User login
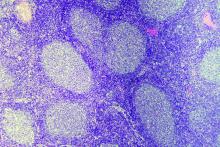
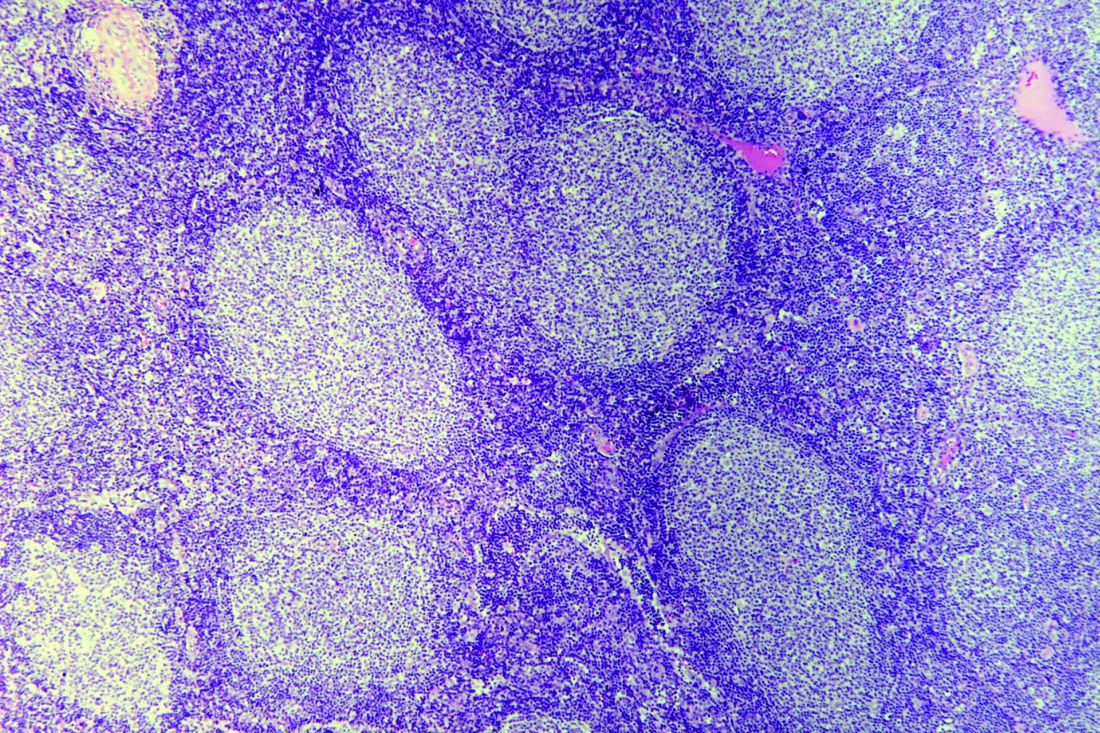
CD23 expression linked to improved survival in MCL
In a large cohort of patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), CD23 expression was associated with significantly improved survival outcomes, according to a retrospective analysis.
“Mantle cell lymphoma has a distinctive immunophenotype, typically positive for pan B-cell markers, CD5 and cyclin D1, but negative for CD10, CD23, and CD200. Although most cases show this immunophenotype, some MCL cases have atypical immunophenotypic features, such as expression of CD10, CD23, or rarely CD200 or lack of expression of CD5,” wrote Annapurna Saksena, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues. Their report is in Human Pathology.
They retrospectively reviewed medical records from a pathology database at MD Anderson from the period of 2008-2016. In all, 798 patients with MCL were identified, of which 103 were classified as CD23-positive via flow cytometry.
The team collected data related to the immunophenotypic and clinicopathologic characteristics of the disease, in addition to survival-related outcomes, including progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). They compared outcomes for the CD23-positive group against 240 patients with CD23-negative MCL.
After analysis, Dr. Saksena and colleagues found that patients with CD23-positive MCL more frequently had bone marrow involvement (89% vs. 78%, P = .02), a leukemic nonnodal presentation (42% vs. 11%, P = .0001), an elevated leukocyte count (33% vs. 18%, P = .009), and stage 4 disease (87% vs. 77%, P = .03).
The researchers reported that CD23 expression was associated with significantly improved PFS and OS (P = .029 and P = .02, respectively) in the univariate analysis.
However, the prognostic significance was partially lost when leukemic nonnodal cases were excluded, the researchers reported.
In addition to the higher frequency of leukemic nonnodal presentation with CD23-positive MCL cases, there was a higher frequency of CD200 expression and a lower frequency of SOX11 expression.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the loss of prognostic significance in the multivariate analysis. Further studies are needed to fully understand the links between CD23 expression and MCL survival, they noted.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Saksena A et al. Hum Pathol. 2019 May 2. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2019.04.010.
In a large cohort of patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), CD23 expression was associated with significantly improved survival outcomes, according to a retrospective analysis.
“Mantle cell lymphoma has a distinctive immunophenotype, typically positive for pan B-cell markers, CD5 and cyclin D1, but negative for CD10, CD23, and CD200. Although most cases show this immunophenotype, some MCL cases have atypical immunophenotypic features, such as expression of CD10, CD23, or rarely CD200 or lack of expression of CD5,” wrote Annapurna Saksena, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues. Their report is in Human Pathology.
They retrospectively reviewed medical records from a pathology database at MD Anderson from the period of 2008-2016. In all, 798 patients with MCL were identified, of which 103 were classified as CD23-positive via flow cytometry.
The team collected data related to the immunophenotypic and clinicopathologic characteristics of the disease, in addition to survival-related outcomes, including progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). They compared outcomes for the CD23-positive group against 240 patients with CD23-negative MCL.
After analysis, Dr. Saksena and colleagues found that patients with CD23-positive MCL more frequently had bone marrow involvement (89% vs. 78%, P = .02), a leukemic nonnodal presentation (42% vs. 11%, P = .0001), an elevated leukocyte count (33% vs. 18%, P = .009), and stage 4 disease (87% vs. 77%, P = .03).
The researchers reported that CD23 expression was associated with significantly improved PFS and OS (P = .029 and P = .02, respectively) in the univariate analysis.
However, the prognostic significance was partially lost when leukemic nonnodal cases were excluded, the researchers reported.
In addition to the higher frequency of leukemic nonnodal presentation with CD23-positive MCL cases, there was a higher frequency of CD200 expression and a lower frequency of SOX11 expression.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the loss of prognostic significance in the multivariate analysis. Further studies are needed to fully understand the links between CD23 expression and MCL survival, they noted.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Saksena A et al. Hum Pathol. 2019 May 2. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2019.04.010.
In a large cohort of patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), CD23 expression was associated with significantly improved survival outcomes, according to a retrospective analysis.
“Mantle cell lymphoma has a distinctive immunophenotype, typically positive for pan B-cell markers, CD5 and cyclin D1, but negative for CD10, CD23, and CD200. Although most cases show this immunophenotype, some MCL cases have atypical immunophenotypic features, such as expression of CD10, CD23, or rarely CD200 or lack of expression of CD5,” wrote Annapurna Saksena, MD, of MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues. Their report is in Human Pathology.
They retrospectively reviewed medical records from a pathology database at MD Anderson from the period of 2008-2016. In all, 798 patients with MCL were identified, of which 103 were classified as CD23-positive via flow cytometry.
The team collected data related to the immunophenotypic and clinicopathologic characteristics of the disease, in addition to survival-related outcomes, including progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). They compared outcomes for the CD23-positive group against 240 patients with CD23-negative MCL.
After analysis, Dr. Saksena and colleagues found that patients with CD23-positive MCL more frequently had bone marrow involvement (89% vs. 78%, P = .02), a leukemic nonnodal presentation (42% vs. 11%, P = .0001), an elevated leukocyte count (33% vs. 18%, P = .009), and stage 4 disease (87% vs. 77%, P = .03).
The researchers reported that CD23 expression was associated with significantly improved PFS and OS (P = .029 and P = .02, respectively) in the univariate analysis.
However, the prognostic significance was partially lost when leukemic nonnodal cases were excluded, the researchers reported.
In addition to the higher frequency of leukemic nonnodal presentation with CD23-positive MCL cases, there was a higher frequency of CD200 expression and a lower frequency of SOX11 expression.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the loss of prognostic significance in the multivariate analysis. Further studies are needed to fully understand the links between CD23 expression and MCL survival, they noted.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Saksena A et al. Hum Pathol. 2019 May 2. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2019.04.010.
FROM HUMAN PATHOLOGY
Lenalidomide may reduce risk of progression from SMM to MM
Lenalidomide can reduce the risk of progression from smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM) to multiple myeloma (MM), according to a phase 2/3 trial.
At 3 years, the rate of progression-free survival (PFS) was 91% in SMM patients randomized to lenalidomide and 66% in those randomized to observation.
However, more than half of patients randomized to lenalidomide discontinued treatment because of toxicity.
These results are scheduled to be presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Sagar Lonial, MD, of Winship Cancer Institute, Emory University, Atlanta, discussed the results in a press briefing in advance of the meeting.
A prior trial suggested that lenalidomide plus dexamethasone can improve time to MM development and overall survival in patients with high-risk SMM (Mateos MV et al. NEJM 2013). However, inferior imaging was used in this trial, and the addition of dexamethasone hindered researchers’ ability to isolate the effects of lenalidomide, Dr. Lonial said.
With their trial (NCT01169337), Dr. Lonial and colleagues tested lenalidomide alone and screened patients using magnetic resonance imaging.
The trial enrolled patients with intermediate or high-risk SMM in two phases. In phase 2, all 44 patients received lenalidomide at 25 mg daily on days 1-21 of a 28-day cycle. They also received aspirin at 325 mg on days 1-28.
In the phase 3 portion of the trial, 182 patients were randomized to observation or lenalidomide and aspirin at the aforementioned dose and schedule. Patients were stratified according to time since SMM diagnosis – 1 year or less vs. more than 1 year.
Safety
Dr. Lonial said, in general, lenalidomide was “very well tolerated.” However, 80% of patients in phase 2 and 51% in phase 3 discontinued lenalidomide due to toxicity.
The rates of treatment-related adverse events (AEs) in the phase 2 portion were 34.1% for grade 3 AEs, 11.4% for grade 4, and 4.5% for grade 5. In the phase 3 portion, 35.2% of patients had grade 3 treatment-related AEs, and 5.7% had grade 4 treatment-related AEs.
Common AEs in phase 3 were grade 4 neutrophil count decrease (4.5%) and grade 3 infections (20.5%), hypertension (9.1%), fatigue (6.8%), skin AEs (5.7%), dyspnea (5.7%), and hypokalemia (3.4%).
Efficacy
“It is worth noting that about 50% of patients had an objective response to lenalidomide in both the phase 2 and the phase 3 trial,” Dr. Lonial said. “I think it’s also important to realize that, in the phase 2 portion of this study, of the 44 patients enrolled, 78% of them did not progress to myeloma with a median follow-up of over 5 years.”
In phase 2, PFS was 98% at 1 year, 87% at 3 years, and 78% at 5 years.
In phase 3, PFS was 98% in the lenalidomide arm and 89% in the observation arm at 1 year. At 2 years, PFS was 93% in the lenalidomide arm and 76% in the observation arm. At 3 years, PFS was 91% in the lenalidomide arm and 66% in the observation arm.
“What’s really quite interesting is that each [risk] group appeared to benefit almost equally from the early intervention of lenalidomide as a single agent,” Dr. Lonial said. “[W]hile the high-risk group may be the target now, this may be a fertile area for investigation in the intermediate-risk group as well.”
Dr. Lonial has relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen Oncology, Juno Therapeutics, Merck, Novartis, and Takeda. The trial was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Lonial S et al. ASCO 2019. Abstract 8001.
Lenalidomide can reduce the risk of progression from smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM) to multiple myeloma (MM), according to a phase 2/3 trial.
At 3 years, the rate of progression-free survival (PFS) was 91% in SMM patients randomized to lenalidomide and 66% in those randomized to observation.
However, more than half of patients randomized to lenalidomide discontinued treatment because of toxicity.
These results are scheduled to be presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Sagar Lonial, MD, of Winship Cancer Institute, Emory University, Atlanta, discussed the results in a press briefing in advance of the meeting.
A prior trial suggested that lenalidomide plus dexamethasone can improve time to MM development and overall survival in patients with high-risk SMM (Mateos MV et al. NEJM 2013). However, inferior imaging was used in this trial, and the addition of dexamethasone hindered researchers’ ability to isolate the effects of lenalidomide, Dr. Lonial said.
With their trial (NCT01169337), Dr. Lonial and colleagues tested lenalidomide alone and screened patients using magnetic resonance imaging.
The trial enrolled patients with intermediate or high-risk SMM in two phases. In phase 2, all 44 patients received lenalidomide at 25 mg daily on days 1-21 of a 28-day cycle. They also received aspirin at 325 mg on days 1-28.
In the phase 3 portion of the trial, 182 patients were randomized to observation or lenalidomide and aspirin at the aforementioned dose and schedule. Patients were stratified according to time since SMM diagnosis – 1 year or less vs. more than 1 year.
Safety
Dr. Lonial said, in general, lenalidomide was “very well tolerated.” However, 80% of patients in phase 2 and 51% in phase 3 discontinued lenalidomide due to toxicity.
The rates of treatment-related adverse events (AEs) in the phase 2 portion were 34.1% for grade 3 AEs, 11.4% for grade 4, and 4.5% for grade 5. In the phase 3 portion, 35.2% of patients had grade 3 treatment-related AEs, and 5.7% had grade 4 treatment-related AEs.
Common AEs in phase 3 were grade 4 neutrophil count decrease (4.5%) and grade 3 infections (20.5%), hypertension (9.1%), fatigue (6.8%), skin AEs (5.7%), dyspnea (5.7%), and hypokalemia (3.4%).
Efficacy
“It is worth noting that about 50% of patients had an objective response to lenalidomide in both the phase 2 and the phase 3 trial,” Dr. Lonial said. “I think it’s also important to realize that, in the phase 2 portion of this study, of the 44 patients enrolled, 78% of them did not progress to myeloma with a median follow-up of over 5 years.”
In phase 2, PFS was 98% at 1 year, 87% at 3 years, and 78% at 5 years.
In phase 3, PFS was 98% in the lenalidomide arm and 89% in the observation arm at 1 year. At 2 years, PFS was 93% in the lenalidomide arm and 76% in the observation arm. At 3 years, PFS was 91% in the lenalidomide arm and 66% in the observation arm.
“What’s really quite interesting is that each [risk] group appeared to benefit almost equally from the early intervention of lenalidomide as a single agent,” Dr. Lonial said. “[W]hile the high-risk group may be the target now, this may be a fertile area for investigation in the intermediate-risk group as well.”
Dr. Lonial has relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen Oncology, Juno Therapeutics, Merck, Novartis, and Takeda. The trial was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Lonial S et al. ASCO 2019. Abstract 8001.
Lenalidomide can reduce the risk of progression from smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM) to multiple myeloma (MM), according to a phase 2/3 trial.
At 3 years, the rate of progression-free survival (PFS) was 91% in SMM patients randomized to lenalidomide and 66% in those randomized to observation.
However, more than half of patients randomized to lenalidomide discontinued treatment because of toxicity.
These results are scheduled to be presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Sagar Lonial, MD, of Winship Cancer Institute, Emory University, Atlanta, discussed the results in a press briefing in advance of the meeting.
A prior trial suggested that lenalidomide plus dexamethasone can improve time to MM development and overall survival in patients with high-risk SMM (Mateos MV et al. NEJM 2013). However, inferior imaging was used in this trial, and the addition of dexamethasone hindered researchers’ ability to isolate the effects of lenalidomide, Dr. Lonial said.
With their trial (NCT01169337), Dr. Lonial and colleagues tested lenalidomide alone and screened patients using magnetic resonance imaging.
The trial enrolled patients with intermediate or high-risk SMM in two phases. In phase 2, all 44 patients received lenalidomide at 25 mg daily on days 1-21 of a 28-day cycle. They also received aspirin at 325 mg on days 1-28.
In the phase 3 portion of the trial, 182 patients were randomized to observation or lenalidomide and aspirin at the aforementioned dose and schedule. Patients were stratified according to time since SMM diagnosis – 1 year or less vs. more than 1 year.
Safety
Dr. Lonial said, in general, lenalidomide was “very well tolerated.” However, 80% of patients in phase 2 and 51% in phase 3 discontinued lenalidomide due to toxicity.
The rates of treatment-related adverse events (AEs) in the phase 2 portion were 34.1% for grade 3 AEs, 11.4% for grade 4, and 4.5% for grade 5. In the phase 3 portion, 35.2% of patients had grade 3 treatment-related AEs, and 5.7% had grade 4 treatment-related AEs.
Common AEs in phase 3 were grade 4 neutrophil count decrease (4.5%) and grade 3 infections (20.5%), hypertension (9.1%), fatigue (6.8%), skin AEs (5.7%), dyspnea (5.7%), and hypokalemia (3.4%).
Efficacy
“It is worth noting that about 50% of patients had an objective response to lenalidomide in both the phase 2 and the phase 3 trial,” Dr. Lonial said. “I think it’s also important to realize that, in the phase 2 portion of this study, of the 44 patients enrolled, 78% of them did not progress to myeloma with a median follow-up of over 5 years.”
In phase 2, PFS was 98% at 1 year, 87% at 3 years, and 78% at 5 years.
In phase 3, PFS was 98% in the lenalidomide arm and 89% in the observation arm at 1 year. At 2 years, PFS was 93% in the lenalidomide arm and 76% in the observation arm. At 3 years, PFS was 91% in the lenalidomide arm and 66% in the observation arm.
“What’s really quite interesting is that each [risk] group appeared to benefit almost equally from the early intervention of lenalidomide as a single agent,” Dr. Lonial said. “[W]hile the high-risk group may be the target now, this may be a fertile area for investigation in the intermediate-risk group as well.”
Dr. Lonial has relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen Oncology, Juno Therapeutics, Merck, Novartis, and Takeda. The trial was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Lonial S et al. ASCO 2019. Abstract 8001.
REPORTING FROM ASCO 2019
Trial follow-up spotlights survival gains in follicular lymphoma
Results from a 13-year follow-up of a trial comparing two types of rituximab-based chemotherapy as upfront treatment for patients with follicular lymphoma show an “extraordinary improvement” in overall survival, compared with the prerituximab era.
In a finding that the researchers termed “somewhat unexpected,” complete remission was the strongest factor in long-term survival.
Between March 2000 and May 2005, researchers enrolled 136 high-risk follicular lymphoma patients in the GITMO-IIL trial to evaluate the superiority of high-dose chemotherapy with rituximab and autograft (R-HDS) versus conventional chemotherapy with rituximab (R-CHOP) as frontline therapy. At a median follow-up of 4 years, there was no survival advantage for R-HDS.
In the current analysis – that had a 13-year median follow-up – median survival had not yet been reached. As of February 2017, two-thirds of all patients were alive at their last follow-up. Overall survival was 68.5% in the R-CHOP arm and 64.5% in the R-HDS arm, Riccardo Bruna, MD, of the European Institute of Oncology in Milano, Italy, and his colleagues, reported in Haematologica.
The main causes of death for the 46 patients who had died as of long-term follow-up were disease progression and secondary malignancies. Other causes included cardiovascular events, infections, graft failure following autograft, anaphylactic shock, and late sudden death.
Complete remission was seen in 98 patients (73.1%) overall – 59.1% in the R-CHOP arm and 86.7% in the R-HDS arm. Achieving durable complete remission was associated with prolonged survival, the researchers reported. Of the 79 patients in complete remission at 2 years after the start of treatment, 65 (82.3%) were alive at 13 years, compared with 21 (58.3%) of 36 patients who had an early relapse (P = .003).
“[Complete remission] achievement was the most important factor for prolonged survival,” the researchers wrote. “The importance of disease response is further emphasized by the first-time observation that [molecular remission] achievement is associated with survival duration and a high proportion of patients had prolonged survival in the absence of disease recurrence.”
The researchers reported that this is longest ever follow-up reported for first-line treatment of follicular lymphoma with rituximab-based chemotherapy.
This work was supported in part by the Ministero Italiano Università e Ricerca and by Banca del Piemonte. The initial clinical trial was supported by Compagnia di San Paolo, Regione Piemonte, and Roche, which provided rituximab for the study.
SOURCE: Bruna R et al. Haematologica. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.209932.
Results from a 13-year follow-up of a trial comparing two types of rituximab-based chemotherapy as upfront treatment for patients with follicular lymphoma show an “extraordinary improvement” in overall survival, compared with the prerituximab era.
In a finding that the researchers termed “somewhat unexpected,” complete remission was the strongest factor in long-term survival.
Between March 2000 and May 2005, researchers enrolled 136 high-risk follicular lymphoma patients in the GITMO-IIL trial to evaluate the superiority of high-dose chemotherapy with rituximab and autograft (R-HDS) versus conventional chemotherapy with rituximab (R-CHOP) as frontline therapy. At a median follow-up of 4 years, there was no survival advantage for R-HDS.
In the current analysis – that had a 13-year median follow-up – median survival had not yet been reached. As of February 2017, two-thirds of all patients were alive at their last follow-up. Overall survival was 68.5% in the R-CHOP arm and 64.5% in the R-HDS arm, Riccardo Bruna, MD, of the European Institute of Oncology in Milano, Italy, and his colleagues, reported in Haematologica.
The main causes of death for the 46 patients who had died as of long-term follow-up were disease progression and secondary malignancies. Other causes included cardiovascular events, infections, graft failure following autograft, anaphylactic shock, and late sudden death.
Complete remission was seen in 98 patients (73.1%) overall – 59.1% in the R-CHOP arm and 86.7% in the R-HDS arm. Achieving durable complete remission was associated with prolonged survival, the researchers reported. Of the 79 patients in complete remission at 2 years after the start of treatment, 65 (82.3%) were alive at 13 years, compared with 21 (58.3%) of 36 patients who had an early relapse (P = .003).
“[Complete remission] achievement was the most important factor for prolonged survival,” the researchers wrote. “The importance of disease response is further emphasized by the first-time observation that [molecular remission] achievement is associated with survival duration and a high proportion of patients had prolonged survival in the absence of disease recurrence.”
The researchers reported that this is longest ever follow-up reported for first-line treatment of follicular lymphoma with rituximab-based chemotherapy.
This work was supported in part by the Ministero Italiano Università e Ricerca and by Banca del Piemonte. The initial clinical trial was supported by Compagnia di San Paolo, Regione Piemonte, and Roche, which provided rituximab for the study.
SOURCE: Bruna R et al. Haematologica. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.209932.
Results from a 13-year follow-up of a trial comparing two types of rituximab-based chemotherapy as upfront treatment for patients with follicular lymphoma show an “extraordinary improvement” in overall survival, compared with the prerituximab era.
In a finding that the researchers termed “somewhat unexpected,” complete remission was the strongest factor in long-term survival.
Between March 2000 and May 2005, researchers enrolled 136 high-risk follicular lymphoma patients in the GITMO-IIL trial to evaluate the superiority of high-dose chemotherapy with rituximab and autograft (R-HDS) versus conventional chemotherapy with rituximab (R-CHOP) as frontline therapy. At a median follow-up of 4 years, there was no survival advantage for R-HDS.
In the current analysis – that had a 13-year median follow-up – median survival had not yet been reached. As of February 2017, two-thirds of all patients were alive at their last follow-up. Overall survival was 68.5% in the R-CHOP arm and 64.5% in the R-HDS arm, Riccardo Bruna, MD, of the European Institute of Oncology in Milano, Italy, and his colleagues, reported in Haematologica.
The main causes of death for the 46 patients who had died as of long-term follow-up were disease progression and secondary malignancies. Other causes included cardiovascular events, infections, graft failure following autograft, anaphylactic shock, and late sudden death.
Complete remission was seen in 98 patients (73.1%) overall – 59.1% in the R-CHOP arm and 86.7% in the R-HDS arm. Achieving durable complete remission was associated with prolonged survival, the researchers reported. Of the 79 patients in complete remission at 2 years after the start of treatment, 65 (82.3%) were alive at 13 years, compared with 21 (58.3%) of 36 patients who had an early relapse (P = .003).
“[Complete remission] achievement was the most important factor for prolonged survival,” the researchers wrote. “The importance of disease response is further emphasized by the first-time observation that [molecular remission] achievement is associated with survival duration and a high proportion of patients had prolonged survival in the absence of disease recurrence.”
The researchers reported that this is longest ever follow-up reported for first-line treatment of follicular lymphoma with rituximab-based chemotherapy.
This work was supported in part by the Ministero Italiano Università e Ricerca and by Banca del Piemonte. The initial clinical trial was supported by Compagnia di San Paolo, Regione Piemonte, and Roche, which provided rituximab for the study.
SOURCE: Bruna R et al. Haematologica. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.209932.
FROM HAEMATOLOGICA
FDA approves venetoclax/obinutuzumab combo for CLL
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the combination of venetoclax (Venclexta) plus obinutuzumab (Gazyva) for patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The approval provides a chemotherapy-free, fixed duration treatment. The FDA based the approval on the results of the phase 3 CLL14 trial, which will be presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Researchers randomized 432 patients to either a 12-month duration of venetoclax with a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab or to a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil and another 6-month duration of chlorambucil.
The newly approved combination reduced the risk of disease progression or death (progression-free survival as assessed by an independent review committee) by 67%, compared with obinutuzumab/chlorambucil (hazard ratio, 0.33; P less than .0001).
Venetoclax/obinutuzumab also had a higher rate of minimal residual disease negativity in bone marrow and peripheral blood, compared to the other combination, according to Genentech.
The most common adverse reactions of any grade reported for venetoclax/obinutuzumab were neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, anemia, and upper respiratory tract infection.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the combination of venetoclax (Venclexta) plus obinutuzumab (Gazyva) for patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The approval provides a chemotherapy-free, fixed duration treatment. The FDA based the approval on the results of the phase 3 CLL14 trial, which will be presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Researchers randomized 432 patients to either a 12-month duration of venetoclax with a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab or to a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil and another 6-month duration of chlorambucil.
The newly approved combination reduced the risk of disease progression or death (progression-free survival as assessed by an independent review committee) by 67%, compared with obinutuzumab/chlorambucil (hazard ratio, 0.33; P less than .0001).
Venetoclax/obinutuzumab also had a higher rate of minimal residual disease negativity in bone marrow and peripheral blood, compared to the other combination, according to Genentech.
The most common adverse reactions of any grade reported for venetoclax/obinutuzumab were neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, anemia, and upper respiratory tract infection.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the combination of venetoclax (Venclexta) plus obinutuzumab (Gazyva) for patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The approval provides a chemotherapy-free, fixed duration treatment. The FDA based the approval on the results of the phase 3 CLL14 trial, which will be presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Researchers randomized 432 patients to either a 12-month duration of venetoclax with a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab or to a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil and another 6-month duration of chlorambucil.
The newly approved combination reduced the risk of disease progression or death (progression-free survival as assessed by an independent review committee) by 67%, compared with obinutuzumab/chlorambucil (hazard ratio, 0.33; P less than .0001).
Venetoclax/obinutuzumab also had a higher rate of minimal residual disease negativity in bone marrow and peripheral blood, compared to the other combination, according to Genentech.
The most common adverse reactions of any grade reported for venetoclax/obinutuzumab were neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, anemia, and upper respiratory tract infection.
FDA panel not ready to recommend quizartinib approval for FLT3-ITD+ AML
SILVER SPRING, MD. – Daiichi Sankyo failed to make the case for approval of its investigational tyrosine kinase inhibitor quizartinib for patients with acute myeloid leukemia bearing the FLT3 internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutation.
Members of the Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) of the Food and Drug Administration voted 8-3 not to recommend approval of the drug at this time, despite the prevailing sentiment among oncologists on the panel that, as one stated, “I need this drug. I want this drug.”
The prevailing majority of committee members agreed that the drug may have a place in the treatment of patients with FLT3-mutated AML, but that more robust data were needed to prove it.
Currently, only one agent, gilteritinib (Xospata) is approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory FLT3-mutated AML.
QuANTUM-R
Daiichi Sankyo sought approval for quizartinib based on results of the phase 3 randomized QuANTUM-R trial. In this trial, single-agent therapy with quizartinib slightly but significantly prolonged survival – compared with salvage chemotherapy – of patients with relapsed/refractory FLT3-ITD positive AML.
Median overall survival (OS), the trial’s primary endpoint, was 6.2 months for 245 patients randomized to quizartinib, compared with 4.7 months for 122 patients assigned to salvage chemotherapy, a difference that translated into a hazard ratio (HR) for death of 0.76 (P = .0177).
The patients were randomly assigned on a 2:1 basis to receive either quizartinib or salvage chemotherapy. Quizartinib was dosed 30 mg per day for 15 days, which could be titrated upward to 60 mg daily if the corrected QT interval by Fredericia (QTcF) was 450 ms or less on day 16.
Chemotherapy was the investigator’s choice of one of three specified regimens: either low-dose cytarabine (LoDAC); mitoxantrone, etoposide, and intermediate-dose cytarabine (MEC); or fludarabine, cytarabine, and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) with idarubicin (FLAG-IDA). Up to 2 cycles of MEC or FLAG-IDA were permitted; quizartinib and LoDAC were given until lack of benefit, unacceptable toxicity, or until the patient went on to hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
Principal investigator Jorge Cortes, MD, from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, speaking in support of the application, said that combined with the phase 2 study results, “these data support a clear and clinically meaningful benefit of quizartinib in this patient population.”
Mark Levis, MD. PhD, from the Johns Hopkins Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center in Baltimore, also spoke in support of the FLT3 inhibitor.
“I have studied both in the lab and in the clinic most FLT3 inhibitors that have been developed, including lestaurtinib, midostaurin, sorafenib and gilteritinib. Quizartinib is the most highly potent and selective FLT3 inhibitor I have ever worked with,” Dr. Levis said.
FDA: Data not up to snuff
But as FDA staff member Kunthel By, PhD, a statistical reviewer in the Office of Biostatistics, pointed out, the upper limit of the hazard ratio favoring quizartinib over chemotherapy was 0.99, and the difference in median overall survival was just 6.5 weeks.
Additionally, the trial data lacked internal consistency, showing no benefits for the drug in either event-free survival (EFS) or in complete response rates.
There were also imbalances in the number of patients with subsequent HSCT between the arms, with more patients on quizartinib undergoing HSCT despite not having a complete remission, than in the chemotherapy group. Also, there were differences in the number of patients who were randomized but not treated and in those censored early. And statistical stress tests indicated “a lack of robustness in the estimated treatment effect,” he said.
Safety issues raised in QuANTUM-R included slow potassium channel (IKs) blockade and related cardiac toxicitites, as well as the differentiation syndrome, acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, and cytopenias, said Aviva Krauss, MD, a clinical reviewer in the FDA’s Office of Hematology and Oncology Products.
“Quizartinib therapy is associated with significant and unique safety concerns in the [proposed population], including the risk of fatal cardiac events that cannot be predicted with certainty using routine QTc measurements,” she said.
She noted that the events occurred in QuANTUM-R despite dose modifications and concomitant medications guidelines in the study protocol.
Reviewers recommended that should the drug receive approval, the package labeling should include contraindication for use with other QT-prolonging agents, and a recommendation for prophylactic beta blockage, although the panelists in general felt that the latter recommendation was not necessary.
‘I believe in this drug’
The ODAC meeting was convened to answer questions about whether the overall survival results were credible based on a single clinical trial and outweighed the risks of treatment with quizartinib, and to assess risk strategies for reducing risks of potentially fatal cardiac toxicities, primarily prolongation of the QT interval.
A. Michael Lincoff, MD, a cardiologist at Case Western Reserve University and the Cleveland Clinic, both in Cleveland, Ohio, voted in favor of approval.
“I’m less concerned about the risk and I do think on the balance there is benefit,” he said.
But most committee members echoed the comments of Anthony D. Sung, MD, from the division of hematologic malignancies and cellular therapy at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
“My vote is based purely on the data I’m shown, and my vote is no,” he said. “But I want the FDA to know that I believe in this drug, and I think it should get approved, and I want to use it.”
The trial was sponsored by Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Cortes reported research funding from Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, Arog, Astellas Pharma and Novartis, and consulting activities for all of the same companies except Arog. Dr. Levis is a paid consultant for Daiichi Sankyo. He and Dr. Cortes stated that they had no financial interests in the outcome of the ODAC meeting.
SILVER SPRING, MD. – Daiichi Sankyo failed to make the case for approval of its investigational tyrosine kinase inhibitor quizartinib for patients with acute myeloid leukemia bearing the FLT3 internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutation.
Members of the Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) of the Food and Drug Administration voted 8-3 not to recommend approval of the drug at this time, despite the prevailing sentiment among oncologists on the panel that, as one stated, “I need this drug. I want this drug.”
The prevailing majority of committee members agreed that the drug may have a place in the treatment of patients with FLT3-mutated AML, but that more robust data were needed to prove it.
Currently, only one agent, gilteritinib (Xospata) is approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory FLT3-mutated AML.
QuANTUM-R
Daiichi Sankyo sought approval for quizartinib based on results of the phase 3 randomized QuANTUM-R trial. In this trial, single-agent therapy with quizartinib slightly but significantly prolonged survival – compared with salvage chemotherapy – of patients with relapsed/refractory FLT3-ITD positive AML.
Median overall survival (OS), the trial’s primary endpoint, was 6.2 months for 245 patients randomized to quizartinib, compared with 4.7 months for 122 patients assigned to salvage chemotherapy, a difference that translated into a hazard ratio (HR) for death of 0.76 (P = .0177).
The patients were randomly assigned on a 2:1 basis to receive either quizartinib or salvage chemotherapy. Quizartinib was dosed 30 mg per day for 15 days, which could be titrated upward to 60 mg daily if the corrected QT interval by Fredericia (QTcF) was 450 ms or less on day 16.
Chemotherapy was the investigator’s choice of one of three specified regimens: either low-dose cytarabine (LoDAC); mitoxantrone, etoposide, and intermediate-dose cytarabine (MEC); or fludarabine, cytarabine, and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) with idarubicin (FLAG-IDA). Up to 2 cycles of MEC or FLAG-IDA were permitted; quizartinib and LoDAC were given until lack of benefit, unacceptable toxicity, or until the patient went on to hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
Principal investigator Jorge Cortes, MD, from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, speaking in support of the application, said that combined with the phase 2 study results, “these data support a clear and clinically meaningful benefit of quizartinib in this patient population.”
Mark Levis, MD. PhD, from the Johns Hopkins Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center in Baltimore, also spoke in support of the FLT3 inhibitor.
“I have studied both in the lab and in the clinic most FLT3 inhibitors that have been developed, including lestaurtinib, midostaurin, sorafenib and gilteritinib. Quizartinib is the most highly potent and selective FLT3 inhibitor I have ever worked with,” Dr. Levis said.
FDA: Data not up to snuff
But as FDA staff member Kunthel By, PhD, a statistical reviewer in the Office of Biostatistics, pointed out, the upper limit of the hazard ratio favoring quizartinib over chemotherapy was 0.99, and the difference in median overall survival was just 6.5 weeks.
Additionally, the trial data lacked internal consistency, showing no benefits for the drug in either event-free survival (EFS) or in complete response rates.
There were also imbalances in the number of patients with subsequent HSCT between the arms, with more patients on quizartinib undergoing HSCT despite not having a complete remission, than in the chemotherapy group. Also, there were differences in the number of patients who were randomized but not treated and in those censored early. And statistical stress tests indicated “a lack of robustness in the estimated treatment effect,” he said.
Safety issues raised in QuANTUM-R included slow potassium channel (IKs) blockade and related cardiac toxicitites, as well as the differentiation syndrome, acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, and cytopenias, said Aviva Krauss, MD, a clinical reviewer in the FDA’s Office of Hematology and Oncology Products.
“Quizartinib therapy is associated with significant and unique safety concerns in the [proposed population], including the risk of fatal cardiac events that cannot be predicted with certainty using routine QTc measurements,” she said.
She noted that the events occurred in QuANTUM-R despite dose modifications and concomitant medications guidelines in the study protocol.
Reviewers recommended that should the drug receive approval, the package labeling should include contraindication for use with other QT-prolonging agents, and a recommendation for prophylactic beta blockage, although the panelists in general felt that the latter recommendation was not necessary.
‘I believe in this drug’
The ODAC meeting was convened to answer questions about whether the overall survival results were credible based on a single clinical trial and outweighed the risks of treatment with quizartinib, and to assess risk strategies for reducing risks of potentially fatal cardiac toxicities, primarily prolongation of the QT interval.
A. Michael Lincoff, MD, a cardiologist at Case Western Reserve University and the Cleveland Clinic, both in Cleveland, Ohio, voted in favor of approval.
“I’m less concerned about the risk and I do think on the balance there is benefit,” he said.
But most committee members echoed the comments of Anthony D. Sung, MD, from the division of hematologic malignancies and cellular therapy at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
“My vote is based purely on the data I’m shown, and my vote is no,” he said. “But I want the FDA to know that I believe in this drug, and I think it should get approved, and I want to use it.”
The trial was sponsored by Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Cortes reported research funding from Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, Arog, Astellas Pharma and Novartis, and consulting activities for all of the same companies except Arog. Dr. Levis is a paid consultant for Daiichi Sankyo. He and Dr. Cortes stated that they had no financial interests in the outcome of the ODAC meeting.
SILVER SPRING, MD. – Daiichi Sankyo failed to make the case for approval of its investigational tyrosine kinase inhibitor quizartinib for patients with acute myeloid leukemia bearing the FLT3 internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutation.
Members of the Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) of the Food and Drug Administration voted 8-3 not to recommend approval of the drug at this time, despite the prevailing sentiment among oncologists on the panel that, as one stated, “I need this drug. I want this drug.”
The prevailing majority of committee members agreed that the drug may have a place in the treatment of patients with FLT3-mutated AML, but that more robust data were needed to prove it.
Currently, only one agent, gilteritinib (Xospata) is approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory FLT3-mutated AML.
QuANTUM-R
Daiichi Sankyo sought approval for quizartinib based on results of the phase 3 randomized QuANTUM-R trial. In this trial, single-agent therapy with quizartinib slightly but significantly prolonged survival – compared with salvage chemotherapy – of patients with relapsed/refractory FLT3-ITD positive AML.
Median overall survival (OS), the trial’s primary endpoint, was 6.2 months for 245 patients randomized to quizartinib, compared with 4.7 months for 122 patients assigned to salvage chemotherapy, a difference that translated into a hazard ratio (HR) for death of 0.76 (P = .0177).
The patients were randomly assigned on a 2:1 basis to receive either quizartinib or salvage chemotherapy. Quizartinib was dosed 30 mg per day for 15 days, which could be titrated upward to 60 mg daily if the corrected QT interval by Fredericia (QTcF) was 450 ms or less on day 16.
Chemotherapy was the investigator’s choice of one of three specified regimens: either low-dose cytarabine (LoDAC); mitoxantrone, etoposide, and intermediate-dose cytarabine (MEC); or fludarabine, cytarabine, and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) with idarubicin (FLAG-IDA). Up to 2 cycles of MEC or FLAG-IDA were permitted; quizartinib and LoDAC were given until lack of benefit, unacceptable toxicity, or until the patient went on to hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
Principal investigator Jorge Cortes, MD, from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, speaking in support of the application, said that combined with the phase 2 study results, “these data support a clear and clinically meaningful benefit of quizartinib in this patient population.”
Mark Levis, MD. PhD, from the Johns Hopkins Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center in Baltimore, also spoke in support of the FLT3 inhibitor.
“I have studied both in the lab and in the clinic most FLT3 inhibitors that have been developed, including lestaurtinib, midostaurin, sorafenib and gilteritinib. Quizartinib is the most highly potent and selective FLT3 inhibitor I have ever worked with,” Dr. Levis said.
FDA: Data not up to snuff
But as FDA staff member Kunthel By, PhD, a statistical reviewer in the Office of Biostatistics, pointed out, the upper limit of the hazard ratio favoring quizartinib over chemotherapy was 0.99, and the difference in median overall survival was just 6.5 weeks.
Additionally, the trial data lacked internal consistency, showing no benefits for the drug in either event-free survival (EFS) or in complete response rates.
There were also imbalances in the number of patients with subsequent HSCT between the arms, with more patients on quizartinib undergoing HSCT despite not having a complete remission, than in the chemotherapy group. Also, there were differences in the number of patients who were randomized but not treated and in those censored early. And statistical stress tests indicated “a lack of robustness in the estimated treatment effect,” he said.
Safety issues raised in QuANTUM-R included slow potassium channel (IKs) blockade and related cardiac toxicitites, as well as the differentiation syndrome, acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, and cytopenias, said Aviva Krauss, MD, a clinical reviewer in the FDA’s Office of Hematology and Oncology Products.
“Quizartinib therapy is associated with significant and unique safety concerns in the [proposed population], including the risk of fatal cardiac events that cannot be predicted with certainty using routine QTc measurements,” she said.
She noted that the events occurred in QuANTUM-R despite dose modifications and concomitant medications guidelines in the study protocol.
Reviewers recommended that should the drug receive approval, the package labeling should include contraindication for use with other QT-prolonging agents, and a recommendation for prophylactic beta blockage, although the panelists in general felt that the latter recommendation was not necessary.
‘I believe in this drug’
The ODAC meeting was convened to answer questions about whether the overall survival results were credible based on a single clinical trial and outweighed the risks of treatment with quizartinib, and to assess risk strategies for reducing risks of potentially fatal cardiac toxicities, primarily prolongation of the QT interval.
A. Michael Lincoff, MD, a cardiologist at Case Western Reserve University and the Cleveland Clinic, both in Cleveland, Ohio, voted in favor of approval.
“I’m less concerned about the risk and I do think on the balance there is benefit,” he said.
But most committee members echoed the comments of Anthony D. Sung, MD, from the division of hematologic malignancies and cellular therapy at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
“My vote is based purely on the data I’m shown, and my vote is no,” he said. “But I want the FDA to know that I believe in this drug, and I think it should get approved, and I want to use it.”
The trial was sponsored by Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Cortes reported research funding from Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, Arog, Astellas Pharma and Novartis, and consulting activities for all of the same companies except Arog. Dr. Levis is a paid consultant for Daiichi Sankyo. He and Dr. Cortes stated that they had no financial interests in the outcome of the ODAC meeting.
Peanut contamination risk prompts Promacta recall
Novartis has recalled three lots of 12.5-mg eltrombopag (Promacta) for oral suspension following discovery of possible contamination with peanut flour at a third-party manufacturing site.
Tablets at doses of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, and 75 mg are unaffected by this recall because they are not manufactured in the same facility. The recalled lots of medication were distributed between January and April 2019, but so far, Novartis has not received any reports of adverse events related to the recall.
Oral suspension of eltrombopag is indicated for certain patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia, hepatitis C–associated thrombocytopenia, and severe aplastic anemia.
More information on the recalled lots and instructions on how to return the product can be found in the full announcement, which is also available through the Food and Drug Administration website.
Novartis has recalled three lots of 12.5-mg eltrombopag (Promacta) for oral suspension following discovery of possible contamination with peanut flour at a third-party manufacturing site.
Tablets at doses of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, and 75 mg are unaffected by this recall because they are not manufactured in the same facility. The recalled lots of medication were distributed between January and April 2019, but so far, Novartis has not received any reports of adverse events related to the recall.
Oral suspension of eltrombopag is indicated for certain patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia, hepatitis C–associated thrombocytopenia, and severe aplastic anemia.
More information on the recalled lots and instructions on how to return the product can be found in the full announcement, which is also available through the Food and Drug Administration website.
Novartis has recalled three lots of 12.5-mg eltrombopag (Promacta) for oral suspension following discovery of possible contamination with peanut flour at a third-party manufacturing site.
Tablets at doses of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, and 75 mg are unaffected by this recall because they are not manufactured in the same facility. The recalled lots of medication were distributed between January and April 2019, but so far, Novartis has not received any reports of adverse events related to the recall.
Oral suspension of eltrombopag is indicated for certain patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia, hepatitis C–associated thrombocytopenia, and severe aplastic anemia.
More information on the recalled lots and instructions on how to return the product can be found in the full announcement, which is also available through the Food and Drug Administration website.
QOL concerns prompt second-line therapy in children with ITP
NEW ORLEANS – In a survey of pediatric hematologists, quality of life was the most frequently cited reason for starting second-line therapy in children with immune thrombocytopenia.
Quality of life (QOL) was an indication for second-line treatment in nearly three-quarters of patients studied, and it ranked among the top three indications – along with bleeding frequency and bleeding severity – for treatment in more than half of patients.
Kristin A. Shimano, MD, of the department of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Dr. Shimano and colleagues surveyed hematologists treating children in the ICON1 study (Am J Hematol. 2019 Apr 3. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25479).
The study enrolled 120 children receiving second-line immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) treatment at 21 centers. The median age at enrollment was 11.7 years (range, 1.2-17.8 years). About half of patients (53%) had chronic ITP, 31% had persistent ITP, and 16% had newly diagnosed ITP. The median number of prior treatments was three (range, zero to eight).
At study entry, the hematologists were asked to provide reasons that patients required second-line treatment. The list of 12 possible reasons included patient or parent QOL; bleeding severity; bleeding frequency; severity of thrombocytopenia; chronicity of ITP; high baseline activity level; involvement in sports; patient age; distance from medical center; and parent, patient, or physician anxiety. The hematologists were asked to choose all reasons that applied and to rank the top three reasons.
QOL was chosen as a reason to treat in 73% of patients (n = 88). QOL was among the top three reasons in 57% of patients (n = 68) and was the most important reason in 27% of patients (n = 32).
The severity and frequency of bleeding were ranked among the top three indications as well. Bleeding severity was a top indication in 29% of cases (n = 35), and bleeding frequency was a top indication in 40% of cases (n = 48).
Reasons for starting second-line treatment varied depending on patients’ phase of disease.
Bleeding severity was significantly more likely to be an indication for treatment among patients who had newly diagnosed or persistent ITP (69%), rather than chronic ITP (31%; P = .0025). Bleeding frequency was also significantly more likely to be an indication among patients with newly diagnosed or persistent ITP (63% vs. 37%; P = .0054).
Conversely, QOL was significantly more likely to be an indication for patients with chronic ITP (65%) rather than newly diagnosed or persistent ITP (35%, P = .0056). Sports participation was a more likely indication among patients with chronic ITP as well (75% vs. 26%, P = .017).
Indications for treatment also varied according to baseline platelet counts. For example, QOL was an indication for treatment in 42% of patients with baseline platelet counts less than 10 x 109/L and 78% of patients with platelet counts of 20 x 109/L or greater. So the higher the baseline platelet count, the more likely QOL was an indication for treatment (P = .006).
On the other hand, the importance hematologists placed on QOL did not appear to correlate with actual health-related QOL as assessed by the Kids ITP Tool. There was no difference reported in baseline health-related QOL, according to the tool, in children for whom QOL was ranked versus unranked by hematologists.
This finding suggests physicians may not be adequately assessing the impact of ITP on QOL, Dr. Shimano said.
“Better clinical measures of the impact of ITP on patient quality of life are needed to assess both need for treatment and treatment response,” she said. “Understanding the effects of individual second-line treatments on quality of life is critical for this patient population in order to best tailor therapy for each patient.”
Dr. Shimano reported involvement in an investigator-initiated trial for eltrombopag in children with ITP. The study, which has not yet opened, is funded by Novartis.
SOURCE: Shimano KA et al. ASPHO 2019, Abstract 2012.
NEW ORLEANS – In a survey of pediatric hematologists, quality of life was the most frequently cited reason for starting second-line therapy in children with immune thrombocytopenia.
Quality of life (QOL) was an indication for second-line treatment in nearly three-quarters of patients studied, and it ranked among the top three indications – along with bleeding frequency and bleeding severity – for treatment in more than half of patients.
Kristin A. Shimano, MD, of the department of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Dr. Shimano and colleagues surveyed hematologists treating children in the ICON1 study (Am J Hematol. 2019 Apr 3. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25479).
The study enrolled 120 children receiving second-line immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) treatment at 21 centers. The median age at enrollment was 11.7 years (range, 1.2-17.8 years). About half of patients (53%) had chronic ITP, 31% had persistent ITP, and 16% had newly diagnosed ITP. The median number of prior treatments was three (range, zero to eight).
At study entry, the hematologists were asked to provide reasons that patients required second-line treatment. The list of 12 possible reasons included patient or parent QOL; bleeding severity; bleeding frequency; severity of thrombocytopenia; chronicity of ITP; high baseline activity level; involvement in sports; patient age; distance from medical center; and parent, patient, or physician anxiety. The hematologists were asked to choose all reasons that applied and to rank the top three reasons.
QOL was chosen as a reason to treat in 73% of patients (n = 88). QOL was among the top three reasons in 57% of patients (n = 68) and was the most important reason in 27% of patients (n = 32).
The severity and frequency of bleeding were ranked among the top three indications as well. Bleeding severity was a top indication in 29% of cases (n = 35), and bleeding frequency was a top indication in 40% of cases (n = 48).
Reasons for starting second-line treatment varied depending on patients’ phase of disease.
Bleeding severity was significantly more likely to be an indication for treatment among patients who had newly diagnosed or persistent ITP (69%), rather than chronic ITP (31%; P = .0025). Bleeding frequency was also significantly more likely to be an indication among patients with newly diagnosed or persistent ITP (63% vs. 37%; P = .0054).
Conversely, QOL was significantly more likely to be an indication for patients with chronic ITP (65%) rather than newly diagnosed or persistent ITP (35%, P = .0056). Sports participation was a more likely indication among patients with chronic ITP as well (75% vs. 26%, P = .017).
Indications for treatment also varied according to baseline platelet counts. For example, QOL was an indication for treatment in 42% of patients with baseline platelet counts less than 10 x 109/L and 78% of patients with platelet counts of 20 x 109/L or greater. So the higher the baseline platelet count, the more likely QOL was an indication for treatment (P = .006).
On the other hand, the importance hematologists placed on QOL did not appear to correlate with actual health-related QOL as assessed by the Kids ITP Tool. There was no difference reported in baseline health-related QOL, according to the tool, in children for whom QOL was ranked versus unranked by hematologists.
This finding suggests physicians may not be adequately assessing the impact of ITP on QOL, Dr. Shimano said.
“Better clinical measures of the impact of ITP on patient quality of life are needed to assess both need for treatment and treatment response,” she said. “Understanding the effects of individual second-line treatments on quality of life is critical for this patient population in order to best tailor therapy for each patient.”
Dr. Shimano reported involvement in an investigator-initiated trial for eltrombopag in children with ITP. The study, which has not yet opened, is funded by Novartis.
SOURCE: Shimano KA et al. ASPHO 2019, Abstract 2012.
NEW ORLEANS – In a survey of pediatric hematologists, quality of life was the most frequently cited reason for starting second-line therapy in children with immune thrombocytopenia.
Quality of life (QOL) was an indication for second-line treatment in nearly three-quarters of patients studied, and it ranked among the top three indications – along with bleeding frequency and bleeding severity – for treatment in more than half of patients.
Kristin A. Shimano, MD, of the department of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Dr. Shimano and colleagues surveyed hematologists treating children in the ICON1 study (Am J Hematol. 2019 Apr 3. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25479).
The study enrolled 120 children receiving second-line immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) treatment at 21 centers. The median age at enrollment was 11.7 years (range, 1.2-17.8 years). About half of patients (53%) had chronic ITP, 31% had persistent ITP, and 16% had newly diagnosed ITP. The median number of prior treatments was three (range, zero to eight).
At study entry, the hematologists were asked to provide reasons that patients required second-line treatment. The list of 12 possible reasons included patient or parent QOL; bleeding severity; bleeding frequency; severity of thrombocytopenia; chronicity of ITP; high baseline activity level; involvement in sports; patient age; distance from medical center; and parent, patient, or physician anxiety. The hematologists were asked to choose all reasons that applied and to rank the top three reasons.
QOL was chosen as a reason to treat in 73% of patients (n = 88). QOL was among the top three reasons in 57% of patients (n = 68) and was the most important reason in 27% of patients (n = 32).
The severity and frequency of bleeding were ranked among the top three indications as well. Bleeding severity was a top indication in 29% of cases (n = 35), and bleeding frequency was a top indication in 40% of cases (n = 48).
Reasons for starting second-line treatment varied depending on patients’ phase of disease.
Bleeding severity was significantly more likely to be an indication for treatment among patients who had newly diagnosed or persistent ITP (69%), rather than chronic ITP (31%; P = .0025). Bleeding frequency was also significantly more likely to be an indication among patients with newly diagnosed or persistent ITP (63% vs. 37%; P = .0054).
Conversely, QOL was significantly more likely to be an indication for patients with chronic ITP (65%) rather than newly diagnosed or persistent ITP (35%, P = .0056). Sports participation was a more likely indication among patients with chronic ITP as well (75% vs. 26%, P = .017).
Indications for treatment also varied according to baseline platelet counts. For example, QOL was an indication for treatment in 42% of patients with baseline platelet counts less than 10 x 109/L and 78% of patients with platelet counts of 20 x 109/L or greater. So the higher the baseline platelet count, the more likely QOL was an indication for treatment (P = .006).
On the other hand, the importance hematologists placed on QOL did not appear to correlate with actual health-related QOL as assessed by the Kids ITP Tool. There was no difference reported in baseline health-related QOL, according to the tool, in children for whom QOL was ranked versus unranked by hematologists.
This finding suggests physicians may not be adequately assessing the impact of ITP on QOL, Dr. Shimano said.
“Better clinical measures of the impact of ITP on patient quality of life are needed to assess both need for treatment and treatment response,” she said. “Understanding the effects of individual second-line treatments on quality of life is critical for this patient population in order to best tailor therapy for each patient.”
Dr. Shimano reported involvement in an investigator-initiated trial for eltrombopag in children with ITP. The study, which has not yet opened, is funded by Novartis.
SOURCE: Shimano KA et al. ASPHO 2019, Abstract 2012.
REPORTING FROM THE 2019 ASPHO CONFERENCE
Key clinical point: Quality of life was the most frequently cited reason for starting second-line therapy in children with immune thrombocytopenia.
Major finding: Quality of life was chosen as a reason to treat in 73% of patients, it was among the top three reasons in 57% of patients, and it was the most important reason in 27%.
Study details: A survey of hematologists treating 120 children in an observational study.
Disclosures: The speaker reported involvement in an investigator-initiated trial for eltrombopag in children with ITP. The study, which has not yet opened, is funded by Novartis.
Source: Shimano KA et al. ASPHO 2019, Abstract 2012.
Master trial seeks to aid drug development for pediatric AML
NEW ORLEANS – Researchers are organizing a master trial in an attempt to improve the treatment of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
The Pediatric Acute Leukemia (PedAL) trial is an effort to collect data on all pediatric AML patients. The plan is to use these data to match patients to clinical trials, better understand pediatric AML, and bring new treatments to this population.
E. Anders Kolb, MD, of Nemours Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders in Wilmington, Del., described the initiative at the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Dr. Kolb noted that several drugs have been approved to treat adult AML in the last 2 years, but most of them are not approved for use in children.
“What we see in childhood AML is a lot different than what we see in adult AML, and this challenges the paradigm that we have traditionally followed where we use the adult as the 'preclinical model' for pediatric AML,” he said. “I think we are learning more and more that children have a unique disease, unique targets, and need unique therapies.”
The PedAL initiative is an attempt to address these unique needs. PedAL is part of the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society’s Children’s Initiative, and it involves researchers from academic centers and the Children’s Oncology Group.
The PedAL initiative includes preclinical, biomarker, and informatics research, as well as the master clinical trial. The main goal of the master trial is to collect genomic, proteomic, metabolomic, flow cytometry, and clinical data from all children with AML and use these data to match patients to clinical trials.
The PedAL trial will leverage Project:EveryChild, an effort by the Children’s Oncology Group to study every child with cancer. Each child enrolled in this program has an identification number that follows the child through all clinical interventions.
The goal is that Project:EveryChild will capture all pediatric AML patients at the time of diagnosis, although patients can join the project at any time. Then, sequencing, clinical, and other data will be collected from these patients and stored in a data commons.
If patients relapse after standard or other therapies, the GEARBOX algorithm (genomic eligibility algorithm at relapse for better outcomes) can be used to match the patient’s information to clinical trial eligibility criteria and provide a list of appropriate trials.
Dr. Kolb said this process should reduce logistical barriers and get relapsed patients to trials more quickly. Additionally, the data collected through PedAL should help researchers design better trials for pediatric patients with relapsed AML.
“Ultimately, we’ll create the largest data set that will give us a better understanding of all the risks and benefits associated with postrelapse AML,” Dr. Kolb said. “No matter what happens to the patient, no matter where that patient enrolls, we’re going to have the capacity to collect data and present that data to the community for analysis for improved understanding of outcomes.”
Dr. Kolb and his colleagues are already working with researchers in Europe and Japan to make this a global effort and create an international data commons. In addition, the researchers are planning to collaborate with the pharmaceutical industry to unite efforts in pediatric AML drug development.
“We can’t just test drugs in kids because they worked in adults,” Dr. Kolb said. “We really need to maintain the integrity of the science and ask relevant questions in children but do so with the intent to make sure these drugs are licensed for use in kids.”
Dr. Kolb reported having no conflicts of interest. The PedAL trial is sponsored by the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society.
NEW ORLEANS – Researchers are organizing a master trial in an attempt to improve the treatment of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
The Pediatric Acute Leukemia (PedAL) trial is an effort to collect data on all pediatric AML patients. The plan is to use these data to match patients to clinical trials, better understand pediatric AML, and bring new treatments to this population.
E. Anders Kolb, MD, of Nemours Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders in Wilmington, Del., described the initiative at the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Dr. Kolb noted that several drugs have been approved to treat adult AML in the last 2 years, but most of them are not approved for use in children.
“What we see in childhood AML is a lot different than what we see in adult AML, and this challenges the paradigm that we have traditionally followed where we use the adult as the 'preclinical model' for pediatric AML,” he said. “I think we are learning more and more that children have a unique disease, unique targets, and need unique therapies.”
The PedAL initiative is an attempt to address these unique needs. PedAL is part of the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society’s Children’s Initiative, and it involves researchers from academic centers and the Children’s Oncology Group.
The PedAL initiative includes preclinical, biomarker, and informatics research, as well as the master clinical trial. The main goal of the master trial is to collect genomic, proteomic, metabolomic, flow cytometry, and clinical data from all children with AML and use these data to match patients to clinical trials.
The PedAL trial will leverage Project:EveryChild, an effort by the Children’s Oncology Group to study every child with cancer. Each child enrolled in this program has an identification number that follows the child through all clinical interventions.
The goal is that Project:EveryChild will capture all pediatric AML patients at the time of diagnosis, although patients can join the project at any time. Then, sequencing, clinical, and other data will be collected from these patients and stored in a data commons.
If patients relapse after standard or other therapies, the GEARBOX algorithm (genomic eligibility algorithm at relapse for better outcomes) can be used to match the patient’s information to clinical trial eligibility criteria and provide a list of appropriate trials.
Dr. Kolb said this process should reduce logistical barriers and get relapsed patients to trials more quickly. Additionally, the data collected through PedAL should help researchers design better trials for pediatric patients with relapsed AML.
“Ultimately, we’ll create the largest data set that will give us a better understanding of all the risks and benefits associated with postrelapse AML,” Dr. Kolb said. “No matter what happens to the patient, no matter where that patient enrolls, we’re going to have the capacity to collect data and present that data to the community for analysis for improved understanding of outcomes.”
Dr. Kolb and his colleagues are already working with researchers in Europe and Japan to make this a global effort and create an international data commons. In addition, the researchers are planning to collaborate with the pharmaceutical industry to unite efforts in pediatric AML drug development.
“We can’t just test drugs in kids because they worked in adults,” Dr. Kolb said. “We really need to maintain the integrity of the science and ask relevant questions in children but do so with the intent to make sure these drugs are licensed for use in kids.”
Dr. Kolb reported having no conflicts of interest. The PedAL trial is sponsored by the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society.
NEW ORLEANS – Researchers are organizing a master trial in an attempt to improve the treatment of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
The Pediatric Acute Leukemia (PedAL) trial is an effort to collect data on all pediatric AML patients. The plan is to use these data to match patients to clinical trials, better understand pediatric AML, and bring new treatments to this population.
E. Anders Kolb, MD, of Nemours Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders in Wilmington, Del., described the initiative at the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Dr. Kolb noted that several drugs have been approved to treat adult AML in the last 2 years, but most of them are not approved for use in children.
“What we see in childhood AML is a lot different than what we see in adult AML, and this challenges the paradigm that we have traditionally followed where we use the adult as the 'preclinical model' for pediatric AML,” he said. “I think we are learning more and more that children have a unique disease, unique targets, and need unique therapies.”
The PedAL initiative is an attempt to address these unique needs. PedAL is part of the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society’s Children’s Initiative, and it involves researchers from academic centers and the Children’s Oncology Group.
The PedAL initiative includes preclinical, biomarker, and informatics research, as well as the master clinical trial. The main goal of the master trial is to collect genomic, proteomic, metabolomic, flow cytometry, and clinical data from all children with AML and use these data to match patients to clinical trials.
The PedAL trial will leverage Project:EveryChild, an effort by the Children’s Oncology Group to study every child with cancer. Each child enrolled in this program has an identification number that follows the child through all clinical interventions.
The goal is that Project:EveryChild will capture all pediatric AML patients at the time of diagnosis, although patients can join the project at any time. Then, sequencing, clinical, and other data will be collected from these patients and stored in a data commons.
If patients relapse after standard or other therapies, the GEARBOX algorithm (genomic eligibility algorithm at relapse for better outcomes) can be used to match the patient’s information to clinical trial eligibility criteria and provide a list of appropriate trials.
Dr. Kolb said this process should reduce logistical barriers and get relapsed patients to trials more quickly. Additionally, the data collected through PedAL should help researchers design better trials for pediatric patients with relapsed AML.
“Ultimately, we’ll create the largest data set that will give us a better understanding of all the risks and benefits associated with postrelapse AML,” Dr. Kolb said. “No matter what happens to the patient, no matter where that patient enrolls, we’re going to have the capacity to collect data and present that data to the community for analysis for improved understanding of outcomes.”
Dr. Kolb and his colleagues are already working with researchers in Europe and Japan to make this a global effort and create an international data commons. In addition, the researchers are planning to collaborate with the pharmaceutical industry to unite efforts in pediatric AML drug development.
“We can’t just test drugs in kids because they worked in adults,” Dr. Kolb said. “We really need to maintain the integrity of the science and ask relevant questions in children but do so with the intent to make sure these drugs are licensed for use in kids.”
Dr. Kolb reported having no conflicts of interest. The PedAL trial is sponsored by the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society.
REPORTING FROM 2019 ASPHO CONFERENCE
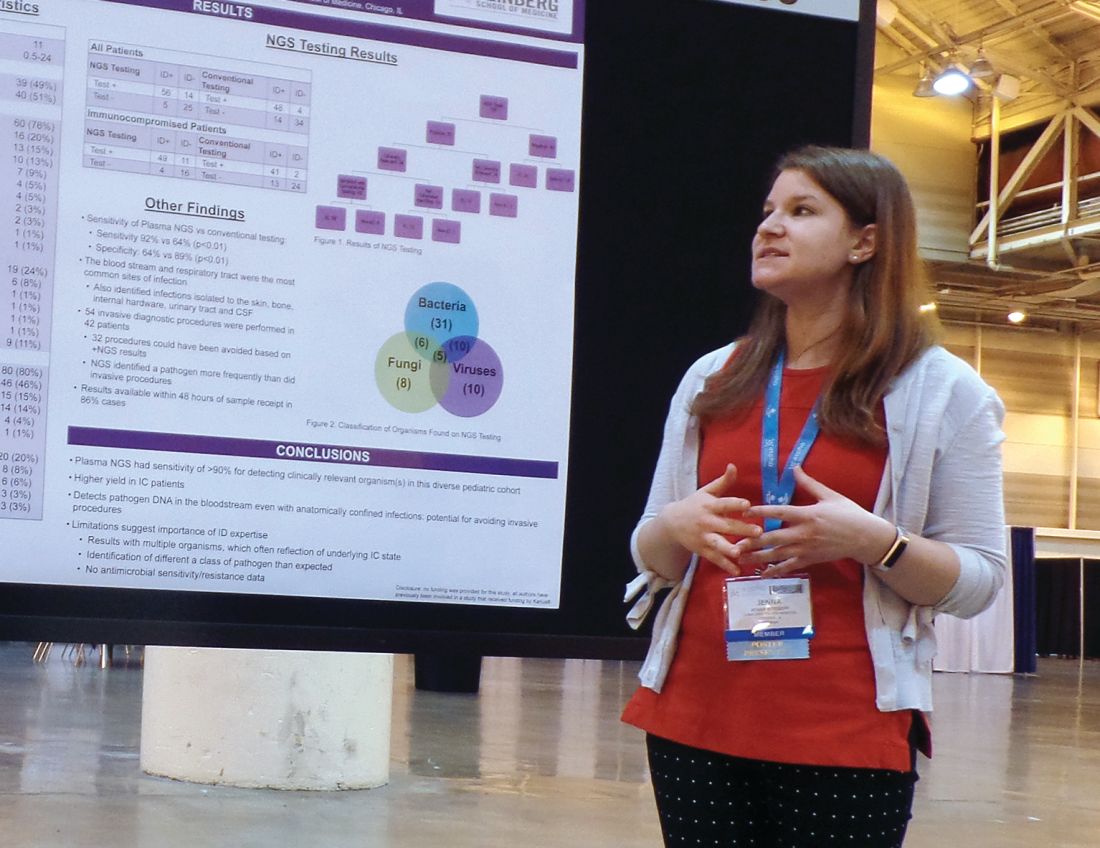
Next-generation sequencing test detects pathogens with high sensitivity
NEW ORLEANS – A next-generation sequencing (NGS) test for pathogen detection demonstrated higher sensitivity than conventional testing methods in a cohort of diverse pediatric patients, according to researchers.
The NGS test, which detects sequences of circulating cell-free DNA in plasma, detected pathogens with 92% sensitivity, compared with 64% sensitivity for all conventional testing methods combined (P less than .01).
“While I think we can all recognize that specificity is important, I think sensitivity is more important to be able to get at sources of infection,” said Jenna Rossoff, MD, of Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues conducted this study and presented the results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Lurie Children’s Hospital began using a commercially available NGS pathogen test, the Karius test, in 2016. Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues set out to evaluate how the test affected patient care by conducting a retrospective analysis of tests performed from December 2016 through August 2018.
The researchers studied 100 NGS tests performed for 79 pediatric patients. The patients had a median age of 11 years (range, 0.5-24 years).
Most patients (n = 60) were immunocompromised, largely due to a hematologic malignancy (n = 16), primary immune deficiency (n = 13), hematopoietic cell transplant (n = 10), or solid organ transplant (n = 7).
The remaining 19 patients were immunocompetent, and 9 of them had no underlying diagnosis. The most common diagnosis for this group was neurologic disorder (n = 6).
Results
Of the 100 NGS tests evaluated, 70 were positive for any organism, and 56 of these were deemed clinically relevant.
“What I think is quite remarkable is that, of those clinically relevant organisms, tests on 14, which is 25% of those, were able to identify clinically relevant or pathogenic organisms when no other conventional testing modality was able to identify them,” Dr. Rossoff said. “And these were often in patients who underwent invasive procedures to try to get at the source of their infectious disease.”
In fact, the study included 42 patients who underwent 54 invasive diagnostic procedures, and 32 of those procedures could have been avoided based on positive NGS results, according to Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues.
Dr. Rossoff noted that the most common sites of infection were the bloodstream and respiratory tract, but the NGS test was able to identify pathogens in the bone, skin, cerebrospinal fluid, and urinary tract. She also pointed out that NGS results were available “in a fairly timely manner,” as 86% of test results were available within 48 hours of sample receipt.
Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues did not receive any funding for this study, but they were previously involved in a study funded by Karius, the company that commercialized the NGS test.
SOURCE: Rossoff J et al. ASPHO 2019. Abstract 439.
NEW ORLEANS – A next-generation sequencing (NGS) test for pathogen detection demonstrated higher sensitivity than conventional testing methods in a cohort of diverse pediatric patients, according to researchers.
The NGS test, which detects sequences of circulating cell-free DNA in plasma, detected pathogens with 92% sensitivity, compared with 64% sensitivity for all conventional testing methods combined (P less than .01).
“While I think we can all recognize that specificity is important, I think sensitivity is more important to be able to get at sources of infection,” said Jenna Rossoff, MD, of Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues conducted this study and presented the results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Lurie Children’s Hospital began using a commercially available NGS pathogen test, the Karius test, in 2016. Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues set out to evaluate how the test affected patient care by conducting a retrospective analysis of tests performed from December 2016 through August 2018.
The researchers studied 100 NGS tests performed for 79 pediatric patients. The patients had a median age of 11 years (range, 0.5-24 years).
Most patients (n = 60) were immunocompromised, largely due to a hematologic malignancy (n = 16), primary immune deficiency (n = 13), hematopoietic cell transplant (n = 10), or solid organ transplant (n = 7).
The remaining 19 patients were immunocompetent, and 9 of them had no underlying diagnosis. The most common diagnosis for this group was neurologic disorder (n = 6).
Results
Of the 100 NGS tests evaluated, 70 were positive for any organism, and 56 of these were deemed clinically relevant.
“What I think is quite remarkable is that, of those clinically relevant organisms, tests on 14, which is 25% of those, were able to identify clinically relevant or pathogenic organisms when no other conventional testing modality was able to identify them,” Dr. Rossoff said. “And these were often in patients who underwent invasive procedures to try to get at the source of their infectious disease.”
In fact, the study included 42 patients who underwent 54 invasive diagnostic procedures, and 32 of those procedures could have been avoided based on positive NGS results, according to Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues.
Dr. Rossoff noted that the most common sites of infection were the bloodstream and respiratory tract, but the NGS test was able to identify pathogens in the bone, skin, cerebrospinal fluid, and urinary tract. She also pointed out that NGS results were available “in a fairly timely manner,” as 86% of test results were available within 48 hours of sample receipt.
Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues did not receive any funding for this study, but they were previously involved in a study funded by Karius, the company that commercialized the NGS test.
SOURCE: Rossoff J et al. ASPHO 2019. Abstract 439.
NEW ORLEANS – A next-generation sequencing (NGS) test for pathogen detection demonstrated higher sensitivity than conventional testing methods in a cohort of diverse pediatric patients, according to researchers.
The NGS test, which detects sequences of circulating cell-free DNA in plasma, detected pathogens with 92% sensitivity, compared with 64% sensitivity for all conventional testing methods combined (P less than .01).
“While I think we can all recognize that specificity is important, I think sensitivity is more important to be able to get at sources of infection,” said Jenna Rossoff, MD, of Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues conducted this study and presented the results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Lurie Children’s Hospital began using a commercially available NGS pathogen test, the Karius test, in 2016. Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues set out to evaluate how the test affected patient care by conducting a retrospective analysis of tests performed from December 2016 through August 2018.
The researchers studied 100 NGS tests performed for 79 pediatric patients. The patients had a median age of 11 years (range, 0.5-24 years).
Most patients (n = 60) were immunocompromised, largely due to a hematologic malignancy (n = 16), primary immune deficiency (n = 13), hematopoietic cell transplant (n = 10), or solid organ transplant (n = 7).
The remaining 19 patients were immunocompetent, and 9 of them had no underlying diagnosis. The most common diagnosis for this group was neurologic disorder (n = 6).
Results
Of the 100 NGS tests evaluated, 70 were positive for any organism, and 56 of these were deemed clinically relevant.
“What I think is quite remarkable is that, of those clinically relevant organisms, tests on 14, which is 25% of those, were able to identify clinically relevant or pathogenic organisms when no other conventional testing modality was able to identify them,” Dr. Rossoff said. “And these were often in patients who underwent invasive procedures to try to get at the source of their infectious disease.”
In fact, the study included 42 patients who underwent 54 invasive diagnostic procedures, and 32 of those procedures could have been avoided based on positive NGS results, according to Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues.
Dr. Rossoff noted that the most common sites of infection were the bloodstream and respiratory tract, but the NGS test was able to identify pathogens in the bone, skin, cerebrospinal fluid, and urinary tract. She also pointed out that NGS results were available “in a fairly timely manner,” as 86% of test results were available within 48 hours of sample receipt.
Dr. Rossoff and her colleagues did not receive any funding for this study, but they were previously involved in a study funded by Karius, the company that commercialized the NGS test.
SOURCE: Rossoff J et al. ASPHO 2019. Abstract 439.
REPORTING FROM 2019 ASPHO CONFERENCE
Atypical case of cutaneous MCL mimics SPTCL
An atypical case of cutaneous mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) with histomorphological features mimicking subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) highlights a “potential pitfall,” according to investigators.
This unusual case stresses the importance of molecular cytogenetics and/or immunohistochemistry for panniculitis-type lymphomas, reported lead author Caroline Laggis, MD of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
“While morphologic features of SPTCL, specifically rimming of adipocytes by neoplastic lymphoid cells, have been documented in other types of lymphomas, this case is exceptional in that the morphologic features of SPTCL are showed in secondary cutaneous involvement by MCL,” the investigators wrote. Their report is in Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.
The patient was a 69-year-old man who presented with 2-year history of night sweats and fever of unknown origin, and, closer to presentation, weight loss and tender bumps under the skin of his pelvic region.
Subsequent computed tomography and excisional lymph node biopsy led to a diagnosis of MCL, with a Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index of 5, suggesting aggressive, intermediate-risk disease. Further imaging showed involvement of the nasopharynx, and cervical and mediastinal lymph nodes.
Bendamustine and rituximab chemotherapy was given unremarkably until the final cycle, at which point the patient presented with tender subcutaneous nodules on his lower legs. Histopathology from punch biopsies revealed “a dense infiltrate of monomorphic, mitotically active lymphoid cells with infiltration between the deep dermal collagen and the adipocytes in subcutaneous fat,” the investigators wrote, noting that the infiltrative cells were blastoid and 70% expressed cyclin D1, supporting cutaneous involvement of his systemic MCL.
Treatment was switched to ibrutinib and selinexor via a clinical trial, which led to temporary improvement of leg lesions; when the lesions returned, biopsy was performed with the same histopathological result. Lenalidomide and rituximab were started, but without success, and disease spread to the central nervous system.
Another biopsy of the skin lesions again supported cutaneous MCL, with tumor cells rimming individual adipocytes.
Because of this atypical morphology, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was conducted, revealing t(11;14)(q13:32) positivity, thereby “confirming the diagnosis of cutaneous involvement by systemic MCL,” the investigators wrote.
Genomic sequencing revealed abnormalities of “ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR), BCL6 corepressor, and FAS-associated factor 1, as well as the expected mutation in IGH-CCND1, leading to cyclin D1 upregulation.”
Subsequent treatment was unsuccessful, and the patient died from his disease.
“The complex and central role that mTOR plays in adipose homeostasis may link our tumor to its preference to the adipose tissue, although further investigation is warranted regarding specific genomic alterations in lymphomas and the implications these mutations have in the involvement of tumor cells with cutaneous and adipose environments,” the investigators wrote.
The investigators did not report conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Laggis C et al. 2019 Apr 8. doi:10.1111/cup.13471.
An atypical case of cutaneous mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) with histomorphological features mimicking subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) highlights a “potential pitfall,” according to investigators.
This unusual case stresses the importance of molecular cytogenetics and/or immunohistochemistry for panniculitis-type lymphomas, reported lead author Caroline Laggis, MD of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
“While morphologic features of SPTCL, specifically rimming of adipocytes by neoplastic lymphoid cells, have been documented in other types of lymphomas, this case is exceptional in that the morphologic features of SPTCL are showed in secondary cutaneous involvement by MCL,” the investigators wrote. Their report is in Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.
The patient was a 69-year-old man who presented with 2-year history of night sweats and fever of unknown origin, and, closer to presentation, weight loss and tender bumps under the skin of his pelvic region.
Subsequent computed tomography and excisional lymph node biopsy led to a diagnosis of MCL, with a Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index of 5, suggesting aggressive, intermediate-risk disease. Further imaging showed involvement of the nasopharynx, and cervical and mediastinal lymph nodes.
Bendamustine and rituximab chemotherapy was given unremarkably until the final cycle, at which point the patient presented with tender subcutaneous nodules on his lower legs. Histopathology from punch biopsies revealed “a dense infiltrate of monomorphic, mitotically active lymphoid cells with infiltration between the deep dermal collagen and the adipocytes in subcutaneous fat,” the investigators wrote, noting that the infiltrative cells were blastoid and 70% expressed cyclin D1, supporting cutaneous involvement of his systemic MCL.
Treatment was switched to ibrutinib and selinexor via a clinical trial, which led to temporary improvement of leg lesions; when the lesions returned, biopsy was performed with the same histopathological result. Lenalidomide and rituximab were started, but without success, and disease spread to the central nervous system.
Another biopsy of the skin lesions again supported cutaneous MCL, with tumor cells rimming individual adipocytes.
Because of this atypical morphology, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was conducted, revealing t(11;14)(q13:32) positivity, thereby “confirming the diagnosis of cutaneous involvement by systemic MCL,” the investigators wrote.
Genomic sequencing revealed abnormalities of “ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR), BCL6 corepressor, and FAS-associated factor 1, as well as the expected mutation in IGH-CCND1, leading to cyclin D1 upregulation.”
Subsequent treatment was unsuccessful, and the patient died from his disease.
“The complex and central role that mTOR plays in adipose homeostasis may link our tumor to its preference to the adipose tissue, although further investigation is warranted regarding specific genomic alterations in lymphomas and the implications these mutations have in the involvement of tumor cells with cutaneous and adipose environments,” the investigators wrote.
The investigators did not report conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Laggis C et al. 2019 Apr 8. doi:10.1111/cup.13471.
An atypical case of cutaneous mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) with histomorphological features mimicking subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) highlights a “potential pitfall,” according to investigators.
This unusual case stresses the importance of molecular cytogenetics and/or immunohistochemistry for panniculitis-type lymphomas, reported lead author Caroline Laggis, MD of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
“While morphologic features of SPTCL, specifically rimming of adipocytes by neoplastic lymphoid cells, have been documented in other types of lymphomas, this case is exceptional in that the morphologic features of SPTCL are showed in secondary cutaneous involvement by MCL,” the investigators wrote. Their report is in Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.
The patient was a 69-year-old man who presented with 2-year history of night sweats and fever of unknown origin, and, closer to presentation, weight loss and tender bumps under the skin of his pelvic region.
Subsequent computed tomography and excisional lymph node biopsy led to a diagnosis of MCL, with a Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index of 5, suggesting aggressive, intermediate-risk disease. Further imaging showed involvement of the nasopharynx, and cervical and mediastinal lymph nodes.
Bendamustine and rituximab chemotherapy was given unremarkably until the final cycle, at which point the patient presented with tender subcutaneous nodules on his lower legs. Histopathology from punch biopsies revealed “a dense infiltrate of monomorphic, mitotically active lymphoid cells with infiltration between the deep dermal collagen and the adipocytes in subcutaneous fat,” the investigators wrote, noting that the infiltrative cells were blastoid and 70% expressed cyclin D1, supporting cutaneous involvement of his systemic MCL.
Treatment was switched to ibrutinib and selinexor via a clinical trial, which led to temporary improvement of leg lesions; when the lesions returned, biopsy was performed with the same histopathological result. Lenalidomide and rituximab were started, but without success, and disease spread to the central nervous system.
Another biopsy of the skin lesions again supported cutaneous MCL, with tumor cells rimming individual adipocytes.
Because of this atypical morphology, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was conducted, revealing t(11;14)(q13:32) positivity, thereby “confirming the diagnosis of cutaneous involvement by systemic MCL,” the investigators wrote.
Genomic sequencing revealed abnormalities of “ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR), BCL6 corepressor, and FAS-associated factor 1, as well as the expected mutation in IGH-CCND1, leading to cyclin D1 upregulation.”
Subsequent treatment was unsuccessful, and the patient died from his disease.
“The complex and central role that mTOR plays in adipose homeostasis may link our tumor to its preference to the adipose tissue, although further investigation is warranted regarding specific genomic alterations in lymphomas and the implications these mutations have in the involvement of tumor cells with cutaneous and adipose environments,” the investigators wrote.
The investigators did not report conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Laggis C et al. 2019 Apr 8. doi:10.1111/cup.13471.
FROM JOURNAL OF CUTANEOUS PATHOLOGY