User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Deployed Airbag Causes Bullous Reaction Following a Motor Vehicle Accident
Airbags are lifesaving during motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), but their deployment has been associated with skin issues such as irritant dermatitis1; lacerations2; abrasions3; and thermal, friction, and chemical burns.4-6 Ocular issues such as alkaline chemical keratitis7 and ocular alkali injuries8 also have been described.
Airbag deployment is triggered by rapid deceleration and impact, which ignite a sodium azide cartridge, causing the woven nylon bag to inflate with hydrocarbon gases.8 This leads to release of sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate, and metallic oxides in an aerosolized form. If a tear in the meshwork of the airbag occurs, exposure to an even larger amount of powder containing caustic alkali chemicals can occur.8
We describe a patient who developed a bullous reaction to airbag contents after he was involved in an MVA in which the airbag deployed.
Case Report
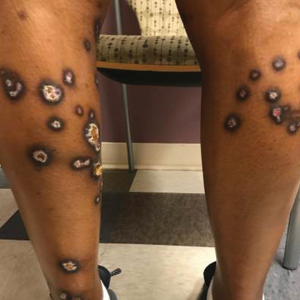
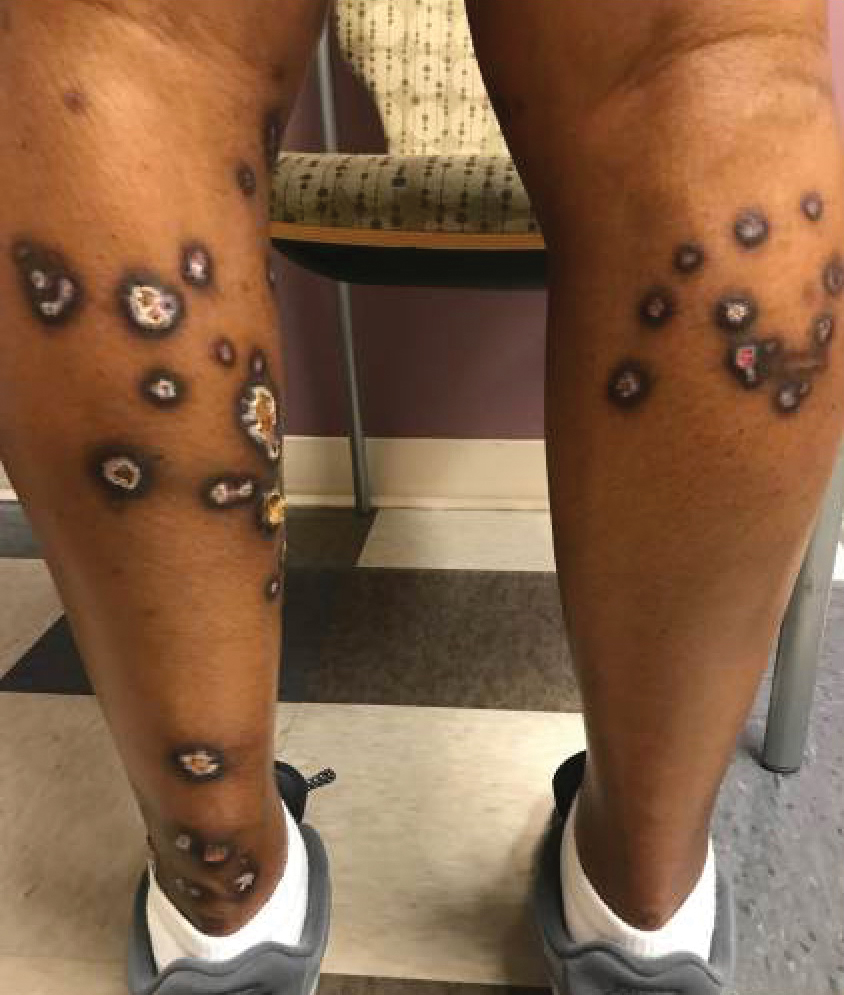
A 35-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis B presented to the dermatology clinic for an evaluation of new-onset blisters. The rash occurred 1 day after the patient was involved in an MVA in which he was exposed to the airbag’s contents after it burst. He had been evaluated twice in the emergency department for the skin eruption before being referred to dermatology. He noted the lesions were pruritic and painful. Prior treatments included silver sulfadiazine cream 1% and clobetasol cream 0.05%, though he discontinued using the latter because of burning with application. Physical examination revealed tense vesicles and bullae on an erythematous base on the right lower flank, forearms, and legs, with the exception of the lower right leg where a cast had been from a prior injury (Figure 1).

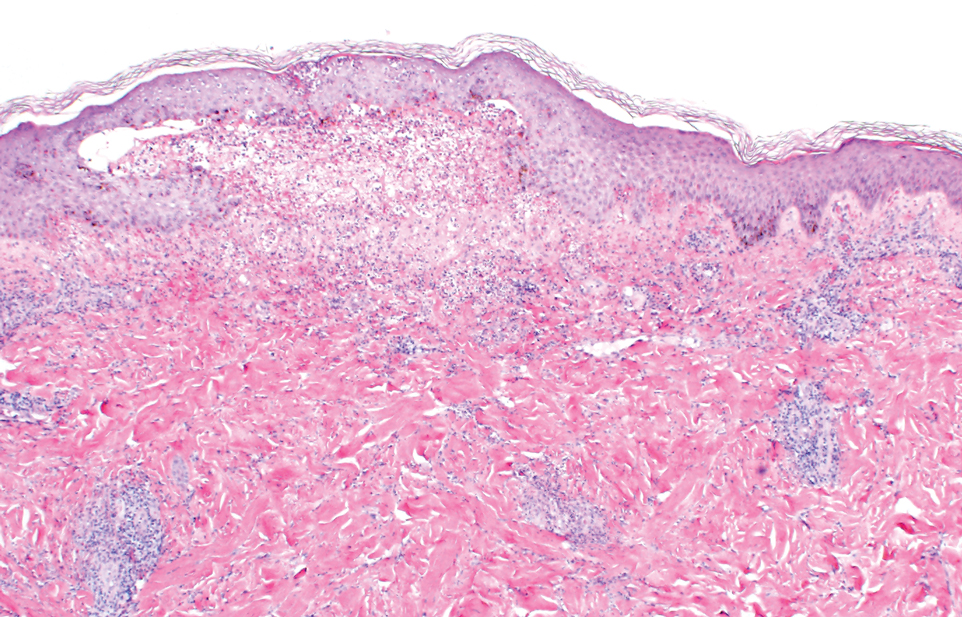
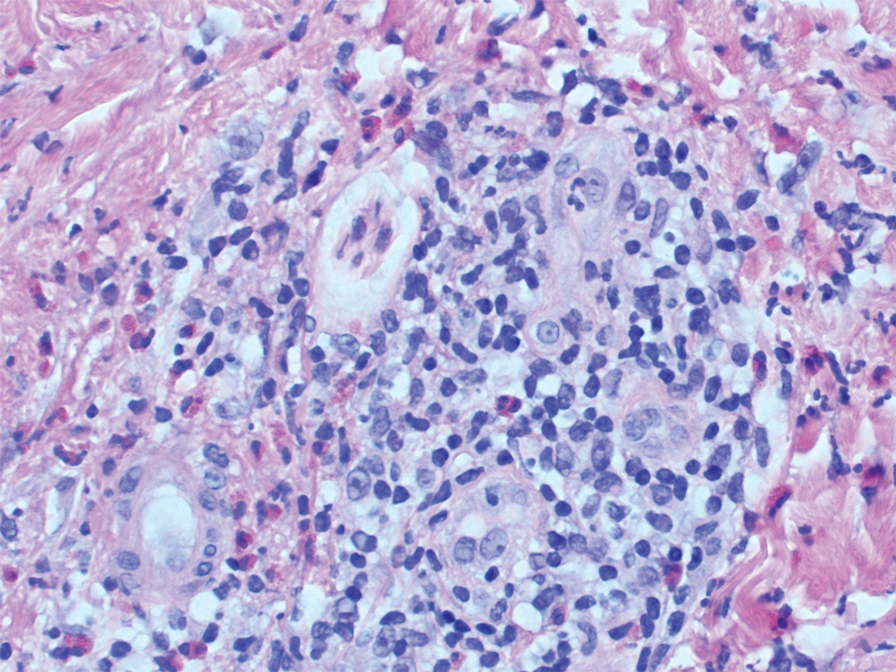
Two punch biopsies of the left arm were performed and sent for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence to rule out bullous diseases, such as bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA, and bullous lupus. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed extensive spongiosis with blister formation and a dense perivascular infiltrate in the superficial and mid dermis composed of lymphocytes with numerous scattered eosinophils (Figures 2 and 3). Direct immunofluorescence studies were negative. Treatment with oral prednisone and oral antihistamines was initiated.
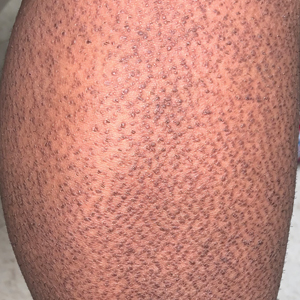
At 10-day follow-up, the patient had a few residual bullae; most lesions were demonstrating various stages of healing (Figure 4). The patient’s cast had been removed, and there were no lesions in this previously covered area. At 6-week follow-up he had continued healing of the bullae and erosions as well as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (Figure 5).

Comment
With the advent of airbags for safety purposes, these potentially lifesaving devices also have been known to cause injury.9 In 1998, the most commonly reported airbag injuries were ocular injuries.10 Cutaneous manifestations of airbag injury are less well known.11
Two cases of airbag deployment with skin blistering have been reported in the literature based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms airbag blistering or airbag bullae12,13; however, the blistering was described in the context of a burn. One case of the effects of airbag deployment residue highlights a patient arriving to the emergency department with erythema and blisters on the hands within 48 hours of airbag deployment in an MVA, and the treatment was standard burn therapy.12 Another case report described a patient with a second-degree burn with a 12-cm blister occurring on the radial side of the hand and distal forearm following an MVA and airbag deployment, which was treated conservatively.13 Cases of thermal burns, chemical burns, and irritant contact dermatitis after airbag deployment have been described in the literature.4-6,11,12,14,15 Our patient’s distal right lower leg was covered with a cast for osteomyelitis, and no blisters had developed in this area. It is likely that the transfer of airbag contents occurred during the process of unbuckling his seatbelt, which could explain the bullae that developed on the right flank. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, individuals should quickly remove clothing and wash their body with large amounts of soap and water following exposure to sodium azide.16
In 1989, the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 208 (occupant crash protection) became effective, stating all cars must have vehicle crash protection.12 Prior to 1993, it was reported that there had been no associated chemical injuries with airbag deployment. Subsequently, a 6-month retrospective study in 1993 showed that dermal injuries were found in connection with the presence of sodium hydroxide in automobile airbags.12 By 2004, it was known that airbags could cause chemical and thermal burns in addition to traumatic injuries from deployment.1 Since 2007, all motor vehicles have been required to have advanced airbags, which are engineered to sense the presence of passengers and determine if the airbag will deploy, and if so, how much to deploy to minimize airbag-related injury.3
The brand of car that our patient drove during the MVA is one with known airbag recalls due to safety defects; however, the year and actual model of the vehicle are not known, so specific information about the airbag in question is not available. It has been noted that some defective airbag inflators that were exposed to excess moisture during the manufacturing process could explode during deployment, causing shrapnel and airbag rupture, which has been linked to nearly 300 injuries worldwide.17
Conclusion
It is evident that the use of airbag devices reduces morbidity and mortality due to MVAs.9 It also had been reported that up to 96% of airbag-related injuries are relatively minor, which many would argue justifies their use.18 Furthermore, it has been reported that 99.8% of skin injuries following airbag deployment are minor.19 In the United States, it is mandated that every vehicle have functional airbags installed.8
This case highlights the potential for substantial airbag-induced skin reactions, specifically a bullous reaction, following airbag deployment. The persistent pruritus and lasting postinflammatory hyperpigmentation seen in this case were certainly worrisome for our patient. We also present this case to remind dermatology providers of possible treatment approaches to these skin reactions. Immediate cleansing of the affected areas of skin may help avoid such reactions.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Zampino MR, et al. Air bags and the skin. Skinmed. 2004;3:256-258.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Virgili A. Effects of airbag deployment: lesions, epidemiology, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5:295-300.
- Kuska TC. Air bag safety: an update. J Emerg Nurs. 2016;42:438-441.
- Ulrich D, Noah EM, Fuchs P, et al. Burn injuries caused by air bag deployment. Burns. 2001;27:196-199.
- Erpenbeck SP, Roy E, Ziembicki JA, et al. A systematic review on airbag-induced burns. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:481-487.
- Skibba KEH, Cleveland CN, Bell DE. Airbag burns: an unfortunate consequence of motor vehicle safety. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:71-73.
- Smally AJ, Binzer A, Dolin S, et al. Alkaline chemical keratitis: eye injury from airbags. Ann Emerg Med. 1992;21:1400-1402.
- Barnes SS, Wong W Jr, Affeldt JC. A case of severe airbag related ocular alkali injury. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2012;71:229-231.
- Wallis LA, Greaves I. Injuries associated with airbag deployment. Emerg Med J. 2002;19:490-493.
- Mohamed AA, Banerjee A. Patterns of injury associated with automobile airbag use. Postgrad Med J. 1998;74:455-458.
- Foley E, Helm TN. Air bag injury and the dermatologist. Cutis. 2000;66:251-252.
- Swanson-Biearman B, Mrvos R, Dean BS, et al. Air bags: lifesaving with toxic potential? Am J Emerg Med. 1993;11:38-39.
- Roth T, Meredith P. Traumatic lesions caused by the “air-bag” system [in French]. Z Unfallchir Versicherungsmed. 1993;86:189-193.
- Wu JJ, Sanchez-Palacios C, Brieva J, et al. A case of air bag dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1383-1384.
- Vitello W, Kim M, Johnson RM, et al. Full-thickness burn to the hand from an automobile airbag. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20:212-215.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facts about sodium azide. Updated April 4, 2018. Accessed May 15, 2022. https://emergency.cdc.gov/agent/sodiumazide/basics/facts.asp
- Shepardson D. Honda to recall 1.2 million vehicles in North America to replace Takata airbags. March 12, 2019. Accessed March 22, 2022. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-honda-takata-recall/honda-to-recall-1-2-million-vehicles-in-north-america-to-replace-takata-airbags-idUSKBN1QT1C9
- Gabauer DJ, Gabler HC. The effects of airbags and seatbelts on occupant injury in longitudinal barrier crashes. J Safety Res. 2010;41:9-15.
- Rath AL, Jernigan MV, Stitzel JD, et al. The effects of depowered airbags on skin injuries in frontal automobile crashes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;115:428-435.
Airbags are lifesaving during motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), but their deployment has been associated with skin issues such as irritant dermatitis1; lacerations2; abrasions3; and thermal, friction, and chemical burns.4-6 Ocular issues such as alkaline chemical keratitis7 and ocular alkali injuries8 also have been described.
Airbag deployment is triggered by rapid deceleration and impact, which ignite a sodium azide cartridge, causing the woven nylon bag to inflate with hydrocarbon gases.8 This leads to release of sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate, and metallic oxides in an aerosolized form. If a tear in the meshwork of the airbag occurs, exposure to an even larger amount of powder containing caustic alkali chemicals can occur.8
We describe a patient who developed a bullous reaction to airbag contents after he was involved in an MVA in which the airbag deployed.
Case Report
A 35-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis B presented to the dermatology clinic for an evaluation of new-onset blisters. The rash occurred 1 day after the patient was involved in an MVA in which he was exposed to the airbag’s contents after it burst. He had been evaluated twice in the emergency department for the skin eruption before being referred to dermatology. He noted the lesions were pruritic and painful. Prior treatments included silver sulfadiazine cream 1% and clobetasol cream 0.05%, though he discontinued using the latter because of burning with application. Physical examination revealed tense vesicles and bullae on an erythematous base on the right lower flank, forearms, and legs, with the exception of the lower right leg where a cast had been from a prior injury (Figure 1).

Two punch biopsies of the left arm were performed and sent for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence to rule out bullous diseases, such as bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA, and bullous lupus. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed extensive spongiosis with blister formation and a dense perivascular infiltrate in the superficial and mid dermis composed of lymphocytes with numerous scattered eosinophils (Figures 2 and 3). Direct immunofluorescence studies were negative. Treatment with oral prednisone and oral antihistamines was initiated.


At 10-day follow-up, the patient had a few residual bullae; most lesions were demonstrating various stages of healing (Figure 4). The patient’s cast had been removed, and there were no lesions in this previously covered area. At 6-week follow-up he had continued healing of the bullae and erosions as well as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (Figure 5).


Comment
With the advent of airbags for safety purposes, these potentially lifesaving devices also have been known to cause injury.9 In 1998, the most commonly reported airbag injuries were ocular injuries.10 Cutaneous manifestations of airbag injury are less well known.11
Two cases of airbag deployment with skin blistering have been reported in the literature based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms airbag blistering or airbag bullae12,13; however, the blistering was described in the context of a burn. One case of the effects of airbag deployment residue highlights a patient arriving to the emergency department with erythema and blisters on the hands within 48 hours of airbag deployment in an MVA, and the treatment was standard burn therapy.12 Another case report described a patient with a second-degree burn with a 12-cm blister occurring on the radial side of the hand and distal forearm following an MVA and airbag deployment, which was treated conservatively.13 Cases of thermal burns, chemical burns, and irritant contact dermatitis after airbag deployment have been described in the literature.4-6,11,12,14,15 Our patient’s distal right lower leg was covered with a cast for osteomyelitis, and no blisters had developed in this area. It is likely that the transfer of airbag contents occurred during the process of unbuckling his seatbelt, which could explain the bullae that developed on the right flank. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, individuals should quickly remove clothing and wash their body with large amounts of soap and water following exposure to sodium azide.16
In 1989, the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 208 (occupant crash protection) became effective, stating all cars must have vehicle crash protection.12 Prior to 1993, it was reported that there had been no associated chemical injuries with airbag deployment. Subsequently, a 6-month retrospective study in 1993 showed that dermal injuries were found in connection with the presence of sodium hydroxide in automobile airbags.12 By 2004, it was known that airbags could cause chemical and thermal burns in addition to traumatic injuries from deployment.1 Since 2007, all motor vehicles have been required to have advanced airbags, which are engineered to sense the presence of passengers and determine if the airbag will deploy, and if so, how much to deploy to minimize airbag-related injury.3
The brand of car that our patient drove during the MVA is one with known airbag recalls due to safety defects; however, the year and actual model of the vehicle are not known, so specific information about the airbag in question is not available. It has been noted that some defective airbag inflators that were exposed to excess moisture during the manufacturing process could explode during deployment, causing shrapnel and airbag rupture, which has been linked to nearly 300 injuries worldwide.17
Conclusion
It is evident that the use of airbag devices reduces morbidity and mortality due to MVAs.9 It also had been reported that up to 96% of airbag-related injuries are relatively minor, which many would argue justifies their use.18 Furthermore, it has been reported that 99.8% of skin injuries following airbag deployment are minor.19 In the United States, it is mandated that every vehicle have functional airbags installed.8
This case highlights the potential for substantial airbag-induced skin reactions, specifically a bullous reaction, following airbag deployment. The persistent pruritus and lasting postinflammatory hyperpigmentation seen in this case were certainly worrisome for our patient. We also present this case to remind dermatology providers of possible treatment approaches to these skin reactions. Immediate cleansing of the affected areas of skin may help avoid such reactions.
Airbags are lifesaving during motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), but their deployment has been associated with skin issues such as irritant dermatitis1; lacerations2; abrasions3; and thermal, friction, and chemical burns.4-6 Ocular issues such as alkaline chemical keratitis7 and ocular alkali injuries8 also have been described.
Airbag deployment is triggered by rapid deceleration and impact, which ignite a sodium azide cartridge, causing the woven nylon bag to inflate with hydrocarbon gases.8 This leads to release of sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate, and metallic oxides in an aerosolized form. If a tear in the meshwork of the airbag occurs, exposure to an even larger amount of powder containing caustic alkali chemicals can occur.8
We describe a patient who developed a bullous reaction to airbag contents after he was involved in an MVA in which the airbag deployed.
Case Report
A 35-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis B presented to the dermatology clinic for an evaluation of new-onset blisters. The rash occurred 1 day after the patient was involved in an MVA in which he was exposed to the airbag’s contents after it burst. He had been evaluated twice in the emergency department for the skin eruption before being referred to dermatology. He noted the lesions were pruritic and painful. Prior treatments included silver sulfadiazine cream 1% and clobetasol cream 0.05%, though he discontinued using the latter because of burning with application. Physical examination revealed tense vesicles and bullae on an erythematous base on the right lower flank, forearms, and legs, with the exception of the lower right leg where a cast had been from a prior injury (Figure 1).

Two punch biopsies of the left arm were performed and sent for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence to rule out bullous diseases, such as bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA, and bullous lupus. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed extensive spongiosis with blister formation and a dense perivascular infiltrate in the superficial and mid dermis composed of lymphocytes with numerous scattered eosinophils (Figures 2 and 3). Direct immunofluorescence studies were negative. Treatment with oral prednisone and oral antihistamines was initiated.


At 10-day follow-up, the patient had a few residual bullae; most lesions were demonstrating various stages of healing (Figure 4). The patient’s cast had been removed, and there were no lesions in this previously covered area. At 6-week follow-up he had continued healing of the bullae and erosions as well as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (Figure 5).


Comment
With the advent of airbags for safety purposes, these potentially lifesaving devices also have been known to cause injury.9 In 1998, the most commonly reported airbag injuries were ocular injuries.10 Cutaneous manifestations of airbag injury are less well known.11
Two cases of airbag deployment with skin blistering have been reported in the literature based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms airbag blistering or airbag bullae12,13; however, the blistering was described in the context of a burn. One case of the effects of airbag deployment residue highlights a patient arriving to the emergency department with erythema and blisters on the hands within 48 hours of airbag deployment in an MVA, and the treatment was standard burn therapy.12 Another case report described a patient with a second-degree burn with a 12-cm blister occurring on the radial side of the hand and distal forearm following an MVA and airbag deployment, which was treated conservatively.13 Cases of thermal burns, chemical burns, and irritant contact dermatitis after airbag deployment have been described in the literature.4-6,11,12,14,15 Our patient’s distal right lower leg was covered with a cast for osteomyelitis, and no blisters had developed in this area. It is likely that the transfer of airbag contents occurred during the process of unbuckling his seatbelt, which could explain the bullae that developed on the right flank. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, individuals should quickly remove clothing and wash their body with large amounts of soap and water following exposure to sodium azide.16
In 1989, the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 208 (occupant crash protection) became effective, stating all cars must have vehicle crash protection.12 Prior to 1993, it was reported that there had been no associated chemical injuries with airbag deployment. Subsequently, a 6-month retrospective study in 1993 showed that dermal injuries were found in connection with the presence of sodium hydroxide in automobile airbags.12 By 2004, it was known that airbags could cause chemical and thermal burns in addition to traumatic injuries from deployment.1 Since 2007, all motor vehicles have been required to have advanced airbags, which are engineered to sense the presence of passengers and determine if the airbag will deploy, and if so, how much to deploy to minimize airbag-related injury.3
The brand of car that our patient drove during the MVA is one with known airbag recalls due to safety defects; however, the year and actual model of the vehicle are not known, so specific information about the airbag in question is not available. It has been noted that some defective airbag inflators that were exposed to excess moisture during the manufacturing process could explode during deployment, causing shrapnel and airbag rupture, which has been linked to nearly 300 injuries worldwide.17
Conclusion
It is evident that the use of airbag devices reduces morbidity and mortality due to MVAs.9 It also had been reported that up to 96% of airbag-related injuries are relatively minor, which many would argue justifies their use.18 Furthermore, it has been reported that 99.8% of skin injuries following airbag deployment are minor.19 In the United States, it is mandated that every vehicle have functional airbags installed.8
This case highlights the potential for substantial airbag-induced skin reactions, specifically a bullous reaction, following airbag deployment. The persistent pruritus and lasting postinflammatory hyperpigmentation seen in this case were certainly worrisome for our patient. We also present this case to remind dermatology providers of possible treatment approaches to these skin reactions. Immediate cleansing of the affected areas of skin may help avoid such reactions.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Zampino MR, et al. Air bags and the skin. Skinmed. 2004;3:256-258.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Virgili A. Effects of airbag deployment: lesions, epidemiology, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5:295-300.
- Kuska TC. Air bag safety: an update. J Emerg Nurs. 2016;42:438-441.
