User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Bronchiectasis: A call to action
AIRWAYS DISORDERS NETWORK
Bronchiectasis Section
For years, the noncystic fibrosis (CF) bronchiectasis community has been trying to organize to provide better care for more than half a million adults with bronchiectasis in the United States. Internationally, the Europeans created the European Bronchiectasis Registry, which has been a powerful tool including nearly 20,000 patients, to answer important epidemiologic and management questions. We must do more for the bronchiectasis community.
Clinicaltrials.gov indicates that there are 8 international phase 3 or 4 clinical trials that are currently enrolling; 3 of those have enrollment sites in the United States. One such study from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill is looking at the use of nebulized hypertonic saline in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis to understand the effect it has on mucociliary clearance. Emory University is looking at the use of elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor (Trikafta) in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis; these patients have only 1 targetable mutation and a phenotype that resembles CF. This 8-week, open-label, single-center study aims to measure both clinical and biomarker outcomes after treatment with Trikafta. Finally, a phase 3 trial out of Florida, the ICoN-1 study, is examining the efficacy and safety of inhaled clofazimine in the treatment of nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM). This double-blind, randomized trial will look at culture conversion and quality of life measures. Additionally, the COPD Foundation has created the Bronchiectasis and NTM Research Registry, an American cohort containing more than 5,000 patients and data from 22 different sites, to answer some of the most important questions for clinicians and patients.
We have made significant progress in bronchiectasis research; however, there is still much to learn. Together, we must make a concerted effort to enroll patients in clinical trials. Doing so will allow us to define our epidemiologic profile more precisely and explore new treatments and airway clearance techniques.
AIRWAYS DISORDERS NETWORK
Bronchiectasis Section
For years, the noncystic fibrosis (CF) bronchiectasis community has been trying to organize to provide better care for more than half a million adults with bronchiectasis in the United States. Internationally, the Europeans created the European Bronchiectasis Registry, which has been a powerful tool including nearly 20,000 patients, to answer important epidemiologic and management questions. We must do more for the bronchiectasis community.
Clinicaltrials.gov indicates that there are 8 international phase 3 or 4 clinical trials that are currently enrolling; 3 of those have enrollment sites in the United States. One such study from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill is looking at the use of nebulized hypertonic saline in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis to understand the effect it has on mucociliary clearance. Emory University is looking at the use of elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor (Trikafta) in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis; these patients have only 1 targetable mutation and a phenotype that resembles CF. This 8-week, open-label, single-center study aims to measure both clinical and biomarker outcomes after treatment with Trikafta. Finally, a phase 3 trial out of Florida, the ICoN-1 study, is examining the efficacy and safety of inhaled clofazimine in the treatment of nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM). This double-blind, randomized trial will look at culture conversion and quality of life measures. Additionally, the COPD Foundation has created the Bronchiectasis and NTM Research Registry, an American cohort containing more than 5,000 patients and data from 22 different sites, to answer some of the most important questions for clinicians and patients.
We have made significant progress in bronchiectasis research; however, there is still much to learn. Together, we must make a concerted effort to enroll patients in clinical trials. Doing so will allow us to define our epidemiologic profile more precisely and explore new treatments and airway clearance techniques.
AIRWAYS DISORDERS NETWORK
Bronchiectasis Section
For years, the noncystic fibrosis (CF) bronchiectasis community has been trying to organize to provide better care for more than half a million adults with bronchiectasis in the United States. Internationally, the Europeans created the European Bronchiectasis Registry, which has been a powerful tool including nearly 20,000 patients, to answer important epidemiologic and management questions. We must do more for the bronchiectasis community.
Clinicaltrials.gov indicates that there are 8 international phase 3 or 4 clinical trials that are currently enrolling; 3 of those have enrollment sites in the United States. One such study from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill is looking at the use of nebulized hypertonic saline in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis to understand the effect it has on mucociliary clearance. Emory University is looking at the use of elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor (Trikafta) in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis; these patients have only 1 targetable mutation and a phenotype that resembles CF. This 8-week, open-label, single-center study aims to measure both clinical and biomarker outcomes after treatment with Trikafta. Finally, a phase 3 trial out of Florida, the ICoN-1 study, is examining the efficacy and safety of inhaled clofazimine in the treatment of nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM). This double-blind, randomized trial will look at culture conversion and quality of life measures. Additionally, the COPD Foundation has created the Bronchiectasis and NTM Research Registry, an American cohort containing more than 5,000 patients and data from 22 different sites, to answer some of the most important questions for clinicians and patients.
We have made significant progress in bronchiectasis research; however, there is still much to learn. Together, we must make a concerted effort to enroll patients in clinical trials. Doing so will allow us to define our epidemiologic profile more precisely and explore new treatments and airway clearance techniques.
The Genetic Side of Interstitial Lung Disease
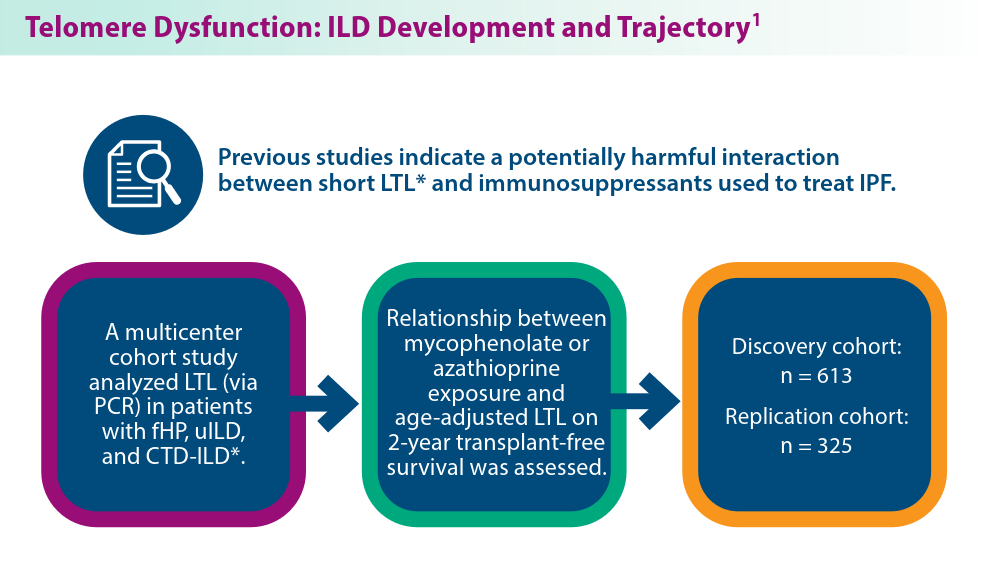
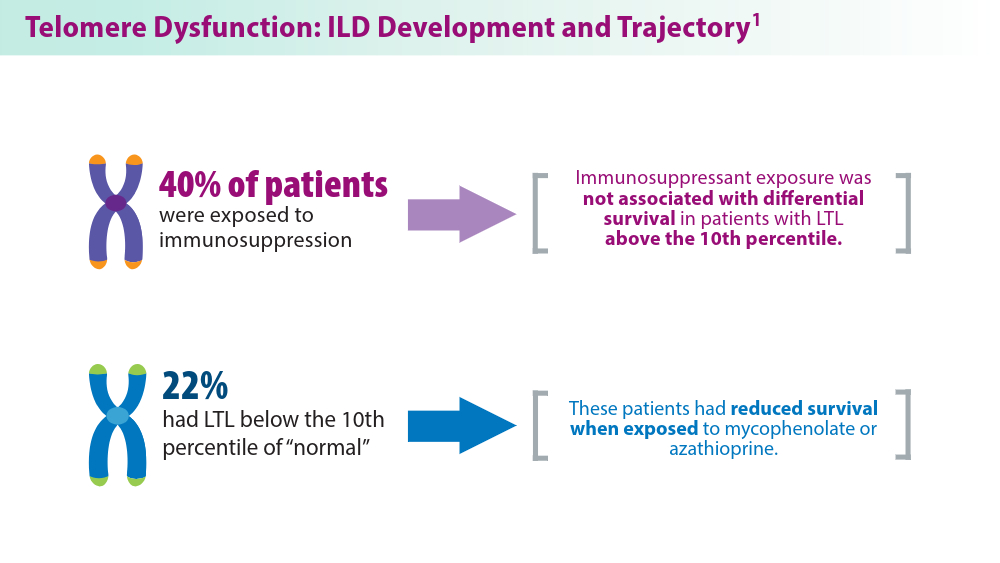
- Zhang D, Adegunsoye A, Oldham JM, et al. Telomere length and immunosuppression in non-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2023;62(5):2300441. doi:10.1183/13993003.00441-2023
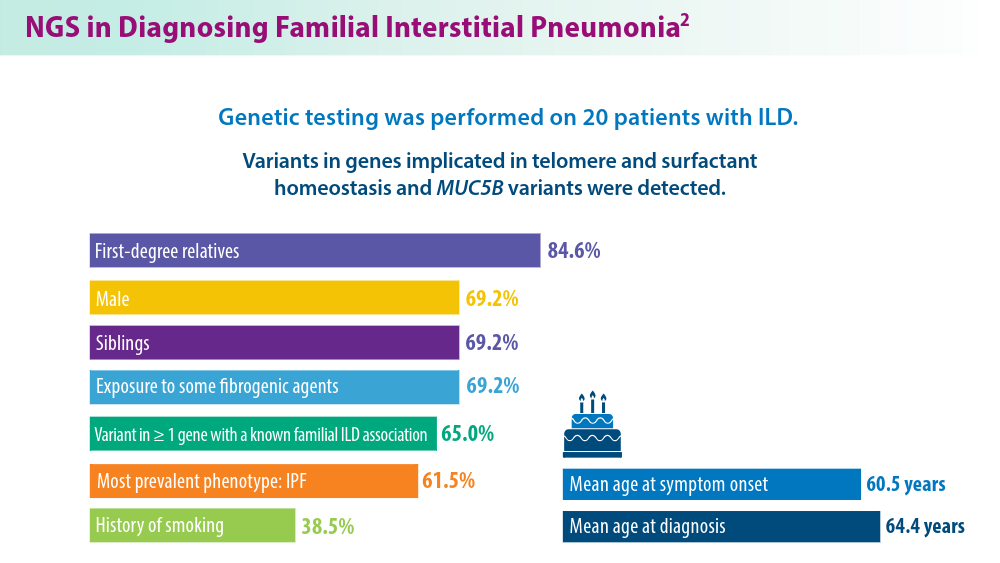
- Gigante AR, Tinoco EM, Fonseca A, et al. Use of next-generation sequencing to support the diagnosis of familial interstitial pneumonia. Genes (Basel). 2023;14(2):326. doi:10.3390/genes14020326
- Adegunsoye A, Kropski JA, Behr J, et al. Genetics and genomics of pulmonary fibrosis: charting the molecular landscape and shaping precision medicine. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. Published online April 4, 2024. doi:10.1164/rccm.202401-0238SO
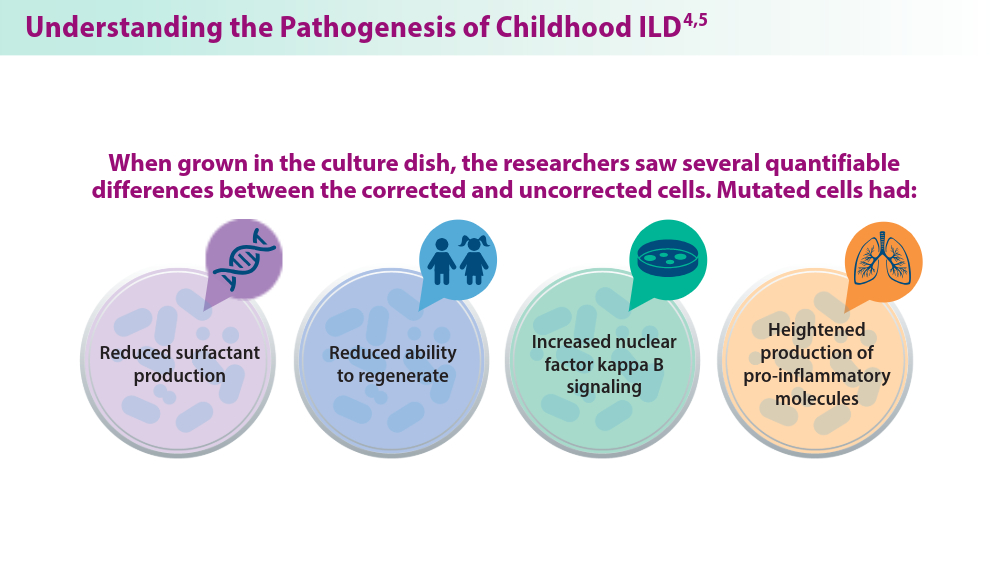
- Sun YL, Hennessey EE, Heins H, et al. Human pluripotent stem cell modeling of alveolar type 2 cell dysfunction caused by ABCA3 mutations. J Clin Invest. 2024;134(2):e164274. doi:10.1172/JCI164274
- Raghu G, Torres JM, Bennett RL. Genetic factors for ILD—the path of precision medicine. Lancet Respir Med. Published online March 20, 2024. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(24)00071-7
- Zhang D, Adegunsoye A, Oldham JM, et al. Telomere length and immunosuppression in non-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2023;62(5):2300441. doi:10.1183/13993003.00441-2023
- Gigante AR, Tinoco EM, Fonseca A, et al. Use of next-generation sequencing to support the diagnosis of familial interstitial pneumonia. Genes (Basel). 2023;14(2):326. doi:10.3390/genes14020326
- Adegunsoye A, Kropski JA, Behr J, et al. Genetics and genomics of pulmonary fibrosis: charting the molecular landscape and shaping precision medicine. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. Published online April 4, 2024. doi:10.1164/rccm.202401-0238SO
- Sun YL, Hennessey EE, Heins H, et al. Human pluripotent stem cell modeling of alveolar type 2 cell dysfunction caused by ABCA3 mutations. J Clin Invest. 2024;134(2):e164274. doi:10.1172/JCI164274
- Raghu G, Torres JM, Bennett RL. Genetic factors for ILD—the path of precision medicine. Lancet Respir Med. Published online March 20, 2024. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(24)00071-7
- Zhang D, Adegunsoye A, Oldham JM, et al. Telomere length and immunosuppression in non-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2023;62(5):2300441. doi:10.1183/13993003.00441-2023
- Gigante AR, Tinoco EM, Fonseca A, et al. Use of next-generation sequencing to support the diagnosis of familial interstitial pneumonia. Genes (Basel). 2023;14(2):326. doi:10.3390/genes14020326
- Adegunsoye A, Kropski JA, Behr J, et al. Genetics and genomics of pulmonary fibrosis: charting the molecular landscape and shaping precision medicine. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. Published online April 4, 2024. doi:10.1164/rccm.202401-0238SO
- Sun YL, Hennessey EE, Heins H, et al. Human pluripotent stem cell modeling of alveolar type 2 cell dysfunction caused by ABCA3 mutations. J Clin Invest. 2024;134(2):e164274. doi:10.1172/JCI164274
- Raghu G, Torres JM, Bennett RL. Genetic factors for ILD—the path of precision medicine. Lancet Respir Med. Published online March 20, 2024. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(24)00071-7
The countdown to CHEST 2024 begins
As we find ourselves in September, I cannot help but dedicate my column to the upcoming CHEST Annual Meeting quickly approaching, October 6 to 9, in Boston.
