User login
Daratumumab shows limited benefit in transfusion-dependent patients with low- to intermediate-risk MDS
Key clinical point: Daratumumab provided some clinical activity in patients with low- to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), who relapsed or were refractory to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESA) treatment. No new safety signals were identified.
Major finding: Eight-week transfusion independence (TI) was achieved by 6.1% (95% confidence interval, 0.7%-20.2%) of patients. Time to 8-week TI was 4–5 weeks after the first daratumumab infusion. Daratumumab-related adverse events were reported by 54.5% of patients, of whom 3 patients experienced 4 serious adverse events. Infusion-related reaction was observed, but none led to treatment discontinuation.
Study details: Findings are from a phase 2, randomized, open-label study involving 34 patients with low- or intermediate-1-risk MDS, who were transfusion dependent and who relapsed or were refractory to ESA treatment. Patients received either daratumumab (n=33) or talacotuzumab (n=1); however, recruitment to talacotuzumab arm was closed after the occurrence of a serious adverse event in the first patient.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Janssen Research & Development. The lead author reported receiving research support from Johnson & Johnson. Some of the coinvestigators reported owning stocks, being an employee, serving on an advisory board, receiving support, and consulting for various pharmaceutical companies including Janssen Research & Development. Six of the coinvestigators declared no potential competing interests.
Source: Garcia‐Manero G et al. Am J Hematol. 2021 Jan 15. doi: 10.1002/ajh.26095.
Key clinical point: Daratumumab provided some clinical activity in patients with low- to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), who relapsed or were refractory to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESA) treatment. No new safety signals were identified.
Major finding: Eight-week transfusion independence (TI) was achieved by 6.1% (95% confidence interval, 0.7%-20.2%) of patients. Time to 8-week TI was 4–5 weeks after the first daratumumab infusion. Daratumumab-related adverse events were reported by 54.5% of patients, of whom 3 patients experienced 4 serious adverse events. Infusion-related reaction was observed, but none led to treatment discontinuation.
Study details: Findings are from a phase 2, randomized, open-label study involving 34 patients with low- or intermediate-1-risk MDS, who were transfusion dependent and who relapsed or were refractory to ESA treatment. Patients received either daratumumab (n=33) or talacotuzumab (n=1); however, recruitment to talacotuzumab arm was closed after the occurrence of a serious adverse event in the first patient.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Janssen Research & Development. The lead author reported receiving research support from Johnson & Johnson. Some of the coinvestigators reported owning stocks, being an employee, serving on an advisory board, receiving support, and consulting for various pharmaceutical companies including Janssen Research & Development. Six of the coinvestigators declared no potential competing interests.
Source: Garcia‐Manero G et al. Am J Hematol. 2021 Jan 15. doi: 10.1002/ajh.26095.
Key clinical point: Daratumumab provided some clinical activity in patients with low- to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), who relapsed or were refractory to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESA) treatment. No new safety signals were identified.
Major finding: Eight-week transfusion independence (TI) was achieved by 6.1% (95% confidence interval, 0.7%-20.2%) of patients. Time to 8-week TI was 4–5 weeks after the first daratumumab infusion. Daratumumab-related adverse events were reported by 54.5% of patients, of whom 3 patients experienced 4 serious adverse events. Infusion-related reaction was observed, but none led to treatment discontinuation.
Study details: Findings are from a phase 2, randomized, open-label study involving 34 patients with low- or intermediate-1-risk MDS, who were transfusion dependent and who relapsed or were refractory to ESA treatment. Patients received either daratumumab (n=33) or talacotuzumab (n=1); however, recruitment to talacotuzumab arm was closed after the occurrence of a serious adverse event in the first patient.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Janssen Research & Development. The lead author reported receiving research support from Johnson & Johnson. Some of the coinvestigators reported owning stocks, being an employee, serving on an advisory board, receiving support, and consulting for various pharmaceutical companies including Janssen Research & Development. Six of the coinvestigators declared no potential competing interests.
Source: Garcia‐Manero G et al. Am J Hematol. 2021 Jan 15. doi: 10.1002/ajh.26095.
MDS: Fractionated busulfan reduces relapse and boosts survival
Key clinical point: A myeloablative, fractionated busulfan (f-Bu) regimen reduces relapse and boosts survival without increasing nonrelapse mortality (NRM) in older patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
Major finding: At 2 years, the f-Bu group had a significantly better progression-free survival than the nonfractionated, lower dose busalfan (Bu) group (45% vs 24%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.6; P = .004), attributed to a significant reduction in progression (34% vs 59%; HR, 0.5; P = .003) without an increase in NRM (21% vs 15%; HR, 1.4; P = .3). Overall survival also improved in the f-Bu group vs the Bu group (51% vs 31%, HR, 0.6; P = .01).
Study details: In an open-label, phase 2 trial, patients with AML or MDS were randomly assigned to either myeloablative f-Bu over 2 weeks (n = 84; median age, 65 years) or a standard Bu regimen over 4 days (n = 78; median age, 66 years).
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by a grant from the National Cancer Institute. Q Bashir, C Hosing, K Rezvani and UR Popat reported relationships with various pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Oran B et al. Cancer. 2021 Jan 20. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33383
Key clinical point: A myeloablative, fractionated busulfan (f-Bu) regimen reduces relapse and boosts survival without increasing nonrelapse mortality (NRM) in older patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
Major finding: At 2 years, the f-Bu group had a significantly better progression-free survival than the nonfractionated, lower dose busalfan (Bu) group (45% vs 24%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.6; P = .004), attributed to a significant reduction in progression (34% vs 59%; HR, 0.5; P = .003) without an increase in NRM (21% vs 15%; HR, 1.4; P = .3). Overall survival also improved in the f-Bu group vs the Bu group (51% vs 31%, HR, 0.6; P = .01).
Study details: In an open-label, phase 2 trial, patients with AML or MDS were randomly assigned to either myeloablative f-Bu over 2 weeks (n = 84; median age, 65 years) or a standard Bu regimen over 4 days (n = 78; median age, 66 years).
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by a grant from the National Cancer Institute. Q Bashir, C Hosing, K Rezvani and UR Popat reported relationships with various pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Oran B et al. Cancer. 2021 Jan 20. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33383
Key clinical point: A myeloablative, fractionated busulfan (f-Bu) regimen reduces relapse and boosts survival without increasing nonrelapse mortality (NRM) in older patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
Major finding: At 2 years, the f-Bu group had a significantly better progression-free survival than the nonfractionated, lower dose busalfan (Bu) group (45% vs 24%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.6; P = .004), attributed to a significant reduction in progression (34% vs 59%; HR, 0.5; P = .003) without an increase in NRM (21% vs 15%; HR, 1.4; P = .3). Overall survival also improved in the f-Bu group vs the Bu group (51% vs 31%, HR, 0.6; P = .01).
Study details: In an open-label, phase 2 trial, patients with AML or MDS were randomly assigned to either myeloablative f-Bu over 2 weeks (n = 84; median age, 65 years) or a standard Bu regimen over 4 days (n = 78; median age, 66 years).
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by a grant from the National Cancer Institute. Q Bashir, C Hosing, K Rezvani and UR Popat reported relationships with various pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Oran B et al. Cancer. 2021 Jan 20. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33383
Baseline and serial molecular profiling can predict outcomes with HMAs in MDS
Key clinical point: Baseline and serial molecular profiling by next-generation sequencing (NGS) can predict outcomes with hypomethylating agents (HMAs) in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Serial molecular profiling during therapy of patients with mutant TP53 can identify patients who may benefit from allogeneic transplantation.
Major finding: Mutations in TET2 and ASXL1 genes emerged as the most informative variables associated with response to HMA therapy (overall response rate, 62.1%; complete remission rate, 34.5%). The number of mutations detected by NGS (hazard ratio [HR], 1.22; P = .02) and mutations in TP53 (HR, 2.33; P = .001) and EZH2 (HR, 2.41; P = .04) were independent covariates associated with inferior overall survival (OS). Serial molecular profiling demonstrated that clearance of TP53 mutations during HMA therapy was associated with superior OS (HR, 0.28; P = .001) and improved outcome in patients proceeding to allogeneic transplantation.
Study details: This study evaluated response and OS in 247 patients molecularly profiled by NGS before first-line HMA therapy; a subset of 108 patients were sequenced serially during treatment.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the S Foundation Young Investigator Grant, the Early Career Award of the Dresner Foundation, and the Edward P. Evans Foundation Award. DA Sallman, E Padron, and AF List received research funding from Celgene. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Hunter AM et al. Blood Adv. 2021 Feb 23. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003508.
Key clinical point: Baseline and serial molecular profiling by next-generation sequencing (NGS) can predict outcomes with hypomethylating agents (HMAs) in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Serial molecular profiling during therapy of patients with mutant TP53 can identify patients who may benefit from allogeneic transplantation.
Major finding: Mutations in TET2 and ASXL1 genes emerged as the most informative variables associated with response to HMA therapy (overall response rate, 62.1%; complete remission rate, 34.5%). The number of mutations detected by NGS (hazard ratio [HR], 1.22; P = .02) and mutations in TP53 (HR, 2.33; P = .001) and EZH2 (HR, 2.41; P = .04) were independent covariates associated with inferior overall survival (OS). Serial molecular profiling demonstrated that clearance of TP53 mutations during HMA therapy was associated with superior OS (HR, 0.28; P = .001) and improved outcome in patients proceeding to allogeneic transplantation.