- Ulrich D, Noah EM, Fuchs P, et al. Burn injuries caused by air bag deployment. Burns. 2001;27:196-199.
- Erpenbeck SP, Roy E, Ziembicki JA, et al. A systematic review on airbag-induced burns. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:481-487.
- Skibba KEH, Cleveland CN, Bell DE. Airbag burns: an unfortunate consequence of motor vehicle safety. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:71-73.
- Smally AJ, Binzer A, Dolin S, et al. Alkaline chemical keratitis: eye injury from airbags. Ann Emerg Med. 1992;21:1400-1402.
- Barnes SS, Wong W Jr, Affeldt JC. A case of severe airbag related ocular alkali injury. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2012;71:229-231.
- Wallis LA, Greaves I. Injuries associated with airbag deployment. Emerg Med J. 2002;19:490-493.
- Mohamed AA, Banerjee A. Patterns of injury associated with automobile airbag use. Postgrad Med J. 1998;74:455-458.
- Foley E, Helm TN. Air bag injury and the dermatologist. Cutis. 2000;66:251-252.
- Swanson-Biearman B, Mrvos R, Dean BS, et al. Air bags: lifesaving with toxic potential? Am J Emerg Med. 1993;11:38-39.
- Roth T, Meredith P. Traumatic lesions caused by the “air-bag” system [in French]. Z Unfallchir Versicherungsmed. 1993;86:189-193.
- Wu JJ, Sanchez-Palacios C, Brieva J, et al. A case of air bag dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1383-1384.
- Vitello W, Kim M, Johnson RM, et al. Full-thickness burn to the hand from an automobile airbag. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20:212-215.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facts about sodium azide. Updated April 4, 2018. Accessed May 15, 2022. https://emergency.cdc.gov/agent/sodiumazide/basics/facts.asp
- Shepardson D. Honda to recall 1.2 million vehicles in North America to replace Takata airbags. March 12, 2019. Accessed March 22, 2022. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-honda-takata-recall/honda-to-recall-1-2-million-vehicles-in-north-america-to-replace-takata-airbags-idUSKBN1QT1C9
- Gabauer DJ, Gabler HC. The effects of airbags and seatbelts on occupant injury in longitudinal barrier crashes. J Safety Res. 2010;41:9-15.
- Rath AL, Jernigan MV, Stitzel JD, et al. The effects of depowered airbags on skin injuries in frontal automobile crashes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;115:428-435.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Zampino MR, et al. Air bags and the skin. Skinmed. 2004;3:256-258.
- Corazza M, Trincone S, Virgili A. Effects of airbag deployment: lesions, epidemiology, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5:295-300.
- Kuska TC. Air bag safety: an update. J Emerg Nurs. 2016;42:438-441.
- Ulrich D, Noah EM, Fuchs P, et al. Burn injuries caused by air bag deployment. Burns. 2001;27:196-199.
- Erpenbeck SP, Roy E, Ziembicki JA, et al. A systematic review on airbag-induced burns. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:481-487.
- Skibba KEH, Cleveland CN, Bell DE. Airbag burns: an unfortunate consequence of motor vehicle safety. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:71-73.
- Smally AJ, Binzer A, Dolin S, et al. Alkaline chemical keratitis: eye injury from airbags. Ann Emerg Med. 1992;21:1400-1402.
- Barnes SS, Wong W Jr, Affeldt JC. A case of severe airbag related ocular alkali injury. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2012;71:229-231.
- Wallis LA, Greaves I. Injuries associated with airbag deployment. Emerg Med J. 2002;19:490-493.
- Mohamed AA, Banerjee A. Patterns of injury associated with automobile airbag use. Postgrad Med J. 1998;74:455-458.
- Foley E, Helm TN. Air bag injury and the dermatologist. Cutis. 2000;66:251-252.
- Swanson-Biearman B, Mrvos R, Dean BS, et al. Air bags: lifesaving with toxic potential? Am J Emerg Med. 1993;11:38-39.
- Roth T, Meredith P. Traumatic lesions caused by the “air-bag” system [in French]. Z Unfallchir Versicherungsmed. 1993;86:189-193.
- Wu JJ, Sanchez-Palacios C, Brieva J, et al. A case of air bag dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1383-1384.
- Vitello W, Kim M, Johnson RM, et al. Full-thickness burn to the hand from an automobile airbag. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20:212-215.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facts about sodium azide. Updated April 4, 2018. Accessed May 15, 2022. https://emergency.cdc.gov/agent/sodiumazide/basics/facts.asp
- Shepardson D. Honda to recall 1.2 million vehicles in North America to replace Takata airbags. March 12, 2019. Accessed March 22, 2022. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-honda-takata-recall/honda-to-recall-1-2-million-vehicles-in-north-america-to-replace-takata-airbags-idUSKBN1QT1C9
- Gabauer DJ, Gabler HC. The effects of airbags and seatbelts on occupant injury in longitudinal barrier crashes. J Safety Res. 2010;41:9-15.
- Rath AL, Jernigan MV, Stitzel JD, et al. The effects of depowered airbags on skin injuries in frontal automobile crashes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;115:428-435.
Practice Points
- This case highlights the potential for a bullous reaction following airbag deployment.
- After airbag deployment, it is important to immediately cleanse the affected areas of skin with soap and water.
The ERAS Supplemental Application: Current Status and Recommendations for Dermatology Applicants and Programs
In the 2021-2022 residency application cycle, the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) piloted a supplemental application to accompany the standard residency application submitted via the AAMC’s Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS).1 Dermatology was 1 of 3 specialties to participate in the pilot alongside internal medicine and general surgery. The goal was to develop a tool that could align applicants with programs that best matched their career goals as well as program and geographic preferences. The Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section was an early advocate for the supplemental application, and members of our leadership were involved in the design, implementation, and evaluation of the pilot supplemental application.
Participating in the supplemental application was optional for both applicants and programs. The supplemental application included a Past Experiences section, which allowed applicants to highlight their 5 most meaningful research, work, and/or volunteer experiences and to describe a challenging life event that might not otherwise be included with their application. The geographic preferences section permitted applicants to select up to 3 regions of interest as well as to indicate an urban vs rural preference. Lastly, a preference-signaling section allowed dermatology applicants to send signals to up to 3 programs of particular interest.
With the close of another application cycle, applicants and programs will begin preparing for the 2022-2023 recruitment season. In this column, we present dermatology-specific data regarding the supplemental application, highlight tentative changes for the upcoming application cycle, and offer tips for applicants and programs as we approach year 2 of the supplemental application.
Results of Supplemental Application Evaluation Surveys
During the 2021-2022 recruitment season, 93% (950/1019) of dermatology applicants submitted the supplemental application, and 87% (117/135) of dermatology residency programs participated in the pilot.2 Surveys conducted by the AAMC between October 2021 and January 2022 showed that a large majority of dermatology programs used supplemental application data during initial application review when deciding who to interview. Eighty-three percent (40/48) of program directors felt that preference signals in particular helped them identify applicants they would have otherwise overlooked. Fifty-seven percent (4288/7516) of applicants across all specialties that participated in the pilot felt that preference signals would help them be noticed by their preferred programs.2 Preference signals were not evenly distributed among dermatology programs. Programs received an average of 23 signals, with a range of 2 to 87 (AAMC, unpublished data, February 2022).
Additional questions remain to be answered: How does the number of signals received affect application review? How often do geographic and program signals convert to interview offers and matches? Regardless, enthusiasm among dermatology programs for the supplemental application remains. In a recent survey of Association of Professors of Dermatology program directors, all 43 respondents planned to participate in the supplemental application again in the upcoming year (Ilana Rosman, MD; unpublished data; February 2022). The pilot will be expanded to include at least 12 other specialties.1As many who reviewed residency applications in 2021-2022 will attest, there was difficulty accessing the supplemental application data because it was not integrated into the Program Directors’ Work Station, the ERAS platform for programs to access applications, which will be remedied for the 2022-2023 iteration. Other tentative changes include modifications to the past experiences sections and timeline of the application.2
Utilizing the Supplemental Application: Recommendations to Applicants
Format of the Application—Applicants should familiarize themselves with the format of the supplemental application in advance and give themselves sufficient time to complete the application. In general, 3 to 4 hours of focused work should be enough time. Applicants should proofread for grammar and spelling before submitting.
Past Experiences—The past experiences section is intended to provide a focused snapshot of an applicant’s most meaningful activities and unique path to residency. Applicants should answer honestly based on their interests. If a student’s focus has been on volunteerism, the bulk of their 5 experiences listed may be related to service. Similarly, a student who has focused on research may preferentially highlight those experiences. In place of the long list of research, volunteer, and work experiences in the traditional ERAS application, applicants can highlight those activities in which they have been most invested. Applicants are encouraged to reflect on all genres of activities at any stage of their careers, even those not medical in nature, including work experience, military service, college athletics, or sustained musical or artistic achievement. Applicants should explain why each experience is meaningful rather than simply describing the activity.
Applicants also have the option to share a notable challenge they have overcome. It is not expected that each applicant will complete this question; in general, applicants who have not faced notable personal or professional obstacles should avoid answering. Additionally, if these challenges have been discussed in other areas of the application—for example, in the personal statement or medical student performance evaluation—it is not necessary to restate them here, though applicants can choose to do so. Examples of topics a student might discuss include being a first-generation college or medical student, growing up in poverty, facing notable personal or family health challenges, or having limited educational opportunities. It is important to share how this experience impacted an applicant’s journey to dermatology residency.
Geographic Preferences—The geographic preferences section can be difficult for applicants to navigate, as it may involve balancing a desire to attend a residency program in a particular region vs a greater desire to simply match in dermatology. In the past, programs may have made assumptions about geographic preferences based on an applicant’s birthplace, hometown, or medical school. In the supplemental application, applicants have the opportunity to directly reveal their preferences. We encourage applicants to be candid. Selecting a geographic region will not necessarily exclude applicants from consideration at other programs. For some applicants, program qualities may be more important than geography, or there may be no regional preferences. Those applicants can choose “no geographic preference.” There is considerable variability in how programs use geographic preferences. For this reason, it is in the best interest of applicants to simply respond honestly.
Preference Signaling—Preference signaling allows applicants to signal up to 3 preferred programs. Dermatology program directors agree that applicants should not signal their home program or programs at which they did in-person away rotations, as those programs would already be aware of the applicant’s interest. Although a signal increases the chances that the application will be reviewed holistically, it does not guarantee an interview offer. Programs may differentially utilize signals depending on multiple factors, including the number of signals received. We encourage applicants to discuss preference signaling strategies with advisors and focus on signaling programs in which they have genuine interest.
Recommendations to Selection Committees and Program Directors
The intent of the supplemental application is to provide a more meaningful picture of applicants and their experiences and preferences, with the goal of optimizing applicant-program fit. Programs should explicitly define for themselves the applicant characteristics and experiences they prioritize as well as their program goals. The supplemental application offers the potential to streamline holistic application review based on these elements. The short essay answers in the past experiences section permit reviewers to quickly scan for important experiences that align with the program’s recruitment goals. Importantly, reviewers should not penalize applicants who have not completed the question regarding other impactful life experiences, as not all applicants will have relevant information to share.
Some programs may find the geographic preferences section more valuable than others. Multiple factors affect how much weight will be given to geographic preferences, including program location and other characteristics that affect the desirability of the program to applicants. The competitiveness of the field, relatively low match rate, and limited number of programs may lead to less emphasis on geographic preferences in dermatology compared to other specialties. The purpose of this section is not to exclude applicants but to give programs more information that may help with alignment.
Anecdotally, many dermatology program directors were most interested in the preference signaling section of the supplemental application. Programs should consider signals to be evidence of strong preliminary interest. Programs may utilize signals differently depending on many factors such as the overall competitiveness of the program, program location, and the total number of signals the program receives. We recommend that programs holistically review all applications accompanied by a signal. Programs that utilize a points system may choose to award a certain number of points for a signal to their program. A signal might have a higher value at a program that receives only a few signals; conversely, a program that receives a large number of signals might not place tremendous value on the signal but may use it as a tiebreaker between similarly qualified applicants. Preference signaling is solely a tool for application review; because applicants’ preferences may change after the interview process, signals should not be utilized during ranking.
Next Steps
For program directors who have excitedly awaited residency application reform, the supplemental ERAS application is an important first step. Ultimately, we hope the supplemental application supplants much of the current residency application, serving as an efficient high-yield tool for holistically evaluating applicants’ academic and service records, accomplishments, and training preferences. Arriving at a new application will undoubtedly take time and discussion among the various stakeholders. Please continue to complete surveys from the AAMC, as feedback is the best method for refining the tool to serve its intended purpose.
Optimization of the application content is only one component of the reforms needed to improve the application process. Even with a revamped application tool, holistic review is challenging when programs are inundated with an ever-increasing number of applications. As such, we encourage stakeholders to simultaneously consider other potential reforms, such as caps on the number of applications, to allow programs and applicants the best opportunity for a mutually successful match.
- Supplemental ERAS application. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed May 9, 2022. https://students-residents.aamc.org/applying-residencies-eras/supplemental-eras-application-eras-2023-cycle
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Supplemental application data and reports. Accessed May 9, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/students-residents/report/supplemental-eras-application-data-and-reports
In the 2021-2022 residency application cycle, the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) piloted a supplemental application to accompany the standard residency application submitted via the AAMC’s Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS).1 Dermatology was 1 of 3 specialties to participate in the pilot alongside internal medicine and general surgery. The goal was to develop a tool that could align applicants with programs that best matched their career goals as well as program and geographic preferences. The Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section was an early advocate for the supplemental application, and members of our leadership were involved in the design, implementation, and evaluation of the pilot supplemental application.
Participating in the supplemental application was optional for both applicants and programs. The supplemental application included a Past Experiences section, which allowed applicants to highlight their 5 most meaningful research, work, and/or volunteer experiences and to describe a challenging life event that might not otherwise be included with their application. The geographic preferences section permitted applicants to select up to 3 regions of interest as well as to indicate an urban vs rural preference. Lastly, a preference-signaling section allowed dermatology applicants to send signals to up to 3 programs of particular interest.
With the close of another application cycle, applicants and programs will begin preparing for the 2022-2023 recruitment season. In this column, we present dermatology-specific data regarding the supplemental application, highlight tentative changes for the upcoming application cycle, and offer tips for applicants and programs as we approach year 2 of the supplemental application.
Results of Supplemental Application Evaluation Surveys
During the 2021-2022 recruitment season, 93% (950/1019) of dermatology applicants submitted the supplemental application, and 87% (117/135) of dermatology residency programs participated in the pilot.2 Surveys conducted by the AAMC between October 2021 and January 2022 showed that a large majority of dermatology programs used supplemental application data during initial application review when deciding who to interview. Eighty-three percent (40/48) of program directors felt that preference signals in particular helped them identify applicants they would have otherwise overlooked. Fifty-seven percent (4288/7516) of applicants across all specialties that participated in the pilot felt that preference signals would help them be noticed by their preferred programs.2 Preference signals were not evenly distributed among dermatology programs. Programs received an average of 23 signals, with a range of 2 to 87 (AAMC, unpublished data, February 2022).
Additional questions remain to be answered: How does the number of signals received affect application review? How often do geographic and program signals convert to interview offers and matches? Regardless, enthusiasm among dermatology programs for the supplemental application remains. In a recent survey of Association of Professors of Dermatology program directors, all 43 respondents planned to participate in the supplemental application again in the upcoming year (Ilana Rosman, MD; unpublished data; February 2022). The pilot will be expanded to include at least 12 other specialties.1As many who reviewed residency applications in 2021-2022 will attest, there was difficulty accessing the supplemental application data because it was not integrated into the Program Directors’ Work Station, the ERAS platform for programs to access applications, which will be remedied for the 2022-2023 iteration. Other tentative changes include modifications to the past experiences sections and timeline of the application.2
Utilizing the Supplemental Application: Recommendations to Applicants
Format of the Application—Applicants should familiarize themselves with the format of the supplemental application in advance and give themselves sufficient time to complete the application. In general, 3 to 4 hours of focused work should be enough time. Applicants should proofread for grammar and spelling before submitting.
Past Experiences—The past experiences section is intended to provide a focused snapshot of an applicant’s most meaningful activities and unique path to residency. Applicants should answer honestly based on their interests. If a student’s focus has been on volunteerism, the bulk of their 5 experiences listed may be related to service. Similarly, a student who has focused on research may preferentially highlight those experiences. In place of the long list of research, volunteer, and work experiences in the traditional ERAS application, applicants can highlight those activities in which they have been most invested. Applicants are encouraged to reflect on all genres of activities at any stage of their careers, even those not medical in nature, including work experience, military service, college athletics, or sustained musical or artistic achievement. Applicants should explain why each experience is meaningful rather than simply describing the activity.
Applicants also have the option to share a notable challenge they have overcome. It is not expected that each applicant will complete this question; in general, applicants who have not faced notable personal or professional obstacles should avoid answering. Additionally, if these challenges have been discussed in other areas of the application—for example, in the personal statement or medical student performance evaluation—it is not necessary to restate them here, though applicants can choose to do so. Examples of topics a student might discuss include being a first-generation college or medical student, growing up in poverty, facing notable personal or family health challenges, or having limited educational opportunities. It is important to share how this experience impacted an applicant’s journey to dermatology residency.
Geographic Preferences—The geographic preferences section can be difficult for applicants to navigate, as it may involve balancing a desire to attend a residency program in a particular region vs a greater desire to simply match in dermatology. In the past, programs may have made assumptions about geographic preferences based on an applicant’s birthplace, hometown, or medical school. In the supplemental application, applicants have the opportunity to directly reveal their preferences. We encourage applicants to be candid. Selecting a geographic region will not necessarily exclude applicants from consideration at other programs. For some applicants, program qualities may be more important than geography, or there may be no regional preferences. Those applicants can choose “no geographic preference.” There is considerable variability in how programs use geographic preferences. For this reason, it is in the best interest of applicants to simply respond honestly.
Preference Signaling—Preference signaling allows applicants to signal up to 3 preferred programs. Dermatology program directors agree that applicants should not signal their home program or programs at which they did in-person away rotations, as those programs would already be aware of the applicant’s interest. Although a signal increases the chances that the application will be reviewed holistically, it does not guarantee an interview offer. Programs may differentially utilize signals depending on multiple factors, including the number of signals received. We encourage applicants to discuss preference signaling strategies with advisors and focus on signaling programs in which they have genuine interest.
Recommendations to Selection Committees and Program Directors
The intent of the supplemental application is to provide a more meaningful picture of applicants and their experiences and preferences, with the goal of optimizing applicant-program fit. Programs should explicitly define for themselves the applicant characteristics and experiences they prioritize as well as their program goals. The supplemental application offers the potential to streamline holistic application review based on these elements. The short essay answers in the past experiences section permit reviewers to quickly scan for important experiences that align with the program’s recruitment goals. Importantly, reviewers should not penalize applicants who have not completed the question regarding other impactful life experiences, as not all applicants will have relevant information to share.
Some programs may find the geographic preferences section more valuable than others. Multiple factors affect how much weight will be given to geographic preferences, including program location and other characteristics that affect the desirability of the program to applicants. The competitiveness of the field, relatively low match rate, and limited number of programs may lead to less emphasis on geographic preferences in dermatology compared to other specialties. The purpose of this section is not to exclude applicants but to give programs more information that may help with alignment.
Anecdotally, many dermatology program directors were most interested in the preference signaling section of the supplemental application. Programs should consider signals to be evidence of strong preliminary interest. Programs may utilize signals differently depending on many factors such as the overall competitiveness of the program, program location, and the total number of signals the program receives. We recommend that programs holistically review all applications accompanied by a signal. Programs that utilize a points system may choose to award a certain number of points for a signal to their program. A signal might have a higher value at a program that receives only a few signals; conversely, a program that receives a large number of signals might not place tremendous value on the signal but may use it as a tiebreaker between similarly qualified applicants. Preference signaling is solely a tool for application review; because applicants’ preferences may change after the interview process, signals should not be utilized during ranking.
Next Steps
For program directors who have excitedly awaited residency application reform, the supplemental ERAS application is an important first step. Ultimately, we hope the supplemental application supplants much of the current residency application, serving as an efficient high-yield tool for holistically evaluating applicants’ academic and service records, accomplishments, and training preferences. Arriving at a new application will undoubtedly take time and discussion among the various stakeholders. Please continue to complete surveys from the AAMC, as feedback is the best method for refining the tool to serve its intended purpose.
Optimization of the application content is only one component of the reforms needed to improve the application process. Even with a revamped application tool, holistic review is challenging when programs are inundated with an ever-increasing number of applications. As such, we encourage stakeholders to simultaneously consider other potential reforms, such as caps on the number of applications, to allow programs and applicants the best opportunity for a mutually successful match.
In the 2021-2022 residency application cycle, the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) piloted a supplemental application to accompany the standard residency application submitted via the AAMC’s Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS).1 Dermatology was 1 of 3 specialties to participate in the pilot alongside internal medicine and general surgery. The goal was to develop a tool that could align applicants with programs that best matched their career goals as well as program and geographic preferences. The Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section was an early advocate for the supplemental application, and members of our leadership were involved in the design, implementation, and evaluation of the pilot supplemental application.
Participating in the supplemental application was optional for both applicants and programs. The supplemental application included a Past Experiences section, which allowed applicants to highlight their 5 most meaningful research, work, and/or volunteer experiences and to describe a challenging life event that might not otherwise be included with their application. The geographic preferences section permitted applicants to select up to 3 regions of interest as well as to indicate an urban vs rural preference. Lastly, a preference-signaling section allowed dermatology applicants to send signals to up to 3 programs of particular interest.
With the close of another application cycle, applicants and programs will begin preparing for the 2022-2023 recruitment season. In this column, we present dermatology-specific data regarding the supplemental application, highlight tentative changes for the upcoming application cycle, and offer tips for applicants and programs as we approach year 2 of the supplemental application.
Results of Supplemental Application Evaluation Surveys
During the 2021-2022 recruitment season, 93% (950/1019) of dermatology applicants submitted the supplemental application, and 87% (117/135) of dermatology residency programs participated in the pilot.2 Surveys conducted by the AAMC between October 2021 and January 2022 showed that a large majority of dermatology programs used supplemental application data during initial application review when deciding who to interview. Eighty-three percent (40/48) of program directors felt that preference signals in particular helped them identify applicants they would have otherwise overlooked. Fifty-seven percent (4288/7516) of applicants across all specialties that participated in the pilot felt that preference signals would help them be noticed by their preferred programs.2 Preference signals were not evenly distributed among dermatology programs. Programs received an average of 23 signals, with a range of 2 to 87 (AAMC, unpublished data, February 2022).
Additional questions remain to be answered: How does the number of signals received affect application review? How often do geographic and program signals convert to interview offers and matches? Regardless, enthusiasm among dermatology programs for the supplemental application remains. In a recent survey of Association of Professors of Dermatology program directors, all 43 respondents planned to participate in the supplemental application again in the upcoming year (Ilana Rosman, MD; unpublished data; February 2022). The pilot will be expanded to include at least 12 other specialties.1As many who reviewed residency applications in 2021-2022 will attest, there was difficulty accessing the supplemental application data because it was not integrated into the Program Directors’ Work Station, the ERAS platform for programs to access applications, which will be remedied for the 2022-2023 iteration. Other tentative changes include modifications to the past experiences sections and timeline of the application.2
Utilizing the Supplemental Application: Recommendations to Applicants
Format of the Application—Applicants should familiarize themselves with the format of the supplemental application in advance and give themselves sufficient time to complete the application. In general, 3 to 4 hours of focused work should be enough time. Applicants should proofread for grammar and spelling before submitting.
Past Experiences—The past experiences section is intended to provide a focused snapshot of an applicant’s most meaningful activities and unique path to residency. Applicants should answer honestly based on their interests. If a student’s focus has been on volunteerism, the bulk of their 5 experiences listed may be related to service. Similarly, a student who has focused on research may preferentially highlight those experiences. In place of the long list of research, volunteer, and work experiences in the traditional ERAS application, applicants can highlight those activities in which they have been most invested. Applicants are encouraged to reflect on all genres of activities at any stage of their careers, even those not medical in nature, including work experience, military service, college athletics, or sustained musical or artistic achievement. Applicants should explain why each experience is meaningful rather than simply describing the activity.
Applicants also have the option to share a notable challenge they have overcome. It is not expected that each applicant will complete this question; in general, applicants who have not faced notable personal or professional obstacles should avoid answering. Additionally, if these challenges have been discussed in other areas of the application—for example, in the personal statement or medical student performance evaluation—it is not necessary to restate them here, though applicants can choose to do so. Examples of topics a student might discuss include being a first-generation college or medical student, growing up in poverty, facing notable personal or family health challenges, or having limited educational opportunities. It is important to share how this experience impacted an applicant’s journey to dermatology residency.