If you haven’t yet been to a CHEST Annual Meeting, it’s an unmatched experience.
For those who have attended, there’s always something new to see. Every year is different, with the culture of the location guiding the way and new opportunities to network while engaging in activity. No matter how many times you have been, attending the CHEST Annual Meeting never gets old.
Leveraging CHEST 2024’s location, we’ll be hosting a Grand Rounds event days before the meeting starts with pulmonary and critical care medicine fellows from the regional Boston programs to learn from visiting CHEST leadership on a variety of influential topics. These fellowship programs held events like this prepandemic, so I’m truly excited we could help restart the tradition and give the local fellows an opportunity to interact with each other from both an academic and social perspective. Personally, I am very much looking forward to meeting and getting to know the fellows from the Boston area.
The meeting has a lot of notable opportunities lined up (see my official “President’s checklist”), including the third year of CHEST After Hours (Monday, October 7)—a unique storytelling event focusing on the humanities of medicine in partnership with The Nocturnists podcast. And for the first time in recent years, CHEST 2024 will feature a 5K run/walk (Tuesday, October 8) in support of CHEST philanthropy and its work to fuel breakthroughs, empower innovation, and drive toward a future where every patient’s well-being is safeguarded. I encourage you to register in advance of the meeting to secure your space and snag a souvenir T-shirt.
First thing Sunday morning (October 6), the meeting kicks off with the Opening Session where we will be celebrating the new fellows of the college (FCCP), honoring trailblazers in chest medicine, and welcoming this year’s keynote speaker.
This year’s keynote address will come from Vanessa Kerry, MD, who will speak on environmental issues and her work to raise awareness of the impact of climate change on health.
With so many things to look forward to, this meeting will be one to remember for all in attendance.
I look forward to seeing you in Boston,
Jack
As we find ourselves in September, I cannot help but dedicate my column to the upcoming CHEST Annual Meeting quickly approaching, October 6 to 9, in Boston.
If you haven’t yet been to a CHEST Annual Meeting, it’s an unmatched experience.
For those who have attended, there’s always something new to see. Every year is different, with the culture of the location guiding the way and new opportunities to network while engaging in activity. No matter how many times you have been, attending the CHEST Annual Meeting never gets old.
Leveraging CHEST 2024’s location, we’ll be hosting a Grand Rounds event days before the meeting starts with pulmonary and critical care medicine fellows from the regional Boston programs to learn from visiting CHEST leadership on a variety of influential topics. These fellowship programs held events like this prepandemic, so I’m truly excited we could help restart the tradition and give the local fellows an opportunity to interact with each other from both an academic and social perspective. Personally, I am very much looking forward to meeting and getting to know the fellows from the Boston area.
The meeting has a lot of notable opportunities lined up (see my official “President’s checklist”), including the third year of CHEST After Hours (Monday, October 7)—a unique storytelling event focusing on the humanities of medicine in partnership with The Nocturnists podcast. And for the first time in recent years, CHEST 2024 will feature a 5K run/walk (Tuesday, October 8) in support of CHEST philanthropy and its work to fuel breakthroughs, empower innovation, and drive toward a future where every patient’s well-being is safeguarded. I encourage you to register in advance of the meeting to secure your space and snag a souvenir T-shirt.
First thing Sunday morning (October 6), the meeting kicks off with the Opening Session where we will be celebrating the new fellows of the college (FCCP), honoring trailblazers in chest medicine, and welcoming this year’s keynote speaker.
This year’s keynote address will come from Vanessa Kerry, MD, who will speak on environmental issues and her work to raise awareness of the impact of climate change on health.
With so many things to look forward to, this meeting will be one to remember for all in attendance.
I look forward to seeing you in Boston,
Jack
As we find ourselves in September, I cannot help but dedicate my column to the upcoming CHEST Annual Meeting quickly approaching, October 6 to 9, in Boston.
If you haven’t yet been to a CHEST Annual Meeting, it’s an unmatched experience.
For those who have attended, there’s always something new to see. Every year is different, with the culture of the location guiding the way and new opportunities to network while engaging in activity. No matter how many times you have been, attending the CHEST Annual Meeting never gets old.
Leveraging CHEST 2024’s location, we’ll be hosting a Grand Rounds event days before the meeting starts with pulmonary and critical care medicine fellows from the regional Boston programs to learn from visiting CHEST leadership on a variety of influential topics. These fellowship programs held events like this prepandemic, so I’m truly excited we could help restart the tradition and give the local fellows an opportunity to interact with each other from both an academic and social perspective. Personally, I am very much looking forward to meeting and getting to know the fellows from the Boston area.
The meeting has a lot of notable opportunities lined up (see my official “President’s checklist”), including the third year of CHEST After Hours (Monday, October 7)—a unique storytelling event focusing on the humanities of medicine in partnership with The Nocturnists podcast. And for the first time in recent years, CHEST 2024 will feature a 5K run/walk (Tuesday, October 8) in support of CHEST philanthropy and its work to fuel breakthroughs, empower innovation, and drive toward a future where every patient’s well-being is safeguarded. I encourage you to register in advance of the meeting to secure your space and snag a souvenir T-shirt.
First thing Sunday morning (October 6), the meeting kicks off with the Opening Session where we will be celebrating the new fellows of the college (FCCP), honoring trailblazers in chest medicine, and welcoming this year’s keynote speaker.
This year’s keynote address will come from Vanessa Kerry, MD, who will speak on environmental issues and her work to raise awareness of the impact of climate change on health.
With so many things to look forward to, this meeting will be one to remember for all in attendance.
I look forward to seeing you in Boston,
Jack
Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Diagnostic Criteria, Treatment, and COVID-19
- Torres A, Cilloniz C, Niederman MS, et al. Pneumonia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):25. doi:10.1038/s41572-021-00259-0
- Niederman MS, Torres A. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. Eur Respir Rev. 2022;31(166):220123. doi:10.1183/16000617.0123-2022
- Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(7):e45-e67. doi:10.1164/rccm.201908-1581ST
- Memon RA, Rashid MA, Avva S, et al. The use of the SMART-COP score in predicting severity outcomes among patients with community-acquired pneumonia: a meta-analysis. Cureus. 2022;14(7):e27248. doi:10.7759/cureus.27248
- Regunath H, Oba Y. Community-acquired pneumonia. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Updated January 26, 2024. Accessed May 14, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430749/
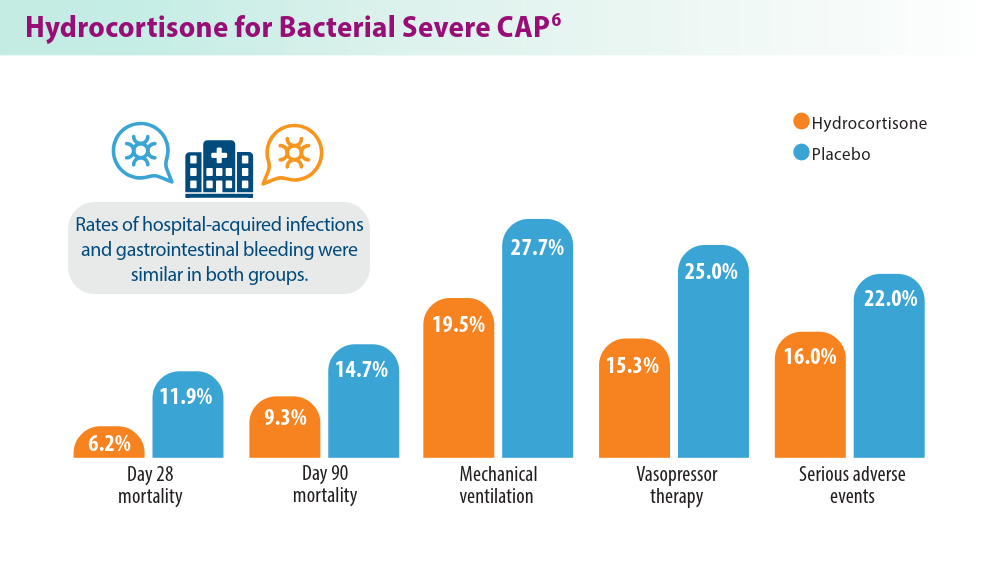
- Dequin PF, Meziani F, Quenot JP, et al; for the CRICS-TriGGERSep Network. Hydrocortisone in severe community-acquired pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(21):1931-1941. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2215145
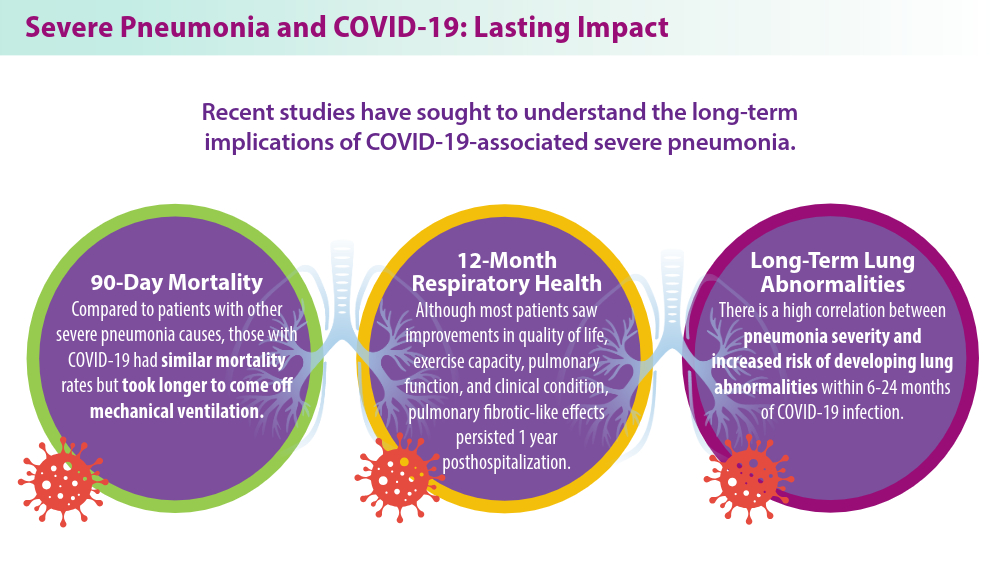
- Eizaguirre S, Sabater G, Belda S, et al. Long-term respiratory consequences of COVID-19 related pneumonia: a cohort study. BMC Pulm Med. 2023;23(1):439. doi:10.1186/s12890-023-02627-w
- Ramirez JA, Wiemken TL, Peyrani P, et al; for the University of Louisville Pneumonia Study Group. Adults hospitalized with pneumonia in the United States: incidence, epidemiology, and mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(11):1806-1812. doi:10.1093/cid/cix647
- Morgan AJ, Glossop AJ. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. BJA Educ. 2016;16(5):167-172. doi:10.1093/bjaed/mkv052
- Haessler S, Guo N, Deshpande A, et al. Etiology, treatments, and outcomes of patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia in a large U.S. sample. Crit Care Med. 2022;50(7):1063-1071. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000005498
- Nolley EP, Sahetya SK, Hochberg CH, et al. Outcomes among mechanically ventilated patients with severe pneumonia and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure from SARS-CoV-2 and other etiologies. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(1):e2250401. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.50401
- Hino T, Nishino M, Valtchinov VI, et al. Severe COVID-19 pneumonia leads to post-COVID-19 lung abnormalities on follow-up CT scans. Eur J Radiol Open. 2023;10:100483. doi:10.1016/j.ejro.2023.100483
- Torres A, Cilloniz C, Niederman MS, et al. Pneumonia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):25. doi:10.1038/s41572-021-00259-0
- Niederman MS, Torres A. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. Eur Respir Rev. 2022;31(166):220123. doi:10.1183/16000617.0123-2022
- Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(7):e45-e67. doi:10.1164/rccm.201908-1581ST
- Memon RA, Rashid MA, Avva S, et al. The use of the SMART-COP score in predicting severity outcomes among patients with community-acquired pneumonia: a meta-analysis. Cureus. 2022;14(7):e27248. doi:10.7759/cureus.27248
- Regunath H, Oba Y. Community-acquired pneumonia. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Updated January 26, 2024. Accessed May 14, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430749/
- Dequin PF, Meziani F, Quenot JP, et al; for the CRICS-TriGGERSep Network. Hydrocortisone in severe community-acquired pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(21):1931-1941. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2215145
- Eizaguirre S, Sabater G, Belda S, et al. Long-term respiratory consequences of COVID-19 related pneumonia: a cohort study. BMC Pulm Med. 2023;23(1):439. doi:10.1186/s12890-023-02627-w
- Ramirez JA, Wiemken TL, Peyrani P, et al; for the University of Louisville Pneumonia Study Group. Adults hospitalized with pneumonia in the United States: incidence, epidemiology, and mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(11):1806-1812. doi:10.1093/cid/cix647
- Morgan AJ, Glossop AJ. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. BJA Educ. 2016;16(5):167-172. doi:10.1093/bjaed/mkv052
- Haessler S, Guo N, Deshpande A, et al. Etiology, treatments, and outcomes of patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia in a large U.S. sample. Crit Care Med. 2022;50(7):1063-1071. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000005498
- Nolley EP, Sahetya SK, Hochberg CH, et al. Outcomes among mechanically ventilated patients with severe pneumonia and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure from SARS-CoV-2 and other etiologies. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(1):e2250401. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.50401
- Hino T, Nishino M, Valtchinov VI, et al. Severe COVID-19 pneumonia leads to post-COVID-19 lung abnormalities on follow-up CT scans. Eur J Radiol Open. 2023;10:100483. doi:10.1016/j.ejro.2023.100483
- Torres A, Cilloniz C, Niederman MS, et al. Pneumonia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):25. doi:10.1038/s41572-021-00259-0
- Niederman MS, Torres A. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. Eur Respir Rev. 2022;31(166):220123. doi:10.1183/16000617.0123-2022
- Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(7):e45-e67. doi:10.1164/rccm.201908-1581ST
- Memon RA, Rashid MA, Avva S, et al. The use of the SMART-COP score in predicting severity outcomes among patients with community-acquired pneumonia: a meta-analysis. Cureus. 2022;14(7):e27248. doi:10.7759/cureus.27248
- Regunath H, Oba Y. Community-acquired pneumonia. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Updated January 26, 2024. Accessed May 14, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430749/
- Dequin PF, Meziani F, Quenot JP, et al; for the CRICS-TriGGERSep Network. Hydrocortisone in severe community-acquired pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(21):1931-1941. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2215145
- Eizaguirre S, Sabater G, Belda S, et al. Long-term respiratory consequences of COVID-19 related pneumonia: a cohort study. BMC Pulm Med. 2023;23(1):439. doi:10.1186/s12890-023-02627-w
- Ramirez JA, Wiemken TL, Peyrani P, et al; for the University of Louisville Pneumonia Study Group. Adults hospitalized with pneumonia in the United States: incidence, epidemiology, and mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(11):1806-1812. doi:10.1093/cid/cix647
- Morgan AJ, Glossop AJ. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. BJA Educ. 2016;16(5):167-172. doi:10.1093/bjaed/mkv052
- Haessler S, Guo N, Deshpande A, et al. Etiology, treatments, and outcomes of patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia in a large U.S. sample. Crit Care Med. 2022;50(7):1063-1071. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000005498
- Nolley EP, Sahetya SK, Hochberg CH, et al. Outcomes among mechanically ventilated patients with severe pneumonia and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure from SARS-CoV-2 and other etiologies. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(1):e2250401. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.50401
- Hino T, Nishino M, Valtchinov VI, et al. Severe COVID-19 pneumonia leads to post-COVID-19 lung abnormalities on follow-up CT scans. Eur J Radiol Open. 2023;10:100483. doi:10.1016/j.ejro.2023.100483
OSA in pregnancy: Who to test, how to screen, and does treatment help?
