User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Nilotinib is safe in moderate and advanced Parkinson’s disease
according to investigators. Nevertheless, other drugs that – like nilotinib – inhibit tyrosine kinase (c-Abl) may have a neuroprotective effect, they added. The study was presented online as part of the American Academy of Neurology’s 2020 Science Highlights.
Research using preclinical models of Parkinson’s disease has indicated that nilotinib offers neuroprotection. Tanya Simuni, MD, the Arthur C. Nielsen Jr., Research Professor of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders at Northwestern University in Chicago, and colleagues conducted a prospective study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of oral nilotinib in patients with moderate or advanced Parkinson’s disease. The investigators also sought to examine nilotinib’s symptomatic effect, as measured by the Movement Disorder Society–Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) part III. In addition, Dr. Simuni and colleagues analyzed the drug’s effect on progression of disability, as measured by various other Parkinson’s disease scales. The study’s exploratory outcomes included cognitive function, quality of life, pharmacokinetic profile, and a battery of serum and spinal fluid biomarkers.
The researchers conducted their randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study at 25 sites in the United States. They randomized 76 patients with Parkinson’s disease in approximately equal groups to a daily dose of placebo, 150 mg of nilotinib, or 300 mg of nilotinib. Safety visits occurred monthly. Patient assessments occurred at 3 months and at 6 months, which was the end of the treatment period. Patients presented off study medication at 1 month and 2 months after the end of the treatment period.
Treatment did not change dopamine levels
Baseline demographics and disease characteristics were balanced between groups. Mean age was about 66 years in the placebo group, 61 years in the 150-mg group, and 67 years in the 300-mg group. The proportion of male participants was 64% in the placebo group, 60% in the 150-mg group, and 81% in the 300-mg group. Disease duration was 9 years in the placebo group, approximately 9 years in the 150-mg group, and approximately 12 years in the 300-mg group. Mean MDS-UPDRS total on score was 46 in the placebo group, 47 in the 150-mg group, and 52 in the 300-mg group.
Tolerability was 84% in the placebo group, 76% in the in the 150-mg group, and 77% in the 300-mg group. The sole treatment-related serious adverse event, arrhythmia, occurred in one patient in the 300-mg group. The rate of any adverse event was 88% in the placebo group, 92% in the 150-mg group, and 88% in the 300-mg group. The rate of any serious adverse event was 8% in the placebo group and 4% in each nilotinib group.
From baseline to 1 month, MDS-UPDRS part III on scores decreased by 0.49 points in the placebo group, increased by 2.08 in the 150-mg group, and increased by 4.67 in the 300-mg group. Differences in other secondary measures (e.g., change in MDS-UPDRS part III on scores from baseline to 6 months and change in MDS-UPDRS part III off score from baseline to 6 months) were not statistically significant.
At 3 months, CSF levels of nilotinib were well below the threshold for c-Abl inhibition (approximately 11 ng/mL). The arithmetic mean levels were 0.91 ng/mL in the 150-mg group and 1.69 ng/mL in the 300-mg group. Nilotinib also failed to alter CSF levels of dopamine or its metabolites at 3 months. Dr. Simuni and colleagues did not see significant differences between treatment groups in the exploratory outcomes of cognitive function and quality of life.
“Nilotinib is not an optimal molecule to assess the therapeutic potential of c-Abl inhibition for Parkinson’s disease,” the investigators concluded.
Nilotinib may be an inappropriate candidate
The data “suggest that the hypothesis wasn’t tested, since the CSF and serum concentration of the drug were insufficient for enzyme inhibition,” said Peter LeWitt, MD, Sastry Foundation Endowed Chair in Neurology and professor of neurology at Wayne State University, Detroit. “A higher dose or a more CNS-penetrant drug would be needed for adequate testing of the hypothesis that c-Abl inhibition could provide disease modification.”
Nilotinib might not be an appropriate drug for this investigation, he continued. “There may be better choices among c-Abl inhibitors for penetration into the CNS, such as dasatinib, or for increased potency of effect, such as imatinib.”
Sun Pharma Advanced Research Company is conducting a clinical trial of KO706, another c-Abl inhibitor, added Dr. LeWitt, who is a researcher in that trial and an editorial adviser to Neurology Reviews. “The studies published recently in JAMA Neurology by Pagan et al. claiming target engagement with nilotinib in Parkinson’s disease patients need to be contrasted with the results of the current investigation. Disease modification with c-Abl inhibition continues to be a promising therapeutic avenue, but both positive and negative study results need careful reassessment and validation.”
The Michael J. Fox Foundation, the Cure Parkinson’s Trust, and Van Andel Research Institute funded the study. Novartis provided the study drug and placebo. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Simuni T et al. AAN 2020. Abstract 43617.
according to investigators. Nevertheless, other drugs that – like nilotinib – inhibit tyrosine kinase (c-Abl) may have a neuroprotective effect, they added. The study was presented online as part of the American Academy of Neurology’s 2020 Science Highlights.
Research using preclinical models of Parkinson’s disease has indicated that nilotinib offers neuroprotection. Tanya Simuni, MD, the Arthur C. Nielsen Jr., Research Professor of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders at Northwestern University in Chicago, and colleagues conducted a prospective study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of oral nilotinib in patients with moderate or advanced Parkinson’s disease. The investigators also sought to examine nilotinib’s symptomatic effect, as measured by the Movement Disorder Society–Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) part III. In addition, Dr. Simuni and colleagues analyzed the drug’s effect on progression of disability, as measured by various other Parkinson’s disease scales. The study’s exploratory outcomes included cognitive function, quality of life, pharmacokinetic profile, and a battery of serum and spinal fluid biomarkers.
The researchers conducted their randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study at 25 sites in the United States. They randomized 76 patients with Parkinson’s disease in approximately equal groups to a daily dose of placebo, 150 mg of nilotinib, or 300 mg of nilotinib. Safety visits occurred monthly. Patient assessments occurred at 3 months and at 6 months, which was the end of the treatment period. Patients presented off study medication at 1 month and 2 months after the end of the treatment period.
Treatment did not change dopamine levels
Baseline demographics and disease characteristics were balanced between groups. Mean age was about 66 years in the placebo group, 61 years in the 150-mg group, and 67 years in the 300-mg group. The proportion of male participants was 64% in the placebo group, 60% in the 150-mg group, and 81% in the 300-mg group. Disease duration was 9 years in the placebo group, approximately 9 years in the 150-mg group, and approximately 12 years in the 300-mg group. Mean MDS-UPDRS total on score was 46 in the placebo group, 47 in the 150-mg group, and 52 in the 300-mg group.
Tolerability was 84% in the placebo group, 76% in the in the 150-mg group, and 77% in the 300-mg group. The sole treatment-related serious adverse event, arrhythmia, occurred in one patient in the 300-mg group. The rate of any adverse event was 88% in the placebo group, 92% in the 150-mg group, and 88% in the 300-mg group. The rate of any serious adverse event was 8% in the placebo group and 4% in each nilotinib group.
From baseline to 1 month, MDS-UPDRS part III on scores decreased by 0.49 points in the placebo group, increased by 2.08 in the 150-mg group, and increased by 4.67 in the 300-mg group. Differences in other secondary measures (e.g., change in MDS-UPDRS part III on scores from baseline to 6 months and change in MDS-UPDRS part III off score from baseline to 6 months) were not statistically significant.
At 3 months, CSF levels of nilotinib were well below the threshold for c-Abl inhibition (approximately 11 ng/mL). The arithmetic mean levels were 0.91 ng/mL in the 150-mg group and 1.69 ng/mL in the 300-mg group. Nilotinib also failed to alter CSF levels of dopamine or its metabolites at 3 months. Dr. Simuni and colleagues did not see significant differences between treatment groups in the exploratory outcomes of cognitive function and quality of life.
“Nilotinib is not an optimal molecule to assess the therapeutic potential of c-Abl inhibition for Parkinson’s disease,” the investigators concluded.
Nilotinib may be an inappropriate candidate
The data “suggest that the hypothesis wasn’t tested, since the CSF and serum concentration of the drug were insufficient for enzyme inhibition,” said Peter LeWitt, MD, Sastry Foundation Endowed Chair in Neurology and professor of neurology at Wayne State University, Detroit. “A higher dose or a more CNS-penetrant drug would be needed for adequate testing of the hypothesis that c-Abl inhibition could provide disease modification.”
Nilotinib might not be an appropriate drug for this investigation, he continued. “There may be better choices among c-Abl inhibitors for penetration into the CNS, such as dasatinib, or for increased potency of effect, such as imatinib.”
Sun Pharma Advanced Research Company is conducting a clinical trial of KO706, another c-Abl inhibitor, added Dr. LeWitt, who is a researcher in that trial and an editorial adviser to Neurology Reviews. “The studies published recently in JAMA Neurology by Pagan et al. claiming target engagement with nilotinib in Parkinson’s disease patients need to be contrasted with the results of the current investigation. Disease modification with c-Abl inhibition continues to be a promising therapeutic avenue, but both positive and negative study results need careful reassessment and validation.”
The Michael J. Fox Foundation, the Cure Parkinson’s Trust, and Van Andel Research Institute funded the study. Novartis provided the study drug and placebo. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Simuni T et al. AAN 2020. Abstract 43617.
according to investigators. Nevertheless, other drugs that – like nilotinib – inhibit tyrosine kinase (c-Abl) may have a neuroprotective effect, they added. The study was presented online as part of the American Academy of Neurology’s 2020 Science Highlights.
Research using preclinical models of Parkinson’s disease has indicated that nilotinib offers neuroprotection. Tanya Simuni, MD, the Arthur C. Nielsen Jr., Research Professor of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders at Northwestern University in Chicago, and colleagues conducted a prospective study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of oral nilotinib in patients with moderate or advanced Parkinson’s disease. The investigators also sought to examine nilotinib’s symptomatic effect, as measured by the Movement Disorder Society–Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) part III. In addition, Dr. Simuni and colleagues analyzed the drug’s effect on progression of disability, as measured by various other Parkinson’s disease scales. The study’s exploratory outcomes included cognitive function, quality of life, pharmacokinetic profile, and a battery of serum and spinal fluid biomarkers.
The researchers conducted their randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study at 25 sites in the United States. They randomized 76 patients with Parkinson’s disease in approximately equal groups to a daily dose of placebo, 150 mg of nilotinib, or 300 mg of nilotinib. Safety visits occurred monthly. Patient assessments occurred at 3 months and at 6 months, which was the end of the treatment period. Patients presented off study medication at 1 month and 2 months after the end of the treatment period.
Treatment did not change dopamine levels
Baseline demographics and disease characteristics were balanced between groups. Mean age was about 66 years in the placebo group, 61 years in the 150-mg group, and 67 years in the 300-mg group. The proportion of male participants was 64% in the placebo group, 60% in the 150-mg group, and 81% in the 300-mg group. Disease duration was 9 years in the placebo group, approximately 9 years in the 150-mg group, and approximately 12 years in the 300-mg group. Mean MDS-UPDRS total on score was 46 in the placebo group, 47 in the 150-mg group, and 52 in the 300-mg group.
Tolerability was 84% in the placebo group, 76% in the in the 150-mg group, and 77% in the 300-mg group. The sole treatment-related serious adverse event, arrhythmia, occurred in one patient in the 300-mg group. The rate of any adverse event was 88% in the placebo group, 92% in the 150-mg group, and 88% in the 300-mg group. The rate of any serious adverse event was 8% in the placebo group and 4% in each nilotinib group.
From baseline to 1 month, MDS-UPDRS part III on scores decreased by 0.49 points in the placebo group, increased by 2.08 in the 150-mg group, and increased by 4.67 in the 300-mg group. Differences in other secondary measures (e.g., change in MDS-UPDRS part III on scores from baseline to 6 months and change in MDS-UPDRS part III off score from baseline to 6 months) were not statistically significant.
At 3 months, CSF levels of nilotinib were well below the threshold for c-Abl inhibition (approximately 11 ng/mL). The arithmetic mean levels were 0.91 ng/mL in the 150-mg group and 1.69 ng/mL in the 300-mg group. Nilotinib also failed to alter CSF levels of dopamine or its metabolites at 3 months. Dr. Simuni and colleagues did not see significant differences between treatment groups in the exploratory outcomes of cognitive function and quality of life.
“Nilotinib is not an optimal molecule to assess the therapeutic potential of c-Abl inhibition for Parkinson’s disease,” the investigators concluded.
Nilotinib may be an inappropriate candidate
The data “suggest that the hypothesis wasn’t tested, since the CSF and serum concentration of the drug were insufficient for enzyme inhibition,” said Peter LeWitt, MD, Sastry Foundation Endowed Chair in Neurology and professor of neurology at Wayne State University, Detroit. “A higher dose or a more CNS-penetrant drug would be needed for adequate testing of the hypothesis that c-Abl inhibition could provide disease modification.”