Geographic Preferences—The geographic preferences section can be difficult for applicants to navigate, as it may involve balancing a desire to attend a residency program in a particular region vs a greater desire to simply match in dermatology. In the past, programs may have made assumptions about geographic preferences based on an applicant’s birthplace, hometown, or medical school. In the supplemental application, applicants have the opportunity to directly reveal their preferences. We encourage applicants to be candid. Selecting a geographic region will not necessarily exclude applicants from consideration at other programs. For some applicants, program qualities may be more important than geography, or there may be no regional preferences. Those applicants can choose “no geographic preference.” There is considerable variability in how programs use geographic preferences. For this reason, it is in the best interest of applicants to simply respond honestly.
Preference Signaling—Preference signaling allows applicants to signal up to 3 preferred programs. Dermatology program directors agree that applicants should not signal their home program or programs at which they did in-person away rotations, as those programs would already be aware of the applicant’s interest. Although a signal increases the chances that the application will be reviewed holistically, it does not guarantee an interview offer. Programs may differentially utilize signals depending on multiple factors, including the number of signals received. We encourage applicants to discuss preference signaling strategies with advisors and focus on signaling programs in which they have genuine interest.
Recommendations to Selection Committees and Program Directors
The intent of the supplemental application is to provide a more meaningful picture of applicants and their experiences and preferences, with the goal of optimizing applicant-program fit. Programs should explicitly define for themselves the applicant characteristics and experiences they prioritize as well as their program goals. The supplemental application offers the potential to streamline holistic application review based on these elements. The short essay answers in the past experiences section permit reviewers to quickly scan for important experiences that align with the program’s recruitment goals. Importantly, reviewers should not penalize applicants who have not completed the question regarding other impactful life experiences, as not all applicants will have relevant information to share.
Some programs may find the geographic preferences section more valuable than others. Multiple factors affect how much weight will be given to geographic preferences, including program location and other characteristics that affect the desirability of the program to applicants. The competitiveness of the field, relatively low match rate, and limited number of programs may lead to less emphasis on geographic preferences in dermatology compared to other specialties. The purpose of this section is not to exclude applicants but to give programs more information that may help with alignment.
Anecdotally, many dermatology program directors were most interested in the preference signaling section of the supplemental application. Programs should consider signals to be evidence of strong preliminary interest. Programs may utilize signals differently depending on many factors such as the overall competitiveness of the program, program location, and the total number of signals the program receives. We recommend that programs holistically review all applications accompanied by a signal. Programs that utilize a points system may choose to award a certain number of points for a signal to their program. A signal might have a higher value at a program that receives only a few signals; conversely, a program that receives a large number of signals might not place tremendous value on the signal but may use it as a tiebreaker between similarly qualified applicants. Preference signaling is solely a tool for application review; because applicants’ preferences may change after the interview process, signals should not be utilized during ranking.
Next Steps
For program directors who have excitedly awaited residency application reform, the supplemental ERAS application is an important first step. Ultimately, we hope the supplemental application supplants much of the current residency application, serving as an efficient high-yield tool for holistically evaluating applicants’ academic and service records, accomplishments, and training preferences. Arriving at a new application will undoubtedly take time and discussion among the various stakeholders. Please continue to complete surveys from the AAMC, as feedback is the best method for refining the tool to serve its intended purpose.
Optimization of the application content is only one component of the reforms needed to improve the application process. Even with a revamped application tool, holistic review is challenging when programs are inundated with an ever-increasing number of applications. As such, we encourage stakeholders to simultaneously consider other potential reforms, such as caps on the number of applications, to allow programs and applicants the best opportunity for a mutually successful match.
- Supplemental ERAS application. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed May 9, 2022. https://students-residents.aamc.org/applying-residencies-eras/supplemental-eras-application-eras-2023-cycle
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Supplemental application data and reports. Accessed May 9, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/students-residents/report/supplemental-eras-application-data-and-reports
- Supplemental ERAS application. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed May 9, 2022. https://students-residents.aamc.org/applying-residencies-eras/supplemental-eras-application-eras-2023-cycle
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Supplemental application data and reports. Accessed May 9, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/students-residents/report/supplemental-eras-application-data-and-reports
Practice Points
- The Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS) Supplemental Application was piloted in the 2021-2022 residency application cycle and was utilized by the vast majority of dermatology applicants and programs.
- Survey data suggested that both applicants and programs found the supplemental application useful, particularly the preference signaling portion.
- The supplemental application will return for the 2022-2023 application cycle and will be integrated into the MyERAS workstation platform for easier access by programs.
Going Beyond Hydroquinone: Alternative Skin Lightening Agents
Disorders of hyperpigmentation—melasma, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, lichen planus pigmentosus, erythema dyschromicum perstans, and pigmented contact dermatitis, among others—are common and challenging to treat. Although they can affect individuals of all skin types, they most commonly are seen in skin of color; in fact, dyspigmentation is one of the most common chief concerns for which individuals of color see a dermatologist.1,2
For many years, hydroquinone (HQ) was one of the main options available for use as a lightening agent. Although effective, it has the risk of causing irritant dermatitis, potentially leading to further dyspigmentation, in addition to the risk of ochronosis with long-term use. It remains an important and useful treatment for pigmentary disorders, but there are numerous other lightening agents that also can be considered in the treatment of disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Herein, we provide recommendations for traditional and newer non-HQ lightening agents that can be considered when treating disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Traditional Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Retinoids—Retinoids are topical vitamin A derivatives that have been used safely and effectively for decades in the treatment of pigmentary disorders. Retinoids have multiple mechanisms of action in improving pigmentation. In addition to impeding tyrosinase induction, they inhibit pigment transfer to keratinocytes and lead to accelerated pigment loss due to epidermal shedding.3 Over-the-counter formulations include retinol, retinaldehyde, and adapalene. Prescription formulations include tretinoin and tazarotene in different strengths and vehicle formulations.4
Glycolic Acid—Glycolic acid is derived from sugarcane and is considered an α-hydroxy acid that leads to rapid desquamation of pigmented keratinocytes.5 Glycolic acid can not only be used in chemical peels but also in topical creams. It is the most common α-hydroxy acid peel and is sometimes paired with HQ and other topical lightening agents for increased penetration. Glycolic acid peels are available in concentrations of 20% to 70% and can be used at various depths. When used incorrectly, it can cause redness, burning, and even skin discoloration; however, when used at the proper concentrations and depth according to Fitzpatrick skin type, there typically are no notable adverse effects, and clinical results are favorable.
Kojic Acid—Kojic acid is a natural metabolite derived from fungi and is widely used in Asian countries. It works by inhibiting the catecholase activity of tyrosinase6 and typically is available in concentrations of 1% to 4%. A study suggested that a concentration of 1% or less typically is safe to use for prolonged periods without adverse effects. Although not more effective than HQ as a monotherapy, kojic acid has been shown to haveimproved efficacy when used in combination with other lightening agents.7
Azelaic Acid—Azelaic acid works by inhibiting tyrosinase, mitochondrial oxidoreductase activation, and DNA synthesis. It preferentially targets heavily pigmented melanocytes and possesses anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.8 A 20% concentration of azelaic acid was compared to HQ 4% for the treatment of melasma, and results revealed that the liposomal form of azelaic acid was considerably more tolerable than HQ 4% and also more effective.9
Licorice Extracts—Licorice extracts have been safely used in several cosmeceutical skin lightening products.10 The main active compounds in licorice root are glabridin and liquiritin, which work to disperse melanin. These compounds often are used topically at concentrations of 10% to 40%. A study by Amer and Metwalli11 found that topical liquiritin produced a reduction of pigmentary intensity, with 80% of patients showing an excellent response, which was described as no difference between the previously pigmented area and the normal skin surrounding it.
Aloesin—Aloesin is a low-molecular-weight glycoprotein found in aloe vera plants. Its mechanism of action includes competitive inhibition of the dihydroxyphenylalanine oxidation site, resulting in the inhibition of tyrosinase.12 It often is combined with arbutin for an enhanced lightening effect.
Niacinamide—Niacinamide is a form of vitamin B3 that works by suppressing the transfer of melanosomes to keratinocytes.13 In addition to its skin lightening effects, it also is photoprotective and antimicrobial, and its tolerability and safety have led to its inclusion in many cosmeceutical and prescription products.14
Ascorbic Acid—Ascorbic acid affects the monopherase activity of tyrosinase, thus reducing the synthesis of melanin. It also serves as an antioxidant in the skin by preventing the production of free radicals that can induce melanogenesis.15 Although it tends to be well tolerated with a low adverse effect profile, its relative instability and varying permeability can present a challenge. It is less effective as a monotherapy, so it often is combined with other lightening ingredients for greater efficacy.
Corticosteroids—Topical corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory and impact melanogenesis, though the mechanism of action of the latter has not been fully elucidated.16,17 Low- to mid-potency topical steroids often are used in conjunction with skin lightening products to diminish irritation and decrease inflammation.18 However, prolonged use of corticosteroids can lead to cutaneous adverse effects such as striae, hypopigmentation, and acne, as well as systemic side effects if there is sufficient absorption over time.
Soybean Extracts—Soybean extracts contain serine protease inhibitors that reduce the transfer of melanosomes into keratinocytes by inhibiting the PAR-2 (protease-activated receptor 2) pathway.19,20
Ellagic Acid—Ellagic acid is found in common plants such as eucalyptus and strawberry as well as green tea.21 It works as an antioxidant and decreases melanogenesis through inhibition of tyrosinase activity.
Paper Mulberry—Paper mulberry extract comes from the roots of the Broussonetia papyrifera tree and functions by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. It is widely used in South Africa and Europe.22
Resveratrol—Resveratrol is an ingredient extracted from Morus alba L and functions as an antimelanogentic agent by directly inhibiting tyrosinase as well as transcriptional and posttranscriptional processing of tyrosinase.23 It also holds antiproliferative, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties and has widely been used for antiaging and skin lightening purposes.24
Newer Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Silymarin—Silymarin (also known as milk thistle [Silybum marianum]), is a polyphenolic flavonoid that possesses anticarcinogenic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. It prevents melanin production in a dose-dependent manner by inhibiting levodopa (L-dopa) oxidation activity of tyrosinase and also reduces the expression of tyrosinase protein.25 In combination with vitamins C and E and hexylresorcinol, silymarin has been found to reduce the effects of photodamage, brighten skin, improve evenness and lines, as well as improve global facial appearance.26
Malassezin—Malassezin is an indole produced by Malessezia furfur yeast and has recently been investigated for melanogenesis suppression. Grimes et al27 assessed the efficacy of topical malassezin in 7 patients with facial hyperpigmentation applied twice daily for 14 weeks. Punch biopsies were taken at weeks 0, 8, 14, and 22. Biopsies from weeks 8 and 14 demonstrated reduced epidermal melanin compared to baseline in all participants; however, at 22 weeks, biopsies showed no difference in melanin content compared to baseline, indicating a temporary process induced by the malassezin.27 More clinical studies are needed to investigate this further.
N-acetyl-glucosamine—N-acetyl-glucosamine is an aminosaccharide that inhibits the glycosylation of tyrosinase as well as its function in melanogenesis.28 It is synthesized and included in topical products for wound healing, rhytides, moisturization, and pigmentation disorders.
Topical Tranexamic Acid—Tranexamic acid traditionally has been used orally for the treatment of menorrhagia but also has been found to be beneficial as a therapy for hyperpigmentation and erythema. Tranexamic acid interferes with plasmin activity, thus indirectly inhibiting melanogenesis while also inhibiting angiogenesis by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors.29 It also leads to an increase in the levels of β-endorphin and μ-opioid receptors as well as the expression of estrogen receptor β on the surface of mast cells.30 Its oral benefit led to the development of topical formulations, typically in 2% to 5% concentrations. It has proven particularly beneficial in the treatment of melasma due to its effects on improving pigmentation, erythema, and skin barrier function.31 Topical tranexamic acid has a relatively high safety profile, with minor side effects such as transient skin irritation and erythema being reported.32
Cysteamine—Cysteamine inhibits tyrosinase, peroxidase, and chelating copper ions necessary for melanogenesis. It has proven to be effective in treating melasma and chronic severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation when used in a 5% cream formulation.33,34 Lima et al35 were the first to compare the effects of topical cysteamine to HQ in the treatment of facial melasma. They found that the mean reduction in modified Melasma Area and Severity Index score was 24% for cysteamine and 41% for HQ after 60 days. There were no severe adverse effects with either treatment group.35
Final Thoughts
Hydroquinone remains the gold standard for treatment of hyperpigmentation; however, its side-effect profile and risk of ochronosis with long-term use has ushered in various other safe and effective skin lightening agents that can be used as monotherapies or in combination with other lightening agents. Many of these products also can be used effectively with procedural treatments such as chemical peels, lasers, and microneedling for enhanced absorption and efficacy. As newer agents are developed, additional well-designed studies will be needed to determine their safety and efficacy in different skin types as well as their role in the treatment of pigmentary disorders.
- Woolery-Lloyd H, Kammer JN. Treatment of hyperpigmentation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:171-175. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2011.06.004
- Desai SR. Hyperpigmentation therapy: a review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:13-17.
- Kligman AM, Willis I. A new formula for depigmenting human skin. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:40-48.
- Kligman AM, Grove GL, Hirose R, et al. Topical tretinoin for photoaged skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15(4 pt 2):836-859. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(86)70242-9
- Sharad J. Glycolic acid peel therapy—a current review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:281-288. doi:10.2147/CCID.S34029
- Nautiyal A, Wairkar S. Management of hyperpigmentation: current treatments and emerging therapies. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:1000-1014. doi:10.1111/pcmr.12986
- Saeedi M, Eslamifar M, Khezri K. Kojic acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:582-593. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.006
- Schulte BC, Wu W, Rosen T. Azelaic acid: evidence-based update on mechanism of action and clinical application. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:964-968.
- Akl EM. Liposomal azelaic acid 20% cream vs hydroquinone 4% cream as adjuvant to oral tranexamic acid in melasma: a comparative study [published online April 7, 2021]. J Dermatol Treat. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.1905765
- Holloway VL. Ethnic cosmetic products. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:743-749. doi:10.1016/s0733-8635(03)00089-5
- Amer M, Metwalli M. Topical liquiritin improves melasma. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:299-301. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00943.x
- Jones K, Hughes J, Hong M, et al. Modulation of melanogenesis by aloesin: a competitive inhibitor of tyrosinase. Pigment Cell Res. 2002;15:335-340. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2002.02014.x
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, et al. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:20-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04834.x
- Wohlrab J, Kreft D. Niacinamide—mechanisms of action and its topical use in dermatology. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;27:311-315. doi:10.1159/000359974
- Fitzpatrick RE, Rostan EF. Double-blind, half-face study comparing topical vitamin C and vehicle for rejuvenation of photodamage. Dermatol Surg. 2002;28:231-236. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.01129.x
- Mehta AB, Nadkarni NJ, Patil SP, et al. Topical corticosteroids in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016;82:371-378. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.178903
- Petit L, Piérard GE. Skin-lightening products revisited. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2003;25:169-181. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2003.00182.x
- Kanwar AJ, Dhar S, Kaur S. Treatment of melasma with potent topical corticosteroids. Dermatol Basel Switz. 1994;188:170. doi:10.1159/000247129
- Paine C, Sharlow E, Liebel F, et al. An alternative approach to depigmentation by soybean extracts via inhibition of the PAR-2 pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:587-595. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2001.01291.x
- Seiberg M, Paine C, Sharlow E, et al. Inhibition of melanosome transfer results in skin lightening. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:162-167. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00035.x
- Shimogaki H, Tanaka Y, Tamai H, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ellagic acid on melanogenesis inhibition. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2000;22:291-303. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2000.00023.x
- Rendon MI, Gaviria JI. Review of skin-lightening agents. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31(7 pt 2):886-889; discussion 889. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31736
- Na JI, Shin JW, Choi HR, et al. Resveratrol as a multifunctional topical hypopigmenting agent [published online February 22, 2019]. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:956. doi:10.3390/ijms20040956
- Ratz-Łyko A, Arct J. Resveratrol as an active ingredient for cosmetic and dermatological applications: a review. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2019;21:84-90. doi:10.1080/14764172.2018.1469767
- Choo SJ, Ryoo IJ, Kim YH, et al. Silymarin inhibits melanin synthesis in melanocyte cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009;61:663-667. doi:10.1211/jpp/61.05.0016
- Draelos ZD, Diaz I, Cohen A, et al. A novel skin brightening topical technology. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:3280-3285. doi:10.1111/jocd.13741
- Grimes P, Bhawan J, Howell M, et al. Histopathological changes induced by malassezin: a novel natural microbiome indole for treatment of facial hyperpigmentation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:141-145. doi:10.36849/jdd.6596
- Bissett DL. Glucosamine: an ingredient with skin and other benefits. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2006;5:309-315. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2006.00277.x
- Zhu JW, Ni YJ, Tong XY, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits angiogenesis and melanogenesis in vitro by targeting VEGF receptors. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17:903-911. doi:10.7150/ijms.44188
- Hiramoto K, Yamate Y, Sugiyama D, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits the plasma and non-irradiated skin markers of photoaging induced by long-term UVA eye irradiation in female mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:54-58. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.146
- da Silva Souza ID, Lampe L, Winn D. New topical tranexamic acid derivative for the improvement of hyperpigmentation and inflammation in the sun-damaged skin. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:561-565. doi:10.1111/jocd.13545
- Kim HJ, Moon SH, Cho SH, et al. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in melasma: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:776-781. doi:10.2340/00015555-2668
- Mathe N, Balogun M, Yoo J. A case report on the use of topical cysteamine 5% cream in the management of refractory postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) resistant to triple combination cream (hydroquinone, topical corticosteroids, and retinoids). J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:204-206. doi:10.1111/jocd.13755
- Mansouri P, Farshi S, Hashemi Z, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of cysteamine 5% cream in the treatment of epidermal melasma: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:209-217. doi:10.1111/bjd.13424
- Lima PB, Dias JAF, Cassiano D, et al. A comparative study of topical 5% cysteamine versus 4% hydroquinone in the treatment of facial melasma in women. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1531-1536. doi:10.1111/ijd.15146
Disorders of hyperpigmentation—melasma, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, lichen planus pigmentosus, erythema dyschromicum perstans, and pigmented contact dermatitis, among others—are common and challenging to treat. Although they can affect individuals of all skin types, they most commonly are seen in skin of color; in fact, dyspigmentation is one of the most common chief concerns for which individuals of color see a dermatologist.1,2
For many years, hydroquinone (HQ) was one of the main options available for use as a lightening agent. Although effective, it has the risk of causing irritant dermatitis, potentially leading to further dyspigmentation, in addition to the risk of ochronosis with long-term use. It remains an important and useful treatment for pigmentary disorders, but there are numerous other lightening agents that also can be considered in the treatment of disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Herein, we provide recommendations for traditional and newer non-HQ lightening agents that can be considered when treating disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Traditional Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Retinoids—Retinoids are topical vitamin A derivatives that have been used safely and effectively for decades in the treatment of pigmentary disorders. Retinoids have multiple mechanisms of action in improving pigmentation. In addition to impeding tyrosinase induction, they inhibit pigment transfer to keratinocytes and lead to accelerated pigment loss due to epidermal shedding.3 Over-the-counter formulations include retinol, retinaldehyde, and adapalene. Prescription formulations include tretinoin and tazarotene in different strengths and vehicle formulations.4
Glycolic Acid—Glycolic acid is derived from sugarcane and is considered an α-hydroxy acid that leads to rapid desquamation of pigmented keratinocytes.5 Glycolic acid can not only be used in chemical peels but also in topical creams. It is the most common α-hydroxy acid peel and is sometimes paired with HQ and other topical lightening agents for increased penetration. Glycolic acid peels are available in concentrations of 20% to 70% and can be used at various depths. When used incorrectly, it can cause redness, burning, and even skin discoloration; however, when used at the proper concentrations and depth according to Fitzpatrick skin type, there typically are no notable adverse effects, and clinical results are favorable.
Kojic Acid—Kojic acid is a natural metabolite derived from fungi and is widely used in Asian countries. It works by inhibiting the catecholase activity of tyrosinase6 and typically is available in concentrations of 1% to 4%. A study suggested that a concentration of 1% or less typically is safe to use for prolonged periods without adverse effects. Although not more effective than HQ as a monotherapy, kojic acid has been shown to haveimproved efficacy when used in combination with other lightening agents.7
Azelaic Acid—Azelaic acid works by inhibiting tyrosinase, mitochondrial oxidoreductase activation, and DNA synthesis. It preferentially targets heavily pigmented melanocytes and possesses anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.8 A 20% concentration of azelaic acid was compared to HQ 4% for the treatment of melasma, and results revealed that the liposomal form of azelaic acid was considerably more tolerable than HQ 4% and also more effective.9
Licorice Extracts—Licorice extracts have been safely used in several cosmeceutical skin lightening products.10 The main active compounds in licorice root are glabridin and liquiritin, which work to disperse melanin. These compounds often are used topically at concentrations of 10% to 40%. A study by Amer and Metwalli11 found that topical liquiritin produced a reduction of pigmentary intensity, with 80% of patients showing an excellent response, which was described as no difference between the previously pigmented area and the normal skin surrounding it.
Aloesin—Aloesin is a low-molecular-weight glycoprotein found in aloe vera plants. Its mechanism of action includes competitive inhibition of the dihydroxyphenylalanine oxidation site, resulting in the inhibition of tyrosinase.12 It often is combined with arbutin for an enhanced lightening effect.
Niacinamide—Niacinamide is a form of vitamin B3 that works by suppressing the transfer of melanosomes to keratinocytes.13 In addition to its skin lightening effects, it also is photoprotective and antimicrobial, and its tolerability and safety have led to its inclusion in many cosmeceutical and prescription products.14
Ascorbic Acid—Ascorbic acid affects the monopherase activity of tyrosinase, thus reducing the synthesis of melanin. It also serves as an antioxidant in the skin by preventing the production of free radicals that can induce melanogenesis.15 Although it tends to be well tolerated with a low adverse effect profile, its relative instability and varying permeability can present a challenge. It is less effective as a monotherapy, so it often is combined with other lightening ingredients for greater efficacy.
Corticosteroids—Topical corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory and impact melanogenesis, though the mechanism of action of the latter has not been fully elucidated.16,17 Low- to mid-potency topical steroids often are used in conjunction with skin lightening products to diminish irritation and decrease inflammation.18 However, prolonged use of corticosteroids can lead to cutaneous adverse effects such as striae, hypopigmentation, and acne, as well as systemic side effects if there is sufficient absorption over time.
Soybean Extracts—Soybean extracts contain serine protease inhibitors that reduce the transfer of melanosomes into keratinocytes by inhibiting the PAR-2 (protease-activated receptor 2) pathway.19,20
Ellagic Acid—Ellagic acid is found in common plants such as eucalyptus and strawberry as well as green tea.21 It works as an antioxidant and decreases melanogenesis through inhibition of tyrosinase activity.
Paper Mulberry—Paper mulberry extract comes from the roots of the Broussonetia papyrifera tree and functions by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. It is widely used in South Africa and Europe.22
Resveratrol—Resveratrol is an ingredient extracted from Morus alba L and functions as an antimelanogentic agent by directly inhibiting tyrosinase as well as transcriptional and posttranscriptional processing of tyrosinase.23 It also holds antiproliferative, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties and has widely been used for antiaging and skin lightening purposes.24
Newer Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Silymarin—Silymarin (also known as milk thistle [Silybum marianum]), is a polyphenolic flavonoid that possesses anticarcinogenic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. It prevents melanin production in a dose-dependent manner by inhibiting levodopa (L-dopa) oxidation activity of tyrosinase and also reduces the expression of tyrosinase protein.25 In combination with vitamins C and E and hexylresorcinol, silymarin has been found to reduce the effects of photodamage, brighten skin, improve evenness and lines, as well as improve global facial appearance.26
Malassezin—Malassezin is an indole produced by Malessezia furfur yeast and has recently been investigated for melanogenesis suppression. Grimes et al27 assessed the efficacy of topical malassezin in 7 patients with facial hyperpigmentation applied twice daily for 14 weeks. Punch biopsies were taken at weeks 0, 8, 14, and 22. Biopsies from weeks 8 and 14 demonstrated reduced epidermal melanin compared to baseline in all participants; however, at 22 weeks, biopsies showed no difference in melanin content compared to baseline, indicating a temporary process induced by the malassezin.27 More clinical studies are needed to investigate this further.
N-acetyl-glucosamine—N-acetyl-glucosamine is an aminosaccharide that inhibits the glycosylation of tyrosinase as well as its function in melanogenesis.28 It is synthesized and included in topical products for wound healing, rhytides, moisturization, and pigmentation disorders.
Topical Tranexamic Acid—Tranexamic acid traditionally has been used orally for the treatment of menorrhagia but also has been found to be beneficial as a therapy for hyperpigmentation and erythema. Tranexamic acid interferes with plasmin activity, thus indirectly inhibiting melanogenesis while also inhibiting angiogenesis by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors.29 It also leads to an increase in the levels of β-endorphin and μ-opioid receptors as well as the expression of estrogen receptor β on the surface of mast cells.30 Its oral benefit led to the development of topical formulations, typically in 2% to 5% concentrations. It has proven particularly beneficial in the treatment of melasma due to its effects on improving pigmentation, erythema, and skin barrier function.31 Topical tranexamic acid has a relatively high safety profile, with minor side effects such as transient skin irritation and erythema being reported.32
Cysteamine—Cysteamine inhibits tyrosinase, peroxidase, and chelating copper ions necessary for melanogenesis. It has proven to be effective in treating melasma and chronic severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation when used in a 5% cream formulation.33,34 Lima et al35 were the first to compare the effects of topical cysteamine to HQ in the treatment of facial melasma. They found that the mean reduction in modified Melasma Area and Severity Index score was 24% for cysteamine and 41% for HQ after 60 days. There were no severe adverse effects with either treatment group.35
Final Thoughts
Hydroquinone remains the gold standard for treatment of hyperpigmentation; however, its side-effect profile and risk of ochronosis with long-term use has ushered in various other safe and effective skin lightening agents that can be used as monotherapies or in combination with other lightening agents. Many of these products also can be used effectively with procedural treatments such as chemical peels, lasers, and microneedling for enhanced absorption and efficacy. As newer agents are developed, additional well-designed studies will be needed to determine their safety and efficacy in different skin types as well as their role in the treatment of pigmentary disorders.
Disorders of hyperpigmentation—melasma, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, lichen planus pigmentosus, erythema dyschromicum perstans, and pigmented contact dermatitis, among others—are common and challenging to treat. Although they can affect individuals of all skin types, they most commonly are seen in skin of color; in fact, dyspigmentation is one of the most common chief concerns for which individuals of color see a dermatologist.1,2
For many years, hydroquinone (HQ) was one of the main options available for use as a lightening agent. Although effective, it has the risk of causing irritant dermatitis, potentially leading to further dyspigmentation, in addition to the risk of ochronosis with long-term use. It remains an important and useful treatment for pigmentary disorders, but there are numerous other lightening agents that also can be considered in the treatment of disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Herein, we provide recommendations for traditional and newer non-HQ lightening agents that can be considered when treating disorders of hyperpigmentation.
Traditional Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Retinoids—Retinoids are topical vitamin A derivatives that have been used safely and effectively for decades in the treatment of pigmentary disorders. Retinoids have multiple mechanisms of action in improving pigmentation. In addition to impeding tyrosinase induction, they inhibit pigment transfer to keratinocytes and lead to accelerated pigment loss due to epidermal shedding.3 Over-the-counter formulations include retinol, retinaldehyde, and adapalene. Prescription formulations include tretinoin and tazarotene in different strengths and vehicle formulations.4
Glycolic Acid—Glycolic acid is derived from sugarcane and is considered an α-hydroxy acid that leads to rapid desquamation of pigmented keratinocytes.5 Glycolic acid can not only be used in chemical peels but also in topical creams. It is the most common α-hydroxy acid peel and is sometimes paired with HQ and other topical lightening agents for increased penetration. Glycolic acid peels are available in concentrations of 20% to 70% and can be used at various depths. When used incorrectly, it can cause redness, burning, and even skin discoloration; however, when used at the proper concentrations and depth according to Fitzpatrick skin type, there typically are no notable adverse effects, and clinical results are favorable.
Kojic Acid—Kojic acid is a natural metabolite derived from fungi and is widely used in Asian countries. It works by inhibiting the catecholase activity of tyrosinase6 and typically is available in concentrations of 1% to 4%. A study suggested that a concentration of 1% or less typically is safe to use for prolonged periods without adverse effects. Although not more effective than HQ as a monotherapy, kojic acid has been shown to haveimproved efficacy when used in combination with other lightening agents.7
Azelaic Acid—Azelaic acid works by inhibiting tyrosinase, mitochondrial oxidoreductase activation, and DNA synthesis. It preferentially targets heavily pigmented melanocytes and possesses anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.8 A 20% concentration of azelaic acid was compared to HQ 4% for the treatment of melasma, and results revealed that the liposomal form of azelaic acid was considerably more tolerable than HQ 4% and also more effective.9
Licorice Extracts—Licorice extracts have been safely used in several cosmeceutical skin lightening products.10 The main active compounds in licorice root are glabridin and liquiritin, which work to disperse melanin. These compounds often are used topically at concentrations of 10% to 40%. A study by Amer and Metwalli11 found that topical liquiritin produced a reduction of pigmentary intensity, with 80% of patients showing an excellent response, which was described as no difference between the previously pigmented area and the normal skin surrounding it.
Aloesin—Aloesin is a low-molecular-weight glycoprotein found in aloe vera plants. Its mechanism of action includes competitive inhibition of the dihydroxyphenylalanine oxidation site, resulting in the inhibition of tyrosinase.12 It often is combined with arbutin for an enhanced lightening effect.
Niacinamide—Niacinamide is a form of vitamin B3 that works by suppressing the transfer of melanosomes to keratinocytes.13 In addition to its skin lightening effects, it also is photoprotective and antimicrobial, and its tolerability and safety have led to its inclusion in many cosmeceutical and prescription products.14
Ascorbic Acid—Ascorbic acid affects the monopherase activity of tyrosinase, thus reducing the synthesis of melanin. It also serves as an antioxidant in the skin by preventing the production of free radicals that can induce melanogenesis.15 Although it tends to be well tolerated with a low adverse effect profile, its relative instability and varying permeability can present a challenge. It is less effective as a monotherapy, so it often is combined with other lightening ingredients for greater efficacy.
Corticosteroids—Topical corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory and impact melanogenesis, though the mechanism of action of the latter has not been fully elucidated.16,17 Low- to mid-potency topical steroids often are used in conjunction with skin lightening products to diminish irritation and decrease inflammation.18 However, prolonged use of corticosteroids can lead to cutaneous adverse effects such as striae, hypopigmentation, and acne, as well as systemic side effects if there is sufficient absorption over time.
Soybean Extracts—Soybean extracts contain serine protease inhibitors that reduce the transfer of melanosomes into keratinocytes by inhibiting the PAR-2 (protease-activated receptor 2) pathway.19,20
Ellagic Acid—Ellagic acid is found in common plants such as eucalyptus and strawberry as well as green tea.21 It works as an antioxidant and decreases melanogenesis through inhibition of tyrosinase activity.
Paper Mulberry—Paper mulberry extract comes from the roots of the Broussonetia papyrifera tree and functions by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. It is widely used in South Africa and Europe.22
Resveratrol—Resveratrol is an ingredient extracted from Morus alba L and functions as an antimelanogentic agent by directly inhibiting tyrosinase as well as transcriptional and posttranscriptional processing of tyrosinase.23 It also holds antiproliferative, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties and has widely been used for antiaging and skin lightening purposes.24
Newer Non-HQ Lightening Agents
Silymarin—Silymarin (also known as milk thistle [Silybum marianum]), is a polyphenolic flavonoid that possesses anticarcinogenic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. It prevents melanin production in a dose-dependent manner by inhibiting levodopa (L-dopa) oxidation activity of tyrosinase and also reduces the expression of tyrosinase protein.25 In combination with vitamins C and E and hexylresorcinol, silymarin has been found to reduce the effects of photodamage, brighten skin, improve evenness and lines, as well as improve global facial appearance.26
Malassezin—Malassezin is an indole produced by Malessezia furfur yeast and has recently been investigated for melanogenesis suppression. Grimes et al27 assessed the efficacy of topical malassezin in 7 patients with facial hyperpigmentation applied twice daily for 14 weeks. Punch biopsies were taken at weeks 0, 8, 14, and 22. Biopsies from weeks 8 and 14 demonstrated reduced epidermal melanin compared to baseline in all participants; however, at 22 weeks, biopsies showed no difference in melanin content compared to baseline, indicating a temporary process induced by the malassezin.27 More clinical studies are needed to investigate this further.
N-acetyl-glucosamine—N-acetyl-glucosamine is an aminosaccharide that inhibits the glycosylation of tyrosinase as well as its function in melanogenesis.28 It is synthesized and included in topical products for wound healing, rhytides, moisturization, and pigmentation disorders.
Topical Tranexamic Acid—Tranexamic acid traditionally has been used orally for the treatment of menorrhagia but also has been found to be beneficial as a therapy for hyperpigmentation and erythema. Tranexamic acid interferes with plasmin activity, thus indirectly inhibiting melanogenesis while also inhibiting angiogenesis by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors.29 It also leads to an increase in the levels of β-endorphin and μ-opioid receptors as well as the expression of estrogen receptor β on the surface of mast cells.30 Its oral benefit led to the development of topical formulations, typically in 2% to 5% concentrations. It has proven particularly beneficial in the treatment of melasma due to its effects on improving pigmentation, erythema, and skin barrier function.31 Topical tranexamic acid has a relatively high safety profile, with minor side effects such as transient skin irritation and erythema being reported.32
Cysteamine—Cysteamine inhibits tyrosinase, peroxidase, and chelating copper ions necessary for melanogenesis. It has proven to be effective in treating melasma and chronic severe postinflammatory hyperpigmentation when used in a 5% cream formulation.33,34 Lima et al35 were the first to compare the effects of topical cysteamine to HQ in the treatment of facial melasma. They found that the mean reduction in modified Melasma Area and Severity Index score was 24% for cysteamine and 41% for HQ after 60 days. There were no severe adverse effects with either treatment group.35
Final Thoughts
Hydroquinone remains the gold standard for treatment of hyperpigmentation; however, its side-effect profile and risk of ochronosis with long-term use has ushered in various other safe and effective skin lightening agents that can be used as monotherapies or in combination with other lightening agents. Many of these products also can be used effectively with procedural treatments such as chemical peels, lasers, and microneedling for enhanced absorption and efficacy. As newer agents are developed, additional well-designed studies will be needed to determine their safety and efficacy in different skin types as well as their role in the treatment of pigmentary disorders.
- Woolery-Lloyd H, Kammer JN. Treatment of hyperpigmentation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:171-175. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2011.06.004
- Desai SR. Hyperpigmentation therapy: a review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:13-17.
- Kligman AM, Willis I. A new formula for depigmenting human skin. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:40-48.
- Kligman AM, Grove GL, Hirose R, et al. Topical tretinoin for photoaged skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15(4 pt 2):836-859. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(86)70242-9
- Sharad J. Glycolic acid peel therapy—a current review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:281-288. doi:10.2147/CCID.S34029
- Nautiyal A, Wairkar S. Management of hyperpigmentation: current treatments and emerging therapies. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:1000-1014. doi:10.1111/pcmr.12986
- Saeedi M, Eslamifar M, Khezri K. Kojic acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:582-593. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.006
- Schulte BC, Wu W, Rosen T. Azelaic acid: evidence-based update on mechanism of action and clinical application. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:964-968.
- Akl EM. Liposomal azelaic acid 20% cream vs hydroquinone 4% cream as adjuvant to oral tranexamic acid in melasma: a comparative study [published online April 7, 2021]. J Dermatol Treat. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.1905765
- Holloway VL. Ethnic cosmetic products. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:743-749. doi:10.1016/s0733-8635(03)00089-5
- Amer M, Metwalli M. Topical liquiritin improves melasma. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:299-301. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00943.x
- Jones K, Hughes J, Hong M, et al. Modulation of melanogenesis by aloesin: a competitive inhibitor of tyrosinase. Pigment Cell Res. 2002;15:335-340. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2002.02014.x
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, et al. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:20-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04834.x
- Wohlrab J, Kreft D. Niacinamide—mechanisms of action and its topical use in dermatology. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;27:311-315. doi:10.1159/000359974
- Fitzpatrick RE, Rostan EF. Double-blind, half-face study comparing topical vitamin C and vehicle for rejuvenation of photodamage. Dermatol Surg. 2002;28:231-236. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.01129.x
- Mehta AB, Nadkarni NJ, Patil SP, et al. Topical corticosteroids in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016;82:371-378. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.178903
- Petit L, Piérard GE. Skin-lightening products revisited. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2003;25:169-181. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2003.00182.x
- Kanwar AJ, Dhar S, Kaur S. Treatment of melasma with potent topical corticosteroids. Dermatol Basel Switz. 1994;188:170. doi:10.1159/000247129
- Paine C, Sharlow E, Liebel F, et al. An alternative approach to depigmentation by soybean extracts via inhibition of the PAR-2 pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:587-595. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2001.01291.x
- Seiberg M, Paine C, Sharlow E, et al. Inhibition of melanosome transfer results in skin lightening. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:162-167. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00035.x
- Shimogaki H, Tanaka Y, Tamai H, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ellagic acid on melanogenesis inhibition. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2000;22:291-303. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2000.00023.x
- Rendon MI, Gaviria JI. Review of skin-lightening agents. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31(7 pt 2):886-889; discussion 889. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31736
- Na JI, Shin JW, Choi HR, et al. Resveratrol as a multifunctional topical hypopigmenting agent [published online February 22, 2019]. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:956. doi:10.3390/ijms20040956
- Ratz-Łyko A, Arct J. Resveratrol as an active ingredient for cosmetic and dermatological applications: a review. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2019;21:84-90. doi:10.1080/14764172.2018.1469767
- Choo SJ, Ryoo IJ, Kim YH, et al. Silymarin inhibits melanin synthesis in melanocyte cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009;61:663-667. doi:10.1211/jpp/61.05.0016
- Draelos ZD, Diaz I, Cohen A, et al. A novel skin brightening topical technology. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:3280-3285. doi:10.1111/jocd.13741
- Grimes P, Bhawan J, Howell M, et al. Histopathological changes induced by malassezin: a novel natural microbiome indole for treatment of facial hyperpigmentation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:141-145. doi:10.36849/jdd.6596
- Bissett DL. Glucosamine: an ingredient with skin and other benefits. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2006;5:309-315. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2006.00277.x
- Zhu JW, Ni YJ, Tong XY, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits angiogenesis and melanogenesis in vitro by targeting VEGF receptors. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17:903-911. doi:10.7150/ijms.44188
- Hiramoto K, Yamate Y, Sugiyama D, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits the plasma and non-irradiated skin markers of photoaging induced by long-term UVA eye irradiation in female mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:54-58. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.146
- da Silva Souza ID, Lampe L, Winn D. New topical tranexamic acid derivative for the improvement of hyperpigmentation and inflammation in the sun-damaged skin. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:561-565. doi:10.1111/jocd.13545
- Kim HJ, Moon SH, Cho SH, et al. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in melasma: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:776-781. doi:10.2340/00015555-2668
- Mathe N, Balogun M, Yoo J. A case report on the use of topical cysteamine 5% cream in the management of refractory postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) resistant to triple combination cream (hydroquinone, topical corticosteroids, and retinoids). J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:204-206. doi:10.1111/jocd.13755
- Mansouri P, Farshi S, Hashemi Z, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of cysteamine 5% cream in the treatment of epidermal melasma: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:209-217. doi:10.1111/bjd.13424
- Lima PB, Dias JAF, Cassiano D, et al. A comparative study of topical 5% cysteamine versus 4% hydroquinone in the treatment of facial melasma in women. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1531-1536. doi:10.1111/ijd.15146
- Woolery-Lloyd H, Kammer JN. Treatment of hyperpigmentation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:171-175. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2011.06.004
- Desai SR. Hyperpigmentation therapy: a review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:13-17.
- Kligman AM, Willis I. A new formula for depigmenting human skin. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:40-48.
- Kligman AM, Grove GL, Hirose R, et al. Topical tretinoin for photoaged skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15(4 pt 2):836-859. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(86)70242-9
- Sharad J. Glycolic acid peel therapy—a current review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:281-288. doi:10.2147/CCID.S34029
- Nautiyal A, Wairkar S. Management of hyperpigmentation: current treatments and emerging therapies. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:1000-1014. doi:10.1111/pcmr.12986
- Saeedi M, Eslamifar M, Khezri K. Kojic acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:582-593. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.006
- Schulte BC, Wu W, Rosen T. Azelaic acid: evidence-based update on mechanism of action and clinical application. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:964-968.
- Akl EM. Liposomal azelaic acid 20% cream vs hydroquinone 4% cream as adjuvant to oral tranexamic acid in melasma: a comparative study [published online April 7, 2021]. J Dermatol Treat. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.1905765
- Holloway VL. Ethnic cosmetic products. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:743-749. doi:10.1016/s0733-8635(03)00089-5
- Amer M, Metwalli M. Topical liquiritin improves melasma. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:299-301. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00943.x
- Jones K, Hughes J, Hong M, et al. Modulation of melanogenesis by aloesin: a competitive inhibitor of tyrosinase. Pigment Cell Res. 2002;15:335-340. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2002.02014.x
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, et al. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:20-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04834.x
- Wohlrab J, Kreft D. Niacinamide—mechanisms of action and its topical use in dermatology. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;27:311-315. doi:10.1159/000359974
- Fitzpatrick RE, Rostan EF. Double-blind, half-face study comparing topical vitamin C and vehicle for rejuvenation of photodamage. Dermatol Surg. 2002;28:231-236. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.01129.x
- Mehta AB, Nadkarni NJ, Patil SP, et al. Topical corticosteroids in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016;82:371-378. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.178903
- Petit L, Piérard GE. Skin-lightening products revisited. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2003;25:169-181. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2003.00182.x
- Kanwar AJ, Dhar S, Kaur S. Treatment of melasma with potent topical corticosteroids. Dermatol Basel Switz. 1994;188:170. doi:10.1159/000247129
- Paine C, Sharlow E, Liebel F, et al. An alternative approach to depigmentation by soybean extracts via inhibition of the PAR-2 pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:587-595. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2001.01291.x
- Seiberg M, Paine C, Sharlow E, et al. Inhibition of melanosome transfer results in skin lightening. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:162-167. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00035.x
- Shimogaki H, Tanaka Y, Tamai H, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ellagic acid on melanogenesis inhibition. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2000;22:291-303. doi:10.1046/j.1467-2494.2000.00023.x
- Rendon MI, Gaviria JI. Review of skin-lightening agents. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31(7 pt 2):886-889; discussion 889. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31736
- Na JI, Shin JW, Choi HR, et al. Resveratrol as a multifunctional topical hypopigmenting agent [published online February 22, 2019]. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:956. doi:10.3390/ijms20040956
- Ratz-Łyko A, Arct J. Resveratrol as an active ingredient for cosmetic and dermatological applications: a review. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2019;21:84-90. doi:10.1080/14764172.2018.1469767
- Choo SJ, Ryoo IJ, Kim YH, et al. Silymarin inhibits melanin synthesis in melanocyte cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009;61:663-667. doi:10.1211/jpp/61.05.0016
- Draelos ZD, Diaz I, Cohen A, et al. A novel skin brightening topical technology. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:3280-3285. doi:10.1111/jocd.13741
- Grimes P, Bhawan J, Howell M, et al. Histopathological changes induced by malassezin: a novel natural microbiome indole for treatment of facial hyperpigmentation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:141-145. doi:10.36849/jdd.6596
- Bissett DL. Glucosamine: an ingredient with skin and other benefits. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2006;5:309-315. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2006.00277.x
- Zhu JW, Ni YJ, Tong XY, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits angiogenesis and melanogenesis in vitro by targeting VEGF receptors. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17:903-911. doi:10.7150/ijms.44188
- Hiramoto K, Yamate Y, Sugiyama D, et al. Tranexamic acid inhibits the plasma and non-irradiated skin markers of photoaging induced by long-term UVA eye irradiation in female mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:54-58. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.146
- da Silva Souza ID, Lampe L, Winn D. New topical tranexamic acid derivative for the improvement of hyperpigmentation and inflammation in the sun-damaged skin. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:561-565. doi:10.1111/jocd.13545
- Kim HJ, Moon SH, Cho SH, et al. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in melasma: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:776-781. doi:10.2340/00015555-2668
- Mathe N, Balogun M, Yoo J. A case report on the use of topical cysteamine 5% cream in the management of refractory postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) resistant to triple combination cream (hydroquinone, topical corticosteroids, and retinoids). J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:204-206. doi:10.1111/jocd.13755
- Mansouri P, Farshi S, Hashemi Z, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of cysteamine 5% cream in the treatment of epidermal melasma: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:209-217. doi:10.1111/bjd.13424
- Lima PB, Dias JAF, Cassiano D, et al. A comparative study of topical 5% cysteamine versus 4% hydroquinone in the treatment of facial melasma in women. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1531-1536. doi:10.1111/ijd.15146
Rippled Macules and Papules on the Legs
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Amyloidosis
A punch biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of cutaneous amyloidosis, which is characterized by the deposition of amyloid proteins in the skin without systemic involvement. Subtypes of cutaneous amyloidosis include lichenoid, macular, and nodular amyloidosis. A mixed or biphasic amyloidosis can occur when both lichenoid and macular lesions are present.1 Lichenoid and macular amyloidosis generally are characterized by moderate to severe pruritus. Lichenoid amyloidosis favors the shins, calves, ankles, and extensor extremities; macular amyloidosis has a predilection for the interscapular area and less frequently the upper arms, chest, and thighs.2 Atypical variants also have been reported, including amyloidosis cutis dyschromica, poikilodermalike amyloidosis, and bullous amyloidosis, as well as incontinentia pigmenti–like, linear, and nevoid types.3 Macular amyloidosis has been reported to occur in association with progressive systemic sclerosis, primary biliary cirrhosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, paronychia, and multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2.2
Acanthosis nigricans typically presents on the neck and intertriginous areas as velvety hyperpigmented plaques. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis also appears as slightly elevated papules; however, it occurs in the intermammary region in a reticulated pattern. Ichthyosis vulgaris also may occur on the lower extremities but presents with adherent large scales rather than papules. Keratosis pilaris may present on the proximal lower extremities with smaller, folliculocentric, fleshcolored to pink papules.
Treatment of cutaneous amyloidosis has long been challenging for dermatologists. The primary focus should be treatment of any underlying disease that is causing the pruritus and subsequent manipulation of skin lesions. Topical calcipotriol, phototherapy, oral cyclophosphamide, and Nd:YAG laser have demonstrated beneficial outcomes. IL-31 antibodies may be a potential future treatment.1
1. Weidner T, Illing T, Elsner P. Primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis: a systematic treatment review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:629-642. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0278-9 2. Rasi A, Khatami A, Javaheri SM. Macular amyloidosis: an assessment of prevalence, sex, and age. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:898-899. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2004.01935.x 3. Hamie L, Haddad I, Nasser N, et al. Primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis of keratinocyte origin: an update with emphasis on atypical clinical variants [published online July 21, 2021]. 2021;22:667-680. Am J Clin Dermatol. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00620-9
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Amyloidosis
A punch biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of cutaneous amyloidosis, which is characterized by the deposition of amyloid proteins in the skin without systemic involvement. Subtypes of cutaneous amyloidosis include lichenoid, macular, and nodular amyloidosis. A mixed or biphasic amyloidosis can occur when both lichenoid and macular lesions are present.1 Lichenoid and macular amyloidosis generally are characterized by moderate to severe pruritus. Lichenoid amyloidosis favors the shins, calves, ankles, and extensor extremities; macular amyloidosis has a predilection for the interscapular area and less frequently the upper arms, chest, and thighs.2 Atypical variants also have been reported, including amyloidosis cutis dyschromica, poikilodermalike amyloidosis, and bullous amyloidosis, as well as incontinentia pigmenti–like, linear, and nevoid types.3 Macular amyloidosis has been reported to occur in association with progressive systemic sclerosis, primary biliary cirrhosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, paronychia, and multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2.2
Acanthosis nigricans typically presents on the neck and intertriginous areas as velvety hyperpigmented plaques. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis also appears as slightly elevated papules; however, it occurs in the intermammary region in a reticulated pattern. Ichthyosis vulgaris also may occur on the lower extremities but presents with adherent large scales rather than papules. Keratosis pilaris may present on the proximal lower extremities with smaller, folliculocentric, fleshcolored to pink papules.