Study details: This study evaluated response and OS in 247 patients molecularly profiled by NGS before first-line HMA therapy; a subset of 108 patients were sequenced serially during treatment.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the S Foundation Young Investigator Grant, the Early Career Award of the Dresner Foundation, and the Edward P. Evans Foundation Award. DA Sallman, E Padron, and AF List received research funding from Celgene. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Hunter AM et al. Blood Adv. 2021 Feb 23. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003508.
Key clinical point: Baseline and serial molecular profiling by next-generation sequencing (NGS) can predict outcomes with hypomethylating agents (HMAs) in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Serial molecular profiling during therapy of patients with mutant TP53 can identify patients who may benefit from allogeneic transplantation.
Major finding: Mutations in TET2 and ASXL1 genes emerged as the most informative variables associated with response to HMA therapy (overall response rate, 62.1%; complete remission rate, 34.5%). The number of mutations detected by NGS (hazard ratio [HR], 1.22; P = .02) and mutations in TP53 (HR, 2.33; P = .001) and EZH2 (HR, 2.41; P = .04) were independent covariates associated with inferior overall survival (OS). Serial molecular profiling demonstrated that clearance of TP53 mutations during HMA therapy was associated with superior OS (HR, 0.28; P = .001) and improved outcome in patients proceeding to allogeneic transplantation.
Study details: This study evaluated response and OS in 247 patients molecularly profiled by NGS before first-line HMA therapy; a subset of 108 patients were sequenced serially during treatment.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the S Foundation Young Investigator Grant, the Early Career Award of the Dresner Foundation, and the Edward P. Evans Foundation Award. DA Sallman, E Padron, and AF List received research funding from Celgene. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Hunter AM et al. Blood Adv. 2021 Feb 23. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003508.
High erythroferrone expression in CD71+ erythroid progenitors predicts superior survival in MDS
Key clinical point: Dysregulated erythroferrone (ERFE) expression in CD71+ erythroid progenitors is associated with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) outcome and predicts patient survival independently of International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) stratification.
Major finding: The expression of ERFE was significantly higher in CD71+ cells of MDS patients vs. healthy donors group (median normalized mean fold change, 2.42 vs. 0.78). Elevated expression of ERFE in erythroid progenitors was associated with superior survival (hazard ratio, 0.35; P = .0017) independently of IPSS stratification. For growth/differentiation factor 15, the result was similar, but not statistically significant (P = .0543).
Study details: The data come from a study of 111 patients with MDS (median age, 73 years; 66.7% males).
Disclosures: This study was supported by funds of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Riabov V et al. Br J Haematol. 2021 Jan 24. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17314.
Key clinical point: Dysregulated erythroferrone (ERFE) expression in CD71+ erythroid progenitors is associated with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) outcome and predicts patient survival independently of International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) stratification.
Major finding: The expression of ERFE was significantly higher in CD71+ cells of MDS patients vs. healthy donors group (median normalized mean fold change, 2.42 vs. 0.78). Elevated expression of ERFE in erythroid progenitors was associated with superior survival (hazard ratio, 0.35; P = .0017) independently of IPSS stratification. For growth/differentiation factor 15, the result was similar, but not statistically significant (P = .0543).
Study details: The data come from a study of 111 patients with MDS (median age, 73 years; 66.7% males).
Disclosures: This study was supported by funds of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Riabov V et al. Br J Haematol. 2021 Jan 24. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17314.
Key clinical point: Dysregulated erythroferrone (ERFE) expression in CD71+ erythroid progenitors is associated with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) outcome and predicts patient survival independently of International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) stratification.
Major finding: The expression of ERFE was significantly higher in CD71+ cells of MDS patients vs. healthy donors group (median normalized mean fold change, 2.42 vs. 0.78). Elevated expression of ERFE in erythroid progenitors was associated with superior survival (hazard ratio, 0.35; P = .0017) independently of IPSS stratification. For growth/differentiation factor 15, the result was similar, but not statistically significant (P = .0543).
Study details: The data come from a study of 111 patients with MDS (median age, 73 years; 66.7% males).
Disclosures: This study was supported by funds of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Riabov V et al. Br J Haematol. 2021 Jan 24. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17314.
MDS: Novel MIPSS-R system improves risk stratification
Key clinical point: A novel risk scoring system termed 'mutation combined with revised international prognostic scoring system (MIPSS-R)' was more effective in predicting prognosis and guiding treatment in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) than the revised international prognostic scoring system (IPSS-R).
Major finding: Kaplan-Meier survival curves demonstrated superiority of MIPSS-R over IPSS-R in separating patients from different groups in the training cohort (P = 1.71e-08 vs P = 1.363e-04) and in the validation cohort (P = 1.788e-04 vs P = 2.757e-03). Area under the receiver operating characteristic of MIPSS-R was 0.79 in the training cohort and 0.62 in the validation cohort.
Study details: MIPSS-R was developed by integrating IPSS-R and the mutation scores. MIPSS-R was further compared with IPSS-R in a training cohort of 63 MDS patients and a validation cohort of 141 MDS patients.
Disclosures: The study was supported in part by The National Natural Science Foundation of China, Jiangsu Provincial Special Program of Medical Science, Jiangsu Province “333” project, The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Milstein Medical Asian American Partnership Foundation Research Project Award in Hematology, and Key Medical of Jiangsu Province. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Gu S et al. BMC Cancer. 2021 Feb 6. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07864-y.
Key clinical point: A novel risk scoring system termed 'mutation combined with revised international prognostic scoring system (MIPSS-R)' was more effective in predicting prognosis and guiding treatment in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) than the revised international prognostic scoring system (IPSS-R).
Major finding: Kaplan-Meier survival curves demonstrated superiority of MIPSS-R over IPSS-R in separating patients from different groups in the training cohort (P = 1.71e-08 vs P = 1.363e-04) and in the validation cohort (P = 1.788e-04 vs P = 2.757e-03). Area under the receiver operating characteristic of MIPSS-R was 0.79 in the training cohort and 0.62 in the validation cohort.
Study details: MIPSS-R was developed by integrating IPSS-R and the mutation scores. MIPSS-R was further compared with IPSS-R in a training cohort of 63 MDS patients and a validation cohort of 141 MDS patients.
Disclosures: The study was supported in part by The National Natural Science Foundation of China, Jiangsu Provincial Special Program of Medical Science, Jiangsu Province “333” project, The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Milstein Medical Asian American Partnership Foundation Research Project Award in Hematology, and Key Medical of Jiangsu Province. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Gu S et al. BMC Cancer. 2021 Feb 6. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07864-y.
Key clinical point: A novel risk scoring system termed 'mutation combined with revised international prognostic scoring system (MIPSS-R)' was more effective in predicting prognosis and guiding treatment in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) than the revised international prognostic scoring system (IPSS-R).
Major finding: Kaplan-Meier survival curves demonstrated superiority of MIPSS-R over IPSS-R in separating patients from different groups in the training cohort (P = 1.71e-08 vs P = 1.363e-04) and in the validation cohort (P = 1.788e-04 vs P = 2.757e-03). Area under the receiver operating characteristic of MIPSS-R was 0.79 in the training cohort and 0.62 in the validation cohort.
Study details: MIPSS-R was developed by integrating IPSS-R and the mutation scores. MIPSS-R was further compared with IPSS-R in a training cohort of 63 MDS patients and a validation cohort of 141 MDS patients.
Disclosures: The study was supported in part by The National Natural Science Foundation of China, Jiangsu Provincial Special Program of Medical Science, Jiangsu Province “333” project, The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Milstein Medical Asian American Partnership Foundation Research Project Award in Hematology, and Key Medical of Jiangsu Province. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Gu S et al. BMC Cancer. 2021 Feb 6. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07864-y.
Impact of conditioning intensity and genomics on relapse after allogeneic HCT in MDS
Key clinical point: In patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) with less than 5% marrow myeloblasts and no leukemic myeloblasts in blood before allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (alloHCT), ultra-deep DNA sequencing for mutations in 10 gene regions previously shown to be high risk in acute myeloid leukemia could help identify which patients are likely to relapse after alloHCT.
Major finding: Twenty (42%) patients had mutations detectable before conditioning treatment. The presence of mutations within a previously identified set of 10 gene regions before alloHCT was associated with increased rates of relapse (3-year relapse, 75% vs. 17%; P = .003) and decreased relapse-free survival (RFS; 3-year RFS, 13% vs. 49%; P = .003) in patients with MDS who received reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) vs. myeloablative conditioning (MAC).
Study details: The researchers performed targeted error-corrected DNA sequencing on preconditioning blood samples from patients with MDS (n=48) from the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network 0901 phase 3 trial before random assignment to MAC (n=25) or RIC (n=23) for alloHCT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) of the National Institutes of Health and by grants to the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network from the NHLBI and the National Cancer Institute. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Dillon LW et al. JCO Precis Oncol. 2021 Jan 25. doi: 10.1200/PO.20.00355.
Key clinical point: In patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) with less than 5% marrow myeloblasts and no leukemic myeloblasts in blood before allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (alloHCT), ultra-deep DNA sequencing for mutations in 10 gene regions previously shown to be high risk in acute myeloid leukemia could help identify which patients are likely to relapse after alloHCT.
Major finding: Twenty (42%) patients had mutations detectable before conditioning treatment. The presence of mutations within a previously identified set of 10 gene regions before alloHCT was associated with increased rates of relapse (3-year relapse, 75% vs. 17%; P = .003) and decreased relapse-free survival (RFS; 3-year RFS, 13% vs. 49%; P = .003) in patients with MDS who received reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) vs. myeloablative conditioning (MAC).