Nilotinib might not be an appropriate drug for this investigation, he continued. “There may be better choices among c-Abl inhibitors for penetration into the CNS, such as dasatinib, or for increased potency of effect, such as imatinib.”
Sun Pharma Advanced Research Company is conducting a clinical trial of KO706, another c-Abl inhibitor, added Dr. LeWitt, who is a researcher in that trial and an editorial adviser to Neurology Reviews. “The studies published recently in JAMA Neurology by Pagan et al. claiming target engagement with nilotinib in Parkinson’s disease patients need to be contrasted with the results of the current investigation. Disease modification with c-Abl inhibition continues to be a promising therapeutic avenue, but both positive and negative study results need careful reassessment and validation.”
The Michael J. Fox Foundation, the Cure Parkinson’s Trust, and Van Andel Research Institute funded the study. Novartis provided the study drug and placebo. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Simuni T et al. AAN 2020. Abstract 43617.
FROM AAN 2020
Ofatumumab shows high elimination of disease activity in MS
, a new study shows.
The drug, which is already approved for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, is currently under review for relapsing MS as a once-per-month self-injected therapy that could offer a convenient alternative to DMTs that require in-office infusion.
The new findings are from a pooled analysis from the phase 3 ASCLEPIOS I/II trials of the use of ofatumumab for patients with relapsing MS. There were 927 patients in the ASCLEPIOS I trial and 955 in the ASCLEPIOS II trial. The trials were conducted in 37 countries and involved patients aged 18-55 years.
The late-breaking research was presented at the virtual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
The studies compared patients who were treated with subcutaneous ofatumumab 20 mg with patients treated with oral teriflunomide 14 mg once daily for up to 30 months. The average duration of follow-up was 18 months.
NEDA-3, commonly used to determine treatment outcomes for patients with relapsing MS, was defined as a composite of having no worsening of disability over a 6-month period (6mCDW), no confirmed MS relapse, no new/enlarging T2 lesions, and no gadolinium-enhancing T1 lesions.
The pooled results showed that the odds of achieving NEDA-3 during the first 12 months were three times greater with ofatumumab than with teriflunomide (47.0% vs. 24.5%; odds ratio [OR], 3.36; P < .001) and were more than eight times greater from months 12 to 24 (87.8% vs. 48.2%; OR, 8.09; P < .001).
In addition, compared with patients who received teriflunomide, a higher proportion of patients who received ofatumumab were free from 6mCDW over 2 years (91.9% vs. 88.9%), as well as from relapses (82.3% vs 69.2%) and lesion activity (54.1% vs. 27.5%).
There was a significantly greater reduction in annualized relapse rate with ofatumumab compared with teriflunomide at all cumulative time intervals, including months 0 to 3 (P = .011), and at all subsequent time intervals from month 0 to 27 (P < .001).
The pooled findings further showed that ofatumumab reduced the mean number of gadolinium-enhancing T1 lesions per scan by 95.9% compared with teriflunomide (P < .001).
“Ofatumumab increased the probability of achieving NEDA-3 and demonstrated superior efficacy vs teriflunomide in patients with relapsing MS,” said the authors, led by Stephen L. Hauser, MD, of the department of neurology, UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, University of California, San Francisco.
Ofatumumab superior in primary, secondary outcomes
As previously reported, subcutaneous ofatumumab also demonstrated superior efficacy over oral teriflunomide in the primary and secondary endpoints in the ASCLEPIOS I/II trials. The annualized relapse rate was reduced by 0.22 in the teriflunomide group, vs 0.11 in the ofatumumab group (50.5% relative reduction; P < .001) in the ASCLEPIOS I trial, and by 0.25 vs. 0.10 (58.5% relative reduction P < .001) in ASCLEPIOS II.
Ofatumumab also reduced the number of gadolinium-enhancing T1 lesions and new or enlarging T2 lesions compared with teriflunomide (all P < .001). It reduced the risk for disability progression by 34.4% over 3 months and by 32.5% over 6 months.
In the studies, the rate of serious infection with ofatumumab was 2.5%, compared with 1.8% with teriflunomide. Rates of malignancies were 0.5% and 0.3%, respectively.
“Ofatumumab demonstrated superior efficacy versus teriflunomide, with an acceptable safety profile, in patients with relapsing MS,” the authors reported.
Adherence rates with self-injection encouraging
An additional analysis from the two trials presented virtually in a separate abstract at the CMSC showed greater adherence to the self-administered regimen.
The analysis shows that in the ASCLEPIOS I study, 86.0% patients who were randomly assigned to receive ofatumumab and 77.7% who received teriflunomide completed the study on the assigned study drug. The proportion of patients who received ofatumumab and who discontinued treatment was 14.0%, versus 21.2% for those in the teriflunomide group. The most common reasons for discontinuation were patient/guardian decision (ofatumumab, 4.9%; teriflunomide, 8.2%), adverse event (ofatumumab, 5.2%; teriflunomide, 5.0%), and physician decision (ofatumumab, 2.2%; teriflunomide, 6.5%).
In the ASCLEPIOS II study, the rates were similar in all measures.
“In ASCLEPIOS trials, compliance with home-administered subcutaneous ofatumumab was high, and fewer patients discontinued ofatumumab as compared to teriflunomide,” the authors concluded.
Comparator drug a weak choice?
In commenting on the research, Stephen Kamin, MD, professor, vice chair, and chief of service, department of neurology, New Jersey Medical School, in Newark, noted that a limitation of the ASCLEPIOS trials is the comparison with teriflunomide.
“The comparator drug, teriflunomide, is one of the least effective DMTs, and one that some clinicians, including myself, don’t use,” he said.
Previously, when asked in an interview about the choice of teriflunomide as the comparator, Dr. Hauser noted that considerable discussion had gone into the decision. “The rationale was that we wanted to have a comparator that would be present not only against focal disease activity but also potentially against progression, and we were also able to blind the study successfully,” he said at the time.
Dr. Kamin said that ofatumumab will nevertheless likely represent a welcome addition to the tool kit of treatment options for MS. “Any new drug is helpful in adding to our choices as a general rule,” he said. “Subcutaneous injection does have increased convenience.”
It is not likely that the drug will be a game changer, he added, although the treatment’s efficacy compared with other drugs remains to be seen. “It all depends upon the relative efficacy of ofatumumab versus ocrelizumab or siponimod,” Dr. Kamin said.
“There has been another subcutaneous monoclonal for MS, daclizumab, although this was withdrawn from the market due to severe adverse effects not related to route of administration,” he added.
Dr. Hauser has relationships with Alector, Annexon, Bionure, Molecular Stethoscope, Symbiotix, and F. Hoffmann-La Roche. Dr. Kamin has received research support from Biogen, Novartis and CMSC.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study shows.
The drug, which is already approved for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, is currently under review for relapsing MS as a once-per-month self-injected therapy that could offer a convenient alternative to DMTs that require in-office infusion.
The new findings are from a pooled analysis from the phase 3 ASCLEPIOS I/II trials of the use of ofatumumab for patients with relapsing MS. There were 927 patients in the ASCLEPIOS I trial and 955 in the ASCLEPIOS II trial. The trials were conducted in 37 countries and involved patients aged 18-55 years.
The late-breaking research was presented at the virtual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
The studies compared patients who were treated with subcutaneous ofatumumab 20 mg with patients treated with oral teriflunomide 14 mg once daily for up to 30 months. The average duration of follow-up was 18 months.
NEDA-3, commonly used to determine treatment outcomes for patients with relapsing MS, was defined as a composite of having no worsening of disability over a 6-month period (6mCDW), no confirmed MS relapse, no new/enlarging T2 lesions, and no gadolinium-enhancing T1 lesions.
The pooled results showed that the odds of achieving NEDA-3 during the first 12 months were three times greater with ofatumumab than with teriflunomide (47.0% vs. 24.5%; odds ratio [OR], 3.36; P < .001) and were more than eight times greater from months 12 to 24 (87.8% vs. 48.2%; OR, 8.09; P < .001).
In addition, compared with patients who received teriflunomide, a higher proportion of patients who received ofatumumab were free from 6mCDW over 2 years (91.9% vs. 88.9%), as well as from relapses (82.3% vs 69.2%) and lesion activity (54.1% vs. 27.5%).
There was a significantly greater reduction in annualized relapse rate with ofatumumab compared with teriflunomide at all cumulative time intervals, including months 0 to 3 (P = .011), and at all subsequent time intervals from month 0 to 27 (P < .001).
The pooled findings further showed that ofatumumab reduced the mean number of gadolinium-enhancing T1 lesions per scan by 95.9% compared with teriflunomide (P < .001).
“Ofatumumab increased the probability of achieving NEDA-3 and demonstrated superior efficacy vs teriflunomide in patients with relapsing MS,” said the authors, led by Stephen L. Hauser, MD, of the department of neurology, UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, University of California, San Francisco.
Ofatumumab superior in primary, secondary outcomes
As previously reported, subcutaneous ofatumumab also demonstrated superior efficacy over oral teriflunomide in the primary and secondary endpoints in the ASCLEPIOS I/II trials. The annualized relapse rate was reduced by 0.22 in the teriflunomide group, vs 0.11 in the ofatumumab group (50.5% relative reduction; P < .001) in the ASCLEPIOS I trial, and by 0.25 vs. 0.10 (58.5% relative reduction P < .001) in ASCLEPIOS II.
Ofatumumab also reduced the number of gadolinium-enhancing T1 lesions and new or enlarging T2 lesions compared with teriflunomide (all P < .001). It reduced the risk for disability progression by 34.4% over 3 months and by 32.5% over 6 months.
In the studies, the rate of serious infection with ofatumumab was 2.5%, compared with 1.8% with teriflunomide. Rates of malignancies were 0.5% and 0.3%, respectively.
“Ofatumumab demonstrated superior efficacy versus teriflunomide, with an acceptable safety profile, in patients with relapsing MS,” the authors reported.
Adherence rates with self-injection encouraging
An additional analysis from the two trials presented virtually in a separate abstract at the CMSC showed greater adherence to the self-administered regimen.
The analysis shows that in the ASCLEPIOS I study, 86.0% patients who were randomly assigned to receive ofatumumab and 77.7% who received teriflunomide completed the study on the assigned study drug. The proportion of patients who received ofatumumab and who discontinued treatment was 14.0%, versus 21.2% for those in the teriflunomide group. The most common reasons for discontinuation were patient/guardian decision (ofatumumab, 4.9%; teriflunomide, 8.2%), adverse event (ofatumumab, 5.2%; teriflunomide, 5.0%), and physician decision (ofatumumab, 2.2%; teriflunomide, 6.5%).
In the ASCLEPIOS II study, the rates were similar in all measures.
“In ASCLEPIOS trials, compliance with home-administered subcutaneous ofatumumab was high, and fewer patients discontinued ofatumumab as compared to teriflunomide,” the authors concluded.
Comparator drug a weak choice?
In commenting on the research, Stephen Kamin, MD, professor, vice chair, and chief of service, department of neurology, New Jersey Medical School, in Newark, noted that a limitation of the ASCLEPIOS trials is the comparison with teriflunomide.
“The comparator drug, teriflunomide, is one of the least effective DMTs, and one that some clinicians, including myself, don’t use,” he said.
Previously, when asked in an interview about the choice of teriflunomide as the comparator, Dr. Hauser noted that considerable discussion had gone into the decision. “The rationale was that we wanted to have a comparator that would be present not only against focal disease activity but also potentially against progression, and we were also able to blind the study successfully,” he said at the time.
Dr. Kamin said that ofatumumab will nevertheless likely represent a welcome addition to the tool kit of treatment options for MS. “Any new drug is helpful in adding to our choices as a general rule,” he said. “Subcutaneous injection does have increased convenience.”
It is not likely that the drug will be a game changer, he added, although the treatment’s efficacy compared with other drugs remains to be seen. “It all depends upon the relative efficacy of ofatumumab versus ocrelizumab or siponimod,” Dr. Kamin said.
“There has been another subcutaneous monoclonal for MS, daclizumab, although this was withdrawn from the market due to severe adverse effects not related to route of administration,” he added.
Dr. Hauser has relationships with Alector, Annexon, Bionure, Molecular Stethoscope, Symbiotix, and F. Hoffmann-La Roche. Dr. Kamin has received research support from Biogen, Novartis and CMSC.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study shows.
The drug, which is already approved for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, is currently under review for relapsing MS as a once-per-month self-injected therapy that could offer a convenient alternative to DMTs that require in-office infusion.
The new findings are from a pooled analysis from the phase 3 ASCLEPIOS I/II trials of the use of ofatumumab for patients with relapsing MS. There were 927 patients in the ASCLEPIOS I trial and 955 in the ASCLEPIOS II trial. The trials were conducted in 37 countries and involved patients aged 18-55 years.