Treatment of cutaneous amyloidosis has long been challenging for dermatologists. The primary focus should be treatment of any underlying disease that is causing the pruritus and subsequent manipulation of skin lesions. Topical calcipotriol, phototherapy, oral cyclophosphamide, and Nd:YAG laser have demonstrated beneficial outcomes. IL-31 antibodies may be a potential future treatment.1
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Amyloidosis
A punch biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of cutaneous amyloidosis, which is characterized by the deposition of amyloid proteins in the skin without systemic involvement. Subtypes of cutaneous amyloidosis include lichenoid, macular, and nodular amyloidosis. A mixed or biphasic amyloidosis can occur when both lichenoid and macular lesions are present.1 Lichenoid and macular amyloidosis generally are characterized by moderate to severe pruritus. Lichenoid amyloidosis favors the shins, calves, ankles, and extensor extremities; macular amyloidosis has a predilection for the interscapular area and less frequently the upper arms, chest, and thighs.2 Atypical variants also have been reported, including amyloidosis cutis dyschromica, poikilodermalike amyloidosis, and bullous amyloidosis, as well as incontinentia pigmenti–like, linear, and nevoid types.3 Macular amyloidosis has been reported to occur in association with progressive systemic sclerosis, primary biliary cirrhosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, paronychia, and multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2.2
Acanthosis nigricans typically presents on the neck and intertriginous areas as velvety hyperpigmented plaques. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis also appears as slightly elevated papules; however, it occurs in the intermammary region in a reticulated pattern. Ichthyosis vulgaris also may occur on the lower extremities but presents with adherent large scales rather than papules. Keratosis pilaris may present on the proximal lower extremities with smaller, folliculocentric, fleshcolored to pink papules.
Treatment of cutaneous amyloidosis has long been challenging for dermatologists. The primary focus should be treatment of any underlying disease that is causing the pruritus and subsequent manipulation of skin lesions. Topical calcipotriol, phototherapy, oral cyclophosphamide, and Nd:YAG laser have demonstrated beneficial outcomes. IL-31 antibodies may be a potential future treatment.1
1. Weidner T, Illing T, Elsner P. Primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis: a systematic treatment review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:629-642. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0278-9 2. Rasi A, Khatami A, Javaheri SM. Macular amyloidosis: an assessment of prevalence, sex, and age. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:898-899. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2004.01935.x 3. Hamie L, Haddad I, Nasser N, et al. Primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis of keratinocyte origin: an update with emphasis on atypical clinical variants [published online July 21, 2021]. 2021;22:667-680. Am J Clin Dermatol. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00620-9
1. Weidner T, Illing T, Elsner P. Primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis: a systematic treatment review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:629-642. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0278-9 2. Rasi A, Khatami A, Javaheri SM. Macular amyloidosis: an assessment of prevalence, sex, and age. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:898-899. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2004.01935.x 3. Hamie L, Haddad I, Nasser N, et al. Primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis of keratinocyte origin: an update with emphasis on atypical clinical variants [published online July 21, 2021]. 2021;22:667-680. Am J Clin Dermatol. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00620-9
A 34-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with an intensely pruritic rash on the legs of 2 years’ duration. The pruritus had waxed and waned in intensity, and the skin lesions were refractory to treatment with low-potency topical steroids. She had no other chronic medical conditions and was not taking any other medications.
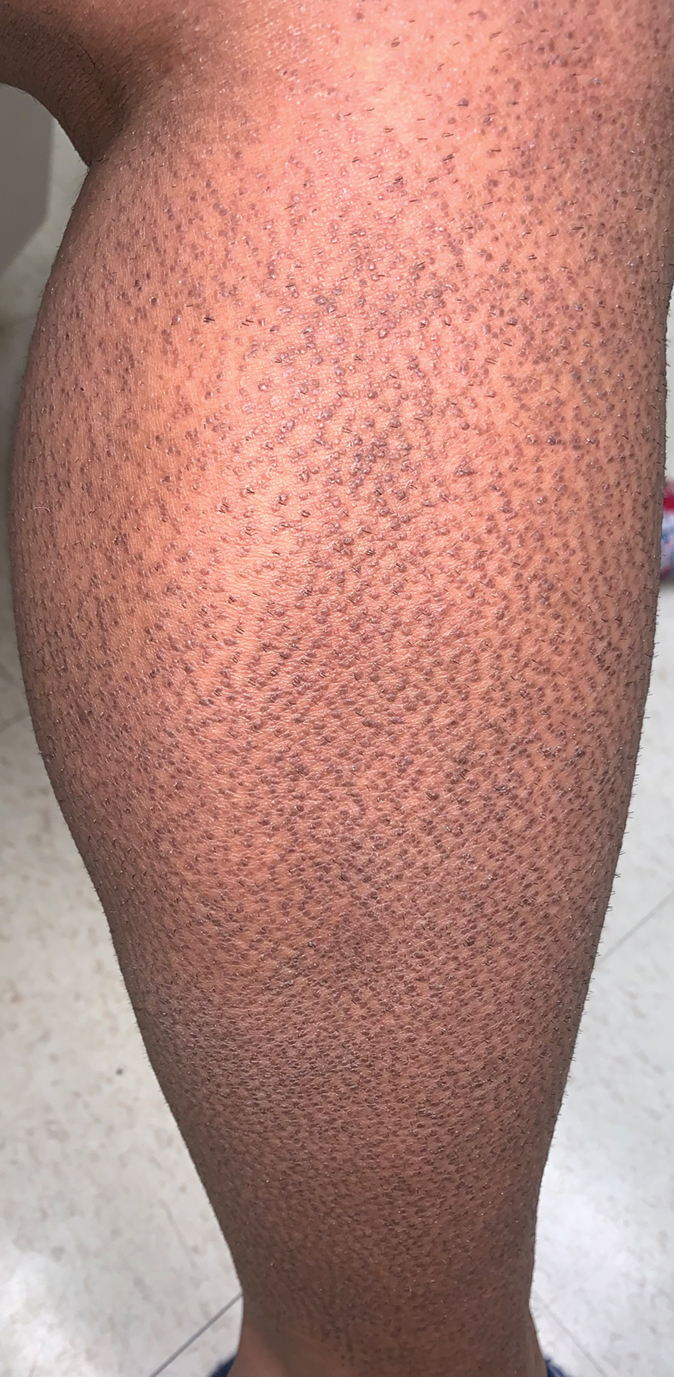
Pending further study, caution recommended in treating vitiligo patients with lasers, IPL
SAN DIEGO – The .
Those are the preliminary conclusions from a systematic review and survey of experts that Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, presented during a clinical abstract session at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
According to Dr. Wolkerstorfer, a dermatologist at Amsterdam University Medical Center, clinicians are reluctant to perform laser/intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments in patients with vitiligo because of the absence of clear guidelines, so he and his colleagues set out to investigate the risks of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo in patients with vitiligo and to seek out international consensus on recommendations from experts. “There is hardly any literature about it and certainly no guidelines,” he pointed out.
Dr. Wolkerstorfer and his colleagues designed three consecutive studies: A systematic review of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo; an international survey among 14 vitiligo experts from 10 countries about the occurrence of laser‐induced vitiligo, and a Delphi technique aimed at establishing a broad consensus about recommendations for safe use of lasers in vitiligo patients. At the time of the meeting, the Delphi process was still being carried out, so he did not discuss that study.
For the systematic review, the researchers found 11,073 unique hits on PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL using the terms “vitiligo,” “depigmentation,” “hypopigmentation,” and “leukoderma.” Only six case reports of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo were included in the final analysis. Of these, three had de novo vitiligo and three had vitiligo/halo nevi. These cases included two that occurred following treatment of port wine stains with the 585-nm laser; one that occurred following treatment of dyspigmentation with IPL; one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 1,064-nm laser, one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 755-nm laser, and one case that occurred following treatment of melasma with the ablative laser.
For the international survey of 14 experts from 10 countries, respondents said they had 10,670 new face-to-face vitiligo consultations in the past year. They reported that 30 of the vitiligo cases (0.3%) were likely caused by laser/IPL. Of these 30 cases, 18 (60%) had de novo vitiligo.
Of these cases, vitiligo occurred most frequently after laser hair reduction (47%), followed by use of the fractional laser (17%), and the ablative laser (13%). The interval between laser/IPL treatment and onset of vitiligo was 0-4 weeks in 27% of cases and 4-12 weeks in 57% of cases. Direct complications such as blistering, crusting, and erosions occurred in 57% of cases.
“Our conclusion is that laser and IPL-induced vitiligo is a rare phenomenon, and it often affects patients without prior vitiligo, which was really a surprise to us,” Dr. Wolkerstorfer said. “Complications seem to increase the risk,” he added.
“Despite the apparently low risk, we recommend caution [in patients with vitiligo], especially with aggressive laser procedures,” he said. “We recommend using conservative settings, not to treat active vitiligo patients ... and to perform test spots prior to treating large areas.” But he characterized this recommendation as “totally preliminary” pending results of the Delphi technique aimed at building consensus about laser/IPL treatments in vitiligo.
In an interview at the meeting, one of the session moderators, Oge Onwudiwe, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Alexandria, Va., said that as clinicians await results of the study’s Delphi consensus, current use of lasers and IPL in patients with vitiligo “is based on your clinical judgment and whether the vitiligo is active or inactive. If the patient has vitiligo and you’re doing laser hair removal in the armpit, they may get active lesions in that area, but they can cover it. So, they may take that as a ‘win’ with the risk. But if it can erupt in other areas, that’s a risk they must be willing to take.”
Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received grant or research funding from Lumenis, Novartis, and Avita Medical. He is an advisory board member for Incyte. Dr. Onwudiwe reported having no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – The .
Those are the preliminary conclusions from a systematic review and survey of experts that Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, presented during a clinical abstract session at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
According to Dr. Wolkerstorfer, a dermatologist at Amsterdam University Medical Center, clinicians are reluctant to perform laser/intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments in patients with vitiligo because of the absence of clear guidelines, so he and his colleagues set out to investigate the risks of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo in patients with vitiligo and to seek out international consensus on recommendations from experts. “There is hardly any literature about it and certainly no guidelines,” he pointed out.
Dr. Wolkerstorfer and his colleagues designed three consecutive studies: A systematic review of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo; an international survey among 14 vitiligo experts from 10 countries about the occurrence of laser‐induced vitiligo, and a Delphi technique aimed at establishing a broad consensus about recommendations for safe use of lasers in vitiligo patients. At the time of the meeting, the Delphi process was still being carried out, so he did not discuss that study.
For the systematic review, the researchers found 11,073 unique hits on PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL using the terms “vitiligo,” “depigmentation,” “hypopigmentation,” and “leukoderma.” Only six case reports of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo were included in the final analysis. Of these, three had de novo vitiligo and three had vitiligo/halo nevi. These cases included two that occurred following treatment of port wine stains with the 585-nm laser; one that occurred following treatment of dyspigmentation with IPL; one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 1,064-nm laser, one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 755-nm laser, and one case that occurred following treatment of melasma with the ablative laser.
For the international survey of 14 experts from 10 countries, respondents said they had 10,670 new face-to-face vitiligo consultations in the past year. They reported that 30 of the vitiligo cases (0.3%) were likely caused by laser/IPL. Of these 30 cases, 18 (60%) had de novo vitiligo.
Of these cases, vitiligo occurred most frequently after laser hair reduction (47%), followed by use of the fractional laser (17%), and the ablative laser (13%). The interval between laser/IPL treatment and onset of vitiligo was 0-4 weeks in 27% of cases and 4-12 weeks in 57% of cases. Direct complications such as blistering, crusting, and erosions occurred in 57% of cases.
“Our conclusion is that laser and IPL-induced vitiligo is a rare phenomenon, and it often affects patients without prior vitiligo, which was really a surprise to us,” Dr. Wolkerstorfer said. “Complications seem to increase the risk,” he added.
“Despite the apparently low risk, we recommend caution [in patients with vitiligo], especially with aggressive laser procedures,” he said. “We recommend using conservative settings, not to treat active vitiligo patients ... and to perform test spots prior to treating large areas.” But he characterized this recommendation as “totally preliminary” pending results of the Delphi technique aimed at building consensus about laser/IPL treatments in vitiligo.
In an interview at the meeting, one of the session moderators, Oge Onwudiwe, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Alexandria, Va., said that as clinicians await results of the study’s Delphi consensus, current use of lasers and IPL in patients with vitiligo “is based on your clinical judgment and whether the vitiligo is active or inactive. If the patient has vitiligo and you’re doing laser hair removal in the armpit, they may get active lesions in that area, but they can cover it. So, they may take that as a ‘win’ with the risk. But if it can erupt in other areas, that’s a risk they must be willing to take.”
Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received grant or research funding from Lumenis, Novartis, and Avita Medical. He is an advisory board member for Incyte. Dr. Onwudiwe reported having no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – The .
Those are the preliminary conclusions from a systematic review and survey of experts that Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, presented during a clinical abstract session at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
According to Dr. Wolkerstorfer, a dermatologist at Amsterdam University Medical Center, clinicians are reluctant to perform laser/intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments in patients with vitiligo because of the absence of clear guidelines, so he and his colleagues set out to investigate the risks of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo in patients with vitiligo and to seek out international consensus on recommendations from experts. “There is hardly any literature about it and certainly no guidelines,” he pointed out.
Dr. Wolkerstorfer and his colleagues designed three consecutive studies: A systematic review of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo; an international survey among 14 vitiligo experts from 10 countries about the occurrence of laser‐induced vitiligo, and a Delphi technique aimed at establishing a broad consensus about recommendations for safe use of lasers in vitiligo patients. At the time of the meeting, the Delphi process was still being carried out, so he did not discuss that study.
For the systematic review, the researchers found 11,073 unique hits on PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL using the terms “vitiligo,” “depigmentation,” “hypopigmentation,” and “leukoderma.” Only six case reports of laser/IPL-induced vitiligo were included in the final analysis. Of these, three had de novo vitiligo and three had vitiligo/halo nevi. These cases included two that occurred following treatment of port wine stains with the 585-nm laser; one that occurred following treatment of dyspigmentation with IPL; one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 1,064-nm laser, one that occurred following treatment of hypertrichosis with the 755-nm laser, and one case that occurred following treatment of melasma with the ablative laser.
For the international survey of 14 experts from 10 countries, respondents said they had 10,670 new face-to-face vitiligo consultations in the past year. They reported that 30 of the vitiligo cases (0.3%) were likely caused by laser/IPL. Of these 30 cases, 18 (60%) had de novo vitiligo.
Of these cases, vitiligo occurred most frequently after laser hair reduction (47%), followed by use of the fractional laser (17%), and the ablative laser (13%). The interval between laser/IPL treatment and onset of vitiligo was 0-4 weeks in 27% of cases and 4-12 weeks in 57% of cases. Direct complications such as blistering, crusting, and erosions occurred in 57% of cases.
“Our conclusion is that laser and IPL-induced vitiligo is a rare phenomenon, and it often affects patients without prior vitiligo, which was really a surprise to us,” Dr. Wolkerstorfer said. “Complications seem to increase the risk,” he added.
“Despite the apparently low risk, we recommend caution [in patients with vitiligo], especially with aggressive laser procedures,” he said. “We recommend using conservative settings, not to treat active vitiligo patients ... and to perform test spots prior to treating large areas.” But he characterized this recommendation as “totally preliminary” pending results of the Delphi technique aimed at building consensus about laser/IPL treatments in vitiligo.
In an interview at the meeting, one of the session moderators, Oge Onwudiwe, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Alexandria, Va., said that as clinicians await results of the study’s Delphi consensus, current use of lasers and IPL in patients with vitiligo “is based on your clinical judgment and whether the vitiligo is active or inactive. If the patient has vitiligo and you’re doing laser hair removal in the armpit, they may get active lesions in that area, but they can cover it. So, they may take that as a ‘win’ with the risk. But if it can erupt in other areas, that’s a risk they must be willing to take.”
Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received grant or research funding from Lumenis, Novartis, and Avita Medical. He is an advisory board member for Incyte. Dr. Onwudiwe reported having no disclosures.
AT ASLMS 2022
Surgical site infections not increased in immunocompromised patients after Mohs surgery
, suggesting that antibiotic prophylaxis, which is often used for these patients, may not be necessary, according to new research.
The retrospective cohort study found that “immunosuppressed patients had similar infection rates as immunocompetent patients following Mohs micrographic surgery,” first author Tuyet A. Nguyen, MD, of the department of dermatology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, told this news organization.
“Therefore, antibiotic prescribing patterns should not change simply due to immunosuppression. Furthermore, immunosuppressed patients appear to respond well to antibiotics and recover similarly to immunocompetent patients,” she said.
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
Mohs surgery is increasingly being performed for patients who are immunosuppressed because of the higher incidence of skin cancer in this group of patients and their higher risk of more aggressive skin cancers.
Overall, the rate of surgical site infections following Mohs surgery generally ranges from 0.5% to 2.4%. However, research is lacking on the risk among patients who are immunosuppressed and on how effective the use of prophylactic antibiotics is for these patients.
For the retrospective study, Dr. Nguyen and her colleagues evaluated data on 5,886 patients who underwent Mohs surgery at Cedars-Sinai between October 2014 and August 2021. Among these patients, 741 (12.6%) were immunocompromised.
Causes of immunosuppression in the cohort included the following: immunosuppression after transplant surgery; having HIV, chronic myeloid leukemia, multiple myeloma, or other hematogenous forms of immunosuppression; or immunosuppression related to other conditions, such as chronic inflammatory diseases.
Overall, postprocedural infections occurred in 1.6% (95) of patients, a rate that mirrors that of the general population, Dr. Nguyen noted. No significant differences in surgical site infection rates were observed between immunocompromised patients (2.1%, n = 15) and those who were immunocompetent (1.6%, n = 80; P = .30).
Importantly, among those who were immunocompromised, the rates of infection were not significantly different between those who did receive antibiotics (3.0%, n = 8) and those who did not receive antibiotics (1.5%, n = 7; P = .19).
The lack of a difference in surgical site infection rates among those who did and those who did not receive antibiotics extended to the entire study population (2.0% vs. 1.4%; P = .12).
The study cohort mainly comprised immunosuppressed transplant patients, notably, heart, lung, and kidney transplant patients. However, “even in this population, we did not see a higher rate of infection,” senior author Nima M. Gharavi, MD, PhD, director of dermatologic surgery and Mohs micrographic surgery and associate professor of medicine and pathology and laboratory medicine at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in an interview.
Yet the risk of infection among those patients has been shown to be high and of consequence. Data indicate that infections account for 13%-16% of deaths among kidney and heart transplant patients and up to 21% of deaths among lung transplant patients. The rate of mortality appears to parallel the level of immunosuppression, Dr. Nguyen explained.
Furthermore, up to 25% of patients who undergo heart and lung transplantation develop bacteremia.
In terms of why worse infections or bacteremia surgeries may not occur in association with Mohs, Dr. Nguyen speculated that, as opposed to other surgeries, those involving the skin may benefit from unique defense mechanisms.
“The skin is a complex system in its defense against foreign pathogens and infectious agents,” she explained during her presentation. “There is the physical barrier, the antimicrobial peptides, and an adaptive as well as innate immune response.”
“In immunosuppressed patients, with the decrease in adaptive immunity, it’s possible this loss is less important because the skin has such a robust immune system in general.”
In her presentation, Dr. Nguyen noted that “further studies are necessary to investigate why patients aren’t presenting with greater severity, and we plan to try to investigate whether the unique nature of skin-mediated immunity makes this organ less susceptible to severe or life-threatening infections in patients on immunosuppression.”
Of note, the rate of prophylactic antibiotic prescriptions was no higher for those who were and those who were not immunosuppressed (37.9% vs. 34.1%; P = .14), which Dr. Nguyen said is consistent with recommendations.
“Immunosuppression is not an indication for antibiotic use, and hence, we did not have a higher rate of antibiotics use in this population,” she told this news organization. However, a 2021 ACMS survey found that a high percentage of Mohs surgeons prescribe antibiotics for procedures in which antibiotics are not indicated so as to reduce the risk of infections and that immunosuppression is a common reason for doing so.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, suggesting that antibiotic prophylaxis, which is often used for these patients, may not be necessary, according to new research.
The retrospective cohort study found that “immunosuppressed patients had similar infection rates as immunocompetent patients following Mohs micrographic surgery,” first author Tuyet A. Nguyen, MD, of the department of dermatology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, told this news organization.
“Therefore, antibiotic prescribing patterns should not change simply due to immunosuppression. Furthermore, immunosuppressed patients appear to respond well to antibiotics and recover similarly to immunocompetent patients,” she said.
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
Mohs surgery is increasingly being performed for patients who are immunosuppressed because of the higher incidence of skin cancer in this group of patients and their higher risk of more aggressive skin cancers.
Overall, the rate of surgical site infections following Mohs surgery generally ranges from 0.5% to 2.4%. However, research is lacking on the risk among patients who are immunosuppressed and on how effective the use of prophylactic antibiotics is for these patients.
For the retrospective study, Dr. Nguyen and her colleagues evaluated data on 5,886 patients who underwent Mohs surgery at Cedars-Sinai between October 2014 and August 2021. Among these patients, 741 (12.6%) were immunocompromised.
Causes of immunosuppression in the cohort included the following: immunosuppression after transplant surgery; having HIV, chronic myeloid leukemia, multiple myeloma, or other hematogenous forms of immunosuppression; or immunosuppression related to other conditions, such as chronic inflammatory diseases.
Overall, postprocedural infections occurred in 1.6% (95) of patients, a rate that mirrors that of the general population, Dr. Nguyen noted. No significant differences in surgical site infection rates were observed between immunocompromised patients (2.1%, n = 15) and those who were immunocompetent (1.6%, n = 80; P = .30).
Importantly, among those who were immunocompromised, the rates of infection were not significantly different between those who did receive antibiotics (3.0%, n = 8) and those who did not receive antibiotics (1.5%, n = 7; P = .19).
The lack of a difference in surgical site infection rates among those who did and those who did not receive antibiotics extended to the entire study population (2.0% vs. 1.4%; P = .12).
The study cohort mainly comprised immunosuppressed transplant patients, notably, heart, lung, and kidney transplant patients. However, “even in this population, we did not see a higher rate of infection,” senior author Nima M. Gharavi, MD, PhD, director of dermatologic surgery and Mohs micrographic surgery and associate professor of medicine and pathology and laboratory medicine at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in an interview.
Yet the risk of infection among those patients has been shown to be high and of consequence. Data indicate that infections account for 13%-16% of deaths among kidney and heart transplant patients and up to 21% of deaths among lung transplant patients. The rate of mortality appears to parallel the level of immunosuppression, Dr. Nguyen explained.
Furthermore, up to 25% of patients who undergo heart and lung transplantation develop bacteremia.
In terms of why worse infections or bacteremia surgeries may not occur in association with Mohs, Dr. Nguyen speculated that, as opposed to other surgeries, those involving the skin may benefit from unique defense mechanisms.
“The skin is a complex system in its defense against foreign pathogens and infectious agents,” she explained during her presentation. “There is the physical barrier, the antimicrobial peptides, and an adaptive as well as innate immune response.”
“In immunosuppressed patients, with the decrease in adaptive immunity, it’s possible this loss is less important because the skin has such a robust immune system in general.”
In her presentation, Dr. Nguyen noted that “further studies are necessary to investigate why patients aren’t presenting with greater severity, and we plan to try to investigate whether the unique nature of skin-mediated immunity makes this organ less susceptible to severe or life-threatening infections in patients on immunosuppression.”
Of note, the rate of prophylactic antibiotic prescriptions was no higher for those who were and those who were not immunosuppressed (37.9% vs. 34.1%; P = .14), which Dr. Nguyen said is consistent with recommendations.
“Immunosuppression is not an indication for antibiotic use, and hence, we did not have a higher rate of antibiotics use in this population,” she told this news organization. However, a 2021 ACMS survey found that a high percentage of Mohs surgeons prescribe antibiotics for procedures in which antibiotics are not indicated so as to reduce the risk of infections and that immunosuppression is a common reason for doing so.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, suggesting that antibiotic prophylaxis, which is often used for these patients, may not be necessary, according to new research.
The retrospective cohort study found that “immunosuppressed patients had similar infection rates as immunocompetent patients following Mohs micrographic surgery,” first author Tuyet A. Nguyen, MD, of the department of dermatology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, told this news organization.
“Therefore, antibiotic prescribing patterns should not change simply due to immunosuppression. Furthermore, immunosuppressed patients appear to respond well to antibiotics and recover similarly to immunocompetent patients,” she said.
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
Mohs surgery is increasingly being performed for patients who are immunosuppressed because of the higher incidence of skin cancer in this group of patients and their higher risk of more aggressive skin cancers.
Overall, the rate of surgical site infections following Mohs surgery generally ranges from 0.5% to 2.4%. However, research is lacking on the risk among patients who are immunosuppressed and on how effective the use of prophylactic antibiotics is for these patients.
For the retrospective study, Dr. Nguyen and her colleagues evaluated data on 5,886 patients who underwent Mohs surgery at Cedars-Sinai between October 2014 and August 2021. Among these patients, 741 (12.6%) were immunocompromised.