The increased prevalence in pregnancy can be explained by physiologic changes impacting the upper airway such as increases in maternal blood volume and reductions in oncotic pressure, as well as increases in circulating levels of estrogen and progesterone. OSA in pregnancy is associated with adverse perinatal outcomes such as hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, severe maternal morbidity abnormalities in fetal growth, preterm birth, and congenital abnormalities in the offspring.2,3 Despite this evidence, guidelines on the screening, diagnosis, and treatment of OSA in pregnancy have only recently been published and will be reviewed here.1
The obstetric subcommittee of the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine that produced these guidelines had expertise in obstetric anesthesiology, sleep medicine and sleep research, high-risk obstetrics, and obstetric medicine. The guideline aimed to answer 3 questions: 1) Who should be screened in pregnancy for OSA, 2) how to make a diagnosis of OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period, and 3) what is the treatment for OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period. Although the estimated number of annual pregnancies in the US declined between 2010 to 2019, these clinical questions remain critical considering the obesity epidemic, the ability to conceive despite advanced maternal age and chronic illnesses with the use of fertility treatments, and the crisis of severe maternal morbidity and mortality. As sleep disordered breathing (SDB) has been associated with many conditions linked to maternal mortality, better management of SDB in this population is key.
Screening for OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline does not support universal screening of all people who are pregnant, but rather suggests that people who are pregnant and at high risk for OSA, such as those with a body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m2 and those with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, or diabetes, in the index pregnancy or a prior pregnancy, be screened for OSA in the first or second trimester.1 Screening for OSA in pregnancy in limited populations is recommended due to the lower yield of universal screening and its potential burden on the health care system. Furthermore, screening for OSA in early pregnancy is suggested given the practical challenges of arranging testing, initiating, and allowing time for patients to become acclimated to therapy in later stages of pregnancy. However, even when timing of diagnosis may not allow for appropriate treatment of OSA during pregnancy, knowing a person’s OSA status before delivery is beneficial, particularly for patients at risk for Cesarean delivery who may require intubation and exposure to sedative medications, as well as those receiving epidural anesthesia, as OSA is a risk factor for respiratory depression.
Although screening was thought to be beneficial in specific populations, there is insufficient evidence to recommend any one screening tool. The guideline made recommendations against the use of the Berlin questionnaire, STOP-BANG questionnaire, Epworth Sleepiness Scale, or the ASA checklist.1 These screening tools were developed and validated in nonpregnant patient populations and their pooled sensitivity and specificity to detect OSA in pregnancy is low. Individual components of these screening tools, such as prepregnancy BMI, frequency and volume of snoring, hypertension, and neck circumference ≥16 inches have, however, been associated with OSA status.
Pregnancy-specific OSA screening tools have been proposed.4,5 The guideline suggests these pregnancy-specific tools may be considered for screening for OSA in pregnancy but still require external validation, especially in high-risk populations. The committee agreed that individuals with BMI >30kg/m2, hypertension, diabetes, and those with a history of difficult intubation or Mallampati score III or IV are considered at risk for OSA in pregnancy.
Diagnosis of OSA in the pregnant population
In the general population, in-laboratory polysomnogram (PSG) is the gold standard diagnostic test. However, for patients in whom uncomplicated OSA is suspected with a moderate to high pretest probability, unattended home sleep apnea testing (HSAT) is a reasonable initial study. On the other hand, in-lab PSG is recommended in mission-critical workers and when coexisting respiratory sleep disorders, or nonrespiratory sleep disorders, are suspected. For individuals who are pregnant and suspected of having OSA, the guideline suggests that HSAT is a reasonable diagnostic tool, as many level III devices have demonstrated good agreement between the respiratory disturbance index (RDI) and apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) measured by PSG.6 Notably, most studies have examined the performance of level III devices in late pregnancy in populations with obesity; hence, the performance of these devices in early pregnancy when risk for OSA is lower, or more subtle forms of SDB may be more common, is less clear but may be an acceptable first-line test.
The guideline did not provide recommendations for next steps following an inconclusive, technically inadequate, or negative HSAT. However, recommendations to proceed with in-lab PSG in individuals with clinical suspicion for OSA and a negative HSAT is a reasonable approach, keeping in mind the time restrictions of pregnancy. The more delayed the diagnosis, the less time there will be for initiation of and acclimation to therapy to maximize potential benefits during pregnancy. HSAT is especially practical and convenient for individuals with young families. The guideline does not recommend the use of overnight oximetry for diagnostic purposes.1
The postpartum period is usually associated with weight loss and reversal of pregnancy physiology. Generally, the decision to perform a repeat sleep study following weight loss is individualized, based on factors such as improved symptoms or sustained, significant weight loss. Though data show improvement in AHI following delivery, small studies show persistent OSA in nearly half of individuals diagnosed in pregnancy. Hence, as pregnancy increases the risk for OSA, and given that the postpartum status is not always associated with resolution of OSA, the guideline recommends considering repeat diagnostic testing in the postpartum period.1 The decision to repeat testing also depends on whether OSA or OSA symptoms predated pregnancy, on the persistence of symptoms, and the degree of weight loss with delivery and the postpartum body habitus.
Treatment of OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline recommends behavior modification in OSA similarly to individuals who are not pregnant (avoidance of sedatives, smoking, and alcohol).1 However, weight loss is not recommended in pregnancy due to the potential for harm to the fetus.
The gold standard treatment for people who are pregnant and have OSA is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). Treatment of OSA in pregnancy is complicated by the fact that very few women are referred to sleep practices due to time restrictions and logistical reasons, and that data demonstrating improved pregnancy outcomes with CPAP are scarce, limiting the prioritization of OSA management. However, expert consensus considers a theoretical benefit in the context of lack of current evidence of harm from treatment. Hence, at this point, the guideline recommends counseling around CPAP therapy be aimed at improvement in symptoms, AHI, and quality of life, rather than pregnancy-specific outcomes.1 This recommendation was based on observations from small case series that demonstrated improved breathing parameters during sleep and symptoms, and small randomized controlled trials (RCT), limited by short-term exposure to the intervention. However, since the publication of this guideline, a large RCT that randomized pregnant women with SDB to CPAP or usual care has demonstrated significantly lower diastolic blood pressure, an altered diastolic blood pressure trajectory, and a lower rate of preeclampsia in the group treated with CPAP compared with usual care.7
This guideline provides helpful insight on who to screen and how to manage OSA in pregnancy but additional research is needed to elucidate benefits of treatment and its effects on maternal and neonatal outcomes. Multidisciplinary collaborations between obstetric and sleep teams are necessary to ensure that screening and diagnostic strategies result in management change for improved outcomes.
References
1. Dominguez JE, Cantrell S, Habib AS, et al. Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine and the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology Consensus Guideline on the screening, diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;142(2):403-423.
2. Bourjeily, G, Danilack C, Bublitz M, Muri J, Rosene-Montella K, Lipkind H. Maternal obstructive sleep apnea and neonatal birth outcomes in a population based sample. Sleep Med. 2000;66:233-240.
3. Malhamé I, Bublitz MH, Wilson D, Sanapo L, Rochin E, Bourjeily G. Sleep disordered breathing and the risk of severe maternal morbidity in women with preeclampsia: a population-based study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022;30:215-220.
4. Izci-Balserak B, Zhu B, Gurubhagavatula I, Keenan BT, Pien GW. A screening algorithm for obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16(10):1286-1294.
5. Louis J, Koch MA, Reddy UM, et al. Predictors of sleep-disordered breathing in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218(5):521.e1.e12.
6. Sharkey K, Waters K, Millman R, Moore R, Martin SM, Bourjeily. Validation of the Apnea Risk Evaluation System (ARES) device against laboratory polysomnogram in pregnant women at risk for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med. 2014;10(5):497-502.
7. Tantrakul V, Ingsathit A, Liamsombut S, et al. Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in high-risk pregnancy: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Respir Res. 2023;24(1):171.
The increased prevalence in pregnancy can be explained by physiologic changes impacting the upper airway such as increases in maternal blood volume and reductions in oncotic pressure, as well as increases in circulating levels of estrogen and progesterone. OSA in pregnancy is associated with adverse perinatal outcomes such as hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, severe maternal morbidity abnormalities in fetal growth, preterm birth, and congenital abnormalities in the offspring.2,3 Despite this evidence, guidelines on the screening, diagnosis, and treatment of OSA in pregnancy have only recently been published and will be reviewed here.1
The obstetric subcommittee of the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine that produced these guidelines had expertise in obstetric anesthesiology, sleep medicine and sleep research, high-risk obstetrics, and obstetric medicine. The guideline aimed to answer 3 questions: 1) Who should be screened in pregnancy for OSA, 2) how to make a diagnosis of OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period, and 3) what is the treatment for OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period. Although the estimated number of annual pregnancies in the US declined between 2010 to 2019, these clinical questions remain critical considering the obesity epidemic, the ability to conceive despite advanced maternal age and chronic illnesses with the use of fertility treatments, and the crisis of severe maternal morbidity and mortality. As sleep disordered breathing (SDB) has been associated with many conditions linked to maternal mortality, better management of SDB in this population is key.
Screening for OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline does not support universal screening of all people who are pregnant, but rather suggests that people who are pregnant and at high risk for OSA, such as those with a body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m2 and those with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, or diabetes, in the index pregnancy or a prior pregnancy, be screened for OSA in the first or second trimester.1 Screening for OSA in pregnancy in limited populations is recommended due to the lower yield of universal screening and its potential burden on the health care system. Furthermore, screening for OSA in early pregnancy is suggested given the practical challenges of arranging testing, initiating, and allowing time for patients to become acclimated to therapy in later stages of pregnancy. However, even when timing of diagnosis may not allow for appropriate treatment of OSA during pregnancy, knowing a person’s OSA status before delivery is beneficial, particularly for patients at risk for Cesarean delivery who may require intubation and exposure to sedative medications, as well as those receiving epidural anesthesia, as OSA is a risk factor for respiratory depression.
Although screening was thought to be beneficial in specific populations, there is insufficient evidence to recommend any one screening tool. The guideline made recommendations against the use of the Berlin questionnaire, STOP-BANG questionnaire, Epworth Sleepiness Scale, or the ASA checklist.1 These screening tools were developed and validated in nonpregnant patient populations and their pooled sensitivity and specificity to detect OSA in pregnancy is low. Individual components of these screening tools, such as prepregnancy BMI, frequency and volume of snoring, hypertension, and neck circumference ≥16 inches have, however, been associated with OSA status.
Pregnancy-specific OSA screening tools have been proposed.4,5 The guideline suggests these pregnancy-specific tools may be considered for screening for OSA in pregnancy but still require external validation, especially in high-risk populations. The committee agreed that individuals with BMI >30kg/m2, hypertension, diabetes, and those with a history of difficult intubation or Mallampati score III or IV are considered at risk for OSA in pregnancy.
Diagnosis of OSA in the pregnant population
In the general population, in-laboratory polysomnogram (PSG) is the gold standard diagnostic test. However, for patients in whom uncomplicated OSA is suspected with a moderate to high pretest probability, unattended home sleep apnea testing (HSAT) is a reasonable initial study. On the other hand, in-lab PSG is recommended in mission-critical workers and when coexisting respiratory sleep disorders, or nonrespiratory sleep disorders, are suspected. For individuals who are pregnant and suspected of having OSA, the guideline suggests that HSAT is a reasonable diagnostic tool, as many level III devices have demonstrated good agreement between the respiratory disturbance index (RDI) and apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) measured by PSG.6 Notably, most studies have examined the performance of level III devices in late pregnancy in populations with obesity; hence, the performance of these devices in early pregnancy when risk for OSA is lower, or more subtle forms of SDB may be more common, is less clear but may be an acceptable first-line test.
The guideline did not provide recommendations for next steps following an inconclusive, technically inadequate, or negative HSAT. However, recommendations to proceed with in-lab PSG in individuals with clinical suspicion for OSA and a negative HSAT is a reasonable approach, keeping in mind the time restrictions of pregnancy. The more delayed the diagnosis, the less time there will be for initiation of and acclimation to therapy to maximize potential benefits during pregnancy. HSAT is especially practical and convenient for individuals with young families. The guideline does not recommend the use of overnight oximetry for diagnostic purposes.1
The postpartum period is usually associated with weight loss and reversal of pregnancy physiology. Generally, the decision to perform a repeat sleep study following weight loss is individualized, based on factors such as improved symptoms or sustained, significant weight loss. Though data show improvement in AHI following delivery, small studies show persistent OSA in nearly half of individuals diagnosed in pregnancy. Hence, as pregnancy increases the risk for OSA, and given that the postpartum status is not always associated with resolution of OSA, the guideline recommends considering repeat diagnostic testing in the postpartum period.1 The decision to repeat testing also depends on whether OSA or OSA symptoms predated pregnancy, on the persistence of symptoms, and the degree of weight loss with delivery and the postpartum body habitus.
Treatment of OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline recommends behavior modification in OSA similarly to individuals who are not pregnant (avoidance of sedatives, smoking, and alcohol).1 However, weight loss is not recommended in pregnancy due to the potential for harm to the fetus.
The gold standard treatment for people who are pregnant and have OSA is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). Treatment of OSA in pregnancy is complicated by the fact that very few women are referred to sleep practices due to time restrictions and logistical reasons, and that data demonstrating improved pregnancy outcomes with CPAP are scarce, limiting the prioritization of OSA management. However, expert consensus considers a theoretical benefit in the context of lack of current evidence of harm from treatment. Hence, at this point, the guideline recommends counseling around CPAP therapy be aimed at improvement in symptoms, AHI, and quality of life, rather than pregnancy-specific outcomes.1 This recommendation was based on observations from small case series that demonstrated improved breathing parameters during sleep and symptoms, and small randomized controlled trials (RCT), limited by short-term exposure to the intervention. However, since the publication of this guideline, a large RCT that randomized pregnant women with SDB to CPAP or usual care has demonstrated significantly lower diastolic blood pressure, an altered diastolic blood pressure trajectory, and a lower rate of preeclampsia in the group treated with CPAP compared with usual care.7
This guideline provides helpful insight on who to screen and how to manage OSA in pregnancy but additional research is needed to elucidate benefits of treatment and its effects on maternal and neonatal outcomes. Multidisciplinary collaborations between obstetric and sleep teams are necessary to ensure that screening and diagnostic strategies result in management change for improved outcomes.
References
1. Dominguez JE, Cantrell S, Habib AS, et al. Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine and the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology Consensus Guideline on the screening, diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;142(2):403-423.
2. Bourjeily, G, Danilack C, Bublitz M, Muri J, Rosene-Montella K, Lipkind H. Maternal obstructive sleep apnea and neonatal birth outcomes in a population based sample. Sleep Med. 2000;66:233-240.
3. Malhamé I, Bublitz MH, Wilson D, Sanapo L, Rochin E, Bourjeily G. Sleep disordered breathing and the risk of severe maternal morbidity in women with preeclampsia: a population-based study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022;30:215-220.
4. Izci-Balserak B, Zhu B, Gurubhagavatula I, Keenan BT, Pien GW. A screening algorithm for obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16(10):1286-1294.
5. Louis J, Koch MA, Reddy UM, et al. Predictors of sleep-disordered breathing in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218(5):521.e1.e12.
6. Sharkey K, Waters K, Millman R, Moore R, Martin SM, Bourjeily. Validation of the Apnea Risk Evaluation System (ARES) device against laboratory polysomnogram in pregnant women at risk for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med. 2014;10(5):497-502.
7. Tantrakul V, Ingsathit A, Liamsombut S, et al. Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in high-risk pregnancy: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Respir Res. 2023;24(1):171.
The increased prevalence in pregnancy can be explained by physiologic changes impacting the upper airway such as increases in maternal blood volume and reductions in oncotic pressure, as well as increases in circulating levels of estrogen and progesterone. OSA in pregnancy is associated with adverse perinatal outcomes such as hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, severe maternal morbidity abnormalities in fetal growth, preterm birth, and congenital abnormalities in the offspring.2,3 Despite this evidence, guidelines on the screening, diagnosis, and treatment of OSA in pregnancy have only recently been published and will be reviewed here.1
The obstetric subcommittee of the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine that produced these guidelines had expertise in obstetric anesthesiology, sleep medicine and sleep research, high-risk obstetrics, and obstetric medicine. The guideline aimed to answer 3 questions: 1) Who should be screened in pregnancy for OSA, 2) how to make a diagnosis of OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period, and 3) what is the treatment for OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period. Although the estimated number of annual pregnancies in the US declined between 2010 to 2019, these clinical questions remain critical considering the obesity epidemic, the ability to conceive despite advanced maternal age and chronic illnesses with the use of fertility treatments, and the crisis of severe maternal morbidity and mortality. As sleep disordered breathing (SDB) has been associated with many conditions linked to maternal mortality, better management of SDB in this population is key.
Screening for OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline does not support universal screening of all people who are pregnant, but rather suggests that people who are pregnant and at high risk for OSA, such as those with a body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m2 and those with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, or diabetes, in the index pregnancy or a prior pregnancy, be screened for OSA in the first or second trimester.1 Screening for OSA in pregnancy in limited populations is recommended due to the lower yield of universal screening and its potential burden on the health care system. Furthermore, screening for OSA in early pregnancy is suggested given the practical challenges of arranging testing, initiating, and allowing time for patients to become acclimated to therapy in later stages of pregnancy. However, even when timing of diagnosis may not allow for appropriate treatment of OSA during pregnancy, knowing a person’s OSA status before delivery is beneficial, particularly for patients at risk for Cesarean delivery who may require intubation and exposure to sedative medications, as well as those receiving epidural anesthesia, as OSA is a risk factor for respiratory depression.
Although screening was thought to be beneficial in specific populations, there is insufficient evidence to recommend any one screening tool. The guideline made recommendations against the use of the Berlin questionnaire, STOP-BANG questionnaire, Epworth Sleepiness Scale, or the ASA checklist.1 These screening tools were developed and validated in nonpregnant patient populations and their pooled sensitivity and specificity to detect OSA in pregnancy is low. Individual components of these screening tools, such as prepregnancy BMI, frequency and volume of snoring, hypertension, and neck circumference ≥16 inches have, however, been associated with OSA status.
Pregnancy-specific OSA screening tools have been proposed.4,5 The guideline suggests these pregnancy-specific tools may be considered for screening for OSA in pregnancy but still require external validation, especially in high-risk populations. The committee agreed that individuals with BMI >30kg/m2, hypertension, diabetes, and those with a history of difficult intubation or Mallampati score III or IV are considered at risk for OSA in pregnancy.
Diagnosis of OSA in the pregnant population
In the general population, in-laboratory polysomnogram (PSG) is the gold standard diagnostic test. However, for patients in whom uncomplicated OSA is suspected with a moderate to high pretest probability, unattended home sleep apnea testing (HSAT) is a reasonable initial study. On the other hand, in-lab PSG is recommended in mission-critical workers and when coexisting respiratory sleep disorders, or nonrespiratory sleep disorders, are suspected. For individuals who are pregnant and suspected of having OSA, the guideline suggests that HSAT is a reasonable diagnostic tool, as many level III devices have demonstrated good agreement between the respiratory disturbance index (RDI) and apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) measured by PSG.6 Notably, most studies have examined the performance of level III devices in late pregnancy in populations with obesity; hence, the performance of these devices in early pregnancy when risk for OSA is lower, or more subtle forms of SDB may be more common, is less clear but may be an acceptable first-line test.
The guideline did not provide recommendations for next steps following an inconclusive, technically inadequate, or negative HSAT. However, recommendations to proceed with in-lab PSG in individuals with clinical suspicion for OSA and a negative HSAT is a reasonable approach, keeping in mind the time restrictions of pregnancy. The more delayed the diagnosis, the less time there will be for initiation of and acclimation to therapy to maximize potential benefits during pregnancy. HSAT is especially practical and convenient for individuals with young families. The guideline does not recommend the use of overnight oximetry for diagnostic purposes.1
The postpartum period is usually associated with weight loss and reversal of pregnancy physiology. Generally, the decision to perform a repeat sleep study following weight loss is individualized, based on factors such as improved symptoms or sustained, significant weight loss. Though data show improvement in AHI following delivery, small studies show persistent OSA in nearly half of individuals diagnosed in pregnancy. Hence, as pregnancy increases the risk for OSA, and given that the postpartum status is not always associated with resolution of OSA, the guideline recommends considering repeat diagnostic testing in the postpartum period.1 The decision to repeat testing also depends on whether OSA or OSA symptoms predated pregnancy, on the persistence of symptoms, and the degree of weight loss with delivery and the postpartum body habitus.
Treatment of OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline recommends behavior modification in OSA similarly to individuals who are not pregnant (avoidance of sedatives, smoking, and alcohol).1 However, weight loss is not recommended in pregnancy due to the potential for harm to the fetus.
The gold standard treatment for people who are pregnant and have OSA is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). Treatment of OSA in pregnancy is complicated by the fact that very few women are referred to sleep practices due to time restrictions and logistical reasons, and that data demonstrating improved pregnancy outcomes with CPAP are scarce, limiting the prioritization of OSA management. However, expert consensus considers a theoretical benefit in the context of lack of current evidence of harm from treatment. Hence, at this point, the guideline recommends counseling around CPAP therapy be aimed at improvement in symptoms, AHI, and quality of life, rather than pregnancy-specific outcomes.1 This recommendation was based on observations from small case series that demonstrated improved breathing parameters during sleep and symptoms, and small randomized controlled trials (RCT), limited by short-term exposure to the intervention. However, since the publication of this guideline, a large RCT that randomized pregnant women with SDB to CPAP or usual care has demonstrated significantly lower diastolic blood pressure, an altered diastolic blood pressure trajectory, and a lower rate of preeclampsia in the group treated with CPAP compared with usual care.7
This guideline provides helpful insight on who to screen and how to manage OSA in pregnancy but additional research is needed to elucidate benefits of treatment and its effects on maternal and neonatal outcomes. Multidisciplinary collaborations between obstetric and sleep teams are necessary to ensure that screening and diagnostic strategies result in management change for improved outcomes.
References
1. Dominguez JE, Cantrell S, Habib AS, et al. Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine and the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology Consensus Guideline on the screening, diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;142(2):403-423.
2. Bourjeily, G, Danilack C, Bublitz M, Muri J, Rosene-Montella K, Lipkind H. Maternal obstructive sleep apnea and neonatal birth outcomes in a population based sample. Sleep Med. 2000;66:233-240.
3. Malhamé I, Bublitz MH, Wilson D, Sanapo L, Rochin E, Bourjeily G. Sleep disordered breathing and the risk of severe maternal morbidity in women with preeclampsia: a population-based study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022;30:215-220.
4. Izci-Balserak B, Zhu B, Gurubhagavatula I, Keenan BT, Pien GW. A screening algorithm for obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16(10):1286-1294.
5. Louis J, Koch MA, Reddy UM, et al. Predictors of sleep-disordered breathing in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218(5):521.e1.e12.
6. Sharkey K, Waters K, Millman R, Moore R, Martin SM, Bourjeily. Validation of the Apnea Risk Evaluation System (ARES) device against laboratory polysomnogram in pregnant women at risk for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med. 2014;10(5):497-502.
7. Tantrakul V, Ingsathit A, Liamsombut S, et al. Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in high-risk pregnancy: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Respir Res. 2023;24(1):171.
Cystic fibrosis: Advances, ongoing challenges
After Rena Barrow-Wells, an African American mother, fought mightily to prevent a repeat of her experience of two decades earlier when her first child’s cystic fibrosis (CF) took 4 years to diagnose, her story became the subject of a New York Times feature covering disparities in diagnostic CF screening. The article highlighted not only her struggles, but also the utter transformation of the CF landscape since the introduction of small molecule mutation-specific drugs. These drugs restore function to defective CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) proteins. By the time Ms. Barrow-Wells’ young son was treated, lung and pancreatic scarring were already significant. So when the 39-mutation variant screening test available in Ms. Barrow-Wells’ Lawrenceville, Georgia, clinic turned out negative for CF, her pediatrician told her to stop worrying despite her new son’s inherent genetic risk, telltale salty skin, foul-smelling diapers, and her pleas to test for sweat chloride. It still took 3 months for a confirmed diagnosis and the initiation of treatment.
Current genetic tests, based largely on older clinical trials that enrolled mostly white children, are highly accurate for identifying CF in white babies (95%), but often fail to identify substantial percentages of mutations originating in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. They miss CF in Asian (44%), Black (22%), and Hispanic, Native American and Alaskan Native babies (14%), the Times article stated. In the United States, the number of CF variants tested for falls into a wide range: from the one variant found mostly in White populations in Mississippi (with a 38% Black populace) to 689 variants in Wisconsin.
Not too far back, CF was thought of as an inherited childhood disease leading often to childhood or adolescent mortality.
Today’s CF challenges
Beyond refinements in screening instruments and policies that broaden access leading to the earliest possible diagnoses, ongoing research needs include finding treatments for other variants, and caring for adult populations living with treated CF and the disease’s multisystem manifestations. “As people with CF live longer, we need to be very focused on optimized adult medical care for this population,” Marc A. Sala, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Adult CF Program, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said in an interview. “For example, we need higher vigilance for liver, microvascular, coronary artery disease, and various cancer screenings. We do not know exactly how these will manifest differently from the way they do in non-CF populations, so this is where more work needs to be done.”
Emphasis on monitoring
The authors of “Future therapies for cystic fibrosis” (Allen et al. Nature Communications, 2023 Feb 8), after citing the ongoing transformative change for people with CF since the introduction of CFTR drugs, gave voice to important cautions. “Disease will progress, albeit more slowly, and will be more challenging to monitor. Effective CFTR modulators will likely slow or, at best, halt disease progression, but will not reverse a disease that has already become fixed.” They cited pancreatic destruction in the majority, bronchiectasis, and absence of the vas deferens, with still recurring (although less frequently) pulmonary exacerbations along with chronic infections and persistent airway inflammation. “It is essential that we do not become complacent about disease progression in this population,” the researchers stated. They cautioned also that effective surveillance for infection is critical in asymptomatic patients, emphasizing that it underpins the management of young healthy children with CF who demonstrate disease progression despite a lack of symptoms.
Among the ~90% for whom Trikafta is suitable and approved (those with least one copy of F508del or specific other responsive mutations), improvements include increased percent predicted FEV1 by 10%-15% or more, decreased exacerbations, and improved quality of life,” Dr. Sala said. “Subsequent ‘real world’ experience shows dramatic reductions in sputum production and decreased frequency of lung transplant.”
Mutation agnostic therapy
Unfortunately, CF mutants, outside the population eligible for Trikafta, are prodigious in number and do not fall into just a few major groups. “Furthermore, although CF is a monogenic disease, it has variable phenotypes even for two individuals with the same mutations,” Dr. Sala said. “Current CFTR modulators act on the dysfunctional CFTR protein (either as channel gating potentiators or molecular chaperones to improve misfolding). That leaves about 10% of the CF population, those with little to no protein production (such as in nonsense mutations) ineligible for treatment with CFTR modulators. “The ideal for efficacy and equity, given that some CFTR mutations only exist in a handful of people, would be to develop a ‘mutation agnostic’ strategy — such as with mRNA or gene delivery. Here you could imagine that regardless of the type of mutation, a patient would then be able to receive the technology to increase CFTR channel function,” Dr. Sala said. Many modifiable factors, including host immunity and non-CFTR genes that impact CFTR indirectly, may underlie the fact that one person has a worse trajectory than another. “New therapies may also be found in this area of research,” Dr. Sala said.
Strategies in testing phases
“For patients with class I (nonsense) mutations there is hope that small molecules will be identified that can facilitate premature truncation codon (PTC) read-through and/or impede mRNA decay allowing for clinically relevant levels of functional CFTR,” the researchers noted. While the most extensively developed, ataluren, an oxadiazole, failed in phase 3 trials after initial promise, other ribosomal read-through drugs are in preclinical and early phase clinical trials. Also, early encouraging results support an alternative strategy, engineered transfer RNAs (tRNAs) that introduce an amino acid to an elongating peptide in place of the termination codon.
While these will address specific mutations, DNA or mRNA replacement strategies would be “mutation agnostic,” the researchers stated. The major challenge: delivery to the respiratory epithelium. Approaches currently in early testing include an inhaled aerosolized, lipid-based nanoparticle carrier for mRNA delivery, viral and non-viral DNA transfer, lipid-mediated CFTR gene transfer, pseudotyped lentiviral vector and adeno-associated vector transfer of CFTR DNA.
Adult CF care
“Adult CF care in general is a completely new frontier,” Meilinh Thi, DO, director of the adult cystic fibrosis program and assistant professor at University of Texas Health at San Antonio, said in an interview. “It’s fairly new to have separate pediatric and adult CF centers. There’s been a shift,” she said. “We’re encountering diseases in CF that we have not in the past had to deal with: diabetes that has features of both type 1 and type 2, increased colon cancer risk, bone disease, and mental health issues. Also, while pregnancy was previously discouraged for women with CF because of lung disease, now many are giving birth without complications and living normal lives,” Dr. Thi said.
“We do encourage our patients to talk to us before becoming pregnant so we can discuss the risk of passing on the gene. And, we do encourage their significant others to get testing. Some patients and their others, however, do decline to get tested,” she added.
The lifetime health issues conferred by CF, Dr. Thi noted, include lung disease with chronic inflammation, infection, respiratory failure (still the most common cause of death), gastrointestinal disorders (including of the pancreas) , colon obstruction and colon cancer, sinus disease, and reproductive system effects. Their permanence, she said, depends on how far their disease has progressed. “So the earlier you can provide these newer therapies — the modulators, for example, or the gene therapy whenever that comes out, then the less damage these organ systems will have, and the patients, we hope, will then do better.”
After Rena Barrow-Wells, an African American mother, fought mightily to prevent a repeat of her experience of two decades earlier when her first child’s cystic fibrosis (CF) took 4 years to diagnose, her story became the subject of a New York Times feature covering disparities in diagnostic CF screening. The article highlighted not only her struggles, but also the utter transformation of the CF landscape since the introduction of small molecule mutation-specific drugs. These drugs restore function to defective CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) proteins. By the time Ms. Barrow-Wells’ young son was treated, lung and pancreatic scarring were already significant. So when the 39-mutation variant screening test available in Ms. Barrow-Wells’ Lawrenceville, Georgia, clinic turned out negative for CF, her pediatrician told her to stop worrying despite her new son’s inherent genetic risk, telltale salty skin, foul-smelling diapers, and her pleas to test for sweat chloride. It still took 3 months for a confirmed diagnosis and the initiation of treatment.
Current genetic tests, based largely on older clinical trials that enrolled mostly white children, are highly accurate for identifying CF in white babies (95%), but often fail to identify substantial percentages of mutations originating in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. They miss CF in Asian (44%), Black (22%), and Hispanic, Native American and Alaskan Native babies (14%), the Times article stated. In the United States, the number of CF variants tested for falls into a wide range: from the one variant found mostly in White populations in Mississippi (with a 38% Black populace) to 689 variants in Wisconsin.
Not too far back, CF was thought of as an inherited childhood disease leading often to childhood or adolescent mortality.
Today’s CF challenges
Beyond refinements in screening instruments and policies that broaden access leading to the earliest possible diagnoses, ongoing research needs include finding treatments for other variants, and caring for adult populations living with treated CF and the disease’s multisystem manifestations. “As people with CF live longer, we need to be very focused on optimized adult medical care for this population,” Marc A. Sala, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Adult CF Program, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said in an interview. “For example, we need higher vigilance for liver, microvascular, coronary artery disease, and various cancer screenings. We do not know exactly how these will manifest differently from the way they do in non-CF populations, so this is where more work needs to be done.”
Emphasis on monitoring
The authors of “Future therapies for cystic fibrosis” (Allen et al. Nature Communications, 2023 Feb 8), after citing the ongoing transformative change for people with CF since the introduction of CFTR drugs, gave voice to important cautions. “Disease will progress, albeit more slowly, and will be more challenging to monitor. Effective CFTR modulators will likely slow or, at best, halt disease progression, but will not reverse a disease that has already become fixed.” They cited pancreatic destruction in the majority, bronchiectasis, and absence of the vas deferens, with still recurring (although less frequently) pulmonary exacerbations along with chronic infections and persistent airway inflammation. “It is essential that we do not become complacent about disease progression in this population,” the researchers stated. They cautioned also that effective surveillance for infection is critical in asymptomatic patients, emphasizing that it underpins the management of young healthy children with CF who demonstrate disease progression despite a lack of symptoms.
Among the ~90% for whom Trikafta is suitable and approved (those with least one copy of F508del or specific other responsive mutations), improvements include increased percent predicted FEV1 by 10%-15% or more, decreased exacerbations, and improved quality of life,” Dr. Sala said. “Subsequent ‘real world’ experience shows dramatic reductions in sputum production and decreased frequency of lung transplant.”
Mutation agnostic therapy
Unfortunately, CF mutants, outside the population eligible for Trikafta, are prodigious in number and do not fall into just a few major groups. “Furthermore, although CF is a monogenic disease, it has variable phenotypes even for two individuals with the same mutations,” Dr. Sala said. “Current CFTR modulators act on the dysfunctional CFTR protein (either as channel gating potentiators or molecular chaperones to improve misfolding). That leaves about 10% of the CF population, those with little to no protein production (such as in nonsense mutations) ineligible for treatment with CFTR modulators. “The ideal for efficacy and equity, given that some CFTR mutations only exist in a handful of people, would be to develop a ‘mutation agnostic’ strategy — such as with mRNA or gene delivery. Here you could imagine that regardless of the type of mutation, a patient would then be able to receive the technology to increase CFTR channel function,” Dr. Sala said. Many modifiable factors, including host immunity and non-CFTR genes that impact CFTR indirectly, may underlie the fact that one person has a worse trajectory than another. “New therapies may also be found in this area of research,” Dr. Sala said.
Strategies in testing phases
“For patients with class I (nonsense) mutations there is hope that small molecules will be identified that can facilitate premature truncation codon (PTC) read-through and/or impede mRNA decay allowing for clinically relevant levels of functional CFTR,” the researchers noted. While the most extensively developed, ataluren, an oxadiazole, failed in phase 3 trials after initial promise, other ribosomal read-through drugs are in preclinical and early phase clinical trials. Also, early encouraging results support an alternative strategy, engineered transfer RNAs (tRNAs) that introduce an amino acid to an elongating peptide in place of the termination codon.
While these will address specific mutations, DNA or mRNA replacement strategies would be “mutation agnostic,” the researchers stated. The major challenge: delivery to the respiratory epithelium. Approaches currently in early testing include an inhaled aerosolized, lipid-based nanoparticle carrier for mRNA delivery, viral and non-viral DNA transfer, lipid-mediated CFTR gene transfer, pseudotyped lentiviral vector and adeno-associated vector transfer of CFTR DNA.
Adult CF care
“Adult CF care in general is a completely new frontier,” Meilinh Thi, DO, director of the adult cystic fibrosis program and assistant professor at University of Texas Health at San Antonio, said in an interview. “It’s fairly new to have separate pediatric and adult CF centers. There’s been a shift,” she said. “We’re encountering diseases in CF that we have not in the past had to deal with: diabetes that has features of both type 1 and type 2, increased colon cancer risk, bone disease, and mental health issues. Also, while pregnancy was previously discouraged for women with CF because of lung disease, now many are giving birth without complications and living normal lives,” Dr. Thi said.
“We do encourage our patients to talk to us before becoming pregnant so we can discuss the risk of passing on the gene. And, we do encourage their significant others to get testing. Some patients and their others, however, do decline to get tested,” she added.
The lifetime health issues conferred by CF, Dr. Thi noted, include lung disease with chronic inflammation, infection, respiratory failure (still the most common cause of death), gastrointestinal disorders (including of the pancreas) , colon obstruction and colon cancer, sinus disease, and reproductive system effects. Their permanence, she said, depends on how far their disease has progressed. “So the earlier you can provide these newer therapies — the modulators, for example, or the gene therapy whenever that comes out, then the less damage these organ systems will have, and the patients, we hope, will then do better.”
After Rena Barrow-Wells, an African American mother, fought mightily to prevent a repeat of her experience of two decades earlier when her first child’s cystic fibrosis (CF) took 4 years to diagnose, her story became the subject of a New York Times feature covering disparities in diagnostic CF screening. The article highlighted not only her struggles, but also the utter transformation of the CF landscape since the introduction of small molecule mutation-specific drugs. These drugs restore function to defective CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) proteins. By the time Ms. Barrow-Wells’ young son was treated, lung and pancreatic scarring were already significant. So when the 39-mutation variant screening test available in Ms. Barrow-Wells’ Lawrenceville, Georgia, clinic turned out negative for CF, her pediatrician told her to stop worrying despite her new son’s inherent genetic risk, telltale salty skin, foul-smelling diapers, and her pleas to test for sweat chloride. It still took 3 months for a confirmed diagnosis and the initiation of treatment.
Current genetic tests, based largely on older clinical trials that enrolled mostly white children, are highly accurate for identifying CF in white babies (95%), but often fail to identify substantial percentages of mutations originating in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. They miss CF in Asian (44%), Black (22%), and Hispanic, Native American and Alaskan Native babies (14%), the Times article stated. In the United States, the number of CF variants tested for falls into a wide range: from the one variant found mostly in White populations in Mississippi (with a 38% Black populace) to 689 variants in Wisconsin.
Not too far back, CF was thought of as an inherited childhood disease leading often to childhood or adolescent mortality.
Today’s CF challenges
Beyond refinements in screening instruments and policies that broaden access leading to the earliest possible diagnoses, ongoing research needs include finding treatments for other variants, and caring for adult populations living with treated CF and the disease’s multisystem manifestations. “As people with CF live longer, we need to be very focused on optimized adult medical care for this population,” Marc A. Sala, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Adult CF Program, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said in an interview. “For example, we need higher vigilance for liver, microvascular, coronary artery disease, and various cancer screenings. We do not know exactly how these will manifest differently from the way they do in non-CF populations, so this is where more work needs to be done.”
Emphasis on monitoring
The authors of “Future therapies for cystic fibrosis” (Allen et al. Nature Communications, 2023 Feb 8), after citing the ongoing transformative change for people with CF since the introduction of CFTR drugs, gave voice to important cautions. “Disease will progress, albeit more slowly, and will be more challenging to monitor. Effective CFTR modulators will likely slow or, at best, halt disease progression, but will not reverse a disease that has already become fixed.” They cited pancreatic destruction in the majority, bronchiectasis, and absence of the vas deferens, with still recurring (although less frequently) pulmonary exacerbations along with chronic infections and persistent airway inflammation. “It is essential that we do not become complacent about disease progression in this population,” the researchers stated. They cautioned also that effective surveillance for infection is critical in asymptomatic patients, emphasizing that it underpins the management of young healthy children with CF who demonstrate disease progression despite a lack of symptoms.
Among the ~90% for whom Trikafta is suitable and approved (those with least one copy of F508del or specific other responsive mutations), improvements include increased percent predicted FEV1 by 10%-15% or more, decreased exacerbations, and improved quality of life,” Dr. Sala said. “Subsequent ‘real world’ experience shows dramatic reductions in sputum production and decreased frequency of lung transplant.”
Mutation agnostic therapy
Unfortunately, CF mutants, outside the population eligible for Trikafta, are prodigious in number and do not fall into just a few major groups. “Furthermore, although CF is a monogenic disease, it has variable phenotypes even for two individuals with the same mutations,” Dr. Sala said. “Current CFTR modulators act on the dysfunctional CFTR protein (either as channel gating potentiators or molecular chaperones to improve misfolding). That leaves about 10% of the CF population, those with little to no protein production (such as in nonsense mutations) ineligible for treatment with CFTR modulators. “The ideal for efficacy and equity, given that some CFTR mutations only exist in a handful of people, would be to develop a ‘mutation agnostic’ strategy — such as with mRNA or gene delivery. Here you could imagine that regardless of the type of mutation, a patient would then be able to receive the technology to increase CFTR channel function,” Dr. Sala said. Many modifiable factors, including host immunity and non-CFTR genes that impact CFTR indirectly, may underlie the fact that one person has a worse trajectory than another. “New therapies may also be found in this area of research,” Dr. Sala said.
Strategies in testing phases
“For patients with class I (nonsense) mutations there is hope that small molecules will be identified that can facilitate premature truncation codon (PTC) read-through and/or impede mRNA decay allowing for clinically relevant levels of functional CFTR,” the researchers noted. While the most extensively developed, ataluren, an oxadiazole, failed in phase 3 trials after initial promise, other ribosomal read-through drugs are in preclinical and early phase clinical trials. Also, early encouraging results support an alternative strategy, engineered transfer RNAs (tRNAs) that introduce an amino acid to an elongating peptide in place of the termination codon.
While these will address specific mutations, DNA or mRNA replacement strategies would be “mutation agnostic,” the researchers stated. The major challenge: delivery to the respiratory epithelium. Approaches currently in early testing include an inhaled aerosolized, lipid-based nanoparticle carrier for mRNA delivery, viral and non-viral DNA transfer, lipid-mediated CFTR gene transfer, pseudotyped lentiviral vector and adeno-associated vector transfer of CFTR DNA.
Adult CF care
“Adult CF care in general is a completely new frontier,” Meilinh Thi, DO, director of the adult cystic fibrosis program and assistant professor at University of Texas Health at San Antonio, said in an interview. “It’s fairly new to have separate pediatric and adult CF centers. There’s been a shift,” she said. “We’re encountering diseases in CF that we have not in the past had to deal with: diabetes that has features of both type 1 and type 2, increased colon cancer risk, bone disease, and mental health issues. Also, while pregnancy was previously discouraged for women with CF because of lung disease, now many are giving birth without complications and living normal lives,” Dr. Thi said.
“We do encourage our patients to talk to us before becoming pregnant so we can discuss the risk of passing on the gene. And, we do encourage their significant others to get testing. Some patients and their others, however, do decline to get tested,” she added.
The lifetime health issues conferred by CF, Dr. Thi noted, include lung disease with chronic inflammation, infection, respiratory failure (still the most common cause of death), gastrointestinal disorders (including of the pancreas) , colon obstruction and colon cancer, sinus disease, and reproductive system effects. Their permanence, she said, depends on how far their disease has progressed. “So the earlier you can provide these newer therapies — the modulators, for example, or the gene therapy whenever that comes out, then the less damage these organ systems will have, and the patients, we hope, will then do better.”
Top reads from the CHEST journal portfolio
Covering the frailty scale in ILD, diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules, and platelet mitochondrial function in sepsis.
Journal CHEST®
By Guler, MD, and colleagues
Life expectancy is a very important factor for patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) and their caregivers. The discussion surrounding prognosis is often wrought with uncertainty and is inherently painful for both patients and clinicians when faced with nonmodifiable traits. This study illustrates the significance of employing a method that succinctly and systematically communicates the degree of functional impairment in patients with fibrotic lung disease. The authors have highlighted the importance of identifying and improving health factors associated with frailty to enhance the survival and quality of life of patients with chronic noncurable fibrotic lung disease. It also presents hope that interventions aimed at improving functional capacity may improve frailty and thus modify prognosis. In the future, longitudinal trends of frailty assessments following interventions aimed at improving both exercise and functional capacity, like pulmonary rehab, should be explored.
– Commentary by Priya Balakrishnan, MD, MS, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Pulmonary
By Michael V. Brown, MD, and colleagues
Brown and colleagues provide a systemic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic yield of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan combined with radial-endobronchial ultrasound (r-EBUS) for the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules. They included 14 studies (865 patients with 882 lesions) with pooled diagnostic yield from CBCT scan and r-EBUS for peripheral pulmonary nodules of 80% (95% CI, 76% to 84%) with complication rates of 2.01% for pneumothorax and 1.08% for bleeding. Amongst the studies selected, confounders (including study design, definition of diagnostic yield, use of ROSE, additional equipment, etc) existed. The important takeaway is that 3D imaging guidance with CBCT scan can corroborate “tool in lesion” and thus potentially improve the outcomes of the different bronchoscopic modalities utilized to diagnose peripheral pulmonary nodules. Future prospective investigations with less heterogeneity in study design and outcomes, as well as comparison with newer technologies such as robotic bronchoscopy, are necessary to corroborate these findings.
– Commentary by Saadia A. Faiz, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Critical Care
Platelet Bioenergetics and Associations With Delirium and Coma in Patients With Sepsis
By Chukwudi A. Onyemekwu, DO, and colleagues
The study by Onyemekwu and colleagues explores the link between platelet mitochondrial function and acute brain dysfunction (delirium and coma) in patients with sepsis. The investigators measured various parameters of platelet mitochondrial respiratory bioenergetics and found that increased spare respiratory capacity was significantly associated with coma but not delirium. These findings suggest that systemic mitochondrial function could influence brain health and indicate a potential link between mitochondrial bioenergetics and coma during sepsis. The study did not find a significant association between platelet bioenergetics and delirium, suggesting that coma and delirium may have different underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms. We must interpret the results with caution, as the associations identified in this observational study do not prove causation. It is possible that the changes seen in platelet mitochondria may be a result of coma rather than a mechanism. Nonetheless, the study provides a foundation for future research to explore the mechanistic role of mitochondria in acute brain dysfunction during sepsis and the potential for developing mitochondrial-targeted therapies as a possible treatment approach for patients with sepsis-induced coma.
– Commentary by Angel O. Coz, MD, FCCP, Editor in Chief of CHEST Physician
Covering the frailty scale in ILD, diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules, and platelet mitochondrial function in sepsis.
Covering the frailty scale in ILD, diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules, and platelet mitochondrial function in sepsis.
Journal CHEST®
By Guler, MD, and colleagues
Life expectancy is a very important factor for patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) and their caregivers. The discussion surrounding prognosis is often wrought with uncertainty and is inherently painful for both patients and clinicians when faced with nonmodifiable traits. This study illustrates the significance of employing a method that succinctly and systematically communicates the degree of functional impairment in patients with fibrotic lung disease. The authors have highlighted the importance of identifying and improving health factors associated with frailty to enhance the survival and quality of life of patients with chronic noncurable fibrotic lung disease. It also presents hope that interventions aimed at improving functional capacity may improve frailty and thus modify prognosis. In the future, longitudinal trends of frailty assessments following interventions aimed at improving both exercise and functional capacity, like pulmonary rehab, should be explored.
– Commentary by Priya Balakrishnan, MD, MS, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Pulmonary
By Michael V. Brown, MD, and colleagues
Brown and colleagues provide a systemic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic yield of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan combined with radial-endobronchial ultrasound (r-EBUS) for the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules. They included 14 studies (865 patients with 882 lesions) with pooled diagnostic yield from CBCT scan and r-EBUS for peripheral pulmonary nodules of 80% (95% CI, 76% to 84%) with complication rates of 2.01% for pneumothorax and 1.08% for bleeding. Amongst the studies selected, confounders (including study design, definition of diagnostic yield, use of ROSE, additional equipment, etc) existed. The important takeaway is that 3D imaging guidance with CBCT scan can corroborate “tool in lesion” and thus potentially improve the outcomes of the different bronchoscopic modalities utilized to diagnose peripheral pulmonary nodules. Future prospective investigations with less heterogeneity in study design and outcomes, as well as comparison with newer technologies such as robotic bronchoscopy, are necessary to corroborate these findings.
– Commentary by Saadia A. Faiz, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Critical Care
Platelet Bioenergetics and Associations With Delirium and Coma in Patients With Sepsis
By Chukwudi A. Onyemekwu, DO, and colleagues
The study by Onyemekwu and colleagues explores the link between platelet mitochondrial function and acute brain dysfunction (delirium and coma) in patients with sepsis. The investigators measured various parameters of platelet mitochondrial respiratory bioenergetics and found that increased spare respiratory capacity was significantly associated with coma but not delirium. These findings suggest that systemic mitochondrial function could influence brain health and indicate a potential link between mitochondrial bioenergetics and coma during sepsis. The study did not find a significant association between platelet bioenergetics and delirium, suggesting that coma and delirium may have different underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms. We must interpret the results with caution, as the associations identified in this observational study do not prove causation. It is possible that the changes seen in platelet mitochondria may be a result of coma rather than a mechanism. Nonetheless, the study provides a foundation for future research to explore the mechanistic role of mitochondria in acute brain dysfunction during sepsis and the potential for developing mitochondrial-targeted therapies as a possible treatment approach for patients with sepsis-induced coma.
– Commentary by Angel O. Coz, MD, FCCP, Editor in Chief of CHEST Physician
Journal CHEST®
By Guler, MD, and colleagues
Life expectancy is a very important factor for patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) and their caregivers. The discussion surrounding prognosis is often wrought with uncertainty and is inherently painful for both patients and clinicians when faced with nonmodifiable traits. This study illustrates the significance of employing a method that succinctly and systematically communicates the degree of functional impairment in patients with fibrotic lung disease. The authors have highlighted the importance of identifying and improving health factors associated with frailty to enhance the survival and quality of life of patients with chronic noncurable fibrotic lung disease. It also presents hope that interventions aimed at improving functional capacity may improve frailty and thus modify prognosis. In the future, longitudinal trends of frailty assessments following interventions aimed at improving both exercise and functional capacity, like pulmonary rehab, should be explored.
– Commentary by Priya Balakrishnan, MD, MS, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Pulmonary
By Michael V. Brown, MD, and colleagues
Brown and colleagues provide a systemic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic yield of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan combined with radial-endobronchial ultrasound (r-EBUS) for the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules. They included 14 studies (865 patients with 882 lesions) with pooled diagnostic yield from CBCT scan and r-EBUS for peripheral pulmonary nodules of 80% (95% CI, 76% to 84%) with complication rates of 2.01% for pneumothorax and 1.08% for bleeding. Amongst the studies selected, confounders (including study design, definition of diagnostic yield, use of ROSE, additional equipment, etc) existed. The important takeaway is that 3D imaging guidance with CBCT scan can corroborate “tool in lesion” and thus potentially improve the outcomes of the different bronchoscopic modalities utilized to diagnose peripheral pulmonary nodules. Future prospective investigations with less heterogeneity in study design and outcomes, as well as comparison with newer technologies such as robotic bronchoscopy, are necessary to corroborate these findings.
– Commentary by Saadia A. Faiz, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Critical Care
Platelet Bioenergetics and Associations With Delirium and Coma in Patients With Sepsis
By Chukwudi A. Onyemekwu, DO, and colleagues
The study by Onyemekwu and colleagues explores the link between platelet mitochondrial function and acute brain dysfunction (delirium and coma) in patients with sepsis. The investigators measured various parameters of platelet mitochondrial respiratory bioenergetics and found that increased spare respiratory capacity was significantly associated with coma but not delirium. These findings suggest that systemic mitochondrial function could influence brain health and indicate a potential link between mitochondrial bioenergetics and coma during sepsis. The study did not find a significant association between platelet bioenergetics and delirium, suggesting that coma and delirium may have different underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms. We must interpret the results with caution, as the associations identified in this observational study do not prove causation. It is possible that the changes seen in platelet mitochondria may be a result of coma rather than a mechanism. Nonetheless, the study provides a foundation for future research to explore the mechanistic role of mitochondria in acute brain dysfunction during sepsis and the potential for developing mitochondrial-targeted therapies as a possible treatment approach for patients with sepsis-induced coma.
– Commentary by Angel O. Coz, MD, FCCP, Editor in Chief of CHEST Physician
Ensifentrine for COPD: Out of reach for many?
Ensifentrine (Ohtuvayre), a novel medication for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration, has been shown to reduce COPD exacerbations and may improve the quality of life for patients, but these potential benefits come at an unreasonably high annual cost, authors of a cost and effectiveness analysis say.
Ensifentrine is a first-in-class selective dual inhibitor of both phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE-3) and PDE-4, combining both bronchodilator and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory effects in a single molecule. The drug is delivered through a standard jet nebulizer.
In the phase 3 ENHANCE 1 and 2 trials, ensifentrine significantly improved lung function based on the primary outcome of average forced expiratory volume in 1 second within 0-12 hours of administration, compared with placebo. In addition, patients were reported to tolerate the inhaled treatment well, with similar proportions of ensifentrine- and placebo-assigned patients reporting treatment-emergent adverse events. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were nasopharyngitis, hypertension, and back pain, reported in < 3% of the ensifentrine group.
High cost barrier
But as authors of the analysis from the Boston, Massachusetts–based Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) found, the therapeutic edge offered by ensifentrine is outweighed by the annual wholesale acquisition cost that its maker, Vernona Pharma, has established: $35,400, which far exceeds the estimated health-benefit price of $7,500-$12,700, according to ICER. ICER is an independent, nonprofit research institute that conducts evidence-based reviews of healthcare interventions, including prescription drugs, other treatments, and diagnostic tests.
“Current evidence shows that ensifentrine decreases COPD exacerbations when used in combination with some current inhaled therapies, but there are uncertainties about how much benefit it may add to unstudied combinations of inhaled treatments,” said David Rind, MD, chief medical officer of ICER in a statement.
In an interview, Dr. Rind noted that the high price of ensifentrine may lead payers to restrict access to an otherwise promising new therapy. “Obviously many drugs in the US are overpriced, and this one, too, looks like it is overpriced. That causes ongoing financial toxicity for individual patients and it causes problems for the entire US health system, because when we pay too much for drugs we don’t have money for other things. So I’m worried about the fact that this price is too high compared to the benefit it provides.”
As previously reported, as many as one in six persons with COPD in the United States miss or delay COPD medication doses because of high drug costs. “I think that the pricing they chose is going to cause lots of barriers to people getting access and that insurance companies will throw up barriers. Primary care physicians like me won’t even try to get approval for a drug like this given the hoops we will be made to jump through, and so fewer people will get this drug,” Dr. Rind said. He pointed out that a lower wholesale acquisition cost could encourage higher-volume sales, affording the drugmaker a comparable profit with the higher-cost but lower-volume option.
Good drug, high price
An independent appraisal committee for ICER determined that “current evidence is adequate to demonstrate a net health benefit for ensifentrine added to maintenance therapy when compared to maintenance therapy alone.”
But ICER also issued an access and affordability alert “to signal to stakeholders and policymakers that the amount of added healthcare costs associated with a new service may be difficult for the health system to absorb over the short term without displacing other needed services.” ICER recommends that payers should include coverage for smoking cessation therapies, and that drug manufacturers “set prices that will foster affordability and good access for all patients by aligning prices with the patient-centered therapeutic value of their treatments.”
“This looks like a pretty good drug,” Dr. Rind said. “It looks quite safe and I think there will be a lot of patients, particularly those who are having frequent exacerbations, who this would be appropriate for, particularly once they’ve maxed out existing therapies, but maybe even earlier than that. And if the price comes down to the point that patients can really access this and providers can access it, people really should look at this as a potential therapy.”
Drug not yet available?
However, providers have not yet had direct experience with the new medication. “We haven’t been able to prescribe it yet,” said Corinne Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, director of Advance Practice Provider and Clinical Services for Colorado Springs Pulmonary Consultants, president and founder of the Association of Pulmonary Advance Practice Providers, and a member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board.
She learned “they were going to release it to select specialty pharmacies in the 3rd quarter of 2024. But all the ones we call do not have it and no one knows who does. They haven’t sent any reps into the field in my area so we don’t have any points of contact either,” she said.
Verona Pharma stated it anticipates ensifentrine to be available in the third quarter of 2024 “through an exclusive network of accredited specialty pharmacies.”
Funding for the ICER report came from nonprofit foundations. No funding came from health insurers, pharmacy benefit managers, or life science companies. Dr. Rind had no relevant disclosures.
Ensifentrine (Ohtuvayre), a novel medication for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration, has been shown to reduce COPD exacerbations and may improve the quality of life for patients, but these potential benefits come at an unreasonably high annual cost, authors of a cost and effectiveness analysis say.
Ensifentrine is a first-in-class selective dual inhibitor of both phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE-3) and PDE-4, combining both bronchodilator and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory effects in a single molecule. The drug is delivered through a standard jet nebulizer.
In the phase 3 ENHANCE 1 and 2 trials, ensifentrine significantly improved lung function based on the primary outcome of average forced expiratory volume in 1 second within 0-12 hours of administration, compared with placebo. In addition, patients were reported to tolerate the inhaled treatment well, with similar proportions of ensifentrine- and placebo-assigned patients reporting treatment-emergent adverse events. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were nasopharyngitis, hypertension, and back pain, reported in < 3% of the ensifentrine group.
High cost barrier
But as authors of the analysis from the Boston, Massachusetts–based Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) found, the therapeutic edge offered by ensifentrine is outweighed by the annual wholesale acquisition cost that its maker, Vernona Pharma, has established: $35,400, which far exceeds the estimated health-benefit price of $7,500-$12,700, according to ICER. ICER is an independent, nonprofit research institute that conducts evidence-based reviews of healthcare interventions, including prescription drugs, other treatments, and diagnostic tests.
“Current evidence shows that ensifentrine decreases COPD exacerbations when used in combination with some current inhaled therapies, but there are uncertainties about how much benefit it may add to unstudied combinations of inhaled treatments,” said David Rind, MD, chief medical officer of ICER in a statement.
In an interview, Dr. Rind noted that the high price of ensifentrine may lead payers to restrict access to an otherwise promising new therapy. “Obviously many drugs in the US are overpriced, and this one, too, looks like it is overpriced. That causes ongoing financial toxicity for individual patients and it causes problems for the entire US health system, because when we pay too much for drugs we don’t have money for other things. So I’m worried about the fact that this price is too high compared to the benefit it provides.”
As previously reported, as many as one in six persons with COPD in the United States miss or delay COPD medication doses because of high drug costs. “I think that the pricing they chose is going to cause lots of barriers to people getting access and that insurance companies will throw up barriers. Primary care physicians like me won’t even try to get approval for a drug like this given the hoops we will be made to jump through, and so fewer people will get this drug,” Dr. Rind said. He pointed out that a lower wholesale acquisition cost could encourage higher-volume sales, affording the drugmaker a comparable profit with the higher-cost but lower-volume option.
Good drug, high price
An independent appraisal committee for ICER determined that “current evidence is adequate to demonstrate a net health benefit for ensifentrine added to maintenance therapy when compared to maintenance therapy alone.”
But ICER also issued an access and affordability alert “to signal to stakeholders and policymakers that the amount of added healthcare costs associated with a new service may be difficult for the health system to absorb over the short term without displacing other needed services.” ICER recommends that payers should include coverage for smoking cessation therapies, and that drug manufacturers “set prices that will foster affordability and good access for all patients by aligning prices with the patient-centered therapeutic value of their treatments.”
“This looks like a pretty good drug,” Dr. Rind said. “It looks quite safe and I think there will be a lot of patients, particularly those who are having frequent exacerbations, who this would be appropriate for, particularly once they’ve maxed out existing therapies, but maybe even earlier than that. And if the price comes down to the point that patients can really access this and providers can access it, people really should look at this as a potential therapy.”
Drug not yet available?
However, providers have not yet had direct experience with the new medication. “We haven’t been able to prescribe it yet,” said Corinne Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, director of Advance Practice Provider and Clinical Services for Colorado Springs Pulmonary Consultants, president and founder of the Association of Pulmonary Advance Practice Providers, and a member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board.
She learned “they were going to release it to select specialty pharmacies in the 3rd quarter of 2024. But all the ones we call do not have it and no one knows who does. They haven’t sent any reps into the field in my area so we don’t have any points of contact either,” she said.
Verona Pharma stated it anticipates ensifentrine to be available in the third quarter of 2024 “through an exclusive network of accredited specialty pharmacies.”
Funding for the ICER report came from nonprofit foundations. No funding came from health insurers, pharmacy benefit managers, or life science companies. Dr. Rind had no relevant disclosures.
Ensifentrine (Ohtuvayre), a novel medication for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration, has been shown to reduce COPD exacerbations and may improve the quality of life for patients, but these potential benefits come at an unreasonably high annual cost, authors of a cost and effectiveness analysis say.
Ensifentrine is a first-in-class selective dual inhibitor of both phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE-3) and PDE-4, combining both bronchodilator and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory effects in a single molecule. The drug is delivered through a standard jet nebulizer.
In the phase 3 ENHANCE 1 and 2 trials, ensifentrine significantly improved lung function based on the primary outcome of average forced expiratory volume in 1 second within 0-12 hours of administration, compared with placebo. In addition, patients were reported to tolerate the inhaled treatment well, with similar proportions of ensifentrine- and placebo-assigned patients reporting treatment-emergent adverse events. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were nasopharyngitis, hypertension, and back pain, reported in < 3% of the ensifentrine group.
High cost barrier
But as authors of the analysis from the Boston, Massachusetts–based Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) found, the therapeutic edge offered by ensifentrine is outweighed by the annual wholesale acquisition cost that its maker, Vernona Pharma, has established: $35,400, which far exceeds the estimated health-benefit price of $7,500-$12,700, according to ICER. ICER is an independent, nonprofit research institute that conducts evidence-based reviews of healthcare interventions, including prescription drugs, other treatments, and diagnostic tests.
“Current evidence shows that ensifentrine decreases COPD exacerbations when used in combination with some current inhaled therapies, but there are uncertainties about how much benefit it may add to unstudied combinations of inhaled treatments,” said David Rind, MD, chief medical officer of ICER in a statement.
In an interview, Dr. Rind noted that the high price of ensifentrine may lead payers to restrict access to an otherwise promising new therapy. “Obviously many drugs in the US are overpriced, and this one, too, looks like it is overpriced. That causes ongoing financial toxicity for individual patients and it causes problems for the entire US health system, because when we pay too much for drugs we don’t have money for other things. So I’m worried about the fact that this price is too high compared to the benefit it provides.”
As previously reported, as many as one in six persons with COPD in the United States miss or delay COPD medication doses because of high drug costs. “I think that the pricing they chose is going to cause lots of barriers to people getting access and that insurance companies will throw up barriers. Primary care physicians like me won’t even try to get approval for a drug like this given the hoops we will be made to jump through, and so fewer people will get this drug,” Dr. Rind said. He pointed out that a lower wholesale acquisition cost could encourage higher-volume sales, affording the drugmaker a comparable profit with the higher-cost but lower-volume option.
Good drug, high price
An independent appraisal committee for ICER determined that “current evidence is adequate to demonstrate a net health benefit for ensifentrine added to maintenance therapy when compared to maintenance therapy alone.”
But ICER also issued an access and affordability alert “to signal to stakeholders and policymakers that the amount of added healthcare costs associated with a new service may be difficult for the health system to absorb over the short term without displacing other needed services.” ICER recommends that payers should include coverage for smoking cessation therapies, and that drug manufacturers “set prices that will foster affordability and good access for all patients by aligning prices with the patient-centered therapeutic value of their treatments.”
“This looks like a pretty good drug,” Dr. Rind said. “It looks quite safe and I think there will be a lot of patients, particularly those who are having frequent exacerbations, who this would be appropriate for, particularly once they’ve maxed out existing therapies, but maybe even earlier than that. And if the price comes down to the point that patients can really access this and providers can access it, people really should look at this as a potential therapy.”
Drug not yet available?
However, providers have not yet had direct experience with the new medication. “We haven’t been able to prescribe it yet,” said Corinne Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, director of Advance Practice Provider and Clinical Services for Colorado Springs Pulmonary Consultants, president and founder of the Association of Pulmonary Advance Practice Providers, and a member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board.
She learned “they were going to release it to select specialty pharmacies in the 3rd quarter of 2024. But all the ones we call do not have it and no one knows who does. They haven’t sent any reps into the field in my area so we don’t have any points of contact either,” she said.
Verona Pharma stated it anticipates ensifentrine to be available in the third quarter of 2024 “through an exclusive network of accredited specialty pharmacies.”
Funding for the ICER report came from nonprofit foundations. No funding came from health insurers, pharmacy benefit managers, or life science companies. Dr. Rind had no relevant disclosures.
The language of AI and its applications in health care
AI is a group of nonhuman techniques that utilize automated learning methods to extract information from datasets through generalization, classification, prediction, and association. In other words, AI is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines. The branches of AI include natural language processing, speech recognition, machine vision, and expert systems. AI can make clinical care more efficient; however, many find its confusing terminology to be a barrier.1 This article provides concise definitions of AI terms and is intended to help physicians better understand how AI methods can be applied to clinical care. The clinical application of natural language processing and machine vision applications are more clinically intuitive than the roles of machine learning algorithms.
Machine learning and algorithms
Machine learning is a branch of AI that uses data and algorithms to mimic human reasoning through classification, pattern recognition, and prediction. Supervised and unsupervised machine-learning algorithms can analyze data and recognize undetected associations and relationships.
Supervised learning involves training models to make predictions using data sets that have correct outcome parameters called labels using predictive fields called features. Machine learning uses iterative analysis including random forest, decision tree, and gradient boosting methods that minimize predictive error metrics (see Table 1). This approach is widely used to improve diagnoses, predict disease progression or exacerbation, and personalize treatment plan modifications.
Supervised machine learning methods can be particularly effective for processing large volumes of medical information to identify patterns and make accurate predictions. In contrast, unsupervised learning techniques can analyze unlabeled data and help clinicians uncover hidden patterns or undetected groupings. Techniques including clustering, exploratory analysis, and anomaly detection are common applications. Both of these machine-learning approaches can be used to extract novel and helpful insights.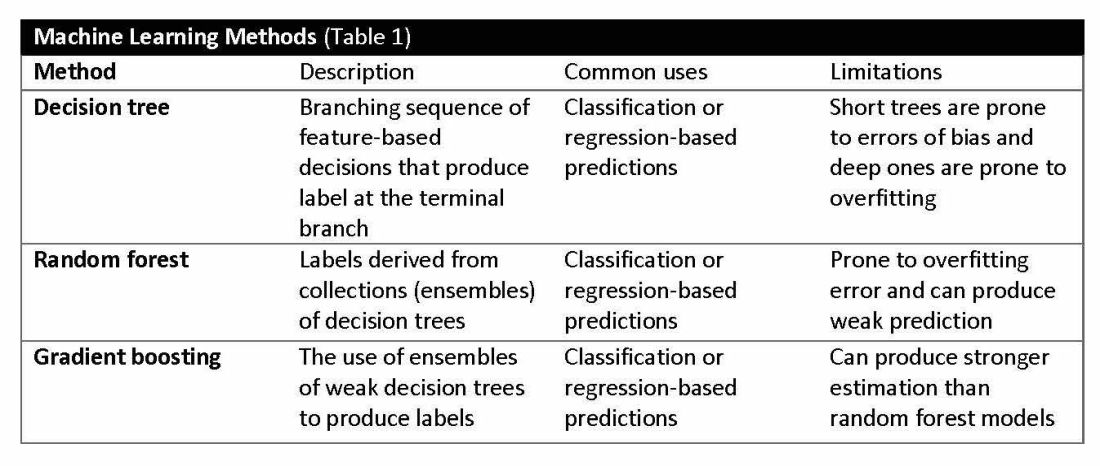
The utility of machine learning analyses depends on the size and accuracy of the available datasets. Small datasets can limit usability, while large datasets require substantial computational power. Predictive models are generated using training datasets and evaluated using separate evaluation datasets. Deep learning models, a subset of machine learning, can automatically readjust themselves to maintain or improve accuracy when analyzing new observations that include accurate labels.
Challenges of algorithms and calibration
Machine learning algorithms vary in complexity and accuracy. For example, a simple logistic regression model using time, date, latitude, and indoor/outdoor location can accurately recommend sunscreen application. This model identifies when solar radiation is high enough to warrant sunscreen use, avoiding unnecessary recommendations during nighttime hours or indoor locations. A more complex model might suffer from model overfitting and inappropriately suggest sunscreen before a tanning salon visit.
Complex machine learning models, like support vector machine (SVM) and decision tree methods, are useful when many features have predictive power. SVMs are useful for small but complex datasets. Features are manipulated in a multidimensional space to maximize the “margins” separating 2 groups. Decision tree analyses are useful when more than 2 groups are being analyzed. SVM and decision tree models can also lose accuracy by data overfitting.
Consider the development of an SVM analysis to predict whether an individual is a fellow or a senior faculty member. One could use high gray hair density feature values to identify senior faculty. When this algorithm is applied to an individual with alopecia, no amount of model adjustment can achieve high levels of discrimination because no hair is present. Rather than overfitting the model by adding more nonpredictive features, individuals with alopecia are analyzed by their own algorithm (tree) that uses the skin wrinkle/solar damage rather than the gray hair density feature.
Decision tree ensemble algorithms like random forest and gradient boosting use feature-based decision trees to process and classify data. Random forests are robust, scalable, and versatile, providing classifications and predictions while protecting against inaccurate data and outliers and have the advantage of being able to handle both categorical and continuous features. Gradient boosting, which uses an ensemble of weak decision trees, often outperforms random forests when individual trees perform only slightly better than random chance. This method incrementally builds the model by optimizing the residual errors of previous trees, leading to more accurate predictions.
In practice, gradient boosting can be used to fine-tune diagnostic models, improving their precision and reliability. A recent example of how gradient boosting of random forest predictions yielded highly accurate predictions for unplanned vasopressor initiation and intubation events 2 to 4 hours before an ICU adult became unstable.2
Assessing the accuracy of algorithms
The value of the data set is directly related to the accuracy of its labels. Traditional methods that measure model performance, such as sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values (PPV and NPV), have important limitations. They provide little insight into how a complex model made its prediction. Understanding which individual features drive model accuracy is key to fostering trust in model predictions. This can be done by comparing model output with and without including individual features. The results of all possible combinations are aggregated according to feature importance, which is summarized in the Shapley value for each model feature. Higher values indicate greater relative importance. SHAP plots help identify how much and how often specific features change the model output, presenting values of individual model estimates with and without a specific feature (see Figure 1).
Promoting AI use
AI and machine learning algorithms are coming to patient care. Understanding the language of AI helps caregivers integrate these tools into their practices. The science of AI faces serious challenges. Algorithms must be recalibrated to keep pace as therapies advance, disease prevalence changes, and our population ages. AI must address new challenges as they confront those suffering from respiratory diseases. This resource encourages clinicians with novel approaches by using AI methodologies to advance their development. We can better address future health care needs by promoting the equitable use of AI technologies, especially among socially disadvantaged developers.
References
1. Lilly CM, Soni AV, Dunlap D, et al. Advancing point of care testing by application of machine learning techniques and artificial intelligence. Chest. 2024 (in press).
2. Lilly CM, Kirk D, Pessach IM, et al. Application of machine learning models to biomedical and information system signals from critically ill adults. Chest. 2024;165(5):1139-1148.
AI is a group of nonhuman techniques that utilize automated learning methods to extract information from datasets through generalization, classification, prediction, and association. In other words, AI is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines. The branches of AI include natural language processing, speech recognition, machine vision, and expert systems. AI can make clinical care more efficient; however, many find its confusing terminology to be a barrier.1 This article provides concise definitions of AI terms and is intended to help physicians better understand how AI methods can be applied to clinical care. The clinical application of natural language processing and machine vision applications are more clinically intuitive than the roles of machine learning algorithms.
Machine learning and algorithms
Machine learning is a branch of AI that uses data and algorithms to mimic human reasoning through classification, pattern recognition, and prediction. Supervised and unsupervised machine-learning algorithms can analyze data and recognize undetected associations and relationships.
Supervised learning involves training models to make predictions using data sets that have correct outcome parameters called labels using predictive fields called features. Machine learning uses iterative analysis including random forest, decision tree, and gradient boosting methods that minimize predictive error metrics (see Table 1). This approach is widely used to improve diagnoses, predict disease progression or exacerbation, and personalize treatment plan modifications.
Supervised machine learning methods can be particularly effective for processing large volumes of medical information to identify patterns and make accurate predictions. In contrast, unsupervised learning techniques can analyze unlabeled data and help clinicians uncover hidden patterns or undetected groupings. Techniques including clustering, exploratory analysis, and anomaly detection are common applications. Both of these machine-learning approaches can be used to extract novel and helpful insights.
The utility of machine learning analyses depends on the size and accuracy of the available datasets. Small datasets can limit usability, while large datasets require substantial computational power. Predictive models are generated using training datasets and evaluated using separate evaluation datasets. Deep learning models, a subset of machine learning, can automatically readjust themselves to maintain or improve accuracy when analyzing new observations that include accurate labels.
Challenges of algorithms and calibration
Machine learning algorithms vary in complexity and accuracy. For example, a simple logistic regression model using time, date, latitude, and indoor/outdoor location can accurately recommend sunscreen application. This model identifies when solar radiation is high enough to warrant sunscreen use, avoiding unnecessary recommendations during nighttime hours or indoor locations. A more complex model might suffer from model overfitting and inappropriately suggest sunscreen before a tanning salon visit.
Complex machine learning models, like support vector machine (SVM) and decision tree methods, are useful when many features have predictive power. SVMs are useful for small but complex datasets. Features are manipulated in a multidimensional space to maximize the “margins” separating 2 groups. Decision tree analyses are useful when more than 2 groups are being analyzed. SVM and decision tree models can also lose accuracy by data overfitting.
Consider the development of an SVM analysis to predict whether an individual is a fellow or a senior faculty member. One could use high gray hair density feature values to identify senior faculty. When this algorithm is applied to an individual with alopecia, no amount of model adjustment can achieve high levels of discrimination because no hair is present. Rather than overfitting the model by adding more nonpredictive features, individuals with alopecia are analyzed by their own algorithm (tree) that uses the skin wrinkle/solar damage rather than the gray hair density feature.
Decision tree ensemble algorithms like random forest and gradient boosting use feature-based decision trees to process and classify data. Random forests are robust, scalable, and versatile, providing classifications and predictions while protecting against inaccurate data and outliers and have the advantage of being able to handle both categorical and continuous features. Gradient boosting, which uses an ensemble of weak decision trees, often outperforms random forests when individual trees perform only slightly better than random chance. This method incrementally builds the model by optimizing the residual errors of previous trees, leading to more accurate predictions.
In practice, gradient boosting can be used to fine-tune diagnostic models, improving their precision and reliability. A recent example of how gradient boosting of random forest predictions yielded highly accurate predictions for unplanned vasopressor initiation and intubation events 2 to 4 hours before an ICU adult became unstable.2
Assessing the accuracy of algorithms
The value of the data set is directly related to the accuracy of its labels. Traditional methods that measure model performance, such as sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values (PPV and NPV), have important limitations. They provide little insight into how a complex model made its prediction. Understanding which individual features drive model accuracy is key to fostering trust in model predictions. This can be done by comparing model output with and without including individual features. The results of all possible combinations are aggregated according to feature importance, which is summarized in the Shapley value for each model feature. Higher values indicate greater relative importance. SHAP plots help identify how much and how often specific features change the model output, presenting values of individual model estimates with and without a specific feature (see Figure 1).
Promoting AI use
AI and machine learning algorithms are coming to patient care. Understanding the language of AI helps caregivers integrate these tools into their practices. The science of AI faces serious challenges. Algorithms must be recalibrated to keep pace as therapies advance, disease prevalence changes, and our population ages. AI must address new challenges as they confront those suffering from respiratory diseases. This resource encourages clinicians with novel approaches by using AI methodologies to advance their development. We can better address future health care needs by promoting the equitable use of AI technologies, especially among socially disadvantaged developers.
References
1. Lilly CM, Soni AV, Dunlap D, et al. Advancing point of care testing by application of machine learning techniques and artificial intelligence. Chest. 2024 (in press).
2. Lilly CM, Kirk D, Pessach IM, et al. Application of machine learning models to biomedical and information system signals from critically ill adults. Chest. 2024;165(5):1139-1148.
AI is a group of nonhuman techniques that utilize automated learning methods to extract information from datasets through generalization, classification, prediction, and association. In other words, AI is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines. The branches of AI include natural language processing, speech recognition, machine vision, and expert systems. AI can make clinical care more efficient; however, many find its confusing terminology to be a barrier.1 This article provides concise definitions of AI terms and is intended to help physicians better understand how AI methods can be applied to clinical care. The clinical application of natural language processing and machine vision applications are more clinically intuitive than the roles of machine learning algorithms.
Machine learning and algorithms
Machine learning is a branch of AI that uses data and algorithms to mimic human reasoning through classification, pattern recognition, and prediction. Supervised and unsupervised machine-learning algorithms can analyze data and recognize undetected associations and relationships.
Supervised learning involves training models to make predictions using data sets that have correct outcome parameters called labels using predictive fields called features. Machine learning uses iterative analysis including random forest, decision tree, and gradient boosting methods that minimize predictive error metrics (see Table 1). This approach is widely used to improve diagnoses, predict disease progression or exacerbation, and personalize treatment plan modifications.
Supervised machine learning methods can be particularly effective for processing large volumes of medical information to identify patterns and make accurate predictions. In contrast, unsupervised learning techniques can analyze unlabeled data and help clinicians uncover hidden patterns or undetected groupings. Techniques including clustering, exploratory analysis, and anomaly detection are common applications. Both of these machine-learning approaches can be used to extract novel and helpful insights.
The utility of machine learning analyses depends on the size and accuracy of the available datasets. Small datasets can limit usability, while large datasets require substantial computational power. Predictive models are generated using training datasets and evaluated using separate evaluation datasets. Deep learning models, a subset of machine learning, can automatically readjust themselves to maintain or improve accuracy when analyzing new observations that include accurate labels.
Challenges of algorithms and calibration
Machine learning algorithms vary in complexity and accuracy. For example, a simple logistic regression model using time, date, latitude, and indoor/outdoor location can accurately recommend sunscreen application. This model identifies when solar radiation is high enough to warrant sunscreen use, avoiding unnecessary recommendations during nighttime hours or indoor locations. A more complex model might suffer from model overfitting and inappropriately suggest sunscreen before a tanning salon visit.
Complex machine learning models, like support vector machine (SVM) and decision tree methods, are useful when many features have predictive power. SVMs are useful for small but complex datasets. Features are manipulated in a multidimensional space to maximize the “margins” separating 2 groups. Decision tree analyses are useful when more than 2 groups are being analyzed. SVM and decision tree models can also lose accuracy by data overfitting.
Consider the development of an SVM analysis to predict whether an individual is a fellow or a senior faculty member. One could use high gray hair density feature values to identify senior faculty. When this algorithm is applied to an individual with alopecia, no amount of model adjustment can achieve high levels of discrimination because no hair is present. Rather than overfitting the model by adding more nonpredictive features, individuals with alopecia are analyzed by their own algorithm (tree) that uses the skin wrinkle/solar damage rather than the gray hair density feature.
Decision tree ensemble algorithms like random forest and gradient boosting use feature-based decision trees to process and classify data. Random forests are robust, scalable, and versatile, providing classifications and predictions while protecting against inaccurate data and outliers and have the advantage of being able to handle both categorical and continuous features. Gradient boosting, which uses an ensemble of weak decision trees, often outperforms random forests when individual trees perform only slightly better than random chance. This method incrementally builds the model by optimizing the residual errors of previous trees, leading to more accurate predictions.
In practice, gradient boosting can be used to fine-tune diagnostic models, improving their precision and reliability. A recent example of how gradient boosting of random forest predictions yielded highly accurate predictions for unplanned vasopressor initiation and intubation events 2 to 4 hours before an ICU adult became unstable.2
Assessing the accuracy of algorithms
The value of the data set is directly related to the accuracy of its labels. Traditional methods that measure model performance, such as sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values (PPV and NPV), have important limitations. They provide little insight into how a complex model made its prediction. Understanding which individual features drive model accuracy is key to fostering trust in model predictions. This can be done by comparing model output with and without including individual features. The results of all possible combinations are aggregated according to feature importance, which is summarized in the Shapley value for each model feature. Higher values indicate greater relative importance. SHAP plots help identify how much and how often specific features change the model output, presenting values of individual model estimates with and without a specific feature (see Figure 1).
Promoting AI use
AI and machine learning algorithms are coming to patient care. Understanding the language of AI helps caregivers integrate these tools into their practices. The science of AI faces serious challenges. Algorithms must be recalibrated to keep pace as therapies advance, disease prevalence changes, and our population ages. AI must address new challenges as they confront those suffering from respiratory diseases. This resource encourages clinicians with novel approaches by using AI methodologies to advance their development. We can better address future health care needs by promoting the equitable use of AI technologies, especially among socially disadvantaged developers.
References
1. Lilly CM, Soni AV, Dunlap D, et al. Advancing point of care testing by application of machine learning techniques and artificial intelligence. Chest. 2024 (in press).
2. Lilly CM, Kirk D, Pessach IM, et al. Application of machine learning models to biomedical and information system signals from critically ill adults. Chest. 2024;165(5):1139-1148.
CHEST releases new guideline on management of central airway obstruction
CHEST recently released a new clinical guideline on central airway obstruction (CAO).
“Central airway obstruction is associated with a poor prognosis, and the management of CAO is highly variable dependent on the provider expertise and local resources. By releasing this guideline, the panel hopes to standardize the definition of CAO and provide guidance for the management of patients to optimize care and improve outcomes,” said Kamran Mahmood, MD, MPH, FCCP, lead author on the guideline. “The guideline recommendations are developed using GRADE methodology and based on thorough evidence review and expert input. But the quality of overall evidence is very low, and the panel calls for well-designed studies and randomized controlled trials for the management of CAO.”
CAO can be caused by a variety of malignant and nonmalignant disorders, and multiple specialists may be involved in the care, including pulmonologists, interventional pulmonologists, radiologists, anesthesiologists, oncologists, radiation oncologists, thoracic surgeons and otolaryngologists, etc. The panel recommends shared decision-making with the patients and a multidisciplinary approach to manage CAO.
Below, you’ll find flowcharts outlining the suggested treatments for patients with a malignant or nonmalignant CAO.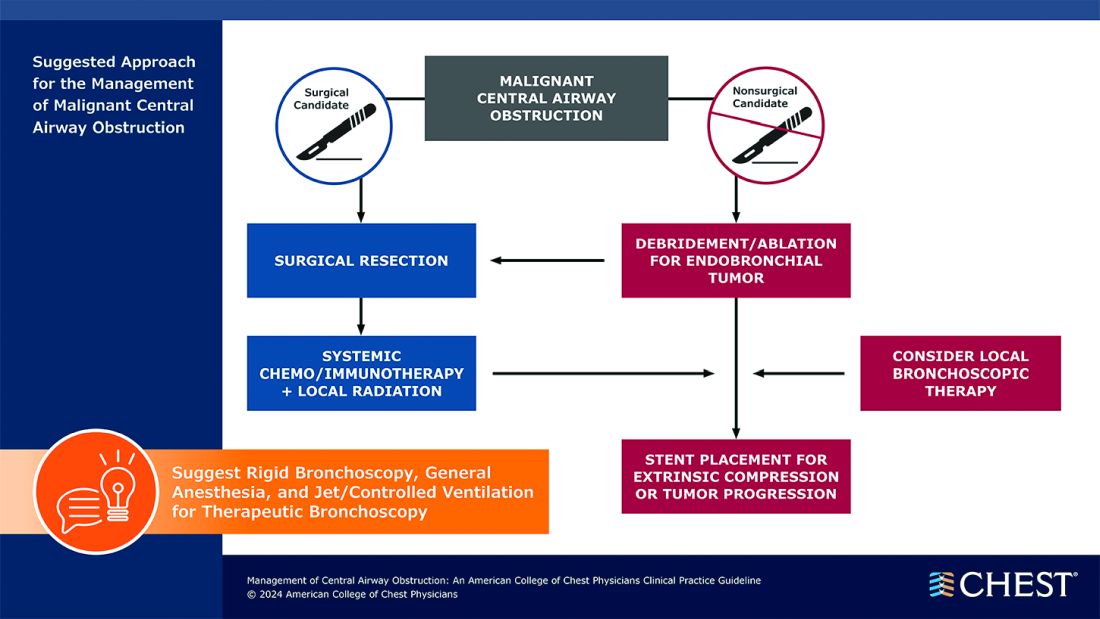
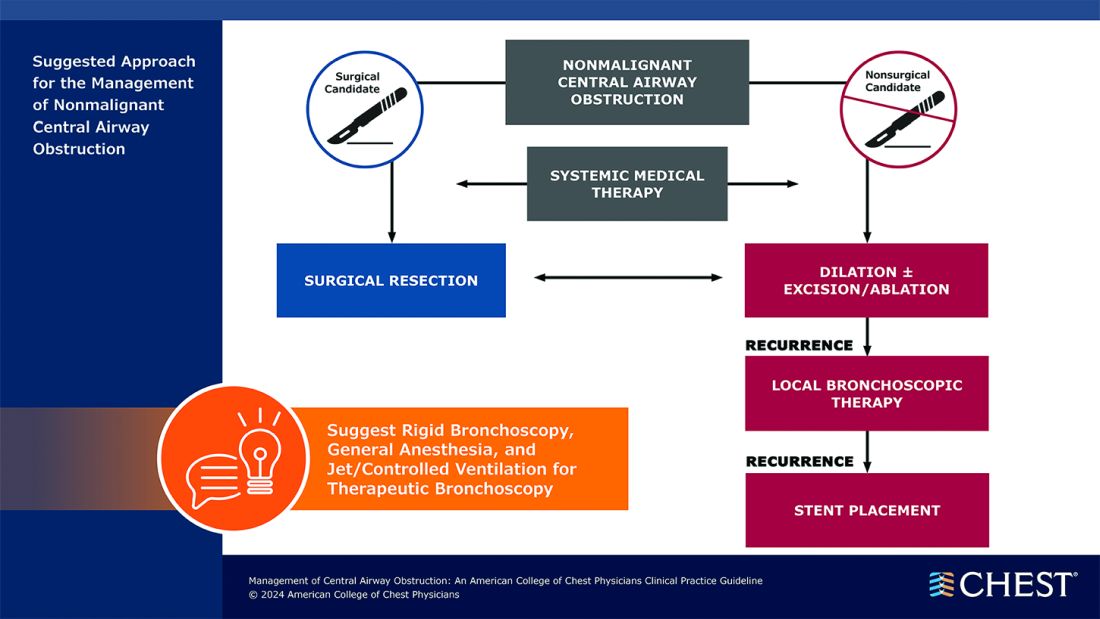
Visit www.chestnet.org/CAO-guideline to download the flowcharts and access the complete guideline.
CHEST recently released a new clinical guideline on central airway obstruction (CAO).
“Central airway obstruction is associated with a poor prognosis, and the management of CAO is highly variable dependent on the provider expertise and local resources. By releasing this guideline, the panel hopes to standardize the definition of CAO and provide guidance for the management of patients to optimize care and improve outcomes,” said Kamran Mahmood, MD, MPH, FCCP, lead author on the guideline. “The guideline recommendations are developed using GRADE methodology and based on thorough evidence review and expert input. But the quality of overall evidence is very low, and the panel calls for well-designed studies and randomized controlled trials for the management of CAO.”
CAO can be caused by a variety of malignant and nonmalignant disorders, and multiple specialists may be involved in the care, including pulmonologists, interventional pulmonologists, radiologists, anesthesiologists, oncologists, radiation oncologists, thoracic surgeons and otolaryngologists, etc. The panel recommends shared decision-making with the patients and a multidisciplinary approach to manage CAO.
Below, you’ll find flowcharts outlining the suggested treatments for patients with a malignant or nonmalignant CAO.

Visit www.chestnet.org/CAO-guideline to download the flowcharts and access the complete guideline.
CHEST recently released a new clinical guideline on central airway obstruction (CAO).
“Central airway obstruction is associated with a poor prognosis, and the management of CAO is highly variable dependent on the provider expertise and local resources. By releasing this guideline, the panel hopes to standardize the definition of CAO and provide guidance for the management of patients to optimize care and improve outcomes,” said Kamran Mahmood, MD, MPH, FCCP, lead author on the guideline. “The guideline recommendations are developed using GRADE methodology and based on thorough evidence review and expert input. But the quality of overall evidence is very low, and the panel calls for well-designed studies and randomized controlled trials for the management of CAO.”
CAO can be caused by a variety of malignant and nonmalignant disorders, and multiple specialists may be involved in the care, including pulmonologists, interventional pulmonologists, radiologists, anesthesiologists, oncologists, radiation oncologists, thoracic surgeons and otolaryngologists, etc. The panel recommends shared decision-making with the patients and a multidisciplinary approach to manage CAO.
Below, you’ll find flowcharts outlining the suggested treatments for patients with a malignant or nonmalignant CAO.

Visit www.chestnet.org/CAO-guideline to download the flowcharts and access the complete guideline.