User login
PPI Prophylaxis Prevents GI Bleed in Ventilated Patients
according to a randomized trial and a systematic review led by researchers at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
Patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) who need mechanical ventilation typically are given a PPI, such as pantoprazole, to prevent upper GI bleeding caused by stress-induced stomach ulcers, but some evidence suggested that their use might increase the risk for pneumonia and death in the most severely ill patients.
As a result, recent guidelines have issued only weak recommendations for stress ulcer prophylaxis, especially with PPIs, in critically ill patients at a high risk for bleeding, Deborah Cook, MD, professor of medicine at McMaster University, and colleagues noted.
To address clinical questions, they investigated the efficacy and safety of PPIs to prevent upper GI bleeding in critically ill patients.
Both the randomized trial in The New England Journal of Medicine and the systematic review in NEJM Evidence were published online in June.
Significantly Lower Bleeding Risk
The REVISE trial, conducted in eight countries, compared pantoprazole 40 mg daily with placebo in critically ill adults on mechanical ventilation.
The primary efficacy outcome was clinically important upper GI bleeding in the ICU at 90 days, and the primary safety outcome was death from any cause at 90 days.
A total of 4821 patients in 68 ICUs were randomly assigned to the pantoprazole group or placebo group.
Clinically important upper GI bleeding occurred in 25 patients (1%) receiving pantoprazole and in 84 patients (3.5%) receiving placebo. At 90 days, 696 patients (29.1%) in the pantoprazole group died, as did 734 (30.9%) in the placebo group.
No significant differences were found on key secondary outcomes, including ventilator-associated pneumonia and Clostridioides difficile infection in the hospital.
The authors concluded that pantoprazole resulted in a significantly lower risk for clinically important upper GI bleeding than placebo, and it had no significant effect on mortality.
Disease Severity as a Possible Factor
The systematic review included 12 randomized controlled trials comparing PPIs with placebo or no prophylaxis for stress ulcers in a total of 9533 critically ill adults. The researchers performed meta-analyses and assessed the certainty of the evidence. They also conducted a subgroup analysis combining within-trial subgroup data from the two largest trials.
They found that PPIs were associated with a reduced incidence of clinically important upper GI bleeding (relative risk [RR], 0.51, with high certainty evidence) and may have little or no effect on mortality (RR, 0.99, with low-certainty evidence).
However, the within-trial subgroup analysis with intermediate credibility suggested that the effect of PPIs on mortality may differ based on disease severity. The results also raised the possibility that PPI use may decrease 90-day mortality in less severely ill patients (RR, 0.89) and increase mortality in more severely ill patients (RR, 1.08). The mechanisms behind this possible signal are likely multifactorial, the authors noted.
In addition, the review found that PPIs may have no effect on pneumonia, duration of ICU stay, or duration of hospital stay, and little or no effect on C difficile infection or duration of mechanical ventilation (low-certainty evidence).
“Physicians, nurses, and pharmacists working in the ICU setting will use this information in practice right away, and the trial results and the updated meta-analysis will be incorporated into international practice guidelines,” Dr. Cook said.
Both studies had limitations. The REVISE trial did not include patient-reported disability outcomes, and the results may not be generalizable to patients with unassisted breathing. The systematic review included studies with diverse definitions of bleeding and pneumonia, and with mortality reported at different milestones, without considering competing risk analyses. Patient-important GI bleeding was available in only one trial. Other potential side effects of PPIs, such as infection with multidrug-resistant organisms, were not reported.
In an editorial accompanying both studies, Samuel M. Brown, MD, a pulmonologist and vice president of research at Intermountain Health, Salt Lake City, Utah, said that the REVISE trial was “well designed and executed, with generalizable eligibility criteria and excellent experimental separation.” He said the researchers had shown that PPIs “slightly but significantly” decrease the risk of important GI bleeding and have a “decent chance” of slightly decreasing mortality in less severely ill patients during mechanical ventilation. At the same time, he noted, PPIs “do not decrease — and may slightly increase — mortality” in severely ill patients.
Dr. Brown wrote that, in his own practice, he intends to prescribe prophylactic PPIs to patients during mechanical ventilation “if they have an APACHE II score of less than 25” or a reasonable equivalent. The APACHE II scoring system is a point-based system that estimates a patient’s risk of death while in an ICU.
“For sicker patients, I would probably reserve the use of proton-pump inhibitors for those who are being treated with antiplatelet agents, especially in the presence of therapeutic anticoagulants,” he added.
REVISE was supported by numerous grants from organizations in several countries. No funding was specified for the systematic review. Author disclosures and other supplementary materials are available with the full text of the article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a randomized trial and a systematic review led by researchers at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
Patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) who need mechanical ventilation typically are given a PPI, such as pantoprazole, to prevent upper GI bleeding caused by stress-induced stomach ulcers, but some evidence suggested that their use might increase the risk for pneumonia and death in the most severely ill patients.
As a result, recent guidelines have issued only weak recommendations for stress ulcer prophylaxis, especially with PPIs, in critically ill patients at a high risk for bleeding, Deborah Cook, MD, professor of medicine at McMaster University, and colleagues noted.
To address clinical questions, they investigated the efficacy and safety of PPIs to prevent upper GI bleeding in critically ill patients.
Both the randomized trial in The New England Journal of Medicine and the systematic review in NEJM Evidence were published online in June.
Significantly Lower Bleeding Risk
The REVISE trial, conducted in eight countries, compared pantoprazole 40 mg daily with placebo in critically ill adults on mechanical ventilation.
The primary efficacy outcome was clinically important upper GI bleeding in the ICU at 90 days, and the primary safety outcome was death from any cause at 90 days.
A total of 4821 patients in 68 ICUs were randomly assigned to the pantoprazole group or placebo group.
Clinically important upper GI bleeding occurred in 25 patients (1%) receiving pantoprazole and in 84 patients (3.5%) receiving placebo. At 90 days, 696 patients (29.1%) in the pantoprazole group died, as did 734 (30.9%) in the placebo group.
No significant differences were found on key secondary outcomes, including ventilator-associated pneumonia and Clostridioides difficile infection in the hospital.
The authors concluded that pantoprazole resulted in a significantly lower risk for clinically important upper GI bleeding than placebo, and it had no significant effect on mortality.
Disease Severity as a Possible Factor
The systematic review included 12 randomized controlled trials comparing PPIs with placebo or no prophylaxis for stress ulcers in a total of 9533 critically ill adults. The researchers performed meta-analyses and assessed the certainty of the evidence. They also conducted a subgroup analysis combining within-trial subgroup data from the two largest trials.
They found that PPIs were associated with a reduced incidence of clinically important upper GI bleeding (relative risk [RR], 0.51, with high certainty evidence) and may have little or no effect on mortality (RR, 0.99, with low-certainty evidence).
However, the within-trial subgroup analysis with intermediate credibility suggested that the effect of PPIs on mortality may differ based on disease severity. The results also raised the possibility that PPI use may decrease 90-day mortality in less severely ill patients (RR, 0.89) and increase mortality in more severely ill patients (RR, 1.08). The mechanisms behind this possible signal are likely multifactorial, the authors noted.
In addition, the review found that PPIs may have no effect on pneumonia, duration of ICU stay, or duration of hospital stay, and little or no effect on C difficile infection or duration of mechanical ventilation (low-certainty evidence).
“Physicians, nurses, and pharmacists working in the ICU setting will use this information in practice right away, and the trial results and the updated meta-analysis will be incorporated into international practice guidelines,” Dr. Cook said.
Both studies had limitations. The REVISE trial did not include patient-reported disability outcomes, and the results may not be generalizable to patients with unassisted breathing. The systematic review included studies with diverse definitions of bleeding and pneumonia, and with mortality reported at different milestones, without considering competing risk analyses. Patient-important GI bleeding was available in only one trial. Other potential side effects of PPIs, such as infection with multidrug-resistant organisms, were not reported.
In an editorial accompanying both studies, Samuel M. Brown, MD, a pulmonologist and vice president of research at Intermountain Health, Salt Lake City, Utah, said that the REVISE trial was “well designed and executed, with generalizable eligibility criteria and excellent experimental separation.” He said the researchers had shown that PPIs “slightly but significantly” decrease the risk of important GI bleeding and have a “decent chance” of slightly decreasing mortality in less severely ill patients during mechanical ventilation. At the same time, he noted, PPIs “do not decrease — and may slightly increase — mortality” in severely ill patients.
Dr. Brown wrote that, in his own practice, he intends to prescribe prophylactic PPIs to patients during mechanical ventilation “if they have an APACHE II score of less than 25” or a reasonable equivalent. The APACHE II scoring system is a point-based system that estimates a patient’s risk of death while in an ICU.
“For sicker patients, I would probably reserve the use of proton-pump inhibitors for those who are being treated with antiplatelet agents, especially in the presence of therapeutic anticoagulants,” he added.
REVISE was supported by numerous grants from organizations in several countries. No funding was specified for the systematic review. Author disclosures and other supplementary materials are available with the full text of the article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a randomized trial and a systematic review led by researchers at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
Patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) who need mechanical ventilation typically are given a PPI, such as pantoprazole, to prevent upper GI bleeding caused by stress-induced stomach ulcers, but some evidence suggested that their use might increase the risk for pneumonia and death in the most severely ill patients.
As a result, recent guidelines have issued only weak recommendations for stress ulcer prophylaxis, especially with PPIs, in critically ill patients at a high risk for bleeding, Deborah Cook, MD, professor of medicine at McMaster University, and colleagues noted.
To address clinical questions, they investigated the efficacy and safety of PPIs to prevent upper GI bleeding in critically ill patients.
Both the randomized trial in The New England Journal of Medicine and the systematic review in NEJM Evidence were published online in June.
Significantly Lower Bleeding Risk
The REVISE trial, conducted in eight countries, compared pantoprazole 40 mg daily with placebo in critically ill adults on mechanical ventilation.
The primary efficacy outcome was clinically important upper GI bleeding in the ICU at 90 days, and the primary safety outcome was death from any cause at 90 days.
A total of 4821 patients in 68 ICUs were randomly assigned to the pantoprazole group or placebo group.
Clinically important upper GI bleeding occurred in 25 patients (1%) receiving pantoprazole and in 84 patients (3.5%) receiving placebo. At 90 days, 696 patients (29.1%) in the pantoprazole group died, as did 734 (30.9%) in the placebo group.
No significant differences were found on key secondary outcomes, including ventilator-associated pneumonia and Clostridioides difficile infection in the hospital.
The authors concluded that pantoprazole resulted in a significantly lower risk for clinically important upper GI bleeding than placebo, and it had no significant effect on mortality.
Disease Severity as a Possible Factor
The systematic review included 12 randomized controlled trials comparing PPIs with placebo or no prophylaxis for stress ulcers in a total of 9533 critically ill adults. The researchers performed meta-analyses and assessed the certainty of the evidence. They also conducted a subgroup analysis combining within-trial subgroup data from the two largest trials.
They found that PPIs were associated with a reduced incidence of clinically important upper GI bleeding (relative risk [RR], 0.51, with high certainty evidence) and may have little or no effect on mortality (RR, 0.99, with low-certainty evidence).
However, the within-trial subgroup analysis with intermediate credibility suggested that the effect of PPIs on mortality may differ based on disease severity. The results also raised the possibility that PPI use may decrease 90-day mortality in less severely ill patients (RR, 0.89) and increase mortality in more severely ill patients (RR, 1.08). The mechanisms behind this possible signal are likely multifactorial, the authors noted.
In addition, the review found that PPIs may have no effect on pneumonia, duration of ICU stay, or duration of hospital stay, and little or no effect on C difficile infection or duration of mechanical ventilation (low-certainty evidence).
“Physicians, nurses, and pharmacists working in the ICU setting will use this information in practice right away, and the trial results and the updated meta-analysis will be incorporated into international practice guidelines,” Dr. Cook said.
Both studies had limitations. The REVISE trial did not include patient-reported disability outcomes, and the results may not be generalizable to patients with unassisted breathing. The systematic review included studies with diverse definitions of bleeding and pneumonia, and with mortality reported at different milestones, without considering competing risk analyses. Patient-important GI bleeding was available in only one trial. Other potential side effects of PPIs, such as infection with multidrug-resistant organisms, were not reported.
In an editorial accompanying both studies, Samuel M. Brown, MD, a pulmonologist and vice president of research at Intermountain Health, Salt Lake City, Utah, said that the REVISE trial was “well designed and executed, with generalizable eligibility criteria and excellent experimental separation.” He said the researchers had shown that PPIs “slightly but significantly” decrease the risk of important GI bleeding and have a “decent chance” of slightly decreasing mortality in less severely ill patients during mechanical ventilation. At the same time, he noted, PPIs “do not decrease — and may slightly increase — mortality” in severely ill patients.
Dr. Brown wrote that, in his own practice, he intends to prescribe prophylactic PPIs to patients during mechanical ventilation “if they have an APACHE II score of less than 25” or a reasonable equivalent. The APACHE II scoring system is a point-based system that estimates a patient’s risk of death while in an ICU.
“For sicker patients, I would probably reserve the use of proton-pump inhibitors for those who are being treated with antiplatelet agents, especially in the presence of therapeutic anticoagulants,” he added.
REVISE was supported by numerous grants from organizations in several countries. No funding was specified for the systematic review. Author disclosures and other supplementary materials are available with the full text of the article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Can Addressing Depression Reduce Chemo Toxicity in Older Adults?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Few Smokers Who Want to Quit Seek Healthcare Provider Help
Approximately half of US adult smokers tried to quit in 2022, but fewer than 40% used counseling or medication, and half received assistance or advice about quitting from clinicians, based on a review in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Previous research has shown that clinician intervention and evidence-based treatment increase the odds that smokers can quit successfully, but the extent to which these interventions are applied in practice has not been well studied, the researchers noted.
Although great progress has been made in reducing cigarette smoking in the United States, disparities remain, both in use and in cessation, with an estimated 28.8 million adults reporting cigarette smoking in 2022, lead author Brenna VanFrank, MD, MSPH, said in an interview.
“Cigarette smoking remains the leading preventable cause of death and disease in the United States,” said Dr. VanFrank, Senior Medical Officer, Office on Smoking and Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
In a new review, the researchers examined data from the 2022 National Health Interview Survey. The study population included 27,651 adults aged 18 years and older. Current smoking was defined as currently smoking each day or some days and ever having smoked at least 100 cigarettes. The survey assessed the individuals’ interest in quitting, past-year quit attempts, recent quitting success, receipt of healthcare professional advice about quitting, use of counseling to help quit, and use of medication to help quit.
In 2022, approximately two thirds (67.7%) of the 28.8 million adult smokers in the United States wanted to quit, half (53.3%) tried to quit, but only 8.8% were successful. Of those who reported trying to quit, 38.3% used counseling or medication. Of these, 36.3% used medication, 7.3% used counseling, and 5.3% used both.
Indicators of smoking cessation varied by health characteristics and sociodemographic factors, with the highest prevalence of attempts to quit smoking in the past year among adults aged 18-24 years and the lowest among those aged 45-64 years (74.4% vs 47.5%).
Rates of successful quitting were highest among individuals with higher levels of education and income, and use of smoking cessation treatment was highest among White adults (42.7%), followed by non-Hispanic adults of another race, Black adults, and Hispanic adults (33.6%, 32.6%, and 28.8%, respectively).
Smokers of menthol cigarettes had similarly low success rates for quitting (< 10%), although they were significantly more likely than nonmenthol cigarette smokers to express interest in quitting (72.2% vs 65.4%). Smokers of menthol cigarettes also had significantly lower prevalences than smokers of nonmenthol cigarettes of receiving clinician advance to quit and using treatment strategies (both P < .05).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of self-reports, which may be subject to bias, and a lack of data on institutionalized adults or adults in the military, which may limit generalizability of the findings to those populations, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that opportunities exist to increase smoking cessation across public health and healthcare sectors by expanding access to and use of services and supports to help smokers quit, they wrote.
Ensuring Support for All Smokers Seeking to Quit
The takeaway for clinical practice remains that quitting smoking “is one of the most important actions people who smoke can take to improve their health,” Dr. VanFrank said in an interview.
“It is important to ensure everyone has an opportunity to quit smoking and has access to proven treatments to help them be successful,” she emphasized. Strategies that include behavioral counseling, cessation medications, and advice and support from healthcare professionals can increase quit success. Given that tobacco dependence is a chronic, relapsing condition driven by addiction to nicotine, quitting successfully often takes multiple tries, and those trying to quit may need long-term support and repeated treatment.
“Health systems changes, such as adoption of treatment protocols and standardized clinical work flows, can systematize clinical treatment delivery, and such changes might also serve to increase treatment access for the 75% of adults who smoke who see a healthcare professional in a given year,” said Dr. VanFrank.
As for additional research, “continued surveillance of tobacco use and cessation-related behaviors will help us monitor progress and identify continued opportunities to eliminate tobacco product use and tobacco-related disparities,” Dr. VanFrank said.
“We know a lot about what works to help people successfully quit smoking and what we can do to support people in making quit attempts,” she said. Including equitable opportunities in all commercial tobacco prevention and control efforts has the potential to reduce tobacco-related health disparities.
Overall smoking prevalence in the United States and the current study shows that most smokers would like to quit, David M. Mannino, MD, a pulmonologist and professor of medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington, said in an interview. The lack of success experienced by many smokers seeking to quit emphasizes the highly addictive nature of nicotine products, which cause death and disease when used as directed, added Dr. Mannino, who was not involved in the study.
The results of the review were not surprising, and reflect where tobacco treatment has been for the past 20 years, said Dr. Mannino. The good news is that smoking prevalence has continued to drop in the United States over the past 15 years. However, some bad news is that use of e-cigarettes/vaping is still increasing, especially in younger populations, and new nicotine delivery systems, such as pouches (Zyn) are addicting a new generation.
Always Ask About Smoking
In practice, “clinicians should always ask patients about cigarette smoking, as well as vaping and other nicotine use, advise them to quit, and refer them to tobacco treatment experts,” Dr. Mannino emphasized.
The bottom line is that better treatments are needed for tobacco/nicotine addiction, Dr. Mannino said. “Although we have come a long way, we have a long way to go as millions of smokers in the US and globally would like to quit.”
Tobacco-related disease continues to be the number one cause of morbidly and mortality in the United States, and although many current smokers want to quit, most are not successful, Jamie Garfield, MD, professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, said in an interview.