Causes of immunosuppression in the cohort included the following: immunosuppression after transplant surgery; having HIV, chronic myeloid leukemia, multiple myeloma, or other hematogenous forms of immunosuppression; or immunosuppression related to other conditions, such as chronic inflammatory diseases.
Overall, postprocedural infections occurred in 1.6% (95) of patients, a rate that mirrors that of the general population, Dr. Nguyen noted. No significant differences in surgical site infection rates were observed between immunocompromised patients (2.1%, n = 15) and those who were immunocompetent (1.6%, n = 80; P = .30).
Importantly, among those who were immunocompromised, the rates of infection were not significantly different between those who did receive antibiotics (3.0%, n = 8) and those who did not receive antibiotics (1.5%, n = 7; P = .19).
The lack of a difference in surgical site infection rates among those who did and those who did not receive antibiotics extended to the entire study population (2.0% vs. 1.4%; P = .12).
The study cohort mainly comprised immunosuppressed transplant patients, notably, heart, lung, and kidney transplant patients. However, “even in this population, we did not see a higher rate of infection,” senior author Nima M. Gharavi, MD, PhD, director of dermatologic surgery and Mohs micrographic surgery and associate professor of medicine and pathology and laboratory medicine at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in an interview.
Yet the risk of infection among those patients has been shown to be high and of consequence. Data indicate that infections account for 13%-16% of deaths among kidney and heart transplant patients and up to 21% of deaths among lung transplant patients. The rate of mortality appears to parallel the level of immunosuppression, Dr. Nguyen explained.
Furthermore, up to 25% of patients who undergo heart and lung transplantation develop bacteremia.
In terms of why worse infections or bacteremia surgeries may not occur in association with Mohs, Dr. Nguyen speculated that, as opposed to other surgeries, those involving the skin may benefit from unique defense mechanisms.
“The skin is a complex system in its defense against foreign pathogens and infectious agents,” she explained during her presentation. “There is the physical barrier, the antimicrobial peptides, and an adaptive as well as innate immune response.”
“In immunosuppressed patients, with the decrease in adaptive immunity, it’s possible this loss is less important because the skin has such a robust immune system in general.”
In her presentation, Dr. Nguyen noted that “further studies are necessary to investigate why patients aren’t presenting with greater severity, and we plan to try to investigate whether the unique nature of skin-mediated immunity makes this organ less susceptible to severe or life-threatening infections in patients on immunosuppression.”
Of note, the rate of prophylactic antibiotic prescriptions was no higher for those who were and those who were not immunosuppressed (37.9% vs. 34.1%; P = .14), which Dr. Nguyen said is consistent with recommendations.
“Immunosuppression is not an indication for antibiotic use, and hence, we did not have a higher rate of antibiotics use in this population,” she told this news organization. However, a 2021 ACMS survey found that a high percentage of Mohs surgeons prescribe antibiotics for procedures in which antibiotics are not indicated so as to reduce the risk of infections and that immunosuppression is a common reason for doing so.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACMS ANNUAL MEETING
Mohs surgery in the elderly: The dilemma of when to treat
As increasing numbers of patients in their 80s, 90s, and even 100s present for possible Mohs micrographic surgery, surgeons are confronted with deciding when the risks of treatment may outweigh the benefits.
In one of two presentations at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery that addressed this topic, Howard W. Rogers, MD, of Advanced Dermatology in Norwich, Conn., said that the crux of the issue is the concern not to undertreat. He noted that reduced access to dermatologic care during the pandemic has provided a stark lesson in the risks of delaying treatment in all age groups. “Mohs surgeons have all seen the consequences of delayed treatment due to the pandemic with enormous, destructive, and sometimes fatal cancers coming to the office in the last year,” he told this news organization.
“Pandemic-related treatment delay has caused increased suffering and morbidity for countless skin cancer patients across the U.S.,” he said. “In general, not treating skin cancer and hoping it’s not going to grow or having significant delays in treatment are a recipe for disastrous outcomes.”
That said, active monitoring may be appropriate “for select small cancers that tend to grow slowly in the very elderly,” added Dr. Rogers, the incoming ACMS president. Among the key situations where the benefits of active monitoring may outweigh the risks of surgery are small, slowly growing cancers, when frailty is an issue.
Frailty has been equated to compromised functionality, which can increase the risk of an array of complications, including prolonged wound healing and secondary complications stemming from immobility. The toll those issues can take on patients’ quality of life can be considerable, Dr. Rogers said.
When weighing treatment options with elderly patients, he emphasized that careful consideration should be given to whether the “time needed to benefit from a Mohs procedure is longer than the patient’s life expectancy.” Furthermore, a decision not to treat does not have to be the last word. “We need to have an honest dialogue on the consequences of nontreatment, but part of that should be that just because we don’t treat today, doesn’t mean we can’t treat it tomorrow, if necessary.”
Of note, he added, “more than 100,00 patients have surgery for basal cell carcinoma [BCC] in their last year of life.” And that figure will likely rise exponentially if population projections come to fruition, considering that the population of people over the age of 85 is predicted to increase to nearly 18 million in 2050, from 5.8 million in 2012, Dr. Rogers said.
Until more research emerges on how to best treat this age group, Dr. Rogers noted that experts recommend that for elderly patients, “treatment should be individualized with consideration of active monitoring of primary BCC that is not in the H-zone, asymptomatic, smaller than 1 cm, with treatment initiated if there is substantial growth or symptoms.” Ultimately, he urged surgeons to “be sensitive and treat our patients like ourselves or our family members.”
When appropriate – Mohs is safe in the very elderly
Taking on the issue in a separate presentation, Deborah MacFarlane, MD, professor of dermatology and head and neck surgery at MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said that for skin cancer cases that warrant treatment, clinicians should not let age alone stand in the way of Mohs surgery.
The evidence of its safety in the elderly dates back to a paper published in 1997 that Dr. MacFarlane coauthored, describing Mohs surgery of BCCs, squamous cell cancers (SCCs), and melanomas among 115 patients aged 90 and older (average, 92.4 years) who had an average of 1.9 comorbid medical conditions, and were taking an average of 2.3 medications. “Overall, we had just one complication among the patients,” she said.
In a subsequent paper, Dr. MacFarlane and her colleagues found that age at the time of Mohs surgery, even in older patients, was unrelated to survival, stage of cancer, or the type of repair. “We have concluded that this rapidly growing segment of the population can undergo Mohs surgery and should not be relegated to less effective treatment out of fear of its affecting their survival,” Dr. MacFarlane said.
She agreed with the concern about frailty and hence functionality, which may need to be factored in when making a decision to perform Mohs surgery. “I think this is something we do intuitively anyway,” she added. “We’re going to offer Mohs to someone who we think will survive and who is in relatively good health,” Dr. MacFarlane noted.
The point is illustrated in a new multicenter study of 1,181 patients at 22 U.S. sites, aged 85 years and older with nonmelanoma skin cancer referred for Mohs surgery. In the study, published in JAMA Dermatology after the ACMS meeting, patients who had Mohs surgery were almost four times more likely to have high functional status (P < .001) and were more likely to have facial tumors (P < .001), compared with those who had an alternate surgery.
The main reasons provided by the surgeons for opting to treat with Mohs included a patient’s desire for treatment with a high cure rate (66%), good/excellent patient functional status for age (57%), and a high risk associated with the tumor based on histology (40%), noted Dr. MacFarlane, one of the authors.
She reiterated the point raised by Dr. Rogers that “this is something we’re going to increasingly face,” noting that people over 85 represent the fastest growing segment of the population. “I have more patients over the age of 100 than I’ve ever had before,” she said.
Nevertheless, her own experience with elderly patients speaks to the safety of Mohs surgery in this population: Dr. MacFarlane reported a review of her practice’s records of 171 patients aged 85 years and older between May 2016 and May 2022, who received 414 separate procedures, without a single complication.
Sharing many of Dr. Rogers’ concerns about using caution in at-risk patients, Dr. MacFarlane offered recommendations for the optimal treatment of elderly patients receiving Mohs, including handling tissue delicately, and “keep undermining to a minimum.” She noted that intermediate closures and full thickness skin grafts are ideal closures for the elderly, while flaps may be performed in selected robust skin. It is also important to involve caretakers from the onset, talk and listen to patients – and play their choice of music during treatment, she said.
Commenting on the debate, comoderator Nahid Y. Vidal, MD, of the department of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that the expanding older population is accompanied by increases in skin cancer, in addition to more immunosenescence that is related to development of infections, autoimmune disease, and malignant tumors.
“In our academic practice, as with both the reference speakers, we do frequently see elderly, and not uncommonly the super-elderly,” she told this news organization. “The take-home point for me is to treat your whole patient, not just the tumor,” considering social factors, frailty/spry factor, and preferences, “and to do the humanistic thing, while also remaining evidence based,” she said.
“Don’t assume that increased age translates to morbidity, worse outcomes, or futility of treatment,” she added. “Chances are, if [a patient] made it to 90 years old with only a few medications and few medical problems, they may make it to 100, so why put the patient at risk for metastasis and death from a treatable/curable skin cancer,” in the case of SCC, she said.
“By the same token, why not perform more conservative treatments such as ED&C [electrodesiccation and curettage] for very low-risk skin cancers in low-risk locations, such as a superficial basal cell carcinoma on the trunk?” Overall, instead of trying to determine how long a super-elderly individual will live, Dr. Vidal said that “it’s better to educate the patient, engage in a discussion about goals of care, and to make few assumptions.”
Dr. Rogers, Dr. MacFarlane, and Dr. Vidal report no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As increasing numbers of patients in their 80s, 90s, and even 100s present for possible Mohs micrographic surgery, surgeons are confronted with deciding when the risks of treatment may outweigh the benefits.
In one of two presentations at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery that addressed this topic, Howard W. Rogers, MD, of Advanced Dermatology in Norwich, Conn., said that the crux of the issue is the concern not to undertreat. He noted that reduced access to dermatologic care during the pandemic has provided a stark lesson in the risks of delaying treatment in all age groups. “Mohs surgeons have all seen the consequences of delayed treatment due to the pandemic with enormous, destructive, and sometimes fatal cancers coming to the office in the last year,” he told this news organization.
“Pandemic-related treatment delay has caused increased suffering and morbidity for countless skin cancer patients across the U.S.,” he said. “In general, not treating skin cancer and hoping it’s not going to grow or having significant delays in treatment are a recipe for disastrous outcomes.”
That said, active monitoring may be appropriate “for select small cancers that tend to grow slowly in the very elderly,” added Dr. Rogers, the incoming ACMS president. Among the key situations where the benefits of active monitoring may outweigh the risks of surgery are small, slowly growing cancers, when frailty is an issue.
Frailty has been equated to compromised functionality, which can increase the risk of an array of complications, including prolonged wound healing and secondary complications stemming from immobility. The toll those issues can take on patients’ quality of life can be considerable, Dr. Rogers said.
When weighing treatment options with elderly patients, he emphasized that careful consideration should be given to whether the “time needed to benefit from a Mohs procedure is longer than the patient’s life expectancy.” Furthermore, a decision not to treat does not have to be the last word. “We need to have an honest dialogue on the consequences of nontreatment, but part of that should be that just because we don’t treat today, doesn’t mean we can’t treat it tomorrow, if necessary.”
Of note, he added, “more than 100,00 patients have surgery for basal cell carcinoma [BCC] in their last year of life.” And that figure will likely rise exponentially if population projections come to fruition, considering that the population of people over the age of 85 is predicted to increase to nearly 18 million in 2050, from 5.8 million in 2012, Dr. Rogers said.
Until more research emerges on how to best treat this age group, Dr. Rogers noted that experts recommend that for elderly patients, “treatment should be individualized with consideration of active monitoring of primary BCC that is not in the H-zone, asymptomatic, smaller than 1 cm, with treatment initiated if there is substantial growth or symptoms.” Ultimately, he urged surgeons to “be sensitive and treat our patients like ourselves or our family members.”
When appropriate – Mohs is safe in the very elderly
Taking on the issue in a separate presentation, Deborah MacFarlane, MD, professor of dermatology and head and neck surgery at MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said that for skin cancer cases that warrant treatment, clinicians should not let age alone stand in the way of Mohs surgery.
The evidence of its safety in the elderly dates back to a paper published in 1997 that Dr. MacFarlane coauthored, describing Mohs surgery of BCCs, squamous cell cancers (SCCs), and melanomas among 115 patients aged 90 and older (average, 92.4 years) who had an average of 1.9 comorbid medical conditions, and were taking an average of 2.3 medications. “Overall, we had just one complication among the patients,” she said.
In a subsequent paper, Dr. MacFarlane and her colleagues found that age at the time of Mohs surgery, even in older patients, was unrelated to survival, stage of cancer, or the type of repair. “We have concluded that this rapidly growing segment of the population can undergo Mohs surgery and should not be relegated to less effective treatment out of fear of its affecting their survival,” Dr. MacFarlane said.
She agreed with the concern about frailty and hence functionality, which may need to be factored in when making a decision to perform Mohs surgery. “I think this is something we do intuitively anyway,” she added. “We’re going to offer Mohs to someone who we think will survive and who is in relatively good health,” Dr. MacFarlane noted.
The point is illustrated in a new multicenter study of 1,181 patients at 22 U.S. sites, aged 85 years and older with nonmelanoma skin cancer referred for Mohs surgery. In the study, published in JAMA Dermatology after the ACMS meeting, patients who had Mohs surgery were almost four times more likely to have high functional status (P < .001) and were more likely to have facial tumors (P < .001), compared with those who had an alternate surgery.
The main reasons provided by the surgeons for opting to treat with Mohs included a patient’s desire for treatment with a high cure rate (66%), good/excellent patient functional status for age (57%), and a high risk associated with the tumor based on histology (40%), noted Dr. MacFarlane, one of the authors.
She reiterated the point raised by Dr. Rogers that “this is something we’re going to increasingly face,” noting that people over 85 represent the fastest growing segment of the population. “I have more patients over the age of 100 than I’ve ever had before,” she said.
Nevertheless, her own experience with elderly patients speaks to the safety of Mohs surgery in this population: Dr. MacFarlane reported a review of her practice’s records of 171 patients aged 85 years and older between May 2016 and May 2022, who received 414 separate procedures, without a single complication.
Sharing many of Dr. Rogers’ concerns about using caution in at-risk patients, Dr. MacFarlane offered recommendations for the optimal treatment of elderly patients receiving Mohs, including handling tissue delicately, and “keep undermining to a minimum.” She noted that intermediate closures and full thickness skin grafts are ideal closures for the elderly, while flaps may be performed in selected robust skin. It is also important to involve caretakers from the onset, talk and listen to patients – and play their choice of music during treatment, she said.
Commenting on the debate, comoderator Nahid Y. Vidal, MD, of the department of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that the expanding older population is accompanied by increases in skin cancer, in addition to more immunosenescence that is related to development of infections, autoimmune disease, and malignant tumors.
“In our academic practice, as with both the reference speakers, we do frequently see elderly, and not uncommonly the super-elderly,” she told this news organization. “The take-home point for me is to treat your whole patient, not just the tumor,” considering social factors, frailty/spry factor, and preferences, “and to do the humanistic thing, while also remaining evidence based,” she said.
“Don’t assume that increased age translates to morbidity, worse outcomes, or futility of treatment,” she added. “Chances are, if [a patient] made it to 90 years old with only a few medications and few medical problems, they may make it to 100, so why put the patient at risk for metastasis and death from a treatable/curable skin cancer,” in the case of SCC, she said.
“By the same token, why not perform more conservative treatments such as ED&C [electrodesiccation and curettage] for very low-risk skin cancers in low-risk locations, such as a superficial basal cell carcinoma on the trunk?” Overall, instead of trying to determine how long a super-elderly individual will live, Dr. Vidal said that “it’s better to educate the patient, engage in a discussion about goals of care, and to make few assumptions.”
Dr. Rogers, Dr. MacFarlane, and Dr. Vidal report no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As increasing numbers of patients in their 80s, 90s, and even 100s present for possible Mohs micrographic surgery, surgeons are confronted with deciding when the risks of treatment may outweigh the benefits.
In one of two presentations at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery that addressed this topic, Howard W. Rogers, MD, of Advanced Dermatology in Norwich, Conn., said that the crux of the issue is the concern not to undertreat. He noted that reduced access to dermatologic care during the pandemic has provided a stark lesson in the risks of delaying treatment in all age groups. “Mohs surgeons have all seen the consequences of delayed treatment due to the pandemic with enormous, destructive, and sometimes fatal cancers coming to the office in the last year,” he told this news organization.
“Pandemic-related treatment delay has caused increased suffering and morbidity for countless skin cancer patients across the U.S.,” he said. “In general, not treating skin cancer and hoping it’s not going to grow or having significant delays in treatment are a recipe for disastrous outcomes.”
That said, active monitoring may be appropriate “for select small cancers that tend to grow slowly in the very elderly,” added Dr. Rogers, the incoming ACMS president. Among the key situations where the benefits of active monitoring may outweigh the risks of surgery are small, slowly growing cancers, when frailty is an issue.
Frailty has been equated to compromised functionality, which can increase the risk of an array of complications, including prolonged wound healing and secondary complications stemming from immobility. The toll those issues can take on patients’ quality of life can be considerable, Dr. Rogers said.
When weighing treatment options with elderly patients, he emphasized that careful consideration should be given to whether the “time needed to benefit from a Mohs procedure is longer than the patient’s life expectancy.” Furthermore, a decision not to treat does not have to be the last word. “We need to have an honest dialogue on the consequences of nontreatment, but part of that should be that just because we don’t treat today, doesn’t mean we can’t treat it tomorrow, if necessary.”
Of note, he added, “more than 100,00 patients have surgery for basal cell carcinoma [BCC] in their last year of life.” And that figure will likely rise exponentially if population projections come to fruition, considering that the population of people over the age of 85 is predicted to increase to nearly 18 million in 2050, from 5.8 million in 2012, Dr. Rogers said.
Until more research emerges on how to best treat this age group, Dr. Rogers noted that experts recommend that for elderly patients, “treatment should be individualized with consideration of active monitoring of primary BCC that is not in the H-zone, asymptomatic, smaller than 1 cm, with treatment initiated if there is substantial growth or symptoms.” Ultimately, he urged surgeons to “be sensitive and treat our patients like ourselves or our family members.”
When appropriate – Mohs is safe in the very elderly
Taking on the issue in a separate presentation, Deborah MacFarlane, MD, professor of dermatology and head and neck surgery at MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said that for skin cancer cases that warrant treatment, clinicians should not let age alone stand in the way of Mohs surgery.
The evidence of its safety in the elderly dates back to a paper published in 1997 that Dr. MacFarlane coauthored, describing Mohs surgery of BCCs, squamous cell cancers (SCCs), and melanomas among 115 patients aged 90 and older (average, 92.4 years) who had an average of 1.9 comorbid medical conditions, and were taking an average of 2.3 medications. “Overall, we had just one complication among the patients,” she said.
In a subsequent paper, Dr. MacFarlane and her colleagues found that age at the time of Mohs surgery, even in older patients, was unrelated to survival, stage of cancer, or the type of repair. “We have concluded that this rapidly growing segment of the population can undergo Mohs surgery and should not be relegated to less effective treatment out of fear of its affecting their survival,” Dr. MacFarlane said.
She agreed with the concern about frailty and hence functionality, which may need to be factored in when making a decision to perform Mohs surgery. “I think this is something we do intuitively anyway,” she added. “We’re going to offer Mohs to someone who we think will survive and who is in relatively good health,” Dr. MacFarlane noted.
The point is illustrated in a new multicenter study of 1,181 patients at 22 U.S. sites, aged 85 years and older with nonmelanoma skin cancer referred for Mohs surgery. In the study, published in JAMA Dermatology after the ACMS meeting, patients who had Mohs surgery were almost four times more likely to have high functional status (P < .001) and were more likely to have facial tumors (P < .001), compared with those who had an alternate surgery.
The main reasons provided by the surgeons for opting to treat with Mohs included a patient’s desire for treatment with a high cure rate (66%), good/excellent patient functional status for age (57%), and a high risk associated with the tumor based on histology (40%), noted Dr. MacFarlane, one of the authors.
She reiterated the point raised by Dr. Rogers that “this is something we’re going to increasingly face,” noting that people over 85 represent the fastest growing segment of the population. “I have more patients over the age of 100 than I’ve ever had before,” she said.
Nevertheless, her own experience with elderly patients speaks to the safety of Mohs surgery in this population: Dr. MacFarlane reported a review of her practice’s records of 171 patients aged 85 years and older between May 2016 and May 2022, who received 414 separate procedures, without a single complication.
Sharing many of Dr. Rogers’ concerns about using caution in at-risk patients, Dr. MacFarlane offered recommendations for the optimal treatment of elderly patients receiving Mohs, including handling tissue delicately, and “keep undermining to a minimum.” She noted that intermediate closures and full thickness skin grafts are ideal closures for the elderly, while flaps may be performed in selected robust skin. It is also important to involve caretakers from the onset, talk and listen to patients – and play their choice of music during treatment, she said.
Commenting on the debate, comoderator Nahid Y. Vidal, MD, of the department of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that the expanding older population is accompanied by increases in skin cancer, in addition to more immunosenescence that is related to development of infections, autoimmune disease, and malignant tumors.
“In our academic practice, as with both the reference speakers, we do frequently see elderly, and not uncommonly the super-elderly,” she told this news organization. “The take-home point for me is to treat your whole patient, not just the tumor,” considering social factors, frailty/spry factor, and preferences, “and to do the humanistic thing, while also remaining evidence based,” she said.
“Don’t assume that increased age translates to morbidity, worse outcomes, or futility of treatment,” she added. “Chances are, if [a patient] made it to 90 years old with only a few medications and few medical problems, they may make it to 100, so why put the patient at risk for metastasis and death from a treatable/curable skin cancer,” in the case of SCC, she said.
“By the same token, why not perform more conservative treatments such as ED&C [electrodesiccation and curettage] for very low-risk skin cancers in low-risk locations, such as a superficial basal cell carcinoma on the trunk?” Overall, instead of trying to determine how long a super-elderly individual will live, Dr. Vidal said that “it’s better to educate the patient, engage in a discussion about goals of care, and to make few assumptions.”
Dr. Rogers, Dr. MacFarlane, and Dr. Vidal report no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACMS 2022
Izokibep improves multiple psoriatic arthritis symptoms in phase 2 study
A host of psoriatic arthritis symptoms can be improved by the investigational interleukin (IL)-17 blocker izokibep, according to the results of a phase 2 trial presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Around half of all participants in the trial who were treated with izokibep achieved a 50% or higher improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR50) at week 16, the trial’s primary endpoint. This was highly significant (P = .0003) when compared to the control group, where only 13% of patients given a placebo achieved an ACR50.
There was also a significant improvement in skin symptoms, as assessed by the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) and resolution of enthesitis in 88% of patients given the highest dose of izokibep.
Aurelie Najm, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Infection, Immunity and Inflammation at the University of Glasgow, who tweeted about the main results, said that the data also looked “promising for the enthesitis domain” with a “safety profile similar to that observed in PsO [psoriasis].”Peter Taylor, MA, PhD, FRCP, FRCPE, of the University of Oxford in England, said: “The improvements demonstrated in arthritis, psoriasis, and enthesitis are exciting relative to responses reported for the current standard of care.”
He continued, in a statement issued jointly by Affibody, Acelyrin, and Immagene Biopharmaceuticals – the three companies assessing izokibep’s therapeutic potential – that the drug “seems promising” and that he was “eager to see its continued development for patients.”
Small and potent, a novel IL-17 inhibitor
Izokibep is an antibody mimetic that inhibits IL-17A designed to “overcome the limitations of monoclonal antibodies,” according to its developers.
Due to its small molecular size – reportedly about one-tenth of the size of a monoclonal antibody – they say that levels of high drug exposure can be achieved from a single, subcutaneous injection rather than an intravenous infusion, which is needed for monoclonal antibodies.
Moreover, izokibep’s small size means it could potentially reach target tissues “that may otherwise be inaccessible to the much larger monoclonal antibodies.”
So far more than 300 patients have been treated with izokibep, some for up to 3 years, but not all have had psoriatic arthritis. Indeed, the drug has been tested in patients with psoriasis, and there are a few actively recruiting trials including one in ankylosing spondylitis, another in noninfective uveitis, and one in the rare and painful skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa.
Testing two doses of izokibep in psoriatic arthritis
The trial presented at the EULAR 2022 Congress tested two doses of izokibep – 40 mg and 80 mg – given by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks – against placebo in 135 adult patients with active psoriatic arthritis. For inclusion in the trial patients had to have at least three swollen and at least three tender joints and have had an inadequate response to prior therapy including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Principle investigator Frank Behrens, MD, of Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany, reported that it was a multicenter effort conducted at 22 European sites with the primary endpoint being an ACR50 response at 16 weeks. This was met by 52% of patients given the 80-mg dose of izokibep, 48% of patients given the 40-mg dose of izokibep, and just 13% of patients who had been randomized to placebo.