The late-breaking research was presented at the virtual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC).
The studies compared patients who were treated with subcutaneous ofatumumab 20 mg with patients treated with oral teriflunomide 14 mg once daily for up to 30 months. The average duration of follow-up was 18 months.
NEDA-3, commonly used to determine treatment outcomes for patients with relapsing MS, was defined as a composite of having no worsening of disability over a 6-month period (6mCDW), no confirmed MS relapse, no new/enlarging T2 lesions, and no gadolinium-enhancing T1 lesions.
The pooled results showed that the odds of achieving NEDA-3 during the first 12 months were three times greater with ofatumumab than with teriflunomide (47.0% vs. 24.5%; odds ratio [OR], 3.36; P < .001) and were more than eight times greater from months 12 to 24 (87.8% vs. 48.2%; OR, 8.09; P < .001).
In addition, compared with patients who received teriflunomide, a higher proportion of patients who received ofatumumab were free from 6mCDW over 2 years (91.9% vs. 88.9%), as well as from relapses (82.3% vs 69.2%) and lesion activity (54.1% vs. 27.5%).
There was a significantly greater reduction in annualized relapse rate with ofatumumab compared with teriflunomide at all cumulative time intervals, including months 0 to 3 (P = .011), and at all subsequent time intervals from month 0 to 27 (P < .001).
The pooled findings further showed that ofatumumab reduced the mean number of gadolinium-enhancing T1 lesions per scan by 95.9% compared with teriflunomide (P < .001).
“Ofatumumab increased the probability of achieving NEDA-3 and demonstrated superior efficacy vs teriflunomide in patients with relapsing MS,” said the authors, led by Stephen L. Hauser, MD, of the department of neurology, UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, University of California, San Francisco.
Ofatumumab superior in primary, secondary outcomes
As previously reported, subcutaneous ofatumumab also demonstrated superior efficacy over oral teriflunomide in the primary and secondary endpoints in the ASCLEPIOS I/II trials. The annualized relapse rate was reduced by 0.22 in the teriflunomide group, vs 0.11 in the ofatumumab group (50.5% relative reduction; P < .001) in the ASCLEPIOS I trial, and by 0.25 vs. 0.10 (58.5% relative reduction P < .001) in ASCLEPIOS II.
Ofatumumab also reduced the number of gadolinium-enhancing T1 lesions and new or enlarging T2 lesions compared with teriflunomide (all P < .001). It reduced the risk for disability progression by 34.4% over 3 months and by 32.5% over 6 months.
In the studies, the rate of serious infection with ofatumumab was 2.5%, compared with 1.8% with teriflunomide. Rates of malignancies were 0.5% and 0.3%, respectively.
“Ofatumumab demonstrated superior efficacy versus teriflunomide, with an acceptable safety profile, in patients with relapsing MS,” the authors reported.
Adherence rates with self-injection encouraging
An additional analysis from the two trials presented virtually in a separate abstract at the CMSC showed greater adherence to the self-administered regimen.
The analysis shows that in the ASCLEPIOS I study, 86.0% patients who were randomly assigned to receive ofatumumab and 77.7% who received teriflunomide completed the study on the assigned study drug. The proportion of patients who received ofatumumab and who discontinued treatment was 14.0%, versus 21.2% for those in the teriflunomide group. The most common reasons for discontinuation were patient/guardian decision (ofatumumab, 4.9%; teriflunomide, 8.2%), adverse event (ofatumumab, 5.2%; teriflunomide, 5.0%), and physician decision (ofatumumab, 2.2%; teriflunomide, 6.5%).
In the ASCLEPIOS II study, the rates were similar in all measures.
“In ASCLEPIOS trials, compliance with home-administered subcutaneous ofatumumab was high, and fewer patients discontinued ofatumumab as compared to teriflunomide,” the authors concluded.
Comparator drug a weak choice?
In commenting on the research, Stephen Kamin, MD, professor, vice chair, and chief of service, department of neurology, New Jersey Medical School, in Newark, noted that a limitation of the ASCLEPIOS trials is the comparison with teriflunomide.
“The comparator drug, teriflunomide, is one of the least effective DMTs, and one that some clinicians, including myself, don’t use,” he said.
Previously, when asked in an interview about the choice of teriflunomide as the comparator, Dr. Hauser noted that considerable discussion had gone into the decision. “The rationale was that we wanted to have a comparator that would be present not only against focal disease activity but also potentially against progression, and we were also able to blind the study successfully,” he said at the time.
Dr. Kamin said that ofatumumab will nevertheless likely represent a welcome addition to the tool kit of treatment options for MS. “Any new drug is helpful in adding to our choices as a general rule,” he said. “Subcutaneous injection does have increased convenience.”
It is not likely that the drug will be a game changer, he added, although the treatment’s efficacy compared with other drugs remains to be seen. “It all depends upon the relative efficacy of ofatumumab versus ocrelizumab or siponimod,” Dr. Kamin said.
“There has been another subcutaneous monoclonal for MS, daclizumab, although this was withdrawn from the market due to severe adverse effects not related to route of administration,” he added.
Dr. Hauser has relationships with Alector, Annexon, Bionure, Molecular Stethoscope, Symbiotix, and F. Hoffmann-La Roche. Dr. Kamin has received research support from Biogen, Novartis and CMSC.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
From CMSC 2020
COVID-19: Putting distance between projection and reality
When it comes to COVID-19, studies show that social distancing flattened the curve.
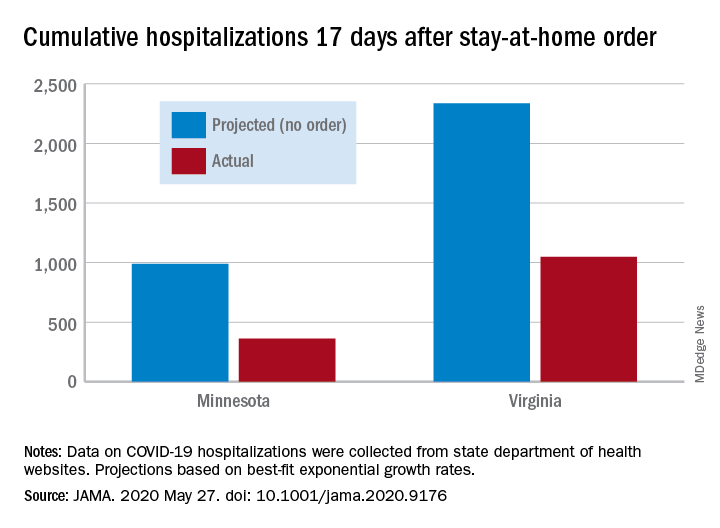
Cumulative hospitalizations in four states with stay-at-home orders were well short of the projected exponential growth curves, Soumya Sen, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and associates reported May 27 in a research letter in JAMA. All states were observed through April 28.
The deviations between observed cases and worst-case projections in the four states – Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia – all began within 8-10 days of the stay-at-home orders. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In Virginia, the corresponding numbers were 1,048 observed and 2,335 projected, they reported.
“Observed hospitalizations consistently fell outside of the 95% prediction bands of the projected exponential growth curve,” Dr. Sen and associates noted.
In a separate Canadian study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention, Ashleigh R. Tuite, PhD, MPH, of the University of Toronto and associates wrote May 27 in a letter in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Their model, based on a 70% reduction in physical contacts for March 19–May 3, projected 2.0 cases per 100,000 population with physical distancing and 37.4 per 100,000 without. Deaths among those ICU patients were projected at 2.5 per 100,000 with distancing and 12.7 per 100,000 without intervention, they reported.
“Our modeling also shows the challenges associated with relaxation of physical distancing measures without a concomitant increase in other public health measures. Specifically, when the number of contacts between persons returns to more than 50% of normal, we expect disease activity to resurge rapidly and ICUs to quickly reach capacity,” they wrote.
The study published in JAMA used publicly available data from the University of Minnesota COVID-19 Hospitalization Project, which is partially funded by the University of Minnesota Office of Academic Clinical Affairs and United Health Foundation.
SOURCES: Sen S et al. JAMA. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9176; Tuite AR et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.7326/M20-2945.
When it comes to COVID-19, studies show that social distancing flattened the curve.

Cumulative hospitalizations in four states with stay-at-home orders were well short of the projected exponential growth curves, Soumya Sen, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and associates reported May 27 in a research letter in JAMA. All states were observed through April 28.
The deviations between observed cases and worst-case projections in the four states – Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia – all began within 8-10 days of the stay-at-home orders. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In Virginia, the corresponding numbers were 1,048 observed and 2,335 projected, they reported.
“Observed hospitalizations consistently fell outside of the 95% prediction bands of the projected exponential growth curve,” Dr. Sen and associates noted.
In a separate Canadian study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention, Ashleigh R. Tuite, PhD, MPH, of the University of Toronto and associates wrote May 27 in a letter in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Their model, based on a 70% reduction in physical contacts for March 19–May 3, projected 2.0 cases per 100,000 population with physical distancing and 37.4 per 100,000 without. Deaths among those ICU patients were projected at 2.5 per 100,000 with distancing and 12.7 per 100,000 without intervention, they reported.
“Our modeling also shows the challenges associated with relaxation of physical distancing measures without a concomitant increase in other public health measures. Specifically, when the number of contacts between persons returns to more than 50% of normal, we expect disease activity to resurge rapidly and ICUs to quickly reach capacity,” they wrote.
The study published in JAMA used publicly available data from the University of Minnesota COVID-19 Hospitalization Project, which is partially funded by the University of Minnesota Office of Academic Clinical Affairs and United Health Foundation.
SOURCES: Sen S et al. JAMA. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9176; Tuite AR et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.7326/M20-2945.
When it comes to COVID-19, studies show that social distancing flattened the curve.

Cumulative hospitalizations in four states with stay-at-home orders were well short of the projected exponential growth curves, Soumya Sen, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and associates reported May 27 in a research letter in JAMA. All states were observed through April 28.
The deviations between observed cases and worst-case projections in the four states – Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia – all began within 8-10 days of the stay-at-home orders. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In Virginia, the corresponding numbers were 1,048 observed and 2,335 projected, they reported.
“Observed hospitalizations consistently fell outside of the 95% prediction bands of the projected exponential growth curve,” Dr. Sen and associates noted.
In a separate Canadian study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention, Ashleigh R. Tuite, PhD, MPH, of the University of Toronto and associates wrote May 27 in a letter in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Their model, based on a 70% reduction in physical contacts for March 19–May 3, projected 2.0 cases per 100,000 population with physical distancing and 37.4 per 100,000 without. Deaths among those ICU patients were projected at 2.5 per 100,000 with distancing and 12.7 per 100,000 without intervention, they reported.
“Our modeling also shows the challenges associated with relaxation of physical distancing measures without a concomitant increase in other public health measures. Specifically, when the number of contacts between persons returns to more than 50% of normal, we expect disease activity to resurge rapidly and ICUs to quickly reach capacity,” they wrote.
The study published in JAMA used publicly available data from the University of Minnesota COVID-19 Hospitalization Project, which is partially funded by the University of Minnesota Office of Academic Clinical Affairs and United Health Foundation.
SOURCES: Sen S et al. JAMA. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9176; Tuite AR et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.7326/M20-2945.
Today’s top news highlights: Coping with addiction during COVID, lung rehab part of recovery
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Long road to recovery includes lung rehab
For seriously ill COVID-19 patients, there may a long recovery period even after leaving the intensive care unit. Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, is one of those patients. For 28 days, he was on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab. “The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University. READ MORE.
Detox unit keeps running during COVID-19
Substance use disorder doesn’t take a break for a pandemic. In fact, the stressors from the current COVID-19 situation have increased substance use. In a commentary published on MDedge, Keji Fagbemi, MD, a hospitalist at the BronxCare Health System, shared how his hospital kept its inpatient detoxification unit running, despite the challenges presented by COVID-19. “At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service,” he wrote. “In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.” READ MORE.
Air pollution linked to MS risk
Air pollution may be another environmental risk factor for developing multiple sclerosis, suggests new research released as part of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020. The findings, which are based on a large cohort study of nearly 550,000 individuals in Italy, appear to confirm the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in prior studies. “Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy. READ MORE.
Trials produce conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease
High-dose aducanumab, a human monoclonal antibody in development for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, significantly reduced clinical decline in people with early disease in one randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. But there was no statistically significant change in outcomes in an identical study. “We believe that the difference between the results was largely due to patients’ greater exposure to the high dose of aducanumab,” said Samantha Budd Haeberlein, PhD, one of the study investigators and senior vice president and head of the neurodegeneration development unit at Biogen, which is developing the drug. READ MORE.
Pregnant patients have asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
The rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16% among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, according to recent study results. “If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” researchers wrote in Obstetrics & Gynecology. READ MORE.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Long road to recovery includes lung rehab
For seriously ill COVID-19 patients, there may a long recovery period even after leaving the intensive care unit. Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, is one of those patients. For 28 days, he was on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab. “The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University. READ MORE.
Detox unit keeps running during COVID-19
Substance use disorder doesn’t take a break for a pandemic. In fact, the stressors from the current COVID-19 situation have increased substance use. In a commentary published on MDedge, Keji Fagbemi, MD, a hospitalist at the BronxCare Health System, shared how his hospital kept its inpatient detoxification unit running, despite the challenges presented by COVID-19. “At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service,” he wrote. “In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.” READ MORE.
Air pollution linked to MS risk
Air pollution may be another environmental risk factor for developing multiple sclerosis, suggests new research released as part of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020. The findings, which are based on a large cohort study of nearly 550,000 individuals in Italy, appear to confirm the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in prior studies. “Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy. READ MORE.
Trials produce conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease
High-dose aducanumab, a human monoclonal antibody in development for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, significantly reduced clinical decline in people with early disease in one randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. But there was no statistically significant change in outcomes in an identical study. “We believe that the difference between the results was largely due to patients’ greater exposure to the high dose of aducanumab,” said Samantha Budd Haeberlein, PhD, one of the study investigators and senior vice president and head of the neurodegeneration development unit at Biogen, which is developing the drug. READ MORE.
Pregnant patients have asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
The rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16% among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, according to recent study results. “If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” researchers wrote in Obstetrics & Gynecology. READ MORE.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Long road to recovery includes lung rehab
For seriously ill COVID-19 patients, there may a long recovery period even after leaving the intensive care unit. Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, is one of those patients. For 28 days, he was on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab. “The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University. READ MORE.
Detox unit keeps running during COVID-19
Substance use disorder doesn’t take a break for a pandemic. In fact, the stressors from the current COVID-19 situation have increased substance use. In a commentary published on MDedge, Keji Fagbemi, MD, a hospitalist at the BronxCare Health System, shared how his hospital kept its inpatient detoxification unit running, despite the challenges presented by COVID-19. “At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service,” he wrote. “In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.” READ MORE.
Air pollution linked to MS risk
Air pollution may be another environmental risk factor for developing multiple sclerosis, suggests new research released as part of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020. The findings, which are based on a large cohort study of nearly 550,000 individuals in Italy, appear to confirm the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in prior studies. “Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy. READ MORE.
Trials produce conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease
High-dose aducanumab, a human monoclonal antibody in development for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, significantly reduced clinical decline in people with early disease in one randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. But there was no statistically significant change in outcomes in an identical study. “We believe that the difference between the results was largely due to patients’ greater exposure to the high dose of aducanumab,” said Samantha Budd Haeberlein, PhD, one of the study investigators and senior vice president and head of the neurodegeneration development unit at Biogen, which is developing the drug. READ MORE.
Pregnant patients have asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
The rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16% among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, according to recent study results. “If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” researchers wrote in Obstetrics & Gynecology. READ MORE.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Natalizumab switch to moderate-efficacy DMT increases disability risk
, new research shows.
“Owing to the vast number of available DMTs, not only understanding DMT performance but answering the question of what can come next if a patient needs to discontinue treatment due to safety or breakthrough disease is important,” said lead author Carrie M. Hersh, DO, of the Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health, Cleveland Clinic, Las Vegas.
The study shows that, “patients transitioning from natalizumab to another high-efficacy therapy have better inflammatory and disability outcomes compared with those who de-escalate their therapy to a moderate-efficacy DMT,” she said.
Natalizumab (Tysabri) offers significant benefits in the treatment of relapsing forms of MS, however, its long-term use is associated with safety concerns, notably an increased risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). Although the risk can be reduced with a switch to a different DMT, the transition can have risks of its own, including a rebound of disease activity that could prove to be worse than the pre-natalizumab treatment period, and there is a lack of consensus on the safest avenues for switching to another DMT following discontinuation of natalizumab.
In research presented at the virtual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers, Dr. Hersh and colleagues explored the issue in a real-world population of 556 patients discontinuing natalizumab at two MS centers. Of these, 270 switched to a moderate DMT (dimethyl fumarate, n = 130; or fingolimod, n = 140) and 130 switched to a highly effective DMT (ocrelizumab, n = 106; rituximab, n = 17; or alemtuzumab, n = 7).
Reasons for switching included a PML risk for 54.9%, breakthrough disease for 15.3%, and adverse effects for 17.3%.
At 24-month follow-up after the switch and after adjustment for propensity score matching, no differences were seen between the moderate and highly effective DMT groups in terms of the annualized relapse rate (ARR; P = 0.33) or the time to first relapse (P = 0.09).
However, significantly higher proportions of patients switching to moderate DMTs showed new T2 lesions (odds ratio, 2.15; P = .01), as well as new gadolinium-enhancing lesions (OR, 1.99; P = .02), and a 20% worsening of the timed 25-foot walk test (T25FW; OR, 1.83; P = .04) and 9-hole peg test (9-HPT; OR, 1.81; P = .04)
Those switching to moderate DMTs also had significantly lower rates of absence of disease activity over the 24 months (OR, 0.41, P = .004), and they had a higher risk of earlier time-to-first gadolinium-enhancing lesion (hazard ratio, 6.67, P = .002), compared with those switching to a high-efficacy DMT.
Other factors that have previously been shown to be associated with rebounds that are worse than pre-natalizumab treatment include washout periods that are longer than 3 months.
The authors noted that there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of mean washout duration, which were relatively short (moderate DMT, 1.4 months; highly effective treatment, 1.8 months; P = .34), In addition, there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of the average duration of natalizumab treatment.
Dr. Hersh speculated that the lack of ARR differences may reflect that the measure is not as objective as the more specific determinants of performance. “One could consider the comparable ARR as a little surprising, but relapse evaluation in a retrospective manner is limited,” she explained.
“Historically, radiographic markers of new inflammation via brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and neuroperformance measures (T25FW and 9-HPT) are more objective compared to assessing clinical relapses, especially in a retrospective cohort where relapses cannot be validated by a central agency or the principal investigator. Therefore, one can surmise that patients transitioning from natalizumab to another high-efficacy DMT fare better than de-escalating treatment to a moderate-efficacy DMT.”
Dr. Hersh and team plan a larger, multicenter study to investigate the short- and long-term effects of post-natalizumab DMT sequencing to help validate the current findings.
Commenting on the research, Stephen Kamin, MD, professor, vice chair and chief of service, department of neurology, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, said the results are consistent with natalizumab’s general profile.
“In general, natalizumab has been used in patients with highly active disease, so I would expect fewer patients with no evidence of disease activity when switched to a moderately active drug rather than a highly active one,” he said in an interview.
Caveats of the findings include the trial’s observational nature, meaning potential confounding factors of baseline characteristics among patients who switched regimens are not known, noted Dr. Kamin, who was not involved with the study.
“Also, the patients were switched to a variety of drugs and even within a class there may be differences in outcome,” he explained.
Dr. Hersh reported consulting or research relationships with Biogen, Genentech, EMD Serono, Genzyme, Novartis, and PCORI. Dr. Kamin has received research support from Biogen, Novartis, and the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
“Owing to the vast number of available DMTs, not only understanding DMT performance but answering the question of what can come next if a patient needs to discontinue treatment due to safety or breakthrough disease is important,” said lead author Carrie M. Hersh, DO, of the Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health, Cleveland Clinic, Las Vegas.
The study shows that, “patients transitioning from natalizumab to another high-efficacy therapy have better inflammatory and disability outcomes compared with those who de-escalate their therapy to a moderate-efficacy DMT,” she said.
Natalizumab (Tysabri) offers significant benefits in the treatment of relapsing forms of MS, however, its long-term use is associated with safety concerns, notably an increased risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). Although the risk can be reduced with a switch to a different DMT, the transition can have risks of its own, including a rebound of disease activity that could prove to be worse than the pre-natalizumab treatment period, and there is a lack of consensus on the safest avenues for switching to another DMT following discontinuation of natalizumab.
In research presented at the virtual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers, Dr. Hersh and colleagues explored the issue in a real-world population of 556 patients discontinuing natalizumab at two MS centers. Of these, 270 switched to a moderate DMT (dimethyl fumarate, n = 130; or fingolimod, n = 140) and 130 switched to a highly effective DMT (ocrelizumab, n = 106; rituximab, n = 17; or alemtuzumab, n = 7).
Reasons for switching included a PML risk for 54.9%, breakthrough disease for 15.3%, and adverse effects for 17.3%.
At 24-month follow-up after the switch and after adjustment for propensity score matching, no differences were seen between the moderate and highly effective DMT groups in terms of the annualized relapse rate (ARR; P = 0.33) or the time to first relapse (P = 0.09).
However, significantly higher proportions of patients switching to moderate DMTs showed new T2 lesions (odds ratio, 2.15; P = .01), as well as new gadolinium-enhancing lesions (OR, 1.99; P = .02), and a 20% worsening of the timed 25-foot walk test (T25FW; OR, 1.83; P = .04) and 9-hole peg test (9-HPT; OR, 1.81; P = .04)
Those switching to moderate DMTs also had significantly lower rates of absence of disease activity over the 24 months (OR, 0.41, P = .004), and they had a higher risk of earlier time-to-first gadolinium-enhancing lesion (hazard ratio, 6.67, P = .002), compared with those switching to a high-efficacy DMT.
Other factors that have previously been shown to be associated with rebounds that are worse than pre-natalizumab treatment include washout periods that are longer than 3 months.
The authors noted that there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of mean washout duration, which were relatively short (moderate DMT, 1.4 months; highly effective treatment, 1.8 months; P = .34), In addition, there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of the average duration of natalizumab treatment.
Dr. Hersh speculated that the lack of ARR differences may reflect that the measure is not as objective as the more specific determinants of performance. “One could consider the comparable ARR as a little surprising, but relapse evaluation in a retrospective manner is limited,” she explained.
“Historically, radiographic markers of new inflammation via brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and neuroperformance measures (T25FW and 9-HPT) are more objective compared to assessing clinical relapses, especially in a retrospective cohort where relapses cannot be validated by a central agency or the principal investigator. Therefore, one can surmise that patients transitioning from natalizumab to another high-efficacy DMT fare better than de-escalating treatment to a moderate-efficacy DMT.”
Dr. Hersh and team plan a larger, multicenter study to investigate the short- and long-term effects of post-natalizumab DMT sequencing to help validate the current findings.
Commenting on the research, Stephen Kamin, MD, professor, vice chair and chief of service, department of neurology, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, said the results are consistent with natalizumab’s general profile.
“In general, natalizumab has been used in patients with highly active disease, so I would expect fewer patients with no evidence of disease activity when switched to a moderately active drug rather than a highly active one,” he said in an interview.
Caveats of the findings include the trial’s observational nature, meaning potential confounding factors of baseline characteristics among patients who switched regimens are not known, noted Dr. Kamin, who was not involved with the study.
“Also, the patients were switched to a variety of drugs and even within a class there may be differences in outcome,” he explained.
Dr. Hersh reported consulting or research relationships with Biogen, Genentech, EMD Serono, Genzyme, Novartis, and PCORI. Dr. Kamin has received research support from Biogen, Novartis, and the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
“Owing to the vast number of available DMTs, not only understanding DMT performance but answering the question of what can come next if a patient needs to discontinue treatment due to safety or breakthrough disease is important,” said lead author Carrie M. Hersh, DO, of the Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health, Cleveland Clinic, Las Vegas.
The study shows that, “patients transitioning from natalizumab to another high-efficacy therapy have better inflammatory and disability outcomes compared with those who de-escalate their therapy to a moderate-efficacy DMT,” she said.
Natalizumab (Tysabri) offers significant benefits in the treatment of relapsing forms of MS, however, its long-term use is associated with safety concerns, notably an increased risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). Although the risk can be reduced with a switch to a different DMT, the transition can have risks of its own, including a rebound of disease activity that could prove to be worse than the pre-natalizumab treatment period, and there is a lack of consensus on the safest avenues for switching to another DMT following discontinuation of natalizumab.
In research presented at the virtual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers, Dr. Hersh and colleagues explored the issue in a real-world population of 556 patients discontinuing natalizumab at two MS centers. Of these, 270 switched to a moderate DMT (dimethyl fumarate, n = 130; or fingolimod, n = 140) and 130 switched to a highly effective DMT (ocrelizumab, n = 106; rituximab, n = 17; or alemtuzumab, n = 7).
Reasons for switching included a PML risk for 54.9%, breakthrough disease for 15.3%, and adverse effects for 17.3%.
At 24-month follow-up after the switch and after adjustment for propensity score matching, no differences were seen between the moderate and highly effective DMT groups in terms of the annualized relapse rate (ARR; P = 0.33) or the time to first relapse (P = 0.09).
However, significantly higher proportions of patients switching to moderate DMTs showed new T2 lesions (odds ratio, 2.15; P = .01), as well as new gadolinium-enhancing lesions (OR, 1.99; P = .02), and a 20% worsening of the timed 25-foot walk test (T25FW; OR, 1.83; P = .04) and 9-hole peg test (9-HPT; OR, 1.81; P = .04)
Those switching to moderate DMTs also had significantly lower rates of absence of disease activity over the 24 months (OR, 0.41, P = .004), and they had a higher risk of earlier time-to-first gadolinium-enhancing lesion (hazard ratio, 6.67, P = .002), compared with those switching to a high-efficacy DMT.
Other factors that have previously been shown to be associated with rebounds that are worse than pre-natalizumab treatment include washout periods that are longer than 3 months.
The authors noted that there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of mean washout duration, which were relatively short (moderate DMT, 1.4 months; highly effective treatment, 1.8 months; P = .34), In addition, there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of the average duration of natalizumab treatment.
Dr. Hersh speculated that the lack of ARR differences may reflect that the measure is not as objective as the more specific determinants of performance. “One could consider the comparable ARR as a little surprising, but relapse evaluation in a retrospective manner is limited,” she explained.
“Historically, radiographic markers of new inflammation via brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and neuroperformance measures (T25FW and 9-HPT) are more objective compared to assessing clinical relapses, especially in a retrospective cohort where relapses cannot be validated by a central agency or the principal investigator. Therefore, one can surmise that patients transitioning from natalizumab to another high-efficacy DMT fare better than de-escalating treatment to a moderate-efficacy DMT.”
Dr. Hersh and team plan a larger, multicenter study to investigate the short- and long-term effects of post-natalizumab DMT sequencing to help validate the current findings.
Commenting on the research, Stephen Kamin, MD, professor, vice chair and chief of service, department of neurology, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, said the results are consistent with natalizumab’s general profile.
“In general, natalizumab has been used in patients with highly active disease, so I would expect fewer patients with no evidence of disease activity when switched to a moderately active drug rather than a highly active one,” he said in an interview.
Caveats of the findings include the trial’s observational nature, meaning potential confounding factors of baseline characteristics among patients who switched regimens are not known, noted Dr. Kamin, who was not involved with the study.
“Also, the patients were switched to a variety of drugs and even within a class there may be differences in outcome,” he explained.
Dr. Hersh reported consulting or research relationships with Biogen, Genentech, EMD Serono, Genzyme, Novartis, and PCORI. Dr. Kamin has received research support from Biogen, Novartis, and the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
High levels of air pollution linked to increased MS risk
, new research suggests. A large cohort study of almost 550,000 individuals living in Italy showed that participants living in areas with high levels of pollutants had a significantly greater risk of developing MS than those who lived in areas with low levels of pollutants.
The findings further confirm a relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in previous research, said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy.
“Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” Dr. Bergamaschi said.
The findings were presented at the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020, which transitioned to a virtual/online meeting because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Toxic pollutants
Several environmental factors may trigger an abnormal immune response that manifests in MS. The most studied of these are low vitamin D level, cigarette smoking, and an unhealthy diet, Dr. Bergamaschi said. However, “other environmental factors deserve to be studied—pollution included,” he added.
Among the most toxic air pollutants are particulate matter (PM), which is a mixture of fine solid and liquid particles suspended in the earth’s atmosphere. PM may range from 2.5 microns (PM2.5) to 10 microns (PM10) in diameter.
The main sources of such pollutants are household and commercial heating (53%) and industrial activities (17%), followed by road vehicle and non–road vehicle use, agriculture, and electricity production.
The World Health Organization estimates that more than 3.2 million individuals worldwide die prematurely every year because of lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, and other diseases related to air pollutants, said Dr. Bergamaschi.
Epidemiologic research has uncovered a relationship between air pollution and MS. A large American study published in 2008 in Science of the Total Environment showed a significant association between MS prevalence and PM10 levels (P < 0.001). Other studies have shown an increase in the number of clinical relapses of MS that were linked to air pollution.
The current investigators assessed the association between PM2.5 levels and MS prevalence in the northern province of Pavia, which has a population of 547,251 individuals in 188 municipalities.
Peculiar features
Pavia is situated in a flat territory that encompasses the highly industrialized regions of Piedmont, Lombardy, Emilia-Romagna, and Veneto. It has a high level of anthropogenic emissions, or environmental pollutants, originating from human activity, Dr. Bergamaschi reported. The region also has “peculiar” geographical features that “favor the accumulation of pollutants,” such as the natural barrier of the Alps in the north and low wind speed, he said.
The researchers identified 927 individuals with MS (315 male and 612 female) in the province. The overall MS prevalence rate was 169.4 per 100,000 population (95% confidence interval [CI], 158.8 – 180.6), which is 10-fold higher than 50 years ago, Dr. Bergamaschi said. In addition, this MS prevalence is higher than that in the United States, which is about 150 per 100,000 population.
Using sophisticated Bayesian disease mapping, the investigators looked for clusters of MS. They also gathered emission data for PM2.5 from 2010 to 2017 from the European Monitoring and Evaluation Programme database. They then divided the region on the basis of average winter concentrations of PM2.5.
Three distinct lateral areas of air pollution were identified. The more northern region, which includes the large urban center of Milan, had the highest level of air pollution. Concentrations decreased the further south the investigators looked.
After adjusting for age, urbanization (population density), and deprivation index, results showed that living in areas with high levels of pollutants was associated with increased MS risk. When controlling for PM2.5 pollution, participants in urban areas had an increased risk for MS compared with rural dwellers (relative risk [RR], 1.16; 95% CI, 1.04 – 1.30; P = 0.003)
Dr. Bergamaschi said it is unclear whether this risk is higher for certain types of MS. “To my knowledge, no study has analyzed possible relationships between MS phenotypes and air pollution,” he noted.
Vitamin D’s role?
Several mechanisms might help explain the relationship between air pollution and MS risk, he added. These include oxidative stress, which results in cell damage, inflammation, and proinflammatory cytokine release. Vitamin D also likely plays some role, Dr. Bergamaschi said. Upon penetrating the lower strata of the earth’s atmosphere, ultraviolet B radiation is absorbed and scattered by suspended pollutants.
Several studies have highlighted the correlation between living in a polluted area and vitamin D hypovitaminosis; “so air pollution can contribute to increasing the risk of MS by reducing vitamin D synthesis,” he said.
Recent research has also shown that air pollution is associated with a higher risk for other autoimmune disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and type 1 diabetes mellitus.
However, pollution alone is only part of the picture. MS prevalence in highly populated and polluted countries such as China and India is low, with no more than 30 to 40 cases per 100,000 population, Dr. Bergamaschi noted. “This discrepancy is explained by different genetic backgrounds. While Caucasians are particularly susceptible to MS, Asians are not,” he said.
Study limitations cited included a possible bias because the analysis did not include other possible contributing risk factors, particularly other pollutants, Dr. Bergamaschi said.
Commenting on the research, Lily Jung Henson, MD, chief of neurology at Piedmont Healthcare in Stockbridge, Georgia, said the findings provide “a fascinating glimpse” into possible causative factors for MS and warrant further investigation.
“This research also suggests other opportunities to look at, such as progression of the degree of air pollution and the incidence of MS over time,” said Dr. Henson, who was not involved with the study.
Drs. Bergamaschi and Dr. Henson have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests. A large cohort study of almost 550,000 individuals living in Italy showed that participants living in areas with high levels of pollutants had a significantly greater risk of developing MS than those who lived in areas with low levels of pollutants.
The findings further confirm a relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in previous research, said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy.
“Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” Dr. Bergamaschi said.
The findings were presented at the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020, which transitioned to a virtual/online meeting because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Toxic pollutants
Several environmental factors may trigger an abnormal immune response that manifests in MS. The most studied of these are low vitamin D level, cigarette smoking, and an unhealthy diet, Dr. Bergamaschi said. However, “other environmental factors deserve to be studied—pollution included,” he added.
Among the most toxic air pollutants are particulate matter (PM), which is a mixture of fine solid and liquid particles suspended in the earth’s atmosphere. PM may range from 2.5 microns (PM2.5) to 10 microns (PM10) in diameter.
The main sources of such pollutants are household and commercial heating (53%) and industrial activities (17%), followed by road vehicle and non–road vehicle use, agriculture, and electricity production.
The World Health Organization estimates that more than 3.2 million individuals worldwide die prematurely every year because of lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, and other diseases related to air pollutants, said Dr. Bergamaschi.
Epidemiologic research has uncovered a relationship between air pollution and MS. A large American study published in 2008 in Science of the Total Environment showed a significant association between MS prevalence and PM10 levels (P < 0.001). Other studies have shown an increase in the number of clinical relapses of MS that were linked to air pollution.
The current investigators assessed the association between PM2.5 levels and MS prevalence in the northern province of Pavia, which has a population of 547,251 individuals in 188 municipalities.
Peculiar features
Pavia is situated in a flat territory that encompasses the highly industrialized regions of Piedmont, Lombardy, Emilia-Romagna, and Veneto. It has a high level of anthropogenic emissions, or environmental pollutants, originating from human activity, Dr. Bergamaschi reported. The region also has “peculiar” geographical features that “favor the accumulation of pollutants,” such as the natural barrier of the Alps in the north and low wind speed, he said.
The researchers identified 927 individuals with MS (315 male and 612 female) in the province. The overall MS prevalence rate was 169.4 per 100,000 population (95% confidence interval [CI], 158.8 – 180.6), which is 10-fold higher than 50 years ago, Dr. Bergamaschi said. In addition, this MS prevalence is higher than that in the United States, which is about 150 per 100,000 population.
Using sophisticated Bayesian disease mapping, the investigators looked for clusters of MS. They also gathered emission data for PM2.5 from 2010 to 2017 from the European Monitoring and Evaluation Programme database. They then divided the region on the basis of average winter concentrations of PM2.5.
Three distinct lateral areas of air pollution were identified. The more northern region, which includes the large urban center of Milan, had the highest level of air pollution. Concentrations decreased the further south the investigators looked.
After adjusting for age, urbanization (population density), and deprivation index, results showed that living in areas with high levels of pollutants was associated with increased MS risk. When controlling for PM2.5 pollution, participants in urban areas had an increased risk for MS compared with rural dwellers (relative risk [RR], 1.16; 95% CI, 1.04 – 1.30; P = 0.003)
Dr. Bergamaschi said it is unclear whether this risk is higher for certain types of MS. “To my knowledge, no study has analyzed possible relationships between MS phenotypes and air pollution,” he noted.
Vitamin D’s role?
Several mechanisms might help explain the relationship between air pollution and MS risk, he added. These include oxidative stress, which results in cell damage, inflammation, and proinflammatory cytokine release. Vitamin D also likely plays some role, Dr. Bergamaschi said. Upon penetrating the lower strata of the earth’s atmosphere, ultraviolet B radiation is absorbed and scattered by suspended pollutants.
Several studies have highlighted the correlation between living in a polluted area and vitamin D hypovitaminosis; “so air pollution can contribute to increasing the risk of MS by reducing vitamin D synthesis,” he said.
Recent research has also shown that air pollution is associated with a higher risk for other autoimmune disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and type 1 diabetes mellitus.
However, pollution alone is only part of the picture. MS prevalence in highly populated and polluted countries such as China and India is low, with no more than 30 to 40 cases per 100,000 population, Dr. Bergamaschi noted. “This discrepancy is explained by different genetic backgrounds. While Caucasians are particularly susceptible to MS, Asians are not,” he said.
Study limitations cited included a possible bias because the analysis did not include other possible contributing risk factors, particularly other pollutants, Dr. Bergamaschi said.
Commenting on the research, Lily Jung Henson, MD, chief of neurology at Piedmont Healthcare in Stockbridge, Georgia, said the findings provide “a fascinating glimpse” into possible causative factors for MS and warrant further investigation.
“This research also suggests other opportunities to look at, such as progression of the degree of air pollution and the incidence of MS over time,” said Dr. Henson, who was not involved with the study.
Drs. Bergamaschi and Dr. Henson have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests. A large cohort study of almost 550,000 individuals living in Italy showed that participants living in areas with high levels of pollutants had a significantly greater risk of developing MS than those who lived in areas with low levels of pollutants.
The findings further confirm a relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in previous research, said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy.
“Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” Dr. Bergamaschi said.
The findings were presented at the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020, which transitioned to a virtual/online meeting because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Toxic pollutants
Several environmental factors may trigger an abnormal immune response that manifests in MS. The most studied of these are low vitamin D level, cigarette smoking, and an unhealthy diet, Dr. Bergamaschi said. However, “other environmental factors deserve to be studied—pollution included,” he added.