“This review highlights the sheer number of current cigarette smokers who want to quit, how many of them attempted to quit, and how many of those were successful,” said Dr. Garfield, who was not involved in the study. Understanding the characteristics of individuals who are more or less likely to successfully quit smoking can help public health and healthcare sectors to increase smoking cessation by expanding access to and use of services and supports.
“We have to do better to control the sale of tobacco products and make tobacco cessation more accessible to everyone,” Dr. Garfield said. In addition, clinicians need to be consistent in asking patients about tobacco use. “If we don’t ask, we will not know who needs help.” Behavioral counseling helps, as does pharmacotherapy, and the two together are more effective than either alone, she added.
Cessation services need to be tailored to the many demographic groups who use tobacco products, said Dr. Garfield. “Just as marketing campaigns directed to older adults will be different from those directed to young adults, so too must cessation resources. Providers need better options to choose from with regard to cessation resources and behavioral counseling sessions. They need to be aware of what motivates one group of people to smoke and how they can be inspired to quit, including which pharmacotherapies are affordable, available, and will work; the same strategies will not work for all people”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Mannino disclosed serving as an expert witness for on tobacco use and tobacco-caused disease on behalf of people suing the tobacco and vaping industries. Dr. Garfield had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approximately half of US adult smokers tried to quit in 2022, but fewer than 40% used counseling or medication, and half received assistance or advice about quitting from clinicians, based on a review in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Previous research has shown that clinician intervention and evidence-based treatment increase the odds that smokers can quit successfully, but the extent to which these interventions are applied in practice has not been well studied, the researchers noted.
Although great progress has been made in reducing cigarette smoking in the United States, disparities remain, both in use and in cessation, with an estimated 28.8 million adults reporting cigarette smoking in 2022, lead author Brenna VanFrank, MD, MSPH, said in an interview.
“Cigarette smoking remains the leading preventable cause of death and disease in the United States,” said Dr. VanFrank, Senior Medical Officer, Office on Smoking and Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
In a new review, the researchers examined data from the 2022 National Health Interview Survey. The study population included 27,651 adults aged 18 years and older. Current smoking was defined as currently smoking each day or some days and ever having smoked at least 100 cigarettes. The survey assessed the individuals’ interest in quitting, past-year quit attempts, recent quitting success, receipt of healthcare professional advice about quitting, use of counseling to help quit, and use of medication to help quit.
In 2022, approximately two thirds (67.7%) of the 28.8 million adult smokers in the United States wanted to quit, half (53.3%) tried to quit, but only 8.8% were successful. Of those who reported trying to quit, 38.3% used counseling or medication. Of these, 36.3% used medication, 7.3% used counseling, and 5.3% used both.
Indicators of smoking cessation varied by health characteristics and sociodemographic factors, with the highest prevalence of attempts to quit smoking in the past year among adults aged 18-24 years and the lowest among those aged 45-64 years (74.4% vs 47.5%).
Rates of successful quitting were highest among individuals with higher levels of education and income, and use of smoking cessation treatment was highest among White adults (42.7%), followed by non-Hispanic adults of another race, Black adults, and Hispanic adults (33.6%, 32.6%, and 28.8%, respectively).
Smokers of menthol cigarettes had similarly low success rates for quitting (< 10%), although they were significantly more likely than nonmenthol cigarette smokers to express interest in quitting (72.2% vs 65.4%). Smokers of menthol cigarettes also had significantly lower prevalences than smokers of nonmenthol cigarettes of receiving clinician advance to quit and using treatment strategies (both P < .05).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of self-reports, which may be subject to bias, and a lack of data on institutionalized adults or adults in the military, which may limit generalizability of the findings to those populations, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that opportunities exist to increase smoking cessation across public health and healthcare sectors by expanding access to and use of services and supports to help smokers quit, they wrote.
Ensuring Support for All Smokers Seeking to Quit
The takeaway for clinical practice remains that quitting smoking “is one of the most important actions people who smoke can take to improve their health,” Dr. VanFrank said in an interview.
“It is important to ensure everyone has an opportunity to quit smoking and has access to proven treatments to help them be successful,” she emphasized. Strategies that include behavioral counseling, cessation medications, and advice and support from healthcare professionals can increase quit success. Given that tobacco dependence is a chronic, relapsing condition driven by addiction to nicotine, quitting successfully often takes multiple tries, and those trying to quit may need long-term support and repeated treatment.
“Health systems changes, such as adoption of treatment protocols and standardized clinical work flows, can systematize clinical treatment delivery, and such changes might also serve to increase treatment access for the 75% of adults who smoke who see a healthcare professional in a given year,” said Dr. VanFrank.
As for additional research, “continued surveillance of tobacco use and cessation-related behaviors will help us monitor progress and identify continued opportunities to eliminate tobacco product use and tobacco-related disparities,” Dr. VanFrank said.
“We know a lot about what works to help people successfully quit smoking and what we can do to support people in making quit attempts,” she said. Including equitable opportunities in all commercial tobacco prevention and control efforts has the potential to reduce tobacco-related health disparities.
Overall smoking prevalence in the United States and the current study shows that most smokers would like to quit, David M. Mannino, MD, a pulmonologist and professor of medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington, said in an interview. The lack of success experienced by many smokers seeking to quit emphasizes the highly addictive nature of nicotine products, which cause death and disease when used as directed, added Dr. Mannino, who was not involved in the study.
The results of the review were not surprising, and reflect where tobacco treatment has been for the past 20 years, said Dr. Mannino. The good news is that smoking prevalence has continued to drop in the United States over the past 15 years. However, some bad news is that use of e-cigarettes/vaping is still increasing, especially in younger populations, and new nicotine delivery systems, such as pouches (Zyn) are addicting a new generation.
Always Ask About Smoking
In practice, “clinicians should always ask patients about cigarette smoking, as well as vaping and other nicotine use, advise them to quit, and refer them to tobacco treatment experts,” Dr. Mannino emphasized.
The bottom line is that better treatments are needed for tobacco/nicotine addiction, Dr. Mannino said. “Although we have come a long way, we have a long way to go as millions of smokers in the US and globally would like to quit.”
Tobacco-related disease continues to be the number one cause of morbidly and mortality in the United States, and although many current smokers want to quit, most are not successful, Jamie Garfield, MD, professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, said in an interview.
“This review highlights the sheer number of current cigarette smokers who want to quit, how many of them attempted to quit, and how many of those were successful,” said Dr. Garfield, who was not involved in the study. Understanding the characteristics of individuals who are more or less likely to successfully quit smoking can help public health and healthcare sectors to increase smoking cessation by expanding access to and use of services and supports.
“We have to do better to control the sale of tobacco products and make tobacco cessation more accessible to everyone,” Dr. Garfield said. In addition, clinicians need to be consistent in asking patients about tobacco use. “If we don’t ask, we will not know who needs help.” Behavioral counseling helps, as does pharmacotherapy, and the two together are more effective than either alone, she added.
Cessation services need to be tailored to the many demographic groups who use tobacco products, said Dr. Garfield. “Just as marketing campaigns directed to older adults will be different from those directed to young adults, so too must cessation resources. Providers need better options to choose from with regard to cessation resources and behavioral counseling sessions. They need to be aware of what motivates one group of people to smoke and how they can be inspired to quit, including which pharmacotherapies are affordable, available, and will work; the same strategies will not work for all people”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Mannino disclosed serving as an expert witness for on tobacco use and tobacco-caused disease on behalf of people suing the tobacco and vaping industries. Dr. Garfield had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approximately half of US adult smokers tried to quit in 2022, but fewer than 40% used counseling or medication, and half received assistance or advice about quitting from clinicians, based on a review in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Previous research has shown that clinician intervention and evidence-based treatment increase the odds that smokers can quit successfully, but the extent to which these interventions are applied in practice has not been well studied, the researchers noted.
Although great progress has been made in reducing cigarette smoking in the United States, disparities remain, both in use and in cessation, with an estimated 28.8 million adults reporting cigarette smoking in 2022, lead author Brenna VanFrank, MD, MSPH, said in an interview.
“Cigarette smoking remains the leading preventable cause of death and disease in the United States,” said Dr. VanFrank, Senior Medical Officer, Office on Smoking and Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
In a new review, the researchers examined data from the 2022 National Health Interview Survey. The study population included 27,651 adults aged 18 years and older. Current smoking was defined as currently smoking each day or some days and ever having smoked at least 100 cigarettes. The survey assessed the individuals’ interest in quitting, past-year quit attempts, recent quitting success, receipt of healthcare professional advice about quitting, use of counseling to help quit, and use of medication to help quit.
In 2022, approximately two thirds (67.7%) of the 28.8 million adult smokers in the United States wanted to quit, half (53.3%) tried to quit, but only 8.8% were successful. Of those who reported trying to quit, 38.3% used counseling or medication. Of these, 36.3% used medication, 7.3% used counseling, and 5.3% used both.
Indicators of smoking cessation varied by health characteristics and sociodemographic factors, with the highest prevalence of attempts to quit smoking in the past year among adults aged 18-24 years and the lowest among those aged 45-64 years (74.4% vs 47.5%).
Rates of successful quitting were highest among individuals with higher levels of education and income, and use of smoking cessation treatment was highest among White adults (42.7%), followed by non-Hispanic adults of another race, Black adults, and Hispanic adults (33.6%, 32.6%, and 28.8%, respectively).
Smokers of menthol cigarettes had similarly low success rates for quitting (< 10%), although they were significantly more likely than nonmenthol cigarette smokers to express interest in quitting (72.2% vs 65.4%). Smokers of menthol cigarettes also had significantly lower prevalences than smokers of nonmenthol cigarettes of receiving clinician advance to quit and using treatment strategies (both P < .05).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of self-reports, which may be subject to bias, and a lack of data on institutionalized adults or adults in the military, which may limit generalizability of the findings to those populations, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that opportunities exist to increase smoking cessation across public health and healthcare sectors by expanding access to and use of services and supports to help smokers quit, they wrote.
Ensuring Support for All Smokers Seeking to Quit
The takeaway for clinical practice remains that quitting smoking “is one of the most important actions people who smoke can take to improve their health,” Dr. VanFrank said in an interview.
“It is important to ensure everyone has an opportunity to quit smoking and has access to proven treatments to help them be successful,” she emphasized. Strategies that include behavioral counseling, cessation medications, and advice and support from healthcare professionals can increase quit success. Given that tobacco dependence is a chronic, relapsing condition driven by addiction to nicotine, quitting successfully often takes multiple tries, and those trying to quit may need long-term support and repeated treatment.
“Health systems changes, such as adoption of treatment protocols and standardized clinical work flows, can systematize clinical treatment delivery, and such changes might also serve to increase treatment access for the 75% of adults who smoke who see a healthcare professional in a given year,” said Dr. VanFrank.
As for additional research, “continued surveillance of tobacco use and cessation-related behaviors will help us monitor progress and identify continued opportunities to eliminate tobacco product use and tobacco-related disparities,” Dr. VanFrank said.
“We know a lot about what works to help people successfully quit smoking and what we can do to support people in making quit attempts,” she said. Including equitable opportunities in all commercial tobacco prevention and control efforts has the potential to reduce tobacco-related health disparities.
Overall smoking prevalence in the United States and the current study shows that most smokers would like to quit, David M. Mannino, MD, a pulmonologist and professor of medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington, said in an interview. The lack of success experienced by many smokers seeking to quit emphasizes the highly addictive nature of nicotine products, which cause death and disease when used as directed, added Dr. Mannino, who was not involved in the study.
The results of the review were not surprising, and reflect where tobacco treatment has been for the past 20 years, said Dr. Mannino. The good news is that smoking prevalence has continued to drop in the United States over the past 15 years. However, some bad news is that use of e-cigarettes/vaping is still increasing, especially in younger populations, and new nicotine delivery systems, such as pouches (Zyn) are addicting a new generation.
Always Ask About Smoking
In practice, “clinicians should always ask patients about cigarette smoking, as well as vaping and other nicotine use, advise them to quit, and refer them to tobacco treatment experts,” Dr. Mannino emphasized.
The bottom line is that better treatments are needed for tobacco/nicotine addiction, Dr. Mannino said. “Although we have come a long way, we have a long way to go as millions of smokers in the US and globally would like to quit.”
Tobacco-related disease continues to be the number one cause of morbidly and mortality in the United States, and although many current smokers want to quit, most are not successful, Jamie Garfield, MD, professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, said in an interview.
“This review highlights the sheer number of current cigarette smokers who want to quit, how many of them attempted to quit, and how many of those were successful,” said Dr. Garfield, who was not involved in the study. Understanding the characteristics of individuals who are more or less likely to successfully quit smoking can help public health and healthcare sectors to increase smoking cessation by expanding access to and use of services and supports.
“We have to do better to control the sale of tobacco products and make tobacco cessation more accessible to everyone,” Dr. Garfield said. In addition, clinicians need to be consistent in asking patients about tobacco use. “If we don’t ask, we will not know who needs help.” Behavioral counseling helps, as does pharmacotherapy, and the two together are more effective than either alone, she added.
Cessation services need to be tailored to the many demographic groups who use tobacco products, said Dr. Garfield. “Just as marketing campaigns directed to older adults will be different from those directed to young adults, so too must cessation resources. Providers need better options to choose from with regard to cessation resources and behavioral counseling sessions. They need to be aware of what motivates one group of people to smoke and how they can be inspired to quit, including which pharmacotherapies are affordable, available, and will work; the same strategies will not work for all people”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Mannino disclosed serving as an expert witness for on tobacco use and tobacco-caused disease on behalf of people suing the tobacco and vaping industries. Dr. Garfield had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE MMWR
Air Pollution and Genetics May Raise Risk for Lupus
TOPLINE:
Chronic exposure to air pollutants such as fine particulate matter ≤ 2.5 μm in diameter (PM2.5), particulate matter ≤ 10 μm in diameter (PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and nitrogen oxides (NOX) increased the risk for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) onset. The risk was highest among those with high genetic risk and high air-pollution exposure.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers prospectively investigated the association between long-term exposure to air pollutants and incident SLE in 459,815 participants from the UK Biobank.
- A land-use regression model was used to quantify the annual average air pollution concentrations, including PM2.5, PM10, NO2, and NOX.
- The genetic susceptibility to lupus was assessed using polygenic risk scores (PRS), and the participants were classified into low–, intermediate–, or high–genetic-risk groups based on the tertiles of PRS.
- The joint effect of air pollutants and genetic susceptibility to lupus on the risk for incident SLE was evaluated, with the reference group consisting of participants with a low genetic risk and low exposure to air pollution.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up period of 11.77 years, 399 new cases of SLE were identified.
- The odds of developing SLE were higher among participants with high genetic risk than among those with low genetic risk (hazard ratio [HR], 3.45; P < .001 for trend).
- The risk for developing SLE was even higher among participants with a high genetic risk and high exposure to PM2.5 (adjusted HR [aHR], 4.16; 95% CI, 2.67-6.49), PM10 (aHR, 5.31; 95% CI, 3.30-8.55), NO2 (aHR, 5.61; 95% CI, 3.45-9.13), and NOX (aHR, 4.80; 95% CI, 3.00-7.66) than among with those with a low genetic risk and low exposure to air pollutants.
IN PRACTICE:
“Findings can inform the development of stricter air quality regulations to mitigate exposure to harmful pollutants, thereby reducing the risk of SLE,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Meiqi Xing, MASc, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China. It was published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study participants were enrolled voluntarily, which may have led to selection bias because they might have been healthier or more health conscious. The study did not consider the specific components of air pollutants, particularly particulate matter, which may have varying effects on the incidence of SLE. Other air pollutants such as ozone, sulfur dioxide, and carbon monoxide were not included in the analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not disclose any funding source. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Chronic exposure to air pollutants such as fine particulate matter ≤ 2.5 μm in diameter (PM2.5), particulate matter ≤ 10 μm in diameter (PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and nitrogen oxides (NOX) increased the risk for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) onset. The risk was highest among those with high genetic risk and high air-pollution exposure.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers prospectively investigated the association between long-term exposure to air pollutants and incident SLE in 459,815 participants from the UK Biobank.
- A land-use regression model was used to quantify the annual average air pollution concentrations, including PM2.5, PM10, NO2, and NOX.
- The genetic susceptibility to lupus was assessed using polygenic risk scores (PRS), and the participants were classified into low–, intermediate–, or high–genetic-risk groups based on the tertiles of PRS.
- The joint effect of air pollutants and genetic susceptibility to lupus on the risk for incident SLE was evaluated, with the reference group consisting of participants with a low genetic risk and low exposure to air pollution.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up period of 11.77 years, 399 new cases of SLE were identified.
- The odds of developing SLE were higher among participants with high genetic risk than among those with low genetic risk (hazard ratio [HR], 3.45; P < .001 for trend).
- The risk for developing SLE was even higher among participants with a high genetic risk and high exposure to PM2.5 (adjusted HR [aHR], 4.16; 95% CI, 2.67-6.49), PM10 (aHR, 5.31; 95% CI, 3.30-8.55), NO2 (aHR, 5.61; 95% CI, 3.45-9.13), and NOX (aHR, 4.80; 95% CI, 3.00-7.66) than among with those with a low genetic risk and low exposure to air pollutants.
IN PRACTICE:
“Findings can inform the development of stricter air quality regulations to mitigate exposure to harmful pollutants, thereby reducing the risk of SLE,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Meiqi Xing, MASc, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China. It was published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study participants were enrolled voluntarily, which may have led to selection bias because they might have been healthier or more health conscious. The study did not consider the specific components of air pollutants, particularly particulate matter, which may have varying effects on the incidence of SLE. Other air pollutants such as ozone, sulfur dioxide, and carbon monoxide were not included in the analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not disclose any funding source. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Chronic exposure to air pollutants such as fine particulate matter ≤ 2.5 μm in diameter (PM2.5), particulate matter ≤ 10 μm in diameter (PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and nitrogen oxides (NOX) increased the risk for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) onset. The risk was highest among those with high genetic risk and high air-pollution exposure.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers prospectively investigated the association between long-term exposure to air pollutants and incident SLE in 459,815 participants from the UK Biobank.
- A land-use regression model was used to quantify the annual average air pollution concentrations, including PM2.5, PM10, NO2, and NOX.
- The genetic susceptibility to lupus was assessed using polygenic risk scores (PRS), and the participants were classified into low–, intermediate–, or high–genetic-risk groups based on the tertiles of PRS.
- The joint effect of air pollutants and genetic susceptibility to lupus on the risk for incident SLE was evaluated, with the reference group consisting of participants with a low genetic risk and low exposure to air pollution.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up period of 11.77 years, 399 new cases of SLE were identified.
- The odds of developing SLE were higher among participants with high genetic risk than among those with low genetic risk (hazard ratio [HR], 3.45; P < .001 for trend).
- The risk for developing SLE was even higher among participants with a high genetic risk and high exposure to PM2.5 (adjusted HR [aHR], 4.16; 95% CI, 2.67-6.49), PM10 (aHR, 5.31; 95% CI, 3.30-8.55), NO2 (aHR, 5.61; 95% CI, 3.45-9.13), and NOX (aHR, 4.80; 95% CI, 3.00-7.66) than among with those with a low genetic risk and low exposure to air pollutants.
IN PRACTICE:
“Findings can inform the development of stricter air quality regulations to mitigate exposure to harmful pollutants, thereby reducing the risk of SLE,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Meiqi Xing, MASc, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China. It was published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study participants were enrolled voluntarily, which may have led to selection bias because they might have been healthier or more health conscious. The study did not consider the specific components of air pollutants, particularly particulate matter, which may have varying effects on the incidence of SLE. Other air pollutants such as ozone, sulfur dioxide, and carbon monoxide were not included in the analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not disclose any funding source. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ozempic Curbs Hunger – And Not Just for Food
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’ve been paying attention only to the headlines, when you think of “Ozempic” you’ll think of a few things: a blockbuster weight loss drug or the tip of the spear of a completely new industry — why not? A drug so popular that the people it was invented for (those with diabetes) can’t even get it.
Ozempic and other GLP-1 receptor agonists are undeniable game changers. Insofar as obesity is the number-one public health risk in the United States, antiobesity drugs hold immense promise even if all they do is reduce obesity.
In 2023, an article in Scientific Reports presented data suggesting that people on Ozempic might be reducing their alcohol intake, not just their total calories.
A 2024 article in Molecular Psychiatry found that the drug might positively impact cannabis use disorder. An article from Brain Sciences suggests that the drug reduces compulsive shopping.
A picture is starting to form, a picture that suggests these drugs curb hunger both literally and figuratively. That GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Mounjaro are fundamentally anticonsumption drugs. In a society that — some would argue — is plagued by overconsumption, these drugs might be just what the doctor ordered.
If only they could stop people from smoking.
Oh, wait — they can.
At least it seems they can, based on a new study appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
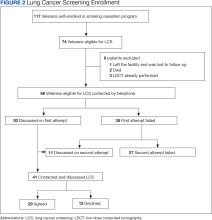
Before we get too excited, this is not a randomized trial. There actually was a small randomized trial of exenatide (Byetta), which is in the same class as Ozempic but probably a bit less potent, with promising results for smoking cessation. 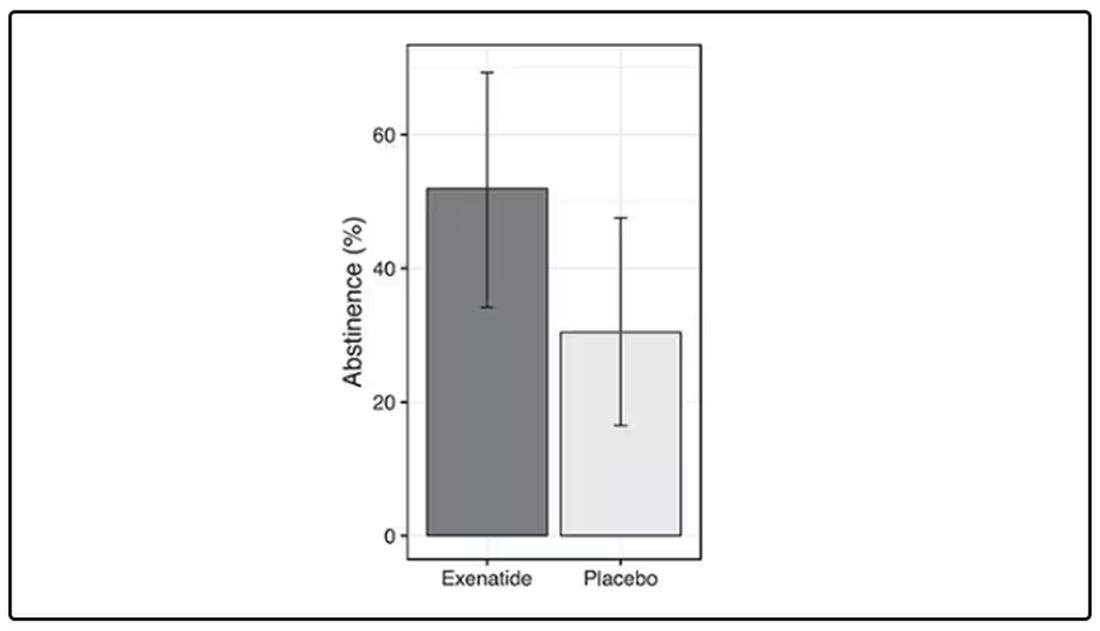
But Byetta is the weaker drug in this class; the market leader is Ozempic. So how can you figure out whether Ozempic can reduce smoking without doing a huge and expensive randomized trial? You can do what Nora Volkow and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse did: a target trial emulation study.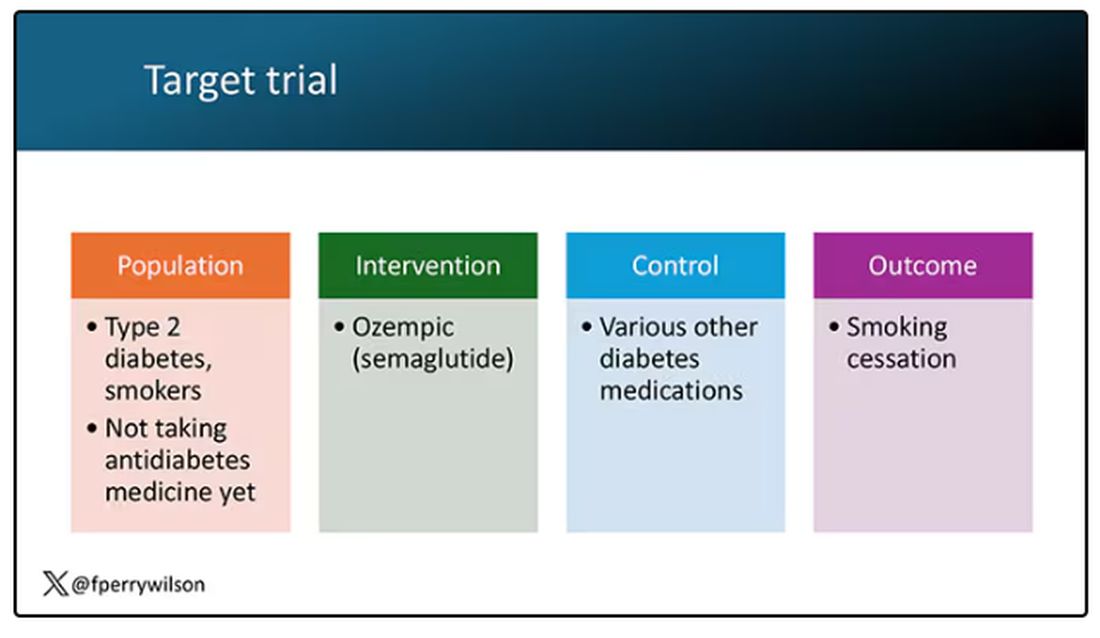
A target trial emulation study is more or less what it sounds like. First, you decide what your dream randomized controlled trial would be and you plan it all out in great detail. You define the population you would recruit, with all the relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria. You define the intervention and the control, and you define the outcome.
But you don’t actually do the trial. You could if someone would lend you $10-$50 million, but assuming you don’t have that lying around, you do the next best thing, which is to dig into a medical record database to find all the people who would be eligible for your imaginary trial. And you analyze them.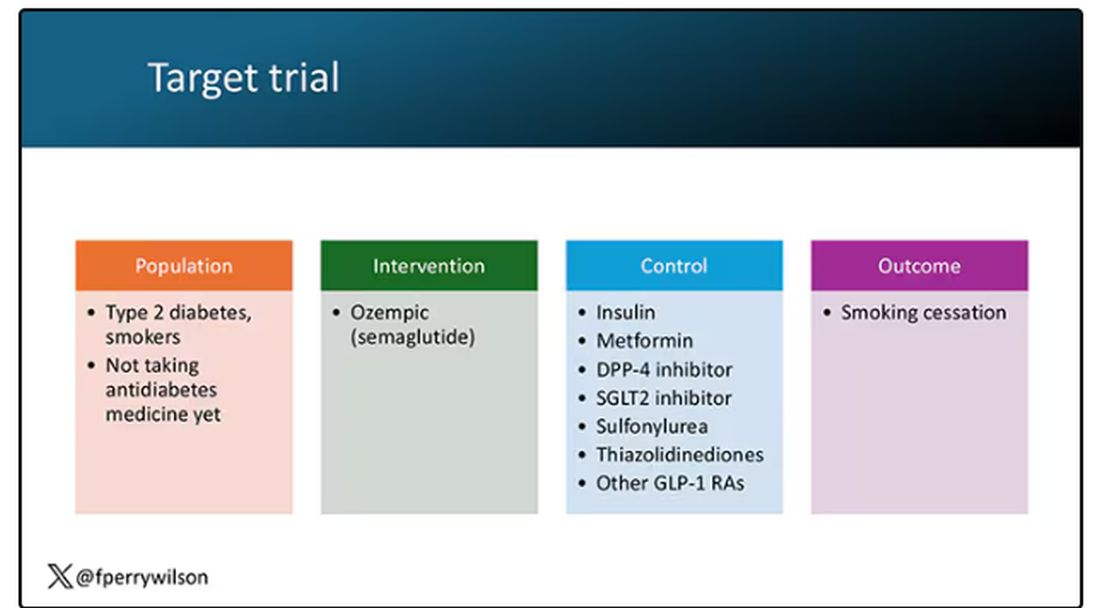
The authors wanted to study the effect of Ozempic on smoking among people with diabetes; that’s why all the comparator agents are antidiabetes drugs. They figured out whether these folks were smoking on the basis of a medical record diagnosis of tobacco use disorder before they started one of the drugs of interest. This code is fairly specific: If a patient has it, you can be pretty sure they are smoking. But it’s not very sensitive; not every smoker has this diagnostic code. This is an age-old limitation of using EHR data instead of asking patients, but it’s part of the tradeoff for not having to spend $50 million.
After applying all those inclusion and exclusion criteria, they have a defined population who could be in their dream trial. And, as luck would have it, some of those people really were treated with Ozempic and some really were treated with those other agents. Although decisions about what to prescribe were not randomized, the authors account for this confounding-by-indication using propensity-score matching. You can find a little explainer on propensity-score matching in an earlier column here. 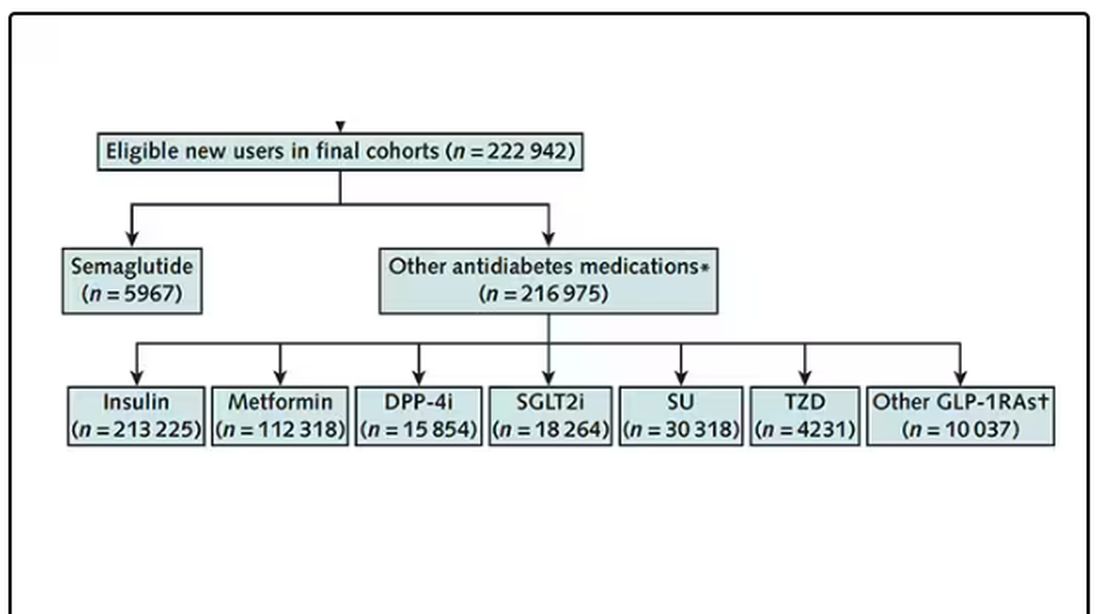
It’s easy enough, using the EHR, to figure out who has diabetes and who got which drug. But how do you know who quit smoking? Remember, everyone had a diagnosis code for tobacco use disorder prior to starting Ozempic or a comparator drug. The authors decided that if the patient had a medical visit where someone again coded tobacco-use disorder, they were still smoking. If someone prescribed smoking cessation meds like a nicotine patch or varenicline, they were obviously still smoking. If someone billed for tobacco-cessation counseling, the patient is still smoking. We’ll get back to the implications of this outcome definition in a minute.
Let’s talk about the results, which are pretty intriguing. 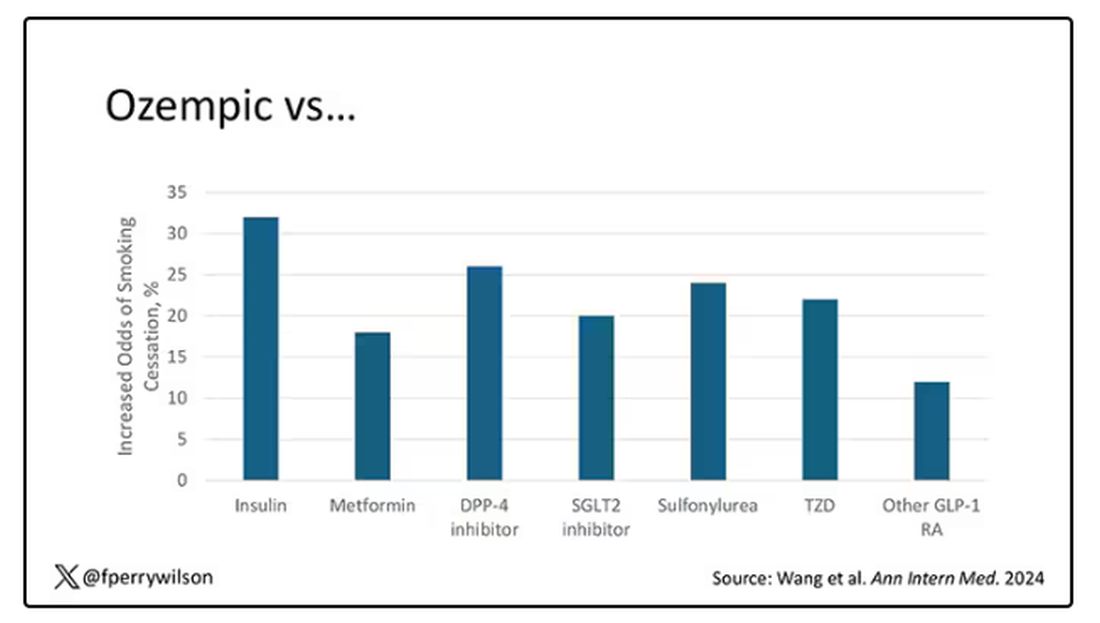
When Ozempic is compared with insulin among smokers with diabetes, those on Ozempic were about 30% more likely to quit smoking. They were about 18% more likely to quit smoking than those who took metformin. They were even slightly more likely to quit smoking than those on other GLP-1 receptor antagonists, though I should note that Mounjaro, which is probably the more potent GLP-1 drug in terms of weight loss, was not among the comparators.
This is pretty impressive for a drug that was not designed to be a smoking cessation drug. It speaks to this emerging idea that these drugs do more than curb appetite by slowing down gastric emptying or something. They work in the brain, modulating some of the reward circuitry that keeps us locked into our bad habits.
There are, of course, some caveats. As I pointed out, this study captured the idea of “still smoking” through the use of administrative codes in the EHR and prescription of smoking cessation aids. You could see similar results if taking Ozempic makes people less likely to address their smoking at all; maybe they shut down the doctor before they even talk about it, or there is too much to discuss during these visits to even get to the subject of smoking. You could also see results like this if people taking Ozempic had fewer visits overall, but the authors showed that that, at least, was not the case.
I’m inclined to believe that this effect is real, simply because we keep seeing signals from multiple sources. If that turns out to be the case, these new “weight loss” drugs may prove to be much more than that; they may turn out to be the drugs that can finally save us from ourselves.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’ve been paying attention only to the headlines, when you think of “Ozempic” you’ll think of a few things: a blockbuster weight loss drug or the tip of the spear of a completely new industry — why not? A drug so popular that the people it was invented for (those with diabetes) can’t even get it.
Ozempic and other GLP-1 receptor agonists are undeniable game changers. Insofar as obesity is the number-one public health risk in the United States, antiobesity drugs hold immense promise even if all they do is reduce obesity.
In 2023, an article in Scientific Reports presented data suggesting that people on Ozempic might be reducing their alcohol intake, not just their total calories.
A 2024 article in Molecular Psychiatry found that the drug might positively impact cannabis use disorder. An article from Brain Sciences suggests that the drug reduces compulsive shopping.
A picture is starting to form, a picture that suggests these drugs curb hunger both literally and figuratively. That GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Mounjaro are fundamentally anticonsumption drugs. In a society that — some would argue — is plagued by overconsumption, these drugs might be just what the doctor ordered.
If only they could stop people from smoking.
Oh, wait — they can.
At least it seems they can, based on a new study appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Before we get too excited, this is not a randomized trial. There actually was a small randomized trial of exenatide (Byetta), which is in the same class as Ozempic but probably a bit less potent, with promising results for smoking cessation. 