ACR20 and ACR70 response were one of several key secondary endpoints tested, again at 16 weeks, with a respective 75%, 60%, and 20% of patients in each group achieving the lower response target and 20%, 32%, and 5%, achieving the more stringent response target.
“Izokibep demonstrated a robust efficacy in the musculoskeletal arthritic domains, but also in the extra-articular musculoskeletal domain,” Dr. Behrens said.
Not only that, but the values were “at the top end” of what’s been demonstrated for drugs currently regarded as the standard of care.
More than 80% of patients achieved a PASI75 response and 57% a PASI50 response with the two doses of izokibep, and 63%-88% achieved a resolution of enthesitis. The latter was measured using the Leeds Enthesitis Index.
There was also improvement in quality of life, measured using the Psoriatic Impact of Disease questionnaire, with a percentage increase beyond the MCID of 31%-41% with izokibep versus 12% for placebo.
“These are the first data of the phase 2 study in psoriatic arthritis,” Dr. Behrens reported.
“The safety profile was consistent with placebo,” with the only “standout aspect” being a higher number of injection-site reactions with izokibep versus placebo; but there were no serious infections, no serious adverse events,” he added.
“The interesting thing is from the preclinical research there was no dose-limiting toxicity with izokibep, therefore, I think the plan in the future is maybe to increase the dose to optimize treatment outcome based on the really robust effectiveness we see here in the first study in this clinical trial,” he said.
As a small study, stratifying results by gender wasn’t an option, Dr. Behrens noted in answering a question during the discussion period, but might be something that will be included in future and larger trials based on the post-hoc findings of other IL-17 trials.
Moving forward, the next step will involve a phase 2b/3 pivotal study which will likely include a higher dosing regimen of 160 mg once weekly alongside the twice-weekly dosing used in this trial.
Izokibep is an investigational treatment being developed by Affibody AB, Sweden, and ACELYRIN, USA. All three companies funded the phase 2 trial and were involved in the study design, conduct and reporting of results.
Dr. Behrens and Dr. Taylor were investigators in the study.
Dr. Behrens disclosed he was a shareholder of Pfizer, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead Sciences, Inc. and Novartis; part of the speakers’ bureau for Amgen, Horizon, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Genzyme, Flexion and AbbVie; a consultant of AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Flexion, Janssen, Pfizer, Sanofi, Regeneron, SUN Pharma Advanced Research, Gilead Sciences, Inc.; and had received grant or research support from Pfizer, Janssen, Chugai, Celgene and Roche
Dr. Taylor acknowledged grant or research support from: Celgene and Galapagos, and acted as a consultant for AbbVie, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Fresenius, Galapagos, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Lilly, Nordic Pharma, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi and UCB.
A host of psoriatic arthritis symptoms can be improved by the investigational interleukin (IL)-17 blocker izokibep, according to the results of a phase 2 trial presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Around half of all participants in the trial who were treated with izokibep achieved a 50% or higher improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR50) at week 16, the trial’s primary endpoint. This was highly significant (P = .0003) when compared to the control group, where only 13% of patients given a placebo achieved an ACR50.
There was also a significant improvement in skin symptoms, as assessed by the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) and resolution of enthesitis in 88% of patients given the highest dose of izokibep.
Aurelie Najm, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Infection, Immunity and Inflammation at the University of Glasgow, who tweeted about the main results, said that the data also looked “promising for the enthesitis domain” with a “safety profile similar to that observed in PsO [psoriasis].”Peter Taylor, MA, PhD, FRCP, FRCPE, of the University of Oxford in England, said: “The improvements demonstrated in arthritis, psoriasis, and enthesitis are exciting relative to responses reported for the current standard of care.”
He continued, in a statement issued jointly by Affibody, Acelyrin, and Immagene Biopharmaceuticals – the three companies assessing izokibep’s therapeutic potential – that the drug “seems promising” and that he was “eager to see its continued development for patients.”
Small and potent, a novel IL-17 inhibitor
Izokibep is an antibody mimetic that inhibits IL-17A designed to “overcome the limitations of monoclonal antibodies,” according to its developers.
Due to its small molecular size – reportedly about one-tenth of the size of a monoclonal antibody – they say that levels of high drug exposure can be achieved from a single, subcutaneous injection rather than an intravenous infusion, which is needed for monoclonal antibodies.
Moreover, izokibep’s small size means it could potentially reach target tissues “that may otherwise be inaccessible to the much larger monoclonal antibodies.”
So far more than 300 patients have been treated with izokibep, some for up to 3 years, but not all have had psoriatic arthritis. Indeed, the drug has been tested in patients with psoriasis, and there are a few actively recruiting trials including one in ankylosing spondylitis, another in noninfective uveitis, and one in the rare and painful skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa.
Testing two doses of izokibep in psoriatic arthritis
The trial presented at the EULAR 2022 Congress tested two doses of izokibep – 40 mg and 80 mg – given by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks – against placebo in 135 adult patients with active psoriatic arthritis. For inclusion in the trial patients had to have at least three swollen and at least three tender joints and have had an inadequate response to prior therapy including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Principle investigator Frank Behrens, MD, of Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany, reported that it was a multicenter effort conducted at 22 European sites with the primary endpoint being an ACR50 response at 16 weeks. This was met by 52% of patients given the 80-mg dose of izokibep, 48% of patients given the 40-mg dose of izokibep, and just 13% of patients who had been randomized to placebo.
ACR20 and ACR70 response were one of several key secondary endpoints tested, again at 16 weeks, with a respective 75%, 60%, and 20% of patients in each group achieving the lower response target and 20%, 32%, and 5%, achieving the more stringent response target.
“Izokibep demonstrated a robust efficacy in the musculoskeletal arthritic domains, but also in the extra-articular musculoskeletal domain,” Dr. Behrens said.
Not only that, but the values were “at the top end” of what’s been demonstrated for drugs currently regarded as the standard of care.
More than 80% of patients achieved a PASI75 response and 57% a PASI50 response with the two doses of izokibep, and 63%-88% achieved a resolution of enthesitis. The latter was measured using the Leeds Enthesitis Index.
There was also improvement in quality of life, measured using the Psoriatic Impact of Disease questionnaire, with a percentage increase beyond the MCID of 31%-41% with izokibep versus 12% for placebo.
“These are the first data of the phase 2 study in psoriatic arthritis,” Dr. Behrens reported.
“The safety profile was consistent with placebo,” with the only “standout aspect” being a higher number of injection-site reactions with izokibep versus placebo; but there were no serious infections, no serious adverse events,” he added.
“The interesting thing is from the preclinical research there was no dose-limiting toxicity with izokibep, therefore, I think the plan in the future is maybe to increase the dose to optimize treatment outcome based on the really robust effectiveness we see here in the first study in this clinical trial,” he said.
As a small study, stratifying results by gender wasn’t an option, Dr. Behrens noted in answering a question during the discussion period, but might be something that will be included in future and larger trials based on the post-hoc findings of other IL-17 trials.
Moving forward, the next step will involve a phase 2b/3 pivotal study which will likely include a higher dosing regimen of 160 mg once weekly alongside the twice-weekly dosing used in this trial.
Izokibep is an investigational treatment being developed by Affibody AB, Sweden, and ACELYRIN, USA. All three companies funded the phase 2 trial and were involved in the study design, conduct and reporting of results.
Dr. Behrens and Dr. Taylor were investigators in the study.
Dr. Behrens disclosed he was a shareholder of Pfizer, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead Sciences, Inc. and Novartis; part of the speakers’ bureau for Amgen, Horizon, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Genzyme, Flexion and AbbVie; a consultant of AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Flexion, Janssen, Pfizer, Sanofi, Regeneron, SUN Pharma Advanced Research, Gilead Sciences, Inc.; and had received grant or research support from Pfizer, Janssen, Chugai, Celgene and Roche
Dr. Taylor acknowledged grant or research support from: Celgene and Galapagos, and acted as a consultant for AbbVie, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Fresenius, Galapagos, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Lilly, Nordic Pharma, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi and UCB.
A host of psoriatic arthritis symptoms can be improved by the investigational interleukin (IL)-17 blocker izokibep, according to the results of a phase 2 trial presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Around half of all participants in the trial who were treated with izokibep achieved a 50% or higher improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR50) at week 16, the trial’s primary endpoint. This was highly significant (P = .0003) when compared to the control group, where only 13% of patients given a placebo achieved an ACR50.
There was also a significant improvement in skin symptoms, as assessed by the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) and resolution of enthesitis in 88% of patients given the highest dose of izokibep.
Aurelie Najm, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Infection, Immunity and Inflammation at the University of Glasgow, who tweeted about the main results, said that the data also looked “promising for the enthesitis domain” with a “safety profile similar to that observed in PsO [psoriasis].”Peter Taylor, MA, PhD, FRCP, FRCPE, of the University of Oxford in England, said: “The improvements demonstrated in arthritis, psoriasis, and enthesitis are exciting relative to responses reported for the current standard of care.”
He continued, in a statement issued jointly by Affibody, Acelyrin, and Immagene Biopharmaceuticals – the three companies assessing izokibep’s therapeutic potential – that the drug “seems promising” and that he was “eager to see its continued development for patients.”
Small and potent, a novel IL-17 inhibitor
Izokibep is an antibody mimetic that inhibits IL-17A designed to “overcome the limitations of monoclonal antibodies,” according to its developers.
Due to its small molecular size – reportedly about one-tenth of the size of a monoclonal antibody – they say that levels of high drug exposure can be achieved from a single, subcutaneous injection rather than an intravenous infusion, which is needed for monoclonal antibodies.
Moreover, izokibep’s small size means it could potentially reach target tissues “that may otherwise be inaccessible to the much larger monoclonal antibodies.”
So far more than 300 patients have been treated with izokibep, some for up to 3 years, but not all have had psoriatic arthritis. Indeed, the drug has been tested in patients with psoriasis, and there are a few actively recruiting trials including one in ankylosing spondylitis, another in noninfective uveitis, and one in the rare and painful skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa.
Testing two doses of izokibep in psoriatic arthritis
The trial presented at the EULAR 2022 Congress tested two doses of izokibep – 40 mg and 80 mg – given by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks – against placebo in 135 adult patients with active psoriatic arthritis. For inclusion in the trial patients had to have at least three swollen and at least three tender joints and have had an inadequate response to prior therapy including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Principle investigator Frank Behrens, MD, of Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany, reported that it was a multicenter effort conducted at 22 European sites with the primary endpoint being an ACR50 response at 16 weeks. This was met by 52% of patients given the 80-mg dose of izokibep, 48% of patients given the 40-mg dose of izokibep, and just 13% of patients who had been randomized to placebo.
ACR20 and ACR70 response were one of several key secondary endpoints tested, again at 16 weeks, with a respective 75%, 60%, and 20% of patients in each group achieving the lower response target and 20%, 32%, and 5%, achieving the more stringent response target.
“Izokibep demonstrated a robust efficacy in the musculoskeletal arthritic domains, but also in the extra-articular musculoskeletal domain,” Dr. Behrens said.
Not only that, but the values were “at the top end” of what’s been demonstrated for drugs currently regarded as the standard of care.
More than 80% of patients achieved a PASI75 response and 57% a PASI50 response with the two doses of izokibep, and 63%-88% achieved a resolution of enthesitis. The latter was measured using the Leeds Enthesitis Index.
There was also improvement in quality of life, measured using the Psoriatic Impact of Disease questionnaire, with a percentage increase beyond the MCID of 31%-41% with izokibep versus 12% for placebo.
“These are the first data of the phase 2 study in psoriatic arthritis,” Dr. Behrens reported.
“The safety profile was consistent with placebo,” with the only “standout aspect” being a higher number of injection-site reactions with izokibep versus placebo; but there were no serious infections, no serious adverse events,” he added.
“The interesting thing is from the preclinical research there was no dose-limiting toxicity with izokibep, therefore, I think the plan in the future is maybe to increase the dose to optimize treatment outcome based on the really robust effectiveness we see here in the first study in this clinical trial,” he said.
As a small study, stratifying results by gender wasn’t an option, Dr. Behrens noted in answering a question during the discussion period, but might be something that will be included in future and larger trials based on the post-hoc findings of other IL-17 trials.
Moving forward, the next step will involve a phase 2b/3 pivotal study which will likely include a higher dosing regimen of 160 mg once weekly alongside the twice-weekly dosing used in this trial.
Izokibep is an investigational treatment being developed by Affibody AB, Sweden, and ACELYRIN, USA. All three companies funded the phase 2 trial and were involved in the study design, conduct and reporting of results.
Dr. Behrens and Dr. Taylor were investigators in the study.
Dr. Behrens disclosed he was a shareholder of Pfizer, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead Sciences, Inc. and Novartis; part of the speakers’ bureau for Amgen, Horizon, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Genzyme, Flexion and AbbVie; a consultant of AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Flexion, Janssen, Pfizer, Sanofi, Regeneron, SUN Pharma Advanced Research, Gilead Sciences, Inc.; and had received grant or research support from Pfizer, Janssen, Chugai, Celgene and Roche
Dr. Taylor acknowledged grant or research support from: Celgene and Galapagos, and acted as a consultant for AbbVie, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Fresenius, Galapagos, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Lilly, Nordic Pharma, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi and UCB.
FROM THE EULAR 2022 CONGRESS
Surgeons, who see it up close, offer ways to stop gun violence
Their strategies can work regardless of where you stand on the Second Amendment of the Constitution, said Patricia Turner, MD. “Our proposals are embraced by both gun owners and non–gun owners alike, and we are unique in that regard.”
These “implementable solutions” could prevent the next massacre, Dr. Turner, executive director of the American College of Surgeons, said during a news briefing the group sponsored on June 2.
“Our future – indeed all of our futures – depend on our ability to find durable, actionable steps that we can implement tomorrow to save lives,” she said.
Firsthand perspective
“Sadly I’m here today as a trauma surgeon who has cared for two of the largest mass shootings in modern U.S. history,” said Ronald Stewart, MD, chair of the department of surgery at University Hospital in San Antonio, Texas.
Dr. Stewart treated victims of the 2017 Sutherland Springs First Baptist Church shooting – where 27 people died, including the shooter – and the recent Uvalde school shooting, both in Texas.
“The injuries inflicted by high-velocity weapons used at both of these attacks are horrific. A high-capacity, magazine-fed automatic rifle such as the AR-15 causes extremely destructive tissue wounds,” he said.
One of the group’s proposals is to increase the regulation of high-velocity weapons, including AR-15s.
“These wounds are horribly lethal at close range, and sadly, most victims do not survive long enough to make it to a trauma center,” Dr. Stewart said.
On a positive note, “all of our current [Uvalde] patients are improving, which really brings us joy in this dark time,” he said. “But all of them have a long road to deal with recovery with both the physical and emotional impact of their injuries.”
Jeffrey Kerby, MD, agreed.
“Trauma surgeons see the short-term physical effects of these injuries and watch patients struggle with the long-term impact of these wounds,” said Dr. Kerby, director of trauma and acute care surgery at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Surgeons feel ‘profound impact’ of shootings
“Firearm violence has a profound impact on surgeons, and we are the undisputed subject matter experts in treating the tragic results,” said Patrick Bailey, MD, medical director for advocacy at the American College of Surgeons.
“This impacts surgeons as well,” said Dr. Kerby, chair of the Committee on Trauma for the surgeons’ group. “We are human, and we can’t help but share in the grief, the pain, and the suffering that our patients endure.
“As a pediatric surgeon ... I have too often witnessed the impact of firearm violence, and obviously, the devastation extends beyond the victims to their families,” he said. “To put it succinctly, in our culture, parents are not supposed to be put in a position of burying their children.”
A public health crisis
“It’s important to recognize that we’ve been talking about a public health approach,” said Eileen Bulger, MD, acting chief of the trauma division at the University of Washington in Seattle. That strategy is important for engaging both firearm owners and communities that have a higher risk for firearm violence, she said.
A committee of the American College of Surgeons developed specific recommendations in 2018, which are still valid today. The group brought together surgeons from across the U.S. including “passionate firearm owners and experts in firearm safety,” Dr. Bulger said.
The committee, for example, agreed on 10 specific recommendations “that we believe are bipartisan and could have an immediate impact in saving lives.”
“I’m a lifelong gun owner,” Dr. Bailey said, emphasizing that the team’s process included participation and perspective from other surgeons “who, like me, are also gun owners, but gun owners who also seek to reduce the impact of firearm violence in our country.”
The recommendations address these areas:
- Gun ownership
- Firearm registration
- Licensure
- Education and training
- Ownership responsibilities
- Mandatory reporting and risk reduction
- Safety innovation and technology
- Research
- The culture of violence
- Social isolation and mental health
For example, “we currently have certain classes of weapons with significant offensive capability,” Dr. Bulger said, “that are appropriately restricted and regulated under the National Firearms Act as Class 3 weapons.”
This group includes fully automatic machine guns, explosive devices, and short-barrel shotguns.
“We recommend a formal reassessment of the firearms designated within each of these national firearms classifications,” Dr. Bulger said.
For example, high-capacity, magazine-fed semiautomatic rifles, such as the AR-15, should be considered for reclassification as NFA Class 3 firearms, or they should get a new designation with tighter regulation.
The ACS endorses formal firearm safety training for all new gun owners. Also, owners who do not provide reasonably safe firearm storage should be held responsible for events related to the discharge of their firearms, Dr. Bulger said. And people who are deemed an imminent threat to themselves or others through firearm ownership should be temporarily or permanently restricted, with due process.
Research and reporting reforms
The ACS is also calling for research on firearm injuries and firearm injury prevention to be federally funded, Dr. Bulger said. The research should be done in a nonpartisan manner, she said.
“We have concerns that the manner and tone in which information is released to the public may lead to copycat mass killers,” she said. “The ACS recommends that law enforcement officials and the press take steps to eliminate the notoriety of the shooter, for example.”
Dr. Bulger also addressed the mental health angle. “We encourage recognition of mental health warning signs and social isolation by teachers, counselors, peers, and parents.” When identified, immediate referral to professionals is needed.
In addition to these recommendations, another team from the American College of Surgeons has published an overview of ways to address the inequities that contribute to violence. “We advocate for federal funding to support the development of hospital-based and community programs for violence intervention and prevention,” Dr. Bulger said.
Dr. Bailey said that as a gun owner himself, he thinks other gun owners would support these recommendations.
“I do not believe that the steps recommended ... pose undue burden on the rights of individual gun owners,” he said.
The time is now
Most firearm injuries are not from mass shooting events, Dr. Kerby said.
“My own trauma center has seen a 40% increase in the number of firearm injuries just in the last 2 years,” he added, “and these numbers continue to grow.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Their strategies can work regardless of where you stand on the Second Amendment of the Constitution, said Patricia Turner, MD. “Our proposals are embraced by both gun owners and non–gun owners alike, and we are unique in that regard.”
These “implementable solutions” could prevent the next massacre, Dr. Turner, executive director of the American College of Surgeons, said during a news briefing the group sponsored on June 2.
“Our future – indeed all of our futures – depend on our ability to find durable, actionable steps that we can implement tomorrow to save lives,” she said.
Firsthand perspective
“Sadly I’m here today as a trauma surgeon who has cared for two of the largest mass shootings in modern U.S. history,” said Ronald Stewart, MD, chair of the department of surgery at University Hospital in San Antonio, Texas.
Dr. Stewart treated victims of the 2017 Sutherland Springs First Baptist Church shooting – where 27 people died, including the shooter – and the recent Uvalde school shooting, both in Texas.
“The injuries inflicted by high-velocity weapons used at both of these attacks are horrific. A high-capacity, magazine-fed automatic rifle such as the AR-15 causes extremely destructive tissue wounds,” he said.
One of the group’s proposals is to increase the regulation of high-velocity weapons, including AR-15s.
“These wounds are horribly lethal at close range, and sadly, most victims do not survive long enough to make it to a trauma center,” Dr. Stewart said.
On a positive note, “all of our current [Uvalde] patients are improving, which really brings us joy in this dark time,” he said. “But all of them have a long road to deal with recovery with both the physical and emotional impact of their injuries.”
Jeffrey Kerby, MD, agreed.
“Trauma surgeons see the short-term physical effects of these injuries and watch patients struggle with the long-term impact of these wounds,” said Dr. Kerby, director of trauma and acute care surgery at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Surgeons feel ‘profound impact’ of shootings
“Firearm violence has a profound impact on surgeons, and we are the undisputed subject matter experts in treating the tragic results,” said Patrick Bailey, MD, medical director for advocacy at the American College of Surgeons.
“This impacts surgeons as well,” said Dr. Kerby, chair of the Committee on Trauma for the surgeons’ group. “We are human, and we can’t help but share in the grief, the pain, and the suffering that our patients endure.
“As a pediatric surgeon ... I have too often witnessed the impact of firearm violence, and obviously, the devastation extends beyond the victims to their families,” he said. “To put it succinctly, in our culture, parents are not supposed to be put in a position of burying their children.”
A public health crisis
“It’s important to recognize that we’ve been talking about a public health approach,” said Eileen Bulger, MD, acting chief of the trauma division at the University of Washington in Seattle. That strategy is important for engaging both firearm owners and communities that have a higher risk for firearm violence, she said.
A committee of the American College of Surgeons developed specific recommendations in 2018, which are still valid today. The group brought together surgeons from across the U.S. including “passionate firearm owners and experts in firearm safety,” Dr. Bulger said.
The committee, for example, agreed on 10 specific recommendations “that we believe are bipartisan and could have an immediate impact in saving lives.”
“I’m a lifelong gun owner,” Dr. Bailey said, emphasizing that the team’s process included participation and perspective from other surgeons “who, like me, are also gun owners, but gun owners who also seek to reduce the impact of firearm violence in our country.”
The recommendations address these areas:
- Gun ownership
- Firearm registration
- Licensure
- Education and training
- Ownership responsibilities
- Mandatory reporting and risk reduction
- Safety innovation and technology
- Research
- The culture of violence
- Social isolation and mental health
For example, “we currently have certain classes of weapons with significant offensive capability,” Dr. Bulger said, “that are appropriately restricted and regulated under the National Firearms Act as Class 3 weapons.”
This group includes fully automatic machine guns, explosive devices, and short-barrel shotguns.
“We recommend a formal reassessment of the firearms designated within each of these national firearms classifications,” Dr. Bulger said.
For example, high-capacity, magazine-fed semiautomatic rifles, such as the AR-15, should be considered for reclassification as NFA Class 3 firearms, or they should get a new designation with tighter regulation.
The ACS endorses formal firearm safety training for all new gun owners. Also, owners who do not provide reasonably safe firearm storage should be held responsible for events related to the discharge of their firearms, Dr. Bulger said. And people who are deemed an imminent threat to themselves or others through firearm ownership should be temporarily or permanently restricted, with due process.
Research and reporting reforms
The ACS is also calling for research on firearm injuries and firearm injury prevention to be federally funded, Dr. Bulger said. The research should be done in a nonpartisan manner, she said.
“We have concerns that the manner and tone in which information is released to the public may lead to copycat mass killers,” she said. “The ACS recommends that law enforcement officials and the press take steps to eliminate the notoriety of the shooter, for example.”
Dr. Bulger also addressed the mental health angle. “We encourage recognition of mental health warning signs and social isolation by teachers, counselors, peers, and parents.” When identified, immediate referral to professionals is needed.
In addition to these recommendations, another team from the American College of Surgeons has published an overview of ways to address the inequities that contribute to violence. “We advocate for federal funding to support the development of hospital-based and community programs for violence intervention and prevention,” Dr. Bulger said.
Dr. Bailey said that as a gun owner himself, he thinks other gun owners would support these recommendations.
“I do not believe that the steps recommended ... pose undue burden on the rights of individual gun owners,” he said.
The time is now
Most firearm injuries are not from mass shooting events, Dr. Kerby said.
“My own trauma center has seen a 40% increase in the number of firearm injuries just in the last 2 years,” he added, “and these numbers continue to grow.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Their strategies can work regardless of where you stand on the Second Amendment of the Constitution, said Patricia Turner, MD. “Our proposals are embraced by both gun owners and non–gun owners alike, and we are unique in that regard.”
These “implementable solutions” could prevent the next massacre, Dr. Turner, executive director of the American College of Surgeons, said during a news briefing the group sponsored on June 2.
“Our future – indeed all of our futures – depend on our ability to find durable, actionable steps that we can implement tomorrow to save lives,” she said.
Firsthand perspective
“Sadly I’m here today as a trauma surgeon who has cared for two of the largest mass shootings in modern U.S. history,” said Ronald Stewart, MD, chair of the department of surgery at University Hospital in San Antonio, Texas.
Dr. Stewart treated victims of the 2017 Sutherland Springs First Baptist Church shooting – where 27 people died, including the shooter – and the recent Uvalde school shooting, both in Texas.
“The injuries inflicted by high-velocity weapons used at both of these attacks are horrific. A high-capacity, magazine-fed automatic rifle such as the AR-15 causes extremely destructive tissue wounds,” he said.
One of the group’s proposals is to increase the regulation of high-velocity weapons, including AR-15s.
“These wounds are horribly lethal at close range, and sadly, most victims do not survive long enough to make it to a trauma center,” Dr. Stewart said.
On a positive note, “all of our current [Uvalde] patients are improving, which really brings us joy in this dark time,” he said. “But all of them have a long road to deal with recovery with both the physical and emotional impact of their injuries.”
Jeffrey Kerby, MD, agreed.
“Trauma surgeons see the short-term physical effects of these injuries and watch patients struggle with the long-term impact of these wounds,” said Dr. Kerby, director of trauma and acute care surgery at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Surgeons feel ‘profound impact’ of shootings
“Firearm violence has a profound impact on surgeons, and we are the undisputed subject matter experts in treating the tragic results,” said Patrick Bailey, MD, medical director for advocacy at the American College of Surgeons.
“This impacts surgeons as well,” said Dr. Kerby, chair of the Committee on Trauma for the surgeons’ group. “We are human, and we can’t help but share in the grief, the pain, and the suffering that our patients endure.
“As a pediatric surgeon ... I have too often witnessed the impact of firearm violence, and obviously, the devastation extends beyond the victims to their families,” he said. “To put it succinctly, in our culture, parents are not supposed to be put in a position of burying their children.”
A public health crisis
“It’s important to recognize that we’ve been talking about a public health approach,” said Eileen Bulger, MD, acting chief of the trauma division at the University of Washington in Seattle. That strategy is important for engaging both firearm owners and communities that have a higher risk for firearm violence, she said.
A committee of the American College of Surgeons developed specific recommendations in 2018, which are still valid today. The group brought together surgeons from across the U.S. including “passionate firearm owners and experts in firearm safety,” Dr. Bulger said.
The committee, for example, agreed on 10 specific recommendations “that we believe are bipartisan and could have an immediate impact in saving lives.”
“I’m a lifelong gun owner,” Dr. Bailey said, emphasizing that the team’s process included participation and perspective from other surgeons “who, like me, are also gun owners, but gun owners who also seek to reduce the impact of firearm violence in our country.”
The recommendations address these areas:
- Gun ownership
- Firearm registration
- Licensure
- Education and training
- Ownership responsibilities
- Mandatory reporting and risk reduction
- Safety innovation and technology
- Research
- The culture of violence
- Social isolation and mental health
For example, “we currently have certain classes of weapons with significant offensive capability,” Dr. Bulger said, “that are appropriately restricted and regulated under the National Firearms Act as Class 3 weapons.”
This group includes fully automatic machine guns, explosive devices, and short-barrel shotguns.
“We recommend a formal reassessment of the firearms designated within each of these national firearms classifications,” Dr. Bulger said.
For example, high-capacity, magazine-fed semiautomatic rifles, such as the AR-15, should be considered for reclassification as NFA Class 3 firearms, or they should get a new designation with tighter regulation.
The ACS endorses formal firearm safety training for all new gun owners. Also, owners who do not provide reasonably safe firearm storage should be held responsible for events related to the discharge of their firearms, Dr. Bulger said. And people who are deemed an imminent threat to themselves or others through firearm ownership should be temporarily or permanently restricted, with due process.
Research and reporting reforms
The ACS is also calling for research on firearm injuries and firearm injury prevention to be federally funded, Dr. Bulger said. The research should be done in a nonpartisan manner, she said.
“We have concerns that the manner and tone in which information is released to the public may lead to copycat mass killers,” she said. “The ACS recommends that law enforcement officials and the press take steps to eliminate the notoriety of the shooter, for example.”
Dr. Bulger also addressed the mental health angle. “We encourage recognition of mental health warning signs and social isolation by teachers, counselors, peers, and parents.” When identified, immediate referral to professionals is needed.
In addition to these recommendations, another team from the American College of Surgeons has published an overview of ways to address the inequities that contribute to violence. “We advocate for federal funding to support the development of hospital-based and community programs for violence intervention and prevention,” Dr. Bulger said.
Dr. Bailey said that as a gun owner himself, he thinks other gun owners would support these recommendations.
“I do not believe that the steps recommended ... pose undue burden on the rights of individual gun owners,” he said.
The time is now
Most firearm injuries are not from mass shooting events, Dr. Kerby said.
“My own trauma center has seen a 40% increase in the number of firearm injuries just in the last 2 years,” he added, “and these numbers continue to grow.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Lupus mutation may unlock targeted drugs for patient subset
Scientists have confirmed that a receptor long suspected to be linked to lupus is, in fact, a major driver of the autoimmune disease for at least some subset of patients, according to a study recently published in Nature. Researchers discovered the crucial role of toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) because of a rare mutation in a pediatric patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who had a particularly severe presentation.
“Sometimes it’s valuable to find these very severe cases where there is one mutation that has a strong effect because if we understand how those mutations work, the lessons we learn can generally tell us about disease mechanisms,” explained senior author Carola G. Vinuesa, MD, PhD, of the Centre for Personalised Immunology at Australian National University in Canberra and The Francis Crick Institute in London.

“It’s quite difficult to find one mutation that can alone cause the entire disease,” Dr. Vinuesa added, but what it reveals about how the disease develops may lead to more effective targeted therapies than the immune suppressants most often used to treat lupus currently.
The mutation they found was in the TLR7 gene that encodes the TLR7 protein. TLR7 is a receptor used by immune cells to identify viral RNA so they can fight off viral infections, including COVID-19. But if the body’s own genetic material binds to TLR7 in susceptible individuals, it can lead to an overproduction of type 1 interferons, which are cytokines that trigger or exacerbate the immune reactions that lead to lupus symptoms. The TLR7 gene occurs on the X chromosome, which may explain men’s greater susceptibility to COVID-19 and the greater incidence of lupus in women, who have two X chromosomes instead of the one that men have, Dr. Vinuesa said.
Previous research had shown an association between TLR7 and lupus, but this new study is the first to provide definitive proof that a TLR7 mutation by itself can directly cause human lupus. After discovering the variant in the patient, Dr. Vinuesa’s team used CRISPR to edit the genome of a mouse model and introduce the same mutation the patient had. “And they developed full-blown disease, just with this one single base-pair substitution – 1 letter in the 3 billion letters of the genome,” Dr. Vinuesa said. “It tells us that these receptors are not just there to recognize viral RNA, that in some circumstances, they could be triggered by our own nucleic acids.”
One pathway among many?
The finding does not mean that every lupus patient has this mutation, which remains rare, but suggests that overactivity in this receptor already reported in many lupus patients may be causally related to disease, Dr. Vinuesa said.
Noa Schwartz, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and director of the Montefiore-Einstein Institute for Lupus Care and Research, said in an interview that lupus is thought of as a syndrome, a collection of different but similar diseases that don’t necessarily have a single cause. But finding a single gene mutation that could potentially lead to lupus is an important piece of the puzzle, said Dr. Schwartz, who was not involved in the study. Based on past research in mice models, “we’ve hypothesized that TLR7 is important in humans as well, but this is the last nail in the coffin.”
One of the key questions this finding has prompted is how many patients’ disease results from TLR7 activity. “Because of the evidence from Ignacio Sanz’s group demonstrating TLR7 overactivity in a significant fraction of SLE patients, we believe that it is probably going to be pretty important,” Dr. Vinuesa said. “My feeling is that it is going to be quite a central pathway in lupus pathogenesis, if not the central pathway.”
Dr. Schwartz was more cautious, noting that it is probably important for a subset of patients but may “have a limited effect on the general lupus population.” While it’s not yet clear how large that subset is, it is possible it will include people with cutaneous lupus, those with primarily dermatologic symptoms.
“Hydroxychloroquine works particularly well for cutaneous manifestations of lupus, and one of the ways that works is by inhibiting TLR7 and TLR9, so this [finding] potentially matters for skin disease and lupus, but it’s very early,” Dr. Schwartz said. If it does turn out that TLR7 activity is particularly associated with cutaneous lupus, it may mean therapies with fewer side effects, she said. “Specifically for cutaneous lupus, the concept of suppressing the entire immune system for skin illness sometimes feels, especially to patients, very extreme, so they are [patients] who directed therapy could be so especially relevant for.”
Laura Lewandowski, MD, an assistant clinical investigator and head of the lupus genomics and global health disparities unit at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Disease, described this study as particularly remarkable in the way it revealed the mechanism leading to lupus symptoms.
“As whole genome sequencing becomes faster and less expensive, more and more people are employing them in their studies,” most of which report changes in certain genes, Dr. Lewandowski said. “One of the most striking findings about this paper was that they took it to the next step and did a really elegant study on the exact way this gain-of-function TLR7 mutation leads to the autoimmunity that we see in lupus. The detail of mechanism in this paper is really unique.”
A step toward personalized medicine
Dr. Lewandowski is part of a team that recently presented a poster related to genomic sequencing in lupus patients at the annual meeting of the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance. Her study reported on the whole genome sequencing of patients with childhood-onset SLE who were already enrolled in the CARRA Lupus Registry. Children with lupus may be more likely than adults to have rare genetic variants, so a registry of childhood-onset SLE patients with fully sequenced genomes provides an opportunity to look for single-gene mutations specifically linked to lupus, said Dr. Lewandowski, who has recently begun a research collaboration with Dr. Vinuesa.
“As we move forward and more and more patients are included in these studies, we will understand a little bit more about the genetic architecture of patients who have rare variations leading to disease, or even common variations,” Dr. Lewandowski said about the intersection between her research and Dr. Vinuesa’s study. The more data they gather, the more they can explore the possible interactions of rare and common variants that play a role in SLE as well as what environmental triggers, such as viral infection or pollution exposure, might tip someone into having an autoimmune disease. “We’re just starting to peek under the hood,” Dr. Lewandowski said.
If further research can reveal the relative contribution of genetics to the disease and what those genetic drivers are, it may allow for greater precision in therapies and “ultimately improve the quality of life for our patients, the ultimate goal of all of these studies,” Dr. Lewandowski said.
Drugs that target TLR7 already exist for other indications, and clinical trials have already begun to see if these TLR7 inhibitors benefit lupus patients.
“If the clinical trials work, this will be quite a nice, targeted therapy with potentially much less side effects than other therapies on the market at the moment,” Dr. Vinuesa said. She is cautiously hopeful, saying it’s likely to make an impact on lupus treatment, but it’s too early to say precisely how much.
“It allows us to understand the disease mechanisms a little bit better and to try and assess what percentage of patients’ disease can be explained by overactivity in this receptor,” Dr. Vinuesa said. She thinks it’s possible that TLR7 over activation may be relevant to other systemic autoimmune diseases as well, such as Sjögren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, or juvenile dermatomyositis, but it will take more studies to find out.
“Right now, we have medicines that broadly inhibit the immune system and aren’t as targeted, but we have a lot more clinical and scientific work to do before we move this field forward for lupus patients,” Dr. Lewandowski said. “This is one case where they were able to find the exact molecular defect, and it’s not the end of the path of precision medicine — it’s the beginning.”
Dr. Vinuesa, Dr. Schwartz, and Dr. Lewandowski reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scientists have confirmed that a receptor long suspected to be linked to lupus is, in fact, a major driver of the autoimmune disease for at least some subset of patients, according to a study recently published in Nature. Researchers discovered the crucial role of toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) because of a rare mutation in a pediatric patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who had a particularly severe presentation.
“Sometimes it’s valuable to find these very severe cases where there is one mutation that has a strong effect because if we understand how those mutations work, the lessons we learn can generally tell us about disease mechanisms,” explained senior author Carola G. Vinuesa, MD, PhD, of the Centre for Personalised Immunology at Australian National University in Canberra and The Francis Crick Institute in London.

“It’s quite difficult to find one mutation that can alone cause the entire disease,” Dr. Vinuesa added, but what it reveals about how the disease develops may lead to more effective targeted therapies than the immune suppressants most often used to treat lupus currently.
The mutation they found was in the TLR7 gene that encodes the TLR7 protein. TLR7 is a receptor used by immune cells to identify viral RNA so they can fight off viral infections, including COVID-19. But if the body’s own genetic material binds to TLR7 in susceptible individuals, it can lead to an overproduction of type 1 interferons, which are cytokines that trigger or exacerbate the immune reactions that lead to lupus symptoms. The TLR7 gene occurs on the X chromosome, which may explain men’s greater susceptibility to COVID-19 and the greater incidence of lupus in women, who have two X chromosomes instead of the one that men have, Dr. Vinuesa said.
Previous research had shown an association between TLR7 and lupus, but this new study is the first to provide definitive proof that a TLR7 mutation by itself can directly cause human lupus. After discovering the variant in the patient, Dr. Vinuesa’s team used CRISPR to edit the genome of a mouse model and introduce the same mutation the patient had. “And they developed full-blown disease, just with this one single base-pair substitution – 1 letter in the 3 billion letters of the genome,” Dr. Vinuesa said. “It tells us that these receptors are not just there to recognize viral RNA, that in some circumstances, they could be triggered by our own nucleic acids.”
One pathway among many?
The finding does not mean that every lupus patient has this mutation, which remains rare, but suggests that overactivity in this receptor already reported in many lupus patients may be causally related to disease, Dr. Vinuesa said.
Noa Schwartz, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and director of the Montefiore-Einstein Institute for Lupus Care and Research, said in an interview that lupus is thought of as a syndrome, a collection of different but similar diseases that don’t necessarily have a single cause. But finding a single gene mutation that could potentially lead to lupus is an important piece of the puzzle, said Dr. Schwartz, who was not involved in the study. Based on past research in mice models, “we’ve hypothesized that TLR7 is important in humans as well, but this is the last nail in the coffin.”
One of the key questions this finding has prompted is how many patients’ disease results from TLR7 activity. “Because of the evidence from Ignacio Sanz’s group demonstrating TLR7 overactivity in a significant fraction of SLE patients, we believe that it is probably going to be pretty important,” Dr. Vinuesa said. “My feeling is that it is going to be quite a central pathway in lupus pathogenesis, if not the central pathway.”
Dr. Schwartz was more cautious, noting that it is probably important for a subset of patients but may “have a limited effect on the general lupus population.” While it’s not yet clear how large that subset is, it is possible it will include people with cutaneous lupus, those with primarily dermatologic symptoms.
“Hydroxychloroquine works particularly well for cutaneous manifestations of lupus, and one of the ways that works is by inhibiting TLR7 and TLR9, so this [finding] potentially matters for skin disease and lupus, but it’s very early,” Dr. Schwartz said. If it does turn out that TLR7 activity is particularly associated with cutaneous lupus, it may mean therapies with fewer side effects, she said. “Specifically for cutaneous lupus, the concept of suppressing the entire immune system for skin illness sometimes feels, especially to patients, very extreme, so they are [patients] who directed therapy could be so especially relevant for.”
Laura Lewandowski, MD, an assistant clinical investigator and head of the lupus genomics and global health disparities unit at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Disease, described this study as particularly remarkable in the way it revealed the mechanism leading to lupus symptoms.
“As whole genome sequencing becomes faster and less expensive, more and more people are employing them in their studies,” most of which report changes in certain genes, Dr. Lewandowski said. “One of the most striking findings about this paper was that they took it to the next step and did a really elegant study on the exact way this gain-of-function TLR7 mutation leads to the autoimmunity that we see in lupus. The detail of mechanism in this paper is really unique.”
A step toward personalized medicine
Dr. Lewandowski is part of a team that recently presented a poster related to genomic sequencing in lupus patients at the annual meeting of the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance. Her study reported on the whole genome sequencing of patients with childhood-onset SLE who were already enrolled in the CARRA Lupus Registry. Children with lupus may be more likely than adults to have rare genetic variants, so a registry of childhood-onset SLE patients with fully sequenced genomes provides an opportunity to look for single-gene mutations specifically linked to lupus, said Dr. Lewandowski, who has recently begun a research collaboration with Dr. Vinuesa.
“As we move forward and more and more patients are included in these studies, we will understand a little bit more about the genetic architecture of patients who have rare variations leading to disease, or even common variations,” Dr. Lewandowski said about the intersection between her research and Dr. Vinuesa’s study. The more data they gather, the more they can explore the possible interactions of rare and common variants that play a role in SLE as well as what environmental triggers, such as viral infection or pollution exposure, might tip someone into having an autoimmune disease. “We’re just starting to peek under the hood,” Dr. Lewandowski said.
If further research can reveal the relative contribution of genetics to the disease and what those genetic drivers are, it may allow for greater precision in therapies and “ultimately improve the quality of life for our patients, the ultimate goal of all of these studies,” Dr. Lewandowski said.
Drugs that target TLR7 already exist for other indications, and clinical trials have already begun to see if these TLR7 inhibitors benefit lupus patients.
“If the clinical trials work, this will be quite a nice, targeted therapy with potentially much less side effects than other therapies on the market at the moment,” Dr. Vinuesa said. She is cautiously hopeful, saying it’s likely to make an impact on lupus treatment, but it’s too early to say precisely how much.
“It allows us to understand the disease mechanisms a little bit better and to try and assess what percentage of patients’ disease can be explained by overactivity in this receptor,” Dr. Vinuesa said. She thinks it’s possible that TLR7 over activation may be relevant to other systemic autoimmune diseases as well, such as Sjögren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, or juvenile dermatomyositis, but it will take more studies to find out.
“Right now, we have medicines that broadly inhibit the immune system and aren’t as targeted, but we have a lot more clinical and scientific work to do before we move this field forward for lupus patients,” Dr. Lewandowski said. “This is one case where they were able to find the exact molecular defect, and it’s not the end of the path of precision medicine — it’s the beginning.”
Dr. Vinuesa, Dr. Schwartz, and Dr. Lewandowski reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scientists have confirmed that a receptor long suspected to be linked to lupus is, in fact, a major driver of the autoimmune disease for at least some subset of patients, according to a study recently published in Nature. Researchers discovered the crucial role of toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) because of a rare mutation in a pediatric patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who had a particularly severe presentation.
“Sometimes it’s valuable to find these very severe cases where there is one mutation that has a strong effect because if we understand how those mutations work, the lessons we learn can generally tell us about disease mechanisms,” explained senior author Carola G. Vinuesa, MD, PhD, of the Centre for Personalised Immunology at Australian National University in Canberra and The Francis Crick Institute in London.

“It’s quite difficult to find one mutation that can alone cause the entire disease,” Dr. Vinuesa added, but what it reveals about how the disease develops may lead to more effective targeted therapies than the immune suppressants most often used to treat lupus currently.
The mutation they found was in the TLR7 gene that encodes the TLR7 protein. TLR7 is a receptor used by immune cells to identify viral RNA so they can fight off viral infections, including COVID-19. But if the body’s own genetic material binds to TLR7 in susceptible individuals, it can lead to an overproduction of type 1 interferons, which are cytokines that trigger or exacerbate the immune reactions that lead to lupus symptoms. The TLR7 gene occurs on the X chromosome, which may explain men’s greater susceptibility to COVID-19 and the greater incidence of lupus in women, who have two X chromosomes instead of the one that men have, Dr. Vinuesa said.
Previous research had shown an association between TLR7 and lupus, but this new study is the first to provide definitive proof that a TLR7 mutation by itself can directly cause human lupus. After discovering the variant in the patient, Dr. Vinuesa’s team used CRISPR to edit the genome of a mouse model and introduce the same mutation the patient had. “And they developed full-blown disease, just with this one single base-pair substitution – 1 letter in the 3 billion letters of the genome,” Dr. Vinuesa said. “It tells us that these receptors are not just there to recognize viral RNA, that in some circumstances, they could be triggered by our own nucleic acids.”
One pathway among many?
The finding does not mean that every lupus patient has this mutation, which remains rare, but suggests that overactivity in this receptor already reported in many lupus patients may be causally related to disease, Dr. Vinuesa said.
Noa Schwartz, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and director of the Montefiore-Einstein Institute for Lupus Care and Research, said in an interview that lupus is thought of as a syndrome, a collection of different but similar diseases that don’t necessarily have a single cause. But finding a single gene mutation that could potentially lead to lupus is an important piece of the puzzle, said Dr. Schwartz, who was not involved in the study. Based on past research in mice models, “we’ve hypothesized that TLR7 is important in humans as well, but this is the last nail in the coffin.”
One of the key questions this finding has prompted is how many patients’ disease results from TLR7 activity. “Because of the evidence from Ignacio Sanz’s group demonstrating TLR7 overactivity in a significant fraction of SLE patients, we believe that it is probably going to be pretty important,” Dr. Vinuesa said. “My feeling is that it is going to be quite a central pathway in lupus pathogenesis, if not the central pathway.”
Dr. Schwartz was more cautious, noting that it is probably important for a subset of patients but may “have a limited effect on the general lupus population.” While it’s not yet clear how large that subset is, it is possible it will include people with cutaneous lupus, those with primarily dermatologic symptoms.
“Hydroxychloroquine works particularly well for cutaneous manifestations of lupus, and one of the ways that works is by inhibiting TLR7 and TLR9, so this [finding] potentially matters for skin disease and lupus, but it’s very early,” Dr. Schwartz said. If it does turn out that TLR7 activity is particularly associated with cutaneous lupus, it may mean therapies with fewer side effects, she said. “Specifically for cutaneous lupus, the concept of suppressing the entire immune system for skin illness sometimes feels, especially to patients, very extreme, so they are [patients] who directed therapy could be so especially relevant for.”
Laura Lewandowski, MD, an assistant clinical investigator and head of the lupus genomics and global health disparities unit at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Disease, described this study as particularly remarkable in the way it revealed the mechanism leading to lupus symptoms.
“As whole genome sequencing becomes faster and less expensive, more and more people are employing them in their studies,” most of which report changes in certain genes, Dr. Lewandowski said. “One of the most striking findings about this paper was that they took it to the next step and did a really elegant study on the exact way this gain-of-function TLR7 mutation leads to the autoimmunity that we see in lupus. The detail of mechanism in this paper is really unique.”
A step toward personalized medicine
Dr. Lewandowski is part of a team that recently presented a poster related to genomic sequencing in lupus patients at the annual meeting of the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance. Her study reported on the whole genome sequencing of patients with childhood-onset SLE who were already enrolled in the CARRA Lupus Registry. Children with lupus may be more likely than adults to have rare genetic variants, so a registry of childhood-onset SLE patients with fully sequenced genomes provides an opportunity to look for single-gene mutations specifically linked to lupus, said Dr. Lewandowski, who has recently begun a research collaboration with Dr. Vinuesa.
“As we move forward and more and more patients are included in these studies, we will understand a little bit more about the genetic architecture of patients who have rare variations leading to disease, or even common variations,” Dr. Lewandowski said about the intersection between her research and Dr. Vinuesa’s study. The more data they gather, the more they can explore the possible interactions of rare and common variants that play a role in SLE as well as what environmental triggers, such as viral infection or pollution exposure, might tip someone into having an autoimmune disease. “We’re just starting to peek under the hood,” Dr. Lewandowski said.
If further research can reveal the relative contribution of genetics to the disease and what those genetic drivers are, it may allow for greater precision in therapies and “ultimately improve the quality of life for our patients, the ultimate goal of all of these studies,” Dr. Lewandowski said.
Drugs that target TLR7 already exist for other indications, and clinical trials have already begun to see if these TLR7 inhibitors benefit lupus patients.
“If the clinical trials work, this will be quite a nice, targeted therapy with potentially much less side effects than other therapies on the market at the moment,” Dr. Vinuesa said. She is cautiously hopeful, saying it’s likely to make an impact on lupus treatment, but it’s too early to say precisely how much.
“It allows us to understand the disease mechanisms a little bit better and to try and assess what percentage of patients’ disease can be explained by overactivity in this receptor,” Dr. Vinuesa said. She thinks it’s possible that TLR7 over activation may be relevant to other systemic autoimmune diseases as well, such as Sjögren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, or juvenile dermatomyositis, but it will take more studies to find out.
“Right now, we have medicines that broadly inhibit the immune system and aren’t as targeted, but we have a lot more clinical and scientific work to do before we move this field forward for lupus patients,” Dr. Lewandowski said. “This is one case where they were able to find the exact molecular defect, and it’s not the end of the path of precision medicine — it’s the beginning.”
Dr. Vinuesa, Dr. Schwartz, and Dr. Lewandowski reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE