User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
Adalimumab for Psoriasis: Study Compares Biosimilars Vs. Originator
TOPLINE:
rate than those who remained on Humira.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cohort study using data on patients with psoriasis who were treated with adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor used to treat moderate to severe psoriasis, from the French National Health Data System, British Association of Dermatologists Biologics and Immunomodulators Register, and Spanish Registry of Systemic Therapy in Psoriasis.
- The analysis included 7387 adalimumab-naive patients who were new users of an adalimumab biosimilar and 3654 patients (switchers) who switched from Humira to a biosimilar. Patients were matched and compared with patients receiving Humira.
- Co-primary outcomes of the study were drug discontinuation and serious adverse events.
- Researchers assessed the following adalimumab biosimilar brands: Amgevita, Imraldi, Hyrimoz, Idacio, and Hulio.
TAKEAWAY:
- All-cause drug discontinuation rates were similar between new users of biosimilars and Humira new users (hazard ratio [HR], 0.99; 95% CI, 0.94-1.04).
- Discontinuation rates were higher among those who switched from Humira to a biosimilar (HR, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.19-1.52) than among those who stayed on Humira. Switching to Amgevita (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.13-1.27), Imraldi (HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.33-1.76), and Hyrimoz (HR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.29-2.52) was associated with higher discontinuation rates.
- Serious adverse events were not significantly different between new users of Humira and biosimilar new users (incidence rate ratio [IRR], 0.91; 95% CI, 0.80-1.05), and between patients who switched from a biosimilar to Humira and those who stayed on Humira (IRR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.83-1.01).
- No significant differences in discontinuation because of ineffectiveness were found between biosimilar and Humira new users (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.88-1.08). Discontinuation because of adverse events was also comparable for all biosimilars among new users, except for Hyrimoz (HR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.35-0.85), which showed fewer discontinuations than Humira.
IN PRACTICE:
“This study found comparable drug survival and safety between adalimumab biosimilars and Humira in adalimumab-naive patients, supporting the use of biosimilars as viable alternatives for new patients,” the authors wrote. However, noting that discontinuation was more likely among those who switched from Humira to a biosimilar, they added: “Changes in treatment response, skin or injection site reactions, and nocebo effects may contribute to treatment discontinuation post-switch. Thus, patients who switch from Humira to biosimilars may require closer monitoring and support to alleviate these challenges.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Duc Binh Phan, Dermatology Centre, Northern Care Alliance NHS Foundation Trust in Manchester, England. It was published online in The British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Unmeasured factors including psychological perceptions, regional policies, and drug availability could influence drug survival, making the results not fully reflective of treatment effectiveness or safety. Most Humira users in registries were enrolled before biosimilars became available, making it impractical to match new users on the basis of treatment initiation years. Additionally, reasons for discontinuation were not available in the French National Health Data System.
DISCLOSURES:
In the United Kingdom, the research was funded by the Psoriasis Association PhD studentship and supported by the NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. In France, the authors are employees of the French National Health Insurance, the French National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products, and the Assistance Publique — Hôpitaux de Paris and received no funding. The authors reported receiving consulting and speaker fees and clinical trial sponsorship from various pharmaceutical companies. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
rate than those who remained on Humira.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cohort study using data on patients with psoriasis who were treated with adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor used to treat moderate to severe psoriasis, from the French National Health Data System, British Association of Dermatologists Biologics and Immunomodulators Register, and Spanish Registry of Systemic Therapy in Psoriasis.
- The analysis included 7387 adalimumab-naive patients who were new users of an adalimumab biosimilar and 3654 patients (switchers) who switched from Humira to a biosimilar. Patients were matched and compared with patients receiving Humira.
- Co-primary outcomes of the study were drug discontinuation and serious adverse events.
- Researchers assessed the following adalimumab biosimilar brands: Amgevita, Imraldi, Hyrimoz, Idacio, and Hulio.
TAKEAWAY:
- All-cause drug discontinuation rates were similar between new users of biosimilars and Humira new users (hazard ratio [HR], 0.99; 95% CI, 0.94-1.04).
- Discontinuation rates were higher among those who switched from Humira to a biosimilar (HR, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.19-1.52) than among those who stayed on Humira. Switching to Amgevita (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.13-1.27), Imraldi (HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.33-1.76), and Hyrimoz (HR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.29-2.52) was associated with higher discontinuation rates.
- Serious adverse events were not significantly different between new users of Humira and biosimilar new users (incidence rate ratio [IRR], 0.91; 95% CI, 0.80-1.05), and between patients who switched from a biosimilar to Humira and those who stayed on Humira (IRR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.83-1.01).
- No significant differences in discontinuation because of ineffectiveness were found between biosimilar and Humira new users (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.88-1.08). Discontinuation because of adverse events was also comparable for all biosimilars among new users, except for Hyrimoz (HR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.35-0.85), which showed fewer discontinuations than Humira.
IN PRACTICE:
“This study found comparable drug survival and safety between adalimumab biosimilars and Humira in adalimumab-naive patients, supporting the use of biosimilars as viable alternatives for new patients,” the authors wrote. However, noting that discontinuation was more likely among those who switched from Humira to a biosimilar, they added: “Changes in treatment response, skin or injection site reactions, and nocebo effects may contribute to treatment discontinuation post-switch. Thus, patients who switch from Humira to biosimilars may require closer monitoring and support to alleviate these challenges.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Duc Binh Phan, Dermatology Centre, Northern Care Alliance NHS Foundation Trust in Manchester, England. It was published online in The British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Unmeasured factors including psychological perceptions, regional policies, and drug availability could influence drug survival, making the results not fully reflective of treatment effectiveness or safety. Most Humira users in registries were enrolled before biosimilars became available, making it impractical to match new users on the basis of treatment initiation years. Additionally, reasons for discontinuation were not available in the French National Health Data System.
DISCLOSURES:
In the United Kingdom, the research was funded by the Psoriasis Association PhD studentship and supported by the NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. In France, the authors are employees of the French National Health Insurance, the French National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products, and the Assistance Publique — Hôpitaux de Paris and received no funding. The authors reported receiving consulting and speaker fees and clinical trial sponsorship from various pharmaceutical companies. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
rate than those who remained on Humira.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cohort study using data on patients with psoriasis who were treated with adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor used to treat moderate to severe psoriasis, from the French National Health Data System, British Association of Dermatologists Biologics and Immunomodulators Register, and Spanish Registry of Systemic Therapy in Psoriasis.
- The analysis included 7387 adalimumab-naive patients who were new users of an adalimumab biosimilar and 3654 patients (switchers) who switched from Humira to a biosimilar. Patients were matched and compared with patients receiving Humira.
- Co-primary outcomes of the study were drug discontinuation and serious adverse events.
- Researchers assessed the following adalimumab biosimilar brands: Amgevita, Imraldi, Hyrimoz, Idacio, and Hulio.
TAKEAWAY:
- All-cause drug discontinuation rates were similar between new users of biosimilars and Humira new users (hazard ratio [HR], 0.99; 95% CI, 0.94-1.04).
- Discontinuation rates were higher among those who switched from Humira to a biosimilar (HR, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.19-1.52) than among those who stayed on Humira. Switching to Amgevita (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.13-1.27), Imraldi (HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.33-1.76), and Hyrimoz (HR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.29-2.52) was associated with higher discontinuation rates.
- Serious adverse events were not significantly different between new users of Humira and biosimilar new users (incidence rate ratio [IRR], 0.91; 95% CI, 0.80-1.05), and between patients who switched from a biosimilar to Humira and those who stayed on Humira (IRR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.83-1.01).
- No significant differences in discontinuation because of ineffectiveness were found between biosimilar and Humira new users (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.88-1.08). Discontinuation because of adverse events was also comparable for all biosimilars among new users, except for Hyrimoz (HR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.35-0.85), which showed fewer discontinuations than Humira.
IN PRACTICE:
“This study found comparable drug survival and safety between adalimumab biosimilars and Humira in adalimumab-naive patients, supporting the use of biosimilars as viable alternatives for new patients,” the authors wrote. However, noting that discontinuation was more likely among those who switched from Humira to a biosimilar, they added: “Changes in treatment response, skin or injection site reactions, and nocebo effects may contribute to treatment discontinuation post-switch. Thus, patients who switch from Humira to biosimilars may require closer monitoring and support to alleviate these challenges.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Duc Binh Phan, Dermatology Centre, Northern Care Alliance NHS Foundation Trust in Manchester, England. It was published online in The British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Unmeasured factors including psychological perceptions, regional policies, and drug availability could influence drug survival, making the results not fully reflective of treatment effectiveness or safety. Most Humira users in registries were enrolled before biosimilars became available, making it impractical to match new users on the basis of treatment initiation years. Additionally, reasons for discontinuation were not available in the French National Health Data System.
DISCLOSURES:
In the United Kingdom, the research was funded by the Psoriasis Association PhD studentship and supported by the NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. In France, the authors are employees of the French National Health Insurance, the French National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products, and the Assistance Publique — Hôpitaux de Paris and received no funding. The authors reported receiving consulting and speaker fees and clinical trial sponsorship from various pharmaceutical companies. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Treating Onychomycosis: Pearls from a Podiatrist
LAS VEGAS —
According to Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM, a professor at the Samuel Merritt University College of Podiatric Medicine, Oakland, California, most cases of onychomycosis are caused by the dermatophytes Trichophyton rubrum and T mentagrophytes, although the cause can also be a mixed infection. “Dermatophytes are going to impact the nails first, and molds may come in and join the party later,” she said at the Society of Dermatology Physician Associates (SDPA) 22nd Annual Fall Dermatology Conference.
“The distal subungual onychomycosis (DSO) type is still the most common, but don’t forget that onychomycosis and nail psoriasis can happen at the same time. What we can’t lose sight of is that onychomycosis is a disease of the nail bed, which ultimately affects the nail plate; it’s not a disease of the nail plate first.”
Her diagnostic approach combines periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining with fungal culture “because I like to know the speciation,” she said. “PAS doesn’t give me the speciation; fungal cultures should. PCR can be expensive, but that can give me speciation.”
How Does This Happen?
Fungal DSO occurs because of exposure to a dermatophyte, which can be as simple as tinea pedis. “Perhaps it’s the environment in the shoe,” said Vlahovic, one of the authors of a textbook on onychomycosis. “That’s something I’m always concentrating on with the patient. What is your foot hygiene like? What’s your shoe and sock wear? What’s your level of physical activity? You can have trauma to the hyponychium, where the skin and the nail meet. Maybe they trim their nails too close to the skin, or maybe there’s another skin condition like psoriasis.”
The dermatophyte, she continued, enters and invades the nail at the hyponychium and uses the keratinase enzyme to digest keratin in the nail bed. Mild inflammation develops, and pH changes cause focal parakeratosis and subungual hyperkeratosis in the form of onycholysis and subungual debris. “Hyphae then invade the lamina of the nail plate, which causes brittle nails,” she said. “The compromised hyponychium creates a reservoir for molds and bacteria.”
Therapies approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for onychomycosis include the topical agents efinaconazole, tavaborole, and ciclopirox; the oral agents terbinafine and itraconazole; and laser therapy. Off-label, Vlahovic said that she sometimes uses oral fluconazole, pulsed dosing for terbinafine, and booster doses of terbinafine or any approved oral antifungal agent. Pulse dosing for itraconazole is FDA-approved for fingernails but not for toenails.
“We don’t have any oral antifungals that are approved for children, but we do have weight-based dosing,” she noted. Other off-label treatments for onychomycosis that patients may come across while browsing the internet but do not penetrate the nail plate, include products containing tolnaftate, tree oil, and undecylenic acid, “which is a very long-chain antifungal,” Vlahovic said. “It’s so huge that it can’t get through the nail plate. These products must get through the nail plate into the nail bed where the infection is.”
According to therapeutic recommendations for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in the United States, published in 2021, terbinafine is the primary choice for oral treatment and efinaconazole 10% for topical treatment. There are no current treatment recommendations for pregnant or lactating patients. “I always defer to the obstetrician,” said Vlahovic, a coauthor of the recommendations. For pediatric patients, there are approved topical medications: Efinaconazole and tavaborole for ages 6 and up and ciclopirox for ages 12 years or older.
Treatment recommendations for adults vary based on clinical presentation and patient characteristics. Questions to consider: Are they older? Do they have diabetes? Are they able to reach their feet to apply medication? What other medications are they taking? Are there any kidney or liver issues that are cause for concern?
Another question to consider is whether they have concurrent nail psoriasis. “When I have those patients, I often treat the onychomycosis first and the nail psoriasis second,” she said.
Evidence for Lasers Weak
Though laser therapy is FDA approved for the temporary increase of clear nails in onychomycosis, Vlahovic is underwhelmed by the evidence of its use for onychomycosis. According to a systematic review of 261 studies, only 1 reported treatment success as 16.7%, and clinical cures ranged from 13% to 16%. “Many of the existing studies were so poorly done in terms of protocols; it was frustrating,” she said. “No study has reported complete cure. There’s a lack of standardization across laser companies and a lack of standardization across protocols.”
Before starting oral antifungal therapy, Vlahovic uses the Onychomycosis Severity Index to determine the number of nails involved and the proportion of nails that are affected. She also wants to know if the patient is taking any medication that might interfere with an oral antifungal and gets baseline liver function tests (LFTs) to document results in the chart. “You want to discuss the pros and cons of oral antifungal therapy, and you want to set realistic expectations,” she added. “These medications are not cosmetic products; they are meant to kill fungus. Sometimes patients lose sight of that.”
Vlahovic routinely offers pulse dosing of terbinafine, which is FDA approved at a dose of 250 mg/d for 90 days. Pulse dosing involves taking terbinafine 250 mg twice a day for 1 week, followed by a 3-week break. This cycle is repeated three or four times. A clinical trial found no significant difference in outcome between patients who received pulsed vs continuous terbinafine dosing for the treatment of dermatophyte onychomycosis.
What About Oral Antifungal Safety?
For patients who ask about the safety of oral antifungals, Vlahovic characterized them as “well tolerated and safe in an immunocompetent population.” In a meta-analysis of 122 studies of about 22,000 patients, the pooled risk for treatment discontinuation because of adverse events was 3.4% for terbinafine 250 mg/d and 4.21% for itraconazole 200 mg/d. The risk for liver injury requiring termination of treatment and the risk of having symptomatic elevation of LFTs were less than 2% for all regimens.
According to the best available published evidence, Vlahovic said, the onychomycosis recurrence rate ranges from 6% to 40%. “That’s a wild number. We really have no idea what the true recurrence rate is, and that’s a problem.”
Vlahovic disclosed having been a consultant to and an investigator for Ortho Dermatologics and Sagis Diagnostics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LAS VEGAS —
According to Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM, a professor at the Samuel Merritt University College of Podiatric Medicine, Oakland, California, most cases of onychomycosis are caused by the dermatophytes Trichophyton rubrum and T mentagrophytes, although the cause can also be a mixed infection. “Dermatophytes are going to impact the nails first, and molds may come in and join the party later,” she said at the Society of Dermatology Physician Associates (SDPA) 22nd Annual Fall Dermatology Conference.
“The distal subungual onychomycosis (DSO) type is still the most common, but don’t forget that onychomycosis and nail psoriasis can happen at the same time. What we can’t lose sight of is that onychomycosis is a disease of the nail bed, which ultimately affects the nail plate; it’s not a disease of the nail plate first.”
Her diagnostic approach combines periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining with fungal culture “because I like to know the speciation,” she said. “PAS doesn’t give me the speciation; fungal cultures should. PCR can be expensive, but that can give me speciation.”
How Does This Happen?
Fungal DSO occurs because of exposure to a dermatophyte, which can be as simple as tinea pedis. “Perhaps it’s the environment in the shoe,” said Vlahovic, one of the authors of a textbook on onychomycosis. “That’s something I’m always concentrating on with the patient. What is your foot hygiene like? What’s your shoe and sock wear? What’s your level of physical activity? You can have trauma to the hyponychium, where the skin and the nail meet. Maybe they trim their nails too close to the skin, or maybe there’s another skin condition like psoriasis.”
The dermatophyte, she continued, enters and invades the nail at the hyponychium and uses the keratinase enzyme to digest keratin in the nail bed. Mild inflammation develops, and pH changes cause focal parakeratosis and subungual hyperkeratosis in the form of onycholysis and subungual debris. “Hyphae then invade the lamina of the nail plate, which causes brittle nails,” she said. “The compromised hyponychium creates a reservoir for molds and bacteria.”
Therapies approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for onychomycosis include the topical agents efinaconazole, tavaborole, and ciclopirox; the oral agents terbinafine and itraconazole; and laser therapy. Off-label, Vlahovic said that she sometimes uses oral fluconazole, pulsed dosing for terbinafine, and booster doses of terbinafine or any approved oral antifungal agent. Pulse dosing for itraconazole is FDA-approved for fingernails but not for toenails.
“We don’t have any oral antifungals that are approved for children, but we do have weight-based dosing,” she noted. Other off-label treatments for onychomycosis that patients may come across while browsing the internet but do not penetrate the nail plate, include products containing tolnaftate, tree oil, and undecylenic acid, “which is a very long-chain antifungal,” Vlahovic said. “It’s so huge that it can’t get through the nail plate. These products must get through the nail plate into the nail bed where the infection is.”
According to therapeutic recommendations for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in the United States, published in 2021, terbinafine is the primary choice for oral treatment and efinaconazole 10% for topical treatment. There are no current treatment recommendations for pregnant or lactating patients. “I always defer to the obstetrician,” said Vlahovic, a coauthor of the recommendations. For pediatric patients, there are approved topical medications: Efinaconazole and tavaborole for ages 6 and up and ciclopirox for ages 12 years or older.
Treatment recommendations for adults vary based on clinical presentation and patient characteristics. Questions to consider: Are they older? Do they have diabetes? Are they able to reach their feet to apply medication? What other medications are they taking? Are there any kidney or liver issues that are cause for concern?
Another question to consider is whether they have concurrent nail psoriasis. “When I have those patients, I often treat the onychomycosis first and the nail psoriasis second,” she said.
Evidence for Lasers Weak
Though laser therapy is FDA approved for the temporary increase of clear nails in onychomycosis, Vlahovic is underwhelmed by the evidence of its use for onychomycosis. According to a systematic review of 261 studies, only 1 reported treatment success as 16.7%, and clinical cures ranged from 13% to 16%. “Many of the existing studies were so poorly done in terms of protocols; it was frustrating,” she said. “No study has reported complete cure. There’s a lack of standardization across laser companies and a lack of standardization across protocols.”
Before starting oral antifungal therapy, Vlahovic uses the Onychomycosis Severity Index to determine the number of nails involved and the proportion of nails that are affected. She also wants to know if the patient is taking any medication that might interfere with an oral antifungal and gets baseline liver function tests (LFTs) to document results in the chart. “You want to discuss the pros and cons of oral antifungal therapy, and you want to set realistic expectations,” she added. “These medications are not cosmetic products; they are meant to kill fungus. Sometimes patients lose sight of that.”
Vlahovic routinely offers pulse dosing of terbinafine, which is FDA approved at a dose of 250 mg/d for 90 days. Pulse dosing involves taking terbinafine 250 mg twice a day for 1 week, followed by a 3-week break. This cycle is repeated three or four times. A clinical trial found no significant difference in outcome between patients who received pulsed vs continuous terbinafine dosing for the treatment of dermatophyte onychomycosis.
What About Oral Antifungal Safety?
For patients who ask about the safety of oral antifungals, Vlahovic characterized them as “well tolerated and safe in an immunocompetent population.” In a meta-analysis of 122 studies of about 22,000 patients, the pooled risk for treatment discontinuation because of adverse events was 3.4% for terbinafine 250 mg/d and 4.21% for itraconazole 200 mg/d. The risk for liver injury requiring termination of treatment and the risk of having symptomatic elevation of LFTs were less than 2% for all regimens.
According to the best available published evidence, Vlahovic said, the onychomycosis recurrence rate ranges from 6% to 40%. “That’s a wild number. We really have no idea what the true recurrence rate is, and that’s a problem.”
Vlahovic disclosed having been a consultant to and an investigator for Ortho Dermatologics and Sagis Diagnostics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LAS VEGAS —
According to Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM, a professor at the Samuel Merritt University College of Podiatric Medicine, Oakland, California, most cases of onychomycosis are caused by the dermatophytes Trichophyton rubrum and T mentagrophytes, although the cause can also be a mixed infection. “Dermatophytes are going to impact the nails first, and molds may come in and join the party later,” she said at the Society of Dermatology Physician Associates (SDPA) 22nd Annual Fall Dermatology Conference.
“The distal subungual onychomycosis (DSO) type is still the most common, but don’t forget that onychomycosis and nail psoriasis can happen at the same time. What we can’t lose sight of is that onychomycosis is a disease of the nail bed, which ultimately affects the nail plate; it’s not a disease of the nail plate first.”
Her diagnostic approach combines periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining with fungal culture “because I like to know the speciation,” she said. “PAS doesn’t give me the speciation; fungal cultures should. PCR can be expensive, but that can give me speciation.”
How Does This Happen?
Fungal DSO occurs because of exposure to a dermatophyte, which can be as simple as tinea pedis. “Perhaps it’s the environment in the shoe,” said Vlahovic, one of the authors of a textbook on onychomycosis. “That’s something I’m always concentrating on with the patient. What is your foot hygiene like? What’s your shoe and sock wear? What’s your level of physical activity? You can have trauma to the hyponychium, where the skin and the nail meet. Maybe they trim their nails too close to the skin, or maybe there’s another skin condition like psoriasis.”
The dermatophyte, she continued, enters and invades the nail at the hyponychium and uses the keratinase enzyme to digest keratin in the nail bed. Mild inflammation develops, and pH changes cause focal parakeratosis and subungual hyperkeratosis in the form of onycholysis and subungual debris. “Hyphae then invade the lamina of the nail plate, which causes brittle nails,” she said. “The compromised hyponychium creates a reservoir for molds and bacteria.”
Therapies approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for onychomycosis include the topical agents efinaconazole, tavaborole, and ciclopirox; the oral agents terbinafine and itraconazole; and laser therapy. Off-label, Vlahovic said that she sometimes uses oral fluconazole, pulsed dosing for terbinafine, and booster doses of terbinafine or any approved oral antifungal agent. Pulse dosing for itraconazole is FDA-approved for fingernails but not for toenails.
“We don’t have any oral antifungals that are approved for children, but we do have weight-based dosing,” she noted. Other off-label treatments for onychomycosis that patients may come across while browsing the internet but do not penetrate the nail plate, include products containing tolnaftate, tree oil, and undecylenic acid, “which is a very long-chain antifungal,” Vlahovic said. “It’s so huge that it can’t get through the nail plate. These products must get through the nail plate into the nail bed where the infection is.”
According to therapeutic recommendations for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in the United States, published in 2021, terbinafine is the primary choice for oral treatment and efinaconazole 10% for topical treatment. There are no current treatment recommendations for pregnant or lactating patients. “I always defer to the obstetrician,” said Vlahovic, a coauthor of the recommendations. For pediatric patients, there are approved topical medications: Efinaconazole and tavaborole for ages 6 and up and ciclopirox for ages 12 years or older.
Treatment recommendations for adults vary based on clinical presentation and patient characteristics. Questions to consider: Are they older? Do they have diabetes? Are they able to reach their feet to apply medication? What other medications are they taking? Are there any kidney or liver issues that are cause for concern?
Another question to consider is whether they have concurrent nail psoriasis. “When I have those patients, I often treat the onychomycosis first and the nail psoriasis second,” she said.
Evidence for Lasers Weak
Though laser therapy is FDA approved for the temporary increase of clear nails in onychomycosis, Vlahovic is underwhelmed by the evidence of its use for onychomycosis. According to a systematic review of 261 studies, only 1 reported treatment success as 16.7%, and clinical cures ranged from 13% to 16%. “Many of the existing studies were so poorly done in terms of protocols; it was frustrating,” she said. “No study has reported complete cure. There’s a lack of standardization across laser companies and a lack of standardization across protocols.”
Before starting oral antifungal therapy, Vlahovic uses the Onychomycosis Severity Index to determine the number of nails involved and the proportion of nails that are affected. She also wants to know if the patient is taking any medication that might interfere with an oral antifungal and gets baseline liver function tests (LFTs) to document results in the chart. “You want to discuss the pros and cons of oral antifungal therapy, and you want to set realistic expectations,” she added. “These medications are not cosmetic products; they are meant to kill fungus. Sometimes patients lose sight of that.”
Vlahovic routinely offers pulse dosing of terbinafine, which is FDA approved at a dose of 250 mg/d for 90 days. Pulse dosing involves taking terbinafine 250 mg twice a day for 1 week, followed by a 3-week break. This cycle is repeated three or four times. A clinical trial found no significant difference in outcome between patients who received pulsed vs continuous terbinafine dosing for the treatment of dermatophyte onychomycosis.
What About Oral Antifungal Safety?
For patients who ask about the safety of oral antifungals, Vlahovic characterized them as “well tolerated and safe in an immunocompetent population.” In a meta-analysis of 122 studies of about 22,000 patients, the pooled risk for treatment discontinuation because of adverse events was 3.4% for terbinafine 250 mg/d and 4.21% for itraconazole 200 mg/d. The risk for liver injury requiring termination of treatment and the risk of having symptomatic elevation of LFTs were less than 2% for all regimens.
According to the best available published evidence, Vlahovic said, the onychomycosis recurrence rate ranges from 6% to 40%. “That’s a wild number. We really have no idea what the true recurrence rate is, and that’s a problem.”
Vlahovic disclosed having been a consultant to and an investigator for Ortho Dermatologics and Sagis Diagnostics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SDPA 2024
Study Finds Different Survival Rates for Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treatments in Children
results from a small single-center study showed.
A previous study found that overall drug survival of adalimumab and infliximab in adults with HS at 12 and 24 months was 56.3% and 30.5%, and 58.3% and 48.6%, respectively. “They also found that older age, longer disease duration, higher body mass index (BMI), and surgery during treatment are associated with increased drug survival,” Robyn Guo, a third-year medical student at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization following the annual Symposium on Hidradenitis Suppurativa Advances, where the study was presented during an oral abstract session. “To our knowledge, the drug survival of biologic therapies in pediatric HS patients has not been previously investigated.”
Adalimumab and infliximab are tumor necrosis factor blockers approved for multiple indications; adalimumab is approved for treating moderate to severe HS in patients aged 12 years or older. Infliximab is not approved for HS but is used to treat the disease.
To determine the drug survival of adalimumab and infliximab in pediatric patients with HS and whether patient comorbidities and HS lesion location are associated with length of biologic survival in pediatric patients with HS, Guo and colleagues used Kaplan-Meier survival curves to calculate biologic survival at 12 and 24 months following biologic initiation and Cox proportional hazards regression to analyze potential factors associated with biologic survival. The study population included 49 pediatric patients in the adalimumab cohort and 11 in the infliximab cohort.
The researchers found that drug survival for adalimumab was 90.6% at 12 months (95% CI, 83.0%-98.8%) and 78.3% at 24 months (95% CI, 67.7%-90.6%), while drug survival for infliximab was 54.5% at 12 months (95% CI, 31.8%-93.6%) and 36.4% at 24 months, an overall difference that reached statistical significance (P = .0009). “Our data suggests that adalimumab survival is significantly higher than infliximab survival in pediatric HS patients,” Guo said.
On univariate Cox regression analysis, gluteal HS lesions were associated with shorter adalimumab survival, and obesity was associated with longer infliximab survival.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including the small sample size and that unadjusted Cox regression analysis did not account for baseline HS severity, biologic therapy dosing, and concomitant medication use. Also, there were patients in both cohorts who were not biologic-naive: Two in the adalimumab cohort were previously treated with infliximab, and five patients in the infliximab cohort were previously treated with adalimumab.
“We plan on conducting further analysis using adjusted Cox regression analysis to account for baseline disease severity measured by Hurley stage, BMI, medication dosing, and concomitant medication use,” Guo said.
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
results from a small single-center study showed.
A previous study found that overall drug survival of adalimumab and infliximab in adults with HS at 12 and 24 months was 56.3% and 30.5%, and 58.3% and 48.6%, respectively. “They also found that older age, longer disease duration, higher body mass index (BMI), and surgery during treatment are associated with increased drug survival,” Robyn Guo, a third-year medical student at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization following the annual Symposium on Hidradenitis Suppurativa Advances, where the study was presented during an oral abstract session. “To our knowledge, the drug survival of biologic therapies in pediatric HS patients has not been previously investigated.”
Adalimumab and infliximab are tumor necrosis factor blockers approved for multiple indications; adalimumab is approved for treating moderate to severe HS in patients aged 12 years or older. Infliximab is not approved for HS but is used to treat the disease.
To determine the drug survival of adalimumab and infliximab in pediatric patients with HS and whether patient comorbidities and HS lesion location are associated with length of biologic survival in pediatric patients with HS, Guo and colleagues used Kaplan-Meier survival curves to calculate biologic survival at 12 and 24 months following biologic initiation and Cox proportional hazards regression to analyze potential factors associated with biologic survival. The study population included 49 pediatric patients in the adalimumab cohort and 11 in the infliximab cohort.
The researchers found that drug survival for adalimumab was 90.6% at 12 months (95% CI, 83.0%-98.8%) and 78.3% at 24 months (95% CI, 67.7%-90.6%), while drug survival for infliximab was 54.5% at 12 months (95% CI, 31.8%-93.6%) and 36.4% at 24 months, an overall difference that reached statistical significance (P = .0009). “Our data suggests that adalimumab survival is significantly higher than infliximab survival in pediatric HS patients,” Guo said.
On univariate Cox regression analysis, gluteal HS lesions were associated with shorter adalimumab survival, and obesity was associated with longer infliximab survival.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including the small sample size and that unadjusted Cox regression analysis did not account for baseline HS severity, biologic therapy dosing, and concomitant medication use. Also, there were patients in both cohorts who were not biologic-naive: Two in the adalimumab cohort were previously treated with infliximab, and five patients in the infliximab cohort were previously treated with adalimumab.
“We plan on conducting further analysis using adjusted Cox regression analysis to account for baseline disease severity measured by Hurley stage, BMI, medication dosing, and concomitant medication use,” Guo said.
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
results from a small single-center study showed.
A previous study found that overall drug survival of adalimumab and infliximab in adults with HS at 12 and 24 months was 56.3% and 30.5%, and 58.3% and 48.6%, respectively. “They also found that older age, longer disease duration, higher body mass index (BMI), and surgery during treatment are associated with increased drug survival,” Robyn Guo, a third-year medical student at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization following the annual Symposium on Hidradenitis Suppurativa Advances, where the study was presented during an oral abstract session. “To our knowledge, the drug survival of biologic therapies in pediatric HS patients has not been previously investigated.”
Adalimumab and infliximab are tumor necrosis factor blockers approved for multiple indications; adalimumab is approved for treating moderate to severe HS in patients aged 12 years or older. Infliximab is not approved for HS but is used to treat the disease.
To determine the drug survival of adalimumab and infliximab in pediatric patients with HS and whether patient comorbidities and HS lesion location are associated with length of biologic survival in pediatric patients with HS, Guo and colleagues used Kaplan-Meier survival curves to calculate biologic survival at 12 and 24 months following biologic initiation and Cox proportional hazards regression to analyze potential factors associated with biologic survival. The study population included 49 pediatric patients in the adalimumab cohort and 11 in the infliximab cohort.
The researchers found that drug survival for adalimumab was 90.6% at 12 months (95% CI, 83.0%-98.8%) and 78.3% at 24 months (95% CI, 67.7%-90.6%), while drug survival for infliximab was 54.5% at 12 months (95% CI, 31.8%-93.6%) and 36.4% at 24 months, an overall difference that reached statistical significance (P = .0009). “Our data suggests that adalimumab survival is significantly higher than infliximab survival in pediatric HS patients,” Guo said.
On univariate Cox regression analysis, gluteal HS lesions were associated with shorter adalimumab survival, and obesity was associated with longer infliximab survival.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including the small sample size and that unadjusted Cox regression analysis did not account for baseline HS severity, biologic therapy dosing, and concomitant medication use. Also, there were patients in both cohorts who were not biologic-naive: Two in the adalimumab cohort were previously treated with infliximab, and five patients in the infliximab cohort were previously treated with adalimumab.
“We plan on conducting further analysis using adjusted Cox regression analysis to account for baseline disease severity measured by Hurley stage, BMI, medication dosing, and concomitant medication use,” Guo said.
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SDPA 24
Varicella Outbreaks: 2022-2024
Practitioners providing care to children are familiar with the childhood immunization schedule and routinely administer varicella vaccine at the 12-month and 4- to 5-year visits. However, when is the last time most of us or any of the current trainees have seen a case?
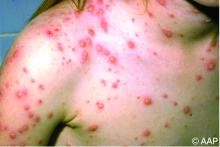
Briefly, varicella is a highly contagious disease caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It is characterized by a generalized pruritic erythematous rash in various stages of development beginning as macules, progressing to papules, and ultimately becoming vesicular lesions on an erythematous base (“dewdrop on a rose petal”) and resolves with crusting of the lesion (Figure 1). It has an incubation period of 10-21 days with symptoms usually developing within 14-16 days after exposure. The vesicular rash must be differentiated from enterovirus, Staphylococcus aureus, contact dermatitis, or insect bites, which initially may be difficult. Approximately 50% of children can have symptoms including fever, malaise, anorexia, headache, and occasionally, mild abdominal pain in the 24-48 hours prior to the appearance of rash. Lesions usually first appear on the scalp, face, or trunk in successive crops over several days. A person with varicella has lesions in various stages.