But Byetta is the weaker drug in this class; the market leader is Ozempic. So how can you figure out whether Ozempic can reduce smoking without doing a huge and expensive randomized trial? You can do what Nora Volkow and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse did: a target trial emulation study.
A target trial emulation study is more or less what it sounds like. First, you decide what your dream randomized controlled trial would be and you plan it all out in great detail. You define the population you would recruit, with all the relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria. You define the intervention and the control, and you define the outcome.
But you don’t actually do the trial. You could if someone would lend you $10-$50 million, but assuming you don’t have that lying around, you do the next best thing, which is to dig into a medical record database to find all the people who would be eligible for your imaginary trial. And you analyze them.
The authors wanted to study the effect of Ozempic on smoking among people with diabetes; that’s why all the comparator agents are antidiabetes drugs. They figured out whether these folks were smoking on the basis of a medical record diagnosis of tobacco use disorder before they started one of the drugs of interest. This code is fairly specific: If a patient has it, you can be pretty sure they are smoking. But it’s not very sensitive; not every smoker has this diagnostic code. This is an age-old limitation of using EHR data instead of asking patients, but it’s part of the tradeoff for not having to spend $50 million.
After applying all those inclusion and exclusion criteria, they have a defined population who could be in their dream trial. And, as luck would have it, some of those people really were treated with Ozempic and some really were treated with those other agents. Although decisions about what to prescribe were not randomized, the authors account for this confounding-by-indication using propensity-score matching. You can find a little explainer on propensity-score matching in an earlier column here. 
It’s easy enough, using the EHR, to figure out who has diabetes and who got which drug. But how do you know who quit smoking? Remember, everyone had a diagnosis code for tobacco use disorder prior to starting Ozempic or a comparator drug. The authors decided that if the patient had a medical visit where someone again coded tobacco-use disorder, they were still smoking. If someone prescribed smoking cessation meds like a nicotine patch or varenicline, they were obviously still smoking. If someone billed for tobacco-cessation counseling, the patient is still smoking. We’ll get back to the implications of this outcome definition in a minute.
Let’s talk about the results, which are pretty intriguing. 
When Ozempic is compared with insulin among smokers with diabetes, those on Ozempic were about 30% more likely to quit smoking. They were about 18% more likely to quit smoking than those who took metformin. They were even slightly more likely to quit smoking than those on other GLP-1 receptor antagonists, though I should note that Mounjaro, which is probably the more potent GLP-1 drug in terms of weight loss, was not among the comparators.
This is pretty impressive for a drug that was not designed to be a smoking cessation drug. It speaks to this emerging idea that these drugs do more than curb appetite by slowing down gastric emptying or something. They work in the brain, modulating some of the reward circuitry that keeps us locked into our bad habits.
There are, of course, some caveats. As I pointed out, this study captured the idea of “still smoking” through the use of administrative codes in the EHR and prescription of smoking cessation aids. You could see similar results if taking Ozempic makes people less likely to address their smoking at all; maybe they shut down the doctor before they even talk about it, or there is too much to discuss during these visits to even get to the subject of smoking. You could also see results like this if people taking Ozempic had fewer visits overall, but the authors showed that that, at least, was not the case.
I’m inclined to believe that this effect is real, simply because we keep seeing signals from multiple sources. If that turns out to be the case, these new “weight loss” drugs may prove to be much more than that; they may turn out to be the drugs that can finally save us from ourselves.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’ve been paying attention only to the headlines, when you think of “Ozempic” you’ll think of a few things: a blockbuster weight loss drug or the tip of the spear of a completely new industry — why not? A drug so popular that the people it was invented for (those with diabetes) can’t even get it.
Ozempic and other GLP-1 receptor agonists are undeniable game changers. Insofar as obesity is the number-one public health risk in the United States, antiobesity drugs hold immense promise even if all they do is reduce obesity.
In 2023, an article in Scientific Reports presented data suggesting that people on Ozempic might be reducing their alcohol intake, not just their total calories.
A 2024 article in Molecular Psychiatry found that the drug might positively impact cannabis use disorder. An article from Brain Sciences suggests that the drug reduces compulsive shopping.
A picture is starting to form, a picture that suggests these drugs curb hunger both literally and figuratively. That GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Mounjaro are fundamentally anticonsumption drugs. In a society that — some would argue — is plagued by overconsumption, these drugs might be just what the doctor ordered.
If only they could stop people from smoking.
Oh, wait — they can.
At least it seems they can, based on a new study appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Before we get too excited, this is not a randomized trial. There actually was a small randomized trial of exenatide (Byetta), which is in the same class as Ozempic but probably a bit less potent, with promising results for smoking cessation. 
But Byetta is the weaker drug in this class; the market leader is Ozempic. So how can you figure out whether Ozempic can reduce smoking without doing a huge and expensive randomized trial? You can do what Nora Volkow and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse did: a target trial emulation study.
A target trial emulation study is more or less what it sounds like. First, you decide what your dream randomized controlled trial would be and you plan it all out in great detail. You define the population you would recruit, with all the relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria. You define the intervention and the control, and you define the outcome.
But you don’t actually do the trial. You could if someone would lend you $10-$50 million, but assuming you don’t have that lying around, you do the next best thing, which is to dig into a medical record database to find all the people who would be eligible for your imaginary trial. And you analyze them.
The authors wanted to study the effect of Ozempic on smoking among people with diabetes; that’s why all the comparator agents are antidiabetes drugs. They figured out whether these folks were smoking on the basis of a medical record diagnosis of tobacco use disorder before they started one of the drugs of interest. This code is fairly specific: If a patient has it, you can be pretty sure they are smoking. But it’s not very sensitive; not every smoker has this diagnostic code. This is an age-old limitation of using EHR data instead of asking patients, but it’s part of the tradeoff for not having to spend $50 million.
After applying all those inclusion and exclusion criteria, they have a defined population who could be in their dream trial. And, as luck would have it, some of those people really were treated with Ozempic and some really were treated with those other agents. Although decisions about what to prescribe were not randomized, the authors account for this confounding-by-indication using propensity-score matching. You can find a little explainer on propensity-score matching in an earlier column here. 
It’s easy enough, using the EHR, to figure out who has diabetes and who got which drug. But how do you know who quit smoking? Remember, everyone had a diagnosis code for tobacco use disorder prior to starting Ozempic or a comparator drug. The authors decided that if the patient had a medical visit where someone again coded tobacco-use disorder, they were still smoking. If someone prescribed smoking cessation meds like a nicotine patch or varenicline, they were obviously still smoking. If someone billed for tobacco-cessation counseling, the patient is still smoking. We’ll get back to the implications of this outcome definition in a minute.
Let’s talk about the results, which are pretty intriguing. 
When Ozempic is compared with insulin among smokers with diabetes, those on Ozempic were about 30% more likely to quit smoking. They were about 18% more likely to quit smoking than those who took metformin. They were even slightly more likely to quit smoking than those on other GLP-1 receptor antagonists, though I should note that Mounjaro, which is probably the more potent GLP-1 drug in terms of weight loss, was not among the comparators.
This is pretty impressive for a drug that was not designed to be a smoking cessation drug. It speaks to this emerging idea that these drugs do more than curb appetite by slowing down gastric emptying or something. They work in the brain, modulating some of the reward circuitry that keeps us locked into our bad habits.
There are, of course, some caveats. As I pointed out, this study captured the idea of “still smoking” through the use of administrative codes in the EHR and prescription of smoking cessation aids. You could see similar results if taking Ozempic makes people less likely to address their smoking at all; maybe they shut down the doctor before they even talk about it, or there is too much to discuss during these visits to even get to the subject of smoking. You could also see results like this if people taking Ozempic had fewer visits overall, but the authors showed that that, at least, was not the case.
I’m inclined to believe that this effect is real, simply because we keep seeing signals from multiple sources. If that turns out to be the case, these new “weight loss” drugs may prove to be much more than that; they may turn out to be the drugs that can finally save us from ourselves.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vasculopathy Can Vary in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Approximately half of adults with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) had nonplexiform vasculopathy characterized in part by severe pulmonary microvascular remodeling, based on data from 50 individuals.
The clinical phenotype of IPAH was historically described as a rapidly progressive rare disease in young women and characterized by plexiform lesions, wrote Esther J. Nossent, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Centers, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues. However, the patient population with IPAH has become older and predominantly men, and the nature of vascular phenotypes and histologic patterns in patients with contemporary IPAH has not been well studied, the researchers said.
In a cross-sectional study published in CHEST, the researchers reviewed lung histology data from 50 adults with IPAH that had been assessed by two experienced pathologists. The mean age of the patients was 52 years and 58% were women. Based on a histopathologic evaluation, 24 patients had nonplexiform vasculopathy (48%) and 26 had plexiform vasculopathy (52%). Notably, microvascular remodeling involving arterioles and venules was substantial in patients with nonplexiform vasculopathy but mild or absent in those with plexiform vasculopathy, the researchers wrote.
The researchers also compared the clinical characteristics of patients with plexiform vs nonplexiform vasculopathy. Hemodynamic parameters were similar in both patient groups. However, those with nonplexiform vasculopathy were significantly older than those with plexiform vasculopathy (60 years vs 44 years), were more likely to be men (67% vs 20%), and had a lower diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO) at diagnosis (all P < .001). Patients with nonplexiform vasculopathy also were significantly more likely than those with plexiform vasculopathy to have a history of smoking (P = .03). Genetic testing revealed no mutations in established PAH genes in the nonplexiform group.
Low DLCO has been associated with worse outcomes regardless of hemodynamic response, the researchers noted. In the current study, “a DLCO of < 45% almost perfectly identified patients with nonplexiform vasculopathy with prominent pulmonary microvascular disease,” they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the small study population and the higher frequency of surgical lung biopsies in the nonplexiform group vs the plexiform group, which is not part of the general workup of patients with IPAH, the researchers noted.
, they said. However, the results suggest that differences between patients with IPAH with plexiform vasculopathy and those with nonplexiform vasculopathy could ultimately inform targeted treatment strategies.
“Recognizing these clinical phenotypes allows revisiting current datasets to understand better the potential future clinical consequences of the vascular phenotypes for treatment response and clinical outcome,” the researchers concluded.
Findings May Inform More Targeted Therapy
“Any investigation that adds substantive insight into a complex disease that can translate into a better understanding of clinical patient phenotypes and eventually into improved treatments and patient outcomes has relevance at any time,” Paul Forfia, MD, professor of medicine at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, said in an interview.
“There is focus on the antiproliferative forms of pulmonary arterial hypertension–specific therapy, and the results of the current study may have implications to these therapies,” said Dr. Forfia, who was not involved in the current study.
“In the current study, the investigators show that 48% of patients that were traditionally categorized as IPAH had a vascular phenotype that is not considered ‘typical’ or classic for IPAH,” Dr. Forfia told this news organization. “These findings highlight a significant heterogeneity of the pulmonary vascular phenotype within IPAH, which raises the question of whether the nonplexiform patient would be less responsive to the novel, antiproliferative forms of therapy,” he said.
The new findings are quite interesting but not surprising, Dr. Forfia said. “The World Symposia diagnostic groupings for pulmonary hypertension are a very important and necessary form of categorization and differentiation amongst forms of PH [pulmonary hypertension], and these groupings make a best attempt based on available evidence to separate patients of varying PH pathophysiology, both in terms of diagnosis and in how PH patients are treated,” he explained.
“However, clinical experts in PH have known that subphenotypes of PH pathophysiology exist within group I PAH, as well as in PH related to left heart disease (group 2), chronic respiratory disease (group 3), and chronic thromboembolic disease (group 4),” he said.
Findings from the current study reinforce the importance of clinical and physiological phenotyping of each patient, which can help in terms of therapy selection and in managing expectations in response to therapy, Dr. Forfia added.
“Perhaps the most evident and important clinical implication from the current study is to remind clinicians treating patients with PH that heterogeneity exists within the vascular phenotype and clinical makeup of patients even within the same type of PAH,” Dr. Forfia said. “With this insight, clinicians are more informed and thus more apt to consider nuances in the diagnosis, treatment, and expectations for treatment response within PAH,” he said.
Dr. Forfia also highlighted the potential implications of the association between cigarette smoking and the nonplexiform vascular phenotype. “This association was present in the absence of radiographic evidence of emphysema and raises the provocative notion that cigarette smoking may lead to pulmonary vascular abnormalities, perhaps even PAH, in patients without a diagnosis of emphysema,” he said.
“An important limitation from the current study is that the vascular phenotypes observed within their cohort of IPAH patients were obtained from histopathology specimens at the time of autopsy, explant at the time of lung transplantation, and surgical lung biopsy spanning over a 22-year period,” Dr. Forfia noted. Additional research is needed to explore how vascular phenotypic differences can be appreciated in the absence of histopathology and how these differences could impact therapy selection and patient outcomes, he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Nossent disclosed receiving speaker fees from Janssen, MSD, and United Therapeutics/Ferrer and consulting fees from Janssen and United Therapeutics/Ferrer. Dr. Forfia had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approximately half of adults with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) had nonplexiform vasculopathy characterized in part by severe pulmonary microvascular remodeling, based on data from 50 individuals.
The clinical phenotype of IPAH was historically described as a rapidly progressive rare disease in young women and characterized by plexiform lesions, wrote Esther J. Nossent, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Centers, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues. However, the patient population with IPAH has become older and predominantly men, and the nature of vascular phenotypes and histologic patterns in patients with contemporary IPAH has not been well studied, the researchers said.
In a cross-sectional study published in CHEST, the researchers reviewed lung histology data from 50 adults with IPAH that had been assessed by two experienced pathologists. The mean age of the patients was 52 years and 58% were women. Based on a histopathologic evaluation, 24 patients had nonplexiform vasculopathy (48%) and 26 had plexiform vasculopathy (52%). Notably, microvascular remodeling involving arterioles and venules was substantial in patients with nonplexiform vasculopathy but mild or absent in those with plexiform vasculopathy, the researchers wrote.
The researchers also compared the clinical characteristics of patients with plexiform vs nonplexiform vasculopathy. Hemodynamic parameters were similar in both patient groups. However, those with nonplexiform vasculopathy were significantly older than those with plexiform vasculopathy (60 years vs 44 years), were more likely to be men (67% vs 20%), and had a lower diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO) at diagnosis (all P < .001). Patients with nonplexiform vasculopathy also were significantly more likely than those with plexiform vasculopathy to have a history of smoking (P = .03). Genetic testing revealed no mutations in established PAH genes in the nonplexiform group.
Low DLCO has been associated with worse outcomes regardless of hemodynamic response, the researchers noted. In the current study, “a DLCO of < 45% almost perfectly identified patients with nonplexiform vasculopathy with prominent pulmonary microvascular disease,” they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the small study population and the higher frequency of surgical lung biopsies in the nonplexiform group vs the plexiform group, which is not part of the general workup of patients with IPAH, the researchers noted.
, they said. However, the results suggest that differences between patients with IPAH with plexiform vasculopathy and those with nonplexiform vasculopathy could ultimately inform targeted treatment strategies.
“Recognizing these clinical phenotypes allows revisiting current datasets to understand better the potential future clinical consequences of the vascular phenotypes for treatment response and clinical outcome,” the researchers concluded.
Findings May Inform More Targeted Therapy
“Any investigation that adds substantive insight into a complex disease that can translate into a better understanding of clinical patient phenotypes and eventually into improved treatments and patient outcomes has relevance at any time,” Paul Forfia, MD, professor of medicine at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, said in an interview.
“There is focus on the antiproliferative forms of pulmonary arterial hypertension–specific therapy, and the results of the current study may have implications to these therapies,” said Dr. Forfia, who was not involved in the current study.
“In the current study, the investigators show that 48% of patients that were traditionally categorized as IPAH had a vascular phenotype that is not considered ‘typical’ or classic for IPAH,” Dr. Forfia told this news organization. “These findings highlight a significant heterogeneity of the pulmonary vascular phenotype within IPAH, which raises the question of whether the nonplexiform patient would be less responsive to the novel, antiproliferative forms of therapy,” he said.
The new findings are quite interesting but not surprising, Dr. Forfia said. “The World Symposia diagnostic groupings for pulmonary hypertension are a very important and necessary form of categorization and differentiation amongst forms of PH [pulmonary hypertension], and these groupings make a best attempt based on available evidence to separate patients of varying PH pathophysiology, both in terms of diagnosis and in how PH patients are treated,” he explained.
“However, clinical experts in PH have known that subphenotypes of PH pathophysiology exist within group I PAH, as well as in PH related to left heart disease (group 2), chronic respiratory disease (group 3), and chronic thromboembolic disease (group 4),” he said.
Findings from the current study reinforce the importance of clinical and physiological phenotyping of each patient, which can help in terms of therapy selection and in managing expectations in response to therapy, Dr. Forfia added.
“Perhaps the most evident and important clinical implication from the current study is to remind clinicians treating patients with PH that heterogeneity exists within the vascular phenotype and clinical makeup of patients even within the same type of PAH,” Dr. Forfia said. “With this insight, clinicians are more informed and thus more apt to consider nuances in the diagnosis, treatment, and expectations for treatment response within PAH,” he said.
Dr. Forfia also highlighted the potential implications of the association between cigarette smoking and the nonplexiform vascular phenotype. “This association was present in the absence of radiographic evidence of emphysema and raises the provocative notion that cigarette smoking may lead to pulmonary vascular abnormalities, perhaps even PAH, in patients without a diagnosis of emphysema,” he said.
“An important limitation from the current study is that the vascular phenotypes observed within their cohort of IPAH patients were obtained from histopathology specimens at the time of autopsy, explant at the time of lung transplantation, and surgical lung biopsy spanning over a 22-year period,” Dr. Forfia noted. Additional research is needed to explore how vascular phenotypic differences can be appreciated in the absence of histopathology and how these differences could impact therapy selection and patient outcomes, he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Nossent disclosed receiving speaker fees from Janssen, MSD, and United Therapeutics/Ferrer and consulting fees from Janssen and United Therapeutics/Ferrer. Dr. Forfia had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approximately half of adults with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) had nonplexiform vasculopathy characterized in part by severe pulmonary microvascular remodeling, based on data from 50 individuals.
The clinical phenotype of IPAH was historically described as a rapidly progressive rare disease in young women and characterized by plexiform lesions, wrote Esther J. Nossent, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Centers, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues. However, the patient population with IPAH has become older and predominantly men, and the nature of vascular phenotypes and histologic patterns in patients with contemporary IPAH has not been well studied, the researchers said.
In a cross-sectional study published in CHEST, the researchers reviewed lung histology data from 50 adults with IPAH that had been assessed by two experienced pathologists. The mean age of the patients was 52 years and 58% were women. Based on a histopathologic evaluation, 24 patients had nonplexiform vasculopathy (48%) and 26 had plexiform vasculopathy (52%). Notably, microvascular remodeling involving arterioles and venules was substantial in patients with nonplexiform vasculopathy but mild or absent in those with plexiform vasculopathy, the researchers wrote.
The researchers also compared the clinical characteristics of patients with plexiform vs nonplexiform vasculopathy. Hemodynamic parameters were similar in both patient groups. However, those with nonplexiform vasculopathy were significantly older than those with plexiform vasculopathy (60 years vs 44 years), were more likely to be men (67% vs 20%), and had a lower diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO) at diagnosis (all P < .001). Patients with nonplexiform vasculopathy also were significantly more likely than those with plexiform vasculopathy to have a history of smoking (P = .03). Genetic testing revealed no mutations in established PAH genes in the nonplexiform group.
Low DLCO has been associated with worse outcomes regardless of hemodynamic response, the researchers noted. In the current study, “a DLCO of < 45% almost perfectly identified patients with nonplexiform vasculopathy with prominent pulmonary microvascular disease,” they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the small study population and the higher frequency of surgical lung biopsies in the nonplexiform group vs the plexiform group, which is not part of the general workup of patients with IPAH, the researchers noted.
, they said. However, the results suggest that differences between patients with IPAH with plexiform vasculopathy and those with nonplexiform vasculopathy could ultimately inform targeted treatment strategies.
“Recognizing these clinical phenotypes allows revisiting current datasets to understand better the potential future clinical consequences of the vascular phenotypes for treatment response and clinical outcome,” the researchers concluded.
Findings May Inform More Targeted Therapy
“Any investigation that adds substantive insight into a complex disease that can translate into a better understanding of clinical patient phenotypes and eventually into improved treatments and patient outcomes has relevance at any time,” Paul Forfia, MD, professor of medicine at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, said in an interview.
“There is focus on the antiproliferative forms of pulmonary arterial hypertension–specific therapy, and the results of the current study may have implications to these therapies,” said Dr. Forfia, who was not involved in the current study.
“In the current study, the investigators show that 48% of patients that were traditionally categorized as IPAH had a vascular phenotype that is not considered ‘typical’ or classic for IPAH,” Dr. Forfia told this news organization. “These findings highlight a significant heterogeneity of the pulmonary vascular phenotype within IPAH, which raises the question of whether the nonplexiform patient would be less responsive to the novel, antiproliferative forms of therapy,” he said.
The new findings are quite interesting but not surprising, Dr. Forfia said. “The World Symposia diagnostic groupings for pulmonary hypertension are a very important and necessary form of categorization and differentiation amongst forms of PH [pulmonary hypertension], and these groupings make a best attempt based on available evidence to separate patients of varying PH pathophysiology, both in terms of diagnosis and in how PH patients are treated,” he explained.
“However, clinical experts in PH have known that subphenotypes of PH pathophysiology exist within group I PAH, as well as in PH related to left heart disease (group 2), chronic respiratory disease (group 3), and chronic thromboembolic disease (group 4),” he said.
Findings from the current study reinforce the importance of clinical and physiological phenotyping of each patient, which can help in terms of therapy selection and in managing expectations in response to therapy, Dr. Forfia added.
“Perhaps the most evident and important clinical implication from the current study is to remind clinicians treating patients with PH that heterogeneity exists within the vascular phenotype and clinical makeup of patients even within the same type of PAH,” Dr. Forfia said. “With this insight, clinicians are more informed and thus more apt to consider nuances in the diagnosis, treatment, and expectations for treatment response within PAH,” he said.
Dr. Forfia also highlighted the potential implications of the association between cigarette smoking and the nonplexiform vascular phenotype. “This association was present in the absence of radiographic evidence of emphysema and raises the provocative notion that cigarette smoking may lead to pulmonary vascular abnormalities, perhaps even PAH, in patients without a diagnosis of emphysema,” he said.
“An important limitation from the current study is that the vascular phenotypes observed within their cohort of IPAH patients were obtained from histopathology specimens at the time of autopsy, explant at the time of lung transplantation, and surgical lung biopsy spanning over a 22-year period,” Dr. Forfia noted. Additional research is needed to explore how vascular phenotypic differences can be appreciated in the absence of histopathology and how these differences could impact therapy selection and patient outcomes, he said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Nossent disclosed receiving speaker fees from Janssen, MSD, and United Therapeutics/Ferrer and consulting fees from Janssen and United Therapeutics/Ferrer. Dr. Forfia had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Could Resistin Predict Death and Disease Severity in PAH?
Resistin, a cytokine expressed in adipocytes, has been associated with poor clinical outcomes in heart failure and cardiovascular disease, Li Gao, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, and colleagues wrote. While mouse studies have shown that human resistin drives pulmonary vascular remodeling and the development of PAH, the role of resistin as a biomarker for PAH remains unclear.
In a study published in Respiratory Research, the researchers reviewed biospecimens and clinical and genetic data from 1121 adults with PAH, 808 with idiopathic PAH (IPAH), and 313 with scleroderma-associated PAH (SSc-PAH). They examined the associations between serum resistin levels and PAH outcomes in multivariate regression models, using machine-learning algorithms to develop models to predict mortality.
Resistin levels were significantly higher in all patients with PAH and patients with the two subtypes than in control participants (all P < .0001). Resistin was also associated with significant discriminative properties, with area under the curve (AUC) measures of 0.84, 0.82, and 0.91 for PAH overall, IPAH, and SSc-PAH, respectively.
Elevated resistin levels (defined as > 4.54 ng/mL) were significantly associated with an increased risk for death (hazard ratio, 2.6; P < .0087) as well as with older age and shorter distance on the 6-minute walk test (P = .001 for both) and reduced cardiac capacity based on the New York Heart Association functional class (P < .014).
Survival models derived from machine learning confirmed the prognostic value of resistin for mortality in PAH as seen in the random forest model, with an AUC of 0.70. “When we used the AUC values of the ROC curve as criteria to evaluate how well resistin levels discerned the presence of PAH, all three tests had excellent discriminative ability (AUCs were 0.84, 0.82, and 0.91 for all PAH, IPAH, and SSc-PAH, respectively),” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also evaluated three RETN genetic variants (rs7408174, rs3219175, and rs3745367) for a specific association with serum resistin levels and measures of PAH severity. Resistin levels were highest among individuals who were carriers of either the rs3219175 or rs3745367 mutation, the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors, including missing data on the 6-minute walk test from several centers, which led to the elimination of that item from the survival analysis. Other limitations included the inability to control for PAH therapy at the time of assessment and the collection of serum at a different time from other clinical variables.
However, “our study provides evidence to support the use of circulating biomarkers as objective and accessible tools for noninvasive PAH risk stratification,” the researchers said. Additional research is needed to strengthen the association, but the findings suggest that resistin represents a novel biomarker for PAH prognostication and risk stratification and may have implications for the development of new treatments.
Biomarker Research Expands Diagnosis and Treatment Horizons
“It is a dynamic time in PAH research and clinical management, given the recent approval and use of the BMP/TGF beta balancing agent sotatercept (Winrevair) as an effective agent to target the molecular origins of this disease,” Stephen Chan, MD, professor of medicine and director of the Vascular Medicine Institute at the University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, said in an interview.
The growing number of medications that can be used to treat patients with PAH will likely be more effective if patients are identified and treated early, said Dr. Chan, who was not involved in the study.
However, the time to diagnosis for patients with PAH is still more than 3 years from the start of symptoms, he said. Factors contributing to the delay include the requirement of an invasive cardiac catheterization procedure to make the final diagnosis, the status of PAH as a borderline orphan disease, and the often nonspecific nature of the initial symptoms of PAH.
Consequently, “there is an unmet need to develop effective and preferably noninvasive tools to aid in early diagnosis of PAH,” Dr. Chan added.
The power of the study is in the number of patients included, as much of previous PAH research has involved small studies of patients that could not be replicated or did not generalize to the larger patient population, Dr. Chan said.
The use of the PAH Biobank allows researchers to access a larger population of patients with PAH. “With that in mind, it is not surprising that some markers would emerge as potentially powerful and clinically meaningful,” he said.
“Currently, we do not have a reliable blood-based biomarker that we use in clinical PAH practice, although there are emerging studies that suggest other markers such as metabolites, RNA molecules, and proteins that may serve in the same capacity. If these studies turn out to be reproducible, generalizable, and specific to PAH in larger populations, measuring resistin could be helpful in making early diagnosis, particularly in areas that do not have invasive catheterization facilities (and globally) and for nonspecialists who are puzzled about the nonspecificity of initial symptoms of PAH,” Dr. Chan said.
Resistin could also be incorporated into existing risk stratification scores, such as the REVEAL risk score, that are already used in PAH clinical practice as guidance for when and how to use currently approved medications, he added.
Limitations of the study included the focus only on resistin alone, not in combination with other molecules that might perform better. Also, no independent validation cohort was used, he noted. “While PAH Biobank certainly offered larger numbers than we typically see, we would have to see validation in large independent cohorts for us to be convinced that measurements of resistin should be used in clinical practice.”
Resistin is not specific to PAH, which makes interpretation of the results more complicated, said Dr. Chan. “In this study, the authors used a smaller healthy control cohort of 50 patients as a comparison to their PAH cohort. However, they did not compare their PAH cohort with other cohorts that represent these other ‘resistin-relevant diseases’ and thus do not know whether they can distinguish PAH from any of these other diseases based on simply the resistin levels.” The frequency of comorbidities in patients with PAH, such as obesity, other inflammatory diseases, and cardiovascular disease, could confound the resistin levels.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Chan had financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Resistin, a cytokine expressed in adipocytes, has been associated with poor clinical outcomes in heart failure and cardiovascular disease, Li Gao, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, and colleagues wrote. While mouse studies have shown that human resistin drives pulmonary vascular remodeling and the development of PAH, the role of resistin as a biomarker for PAH remains unclear.
In a study published in Respiratory Research, the researchers reviewed biospecimens and clinical and genetic data from 1121 adults with PAH, 808 with idiopathic PAH (IPAH), and 313 with scleroderma-associated PAH (SSc-PAH). They examined the associations between serum resistin levels and PAH outcomes in multivariate regression models, using machine-learning algorithms to develop models to predict mortality.
Resistin levels were significantly higher in all patients with PAH and patients with the two subtypes than in control participants (all P < .0001). Resistin was also associated with significant discriminative properties, with area under the curve (AUC) measures of 0.84, 0.82, and 0.91 for PAH overall, IPAH, and SSc-PAH, respectively.
Elevated resistin levels (defined as > 4.54 ng/mL) were significantly associated with an increased risk for death (hazard ratio, 2.6; P < .0087) as well as with older age and shorter distance on the 6-minute walk test (P = .001 for both) and reduced cardiac capacity based on the New York Heart Association functional class (P < .014).
Survival models derived from machine learning confirmed the prognostic value of resistin for mortality in PAH as seen in the random forest model, with an AUC of 0.70. “When we used the AUC values of the ROC curve as criteria to evaluate how well resistin levels discerned the presence of PAH, all three tests had excellent discriminative ability (AUCs were 0.84, 0.82, and 0.91 for all PAH, IPAH, and SSc-PAH, respectively),” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also evaluated three RETN genetic variants (rs7408174, rs3219175, and rs3745367) for a specific association with serum resistin levels and measures of PAH severity. Resistin levels were highest among individuals who were carriers of either the rs3219175 or rs3745367 mutation, the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors, including missing data on the 6-minute walk test from several centers, which led to the elimination of that item from the survival analysis. Other limitations included the inability to control for PAH therapy at the time of assessment and the collection of serum at a different time from other clinical variables.
However, “our study provides evidence to support the use of circulating biomarkers as objective and accessible tools for noninvasive PAH risk stratification,” the researchers said. Additional research is needed to strengthen the association, but the findings suggest that resistin represents a novel biomarker for PAH prognostication and risk stratification and may have implications for the development of new treatments.
Biomarker Research Expands Diagnosis and Treatment Horizons
“It is a dynamic time in PAH research and clinical management, given the recent approval and use of the BMP/TGF beta balancing agent sotatercept (Winrevair) as an effective agent to target the molecular origins of this disease,” Stephen Chan, MD, professor of medicine and director of the Vascular Medicine Institute at the University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, said in an interview.
The growing number of medications that can be used to treat patients with PAH will likely be more effective if patients are identified and treated early, said Dr. Chan, who was not involved in the study.
However, the time to diagnosis for patients with PAH is still more than 3 years from the start of symptoms, he said. Factors contributing to the delay include the requirement of an invasive cardiac catheterization procedure to make the final diagnosis, the status of PAH as a borderline orphan disease, and the often nonspecific nature of the initial symptoms of PAH.
Consequently, “there is an unmet need to develop effective and preferably noninvasive tools to aid in early diagnosis of PAH,” Dr. Chan added.
The power of the study is in the number of patients included, as much of previous PAH research has involved small studies of patients that could not be replicated or did not generalize to the larger patient population, Dr. Chan said.
The use of the PAH Biobank allows researchers to access a larger population of patients with PAH. “With that in mind, it is not surprising that some markers would emerge as potentially powerful and clinically meaningful,” he said.
“Currently, we do not have a reliable blood-based biomarker that we use in clinical PAH practice, although there are emerging studies that suggest other markers such as metabolites, RNA molecules, and proteins that may serve in the same capacity. If these studies turn out to be reproducible, generalizable, and specific to PAH in larger populations, measuring resistin could be helpful in making early diagnosis, particularly in areas that do not have invasive catheterization facilities (and globally) and for nonspecialists who are puzzled about the nonspecificity of initial symptoms of PAH,” Dr. Chan said.
Resistin could also be incorporated into existing risk stratification scores, such as the REVEAL risk score, that are already used in PAH clinical practice as guidance for when and how to use currently approved medications, he added.
Limitations of the study included the focus only on resistin alone, not in combination with other molecules that might perform better. Also, no independent validation cohort was used, he noted. “While PAH Biobank certainly offered larger numbers than we typically see, we would have to see validation in large independent cohorts for us to be convinced that measurements of resistin should be used in clinical practice.”
Resistin is not specific to PAH, which makes interpretation of the results more complicated, said Dr. Chan. “In this study, the authors used a smaller healthy control cohort of 50 patients as a comparison to their PAH cohort. However, they did not compare their PAH cohort with other cohorts that represent these other ‘resistin-relevant diseases’ and thus do not know whether they can distinguish PAH from any of these other diseases based on simply the resistin levels.” The frequency of comorbidities in patients with PAH, such as obesity, other inflammatory diseases, and cardiovascular disease, could confound the resistin levels.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Chan had financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Resistin, a cytokine expressed in adipocytes, has been associated with poor clinical outcomes in heart failure and cardiovascular disease, Li Gao, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, and colleagues wrote. While mouse studies have shown that human resistin drives pulmonary vascular remodeling and the development of PAH, the role of resistin as a biomarker for PAH remains unclear.
In a study published in Respiratory Research, the researchers reviewed biospecimens and clinical and genetic data from 1121 adults with PAH, 808 with idiopathic PAH (IPAH), and 313 with scleroderma-associated PAH (SSc-PAH). They examined the associations between serum resistin levels and PAH outcomes in multivariate regression models, using machine-learning algorithms to develop models to predict mortality.
Resistin levels were significantly higher in all patients with PAH and patients with the two subtypes than in control participants (all P < .0001). Resistin was also associated with significant discriminative properties, with area under the curve (AUC) measures of 0.84, 0.82, and 0.91 for PAH overall, IPAH, and SSc-PAH, respectively.
Elevated resistin levels (defined as > 4.54 ng/mL) were significantly associated with an increased risk for death (hazard ratio, 2.6; P < .0087) as well as with older age and shorter distance on the 6-minute walk test (P = .001 for both) and reduced cardiac capacity based on the New York Heart Association functional class (P < .014).
Survival models derived from machine learning confirmed the prognostic value of resistin for mortality in PAH as seen in the random forest model, with an AUC of 0.70. “When we used the AUC values of the ROC curve as criteria to evaluate how well resistin levels discerned the presence of PAH, all three tests had excellent discriminative ability (AUCs were 0.84, 0.82, and 0.91 for all PAH, IPAH, and SSc-PAH, respectively),” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also evaluated three RETN genetic variants (rs7408174, rs3219175, and rs3745367) for a specific association with serum resistin levels and measures of PAH severity. Resistin levels were highest among individuals who were carriers of either the rs3219175 or rs3745367 mutation, the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors, including missing data on the 6-minute walk test from several centers, which led to the elimination of that item from the survival analysis. Other limitations included the inability to control for PAH therapy at the time of assessment and the collection of serum at a different time from other clinical variables.
However, “our study provides evidence to support the use of circulating biomarkers as objective and accessible tools for noninvasive PAH risk stratification,” the researchers said. Additional research is needed to strengthen the association, but the findings suggest that resistin represents a novel biomarker for PAH prognostication and risk stratification and may have implications for the development of new treatments.
Biomarker Research Expands Diagnosis and Treatment Horizons
“It is a dynamic time in PAH research and clinical management, given the recent approval and use of the BMP/TGF beta balancing agent sotatercept (Winrevair) as an effective agent to target the molecular origins of this disease,” Stephen Chan, MD, professor of medicine and director of the Vascular Medicine Institute at the University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, said in an interview.
The growing number of medications that can be used to treat patients with PAH will likely be more effective if patients are identified and treated early, said Dr. Chan, who was not involved in the study.
However, the time to diagnosis for patients with PAH is still more than 3 years from the start of symptoms, he said. Factors contributing to the delay include the requirement of an invasive cardiac catheterization procedure to make the final diagnosis, the status of PAH as a borderline orphan disease, and the often nonspecific nature of the initial symptoms of PAH.
Consequently, “there is an unmet need to develop effective and preferably noninvasive tools to aid in early diagnosis of PAH,” Dr. Chan added.
The power of the study is in the number of patients included, as much of previous PAH research has involved small studies of patients that could not be replicated or did not generalize to the larger patient population, Dr. Chan said.
The use of the PAH Biobank allows researchers to access a larger population of patients with PAH. “With that in mind, it is not surprising that some markers would emerge as potentially powerful and clinically meaningful,” he said.
“Currently, we do not have a reliable blood-based biomarker that we use in clinical PAH practice, although there are emerging studies that suggest other markers such as metabolites, RNA molecules, and proteins that may serve in the same capacity. If these studies turn out to be reproducible, generalizable, and specific to PAH in larger populations, measuring resistin could be helpful in making early diagnosis, particularly in areas that do not have invasive catheterization facilities (and globally) and for nonspecialists who are puzzled about the nonspecificity of initial symptoms of PAH,” Dr. Chan said.
Resistin could also be incorporated into existing risk stratification scores, such as the REVEAL risk score, that are already used in PAH clinical practice as guidance for when and how to use currently approved medications, he added.
Limitations of the study included the focus only on resistin alone, not in combination with other molecules that might perform better. Also, no independent validation cohort was used, he noted. “While PAH Biobank certainly offered larger numbers than we typically see, we would have to see validation in large independent cohorts for us to be convinced that measurements of resistin should be used in clinical practice.”
Resistin is not specific to PAH, which makes interpretation of the results more complicated, said Dr. Chan. “In this study, the authors used a smaller healthy control cohort of 50 patients as a comparison to their PAH cohort. However, they did not compare their PAH cohort with other cohorts that represent these other ‘resistin-relevant diseases’ and thus do not know whether they can distinguish PAH from any of these other diseases based on simply the resistin levels.” The frequency of comorbidities in patients with PAH, such as obesity, other inflammatory diseases, and cardiovascular disease, could confound the resistin levels.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Chan had financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Using Telehealth to Increase Lung Cancer Screening Referrals for At-Risk Veterans in Rural Communities
Annual lung cancer screening (LCS) with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) of the chest has been shown to reduce mortality rates for individuals at risk for lung cancer.1 Despite the benefits, < 5% of those who were eligible for LCS in the United States were screened in 2022.2 Implementation of a LCS program in rural communities is especially challenging because they are sparsely populated, medically underserved, and located far from urban centers.2-7 It is estimated that 1 in 5 people live in rural areas. Rates of tobacco smoking and cancer are higher in rural communities when compared with urban communities.8,9 The scarcity of physicians in rural areas who are familiar with LCS may further impede individuals who are at risk from accessing this life saving service.5,6 As a result, these individuals may not regularly undergo LCS as recommended.9
Telehealth, or the remote delivery of health care services via telecommunications, is an emerging approach for addressing unmet medical needs in rural communities and is being utilized widely by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA).4,10-15 The Veterans Integrated Service Network 12 (Great Lakes Network) has established the Clinical Resource Hub (CRH), a telehealth network comprising of licensed independent physicians, nurse practitioners, registered nurses, and ancillary staff. The CRH offers regular, remote health care services to several community-based outpatient clinics (CBOC) primary care clinics located in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.10,14
The utility of telehealth in promoting LCS among at-risk veterans living in rural communities has not been firmly established.4-6 To address this issue, we conducted a proof-of-principle quality improvement project to determine whether a telehealth intervention would increase referrals among at-risk veterans who reside in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan who are self-enrolled in a CBOC smoking cessation program in Green Bay, Wisconsin. The CBOC provides primary health care to veterans residing in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan as defined by US Department of Agriculture rural-urban commuting area codes.16 The intervention aimed to refer these individuals to the closest available and centralized LCS program, which is located at the Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
METHODS
We reviewed electronic health records (EHR) of LCS-eligible veterans treated by 2 authors (SH and TB) who were self-enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the Green Bay CBOC between October 1, 2020, and September 30, 2021. The program provides comprehensive evidence-based tobacco use treatment, online self-help resources, behavioral counseling, and medicines for smoking cessation.17 Veterans aged 50 to 80 years with a smoking history of ≥ 20 pack-years, who currently smoke cigarettes or quit within the past 15 years, were considered at risk for lung cancer and eligible for LCS. After confirming eligibility, pertinent demographic data were abstracted from each EHR.
Telehealth Intervention
The CJZVAMC centralized LCS program manages all delivery processes and has been previously shown to increase uptake of LCS and improve patient outcomes among veterans as compared to a decentralized approach.18,19 In the centralized approach, eligible veterans were referred by a CBOC primary care practitioner (PCP) to a designated centralized LCS program. The centralized LCS program provides further evaluation and disposition, which includes structured and shared decision making, ordering LDCT of the chest, reporting LDCT results to the patient and PCP, devising a goal-directed care plan, and managing follow-up LDCTs as indicated (Figure 1).18,19
This intervention was initiated before other measures aimed to increase the LCS enrollment for at-risk rural veterans at the CBOC, (eg, mailing LCS education fact sheet to veterans).20 After reviewing prospective veterans’ EHRs, 1 author (TB) contacted LCS-eligible veterans by telephone and left a voicemail if contact could not be established. A second telephone call was placed within 2 months of the initial call if no call back was documented in the EHR. When verbal contact was established, the goals of the centralized LCS program were described and the veteran was invited to participate.21
Veterans were seen at CBOCs affiliated with CJZVAMC. The CJZVAMC LCS coordinator was notified whenever a veteran agreed to enroll into LCS and then ordered LDCT, which was performed and read at CJZVAMC. Once LDCT has been ordered, 1 author (TB) reviewed the veteran’s EHR for LDCT completion over the next 4 months.Upon conclusion of the intervention period, the number of veterans referred for LDCT and the number of LDCTs performed were recorded. Each LDCT was reviewed and coded by medical imaging clinicians according to Lung CT Screening Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS) version 1.1 and coded as 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 based on the nodule with the highest degree of suspicion.22 The LDCT and reports were also reviewed by pulmonary physicians at the CJZVAMC Lung Nodule Clinic with recommendations issued and reported to the PCP treating the veteran, such as annual follow-up with LDCT or referral to specialty care for further evaluation as indicated.
RESULTS
Of 117 veterans enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the CBOC during the intervention period, 74 (63%) were eligible to undergo LCS, and 68 (58%) were contacted by telephone (Figure 2). Eligible patients were primarily White male veterans; their mean (SD) age was 65.0 years (7.6). Participation in LCS was discussed with 41 (60%) veterans either during the initial or second telephone call of which 29 (71%) agreed to enroll and 12 (29%) declined. Veterans did not provide reasons for declining participation at the time of the telephone call.
Among the 74 eligible veterans who attended the smoking cessation program, only 3 had LDCT performed before initiation of this project (4%). At the conclusion of the telehealth intervention period, 19 veterans had LDCT performed (26%). Ten LDCTs were coded Lung-RADS 1, 7 Lung-RADS 2, 1 Lung-RADS 3, and 1 Lung-RADS 4B. In each case, annual follow-up LDCT or referral to a LCS clinician was pursued as indicated.22
DISCUSSION
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that a high percentage (66%) of individuals in rural communities who were contacted via telehealth agreed to participate in a regional LCS program. The program reviewed LDCT results, ordered follow-up LDCTs, and recommended further evaluations.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process could also promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians, if abnormal imaging findings are detected, remains unclear.
It has been well established LDCT LCS reduces lung cancer-specific and overall mortality rates among eligible current and former smokers.1,9,23 The 5-year relative survival rate of veterans diagnosed with localized non-small cell lung cancer is 63%; that number drops to 7% in those with advanced disease attesting to the utility of LCS in detecting early stage lung cancer.2 Despite these favorable observations, however, screening rates with free LDCT remains low in rural communities.3-7
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that telehealth intervention may increase referrals of at-risk veterans who reside in rural communities to the closest centralized LCS program located at aregional VAMC. This program is responsible for reviewing the results of the initial LDCT, ordering follow-up LDCT, and recommending further evaluation as indicated.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process would promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians if abnormal imaging findings are detected is yet to be determined.
We found that among 74 LCS-eligible rural veterans attending a CBOC-based smoking cessation program, only 3 (4%) underwent LDCT screening before this telehealth intervention was launched. This low LCS rate among veterans attempting to quit smoking may have been related, in part, to a lack of awareness of this intervention and/or barriers to LCS access.7,10,21,24 Deploying a telehealth intervention targeting LCS could address this life threatening and unmet medical need in rural communities.25 The results of this proof-of-principle quality improvement project support this contention with the reported increased referrals to and completion of initial LDCT within 4 months of the telehealth encounter.
Limitations
This was a small, single site project composed of predominantly White male rural veterans participating in a smoking cessation program associated with a VA facility.26,27 It is not clear whether similar outcomes would be observed in at-risk veterans who do not participate in a smoking cessation program or in more diverse communities. We were unable to contact 40% of LCS-eligible rural veterans by telephone. Twelve veterans reached by telephone declined to participate in LCS without providing a reason, and only 19 of 68 eligible veterans (28%) underwent LDCT screening during the 4-month telehealth intervention. The reasons underlying this overall low accrual rate and whether rural veterans prefer other means of personal communication regarding LCS were not determined. Lastly, generalizability of our initial observations to other veterans living in rural communities is limited because the project was conducted only in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.
Conclusions
At-risk rural veterans may be willing to participate in a centralized LCS program at a regional VA medical facility when contacted and coordinated using telehealth modalities. These findings offer support for future prospective, multisite, VA telehealth-based studies to be conducted in rural areas. The results of this project also suggest that telehealth intervention could increase referrals of at-risk rural veterans to the closest centralized LCS program located at a regional VA medical facility.
1. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team, Aberle DR, Adams AM, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(5):395-409. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
2. State of Lung Cancer: 2023 Report. American Lung Association. November 14, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.lung.org/getmedia/186786b6-18c3-46a9-a7e7-810f3ce4deda/SOLC-2023-Print-Report.pdf
3. Okereke IC, Nishi S, Zhou J, Goodwin JS. Trends in lung cancer screening in the United States, 2016-2017. J Thorac Dis. 2019;11(3):873-881. doi:10.21037/jtd.2019.01.105
4. Petraglia AF, Olazagasti JM, Strong A, Dunn B, Anderson RT, Hanley M. Establishing satellite lung cancer screening sites with telehealth to address disparities between high-risk smokers and American College of Radiology-approved Centers of Designation. J Thorac Imaging. 2021;36(1):2-5. doi:10.1097/RTI.0000000000000520
5. Odahowski CL, Zahnd WE, Eberth JM. Challenges and opportunities for lung cancer screening in rural America. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(4 Pt B):590-595. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2019.01.001
6. Rohatgi KW, Marx CM, Lewis-Thames MW, Liu J, Colditz GA, James AS. Urban-rural disparities in access to low-dose computed tomography lung cancer screening in Missouri and Illinois. Prev Chronic Dis. 2020;17:E140. doi:10.5888/pcd17.200202
7. Boudreau JH, Miller DR, Qian S, Nunez ER, Caverly TJ, Wiener RS. Access to lung cancer screening in the Veterans Health Administration: does geographic distribution match need in the population? Chest. 2021;160(1):358-367. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.02.016
8. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al, eds. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017. National Cancer Institute, US Dept of Health and Human Services; April 15, 2020. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2017/index.html
9. US Preventive Services Task Force, Krist AH, Davidson KW, et al. Screening for Lung Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2021;325(10):962-970. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1117
10. Gopal RK, Solanki P, Bokhour BG, et al. Provider, staff, and patient perspectives on medical visits using clinical video telehealth: a foundation for educational initiatives to improve medical care in telehealth. J Nurse Pract. 2021;17(5):582-587. doi:10.1016/j.nurpra.2021.02.020
11. Yacoub JH, Swanson CE, Jay AK, Cooper C, Spies J, Krishnan P. The radiology virtual reading room: during and beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. J Digit Imaging. 2021;34(2):308-319. doi:10.1007/s10278-021-00427-4
12. Beswick DM, Vashi A, Song Y, et al. Consultation via telemedicine and access to operative care for patients with head and neck cancer in a Veterans Health Administration population. Head Neck. 2016;38(6):925-929. doi:10.1002/hed.24386
13. Ruco A, Dossa F, Tinmouth J, et al. Social media and mHealth technology for cancer screening: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(7):e26759. doi:10.2196/26759
14. Raza T, Joshi M, Schapira RM, Agha Z. Pulmonary telemedicine - a model to access the subspecialist services in underserved rural areas. Int J Med Inform. 2009;78(1):53-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2008.07.010
15. Chen A, Ayub MH, Mishuris RG, et al. Telehealth policy, practice, and education: a position statement of the Society of General Internal Medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(11):2613-2620. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08190-8
16. Rural-Urban Commuting Area Codes. Economic Research Service, US Dept of Agriculture. Updated September 25, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes/
17. VHA Directive 1056: National Smoking and Tobacco Use Cessation Program. Veterans Health Administration, US Dept of Veterans Affairs; September 5, 2019. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=8488
18. Smith HB, Ward R, Frazier C, Angotti J, Tanner NT. Guideline-recommended lung cancer screening adherence is superior with a centralized approach. Chest. 2022;161(3):818-825. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.09.002
19. Lewis JA, Samuels LR, Denton J, et al. The association of health care system resources with lung cancer screening implementation: a cohort study. Chest. 2022;162(3):701-711. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2022.03.050
20. US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Lung cancer screening: patient education fact sheet. Accessed July 8, 2024. https://www.cancer.va.gov/assets/pdf/survey/LCSflyer.pdf
21. Melzer AC, Golden SE, Ono SS, Datta S, Crothers K, Slatore CG. What exactly is shared decision-making? A qualitative study of shared decision-making in lung cancer screening. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(2):546-553. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05516-3
22. Chelala L, Hossain R, Kazerooni EA, Christensen JD, Dyer DS, White CS. Lung-RADS Version 1.1: challenges and a look ahead, from the AJR special series on radiology reporting and data systems. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216(6):1411-1422. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.24807
23. Ritzwoller DP, Meza R, Carroll NM, et al. Evaluation of population-level changes associated with the 2021 US Preventive Services Task Force lung cancer screening recommendations in community-based health care systems. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(10):e2128176. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28176
24. Golden SE, Ono SS, Thakurta SG, et al. “I’m putting my trust in their hands”: a qualitative study of patients’ views on clinician initial communication about lung cancer screening. Chest. 2020;158(3):1260-1267. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.02.072
25. Park ER, Chiles C, Cinciripini PM, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on telehealth research in cancer prevention and care: a call to sustain telehealth advances. Cancer. 2021;127(3):334-338. doi:10.1002/cncr.33227
26. Tremblay A, Taghizadeh N, Huang J, et al. A randomized controlled study of integrated smoking cessation in a lung cancer screening program. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14(9):1528-1537. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2019.04.024
27. Neil JM, Marotta C, Gonzalez I, et al. Integrating tobacco treatment into lung cancer screening practices: study protocol for the Screen ASSIST randomized clinical trial. Contemp Clin Trials. 2021;111:106586. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2021.106586
Annual lung cancer screening (LCS) with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) of the chest has been shown to reduce mortality rates for individuals at risk for lung cancer.1 Despite the benefits, < 5% of those who were eligible for LCS in the United States were screened in 2022.2 Implementation of a LCS program in rural communities is especially challenging because they are sparsely populated, medically underserved, and located far from urban centers.2-7 It is estimated that 1 in 5 people live in rural areas. Rates of tobacco smoking and cancer are higher in rural communities when compared with urban communities.8,9 The scarcity of physicians in rural areas who are familiar with LCS may further impede individuals who are at risk from accessing this life saving service.5,6 As a result, these individuals may not regularly undergo LCS as recommended.9
Telehealth, or the remote delivery of health care services via telecommunications, is an emerging approach for addressing unmet medical needs in rural communities and is being utilized widely by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA).4,10-15 The Veterans Integrated Service Network 12 (Great Lakes Network) has established the Clinical Resource Hub (CRH), a telehealth network comprising of licensed independent physicians, nurse practitioners, registered nurses, and ancillary staff. The CRH offers regular, remote health care services to several community-based outpatient clinics (CBOC) primary care clinics located in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.10,14
The utility of telehealth in promoting LCS among at-risk veterans living in rural communities has not been firmly established.4-6 To address this issue, we conducted a proof-of-principle quality improvement project to determine whether a telehealth intervention would increase referrals among at-risk veterans who reside in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan who are self-enrolled in a CBOC smoking cessation program in Green Bay, Wisconsin. The CBOC provides primary health care to veterans residing in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan as defined by US Department of Agriculture rural-urban commuting area codes.16 The intervention aimed to refer these individuals to the closest available and centralized LCS program, which is located at the Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
METHODS
We reviewed electronic health records (EHR) of LCS-eligible veterans treated by 2 authors (SH and TB) who were self-enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the Green Bay CBOC between October 1, 2020, and September 30, 2021. The program provides comprehensive evidence-based tobacco use treatment, online self-help resources, behavioral counseling, and medicines for smoking cessation.17 Veterans aged 50 to 80 years with a smoking history of ≥ 20 pack-years, who currently smoke cigarettes or quit within the past 15 years, were considered at risk for lung cancer and eligible for LCS. After confirming eligibility, pertinent demographic data were abstracted from each EHR.
Telehealth Intervention
The CJZVAMC centralized LCS program manages all delivery processes and has been previously shown to increase uptake of LCS and improve patient outcomes among veterans as compared to a decentralized approach.18,19 In the centralized approach, eligible veterans were referred by a CBOC primary care practitioner (PCP) to a designated centralized LCS program. The centralized LCS program provides further evaluation and disposition, which includes structured and shared decision making, ordering LDCT of the chest, reporting LDCT results to the patient and PCP, devising a goal-directed care plan, and managing follow-up LDCTs as indicated (Figure 1).18,19
This intervention was initiated before other measures aimed to increase the LCS enrollment for at-risk rural veterans at the CBOC, (eg, mailing LCS education fact sheet to veterans).20 After reviewing prospective veterans’ EHRs, 1 author (TB) contacted LCS-eligible veterans by telephone and left a voicemail if contact could not be established. A second telephone call was placed within 2 months of the initial call if no call back was documented in the EHR. When verbal contact was established, the goals of the centralized LCS program were described and the veteran was invited to participate.21
Veterans were seen at CBOCs affiliated with CJZVAMC. The CJZVAMC LCS coordinator was notified whenever a veteran agreed to enroll into LCS and then ordered LDCT, which was performed and read at CJZVAMC. Once LDCT has been ordered, 1 author (TB) reviewed the veteran’s EHR for LDCT completion over the next 4 months.Upon conclusion of the intervention period, the number of veterans referred for LDCT and the number of LDCTs performed were recorded. Each LDCT was reviewed and coded by medical imaging clinicians according to Lung CT Screening Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS) version 1.1 and coded as 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 based on the nodule with the highest degree of suspicion.22 The LDCT and reports were also reviewed by pulmonary physicians at the CJZVAMC Lung Nodule Clinic with recommendations issued and reported to the PCP treating the veteran, such as annual follow-up with LDCT or referral to specialty care for further evaluation as indicated.
RESULTS
Of 117 veterans enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the CBOC during the intervention period, 74 (63%) were eligible to undergo LCS, and 68 (58%) were contacted by telephone (Figure 2). Eligible patients were primarily White male veterans; their mean (SD) age was 65.0 years (7.6). Participation in LCS was discussed with 41 (60%) veterans either during the initial or second telephone call of which 29 (71%) agreed to enroll and 12 (29%) declined. Veterans did not provide reasons for declining participation at the time of the telephone call.
Among the 74 eligible veterans who attended the smoking cessation program, only 3 had LDCT performed before initiation of this project (4%). At the conclusion of the telehealth intervention period, 19 veterans had LDCT performed (26%). Ten LDCTs were coded Lung-RADS 1, 7 Lung-RADS 2, 1 Lung-RADS 3, and 1 Lung-RADS 4B. In each case, annual follow-up LDCT or referral to a LCS clinician was pursued as indicated.22
DISCUSSION
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that a high percentage (66%) of individuals in rural communities who were contacted via telehealth agreed to participate in a regional LCS program. The program reviewed LDCT results, ordered follow-up LDCTs, and recommended further evaluations.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process could also promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians, if abnormal imaging findings are detected, remains unclear.
It has been well established LDCT LCS reduces lung cancer-specific and overall mortality rates among eligible current and former smokers.1,9,23 The 5-year relative survival rate of veterans diagnosed with localized non-small cell lung cancer is 63%; that number drops to 7% in those with advanced disease attesting to the utility of LCS in detecting early stage lung cancer.2 Despite these favorable observations, however, screening rates with free LDCT remains low in rural communities.3-7
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that telehealth intervention may increase referrals of at-risk veterans who reside in rural communities to the closest centralized LCS program located at aregional VAMC. This program is responsible for reviewing the results of the initial LDCT, ordering follow-up LDCT, and recommending further evaluation as indicated.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process would promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians if abnormal imaging findings are detected is yet to be determined.
We found that among 74 LCS-eligible rural veterans attending a CBOC-based smoking cessation program, only 3 (4%) underwent LDCT screening before this telehealth intervention was launched. This low LCS rate among veterans attempting to quit smoking may have been related, in part, to a lack of awareness of this intervention and/or barriers to LCS access.7,10,21,24 Deploying a telehealth intervention targeting LCS could address this life threatening and unmet medical need in rural communities.25 The results of this proof-of-principle quality improvement project support this contention with the reported increased referrals to and completion of initial LDCT within 4 months of the telehealth encounter.
Limitations
This was a small, single site project composed of predominantly White male rural veterans participating in a smoking cessation program associated with a VA facility.26,27 It is not clear whether similar outcomes would be observed in at-risk veterans who do not participate in a smoking cessation program or in more diverse communities. We were unable to contact 40% of LCS-eligible rural veterans by telephone. Twelve veterans reached by telephone declined to participate in LCS without providing a reason, and only 19 of 68 eligible veterans (28%) underwent LDCT screening during the 4-month telehealth intervention. The reasons underlying this overall low accrual rate and whether rural veterans prefer other means of personal communication regarding LCS were not determined. Lastly, generalizability of our initial observations to other veterans living in rural communities is limited because the project was conducted only in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.
Conclusions
At-risk rural veterans may be willing to participate in a centralized LCS program at a regional VA medical facility when contacted and coordinated using telehealth modalities. These findings offer support for future prospective, multisite, VA telehealth-based studies to be conducted in rural areas. The results of this project also suggest that telehealth intervention could increase referrals of at-risk rural veterans to the closest centralized LCS program located at a regional VA medical facility.
Annual lung cancer screening (LCS) with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) of the chest has been shown to reduce mortality rates for individuals at risk for lung cancer.1 Despite the benefits, < 5% of those who were eligible for LCS in the United States were screened in 2022.2 Implementation of a LCS program in rural communities is especially challenging because they are sparsely populated, medically underserved, and located far from urban centers.2-7 It is estimated that 1 in 5 people live in rural areas. Rates of tobacco smoking and cancer are higher in rural communities when compared with urban communities.8,9 The scarcity of physicians in rural areas who are familiar with LCS may further impede individuals who are at risk from accessing this life saving service.5,6 As a result, these individuals may not regularly undergo LCS as recommended.9
Telehealth, or the remote delivery of health care services via telecommunications, is an emerging approach for addressing unmet medical needs in rural communities and is being utilized widely by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA).4,10-15 The Veterans Integrated Service Network 12 (Great Lakes Network) has established the Clinical Resource Hub (CRH), a telehealth network comprising of licensed independent physicians, nurse practitioners, registered nurses, and ancillary staff. The CRH offers regular, remote health care services to several community-based outpatient clinics (CBOC) primary care clinics located in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.10,14
The utility of telehealth in promoting LCS among at-risk veterans living in rural communities has not been firmly established.4-6 To address this issue, we conducted a proof-of-principle quality improvement project to determine whether a telehealth intervention would increase referrals among at-risk veterans who reside in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan who are self-enrolled in a CBOC smoking cessation program in Green Bay, Wisconsin. The CBOC provides primary health care to veterans residing in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan as defined by US Department of Agriculture rural-urban commuting area codes.16 The intervention aimed to refer these individuals to the closest available and centralized LCS program, which is located at the Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
METHODS
We reviewed electronic health records (EHR) of LCS-eligible veterans treated by 2 authors (SH and TB) who were self-enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the Green Bay CBOC between October 1, 2020, and September 30, 2021. The program provides comprehensive evidence-based tobacco use treatment, online self-help resources, behavioral counseling, and medicines for smoking cessation.17 Veterans aged 50 to 80 years with a smoking history of ≥ 20 pack-years, who currently smoke cigarettes or quit within the past 15 years, were considered at risk for lung cancer and eligible for LCS. After confirming eligibility, pertinent demographic data were abstracted from each EHR.
Telehealth Intervention
The CJZVAMC centralized LCS program manages all delivery processes and has been previously shown to increase uptake of LCS and improve patient outcomes among veterans as compared to a decentralized approach.18,19 In the centralized approach, eligible veterans were referred by a CBOC primary care practitioner (PCP) to a designated centralized LCS program. The centralized LCS program provides further evaluation and disposition, which includes structured and shared decision making, ordering LDCT of the chest, reporting LDCT results to the patient and PCP, devising a goal-directed care plan, and managing follow-up LDCTs as indicated (Figure 1).18,19
This intervention was initiated before other measures aimed to increase the LCS enrollment for at-risk rural veterans at the CBOC, (eg, mailing LCS education fact sheet to veterans).20 After reviewing prospective veterans’ EHRs, 1 author (TB) contacted LCS-eligible veterans by telephone and left a voicemail if contact could not be established. A second telephone call was placed within 2 months of the initial call if no call back was documented in the EHR. When verbal contact was established, the goals of the centralized LCS program were described and the veteran was invited to participate.21
Veterans were seen at CBOCs affiliated with CJZVAMC. The CJZVAMC LCS coordinator was notified whenever a veteran agreed to enroll into LCS and then ordered LDCT, which was performed and read at CJZVAMC. Once LDCT has been ordered, 1 author (TB) reviewed the veteran’s EHR for LDCT completion over the next 4 months.Upon conclusion of the intervention period, the number of veterans referred for LDCT and the number of LDCTs performed were recorded. Each LDCT was reviewed and coded by medical imaging clinicians according to Lung CT Screening Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS) version 1.1 and coded as 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 based on the nodule with the highest degree of suspicion.22 The LDCT and reports were also reviewed by pulmonary physicians at the CJZVAMC Lung Nodule Clinic with recommendations issued and reported to the PCP treating the veteran, such as annual follow-up with LDCT or referral to specialty care for further evaluation as indicated.
RESULTS
Of 117 veterans enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the CBOC during the intervention period, 74 (63%) were eligible to undergo LCS, and 68 (58%) were contacted by telephone (Figure 2). Eligible patients were primarily White male veterans; their mean (SD) age was 65.0 years (7.6). Participation in LCS was discussed with 41 (60%) veterans either during the initial or second telephone call of which 29 (71%) agreed to enroll and 12 (29%) declined. Veterans did not provide reasons for declining participation at the time of the telephone call.
Among the 74 eligible veterans who attended the smoking cessation program, only 3 had LDCT performed before initiation of this project (4%). At the conclusion of the telehealth intervention period, 19 veterans had LDCT performed (26%). Ten LDCTs were coded Lung-RADS 1, 7 Lung-RADS 2, 1 Lung-RADS 3, and 1 Lung-RADS 4B. In each case, annual follow-up LDCT or referral to a LCS clinician was pursued as indicated.22
DISCUSSION
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that a high percentage (66%) of individuals in rural communities who were contacted via telehealth agreed to participate in a regional LCS program. The program reviewed LDCT results, ordered follow-up LDCTs, and recommended further evaluations.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process could also promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians, if abnormal imaging findings are detected, remains unclear.
It has been well established LDCT LCS reduces lung cancer-specific and overall mortality rates among eligible current and former smokers.1,9,23 The 5-year relative survival rate of veterans diagnosed with localized non-small cell lung cancer is 63%; that number drops to 7% in those with advanced disease attesting to the utility of LCS in detecting early stage lung cancer.2 Despite these favorable observations, however, screening rates with free LDCT remains low in rural communities.3-7
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that telehealth intervention may increase referrals of at-risk veterans who reside in rural communities to the closest centralized LCS program located at aregional VAMC. This program is responsible for reviewing the results of the initial LDCT, ordering follow-up LDCT, and recommending further evaluation as indicated.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process would promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians if abnormal imaging findings are detected is yet to be determined.
We found that among 74 LCS-eligible rural veterans attending a CBOC-based smoking cessation program, only 3 (4%) underwent LDCT screening before this telehealth intervention was launched. This low LCS rate among veterans attempting to quit smoking may have been related, in part, to a lack of awareness of this intervention and/or barriers to LCS access.7,10,21,24 Deploying a telehealth intervention targeting LCS could address this life threatening and unmet medical need in rural communities.25 The results of this proof-of-principle quality improvement project support this contention with the reported increased referrals to and completion of initial LDCT within 4 months of the telehealth encounter.
Limitations
This was a small, single site project composed of predominantly White male rural veterans participating in a smoking cessation program associated with a VA facility.26,27 It is not clear whether similar outcomes would be observed in at-risk veterans who do not participate in a smoking cessation program or in more diverse communities. We were unable to contact 40% of LCS-eligible rural veterans by telephone. Twelve veterans reached by telephone declined to participate in LCS without providing a reason, and only 19 of 68 eligible veterans (28%) underwent LDCT screening during the 4-month telehealth intervention. The reasons underlying this overall low accrual rate and whether rural veterans prefer other means of personal communication regarding LCS were not determined. Lastly, generalizability of our initial observations to other veterans living in rural communities is limited because the project was conducted only in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.
Conclusions
At-risk rural veterans may be willing to participate in a centralized LCS program at a regional VA medical facility when contacted and coordinated using telehealth modalities. These findings offer support for future prospective, multisite, VA telehealth-based studies to be conducted in rural areas. The results of this project also suggest that telehealth intervention could increase referrals of at-risk rural veterans to the closest centralized LCS program located at a regional VA medical facility.
1. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team, Aberle DR, Adams AM, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(5):395-409. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
2. State of Lung Cancer: 2023 Report. American Lung Association. November 14, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.lung.org/getmedia/186786b6-18c3-46a9-a7e7-810f3ce4deda/SOLC-2023-Print-Report.pdf
3. Okereke IC, Nishi S, Zhou J, Goodwin JS. Trends in lung cancer screening in the United States, 2016-2017. J Thorac Dis. 2019;11(3):873-881. doi:10.21037/jtd.2019.01.105
4. Petraglia AF, Olazagasti JM, Strong A, Dunn B, Anderson RT, Hanley M. Establishing satellite lung cancer screening sites with telehealth to address disparities between high-risk smokers and American College of Radiology-approved Centers of Designation. J Thorac Imaging. 2021;36(1):2-5. doi:10.1097/RTI.0000000000000520
5. Odahowski CL, Zahnd WE, Eberth JM. Challenges and opportunities for lung cancer screening in rural America. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(4 Pt B):590-595. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2019.01.001
6. Rohatgi KW, Marx CM, Lewis-Thames MW, Liu J, Colditz GA, James AS. Urban-rural disparities in access to low-dose computed tomography lung cancer screening in Missouri and Illinois. Prev Chronic Dis. 2020;17:E140. doi:10.5888/pcd17.200202
7. Boudreau JH, Miller DR, Qian S, Nunez ER, Caverly TJ, Wiener RS. Access to lung cancer screening in the Veterans Health Administration: does geographic distribution match need in the population? Chest. 2021;160(1):358-367. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.02.016
8. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al, eds. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017. National Cancer Institute, US Dept of Health and Human Services; April 15, 2020. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2017/index.html
9. US Preventive Services Task Force, Krist AH, Davidson KW, et al. Screening for Lung Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2021;325(10):962-970. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1117
10. Gopal RK, Solanki P, Bokhour BG, et al. Provider, staff, and patient perspectives on medical visits using clinical video telehealth: a foundation for educational initiatives to improve medical care in telehealth. J Nurse Pract. 2021;17(5):582-587. doi:10.1016/j.nurpra.2021.02.020
11. Yacoub JH, Swanson CE, Jay AK, Cooper C, Spies J, Krishnan P. The radiology virtual reading room: during and beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. J Digit Imaging. 2021;34(2):308-319. doi:10.1007/s10278-021-00427-4
12. Beswick DM, Vashi A, Song Y, et al. Consultation via telemedicine and access to operative care for patients with head and neck cancer in a Veterans Health Administration population. Head Neck. 2016;38(6):925-929. doi:10.1002/hed.24386
13. Ruco A, Dossa F, Tinmouth J, et al. Social media and mHealth technology for cancer screening: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(7):e26759. doi:10.2196/26759
14. Raza T, Joshi M, Schapira RM, Agha Z. Pulmonary telemedicine - a model to access the subspecialist services in underserved rural areas. Int J Med Inform. 2009;78(1):53-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2008.07.010
15. Chen A, Ayub MH, Mishuris RG, et al. Telehealth policy, practice, and education: a position statement of the Society of General Internal Medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(11):2613-2620. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08190-8
16. Rural-Urban Commuting Area Codes. Economic Research Service, US Dept of Agriculture. Updated September 25, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes/
17. VHA Directive 1056: National Smoking and Tobacco Use Cessation Program. Veterans Health Administration, US Dept of Veterans Affairs; September 5, 2019. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=8488
18. Smith HB, Ward R, Frazier C, Angotti J, Tanner NT. Guideline-recommended lung cancer screening adherence is superior with a centralized approach. Chest. 2022;161(3):818-825. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.09.002
19. Lewis JA, Samuels LR, Denton J, et al. The association of health care system resources with lung cancer screening implementation: a cohort study. Chest. 2022;162(3):701-711. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2022.03.050
20. US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Lung cancer screening: patient education fact sheet. Accessed July 8, 2024. https://www.cancer.va.gov/assets/pdf/survey/LCSflyer.pdf
21. Melzer AC, Golden SE, Ono SS, Datta S, Crothers K, Slatore CG. What exactly is shared decision-making? A qualitative study of shared decision-making in lung cancer screening. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(2):546-553. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05516-3
22. Chelala L, Hossain R, Kazerooni EA, Christensen JD, Dyer DS, White CS. Lung-RADS Version 1.1: challenges and a look ahead, from the AJR special series on radiology reporting and data systems. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216(6):1411-1422. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.24807
23. Ritzwoller DP, Meza R, Carroll NM, et al. Evaluation of population-level changes associated with the 2021 US Preventive Services Task Force lung cancer screening recommendations in community-based health care systems. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(10):e2128176. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28176
24. Golden SE, Ono SS, Thakurta SG, et al. “I’m putting my trust in their hands”: a qualitative study of patients’ views on clinician initial communication about lung cancer screening. Chest. 2020;158(3):1260-1267. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.02.072
25. Park ER, Chiles C, Cinciripini PM, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on telehealth research in cancer prevention and care: a call to sustain telehealth advances. Cancer. 2021;127(3):334-338. doi:10.1002/cncr.33227
26. Tremblay A, Taghizadeh N, Huang J, et al. A randomized controlled study of integrated smoking cessation in a lung cancer screening program. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14(9):1528-1537. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2019.04.024
27. Neil JM, Marotta C, Gonzalez I, et al. Integrating tobacco treatment into lung cancer screening practices: study protocol for the Screen ASSIST randomized clinical trial. Contemp Clin Trials. 2021;111:106586. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2021.106586
1. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team, Aberle DR, Adams AM, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(5):395-409. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
2. State of Lung Cancer: 2023 Report. American Lung Association. November 14, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.lung.org/getmedia/186786b6-18c3-46a9-a7e7-810f3ce4deda/SOLC-2023-Print-Report.pdf
3. Okereke IC, Nishi S, Zhou J, Goodwin JS. Trends in lung cancer screening in the United States, 2016-2017. J Thorac Dis. 2019;11(3):873-881. doi:10.21037/jtd.2019.01.105
4. Petraglia AF, Olazagasti JM, Strong A, Dunn B, Anderson RT, Hanley M. Establishing satellite lung cancer screening sites with telehealth to address disparities between high-risk smokers and American College of Radiology-approved Centers of Designation. J Thorac Imaging. 2021;36(1):2-5. doi:10.1097/RTI.0000000000000520
5. Odahowski CL, Zahnd WE, Eberth JM. Challenges and opportunities for lung cancer screening in rural America. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(4 Pt B):590-595. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2019.01.001
6. Rohatgi KW, Marx CM, Lewis-Thames MW, Liu J, Colditz GA, James AS. Urban-rural disparities in access to low-dose computed tomography lung cancer screening in Missouri and Illinois. Prev Chronic Dis. 2020;17:E140. doi:10.5888/pcd17.200202
7. Boudreau JH, Miller DR, Qian S, Nunez ER, Caverly TJ, Wiener RS. Access to lung cancer screening in the Veterans Health Administration: does geographic distribution match need in the population? Chest. 2021;160(1):358-367. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.02.016
8. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al, eds. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017. National Cancer Institute, US Dept of Health and Human Services; April 15, 2020. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2017/index.html
9. US Preventive Services Task Force, Krist AH, Davidson KW, et al. Screening for Lung Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2021;325(10):962-970. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1117
10. Gopal RK, Solanki P, Bokhour BG, et al. Provider, staff, and patient perspectives on medical visits using clinical video telehealth: a foundation for educational initiatives to improve medical care in telehealth. J Nurse Pract. 2021;17(5):582-587. doi:10.1016/j.nurpra.2021.02.020
11. Yacoub JH, Swanson CE, Jay AK, Cooper C, Spies J, Krishnan P. The radiology virtual reading room: during and beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. J Digit Imaging. 2021;34(2):308-319. doi:10.1007/s10278-021-00427-4
12. Beswick DM, Vashi A, Song Y, et al. Consultation via telemedicine and access to operative care for patients with head and neck cancer in a Veterans Health Administration population. Head Neck. 2016;38(6):925-929. doi:10.1002/hed.24386
13. Ruco A, Dossa F, Tinmouth J, et al. Social media and mHealth technology for cancer screening: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(7):e26759. doi:10.2196/26759
14. Raza T, Joshi M, Schapira RM, Agha Z. Pulmonary telemedicine - a model to access the subspecialist services in underserved rural areas. Int J Med Inform. 2009;78(1):53-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2008.07.010
15. Chen A, Ayub MH, Mishuris RG, et al. Telehealth policy, practice, and education: a position statement of the Society of General Internal Medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(11):2613-2620. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08190-8
16. Rural-Urban Commuting Area Codes. Economic Research Service, US Dept of Agriculture. Updated September 25, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes/
17. VHA Directive 1056: National Smoking and Tobacco Use Cessation Program. Veterans Health Administration, US Dept of Veterans Affairs; September 5, 2019. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=8488
18. Smith HB, Ward R, Frazier C, Angotti J, Tanner NT. Guideline-recommended lung cancer screening adherence is superior with a centralized approach. Chest. 2022;161(3):818-825. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.09.002
19. Lewis JA, Samuels LR, Denton J, et al. The association of health care system resources with lung cancer screening implementation: a cohort study. Chest. 2022;162(3):701-711. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2022.03.050
20. US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Lung cancer screening: patient education fact sheet. Accessed July 8, 2024. https://www.cancer.va.gov/assets/pdf/survey/LCSflyer.pdf
21. Melzer AC, Golden SE, Ono SS, Datta S, Crothers K, Slatore CG. What exactly is shared decision-making? A qualitative study of shared decision-making in lung cancer screening. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(2):546-553. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05516-3
22. Chelala L, Hossain R, Kazerooni EA, Christensen JD, Dyer DS, White CS. Lung-RADS Version 1.1: challenges and a look ahead, from the AJR special series on radiology reporting and data systems. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216(6):1411-1422. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.24807
23. Ritzwoller DP, Meza R, Carroll NM, et al. Evaluation of population-level changes associated with the 2021 US Preventive Services Task Force lung cancer screening recommendations in community-based health care systems. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(10):e2128176. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28176
24. Golden SE, Ono SS, Thakurta SG, et al. “I’m putting my trust in their hands”: a qualitative study of patients’ views on clinician initial communication about lung cancer screening. Chest. 2020;158(3):1260-1267. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.02.072
25. Park ER, Chiles C, Cinciripini PM, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on telehealth research in cancer prevention and care: a call to sustain telehealth advances. Cancer. 2021;127(3):334-338. doi:10.1002/cncr.33227
26. Tremblay A, Taghizadeh N, Huang J, et al. A randomized controlled study of integrated smoking cessation in a lung cancer screening program. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14(9):1528-1537. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2019.04.024
27. Neil JM, Marotta C, Gonzalez I, et al. Integrating tobacco treatment into lung cancer screening practices: study protocol for the Screen ASSIST randomized clinical trial. Contemp Clin Trials. 2021;111:106586. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2021.106586
Are Beta-Blockers Safe for COPD?
Everyone takes a pharmacology class in medical school that includes a lecture on beta receptors. They’re in the heart (beta-1) and lungs (beta-2), and drug compounds agonize or antagonize one or both. The professor will caution against using antagonists (beta blockade) for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) lest they further impair the patient’s irreversibly narrowed airways. Obsequious students mature into obsequious doctors, intent on “doing no harm.” For better or worse, you withhold beta-blockers from your patient with COPD and comorbid cardiac disease.
Perhaps because the pulmonologist isn’t usually the one who decides whether a beta-blocker is prescribed, I’ve been napping on this topic since training. Early in fellowship, I read an ACP Journal Club article about a Cochrane systematic review (yes, I read a review of a review) that concluded that beta-blockers are fine in patients with COPD. The summary appealed to my bias towards evidence-based medicine (EBM) supplanting physiology, medical school, and everything else. I was more apt to believe my stodgy residency attendings than the stodgy pharmacology professor. Even though COPD and cardiovascular disease share multiple risk factors, I had never reinvestigated the relationship between beta-blockers and COPD.
Turns out that while I was sleeping, the debate continued. Go figure. Just last month a prospective, observational study published in JAMA Network Open found that beta-blockers did not increase the risk for cardiovascular or respiratory events among patients with COPD being discharged after hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction. Although this could be viewed as a triumph for EBM over physiology and a validation of my decade-plus of intellectual laziness, the results are actually pretty thin. These studies, in which patients with an indication for a therapy (a beta-blocker in this case) are analyzed by whether or not they received it, are problematic. The fanciest statistics — in this case, they used propensity scores — can’t control for residual confounding. What drove the physicians to prescribe in some cases but not others? We can only guess.
This might be okay if there hadn’t been a randomized controlled trial (RCT) published in 2019 in The New England Journal of Medicine that found that beta-blockers increase the risk for severe COPD exacerbations. In EBM, the RCT trumps all. Ironically, this trial was designed to test whether beta-blockers reduce severe COPD exacerbations. Yes, we’d come full circle. There was enough biologic plausibility to support a positive effect, or so thought the study authors and the Department of Defense (DOD) — for reasons I can’t possibly guess, the DOD funded this RCT. My pharmacology professor must be rolling over in his tenure.
The RCT did leave beta-blockers some wiggle room. The authors purposely excluded anyone with a cardiovascular indication for a beta-blocker. The intent was to ensure beneficial effects were isolated to respiratory and not cardiovascular outcomes. Of course, the reason I’m writing and you’re reading this is that COPD and cardiovascular disease co-occur at a high rate. The RCT notwithstanding, we prescribe beta-blockers to patients with COPD because they have a cardiac indication, not to reduce acute COPD exacerbations. So, it’s possible there’d be a net beta-blocker benefit in patients with COPD and comorbid heart disease.
That’s where the JAMA Network Open study comes in, but as discussed, methodologic weaknesses preclude its being the final word. That said, I think it’s unlikely we’ll see a COPD with comorbid cardiac disease RCT performed to assess whether beta-blockers provide a net benefit, unless maybe the DOD wants to fund another one of these. In the meantime, I’m calling clinical equipoise and punting. Fortunately for me, I don’t have to prescribe beta-blockers.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University in Bethesda, Maryland, and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington, DC. He reported conflicts of interest with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Everyone takes a pharmacology class in medical school that includes a lecture on beta receptors. They’re in the heart (beta-1) and lungs (beta-2), and drug compounds agonize or antagonize one or both. The professor will caution against using antagonists (beta blockade) for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) lest they further impair the patient’s irreversibly narrowed airways. Obsequious students mature into obsequious doctors, intent on “doing no harm.” For better or worse, you withhold beta-blockers from your patient with COPD and comorbid cardiac disease.
Perhaps because the pulmonologist isn’t usually the one who decides whether a beta-blocker is prescribed, I’ve been napping on this topic since training. Early in fellowship, I read an ACP Journal Club article about a Cochrane systematic review (yes, I read a review of a review) that concluded that beta-blockers are fine in patients with COPD. The summary appealed to my bias towards evidence-based medicine (EBM) supplanting physiology, medical school, and everything else. I was more apt to believe my stodgy residency attendings than the stodgy pharmacology professor. Even though COPD and cardiovascular disease share multiple risk factors, I had never reinvestigated the relationship between beta-blockers and COPD.
Turns out that while I was sleeping, the debate continued. Go figure. Just last month a prospective, observational study published in JAMA Network Open found that beta-blockers did not increase the risk for cardiovascular or respiratory events among patients with COPD being discharged after hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction. Although this could be viewed as a triumph for EBM over physiology and a validation of my decade-plus of intellectual laziness, the results are actually pretty thin. These studies, in which patients with an indication for a therapy (a beta-blocker in this case) are analyzed by whether or not they received it, are problematic. The fanciest statistics — in this case, they used propensity scores — can’t control for residual confounding. What drove the physicians to prescribe in some cases but not others? We can only guess.
This might be okay if there hadn’t been a randomized controlled trial (RCT) published in 2019 in The New England Journal of Medicine that found that beta-blockers increase the risk for severe COPD exacerbations. In EBM, the RCT trumps all. Ironically, this trial was designed to test whether beta-blockers reduce severe COPD exacerbations. Yes, we’d come full circle. There was enough biologic plausibility to support a positive effect, or so thought the study authors and the Department of Defense (DOD) — for reasons I can’t possibly guess, the DOD funded this RCT. My pharmacology professor must be rolling over in his tenure.
The RCT did leave beta-blockers some wiggle room. The authors purposely excluded anyone with a cardiovascular indication for a beta-blocker. The intent was to ensure beneficial effects were isolated to respiratory and not cardiovascular outcomes. Of course, the reason I’m writing and you’re reading this is that COPD and cardiovascular disease co-occur at a high rate. The RCT notwithstanding, we prescribe beta-blockers to patients with COPD because they have a cardiac indication, not to reduce acute COPD exacerbations. So, it’s possible there’d be a net beta-blocker benefit in patients with COPD and comorbid heart disease.
That’s where the JAMA Network Open study comes in, but as discussed, methodologic weaknesses preclude its being the final word. That said, I think it’s unlikely we’ll see a COPD with comorbid cardiac disease RCT performed to assess whether beta-blockers provide a net benefit, unless maybe the DOD wants to fund another one of these. In the meantime, I’m calling clinical equipoise and punting. Fortunately for me, I don’t have to prescribe beta-blockers.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University in Bethesda, Maryland, and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington, DC. He reported conflicts of interest with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Everyone takes a pharmacology class in medical school that includes a lecture on beta receptors. They’re in the heart (beta-1) and lungs (beta-2), and drug compounds agonize or antagonize one or both. The professor will caution against using antagonists (beta blockade) for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) lest they further impair the patient’s irreversibly narrowed airways. Obsequious students mature into obsequious doctors, intent on “doing no harm.” For better or worse, you withhold beta-blockers from your patient with COPD and comorbid cardiac disease.
Perhaps because the pulmonologist isn’t usually the one who decides whether a beta-blocker is prescribed, I’ve been napping on this topic since training. Early in fellowship, I read an ACP Journal Club article about a Cochrane systematic review (yes, I read a review of a review) that concluded that beta-blockers are fine in patients with COPD. The summary appealed to my bias towards evidence-based medicine (EBM) supplanting physiology, medical school, and everything else. I was more apt to believe my stodgy residency attendings than the stodgy pharmacology professor. Even though COPD and cardiovascular disease share multiple risk factors, I had never reinvestigated the relationship between beta-blockers and COPD.
Turns out that while I was sleeping, the debate continued. Go figure. Just last month a prospective, observational study published in JAMA Network Open found that beta-blockers did not increase the risk for cardiovascular or respiratory events among patients with COPD being discharged after hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction. Although this could be viewed as a triumph for EBM over physiology and a validation of my decade-plus of intellectual laziness, the results are actually pretty thin. These studies, in which patients with an indication for a therapy (a beta-blocker in this case) are analyzed by whether or not they received it, are problematic. The fanciest statistics — in this case, they used propensity scores — can’t control for residual confounding. What drove the physicians to prescribe in some cases but not others? We can only guess.
This might be okay if there hadn’t been a randomized controlled trial (RCT) published in 2019 in The New England Journal of Medicine that found that beta-blockers increase the risk for severe COPD exacerbations. In EBM, the RCT trumps all. Ironically, this trial was designed to test whether beta-blockers reduce severe COPD exacerbations. Yes, we’d come full circle. There was enough biologic plausibility to support a positive effect, or so thought the study authors and the Department of Defense (DOD) — for reasons I can’t possibly guess, the DOD funded this RCT. My pharmacology professor must be rolling over in his tenure.
The RCT did leave beta-blockers some wiggle room. The authors purposely excluded anyone with a cardiovascular indication for a beta-blocker. The intent was to ensure beneficial effects were isolated to respiratory and not cardiovascular outcomes. Of course, the reason I’m writing and you’re reading this is that COPD and cardiovascular disease co-occur at a high rate. The RCT notwithstanding, we prescribe beta-blockers to patients with COPD because they have a cardiac indication, not to reduce acute COPD exacerbations. So, it’s possible there’d be a net beta-blocker benefit in patients with COPD and comorbid heart disease.
That’s where the JAMA Network Open study comes in, but as discussed, methodologic weaknesses preclude its being the final word. That said, I think it’s unlikely we’ll see a COPD with comorbid cardiac disease RCT performed to assess whether beta-blockers provide a net benefit, unless maybe the DOD wants to fund another one of these. In the meantime, I’m calling clinical equipoise and punting. Fortunately for me, I don’t have to prescribe beta-blockers.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University in Bethesda, Maryland, and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington, DC. He reported conflicts of interest with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More Illnesses Possible Related Linked to Counterfeit Botulinum Toxin Reported
— two in the intensive care unit. None of the cases required intubation, according to an announcement of an investigation into these reports in by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The report, published online in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, notes that the four patients in Tennessee received counterfeit BoNT, while product information was not available for the three cases in New York City. “However, one person reported paying less than US wholesale acquisition cost for the administered product, and another reported that the product had been purchased overseas,” the authors of the report wrote. The development underscores that BoNT injections “should be administered only by licensed and trained providers using recommended doses of FDA [Food and Drug Admininstration]-approved products.”
This report follows a CDC advisory published in April 2024 of at least 22 people from 11 states who reported serious reactions after receiving botulinum toxin injections from unlicensed or untrained individuals or in nonhealthcare settings, such as homes and spas.
The median age of the women in the July report was 48 years, and signs and symptoms included ptosis, dry mouth, dysphagia, shortness of breath, and weakness. Onset occurred between February 23 and March 7, 2024.
“This investigation did not determine why these illnesses occurred after cosmetic BoNT injections; potential reasons might include use of counterfeit BoNT, which might be more potent or contain harmful additional ingredients or higher susceptibility to BoNT effects among some persons,” the investigators wrote. They recommended further studies to describe the clinical spectrum of cosmetic BoNT injection effects such as severity of signs and symptoms.
For cases of suspected systemic botulism, the CDC recommends calling the local or state health department for consultation and antitoxin release (as well as information on reporting adverse events). Alternatively, the 24/7 phone number for the CDC clinical botulism service is 770-488-7100.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
— two in the intensive care unit. None of the cases required intubation, according to an announcement of an investigation into these reports in by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The report, published online in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, notes that the four patients in Tennessee received counterfeit BoNT, while product information was not available for the three cases in New York City. “However, one person reported paying less than US wholesale acquisition cost for the administered product, and another reported that the product had been purchased overseas,” the authors of the report wrote. The development underscores that BoNT injections “should be administered only by licensed and trained providers using recommended doses of FDA [Food and Drug Admininstration]-approved products.”
This report follows a CDC advisory published in April 2024 of at least 22 people from 11 states who reported serious reactions after receiving botulinum toxin injections from unlicensed or untrained individuals or in nonhealthcare settings, such as homes and spas.
The median age of the women in the July report was 48 years, and signs and symptoms included ptosis, dry mouth, dysphagia, shortness of breath, and weakness. Onset occurred between February 23 and March 7, 2024.
“This investigation did not determine why these illnesses occurred after cosmetic BoNT injections; potential reasons might include use of counterfeit BoNT, which might be more potent or contain harmful additional ingredients or higher susceptibility to BoNT effects among some persons,” the investigators wrote. They recommended further studies to describe the clinical spectrum of cosmetic BoNT injection effects such as severity of signs and symptoms.
For cases of suspected systemic botulism, the CDC recommends calling the local or state health department for consultation and antitoxin release (as well as information on reporting adverse events). Alternatively, the 24/7 phone number for the CDC clinical botulism service is 770-488-7100.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
— two in the intensive care unit. None of the cases required intubation, according to an announcement of an investigation into these reports in by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The report, published online in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, notes that the four patients in Tennessee received counterfeit BoNT, while product information was not available for the three cases in New York City. “However, one person reported paying less than US wholesale acquisition cost for the administered product, and another reported that the product had been purchased overseas,” the authors of the report wrote. The development underscores that BoNT injections “should be administered only by licensed and trained providers using recommended doses of FDA [Food and Drug Admininstration]-approved products.”
This report follows a CDC advisory published in April 2024 of at least 22 people from 11 states who reported serious reactions after receiving botulinum toxin injections from unlicensed or untrained individuals or in nonhealthcare settings, such as homes and spas.
The median age of the women in the July report was 48 years, and signs and symptoms included ptosis, dry mouth, dysphagia, shortness of breath, and weakness. Onset occurred between February 23 and March 7, 2024.
“This investigation did not determine why these illnesses occurred after cosmetic BoNT injections; potential reasons might include use of counterfeit BoNT, which might be more potent or contain harmful additional ingredients or higher susceptibility to BoNT effects among some persons,” the investigators wrote. They recommended further studies to describe the clinical spectrum of cosmetic BoNT injection effects such as severity of signs and symptoms.
For cases of suspected systemic botulism, the CDC recommends calling the local or state health department for consultation and antitoxin release (as well as information on reporting adverse events). Alternatively, the 24/7 phone number for the CDC clinical botulism service is 770-488-7100.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE MMWR