Study details: The researchers performed targeted error-corrected DNA sequencing on preconditioning blood samples from patients with MDS (n=48) from the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network 0901 phase 3 trial before random assignment to MAC (n=25) or RIC (n=23) for alloHCT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) of the National Institutes of Health and by grants to the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network from the NHLBI and the National Cancer Institute. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Dillon LW et al. JCO Precis Oncol. 2021 Jan 25. doi: 10.1200/PO.20.00355.
Key clinical point: In patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) with less than 5% marrow myeloblasts and no leukemic myeloblasts in blood before allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (alloHCT), ultra-deep DNA sequencing for mutations in 10 gene regions previously shown to be high risk in acute myeloid leukemia could help identify which patients are likely to relapse after alloHCT.
Major finding: Twenty (42%) patients had mutations detectable before conditioning treatment. The presence of mutations within a previously identified set of 10 gene regions before alloHCT was associated with increased rates of relapse (3-year relapse, 75% vs. 17%; P = .003) and decreased relapse-free survival (RFS; 3-year RFS, 13% vs. 49%; P = .003) in patients with MDS who received reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) vs. myeloablative conditioning (MAC).
Study details: The researchers performed targeted error-corrected DNA sequencing on preconditioning blood samples from patients with MDS (n=48) from the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network 0901 phase 3 trial before random assignment to MAC (n=25) or RIC (n=23) for alloHCT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) of the National Institutes of Health and by grants to the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network from the NHLBI and the National Cancer Institute. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Dillon LW et al. JCO Precis Oncol. 2021 Jan 25. doi: 10.1200/PO.20.00355.
Eprenetapopt and azacitidine combination yields high response rates in TP53-mutant MDS
Key clinical point: Eprenetapopt in combination with azacitidine yielded high rates of clinical response and complete remission (CR) and was well tolerated in patients with TP53-mutant myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
Major finding: Overall response rate in patients with MDS was 73% (95% confidence, [CI], 56%-85%) with 50% (95% CI, 34%-66%) of patients achieving CR. The median time to first response and CR was 1.9 and 3.1 months, respectively. Adverse events were similar to those reported for azacitidine or eprenetapopt monotherapies.
Study details: Findings come from a phase 1b/2 open-label, dose-escalation/expansion study that assessed safety, recommended dose, and efficacy of eprenetapopt and azacitidine combination in 55 patients with TP53-mutant MDS (n=40) or acute myeloid leukemia with 20%-30% marrow blasts.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the MDS Foundation Young Investigator Grant, the Early Career Award of the Dresner Foundation (DAS), and the Edward P. Evans MDS Clinical Research Consortium. The study was supported in part by the Flow Cytometry and Molecular Genomics Core Facilities at the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute. Some of the authors reported relationships with various pharmaceutical companies while some others declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Sallman DA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Jan 15. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02341.
Key clinical point: Eprenetapopt in combination with azacitidine yielded high rates of clinical response and complete remission (CR) and was well tolerated in patients with TP53-mutant myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
Major finding: Overall response rate in patients with MDS was 73% (95% confidence, [CI], 56%-85%) with 50% (95% CI, 34%-66%) of patients achieving CR. The median time to first response and CR was 1.9 and 3.1 months, respectively. Adverse events were similar to those reported for azacitidine or eprenetapopt monotherapies.
Study details: Findings come from a phase 1b/2 open-label, dose-escalation/expansion study that assessed safety, recommended dose, and efficacy of eprenetapopt and azacitidine combination in 55 patients with TP53-mutant MDS (n=40) or acute myeloid leukemia with 20%-30% marrow blasts.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the MDS Foundation Young Investigator Grant, the Early Career Award of the Dresner Foundation (DAS), and the Edward P. Evans MDS Clinical Research Consortium. The study was supported in part by the Flow Cytometry and Molecular Genomics Core Facilities at the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute. Some of the authors reported relationships with various pharmaceutical companies while some others declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Sallman DA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Jan 15. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02341.
Key clinical point: Eprenetapopt in combination with azacitidine yielded high rates of clinical response and complete remission (CR) and was well tolerated in patients with TP53-mutant myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
Major finding: Overall response rate in patients with MDS was 73% (95% confidence, [CI], 56%-85%) with 50% (95% CI, 34%-66%) of patients achieving CR. The median time to first response and CR was 1.9 and 3.1 months, respectively. Adverse events were similar to those reported for azacitidine or eprenetapopt monotherapies.
Study details: Findings come from a phase 1b/2 open-label, dose-escalation/expansion study that assessed safety, recommended dose, and efficacy of eprenetapopt and azacitidine combination in 55 patients with TP53-mutant MDS (n=40) or acute myeloid leukemia with 20%-30% marrow blasts.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the MDS Foundation Young Investigator Grant, the Early Career Award of the Dresner Foundation (DAS), and the Edward P. Evans MDS Clinical Research Consortium. The study was supported in part by the Flow Cytometry and Molecular Genomics Core Facilities at the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute. Some of the authors reported relationships with various pharmaceutical companies while some others declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Sallman DA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Jan 15. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02341.
The COVID-19 Pandemic and Changes in Healthcare Utilization for Pediatric Respiratory and Nonrespiratory Illnesses in the United States
In the United States, respiratory illnesses are the most common cause of emergency department (ED) visits and hospitalizations in children.1 In response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, several public health interventions, including school and business closures, stay-at-home orders, and mask mandates, were implemented to limit transmission of SARS-CoV-2.2,3 Studies have shown that children can contribute to the spread of SARS-CoV-2 infections, especially within households.4-6 Recent data suggest that COVID-19, and the associated public health measures enacted to slow its spread, may have affected the transmission of other respiratory pathogens.7 Similarly, the pandemic has likely affected healthcare utilization for nonrespiratory illnesses through adoption of social distancing recommendations, suspension and delays in nonemergent elective care, avoidance of healthcare settings, and the effect of decreased respiratory disease on exacerbation of chronic illness.8 The objective of this study was to examine associations between the COVID-19 pandemic and healthcare utilization for pediatric respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses at US pediatric hospitals.
METHODS
Study Design
This is a multicenter, cross-sectional study of encounters at 44 pediatric hospitals that reported data to the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database maintained by the Children’s Hospital Association (Lenexa, Kansas).
Study Population
Children 2 months to 18 years of age discharged from ED or inpatient settings with a nonsurgical diagnosis from January 1 to September 30 over a 4-year period (2017-2020) were included.
Exposure
The primary exposure was the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic time, divided into three periods: pre-COVID-19 (January-February 2020, the period prior to the pandemic in the United States), early COVID-19 (March-April 2020, coinciding with the first reported US pediatric case of COVID-19 on March 2, 2020), and COVID-19 (May-September 2020, marked by the implementation of at least two of the following containment measures in every US state: stay-at-home/shelter orders, school closures, nonessential business closures, restaurant closures, or prohibition of gatherings of more than 10 people).2
Outcomes
Statistical Analysis
Categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and percentages and compared using chi-square tests. Continuous variables were summarized as median and interquartile range (IQR) and compared using Wilcoxon rank sum tests. Weekly observed-to-expected (O:E) ratios were calculated for each hospital by dividing the number of observed respiratory illness and nonrespiratory illness encounters in a given week in 2020 (observed) by the average number of encounters for that same week during 2017-2019 (expected). O:E ratios were then aggregated over the three COVID-19 study periods, and 95% confidence intervals were established around mean O:E ratios across individual hospitals. Outcomes were then stratified by respiratory illness subgroups, geographic region, and age. Additional details can be found in the Supplemental Methods in the Appendix.
RESULTS
Study Population
A total of 9,051,980 encounters were included in the study, 6,811,799 with nonrespiratory illnesses and 2,240,181 with respiratory illnesses. Median age was 5 years (IQR, 1-11 years), and 52.7% of the population was male (Appendix Table 2 and Appendix Table 3).
Respiratory vs Nonrespiratory Illness During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Over the study period, fewer respiratory and nonrespiratory illness encounters were observed than expected, with a larger decrease in respiratory illness encounters (Table, Appendix Table 4). 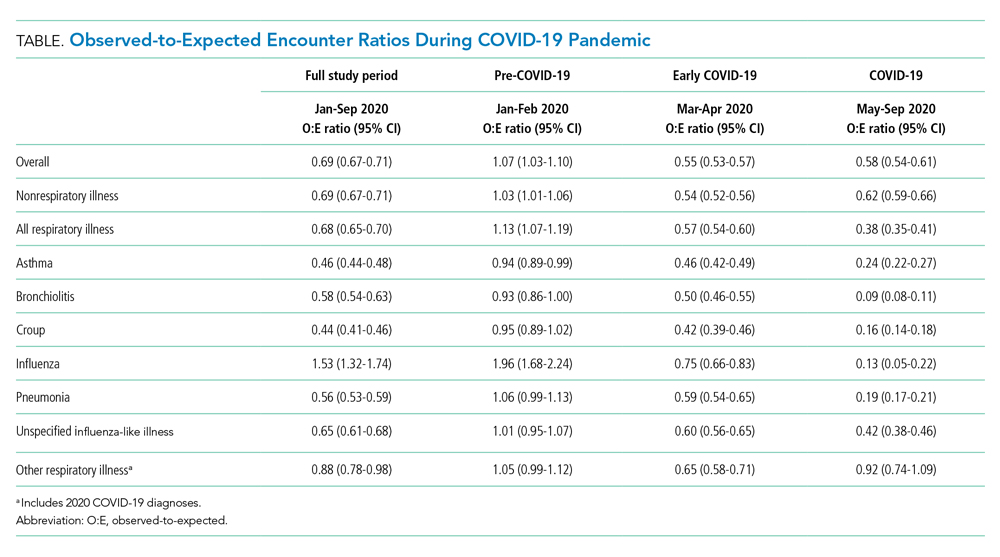

Respiratory Subgroup Analyses
The O:E ratio decreased for all respiratory subgroups over the study period (Table, Appendix Table 4). There were significant differences in specific respiratory subgroups, including asthma, bronchiolitis, croup, influenza, and pneumonia (Appendix Figure 1A). Temporal trends in respiratory encounters were consistent across hospital settings, ages, and geographic regions (Appendix Figure 1B-D). When comparing the with and without COVID-19 subgroups in the “other respiratory illnesses” cohort, other respiratory illness without COVID-19 decreased and remained lower than expected over the rest of the study period, while other respiratory illness with COVID-19 increased markedly during the summer months and declined thereafter (Appendix Figure 2).
All age groups had reductions in respiratory illness encounters during the early COVID-19 and COVID-19 periods, although the decline was less pronounced in the 12- to 17-year-old group (Appendix Figure 1B). Similarly, while all age groups experienced increases in encounters for respiratory illnesses during the summer months, only children in the 12- to 17-year-old group experienced increases beyond pre-COVID-19 levels. Importantly, this increase in respiratory encounters was largely driven by COVID-19 diagnoses (Appendix Figure 3). The trend in nonrespiratory illness encounters stratified by age is shown in Appendix Figure 4.
When patients were stratified by hospital setting, there were no differences between those hospitalized and those discharged from the ED (Appendix Figure 1C). Patterns in respiratory illnesses by geographic location were qualitatively similar until the beginning of the summer 2020, after which geographical variation became more evident (Appendix Figure 1D).
DISCUSSION
In this large, multicenter study evaluating ED visits and hospitalizations for respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses at US pediatric hospitals during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, we found a significant and substantial decrease in healthcare encounters for respiratory illnesses. A rapid and marked decline in encounters for respiratory illness in a relatively short period of time (March 12-April 2) was observed across all hospitals and US regions. Declines were consistent across common respiratory illnesses. More modest, yet still substantial, declines were also observed for nonrespiratory illnesses.
There are likely multiple underlying reasons for the observed reductions. Social distancing measures almost certainly played an important role in interrupting respiratory infection transmission. Rapid reduction in influenza transmission during the early COVID-19 period has been attributed to social distancing measures,3 and influenza transmission in children decreases with school closures.9 It is also possible that some families delayed seeking care at hospitals due to COVID-19, leading to less frequent encounters but more severe illness. The similar decrease in O:E ratio for ED visits and hospitalizations, however, is inconsistent with this explanation.
We also found relative differences in changes in encounters for respiratory illness by age. Adolescents’ levels of respiratory healthcare use declined less and recovered at a faster rate than those of younger children, returning to pre-COVID-19 levels by the end of the study period. The reason for this age differential is likely multifaceted. Infections, such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia, are more likely to be a source of respiratory illness in younger than in older children. It is also likely that disproportionate relaxation of social distancing measures among adolescents, who are known to have a stronger pattern of social interaction, contributed to the faster rise in respiratory illness–related encounters in this age group.11 Adolescents have been reported to be more susceptible to, and more likely to transmit, SARS-CoV-2 compared to younger age groups.12 More modest, albeit similar, age-based changes were observed in encounters for nonrespiratory illnesses
Emerging evidence suggests that school-age children may play an important role in SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the community.4,14 Our finding that, compared to younger children, adolescents had significantly fewer reductions in respiratory illness encounters is concerning. These findings suggest that community-based efforts to help prevent respiratory illnesses, especially COVID-19, should focus on adolescents, who are most likely to maintain social interactions and transmit respiratory infections in the school setting and their households.
This study is limited by the inclusion of only tertiary care children’s hospitals, which may not be nationally representative, and the inability to assess the precise timing of when specific public health interventions were introduced. Moreover, previous studies suggest that social distancing behaviors may have changed even before formal recommendations were enacted.15 Future studies should investigate the local impact of state- and municipality-specific mandates on the burden of COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses.
The COVID-19 pandemic was associated with substantial reductions in encounters for respiratory diseases, and also with more modest but still sizable reductions in encounters for nonrespiratory diseases. These reductions varied by age. Encounters among adolescents declined less and returned to previous levels faster compared with those of younger children.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This publication is dedicated to the memory of our coauthor, Dr. Michael Bendel-Stenzel. Dr. Bendel-Stenzel was dedicated to bettering the lives of children and advancing our knowledge of pediatrics through his research.
1. Leyenaar JK, Ralston SL, Shieh MS, Pekow PS, Mangione-Smith R, Lindenauer PK. Epidemiology of pediatric hospitalizations at general hospitals and freestanding children’s hospitals in the United States. J Hosp Med. 2016;11(11):743-749. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2624
2. Auger KA, Shah SS, Richardson T, et al. Association between statewide school closure and COVID-19 incidence and mortality in the US. JAMA. 2020;324(9):859-870. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.14348
3. Wiese AD, Everson J, Grijalva CG. Social distancing measures: evidence of interruption of seasonal influenza activity and early lessons of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Clin Infect Dis. Published online June 20, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa834
4. Grijalva CG, Rolfes MA, Zhu Y, et al. Transmission of SARS-COV-2 infections in households - Tennessee and Wisconsin, April-September 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(44):1631-1634. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6944e1
5. Worby CJ, Chaves SS, Wallinga J, Lipsitch M, Finelli L, Goldstein E. On the relative role of different age groups in influenza epidemics. Epidemics. 2015;13:10-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epidem.2015.04.003
6. Zimmerman KO, Akinboyo IC, Brookhart MA, et al. Incidence and secondary transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infections in schools. Pediatrics. Published online January 8, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-048090
7. Hatoun J, Correa ET, Donahue SMA, Vernacchio L. Social distancing for COVID-19 and diagnoses of other infectious diseases in children. Pediatrics. 2020;146(4):e2020006460. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-006460
8. Chaiyachati BH, Agawu A, Zorc JJ, Balamuth F. Trends in pediatric emergency department utilization after institution of coronavirus disease-19 mandatory social distancing. J Pediatr. 2020;226:274-277.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.07.048
9. Luca G, Kerckhove KV, Coletti P, et al. The impact of regular school closure on seasonal influenza epidemics: a data-driven spatial transmission model for Belgium. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2934-3
10. Taquechel K, Diwadkar AR, Sayed S, et al. Pediatric asthma healthcare utilization, viral testing, and air pollution changes during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020;8(10):3378-3387.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2020.07.057
11. Park YJ, Choe YJ, Park O, et al. Contact tracing during coronavirus disease outbreak, South Korea, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26(10):2465-2468. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2610.201315
12. Davies NG, Klepac P, Liu Y, et al. Age-dependent effects in the transmission and control of COVID-19 epidemics. Nat Med. 2020;26(8):1205-1211. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0962-9
13. Hill RM, Rufino K, Kurian S, Saxena J, Saxena K, Williams L. Suicide ideation and attempts in a pediatric emergency department before and during COVID-19. Pediatrics. Published online December 16, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-029280
14. Flasche S, Edmunds WJ. The role of schools and school-aged children in SARS-CoV-2 transmission. Lancet Infect Dis. Published online December 8, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30927-0
15. Sehra ST, George M, Wiebe DJ, Fundin S, Baker JF. Cell phone activity in categories of places and associations with growth in cases of COVID-19 in the US. JAMA Intern Med. Published online August 31, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.4288
In the United States, respiratory illnesses are the most common cause of emergency department (ED) visits and hospitalizations in children.1 In response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, several public health interventions, including school and business closures, stay-at-home orders, and mask mandates, were implemented to limit transmission of SARS-CoV-2.2,3 Studies have shown that children can contribute to the spread of SARS-CoV-2 infections, especially within households.4-6 Recent data suggest that COVID-19, and the associated public health measures enacted to slow its spread, may have affected the transmission of other respiratory pathogens.7 Similarly, the pandemic has likely affected healthcare utilization for nonrespiratory illnesses through adoption of social distancing recommendations, suspension and delays in nonemergent elective care, avoidance of healthcare settings, and the effect of decreased respiratory disease on exacerbation of chronic illness.8 The objective of this study was to examine associations between the COVID-19 pandemic and healthcare utilization for pediatric respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses at US pediatric hospitals.
METHODS
Study Design
This is a multicenter, cross-sectional study of encounters at 44 pediatric hospitals that reported data to the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database maintained by the Children’s Hospital Association (Lenexa, Kansas).
Study Population
Children 2 months to 18 years of age discharged from ED or inpatient settings with a nonsurgical diagnosis from January 1 to September 30 over a 4-year period (2017-2020) were included.
Exposure
The primary exposure was the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic time, divided into three periods: pre-COVID-19 (January-February 2020, the period prior to the pandemic in the United States), early COVID-19 (March-April 2020, coinciding with the first reported US pediatric case of COVID-19 on March 2, 2020), and COVID-19 (May-September 2020, marked by the implementation of at least two of the following containment measures in every US state: stay-at-home/shelter orders, school closures, nonessential business closures, restaurant closures, or prohibition of gatherings of more than 10 people).2
Outcomes
Statistical Analysis
Categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and percentages and compared using chi-square tests. Continuous variables were summarized as median and interquartile range (IQR) and compared using Wilcoxon rank sum tests. Weekly observed-to-expected (O:E) ratios were calculated for each hospital by dividing the number of observed respiratory illness and nonrespiratory illness encounters in a given week in 2020 (observed) by the average number of encounters for that same week during 2017-2019 (expected). O:E ratios were then aggregated over the three COVID-19 study periods, and 95% confidence intervals were established around mean O:E ratios across individual hospitals. Outcomes were then stratified by respiratory illness subgroups, geographic region, and age. Additional details can be found in the Supplemental Methods in the Appendix.
RESULTS
Study Population
A total of 9,051,980 encounters were included in the study, 6,811,799 with nonrespiratory illnesses and 2,240,181 with respiratory illnesses. Median age was 5 years (IQR, 1-11 years), and 52.7% of the population was male (Appendix Table 2 and Appendix Table 3).
Respiratory vs Nonrespiratory Illness During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Over the study period, fewer respiratory and nonrespiratory illness encounters were observed than expected, with a larger decrease in respiratory illness encounters (Table, Appendix Table 4). 

Respiratory Subgroup Analyses
The O:E ratio decreased for all respiratory subgroups over the study period (Table, Appendix Table 4). There were significant differences in specific respiratory subgroups, including asthma, bronchiolitis, croup, influenza, and pneumonia (Appendix Figure 1A). Temporal trends in respiratory encounters were consistent across hospital settings, ages, and geographic regions (Appendix Figure 1B-D). When comparing the with and without COVID-19 subgroups in the “other respiratory illnesses” cohort, other respiratory illness without COVID-19 decreased and remained lower than expected over the rest of the study period, while other respiratory illness with COVID-19 increased markedly during the summer months and declined thereafter (Appendix Figure 2).
All age groups had reductions in respiratory illness encounters during the early COVID-19 and COVID-19 periods, although the decline was less pronounced in the 12- to 17-year-old group (Appendix Figure 1B). Similarly, while all age groups experienced increases in encounters for respiratory illnesses during the summer months, only children in the 12- to 17-year-old group experienced increases beyond pre-COVID-19 levels. Importantly, this increase in respiratory encounters was largely driven by COVID-19 diagnoses (Appendix Figure 3). The trend in nonrespiratory illness encounters stratified by age is shown in Appendix Figure 4.
When patients were stratified by hospital setting, there were no differences between those hospitalized and those discharged from the ED (Appendix Figure 1C). Patterns in respiratory illnesses by geographic location were qualitatively similar until the beginning of the summer 2020, after which geographical variation became more evident (Appendix Figure 1D).
DISCUSSION
In this large, multicenter study evaluating ED visits and hospitalizations for respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses at US pediatric hospitals during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, we found a significant and substantial decrease in healthcare encounters for respiratory illnesses. A rapid and marked decline in encounters for respiratory illness in a relatively short period of time (March 12-April 2) was observed across all hospitals and US regions. Declines were consistent across common respiratory illnesses. More modest, yet still substantial, declines were also observed for nonrespiratory illnesses.
There are likely multiple underlying reasons for the observed reductions. Social distancing measures almost certainly played an important role in interrupting respiratory infection transmission. Rapid reduction in influenza transmission during the early COVID-19 period has been attributed to social distancing measures,3 and influenza transmission in children decreases with school closures.9 It is also possible that some families delayed seeking care at hospitals due to COVID-19, leading to less frequent encounters but more severe illness. The similar decrease in O:E ratio for ED visits and hospitalizations, however, is inconsistent with this explanation.
We also found relative differences in changes in encounters for respiratory illness by age. Adolescents’ levels of respiratory healthcare use declined less and recovered at a faster rate than those of younger children, returning to pre-COVID-19 levels by the end of the study period. The reason for this age differential is likely multifaceted. Infections, such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia, are more likely to be a source of respiratory illness in younger than in older children. It is also likely that disproportionate relaxation of social distancing measures among adolescents, who are known to have a stronger pattern of social interaction, contributed to the faster rise in respiratory illness–related encounters in this age group.11 Adolescents have been reported to be more susceptible to, and more likely to transmit, SARS-CoV-2 compared to younger age groups.12 More modest, albeit similar, age-based changes were observed in encounters for nonrespiratory illnesses
Emerging evidence suggests that school-age children may play an important role in SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the community.4,14 Our finding that, compared to younger children, adolescents had significantly fewer reductions in respiratory illness encounters is concerning. These findings suggest that community-based efforts to help prevent respiratory illnesses, especially COVID-19, should focus on adolescents, who are most likely to maintain social interactions and transmit respiratory infections in the school setting and their households.
This study is limited by the inclusion of only tertiary care children’s hospitals, which may not be nationally representative, and the inability to assess the precise timing of when specific public health interventions were introduced. Moreover, previous studies suggest that social distancing behaviors may have changed even before formal recommendations were enacted.15 Future studies should investigate the local impact of state- and municipality-specific mandates on the burden of COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses.
The COVID-19 pandemic was associated with substantial reductions in encounters for respiratory diseases, and also with more modest but still sizable reductions in encounters for nonrespiratory diseases. These reductions varied by age. Encounters among adolescents declined less and returned to previous levels faster compared with those of younger children.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This publication is dedicated to the memory of our coauthor, Dr. Michael Bendel-Stenzel. Dr. Bendel-Stenzel was dedicated to bettering the lives of children and advancing our knowledge of pediatrics through his research.
In the United States, respiratory illnesses are the most common cause of emergency department (ED) visits and hospitalizations in children.1 In response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, several public health interventions, including school and business closures, stay-at-home orders, and mask mandates, were implemented to limit transmission of SARS-CoV-2.2,3 Studies have shown that children can contribute to the spread of SARS-CoV-2 infections, especially within households.4-6 Recent data suggest that COVID-19, and the associated public health measures enacted to slow its spread, may have affected the transmission of other respiratory pathogens.7 Similarly, the pandemic has likely affected healthcare utilization for nonrespiratory illnesses through adoption of social distancing recommendations, suspension and delays in nonemergent elective care, avoidance of healthcare settings, and the effect of decreased respiratory disease on exacerbation of chronic illness.8 The objective of this study was to examine associations between the COVID-19 pandemic and healthcare utilization for pediatric respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses at US pediatric hospitals.
METHODS
Study Design
This is a multicenter, cross-sectional study of encounters at 44 pediatric hospitals that reported data to the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database maintained by the Children’s Hospital Association (Lenexa, Kansas).
Study Population
Children 2 months to 18 years of age discharged from ED or inpatient settings with a nonsurgical diagnosis from January 1 to September 30 over a 4-year period (2017-2020) were included.
Exposure
The primary exposure was the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic time, divided into three periods: pre-COVID-19 (January-February 2020, the period prior to the pandemic in the United States), early COVID-19 (March-April 2020, coinciding with the first reported US pediatric case of COVID-19 on March 2, 2020), and COVID-19 (May-September 2020, marked by the implementation of at least two of the following containment measures in every US state: stay-at-home/shelter orders, school closures, nonessential business closures, restaurant closures, or prohibition of gatherings of more than 10 people).2
Outcomes
Statistical Analysis
Categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and percentages and compared using chi-square tests. Continuous variables were summarized as median and interquartile range (IQR) and compared using Wilcoxon rank sum tests. Weekly observed-to-expected (O:E) ratios were calculated for each hospital by dividing the number of observed respiratory illness and nonrespiratory illness encounters in a given week in 2020 (observed) by the average number of encounters for that same week during 2017-2019 (expected). O:E ratios were then aggregated over the three COVID-19 study periods, and 95% confidence intervals were established around mean O:E ratios across individual hospitals. Outcomes were then stratified by respiratory illness subgroups, geographic region, and age. Additional details can be found in the Supplemental Methods in the Appendix.
RESULTS
Study Population
A total of 9,051,980 encounters were included in the study, 6,811,799 with nonrespiratory illnesses and 2,240,181 with respiratory illnesses. Median age was 5 years (IQR, 1-11 years), and 52.7% of the population was male (Appendix Table 2 and Appendix Table 3).
Respiratory vs Nonrespiratory Illness During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Over the study period, fewer respiratory and nonrespiratory illness encounters were observed than expected, with a larger decrease in respiratory illness encounters (Table, Appendix Table 4). 

Respiratory Subgroup Analyses
The O:E ratio decreased for all respiratory subgroups over the study period (Table, Appendix Table 4). There were significant differences in specific respiratory subgroups, including asthma, bronchiolitis, croup, influenza, and pneumonia (Appendix Figure 1A). Temporal trends in respiratory encounters were consistent across hospital settings, ages, and geographic regions (Appendix Figure 1B-D). When comparing the with and without COVID-19 subgroups in the “other respiratory illnesses” cohort, other respiratory illness without COVID-19 decreased and remained lower than expected over the rest of the study period, while other respiratory illness with COVID-19 increased markedly during the summer months and declined thereafter (Appendix Figure 2).
All age groups had reductions in respiratory illness encounters during the early COVID-19 and COVID-19 periods, although the decline was less pronounced in the 12- to 17-year-old group (Appendix Figure 1B). Similarly, while all age groups experienced increases in encounters for respiratory illnesses during the summer months, only children in the 12- to 17-year-old group experienced increases beyond pre-COVID-19 levels. Importantly, this increase in respiratory encounters was largely driven by COVID-19 diagnoses (Appendix Figure 3). The trend in nonrespiratory illness encounters stratified by age is shown in Appendix Figure 4.
When patients were stratified by hospital setting, there were no differences between those hospitalized and those discharged from the ED (Appendix Figure 1C). Patterns in respiratory illnesses by geographic location were qualitatively similar until the beginning of the summer 2020, after which geographical variation became more evident (Appendix Figure 1D).
DISCUSSION
In this large, multicenter study evaluating ED visits and hospitalizations for respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses at US pediatric hospitals during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, we found a significant and substantial decrease in healthcare encounters for respiratory illnesses. A rapid and marked decline in encounters for respiratory illness in a relatively short period of time (March 12-April 2) was observed across all hospitals and US regions. Declines were consistent across common respiratory illnesses. More modest, yet still substantial, declines were also observed for nonrespiratory illnesses.
There are likely multiple underlying reasons for the observed reductions. Social distancing measures almost certainly played an important role in interrupting respiratory infection transmission. Rapid reduction in influenza transmission during the early COVID-19 period has been attributed to social distancing measures,3 and influenza transmission in children decreases with school closures.9 It is also possible that some families delayed seeking care at hospitals due to COVID-19, leading to less frequent encounters but more severe illness. The similar decrease in O:E ratio for ED visits and hospitalizations, however, is inconsistent with this explanation.
We also found relative differences in changes in encounters for respiratory illness by age. Adolescents’ levels of respiratory healthcare use declined less and recovered at a faster rate than those of younger children, returning to pre-COVID-19 levels by the end of the study period. The reason for this age differential is likely multifaceted. Infections, such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia, are more likely to be a source of respiratory illness in younger than in older children. It is also likely that disproportionate relaxation of social distancing measures among adolescents, who are known to have a stronger pattern of social interaction, contributed to the faster rise in respiratory illness–related encounters in this age group.11 Adolescents have been reported to be more susceptible to, and more likely to transmit, SARS-CoV-2 compared to younger age groups.12 More modest, albeit similar, age-based changes were observed in encounters for nonrespiratory illnesses
Emerging evidence suggests that school-age children may play an important role in SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the community.4,14 Our finding that, compared to younger children, adolescents had significantly fewer reductions in respiratory illness encounters is concerning. These findings suggest that community-based efforts to help prevent respiratory illnesses, especially COVID-19, should focus on adolescents, who are most likely to maintain social interactions and transmit respiratory infections in the school setting and their households.
This study is limited by the inclusion of only tertiary care children’s hospitals, which may not be nationally representative, and the inability to assess the precise timing of when specific public health interventions were introduced. Moreover, previous studies suggest that social distancing behaviors may have changed even before formal recommendations were enacted.15 Future studies should investigate the local impact of state- and municipality-specific mandates on the burden of COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses.
The COVID-19 pandemic was associated with substantial reductions in encounters for respiratory diseases, and also with more modest but still sizable reductions in encounters for nonrespiratory diseases. These reductions varied by age. Encounters among adolescents declined less and returned to previous levels faster compared with those of younger children.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This publication is dedicated to the memory of our coauthor, Dr. Michael Bendel-Stenzel. Dr. Bendel-Stenzel was dedicated to bettering the lives of children and advancing our knowledge of pediatrics through his research.
1. Leyenaar JK, Ralston SL, Shieh MS, Pekow PS, Mangione-Smith R, Lindenauer PK. Epidemiology of pediatric hospitalizations at general hospitals and freestanding children’s hospitals in the United States. J Hosp Med. 2016;11(11):743-749. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2624
2. Auger KA, Shah SS, Richardson T, et al. Association between statewide school closure and COVID-19 incidence and mortality in the US. JAMA. 2020;324(9):859-870. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.14348
3. Wiese AD, Everson J, Grijalva CG. Social distancing measures: evidence of interruption of seasonal influenza activity and early lessons of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Clin Infect Dis. Published online June 20, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa834
4. Grijalva CG, Rolfes MA, Zhu Y, et al. Transmission of SARS-COV-2 infections in households - Tennessee and Wisconsin, April-September 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(44):1631-1634. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6944e1
5. Worby CJ, Chaves SS, Wallinga J, Lipsitch M, Finelli L, Goldstein E. On the relative role of different age groups in influenza epidemics. Epidemics. 2015;13:10-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epidem.2015.04.003
6. Zimmerman KO, Akinboyo IC, Brookhart MA, et al. Incidence and secondary transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infections in schools. Pediatrics. Published online January 8, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-048090
7. Hatoun J, Correa ET, Donahue SMA, Vernacchio L. Social distancing for COVID-19 and diagnoses of other infectious diseases in children. Pediatrics. 2020;146(4):e2020006460. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-006460
8. Chaiyachati BH, Agawu A, Zorc JJ, Balamuth F. Trends in pediatric emergency department utilization after institution of coronavirus disease-19 mandatory social distancing. J Pediatr. 2020;226:274-277.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.07.048
9. Luca G, Kerckhove KV, Coletti P, et al. The impact of regular school closure on seasonal influenza epidemics: a data-driven spatial transmission model for Belgium. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2934-3
10. Taquechel K, Diwadkar AR, Sayed S, et al. Pediatric asthma healthcare utilization, viral testing, and air pollution changes during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020;8(10):3378-3387.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2020.07.057
11. Park YJ, Choe YJ, Park O, et al. Contact tracing during coronavirus disease outbreak, South Korea, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26(10):2465-2468. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2610.201315
12. Davies NG, Klepac P, Liu Y, et al. Age-dependent effects in the transmission and control of COVID-19 epidemics. Nat Med. 2020;26(8):1205-1211. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0962-9
13. Hill RM, Rufino K, Kurian S, Saxena J, Saxena K, Williams L. Suicide ideation and attempts in a pediatric emergency department before and during COVID-19. Pediatrics. Published online December 16, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-029280
14. Flasche S, Edmunds WJ. The role of schools and school-aged children in SARS-CoV-2 transmission. Lancet Infect Dis. Published online December 8, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30927-0
15. Sehra ST, George M, Wiebe DJ, Fundin S, Baker JF. Cell phone activity in categories of places and associations with growth in cases of COVID-19 in the US. JAMA Intern Med. Published online August 31, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.4288
1. Leyenaar JK, Ralston SL, Shieh MS, Pekow PS, Mangione-Smith R, Lindenauer PK. Epidemiology of pediatric hospitalizations at general hospitals and freestanding children’s hospitals in the United States. J Hosp Med. 2016;11(11):743-749. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2624
2. Auger KA, Shah SS, Richardson T, et al. Association between statewide school closure and COVID-19 incidence and mortality in the US. JAMA. 2020;324(9):859-870. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.14348
3. Wiese AD, Everson J, Grijalva CG. Social distancing measures: evidence of interruption of seasonal influenza activity and early lessons of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Clin Infect Dis. Published online June 20, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa834
4. Grijalva CG, Rolfes MA, Zhu Y, et al. Transmission of SARS-COV-2 infections in households - Tennessee and Wisconsin, April-September 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(44):1631-1634. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6944e1
5. Worby CJ, Chaves SS, Wallinga J, Lipsitch M, Finelli L, Goldstein E. On the relative role of different age groups in influenza epidemics. Epidemics. 2015;13:10-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epidem.2015.04.003
6. Zimmerman KO, Akinboyo IC, Brookhart MA, et al. Incidence and secondary transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infections in schools. Pediatrics. Published online January 8, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-048090
7. Hatoun J, Correa ET, Donahue SMA, Vernacchio L. Social distancing for COVID-19 and diagnoses of other infectious diseases in children. Pediatrics. 2020;146(4):e2020006460. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-006460
8. Chaiyachati BH, Agawu A, Zorc JJ, Balamuth F. Trends in pediatric emergency department utilization after institution of coronavirus disease-19 mandatory social distancing. J Pediatr. 2020;226:274-277.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.07.048
9. Luca G, Kerckhove KV, Coletti P, et al. The impact of regular school closure on seasonal influenza epidemics: a data-driven spatial transmission model for Belgium. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2934-3
10. Taquechel K, Diwadkar AR, Sayed S, et al. Pediatric asthma healthcare utilization, viral testing, and air pollution changes during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020;8(10):3378-3387.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2020.07.057
11. Park YJ, Choe YJ, Park O, et al. Contact tracing during coronavirus disease outbreak, South Korea, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26(10):2465-2468. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2610.201315
12. Davies NG, Klepac P, Liu Y, et al. Age-dependent effects in the transmission and control of COVID-19 epidemics. Nat Med. 2020;26(8):1205-1211. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0962-9
13. Hill RM, Rufino K, Kurian S, Saxena J, Saxena K, Williams L. Suicide ideation and attempts in a pediatric emergency department before and during COVID-19. Pediatrics. Published online December 16, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-029280
14. Flasche S, Edmunds WJ. The role of schools and school-aged children in SARS-CoV-2 transmission. Lancet Infect Dis. Published online December 8, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30927-0
15. Sehra ST, George M, Wiebe DJ, Fundin S, Baker JF. Cell phone activity in categories of places and associations with growth in cases of COVID-19 in the US. JAMA Intern Med. Published online August 31, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.4288
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Breast cancer mortality in under 40s resparks screening debate
In the United States, breast cancer mortality rates dropped every year for women across all age groups between 1989 and 2010, but after that, the trend stalled for those younger than 40 years.
“It’s clear that mortality rates in women under 40 are no longer decreasing,” lead author R. Edward Hendrick, PhD, clinical professor from the department of radiology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, stated in a press release. “I estimate that, in 2-3 years, the mortality rate will be increasing significantly in these women.”
These findings were published online Feb. 9, 2021, in Radiology.
The authors speculate that the findings may be related to recommendations for mammography screening.
For their study, the authors analyzed National Center for Health Statistics data for 1969-2017 and delay-adjusted invasive breast cancer incidence rates from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program.
They found that breast cancer mortality rates decreased significantly by 1.5%-3.4% per year for all age groups from 1989 to 2010, and by 1.2%-2.2% per year after 2010 for those aged 40-79 years. However, the rates increased after 2010 by a nonsignificant 2.8% per year for women aged 20-29 years and 0.3% per year for those aged 30-39 years.
Distant-stage breast cancer incidence rates increased by more than 4% per year after the year 2000 in women aged 20-39 years.
“Our hope is that these findings focus more attention and research on breast cancer in younger women and what is behind this rapid increase in late-stage cancers,” Dr. Hendrick stated in the press release.
He and his colleagues speculate that the contrast between the upward trend in women aged younger than 40 years and the downward trend in older women highlights the value of mammography and may reflect the benefits of regular screening, which is not currently recommended for women younger than 40 who are not at high risk for breast cancer.
However, other groups, including the American College of Radiology and the Society for Breast Imaging, support starting annual mammograms at age 40 years.
An expert who was approached for comment noted that the incidence of breast cancer increases with age.
It is more common in women as they age, so screening recommendations do not include women aged younger than 40 years unless they are at very high risk for breast cancer, noted Joann G. Elmore, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
“The majority of deaths due to breast cancer are in women over age 40. The breast cancer mortality rates per 100,000 as shown [in this study] are about 3 patients/100,000 for the under 40 age group, about 30/100,000 in the 40-69 age group, and about 80/100,000 in the 70 and above age group,” she pointed out.
Dr. Elmore was a coauthor of an editorial regarding the 2019 evidence-based guidance statement from the American College of Physicians . That guidance, which was endorsed by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, recommended screening every other year for average-risk women aged 50-74 years, as reported by this news organization.
In their editorial, Dr. Elmore and coauthor Christoph Lee, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, applauded the ACP’s approach but stressed that the guidance is not a perfect product and does not “clearly illuminate the full path ahead for every woman.”
Breast cancer screening guidelines continue to evolve, they said, concluding that “physicians are left to use their best judgment based on available research and expert recommendations.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the United States, breast cancer mortality rates dropped every year for women across all age groups between 1989 and 2010, but after that, the trend stalled for those younger than 40 years.
“It’s clear that mortality rates in women under 40 are no longer decreasing,” lead author R. Edward Hendrick, PhD, clinical professor from the department of radiology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, stated in a press release. “I estimate that, in 2-3 years, the mortality rate will be increasing significantly in these women.”
These findings were published online Feb. 9, 2021, in Radiology.
The authors speculate that the findings may be related to recommendations for mammography screening.
For their study, the authors analyzed National Center for Health Statistics data for 1969-2017 and delay-adjusted invasive breast cancer incidence rates from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program.
They found that breast cancer mortality rates decreased significantly by 1.5%-3.4% per year for all age groups from 1989 to 2010, and by 1.2%-2.2% per year after 2010 for those aged 40-79 years. However, the rates increased after 2010 by a nonsignificant 2.8% per year for women aged 20-29 years and 0.3% per year for those aged 30-39 years.
Distant-stage breast cancer incidence rates increased by more than 4% per year after the year 2000 in women aged 20-39 years.
“Our hope is that these findings focus more attention and research on breast cancer in younger women and what is behind this rapid increase in late-stage cancers,” Dr. Hendrick stated in the press release.
He and his colleagues speculate that the contrast between the upward trend in women aged younger than 40 years and the downward trend in older women highlights the value of mammography and may reflect the benefits of regular screening, which is not currently recommended for women younger than 40 who are not at high risk for breast cancer.
However, other groups, including the American College of Radiology and the Society for Breast Imaging, support starting annual mammograms at age 40 years.
An expert who was approached for comment noted that the incidence of breast cancer increases with age.
It is more common in women as they age, so screening recommendations do not include women aged younger than 40 years unless they are at very high risk for breast cancer, noted Joann G. Elmore, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
“The majority of deaths due to breast cancer are in women over age 40. The breast cancer mortality rates per 100,000 as shown [in this study] are about 3 patients/100,000 for the under 40 age group, about 30/100,000 in the 40-69 age group, and about 80/100,000 in the 70 and above age group,” she pointed out.
Dr. Elmore was a coauthor of an editorial regarding the 2019 evidence-based guidance statement from the American College of Physicians . That guidance, which was endorsed by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, recommended screening every other year for average-risk women aged 50-74 years, as reported by this news organization.
In their editorial, Dr. Elmore and coauthor Christoph Lee, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, applauded the ACP’s approach but stressed that the guidance is not a perfect product and does not “clearly illuminate the full path ahead for every woman.”
Breast cancer screening guidelines continue to evolve, they said, concluding that “physicians are left to use their best judgment based on available research and expert recommendations.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the United States, breast cancer mortality rates dropped every year for women across all age groups between 1989 and 2010, but after that, the trend stalled for those younger than 40 years.
“It’s clear that mortality rates in women under 40 are no longer decreasing,” lead author R. Edward Hendrick, PhD, clinical professor from the department of radiology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, stated in a press release. “I estimate that, in 2-3 years, the mortality rate will be increasing significantly in these women.”
These findings were published online Feb. 9, 2021, in Radiology.
The authors speculate that the findings may be related to recommendations for mammography screening.
For their study, the authors analyzed National Center for Health Statistics data for 1969-2017 and delay-adjusted invasive breast cancer incidence rates from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program.
They found that breast cancer mortality rates decreased significantly by 1.5%-3.4% per year for all age groups from 1989 to 2010, and by 1.2%-2.2% per year after 2010 for those aged 40-79 years. However, the rates increased after 2010 by a nonsignificant 2.8% per year for women aged 20-29 years and 0.3% per year for those aged 30-39 years.
Distant-stage breast cancer incidence rates increased by more than 4% per year after the year 2000 in women aged 20-39 years.
“Our hope is that these findings focus more attention and research on breast cancer in younger women and what is behind this rapid increase in late-stage cancers,” Dr. Hendrick stated in the press release.
He and his colleagues speculate that the contrast between the upward trend in women aged younger than 40 years and the downward trend in older women highlights the value of mammography and may reflect the benefits of regular screening, which is not currently recommended for women younger than 40 who are not at high risk for breast cancer.
However, other groups, including the American College of Radiology and the Society for Breast Imaging, support starting annual mammograms at age 40 years.
An expert who was approached for comment noted that the incidence of breast cancer increases with age.
It is more common in women as they age, so screening recommendations do not include women aged younger than 40 years unless they are at very high risk for breast cancer, noted Joann G. Elmore, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
“The majority of deaths due to breast cancer are in women over age 40. The breast cancer mortality rates per 100,000 as shown [in this study] are about 3 patients/100,000 for the under 40 age group, about 30/100,000 in the 40-69 age group, and about 80/100,000 in the 70 and above age group,” she pointed out.
Dr. Elmore was a coauthor of an editorial regarding the 2019 evidence-based guidance statement from the American College of Physicians . That guidance, which was endorsed by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, recommended screening every other year for average-risk women aged 50-74 years, as reported by this news organization.
In their editorial, Dr. Elmore and coauthor Christoph Lee, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, applauded the ACP’s approach but stressed that the guidance is not a perfect product and does not “clearly illuminate the full path ahead for every woman.”
Breast cancer screening guidelines continue to evolve, they said, concluding that “physicians are left to use their best judgment based on available research and expert recommendations.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Confirmed: Diet influences colorectal cancer risk
It’s now confirmed: What you eat does affect your risk of developing colorectal cancer (CRC).
An umbrella review of studies and meta-analyses found “convincing evidence of an association between a lower CRC risk and higher intakes of dietary fiber, dietary calcium, and yogurt and lower intakes of alcohol and red meat.”
However, more research is needed to address the link between CRC and other foods, including dairy products, whole grains, processed meat, and specific dietary patterns, the authors conclude.
“We can say that the existing recommendations for diet in the primary prevention of colorectal cancer is confirmed,” said lead author Nathorn Chaiyakunapruk, PharmD, PhD, professor of pharmacology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
“It makes sense to encourage healthy diet, including those rich in fruits, vegetables, grains, and low-fat dairy, and reducing red meat and alcohol intake,” he said in an interview. “However, some of them may not yet have convincing evidence to fully support the claim.”
Other lifestyle factors, including excess weight and physical inactivity, also play a role in cancer risk. Dr. Chaiyakunapruk pointed out that their review was focused only on diet and that they had set out to confirm factors for which there was strong and convincing evidence.
The review was published online in JAMA Network Open.
The umbrella review of 45 meta-analyses found 109 associations. Overall, 35 of these 109 associations (32.1%) were nominally statistically significant, as determined on the basis of random-effects meta-analysis models, the researchers explained.
Convincing evidence was found for an increase in the risk for CRC with higher versus lower red meat consumption and with heavy alcohol intake (defined as more than four drinks per day, compared with no drinks per day or occasional drinks).
In addition, convincing evidence was found for three inverse associations: a decrease in the risk for CRC was associated with higher versus lower intake of total dietary fiber, calcium, and yogurt.
The researchers noted that, although not completely convincing, there was highly suggestive evidence for another association: a link between diet and CRC incidence. A higher intake of total dairy products (e.g., milk, cheese, and yogurt) was associated with significant risk reduction, in comparison with lower intake. A moderate intake of alcohol (from one to three drinks but not more than four per day) was associated with an increase in incidence in comparison with no drinks or an occasional drink.
Evidence suggested a reduced risk in association with several lifestyle behaviors, including adherence to a Mediterranean diet, a healthy diet, a pesco-vegetarian or semivegetarian diet, and the intake of whole grains, nonfermented milk, and supplemental calcium.
The evidence suggested that adherence to a Western diet and intake of processed meat were associated with an increased risk for CRC.
There was weak or no evidence for the remaining associations.
Existing cancer prevention guidelines
The findings support the existing cancer prevention dietary guidance and recommendations from the American Institute for Cancer Research, commented the institute’s director of nutrition programs, Sheena Swanner Patel, MS, RDN. The study confirms that dietary factors play a strong role in lowering CRC risk.
“AICR’s report found strong evidence for whole grains, foods containing dietary fiber, dairy products, and calcium supplements decreasing risk for colorectal cancer,” she said. “Specifically, eating 90 g or three servings of whole grains per day is associated with a 17% decrease in colorectal cancer risk.”
Ms. Patel added that the AICR’s report also suggested there was strong evidence that eating large amounts of red and processed meat, drinking alcohol excessively, and carrying extra body weight increased the risk for CRC.
Many previous studies have suggested a link between diet and CRC risk. One recent study suggested that, among all cancers, CRC has the highest proportion of diet-related cases (38.3%). The next highest were cancers of the mouth, pharynx, and larynx, for which almost 26% of cases were linked to diet, followed by endometrial cancer, postmenopausal breast cancer, and cancers of the kidney, stomach, liver, pancreas, and esophagus.
Neither Dr. Chaiyakunapruk and coauthors nor Ms. Patel disclosed any relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Help your patients understand colorectal cancer prevention and screening options by sharing AGA’s patient education from the GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/CRC.
It’s now confirmed: What you eat does affect your risk of developing colorectal cancer (CRC).
An umbrella review of studies and meta-analyses found “convincing evidence of an association between a lower CRC risk and higher intakes of dietary fiber, dietary calcium, and yogurt and lower intakes of alcohol and red meat.”
However, more research is needed to address the link between CRC and other foods, including dairy products, whole grains, processed meat, and specific dietary patterns, the authors conclude.
“We can say that the existing recommendations for diet in the primary prevention of colorectal cancer is confirmed,” said lead author Nathorn Chaiyakunapruk, PharmD, PhD, professor of pharmacology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
“It makes sense to encourage healthy diet, including those rich in fruits, vegetables, grains, and low-fat dairy, and reducing red meat and alcohol intake,” he said in an interview. “However, some of them may not yet have convincing evidence to fully support the claim.”
Other lifestyle factors, including excess weight and physical inactivity, also play a role in cancer risk. Dr. Chaiyakunapruk pointed out that their review was focused only on diet and that they had set out to confirm factors for which there was strong and convincing evidence.
The review was published online in JAMA Network Open.
The umbrella review of 45 meta-analyses found 109 associations. Overall, 35 of these 109 associations (32.1%) were nominally statistically significant, as determined on the basis of random-effects meta-analysis models, the researchers explained.
Convincing evidence was found for an increase in the risk for CRC with higher versus lower red meat consumption and with heavy alcohol intake (defined as more than four drinks per day, compared with no drinks per day or occasional drinks).
In addition, convincing evidence was found for three inverse associations: a decrease in the risk for CRC was associated with higher versus lower intake of total dietary fiber, calcium, and yogurt.
The researchers noted that, although not completely convincing, there was highly suggestive evidence for another association: a link between diet and CRC incidence. A higher intake of total dairy products (e.g., milk, cheese, and yogurt) was associated with significant risk reduction, in comparison with lower intake. A moderate intake of alcohol (from one to three drinks but not more than four per day) was associated with an increase in incidence in comparison with no drinks or an occasional drink.
Evidence suggested a reduced risk in association with several lifestyle behaviors, including adherence to a Mediterranean diet, a healthy diet, a pesco-vegetarian or semivegetarian diet, and the intake of whole grains, nonfermented milk, and supplemental calcium.
The evidence suggested that adherence to a Western diet and intake of processed meat were associated with an increased risk for CRC.
There was weak or no evidence for the remaining associations.
Existing cancer prevention guidelines
The findings support the existing cancer prevention dietary guidance and recommendations from the American Institute for Cancer Research, commented the institute’s director of nutrition programs, Sheena Swanner Patel, MS, RDN. The study confirms that dietary factors play a strong role in lowering CRC risk.
“AICR’s report found strong evidence for whole grains, foods containing dietary fiber, dairy products, and calcium supplements decreasing risk for colorectal cancer,” she said. “Specifically, eating 90 g or three servings of whole grains per day is associated with a 17% decrease in colorectal cancer risk.”
Ms. Patel added that the AICR’s report also suggested there was strong evidence that eating large amounts of red and processed meat, drinking alcohol excessively, and carrying extra body weight increased the risk for CRC.
Many previous studies have suggested a link between diet and CRC risk. One recent study suggested that, among all cancers, CRC has the highest proportion of diet-related cases (38.3%). The next highest were cancers of the mouth, pharynx, and larynx, for which almost 26% of cases were linked to diet, followed by endometrial cancer, postmenopausal breast cancer, and cancers of the kidney, stomach, liver, pancreas, and esophagus.
Neither Dr. Chaiyakunapruk and coauthors nor Ms. Patel disclosed any relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Help your patients understand colorectal cancer prevention and screening options by sharing AGA’s patient education from the GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/CRC.
It’s now confirmed: What you eat does affect your risk of developing colorectal cancer (CRC).
An umbrella review of studies and meta-analyses found “convincing evidence of an association between a lower CRC risk and higher intakes of dietary fiber, dietary calcium, and yogurt and lower intakes of alcohol and red meat.”
However, more research is needed to address the link between CRC and other foods, including dairy products, whole grains, processed meat, and specific dietary patterns, the authors conclude.
“We can say that the existing recommendations for diet in the primary prevention of colorectal cancer is confirmed,” said lead author Nathorn Chaiyakunapruk, PharmD, PhD, professor of pharmacology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
“It makes sense to encourage healthy diet, including those rich in fruits, vegetables, grains, and low-fat dairy, and reducing red meat and alcohol intake,” he said in an interview. “However, some of them may not yet have convincing evidence to fully support the claim.”
Other lifestyle factors, including excess weight and physical inactivity, also play a role in cancer risk. Dr. Chaiyakunapruk pointed out that their review was focused only on diet and that they had set out to confirm factors for which there was strong and convincing evidence.
The review was published online in JAMA Network Open.
The umbrella review of 45 meta-analyses found 109 associations. Overall, 35 of these 109 associations (32.1%) were nominally statistically significant, as determined on the basis of random-effects meta-analysis models, the researchers explained.
Convincing evidence was found for an increase in the risk for CRC with higher versus lower red meat consumption and with heavy alcohol intake (defined as more than four drinks per day, compared with no drinks per day or occasional drinks).
In addition, convincing evidence was found for three inverse associations: a decrease in the risk for CRC was associated with higher versus lower intake of total dietary fiber, calcium, and yogurt.
The researchers noted that, although not completely convincing, there was highly suggestive evidence for another association: a link between diet and CRC incidence. A higher intake of total dairy products (e.g., milk, cheese, and yogurt) was associated with significant risk reduction, in comparison with lower intake. A moderate intake of alcohol (from one to three drinks but not more than four per day) was associated with an increase in incidence in comparison with no drinks or an occasional drink.
Evidence suggested a reduced risk in association with several lifestyle behaviors, including adherence to a Mediterranean diet, a healthy diet, a pesco-vegetarian or semivegetarian diet, and the intake of whole grains, nonfermented milk, and supplemental calcium.
The evidence suggested that adherence to a Western diet and intake of processed meat were associated with an increased risk for CRC.
There was weak or no evidence for the remaining associations.
Existing cancer prevention guidelines
The findings support the existing cancer prevention dietary guidance and recommendations from the American Institute for Cancer Research, commented the institute’s director of nutrition programs, Sheena Swanner Patel, MS, RDN. The study confirms that dietary factors play a strong role in lowering CRC risk.
“AICR’s report found strong evidence for whole grains, foods containing dietary fiber, dairy products, and calcium supplements decreasing risk for colorectal cancer,” she said. “Specifically, eating 90 g or three servings of whole grains per day is associated with a 17% decrease in colorectal cancer risk.”
Ms. Patel added that the AICR’s report also suggested there was strong evidence that eating large amounts of red and processed meat, drinking alcohol excessively, and carrying extra body weight increased the risk for CRC.
Many previous studies have suggested a link between diet and CRC risk. One recent study suggested that, among all cancers, CRC has the highest proportion of diet-related cases (38.3%). The next highest were cancers of the mouth, pharynx, and larynx, for which almost 26% of cases were linked to diet, followed by endometrial cancer, postmenopausal breast cancer, and cancers of the kidney, stomach, liver, pancreas, and esophagus.
Neither Dr. Chaiyakunapruk and coauthors nor Ms. Patel disclosed any relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Help your patients understand colorectal cancer prevention and screening options by sharing AGA’s patient education from the GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/CRC.