In a normal host, new vesicle formation usually stops within 4 days, and most lesions have fully crusted by day 6. VZV establishes latency in sensory ganglia and may reactivate years or decades later to cause herpes zoster (HZ). Most healthy children with varicella recover without sequelae so the disease is generally regarded as benign. However, varicella can lead to serious complications and deaths in healthy as well as immunocompromised persons.
Complications of Varicella: bacterial superinfection of skin lesions most often with Streptococcus pyogenes or S aureus manifested as cellulitis, myositis, or necrotizing fasciitis; neurologic complications include cerebellar ataxia and encephalitis with the latter seen most often in adults. Pneumonia occurs most often in adults, especially those infected during pregnancy. Another concern, infection during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy can lead to fetal death or severe birth defects, including limb hypoplasia, cutaneous scarring, ocular abnormalities, and central nervous system damage (congenital varicella syndrome).
The risk for development of severe disseminated disease was first noted in the 1960s as treatments for leukemia in children improved. They were surviving their cancer only to develop severe and often fatal varicella. Today it is recognized that development of disseminated disease is a risk for all infected persons with impaired T cell function, malignancies, HIV, or receiving immunosuppressive therapy.
Reye’s syndrome is rarely seen today since taking salicylates while infected with VZV was identified as a predisposing factor for development.
VZV is only found in humans and transmission is person to person or airborne. The secondary household attack rate is approximately 90%. In contrast, the secondary attack rates in classrooms may be as low as 12%-33%. Transmission rates in the tropics for unexplained reasons are also lower.
Vaccine History: Why do we rarely see this disease anymore? Varicella, a live attenuated vaccine, was developed in 1974 by Dr. Michiaki Takahashi. It remains the only vaccine directed against a herpes group virus. In 1979, the Collaborative Varicella Vaccine Study Group was established at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and additional safety and efficacy trials were conducted in the United States initially in leukemic patients in remission and later in healthy children, which supported Takahashi’s data. Licensure of varicella vaccine was granted in 1995. That same year, due to continuing disease and societal burden, the United States was the first country to incorporate varicella into the routine childhood immunization schedule, which resulted in significant reductions in cases. To further improve control of varicella, in 2007 vaccine recommendations were revised and a routine two-dose schedule was implemented. The impact of varicella disease pre- and post-vaccine licensure is illustrated in Figure 2. Not listed, is that in the pre-vaccine era, there were approximately 44 cases of congenital varicella syndrome annually.

As of 2023 only 23% (45/195) of nations routinely administer this vaccine and 4% (8/195) have restricted recommendations. The remaining 73% of countries do not offer the vaccine, including all countries on the African continent, and Cuba, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, India, Jordan, Lebanon, Philippines, Portugal, and Venezuela to list a few.
Varicella Outbreak: In October 2022, New York City (NYC) identified a varicella outbreak primarily involving persons who recently migrated from Central and South America and lived in a shelter in NYC or residential facility (n = 105); the outbreak is ongoing. As of March 8, 2024, 873 cases (53%) were among children aged 4-18 years and 91.9% had no documentation of varicella vaccine at time of symptom onset. There were 28 hospitalizations, and no deaths reported. The most common sources of transmission were the residential facilities (41.3%) and importation or possible importation (39.4%). School transmission accounted for only 1.2% of cases.
Most migrants arrived from countries where varicella vaccination is not part of the routine childhood immunization schedule. Although most cases occurred in children, almost 30% occurred in adults. Many of the migrants arrived from tropical countries where susceptibility rates are also higher in adults. This outbreak is a reminder of the importance of limiting disease transmission by maintaining high vaccination rates. To curtail this outbreak, approximately 27,000 doses of varicella vaccine were administered to the arriving migrants. In addition, MMR, COVID-19, influenza, and all routine pediatric vaccines required for school entry were administered. Temporary closure of the residential facilities were required. Education was provided to residents regarding immunizations as well as assistance to help them establish a primary care home. Multiple agencies were mobilized to successfully coordinate these efforts.
Take Home Message
1. Each country has its own routine immunization schedule. It may not include all vaccines recommended in the US schedule. When questioned I’m frequently told that immunizations are up to date, only to review records and find they are not, especially when it is related to MMR. It is often administered at 9 months and/or MR or MM is administered depending on the country. As reported here, varicella is a routine vaccine in only 45 countries.
2.
3. Once an outbreak has been identified, the infrastructure to manage and contain it must already be established. In most instances there will be a need for a rapid and often large-scale effort involving multiple agencies including local health care providers.
4. Not all diseases are reportable. Only deaths by varicella are nationally notifiable. Otherwise, cases are reported voluntarily. As of November 2, 2024, there have been 5,157 cases of varicella reported, excluding any cases from NYC.
Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
CDC. Nationally Notifiable Infectious Diseases and Conditions, United States: Weekly Tables. https://wonder.cdc.gov/nndss/nndss_weekly_tables_menu.asp.
Graham KA et al. Varicella Outbreak Among Recent Arrivals to New York City, 2022-2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024 May 30;73(21):478-483. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7321a1.
Marin M et al. Health and Economic Impact of the United States Varicella Vaccination Program, 1996-2020. J Infect Dis. 2022 Oct 21;226(Suppl 4):S463-S469. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac271.
Varicella-Zoster Virus Infections in Kimberkin DW et al, eds. Red Book: 2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 33rd Edition. American Academy of Pediatrics, 2024:938-951. https://www.aap.org/Red-Book-2024-Report-of-the-Committee-on-Infectious-Diseases-33rd-Edition-Paperback?srsltid=AfmBOoqyF60rR9ZwQ5jA8AouNhtRRTyPLnc_r7HWw7JVYV8v33Hr2vQS.
Practitioners providing care to children are familiar with the childhood immunization schedule and routinely administer varicella vaccine at the 12-month and 4- to 5-year visits. However, when is the last time most of us or any of the current trainees have seen a case?
Briefly, varicella is a highly contagious disease caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It is characterized by a generalized pruritic erythematous rash in various stages of development beginning as macules, progressing to papules, and ultimately becoming vesicular lesions on an erythematous base (“dewdrop on a rose petal”) and resolves with crusting of the lesion (Figure 1). It has an incubation period of 10-21 days with symptoms usually developing within 14-16 days after exposure. The vesicular rash must be differentiated from enterovirus, Staphylococcus aureus, contact dermatitis, or insect bites, which initially may be difficult. Approximately 50% of children can have symptoms including fever, malaise, anorexia, headache, and occasionally, mild abdominal pain in the 24-48 hours prior to the appearance of rash. Lesions usually first appear on the scalp, face, or trunk in successive crops over several days. A person with varicella has lesions in various stages.
In a normal host, new vesicle formation usually stops within 4 days, and most lesions have fully crusted by day 6. VZV establishes latency in sensory ganglia and may reactivate years or decades later to cause herpes zoster (HZ). Most healthy children with varicella recover without sequelae so the disease is generally regarded as benign. However, varicella can lead to serious complications and deaths in healthy as well as immunocompromised persons.
Complications of Varicella: bacterial superinfection of skin lesions most often with Streptococcus pyogenes or S aureus manifested as cellulitis, myositis, or necrotizing fasciitis; neurologic complications include cerebellar ataxia and encephalitis with the latter seen most often in adults. Pneumonia occurs most often in adults, especially those infected during pregnancy. Another concern, infection during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy can lead to fetal death or severe birth defects, including limb hypoplasia, cutaneous scarring, ocular abnormalities, and central nervous system damage (congenital varicella syndrome).
The risk for development of severe disseminated disease was first noted in the 1960s as treatments for leukemia in children improved. They were surviving their cancer only to develop severe and often fatal varicella. Today it is recognized that development of disseminated disease is a risk for all infected persons with impaired T cell function, malignancies, HIV, or receiving immunosuppressive therapy.
Reye’s syndrome is rarely seen today since taking salicylates while infected with VZV was identified as a predisposing factor for development.
VZV is only found in humans and transmission is person to person or airborne. The secondary household attack rate is approximately 90%. In contrast, the secondary attack rates in classrooms may be as low as 12%-33%. Transmission rates in the tropics for unexplained reasons are also lower.
Vaccine History: Why do we rarely see this disease anymore? Varicella, a live attenuated vaccine, was developed in 1974 by Dr. Michiaki Takahashi. It remains the only vaccine directed against a herpes group virus. In 1979, the Collaborative Varicella Vaccine Study Group was established at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and additional safety and efficacy trials were conducted in the United States initially in leukemic patients in remission and later in healthy children, which supported Takahashi’s data. Licensure of varicella vaccine was granted in 1995. That same year, due to continuing disease and societal burden, the United States was the first country to incorporate varicella into the routine childhood immunization schedule, which resulted in significant reductions in cases. To further improve control of varicella, in 2007 vaccine recommendations were revised and a routine two-dose schedule was implemented. The impact of varicella disease pre- and post-vaccine licensure is illustrated in Figure 2. Not listed, is that in the pre-vaccine era, there were approximately 44 cases of congenital varicella syndrome annually.

As of 2023 only 23% (45/195) of nations routinely administer this vaccine and 4% (8/195) have restricted recommendations. The remaining 73% of countries do not offer the vaccine, including all countries on the African continent, and Cuba, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, India, Jordan, Lebanon, Philippines, Portugal, and Venezuela to list a few.
Varicella Outbreak: In October 2022, New York City (NYC) identified a varicella outbreak primarily involving persons who recently migrated from Central and South America and lived in a shelter in NYC or residential facility (n = 105); the outbreak is ongoing. As of March 8, 2024, 873 cases (53%) were among children aged 4-18 years and 91.9% had no documentation of varicella vaccine at time of symptom onset. There were 28 hospitalizations, and no deaths reported. The most common sources of transmission were the residential facilities (41.3%) and importation or possible importation (39.4%). School transmission accounted for only 1.2% of cases.
Most migrants arrived from countries where varicella vaccination is not part of the routine childhood immunization schedule. Although most cases occurred in children, almost 30% occurred in adults. Many of the migrants arrived from tropical countries where susceptibility rates are also higher in adults. This outbreak is a reminder of the importance of limiting disease transmission by maintaining high vaccination rates. To curtail this outbreak, approximately 27,000 doses of varicella vaccine were administered to the arriving migrants. In addition, MMR, COVID-19, influenza, and all routine pediatric vaccines required for school entry were administered. Temporary closure of the residential facilities were required. Education was provided to residents regarding immunizations as well as assistance to help them establish a primary care home. Multiple agencies were mobilized to successfully coordinate these efforts.
Take Home Message
1. Each country has its own routine immunization schedule. It may not include all vaccines recommended in the US schedule. When questioned I’m frequently told that immunizations are up to date, only to review records and find they are not, especially when it is related to MMR. It is often administered at 9 months and/or MR or MM is administered depending on the country. As reported here, varicella is a routine vaccine in only 45 countries.
2.
3. Once an outbreak has been identified, the infrastructure to manage and contain it must already be established. In most instances there will be a need for a rapid and often large-scale effort involving multiple agencies including local health care providers.
4. Not all diseases are reportable. Only deaths by varicella are nationally notifiable. Otherwise, cases are reported voluntarily. As of November 2, 2024, there have been 5,157 cases of varicella reported, excluding any cases from NYC.
Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
CDC. Nationally Notifiable Infectious Diseases and Conditions, United States: Weekly Tables. https://wonder.cdc.gov/nndss/nndss_weekly_tables_menu.asp.
Graham KA et al. Varicella Outbreak Among Recent Arrivals to New York City, 2022-2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024 May 30;73(21):478-483. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7321a1.
Marin M et al. Health and Economic Impact of the United States Varicella Vaccination Program, 1996-2020. J Infect Dis. 2022 Oct 21;226(Suppl 4):S463-S469. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac271.
Varicella-Zoster Virus Infections in Kimberkin DW et al, eds. Red Book: 2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 33rd Edition. American Academy of Pediatrics, 2024:938-951. https://www.aap.org/Red-Book-2024-Report-of-the-Committee-on-Infectious-Diseases-33rd-Edition-Paperback?srsltid=AfmBOoqyF60rR9ZwQ5jA8AouNhtRRTyPLnc_r7HWw7JVYV8v33Hr2vQS.
Practitioners providing care to children are familiar with the childhood immunization schedule and routinely administer varicella vaccine at the 12-month and 4- to 5-year visits. However, when is the last time most of us or any of the current trainees have seen a case?
Briefly, varicella is a highly contagious disease caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It is characterized by a generalized pruritic erythematous rash in various stages of development beginning as macules, progressing to papules, and ultimately becoming vesicular lesions on an erythematous base (“dewdrop on a rose petal”) and resolves with crusting of the lesion (Figure 1). It has an incubation period of 10-21 days with symptoms usually developing within 14-16 days after exposure. The vesicular rash must be differentiated from enterovirus, Staphylococcus aureus, contact dermatitis, or insect bites, which initially may be difficult. Approximately 50% of children can have symptoms including fever, malaise, anorexia, headache, and occasionally, mild abdominal pain in the 24-48 hours prior to the appearance of rash. Lesions usually first appear on the scalp, face, or trunk in successive crops over several days. A person with varicella has lesions in various stages.
In a normal host, new vesicle formation usually stops within 4 days, and most lesions have fully crusted by day 6. VZV establishes latency in sensory ganglia and may reactivate years or decades later to cause herpes zoster (HZ). Most healthy children with varicella recover without sequelae so the disease is generally regarded as benign. However, varicella can lead to serious complications and deaths in healthy as well as immunocompromised persons.
Complications of Varicella: bacterial superinfection of skin lesions most often with Streptococcus pyogenes or S aureus manifested as cellulitis, myositis, or necrotizing fasciitis; neurologic complications include cerebellar ataxia and encephalitis with the latter seen most often in adults. Pneumonia occurs most often in adults, especially those infected during pregnancy. Another concern, infection during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy can lead to fetal death or severe birth defects, including limb hypoplasia, cutaneous scarring, ocular abnormalities, and central nervous system damage (congenital varicella syndrome).
The risk for development of severe disseminated disease was first noted in the 1960s as treatments for leukemia in children improved. They were surviving their cancer only to develop severe and often fatal varicella. Today it is recognized that development of disseminated disease is a risk for all infected persons with impaired T cell function, malignancies, HIV, or receiving immunosuppressive therapy.
Reye’s syndrome is rarely seen today since taking salicylates while infected with VZV was identified as a predisposing factor for development.
VZV is only found in humans and transmission is person to person or airborne. The secondary household attack rate is approximately 90%. In contrast, the secondary attack rates in classrooms may be as low as 12%-33%. Transmission rates in the tropics for unexplained reasons are also lower.
Vaccine History: Why do we rarely see this disease anymore? Varicella, a live attenuated vaccine, was developed in 1974 by Dr. Michiaki Takahashi. It remains the only vaccine directed against a herpes group virus. In 1979, the Collaborative Varicella Vaccine Study Group was established at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and additional safety and efficacy trials were conducted in the United States initially in leukemic patients in remission and later in healthy children, which supported Takahashi’s data. Licensure of varicella vaccine was granted in 1995. That same year, due to continuing disease and societal burden, the United States was the first country to incorporate varicella into the routine childhood immunization schedule, which resulted in significant reductions in cases. To further improve control of varicella, in 2007 vaccine recommendations were revised and a routine two-dose schedule was implemented. The impact of varicella disease pre- and post-vaccine licensure is illustrated in Figure 2. Not listed, is that in the pre-vaccine era, there were approximately 44 cases of congenital varicella syndrome annually.

As of 2023 only 23% (45/195) of nations routinely administer this vaccine and 4% (8/195) have restricted recommendations. The remaining 73% of countries do not offer the vaccine, including all countries on the African continent, and Cuba, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, India, Jordan, Lebanon, Philippines, Portugal, and Venezuela to list a few.
Varicella Outbreak: In October 2022, New York City (NYC) identified a varicella outbreak primarily involving persons who recently migrated from Central and South America and lived in a shelter in NYC or residential facility (n = 105); the outbreak is ongoing. As of March 8, 2024, 873 cases (53%) were among children aged 4-18 years and 91.9% had no documentation of varicella vaccine at time of symptom onset. There were 28 hospitalizations, and no deaths reported. The most common sources of transmission were the residential facilities (41.3%) and importation or possible importation (39.4%). School transmission accounted for only 1.2% of cases.
Most migrants arrived from countries where varicella vaccination is not part of the routine childhood immunization schedule. Although most cases occurred in children, almost 30% occurred in adults. Many of the migrants arrived from tropical countries where susceptibility rates are also higher in adults. This outbreak is a reminder of the importance of limiting disease transmission by maintaining high vaccination rates. To curtail this outbreak, approximately 27,000 doses of varicella vaccine were administered to the arriving migrants. In addition, MMR, COVID-19, influenza, and all routine pediatric vaccines required for school entry were administered. Temporary closure of the residential facilities were required. Education was provided to residents regarding immunizations as well as assistance to help them establish a primary care home. Multiple agencies were mobilized to successfully coordinate these efforts.
Take Home Message
1. Each country has its own routine immunization schedule. It may not include all vaccines recommended in the US schedule. When questioned I’m frequently told that immunizations are up to date, only to review records and find they are not, especially when it is related to MMR. It is often administered at 9 months and/or MR or MM is administered depending on the country. As reported here, varicella is a routine vaccine in only 45 countries.
2.
3. Once an outbreak has been identified, the infrastructure to manage and contain it must already be established. In most instances there will be a need for a rapid and often large-scale effort involving multiple agencies including local health care providers.
4. Not all diseases are reportable. Only deaths by varicella are nationally notifiable. Otherwise, cases are reported voluntarily. As of November 2, 2024, there have been 5,157 cases of varicella reported, excluding any cases from NYC.
Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
CDC. Nationally Notifiable Infectious Diseases and Conditions, United States: Weekly Tables. https://wonder.cdc.gov/nndss/nndss_weekly_tables_menu.asp.
Graham KA et al. Varicella Outbreak Among Recent Arrivals to New York City, 2022-2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024 May 30;73(21):478-483. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7321a1.
Marin M et al. Health and Economic Impact of the United States Varicella Vaccination Program, 1996-2020. J Infect Dis. 2022 Oct 21;226(Suppl 4):S463-S469. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac271.
Varicella-Zoster Virus Infections in Kimberkin DW et al, eds. Red Book: 2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 33rd Edition. American Academy of Pediatrics, 2024:938-951. https://www.aap.org/Red-Book-2024-Report-of-the-Committee-on-Infectious-Diseases-33rd-Edition-Paperback?srsltid=AfmBOoqyF60rR9ZwQ5jA8AouNhtRRTyPLnc_r7HWw7JVYV8v33Hr2vQS.
‘Being a Doctor Isn’t Healthy’: Train Your Body to Handle It
Heather K. Schopper, MD, a head and neck surgeon at Penn State Health, Hershey, Pennsylvania, wasn’t long into her career when she began feeling its physical demands. Standing for 12 hours at a time, holding awkward positions for long periods, and working with surgical tables and instruments made for doctors much taller and larger meant severe back, shoulder, and neck pain at the end of every shift.
“You just want to lie down on the floor at the end of the day,” Schopper explained. “The wear and tear of our profession is really challenging.”
Here’s the thing: At the time Schopper wasn’t particularly out of shape. She only knew she needed to build up her body for long days and a long career. What, physically, would that look like?
This was the catalyst for what she calls a “health and fitness journey” that transformed the way she practices.
“Medicine is unique in its physical demands,” said Meghan Wieser, PT, DPT, a doctor of physical therapy at Recharge Health and Fitness in Ellicott City, Maryland. Wieser frequently works with physicians and others in high-stress career environments, and she’s observed the serious toll that physically demanding medical practice can take on the body.
It’s not just about preventing acute or chronic injury, she said. It’s about performing better for longer periods. And every doctor knows the only way to build a more functional body is training.
The Fantasy of Physical Perfection vs the Reality of, Well, Reality
Jordan D. Metzl, MD, is a sports medicine physician at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) in New York City. He’s also a lifelong triathlete and marathon runner and has parlayed that passion into an online fitness community of more than 10,000 people called Ironstrength. Through that, Metzl has led free exercise classes in Central Park for years. He doesn’t dabble. Three times a year he leads a boot camp class of more than 1000 people on the flight deck of the USS Intrepid on the Hudson River.
“I get it, being a doctor is all about the hours,” he said. “The time sacrifices get brutal and you have to cut something out, sometimes every day. For a lot of us, that’s exercise.”
Metzl understands it so well that he recently began leading twice-monthly boot camp classes just for his HSS physician colleagues on Wednesday mornings. He says those doctors both want and need that extra boost and will be aggressive about making time for it.
“The better shape you’re in, the better job you’ll do as a physician,” he said. “You’ll feel better when the hours get long. In my own career, I have always been a better doctor when I’m active and in shape.”
Knowledge isn’t really the issue for physicians. Reality is. And reality dictates that doctors have just as much issue with achieving consistency as any patient they prescribe exercise to.
Metzl suggests total body functional training to mimic real-world movement, particularly core and lower body to keep you upright for hours at a time. How do you schedule that? He uses early mornings and weekends to train for his races and run his fitness classes, which is why his primary advice is to focus not on the activity, but on time.
“Schedule full workouts when you can and steal the rest,” he said.
Schopper agrees. “You may not be able to fit in 60 minutes of exercise every day, but 20-30 minutes of intentional movement is key,” she explained. “When you have a day off, prioritize a longer session of something you can’t fit in on workdays.”
Those shorter bouts of exercise might include “bookending” the day with 10 minutes of burpees in the morning and then 10 minutes of bodyweight strength moves like planks, push-ups, and air squats in the evening.
“Bodyweight exercises are low-hanging fruit,” said Wieser. “If you’ve got a short window, aim for something that can shoot your heart rate up quickly.”
You can also throw in “movement snacks” throughout the day — skip the elevator and run up a flight of stairs, walk around during a quick lunch break, or throw in a set of jumping jacks between patients. (Don’t worry — you won’t be dripping sweat when they walk in.)
Remember, the rehab room in the orthopedic wing may have a few dumbbells and exercise bands you can utilize when you have 5 extra minutes in your day. “Any way you can squeeze in extra movement counts,” said Wieser.
Feats of Strength? Neighborhood Sprints? It All Matters
Kissinger Goldman, DO, a Florida-based ER physician, began his dedication to exercise 17 years ago, after a high-cholesterol diagnosis. “Did I have time to exercise in medical school and residency? Yes,” Goldman admitted. “But I didn’t have the same commitment to my health until I received that number. I set about to change everything.”
Goldman follows the approach of dividing up his exercise routine into short or long sessions, depending on his schedule. “If I’m off, I’ll aim for 30 minutes of cardio and 30 minutes of strength and core work,” he explained. “When I have to work, I’ll do a compressed version of that routine as soon as I wake up, and make sure the cardio is very intense — I’ll sprint in my neighborhood, for instance.”
Matt Klein, a doctor of physical therapy and professor at George Fox University in Newberg, Oregon, who has treated many doctors, says that, when pushed for time, just 20 minutes of “heavy” strength training can deliver good results. “The definition of heavy will vary, but aim for a weight that is challenging, whether a beginner or a more experienced exerciser,” he said. “Most doctors won’t have time to go to the gym, so a simple set of dumbbells or kettlebells will work just fine. The easier it is to access, the more likely you are to do it consistently.”
Klein is a fan of strength training with good reason: “Strength is a predictor of chronic disease, so doing some high-level strength training or power training can go a long way,” he said.
The endorphin high and overall sense of improved well-being are an extra bonus. Goldman credits it with ensuring he rarely misses a workout.
Get Hardcore About Sleep
Consider the following passage: “There are clear negative effects of sleep deprivation on performance, including reaction time, accuracy, vigor, submaximal strength, and endurance. Cognitive functions such as judgment and decision-making also suffer.”
Does that sound like how you feel on suboptimal sleep? That’s from an International Journal of Sports Medicine study on the effects of sleep deprivation on athletes.
Athletes aren’t doctors — but when you consider “reaction time, accuracy, endurance, judgment, and decision-making” — doctors could certainly benefit by thinking like athletes.
Schopper is serious about sleep and sets firm boundaries.
“It’s hard,” she admitted. “We want to work, see our families, have fun. But I work hard to say, ‘I’m done,’ and go to bed.”
“Rest is crucial for this job,” agreed Goldman. “If you don’t have adequate sleep, your cortisone levels are going to go up. When you’re exhausted and you’re working, you’re likely to miss something.” Goldman is consistent with early bedtimes around 9:00 or 9:30 PM, and he allows for a bit of “wind-down” time by reading for about 20 minutes before nodding off.
Goldman also sees a link between rest and improved interactions with patients. “There’s a direct correlation between number of hours worked in a row with respect to ‘customer service’ with patients,” he said.
But don’t aim for perfection. Allow some wiggle room for the time you spend asleep, Klein recommends. “We’ve always aimed for 8 hours, but there’s evidence that even 6 or 7 hours can be enough to allow you to recover as needed,” he said. “Optimally, you want that to be uninterrupted, but if not, a 10-minute power nap can help with mental clarity.”
Keep Searching, Keep Trying, Keep Training
Schopper was never, nor has she become, a gym rat. Still, “I knew I needed to build upper body strength,” she said. That meant expanding her fitness possibilities beyond the obvious. She discovered aerial arts — intense workouts using straps and other suspension tools to work every muscle in her body while hanging from the ceiling. Increased strength was a given, but she also seriously increased her range of motion.
For Schopper, the improvements to her lifestyle have been game changers. “I still have long days, but I’m no longer sore and tired after them,” she said. “I sleep better and have more energy. I’m proud of myself for putting the effort into this.”
A journey toward health and fitness may look different for everyone, but (as doctors frequently tell their patients) it’s a path anyone can follow.
“Being a doctor is not necessarily good for your health,” said Klein. “The body can handle the job, however, if you train for it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heather K. Schopper, MD, a head and neck surgeon at Penn State Health, Hershey, Pennsylvania, wasn’t long into her career when she began feeling its physical demands. Standing for 12 hours at a time, holding awkward positions for long periods, and working with surgical tables and instruments made for doctors much taller and larger meant severe back, shoulder, and neck pain at the end of every shift.
“You just want to lie down on the floor at the end of the day,” Schopper explained. “The wear and tear of our profession is really challenging.”
Here’s the thing: At the time Schopper wasn’t particularly out of shape. She only knew she needed to build up her body for long days and a long career. What, physically, would that look like?
This was the catalyst for what she calls a “health and fitness journey” that transformed the way she practices.
“Medicine is unique in its physical demands,” said Meghan Wieser, PT, DPT, a doctor of physical therapy at Recharge Health and Fitness in Ellicott City, Maryland. Wieser frequently works with physicians and others in high-stress career environments, and she’s observed the serious toll that physically demanding medical practice can take on the body.
It’s not just about preventing acute or chronic injury, she said. It’s about performing better for longer periods. And every doctor knows the only way to build a more functional body is training.
The Fantasy of Physical Perfection vs the Reality of, Well, Reality
Jordan D. Metzl, MD, is a sports medicine physician at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) in New York City. He’s also a lifelong triathlete and marathon runner and has parlayed that passion into an online fitness community of more than 10,000 people called Ironstrength. Through that, Metzl has led free exercise classes in Central Park for years. He doesn’t dabble. Three times a year he leads a boot camp class of more than 1000 people on the flight deck of the USS Intrepid on the Hudson River.
“I get it, being a doctor is all about the hours,” he said. “The time sacrifices get brutal and you have to cut something out, sometimes every day. For a lot of us, that’s exercise.”
Metzl understands it so well that he recently began leading twice-monthly boot camp classes just for his HSS physician colleagues on Wednesday mornings. He says those doctors both want and need that extra boost and will be aggressive about making time for it.
“The better shape you’re in, the better job you’ll do as a physician,” he said. “You’ll feel better when the hours get long. In my own career, I have always been a better doctor when I’m active and in shape.”
Knowledge isn’t really the issue for physicians. Reality is. And reality dictates that doctors have just as much issue with achieving consistency as any patient they prescribe exercise to.
Metzl suggests total body functional training to mimic real-world movement, particularly core and lower body to keep you upright for hours at a time. How do you schedule that? He uses early mornings and weekends to train for his races and run his fitness classes, which is why his primary advice is to focus not on the activity, but on time.
“Schedule full workouts when you can and steal the rest,” he said.
Schopper agrees. “You may not be able to fit in 60 minutes of exercise every day, but 20-30 minutes of intentional movement is key,” she explained. “When you have a day off, prioritize a longer session of something you can’t fit in on workdays.”
Those shorter bouts of exercise might include “bookending” the day with 10 minutes of burpees in the morning and then 10 minutes of bodyweight strength moves like planks, push-ups, and air squats in the evening.
“Bodyweight exercises are low-hanging fruit,” said Wieser. “If you’ve got a short window, aim for something that can shoot your heart rate up quickly.”
You can also throw in “movement snacks” throughout the day — skip the elevator and run up a flight of stairs, walk around during a quick lunch break, or throw in a set of jumping jacks between patients. (Don’t worry — you won’t be dripping sweat when they walk in.)
Remember, the rehab room in the orthopedic wing may have a few dumbbells and exercise bands you can utilize when you have 5 extra minutes in your day. “Any way you can squeeze in extra movement counts,” said Wieser.
Feats of Strength? Neighborhood Sprints? It All Matters
Kissinger Goldman, DO, a Florida-based ER physician, began his dedication to exercise 17 years ago, after a high-cholesterol diagnosis. “Did I have time to exercise in medical school and residency? Yes,” Goldman admitted. “But I didn’t have the same commitment to my health until I received that number. I set about to change everything.”
Goldman follows the approach of dividing up his exercise routine into short or long sessions, depending on his schedule. “If I’m off, I’ll aim for 30 minutes of cardio and 30 minutes of strength and core work,” he explained. “When I have to work, I’ll do a compressed version of that routine as soon as I wake up, and make sure the cardio is very intense — I’ll sprint in my neighborhood, for instance.”
Matt Klein, a doctor of physical therapy and professor at George Fox University in Newberg, Oregon, who has treated many doctors, says that, when pushed for time, just 20 minutes of “heavy” strength training can deliver good results. “The definition of heavy will vary, but aim for a weight that is challenging, whether a beginner or a more experienced exerciser,” he said. “Most doctors won’t have time to go to the gym, so a simple set of dumbbells or kettlebells will work just fine. The easier it is to access, the more likely you are to do it consistently.”
Klein is a fan of strength training with good reason: “Strength is a predictor of chronic disease, so doing some high-level strength training or power training can go a long way,” he said.
The endorphin high and overall sense of improved well-being are an extra bonus. Goldman credits it with ensuring he rarely misses a workout.
Get Hardcore About Sleep
Consider the following passage: “There are clear negative effects of sleep deprivation on performance, including reaction time, accuracy, vigor, submaximal strength, and endurance. Cognitive functions such as judgment and decision-making also suffer.”
Does that sound like how you feel on suboptimal sleep? That’s from an International Journal of Sports Medicine study on the effects of sleep deprivation on athletes.
Athletes aren’t doctors — but when you consider “reaction time, accuracy, endurance, judgment, and decision-making” — doctors could certainly benefit by thinking like athletes.
Schopper is serious about sleep and sets firm boundaries.
“It’s hard,” she admitted. “We want to work, see our families, have fun. But I work hard to say, ‘I’m done,’ and go to bed.”
“Rest is crucial for this job,” agreed Goldman. “If you don’t have adequate sleep, your cortisone levels are going to go up. When you’re exhausted and you’re working, you’re likely to miss something.” Goldman is consistent with early bedtimes around 9:00 or 9:30 PM, and he allows for a bit of “wind-down” time by reading for about 20 minutes before nodding off.
Goldman also sees a link between rest and improved interactions with patients. “There’s a direct correlation between number of hours worked in a row with respect to ‘customer service’ with patients,” he said.
But don’t aim for perfection. Allow some wiggle room for the time you spend asleep, Klein recommends. “We’ve always aimed for 8 hours, but there’s evidence that even 6 or 7 hours can be enough to allow you to recover as needed,” he said. “Optimally, you want that to be uninterrupted, but if not, a 10-minute power nap can help with mental clarity.”
Keep Searching, Keep Trying, Keep Training
Schopper was never, nor has she become, a gym rat. Still, “I knew I needed to build upper body strength,” she said. That meant expanding her fitness possibilities beyond the obvious. She discovered aerial arts — intense workouts using straps and other suspension tools to work every muscle in her body while hanging from the ceiling. Increased strength was a given, but she also seriously increased her range of motion.
For Schopper, the improvements to her lifestyle have been game changers. “I still have long days, but I’m no longer sore and tired after them,” she said. “I sleep better and have more energy. I’m proud of myself for putting the effort into this.”
A journey toward health and fitness may look different for everyone, but (as doctors frequently tell their patients) it’s a path anyone can follow.
“Being a doctor is not necessarily good for your health,” said Klein. “The body can handle the job, however, if you train for it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heather K. Schopper, MD, a head and neck surgeon at Penn State Health, Hershey, Pennsylvania, wasn’t long into her career when she began feeling its physical demands. Standing for 12 hours at a time, holding awkward positions for long periods, and working with surgical tables and instruments made for doctors much taller and larger meant severe back, shoulder, and neck pain at the end of every shift.
“You just want to lie down on the floor at the end of the day,” Schopper explained. “The wear and tear of our profession is really challenging.”
Here’s the thing: At the time Schopper wasn’t particularly out of shape. She only knew she needed to build up her body for long days and a long career. What, physically, would that look like?
This was the catalyst for what she calls a “health and fitness journey” that transformed the way she practices.
“Medicine is unique in its physical demands,” said Meghan Wieser, PT, DPT, a doctor of physical therapy at Recharge Health and Fitness in Ellicott City, Maryland. Wieser frequently works with physicians and others in high-stress career environments, and she’s observed the serious toll that physically demanding medical practice can take on the body.
It’s not just about preventing acute or chronic injury, she said. It’s about performing better for longer periods. And every doctor knows the only way to build a more functional body is training.
The Fantasy of Physical Perfection vs the Reality of, Well, Reality
Jordan D. Metzl, MD, is a sports medicine physician at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) in New York City. He’s also a lifelong triathlete and marathon runner and has parlayed that passion into an online fitness community of more than 10,000 people called Ironstrength. Through that, Metzl has led free exercise classes in Central Park for years. He doesn’t dabble. Three times a year he leads a boot camp class of more than 1000 people on the flight deck of the USS Intrepid on the Hudson River.
“I get it, being a doctor is all about the hours,” he said. “The time sacrifices get brutal and you have to cut something out, sometimes every day. For a lot of us, that’s exercise.”
Metzl understands it so well that he recently began leading twice-monthly boot camp classes just for his HSS physician colleagues on Wednesday mornings. He says those doctors both want and need that extra boost and will be aggressive about making time for it.
“The better shape you’re in, the better job you’ll do as a physician,” he said. “You’ll feel better when the hours get long. In my own career, I have always been a better doctor when I’m active and in shape.”
Knowledge isn’t really the issue for physicians. Reality is. And reality dictates that doctors have just as much issue with achieving consistency as any patient they prescribe exercise to.
Metzl suggests total body functional training to mimic real-world movement, particularly core and lower body to keep you upright for hours at a time. How do you schedule that? He uses early mornings and weekends to train for his races and run his fitness classes, which is why his primary advice is to focus not on the activity, but on time.
“Schedule full workouts when you can and steal the rest,” he said.
Schopper agrees. “You may not be able to fit in 60 minutes of exercise every day, but 20-30 minutes of intentional movement is key,” she explained. “When you have a day off, prioritize a longer session of something you can’t fit in on workdays.”
Those shorter bouts of exercise might include “bookending” the day with 10 minutes of burpees in the morning and then 10 minutes of bodyweight strength moves like planks, push-ups, and air squats in the evening.
“Bodyweight exercises are low-hanging fruit,” said Wieser. “If you’ve got a short window, aim for something that can shoot your heart rate up quickly.”
You can also throw in “movement snacks” throughout the day — skip the elevator and run up a flight of stairs, walk around during a quick lunch break, or throw in a set of jumping jacks between patients. (Don’t worry — you won’t be dripping sweat when they walk in.)
Remember, the rehab room in the orthopedic wing may have a few dumbbells and exercise bands you can utilize when you have 5 extra minutes in your day. “Any way you can squeeze in extra movement counts,” said Wieser.
Feats of Strength? Neighborhood Sprints? It All Matters
Kissinger Goldman, DO, a Florida-based ER physician, began his dedication to exercise 17 years ago, after a high-cholesterol diagnosis. “Did I have time to exercise in medical school and residency? Yes,” Goldman admitted. “But I didn’t have the same commitment to my health until I received that number. I set about to change everything.”
Goldman follows the approach of dividing up his exercise routine into short or long sessions, depending on his schedule. “If I’m off, I’ll aim for 30 minutes of cardio and 30 minutes of strength and core work,” he explained. “When I have to work, I’ll do a compressed version of that routine as soon as I wake up, and make sure the cardio is very intense — I’ll sprint in my neighborhood, for instance.”
Matt Klein, a doctor of physical therapy and professor at George Fox University in Newberg, Oregon, who has treated many doctors, says that, when pushed for time, just 20 minutes of “heavy” strength training can deliver good results. “The definition of heavy will vary, but aim for a weight that is challenging, whether a beginner or a more experienced exerciser,” he said. “Most doctors won’t have time to go to the gym, so a simple set of dumbbells or kettlebells will work just fine. The easier it is to access, the more likely you are to do it consistently.”
Klein is a fan of strength training with good reason: “Strength is a predictor of chronic disease, so doing some high-level strength training or power training can go a long way,” he said.
The endorphin high and overall sense of improved well-being are an extra bonus. Goldman credits it with ensuring he rarely misses a workout.
Get Hardcore About Sleep
Consider the following passage: “There are clear negative effects of sleep deprivation on performance, including reaction time, accuracy, vigor, submaximal strength, and endurance. Cognitive functions such as judgment and decision-making also suffer.”
Does that sound like how you feel on suboptimal sleep? That’s from an International Journal of Sports Medicine study on the effects of sleep deprivation on athletes.
Athletes aren’t doctors — but when you consider “reaction time, accuracy, endurance, judgment, and decision-making” — doctors could certainly benefit by thinking like athletes.
Schopper is serious about sleep and sets firm boundaries.
“It’s hard,” she admitted. “We want to work, see our families, have fun. But I work hard to say, ‘I’m done,’ and go to bed.”
“Rest is crucial for this job,” agreed Goldman. “If you don’t have adequate sleep, your cortisone levels are going to go up. When you’re exhausted and you’re working, you’re likely to miss something.” Goldman is consistent with early bedtimes around 9:00 or 9:30 PM, and he allows for a bit of “wind-down” time by reading for about 20 minutes before nodding off.
Goldman also sees a link between rest and improved interactions with patients. “There’s a direct correlation between number of hours worked in a row with respect to ‘customer service’ with patients,” he said.
But don’t aim for perfection. Allow some wiggle room for the time you spend asleep, Klein recommends. “We’ve always aimed for 8 hours, but there’s evidence that even 6 or 7 hours can be enough to allow you to recover as needed,” he said. “Optimally, you want that to be uninterrupted, but if not, a 10-minute power nap can help with mental clarity.”
Keep Searching, Keep Trying, Keep Training
Schopper was never, nor has she become, a gym rat. Still, “I knew I needed to build upper body strength,” she said. That meant expanding her fitness possibilities beyond the obvious. She discovered aerial arts — intense workouts using straps and other suspension tools to work every muscle in her body while hanging from the ceiling. Increased strength was a given, but she also seriously increased her range of motion.
For Schopper, the improvements to her lifestyle have been game changers. “I still have long days, but I’m no longer sore and tired after them,” she said. “I sleep better and have more energy. I’m proud of myself for putting the effort into this.”
A journey toward health and fitness may look different for everyone, but (as doctors frequently tell their patients) it’s a path anyone can follow.
“Being a doctor is not necessarily good for your health,” said Klein. “The body can handle the job, however, if you train for it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Trump Nominations for US Health Agencies Spark Controversy, Criticism, Praise
President-elect Donald Trump’s vision for the nation’s top health agencies is coming into focus with three nominations announced Nov. 22 that drew both criticism and praise:
- Surgeon and health researcher Martin A. Makary, MD, MPH, to lead the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- Former Republican congressman and physician David J. Weldon, MD, for director of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- Fox News contributor Janette Nesheiwat, MD, for surgeon general.
Earlier in November, Trump nominated vaccine skeptic and former presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. to lead the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
Here’s what to know about the latest nominees, who, like Kennedy, must be confirmed by the US Senate.
Martin A. Makary
Currently a professor at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and chief of islet transplant surgery at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Makary co-invented in 2006 a surgery checklist that became a widely-used patient safety tool.
As a US FDA commissioner, Makary would preside over a $6.5 billion agency with more than 18,000 employees. The agency, part of HHS, oversees human and animal drugs and vaccines, medical devices, food, tobacco and other products. Some of Makary’s views align closely with those of HHS nominee Kennedy.
Makary is also chief medical officer of telehealth platform Sesame.
Makary was primarily known as a health researcher and author of books about price transparency and the cost of health care until the COVID-19 pandemic, when he became an outspoken critic of the federal response, lambasting restrictions and mandates advocated by the CDC and other public health officials.
In 2023, Makary told the House Select Subcommittee on the COVID Pandemic that federal officials had ignored what he called “natural immunity.” Studies have shown that natural immunity is “at least as effective as vaccinated immunity, and probably better,” testified Makary.
Makary called for an overhaul of the US FDA in a 2021 Fox News opinion, saying that its culture was “defined by counterproductive rigidity and a refusal to adapt.”
Blind Spots, his most recent book, takes on what he calls “medical dogma” and challenges conventional views on subjects ranging from the microbiome to marijuana to cancer prevention, hormone replacement therapy, antibiotics and peanut allergies.
In an interview he posted to X, Makary blames inappropriate use of antibiotics for a variety of childhood illnesses. He cites increases in obesity, learning disabilities, attention deficit disorder, asthma, celiac disease, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease as all potentially causally related to antibiotics given in childhood.
Makary is an advisor to two conservative think tanks, the Foundation for Research on Equal Opportunity, and to Paragon Health Institute, begun in 2021 by two former top officials in the previous Trump administration.
Makary would “cut the bureaucratic red tape at the agency to make sure Americans get the medical cures and treatments they deserve,” Trump said on his social media platform, Truth Social, and in a press release.
While Los Angeles Times owner and physician-entrepreneur Patrick Soon-Shiong, MBBCh, MSc, praised the nomination of Makary (and the two other nominees) as “inspired,” other physicians criticized Makary for his anti-COVID mandate views and “fear-mongering” over COVID vaccine side effects.
Janette Nesheiwat
As surgeon general, Nesheiwat would serve as the top “health communicator in chief” and oversee the 6000 member US Public Health Service Commissioned Corps.
She is a frequent medical contributor to Fox News and serves as a medical director for a group of urgent care clinics in New York. She received her medical degree from the American University of the Caribbean School of Medicine and completed a family medicine residency at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. She is board-certified in family medicine.
Nesheiwat sells vitamin supplements on her website and in December will publish a book on “miracles in medicine” and her Christian faith.
Trump said in a statement that Nesheiwat “is a fierce advocate and strong communicator for preventive medicine and public health. She is committed to ensuring that Americans have access to affordable, quality healthcare, and believes in empowering individuals to take charge of their health to live longer, healthier lives.”
While Nesheiwat was critical of COVID mandates, she voiced more support for COVID vaccines and mask-wearing during the pandemic than her fellow nominees, leading some Trump supporters to criticize her nomination.
“A good appointment, happy about this: I got to know @DoctorJanette during the pandemic, exchanging information. She is very smart, thoughtful, interested in learning, and a compassionate doctor, and…a truly nice person,” noted vaccine researcher Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, said on X.
David J. Weldon
If confirmed, former congressman Weldon would oversee the sprawling CDC, an agency with a roughly $17 billion budget, 15,000 employees or contractors, and numerous centers covering everything from health statistics to vaccines to epidemiology.
After earning his medical degree from the University at Buffalo School of Medicine, Weldon served in the US Army and US Army reserve. The Republican later served for 14 years in Congress representing Florida’s 15th district, which covers the Tampa region.
He now practices as an internist in Brevard County, Florida.
In Congress, Weldon raised concerns about the safety of some vaccines and promoted the false narrative that a former vaccine ingredient, thimerosal, caused autism, the Washington Post reported. Thimerosal has not been used in child vaccines for more than two decades. He also introduced a bill to move vaccine safety oversight from the CDC to an independent agency within HHS.
Trump said in a statement that Weldon “will proudly restore the CDC to its true purpose, and will work to end the Chronic Disease Epidemic.”
But some physicians criticized Weldon for what they called his anti-vaccine views.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President-elect Donald Trump’s vision for the nation’s top health agencies is coming into focus with three nominations announced Nov. 22 that drew both criticism and praise:
- Surgeon and health researcher Martin A. Makary, MD, MPH, to lead the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- Former Republican congressman and physician David J. Weldon, MD, for director of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- Fox News contributor Janette Nesheiwat, MD, for surgeon general.
Earlier in November, Trump nominated vaccine skeptic and former presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. to lead the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
Here’s what to know about the latest nominees, who, like Kennedy, must be confirmed by the US Senate.
Martin A. Makary
Currently a professor at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and chief of islet transplant surgery at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Makary co-invented in 2006 a surgery checklist that became a widely-used patient safety tool.
As a US FDA commissioner, Makary would preside over a $6.5 billion agency with more than 18,000 employees. The agency, part of HHS, oversees human and animal drugs and vaccines, medical devices, food, tobacco and other products. Some of Makary’s views align closely with those of HHS nominee Kennedy.
Makary is also chief medical officer of telehealth platform Sesame.
Makary was primarily known as a health researcher and author of books about price transparency and the cost of health care until the COVID-19 pandemic, when he became an outspoken critic of the federal response, lambasting restrictions and mandates advocated by the CDC and other public health officials.
In 2023, Makary told the House Select Subcommittee on the COVID Pandemic that federal officials had ignored what he called “natural immunity.” Studies have shown that natural immunity is “at least as effective as vaccinated immunity, and probably better,” testified Makary.
Makary called for an overhaul of the US FDA in a 2021 Fox News opinion, saying that its culture was “defined by counterproductive rigidity and a refusal to adapt.”
Blind Spots, his most recent book, takes on what he calls “medical dogma” and challenges conventional views on subjects ranging from the microbiome to marijuana to cancer prevention, hormone replacement therapy, antibiotics and peanut allergies.
In an interview he posted to X, Makary blames inappropriate use of antibiotics for a variety of childhood illnesses. He cites increases in obesity, learning disabilities, attention deficit disorder, asthma, celiac disease, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease as all potentially causally related to antibiotics given in childhood.
Makary is an advisor to two conservative think tanks, the Foundation for Research on Equal Opportunity, and to Paragon Health Institute, begun in 2021 by two former top officials in the previous Trump administration.
Makary would “cut the bureaucratic red tape at the agency to make sure Americans get the medical cures and treatments they deserve,” Trump said on his social media platform, Truth Social, and in a press release.
While Los Angeles Times owner and physician-entrepreneur Patrick Soon-Shiong, MBBCh, MSc, praised the nomination of Makary (and the two other nominees) as “inspired,” other physicians criticized Makary for his anti-COVID mandate views and “fear-mongering” over COVID vaccine side effects.
Janette Nesheiwat
As surgeon general, Nesheiwat would serve as the top “health communicator in chief” and oversee the 6000 member US Public Health Service Commissioned Corps.
She is a frequent medical contributor to Fox News and serves as a medical director for a group of urgent care clinics in New York. She received her medical degree from the American University of the Caribbean School of Medicine and completed a family medicine residency at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. She is board-certified in family medicine.
Nesheiwat sells vitamin supplements on her website and in December will publish a book on “miracles in medicine” and her Christian faith.
Trump said in a statement that Nesheiwat “is a fierce advocate and strong communicator for preventive medicine and public health. She is committed to ensuring that Americans have access to affordable, quality healthcare, and believes in empowering individuals to take charge of their health to live longer, healthier lives.”
While Nesheiwat was critical of COVID mandates, she voiced more support for COVID vaccines and mask-wearing during the pandemic than her fellow nominees, leading some Trump supporters to criticize her nomination.
“A good appointment, happy about this: I got to know @DoctorJanette during the pandemic, exchanging information. She is very smart, thoughtful, interested in learning, and a compassionate doctor, and…a truly nice person,” noted vaccine researcher Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, said on X.
David J. Weldon
If confirmed, former congressman Weldon would oversee the sprawling CDC, an agency with a roughly $17 billion budget, 15,000 employees or contractors, and numerous centers covering everything from health statistics to vaccines to epidemiology.
After earning his medical degree from the University at Buffalo School of Medicine, Weldon served in the US Army and US Army reserve. The Republican later served for 14 years in Congress representing Florida’s 15th district, which covers the Tampa region.
He now practices as an internist in Brevard County, Florida.
In Congress, Weldon raised concerns about the safety of some vaccines and promoted the false narrative that a former vaccine ingredient, thimerosal, caused autism, the Washington Post reported. Thimerosal has not been used in child vaccines for more than two decades. He also introduced a bill to move vaccine safety oversight from the CDC to an independent agency within HHS.
Trump said in a statement that Weldon “will proudly restore the CDC to its true purpose, and will work to end the Chronic Disease Epidemic.”
But some physicians criticized Weldon for what they called his anti-vaccine views.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President-elect Donald Trump’s vision for the nation’s top health agencies is coming into focus with three nominations announced Nov. 22 that drew both criticism and praise:
- Surgeon and health researcher Martin A. Makary, MD, MPH, to lead the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- Former Republican congressman and physician David J. Weldon, MD, for director of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- Fox News contributor Janette Nesheiwat, MD, for surgeon general.
Earlier in November, Trump nominated vaccine skeptic and former presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. to lead the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
Here’s what to know about the latest nominees, who, like Kennedy, must be confirmed by the US Senate.
Martin A. Makary
Currently a professor at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and chief of islet transplant surgery at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Makary co-invented in 2006 a surgery checklist that became a widely-used patient safety tool.
As a US FDA commissioner, Makary would preside over a $6.5 billion agency with more than 18,000 employees. The agency, part of HHS, oversees human and animal drugs and vaccines, medical devices, food, tobacco and other products. Some of Makary’s views align closely with those of HHS nominee Kennedy.
Makary is also chief medical officer of telehealth platform Sesame.
Makary was primarily known as a health researcher and author of books about price transparency and the cost of health care until the COVID-19 pandemic, when he became an outspoken critic of the federal response, lambasting restrictions and mandates advocated by the CDC and other public health officials.
In 2023, Makary told the House Select Subcommittee on the COVID Pandemic that federal officials had ignored what he called “natural immunity.” Studies have shown that natural immunity is “at least as effective as vaccinated immunity, and probably better,” testified Makary.
Makary called for an overhaul of the US FDA in a 2021 Fox News opinion, saying that its culture was “defined by counterproductive rigidity and a refusal to adapt.”
Blind Spots, his most recent book, takes on what he calls “medical dogma” and challenges conventional views on subjects ranging from the microbiome to marijuana to cancer prevention, hormone replacement therapy, antibiotics and peanut allergies.
In an interview he posted to X, Makary blames inappropriate use of antibiotics for a variety of childhood illnesses. He cites increases in obesity, learning disabilities, attention deficit disorder, asthma, celiac disease, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease as all potentially causally related to antibiotics given in childhood.
Makary is an advisor to two conservative think tanks, the Foundation for Research on Equal Opportunity, and to Paragon Health Institute, begun in 2021 by two former top officials in the previous Trump administration.
Makary would “cut the bureaucratic red tape at the agency to make sure Americans get the medical cures and treatments they deserve,” Trump said on his social media platform, Truth Social, and in a press release.
While Los Angeles Times owner and physician-entrepreneur Patrick Soon-Shiong, MBBCh, MSc, praised the nomination of Makary (and the two other nominees) as “inspired,” other physicians criticized Makary for his anti-COVID mandate views and “fear-mongering” over COVID vaccine side effects.
Janette Nesheiwat
As surgeon general, Nesheiwat would serve as the top “health communicator in chief” and oversee the 6000 member US Public Health Service Commissioned Corps.
She is a frequent medical contributor to Fox News and serves as a medical director for a group of urgent care clinics in New York. She received her medical degree from the American University of the Caribbean School of Medicine and completed a family medicine residency at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. She is board-certified in family medicine.
Nesheiwat sells vitamin supplements on her website and in December will publish a book on “miracles in medicine” and her Christian faith.
Trump said in a statement that Nesheiwat “is a fierce advocate and strong communicator for preventive medicine and public health. She is committed to ensuring that Americans have access to affordable, quality healthcare, and believes in empowering individuals to take charge of their health to live longer, healthier lives.”
While Nesheiwat was critical of COVID mandates, she voiced more support for COVID vaccines and mask-wearing during the pandemic than her fellow nominees, leading some Trump supporters to criticize her nomination.
“A good appointment, happy about this: I got to know @DoctorJanette during the pandemic, exchanging information. She is very smart, thoughtful, interested in learning, and a compassionate doctor, and…a truly nice person,” noted vaccine researcher Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, said on X.
David J. Weldon
If confirmed, former congressman Weldon would oversee the sprawling CDC, an agency with a roughly $17 billion budget, 15,000 employees or contractors, and numerous centers covering everything from health statistics to vaccines to epidemiology.
After earning his medical degree from the University at Buffalo School of Medicine, Weldon served in the US Army and US Army reserve. The Republican later served for 14 years in Congress representing Florida’s 15th district, which covers the Tampa region.
He now practices as an internist in Brevard County, Florida.
In Congress, Weldon raised concerns about the safety of some vaccines and promoted the false narrative that a former vaccine ingredient, thimerosal, caused autism, the Washington Post reported. Thimerosal has not been used in child vaccines for more than two decades. He also introduced a bill to move vaccine safety oversight from the CDC to an independent agency within HHS.
Trump said in a statement that Weldon “will proudly restore the CDC to its true purpose, and will work to end the Chronic Disease Epidemic.”
But some physicians criticized Weldon for what they called his anti-vaccine views.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low-Dose Oral Minoxidil: Expert Consensus Provide Guidance for Treating Hair Loss
. With large randomized, controlled trials lacking, the guidelines authors and other dermatologists said the paper provides practical pointers that should increase clinicians’ confidence in prescribing LDOM for hair loss.
Comfort and Confidence
Benjamin N. Ungar, MD, director of the Alopecia Center of Excellence at Mount Sinai Icahn School of Medicine, New York City, said he hopes that the guidelines will “make dermatologists in practice more comfortable with the use of low-dose oral minoxidil to treat different kinds of hair loss, and therefore, more patients will benefit.” He was not an author of the paper, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology on November 20, but was asked to comment.
Members of the multidisciplinary Low-Dose Oral Minoxidil Initiation steering committee recruited dermatologists with hair loss expertise from 12 countries. Using a modified four-round Delphi process that required at least 70% agreement, the group of 43 dermatologists crafted 76 consensus statements. “Notably,” said Co-senior author Jennifer Fu, MD, director of the Hair Disorders Clinic at the University of California, San Francisco, “27 items achieved at least 90% consensus after the first two rounds, indicating broad agreement in expert practice.”
Indications for LDOM
At least 90% of experts concurred regarding the appropriateness of LDOM use for androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and age-related thinning and in cases where topical minoxidil proves ineffective or problematic. Additional situations in which LDOM might provide direct benefit involve follicular miniaturization, such as alopecia areata, or hair cycle disruption, such as chemotherapy. The authors also recommended considering LDOM over topical minoxidil when the latter is more expensive and when patients desire enhanced hypertrichosis.
Contraindications and Precautions
Before prescribing LDOM, the authors wrote, clinicians may consult with primary care or cardiology when contraindications (cardiovascular issues, pregnancy/nursing, and potential drug interactions) or precautions (history of tachycardia or arrhythmia, hypotension, or impaired kidney function) exist. Patients with precautions may require blood pressure monitoring, as well as monitoring for adverse effects of treatment. The panel also suggested the latter for all patients at the time of LDOM initiation and dose escalation. The authors advised against routine baseline laboratory and EKG testing in cases without relevant precautions.
Dosing Considerations
Along with systemic adverse event risk and baseline hair loss severity, key dosing considerations include patient age, sex, and whether patients desire hypertrichosis. Consensus on daily doses for adolescent females and males begins at 0.625 mg and 1.25 mg, respectively, and ranges up to 2.5 mg for adolescent females vs 5 mg for adult females and adolescent and adult males.
Presently, said Ungar, many dermatologists — including some who prescribe LDOM — remain uncomfortable even with very low doses, perhaps because of an invalid perception of cardiovascular safety issues including potential hypotension and pericardial effusions. However, recently published data include a review published November 7 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which showed no significant effect of LDOM on blood pressure. And in a September Journal of Drugs in Dermatology article the authors found no impact on pericardial effusions in a 100-patient cohort.
Some dermatologists worry about the impact hypertrichosis may have on patients, Ungar added. Although incidence estimates range from 15% to 30%, he said, more than half of his patients experience hypertrichosis. “However, most continue treatment because the beneficial effects outweigh the effect of hypertrichosis.”
Practical Roadmap
Adam Friedman, MD, who was not involved with the publication, applauds its inclusion of pragmatic clinical guidance, which he said consensus papers often lack. “This paper sets a great roadmap for working low-dose oral minoxidil into your clinical practice, Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
Rather than limiting LDOM use to AGA, he said, the paper is most helpful in showing the spectrum of disease states for which the expert panel prescribes LDOM. “We use it as adjunctive therapy for many other things, both scarring and nonscarring hair loss,” he added.
In appropriate clinical contexts, the authors wrote, clinicians may consider combining LDOM with spironolactone or beta-blockers. Friedman said that in his hands, combining LDOM with a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor (5ARI) is “absolutely outstanding.” Minoxidil increases blood flow to the scalp, he explained, while 5ARIs prevent production of dihydrotestosterone, which miniaturizes hair.
Fu said, “We hope these consensus outcomes will be helpful to dermatology colleagues as they consider using LDOM to treat hair loss in their adult and adolescent patient populations. We anticipate that these guidelines will be updated as additional evidence-based data emerges and are encouraged that we are already seeing new publications on this topic.”
Important areas for future research, she noted, include pediatric use of LDOM, the comparative efficacy of topical vs oral minoxidil, the safety of oral minoxidil for patients with a history of allergic contact dermatitis to topical minoxidil, and the use of other off-label forms of minoxidil, such as compounded oral minoxidil and sublingual minoxidil.
The study was funded by the University of California, San Francisco, Department of Dermatology Medical Student Summer Research Fellowship Program. Fu reported personal fees from Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, and Sun Pharma outside of the study. The full list of author disclosures can be found in the paper. Ungar and Friedman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
. With large randomized, controlled trials lacking, the guidelines authors and other dermatologists said the paper provides practical pointers that should increase clinicians’ confidence in prescribing LDOM for hair loss.
Comfort and Confidence
Benjamin N. Ungar, MD, director of the Alopecia Center of Excellence at Mount Sinai Icahn School of Medicine, New York City, said he hopes that the guidelines will “make dermatologists in practice more comfortable with the use of low-dose oral minoxidil to treat different kinds of hair loss, and therefore, more patients will benefit.” He was not an author of the paper, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology on November 20, but was asked to comment.
Members of the multidisciplinary Low-Dose Oral Minoxidil Initiation steering committee recruited dermatologists with hair loss expertise from 12 countries. Using a modified four-round Delphi process that required at least 70% agreement, the group of 43 dermatologists crafted 76 consensus statements. “Notably,” said Co-senior author Jennifer Fu, MD, director of the Hair Disorders Clinic at the University of California, San Francisco, “27 items achieved at least 90% consensus after the first two rounds, indicating broad agreement in expert practice.”
Indications for LDOM
At least 90% of experts concurred regarding the appropriateness of LDOM use for androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and age-related thinning and in cases where topical minoxidil proves ineffective or problematic. Additional situations in which LDOM might provide direct benefit involve follicular miniaturization, such as alopecia areata, or hair cycle disruption, such as chemotherapy. The authors also recommended considering LDOM over topical minoxidil when the latter is more expensive and when patients desire enhanced hypertrichosis.
Contraindications and Precautions
Before prescribing LDOM, the authors wrote, clinicians may consult with primary care or cardiology when contraindications (cardiovascular issues, pregnancy/nursing, and potential drug interactions) or precautions (history of tachycardia or arrhythmia, hypotension, or impaired kidney function) exist. Patients with precautions may require blood pressure monitoring, as well as monitoring for adverse effects of treatment. The panel also suggested the latter for all patients at the time of LDOM initiation and dose escalation. The authors advised against routine baseline laboratory and EKG testing in cases without relevant precautions.
Dosing Considerations
Along with systemic adverse event risk and baseline hair loss severity, key dosing considerations include patient age, sex, and whether patients desire hypertrichosis. Consensus on daily doses for adolescent females and males begins at 0.625 mg and 1.25 mg, respectively, and ranges up to 2.5 mg for adolescent females vs 5 mg for adult females and adolescent and adult males.
Presently, said Ungar, many dermatologists — including some who prescribe LDOM — remain uncomfortable even with very low doses, perhaps because of an invalid perception of cardiovascular safety issues including potential hypotension and pericardial effusions. However, recently published data include a review published November 7 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which showed no significant effect of LDOM on blood pressure. And in a September Journal of Drugs in Dermatology article the authors found no impact on pericardial effusions in a 100-patient cohort.
Some dermatologists worry about the impact hypertrichosis may have on patients, Ungar added. Although incidence estimates range from 15% to 30%, he said, more than half of his patients experience hypertrichosis. “However, most continue treatment because the beneficial effects outweigh the effect of hypertrichosis.”
Practical Roadmap
Adam Friedman, MD, who was not involved with the publication, applauds its inclusion of pragmatic clinical guidance, which he said consensus papers often lack. “This paper sets a great roadmap for working low-dose oral minoxidil into your clinical practice, Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
Rather than limiting LDOM use to AGA, he said, the paper is most helpful in showing the spectrum of disease states for which the expert panel prescribes LDOM. “We use it as adjunctive therapy for many other things, both scarring and nonscarring hair loss,” he added.
In appropriate clinical contexts, the authors wrote, clinicians may consider combining LDOM with spironolactone or beta-blockers. Friedman said that in his hands, combining LDOM with a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor (5ARI) is “absolutely outstanding.” Minoxidil increases blood flow to the scalp, he explained, while 5ARIs prevent production of dihydrotestosterone, which miniaturizes hair.
Fu said, “We hope these consensus outcomes will be helpful to dermatology colleagues as they consider using LDOM to treat hair loss in their adult and adolescent patient populations. We anticipate that these guidelines will be updated as additional evidence-based data emerges and are encouraged that we are already seeing new publications on this topic.”
Important areas for future research, she noted, include pediatric use of LDOM, the comparative efficacy of topical vs oral minoxidil, the safety of oral minoxidil for patients with a history of allergic contact dermatitis to topical minoxidil, and the use of other off-label forms of minoxidil, such as compounded oral minoxidil and sublingual minoxidil.
The study was funded by the University of California, San Francisco, Department of Dermatology Medical Student Summer Research Fellowship Program. Fu reported personal fees from Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, and Sun Pharma outside of the study. The full list of author disclosures can be found in the paper. Ungar and Friedman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
. With large randomized, controlled trials lacking, the guidelines authors and other dermatologists said the paper provides practical pointers that should increase clinicians’ confidence in prescribing LDOM for hair loss.
Comfort and Confidence
Benjamin N. Ungar, MD, director of the Alopecia Center of Excellence at Mount Sinai Icahn School of Medicine, New York City, said he hopes that the guidelines will “make dermatologists in practice more comfortable with the use of low-dose oral minoxidil to treat different kinds of hair loss, and therefore, more patients will benefit.” He was not an author of the paper, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology on November 20, but was asked to comment.
Members of the multidisciplinary Low-Dose Oral Minoxidil Initiation steering committee recruited dermatologists with hair loss expertise from 12 countries. Using a modified four-round Delphi process that required at least 70% agreement, the group of 43 dermatologists crafted 76 consensus statements. “Notably,” said Co-senior author Jennifer Fu, MD, director of the Hair Disorders Clinic at the University of California, San Francisco, “27 items achieved at least 90% consensus after the first two rounds, indicating broad agreement in expert practice.”
Indications for LDOM
At least 90% of experts concurred regarding the appropriateness of LDOM use for androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and age-related thinning and in cases where topical minoxidil proves ineffective or problematic. Additional situations in which LDOM might provide direct benefit involve follicular miniaturization, such as alopecia areata, or hair cycle disruption, such as chemotherapy. The authors also recommended considering LDOM over topical minoxidil when the latter is more expensive and when patients desire enhanced hypertrichosis.
Contraindications and Precautions
Before prescribing LDOM, the authors wrote, clinicians may consult with primary care or cardiology when contraindications (cardiovascular issues, pregnancy/nursing, and potential drug interactions) or precautions (history of tachycardia or arrhythmia, hypotension, or impaired kidney function) exist. Patients with precautions may require blood pressure monitoring, as well as monitoring for adverse effects of treatment. The panel also suggested the latter for all patients at the time of LDOM initiation and dose escalation. The authors advised against routine baseline laboratory and EKG testing in cases without relevant precautions.
Dosing Considerations
Along with systemic adverse event risk and baseline hair loss severity, key dosing considerations include patient age, sex, and whether patients desire hypertrichosis. Consensus on daily doses for adolescent females and males begins at 0.625 mg and 1.25 mg, respectively, and ranges up to 2.5 mg for adolescent females vs 5 mg for adult females and adolescent and adult males.
Presently, said Ungar, many dermatologists — including some who prescribe LDOM — remain uncomfortable even with very low doses, perhaps because of an invalid perception of cardiovascular safety issues including potential hypotension and pericardial effusions. However, recently published data include a review published November 7 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which showed no significant effect of LDOM on blood pressure. And in a September Journal of Drugs in Dermatology article the authors found no impact on pericardial effusions in a 100-patient cohort.
Some dermatologists worry about the impact hypertrichosis may have on patients, Ungar added. Although incidence estimates range from 15% to 30%, he said, more than half of his patients experience hypertrichosis. “However, most continue treatment because the beneficial effects outweigh the effect of hypertrichosis.”
Practical Roadmap
Adam Friedman, MD, who was not involved with the publication, applauds its inclusion of pragmatic clinical guidance, which he said consensus papers often lack. “This paper sets a great roadmap for working low-dose oral minoxidil into your clinical practice, Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
Rather than limiting LDOM use to AGA, he said, the paper is most helpful in showing the spectrum of disease states for which the expert panel prescribes LDOM. “We use it as adjunctive therapy for many other things, both scarring and nonscarring hair loss,” he added.
In appropriate clinical contexts, the authors wrote, clinicians may consider combining LDOM with spironolactone or beta-blockers. Friedman said that in his hands, combining LDOM with a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor (5ARI) is “absolutely outstanding.” Minoxidil increases blood flow to the scalp, he explained, while 5ARIs prevent production of dihydrotestosterone, which miniaturizes hair.
Fu said, “We hope these consensus outcomes will be helpful to dermatology colleagues as they consider using LDOM to treat hair loss in their adult and adolescent patient populations. We anticipate that these guidelines will be updated as additional evidence-based data emerges and are encouraged that we are already seeing new publications on this topic.”
Important areas for future research, she noted, include pediatric use of LDOM, the comparative efficacy of topical vs oral minoxidil, the safety of oral minoxidil for patients with a history of allergic contact dermatitis to topical minoxidil, and the use of other off-label forms of minoxidil, such as compounded oral minoxidil and sublingual minoxidil.
The study was funded by the University of California, San Francisco, Department of Dermatology Medical Student Summer Research Fellowship Program. Fu reported personal fees from Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, and Sun Pharma outside of the study. The full list of author disclosures can be found in the paper. Ungar and Friedman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Phase 3 Lupus Trial Shows Promising Results for Dapirolizumab Pegol
WASHINGTON — The investigational anti-CD40 ligand agent dapirolizumab pegol (DZP) outperformed placebo in improving disease activity and reducing high-dose corticosteroid use in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in the phase 3 PHOENYCS GO trial.
“We really think that dapirolizumab pegol may represent a novel treatment for lupus, particularly given its broad immune modulatory effects,” said Megan Clowse, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine and chief of the Division of Rheumatology and Immunology at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina. She presented the study in a late-breaking poster session at the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 2024 Annual Meeting.
There is a “huge unmet need” for drugs for lupus, Clowse told this news organization. Patients with SLE continue to have high disease burden, including ongoing symptoms often driven by inflammation. Corticosteroids are often the best medications to control disease activity, she said, but they can result in long-term toxicity.
What Makes DZP Unique?
Through CD40 ligand signaling, DZP has been shown to reduce B- and T-cell activation and to downregulate interferon pathways. Previous antibodies targeting the CD40 ligand have been associated with an increased risk for thromboembolic events. However, DZP lacks the Fc portion of the antibody, which can bind to platelets and cause clotting. Data from phase 1, 2, and 3 trials thus far do not show an elevated risk for these events, Clowse explained. In fact, safety signals were strong enough that patients with antiphospholipid antibodies — a key driver for blood clots in patients with SLE — were included in the trial.
In PHOENYCS GO, investigators enrolled 321 patients with moderate to severe SLE with persistently active or frequently flaring/relapsing-remitting disease activity despite stable standard of care (SOC) medications such as antimalarials, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants.
Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive intravenous DZP (24 mg/kg) plus SOC or intravenous placebo plus SOC every 4 weeks, with patients and investigators blinded to treatment assignments.
Patients taking a corticosteroid dose > 7.5 mg/day began a mandatory steroid taper by week 8 of the trial, with the goal of reducing that to < 7.5 mg/day. The tapering regimen was at the discretion of providers and was adapted to each patient’s individual disease activity.
The primary endpoint was British Isles Lupus Assessment Group–based Composite Lupus Assessment (BICLA) response at week 48.
Patients in the DZP and placebo groups were on average 43.5 and 41.5 years old, respectively. More than 90% of patients were women, all on concomitant SLE medications. About half of the participants took a daily corticosteroid dose > 7.5 mg.
At 48 weeks, half of the DZP group (49.5%) achieved BICLA response compared with 34.6% in the placebo group (P = .0110). A higher proportion of patients taking DZP achieved SLE Responder Index-4 response than those taking placebo (60.1% vs 41.1%, respectively; P = .0014), and the rate of severe British Isles Lupus Assessment Group flares in the DZP group was half that of the placebo group (11.6% vs 23.4%; P = .0257). In the subgroup of patients who underwent corticosteroid tapering, 72.4% receiving DZP and 52.9% taking placebo reduced their dose to < 7.5 mg/day by 48 weeks (P = .0404).
DZP was generally well tolerated. Over 48 weeks, 82.6% of the DZP group and 75% of the placebo group reported treatment-emergent adverse events, but serious occurrences were more common in the placebo group (14.8%) than in the DZP group (9.9%). Herpes viral infections were higher in the placebo group, although there were three ophthalmic herpes cases in the DZP group. There was one case of acute myocardial infarction and one death linked to gangrene-related sepsis in patients receiving DZP.
A ‘Mild to Moderate’ Response
Although these are definitely positive results, they show a “mild to moderate response” to DZP, commented Gregory Gardner, MD, an emeritus professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, and chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s annual meeting planning committee. He moderated the session where the research was presented. Although DZP showed efficacy among some patients, he noted, “there were still 51% patients that it didn’t work for.”
The drug uses an alternative pathway to current lupus drugs, Gardner added, and more research is needed to understand how best to use this medication in practice.
Clowse noted that DZP could be particularly beneficial for patients with SLE who want to get pregnant. Many drugs used to treat the disease are teratogenic; however, “because of the lack of Fc portion on this drug, it very likely does not cross the placenta in any kind of significant amount,” she said. Although there are not yet any reproductive safety data on DZP, she added, “that is a great potential niche.”
Biogen and UCB, which are jointly developing DZP, aim to start a second phase 3 trial of DZP in patients with SLE, called PHOENYCS FLY, in 2024.
The trial was sponsored by UCB. Clowse is a consultant and has received grant/research support from GSK and UCB. Gardner had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — The investigational anti-CD40 ligand agent dapirolizumab pegol (DZP) outperformed placebo in improving disease activity and reducing high-dose corticosteroid use in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in the phase 3 PHOENYCS GO trial.
“We really think that dapirolizumab pegol may represent a novel treatment for lupus, particularly given its broad immune modulatory effects,” said Megan Clowse, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine and chief of the Division of Rheumatology and Immunology at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina. She presented the study in a late-breaking poster session at the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 2024 Annual Meeting.
There is a “huge unmet need” for drugs for lupus, Clowse told this news organization. Patients with SLE continue to have high disease burden, including ongoing symptoms often driven by inflammation. Corticosteroids are often the best medications to control disease activity, she said, but they can result in long-term toxicity.
What Makes DZP Unique?
Through CD40 ligand signaling, DZP has been shown to reduce B- and T-cell activation and to downregulate interferon pathways. Previous antibodies targeting the CD40 ligand have been associated with an increased risk for thromboembolic events. However, DZP lacks the Fc portion of the antibody, which can bind to platelets and cause clotting. Data from phase 1, 2, and 3 trials thus far do not show an elevated risk for these events, Clowse explained. In fact, safety signals were strong enough that patients with antiphospholipid antibodies — a key driver for blood clots in patients with SLE — were included in the trial.
In PHOENYCS GO, investigators enrolled 321 patients with moderate to severe SLE with persistently active or frequently flaring/relapsing-remitting disease activity despite stable standard of care (SOC) medications such as antimalarials, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants.
Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive intravenous DZP (24 mg/kg) plus SOC or intravenous placebo plus SOC every 4 weeks, with patients and investigators blinded to treatment assignments.
Patients taking a corticosteroid dose > 7.5 mg/day began a mandatory steroid taper by week 8 of the trial, with the goal of reducing that to < 7.5 mg/day. The tapering regimen was at the discretion of providers and was adapted to each patient’s individual disease activity.
The primary endpoint was British Isles Lupus Assessment Group–based Composite Lupus Assessment (BICLA) response at week 48.
Patients in the DZP and placebo groups were on average 43.5 and 41.5 years old, respectively. More than 90% of patients were women, all on concomitant SLE medications. About half of the participants took a daily corticosteroid dose > 7.5 mg.
At 48 weeks, half of the DZP group (49.5%) achieved BICLA response compared with 34.6% in the placebo group (P = .0110). A higher proportion of patients taking DZP achieved SLE Responder Index-4 response than those taking placebo (60.1% vs 41.1%, respectively; P = .0014), and the rate of severe British Isles Lupus Assessment Group flares in the DZP group was half that of the placebo group (11.6% vs 23.4%; P = .0257). In the subgroup of patients who underwent corticosteroid tapering, 72.4% receiving DZP and 52.9% taking placebo reduced their dose to < 7.5 mg/day by 48 weeks (P = .0404).
DZP was generally well tolerated. Over 48 weeks, 82.6% of the DZP group and 75% of the placebo group reported treatment-emergent adverse events, but serious occurrences were more common in the placebo group (14.8%) than in the DZP group (9.9%). Herpes viral infections were higher in the placebo group, although there were three ophthalmic herpes cases in the DZP group. There was one case of acute myocardial infarction and one death linked to gangrene-related sepsis in patients receiving DZP.
A ‘Mild to Moderate’ Response
Although these are definitely positive results, they show a “mild to moderate response” to DZP, commented Gregory Gardner, MD, an emeritus professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, and chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s annual meeting planning committee. He moderated the session where the research was presented. Although DZP showed efficacy among some patients, he noted, “there were still 51% patients that it didn’t work for.”
The drug uses an alternative pathway to current lupus drugs, Gardner added, and more research is needed to understand how best to use this medication in practice.
Clowse noted that DZP could be particularly beneficial for patients with SLE who want to get pregnant. Many drugs used to treat the disease are teratogenic; however, “because of the lack of Fc portion on this drug, it very likely does not cross the placenta in any kind of significant amount,” she said. Although there are not yet any reproductive safety data on DZP, she added, “that is a great potential niche.”
Biogen and UCB, which are jointly developing DZP, aim to start a second phase 3 trial of DZP in patients with SLE, called PHOENYCS FLY, in 2024.
The trial was sponsored by UCB. Clowse is a consultant and has received grant/research support from GSK and UCB. Gardner had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — The investigational anti-CD40 ligand agent dapirolizumab pegol (DZP) outperformed placebo in improving disease activity and reducing high-dose corticosteroid use in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in the phase 3 PHOENYCS GO trial.
“We really think that dapirolizumab pegol may represent a novel treatment for lupus, particularly given its broad immune modulatory effects,” said Megan Clowse, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine and chief of the Division of Rheumatology and Immunology at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina. She presented the study in a late-breaking poster session at the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 2024 Annual Meeting.
There is a “huge unmet need” for drugs for lupus, Clowse told this news organization. Patients with SLE continue to have high disease burden, including ongoing symptoms often driven by inflammation. Corticosteroids are often the best medications to control disease activity, she said, but they can result in long-term toxicity.
What Makes DZP Unique?
Through CD40 ligand signaling, DZP has been shown to reduce B- and T-cell activation and to downregulate interferon pathways. Previous antibodies targeting the CD40 ligand have been associated with an increased risk for thromboembolic events. However, DZP lacks the Fc portion of the antibody, which can bind to platelets and cause clotting. Data from phase 1, 2, and 3 trials thus far do not show an elevated risk for these events, Clowse explained. In fact, safety signals were strong enough that patients with antiphospholipid antibodies — a key driver for blood clots in patients with SLE — were included in the trial.
In PHOENYCS GO, investigators enrolled 321 patients with moderate to severe SLE with persistently active or frequently flaring/relapsing-remitting disease activity despite stable standard of care (SOC) medications such as antimalarials, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants.
Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive intravenous DZP (24 mg/kg) plus SOC or intravenous placebo plus SOC every 4 weeks, with patients and investigators blinded to treatment assignments.
Patients taking a corticosteroid dose > 7.5 mg/day began a mandatory steroid taper by week 8 of the trial, with the goal of reducing that to < 7.5 mg/day. The tapering regimen was at the discretion of providers and was adapted to each patient’s individual disease activity.
The primary endpoint was British Isles Lupus Assessment Group–based Composite Lupus Assessment (BICLA) response at week 48.
Patients in the DZP and placebo groups were on average 43.5 and 41.5 years old, respectively. More than 90% of patients were women, all on concomitant SLE medications. About half of the participants took a daily corticosteroid dose > 7.5 mg.
At 48 weeks, half of the DZP group (49.5%) achieved BICLA response compared with 34.6% in the placebo group (P = .0110). A higher proportion of patients taking DZP achieved SLE Responder Index-4 response than those taking placebo (60.1% vs 41.1%, respectively; P = .0014), and the rate of severe British Isles Lupus Assessment Group flares in the DZP group was half that of the placebo group (11.6% vs 23.4%; P = .0257). In the subgroup of patients who underwent corticosteroid tapering, 72.4% receiving DZP and 52.9% taking placebo reduced their dose to < 7.5 mg/day by 48 weeks (P = .0404).
DZP was generally well tolerated. Over 48 weeks, 82.6% of the DZP group and 75% of the placebo group reported treatment-emergent adverse events, but serious occurrences were more common in the placebo group (14.8%) than in the DZP group (9.9%). Herpes viral infections were higher in the placebo group, although there were three ophthalmic herpes cases in the DZP group. There was one case of acute myocardial infarction and one death linked to gangrene-related sepsis in patients receiving DZP.
A ‘Mild to Moderate’ Response
Although these are definitely positive results, they show a “mild to moderate response” to DZP, commented Gregory Gardner, MD, an emeritus professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, and chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s annual meeting planning committee. He moderated the session where the research was presented. Although DZP showed efficacy among some patients, he noted, “there were still 51% patients that it didn’t work for.”
The drug uses an alternative pathway to current lupus drugs, Gardner added, and more research is needed to understand how best to use this medication in practice.
Clowse noted that DZP could be particularly beneficial for patients with SLE who want to get pregnant. Many drugs used to treat the disease are teratogenic; however, “because of the lack of Fc portion on this drug, it very likely does not cross the placenta in any kind of significant amount,” she said. Although there are not yet any reproductive safety data on DZP, she added, “that is a great potential niche.”
Biogen and UCB, which are jointly developing DZP, aim to start a second phase 3 trial of DZP in patients with SLE, called PHOENYCS FLY, in 2024.
The trial was sponsored by UCB. Clowse is a consultant and has received grant/research support from GSK and UCB. Gardner had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
A 58-year-old White male presented with lesions on his index and middle finger for 3 months
Syphilis
Two biopsies by punch technique were performed; one for pathology and one for tissue culture (fungal and atypical mycobacteria). Tissue cultures showed no growth at 4 and 6 weeks, respectively. The lesions were swabbed for bacterial and viral cultures. Bacterial culture was positive for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and group C Streptococcus. Viral culture for herpes simplex virus (HSV) and varicella zoster virus (VZV) was negative. Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of syphilis. Immunoperoxidase stain was positive for Treponema pallidum, and negative for HSV-1, HSV-2, and VZV. Special stains for PAS, GMS, Fite, and AFB were negative for organisms.
Syphilis, also known as Lues disease, is a contagious, sexually acquired disease caused by the spirochete T pallidum. The skin and mucous membranes are primarily infected. There are primary, secondary, and tertiary stages. In the primary or initial stage of syphilis, a chancre appears, usually 3-4 weeks after infection. The chancre is a painless papule or erosion that progresses to a firm ulceration. Lymphadenopathy may be present. Less often, multiple chancres may be present. Primary chancre on the finger has been reported in the literature, although it is far less common to have extragenital primary syphilis. The incidence ranges from 2% to 10%. Other extragenital areas that can be affected include lips, intraoral lesions, and the anus. Atypical chancres can be formed when other microbial agents are also present. Generally, an untreated chancre will heal spontaneously within a few months.
The patient referred to the department of health for treatment with penicillin G and further workup of sexually transmitted diseases. He was also seen by infectious disease for treatment of the superimposed bacterial infections and treated with an antibiotic regimen.
The case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Ramoni S et al. Sex Transm Dis. 2010 Jul;37(7):468. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181e2cfac.
Starzycki Z. Br J Vener Dis. 1983 Jun;59(3):169-71. doi: 10.1136/sti.59.3.169.
Syphilis
Two biopsies by punch technique were performed; one for pathology and one for tissue culture (fungal and atypical mycobacteria). Tissue cultures showed no growth at 4 and 6 weeks, respectively. The lesions were swabbed for bacterial and viral cultures. Bacterial culture was positive for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and group C Streptococcus. Viral culture for herpes simplex virus (HSV) and varicella zoster virus (VZV) was negative. Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of syphilis. Immunoperoxidase stain was positive for Treponema pallidum, and negative for HSV-1, HSV-2, and VZV. Special stains for PAS, GMS, Fite, and AFB were negative for organisms.
Syphilis, also known as Lues disease, is a contagious, sexually acquired disease caused by the spirochete T pallidum. The skin and mucous membranes are primarily infected. There are primary, secondary, and tertiary stages. In the primary or initial stage of syphilis, a chancre appears, usually 3-4 weeks after infection. The chancre is a painless papule or erosion that progresses to a firm ulceration. Lymphadenopathy may be present. Less often, multiple chancres may be present. Primary chancre on the finger has been reported in the literature, although it is far less common to have extragenital primary syphilis. The incidence ranges from 2% to 10%. Other extragenital areas that can be affected include lips, intraoral lesions, and the anus. Atypical chancres can be formed when other microbial agents are also present. Generally, an untreated chancre will heal spontaneously within a few months.
The patient referred to the department of health for treatment with penicillin G and further workup of sexually transmitted diseases. He was also seen by infectious disease for treatment of the superimposed bacterial infections and treated with an antibiotic regimen.
The case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Ramoni S et al. Sex Transm Dis. 2010 Jul;37(7):468. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181e2cfac.
Starzycki Z. Br J Vener Dis. 1983 Jun;59(3):169-71. doi: 10.1136/sti.59.3.169.
Syphilis
Two biopsies by punch technique were performed; one for pathology and one for tissue culture (fungal and atypical mycobacteria). Tissue cultures showed no growth at 4 and 6 weeks, respectively. The lesions were swabbed for bacterial and viral cultures. Bacterial culture was positive for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and group C Streptococcus. Viral culture for herpes simplex virus (HSV) and varicella zoster virus (VZV) was negative. Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of syphilis. Immunoperoxidase stain was positive for Treponema pallidum, and negative for HSV-1, HSV-2, and VZV. Special stains for PAS, GMS, Fite, and AFB were negative for organisms.
Syphilis, also known as Lues disease, is a contagious, sexually acquired disease caused by the spirochete T pallidum. The skin and mucous membranes are primarily infected. There are primary, secondary, and tertiary stages. In the primary or initial stage of syphilis, a chancre appears, usually 3-4 weeks after infection. The chancre is a painless papule or erosion that progresses to a firm ulceration. Lymphadenopathy may be present. Less often, multiple chancres may be present. Primary chancre on the finger has been reported in the literature, although it is far less common to have extragenital primary syphilis. The incidence ranges from 2% to 10%. Other extragenital areas that can be affected include lips, intraoral lesions, and the anus. Atypical chancres can be formed when other microbial agents are also present. Generally, an untreated chancre will heal spontaneously within a few months.
The patient referred to the department of health for treatment with penicillin G and further workup of sexually transmitted diseases. He was also seen by infectious disease for treatment of the superimposed bacterial infections and treated with an antibiotic regimen.
The case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Ramoni S et al. Sex Transm Dis. 2010 Jul;37(7):468. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181e2cfac.
Starzycki Z. Br J Vener Dis. 1983 Jun;59(3):169-71. doi: 10.1136/sti.59.3.169.
A 58-year-old White male with no significant past medical history presented with lesions on his right index and middle fingers, which had been present for 3 months. The lesions were painless. The patient has a history of hand dermatitis. Upon questioning, the patient said he had not fished or cleaned fish tanks. He did garden occasionally (no roses). He has been using Neosporin on the lesions. He denied any fever or systemic symptoms and had no lymphadenopathy.
What's your diagnosis?
Managing Rosacea: Tips for Reducing Facial Erythema, Flushing
LAS VEGAS —
These agents “work fast” and “improve redness quickly,” Harper, a dermatologist who practices in Birmingham, Alabama, said at the Society of Dermatology Physician Associates (SDPA) 22nd Annual Fall Dermatology Conference. In addition, “you’re going to know within 30 minutes or an hour whether it’s going to work or not.”
Brimonidine 0.33% gel, an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2014 for persistent facial erythema of rosacea. It does not treat telangiectasia and is not approved for flushing (transient erythema). Patients are advised to apply the gel daily in the morning. In phase 3 pivotal trials of patients with moderate to severe erythema of rosacea, which excluded individuals with more than two papules, a composite (investigator- and patient-reported) 2-grade improvement was seen as early as 30 minutes after application on day 1, and erythema was reduced for 9-12 hours.
Oxymetazoline 1% cream, an alpha-1a adrenergic receptor agonist, was approved by the FDA in 2017 for persistent facial erythema of rosacea. It neither treats telangiectasia nor is approved for flushing. Phase 3 trials of patients with moderate to severe persistent erythema of rosacea excluded individuals with more than three inflammatory papules or pustules. A composite (investigator- and subject-reported) 2-grade improvement was seen as early as 1 hour after application on day 1, and erythema was reduced for 9-12 hours.
Receptor Selectivity Differences
According to Harper, there are more reports of worsening erythema with brimonidine 0.33% gel than with oxymetazoline 1% cream, perhaps because of the different receptor selectivity between the two products. She explained that alpha-1 receptors are located only postsynaptically in vascular smooth muscle, while alpha-2 receptors are located presynaptically, which can inhibit norepinephrine and lead to vasodilation. Alpha-2 receptors are also located postsynaptically in vascular smooth muscle and in the endothelial wall, which can mediate nitric oxide release and cause vasodilation.
No head-to-head studies exist that compare brimonidine 0.33% gel with oxymetazoline 1% cream. But in a 52-week study of oxymetazoline 1% cream for persistent facial erythema associated with rosacea published in 2018, at week 52, 36.7% and 43.4% of patients achieved a 2-grade or greater composite improvement from baseline in both Clinician Erythema Assessment and Subject Self-Assessment 3 and 6 hours after a dose, respectively. Also, fewer than 1% of patients experienced a rebound effect following treatment cessation.
“What we learned from this study is that maybe patients do better if they use oxymetazoline 1% cream consistently,” Harper said. “Does that mean that everybody I give this to uses it daily? Probably not, but I think we can change the vascular tone by using it consistently every day.”
Oral Beta-Blockers Another Option
Alpha agonists can also help quell flushing associated with rosacea, Harper continued, but oral beta-blockers may be the better choice. In a 2020 review that drew from nine studies, researchers evaluated the use of carvedilol, propranolol, nadolol, and beta-blockers in general for rosacea-associated facial erythema and flushing. Articles studying carvedilol and propranolol showed a large reduction of erythema and flushing during treatment with a rapid onset of symptom control, while bradycardia and hypotension were the most commonly reported adverse events. “All of these agents are studied in rosacea, but none of them are FDA approved for rosacea,” Harper noted.
In a separate study, five patients with rosacea who had either severe frequent flushing episodes or persistent erythema and burning sensations were treated with carvedilol, a nonselective beta-blocker. Prior treatments included cetirizine and doxycycline, or isotretinoin combined with topical application of metronidazole gel or ivermectin without sufficient improvement in erythema. Carvedilol was added to the above treatments and titrated up to 12.5 mg twice a day and continued for at least 6 months.
The Clinician Erythema Assessment 5-point scale before therapy was 3.4 and dropped to 0.4 during therapy, while the patient self-assessment before therapy was 3.8 and dropped to 0.8 during therapy.
Another study evaluated the use of propranolol and/or doxycycline in 78 patients with rosacea. The propranolol and combination treatment groups showed more rapid improvement at weeks 4 and 8, but there was no statistically significant difference between them by week 12. Rosacea clinical scores also decreased in all groups, but there were no significant differences between them. Reduction of Assessment of Rosacea Clinical Score was 51%, 52.2%, and 57.3% in the propranolol, doxycycline, and combination groups, respectively.
Harper disclosed ties with Almirall, Cutera, Galderma, Journey, Ortho Dermatologics, and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LAS VEGAS —
These agents “work fast” and “improve redness quickly,” Harper, a dermatologist who practices in Birmingham, Alabama, said at the Society of Dermatology Physician Associates (SDPA) 22nd Annual Fall Dermatology Conference. In addition, “you’re going to know within 30 minutes or an hour whether it’s going to work or not.”
Brimonidine 0.33% gel, an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2014 for persistent facial erythema of rosacea. It does not treat telangiectasia and is not approved for flushing (transient erythema). Patients are advised to apply the gel daily in the morning. In phase 3 pivotal trials of patients with moderate to severe erythema of rosacea, which excluded individuals with more than two papules, a composite (investigator- and patient-reported) 2-grade improvement was seen as early as 30 minutes after application on day 1, and erythema was reduced for 9-12 hours.
Oxymetazoline 1% cream, an alpha-1a adrenergic receptor agonist, was approved by the FDA in 2017 for persistent facial erythema of rosacea. It neither treats telangiectasia nor is approved for flushing. Phase 3 trials of patients with moderate to severe persistent erythema of rosacea excluded individuals with more than three inflammatory papules or pustules. A composite (investigator- and subject-reported) 2-grade improvement was seen as early as 1 hour after application on day 1, and erythema was reduced for 9-12 hours.
Receptor Selectivity Differences
According to Harper, there are more reports of worsening erythema with brimonidine 0.33% gel than with oxymetazoline 1% cream, perhaps because of the different receptor selectivity between the two products. She explained that alpha-1 receptors are located only postsynaptically in vascular smooth muscle, while alpha-2 receptors are located presynaptically, which can inhibit norepinephrine and lead to vasodilation. Alpha-2 receptors are also located postsynaptically in vascular smooth muscle and in the endothelial wall, which can mediate nitric oxide release and cause vasodilation.
No head-to-head studies exist that compare brimonidine 0.33% gel with oxymetazoline 1% cream. But in a 52-week study of oxymetazoline 1% cream for persistent facial erythema associated with rosacea published in 2018, at week 52, 36.7% and 43.4% of patients achieved a 2-grade or greater composite improvement from baseline in both Clinician Erythema Assessment and Subject Self-Assessment 3 and 6 hours after a dose, respectively. Also, fewer than 1% of patients experienced a rebound effect following treatment cessation.
“What we learned from this study is that maybe patients do better if they use oxymetazoline 1% cream consistently,” Harper said. “Does that mean that everybody I give this to uses it daily? Probably not, but I think we can change the vascular tone by using it consistently every day.”
Oral Beta-Blockers Another Option
Alpha agonists can also help quell flushing associated with rosacea, Harper continued, but oral beta-blockers may be the better choice. In a 2020 review that drew from nine studies, researchers evaluated the use of carvedilol, propranolol, nadolol, and beta-blockers in general for rosacea-associated facial erythema and flushing. Articles studying carvedilol and propranolol showed a large reduction of erythema and flushing during treatment with a rapid onset of symptom control, while bradycardia and hypotension were the most commonly reported adverse events. “All of these agents are studied in rosacea, but none of them are FDA approved for rosacea,” Harper noted.
In a separate study, five patients with rosacea who had either severe frequent flushing episodes or persistent erythema and burning sensations were treated with carvedilol, a nonselective beta-blocker. Prior treatments included cetirizine and doxycycline, or isotretinoin combined with topical application of metronidazole gel or ivermectin without sufficient improvement in erythema. Carvedilol was added to the above treatments and titrated up to 12.5 mg twice a day and continued for at least 6 months.
The Clinician Erythema Assessment 5-point scale before therapy was 3.4 and dropped to 0.4 during therapy, while the patient self-assessment before therapy was 3.8 and dropped to 0.8 during therapy.
Another study evaluated the use of propranolol and/or doxycycline in 78 patients with rosacea. The propranolol and combination treatment groups showed more rapid improvement at weeks 4 and 8, but there was no statistically significant difference between them by week 12. Rosacea clinical scores also decreased in all groups, but there were no significant differences between them. Reduction of Assessment of Rosacea Clinical Score was 51%, 52.2%, and 57.3% in the propranolol, doxycycline, and combination groups, respectively.
Harper disclosed ties with Almirall, Cutera, Galderma, Journey, Ortho Dermatologics, and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LAS VEGAS —
These agents “work fast” and “improve redness quickly,” Harper, a dermatologist who practices in Birmingham, Alabama, said at the Society of Dermatology Physician Associates (SDPA) 22nd Annual Fall Dermatology Conference. In addition, “you’re going to know within 30 minutes or an hour whether it’s going to work or not.”
Brimonidine 0.33% gel, an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2014 for persistent facial erythema of rosacea. It does not treat telangiectasia and is not approved for flushing (transient erythema). Patients are advised to apply the gel daily in the morning. In phase 3 pivotal trials of patients with moderate to severe erythema of rosacea, which excluded individuals with more than two papules, a composite (investigator- and patient-reported) 2-grade improvement was seen as early as 30 minutes after application on day 1, and erythema was reduced for 9-12 hours.
Oxymetazoline 1% cream, an alpha-1a adrenergic receptor agonist, was approved by the FDA in 2017 for persistent facial erythema of rosacea. It neither treats telangiectasia nor is approved for flushing. Phase 3 trials of patients with moderate to severe persistent erythema of rosacea excluded individuals with more than three inflammatory papules or pustules. A composite (investigator- and subject-reported) 2-grade improvement was seen as early as 1 hour after application on day 1, and erythema was reduced for 9-12 hours.
Receptor Selectivity Differences
According to Harper, there are more reports of worsening erythema with brimonidine 0.33% gel than with oxymetazoline 1% cream, perhaps because of the different receptor selectivity between the two products. She explained that alpha-1 receptors are located only postsynaptically in vascular smooth muscle, while alpha-2 receptors are located presynaptically, which can inhibit norepinephrine and lead to vasodilation. Alpha-2 receptors are also located postsynaptically in vascular smooth muscle and in the endothelial wall, which can mediate nitric oxide release and cause vasodilation.
No head-to-head studies exist that compare brimonidine 0.33% gel with oxymetazoline 1% cream. But in a 52-week study of oxymetazoline 1% cream for persistent facial erythema associated with rosacea published in 2018, at week 52, 36.7% and 43.4% of patients achieved a 2-grade or greater composite improvement from baseline in both Clinician Erythema Assessment and Subject Self-Assessment 3 and 6 hours after a dose, respectively. Also, fewer than 1% of patients experienced a rebound effect following treatment cessation.
“What we learned from this study is that maybe patients do better if they use oxymetazoline 1% cream consistently,” Harper said. “Does that mean that everybody I give this to uses it daily? Probably not, but I think we can change the vascular tone by using it consistently every day.”
Oral Beta-Blockers Another Option
Alpha agonists can also help quell flushing associated with rosacea, Harper continued, but oral beta-blockers may be the better choice. In a 2020 review that drew from nine studies, researchers evaluated the use of carvedilol, propranolol, nadolol, and beta-blockers in general for rosacea-associated facial erythema and flushing. Articles studying carvedilol and propranolol showed a large reduction of erythema and flushing during treatment with a rapid onset of symptom control, while bradycardia and hypotension were the most commonly reported adverse events. “All of these agents are studied in rosacea, but none of them are FDA approved for rosacea,” Harper noted.
In a separate study, five patients with rosacea who had either severe frequent flushing episodes or persistent erythema and burning sensations were treated with carvedilol, a nonselective beta-blocker. Prior treatments included cetirizine and doxycycline, or isotretinoin combined with topical application of metronidazole gel or ivermectin without sufficient improvement in erythema. Carvedilol was added to the above treatments and titrated up to 12.5 mg twice a day and continued for at least 6 months.
The Clinician Erythema Assessment 5-point scale before therapy was 3.4 and dropped to 0.4 during therapy, while the patient self-assessment before therapy was 3.8 and dropped to 0.8 during therapy.
Another study evaluated the use of propranolol and/or doxycycline in 78 patients with rosacea. The propranolol and combination treatment groups showed more rapid improvement at weeks 4 and 8, but there was no statistically significant difference between them by week 12. Rosacea clinical scores also decreased in all groups, but there were no significant differences between them. Reduction of Assessment of Rosacea Clinical Score was 51%, 52.2%, and 57.3% in the propranolol, doxycycline, and combination groups, respectively.
Harper disclosed ties with Almirall, Cutera, Galderma, Journey, Ortho Dermatologics, and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SDPA 2024