User login
ID Practitioner is an independent news source that provides infectious disease specialists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the infectious disease specialist’s practice. Specialty focus topics include antimicrobial resistance, emerging infections, global ID, hepatitis, HIV, hospital-acquired infections, immunizations and vaccines, influenza, mycoses, pediatric infections, and STIs. Infectious Diseases News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
sofosbuvir
ritonavir with dasabuvir
discount
support path
program
ritonavir
greedy
ledipasvir
assistance
viekira pak
vpak
advocacy
needy
protest
abbvie
paritaprevir
ombitasvir
direct-acting antivirals
dasabuvir
gilead
fake-ovir
support
v pak
oasis
harvoni
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-medstat-latest-articles-articles-section')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-idp')]
Despite strict controls, some infants born to mothers with COVID-19 appear infected
Despite implementation of strict infection control and prevention procedures in a hospital in Wuhan, China, according to Lingkong Zeng, MD, of the department of neonatology at Wuhan Children’s Hospital, and associates.
Thirty-three neonates born to mothers with COVID-19 were included in the study, published as a research letter in JAMA Pediatrics. Of this group, three neonates (9%) were confirmed to be infected with the novel coronavirus 2019 at 2 and 4 days of life through nasopharyngeal and anal swabs.
Of the three infected neonates, two were born at 40 weeks’ gestation and the third was born at 31 weeks. The two full-term infants had mild symptoms such as lethargy and fever and were negative for the virus at 6 days of life. The preterm infant had somewhat worse symptoms, but the investigators acknowledged that “the most seriously ill neonate may have been symptomatic from prematurity, asphyxia, and sepsis, rather than [the novel coronavirus 2019] infection.” They added that outcomes for all three neonates were favorable, consistent with past research.
“Because strict infection control and prevention procedures were implemented during the delivery, it is likely that the sources of [novel coronavirus 2019] in the neonates’ upper respiratory tracts or anuses were maternal in origin,” Dr. Zeng and associates surmised.
While previous studies have shown no evidence of COVID-19 transmission between mothers and neonates, and all samples, including amniotic fluid, cord blood, and breast milk, were negative for the novel coronavirus 2019, “vertical maternal-fetal transmission cannot be ruled out in the current cohort. Therefore, it is crucial to screen pregnant women and implement strict infection control measures, quarantine of infected mothers, and close monitoring of neonates at risk of COVID-19,” the investigators concluded.
The study authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zeng L et al. JAMA Pediatrics. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.0878.
Despite implementation of strict infection control and prevention procedures in a hospital in Wuhan, China, according to Lingkong Zeng, MD, of the department of neonatology at Wuhan Children’s Hospital, and associates.
Thirty-three neonates born to mothers with COVID-19 were included in the study, published as a research letter in JAMA Pediatrics. Of this group, three neonates (9%) were confirmed to be infected with the novel coronavirus 2019 at 2 and 4 days of life through nasopharyngeal and anal swabs.
Of the three infected neonates, two were born at 40 weeks’ gestation and the third was born at 31 weeks. The two full-term infants had mild symptoms such as lethargy and fever and were negative for the virus at 6 days of life. The preterm infant had somewhat worse symptoms, but the investigators acknowledged that “the most seriously ill neonate may have been symptomatic from prematurity, asphyxia, and sepsis, rather than [the novel coronavirus 2019] infection.” They added that outcomes for all three neonates were favorable, consistent with past research.
“Because strict infection control and prevention procedures were implemented during the delivery, it is likely that the sources of [novel coronavirus 2019] in the neonates’ upper respiratory tracts or anuses were maternal in origin,” Dr. Zeng and associates surmised.
While previous studies have shown no evidence of COVID-19 transmission between mothers and neonates, and all samples, including amniotic fluid, cord blood, and breast milk, were negative for the novel coronavirus 2019, “vertical maternal-fetal transmission cannot be ruled out in the current cohort. Therefore, it is crucial to screen pregnant women and implement strict infection control measures, quarantine of infected mothers, and close monitoring of neonates at risk of COVID-19,” the investigators concluded.
The study authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zeng L et al. JAMA Pediatrics. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.0878.
Despite implementation of strict infection control and prevention procedures in a hospital in Wuhan, China, according to Lingkong Zeng, MD, of the department of neonatology at Wuhan Children’s Hospital, and associates.
Thirty-three neonates born to mothers with COVID-19 were included in the study, published as a research letter in JAMA Pediatrics. Of this group, three neonates (9%) were confirmed to be infected with the novel coronavirus 2019 at 2 and 4 days of life through nasopharyngeal and anal swabs.
Of the three infected neonates, two were born at 40 weeks’ gestation and the third was born at 31 weeks. The two full-term infants had mild symptoms such as lethargy and fever and were negative for the virus at 6 days of life. The preterm infant had somewhat worse symptoms, but the investigators acknowledged that “the most seriously ill neonate may have been symptomatic from prematurity, asphyxia, and sepsis, rather than [the novel coronavirus 2019] infection.” They added that outcomes for all three neonates were favorable, consistent with past research.
“Because strict infection control and prevention procedures were implemented during the delivery, it is likely that the sources of [novel coronavirus 2019] in the neonates’ upper respiratory tracts or anuses were maternal in origin,” Dr. Zeng and associates surmised.
While previous studies have shown no evidence of COVID-19 transmission between mothers and neonates, and all samples, including amniotic fluid, cord blood, and breast milk, were negative for the novel coronavirus 2019, “vertical maternal-fetal transmission cannot be ruled out in the current cohort. Therefore, it is crucial to screen pregnant women and implement strict infection control measures, quarantine of infected mothers, and close monitoring of neonates at risk of COVID-19,” the investigators concluded.
The study authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zeng L et al. JAMA Pediatrics. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.0878.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Wuhan data link COVID-19 with myocardial damage
The first data on myocardial injury linked with COVID-19 disease during the start of the pandemic in Wuhan, China serves as a “wake up call” for clinicians and the general public on what the United States and other Western countries can expect as the SARS-CoV-2 virus spreads and case numbers mount: a potentially “daunting” toll of deaths as an infection with a tendency to be most severe in patients with underlying cardiovascular disease hits populations that include large numbers of such patients.
“A consistent picture emerges” from two reports on a total of 603 COVID-19 patients treated at two academic hospitals in Wuhan, which described “remarkably similar characteristics of patients who develop myocardial injury” associated with their infection. “Patients who develop myocardial injury with COVID-19 have clinical evidence of higher acuity, with a higher incidence of acute respiratory distress syndrome and more frequent need for assisted ventilation than those without myocardial injury, and the patients who are more prone to have myocardial injury are “older patients with preexisting cardiovascular complications and diabetes,” Robert O. Bonow, MD, and coauthors wrote in an editorial published online (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Mar 27. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1105).
These new findings have special relevance to the United States and other Western countries because of their substantial numbers of elderly patients with cardiovascular diseases, said Dr. Bonow, professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, and coauthors.
One of the two reports cited in the editorial reviewed 416 patients hospitalized at Renmin Hospital in Wuhan during the period of Jan. 20 to Feb. 10, 2020, with confirmed COVID-19 disease, and found that 20% of the cohort had evidence of cardiac injury, defined as blood levels of the high-sensitivity troponin I cardiac biomarker above the 99th-percentile upper reference limit, regardless of new abnormalities in electrocardiography and echocardiography.
The analysis also showed that patients with myocardial injury had a significantly higher in-hospital mortality rate, 51%, compared with a 5% mortality rate among patients without myocardial injury, and among patients with myocardial injury those with elevated high-sensitivity troponin I had an even higher mortality rate (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Mar 25. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0950).
A second review of 187 confirmed COVID-19 cases at Seventh Hospital in Wuhan during the period of Jan. 23 to Feb. 23, 2020, showed similar findings, with a 28% prevalence of myocardial injury at admission based on an elevated level of plasma troponin T (TnT), and 35% had cardiovascular disease (CVD) including hypertension, coronary heart disease, and cardiomyopathy. Elevated TnT levels and CVD at entry each linked with substantially increased mortality. The incidence of death among patients with elevated TnT and no underlying CVD was 38% compared with 8% among patients without elevated TnT or underlying CVD. Among patients admitted with underlying CVD those who also had an elevated TnT had a 69% death rate during hospitalization compared with a 13% rate in those without TnT elevation (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Mar 27. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1017).
Dr. Bonow and coauthors noted that patients with chronic coronary artery disease have a heightened risk for developing acute coronary syndrome during acute infection, potentially resulting from a severe increase in myocardial demand during infection, or severe systemic inflammatory stress that could result in atherosclerotic plaque instability and rupture as well as vascular and myocardial inflammation.
In addition, patients with heart failure are prone to hemodynamic instability during severe infection. “Thus it is anticipated that patients with underlying cardiovascular diseases, which are more prevalent in older adults, would be susceptible to higher risks of adverse outcomes and death during the severe and aggressive inflammatory responses to COVID-19 than individuals who are younger and healthier,” they wrote.
They also cited the potential for acute or fulminant myocarditis as well as new-onset heart failure caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 disease based on experience with the related Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Another concerning observation is that the SARS-CoV-2 virus binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protein on cell surfaces as its main entry receptor, “raising the possibility of direct viral infection of vascular endothelium and myocardium,” a process that itself could produce myocardial injury and myocarditis.
These new findings from COVID-19 patients in Wuhan represent early data from what has become a global pandemic, and raise questions about generalizability, but for the time being a key message from these early cases is that prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection is paramount. “Until we know more, the populations described in these primary data reports should be most observant of strict hand hygiene, social distancing, and, where available, COVID-19 testing,” the authors said.
Dr. Bonow and coauthors had no disclosures.
The first data on myocardial injury linked with COVID-19 disease during the start of the pandemic in Wuhan, China serves as a “wake up call” for clinicians and the general public on what the United States and other Western countries can expect as the SARS-CoV-2 virus spreads and case numbers mount: a potentially “daunting” toll of deaths as an infection with a tendency to be most severe in patients with underlying cardiovascular disease hits populations that include large numbers of such patients.
“A consistent picture emerges” from two reports on a total of 603 COVID-19 patients treated at two academic hospitals in Wuhan, which described “remarkably similar characteristics of patients who develop myocardial injury” associated with their infection. “Patients who develop myocardial injury with COVID-19 have clinical evidence of higher acuity, with a higher incidence of acute respiratory distress syndrome and more frequent need for assisted ventilation than those without myocardial injury, and the patients who are more prone to have myocardial injury are “older patients with preexisting cardiovascular complications and diabetes,” Robert O. Bonow, MD, and coauthors wrote in an editorial published online (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Mar 27. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1105).
These new findings have special relevance to the United States and other Western countries because of their substantial numbers of elderly patients with cardiovascular diseases, said Dr. Bonow, professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, and coauthors.
One of the two reports cited in the editorial reviewed 416 patients hospitalized at Renmin Hospital in Wuhan during the period of Jan. 20 to Feb. 10, 2020, with confirmed COVID-19 disease, and found that 20% of the cohort had evidence of cardiac injury, defined as blood levels of the high-sensitivity troponin I cardiac biomarker above the 99th-percentile upper reference limit, regardless of new abnormalities in electrocardiography and echocardiography.
The analysis also showed that patients with myocardial injury had a significantly higher in-hospital mortality rate, 51%, compared with a 5% mortality rate among patients without myocardial injury, and among patients with myocardial injury those with elevated high-sensitivity troponin I had an even higher mortality rate (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Mar 25. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0950).
A second review of 187 confirmed COVID-19 cases at Seventh Hospital in Wuhan during the period of Jan. 23 to Feb. 23, 2020, showed similar findings, with a 28% prevalence of myocardial injury at admission based on an elevated level of plasma troponin T (TnT), and 35% had cardiovascular disease (CVD) including hypertension, coronary heart disease, and cardiomyopathy. Elevated TnT levels and CVD at entry each linked with substantially increased mortality. The incidence of death among patients with elevated TnT and no underlying CVD was 38% compared with 8% among patients without elevated TnT or underlying CVD. Among patients admitted with underlying CVD those who also had an elevated TnT had a 69% death rate during hospitalization compared with a 13% rate in those without TnT elevation (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Mar 27. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1017).
Dr. Bonow and coauthors noted that patients with chronic coronary artery disease have a heightened risk for developing acute coronary syndrome during acute infection, potentially resulting from a severe increase in myocardial demand during infection, or severe systemic inflammatory stress that could result in atherosclerotic plaque instability and rupture as well as vascular and myocardial inflammation.
In addition, patients with heart failure are prone to hemodynamic instability during severe infection. “Thus it is anticipated that patients with underlying cardiovascular diseases, which are more prevalent in older adults, would be susceptible to higher risks of adverse outcomes and death during the severe and aggressive inflammatory responses to COVID-19 than individuals who are younger and healthier,” they wrote.
They also cited the potential for acute or fulminant myocarditis as well as new-onset heart failure caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 disease based on experience with the related Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Another concerning observation is that the SARS-CoV-2 virus binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protein on cell surfaces as its main entry receptor, “raising the possibility of direct viral infection of vascular endothelium and myocardium,” a process that itself could produce myocardial injury and myocarditis.