Among the most toxic air pollutants are particulate matter (PM), which is a mixture of fine solid and liquid particles suspended in the earth’s atmosphere. PM may range from 2.5 microns (PM2.5) to 10 microns (PM10) in diameter.
The main sources of such pollutants are household and commercial heating (53%) and industrial activities (17%), followed by road vehicle and non–road vehicle use, agriculture, and electricity production.
The World Health Organization estimates that more than 3.2 million individuals worldwide die prematurely every year because of lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, and other diseases related to air pollutants, said Dr. Bergamaschi.
Epidemiologic research has uncovered a relationship between air pollution and MS. A large American study published in 2008 in Science of the Total Environment showed a significant association between MS prevalence and PM10 levels (P < 0.001). Other studies have shown an increase in the number of clinical relapses of MS that were linked to air pollution.
The current investigators assessed the association between PM2.5 levels and MS prevalence in the northern province of Pavia, which has a population of 547,251 individuals in 188 municipalities.
Peculiar features
Pavia is situated in a flat territory that encompasses the highly industrialized regions of Piedmont, Lombardy, Emilia-Romagna, and Veneto. It has a high level of anthropogenic emissions, or environmental pollutants, originating from human activity, Dr. Bergamaschi reported. The region also has “peculiar” geographical features that “favor the accumulation of pollutants,” such as the natural barrier of the Alps in the north and low wind speed, he said.
The researchers identified 927 individuals with MS (315 male and 612 female) in the province. The overall MS prevalence rate was 169.4 per 100,000 population (95% confidence interval [CI], 158.8 – 180.6), which is 10-fold higher than 50 years ago, Dr. Bergamaschi said. In addition, this MS prevalence is higher than that in the United States, which is about 150 per 100,000 population.
Using sophisticated Bayesian disease mapping, the investigators looked for clusters of MS. They also gathered emission data for PM2.5 from 2010 to 2017 from the European Monitoring and Evaluation Programme database. They then divided the region on the basis of average winter concentrations of PM2.5.
Three distinct lateral areas of air pollution were identified. The more northern region, which includes the large urban center of Milan, had the highest level of air pollution. Concentrations decreased the further south the investigators looked.
After adjusting for age, urbanization (population density), and deprivation index, results showed that living in areas with high levels of pollutants was associated with increased MS risk. When controlling for PM2.5 pollution, participants in urban areas had an increased risk for MS compared with rural dwellers (relative risk [RR], 1.16; 95% CI, 1.04 – 1.30; P = 0.003)
Dr. Bergamaschi said it is unclear whether this risk is higher for certain types of MS. “To my knowledge, no study has analyzed possible relationships between MS phenotypes and air pollution,” he noted.
Vitamin D’s role?
Several mechanisms might help explain the relationship between air pollution and MS risk, he added. These include oxidative stress, which results in cell damage, inflammation, and proinflammatory cytokine release. Vitamin D also likely plays some role, Dr. Bergamaschi said. Upon penetrating the lower strata of the earth’s atmosphere, ultraviolet B radiation is absorbed and scattered by suspended pollutants.
Several studies have highlighted the correlation between living in a polluted area and vitamin D hypovitaminosis; “so air pollution can contribute to increasing the risk of MS by reducing vitamin D synthesis,” he said.
Recent research has also shown that air pollution is associated with a higher risk for other autoimmune disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and type 1 diabetes mellitus.
However, pollution alone is only part of the picture. MS prevalence in highly populated and polluted countries such as China and India is low, with no more than 30 to 40 cases per 100,000 population, Dr. Bergamaschi noted. “This discrepancy is explained by different genetic backgrounds. While Caucasians are particularly susceptible to MS, Asians are not,” he said.
Study limitations cited included a possible bias because the analysis did not include other possible contributing risk factors, particularly other pollutants, Dr. Bergamaschi said.
Commenting on the research, Lily Jung Henson, MD, chief of neurology at Piedmont Healthcare in Stockbridge, Georgia, said the findings provide “a fascinating glimpse” into possible causative factors for MS and warrant further investigation.
“This research also suggests other opportunities to look at, such as progression of the degree of air pollution and the incidence of MS over time,” said Dr. Henson, who was not involved with the study.
Drs. Bergamaschi and Dr. Henson have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EAN 2020
New York City inpatient detox unit keeps running: Here’s how
Substance use disorder and its daily consequences take no breaks even during a pandemic. The stressors created by COVID-19, including deaths of loved ones and the disruptions to normal life from policies aimed at flattening the curve, seem to have increased substance use.
I practice as a hospitalist with an internal medicine background and specialty in addiction medicine at BronxCare Health System’s inpatient detoxification unit, a 24/7, 20-bed medically-supervised unit in South Bronx in New York City. It is one of the comprehensive services provided by the BronxCare’s life recovery center and addiction services, which also includes an outpatient clinic, opioid treatment program, inpatient rehab, and a half-way house. Inpatient detoxification units like ours are designed to treat serious addictions and chemical dependency and prevent and treat life-threatening withdrawal symptoms and signs or complications. Our patients come from all over the city and its adjoining suburbs, including from emergency room referrals, referral clinics, courts and the justice system, walk-ins, and self-referrals.
At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service. In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.
Individuals with substance use disorder have historically been a vulnerable and underserved population and possess high risk for multiple health problems as well as preexisting conditions. Many have limited life options financially, educationally, and with housing, and encounter barriers to accessing primary health care services, including preventive services. The introduction of the COVID-19 pandemic into these patients’ precarious health situations only made things worse as many of the limited resources for patients with substance use disorder were diverted to battling the pandemic. Numerous inpatient and outpatient addiction services, for example, were temporarily shut down. This has led to an increase in domestic violence, and psychiatric decompensation, including psychosis, suicidal attempts, and worsening of medical comorbidities in these patients.
Our wake-up call came when the first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in New York in early March. Within a short period of time the state became the epicenter for COVID-19. With the projection of millions of cases being positive and the number of new cases doubling every third day at the onset in New York City, we knew we had a battle brewing and needed to radically transform our mode of operation fast.
Our first task was to ensure the safety of our patients and the dedicated health workers attending to them. We streamlined the patient point of entry through one screening site, while also brushing up on our history-taking to intently screen for COVID-19. This included not just focusing on travels from China, but from Europe and other parts of the world.
Yes, we did ask patients about cough, fever, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling fatigued, severe body ache, and possible contact with someone who is sick or has traveled overseas. But we were also attuned to the increased rate of community spread and the presentation of other symptoms, such as loss of taste and smell, early in the process. Hence we were able to triage patients with suspected cases to the appropriate sections of the hospital for further screening, testing, and evaluation, instead of having those patients admitted to the detox unit.
Early in the process a huddle team was instituted with daily briefing of staff lasting 30 minutes or less. This team consists of physicians, nurses, a physician assistant, a social worker, and a counselor. In addition to discussing treatment plans for the patient, they deliberate on the public health information from the hospital’s COVID-19 command center, New York State Department of Health, the Office of Mental Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the latest evidence-based information. These discussions have helped us modify our policies and practices.
We instituted a no visiting rule during a short hospital stay of 5-7 days, and this was initiated weeks in advance of many institutions, including nursing homes with vulnerable populations. Our admitting criteria was reviewed to allow for admission of only those patients who absolutely needed inpatient substance use disorder treatment, including patients with severe withdrawal symptoms and signs, comorbidities, or neuropsychiatric manifestations that made them unsafe for outpatient or home detoxification. Others were triaged to the outpatient services which was amply supported with telemedicine. Rooms and designated areas of the building were earmarked as places for isolation/quarantine if suspected COVID-19 cases were identified pending testing. To assess patients’ risk of COVID-19, we do point-of-care nasopharyngeal swab testing with polymerase chain reaction.
Regarding face masks, patients and staff were fitted with ones early in the process. Additionally, staff were trained on the importance of face mask use and how to ensure you have a tight seal around the mouth and nose and were provided with other appropriate personal protective equipment. Concerning social distancing, we reduced the patient population capacity for the unit down to 50% and offered only single room admissions. Social distancing was encouraged in the unit, including in the television and recreation room and dining room, and during small treatment groups of less than six individuals. Daily temperature checks with noncontact handheld thermometers were enforced for staff and anyone coming into the life recovery center.
Patients are continuously being educated on the presentations of COVID-19 and encouraged to report any symptoms. Any staff feeling sick or having symptoms are encouraged to stay home. Rigorous and continuous cleaning of surfaces, especially of areas subjected to common use, is done frequently by the hospital housekeeping and environmental crew and is the order of the day.
Dr. Fagbemi is a hospitalist at BronxCare Health System, a not-for-profit health and teaching hospital system serving South and Central Bronx in New York. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Substance use disorder and its daily consequences take no breaks even during a pandemic. The stressors created by COVID-19, including deaths of loved ones and the disruptions to normal life from policies aimed at flattening the curve, seem to have increased substance use.
I practice as a hospitalist with an internal medicine background and specialty in addiction medicine at BronxCare Health System’s inpatient detoxification unit, a 24/7, 20-bed medically-supervised unit in South Bronx in New York City. It is one of the comprehensive services provided by the BronxCare’s life recovery center and addiction services, which also includes an outpatient clinic, opioid treatment program, inpatient rehab, and a half-way house. Inpatient detoxification units like ours are designed to treat serious addictions and chemical dependency and prevent and treat life-threatening withdrawal symptoms and signs or complications. Our patients come from all over the city and its adjoining suburbs, including from emergency room referrals, referral clinics, courts and the justice system, walk-ins, and self-referrals.
At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service. In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.
Individuals with substance use disorder have historically been a vulnerable and underserved population and possess high risk for multiple health problems as well as preexisting conditions. Many have limited life options financially, educationally, and with housing, and encounter barriers to accessing primary health care services, including preventive services. The introduction of the COVID-19 pandemic into these patients’ precarious health situations only made things worse as many of the limited resources for patients with substance use disorder were diverted to battling the pandemic. Numerous inpatient and outpatient addiction services, for example, were temporarily shut down. This has led to an increase in domestic violence, and psychiatric decompensation, including psychosis, suicidal attempts, and worsening of medical comorbidities in these patients.
Our wake-up call came when the first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in New York in early March. Within a short period of time the state became the epicenter for COVID-19. With the projection of millions of cases being positive and the number of new cases doubling every third day at the onset in New York City, we knew we had a battle brewing and needed to radically transform our mode of operation fast.
Our first task was to ensure the safety of our patients and the dedicated health workers attending to them. We streamlined the patient point of entry through one screening site, while also brushing up on our history-taking to intently screen for COVID-19. This included not just focusing on travels from China, but from Europe and other parts of the world.
Yes, we did ask patients about cough, fever, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling fatigued, severe body ache, and possible contact with someone who is sick or has traveled overseas. But we were also attuned to the increased rate of community spread and the presentation of other symptoms, such as loss of taste and smell, early in the process. Hence we were able to triage patients with suspected cases to the appropriate sections of the hospital for further screening, testing, and evaluation, instead of having those patients admitted to the detox unit.
Early in the process a huddle team was instituted with daily briefing of staff lasting 30 minutes or less. This team consists of physicians, nurses, a physician assistant, a social worker, and a counselor. In addition to discussing treatment plans for the patient, they deliberate on the public health information from the hospital’s COVID-19 command center, New York State Department of Health, the Office of Mental Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the latest evidence-based information. These discussions have helped us modify our policies and practices.
We instituted a no visiting rule during a short hospital stay of 5-7 days, and this was initiated weeks in advance of many institutions, including nursing homes with vulnerable populations. Our admitting criteria was reviewed to allow for admission of only those patients who absolutely needed inpatient substance use disorder treatment, including patients with severe withdrawal symptoms and signs, comorbidities, or neuropsychiatric manifestations that made them unsafe for outpatient or home detoxification. Others were triaged to the outpatient services which was amply supported with telemedicine. Rooms and designated areas of the building were earmarked as places for isolation/quarantine if suspected COVID-19 cases were identified pending testing. To assess patients’ risk of COVID-19, we do point-of-care nasopharyngeal swab testing with polymerase chain reaction.
Regarding face masks, patients and staff were fitted with ones early in the process. Additionally, staff were trained on the importance of face mask use and how to ensure you have a tight seal around the mouth and nose and were provided with other appropriate personal protective equipment. Concerning social distancing, we reduced the patient population capacity for the unit down to 50% and offered only single room admissions. Social distancing was encouraged in the unit, including in the television and recreation room and dining room, and during small treatment groups of less than six individuals. Daily temperature checks with noncontact handheld thermometers were enforced for staff and anyone coming into the life recovery center.
Patients are continuously being educated on the presentations of COVID-19 and encouraged to report any symptoms. Any staff feeling sick or having symptoms are encouraged to stay home. Rigorous and continuous cleaning of surfaces, especially of areas subjected to common use, is done frequently by the hospital housekeeping and environmental crew and is the order of the day.
Dr. Fagbemi is a hospitalist at BronxCare Health System, a not-for-profit health and teaching hospital system serving South and Central Bronx in New York. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Substance use disorder and its daily consequences take no breaks even during a pandemic. The stressors created by COVID-19, including deaths of loved ones and the disruptions to normal life from policies aimed at flattening the curve, seem to have increased substance use.
I practice as a hospitalist with an internal medicine background and specialty in addiction medicine at BronxCare Health System’s inpatient detoxification unit, a 24/7, 20-bed medically-supervised unit in South Bronx in New York City. It is one of the comprehensive services provided by the BronxCare’s life recovery center and addiction services, which also includes an outpatient clinic, opioid treatment program, inpatient rehab, and a half-way house. Inpatient detoxification units like ours are designed to treat serious addictions and chemical dependency and prevent and treat life-threatening withdrawal symptoms and signs or complications. Our patients come from all over the city and its adjoining suburbs, including from emergency room referrals, referral clinics, courts and the justice system, walk-ins, and self-referrals.
At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service. In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.
Individuals with substance use disorder have historically been a vulnerable and underserved population and possess high risk for multiple health problems as well as preexisting conditions. Many have limited life options financially, educationally, and with housing, and encounter barriers to accessing primary health care services, including preventive services. The introduction of the COVID-19 pandemic into these patients’ precarious health situations only made things worse as many of the limited resources for patients with substance use disorder were diverted to battling the pandemic. Numerous inpatient and outpatient addiction services, for example, were temporarily shut down. This has led to an increase in domestic violence, and psychiatric decompensation, including psychosis, suicidal attempts, and worsening of medical comorbidities in these patients.
Our wake-up call came when the first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in New York in early March. Within a short period of time the state became the epicenter for COVID-19. With the projection of millions of cases being positive and the number of new cases doubling every third day at the onset in New York City, we knew we had a battle brewing and needed to radically transform our mode of operation fast.
Our first task was to ensure the safety of our patients and the dedicated health workers attending to them. We streamlined the patient point of entry through one screening site, while also brushing up on our history-taking to intently screen for COVID-19. This included not just focusing on travels from China, but from Europe and other parts of the world.
Yes, we did ask patients about cough, fever, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling fatigued, severe body ache, and possible contact with someone who is sick or has traveled overseas. But we were also attuned to the increased rate of community spread and the presentation of other symptoms, such as loss of taste and smell, early in the process. Hence we were able to triage patients with suspected cases to the appropriate sections of the hospital for further screening, testing, and evaluation, instead of having those patients admitted to the detox unit.
Early in the process a huddle team was instituted with daily briefing of staff lasting 30 minutes or less. This team consists of physicians, nurses, a physician assistant, a social worker, and a counselor. In addition to discussing treatment plans for the patient, they deliberate on the public health information from the hospital’s COVID-19 command center, New York State Department of Health, the Office of Mental Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the latest evidence-based information. These discussions have helped us modify our policies and practices.
We instituted a no visiting rule during a short hospital stay of 5-7 days, and this was initiated weeks in advance of many institutions, including nursing homes with vulnerable populations. Our admitting criteria was reviewed to allow for admission of only those patients who absolutely needed inpatient substance use disorder treatment, including patients with severe withdrawal symptoms and signs, comorbidities, or neuropsychiatric manifestations that made them unsafe for outpatient or home detoxification. Others were triaged to the outpatient services which was amply supported with telemedicine. Rooms and designated areas of the building were earmarked as places for isolation/quarantine if suspected COVID-19 cases were identified pending testing. To assess patients’ risk of COVID-19, we do point-of-care nasopharyngeal swab testing with polymerase chain reaction.
Regarding face masks, patients and staff were fitted with ones early in the process. Additionally, staff were trained on the importance of face mask use and how to ensure you have a tight seal around the mouth and nose and were provided with other appropriate personal protective equipment. Concerning social distancing, we reduced the patient population capacity for the unit down to 50% and offered only single room admissions. Social distancing was encouraged in the unit, including in the television and recreation room and dining room, and during small treatment groups of less than six individuals. Daily temperature checks with noncontact handheld thermometers were enforced for staff and anyone coming into the life recovery center.
Patients are continuously being educated on the presentations of COVID-19 and encouraged to report any symptoms. Any staff feeling sick or having symptoms are encouraged to stay home. Rigorous and continuous cleaning of surfaces, especially of areas subjected to common use, is done frequently by the hospital housekeeping and environmental crew and is the order of the day.
Dr. Fagbemi is a hospitalist at BronxCare Health System, a not-for-profit health and teaching hospital system serving South and Central Bronx in New York. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Placental injury reported in women with COVID-19
Neonates appear healthy so far
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
Neonates appear healthy so far
Neonates appear healthy so far
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY
SARS-CoV-2 infection rate 16% in asymptomatic pregnant women at delivery
Among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, the rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Among the patients’ designated support persons, the asymptomatic carrier rate was 10%.
“If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” wrote the researchers affiliated with the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Angela Bianco, MD, and colleagues conducted an observational study of women who were scheduled for a planned delivery within the Mount Sinai Health System between April 4 and April 15, 2020. Patients and their designated support person completed a telephone screen and underwent COVID-19 testing the day before a scheduled delivery. If support persons screened positive during the telephone interview about COVID-19 symptoms, they could not attend the birth, and patients could contact a different support person to be screened and tested. “All patients and their support persons were informed of their SARS-CoV-2 test results before admission,” the investigators wrote. “Those who tested positive were counseled regarding symptomatology that should prompt medical attention.”
In all, researchers screened 158 patients with a planned delivery, and 155 agreed to undergo COVID-19 testing. Of the 155 women tested, 24 (16%) tested positive for SARS CoV-2 infection. Among 146 support persons who had a negative interview screen and underwent SARS-CoV-2 testing, 14 (10%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Test results were substantially concordant among patient and support person pairs. “Among patients who tested positive for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, 11 of 19 (58%) support persons also tested positive for COVID-19 infection,” the authors reported. “Among patients who tested negative for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, only 3 of 127 (2.4%) support persons tested positive for COVID-19 infection.”
Telephone screening did not identify any of the COVID-19–positive cases. Of the 24 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, none of their newborns tested positive at birth.
“Universal testing ... provides a mechanism for more accurate counseling of patients regarding issues such as newborn skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding,” noted Dr. Bianco and colleagues. At their institution, parents with COVID-19 are instructed to wear a mask and practice proper hand hygiene when caring for their newborns.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, said in an interview that the study by Bianco et al. underscores the high rate of asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic COVID-19 infections detected with universal screening in a hospital at the U.S. epicenter of the pandemic. “Each state and hospital will need to evaluate their own data to determine the value of universal screening for their patient population. In rural parts of America that have yet to see cases, universal screening may not make sense, but these areas are likely to be few and far between. The rest of America will need to quickly get on board with universal screening to protect their labor and delivery staff.”
Testing the partner was a strength of the study. “It is reassuring that when a pregnant woman tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the rate was very, very low (2.4%) that her partner would test positive. However, it was disconcerting that telephone screening for common symptoms associated with COVID-19 was not very helpful in identifying cases,” said Dr. Waldorf, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. She was not involved in the study by Bianco et al.
One study author receives payment from the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology for serving as a board examiner, receives payment from UpToDate, and serves as an expert witness in malpractice and products liability cases. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bianco A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003985.
Among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, the rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Among the patients’ designated support persons, the asymptomatic carrier rate was 10%.
“If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” wrote the researchers affiliated with the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Angela Bianco, MD, and colleagues conducted an observational study of women who were scheduled for a planned delivery within the Mount Sinai Health System between April 4 and April 15, 2020. Patients and their designated support person completed a telephone screen and underwent COVID-19 testing the day before a scheduled delivery. If support persons screened positive during the telephone interview about COVID-19 symptoms, they could not attend the birth, and patients could contact a different support person to be screened and tested. “All patients and their support persons were informed of their SARS-CoV-2 test results before admission,” the investigators wrote. “Those who tested positive were counseled regarding symptomatology that should prompt medical attention.”
In all, researchers screened 158 patients with a planned delivery, and 155 agreed to undergo COVID-19 testing. Of the 155 women tested, 24 (16%) tested positive for SARS CoV-2 infection. Among 146 support persons who had a negative interview screen and underwent SARS-CoV-2 testing, 14 (10%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Test results were substantially concordant among patient and support person pairs. “Among patients who tested positive for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, 11 of 19 (58%) support persons also tested positive for COVID-19 infection,” the authors reported. “Among patients who tested negative for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, only 3 of 127 (2.4%) support persons tested positive for COVID-19 infection.”
Telephone screening did not identify any of the COVID-19–positive cases. Of the 24 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, none of their newborns tested positive at birth.
“Universal testing ... provides a mechanism for more accurate counseling of patients regarding issues such as newborn skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding,” noted Dr. Bianco and colleagues. At their institution, parents with COVID-19 are instructed to wear a mask and practice proper hand hygiene when caring for their newborns.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, said in an interview that the study by Bianco et al. underscores the high rate of asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic COVID-19 infections detected with universal screening in a hospital at the U.S. epicenter of the pandemic. “Each state and hospital will need to evaluate their own data to determine the value of universal screening for their patient population. In rural parts of America that have yet to see cases, universal screening may not make sense, but these areas are likely to be few and far between. The rest of America will need to quickly get on board with universal screening to protect their labor and delivery staff.”
Testing the partner was a strength of the study. “It is reassuring that when a pregnant woman tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the rate was very, very low (2.4%) that her partner would test positive. However, it was disconcerting that telephone screening for common symptoms associated with COVID-19 was not very helpful in identifying cases,” said Dr. Waldorf, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. She was not involved in the study by Bianco et al.
One study author receives payment from the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology for serving as a board examiner, receives payment from UpToDate, and serves as an expert witness in malpractice and products liability cases. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bianco A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003985.
Among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, the rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Among the patients’ designated support persons, the asymptomatic carrier rate was 10%.
“If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” wrote the researchers affiliated with the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Angela Bianco, MD, and colleagues conducted an observational study of women who were scheduled for a planned delivery within the Mount Sinai Health System between April 4 and April 15, 2020. Patients and their designated support person completed a telephone screen and underwent COVID-19 testing the day before a scheduled delivery. If support persons screened positive during the telephone interview about COVID-19 symptoms, they could not attend the birth, and patients could contact a different support person to be screened and tested. “All patients and their support persons were informed of their SARS-CoV-2 test results before admission,” the investigators wrote. “Those who tested positive were counseled regarding symptomatology that should prompt medical attention.”
In all, researchers screened 158 patients with a planned delivery, and 155 agreed to undergo COVID-19 testing. Of the 155 women tested, 24 (16%) tested positive for SARS CoV-2 infection. Among 146 support persons who had a negative interview screen and underwent SARS-CoV-2 testing, 14 (10%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Test results were substantially concordant among patient and support person pairs. “Among patients who tested positive for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, 11 of 19 (58%) support persons also tested positive for COVID-19 infection,” the authors reported. “Among patients who tested negative for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, only 3 of 127 (2.4%) support persons tested positive for COVID-19 infection.”
Telephone screening did not identify any of the COVID-19–positive cases. Of the 24 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, none of their newborns tested positive at birth.
“Universal testing ... provides a mechanism for more accurate counseling of patients regarding issues such as newborn skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding,” noted Dr. Bianco and colleagues. At their institution, parents with COVID-19 are instructed to wear a mask and practice proper hand hygiene when caring for their newborns.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, said in an interview that the study by Bianco et al. underscores the high rate of asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic COVID-19 infections detected with universal screening in a hospital at the U.S. epicenter of the pandemic. “Each state and hospital will need to evaluate their own data to determine the value of universal screening for their patient population. In rural parts of America that have yet to see cases, universal screening may not make sense, but these areas are likely to be few and far between. The rest of America will need to quickly get on board with universal screening to protect their labor and delivery staff.”
Testing the partner was a strength of the study. “It is reassuring that when a pregnant woman tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the rate was very, very low (2.4%) that her partner would test positive. However, it was disconcerting that telephone screening for common symptoms associated with COVID-19 was not very helpful in identifying cases,” said Dr. Waldorf, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. She was not involved in the study by Bianco et al.
One study author receives payment from the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology for serving as a board examiner, receives payment from UpToDate, and serves as an expert witness in malpractice and products liability cases. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bianco A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003985.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Whether to test laboring women for SARS-CoV-2 may hinge on regional prevalence
at the time of admission, research published online in Obstetrics & Gynecology suggests.
