the board of the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance and the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative.
INDIANAPOLIS – and a higher proportion responded at week 52, results from a pooled analysis of phase 3 data showed.
Currently, there is no treatment approved by the Food and Drug Administration to repigment patients with vitiligo, but the cream formulation of the Janus kinase inhibitor ruxolitinib was shown to be effective and have a favorable safety profile in patients aged 12 years and up in the phase 3 clinical trials, TRuE-V1 and TruE-V2. “We know that about half of patients will develop vitiligo by the age of 20, so there is a significant need to have treatments available for the pediatric population,” lead study author David Rosmarin, MD, told this news organization in advance of the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In September 2021, topical ruxolitinib (Opzelura) was approved by the FDA for treating atopic dermatitis in nonimmunocompromised patients aged 12 years and older. The manufacturer, Incyte, has submitted an application for approval to the agency for treating vitiligo in patients ages 12 years and older based on 24-week results; the FDA is expected to make a decision by July 18.
For the current study, presented during a poster session at the meeting, Dr. Rosmarin, of the department of dermatology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, and colleagues pooled efficacy and safety data for adolescent patients aged 12-17 years from the TRuE-V studies, which enrolled patients 12 years of age and older diagnosed with nonsegmental vitiligo with depigmentation covering up to 10% of total body surface area (BSA), including facial and total Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI/T-VASI) scores of ≥ 0.5/≥ 3. Investigators randomized patients 2:1 to twice-daily 1.5% ruxolitinib cream or vehicle for 24 weeks, after which all patients could apply 1.5% ruxolitinib cream through week 52. Efficacy endpoints included the proportions of patients who achieved at least 75%, 50%, and 90% improvement from baseline in F-VASI scores (F-VASI75, F-VASI50, F-VASI90); the proportion of patients who achieved at least a 50% improvement from baseline in T-VASI (T-VASI50); the proportion of patients who achieved a Vitiligo Noticeability Scale (VNS) rating of 4 or 5; and percentage change from baseline in facial BSA (F-BSA). Safety and tolerability were also assessed.
For the pooled analysis, Dr. Rosmarin and colleagues reported results on 72 adolescents: 55 who received ruxolitinib cream and 17 who received vehicle. At week 24, 32.1% of adolescents treated with ruxolitinib cream achieved F-VASI75, compared with none of those in the vehicle group. Further, response rates at week 52 for patients who applied ruxolitinib cream from day 1 were as follows: F-VASI75, 48.0%; F-VASI50, 70.0%; F-VASI90, 24.0%; T-VASI50, 60.0%; VNS score of 4/5, 56.0%; and F-BSA mean percentage change from baseline, –41.9%.
Efficacy at week 52 among crossover patients (after 28 weeks of ruxolitinib cream) was consistent with week 24 data in patients who applied ruxolitinib cream from day 1.
“As we know that repigmentation takes time, about half of the patients achieved the F-VASI75 at the 52-week endpoint,” said Dr. Rosmarin, who is also vice-chair for research and education at Tufts Medical Center, Boston. “Particularly remarkable is that 60% of adolescents achieved a T-VASI50 [50% or more repigmentation of the whole body at the year mark] and over half the patients described their vitiligo as a lot less noticeable or no longer noticeable at the year mark.”
In terms of safety, treatment-related adverse events occurred in 12.9% of patients treated with ruxolitinib (no information was available on the specific events). Serious adverse events occurred in 1.4% of patients; none were considered related to treatment.
“Overall, these results are quite impressive,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “While it can be very challenging to repigment patients with vitiligo, ruxolitinib cream provides an effective option which can help many of my patients.” He acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including the fact that the TRuE-V studies were conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, “which may have contributed to patients being lost to follow-up. Also, the majority of the patients had skin phototypes 1-3.”
Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that patients with vitiligo need treatment options that are well-studied and covered by insurance. “This study is a great step forward in developing medications for this underserved patient population,” said Dr. Coughlin, who directs the section of pediatric dermatology at Washington University/St. Louis Children’s Hospital.
However, she continued, “the authors mention approximately 13% of patients had a treatment-related adverse reaction, but the abstract does not delineate these reactions.” In addition, the study was limited to children who had less than or equal to 10% body surface area involvement of vitiligo, she noted, adding that “more work is needed to learn about safety of application to larger surface areas.”
Going forward, “it will be important to learn the durability of response,” said Dr. Coughlin, who is also assistant professor of dermatology at Washington University in St. Louis. “Does the vitiligo return if patients stop applying the ruxolitinib cream?”
Dr. Rosmarin disclosed that he has received honoraria as a consultant for Incyte, AbbVie, Abcuro, AltruBio, Arena, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Celgene, Concert, CSL Behring, Dermavant, Dermira, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Revolo Biotherapeutics, Sanofi, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and VielaBio. He has also received research support from Incyte, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Dermira, Galderma, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Regeneron; and has served as a paid speaker for Incyte, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Incyte, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Coughlin is on the board of the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance and the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative.
AT SPD 2022
Assessing Treatment Delays for Vitiligo Patients: A Retrospective Chart Review
Similar to other dermatologic conditions, barriers to early care in patients with vitiligo can exacerbate health disparities.1 Delayed treatment of vitiligo is known to hamper successful disease stabilization and repigmentation, as therapies tend to work more effectively in early stages of the disease.2
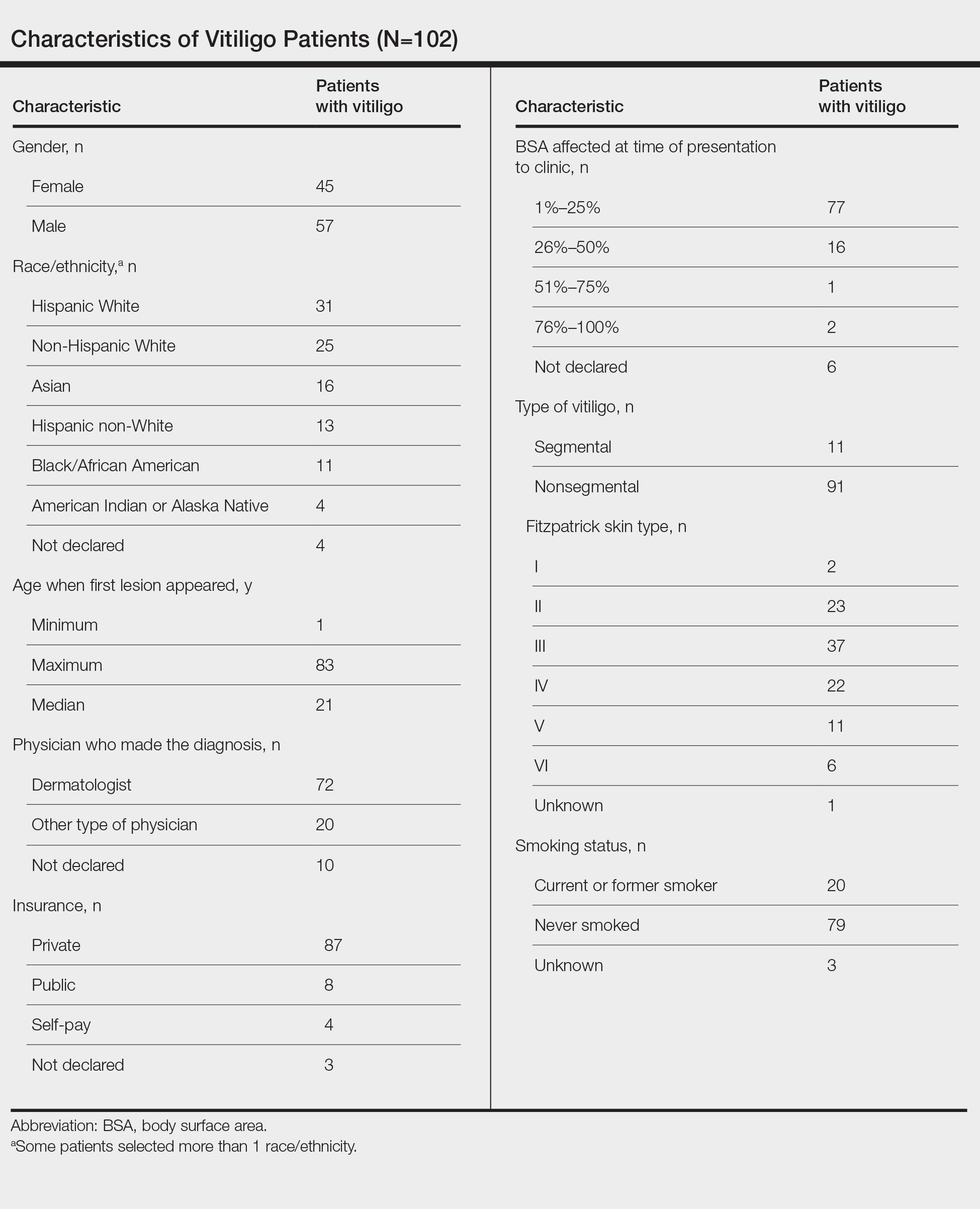
To investigate the factors associated with treatment delays for patients with vitiligo, we conducted a retrospective chart review of 102 consecutive patients with vitiligo attending an academic outpatient clinic in Austin, Texas, over 36 months.
Methods
Our sample included 102 consecutive patients with vitiligo who attended an academic outpatient clinic in Austin, Texas, from January 2017 to January 2020. Demographic information, clinical characteristics of vitiligo, and treatment data were self-reported via a standardized questionnaire given to all patients with vitiligo and gathered from medical chart review. Patient characteristics are outlined in the Table. The delay to treatment was the time (in months) from the date the patient first noticed the lesion to the start date of first treatment. This retrospective chart review was reviewed by the University of Texas at Austin institutional review board and was determined to be exempt.
Statistical Analysis—The data were analyzed descriptively with a Wilcoxon rank sum test (type I error rate of .05).
Results
Of the 102 charts that were analyzed, 45 were females and 57 were males. More than half of the patients (54.9% [56/102]) were White. Sixteen were Asian, 13 were Hispanic non-White, 11 were Black/African American, and 4 were American Indian/Alaska Native. The median age of disease onset was 21 years, minimum age was 1 year, and maximum age was 83 years. The diagnosis of vitiligo was made by a dermatologist for 72 patients and by a physician of another specialty for 20 patients. Ten patients did not declare the specialty of the diagnosing physician.
Individuals older than 21 years when their disease started had a shorter delay to treatment than individuals who noticed their first lesion at an age younger than 21 years (median, 75 months vs 13 months; P<.01). Individuals diagnosed by a dermatologist had a shorter delay to treatment than individuals diagnosed by a physician of another specialty (median, 13 months vs 58 months; P<.05). White individuals had a shorter delay to treatment than individuals with skin of color (median, 13 months vs 31 months; P=.08), though this trend did not reach statistical significance. Individuals with 1% to 25% of body surface area (BSA) affected at time of presentation to clinic also had a shorter delay to treatment than those with a greater BSA affected (median, 13 months vs 74 months; P<.06), though this trend did not reach statistical significance. Type of vitiligo (P<.8), Fitzpatrick skin type (P<.6), and smoking status (P<.7) were not associated with differential delays.
Comment
Impact of Age on Vitiligo Treatment—Our data suggest that individuals who develop vitiligo at a younger age experience longer treatment delays compared to older individuals. Reasons for this are uncertain but could include access issues, medical decision-making agency, and younger patients not remembering being treated during their youth. Our data also could be influenced by some of the adult patients in our study first noticing their lesions many years ago when treatments for vitiligo were more limited. Nevertheless, detrimental effects on quality of life in children and adolescents with vitiligo suggest that motivating younger individuals with vitiligo to seek treatment or proactively making them aware of treatment opportunities may be beneficial.3
Diagnosis of Vitiligo by Nondermatologists—The increase in delay to treatment when a nondermatologist diagnoses vitiligo suggests that prompt initiation of treatment or referrals to dermatology by primary care providers may not routinely be occurring.4 Our data indicate the need to educate primary care providers on treatment opportunities for individuals with vitiligo and that early treatment generally is more effective.5
Impact of Race/Ethnicity on Vitiligo Treatment—Our data also show trends for longer treatment delays for individuals with skin of color. Although this did not reach statistical significance, we hope future studies will investigate this issue, especially because patients with skin of color experience more stigmatization and quality-of-life impacts by vitiligo than White patients.5
Impact of BSA on Vitiligo Treatment—Our data show that patients with a smaller BSA had a shorter delay to treatment than those with a greater BSA affected. This was a unique finding given it initially was hypothesized that patients with greater BSA would seek treatment earlier because of the associated increase in quality of life impact. This trend was not statistically significant, but further investigation would be helpful to analyze the reason behind treatment delays in patients with greater BSA affected.
Conclusion
The delay to treatment in our study population was correlated with the diagnosing physician’s specialty and patient age at disease onset, with trends also observed for race and BSA affected. These findings emphasize the need to investigate specific causes of barriers to early care to promote health equity among individuals with vitiligo.
- Tripathi R, Archibald LK, Mazmudar RS, et al. Racial differences in time to treatment for melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:854-859.
- Boniface K, Seneschal J. Vitiligo as a skin memory disease: the need for early intervention with immunomodulating agents and a maintenance therapy to target resident memory T cells. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:656-661.
- Silverberg JI, Silverberg NB. Quality of life impairment in children and adolescents with vitiligo. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:309-318.
- Amer AA, Gao XH. Quality of life in patients with vitiligo: an analysis of the dermatology life quality index outcome over the past two decades. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:608-614.
- Weibel L, Laguda B, Atherton D, et al. Misdiagnosis and delay in referral of children with localized scleroderma. Br J Dermatol. 2011;165:1308-1313.
Similar to other dermatologic conditions, barriers to early care in patients with vitiligo can exacerbate health disparities.1 Delayed treatment of vitiligo is known to hamper successful disease stabilization and repigmentation, as therapies tend to work more effectively in early stages of the disease.2
To investigate the factors associated with treatment delays for patients with vitiligo, we conducted a retrospective chart review of 102 consecutive patients with vitiligo attending an academic outpatient clinic in Austin, Texas, over 36 months.
Methods
Our sample included 102 consecutive patients with vitiligo who attended an academic outpatient clinic in Austin, Texas, from January 2017 to January 2020. Demographic information, clinical characteristics of vitiligo, and treatment data were self-reported via a standardized questionnaire given to all patients with vitiligo and gathered from medical chart review. Patient characteristics are outlined in the Table. The delay to treatment was the time (in months) from the date the patient first noticed the lesion to the start date of first treatment. This retrospective chart review was reviewed by the University of Texas at Austin institutional review board and was determined to be exempt.

Statistical Analysis—The data were analyzed descriptively with a Wilcoxon rank sum test (type I error rate of .05).
Results
Of the 102 charts that were analyzed, 45 were females and 57 were males. More than half of the patients (54.9% [56/102]) were White. Sixteen were Asian, 13 were Hispanic non-White, 11 were Black/African American, and 4 were American Indian/Alaska Native. The median age of disease onset was 21 years, minimum age was 1 year, and maximum age was 83 years. The diagnosis of vitiligo was made by a dermatologist for 72 patients and by a physician of another specialty for 20 patients. Ten patients did not declare the specialty of the diagnosing physician.
Individuals older than 21 years when their disease started had a shorter delay to treatment than individuals who noticed their first lesion at an age younger than 21 years (median, 75 months vs 13 months; P<.01). Individuals diagnosed by a dermatologist had a shorter delay to treatment than individuals diagnosed by a physician of another specialty (median, 13 months vs 58 months; P<.05). White individuals had a shorter delay to treatment than individuals with skin of color (median, 13 months vs 31 months; P=.08), though this trend did not reach statistical significance. Individuals with 1% to 25% of body surface area (BSA) affected at time of presentation to clinic also had a shorter delay to treatment than those with a greater BSA affected (median, 13 months vs 74 months; P<.06), though this trend did not reach statistical significance. Type of vitiligo (P<.8), Fitzpatrick skin type (P<.6), and smoking status (P<.7) were not associated with differential delays.
Comment
Impact of Age on Vitiligo Treatment—Our data suggest that individuals who develop vitiligo at a younger age experience longer treatment delays compared to older individuals. Reasons for this are uncertain but could include access issues, medical decision-making agency, and younger patients not remembering being treated during their youth. Our data also could be influenced by some of the adult patients in our study first noticing their lesions many years ago when treatments for vitiligo were more limited. Nevertheless, detrimental effects on quality of life in children and adolescents with vitiligo suggest that motivating younger individuals with vitiligo to seek treatment or proactively making them aware of treatment opportunities may be beneficial.3
Diagnosis of Vitiligo by Nondermatologists—The increase in delay to treatment when a nondermatologist diagnoses vitiligo suggests that prompt initiation of treatment or referrals to dermatology by primary care providers may not routinely be occurring.4 Our data indicate the need to educate primary care providers on treatment opportunities for individuals with vitiligo and that early treatment generally is more effective.5
Impact of Race/Ethnicity on Vitiligo Treatment—Our data also show trends for longer treatment delays for individuals with skin of color. Although this did not reach statistical significance, we hope future studies will investigate this issue, especially because patients with skin of color experience more stigmatization and quality-of-life impacts by vitiligo than White patients.5
Impact of BSA on Vitiligo Treatment—Our data show that patients with a smaller BSA had a shorter delay to treatment than those with a greater BSA affected. This was a unique finding given it initially was hypothesized that patients with greater BSA would seek treatment earlier because of the associated increase in quality of life impact. This trend was not statistically significant, but further investigation would be helpful to analyze the reason behind treatment delays in patients with greater BSA affected.
Conclusion
The delay to treatment in our study population was correlated with the diagnosing physician’s specialty and patient age at disease onset, with trends also observed for race and BSA affected. These findings emphasize the need to investigate specific causes of barriers to early care to promote health equity among individuals with vitiligo.
Similar to other dermatologic conditions, barriers to early care in patients with vitiligo can exacerbate health disparities.1 Delayed treatment of vitiligo is known to hamper successful disease stabilization and repigmentation, as therapies tend to work more effectively in early stages of the disease.2
To investigate the factors associated with treatment delays for patients with vitiligo, we conducted a retrospective chart review of 102 consecutive patients with vitiligo attending an academic outpatient clinic in Austin, Texas, over 36 months.
Methods
Our sample included 102 consecutive patients with vitiligo who attended an academic outpatient clinic in Austin, Texas, from January 2017 to January 2020. Demographic information, clinical characteristics of vitiligo, and treatment data were self-reported via a standardized questionnaire given to all patients with vitiligo and gathered from medical chart review. Patient characteristics are outlined in the Table. The delay to treatment was the time (in months) from the date the patient first noticed the lesion to the start date of first treatment. This retrospective chart review was reviewed by the University of Texas at Austin institutional review board and was determined to be exempt.

Statistical Analysis—The data were analyzed descriptively with a Wilcoxon rank sum test (type I error rate of .05).
Results
Of the 102 charts that were analyzed, 45 were females and 57 were males. More than half of the patients (54.9% [56/102]) were White. Sixteen were Asian, 13 were Hispanic non-White, 11 were Black/African American, and 4 were American Indian/Alaska Native. The median age of disease onset was 21 years, minimum age was 1 year, and maximum age was 83 years. The diagnosis of vitiligo was made by a dermatologist for 72 patients and by a physician of another specialty for 20 patients. Ten patients did not declare the specialty of the diagnosing physician.
Individuals older than 21 years when their disease started had a shorter delay to treatment than individuals who noticed their first lesion at an age younger than 21 years (median, 75 months vs 13 months; P<.01). Individuals diagnosed by a dermatologist had a shorter delay to treatment than individuals diagnosed by a physician of another specialty (median, 13 months vs 58 months; P<.05). White individuals had a shorter delay to treatment than individuals with skin of color (median, 13 months vs 31 months; P=.08), though this trend did not reach statistical significance. Individuals with 1% to 25% of body surface area (BSA) affected at time of presentation to clinic also had a shorter delay to treatment than those with a greater BSA affected (median, 13 months vs 74 months; P<.06), though this trend did not reach statistical significance. Type of vitiligo (P<.8), Fitzpatrick skin type (P<.6), and smoking status (P<.7) were not associated with differential delays.
Comment
Impact of Age on Vitiligo Treatment—Our data suggest that individuals who develop vitiligo at a younger age experience longer treatment delays compared to older individuals. Reasons for this are uncertain but could include access issues, medical decision-making agency, and younger patients not remembering being treated during their youth. Our data also could be influenced by some of the adult patients in our study first noticing their lesions many years ago when treatments for vitiligo were more limited. Nevertheless, detrimental effects on quality of life in children and adolescents with vitiligo suggest that motivating younger individuals with vitiligo to seek treatment or proactively making them aware of treatment opportunities may be beneficial.3
Diagnosis of Vitiligo by Nondermatologists—The increase in delay to treatment when a nondermatologist diagnoses vitiligo suggests that prompt initiation of treatment or referrals to dermatology by primary care providers may not routinely be occurring.4 Our data indicate the need to educate primary care providers on treatment opportunities for individuals with vitiligo and that early treatment generally is more effective.5
Impact of Race/Ethnicity on Vitiligo Treatment—Our data also show trends for longer treatment delays for individuals with skin of color. Although this did not reach statistical significance, we hope future studies will investigate this issue, especially because patients with skin of color experience more stigmatization and quality-of-life impacts by vitiligo than White patients.5
Impact of BSA on Vitiligo Treatment—Our data show that patients with a smaller BSA had a shorter delay to treatment than those with a greater BSA affected. This was a unique finding given it initially was hypothesized that patients with greater BSA would seek treatment earlier because of the associated increase in quality of life impact. This trend was not statistically significant, but further investigation would be helpful to analyze the reason behind treatment delays in patients with greater BSA affected.
Conclusion
The delay to treatment in our study population was correlated with the diagnosing physician’s specialty and patient age at disease onset, with trends also observed for race and BSA affected. These findings emphasize the need to investigate specific causes of barriers to early care to promote health equity among individuals with vitiligo.
- Tripathi R, Archibald LK, Mazmudar RS, et al. Racial differences in time to treatment for melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:854-859.
- Boniface K, Seneschal J. Vitiligo as a skin memory disease: the need for early intervention with immunomodulating agents and a maintenance therapy to target resident memory T cells. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:656-661.
- Silverberg JI, Silverberg NB. Quality of life impairment in children and adolescents with vitiligo. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:309-318.
- Amer AA, Gao XH. Quality of life in patients with vitiligo: an analysis of the dermatology life quality index outcome over the past two decades. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:608-614.
- Weibel L, Laguda B, Atherton D, et al. Misdiagnosis and delay in referral of children with localized scleroderma. Br J Dermatol. 2011;165:1308-1313.
- Tripathi R, Archibald LK, Mazmudar RS, et al. Racial differences in time to treatment for melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:854-859.
- Boniface K, Seneschal J. Vitiligo as a skin memory disease: the need for early intervention with immunomodulating agents and a maintenance therapy to target resident memory T cells. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:656-661.
- Silverberg JI, Silverberg NB. Quality of life impairment in children and adolescents with vitiligo. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:309-318.
- Amer AA, Gao XH. Quality of life in patients with vitiligo: an analysis of the dermatology life quality index outcome over the past two decades. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:608-614.
- Weibel L, Laguda B, Atherton D, et al. Misdiagnosis and delay in referral of children with localized scleroderma. Br J Dermatol. 2011;165:1308-1313.
Practice Points
- The medical community should be aware of factors associated with delay to treatment in patients with vitiligo, such as the diagnosing physician’s specialty and patient age at disease onset.
- Race and percentage of body surface area affected at time of presentation also demonstrate trends regarding treatment delays in patients with vitiligo.
FDA cautions against using OTC products to remove skin spots, moles
Those moles, skin tags, and liver spots should stay on your skin until you see a doctor, according to a new alert from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The alert warns against the use of over-the-counter products for removing moles, seborrheic keratoses (wart-like growths that are often brown), or skin tags, emphasizing that none are approved by the FDA for at-home use.
Dermatologists and the FDA say these products may lead to scarring and disfigurement.
Risks include “skin injuries, infection requiring antibiotics, scarring, and delayed skin cancer diagnosis and treatment,” according to the alert, which adds that the agency has received reports of people “who developed permanent skin injuries and infections after using products marketed as mole or skin tag removers. “
These products come in the form of gels, liquids, sticks, or ointments and commonly contain ingredients like salicylic acid, which are cytotoxic, or cell-killing. These chemicals are what make the products potentially dangerous, as each contains unregulated, and likely very high, amounts of these corrosive agents. Even products marketed as natural or organic have these same issues, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who notes that bloodroot is another ingredient found in these products.
Dr. Friedman explained that using these products without the supervision of a health care provider can create a chemical burn in the skin, leading to scarring. He’s treated patients for open wounds and infected ulcers caused by these products. “Over my career, I’ve seen many cases of patients coming in with self-inflicted harm due to using these quote, unquote, safe and natural products to remove benign, or even worse, potentially malignant neoplasms,” he told this news organization.
Another concern is that these spots on the skin are often the only sign of a serious issue – cancer. Early signs of melanoma, a type of skin cancer, include large, misshapen, or rapidly changing moles. Dr. Friedman said that if a patient uses one of these products on what is actually a cancerous mole, they will likely only remove the surface, and in turn, destroy the only sign of cancer – effectively killing the canary in the coal mine.
There’s a good chance that the root of the mole has been left intact under the skin surface, and as a result, the cancer has the potential to spread unnoticed. “If people aren’t going to a dermatologist to be properly diagnosed and properly managed, they’re going to cause more harm by thinking that they’ve taken care of a problem,” he said.
If you are concerned about any type of spot on your skin, a visit to the dermatologist will prove much simpler and safer for treating it than doing so at home. In the office, Dr. Friedman said, providers can use a range of highly studied techniques to remove skin lesions with minimal pain and scarring. From freezing, burning, snipping, or a quick moment under a scalpel, you’ll be healed in no time.
Anyone who has experienced an adverse event with one of these products and health care professionals should report cases to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting Program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Those moles, skin tags, and liver spots should stay on your skin until you see a doctor, according to a new alert from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The alert warns against the use of over-the-counter products for removing moles, seborrheic keratoses (wart-like growths that are often brown), or skin tags, emphasizing that none are approved by the FDA for at-home use.
Dermatologists and the FDA say these products may lead to scarring and disfigurement.
Risks include “skin injuries, infection requiring antibiotics, scarring, and delayed skin cancer diagnosis and treatment,” according to the alert, which adds that the agency has received reports of people “who developed permanent skin injuries and infections after using products marketed as mole or skin tag removers. “
These products come in the form of gels, liquids, sticks, or ointments and commonly contain ingredients like salicylic acid, which are cytotoxic, or cell-killing. These chemicals are what make the products potentially dangerous, as each contains unregulated, and likely very high, amounts of these corrosive agents. Even products marketed as natural or organic have these same issues, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who notes that bloodroot is another ingredient found in these products.
Dr. Friedman explained that using these products without the supervision of a health care provider can create a chemical burn in the skin, leading to scarring. He’s treated patients for open wounds and infected ulcers caused by these products. “Over my career, I’ve seen many cases of patients coming in with self-inflicted harm due to using these quote, unquote, safe and natural products to remove benign, or even worse, potentially malignant neoplasms,” he told this news organization.
Another concern is that these spots on the skin are often the only sign of a serious issue – cancer. Early signs of melanoma, a type of skin cancer, include large, misshapen, or rapidly changing moles. Dr. Friedman said that if a patient uses one of these products on what is actually a cancerous mole, they will likely only remove the surface, and in turn, destroy the only sign of cancer – effectively killing the canary in the coal mine.
There’s a good chance that the root of the mole has been left intact under the skin surface, and as a result, the cancer has the potential to spread unnoticed. “If people aren’t going to a dermatologist to be properly diagnosed and properly managed, they’re going to cause more harm by thinking that they’ve taken care of a problem,” he said.
If you are concerned about any type of spot on your skin, a visit to the dermatologist will prove much simpler and safer for treating it than doing so at home. In the office, Dr. Friedman said, providers can use a range of highly studied techniques to remove skin lesions with minimal pain and scarring. From freezing, burning, snipping, or a quick moment under a scalpel, you’ll be healed in no time.
Anyone who has experienced an adverse event with one of these products and health care professionals should report cases to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting Program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Those moles, skin tags, and liver spots should stay on your skin until you see a doctor, according to a new alert from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The alert warns against the use of over-the-counter products for removing moles, seborrheic keratoses (wart-like growths that are often brown), or skin tags, emphasizing that none are approved by the FDA for at-home use.
Dermatologists and the FDA say these products may lead to scarring and disfigurement.
Risks include “skin injuries, infection requiring antibiotics, scarring, and delayed skin cancer diagnosis and treatment,” according to the alert, which adds that the agency has received reports of people “who developed permanent skin injuries and infections after using products marketed as mole or skin tag removers. “
These products come in the form of gels, liquids, sticks, or ointments and commonly contain ingredients like salicylic acid, which are cytotoxic, or cell-killing. These chemicals are what make the products potentially dangerous, as each contains unregulated, and likely very high, amounts of these corrosive agents. Even products marketed as natural or organic have these same issues, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who notes that bloodroot is another ingredient found in these products.
Dr. Friedman explained that using these products without the supervision of a health care provider can create a chemical burn in the skin, leading to scarring. He’s treated patients for open wounds and infected ulcers caused by these products. “Over my career, I’ve seen many cases of patients coming in with self-inflicted harm due to using these quote, unquote, safe and natural products to remove benign, or even worse, potentially malignant neoplasms,” he told this news organization.
Another concern is that these spots on the skin are often the only sign of a serious issue – cancer. Early signs of melanoma, a type of skin cancer, include large, misshapen, or rapidly changing moles. Dr. Friedman said that if a patient uses one of these products on what is actually a cancerous mole, they will likely only remove the surface, and in turn, destroy the only sign of cancer – effectively killing the canary in the coal mine.
There’s a good chance that the root of the mole has been left intact under the skin surface, and as a result, the cancer has the potential to spread unnoticed. “If people aren’t going to a dermatologist to be properly diagnosed and properly managed, they’re going to cause more harm by thinking that they’ve taken care of a problem,” he said.
If you are concerned about any type of spot on your skin, a visit to the dermatologist will prove much simpler and safer for treating it than doing so at home. In the office, Dr. Friedman said, providers can use a range of highly studied techniques to remove skin lesions with minimal pain and scarring. From freezing, burning, snipping, or a quick moment under a scalpel, you’ll be healed in no time.
Anyone who has experienced an adverse event with one of these products and health care professionals should report cases to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting Program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Deployed Airbag Causes Bullous Reaction Following a Motor Vehicle Accident
Airbags are lifesaving during motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), but their deployment has been associated with skin issues such as irritant dermatitis1; lacerations2; abrasions3; and thermal, friction, and chemical burns.4-6 Ocular issues such as alkaline chemical keratitis7 and ocular alkali injuries8 also have been described.
Airbag deployment is triggered by rapid deceleration and impact, which ignite a sodium azide cartridge, causing the woven nylon bag to inflate with hydrocarbon gases.8 This leads to release of sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate, and metallic oxides in an aerosolized form. If a tear in the meshwork of the airbag occurs, exposure to an even larger amount of powder containing caustic alkali chemicals can occur.8
We describe a patient who developed a bullous reaction to airbag contents after he was involved in an MVA in which the airbag deployed.
Case Report
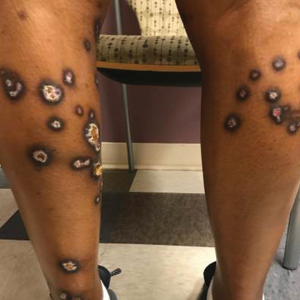
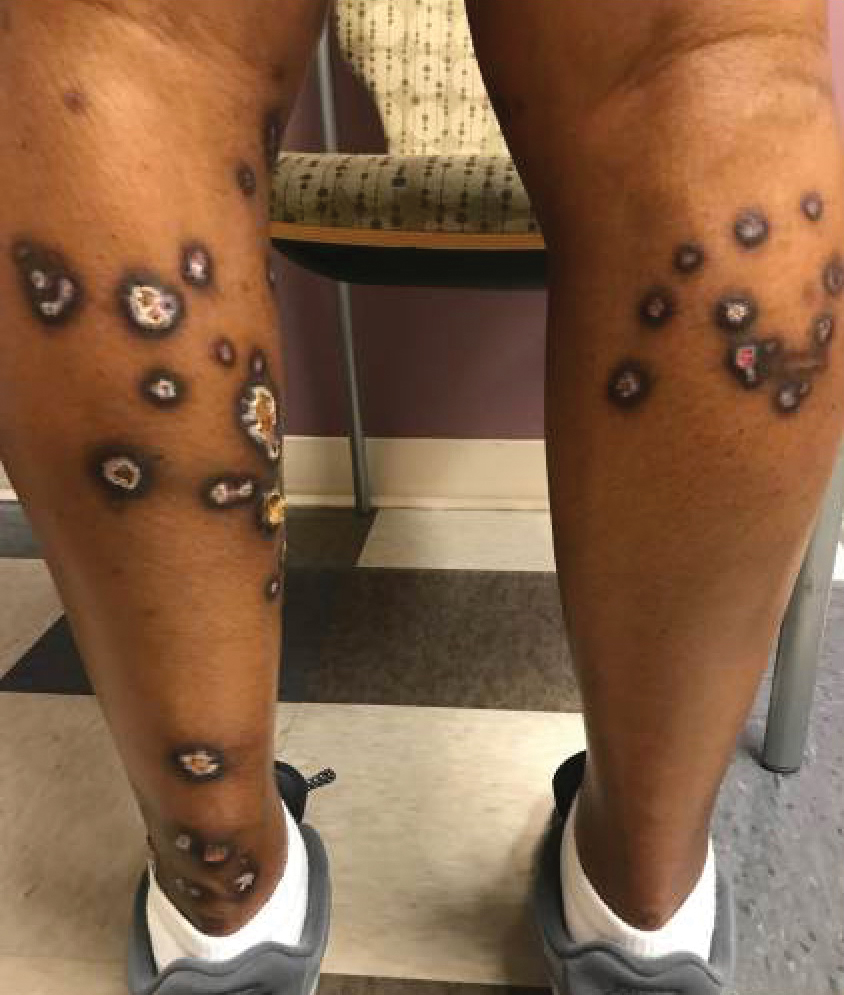
A 35-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis B presented to the dermatology clinic for an evaluation of new-onset blisters. The rash occurred 1 day after the patient was involved in an MVA in which he was exposed to the airbag’s contents after it burst. He had been evaluated twice in the emergency department for the skin eruption before being referred to dermatology. He noted the lesions were pruritic and painful. Prior treatments included silver sulfadiazine cream 1% and clobetasol cream 0.05%, though he discontinued using the latter because of burning with application. Physical examination revealed tense vesicles and bullae on an erythematous base on the right lower flank, forearms, and legs, with the exception of the lower right leg where a cast had been from a prior injury (Figure 1).

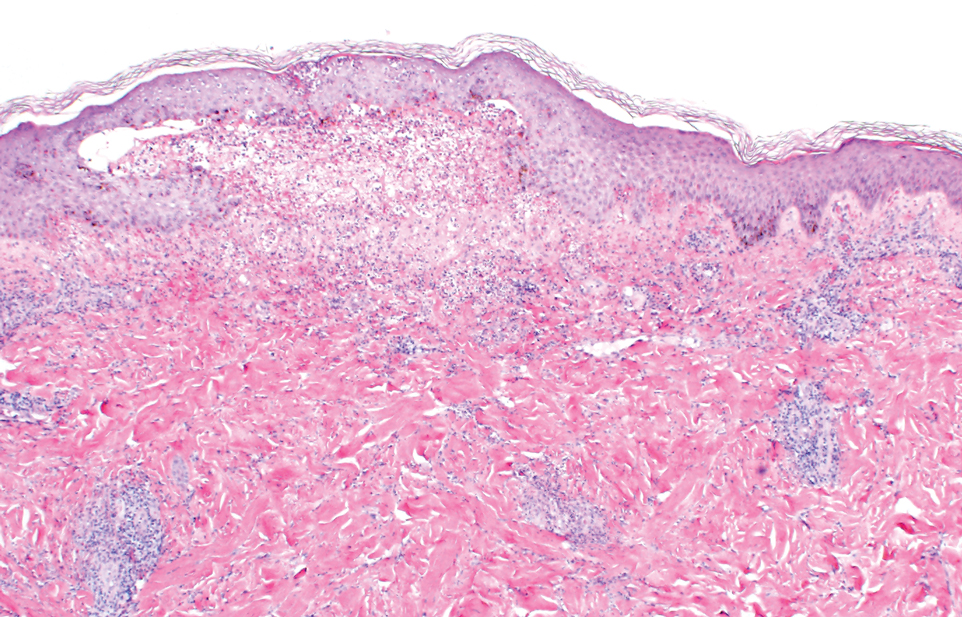
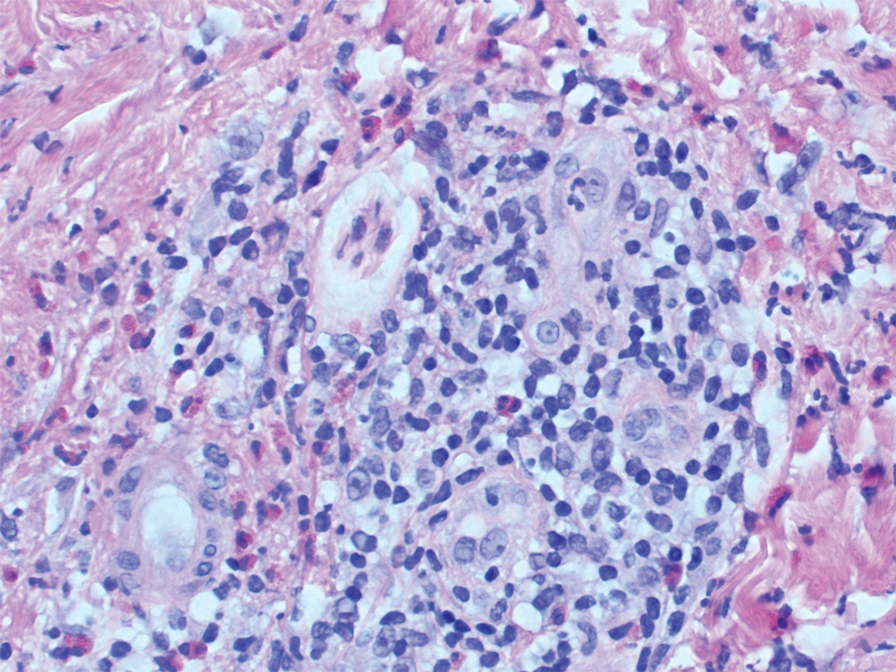
Two punch biopsies of the left arm were performed and sent for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence to rule out bullous diseases, such as bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA, and bullous lupus. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed extensive spongiosis with blister formation and a dense perivascular infiltrate in the superficial and mid dermis composed of lymphocytes with numerous scattered eosinophils (Figures 2 and 3). Direct immunofluorescence studies were negative. Treatment with oral prednisone and oral antihistamines was initiated.
At 10-day follow-up, the patient had a few residual bullae; most lesions were demonstrating various stages of healing (Figure 4). The patient’s cast had been removed, and there were no lesions in this previously covered area. At 6-week follow-up he had continued healing of the bullae and erosions as well as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (Figure 5).

Comment
With the advent of airbags for safety purposes, these potentially lifesaving devices also have been known to cause injury.9 In 1998, the most commonly reported airbag injuries were ocular injuries.10 Cutaneous manifestations of airbag injury are less well known.11
Two cases of airbag deployment with skin blistering have been reported in the literature based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms airbag blistering or airbag bullae12,13; however, the blistering was described in the context of a burn. One case of the effects of airbag deployment residue highlights a patient arriving to the emergency department with erythema and blisters on the hands within 48 hours of airbag deployment in an MVA, and the treatment was standard burn therapy.12 Another case report described a patient with a second-degree burn with a 12-cm blister occurring on the radial side of the hand and distal forearm following an MVA and airbag deployment, which was treated conservatively.13 Cases of thermal burns, chemical burns, and irritant contact dermatitis after airbag deployment have been described in the literature.4-6,11,12,14,15 Our patient’s distal right lower leg was covered with a cast for osteomyelitis, and no blisters had developed in this area. It is likely that the transfer of airbag contents occurred during the process of unbuckling his seatbelt, which could explain the bullae that developed on the right flank. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, individuals should quickly remove clothing and wash their body with large amounts of soap and water following exposure to sodium azide.16
In 1989, the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 208 (occupant crash protection) became effective, stating all cars must have vehicle crash protection.12 Prior to 1993, it was reported that there had been no associated chemical injuries with airbag deployment. Subsequently, a 6-month retrospective study in 1993 showed that dermal injuries were found in connection with the presence of sodium hydroxide in automobile airbags.12 By 2004, it was known that airbags could cause chemical and thermal burns in addition to traumatic injuries from deployment.1 Since 2007, all motor vehicles have been required to have advanced airbags, which are engineered to sense the presence of passengers and determine if the airbag will deploy, and if so, how much to deploy to minimize airbag-related injury.3
The brand of car that our patient drove during the MVA is one with known airbag recalls due to safety defects; however, the year and actual model of the vehicle are not known, so specific information about the airbag in question is not available. It has been noted that some defective airbag inflators that were exposed to excess moisture during the manufacturing process could explode during deployment, causing shrapnel and airbag rupture, which has been linked to nearly 300 injuries worldwide.17
Conclusion
It is evident that the use of airbag devices reduces morbidity and mortality due to MVAs.9 It also had been reported that up to 96% of airbag-related injuries are relatively minor, which many would argue justifies their use.18 Furthermore, it has been reported that 99.8% of skin injuries following airbag deployment are minor.19 In the United States, it is mandated that every vehicle have functional airbags installed.8
This case highlights the potential for substantial airbag-induced skin reactions, specifically a bullous reaction, following airbag deployment. The persistent pruritus and lasting postinflammatory hyperpigmentation seen in this case were certainly worrisome for our patient. We also present this case to remind dermatology providers of possible treatment approaches to these skin reactions. Immediate cleansing of the affected areas of skin may help avoid such reactions.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Zampino MR, et al. Air bags and the skin. Skinmed. 2004;3:256-258.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Virgili A. Effects of airbag deployment: lesions, epidemiology, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5:295-300.
- Kuska TC. Air bag safety: an update. J Emerg Nurs. 2016;42:438-441.
- Ulrich D, Noah EM, Fuchs P, et al. Burn injuries caused by air bag deployment. Burns. 2001;27:196-199.
- Erpenbeck SP, Roy E, Ziembicki JA, et al. A systematic review on airbag-induced burns. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:481-487.
- Skibba KEH, Cleveland CN, Bell DE. Airbag burns: an unfortunate consequence of motor vehicle safety. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:71-73.
- Smally AJ, Binzer A, Dolin S, et al. Alkaline chemical keratitis: eye injury from airbags. Ann Emerg Med. 1992;21:1400-1402.
- Barnes SS, Wong W Jr, Affeldt JC. A case of severe airbag related ocular alkali injury. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2012;71:229-231.
- Wallis LA, Greaves I. Injuries associated with airbag deployment. Emerg Med J. 2002;19:490-493.
- Mohamed AA, Banerjee A. Patterns of injury associated with automobile airbag use. Postgrad Med J. 1998;74:455-458.
- Foley E, Helm TN. Air bag injury and the dermatologist. Cutis. 2000;66:251-252.
- Swanson-Biearman B, Mrvos R, Dean BS, et al. Air bags: lifesaving with toxic potential? Am J Emerg Med. 1993;11:38-39.
- Roth T, Meredith P. Traumatic lesions caused by the “air-bag” system [in French]. Z Unfallchir Versicherungsmed. 1993;86:189-193.
- Wu JJ, Sanchez-Palacios C, Brieva J, et al. A case of air bag dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1383-1384.
- Vitello W, Kim M, Johnson RM, et al. Full-thickness burn to the hand from an automobile airbag. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20:212-215.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facts about sodium azide. Updated April 4, 2018. Accessed May 15, 2022. https://emergency.cdc.gov/agent/sodiumazide/basics/facts.asp
- Shepardson D. Honda to recall 1.2 million vehicles in North America to replace Takata airbags. March 12, 2019. Accessed March 22, 2022. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-honda-takata-recall/honda-to-recall-1-2-million-vehicles-in-north-america-to-replace-takata-airbags-idUSKBN1QT1C9
- Gabauer DJ, Gabler HC. The effects of airbags and seatbelts on occupant injury in longitudinal barrier crashes. J Safety Res. 2010;41:9-15.
- Rath AL, Jernigan MV, Stitzel JD, et al. The effects of depowered airbags on skin injuries in frontal automobile crashes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;115:428-435.
Airbags are lifesaving during motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), but their deployment has been associated with skin issues such as irritant dermatitis1; lacerations2; abrasions3; and thermal, friction, and chemical burns.4-6 Ocular issues such as alkaline chemical keratitis7 and ocular alkali injuries8 also have been described.
Airbag deployment is triggered by rapid deceleration and impact, which ignite a sodium azide cartridge, causing the woven nylon bag to inflate with hydrocarbon gases.8 This leads to release of sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate, and metallic oxides in an aerosolized form. If a tear in the meshwork of the airbag occurs, exposure to an even larger amount of powder containing caustic alkali chemicals can occur.8
We describe a patient who developed a bullous reaction to airbag contents after he was involved in an MVA in which the airbag deployed.
Case Report
A 35-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis B presented to the dermatology clinic for an evaluation of new-onset blisters. The rash occurred 1 day after the patient was involved in an MVA in which he was exposed to the airbag’s contents after it burst. He had been evaluated twice in the emergency department for the skin eruption before being referred to dermatology. He noted the lesions were pruritic and painful. Prior treatments included silver sulfadiazine cream 1% and clobetasol cream 0.05%, though he discontinued using the latter because of burning with application. Physical examination revealed tense vesicles and bullae on an erythematous base on the right lower flank, forearms, and legs, with the exception of the lower right leg where a cast had been from a prior injury (Figure 1).

Two punch biopsies of the left arm were performed and sent for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence to rule out bullous diseases, such as bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA, and bullous lupus. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed extensive spongiosis with blister formation and a dense perivascular infiltrate in the superficial and mid dermis composed of lymphocytes with numerous scattered eosinophils (Figures 2 and 3). Direct immunofluorescence studies were negative. Treatment with oral prednisone and oral antihistamines was initiated.


At 10-day follow-up, the patient had a few residual bullae; most lesions were demonstrating various stages of healing (Figure 4). The patient’s cast had been removed, and there were no lesions in this previously covered area. At 6-week follow-up he had continued healing of the bullae and erosions as well as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (Figure 5).


Comment
With the advent of airbags for safety purposes, these potentially lifesaving devices also have been known to cause injury.9 In 1998, the most commonly reported airbag injuries were ocular injuries.10 Cutaneous manifestations of airbag injury are less well known.11
Two cases of airbag deployment with skin blistering have been reported in the literature based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms airbag blistering or airbag bullae12,13; however, the blistering was described in the context of a burn. One case of the effects of airbag deployment residue highlights a patient arriving to the emergency department with erythema and blisters on the hands within 48 hours of airbag deployment in an MVA, and the treatment was standard burn therapy.12 Another case report described a patient with a second-degree burn with a 12-cm blister occurring on the radial side of the hand and distal forearm following an MVA and airbag deployment, which was treated conservatively.13 Cases of thermal burns, chemical burns, and irritant contact dermatitis after airbag deployment have been described in the literature.4-6,11,12,14,15 Our patient’s distal right lower leg was covered with a cast for osteomyelitis, and no blisters had developed in this area. It is likely that the transfer of airbag contents occurred during the process of unbuckling his seatbelt, which could explain the bullae that developed on the right flank. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, individuals should quickly remove clothing and wash their body with large amounts of soap and water following exposure to sodium azide.16
In 1989, the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 208 (occupant crash protection) became effective, stating all cars must have vehicle crash protection.12 Prior to 1993, it was reported that there had been no associated chemical injuries with airbag deployment. Subsequently, a 6-month retrospective study in 1993 showed that dermal injuries were found in connection with the presence of sodium hydroxide in automobile airbags.12 By 2004, it was known that airbags could cause chemical and thermal burns in addition to traumatic injuries from deployment.1 Since 2007, all motor vehicles have been required to have advanced airbags, which are engineered to sense the presence of passengers and determine if the airbag will deploy, and if so, how much to deploy to minimize airbag-related injury.3
The brand of car that our patient drove during the MVA is one with known airbag recalls due to safety defects; however, the year and actual model of the vehicle are not known, so specific information about the airbag in question is not available. It has been noted that some defective airbag inflators that were exposed to excess moisture during the manufacturing process could explode during deployment, causing shrapnel and airbag rupture, which has been linked to nearly 300 injuries worldwide.17
Conclusion
It is evident that the use of airbag devices reduces morbidity and mortality due to MVAs.9 It also had been reported that up to 96% of airbag-related injuries are relatively minor, which many would argue justifies their use.18 Furthermore, it has been reported that 99.8% of skin injuries following airbag deployment are minor.19 In the United States, it is mandated that every vehicle have functional airbags installed.8
This case highlights the potential for substantial airbag-induced skin reactions, specifically a bullous reaction, following airbag deployment. The persistent pruritus and lasting postinflammatory hyperpigmentation seen in this case were certainly worrisome for our patient. We also present this case to remind dermatology providers of possible treatment approaches to these skin reactions. Immediate cleansing of the affected areas of skin may help avoid such reactions.
Airbags are lifesaving during motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), but their deployment has been associated with skin issues such as irritant dermatitis1; lacerations2; abrasions3; and thermal, friction, and chemical burns.4-6 Ocular issues such as alkaline chemical keratitis7 and ocular alkali injuries8 also have been described.
Airbag deployment is triggered by rapid deceleration and impact, which ignite a sodium azide cartridge, causing the woven nylon bag to inflate with hydrocarbon gases.8 This leads to release of sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate, and metallic oxides in an aerosolized form. If a tear in the meshwork of the airbag occurs, exposure to an even larger amount of powder containing caustic alkali chemicals can occur.8
We describe a patient who developed a bullous reaction to airbag contents after he was involved in an MVA in which the airbag deployed.
Case Report
A 35-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis B presented to the dermatology clinic for an evaluation of new-onset blisters. The rash occurred 1 day after the patient was involved in an MVA in which he was exposed to the airbag’s contents after it burst. He had been evaluated twice in the emergency department for the skin eruption before being referred to dermatology. He noted the lesions were pruritic and painful. Prior treatments included silver sulfadiazine cream 1% and clobetasol cream 0.05%, though he discontinued using the latter because of burning with application. Physical examination revealed tense vesicles and bullae on an erythematous base on the right lower flank, forearms, and legs, with the exception of the lower right leg where a cast had been from a prior injury (Figure 1).

Two punch biopsies of the left arm were performed and sent for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence to rule out bullous diseases, such as bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA, and bullous lupus. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed extensive spongiosis with blister formation and a dense perivascular infiltrate in the superficial and mid dermis composed of lymphocytes with numerous scattered eosinophils (Figures 2 and 3). Direct immunofluorescence studies were negative. Treatment with oral prednisone and oral antihistamines was initiated.


At 10-day follow-up, the patient had a few residual bullae; most lesions were demonstrating various stages of healing (Figure 4). The patient’s cast had been removed, and there were no lesions in this previously covered area. At 6-week follow-up he had continued healing of the bullae and erosions as well as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (Figure 5).


Comment
With the advent of airbags for safety purposes, these potentially lifesaving devices also have been known to cause injury.9 In 1998, the most commonly reported airbag injuries were ocular injuries.10 Cutaneous manifestations of airbag injury are less well known.11
Two cases of airbag deployment with skin blistering have been reported in the literature based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms airbag blistering or airbag bullae12,13; however, the blistering was described in the context of a burn. One case of the effects of airbag deployment residue highlights a patient arriving to the emergency department with erythema and blisters on the hands within 48 hours of airbag deployment in an MVA, and the treatment was standard burn therapy.12 Another case report described a patient with a second-degree burn with a 12-cm blister occurring on the radial side of the hand and distal forearm following an MVA and airbag deployment, which was treated conservatively.13 Cases of thermal burns, chemical burns, and irritant contact dermatitis after airbag deployment have been described in the literature.4-6,11,12,14,15 Our patient’s distal right lower leg was covered with a cast for osteomyelitis, and no blisters had developed in this area. It is likely that the transfer of airbag contents occurred during the process of unbuckling his seatbelt, which could explain the bullae that developed on the right flank. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, individuals should quickly remove clothing and wash their body with large amounts of soap and water following exposure to sodium azide.16
In 1989, the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 208 (occupant crash protection) became effective, stating all cars must have vehicle crash protection.12 Prior to 1993, it was reported that there had been no associated chemical injuries with airbag deployment. Subsequently, a 6-month retrospective study in 1993 showed that dermal injuries were found in connection with the presence of sodium hydroxide in automobile airbags.12 By 2004, it was known that airbags could cause chemical and thermal burns in addition to traumatic injuries from deployment.1 Since 2007, all motor vehicles have been required to have advanced airbags, which are engineered to sense the presence of passengers and determine if the airbag will deploy, and if so, how much to deploy to minimize airbag-related injury.3
The brand of car that our patient drove during the MVA is one with known airbag recalls due to safety defects; however, the year and actual model of the vehicle are not known, so specific information about the airbag in question is not available. It has been noted that some defective airbag inflators that were exposed to excess moisture during the manufacturing process could explode during deployment, causing shrapnel and airbag rupture, which has been linked to nearly 300 injuries worldwide.17
Conclusion
It is evident that the use of airbag devices reduces morbidity and mortality due to MVAs.9 It also had been reported that up to 96% of airbag-related injuries are relatively minor, which many would argue justifies their use.18 Furthermore, it has been reported that 99.8% of skin injuries following airbag deployment are minor.19 In the United States, it is mandated that every vehicle have functional airbags installed.8
This case highlights the potential for substantial airbag-induced skin reactions, specifically a bullous reaction, following airbag deployment. The persistent pruritus and lasting postinflammatory hyperpigmentation seen in this case were certainly worrisome for our patient. We also present this case to remind dermatology providers of possible treatment approaches to these skin reactions. Immediate cleansing of the affected areas of skin may help avoid such reactions.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Zampino MR, et al. Air bags and the skin. Skinmed. 2004;3:256-258.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Virgili A. Effects of airbag deployment: lesions, epidemiology, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5:295-300.
- Kuska TC. Air bag safety: an update. J Emerg Nurs. 2016;42:438-441.
- Ulrich D, Noah EM, Fuchs P, et al. Burn injuries caused by air bag deployment. Burns. 2001;27:196-199.
- Erpenbeck SP, Roy E, Ziembicki JA, et al. A systematic review on airbag-induced burns. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:481-487.
- Skibba KEH, Cleveland CN, Bell DE. Airbag burns: an unfortunate consequence of motor vehicle safety. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:71-73.
- Smally AJ, Binzer A, Dolin S, et al. Alkaline chemical keratitis: eye injury from airbags. Ann Emerg Med. 1992;21:1400-1402.
- Barnes SS, Wong W Jr, Affeldt JC. A case of severe airbag related ocular alkali injury. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2012;71:229-231.
- Wallis LA, Greaves I. Injuries associated with airbag deployment. Emerg Med J. 2002;19:490-493.
- Mohamed AA, Banerjee A. Patterns of injury associated with automobile airbag use. Postgrad Med J. 1998;74:455-458.
- Foley E, Helm TN. Air bag injury and the dermatologist. Cutis. 2000;66:251-252.
- Swanson-Biearman B, Mrvos R, Dean BS, et al. Air bags: lifesaving with toxic potential? Am J Emerg Med. 1993;11:38-39.
- Roth T, Meredith P. Traumatic lesions caused by the “air-bag” system [in French]. Z Unfallchir Versicherungsmed. 1993;86:189-193.
- Wu JJ, Sanchez-Palacios C, Brieva J, et al. A case of air bag dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1383-1384.
- Vitello W, Kim M, Johnson RM, et al. Full-thickness burn to the hand from an automobile airbag. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20:212-215.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facts about sodium azide. Updated April 4, 2018. Accessed May 15, 2022. https://emergency.cdc.gov/agent/sodiumazide/basics/facts.asp
- Shepardson D. Honda to recall 1.2 million vehicles in North America to replace Takata airbags. March 12, 2019. Accessed March 22, 2022. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-honda-takata-recall/honda-to-recall-1-2-million-vehicles-in-north-america-to-replace-takata-airbags-idUSKBN1QT1C9
- Gabauer DJ, Gabler HC. The effects of airbags and seatbelts on occupant injury in longitudinal barrier crashes. J Safety Res. 2010;41:9-15.
- Rath AL, Jernigan MV, Stitzel JD, et al. The effects of depowered airbags on skin injuries in frontal automobile crashes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;115:428-435.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Zampino MR, et al. Air bags and the skin. Skinmed. 2004;3:256-258.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Virgili A. Effects of airbag deployment: lesions, epidemiology, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5:295-300.
- Kuska TC. Air bag safety: an update. J Emerg Nurs. 2016;42:438-441.
- Ulrich D, Noah EM, Fuchs P, et al. Burn injuries caused by air bag deployment. Burns. 2001;27:196-199.
- Erpenbeck SP, Roy E, Ziembicki JA, et al. A systematic review on airbag-induced burns. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:481-487.
- Skibba KEH, Cleveland CN, Bell DE. Airbag burns: an unfortunate consequence of motor vehicle safety. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:71-73.
- Smally AJ, Binzer A, Dolin S, et al. Alkaline chemical keratitis: eye injury from airbags. Ann Emerg Med. 1992;21:1400-1402.
- Barnes SS, Wong W Jr, Affeldt JC. A case of severe airbag related ocular alkali injury. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2012;71:229-231.
- Wallis LA, Greaves I. Injuries associated with airbag deployment. Emerg Med J. 2002;19:490-493.
- Mohamed AA, Banerjee A. Patterns of injury associated with automobile airbag use. Postgrad Med J. 1998;74:455-458.
- Foley E, Helm TN. Air bag injury and the dermatologist. Cutis. 2000;66:251-252.
- Swanson-Biearman B, Mrvos R, Dean BS, et al. Air bags: lifesaving with toxic potential? Am J Emerg Med. 1993;11:38-39.
- Roth T, Meredith P. Traumatic lesions caused by the “air-bag” system [in French]. Z Unfallchir Versicherungsmed. 1993;86:189-193.
- Wu JJ, Sanchez-Palacios C, Brieva J, et al. A case of air bag dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1383-1384.
- Vitello W, Kim M, Johnson RM, et al. Full-thickness burn to the hand from an automobile airbag. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20:212-215.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facts about sodium azide. Updated April 4, 2018. Accessed May 15, 2022. https://emergency.cdc.gov/agent/sodiumazide/basics/facts.asp
- Shepardson D. Honda to recall 1.2 million vehicles in North America to replace Takata airbags. March 12, 2019. Accessed March 22, 2022. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-honda-takata-recall/honda-to-recall-1-2-million-vehicles-in-north-america-to-replace-takata-airbags-idUSKBN1QT1C9
- Gabauer DJ, Gabler HC. The effects of airbags and seatbelts on occupant injury in longitudinal barrier crashes. J Safety Res. 2010;41:9-15.
- Rath AL, Jernigan MV, Stitzel JD, et al. The effects of depowered airbags on skin injuries in frontal automobile crashes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;115:428-435.
Practice Points
- This case highlights the potential for a bullous reaction following airbag deployment.
- After airbag deployment, it is important to immediately cleanse the affected areas of skin with soap and water.
Going Beyond Hydroquinone: Alternative Skin Lightening Agents
Disorders of hyperpigmentation—melasma, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, lichen planus pigmentosus, erythema dyschromicum perstans, and pigmented contact dermatitis, among others—are common and challenging to treat. Although they can affect individuals of all skin types, they most commonly are seen in skin of color; in fact, dyspigmentation is one of the most common chief concerns for which individuals of color see a dermatologist.1,2
For many years, hydroquinone (HQ) was one of the main options available for use as a lightening agent. Although effective, it has the risk of causing irritant dermatitis, potentially leading to further dyspigmentation, in addition to the risk of ochronosis with long-term use. It remains an important and useful treatment for pigmentary disorders, but there are numerous other lightening agents that also can be considered in the treatment of disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Herein, we provide recommendations for traditional and newer non-HQ lightening agents that can be considered when treating disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Traditional Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Retinoids—Retinoids are topical vitamin A derivatives that have been used safely and effectively for decades in the treatment of pigmentary disorders. Retinoids have multiple mechanisms of action in improving pigmentation. In addition to impeding tyrosinase induction, they inhibit pigment transfer to keratinocytes and lead to accelerated pigment loss due to epidermal shedding.3 Over-the-counter formulations include retinol, retinaldehyde, and adapalene. Prescription formulations include tretinoin and tazarotene in different strengths and vehicle formulations.4
Glycolic Acid—Glycolic acid is derived from sugarcane and is considered an α-hydroxy acid that leads to rapid desquamation of pigmented keratinocytes.5 Glycolic acid can not only be used in chemical peels but also in topical creams. It is the most common α-hydroxy acid peel and is sometimes paired with HQ and other topical lightening agents for increased penetration. Glycolic acid peels are available in concentrations of 20% to 70% and can be used at various depths. When used incorrectly, it can cause redness, burning, and even skin discoloration; however, when used at the proper concentrations and depth according to Fitzpatrick skin type, there typically are no notable adverse effects, and clinical results are favorable.
Kojic Acid—Kojic acid is a natural metabolite derived from fungi and is widely used in Asian countries. It works by inhibiting the catecholase activity of tyrosinase6 and typically is available in concentrations of 1% to 4%. A study suggested that a concentration of 1% or less typically is safe to use for prolonged periods without adverse effects. Although not more effective than HQ as a monotherapy, kojic acid has been shown to haveimproved efficacy when used in combination with other lightening agents.7
Azelaic Acid—Azelaic acid works by inhibiting tyrosinase, mitochondrial oxidoreductase activation, and DNA synthesis. It preferentially targets heavily pigmented melanocytes and possesses anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.8 A 20% concentration of azelaic acid was compared to HQ 4% for the treatment of melasma, and results revealed that the liposomal form of azelaic acid was considerably more tolerable than HQ 4% and also more effective.9
Licorice Extracts—Licorice extracts have been safely used in several cosmeceutical skin lightening products.10 The main active compounds in licorice root are glabridin and liquiritin, which work to disperse melanin. These compounds often are used topically at concentrations of 10% to 40%. A study by Amer and Metwalli11 found that topical liquiritin produced a reduction of pigmentary intensity, with 80% of patients showing an excellent response, which was described as no difference between the previously pigmented area and the normal skin surrounding it.
Aloesin—Aloesin is a low-molecular-weight glycoprotein found in aloe vera plants. Its mechanism of action includes competitive inhibition of the dihydroxyphenylalanine oxidation site, resulting in the inhibition of tyrosinase.12 It often is combined with arbutin for an enhanced lightening effect.
Niacinamide—Niacinamide is a form of vitamin B3 that works by suppressing the transfer of melanosomes to keratinocytes.13 In addition to its skin lightening effects, it also is photoprotective and antimicrobial, and its tolerability and safety have led to its inclusion in many cosmeceutical and prescription products.14
Ascorbic Acid—Ascorbic acid affects the monopherase activity of tyrosinase, thus reducing the synthesis of melanin. It also serves as an antioxidant in the skin by preventing the production of free radicals that can induce melanogenesis.15 Although it tends to be well tolerated with a low adverse effect profile, its relative instability and varying permeability can present a challenge. It is less effective as a monotherapy, so it often is combined with other lightening ingredients for greater efficacy.
Corticosteroids—Topical corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory and impact melanogenesis, though the mechanism of action of the latter has not been fully elucidated.16,17 Low- to mid-potency topical steroids often are used in conjunction with skin lightening products to diminish irritation and decrease inflammation.18 However, prolonged use of corticosteroids can lead to cutaneous adverse effects such as striae, hypopigmentation, and acne, as well as systemic side effects if there is sufficient absorption over time.
Soybean Extracts—Soybean extracts contain serine protease inhibitors that reduce the transfer of melanosomes into keratinocytes by inhibiting the PAR-2 (protease-activated receptor 2) pathway.19,20
Ellagic Acid—Ellagic acid is found in common plants such as eucalyptus and strawberry as well as green tea.21 It works as an antioxidant and decreases melanogenesis through inhibition of tyrosinase activity.
Paper Mulberry—Paper mulberry extract comes from the roots of the Broussonetia papyrifera tree and functions by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. It is widely used in South Africa and Europe.22
Resveratrol—Resveratrol is an ingredient extracted from Morus alba L and functions as an antimelanogentic agent by directly inhibiting tyrosinase as well as transcriptional and posttranscriptional processing of tyrosinase.23 It also holds antiproliferative, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties and has widely been used for antiaging and skin lightening purposes.24
Newer Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Silymarin—Silymarin (also known as milk thistle [Silybum marianum]), is a polyphenolic flavonoid that possesses anticarcinogenic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. It prevents melanin production in a dose-dependent manner by inhibiting levodopa (L-dopa) oxidation activity of tyrosinase and also reduces the expression of tyrosinase protein.25 In combination with vitamins C and E and hexylresorcinol, silymarin has been found to reduce the effects of photodamage, brighten skin, improve evenness and lines, as well as improve global facial appearance.26
Malassezin—Malassezin is an indole produced by Malessezia furfur yeast and has recently been investigated for melanogenesis suppression. Grimes et al27 assessed the efficacy of topical malassezin in 7 patients with facial hyperpigmentation applied twice daily for 14 weeks. Punch biopsies were taken at weeks 0, 8, 14, and 22. Biopsies from weeks 8 and 14 demonstrated reduced epidermal melanin compared to baseline in all participants; however, at 22 weeks, biopsies showed no difference in melanin content compared to baseline, indicating a temporary process induced by the malassezin.27 More clinical studies are needed to investigate this further.
N-acetyl-glucosamine—N-acetyl-glucosamine is an aminosaccharide that inhibits the glycosylation of tyrosinase as well as its function in melanogenesis.28 It is synthesized and included in topical products for wound healing, rhytides, moisturization, and pigmentation disorders.
Topical Tranexamic Acid—Tranexamic acid traditionally has been used orally for the treatment of menorrhagia but also has been found to be beneficial as a therapy for hyperpigmentation and erythema. Tranexamic acid interferes with plasmin activity, thus indirectly inhibiting melanogenesis while also inhibiting angiogenesis by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors.29 It also leads to an increase in the levels of β-endorphin and μ-opioid receptors as well as the expression of estrogen receptor β on the surface of mast cells.30 Its oral benefit led to the development of topical formulations, typically in 2% to 5% concentrations. It has proven particularly beneficial in the treatment of melasma due to its effects on improving pigmentation, erythema, and skin barrier function.31 Topical tranexamic acid has a relatively high safety profile, with minor side effects such as transient skin irritation and erythema being reported.32
Cysteamine—Cysteamine inhibits tyrosinase, peroxidase, and chelating copper ions necessary for melanogenesis. It has proven to be effective in treating melasma and chronic severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation when used in a 5% cream formulation.33,34 Lima et al35 were the first to compare the effects of topical cysteamine to HQ in the treatment of facial melasma. They found that the mean reduction in modified Melasma Area and Severity Index score was 24% for cysteamine and 41% for HQ after 60 days. There were no severe adverse effects with either treatment group.35
Final Thoughts
Hydroquinone remains the gold standard for treatment of hyperpigmentation; however, its side-effect profile and risk of ochronosis with long-term use has ushered in various other safe and effective skin lightening agents that can be used as monotherapies or in combination with other lightening agents. Many of these products also can be used effectively with procedural treatments such as chemical peels, lasers, and microneedling for enhanced absorption and efficacy. As newer agents are developed, additional well-designed studies will be needed to determine their safety and efficacy in different skin types as well as their role in the treatment of pigmentary disorders.
- Woolery-Lloyd H, Kammer JN. Treatment of hyperpigmentation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:171-175. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2011.06.004
- Desai SR. Hyperpigmentation therapy: a review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:13-17.
- Kligman AM, Willis I. A new formula for depigmenting human skin. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:40-48.
- Kligman AM, Grove GL, Hirose R, et al. Topical tretinoin for photoaged skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15(4 pt 2):836-859. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(86)70242-9
- Sharad J. Glycolic acid peel therapy—a current review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:281-288. doi:10.2147/CCID.S34029
- Nautiyal A, Wairkar S. Management of hyperpigmentation: current treatments and emerging therapies. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:1000-1014. doi:10.1111/pcmr.12986
- Saeedi M, Eslamifar M, Khezri K. Kojic acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:582-593. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.006
- Schulte BC, Wu W, Rosen T. Azelaic acid: evidence-based update on mechanism of action and clinical application. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:964-968.
- Akl EM. Liposomal azelaic acid 20% cream vs hydroquinone 4% cream as adjuvant to oral tranexamic acid in melasma: a comparative study [published online April 7, 2021]. J Dermatol Treat. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.1905765
- Holloway VL. Ethnic cosmetic products. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:743-749. doi:10.1016/s0733-8635(03)00089-5
- Amer M, Metwalli M. Topical liquiritin improves melasma. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:299-301. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00943.x
- Jones K, Hughes J, Hong M, et al. Modulation of melanogenesis by aloesin: a competitive inhibitor of tyrosinase. Pigment Cell Res. 2002;15:335-340. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2002.02014.x
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, et al. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:20-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04834.x
- Wohlrab J, Kreft D. Niacinamide—mechanisms of action and its topical use in dermatology. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;27:311-315. doi:10.1159/000359974
- Fitzpatrick RE, Rostan EF. Double-blind, half-face study comparing topical vitamin C and vehicle for rejuvenation of photodamage. Dermatol Surg. 2002;28:231-236. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.01129.x
- Mehta AB, Nadkarni NJ, Patil SP, et al. Topical corticosteroids in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016;82:371-378. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.178903
- Petit L, Piérard GE. Skin-lightening products revisited. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2003;25:169-181. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2003.00182.x
- Kanwar AJ, Dhar S, Kaur S. Treatment of melasma with potent topical corticosteroids. Dermatol Basel Switz. 1994;188:170. doi:10.1159/000247129
- Paine C, Sharlow E, Liebel F, et al. An alternative approach to depigmentation by soybean extracts via inhibition of the PAR-2 pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:587-595. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2001.01291.x
- Seiberg M, Paine C, Sharlow E, et al. Inhibition of melanosome transfer results in skin lightening. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:162-167. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00035.x
- Shimogaki H, Tanaka Y, Tamai H, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ellagic acid on melanogenesis inhibition. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2000;22:291-303. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2000.00023.x
- Rendon MI, Gaviria JI. Review of skin-lightening agents. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31(7 pt 2):886-889; discussion 889. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31736
- Na JI, Shin JW, Choi HR, et al. Resveratrol as a multifunctional topical hypopigmenting agent [published online February 22, 2019]. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:956. doi:10.3390/ijms20040956
- Ratz-Łyko A, Arct J. Resveratrol as an active ingredient for cosmetic and dermatological applications: a review. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2019;21:84-90. doi:10.1080/14764172.2018.1469767
- Choo SJ, Ryoo IJ, Kim YH, et al. Silymarin inhibits melanin synthesis in melanocyte cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009;61:663-667. doi:10.1211/jpp/61.05.0016
- Draelos ZD, Diaz I, Cohen A, et al. A novel skin brightening topical technology. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:3280-3285. doi:10.1111/jocd.13741
- Grimes P, Bhawan J, Howell M, et al. Histopathological changes induced by malassezin: a novel natural microbiome indole for treatment of facial hyperpigmentation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:141-145. doi:10.36849/jdd.6596
- Bissett DL. Glucosamine: an ingredient with skin and other benefits. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2006;5:309-315. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2006.00277.x
- Zhu JW, Ni YJ, Tong XY, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits angiogenesis and melanogenesis in vitro by targeting VEGF receptors. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17:903-911. doi:10.7150/ijms.44188
- Hiramoto K, Yamate Y, Sugiyama D, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits the plasma and non-irradiated skin markers of photoaging induced by long-term UVA eye irradiation in female mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:54-58. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.146
- da Silva Souza ID, Lampe L, Winn D. New topical tranexamic acid derivative for the improvement of hyperpigmentation and inflammation in the sun-damaged skin. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:561-565. doi:10.1111/jocd.13545
- Kim HJ, Moon SH, Cho SH, et al. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in melasma: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:776-781. doi:10.2340/00015555-2668
- Mathe N, Balogun M, Yoo J. A case report on the use of topical cysteamine 5% cream in the management of refractory postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) resistant to triple combination cream (hydroquinone, topical corticosteroids, and retinoids). J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:204-206. doi:10.1111/jocd.13755
- Mansouri P, Farshi S, Hashemi Z, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of cysteamine 5% cream in the treatment of epidermal melasma: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:209-217. doi:10.1111/bjd.13424
- Lima PB, Dias JAF, Cassiano D, et al. A comparative study of topical 5% cysteamine versus 4% hydroquinone in the treatment of facial melasma in women. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1531-1536. doi:10.1111/ijd.15146
Disorders of hyperpigmentation—melasma, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, lichen planus pigmentosus, erythema dyschromicum perstans, and pigmented contact dermatitis, among others—are common and challenging to treat. Although they can affect individuals of all skin types, they most commonly are seen in skin of color; in fact, dyspigmentation is one of the most common chief concerns for which individuals of color see a dermatologist.1,2
For many years, hydroquinone (HQ) was one of the main options available for use as a lightening agent. Although effective, it has the risk of causing irritant dermatitis, potentially leading to further dyspigmentation, in addition to the risk of ochronosis with long-term use. It remains an important and useful treatment for pigmentary disorders, but there are numerous other lightening agents that also can be considered in the treatment of disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Herein, we provide recommendations for traditional and newer non-HQ lightening agents that can be considered when treating disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Traditional Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Retinoids—Retinoids are topical vitamin A derivatives that have been used safely and effectively for decades in the treatment of pigmentary disorders. Retinoids have multiple mechanisms of action in improving pigmentation. In addition to impeding tyrosinase induction, they inhibit pigment transfer to keratinocytes and lead to accelerated pigment loss due to epidermal shedding.3 Over-the-counter formulations include retinol, retinaldehyde, and adapalene. Prescription formulations include tretinoin and tazarotene in different strengths and vehicle formulations.4
Glycolic Acid—Glycolic acid is derived from sugarcane and is considered an α-hydroxy acid that leads to rapid desquamation of pigmented keratinocytes.5 Glycolic acid can not only be used in chemical peels but also in topical creams. It is the most common α-hydroxy acid peel and is sometimes paired with HQ and other topical lightening agents for increased penetration. Glycolic acid peels are available in concentrations of 20% to 70% and can be used at various depths. When used incorrectly, it can cause redness, burning, and even skin discoloration; however, when used at the proper concentrations and depth according to Fitzpatrick skin type, there typically are no notable adverse effects, and clinical results are favorable.
Kojic Acid—Kojic acid is a natural metabolite derived from fungi and is widely used in Asian countries. It works by inhibiting the catecholase activity of tyrosinase6 and typically is available in concentrations of 1% to 4%. A study suggested that a concentration of 1% or less typically is safe to use for prolonged periods without adverse effects. Although not more effective than HQ as a monotherapy, kojic acid has been shown to haveimproved efficacy when used in combination with other lightening agents.7
Azelaic Acid—Azelaic acid works by inhibiting tyrosinase, mitochondrial oxidoreductase activation, and DNA synthesis. It preferentially targets heavily pigmented melanocytes and possesses anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.8 A 20% concentration of azelaic acid was compared to HQ 4% for the treatment of melasma, and results revealed that the liposomal form of azelaic acid was considerably more tolerable than HQ 4% and also more effective.9
Licorice Extracts—Licorice extracts have been safely used in several cosmeceutical skin lightening products.10 The main active compounds in licorice root are glabridin and liquiritin, which work to disperse melanin. These compounds often are used topically at concentrations of 10% to 40%. A study by Amer and Metwalli11 found that topical liquiritin produced a reduction of pigmentary intensity, with 80% of patients showing an excellent response, which was described as no difference between the previously pigmented area and the normal skin surrounding it.
Aloesin—Aloesin is a low-molecular-weight glycoprotein found in aloe vera plants. Its mechanism of action includes competitive inhibition of the dihydroxyphenylalanine oxidation site, resulting in the inhibition of tyrosinase.12 It often is combined with arbutin for an enhanced lightening effect.
Niacinamide—Niacinamide is a form of vitamin B3 that works by suppressing the transfer of melanosomes to keratinocytes.13 In addition to its skin lightening effects, it also is photoprotective and antimicrobial, and its tolerability and safety have led to its inclusion in many cosmeceutical and prescription products.14
Ascorbic Acid—Ascorbic acid affects the monopherase activity of tyrosinase, thus reducing the synthesis of melanin. It also serves as an antioxidant in the skin by preventing the production of free radicals that can induce melanogenesis.15 Although it tends to be well tolerated with a low adverse effect profile, its relative instability and varying permeability can present a challenge. It is less effective as a monotherapy, so it often is combined with other lightening ingredients for greater efficacy.
Corticosteroids—Topical corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory and impact melanogenesis, though the mechanism of action of the latter has not been fully elucidated.16,17 Low- to mid-potency topical steroids often are used in conjunction with skin lightening products to diminish irritation and decrease inflammation.18 However, prolonged use of corticosteroids can lead to cutaneous adverse effects such as striae, hypopigmentation, and acne, as well as systemic side effects if there is sufficient absorption over time.
Soybean Extracts—Soybean extracts contain serine protease inhibitors that reduce the transfer of melanosomes into keratinocytes by inhibiting the PAR-2 (protease-activated receptor 2) pathway.19,20
Ellagic Acid—Ellagic acid is found in common plants such as eucalyptus and strawberry as well as green tea.21 It works as an antioxidant and decreases melanogenesis through inhibition of tyrosinase activity.
Paper Mulberry—Paper mulberry extract comes from the roots of the Broussonetia papyrifera tree and functions by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. It is widely used in South Africa and Europe.22
Resveratrol—Resveratrol is an ingredient extracted from Morus alba L and functions as an antimelanogentic agent by directly inhibiting tyrosinase as well as transcriptional and posttranscriptional processing of tyrosinase.23 It also holds antiproliferative, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties and has widely been used for antiaging and skin lightening purposes.24
Newer Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Silymarin—Silymarin (also known as milk thistle [Silybum marianum]), is a polyphenolic flavonoid that possesses anticarcinogenic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. It prevents melanin production in a dose-dependent manner by inhibiting levodopa (L-dopa) oxidation activity of tyrosinase and also reduces the expression of tyrosinase protein.25 In combination with vitamins C and E and hexylresorcinol, silymarin has been found to reduce the effects of photodamage, brighten skin, improve evenness and lines, as well as improve global facial appearance.26
Malassezin—Malassezin is an indole produced by Malessezia furfur yeast and has recently been investigated for melanogenesis suppression. Grimes et al27 assessed the efficacy of topical malassezin in 7 patients with facial hyperpigmentation applied twice daily for 14 weeks. Punch biopsies were taken at weeks 0, 8, 14, and 22. Biopsies from weeks 8 and 14 demonstrated reduced epidermal melanin compared to baseline in all participants; however, at 22 weeks, biopsies showed no difference in melanin content compared to baseline, indicating a temporary process induced by the malassezin.27 More clinical studies are needed to investigate this further.
N-acetyl-glucosamine—N-acetyl-glucosamine is an aminosaccharide that inhibits the glycosylation of tyrosinase as well as its function in melanogenesis.28 It is synthesized and included in topical products for wound healing, rhytides, moisturization, and pigmentation disorders.
Topical Tranexamic Acid—Tranexamic acid traditionally has been used orally for the treatment of menorrhagia but also has been found to be beneficial as a therapy for hyperpigmentation and erythema. Tranexamic acid interferes with plasmin activity, thus indirectly inhibiting melanogenesis while also inhibiting angiogenesis by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors.29 It also leads to an increase in the levels of β-endorphin and μ-opioid receptors as well as the expression of estrogen receptor β on the surface of mast cells.30 Its oral benefit led to the development of topical formulations, typically in 2% to 5% concentrations. It has proven particularly beneficial in the treatment of melasma due to its effects on improving pigmentation, erythema, and skin barrier function.31 Topical tranexamic acid has a relatively high safety profile, with minor side effects such as transient skin irritation and erythema being reported.32
Cysteamine—Cysteamine inhibits tyrosinase, peroxidase, and chelating copper ions necessary for melanogenesis. It has proven to be effective in treating melasma and chronic severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation when used in a 5% cream formulation.33,34 Lima et al35 were the first to compare the effects of topical cysteamine to HQ in the treatment of facial melasma. They found that the mean reduction in modified Melasma Area and Severity Index score was 24% for cysteamine and 41% for HQ after 60 days. There were no severe adverse effects with either treatment group.35
Final Thoughts
Hydroquinone remains the gold standard for treatment of hyperpigmentation; however, its side-effect profile and risk of ochronosis with long-term use has ushered in various other safe and effective skin lightening agents that can be used as monotherapies or in combination with other lightening agents. Many of these products also can be used effectively with procedural treatments such as chemical peels, lasers, and microneedling for enhanced absorption and efficacy. As newer agents are developed, additional well-designed studies will be needed to determine their safety and efficacy in different skin types as well as their role in the treatment of pigmentary disorders.
Disorders of hyperpigmentation—melasma, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, lichen planus pigmentosus, erythema dyschromicum perstans, and pigmented contact dermatitis, among others—are common and challenging to treat. Although they can affect individuals of all skin types, they most commonly are seen in skin of color; in fact, dyspigmentation is one of the most common chief concerns for which individuals of color see a dermatologist.1,2
For many years, hydroquinone (HQ) was one of the main options available for use as a lightening agent. Although effective, it has the risk of causing irritant dermatitis, potentially leading to further dyspigmentation, in addition to the risk of ochronosis with long-term use. It remains an important and useful treatment for pigmentary disorders, but there are numerous other lightening agents that also can be considered in the treatment of disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Herein, we provide recommendations for traditional and newer non-HQ lightening agents that can be considered when treating disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Traditional Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Retinoids—Retinoids are topical vitamin A derivatives that have been used safely and effectively for decades in the treatment of pigmentary disorders. Retinoids have multiple mechanisms of action in improving pigmentation. In addition to impeding tyrosinase induction, they inhibit pigment transfer to keratinocytes and lead to accelerated pigment loss due to epidermal shedding.3 Over-the-counter formulations include retinol, retinaldehyde, and adapalene. Prescription formulations include tretinoin and tazarotene in different strengths and vehicle formulations.4
Glycolic Acid—Glycolic acid is derived from sugarcane and is considered an α-hydroxy acid that leads to rapid desquamation of pigmented keratinocytes.5 Glycolic acid can not only be used in chemical peels but also in topical creams. It is the most common α-hydroxy acid peel and is sometimes paired with HQ and other topical lightening agents for increased penetration. Glycolic acid peels are available in concentrations of 20% to 70% and can be used at various depths. When used incorrectly, it can cause redness, burning, and even skin discoloration; however, when used at the proper concentrations and depth according to Fitzpatrick skin type, there typically are no notable adverse effects, and clinical results are favorable.
Kojic Acid—Kojic acid is a natural metabolite derived from fungi and is widely used in Asian countries. It works by inhibiting the catecholase activity of tyrosinase6 and typically is available in concentrations of 1% to 4%. A study suggested that a concentration of 1% or less typically is safe to use for prolonged periods without adverse effects. Although not more effective than HQ as a monotherapy, kojic acid has been shown to haveimproved efficacy when used in combination with other lightening agents.7
Azelaic Acid—Azelaic acid works by inhibiting tyrosinase, mitochondrial oxidoreductase activation, and DNA synthesis. It preferentially targets heavily pigmented melanocytes and possesses anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.8 A 20% concentration of azelaic acid was compared to HQ 4% for the treatment of melasma, and results revealed that the liposomal form of azelaic acid was considerably more tolerable than HQ 4% and also more effective.9
Licorice Extracts—Licorice extracts have been safely used in several cosmeceutical skin lightening products.10 The main active compounds in licorice root are glabridin and liquiritin, which work to disperse melanin. These compounds often are used topically at concentrations of 10% to 40%. A study by Amer and Metwalli11 found that topical liquiritin produced a reduction of pigmentary intensity, with 80% of patients showing an excellent response, which was described as no difference between the previously pigmented area and the normal skin surrounding it.
Aloesin—Aloesin is a low-molecular-weight glycoprotein found in aloe vera plants. Its mechanism of action includes competitive inhibition of the dihydroxyphenylalanine oxidation site, resulting in the inhibition of tyrosinase.12 It often is combined with arbutin for an enhanced lightening effect.
Niacinamide—Niacinamide is a form of vitamin B3 that works by suppressing the transfer of melanosomes to keratinocytes.13 In addition to its skin lightening effects, it also is photoprotective and antimicrobial, and its tolerability and safety have led to its inclusion in many cosmeceutical and prescription products.14
Ascorbic Acid—Ascorbic acid affects the monopherase activity of tyrosinase, thus reducing the synthesis of melanin. It also serves as an antioxidant in the skin by preventing the production of free radicals that can induce melanogenesis.15 Although it tends to be well tolerated with a low adverse effect profile, its relative instability and varying permeability can present a challenge. It is less effective as a monotherapy, so it often is combined with other lightening ingredients for greater efficacy.
Corticosteroids—Topical corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory and impact melanogenesis, though the mechanism of action of the latter has not been fully elucidated.16,17 Low- to mid-potency topical steroids often are used in conjunction with skin lightening products to diminish irritation and decrease inflammation.18 However, prolonged use of corticosteroids can lead to cutaneous adverse effects such as striae, hypopigmentation, and acne, as well as systemic side effects if there is sufficient absorption over time.
Soybean Extracts—Soybean extracts contain serine protease inhibitors that reduce the transfer of melanosomes into keratinocytes by inhibiting the PAR-2 (protease-activated receptor 2) pathway.19,20
Ellagic Acid—Ellagic acid is found in common plants such as eucalyptus and strawberry as well as green tea.21 It works as an antioxidant and decreases melanogenesis through inhibition of tyrosinase activity.
Paper Mulberry—Paper mulberry extract comes from the roots of the Broussonetia papyrifera tree and functions by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. It is widely used in South Africa and Europe.22
Resveratrol—Resveratrol is an ingredient extracted from Morus alba L and functions as an antimelanogentic agent by directly inhibiting tyrosinase as well as transcriptional and posttranscriptional processing of tyrosinase.23 It also holds antiproliferative, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties and has widely been used for antiaging and skin lightening purposes.24
Newer Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Silymarin—Silymarin (also known as milk thistle [Silybum marianum]), is a polyphenolic flavonoid that possesses anticarcinogenic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. It prevents melanin production in a dose-dependent manner by inhibiting levodopa (L-dopa) oxidation activity of tyrosinase and also reduces the expression of tyrosinase protein.25 In combination with vitamins C and E and hexylresorcinol, silymarin has been found to reduce the effects of photodamage, brighten skin, improve evenness and lines, as well as improve global facial appearance.26
Malassezin—Malassezin is an indole produced by Malessezia furfur yeast and has recently been investigated for melanogenesis suppression. Grimes et al27 assessed the efficacy of topical malassezin in 7 patients with facial hyperpigmentation applied twice daily for 14 weeks. Punch biopsies were taken at weeks 0, 8, 14, and 22. Biopsies from weeks 8 and 14 demonstrated reduced epidermal melanin compared to baseline in all participants; however, at 22 weeks, biopsies showed no difference in melanin content compared to baseline, indicating a temporary process induced by the malassezin.27 More clinical studies are needed to investigate this further.
N-acetyl-glucosamine—N-acetyl-glucosamine is an aminosaccharide that inhibits the glycosylation of tyrosinase as well as its function in melanogenesis.28 It is synthesized and included in topical products for wound healing, rhytides, moisturization, and pigmentation disorders.
Topical Tranexamic Acid—Tranexamic acid traditionally has been used orally for the treatment of menorrhagia but also has been found to be beneficial as a therapy for hyperpigmentation and erythema. Tranexamic acid interferes with plasmin activity, thus indirectly inhibiting melanogenesis while also inhibiting angiogenesis by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors.29 It also leads to an increase in the levels of β-endorphin and μ-opioid receptors as well as the expression of estrogen receptor β on the surface of mast cells.30 Its oral benefit led to the development of topical formulations, typically in 2% to 5% concentrations. It has proven particularly beneficial in the treatment of melasma due to its effects on improving pigmentation, erythema, and skin barrier function.31 Topical tranexamic acid has a relatively high safety profile, with minor side effects such as transient skin irritation and erythema being reported.32
Cysteamine—Cysteamine inhibits tyrosinase, peroxidase, and chelating copper ions necessary for melanogenesis. It has proven to be effective in treating melasma and chronic severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation when used in a 5% cream formulation.33,34 Lima et al35 were the first to compare the effects of topical cysteamine to HQ in the treatment of facial melasma. They found that the mean reduction in modified Melasma Area and Severity Index score was 24% for cysteamine and 41% for HQ after 60 days. There were no severe adverse effects with either treatment group.35
Final Thoughts
Hydroquinone remains the gold standard for treatment of hyperpigmentation; however, its side-effect profile and risk of ochronosis with long-term use has ushered in various other safe and effective skin lightening agents that can be used as monotherapies or in combination with other lightening agents. Many of these products also can be used effectively with procedural treatments such as chemical peels, lasers, and microneedling for enhanced absorption and efficacy. As newer agents are developed, additional well-designed studies will be needed to determine their safety and efficacy in different skin types as well as their role in the treatment of pigmentary disorders.
- Woolery-Lloyd H, Kammer JN. Treatment of hyperpigmentation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:171-175. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2011.06.004
- Desai SR. Hyperpigmentation therapy: a review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:13-17.
- Kligman AM, Willis I. A new formula for depigmenting human skin. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:40-48.
- Kligman AM, Grove GL, Hirose R, et al. Topical tretinoin for photoaged skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15(4 pt 2):836-859. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(86)70242-9
- Sharad J. Glycolic acid peel therapy—a current review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:281-288. doi:10.2147/CCID.S34029
- Nautiyal A, Wairkar S. Management of hyperpigmentation: current treatments and emerging therapies. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:1000-1014. doi:10.1111/pcmr.12986
- Saeedi M, Eslamifar M, Khezri K. Kojic acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:582-593. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.006
- Schulte BC, Wu W, Rosen T. Azelaic acid: evidence-based update on mechanism of action and clinical application. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:964-968.
- Akl EM. Liposomal azelaic acid 20% cream vs hydroquinone 4% cream as adjuvant to oral tranexamic acid in melasma: a comparative study [published online April 7, 2021]. J Dermatol Treat. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.1905765
- Holloway VL. Ethnic cosmetic products. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:743-749. doi:10.1016/s0733-8635(03)00089-5
- Amer M, Metwalli M. Topical liquiritin improves melasma. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:299-301. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00943.x
- Jones K, Hughes J, Hong M, et al. Modulation of melanogenesis by aloesin: a competitive inhibitor of tyrosinase. Pigment Cell Res. 2002;15:335-340. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2002.02014.x
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, et al. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:20-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04834.x
- Wohlrab J, Kreft D. Niacinamide—mechanisms of action and its topical use in dermatology. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;27:311-315. doi:10.1159/000359974
- Fitzpatrick RE, Rostan EF. Double-blind, half-face study comparing topical vitamin C and vehicle for rejuvenation of photodamage. Dermatol Surg. 2002;28:231-236. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.01129.x
- Mehta AB, Nadkarni NJ, Patil SP, et al. Topical corticosteroids in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016;82:371-378. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.178903
- Petit L, Piérard GE. Skin-lightening products revisited. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2003;25:169-181. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2003.00182.x
- Kanwar AJ, Dhar S, Kaur S. Treatment of melasma with potent topical corticosteroids. Dermatol Basel Switz. 1994;188:170. doi:10.1159/000247129
- Paine C, Sharlow E, Liebel F, et al. An alternative approach to depigmentation by soybean extracts via inhibition of the PAR-2 pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:587-595. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2001.01291.x
- Seiberg M, Paine C, Sharlow E, et al. Inhibition of melanosome transfer results in skin lightening. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:162-167. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00035.x
- Shimogaki H, Tanaka Y, Tamai H, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ellagic acid on melanogenesis inhibition. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2000;22:291-303. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2000.00023.x
- Rendon MI, Gaviria JI. Review of skin-lightening agents. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31(7 pt 2):886-889; discussion 889. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31736
- Na JI, Shin JW, Choi HR, et al. Resveratrol as a multifunctional topical hypopigmenting agent [published online February 22, 2019]. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:956. doi:10.3390/ijms20040956
- Ratz-Łyko A, Arct J. Resveratrol as an active ingredient for cosmetic and dermatological applications: a review. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2019;21:84-90. doi:10.1080/14764172.2018.1469767
- Choo SJ, Ryoo IJ, Kim YH, et al. Silymarin inhibits melanin synthesis in melanocyte cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009;61:663-667. doi:10.1211/jpp/61.05.0016
- Draelos ZD, Diaz I, Cohen A, et al. A novel skin brightening topical technology. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:3280-3285. doi:10.1111/jocd.13741
- Grimes P, Bhawan J, Howell M, et al. Histopathological changes induced by malassezin: a novel natural microbiome indole for treatment of facial hyperpigmentation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:141-145. doi:10.36849/jdd.6596
- Bissett DL. Glucosamine: an ingredient with skin and other benefits. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2006;5:309-315. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2006.00277.x
- Zhu JW, Ni YJ, Tong XY, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits angiogenesis and melanogenesis in vitro by targeting VEGF receptors. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17:903-911. doi:10.7150/ijms.44188
- Hiramoto K, Yamate Y, Sugiyama D, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits the plasma and non-irradiated skin markers of photoaging induced by long-term UVA eye irradiation in female mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:54-58. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.146
- da Silva Souza ID, Lampe L, Winn D. New topical tranexamic acid derivative for the improvement of hyperpigmentation and inflammation in the sun-damaged skin. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:561-565. doi:10.1111/jocd.13545
- Kim HJ, Moon SH, Cho SH, et al. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in melasma: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:776-781. doi:10.2340/00015555-2668
- Mathe N, Balogun M, Yoo J. A case report on the use of topical cysteamine 5% cream in the management of refractory postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) resistant to triple combination cream (hydroquinone, topical corticosteroids, and retinoids). J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:204-206. doi:10.1111/jocd.13755
- Mansouri P, Farshi S, Hashemi Z, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of cysteamine 5% cream in the treatment of epidermal melasma: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:209-217. doi:10.1111/bjd.13424
- Lima PB, Dias JAF, Cassiano D, et al. A comparative study of topical 5% cysteamine versus 4% hydroquinone in the treatment of facial melasma in women. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1531-1536. doi:10.1111/ijd.15146
- Woolery-Lloyd H, Kammer JN. Treatment of hyperpigmentation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:171-175. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2011.06.004
- Desai SR. Hyperpigmentation therapy: a review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:13-17.
- Kligman AM, Willis I. A new formula for depigmenting human skin. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:40-48.
- Kligman AM, Grove GL, Hirose R, et al. Topical tretinoin for photoaged skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15(4 pt 2):836-859. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(86)70242-9
- Sharad J. Glycolic acid peel therapy—a current review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:281-288. doi:10.2147/CCID.S34029
- Nautiyal A, Wairkar S. Management of hyperpigmentation: current treatments and emerging therapies. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:1000-1014. doi:10.1111/pcmr.12986
- Saeedi M, Eslamifar M, Khezri K. Kojic acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:582-593. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.006
- Schulte BC, Wu W, Rosen T. Azelaic acid: evidence-based update on mechanism of action and clinical application. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:964-968.
- Akl EM. Liposomal azelaic acid 20% cream vs hydroquinone 4% cream as adjuvant to oral tranexamic acid in melasma: a comparative study [published online April 7, 2021]. J Dermatol Treat. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.1905765
- Holloway VL. Ethnic cosmetic products. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:743-749. doi:10.1016/s0733-8635(03)00089-5
- Amer M, Metwalli M. Topical liquiritin improves melasma. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:299-301. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00943.x
- Jones K, Hughes J, Hong M, et al. Modulation of melanogenesis by aloesin: a competitive inhibitor of tyrosinase. Pigment Cell Res. 2002;15:335-340. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2002.02014.x
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, et al. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:20-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04834.x
- Wohlrab J, Kreft D. Niacinamide—mechanisms of action and its topical use in dermatology. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;27:311-315. doi:10.1159/000359974
- Fitzpatrick RE, Rostan EF. Double-blind, half-face study comparing topical vitamin C and vehicle for rejuvenation of photodamage. Dermatol Surg. 2002;28:231-236. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.01129.x
- Mehta AB, Nadkarni NJ, Patil SP, et al. Topical corticosteroids in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016;82:371-378. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.178903
- Petit L, Piérard GE. Skin-lightening products revisited. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2003;25:169-181. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2003.00182.x
- Kanwar AJ, Dhar S, Kaur S. Treatment of melasma with potent topical corticosteroids. Dermatol Basel Switz. 1994;188:170. doi:10.1159/000247129
- Paine C, Sharlow E, Liebel F, et al. An alternative approach to depigmentation by soybean extracts via inhibition of the PAR-2 pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:587-595. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2001.01291.x
- Seiberg M, Paine C, Sharlow E, et al. Inhibition of melanosome transfer results in skin lightening. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:162-167. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00035.x
- Shimogaki H, Tanaka Y, Tamai H, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ellagic acid on melanogenesis inhibition. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2000;22:291-303. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2000.00023.x
- Rendon MI, Gaviria JI. Review of skin-lightening agents. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31(7 pt 2):886-889; discussion 889. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31736
- Na JI, Shin JW, Choi HR, et al. Resveratrol as a multifunctional topical hypopigmenting agent [published online February 22, 2019]. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:956. doi:10.3390/ijms20040956
- Ratz-Łyko A, Arct J. Resveratrol as an active ingredient for cosmetic and dermatological applications: a review. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2019;21:84-90. doi:10.1080/14764172.2018.1469767
- Choo SJ, Ryoo IJ, Kim YH, et al. Silymarin inhibits melanin synthesis in melanocyte cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009;61:663-667. doi:10.1211/jpp/61.05.0016
- Draelos ZD, Diaz I, Cohen A, et al. A novel skin brightening topical technology. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:3280-3285. doi:10.1111/jocd.13741
- Grimes P, Bhawan J, Howell M, et al. Histopathological changes induced by malassezin: a novel natural microbiome indole for treatment of facial hyperpigmentation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:141-145. doi:10.36849/jdd.6596
- Bissett DL. Glucosamine: an ingredient with skin and other benefits. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2006;5:309-315. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2006.00277.x
- Zhu JW, Ni YJ, Tong XY, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits angiogenesis and melanogenesis in vitro by targeting VEGF receptors. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17:903-911. doi:10.7150/ijms.44188
- Hiramoto K, Yamate Y, Sugiyama D, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits the plasma and non-irradiated skin markers of photoaging induced by long-term UVA eye irradiation in female mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:54-58. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.146
- da Silva Souza ID, Lampe L, Winn D. New topical tranexamic acid derivative for the improvement of hyperpigmentation and inflammation in the sun-damaged skin. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:561-565. doi:10.1111/jocd.13545
- Kim HJ, Moon SH, Cho SH, et al. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in melasma: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:776-781. doi:10.2340/00015555-2668
- Mathe N, Balogun M, Yoo J. A case report on the use of topical cysteamine 5% cream in the management of refractory postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) resistant to triple combination cream (hydroquinone, topical corticosteroids, and retinoids). J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:204-206. doi:10.1111/jocd.13755
- Mansouri P, Farshi S, Hashemi Z, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of cysteamine 5% cream in the treatment of epidermal melasma: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:209-217. doi:10.1111/bjd.13424
- Lima PB, Dias JAF, Cassiano D, et al. A comparative study of topical 5% cysteamine versus 4% hydroquinone in the treatment of facial melasma in women. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1531-1536. doi:10.1111/ijd.15146
Pending further study, caution recommended in treating vitiligo patients with lasers, IPL
SAN DIEGO – The .
Those are the preliminary conclusions from a systematic review and survey of experts that Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, presented during a clinical abstract session at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
According to Dr. Wolkerstorfer, a dermatologist at Amsterdam University Medical Center, clinicians are reluctant to perform laser/intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments in patients with vitiligo because of the absence of clear guidelines, so he and his colleagues set out to investigate the risks of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo in patients with vitiligo and to seek out international consensus on recommendations from experts. “There is hardly any literature about it and certainly no guidelines,” he pointed out.
Dr. Wolkerstorfer and his colleagues designed three consecutive studies: A systematic review of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo; an international survey among 14 vitiligo experts from 10 countries about the occurrence of laser‐induced vitiligo, and a Delphi technique aimed at establishing a broad consensus about recommendations for safe use of lasers in vitiligo patients. At the time of the meeting, the Delphi process was still being carried out, so he did not discuss that study.
For the systematic review, the researchers found 11,073 unique hits on PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL using the terms “vitiligo,” “depigmentation,” “hypopigmentation,” and “leukoderma.” Only six case reports of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo were included in the final analysis. Of these, three had de novo vitiligo and three had vitiligo/halo nevi. These cases included two that occurred following treatment of port wine stains with the 585-nm laser; one that occurred following treatment of dyspigmentation with IPL; one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 1,064-nm laser, one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 755-nm laser, and one case that occurred following treatment of melasma with the ablative laser.
For the international survey of 14 experts from 10 countries, respondents said they had 10,670 new face-to-face vitiligo consultations in the past year. They reported that 30 of the vitiligo cases (0.3%) were likely caused by laser/IPL. Of these 30 cases, 18 (60%) had de novo vitiligo.
Of these cases, vitiligo occurred most frequently after laser hair reduction (47%), followed by use of the fractional laser (17%), and the ablative laser (13%). The interval between laser/IPL treatment and onset of vitiligo was 0-4 weeks in 27% of cases and 4-12 weeks in 57% of cases. Direct complications such as blistering, crusting, and erosions occurred in 57% of cases.
“Our conclusion is that laser and IPL-induced vitiligo is a rare phenomenon, and it often affects patients without prior vitiligo, which was really a surprise to us,” Dr. Wolkerstorfer said. “Complications seem to increase the risk,” he added.
“Despite the apparently low risk, we recommend caution [in patients with vitiligo], especially with aggressive laser procedures,” he said. “We recommend using conservative settings, not to treat active vitiligo patients ... and to perform test spots prior to treating large areas.” But he characterized this recommendation as “totally preliminary” pending results of the Delphi technique aimed at building consensus about laser/IPL treatments in vitiligo.
In an interview at the meeting, one of the session moderators, Oge Onwudiwe, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Alexandria, Va., said that as clinicians await results of the study’s Delphi consensus, current use of lasers and IPL in patients with vitiligo “is based on your clinical judgment and whether the vitiligo is active or inactive. If the patient has vitiligo and you’re doing laser hair removal in the armpit, they may get active lesions in that area, but they can cover it. So, they may take that as a ‘win’ with the risk. But if it can erupt in other areas, that’s a risk they must be willing to take.”
Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received grant or research funding from Lumenis, Novartis, and Avita Medical. He is an advisory board member for Incyte. Dr. Onwudiwe reported having no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – The .
Those are the preliminary conclusions from a systematic review and survey of experts that Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, presented during a clinical abstract session at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
According to Dr. Wolkerstorfer, a dermatologist at Amsterdam University Medical Center, clinicians are reluctant to perform laser/intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments in patients with vitiligo because of the absence of clear guidelines, so he and his colleagues set out to investigate the risks of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo in patients with vitiligo and to seek out international consensus on recommendations from experts. “There is hardly any literature about it and certainly no guidelines,” he pointed out.
Dr. Wolkerstorfer and his colleagues designed three consecutive studies: A systematic review of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo; an international survey among 14 vitiligo experts from 10 countries about the occurrence of laser‐induced vitiligo, and a Delphi technique aimed at establishing a broad consensus about recommendations for safe use of lasers in vitiligo patients. At the time of the meeting, the Delphi process was still being carried out, so he did not discuss that study.
For the systematic review, the researchers found 11,073 unique hits on PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL using the terms “vitiligo,” “depigmentation,” “hypopigmentation,” and “leukoderma.” Only six case reports of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo were included in the final analysis. Of these, three had de novo vitiligo and three had vitiligo/halo nevi. These cases included two that occurred following treatment of port wine stains with the 585-nm laser; one that occurred following treatment of dyspigmentation with IPL; one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 1,064-nm laser, one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 755-nm laser, and one case that occurred following treatment of melasma with the ablative laser.
For the international survey of 14 experts from 10 countries, respondents said they had 10,670 new face-to-face vitiligo consultations in the past year. They reported that 30 of the vitiligo cases (0.3%) were likely caused by laser/IPL. Of these 30 cases, 18 (60%) had de novo vitiligo.
Of these cases, vitiligo occurred most frequently after laser hair reduction (47%), followed by use of the fractional laser (17%), and the ablative laser (13%). The interval between laser/IPL treatment and onset of vitiligo was 0-4 weeks in 27% of cases and 4-12 weeks in 57% of cases. Direct complications such as blistering, crusting, and erosions occurred in 57% of cases.
“Our conclusion is that laser and IPL-induced vitiligo is a rare phenomenon, and it often affects patients without prior vitiligo, which was really a surprise to us,” Dr. Wolkerstorfer said. “Complications seem to increase the risk,” he added.
“Despite the apparently low risk, we recommend caution [in patients with vitiligo], especially with aggressive laser procedures,” he said. “We recommend using conservative settings, not to treat active vitiligo patients ... and to perform test spots prior to treating large areas.” But he characterized this recommendation as “totally preliminary” pending results of the Delphi technique aimed at building consensus about laser/IPL treatments in vitiligo.
In an interview at the meeting, one of the session moderators, Oge Onwudiwe, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Alexandria, Va., said that as clinicians await results of the study’s Delphi consensus, current use of lasers and IPL in patients with vitiligo “is based on your clinical judgment and whether the vitiligo is active or inactive. If the patient has vitiligo and you’re doing laser hair removal in the armpit, they may get active lesions in that area, but they can cover it. So, they may take that as a ‘win’ with the risk. But if it can erupt in other areas, that’s a risk they must be willing to take.”
Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received grant or research funding from Lumenis, Novartis, and Avita Medical. He is an advisory board member for Incyte. Dr. Onwudiwe reported having no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – The .
Those are the preliminary conclusions from a systematic review and survey of experts that Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, presented during a clinical abstract session at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
According to Dr. Wolkerstorfer, a dermatologist at Amsterdam University Medical Center, clinicians are reluctant to perform laser/intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments in patients with vitiligo because of the absence of clear guidelines, so he and his colleagues set out to investigate the risks of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo in patients with vitiligo and to seek out international consensus on recommendations from experts. “There is hardly any literature about it and certainly no guidelines,” he pointed out.
Dr. Wolkerstorfer and his colleagues designed three consecutive studies: A systematic review of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo; an international survey among 14 vitiligo experts from 10 countries about the occurrence of laser‐induced vitiligo, and a Delphi technique aimed at establishing a broad consensus about recommendations for safe use of lasers in vitiligo patients. At the time of the meeting, the Delphi process was still being carried out, so he did not discuss that study.
For the systematic review, the researchers found 11,073 unique hits on PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL using the terms “vitiligo,” “depigmentation,” “hypopigmentation,” and “leukoderma.” Only six case reports of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo were included in the final analysis. Of these, three had de novo vitiligo and three had vitiligo/halo nevi. These cases included two that occurred following treatment of port wine stains with the 585-nm laser; one that occurred following treatment of dyspigmentation with IPL; one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 1,064-nm laser, one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 755-nm laser, and one case that occurred following treatment of melasma with the ablative laser.
For the international survey of 14 experts from 10 countries, respondents said they had 10,670 new face-to-face vitiligo consultations in the past year. They reported that 30 of the vitiligo cases (0.3%) were likely caused by laser/IPL. Of these 30 cases, 18 (60%) had de novo vitiligo.
Of these cases, vitiligo occurred most frequently after laser hair reduction (47%), followed by use of the fractional laser (17%), and the ablative laser (13%). The interval between laser/IPL treatment and onset of vitiligo was 0-4 weeks in 27% of cases and 4-12 weeks in 57% of cases. Direct complications such as blistering, crusting, and erosions occurred in 57% of cases.
“Our conclusion is that laser and IPL-induced vitiligo is a rare phenomenon, and it often affects patients without prior vitiligo, which was really a surprise to us,” Dr. Wolkerstorfer said. “Complications seem to increase the risk,” he added.
“Despite the apparently low risk, we recommend caution [in patients with vitiligo], especially with aggressive laser procedures,” he said. “We recommend using conservative settings, not to treat active vitiligo patients ... and to perform test spots prior to treating large areas.” But he characterized this recommendation as “totally preliminary” pending results of the Delphi technique aimed at building consensus about laser/IPL treatments in vitiligo.
In an interview at the meeting, one of the session moderators, Oge Onwudiwe, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Alexandria, Va., said that as clinicians await results of the study’s Delphi consensus, current use of lasers and IPL in patients with vitiligo “is based on your clinical judgment and whether the vitiligo is active or inactive. If the patient has vitiligo and you’re doing laser hair removal in the armpit, they may get active lesions in that area, but they can cover it. So, they may take that as a ‘win’ with the risk. But if it can erupt in other areas, that’s a risk they must be willing to take.”
Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received grant or research funding from Lumenis, Novartis, and Avita Medical. He is an advisory board member for Incyte. Dr. Onwudiwe reported having no disclosures.
AT ASLMS 2022
PIH in patients with dark skin responds to laser treatment: Small case series
SAN DIEGO – , results from a small retrospective case series suggest.
“Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a leading chief of complaint of many skin of color persons seeking a dermatologist,” Elizabeth J. Kream, MD, told this news organization in advance of the annual conference of American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “I describe PIH to patients as the ‘ashes after a fire is extinguished.’ It’s the stubborn brown to gray/black spots that persist after conditions like acne and folliculitis, but it can be caused by any insult to the skin including external injury. In fact, there’s a risk of inciting PIH with lasers and energy-based devices and this risk is greater in skin of color given the greater melanin content. Unfortunately, we see patients present after visiting a med spa who were treated with the wrong devices and/or the wrong settings and they have disfiguring scarring and/or dyspigmentation.”
During an abstract session at the meeting, Dr. Kream, a dermatology resident at the University of Illinois at Chicago, discussed three patients with recalcitrant PIH and Fitzpatrick skin phototype V and VI who were treated in San Diego with a combination of topical and laser therapies. She presented the case series on behalf of coauthors Monica Boen, MD and Douglas C. Wu, MD, dermatologists who practice in San Diego.
The first patient was a 37-year-old Black female who presented for evaluation of longstanding hyperpigmentation on the face and neck determined to be PIH secondary to folliculitis on the chin and neck. She was started on 8% hydroquinone with kojic acid daily and received four treatments spaced 4-8 weeks apart with the 1,927-nm fractional nonablative diode laser. Laser settings were 5 mJ pulse energy and 5% coverage after eight passes. Triamcinolone 0.1% ointment was applied immediately after treatment and for 3 days following treatment, and the “patient experienced near complete resolution of PIH with no unexpected adverse events,” Dr. Kream said.
The second patient was a 20-year-old Black male who presented with a 3-month history of facial hyperpigmentation after suffering a laser-induced injury. He was started on a non-hydroquinone topical lightening agent and received five treatments spaced 2 weeks apart with a 1,927-nm fractional nonablative diode laser. The laser settings were 5 mJ pulse energy and 5% coverage after eight passes. The patient experienced 80%-90% resolution of his PIH with no unexpected adverse reactions.
The third patient in the series was a 39-year-old Black male who presented with a 6-month history of hyperpigmentation on his right shin and calf, secondary to minor occupational-related trauma. Treatment was initiated with a fractional 1,064-nm picosecond laser. The laser settings were 2.1 mJ per microbeam microwave pulse energy and a 450 picosecond pulse duration delivered at 2 Hz through a holographic beam splitter with a 6 x 6–mm spot size containing 101 microbeams, for an estimated coverage of 4% per pulse. Four passes were performed for each area. The endpoint was a mild erythema to several treated areas a few minutes following laser treatment. Postoperative care consisted of applying a non-hydroquinone topical lightening agent twice daily to the affected area for 1 month. Near-complete resolution of the PIH was achieved, with no unexpected adverse reactions.
“In our clinical experience, PIH can be treated with the combination of topical skin lighteners and low density, low fluence laser therapy in almost all skin types,” Dr. Kream said. “The rationale behind this combination is to treat and remove existing pigment with the laser therapy while minimizing and preventing any pigmentary recurrence with diligent topical therapy and photoprotection.”
It is important to identify the cause of PIH “because some cases are trickier than others,” such as a lichenoid process that deposits pigment “a little bit deeper into the dermis,” she said. “When selecting an appropriate laser modality for the treatment of PIH in skin types V and VI, it’s especially important to consider the mechanism of action, depth of penetration, degree of tissue damage, and the extent of disruption to the dermal-epidermal junction.”
Following the presentation, one of the session moderators, Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Amsterdam University Medical Center, the Netherlands, emphasized the importance of proper patient selection for laser treatment of PIH. “Not every patient with PIH is adapted to treatment with the laser,” Dr. Wolkerstorfer said. “I think it’s also important to choose stable PIH, meaning you often see patients with an underlying disorder who want to get rid of the pigment. They often believe that the laser is the solution, but it often isn’t.”
During a question-and-answer session, a meeting attendee pointed out that the study lacked a control area to compare the treatment results to. “This was a retrospective case series,” Dr. Kream replied. “I’d like to see more elegant studies in the future, with a control [area],” she said.
Dr. Kream reported having no financial disclosures, Dr. Boen has no disclosures, and Dr. Wu has conducted research for many pharmaceutical and device companies. Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received grant or research funding from Lumenis, Novartis, and Avita Medical, and is an advisory board member for Incyte.
SAN DIEGO – , results from a small retrospective case series suggest.
“Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a leading chief of complaint of many skin of color persons seeking a dermatologist,” Elizabeth J. Kream, MD, told this news organization in advance of the annual conference of American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “I describe PIH to patients as the ‘ashes after a fire is extinguished.’ It’s the stubborn brown to gray/black spots that persist after conditions like acne and folliculitis, but it can be caused by any insult to the skin including external injury. In fact, there’s a risk of inciting PIH with lasers and energy-based devices and this risk is greater in skin of color given the greater melanin content. Unfortunately, we see patients present after visiting a med spa who were treated with the wrong devices and/or the wrong settings and they have disfiguring scarring and/or dyspigmentation.”
During an abstract session at the meeting, Dr. Kream, a dermatology resident at the University of Illinois at Chicago, discussed three patients with recalcitrant PIH and Fitzpatrick skin phototype V and VI who were treated in San Diego with a combination of topical and laser therapies. She presented the case series on behalf of coauthors Monica Boen, MD and Douglas C. Wu, MD, dermatologists who practice in San Diego.
The first patient was a 37-year-old Black female who presented for evaluation of longstanding hyperpigmentation on the face and neck determined to be PIH secondary to folliculitis on the chin and neck. She was started on 8% hydroquinone with kojic acid daily and received four treatments spaced 4-8 weeks apart with the 1,927-nm fractional nonablative diode laser. Laser settings were 5 mJ pulse energy and 5% coverage after eight passes. Triamcinolone 0.1% ointment was applied immediately after treatment and for 3 days following treatment, and the “patient experienced near complete resolution of PIH with no unexpected adverse events,” Dr. Kream said.
The second patient was a 20-year-old Black male who presented with a 3-month history of facial hyperpigmentation after suffering a laser-induced injury. He was started on a non-hydroquinone topical lightening agent and received five treatments spaced 2 weeks apart with a 1,927-nm fractional nonablative diode laser. The laser settings were 5 mJ pulse energy and 5% coverage after eight passes. The patient experienced 80%-90% resolution of his PIH with no unexpected adverse reactions.
The third patient in the series was a 39-year-old Black male who presented with a 6-month history of hyperpigmentation on his right shin and calf, secondary to minor occupational-related trauma. Treatment was initiated with a fractional 1,064-nm picosecond laser. The laser settings were 2.1 mJ per microbeam microwave pulse energy and a 450 picosecond pulse duration delivered at 2 Hz through a holographic beam splitter with a 6 x 6–mm spot size containing 101 microbeams, for an estimated coverage of 4% per pulse. Four passes were performed for each area. The endpoint was a mild erythema to several treated areas a few minutes following laser treatment. Postoperative care consisted of applying a non-hydroquinone topical lightening agent twice daily to the affected area for 1 month. Near-complete resolution of the PIH was achieved, with no unexpected adverse reactions.
“In our clinical experience, PIH can be treated with the combination of topical skin lighteners and low density, low fluence laser therapy in almost all skin types,” Dr. Kream said. “The rationale behind this combination is to treat and remove existing pigment with the laser therapy while minimizing and preventing any pigmentary recurrence with diligent topical therapy and photoprotection.”
It is important to identify the cause of PIH “because some cases are trickier than others,” such as a lichenoid process that deposits pigment “a little bit deeper into the dermis,” she said. “When selecting an appropriate laser modality for the treatment of PIH in skin types V and VI, it’s especially important to consider the mechanism of action, depth of penetration, degree of tissue damage, and the extent of disruption to the dermal-epidermal junction.”
Following the presentation, one of the session moderators, Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Amsterdam University Medical Center, the Netherlands, emphasized the importance of proper patient selection for laser treatment of PIH. “Not every patient with PIH is adapted to treatment with the laser,” Dr. Wolkerstorfer said. “I think it’s also important to choose stable PIH, meaning you often see patients with an underlying disorder who want to get rid of the pigment. They often believe that the laser is the solution, but it often isn’t.”
During a question-and-answer session, a meeting attendee pointed out that the study lacked a control area to compare the treatment results to. “This was a retrospective case series,” Dr. Kream replied. “I’d like to see more elegant studies in the future, with a control [area],” she said.
Dr. Kream reported having no financial disclosures, Dr. Boen has no disclosures, and Dr. Wu has conducted research for many pharmaceutical and device companies. Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received grant or research funding from Lumenis, Novartis, and Avita Medical, and is an advisory board member for Incyte.
SAN DIEGO – , results from a small retrospective case series suggest.
“Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a leading chief of complaint of many skin of color persons seeking a dermatologist,” Elizabeth J. Kream, MD, told this news organization in advance of the annual conference of American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “I describe PIH to patients as the ‘ashes after a fire is extinguished.’ It’s the stubborn brown to gray/black spots that persist after conditions like acne and folliculitis, but it can be caused by any insult to the skin including external injury. In fact, there’s a risk of inciting PIH with lasers and energy-based devices and this risk is greater in skin of color given the greater melanin content. Unfortunately, we see patients present after visiting a med spa who were treated with the wrong devices and/or the wrong settings and they have disfiguring scarring and/or dyspigmentation.”
During an abstract session at the meeting, Dr. Kream, a dermatology resident at the University of Illinois at Chicago, discussed three patients with recalcitrant PIH and Fitzpatrick skin phototype V and VI who were treated in San Diego with a combination of topical and laser therapies. She presented the case series on behalf of coauthors Monica Boen, MD and Douglas C. Wu, MD, dermatologists who practice in San Diego.
The first patient was a 37-year-old Black female who presented for evaluation of longstanding hyperpigmentation on the face and neck determined to be PIH secondary to folliculitis on the chin and neck. She was started on 8% hydroquinone with kojic acid daily and received four treatments spaced 4-8 weeks apart with the 1,927-nm fractional nonablative diode laser. Laser settings were 5 mJ pulse energy and 5% coverage after eight passes. Triamcinolone 0.1% ointment was applied immediately after treatment and for 3 days following treatment, and the “patient experienced near complete resolution of PIH with no unexpected adverse events,” Dr. Kream said.
The second patient was a 20-year-old Black male who presented with a 3-month history of facial hyperpigmentation after suffering a laser-induced injury. He was started on a non-hydroquinone topical lightening agent and received five treatments spaced 2 weeks apart with a 1,927-nm fractional nonablative diode laser. The laser settings were 5 mJ pulse energy and 5% coverage after eight passes. The patient experienced 80%-90% resolution of his PIH with no unexpected adverse reactions.
The third patient in the series was a 39-year-old Black male who presented with a 6-month history of hyperpigmentation on his right shin and calf, secondary to minor occupational-related trauma. Treatment was initiated with a fractional 1,064-nm picosecond laser. The laser settings were 2.1 mJ per microbeam microwave pulse energy and a 450 picosecond pulse duration delivered at 2 Hz through a holographic beam splitter with a 6 x 6–mm spot size containing 101 microbeams, for an estimated coverage of 4% per pulse. Four passes were performed for each area. The endpoint was a mild erythema to several treated areas a few minutes following laser treatment. Postoperative care consisted of applying a non-hydroquinone topical lightening agent twice daily to the affected area for 1 month. Near-complete resolution of the PIH was achieved, with no unexpected adverse reactions.
“In our clinical experience, PIH can be treated with the combination of topical skin lighteners and low density, low fluence laser therapy in almost all skin types,” Dr. Kream said. “The rationale behind this combination is to treat and remove existing pigment with the laser therapy while minimizing and preventing any pigmentary recurrence with diligent topical therapy and photoprotection.”
It is important to identify the cause of PIH “because some cases are trickier than others,” such as a lichenoid process that deposits pigment “a little bit deeper into the dermis,” she said. “When selecting an appropriate laser modality for the treatment of PIH in skin types V and VI, it’s especially important to consider the mechanism of action, depth of penetration, degree of tissue damage, and the extent of disruption to the dermal-epidermal junction.”
Following the presentation, one of the session moderators, Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Amsterdam University Medical Center, the Netherlands, emphasized the importance of proper patient selection for laser treatment of PIH. “Not every patient with PIH is adapted to treatment with the laser,” Dr. Wolkerstorfer said. “I think it’s also important to choose stable PIH, meaning you often see patients with an underlying disorder who want to get rid of the pigment. They often believe that the laser is the solution, but it often isn’t.”
During a question-and-answer session, a meeting attendee pointed out that the study lacked a control area to compare the treatment results to. “This was a retrospective case series,” Dr. Kream replied. “I’d like to see more elegant studies in the future, with a control [area],” she said.
Dr. Kream reported having no financial disclosures, Dr. Boen has no disclosures, and Dr. Wu has conducted research for many pharmaceutical and device companies. Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received grant or research funding from Lumenis, Novartis, and Avita Medical, and is an advisory board member for Incyte.
AT ASLMS 2022
Synthetic, botanical agents emerging as promising melasma treatments
BOSTON – Though, according to Nada Elbuluk, MD, MSc.
One such agent is topical tranexamic acid, an antifibrinolytic medication that inhibits plasminogen activator from converting plasminogen in epidermal basal cells and keratinocytes to plasmin. “What makes tranexamic acid exciting is that it’s not just targeting melanogenesis; it’s also targeting the vascular component of melasma,” Dr. Elbuluk, director of the University of Southern California Skin of Color Center and Pigmentary Disorders Program, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “We really don’t have any topical agents that are doing that.”
Topical tranexamic acid is available in cream and solution formulations ranging from 2% to 5%. It has been studied in different drug delivery carriers (liposomal, liquid crystalline nanoparticle, and glycol co-enhancer carriers), has been combined with other lightening agents, and has been found to reduce Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI) scores and reduce melanin while also improving erythema. “That’s where it really stands out from hydroquinone and triple combination cream,” Dr. Elbuluk said.
One study of patients with melasma found that topical tranexamic acid can decrease the number of CD31-positive vessels and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and downregulated endothelin-1.
“Compared to hydroquinone, some studies have found a similar efficacy; others have found it inferior,” she continued. “But none of our patients can be on hydroquinone yearlong, so you have to bring in other agents that are efficacious. This is why you could consider having patients on topical tranexamic acid at different times of the year. It can cause some irritation for patients, but overall, it’s pretty well tolerated, and patients are often very happy with the overall improvement in the texture and appearance of their skin.”
Another emerging option, flutamide, is an anti-androgenic agent used topically and orally to treat acne, hirsutism, and hair loss. “It has not been excessively studied for melasma, but it may improve the condition through modifying alpha-MSH [alpha melanocyte-stimulating hormone] or cAMP [cyclic adenosine monophosphate] agents that play a role in melanin synthesis,” Dr. Elbuluk said. A randomized, controlled trial of 74 women with melasma treated with 1% flutamide vs. 4% hydroquinone showed a significant improvement in the MASI score and patient satisfaction but no difference in the mexameter melanin assay results.
“We need more data, but I think this is the right approach for us to start thinking about different factors that are addressing all of the components of the pathogenesis of melasma,” she said.
Other synthetic topicals that are being used or studied for melasma include N-acetyl glucosamine, linoleic acid, pidobenzone, methimazole, metformin, magnolignan, N-acetyl-4-S-cysteaminylphenol, dioic acid, melatonin, and silymarin.
Botanicals
Botanically-derived topicals for melasma are also being evaluated, including niacinamide, an anti-inflammatory agent that inhibits melanosome transfer to keratinocytes. Niacinamide decreases mast cell infiltrate and solar elastosis and enhances the epidermal barrier.
The antioxidants ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and zinc are also being studied. Ascorbic acid has photoprotective effects, inhibits tyrosinase, and promotes collagen synthesis. “One of the challenges with vitamin C is that it’s not very stable and it has limited permeability and bioavailability in the skin,” Dr. Elbuluk said. Zinc, meanwhile, boasts anti-inflammatory, photoprotective, and exfoliative properties and is a cofactor in wound healing.
Other botanical lightening agents being studied, in addition to silymarin, include arbutin, aloe vera, bakuchiol, soy, Ananas comosus (pineapple), parsley, Bellis perennis (daisy), mulberry extract, ellagic acid, gentisic acid, cinnamic acid, Hippophae rhamnoides (sea buckthorn), Cassia fistula extracts, licorice root extract, lignin peroxidase, and Polypodium leucotomos.
“I do think there really is a place for these in our therapeutic armamentarium, but we need more studies,” she said. “There aren’t many randomized, controlled studies looking at these agents specifically.” A recent systematic review on the efficacy and safety of topical therapy with botanical products for treating melasma included 12 trials composed of 695 patients from seven countries. The authors concluded that the trials lacked sufficient pooled evidence on efficacy and safety. However, many of the studies showed that these agents did improve melasma and MASI scores.
Platelet-rich plasma
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is being used as monotherapy and adjuvant therapy for melasma. “It’s believed to release platelet-derived growth factors, which can affect collagen synthesis,” Dr. Elbuluk explained. “It also has effects on TGF-B1 [transforming growth factor-beta 1], which inhibits melanin synthesis and epidermal growth factor, which has a downstream effect on lowering melanin production.”
A 2021 systematic review of 10 studies involving 395 adults with melasma found that PRP plus microneedling was most efficacious compared with PRP alone or combined with intradermal injection.
A separate systematic review of seven trials evaluating PRP for melasma found that most studies showed moderate improvements in melasma, which led the researchers to assign a moderate grade recommendation to PRP for melasma.
“I think we need more studies, but you may see PRP being used more commonly for melasma,” Dr. Elbuluk said. “The reality with melasma is that you are rarely using just one agent. Combination therapies are often superior to monotherapies in efficacy.” Combination therapy does not include just topicals, she added, but consideration of topicals with procedural modalities “and figuring out what your patient can tolerate and what they can afford.”
Since melasma is a chronic condition, “you want to emphasize to your patients that there is no cure for melasma. We are constantly trying to keep it in remission and keep it in control. That’s an active process.”
Other emerging topical therapies
Meanwhile, researchers continue to evaluate new targets for emerging treatments including a topical combination of an anti-estrogen with a VEGF inhibitor. In a separate pilot study of six women with melasma, investigators described treatment success with a novel combination of 12% hydroquinone, 6% kojic acid, and 5% vitamin C cream. “It’s the right thinking, combining different factors that address different aspects of pathogenesis of melasma,” Dr. Elbuluk said.
The mode of topical drug delivery also plays a role in treatment success. For example, she said, liposomal formulations have been found to enhance drug delivery and skin permeation and to improve the moisturizing effect, stability, and tolerability.
Dr. Elbuluk disclosed that she is a consultant for Avita, Scientis, VisualDx, Zosana, Incyte, La Roche-Posay, and Beiersdorf. She is an advisory board member for Allergan, Galderma, Incyte, and Janssen.
BOSTON – Though, according to Nada Elbuluk, MD, MSc.
One such agent is topical tranexamic acid, an antifibrinolytic medication that inhibits plasminogen activator from converting plasminogen in epidermal basal cells and keratinocytes to plasmin. “What makes tranexamic acid exciting is that it’s not just targeting melanogenesis; it’s also targeting the vascular component of melasma,” Dr. Elbuluk, director of the University of Southern California Skin of Color Center and Pigmentary Disorders Program, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “We really don’t have any topical agents that are doing that.”
Topical tranexamic acid is available in cream and solution formulations ranging from 2% to 5%. It has been studied in different drug delivery carriers (liposomal, liquid crystalline nanoparticle, and glycol co-enhancer carriers), has been combined with other lightening agents, and has been found to reduce Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI) scores and reduce melanin while also improving erythema. “That’s where it really stands out from hydroquinone and triple combination cream,” Dr. Elbuluk said.
One study of patients with melasma found that topical tranexamic acid can decrease the number of CD31-positive vessels and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and downregulated endothelin-1.
“Compared to hydroquinone, some studies have found a similar efficacy; others have found it inferior,” she continued. “But none of our patients can be on hydroquinone yearlong, so you have to bring in other agents that are efficacious. This is why you could consider having patients on topical tranexamic acid at different times of the year. It can cause some irritation for patients, but overall, it’s pretty well tolerated, and patients are often very happy with the overall improvement in the texture and appearance of their skin.”
Another emerging option, flutamide, is an anti-androgenic agent used topically and orally to treat acne, hirsutism, and hair loss. “It has not been excessively studied for melasma, but it may improve the condition through modifying alpha-MSH [alpha melanocyte-stimulating hormone] or cAMP [cyclic adenosine monophosphate] agents that play a role in melanin synthesis,” Dr. Elbuluk said. A randomized, controlled trial of 74 women with melasma treated with 1% flutamide vs. 4% hydroquinone showed a significant improvement in the MASI score and patient satisfaction but no difference in the mexameter melanin assay results.
“We need more data, but I think this is the right approach for us to start thinking about different factors that are addressing all of the components of the pathogenesis of melasma,” she said.
Other synthetic topicals that are being used or studied for melasma include N-acetyl glucosamine, linoleic acid, pidobenzone, methimazole, metformin, magnolignan, N-acetyl-4-S-cysteaminylphenol, dioic acid, melatonin, and silymarin.
Botanicals
Botanically-derived topicals for melasma are also being evaluated, including niacinamide, an anti-inflammatory agent that inhibits melanosome transfer to keratinocytes. Niacinamide decreases mast cell infiltrate and solar elastosis and enhances the epidermal barrier.
The antioxidants ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and zinc are also being studied. Ascorbic acid has photoprotective effects, inhibits tyrosinase, and promotes collagen synthesis. “One of the challenges with vitamin C is that it’s not very stable and it has limited permeability and bioavailability in the skin,” Dr. Elbuluk said. Zinc, meanwhile, boasts anti-inflammatory, photoprotective, and exfoliative properties and is a cofactor in wound healing.
Other botanical lightening agents being studied, in addition to silymarin, include arbutin, aloe vera, bakuchiol, soy, Ananas comosus (pineapple), parsley, Bellis perennis (daisy), mulberry extract, ellagic acid, gentisic acid, cinnamic acid, Hippophae rhamnoides (sea buckthorn), Cassia fistula extracts, licorice root extract, lignin peroxidase, and Polypodium leucotomos.
“I do think there really is a place for these in our therapeutic armamentarium, but we need more studies,” she said. “There aren’t many randomized, controlled studies looking at these agents specifically.” A recent systematic review on the efficacy and safety of topical therapy with botanical products for treating melasma included 12 trials composed of 695 patients from seven countries. The authors concluded that the trials lacked sufficient pooled evidence on efficacy and safety. However, many of the studies showed that these agents did improve melasma and MASI scores.
Platelet-rich plasma
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is being used as monotherapy and adjuvant therapy for melasma. “It’s believed to release platelet-derived growth factors, which can affect collagen synthesis,” Dr. Elbuluk explained. “It also has effects on TGF-B1 [transforming growth factor-beta 1], which inhibits melanin synthesis and epidermal growth factor, which has a downstream effect on lowering melanin production.”
A 2021 systematic review of 10 studies involving 395 adults with melasma found that PRP plus microneedling was most efficacious compared with PRP alone or combined with intradermal injection.
A separate systematic review of seven trials evaluating PRP for melasma found that most studies showed moderate improvements in melasma, which led the researchers to assign a moderate grade recommendation to PRP for melasma.
“I think we need more studies, but you may see PRP being used more commonly for melasma,” Dr. Elbuluk said. “The reality with melasma is that you are rarely using just one agent. Combination therapies are often superior to monotherapies in efficacy.” Combination therapy does not include just topicals, she added, but consideration of topicals with procedural modalities “and figuring out what your patient can tolerate and what they can afford.”
Since melasma is a chronic condition, “you want to emphasize to your patients that there is no cure for melasma. We are constantly trying to keep it in remission and keep it in control. That’s an active process.”
Other emerging topical therapies
Meanwhile, researchers continue to evaluate new targets for emerging treatments including a topical combination of an anti-estrogen with a VEGF inhibitor. In a separate pilot study of six women with melasma, investigators described treatment success with a novel combination of 12% hydroquinone, 6% kojic acid, and 5% vitamin C cream. “It’s the right thinking, combining different factors that address different aspects of pathogenesis of melasma,” Dr. Elbuluk said.
The mode of topical drug delivery also plays a role in treatment success. For example, she said, liposomal formulations have been found to enhance drug delivery and skin permeation and to improve the moisturizing effect, stability, and tolerability.
Dr. Elbuluk disclosed that she is a consultant for Avita, Scientis, VisualDx, Zosana, Incyte, La Roche-Posay, and Beiersdorf. She is an advisory board member for Allergan, Galderma, Incyte, and Janssen.
BOSTON – Though, according to Nada Elbuluk, MD, MSc.
One such agent is topical tranexamic acid, an antifibrinolytic medication that inhibits plasminogen activator from converting plasminogen in epidermal basal cells and keratinocytes to plasmin. “What makes tranexamic acid exciting is that it’s not just targeting melanogenesis; it’s also targeting the vascular component of melasma,” Dr. Elbuluk, director of the University of Southern California Skin of Color Center and Pigmentary Disorders Program, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. “We really don’t have any topical agents that are doing that.”
Topical tranexamic acid is available in cream and solution formulations ranging from 2% to 5%. It has been studied in different drug delivery carriers (liposomal, liquid crystalline nanoparticle, and glycol co-enhancer carriers), has been combined with other lightening agents, and has been found to reduce Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI) scores and reduce melanin while also improving erythema. “That’s where it really stands out from hydroquinone and triple combination cream,” Dr. Elbuluk said.
One study of patients with melasma found that topical tranexamic acid can decrease the number of CD31-positive vessels and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and downregulated endothelin-1.
“Compared to hydroquinone, some studies have found a similar efficacy; others have found it inferior,” she continued. “But none of our patients can be on hydroquinone yearlong, so you have to bring in other agents that are efficacious. This is why you could consider having patients on topical tranexamic acid at different times of the year. It can cause some irritation for patients, but overall, it’s pretty well tolerated, and patients are often very happy with the overall improvement in the texture and appearance of their skin.”
Another emerging option, flutamide, is an anti-androgenic agent used topically and orally to treat acne, hirsutism, and hair loss. “It has not been excessively studied for melasma, but it may improve the condition through modifying alpha-MSH [alpha melanocyte-stimulating hormone] or cAMP [cyclic adenosine monophosphate] agents that play a role in melanin synthesis,” Dr. Elbuluk said. A randomized, controlled trial of 74 women with melasma treated with 1% flutamide vs. 4% hydroquinone showed a significant improvement in the MASI score and patient satisfaction but no difference in the mexameter melanin assay results.
“We need more data, but I think this is the right approach for us to start thinking about different factors that are addressing all of the components of the pathogenesis of melasma,” she said.
Other synthetic topicals that are being used or studied for melasma include N-acetyl glucosamine, linoleic acid, pidobenzone, methimazole, metformin, magnolignan, N-acetyl-4-S-cysteaminylphenol, dioic acid, melatonin, and silymarin.
Botanicals
Botanically-derived topicals for melasma are also being evaluated, including niacinamide, an anti-inflammatory agent that inhibits melanosome transfer to keratinocytes. Niacinamide decreases mast cell infiltrate and solar elastosis and enhances the epidermal barrier.
The antioxidants ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and zinc are also being studied. Ascorbic acid has photoprotective effects, inhibits tyrosinase, and promotes collagen synthesis. “One of the challenges with vitamin C is that it’s not very stable and it has limited permeability and bioavailability in the skin,” Dr. Elbuluk said. Zinc, meanwhile, boasts anti-inflammatory, photoprotective, and exfoliative properties and is a cofactor in wound healing.
Other botanical lightening agents being studied, in addition to silymarin, include arbutin, aloe vera, bakuchiol, soy, Ananas comosus (pineapple), parsley, Bellis perennis (daisy), mulberry extract, ellagic acid, gentisic acid, cinnamic acid, Hippophae rhamnoides (sea buckthorn), Cassia fistula extracts, licorice root extract, lignin peroxidase, and Polypodium leucotomos.
“I do think there really is a place for these in our therapeutic armamentarium, but we need more studies,” she said. “There aren’t many randomized, controlled studies looking at these agents specifically.” A recent systematic review on the efficacy and safety of topical therapy with botanical products for treating melasma included 12 trials composed of 695 patients from seven countries. The authors concluded that the trials lacked sufficient pooled evidence on efficacy and safety. However, many of the studies showed that these agents did improve melasma and MASI scores.
Platelet-rich plasma
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is being used as monotherapy and adjuvant therapy for melasma. “It’s believed to release platelet-derived growth factors, which can affect collagen synthesis,” Dr. Elbuluk explained. “It also has effects on TGF-B1 [transforming growth factor-beta 1], which inhibits melanin synthesis and epidermal growth factor, which has a downstream effect on lowering melanin production.”
A 2021 systematic review of 10 studies involving 395 adults with melasma found that PRP plus microneedling was most efficacious compared with PRP alone or combined with intradermal injection.
A separate systematic review of seven trials evaluating PRP for melasma found that most studies showed moderate improvements in melasma, which led the researchers to assign a moderate grade recommendation to PRP for melasma.
“I think we need more studies, but you may see PRP being used more commonly for melasma,” Dr. Elbuluk said. “The reality with melasma is that you are rarely using just one agent. Combination therapies are often superior to monotherapies in efficacy.” Combination therapy does not include just topicals, she added, but consideration of topicals with procedural modalities “and figuring out what your patient can tolerate and what they can afford.”
Since melasma is a chronic condition, “you want to emphasize to your patients that there is no cure for melasma. We are constantly trying to keep it in remission and keep it in control. That’s an active process.”
Other emerging topical therapies
Meanwhile, researchers continue to evaluate new targets for emerging treatments including a topical combination of an anti-estrogen with a VEGF inhibitor. In a separate pilot study of six women with melasma, investigators described treatment success with a novel combination of 12% hydroquinone, 6% kojic acid, and 5% vitamin C cream. “It’s the right thinking, combining different factors that address different aspects of pathogenesis of melasma,” Dr. Elbuluk said.
The mode of topical drug delivery also plays a role in treatment success. For example, she said, liposomal formulations have been found to enhance drug delivery and skin permeation and to improve the moisturizing effect, stability, and tolerability.
Dr. Elbuluk disclosed that she is a consultant for Avita, Scientis, VisualDx, Zosana, Incyte, La Roche-Posay, and Beiersdorf. She is an advisory board member for Allergan, Galderma, Incyte, and Janssen.
AT AAD 22