These new findings from COVID-19 patients in Wuhan represent early data from what has become a global pandemic, and raise questions about generalizability, but for the time being a key message from these early cases is that prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection is paramount. “Until we know more, the populations described in these primary data reports should be most observant of strict hand hygiene, social distancing, and, where available, COVID-19 testing,” the authors said.
Dr. Bonow and coauthors had no disclosures.
The first data on myocardial injury linked with COVID-19 disease during the start of the pandemic in Wuhan, China serves as a “wake up call” for clinicians and the general public on what the United States and other Western countries can expect as the SARS-CoV-2 virus spreads and case numbers mount: a potentially “daunting” toll of deaths as an infection with a tendency to be most severe in patients with underlying cardiovascular disease hits populations that include large numbers of such patients.
“A consistent picture emerges” from two reports on a total of 603 COVID-19 patients treated at two academic hospitals in Wuhan, which described “remarkably similar characteristics of patients who develop myocardial injury” associated with their infection. “Patients who develop myocardial injury with COVID-19 have clinical evidence of higher acuity, with a higher incidence of acute respiratory distress syndrome and more frequent need for assisted ventilation than those without myocardial injury, and the patients who are more prone to have myocardial injury are “older patients with preexisting cardiovascular complications and diabetes,” Robert O. Bonow, MD, and coauthors wrote in an editorial published online (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Mar 27. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1105).
These new findings have special relevance to the United States and other Western countries because of their substantial numbers of elderly patients with cardiovascular diseases, said Dr. Bonow, professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, and coauthors.
One of the two reports cited in the editorial reviewed 416 patients hospitalized at Renmin Hospital in Wuhan during the period of Jan. 20 to Feb. 10, 2020, with confirmed COVID-19 disease, and found that 20% of the cohort had evidence of cardiac injury, defined as blood levels of the high-sensitivity troponin I cardiac biomarker above the 99th-percentile upper reference limit, regardless of new abnormalities in electrocardiography and echocardiography.
The analysis also showed that patients with myocardial injury had a significantly higher in-hospital mortality rate, 51%, compared with a 5% mortality rate among patients without myocardial injury, and among patients with myocardial injury those with elevated high-sensitivity troponin I had an even higher mortality rate (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Mar 25. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0950).
A second review of 187 confirmed COVID-19 cases at Seventh Hospital in Wuhan during the period of Jan. 23 to Feb. 23, 2020, showed similar findings, with a 28% prevalence of myocardial injury at admission based on an elevated level of plasma troponin T (TnT), and 35% had cardiovascular disease (CVD) including hypertension, coronary heart disease, and cardiomyopathy. Elevated TnT levels and CVD at entry each linked with substantially increased mortality. The incidence of death among patients with elevated TnT and no underlying CVD was 38% compared with 8% among patients without elevated TnT or underlying CVD. Among patients admitted with underlying CVD those who also had an elevated TnT had a 69% death rate during hospitalization compared with a 13% rate in those without TnT elevation (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Mar 27. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1017).
Dr. Bonow and coauthors noted that patients with chronic coronary artery disease have a heightened risk for developing acute coronary syndrome during acute infection, potentially resulting from a severe increase in myocardial demand during infection, or severe systemic inflammatory stress that could result in atherosclerotic plaque instability and rupture as well as vascular and myocardial inflammation.
In addition, patients with heart failure are prone to hemodynamic instability during severe infection. “Thus it is anticipated that patients with underlying cardiovascular diseases, which are more prevalent in older adults, would be susceptible to higher risks of adverse outcomes and death during the severe and aggressive inflammatory responses to COVID-19 than individuals who are younger and healthier,” they wrote.
They also cited the potential for acute or fulminant myocarditis as well as new-onset heart failure caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 disease based on experience with the related Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Another concerning observation is that the SARS-CoV-2 virus binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protein on cell surfaces as its main entry receptor, “raising the possibility of direct viral infection of vascular endothelium and myocardium,” a process that itself could produce myocardial injury and myocarditis.
These new findings from COVID-19 patients in Wuhan represent early data from what has become a global pandemic, and raise questions about generalizability, but for the time being a key message from these early cases is that prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection is paramount. “Until we know more, the populations described in these primary data reports should be most observant of strict hand hygiene, social distancing, and, where available, COVID-19 testing,” the authors said.
Dr. Bonow and coauthors had no disclosures.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
HCV screening risk factors in pregnant women need updating
“Because risk-factor screening has obvious limitations, universal screening in pregnancy has been suggested to allow for linkage to postpartum care and identification of children for future testing and treatment,” wrote Mona Prasad, DO, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and colleagues.
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from women with singleton pregnancies presenting for prenatal care prior to 23 weeks’ gestation during 2012-2015. Of these, 254 tested positive for the hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody, for a seroprevalence rate of 2.4 cases per 1,000 women.
The researchers conducted a case-control analysis of 131 women who tested positive and 251 controls to identify HCV infection risk factors based on interviews and chart reviews. They found that risk factors significantly associated with positive HCV antibodies included injection drug use (adjusted odds ratio, 22.9), a history of blood transfusion (aOR, 3.7), having an HCV-infected partner (aOR, 6.3), having had more than three sexual partners (aOR, 5.3), and smoking during pregnancy (aOR, 2.4).
In an unadjusted analysis, the researchers confirmed two of the risk factors currently recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for screening for HCV: injection drug use and being born to a mother with HCV infection, but not dialysis, organ transplantation, or HIV infection.
“Our results demonstrate that current risk factors could be contemporized,” Dr. Prasad and colleagues noted. “The currently accepted risk factors such as exposure to clotting factors, dialysis, and organ transplants are unlikely to be found. A thorough assessment of injection drug use history, smoking, transfusions, number of sexual partners, and partners with HCV infection is more sensitive in an obstetric population.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including possible selection bias and inclusion of only 65% of eligible women who were HCV positive, as well as a lack of screening data from 2016 to the present, which may not reflect the impact of the recent opioid epidemic, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and the generalizability of the study population.
“Our results regarding prevalence rates and risk factors of HCV antibody among pregnant women in the United States will be valuable to policymakers as they weigh the costs and benefits of universal screening,” Dr. Prasad and associates concluded.
Although universal screening has the potential to be more cost effective, given the small population of pregnant women eligible for treatment and lack of an available treatment, “the rationale is weaker for unique universal HCV screening recommendations for pregnant women,” they said.
By contrast, Sammy Saab, MD, MPH, of the University of California, Los Angeles; Ravina Kullar, PharmD, MPH, of Gilead Sciences, Foster City, Calif.; and Prabhu Gounder, MD, MPH, of the Los Angeles Department of Public Health, wrote an accompanying commentary in favor of universal HCV screening for pregnant women, in part because of the increase in HCV in the younger population overall.
“For many women of reproductive age, pregnancy is one of their few points of contact with their health care provider; therefore, pregnancy could provide a crucial time for targeting this population,” they noted.
Risk-based screening is of limited effectiveness because patients are not identified by way of current screening tools or they decline to reveal risk factors that providers might miss, the editorialists said. Pregnancy has not been shown to affect the accuracy of HCV tests, and identifying infections in mothers allows for screening in children as well.
“The perinatal hepatitis B virus infection program, which has been implemented in several state and local public health departments, could serve as an example for how to conduct surveillance for mothers with HCV infection and to ensure that HCV-exposed children receive appropriate follow-up testing and linkage to care,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported in part by multiple grants from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Prasad disclosed funding from Ohio State University and from Gilead. Coauthors had links with pharmaceutical companies, associations, and organizations – most unrelated to this study. The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCES: Prasad M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:778-88; Saab S et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:773-7.
“Because risk-factor screening has obvious limitations, universal screening in pregnancy has been suggested to allow for linkage to postpartum care and identification of children for future testing and treatment,” wrote Mona Prasad, DO, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and colleagues.
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from women with singleton pregnancies presenting for prenatal care prior to 23 weeks’ gestation during 2012-2015. Of these, 254 tested positive for the hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody, for a seroprevalence rate of 2.4 cases per 1,000 women.
The researchers conducted a case-control analysis of 131 women who tested positive and 251 controls to identify HCV infection risk factors based on interviews and chart reviews. They found that risk factors significantly associated with positive HCV antibodies included injection drug use (adjusted odds ratio, 22.9), a history of blood transfusion (aOR, 3.7), having an HCV-infected partner (aOR, 6.3), having had more than three sexual partners (aOR, 5.3), and smoking during pregnancy (aOR, 2.4).
In an unadjusted analysis, the researchers confirmed two of the risk factors currently recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for screening for HCV: injection drug use and being born to a mother with HCV infection, but not dialysis, organ transplantation, or HIV infection.
“Our results demonstrate that current risk factors could be contemporized,” Dr. Prasad and colleagues noted. “The currently accepted risk factors such as exposure to clotting factors, dialysis, and organ transplants are unlikely to be found. A thorough assessment of injection drug use history, smoking, transfusions, number of sexual partners, and partners with HCV infection is more sensitive in an obstetric population.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including possible selection bias and inclusion of only 65% of eligible women who were HCV positive, as well as a lack of screening data from 2016 to the present, which may not reflect the impact of the recent opioid epidemic, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and the generalizability of the study population.
“Our results regarding prevalence rates and risk factors of HCV antibody among pregnant women in the United States will be valuable to policymakers as they weigh the costs and benefits of universal screening,” Dr. Prasad and associates concluded.
Although universal screening has the potential to be more cost effective, given the small population of pregnant women eligible for treatment and lack of an available treatment, “the rationale is weaker for unique universal HCV screening recommendations for pregnant women,” they said.
By contrast, Sammy Saab, MD, MPH, of the University of California, Los Angeles; Ravina Kullar, PharmD, MPH, of Gilead Sciences, Foster City, Calif.; and Prabhu Gounder, MD, MPH, of the Los Angeles Department of Public Health, wrote an accompanying commentary in favor of universal HCV screening for pregnant women, in part because of the increase in HCV in the younger population overall.
“For many women of reproductive age, pregnancy is one of their few points of contact with their health care provider; therefore, pregnancy could provide a crucial time for targeting this population,” they noted.
Risk-based screening is of limited effectiveness because patients are not identified by way of current screening tools or they decline to reveal risk factors that providers might miss, the editorialists said. Pregnancy has not been shown to affect the accuracy of HCV tests, and identifying infections in mothers allows for screening in children as well.
“The perinatal hepatitis B virus infection program, which has been implemented in several state and local public health departments, could serve as an example for how to conduct surveillance for mothers with HCV infection and to ensure that HCV-exposed children receive appropriate follow-up testing and linkage to care,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported in part by multiple grants from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Prasad disclosed funding from Ohio State University and from Gilead. Coauthors had links with pharmaceutical companies, associations, and organizations – most unrelated to this study. The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCES: Prasad M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:778-88; Saab S et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:773-7.
“Because risk-factor screening has obvious limitations, universal screening in pregnancy has been suggested to allow for linkage to postpartum care and identification of children for future testing and treatment,” wrote Mona Prasad, DO, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and colleagues.
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from women with singleton pregnancies presenting for prenatal care prior to 23 weeks’ gestation during 2012-2015. Of these, 254 tested positive for the hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody, for a seroprevalence rate of 2.4 cases per 1,000 women.
The researchers conducted a case-control analysis of 131 women who tested positive and 251 controls to identify HCV infection risk factors based on interviews and chart reviews. They found that risk factors significantly associated with positive HCV antibodies included injection drug use (adjusted odds ratio, 22.9), a history of blood transfusion (aOR, 3.7), having an HCV-infected partner (aOR, 6.3), having had more than three sexual partners (aOR, 5.3), and smoking during pregnancy (aOR, 2.4).
In an unadjusted analysis, the researchers confirmed two of the risk factors currently recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for screening for HCV: injection drug use and being born to a mother with HCV infection, but not dialysis, organ transplantation, or HIV infection.
“Our results demonstrate that current risk factors could be contemporized,” Dr. Prasad and colleagues noted. “The currently accepted risk factors such as exposure to clotting factors, dialysis, and organ transplants are unlikely to be found. A thorough assessment of injection drug use history, smoking, transfusions, number of sexual partners, and partners with HCV infection is more sensitive in an obstetric population.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including possible selection bias and inclusion of only 65% of eligible women who were HCV positive, as well as a lack of screening data from 2016 to the present, which may not reflect the impact of the recent opioid epidemic, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and the generalizability of the study population.
“Our results regarding prevalence rates and risk factors of HCV antibody among pregnant women in the United States will be valuable to policymakers as they weigh the costs and benefits of universal screening,” Dr. Prasad and associates concluded.
Although universal screening has the potential to be more cost effective, given the small population of pregnant women eligible for treatment and lack of an available treatment, “the rationale is weaker for unique universal HCV screening recommendations for pregnant women,” they said.
By contrast, Sammy Saab, MD, MPH, of the University of California, Los Angeles; Ravina Kullar, PharmD, MPH, of Gilead Sciences, Foster City, Calif.; and Prabhu Gounder, MD, MPH, of the Los Angeles Department of Public Health, wrote an accompanying commentary in favor of universal HCV screening for pregnant women, in part because of the increase in HCV in the younger population overall.
“For many women of reproductive age, pregnancy is one of their few points of contact with their health care provider; therefore, pregnancy could provide a crucial time for targeting this population,” they noted.
Risk-based screening is of limited effectiveness because patients are not identified by way of current screening tools or they decline to reveal risk factors that providers might miss, the editorialists said. Pregnancy has not been shown to affect the accuracy of HCV tests, and identifying infections in mothers allows for screening in children as well.
“The perinatal hepatitis B virus infection program, which has been implemented in several state and local public health departments, could serve as an example for how to conduct surveillance for mothers with HCV infection and to ensure that HCV-exposed children receive appropriate follow-up testing and linkage to care,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported in part by multiple grants from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Prasad disclosed funding from Ohio State University and from Gilead. Coauthors had links with pharmaceutical companies, associations, and organizations – most unrelated to this study. The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCES: Prasad M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:778-88; Saab S et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:773-7.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
In older HIV patients, B/F/TAF regimen was noninferior to others
The single-tablet antiretroviral regimen of bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF) was assessed as being noninferior to two dolutegravir (DTG)-containing regimens among adults aged 50 and over living with HIV, according to a new study.
The study pooled data from two phase 3, randomized, double-blind B/F/TAF studies comparing that regimen with DTG-containing regimens for adults living with HIV who were treatment naive. Anthony Mills, MD, a physician in private practice in West Hollywood, Calif., and his associates reported results at the 144-week mark for the two studies in a poster that was presented as part of the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
In the two trials, the B/F/TAF regimen was compared with a DTG and abacavir/lamivudine (DTG + ABC/3TC) regimen, as well as with DTG plus emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (DTG + F/TAF). A total of 629 patients were enrolled in the first study, and 645 in the second. Of these, a total of 196 patients were aged 50 years or older. Across all study arms, most participants (73%-92%) were male, and 20%-37% were black or of African descent. Participants identifying as Hispanic or being of Latino ancestry made up 11%-27% of participants.
About 80%-90% of patients had asymptomatic HIV infection at the time of enrollment, with median CD4 counts ranging from 405-534 cells/mcL across study arms. Patients had a median 4.27-4.53 log (base 10) copies/mL at baseline. In both studies, patients had to have at least 500 HIV-1 RNA copies per mL, and couldn’t have known resistance to any of the study drugs.
At week 144, there were no statistically significant differences in virologic outcomes across study arms in the younger or older age subgroups: 81% of the B/F/TAF patients older than 50 years had fewer than 50 copies/mL of HIV-1 RNA, compared with 83% and 88% of the younger DTG/ABC/3TC and DTG + F/TAF groups meeting this mark, respectively.
Results were similar for the patients aged younger than 50 years, with 82%, 84%, and 83% of the B/F/TAF, DTG/ABC/3TC, and DTG + F/TAF groups having fewer than 50 copies/mL of HIV-1 RNA, respectively.
No patients in either age group showed resistance to any components of the treatment regimens. No treatment-emergent resistance was seen in any study participants, and few adverse events occurred. Those that were seen didn’t occur more frequently in older patients, compared with younger patients, and no patients discontinued their treatment because of renal issues.
Bone mineral density (BMD) was only measured in the study that compared B/F/TAF with DTG/ABC/3TC. Hip BMD decreased slightly in both groups, but the changes were comparable between older and younger participants. For both age groups, differences weren’t significant between the B/F/TAF group and those taking DTG/ABC/3TC. Spine density actually increased slightly in older patients taking B/F/TAF, but the difference between this measure and the slight decrease in older patients taking DTG/ABC/3TC was not significant.
Weight increased over time for all groups, ranging from a gain of 3.4 kg at 144 weeks for older patients taking DTG + F/TAF to 5.3 kg for the same regimen in younger patients, but none of the between-group differences were significant.
All fasting lipids rose for each study arm in both older and younger patients. Some of the between-group differences were statistically significant, but “there were no clinically significant differences in median changes from baseline in fasting lipids” among those aged 50 years or older, noted Dr. Mills and associates.
In terms of safety, no study drug-related discontinuations for renal adverse events occurred in either the B/F/TAF or the DTG + F/TAF groups, and the investigators saw no proximal renal tubulopathy.
The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using the Cockroft-Gault equation. All three antiviral regimens were associated with early drops in eGFR, “consistent with inhibition of tubular creatinine secretion via organic cation transporter 2,” noted Dr. Mills and associates.
Other adverse events were rare in all groups in both older and younger patients, without significant differences between therapies.
The study was supported by Gilead Sciences, which also provided support to Dr. Mills. One coauthor is a Gilead employee.
SOURCE: Mills A et al. CROI 2020, Abstract 2886.
The single-tablet antiretroviral regimen of bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF) was assessed as being noninferior to two dolutegravir (DTG)-containing regimens among adults aged 50 and over living with HIV, according to a new study.
The study pooled data from two phase 3, randomized, double-blind B/F/TAF studies comparing that regimen with DTG-containing regimens for adults living with HIV who were treatment naive. Anthony Mills, MD, a physician in private practice in West Hollywood, Calif., and his associates reported results at the 144-week mark for the two studies in a poster that was presented as part of the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
In the two trials, the B/F/TAF regimen was compared with a DTG and abacavir/lamivudine (DTG + ABC/3TC) regimen, as well as with DTG plus emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (DTG + F/TAF). A total of 629 patients were enrolled in the first study, and 645 in the second. Of these, a total of 196 patients were aged 50 years or older. Across all study arms, most participants (73%-92%) were male, and 20%-37% were black or of African descent. Participants identifying as Hispanic or being of Latino ancestry made up 11%-27% of participants.
About 80%-90% of patients had asymptomatic HIV infection at the time of enrollment, with median CD4 counts ranging from 405-534 cells/mcL across study arms. Patients had a median 4.27-4.53 log (base 10) copies/mL at baseline. In both studies, patients had to have at least 500 HIV-1 RNA copies per mL, and couldn’t have known resistance to any of the study drugs.
At week 144, there were no statistically significant differences in virologic outcomes across study arms in the younger or older age subgroups: 81% of the B/F/TAF patients older than 50 years had fewer than 50 copies/mL of HIV-1 RNA, compared with 83% and 88% of the younger DTG/ABC/3TC and DTG + F/TAF groups meeting this mark, respectively.
Results were similar for the patients aged younger than 50 years, with 82%, 84%, and 83% of the B/F/TAF, DTG/ABC/3TC, and DTG + F/TAF groups having fewer than 50 copies/mL of HIV-1 RNA, respectively.
No patients in either age group showed resistance to any components of the treatment regimens. No treatment-emergent resistance was seen in any study participants, and few adverse events occurred. Those that were seen didn’t occur more frequently in older patients, compared with younger patients, and no patients discontinued their treatment because of renal issues.
Bone mineral density (BMD) was only measured in the study that compared B/F/TAF with DTG/ABC/3TC. Hip BMD decreased slightly in both groups, but the changes were comparable between older and younger participants. For both age groups, differences weren’t significant between the B/F/TAF group and those taking DTG/ABC/3TC. Spine density actually increased slightly in older patients taking B/F/TAF, but the difference between this measure and the slight decrease in older patients taking DTG/ABC/3TC was not significant.
Weight increased over time for all groups, ranging from a gain of 3.4 kg at 144 weeks for older patients taking DTG + F/TAF to 5.3 kg for the same regimen in younger patients, but none of the between-group differences were significant.
All fasting lipids rose for each study arm in both older and younger patients. Some of the between-group differences were statistically significant, but “there were no clinically significant differences in median changes from baseline in fasting lipids” among those aged 50 years or older, noted Dr. Mills and associates.
In terms of safety, no study drug-related discontinuations for renal adverse events occurred in either the B/F/TAF or the DTG + F/TAF groups, and the investigators saw no proximal renal tubulopathy.
The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using the Cockroft-Gault equation. All three antiviral regimens were associated with early drops in eGFR, “consistent with inhibition of tubular creatinine secretion via organic cation transporter 2,” noted Dr. Mills and associates.
Other adverse events were rare in all groups in both older and younger patients, without significant differences between therapies.
The study was supported by Gilead Sciences, which also provided support to Dr. Mills. One coauthor is a Gilead employee.
SOURCE: Mills A et al. CROI 2020, Abstract 2886.
The single-tablet antiretroviral regimen of bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF) was assessed as being noninferior to two dolutegravir (DTG)-containing regimens among adults aged 50 and over living with HIV, according to a new study.
The study pooled data from two phase 3, randomized, double-blind B/F/TAF studies comparing that regimen with DTG-containing regimens for adults living with HIV who were treatment naive. Anthony Mills, MD, a physician in private practice in West Hollywood, Calif., and his associates reported results at the 144-week mark for the two studies in a poster that was presented as part of the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
In the two trials, the B/F/TAF regimen was compared with a DTG and abacavir/lamivudine (DTG + ABC/3TC) regimen, as well as with DTG plus emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (DTG + F/TAF). A total of 629 patients were enrolled in the first study, and 645 in the second. Of these, a total of 196 patients were aged 50 years or older. Across all study arms, most participants (73%-92%) were male, and 20%-37% were black or of African descent. Participants identifying as Hispanic or being of Latino ancestry made up 11%-27% of participants.
About 80%-90% of patients had asymptomatic HIV infection at the time of enrollment, with median CD4 counts ranging from 405-534 cells/mcL across study arms. Patients had a median 4.27-4.53 log (base 10) copies/mL at baseline. In both studies, patients had to have at least 500 HIV-1 RNA copies per mL, and couldn’t have known resistance to any of the study drugs.
At week 144, there were no statistically significant differences in virologic outcomes across study arms in the younger or older age subgroups: 81% of the B/F/TAF patients older than 50 years had fewer than 50 copies/mL of HIV-1 RNA, compared with 83% and 88% of the younger DTG/ABC/3TC and DTG + F/TAF groups meeting this mark, respectively.
Results were similar for the patients aged younger than 50 years, with 82%, 84%, and 83% of the B/F/TAF, DTG/ABC/3TC, and DTG + F/TAF groups having fewer than 50 copies/mL of HIV-1 RNA, respectively.
No patients in either age group showed resistance to any components of the treatment regimens. No treatment-emergent resistance was seen in any study participants, and few adverse events occurred. Those that were seen didn’t occur more frequently in older patients, compared with younger patients, and no patients discontinued their treatment because of renal issues.
Bone mineral density (BMD) was only measured in the study that compared B/F/TAF with DTG/ABC/3TC. Hip BMD decreased slightly in both groups, but the changes were comparable between older and younger participants. For both age groups, differences weren’t significant between the B/F/TAF group and those taking DTG/ABC/3TC. Spine density actually increased slightly in older patients taking B/F/TAF, but the difference between this measure and the slight decrease in older patients taking DTG/ABC/3TC was not significant.
Weight increased over time for all groups, ranging from a gain of 3.4 kg at 144 weeks for older patients taking DTG + F/TAF to 5.3 kg for the same regimen in younger patients, but none of the between-group differences were significant.
All fasting lipids rose for each study arm in both older and younger patients. Some of the between-group differences were statistically significant, but “there were no clinically significant differences in median changes from baseline in fasting lipids” among those aged 50 years or older, noted Dr. Mills and associates.
In terms of safety, no study drug-related discontinuations for renal adverse events occurred in either the B/F/TAF or the DTG + F/TAF groups, and the investigators saw no proximal renal tubulopathy.
The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using the Cockroft-Gault equation. All three antiviral regimens were associated with early drops in eGFR, “consistent with inhibition of tubular creatinine secretion via organic cation transporter 2,” noted Dr. Mills and associates.
Other adverse events were rare in all groups in both older and younger patients, without significant differences between therapies.
The study was supported by Gilead Sciences, which also provided support to Dr. Mills. One coauthor is a Gilead employee.
SOURCE: Mills A et al. CROI 2020, Abstract 2886.
FROM CROI 2020
Rheumatologists seek to reassure amid hydroxychloroquine shortage
Physicians and pharmacists are reporting shortages of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine following President Trump’s promotion of the medications as potential COVID-19 treatments, leaving patients with rheumatic diseases wondering how it will impact their access.
The American Medical Association, the American Pharmacists Association, and the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, issued a joint statement that strongly opposed prophylactic prescribing of these medications for COVID-19 or stockpiling them in anticipation of use for COVID-19. The concerns over shortages have also prompted the American College of Rheumatology, American Academy of Dermatology, Arthritis Foundation, and Lupus Foundation of America to send a joint statement to the Trump administration and the nation’s governors highlighting critical hydroxychloroquine access issues and asking policymakers to work together with health care providers and patient communities to ensure continued availability of these drugs.
Now
In a Q and A interview, NYU Langone Health rheumatology division director and Lupus Center director Jill P. Buyon, MD, and associate professor of rheumatology, Peter M. Izmirly, MD, noted that, while shortages have been reported across the United States because of large increases in off-label prescribing, many of the drugs’ manufacturers have committed to donating millions of doses and/or stepping up production to meet demand.
Later in this article, Michael H. Pillinger, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine, biochemistry, and molecular pharmacology at NYU Langone Health, New York, answered questions about a new multicenter study called COLCORONA getting underway to test the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine. The answers in this Q&A have been edited for length and clarity.
Questions about hydroxychloroquine shortage
Q: What is the current situation with hydroxychloroquine in your practice?
A: We have been getting calls from our patients asking about getting refills for hydroxychloroquine. Our group has been calling local pharmacies asking about the availability of hydroxychloroquine, and we are compiling a list of pharmacies in New York with current availabilities to share with patients. We are somewhat limited by our electronic health record system, Epic, which can only send a prescription to one pharmacy, so that has placed some limitations on knowing where it is available. Some pharmacies have not had hydroxychloroquine available, while others have. We have also been encouraging patients to check online and look for mail-order possibilities for 90-day supplies.
Nearly all prescriptions are for generic hydroxychloroquine. Branded hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) is much more expensive, and we can run into obstacles with getting it approved by insurers, too.
Q: What are you telling patients who seek to refill their prescription or call with concerns? Is it feasible for patients to stop hydroxychloroquine or cut their dosage if necessary?
A: If someone’s been on hydroxychloroquine and has benefited from its use there’s no reason to come off it at this time, and given the possibility that it may have an effect on COVID-19, that is all the better. But we want to reassure patients that they can get the drug and that it is not difficult to manufacture.
Given the significantly higher risk of disease flare that was first described in lupus patients who discontinued hydroxychloroquine in the Canadian Hydroxychloroquine Study Group’s 1991 randomized, controlled trial, it is not advisable for patients to stop the drug.
Some patients do split their dosage day-to-day if they are taking less than 400 mg daily, such that someone taking 300 mg daily may take two 200-mg tablets one day and just one 200-mg tablet the next day, and so on. To avoid eye toxicity that can occur after years of taking the drug, hydroxychloroquine is generally prescribed based on weight at 5 mg/kg.
The drug also stays in the body for quite a while [often up to 3 months and even longer], so that is helpful for patients to know.
Given the current situation and the possibility of its effectiveness against COVID-19, it is ironic that we are actually trying to recruit older lupus patients who have had long-term stable disease while on hydroxychloroquine to a trial of stopping the drug to reduce the risk of developing the side effect of retinopathy. We want to see if patients can safely withdraw hydroxychloroquine without flaring, so we hope to not run into enrollment difficulties based on the current situation with COVID-19.
Q: How do you view the balance between having enough hydroxychloroquine for patients with lupus or other rheumatic diseases and its use in COVID-19 patients?
A: We want to reassure patients that hydroxychloroquine will be available, and there is no reason to hoard the drug or to worry excessively about being unable to obtain it. Efforts to increase production by Mylan, Teva, Sanofi, Novartis, and other manufacturers of hydroxychloroquine should really help out.
Q: Are there pharmacy restrictions on prescription amounts?
A: This is not universal at this time, but some institutions are cutting back and offering only 1-month supplies.
Colchicine COVID-19 trial underway
Dr. Pillinger, of NYU Langone Health, explored the COLCORONA study of colchicine as a treatment for people infected with COVID-19 and the worry that shortage concerns may arise for it, too.
Q: What is the general availability of colchicine and its susceptibility to shortage?
A: There are two major manufacturers of colchicine in the United States, Takeda and Hikma, who together manufacture the majority of the drug.
The greatest use of colchicine in the United States is for gout, which affects approximately 4 million Americans, but the drug is not used chronically, so a much smaller number of patients are using colchicine at any one time. Colchicine is also used for other inflammatory conditions, primarily calcium pyrophosphate crystal disease and familial Mediterranean fever (FMF is rare in the United States). Cardiologists also regularly prescribe colchicine in pericarditis for short-term use. Physicians may use it off label for other purposes, too.
Overall, the number of patients using colchicine is much larger than that for the use of hydroxychloroquine, for example, suggesting that the immediate risk of shortage could be lower. However, if individuals started using it off label, or prescribing inappropriately for the COVID-19 indication, the supply would rapidly run short.
Q: What other points are there to consider regarding the use of colchicine to treat COVID-19?
A: There is no evidence – zero – that colchicine has any benefit for COVID-19, not even case reports. There is some rationale that it might be beneficial, but that is exactly why the COLCORONA trial would be logical to try.
The COLCORONA trial is exactly the kind of trial that would be needed for assessing colchicine, and it is big enough and happening quickly enough to get an answer. But if people start to use colchicine off label, we may never know the truth.
While colchicine can be used safely in most people, it can be very problematic and requires an experienced doctor’s supervision. Overdoses can be fatal, and colchicine interacts with many drugs, all of which require dose adjustment and some of which must be stopped in order to use colchicine – it isn’t candy. Some of the other drugs being looked at for COVID-19 in fact may interact with colchicine.
Colchicine must also be dose adjusted for kidney disease, and, in some of the COVID-19 patients, kidney function changes rapidly. So again, its use would require expert supervision even if there were evidence for its utility.
The side effects of colchicine, if mis-dosed, can be very unpleasant, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Even at the apparent right dose, some people will get these side effects, so colchicine has to be something that works to make the risk/benefit ratio worth it.
Some preparations of colchicine are made combined with probenecid, a gout drug. This is even more problematic because probenecid can raise the level of drugs excreted by the kidney and could affect other treatments.
So in sum, what may be a good idea in theory can turn out to be a disastrous idea in practice, and here we have nothing but theory. This is not an agent to use randomly; the studies will be rushed out quickly and hopefully will give us the knowledge to know what to do.
Dr. Izmirly and Dr. Buyon said they have research grants with the National Institutes of Health to study hydroxychloroquine in patients with lupus and in anti–SSA/Ro-positive pregnant women with a previous child with congenital heart block. Dr. Pillinger reports that he has an investigator-initiated grant from Hikma to study colchicine in osteoarthritis.
This article was reformatted on 3/30/2020 for clarity.
Physicians and pharmacists are reporting shortages of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine following President Trump’s promotion of the medications as potential COVID-19 treatments, leaving patients with rheumatic diseases wondering how it will impact their access.
The American Medical Association, the American Pharmacists Association, and the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, issued a joint statement that strongly opposed prophylactic prescribing of these medications for COVID-19 or stockpiling them in anticipation of use for COVID-19. The concerns over shortages have also prompted the American College of Rheumatology, American Academy of Dermatology, Arthritis Foundation, and Lupus Foundation of America to send a joint statement to the Trump administration and the nation’s governors highlighting critical hydroxychloroquine access issues and asking policymakers to work together with health care providers and patient communities to ensure continued availability of these drugs.
Now
In a Q and A interview, NYU Langone Health rheumatology division director and Lupus Center director Jill P. Buyon, MD, and associate professor of rheumatology, Peter M. Izmirly, MD, noted that, while shortages have been reported across the United States because of large increases in off-label prescribing, many of the drugs’ manufacturers have committed to donating millions of doses and/or stepping up production to meet demand.
Later in this article, Michael H. Pillinger, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine, biochemistry, and molecular pharmacology at NYU Langone Health, New York, answered questions about a new multicenter study called COLCORONA getting underway to test the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine. The answers in this Q&A have been edited for length and clarity.
Questions about hydroxychloroquine shortage
Q: What is the current situation with hydroxychloroquine in your practice?
A: We have been getting calls from our patients asking about getting refills for hydroxychloroquine. Our group has been calling local pharmacies asking about the availability of hydroxychloroquine, and we are compiling a list of pharmacies in New York with current availabilities to share with patients. We are somewhat limited by our electronic health record system, Epic, which can only send a prescription to one pharmacy, so that has placed some limitations on knowing where it is available. Some pharmacies have not had hydroxychloroquine available, while others have. We have also been encouraging patients to check online and look for mail-order possibilities for 90-day supplies.
Nearly all prescriptions are for generic hydroxychloroquine. Branded hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) is much more expensive, and we can run into obstacles with getting it approved by insurers, too.
Q: What are you telling patients who seek to refill their prescription or call with concerns? Is it feasible for patients to stop hydroxychloroquine or cut their dosage if necessary?
A: If someone’s been on hydroxychloroquine and has benefited from its use there’s no reason to come off it at this time, and given the possibility that it may have an effect on COVID-19, that is all the better. But we want to reassure patients that they can get the drug and that it is not difficult to manufacture.
Given the significantly higher risk of disease flare that was first described in lupus patients who discontinued hydroxychloroquine in the Canadian Hydroxychloroquine Study Group’s 1991 randomized, controlled trial, it is not advisable for patients to stop the drug.
Some patients do split their dosage day-to-day if they are taking less than 400 mg daily, such that someone taking 300 mg daily may take two 200-mg tablets one day and just one 200-mg tablet the next day, and so on. To avoid eye toxicity that can occur after years of taking the drug, hydroxychloroquine is generally prescribed based on weight at 5 mg/kg.
The drug also stays in the body for quite a while [often up to 3 months and even longer], so that is helpful for patients to know.
Given the current situation and the possibility of its effectiveness against COVID-19, it is ironic that we are actually trying to recruit older lupus patients who have had long-term stable disease while on hydroxychloroquine to a trial of stopping the drug to reduce the risk of developing the side effect of retinopathy. We want to see if patients can safely withdraw hydroxychloroquine without flaring, so we hope to not run into enrollment difficulties based on the current situation with COVID-19.
Q: How do you view the balance between having enough hydroxychloroquine for patients with lupus or other rheumatic diseases and its use in COVID-19 patients?
A: We want to reassure patients that hydroxychloroquine will be available, and there is no reason to hoard the drug or to worry excessively about being unable to obtain it. Efforts to increase production by Mylan, Teva, Sanofi, Novartis, and other manufacturers of hydroxychloroquine should really help out.
Q: Are there pharmacy restrictions on prescription amounts?
A: This is not universal at this time, but some institutions are cutting back and offering only 1-month supplies.
Colchicine COVID-19 trial underway
Dr. Pillinger, of NYU Langone Health, explored the COLCORONA study of colchicine as a treatment for people infected with COVID-19 and the worry that shortage concerns may arise for it, too.
Q: What is the general availability of colchicine and its susceptibility to shortage?
A: There are two major manufacturers of colchicine in the United States, Takeda and Hikma, who together manufacture the majority of the drug.
The greatest use of colchicine in the United States is for gout, which affects approximately 4 million Americans, but the drug is not used chronically, so a much smaller number of patients are using colchicine at any one time. Colchicine is also used for other inflammatory conditions, primarily calcium pyrophosphate crystal disease and familial Mediterranean fever (FMF is rare in the United States). Cardiologists also regularly prescribe colchicine in pericarditis for short-term use. Physicians may use it off label for other purposes, too.
Overall, the number of patients using colchicine is much larger than that for the use of hydroxychloroquine, for example, suggesting that the immediate risk of shortage could be lower. However, if individuals started using it off label, or prescribing inappropriately for the COVID-19 indication, the supply would rapidly run short.
Q: What other points are there to consider regarding the use of colchicine to treat COVID-19?
A: There is no evidence – zero – that colchicine has any benefit for COVID-19, not even case reports. There is some rationale that it might be beneficial, but that is exactly why the COLCORONA trial would be logical to try.
The COLCORONA trial is exactly the kind of trial that would be needed for assessing colchicine, and it is big enough and happening quickly enough to get an answer. But if people start to use colchicine off label, we may never know the truth.
While colchicine can be used safely in most people, it can be very problematic and requires an experienced doctor’s supervision. Overdoses can be fatal, and colchicine interacts with many drugs, all of which require dose adjustment and some of which must be stopped in order to use colchicine – it isn’t candy. Some of the other drugs being looked at for COVID-19 in fact may interact with colchicine.
Colchicine must also be dose adjusted for kidney disease, and, in some of the COVID-19 patients, kidney function changes rapidly. So again, its use would require expert supervision even if there were evidence for its utility.
The side effects of colchicine, if mis-dosed, can be very unpleasant, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Even at the apparent right dose, some people will get these side effects, so colchicine has to be something that works to make the risk/benefit ratio worth it.
Some preparations of colchicine are made combined with probenecid, a gout drug. This is even more problematic because probenecid can raise the level of drugs excreted by the kidney and could affect other treatments.
So in sum, what may be a good idea in theory can turn out to be a disastrous idea in practice, and here we have nothing but theory. This is not an agent to use randomly; the studies will be rushed out quickly and hopefully will give us the knowledge to know what to do.
Dr. Izmirly and Dr. Buyon said they have research grants with the National Institutes of Health to study hydroxychloroquine in patients with lupus and in anti–SSA/Ro-positive pregnant women with a previous child with congenital heart block. Dr. Pillinger reports that he has an investigator-initiated grant from Hikma to study colchicine in osteoarthritis.
This article was reformatted on 3/30/2020 for clarity.
Physicians and pharmacists are reporting shortages of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine following President Trump’s promotion of the medications as potential COVID-19 treatments, leaving patients with rheumatic diseases wondering how it will impact their access.
The American Medical Association, the American Pharmacists Association, and the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, issued a joint statement that strongly opposed prophylactic prescribing of these medications for COVID-19 or stockpiling them in anticipation of use for COVID-19. The concerns over shortages have also prompted the American College of Rheumatology, American Academy of Dermatology, Arthritis Foundation, and Lupus Foundation of America to send a joint statement to the Trump administration and the nation’s governors highlighting critical hydroxychloroquine access issues and asking policymakers to work together with health care providers and patient communities to ensure continued availability of these drugs.
Now
In a Q and A interview, NYU Langone Health rheumatology division director and Lupus Center director Jill P. Buyon, MD, and associate professor of rheumatology, Peter M. Izmirly, MD, noted that, while shortages have been reported across the United States because of large increases in off-label prescribing, many of the drugs’ manufacturers have committed to donating millions of doses and/or stepping up production to meet demand.
Later in this article, Michael H. Pillinger, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine, biochemistry, and molecular pharmacology at NYU Langone Health, New York, answered questions about a new multicenter study called COLCORONA getting underway to test the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine. The answers in this Q&A have been edited for length and clarity.
Questions about hydroxychloroquine shortage
Q: What is the current situation with hydroxychloroquine in your practice?
A: We have been getting calls from our patients asking about getting refills for hydroxychloroquine. Our group has been calling local pharmacies asking about the availability of hydroxychloroquine, and we are compiling a list of pharmacies in New York with current availabilities to share with patients. We are somewhat limited by our electronic health record system, Epic, which can only send a prescription to one pharmacy, so that has placed some limitations on knowing where it is available. Some pharmacies have not had hydroxychloroquine available, while others have. We have also been encouraging patients to check online and look for mail-order possibilities for 90-day supplies.
Nearly all prescriptions are for generic hydroxychloroquine. Branded hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) is much more expensive, and we can run into obstacles with getting it approved by insurers, too.
Q: What are you telling patients who seek to refill their prescription or call with concerns? Is it feasible for patients to stop hydroxychloroquine or cut their dosage if necessary?
A: If someone’s been on hydroxychloroquine and has benefited from its use there’s no reason to come off it at this time, and given the possibility that it may have an effect on COVID-19, that is all the better. But we want to reassure patients that they can get the drug and that it is not difficult to manufacture.
Given the significantly higher risk of disease flare that was first described in lupus patients who discontinued hydroxychloroquine in the Canadian Hydroxychloroquine Study Group’s 1991 randomized, controlled trial, it is not advisable for patients to stop the drug.
Some patients do split their dosage day-to-day if they are taking less than 400 mg daily, such that someone taking 300 mg daily may take two 200-mg tablets one day and just one 200-mg tablet the next day, and so on. To avoid eye toxicity that can occur after years of taking the drug, hydroxychloroquine is generally prescribed based on weight at 5 mg/kg.
The drug also stays in the body for quite a while [often up to 3 months and even longer], so that is helpful for patients to know.
Given the current situation and the possibility of its effectiveness against COVID-19, it is ironic that we are actually trying to recruit older lupus patients who have had long-term stable disease while on hydroxychloroquine to a trial of stopping the drug to reduce the risk of developing the side effect of retinopathy. We want to see if patients can safely withdraw hydroxychloroquine without flaring, so we hope to not run into enrollment difficulties based on the current situation with COVID-19.
Q: How do you view the balance between having enough hydroxychloroquine for patients with lupus or other rheumatic diseases and its use in COVID-19 patients?
A: We want to reassure patients that hydroxychloroquine will be available, and there is no reason to hoard the drug or to worry excessively about being unable to obtain it. Efforts to increase production by Mylan, Teva, Sanofi, Novartis, and other manufacturers of hydroxychloroquine should really help out.
Q: Are there pharmacy restrictions on prescription amounts?
A: This is not universal at this time, but some institutions are cutting back and offering only 1-month supplies.
Colchicine COVID-19 trial underway
Dr. Pillinger, of NYU Langone Health, explored the COLCORONA study of colchicine as a treatment for people infected with COVID-19 and the worry that shortage concerns may arise for it, too.
Q: What is the general availability of colchicine and its susceptibility to shortage?
A: There are two major manufacturers of colchicine in the United States, Takeda and Hikma, who together manufacture the majority of the drug.
The greatest use of colchicine in the United States is for gout, which affects approximately 4 million Americans, but the drug is not used chronically, so a much smaller number of patients are using colchicine at any one time. Colchicine is also used for other inflammatory conditions, primarily calcium pyrophosphate crystal disease and familial Mediterranean fever (FMF is rare in the United States). Cardiologists also regularly prescribe colchicine in pericarditis for short-term use. Physicians may use it off label for other purposes, too.
Overall, the number of patients using colchicine is much larger than that for the use of hydroxychloroquine, for example, suggesting that the immediate risk of shortage could be lower. However, if individuals started using it off label, or prescribing inappropriately for the COVID-19 indication, the supply would rapidly run short.
Q: What other points are there to consider regarding the use of colchicine to treat COVID-19?
A: There is no evidence – zero – that colchicine has any benefit for COVID-19, not even case reports. There is some rationale that it might be beneficial, but that is exactly why the COLCORONA trial would be logical to try.
The COLCORONA trial is exactly the kind of trial that would be needed for assessing colchicine, and it is big enough and happening quickly enough to get an answer. But if people start to use colchicine off label, we may never know the truth.
While colchicine can be used safely in most people, it can be very problematic and requires an experienced doctor’s supervision. Overdoses can be fatal, and colchicine interacts with many drugs, all of which require dose adjustment and some of which must be stopped in order to use colchicine – it isn’t candy. Some of the other drugs being looked at for COVID-19 in fact may interact with colchicine.
Colchicine must also be dose adjusted for kidney disease, and, in some of the COVID-19 patients, kidney function changes rapidly. So again, its use would require expert supervision even if there were evidence for its utility.
The side effects of colchicine, if mis-dosed, can be very unpleasant, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Even at the apparent right dose, some people will get these side effects, so colchicine has to be something that works to make the risk/benefit ratio worth it.
Some preparations of colchicine are made combined with probenecid, a gout drug. This is even more problematic because probenecid can raise the level of drugs excreted by the kidney and could affect other treatments.
So in sum, what may be a good idea in theory can turn out to be a disastrous idea in practice, and here we have nothing but theory. This is not an agent to use randomly; the studies will be rushed out quickly and hopefully will give us the knowledge to know what to do.
Dr. Izmirly and Dr. Buyon said they have research grants with the National Institutes of Health to study hydroxychloroquine in patients with lupus and in anti–SSA/Ro-positive pregnant women with a previous child with congenital heart block. Dr. Pillinger reports that he has an investigator-initiated grant from Hikma to study colchicine in osteoarthritis.
This article was reformatted on 3/30/2020 for clarity.
HIV shortens life expectancy 9 years, healthy life expectancy 16 years
Despite highly effective antiretroviral therapy, HIV still shortens life expectancy by 9 years and healthy life expectancy free of comorbidities 16 years, according to a review of HIV patients and matched controls at Kaiser Permanente facilities in California and the mid-Atlantic states during 2000-2016.
The good news is that starting antiretroviral therapy (ART) when CD4 counts are 500 cells/mm3 or higher closes the mortality gap. People who do so can expect to live into their mid-80s, the same as people without HIV, and the years they can expect to be free of diabetes and cancer is catching up to uninfected people, although the gap for other comorbidities hasn’t changed and the overall comorbidity gap remains 16 years, according to the report, which was presented at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections
“We were excited about finding no difference in lifespan for people starting ART with high CD4 counts, but we were surprised by how wide the gap was for the number of comorbidity free years. Greater attention to comorbidity prevention is needed,” said study lead Julia Marcus, PhD, an infectious disease epidemiologist and assistant professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The team estimated the average number of total and comorbidity-free years of life remaining at age 21 for 39,000 people with HIV who were matched 1:10 with 387,767 uninfected adults by sex, race/ethnicity, year, and medical center.
Overall, adults with HIV could expect to live until they were 77 years old, versus 86 years for people without HIV, during 2014-2016. It’s a large improvement over the 22 year gap during 2000-2003, when the numbers were 59 versus 81 years, respectively, Dr. Marcus reported at the virtual meeting, which was scheduled to be in Boston, but held online this year because of concerns about spreading the COVID-19 virus.
But the overall comorbidity gap didn’t budge during 2000-2016. People with HIV during 2014-2016 could expect to be comorbidity free until age 36 years, versus 52 years for the general population, the same 16-year difference during 2000-2003, when the numbers were age 32 versus age 48 years.
During 2014-2016, liver disease came 24 years sooner with HIV, and chronic kidney disease 17 years, chronic lung disease 16 years, cancer 9 years, and diabetes and cancer both 8 years sooner. Early ART didn’t narrow the gap for most comorbidities. Dr. Marcus didn’t address the reasons for the differences, except to note that “smoking rates were definitely higher among people with HIV.”
The results weren’t broken down by sex, but the majority of subjects, 88%, were men. The mean age was 41 years, and about half were white, with most of the rest either black or Hispanic. Transmission was among men who have sex with men in 70% of the cases, heterosexual sex in 20%, and IV drug accounted for the rest. Almost a third of the subjects started ART with CD4 counts at or above 500 cells/mm3.
Dr. Marcus said the results are likely generalizable to most insured people with HIV, but also that comorbidity screening might be higher in the HIV population, which could have affected the results.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Marcus is an adviser for Gilead.
SOURCE: Marcus JL et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 151.
Despite highly effective antiretroviral therapy, HIV still shortens life expectancy by 9 years and healthy life expectancy free of comorbidities 16 years, according to a review of HIV patients and matched controls at Kaiser Permanente facilities in California and the mid-Atlantic states during 2000-2016.
The good news is that starting antiretroviral therapy (ART) when CD4 counts are 500 cells/mm3 or higher closes the mortality gap. People who do so can expect to live into their mid-80s, the same as people without HIV, and the years they can expect to be free of diabetes and cancer is catching up to uninfected people, although the gap for other comorbidities hasn’t changed and the overall comorbidity gap remains 16 years, according to the report, which was presented at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections
“We were excited about finding no difference in lifespan for people starting ART with high CD4 counts, but we were surprised by how wide the gap was for the number of comorbidity free years. Greater attention to comorbidity prevention is needed,” said study lead Julia Marcus, PhD, an infectious disease epidemiologist and assistant professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The team estimated the average number of total and comorbidity-free years of life remaining at age 21 for 39,000 people with HIV who were matched 1:10 with 387,767 uninfected adults by sex, race/ethnicity, year, and medical center.
Overall, adults with HIV could expect to live until they were 77 years old, versus 86 years for people without HIV, during 2014-2016. It’s a large improvement over the 22 year gap during 2000-2003, when the numbers were 59 versus 81 years, respectively, Dr. Marcus reported at the virtual meeting, which was scheduled to be in Boston, but held online this year because of concerns about spreading the COVID-19 virus.
But the overall comorbidity gap didn’t budge during 2000-2016. People with HIV during 2014-2016 could expect to be comorbidity free until age 36 years, versus 52 years for the general population, the same 16-year difference during 2000-2003, when the numbers were age 32 versus age 48 years.
During 2014-2016, liver disease came 24 years sooner with HIV, and chronic kidney disease 17 years, chronic lung disease 16 years, cancer 9 years, and diabetes and cancer both 8 years sooner. Early ART didn’t narrow the gap for most comorbidities. Dr. Marcus didn’t address the reasons for the differences, except to note that “smoking rates were definitely higher among people with HIV.”
The results weren’t broken down by sex, but the majority of subjects, 88%, were men. The mean age was 41 years, and about half were white, with most of the rest either black or Hispanic. Transmission was among men who have sex with men in 70% of the cases, heterosexual sex in 20%, and IV drug accounted for the rest. Almost a third of the subjects started ART with CD4 counts at or above 500 cells/mm3.
Dr. Marcus said the results are likely generalizable to most insured people with HIV, but also that comorbidity screening might be higher in the HIV population, which could have affected the results.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Marcus is an adviser for Gilead.
SOURCE: Marcus JL et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 151.
Despite highly effective antiretroviral therapy, HIV still shortens life expectancy by 9 years and healthy life expectancy free of comorbidities 16 years, according to a review of HIV patients and matched controls at Kaiser Permanente facilities in California and the mid-Atlantic states during 2000-2016.
The good news is that starting antiretroviral therapy (ART) when CD4 counts are 500 cells/mm3 or higher closes the mortality gap. People who do so can expect to live into their mid-80s, the same as people without HIV, and the years they can expect to be free of diabetes and cancer is catching up to uninfected people, although the gap for other comorbidities hasn’t changed and the overall comorbidity gap remains 16 years, according to the report, which was presented at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections
“We were excited about finding no difference in lifespan for people starting ART with high CD4 counts, but we were surprised by how wide the gap was for the number of comorbidity free years. Greater attention to comorbidity prevention is needed,” said study lead Julia Marcus, PhD, an infectious disease epidemiologist and assistant professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The team estimated the average number of total and comorbidity-free years of life remaining at age 21 for 39,000 people with HIV who were matched 1:10 with 387,767 uninfected adults by sex, race/ethnicity, year, and medical center.
Overall, adults with HIV could expect to live until they were 77 years old, versus 86 years for people without HIV, during 2014-2016. It’s a large improvement over the 22 year gap during 2000-2003, when the numbers were 59 versus 81 years, respectively, Dr. Marcus reported at the virtual meeting, which was scheduled to be in Boston, but held online this year because of concerns about spreading the COVID-19 virus.
But the overall comorbidity gap didn’t budge during 2000-2016. People with HIV during 2014-2016 could expect to be comorbidity free until age 36 years, versus 52 years for the general population, the same 16-year difference during 2000-2003, when the numbers were age 32 versus age 48 years.
During 2014-2016, liver disease came 24 years sooner with HIV, and chronic kidney disease 17 years, chronic lung disease 16 years, cancer 9 years, and diabetes and cancer both 8 years sooner. Early ART didn’t narrow the gap for most comorbidities. Dr. Marcus didn’t address the reasons for the differences, except to note that “smoking rates were definitely higher among people with HIV.”
The results weren’t broken down by sex, but the majority of subjects, 88%, were men. The mean age was 41 years, and about half were white, with most of the rest either black or Hispanic. Transmission was among men who have sex with men in 70% of the cases, heterosexual sex in 20%, and IV drug accounted for the rest. Almost a third of the subjects started ART with CD4 counts at or above 500 cells/mm3.
Dr. Marcus said the results are likely generalizable to most insured people with HIV, but also that comorbidity screening might be higher in the HIV population, which could have affected the results.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Marcus is an adviser for Gilead.
SOURCE: Marcus JL et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 151.
FROM CROI 2020
Physicians pessimistic despite increased COVID-19 test kits
according to a survey.
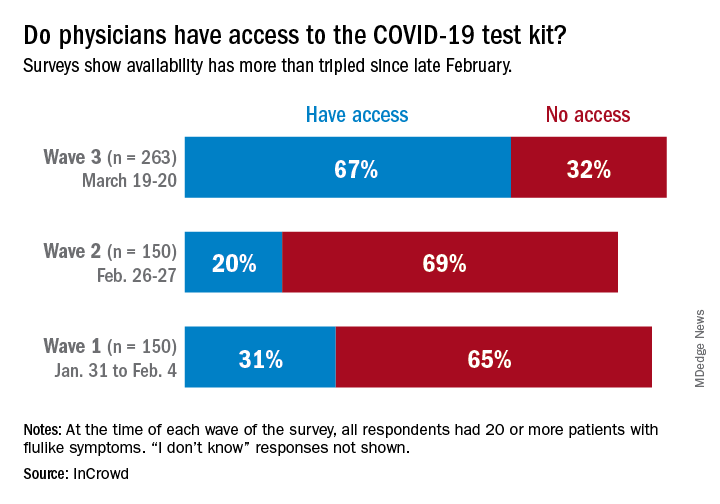
One positive finding from the physicians who participated in this survey March 19-20 was that the availability of COVID-19 test kits has more than doubled since late February.
Reported access to test kits went from 31% in the first wave of a series of surveys (Jan. 31–Feb. 4), down to 20% in the second (Feb. 26-27), and then jumped to 67% by the third wave (March 19-20), InCrowd reported March 26.
Views on several other COVID-related topics were negative among the majority of responding physicians – all of whom had or were currently treating 20 or more patients with flu-like symptoms at the time of the survey.
“Their frustrations and concerns about their ability to protect themselves while meeting upcoming patient care levels has increased significantly in the last 3 months,” Daniel S. Fitzgerald, CEO and president of InCrowd, said in a written statement.
In the third wave, 78% of respondents were “concerned for the safety of loved ones due to my exposure as a physician to COVID-19” and only 16% believed that their facility was “staffed adequately to treat the influx of patients anticipated in the next 30 days,” InCrowd said.
One primary care physician from California elaborated on the issue of safety equipment: “First, [the CDC] said we need N95 masks and other masks would not protect us. As those are running out then they said just use regular surgical masks. Now they are saying use bandannas and scarves! It’s like they don’t care about the safety of the people who will be treating the ill! We don’t want to bring it home to our families!”
“Overall, morale appears low, with few optimistic about the efficacy of public-private collaboration (21%), their own safety given current PPE [personal protective equipment] supply (13%), and the U.S.’s ability to ‘flatten the curve’ (12%),” InCrowd noted in the report.
The first two waves each had 150 respondents, but the number increased to 263 for wave 3, with similar proportions – about 50% emergency medicine or critical care specialists, 25% pediatricians, and 25% primary care physicians – in all three.
according to a survey.

One positive finding from the physicians who participated in this survey March 19-20 was that the availability of COVID-19 test kits has more than doubled since late February.
Reported access to test kits went from 31% in the first wave of a series of surveys (Jan. 31–Feb. 4), down to 20% in the second (Feb. 26-27), and then jumped to 67% by the third wave (March 19-20), InCrowd reported March 26.
Views on several other COVID-related topics were negative among the majority of responding physicians – all of whom had or were currently treating 20 or more patients with flu-like symptoms at the time of the survey.
“Their frustrations and concerns about their ability to protect themselves while meeting upcoming patient care levels has increased significantly in the last 3 months,” Daniel S. Fitzgerald, CEO and president of InCrowd, said in a written statement.
In the third wave, 78% of respondents were “concerned for the safety of loved ones due to my exposure as a physician to COVID-19” and only 16% believed that their facility was “staffed adequately to treat the influx of patients anticipated in the next 30 days,” InCrowd said.
One primary care physician from California elaborated on the issue of safety equipment: “First, [the CDC] said we need N95 masks and other masks would not protect us. As those are running out then they said just use regular surgical masks. Now they are saying use bandannas and scarves! It’s like they don’t care about the safety of the people who will be treating the ill! We don’t want to bring it home to our families!”
“Overall, morale appears low, with few optimistic about the efficacy of public-private collaboration (21%), their own safety given current PPE [personal protective equipment] supply (13%), and the U.S.’s ability to ‘flatten the curve’ (12%),” InCrowd noted in the report.
The first two waves each had 150 respondents, but the number increased to 263 for wave 3, with similar proportions – about 50% emergency medicine or critical care specialists, 25% pediatricians, and 25% primary care physicians – in all three.
according to a survey.

One positive finding from the physicians who participated in this survey March 19-20 was that the availability of COVID-19 test kits has more than doubled since late February.
Reported access to test kits went from 31% in the first wave of a series of surveys (Jan. 31–Feb. 4), down to 20% in the second (Feb. 26-27), and then jumped to 67% by the third wave (March 19-20), InCrowd reported March 26.
Views on several other COVID-related topics were negative among the majority of responding physicians – all of whom had or were currently treating 20 or more patients with flu-like symptoms at the time of the survey.
“Their frustrations and concerns about their ability to protect themselves while meeting upcoming patient care levels has increased significantly in the last 3 months,” Daniel S. Fitzgerald, CEO and president of InCrowd, said in a written statement.
In the third wave, 78% of respondents were “concerned for the safety of loved ones due to my exposure as a physician to COVID-19” and only 16% believed that their facility was “staffed adequately to treat the influx of patients anticipated in the next 30 days,” InCrowd said.
One primary care physician from California elaborated on the issue of safety equipment: “First, [the CDC] said we need N95 masks and other masks would not protect us. As those are running out then they said just use regular surgical masks. Now they are saying use bandannas and scarves! It’s like they don’t care about the safety of the people who will be treating the ill! We don’t want to bring it home to our families!”
“Overall, morale appears low, with few optimistic about the efficacy of public-private collaboration (21%), their own safety given current PPE [personal protective equipment] supply (13%), and the U.S.’s ability to ‘flatten the curve’ (12%),” InCrowd noted in the report.
The first two waves each had 150 respondents, but the number increased to 263 for wave 3, with similar proportions – about 50% emergency medicine or critical care specialists, 25% pediatricians, and 25% primary care physicians – in all three.
Keep calm: Under 25s with diabetes aren't being hospitalized for COVID-19
Reports from pediatric endocrinologists in COVID-19 hot spots globally indicate that children, adolescents, and young adults with diabetes have so far not shown a different disease pattern with the virus compared to children and younger people who do not have diabetes.
Indeed, to date [as of March 24]” according to a new statement from the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD), which currently has about 1,300 members around the globe and has instituted a discussion forum about the topic of treating children with both diabetes and COVID-19.
“We find these reports [from colleagues around the world], though anecdotal, to be reassuring,” it notes. However, there are real worries regarding other potentially dangerous effects. ISPAD has expressed concern, for example, that the COVID-19 pandemic will prevent youngsters with existing diabetes who are having diabetic emergencies from seeking hospital care.
Chinese physicians have reported to ISPAD a number of cases of delayed hospital admissions for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in children with known type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Andrea Scaramuzza, MD, a pediatric endocrinologist at Ospedale Maggiore di Cremona, Italy, has similarly reported multiple cases of patients presenting to emergency services there with severe DKA.
“These experiences reinforce the importance of continued attentiveness to standard diabetes care to avoid the need for hospitalization and emergency or urgent care visits,” says ISPAD, under the strapline: “Keep calm and mind your diabetes care.”
But it nevertheless stresses that these resources should be used “if needed.”
Worries that new-onset diabetes will be missed during COVID-19
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that there also are concerns regarding delays in diagnoses of new cases of type 1 diabetes “due to the fear families have to go to the emergency department because of COVID-19.”
Indeed, in Italy, a few patients have arrived with very serious DKA, he said. Dr. Scaramuzza noted a colleague from Naples, Dario Iafusco, MD, and colleagues have made a video to keep awareness high regarding new-onset diabetes.
“This coronavirus pandemic can be defeated if you stay at home, but if you know of a child who has excessive thirst, frequent urination, or who starts vomiting,” seek health care advice immediately. “This child could have [type 1] diabetes. Prevent severe DKA, or worse, death,” Dr. Iafusco of the Regional Centre of Paediatric Diabetology G.Stoppoloni Via S. Andrea delle Dame, Naples, said in the video.
Physicians from China have similar observations, reporting to ISPAD several cases of delayed admissions of newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Keep calm and mind your diabetes care; physicians use telemedicine
Meanwhile, last week ISPAD issued guidance for young people with diabetes and their carers about what to do if COVID-19 infection is suspected.
Most advice is the same as for the general public because reports of COVID-19 infection suggest it is much less severe in children and adolescents, and the summary currently serves “as reassurance that youth with diabetes are not more affected by COVID-19 than peers,” it adds.
“Our approach to treating a child with diabetes would be to follow the ISPAD sick-day guidelines, which provide generalized diabetes management in any flu-like illness. We wouldn’t do anything very different right now,” one of the authors, Jamie Wood, MD, associate professor of clinical pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
“Any illness makes diabetes more difficult to manage and can increase the risk of DKA,” she emphasized.
“We would reinforce frequent monitoring of blood glucose and ketone levels, to never stop insulin – in fact, when most people are ill, the body is stressed and requires more insulin – and to stay hydrated and treat the underlying symptoms.”
And make sure to “treat the fever,” she stressed. “When patients with type 1 diabetes get fever, they have a tendency to make more ketones, so we recommend aggressive control of fever.”
ISPAD recommends young people aim to keep blood glucose levels between 4 and 10 mmol/L (72-180 mg/dL) and blood ketones below 0.6 mmol/L (10.8 mg/dL) during illness and to never stop insulin.
Guidance is provided on when to seek urgent specialist advice with possible referral to emergency care, for example, in cases in which the patient has DKA symptoms, such as persistent and/or worsened fruity breath odor or vomiting.
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that, in Italy, he and his colleagues have increased their use of telemedicine to keep monitoring their patients with diabetes even from a distance and that it was working very well.
“Technology – such as downloading [records from] insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitoring systems, and the possibility to use Skype or other platforms – really helps,” he noted.
“There has been a rapid increase in telehealth as a way to continue to care for youth with diabetes and decrease risk for infection,” said ISPAD.
“Communication between patients, families, and health care teams is vitally important. Methods to do so that avoid visits to clinics or hospitals can provide needed diabetes advice and reduce risk for COVID-19 transmission.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Reports from pediatric endocrinologists in COVID-19 hot spots globally indicate that children, adolescents, and young adults with diabetes have so far not shown a different disease pattern with the virus compared to children and younger people who do not have diabetes.
Indeed, to date [as of March 24]” according to a new statement from the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD), which currently has about 1,300 members around the globe and has instituted a discussion forum about the topic of treating children with both diabetes and COVID-19.
“We find these reports [from colleagues around the world], though anecdotal, to be reassuring,” it notes. However, there are real worries regarding other potentially dangerous effects. ISPAD has expressed concern, for example, that the COVID-19 pandemic will prevent youngsters with existing diabetes who are having diabetic emergencies from seeking hospital care.
Chinese physicians have reported to ISPAD a number of cases of delayed hospital admissions for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in children with known type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Andrea Scaramuzza, MD, a pediatric endocrinologist at Ospedale Maggiore di Cremona, Italy, has similarly reported multiple cases of patients presenting to emergency services there with severe DKA.
“These experiences reinforce the importance of continued attentiveness to standard diabetes care to avoid the need for hospitalization and emergency or urgent care visits,” says ISPAD, under the strapline: “Keep calm and mind your diabetes care.”
But it nevertheless stresses that these resources should be used “if needed.”
Worries that new-onset diabetes will be missed during COVID-19
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that there also are concerns regarding delays in diagnoses of new cases of type 1 diabetes “due to the fear families have to go to the emergency department because of COVID-19.”
Indeed, in Italy, a few patients have arrived with very serious DKA, he said. Dr. Scaramuzza noted a colleague from Naples, Dario Iafusco, MD, and colleagues have made a video to keep awareness high regarding new-onset diabetes.
“This coronavirus pandemic can be defeated if you stay at home, but if you know of a child who has excessive thirst, frequent urination, or who starts vomiting,” seek health care advice immediately. “This child could have [type 1] diabetes. Prevent severe DKA, or worse, death,” Dr. Iafusco of the Regional Centre of Paediatric Diabetology G.Stoppoloni Via S. Andrea delle Dame, Naples, said in the video.
Physicians from China have similar observations, reporting to ISPAD several cases of delayed admissions of newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Keep calm and mind your diabetes care; physicians use telemedicine
Meanwhile, last week ISPAD issued guidance for young people with diabetes and their carers about what to do if COVID-19 infection is suspected.
Most advice is the same as for the general public because reports of COVID-19 infection suggest it is much less severe in children and adolescents, and the summary currently serves “as reassurance that youth with diabetes are not more affected by COVID-19 than peers,” it adds.
“Our approach to treating a child with diabetes would be to follow the ISPAD sick-day guidelines, which provide generalized diabetes management in any flu-like illness. We wouldn’t do anything very different right now,” one of the authors, Jamie Wood, MD, associate professor of clinical pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
“Any illness makes diabetes more difficult to manage and can increase the risk of DKA,” she emphasized.
“We would reinforce frequent monitoring of blood glucose and ketone levels, to never stop insulin – in fact, when most people are ill, the body is stressed and requires more insulin – and to stay hydrated and treat the underlying symptoms.”
And make sure to “treat the fever,” she stressed. “When patients with type 1 diabetes get fever, they have a tendency to make more ketones, so we recommend aggressive control of fever.”
ISPAD recommends young people aim to keep blood glucose levels between 4 and 10 mmol/L (72-180 mg/dL) and blood ketones below 0.6 mmol/L (10.8 mg/dL) during illness and to never stop insulin.
Guidance is provided on when to seek urgent specialist advice with possible referral to emergency care, for example, in cases in which the patient has DKA symptoms, such as persistent and/or worsened fruity breath odor or vomiting.
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that, in Italy, he and his colleagues have increased their use of telemedicine to keep monitoring their patients with diabetes even from a distance and that it was working very well.
“Technology – such as downloading [records from] insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitoring systems, and the possibility to use Skype or other platforms – really helps,” he noted.
“There has been a rapid increase in telehealth as a way to continue to care for youth with diabetes and decrease risk for infection,” said ISPAD.
“Communication between patients, families, and health care teams is vitally important. Methods to do so that avoid visits to clinics or hospitals can provide needed diabetes advice and reduce risk for COVID-19 transmission.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Reports from pediatric endocrinologists in COVID-19 hot spots globally indicate that children, adolescents, and young adults with diabetes have so far not shown a different disease pattern with the virus compared to children and younger people who do not have diabetes.
Indeed, to date [as of March 24]” according to a new statement from the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD), which currently has about 1,300 members around the globe and has instituted a discussion forum about the topic of treating children with both diabetes and COVID-19.
“We find these reports [from colleagues around the world], though anecdotal, to be reassuring,” it notes. However, there are real worries regarding other potentially dangerous effects. ISPAD has expressed concern, for example, that the COVID-19 pandemic will prevent youngsters with existing diabetes who are having diabetic emergencies from seeking hospital care.
Chinese physicians have reported to ISPAD a number of cases of delayed hospital admissions for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in children with known type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Andrea Scaramuzza, MD, a pediatric endocrinologist at Ospedale Maggiore di Cremona, Italy, has similarly reported multiple cases of patients presenting to emergency services there with severe DKA.
“These experiences reinforce the importance of continued attentiveness to standard diabetes care to avoid the need for hospitalization and emergency or urgent care visits,” says ISPAD, under the strapline: “Keep calm and mind your diabetes care.”
But it nevertheless stresses that these resources should be used “if needed.”
Worries that new-onset diabetes will be missed during COVID-19
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that there also are concerns regarding delays in diagnoses of new cases of type 1 diabetes “due to the fear families have to go to the emergency department because of COVID-19.”
Indeed, in Italy, a few patients have arrived with very serious DKA, he said. Dr. Scaramuzza noted a colleague from Naples, Dario Iafusco, MD, and colleagues have made a video to keep awareness high regarding new-onset diabetes.
“This coronavirus pandemic can be defeated if you stay at home, but if you know of a child who has excessive thirst, frequent urination, or who starts vomiting,” seek health care advice immediately. “This child could have [type 1] diabetes. Prevent severe DKA, or worse, death,” Dr. Iafusco of the Regional Centre of Paediatric Diabetology G.Stoppoloni Via S. Andrea delle Dame, Naples, said in the video.
Physicians from China have similar observations, reporting to ISPAD several cases of delayed admissions of newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Keep calm and mind your diabetes care; physicians use telemedicine
Meanwhile, last week ISPAD issued guidance for young people with diabetes and their carers about what to do if COVID-19 infection is suspected.
Most advice is the same as for the general public because reports of COVID-19 infection suggest it is much less severe in children and adolescents, and the summary currently serves “as reassurance that youth with diabetes are not more affected by COVID-19 than peers,” it adds.
“Our approach to treating a child with diabetes would be to follow the ISPAD sick-day guidelines, which provide generalized diabetes management in any flu-like illness. We wouldn’t do anything very different right now,” one of the authors, Jamie Wood, MD, associate professor of clinical pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
“Any illness makes diabetes more difficult to manage and can increase the risk of DKA,” she emphasized.
“We would reinforce frequent monitoring of blood glucose and ketone levels, to never stop insulin – in fact, when most people are ill, the body is stressed and requires more insulin – and to stay hydrated and treat the underlying symptoms.”
And make sure to “treat the fever,” she stressed. “When patients with type 1 diabetes get fever, they have a tendency to make more ketones, so we recommend aggressive control of fever.”
ISPAD recommends young people aim to keep blood glucose levels between 4 and 10 mmol/L (72-180 mg/dL) and blood ketones below 0.6 mmol/L (10.8 mg/dL) during illness and to never stop insulin.
Guidance is provided on when to seek urgent specialist advice with possible referral to emergency care, for example, in cases in which the patient has DKA symptoms, such as persistent and/or worsened fruity breath odor or vomiting.
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that, in Italy, he and his colleagues have increased their use of telemedicine to keep monitoring their patients with diabetes even from a distance and that it was working very well.
“Technology – such as downloading [records from] insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitoring systems, and the possibility to use Skype or other platforms – really helps,” he noted.
“There has been a rapid increase in telehealth as a way to continue to care for youth with diabetes and decrease risk for infection,” said ISPAD.
“Communication between patients, families, and health care teams is vitally important. Methods to do so that avoid visits to clinics or hospitals can provide needed diabetes advice and reduce risk for COVID-19 transmission.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Less pain with a cancer drug to treat anal HPV, but it’s expensive
At the end of 6 months of low-dose pomalidomide (Pomalyst), more than half of men who have sex with men had partial or complete clearance of long-standing, grade 3 anal lesions from human papillomavirus, irrespective of HIV status; the number increased to almost two-thirds when they were checked at 12 months, according to a 26-subject study said in video presentation of his research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
“Therapy induced durable and continuous clearance of anal HSIL [high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions]. Further study in HPV-associated premalignancy is warranted to follow up this small, single arm study,” said study lead Mark Polizzotto, MD, PhD, head of the therapeutic and vaccine research program at the Kirby Institute in Sydney.
HPV anal lesions, and subsequent HSIL and progression to anal cancer, are prevalent among men who have sex with men. The risk increases with chronic lesions and concomitant HIV infection.
Pomalidomide is potentially a less painful alternative to options such as freezing and laser ablation, and it may have a lower rate of recurrence, but it’s expensive. Copays range upward from $5,000 for a month supply, according to GoodRx. Celgene, the maker of the drug, offers financial assistance.
Pomalidomide is a derivative of thalidomide that’s approved for multiple myeloma and also has shown effect against a viral lesion associated with HIV, Kaposi sarcoma. The drug is a T-cell activator, and since T-cell activation also is key to spontaneous anal HSIL clearance, Dr. Polizzotto and team wanted to take a look to see if it could help, he said.
The men in the study were at high risk for progression to anal cancer. With a median lesion duration of more than 3 years, and at least one case out past 7 years, spontaneous clearance wasn’t in the cards. The lesions were all grade 3 HSIL, which means severe dysplasia, and more than half of the subjects had HPV genotype 16, and the rest had other risky genotypes. Ten subjects also had HIV, which also increases the risk of anal cancer.
Pomalidomide was given in back-to-back cycles for 6 months, each consisting of 2 mg orally for 3 weeks, then 1 week off, along with a thrombolytic, usually aspirin, given the black box warning of blood clots. The dose was half the 5-mg cycle for Kaposi’s.
The overall response rate – complete clearance or a partial clearance of at least a 50% on high-resolution anoscopy – was 50% at 6 months (12/24), including four complete responses (4/15, 27%) in subjects without HIV, as well as four in the HIV group (4/9, 44%).
On follow-up at month 12, “we saw something we did not expect. Strikingly, with no additional therapy in the interim, we saw a deepening of response in a number of subjects.” The overall response rate climbed to 63% (15/24), including 33% complete response in the HIV-free group (5/15) and HIV-positive group (3/9).
Some did lose their response in the interim, however, and the study team is working to figure out if it was do to a recurrence or a new infection.
A general pattern of immune activation on treatment, including increased systemic CD4+ T-cell responses to HPV during therapy, supported the investigator’s hunch of an immunologic mechanism of action, Dr. Polizzotto said.
There were four instances of grade 3 neutropenia over eight treatment cycles, and one possibly related angina attack, but other than that, adverse reactions were generally mild and self-limited, mostly to grade 1 or 2 neutropenia, constipation, fatigue, and rash, with no idiosyncratic reactions in the HIV group or loss of viral suppression, and no discontinuations because of side effects.
The men in the study were aged 40-50 years, with a median age of 54 years; all but one were white. The median lesion involved a quarter of the anal ring, but sometimes more than half.
The work was funded by the Cancer Institute of New South Wales, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Celgene. Dr. Polizzotto disclosed patents with Celgene and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Polizzotto M et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 70
At the end of 6 months of low-dose pomalidomide (Pomalyst), more than half of men who have sex with men had partial or complete clearance of long-standing, grade 3 anal lesions from human papillomavirus, irrespective of HIV status; the number increased to almost two-thirds when they were checked at 12 months, according to a 26-subject study said in video presentation of his research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
“Therapy induced durable and continuous clearance of anal HSIL [high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions]. Further study in HPV-associated premalignancy is warranted to follow up this small, single arm study,” said study lead Mark Polizzotto, MD, PhD, head of the therapeutic and vaccine research program at the Kirby Institute in Sydney.
HPV anal lesions, and subsequent HSIL and progression to anal cancer, are prevalent among men who have sex with men. The risk increases with chronic lesions and concomitant HIV infection.
Pomalidomide is potentially a less painful alternative to options such as freezing and laser ablation, and it may have a lower rate of recurrence, but it’s expensive. Copays range upward from $5,000 for a month supply, according to GoodRx. Celgene, the maker of the drug, offers financial assistance.
Pomalidomide is a derivative of thalidomide that’s approved for multiple myeloma and also has shown effect against a viral lesion associated with HIV, Kaposi sarcoma. The drug is a T-cell activator, and since T-cell activation also is key to spontaneous anal HSIL clearance, Dr. Polizzotto and team wanted to take a look to see if it could help, he said.
The men in the study were at high risk for progression to anal cancer. With a median lesion duration of more than 3 years, and at least one case out past 7 years, spontaneous clearance wasn’t in the cards. The lesions were all grade 3 HSIL, which means severe dysplasia, and more than half of the subjects had HPV genotype 16, and the rest had other risky genotypes. Ten subjects also had HIV, which also increases the risk of anal cancer.
Pomalidomide was given in back-to-back cycles for 6 months, each consisting of 2 mg orally for 3 weeks, then 1 week off, along with a thrombolytic, usually aspirin, given the black box warning of blood clots. The dose was half the 5-mg cycle for Kaposi’s.
The overall response rate – complete clearance or a partial clearance of at least a 50% on high-resolution anoscopy – was 50% at 6 months (12/24), including four complete responses (4/15, 27%) in subjects without HIV, as well as four in the HIV group (4/9, 44%).
On follow-up at month 12, “we saw something we did not expect. Strikingly, with no additional therapy in the interim, we saw a deepening of response in a number of subjects.” The overall response rate climbed to 63% (15/24), including 33% complete response in the HIV-free group (5/15) and HIV-positive group (3/9).
Some did lose their response in the interim, however, and the study team is working to figure out if it was do to a recurrence or a new infection.
A general pattern of immune activation on treatment, including increased systemic CD4+ T-cell responses to HPV during therapy, supported the investigator’s hunch of an immunologic mechanism of action, Dr. Polizzotto said.
There were four instances of grade 3 neutropenia over eight treatment cycles, and one possibly related angina attack, but other than that, adverse reactions were generally mild and self-limited, mostly to grade 1 or 2 neutropenia, constipation, fatigue, and rash, with no idiosyncratic reactions in the HIV group or loss of viral suppression, and no discontinuations because of side effects.
The men in the study were aged 40-50 years, with a median age of 54 years; all but one were white. The median lesion involved a quarter of the anal ring, but sometimes more than half.
The work was funded by the Cancer Institute of New South Wales, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Celgene. Dr. Polizzotto disclosed patents with Celgene and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Polizzotto M et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 70
At the end of 6 months of low-dose pomalidomide (Pomalyst), more than half of men who have sex with men had partial or complete clearance of long-standing, grade 3 anal lesions from human papillomavirus, irrespective of HIV status; the number increased to almost two-thirds when they were checked at 12 months, according to a 26-subject study said in video presentation of his research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
“Therapy induced durable and continuous clearance of anal HSIL [high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions]. Further study in HPV-associated premalignancy is warranted to follow up this small, single arm study,” said study lead Mark Polizzotto, MD, PhD, head of the therapeutic and vaccine research program at the Kirby Institute in Sydney.
HPV anal lesions, and subsequent HSIL and progression to anal cancer, are prevalent among men who have sex with men. The risk increases with chronic lesions and concomitant HIV infection.
Pomalidomide is potentially a less painful alternative to options such as freezing and laser ablation, and it may have a lower rate of recurrence, but it’s expensive. Copays range upward from $5,000 for a month supply, according to GoodRx. Celgene, the maker of the drug, offers financial assistance.
Pomalidomide is a derivative of thalidomide that’s approved for multiple myeloma and also has shown effect against a viral lesion associated with HIV, Kaposi sarcoma. The drug is a T-cell activator, and since T-cell activation also is key to spontaneous anal HSIL clearance, Dr. Polizzotto and team wanted to take a look to see if it could help, he said.
The men in the study were at high risk for progression to anal cancer. With a median lesion duration of more than 3 years, and at least one case out past 7 years, spontaneous clearance wasn’t in the cards. The lesions were all grade 3 HSIL, which means severe dysplasia, and more than half of the subjects had HPV genotype 16, and the rest had other risky genotypes. Ten subjects also had HIV, which also increases the risk of anal cancer.
Pomalidomide was given in back-to-back cycles for 6 months, each consisting of 2 mg orally for 3 weeks, then 1 week off, along with a thrombolytic, usually aspirin, given the black box warning of blood clots. The dose was half the 5-mg cycle for Kaposi’s.
The overall response rate – complete clearance or a partial clearance of at least a 50% on high-resolution anoscopy – was 50% at 6 months (12/24), including four complete responses (4/15, 27%) in subjects without HIV, as well as four in the HIV group (4/9, 44%).
On follow-up at month 12, “we saw something we did not expect. Strikingly, with no additional therapy in the interim, we saw a deepening of response in a number of subjects.” The overall response rate climbed to 63% (15/24), including 33% complete response in the HIV-free group (5/15) and HIV-positive group (3/9).
Some did lose their response in the interim, however, and the study team is working to figure out if it was do to a recurrence or a new infection.
A general pattern of immune activation on treatment, including increased systemic CD4+ T-cell responses to HPV during therapy, supported the investigator’s hunch of an immunologic mechanism of action, Dr. Polizzotto said.
There were four instances of grade 3 neutropenia over eight treatment cycles, and one possibly related angina attack, but other than that, adverse reactions were generally mild and self-limited, mostly to grade 1 or 2 neutropenia, constipation, fatigue, and rash, with no idiosyncratic reactions in the HIV group or loss of viral suppression, and no discontinuations because of side effects.
The men in the study were aged 40-50 years, with a median age of 54 years; all but one were white. The median lesion involved a quarter of the anal ring, but sometimes more than half.
The work was funded by the Cancer Institute of New South Wales, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Celgene. Dr. Polizzotto disclosed patents with Celgene and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Polizzotto M et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 70
FROM CROI 2020
Visceral fat predicts NAFLD fibrosis, progression in HIV
Increased visceral fat predicts both the presence of hepatic fibrosis in HIV patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and also its progression, according to a report at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
Among 58 people with NAFLD and well-controlled HIV, mostly men, a “striking 43% had evidence of fibrosis” on liver biopsy, a quarter with severe stage 3 fibrosis. Visceral fat content on MRI predicted fibrosis (284 cm2 among fibrotic patients vs. 212 cm2 among nonfibrotic patients, P = .005), but body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, subcutaneous fat, and hepatic fat content did not, said investigators led by Lindsay Fourman, MD, an attending physician at the Neuroendocrine & Pituitary Tumor Clinical Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Among 24 subjects with a second liver biopsy a year later, 38% had fibrosis progression, more than half from no fibrosis at baseline. Baseline visceral fat (306 cm2 among progressors versus 212 cm2, P = .04) again predicted progression, after adjustment for baseline BMI, hepatic fat content, and NAFLD activity score.
For every 25 cm2 rise in baseline visceral fat, the team found a 40% increased odds of fibrosis progression (P = .03). Body mass index was stable among subjects, so progression was not related to sudden weight gain. Dr. Fourman noted that people with HIV can have normal BMIs, but still significant accumulation of visceral fat.
The mean rate of progression was 0.2 stages per year. “To put this into perspective, the rate of fibrosis progression among NAFLD in the general population has been quoted to be about 0.03 stages per year.” Among HIV patients, it’s “more than sixfold higher,” she said in a video presentation of her research at the meeting, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting due to concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
Overall, visceral adiposity is “a novel clinical predictor of accelerated” progression in people with HIV. “Therapies to reduce visceral fat may be particularly effective in HIV-associated NAFLD,” she said.
The findings come from a trial of one such therapy, the growth hormone releasing hormone analogue tesamorelin (Egrifta). It’s approved for reduction of excess abdominal fat in HIV patients with lipodystrophy. Dr. Fourman and her colleagues recently reported a more than 30% reduction in liver fat, versus placebo, among HIV patients with NAFLD after a year of treatment, and a lower rate of fibrosis progression at 10.5% versus 37.5% (Lancet HIV. 2019 Dec;6[12]:e821-30).
In their follow-up study reported at the meeting, people with fibrosis at baseline also had higher NAFLD activity scores (3.6 points vs. 2.0 points; P < .0001), as well as higher ALT (41 U/L vs. 23 U/L, P = .002) and AST levels (44 U/L vs. 24 U/L; P = .0003).
Baseline BMI, liver fat content, NAFLD activity score, liver enzymes, waist circumference, CD4 count, and HIV duration, a median of 16 years in the study, did not predict progression, but activity scores, hemoglobin A1C, and C-reactive protein increased as fibrosis progressed.
“We really can’t speak from our own data” if HIV regimens might have had a role in progression. Sixty-two percent of the subjects were on integrase inhibitors, and integrase inhibitors are associated with weight gain, but their effect on visceral weight gain is unclear, plus BMIs were stable. Also, there was no difference in HIV regimens among the more than 100 people screened for the study between those with NAFDL and those without.
The subjects were 54 years old, on average. The average liver fat content at baseline was about 14%, and average baseline BMI just over 30 kg/m2. In addition to the 62% on integrase inhibitors, 40% were on nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, and 24% were on protease inhibitors.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Fourman is a paid consultant to Theratechnologies, maker of tesamorelin.
SOURCE: Fourman LT et al. CROI 2020, Abstract 128
Increased visceral fat predicts both the presence of hepatic fibrosis in HIV patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and also its progression, according to a report at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
Among 58 people with NAFLD and well-controlled HIV, mostly men, a “striking 43% had evidence of fibrosis” on liver biopsy, a quarter with severe stage 3 fibrosis. Visceral fat content on MRI predicted fibrosis (284 cm2 among fibrotic patients vs. 212 cm2 among nonfibrotic patients, P = .005), but body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, subcutaneous fat, and hepatic fat content did not, said investigators led by Lindsay Fourman, MD, an attending physician at the Neuroendocrine & Pituitary Tumor Clinical Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Among 24 subjects with a second liver biopsy a year later, 38% had fibrosis progression, more than half from no fibrosis at baseline. Baseline visceral fat (306 cm2 among progressors versus 212 cm2, P = .04) again predicted progression, after adjustment for baseline BMI, hepatic fat content, and NAFLD activity score.
For every 25 cm2 rise in baseline visceral fat, the team found a 40% increased odds of fibrosis progression (P = .03). Body mass index was stable among subjects, so progression was not related to sudden weight gain. Dr. Fourman noted that people with HIV can have normal BMIs, but still significant accumulation of visceral fat.
The mean rate of progression was 0.2 stages per year. “To put this into perspective, the rate of fibrosis progression among NAFLD in the general population has been quoted to be about 0.03 stages per year.” Among HIV patients, it’s “more than sixfold higher,” she said in a video presentation of her research at the meeting, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting due to concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
Overall, visceral adiposity is “a novel clinical predictor of accelerated” progression in people with HIV. “Therapies to reduce visceral fat may be particularly effective in HIV-associated NAFLD,” she said.
The findings come from a trial of one such therapy, the growth hormone releasing hormone analogue tesamorelin (Egrifta). It’s approved for reduction of excess abdominal fat in HIV patients with lipodystrophy. Dr. Fourman and her colleagues recently reported a more than 30% reduction in liver fat, versus placebo, among HIV patients with NAFLD after a year of treatment, and a lower rate of fibrosis progression at 10.5% versus 37.5% (Lancet HIV. 2019 Dec;6[12]:e821-30).
In their follow-up study reported at the meeting, people with fibrosis at baseline also had higher NAFLD activity scores (3.6 points vs. 2.0 points; P < .0001), as well as higher ALT (41 U/L vs. 23 U/L, P = .002) and AST levels (44 U/L vs. 24 U/L; P = .0003).
Baseline BMI, liver fat content, NAFLD activity score, liver enzymes, waist circumference, CD4 count, and HIV duration, a median of 16 years in the study, did not predict progression, but activity scores, hemoglobin A1C, and C-reactive protein increased as fibrosis progressed.
“We really can’t speak from our own data” if HIV regimens might have had a role in progression. Sixty-two percent of the subjects were on integrase inhibitors, and integrase inhibitors are associated with weight gain, but their effect on visceral weight gain is unclear, plus BMIs were stable. Also, there was no difference in HIV regimens among the more than 100 people screened for the study between those with NAFDL and those without.
The subjects were 54 years old, on average. The average liver fat content at baseline was about 14%, and average baseline BMI just over 30 kg/m2. In addition to the 62% on integrase inhibitors, 40% were on nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, and 24% were on protease inhibitors.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Fourman is a paid consultant to Theratechnologies, maker of tesamorelin.
SOURCE: Fourman LT et al. CROI 2020, Abstract 128
Increased visceral fat predicts both the presence of hepatic fibrosis in HIV patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and also its progression, according to a report at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
Among 58 people with NAFLD and well-controlled HIV, mostly men, a “striking 43% had evidence of fibrosis” on liver biopsy, a quarter with severe stage 3 fibrosis. Visceral fat content on MRI predicted fibrosis (284 cm2 among fibrotic patients vs. 212 cm2 among nonfibrotic patients, P = .005), but body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, subcutaneous fat, and hepatic fat content did not, said investigators led by Lindsay Fourman, MD, an attending physician at the Neuroendocrine & Pituitary Tumor Clinical Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Among 24 subjects with a second liver biopsy a year later, 38% had fibrosis progression, more than half from no fibrosis at baseline. Baseline visceral fat (306 cm2 among progressors versus 212 cm2, P = .04) again predicted progression, after adjustment for baseline BMI, hepatic fat content, and NAFLD activity score.
For every 25 cm2 rise in baseline visceral fat, the team found a 40% increased odds of fibrosis progression (P = .03). Body mass index was stable among subjects, so progression was not related to sudden weight gain. Dr. Fourman noted that people with HIV can have normal BMIs, but still significant accumulation of visceral fat.
The mean rate of progression was 0.2 stages per year. “To put this into perspective, the rate of fibrosis progression among NAFLD in the general population has been quoted to be about 0.03 stages per year.” Among HIV patients, it’s “more than sixfold higher,” she said in a video presentation of her research at the meeting, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting due to concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
Overall, visceral adiposity is “a novel clinical predictor of accelerated” progression in people with HIV. “Therapies to reduce visceral fat may be particularly effective in HIV-associated NAFLD,” she said.
The findings come from a trial of one such therapy, the growth hormone releasing hormone analogue tesamorelin (Egrifta). It’s approved for reduction of excess abdominal fat in HIV patients with lipodystrophy. Dr. Fourman and her colleagues recently reported a more than 30% reduction in liver fat, versus placebo, among HIV patients with NAFLD after a year of treatment, and a lower rate of fibrosis progression at 10.5% versus 37.5% (Lancet HIV. 2019 Dec;6[12]:e821-30).
In their follow-up study reported at the meeting, people with fibrosis at baseline also had higher NAFLD activity scores (3.6 points vs. 2.0 points; P < .0001), as well as higher ALT (41 U/L vs. 23 U/L, P = .002) and AST levels (44 U/L vs. 24 U/L; P = .0003).
Baseline BMI, liver fat content, NAFLD activity score, liver enzymes, waist circumference, CD4 count, and HIV duration, a median of 16 years in the study, did not predict progression, but activity scores, hemoglobin A1C, and C-reactive protein increased as fibrosis progressed.
“We really can’t speak from our own data” if HIV regimens might have had a role in progression. Sixty-two percent of the subjects were on integrase inhibitors, and integrase inhibitors are associated with weight gain, but their effect on visceral weight gain is unclear, plus BMIs were stable. Also, there was no difference in HIV regimens among the more than 100 people screened for the study between those with NAFDL and those without.
The subjects were 54 years old, on average. The average liver fat content at baseline was about 14%, and average baseline BMI just over 30 kg/m2. In addition to the 62% on integrase inhibitors, 40% were on nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, and 24% were on protease inhibitors.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Fourman is a paid consultant to Theratechnologies, maker of tesamorelin.
SOURCE: Fourman LT et al. CROI 2020, Abstract 128
FROM CROI 2020