In Los Angeles, researchers stopped universal testing after none of the first 80 asymptomatic women had positive results. Researchers in Chicago, on the other hand, found a positive rate of approximately 1.6% among 614 asymptomatic patients and continue to test all patients.
“Decisions regarding universal testing need to be made in the context of regional prevalence of COVID-19 infection, with recognition that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach is unlikely to be justifiable,” Torri D. Metz, MD,of University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City said in an editorial accompanying research letters that described the experience in Los Angeles and Chicago. “In the setting of low population prevalence of COVID-19 infection or in locations with limited testing availability, deferring universal testing may represent the better part of valor when weighing risks, benefits, economic burden, and unintended consequences of testing for SARS-CoV-2 infection. In high-prevalence regions, universal testing may be a valuable addition to obstetric care that will prevent infections in health care workers and neonates.”
Testing all patients also may provide valuable population-level surveillance, added Dr. Metz, who is an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist, and vice-chair of research in obstetrics and gynecology.
One week of data
After New York hospitals reported an approximately 13% prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among asymptomatic laboring women, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles changed its policy from testing only women with COVID-19 symptoms to testing all women beginning April 4, 2020. “Data from New York made us very concerned about the possibility of asymptomatic infections among our own pregnant patients,” Mariam Naqvi, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in a news release. “This would have implications for them, their babies, their households, and for the health of our staff caring for them.”
In 1 week, 82 pregnant women admitted to the obstetric unit were tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of two women who reported COVID-19 symptoms, one tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Of the remaining 80 asymptomatic women, none tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and all remained symptom free throughout their hospitalizations,” Dr. Naqvi and colleagues reported. “One asymptomatic patient had an inadequate nasopharyngeal specimen and declined repeat testing.”
Precautions taken during universal testing meant that all members of the treatment team used valuable personal protective equipment. In some cases, mothers and newborns were separated until test results were available.
“We discontinued universal testing after a 7-day period, because we could not justify continued testing of asymptomatic women in the absence of positive test results for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” they noted. “Though universal testing did not yield enough positive results on our obstetric unit to warrant continued testing at this time, our approach may change if local rates of infection increase.”
20 days of testing
In a prospective case series of pregnant women admitted to Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago from April 8 to April 27, 2020, universal testing did detect asymptomatic infections. Women with scheduled admissions were tested 12-36 hours before admission in a drive-through testing center, and women with unscheduled admissions received a test that has a 2- to 3-hour turnaround time. In addition, patients were screened for symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, cough, sore throat, body aches, chills, new-onset vomiting, diarrhea, loss of taste or smell, and red or painful eyes.
“Asymptomatic women with pending tests were managed on the routine labor floor, but health care workers used personal protective equipment that included a respirator during the second stage of labor and delivery until the test result became available,” wrote Emily S. Miller, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues.
During the first 20 days of universal testing, 635 pregnant women were admitted, and 23 (3.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 21 women with COVID-19 symptoms, 13 (62%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 614 women who were asymptomatic, 10 (1.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Our data corroborate the observation that pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection on admission do not seem to be reliably identified using symptom screening alone,” the researchers wrote.
Unintended consequences
Despite a lack of effective treatments for mild to moderate COVID-19, “knowledge of the disease state allows ... health care workers to wear appropriate personal protective equipment to avoid exposure,” Dr. Metz wrote. It also allows “women to be counseled about ways to decrease transmission to neonates” and enables close monitoring of patients with infection.
At the same time, universal testing may have unintended consequences for infected patients, such as stigmatization, separation from the newborn, and delays in care related to health care providers spending more time donning personal protective equipment or changes in medical decision-making regarding cesarean delivery, she emphasized.
“Obstetricians should remain aware of disease prevalence in their communities and consider universal screening of asymptomatic women on an ongoing basis as new ‘hot spots’ for COVID-19 infection are identified,” Dr. Metz concluded.
One of Dr. Naqvi’s coauthors disclosed receiving funds from Contemporary OB/GYN, Keneka, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and serving as a board examiner for the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology; her coauthors did not report any relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metz disclosed that money was paid to her institution from Pfizer and GestVision for work related to an RSV vaccination trial and a preeclampsia test, respectively. Dr. Miller and colleagues did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Naqvi M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003987; Miller ES et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003983; Metz TD. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003972.
at the time of admission, research published online in Obstetrics & Gynecology suggests.
In Los Angeles, researchers stopped universal testing after none of the first 80 asymptomatic women had positive results. Researchers in Chicago, on the other hand, found a positive rate of approximately 1.6% among 614 asymptomatic patients and continue to test all patients.
“Decisions regarding universal testing need to be made in the context of regional prevalence of COVID-19 infection, with recognition that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach is unlikely to be justifiable,” Torri D. Metz, MD,of University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City said in an editorial accompanying research letters that described the experience in Los Angeles and Chicago. “In the setting of low population prevalence of COVID-19 infection or in locations with limited testing availability, deferring universal testing may represent the better part of valor when weighing risks, benefits, economic burden, and unintended consequences of testing for SARS-CoV-2 infection. In high-prevalence regions, universal testing may be a valuable addition to obstetric care that will prevent infections in health care workers and neonates.”
Testing all patients also may provide valuable population-level surveillance, added Dr. Metz, who is an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist, and vice-chair of research in obstetrics and gynecology.
One week of data
After New York hospitals reported an approximately 13% prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among asymptomatic laboring women, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles changed its policy from testing only women with COVID-19 symptoms to testing all women beginning April 4, 2020. “Data from New York made us very concerned about the possibility of asymptomatic infections among our own pregnant patients,” Mariam Naqvi, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in a news release. “This would have implications for them, their babies, their households, and for the health of our staff caring for them.”
In 1 week, 82 pregnant women admitted to the obstetric unit were tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of two women who reported COVID-19 symptoms, one tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Of the remaining 80 asymptomatic women, none tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and all remained symptom free throughout their hospitalizations,” Dr. Naqvi and colleagues reported. “One asymptomatic patient had an inadequate nasopharyngeal specimen and declined repeat testing.”
Precautions taken during universal testing meant that all members of the treatment team used valuable personal protective equipment. In some cases, mothers and newborns were separated until test results were available.
“We discontinued universal testing after a 7-day period, because we could not justify continued testing of asymptomatic women in the absence of positive test results for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” they noted. “Though universal testing did not yield enough positive results on our obstetric unit to warrant continued testing at this time, our approach may change if local rates of infection increase.”
20 days of testing
In a prospective case series of pregnant women admitted to Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago from April 8 to April 27, 2020, universal testing did detect asymptomatic infections. Women with scheduled admissions were tested 12-36 hours before admission in a drive-through testing center, and women with unscheduled admissions received a test that has a 2- to 3-hour turnaround time. In addition, patients were screened for symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, cough, sore throat, body aches, chills, new-onset vomiting, diarrhea, loss of taste or smell, and red or painful eyes.
“Asymptomatic women with pending tests were managed on the routine labor floor, but health care workers used personal protective equipment that included a respirator during the second stage of labor and delivery until the test result became available,” wrote Emily S. Miller, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues.
During the first 20 days of universal testing, 635 pregnant women were admitted, and 23 (3.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 21 women with COVID-19 symptoms, 13 (62%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 614 women who were asymptomatic, 10 (1.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Our data corroborate the observation that pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection on admission do not seem to be reliably identified using symptom screening alone,” the researchers wrote.
Unintended consequences
Despite a lack of effective treatments for mild to moderate COVID-19, “knowledge of the disease state allows ... health care workers to wear appropriate personal protective equipment to avoid exposure,” Dr. Metz wrote. It also allows “women to be counseled about ways to decrease transmission to neonates” and enables close monitoring of patients with infection.
At the same time, universal testing may have unintended consequences for infected patients, such as stigmatization, separation from the newborn, and delays in care related to health care providers spending more time donning personal protective equipment or changes in medical decision-making regarding cesarean delivery, she emphasized.
“Obstetricians should remain aware of disease prevalence in their communities and consider universal screening of asymptomatic women on an ongoing basis as new ‘hot spots’ for COVID-19 infection are identified,” Dr. Metz concluded.
One of Dr. Naqvi’s coauthors disclosed receiving funds from Contemporary OB/GYN, Keneka, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and serving as a board examiner for the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology; her coauthors did not report any relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metz disclosed that money was paid to her institution from Pfizer and GestVision for work related to an RSV vaccination trial and a preeclampsia test, respectively. Dr. Miller and colleagues did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Naqvi M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003987; Miller ES et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003983; Metz TD. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003972.
at the time of admission, research published online in Obstetrics & Gynecology suggests.
In Los Angeles, researchers stopped universal testing after none of the first 80 asymptomatic women had positive results. Researchers in Chicago, on the other hand, found a positive rate of approximately 1.6% among 614 asymptomatic patients and continue to test all patients.
“Decisions regarding universal testing need to be made in the context of regional prevalence of COVID-19 infection, with recognition that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach is unlikely to be justifiable,” Torri D. Metz, MD,of University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City said in an editorial accompanying research letters that described the experience in Los Angeles and Chicago. “In the setting of low population prevalence of COVID-19 infection or in locations with limited testing availability, deferring universal testing may represent the better part of valor when weighing risks, benefits, economic burden, and unintended consequences of testing for SARS-CoV-2 infection. In high-prevalence regions, universal testing may be a valuable addition to obstetric care that will prevent infections in health care workers and neonates.”
Testing all patients also may provide valuable population-level surveillance, added Dr. Metz, who is an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist, and vice-chair of research in obstetrics and gynecology.
One week of data
After New York hospitals reported an approximately 13% prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among asymptomatic laboring women, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles changed its policy from testing only women with COVID-19 symptoms to testing all women beginning April 4, 2020. “Data from New York made us very concerned about the possibility of asymptomatic infections among our own pregnant patients,” Mariam Naqvi, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in a news release. “This would have implications for them, their babies, their households, and for the health of our staff caring for them.”
In 1 week, 82 pregnant women admitted to the obstetric unit were tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of two women who reported COVID-19 symptoms, one tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Of the remaining 80 asymptomatic women, none tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and all remained symptom free throughout their hospitalizations,” Dr. Naqvi and colleagues reported. “One asymptomatic patient had an inadequate nasopharyngeal specimen and declined repeat testing.”
Precautions taken during universal testing meant that all members of the treatment team used valuable personal protective equipment. In some cases, mothers and newborns were separated until test results were available.
“We discontinued universal testing after a 7-day period, because we could not justify continued testing of asymptomatic women in the absence of positive test results for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” they noted. “Though universal testing did not yield enough positive results on our obstetric unit to warrant continued testing at this time, our approach may change if local rates of infection increase.”
20 days of testing
In a prospective case series of pregnant women admitted to Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago from April 8 to April 27, 2020, universal testing did detect asymptomatic infections. Women with scheduled admissions were tested 12-36 hours before admission in a drive-through testing center, and women with unscheduled admissions received a test that has a 2- to 3-hour turnaround time. In addition, patients were screened for symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, cough, sore throat, body aches, chills, new-onset vomiting, diarrhea, loss of taste or smell, and red or painful eyes.
“Asymptomatic women with pending tests were managed on the routine labor floor, but health care workers used personal protective equipment that included a respirator during the second stage of labor and delivery until the test result became available,” wrote Emily S. Miller, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues.
During the first 20 days of universal testing, 635 pregnant women were admitted, and 23 (3.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 21 women with COVID-19 symptoms, 13 (62%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 614 women who were asymptomatic, 10 (1.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Our data corroborate the observation that pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection on admission do not seem to be reliably identified using symptom screening alone,” the researchers wrote.
Unintended consequences
Despite a lack of effective treatments for mild to moderate COVID-19, “knowledge of the disease state allows ... health care workers to wear appropriate personal protective equipment to avoid exposure,” Dr. Metz wrote. It also allows “women to be counseled about ways to decrease transmission to neonates” and enables close monitoring of patients with infection.
At the same time, universal testing may have unintended consequences for infected patients, such as stigmatization, separation from the newborn, and delays in care related to health care providers spending more time donning personal protective equipment or changes in medical decision-making regarding cesarean delivery, she emphasized.
“Obstetricians should remain aware of disease prevalence in their communities and consider universal screening of asymptomatic women on an ongoing basis as new ‘hot spots’ for COVID-19 infection are identified,” Dr. Metz concluded.
One of Dr. Naqvi’s coauthors disclosed receiving funds from Contemporary OB/GYN, Keneka, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and serving as a board examiner for the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology; her coauthors did not report any relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metz disclosed that money was paid to her institution from Pfizer and GestVision for work related to an RSV vaccination trial and a preeclampsia test, respectively. Dr. Miller and colleagues did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Naqvi M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003987; Miller ES et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003983; Metz TD. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003972.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY