User login
mAb granted breakthrough designation for MM
Photo courtesy of Janssen
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted breakthrough therapy designation for daratumumab (Darzalex), a CD38-directed monoclonal antibody (mAb), as part of combination therapy for patients with multiple myeloma (MM).
The designation is for daratumumab in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone or bortezomib and dexamethasone for the treatment of MM patients who have received at least 1 prior therapy.
This is the second breakthrough designation the FDA has granted to daratumumab.
The FDA’s breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of new therapies for serious or life-threatening conditions.
To earn the designation, a treatment must show encouraging early clinical results demonstrating substantial improvement over available therapies with regard to a clinically significant endpoint, or it must fulfill an unmet need.
In May 2013, the FDA granted daratumumab breakthrough designation for the treatment of MM patients who have received at least 3 prior lines of therapy, including a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent, or who are double-refractory to a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent.
In November 2015, daratumumab received accelerated approval from the FDA for this indication. Continued approval of the mAb may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Phase 3 trials
The newest breakthrough designation for daratumumab was based on data from two phase 3 studies—CASTOR (MMY3004) and POLLUX (MMY3003). Both studies were sponsored by Janssen Biotech, Inc., the company developing daratumumab.
In the CASTOR trial, researchers compared daratumumab-bortezomib-dexamethasone to bortezomib-dexamethasone in MM patients who had received at least 1 prior therapy.
The researchers said the addition of daratumumab significantly improved progression-free survival without increasing the cumulative toxicity or the toxicity of the bortezomib-dexamethasone combination.
Results from this trial were presented at the 2016 ASCO Annual Meeting.
In the POLLUX trial, researchers compared daratumumab-lenalidomide-dexamethasone to lenalidomide-dexamethasone in MM patients who had received at least 1 prior therapy.
According to the researchers, daratumumab-lenalidomide-dexamethasone conferred the highest response rate reported to date in the treatment of relapsed/refractory MM, significantly improved progression-free survival compared to lenalidomide-dexamethasone, and had a manageable safety profile.
These results were presented at the 21st Congress of the European Hematology Association. ![]()

Photo courtesy of Janssen
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted breakthrough therapy designation for daratumumab (Darzalex), a CD38-directed monoclonal antibody (mAb), as part of combination therapy for patients with multiple myeloma (MM).
The designation is for daratumumab in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone or bortezomib and dexamethasone for the treatment of MM patients who have received at least 1 prior therapy.
This is the second breakthrough designation the FDA has granted to daratumumab.
The FDA’s breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of new therapies for serious or life-threatening conditions.
To earn the designation, a treatment must show encouraging early clinical results demonstrating substantial improvement over available therapies with regard to a clinically significant endpoint, or it must fulfill an unmet need.
In May 2013, the FDA granted daratumumab breakthrough designation for the treatment of MM patients who have received at least 3 prior lines of therapy, including a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent, or who are double-refractory to a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent.
In November 2015, daratumumab received accelerated approval from the FDA for this indication. Continued approval of the mAb may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Phase 3 trials
The newest breakthrough designation for daratumumab was based on data from two phase 3 studies—CASTOR (MMY3004) and POLLUX (MMY3003). Both studies were sponsored by Janssen Biotech, Inc., the company developing daratumumab.
In the CASTOR trial, researchers compared daratumumab-bortezomib-dexamethasone to bortezomib-dexamethasone in MM patients who had received at least 1 prior therapy.
The researchers said the addition of daratumumab significantly improved progression-free survival without increasing the cumulative toxicity or the toxicity of the bortezomib-dexamethasone combination.
Results from this trial were presented at the 2016 ASCO Annual Meeting.
In the POLLUX trial, researchers compared daratumumab-lenalidomide-dexamethasone to lenalidomide-dexamethasone in MM patients who had received at least 1 prior therapy.
According to the researchers, daratumumab-lenalidomide-dexamethasone conferred the highest response rate reported to date in the treatment of relapsed/refractory MM, significantly improved progression-free survival compared to lenalidomide-dexamethasone, and had a manageable safety profile.
These results were presented at the 21st Congress of the European Hematology Association. ![]()

Photo courtesy of Janssen
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted breakthrough therapy designation for daratumumab (Darzalex), a CD38-directed monoclonal antibody (mAb), as part of combination therapy for patients with multiple myeloma (MM).
The designation is for daratumumab in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone or bortezomib and dexamethasone for the treatment of MM patients who have received at least 1 prior therapy.
This is the second breakthrough designation the FDA has granted to daratumumab.
The FDA’s breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of new therapies for serious or life-threatening conditions.
To earn the designation, a treatment must show encouraging early clinical results demonstrating substantial improvement over available therapies with regard to a clinically significant endpoint, or it must fulfill an unmet need.
In May 2013, the FDA granted daratumumab breakthrough designation for the treatment of MM patients who have received at least 3 prior lines of therapy, including a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent, or who are double-refractory to a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent.
In November 2015, daratumumab received accelerated approval from the FDA for this indication. Continued approval of the mAb may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Phase 3 trials
The newest breakthrough designation for daratumumab was based on data from two phase 3 studies—CASTOR (MMY3004) and POLLUX (MMY3003). Both studies were sponsored by Janssen Biotech, Inc., the company developing daratumumab.
In the CASTOR trial, researchers compared daratumumab-bortezomib-dexamethasone to bortezomib-dexamethasone in MM patients who had received at least 1 prior therapy.
The researchers said the addition of daratumumab significantly improved progression-free survival without increasing the cumulative toxicity or the toxicity of the bortezomib-dexamethasone combination.
Results from this trial were presented at the 2016 ASCO Annual Meeting.
In the POLLUX trial, researchers compared daratumumab-lenalidomide-dexamethasone to lenalidomide-dexamethasone in MM patients who had received at least 1 prior therapy.
According to the researchers, daratumumab-lenalidomide-dexamethasone conferred the highest response rate reported to date in the treatment of relapsed/refractory MM, significantly improved progression-free survival compared to lenalidomide-dexamethasone, and had a manageable safety profile.
These results were presented at the 21st Congress of the European Hematology Association. ![]()
1-800-Zap-My-Zits
ANSWERThe correct diagnosis is discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE; choice “c”). For those unfamiliar with DLE, it is often mistaken for the other items listed. Biopsy can distinguish among them.
Fungal infection (dermatophytosis; choice “a”) of the face is unusual and would have responded in some way to the antifungal cream. Likewise, the use of steroid creams would have markedly worsened a fungal infection.
Although this could have been psoriasis (choice “b”), it’s rare for that condition to be confined to the face. It almost always appears elsewhere—the scalp, elbows, knees, and/or nails.
Dermatomyositis (choice “d”), an autoimmune condition, can certainly present with a bimalar rash. However, it is usually accompanied by additional symptoms, such as progressive weakness and muscle pain.
DISCUSSION
DLE can represent a stand-alone diagnosis, or it can be a manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). When present in this bimalar form, the lesions are often mistaken for the “butterfly rash” commonly seen in SLE.
This patient was thoroughly tested for SLE, and no evidence of it was found. Biopsy did, however, show changes consistent with DLE (interface dermatitis with increased mucin formation, among others).
The treatment for DLE is rather simple: It consists of sun protection and oral hydroxychloroquine. This helps reduce inflammation, although the patient will still have residual scarring.
ANSWERThe correct diagnosis is discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE; choice “c”). For those unfamiliar with DLE, it is often mistaken for the other items listed. Biopsy can distinguish among them.
Fungal infection (dermatophytosis; choice “a”) of the face is unusual and would have responded in some way to the antifungal cream. Likewise, the use of steroid creams would have markedly worsened a fungal infection.
Although this could have been psoriasis (choice “b”), it’s rare for that condition to be confined to the face. It almost always appears elsewhere—the scalp, elbows, knees, and/or nails.
Dermatomyositis (choice “d”), an autoimmune condition, can certainly present with a bimalar rash. However, it is usually accompanied by additional symptoms, such as progressive weakness and muscle pain.
DISCUSSION
DLE can represent a stand-alone diagnosis, or it can be a manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). When present in this bimalar form, the lesions are often mistaken for the “butterfly rash” commonly seen in SLE.
This patient was thoroughly tested for SLE, and no evidence of it was found. Biopsy did, however, show changes consistent with DLE (interface dermatitis with increased mucin formation, among others).
The treatment for DLE is rather simple: It consists of sun protection and oral hydroxychloroquine. This helps reduce inflammation, although the patient will still have residual scarring.
ANSWERThe correct diagnosis is discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE; choice “c”). For those unfamiliar with DLE, it is often mistaken for the other items listed. Biopsy can distinguish among them.
Fungal infection (dermatophytosis; choice “a”) of the face is unusual and would have responded in some way to the antifungal cream. Likewise, the use of steroid creams would have markedly worsened a fungal infection.
Although this could have been psoriasis (choice “b”), it’s rare for that condition to be confined to the face. It almost always appears elsewhere—the scalp, elbows, knees, and/or nails.
Dermatomyositis (choice “d”), an autoimmune condition, can certainly present with a bimalar rash. However, it is usually accompanied by additional symptoms, such as progressive weakness and muscle pain.
DISCUSSION
DLE can represent a stand-alone diagnosis, or it can be a manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). When present in this bimalar form, the lesions are often mistaken for the “butterfly rash” commonly seen in SLE.
This patient was thoroughly tested for SLE, and no evidence of it was found. Biopsy did, however, show changes consistent with DLE (interface dermatitis with increased mucin formation, among others).
The treatment for DLE is rather simple: It consists of sun protection and oral hydroxychloroquine. This helps reduce inflammation, although the patient will still have residual scarring.
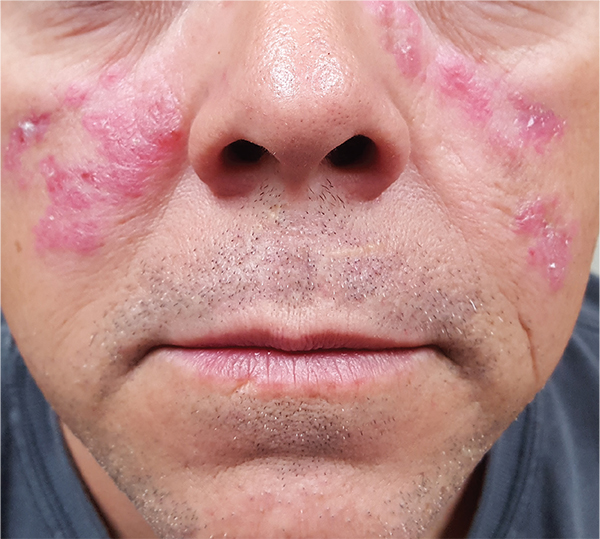
A 52-year-old man is referred to dermatology by his primary care provider for evaluation of facial lesions that first appeared almost a year ago. The patient, who works as a welder, has noticed that sun exposure tends to exacerbate the problem. He denies joint pain, fever, and malaise. He self-diagnosed the condition as acne and ordered a product from a TV ad, but this cream only made things worse. The asymptomatic lesions persist, despite application of a number of prescription products (2.5% hydrocortisone cream, adapalene gel, and antifungal creams, including tolnaftate and clotrimazole). The eruption—comprised of discrete, round, scaly lesions—covers a good portion of the bimalar areas of his face. The lesions are purplish red, and on closer inspection, you observe patulous follicular orifices. Some of the older lesions have focal atrophy. The rest of the examination is unremarkable.
An Exhausting Case of “Smoker’s Cough”
ANSWER
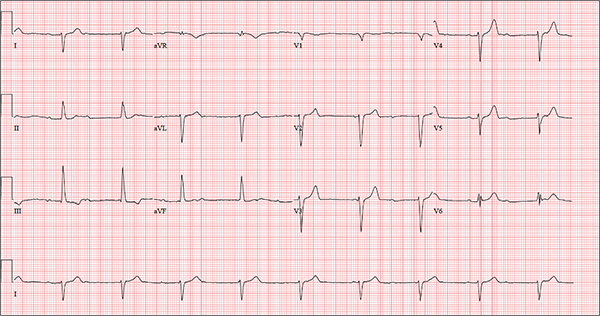
The correct interpretation includes sinus rhythm with complete heart block and a junctional rhythm, a rightward axis, and evidence of an anterior myocardial infarction (MI).
Sinus rhythm is evidenced by the regular rate and rhythm of the P waves.
Complete heart block is identified by the atrioventricular (AV) dissociation (QRS independent of the P wave), while the normal QRS duration—despite AV dissociation—confirms the existence of a junctional rhythm.
A positive R-wave axis slightly above the upper limit of normal, as seen with this patient, constitutes a rightward axis.
Finally, the posteriorly directed forces in the anterior precordial leads with poor R-wave progression denote an anterior MI.
ANSWER
The correct interpretation includes sinus rhythm with complete heart block and a junctional rhythm, a rightward axis, and evidence of an anterior myocardial infarction (MI).
Sinus rhythm is evidenced by the regular rate and rhythm of the P waves.
Complete heart block is identified by the atrioventricular (AV) dissociation (QRS independent of the P wave), while the normal QRS duration—despite AV dissociation—confirms the existence of a junctional rhythm.
A positive R-wave axis slightly above the upper limit of normal, as seen with this patient, constitutes a rightward axis.
Finally, the posteriorly directed forces in the anterior precordial leads with poor R-wave progression denote an anterior MI.
ANSWER
The correct interpretation includes sinus rhythm with complete heart block and a junctional rhythm, a rightward axis, and evidence of an anterior myocardial infarction (MI).
Sinus rhythm is evidenced by the regular rate and rhythm of the P waves.
Complete heart block is identified by the atrioventricular (AV) dissociation (QRS independent of the P wave), while the normal QRS duration—despite AV dissociation—confirms the existence of a junctional rhythm.
A positive R-wave axis slightly above the upper limit of normal, as seen with this patient, constitutes a rightward axis.
Finally, the posteriorly directed forces in the anterior precordial leads with poor R-wave progression denote an anterior MI.
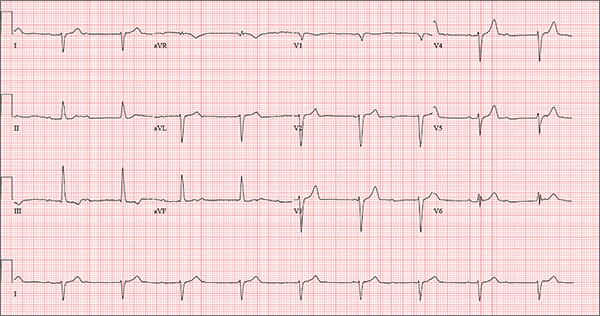
One week ago, a 67-year-old African-American woman with a history of diabetes, hypertension, and smoking developed a nonproductive cough and chest discomfort. Over the past 24 hours, her symptoms have progressed, with increasing fatigue. She has delayed seeking care to spend time with visiting family, but this morning she calls for an appointment. At presentation, she describes her chest discomfort as a “vague, dull ache.” She denies sharp chest pain, radiation, syncope, near-syncope, and palpitations. She says her cough has resolved, aside from her usual early-morning “smoker’s cough.” However, she still experiences fatigue with exertion and must stop to rest after walking up one flight of stairs or about half a block on level ground. When asked about gardening, her favorite hobby, she tells you she stopped last week because she “didn’t have the energy” for it. Her medical history is remarkable for type 2 diabetes (for the past 10 years) and hypertension, for which she has been treated her entire adult life. She also has osteoarthritis. In the 20 years she has been in your patient panel, she has closely monitored her health and been vigilant about taking her medications. Her surgical history is remarkable for hysterectomy, cholecystectomy, and bilateral bunion resections. The patient retired two years ago after a 20-year career as a tax attorney. Her husband died of a myocardial infarction at age 56. She has two adult children, who also have hypertension. She has a 50–pack-year history of tobacco use and smokes up to one full pack of cigarettes per day. She denies alcohol and illicit drug use, aside from the occasional “nip” of brandy and infrequent marijuana use. Her medication list includes metformin, glyburide, hydrochlorothiazide, and lisinopril. She is allergic to sulfa. The review of systems is remarkable for hearing loss, diabetic neuropathy in both feet, and chronic loose stools. Vital signs include a blood pressure of 148/88 mm Hg—higher than measurements from her past three visits. Her pulse is 60 beats/min; respiratory rate, 14 breaths/min-1; and temperature, 98.8°F. On physical exam, her weight is 201 lb and her height is 68 in; her weight has remained stable over the past two years. The HEENT exam findings include corrective lenses, bilateral hearing aids, and extensive dental work (including veneers). The neck is supple, without thyromegaly or jugular venous distention. The lungs are clear in all fields, apart from occasional crackles in both bases that clear with coughing. Her cardiac exam reveals a regular rate with no extra heart sounds or rubs, but a soft, early diastolic murmur at the left lower sternal border. The abdomen is soft and nontender with well-healed surgical scars and no palpable masses. Osteoarthritis is present in both hands, and her left hip has decreased range of motion, compared to her right. Peripheral pulses are strong bilaterally, and her neurologic exam is intact. You draw laboratory specimens and order a chest x-ray and ECG, which reveals a ventricular rate of 56 beats/min; PR interval, unmeasurable; QRS duration, 106 ms; QT/QTc interval, 400/386 ms; P axis, 36°; R axis, 120°; and T axis, 7°. What is your interpretation of this ECG?
Terrorist Activity: Are You Ready?
I was relaxing after work in my local American Legion a few weeks ago when a quiet young man entered with a backpack. He set it down to use the restroom, and when he returned a few minutes later, he picked up the backpack and walked away. After he left, a group of us discussed how lax we were about this situation. Yes, it was probably innocent—but what if it wasn’t? A sign over the bar reads, “Don’t let anyone leave a stranger.” The purpose of that sign is, of course, to make everyone feel welcome, but these days I think it also means to be aware of your surroundings. I have seen too many American flags at half-staff this year to overlook a potential tragedy.
Today, clinicians must be prepared for all possible emergencies, including terrorism. Acts of terrorism (as the word implies) are designed to instill terror and panic, disrupt security and communication systems, destroy property, and kill or injure innocent civilians.
Recent terrorist attacks in 2016, while shocking in their brutality, were not inconceivable—public locations where large groups gather are logical targets. Terrorists often target high-traffic areas, such as airports or shopping malls, where they can quickly disappear into a crowd if necessary (hence the concern circling the Olympic Games to be held in Brazil this month).
Attacks at restaurants, airports, and other public “hot spots” are especially frightening. With terrorist attack locations in the past year ranging from nightclubs (the Pulse Nightclub shooting in Orlando, Florida, left 49 dead) to restaurants (a bomb in Dhaka, Bangladesh, killed 20) to conference rooms (a shooting in San Bernardino, California, left 14 dead and 21 injured), it’s clear that the fundamental message terrorists want to send is: You are not safe—anywhere!
While organized events and big crowds are a bull’s-eye for terrorists, our personal surroundings have risk factors, too. Because a terrorist attack can happen anywhere at any time, you need to be prepared by knowing what to do and how to maximize your chances of survival.
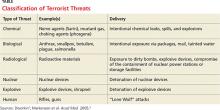
As this year’s attacks exemplify, we shouldn’t assume we understand the “logic” or thinking of terrorist organizations or individuals. Preparation for a terrorist attack boils down to being aware of the warning signs and being cautious and alert. Terrorists use a range of weapons and tactics, including bombs, arson, hijacking, and kidnapping (see Table).1,2
According to Dr. Howard Mell, an EMS director in North Carolina, the overwhelming majority of gunfire in the emergency department—or anywhere—is not the result of an active shooter. Most gunfire is targeted at a specific goal (ie, escaping or avoiding capture) or person. However, should there be an active shooter, he recommends three steps to take: Run (if the path is open), hide (if your exit is blocked), or fight (if there are no other alternatives).3
Wherever you are, always have multiple potential escape routes in mind. If you run, leave all belongings behind. Help others escape if possible, and take steps to prevent others from entering once you have left the area.
If you are unable to run, decide where to hide. If possible, barricade the area; if you are in a room, turn out the lights and stay away from the door. Be silent and put your cell phone on silent. While you are hiding, prepare to fight.
Fighting is the last resort. Act aggressively and improvise weapons to use against the assailant. If you have family, friends, or colleagues with you, put them to work!
When law enforcement officers arrive, understand that their job is to go right to the source and contain the danger. Keep your hands visible at all times, with fingers spread. Do not grab them for protection, and avoid yelling or pointing. Be prepared to give the authorities any pertinent information (eg, shooter description, last known location, direction of travel, or weapons seen).
Many health care facilities and organizations have valuable disaster and terrorism training programs, which include emergency evacuation procedures. I encourage you to take advantage of them, particularly if you travel internationally.4
Continue for personal preparedness >>
This is about personal preparedness. While I am not promoting paranoia, I do believe the risk for terrorist activity has increased in recent years.
I therefore urge you to have a healthy suspicion when you see or hear people
• Asking unusual questions about safety procedures at work
• Engaging in behaviors that provoke suspicion
• Loitering, parking, or standing in the same area over multiple days
• Attempting to disguise themselves from visit to visit
• Obtaining unusual quantities of weapons, ammunition, or explosive precursors
• Wearing clothing not appropriate for the season
• Leaving items, including backpacks or packages, unattended
• Leaving anonymous threats via telephone or e-mail
If after conducting a risk assessment of your surroundings, you believe you could (directly or indirectly) be impacted by terrorism, you must implement evacuation plans, notification of appropriate personnel, and personal safety measures.
In the event of a terrorist incident, remain calm, follow the advice of local emergency officials, and follow radio, television, and cell phone updates for news and instructions. 5
If an attack occurs near you or your home, here are practical steps you can take: Check for injuries. Give first aid and get help for seriously injured people. Check for damage using a flashlight—do not light matches or candles, or use electrical switches. Check for fires, fire hazards, and other household hazards. Sniff for gas leaks, starting at the water heater. If you smell gas or suspect a leak, turn off the main gas valve, open windows, and evacuate quickly. Shut off any damaged utilities, and confine or secure your pets. Call your family contact—but do not use the telephone again unless it is a life-threatening emergency. Cell phones may or may not be working. Check on your neighbors, especially those who are elderly or disabled.
Terrorist attacks leave citizens concerned about future incidents of terrorism in the United States and their potential impact. They raise ambiguity about what might happen next and increase stress levels. You can take steps to prepare for terrorist attacks and reduce the stress you may feel, now and later, should an emergency arise. Taking preparatory action can reassure you, your family, and your children that you have a measure of control—even in the face of terrorism. If you have additional suggestions for terrorist defense preparation, you can email your ideas to [email protected].
References
1. Dworkin RW. Preparing hospitals, doctors, and nurses for a terrorist attack. Hudson Institute. www.hudson.org/content/researchattach ments/attachment/291/dworkin_white_paper.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2016.
2. Markenson F, DiMaggio C, Redlener I. Preparing health professions students for terrorism, disaster, and public health emergencies: core competencies. Acad Med. 2005;80(6):517-526.
3. Mell HK. Run, hide, fight: how to react when there’s gunfire in the emergency department. ACEP NOW. June 21, 2016. www.acepnow.com/react-theres-gunfire-emergency-department/?elq_mid=10369&elq_cid=5274988. Accessed July 6, 2016.
4. Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Center for the Study of Traumatic Stress. Workplace preparedness for terrorism. www.cstsonline.org/assets/media/docu ments/CSTS_report_sloan_workplace_prepare_terrorism_preparedness.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2016.
5. American Red Cross. Terrorism Preparedness. www.redcross.org/prepare/disaster/terrorism. Accessed July 6, 2016.
I was relaxing after work in my local American Legion a few weeks ago when a quiet young man entered with a backpack. He set it down to use the restroom, and when he returned a few minutes later, he picked up the backpack and walked away. After he left, a group of us discussed how lax we were about this situation. Yes, it was probably innocent—but what if it wasn’t? A sign over the bar reads, “Don’t let anyone leave a stranger.” The purpose of that sign is, of course, to make everyone feel welcome, but these days I think it also means to be aware of your surroundings. I have seen too many American flags at half-staff this year to overlook a potential tragedy.
Today, clinicians must be prepared for all possible emergencies, including terrorism. Acts of terrorism (as the word implies) are designed to instill terror and panic, disrupt security and communication systems, destroy property, and kill or injure innocent civilians.
Recent terrorist attacks in 2016, while shocking in their brutality, were not inconceivable—public locations where large groups gather are logical targets. Terrorists often target high-traffic areas, such as airports or shopping malls, where they can quickly disappear into a crowd if necessary (hence the concern circling the Olympic Games to be held in Brazil this month).
Attacks at restaurants, airports, and other public “hot spots” are especially frightening. With terrorist attack locations in the past year ranging from nightclubs (the Pulse Nightclub shooting in Orlando, Florida, left 49 dead) to restaurants (a bomb in Dhaka, Bangladesh, killed 20) to conference rooms (a shooting in San Bernardino, California, left 14 dead and 21 injured), it’s clear that the fundamental message terrorists want to send is: You are not safe—anywhere!
While organized events and big crowds are a bull’s-eye for terrorists, our personal surroundings have risk factors, too. Because a terrorist attack can happen anywhere at any time, you need to be prepared by knowing what to do and how to maximize your chances of survival.
As this year’s attacks exemplify, we shouldn’t assume we understand the “logic” or thinking of terrorist organizations or individuals. Preparation for a terrorist attack boils down to being aware of the warning signs and being cautious and alert. Terrorists use a range of weapons and tactics, including bombs, arson, hijacking, and kidnapping (see Table).1,2
According to Dr. Howard Mell, an EMS director in North Carolina, the overwhelming majority of gunfire in the emergency department—or anywhere—is not the result of an active shooter. Most gunfire is targeted at a specific goal (ie, escaping or avoiding capture) or person. However, should there be an active shooter, he recommends three steps to take: Run (if the path is open), hide (if your exit is blocked), or fight (if there are no other alternatives).3
Wherever you are, always have multiple potential escape routes in mind. If you run, leave all belongings behind. Help others escape if possible, and take steps to prevent others from entering once you have left the area.
If you are unable to run, decide where to hide. If possible, barricade the area; if you are in a room, turn out the lights and stay away from the door. Be silent and put your cell phone on silent. While you are hiding, prepare to fight.
Fighting is the last resort. Act aggressively and improvise weapons to use against the assailant. If you have family, friends, or colleagues with you, put them to work!
When law enforcement officers arrive, understand that their job is to go right to the source and contain the danger. Keep your hands visible at all times, with fingers spread. Do not grab them for protection, and avoid yelling or pointing. Be prepared to give the authorities any pertinent information (eg, shooter description, last known location, direction of travel, or weapons seen).
Many health care facilities and organizations have valuable disaster and terrorism training programs, which include emergency evacuation procedures. I encourage you to take advantage of them, particularly if you travel internationally.4
Continue for personal preparedness >>
This is about personal preparedness. While I am not promoting paranoia, I do believe the risk for terrorist activity has increased in recent years.
I therefore urge you to have a healthy suspicion when you see or hear people
• Asking unusual questions about safety procedures at work
• Engaging in behaviors that provoke suspicion
• Loitering, parking, or standing in the same area over multiple days
• Attempting to disguise themselves from visit to visit
• Obtaining unusual quantities of weapons, ammunition, or explosive precursors
• Wearing clothing not appropriate for the season
• Leaving items, including backpacks or packages, unattended
• Leaving anonymous threats via telephone or e-mail
If after conducting a risk assessment of your surroundings, you believe you could (directly or indirectly) be impacted by terrorism, you must implement evacuation plans, notification of appropriate personnel, and personal safety measures.
In the event of a terrorist incident, remain calm, follow the advice of local emergency officials, and follow radio, television, and cell phone updates for news and instructions. 5
If an attack occurs near you or your home, here are practical steps you can take: Check for injuries. Give first aid and get help for seriously injured people. Check for damage using a flashlight—do not light matches or candles, or use electrical switches. Check for fires, fire hazards, and other household hazards. Sniff for gas leaks, starting at the water heater. If you smell gas or suspect a leak, turn off the main gas valve, open windows, and evacuate quickly. Shut off any damaged utilities, and confine or secure your pets. Call your family contact—but do not use the telephone again unless it is a life-threatening emergency. Cell phones may or may not be working. Check on your neighbors, especially those who are elderly or disabled.
Terrorist attacks leave citizens concerned about future incidents of terrorism in the United States and their potential impact. They raise ambiguity about what might happen next and increase stress levels. You can take steps to prepare for terrorist attacks and reduce the stress you may feel, now and later, should an emergency arise. Taking preparatory action can reassure you, your family, and your children that you have a measure of control—even in the face of terrorism. If you have additional suggestions for terrorist defense preparation, you can email your ideas to [email protected].
References
1. Dworkin RW. Preparing hospitals, doctors, and nurses for a terrorist attack. Hudson Institute. www.hudson.org/content/researchattach ments/attachment/291/dworkin_white_paper.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2016.
2. Markenson F, DiMaggio C, Redlener I. Preparing health professions students for terrorism, disaster, and public health emergencies: core competencies. Acad Med. 2005;80(6):517-526.
3. Mell HK. Run, hide, fight: how to react when there’s gunfire in the emergency department. ACEP NOW. June 21, 2016. www.acepnow.com/react-theres-gunfire-emergency-department/?elq_mid=10369&elq_cid=5274988. Accessed July 6, 2016.
4. Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Center for the Study of Traumatic Stress. Workplace preparedness for terrorism. www.cstsonline.org/assets/media/docu ments/CSTS_report_sloan_workplace_prepare_terrorism_preparedness.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2016.
5. American Red Cross. Terrorism Preparedness. www.redcross.org/prepare/disaster/terrorism. Accessed July 6, 2016.
I was relaxing after work in my local American Legion a few weeks ago when a quiet young man entered with a backpack. He set it down to use the restroom, and when he returned a few minutes later, he picked up the backpack and walked away. After he left, a group of us discussed how lax we were about this situation. Yes, it was probably innocent—but what if it wasn’t? A sign over the bar reads, “Don’t let anyone leave a stranger.” The purpose of that sign is, of course, to make everyone feel welcome, but these days I think it also means to be aware of your surroundings. I have seen too many American flags at half-staff this year to overlook a potential tragedy.
Today, clinicians must be prepared for all possible emergencies, including terrorism. Acts of terrorism (as the word implies) are designed to instill terror and panic, disrupt security and communication systems, destroy property, and kill or injure innocent civilians.
Recent terrorist attacks in 2016, while shocking in their brutality, were not inconceivable—public locations where large groups gather are logical targets. Terrorists often target high-traffic areas, such as airports or shopping malls, where they can quickly disappear into a crowd if necessary (hence the concern circling the Olympic Games to be held in Brazil this month).
Attacks at restaurants, airports, and other public “hot spots” are especially frightening. With terrorist attack locations in the past year ranging from nightclubs (the Pulse Nightclub shooting in Orlando, Florida, left 49 dead) to restaurants (a bomb in Dhaka, Bangladesh, killed 20) to conference rooms (a shooting in San Bernardino, California, left 14 dead and 21 injured), it’s clear that the fundamental message terrorists want to send is: You are not safe—anywhere!
While organized events and big crowds are a bull’s-eye for terrorists, our personal surroundings have risk factors, too. Because a terrorist attack can happen anywhere at any time, you need to be prepared by knowing what to do and how to maximize your chances of survival.
As this year’s attacks exemplify, we shouldn’t assume we understand the “logic” or thinking of terrorist organizations or individuals. Preparation for a terrorist attack boils down to being aware of the warning signs and being cautious and alert. Terrorists use a range of weapons and tactics, including bombs, arson, hijacking, and kidnapping (see Table).1,2
According to Dr. Howard Mell, an EMS director in North Carolina, the overwhelming majority of gunfire in the emergency department—or anywhere—is not the result of an active shooter. Most gunfire is targeted at a specific goal (ie, escaping or avoiding capture) or person. However, should there be an active shooter, he recommends three steps to take: Run (if the path is open), hide (if your exit is blocked), or fight (if there are no other alternatives).3
Wherever you are, always have multiple potential escape routes in mind. If you run, leave all belongings behind. Help others escape if possible, and take steps to prevent others from entering once you have left the area.
If you are unable to run, decide where to hide. If possible, barricade the area; if you are in a room, turn out the lights and stay away from the door. Be silent and put your cell phone on silent. While you are hiding, prepare to fight.
Fighting is the last resort. Act aggressively and improvise weapons to use against the assailant. If you have family, friends, or colleagues with you, put them to work!
When law enforcement officers arrive, understand that their job is to go right to the source and contain the danger. Keep your hands visible at all times, with fingers spread. Do not grab them for protection, and avoid yelling or pointing. Be prepared to give the authorities any pertinent information (eg, shooter description, last known location, direction of travel, or weapons seen).
Many health care facilities and organizations have valuable disaster and terrorism training programs, which include emergency evacuation procedures. I encourage you to take advantage of them, particularly if you travel internationally.4
Continue for personal preparedness >>
This is about personal preparedness. While I am not promoting paranoia, I do believe the risk for terrorist activity has increased in recent years.
I therefore urge you to have a healthy suspicion when you see or hear people
• Asking unusual questions about safety procedures at work
• Engaging in behaviors that provoke suspicion
• Loitering, parking, or standing in the same area over multiple days
• Attempting to disguise themselves from visit to visit
• Obtaining unusual quantities of weapons, ammunition, or explosive precursors
• Wearing clothing not appropriate for the season
• Leaving items, including backpacks or packages, unattended
• Leaving anonymous threats via telephone or e-mail
If after conducting a risk assessment of your surroundings, you believe you could (directly or indirectly) be impacted by terrorism, you must implement evacuation plans, notification of appropriate personnel, and personal safety measures.
In the event of a terrorist incident, remain calm, follow the advice of local emergency officials, and follow radio, television, and cell phone updates for news and instructions. 5
If an attack occurs near you or your home, here are practical steps you can take: Check for injuries. Give first aid and get help for seriously injured people. Check for damage using a flashlight—do not light matches or candles, or use electrical switches. Check for fires, fire hazards, and other household hazards. Sniff for gas leaks, starting at the water heater. If you smell gas or suspect a leak, turn off the main gas valve, open windows, and evacuate quickly. Shut off any damaged utilities, and confine or secure your pets. Call your family contact—but do not use the telephone again unless it is a life-threatening emergency. Cell phones may or may not be working. Check on your neighbors, especially those who are elderly or disabled.
Terrorist attacks leave citizens concerned about future incidents of terrorism in the United States and their potential impact. They raise ambiguity about what might happen next and increase stress levels. You can take steps to prepare for terrorist attacks and reduce the stress you may feel, now and later, should an emergency arise. Taking preparatory action can reassure you, your family, and your children that you have a measure of control—even in the face of terrorism. If you have additional suggestions for terrorist defense preparation, you can email your ideas to [email protected].
References
1. Dworkin RW. Preparing hospitals, doctors, and nurses for a terrorist attack. Hudson Institute. www.hudson.org/content/researchattach ments/attachment/291/dworkin_white_paper.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2016.
2. Markenson F, DiMaggio C, Redlener I. Preparing health professions students for terrorism, disaster, and public health emergencies: core competencies. Acad Med. 2005;80(6):517-526.
3. Mell HK. Run, hide, fight: how to react when there’s gunfire in the emergency department. ACEP NOW. June 21, 2016. www.acepnow.com/react-theres-gunfire-emergency-department/?elq_mid=10369&elq_cid=5274988. Accessed July 6, 2016.
4. Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Center for the Study of Traumatic Stress. Workplace preparedness for terrorism. www.cstsonline.org/assets/media/docu ments/CSTS_report_sloan_workplace_prepare_terrorism_preparedness.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2016.
5. American Red Cross. Terrorism Preparedness. www.redcross.org/prepare/disaster/terrorism. Accessed July 6, 2016.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Devastatingly Deceptive Disease
CE/CME No: CR-1608
PROGRAM OVERVIEW
Earn credit by reading this article and successfully completing the posttest and evaluation. Successful completion is defined as a cumulative score of at least 70% correct.
EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES
• Describe the pathophysiology and explain the various clinical manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
• Define the differential diagnosis for SLE.
• List the elements of the laboratory work-up used in the diagnosis of lupus.
• Describe the therapeutic options for patients with SLE.
FACULTY
Michael Felz is an Assistant Professor at Augusta University (formerly Georgia Regents University) in Augusta, Georgia. Mary Bailey Wickham is a PA student in her final year at Augusta University.
The authors have no financial relationships to disclose.
ACCREDITATION STATEMENT
This program has been reviewed and is approved for a maximum of 1.0 hour of American Academy of Physician Assistants (AAPA) Category 1 CME credit by the Physician Assistant Review Panel. [NPs: Both ANCC and the AANP Certification Program recognize AAPA as an approved provider of Category 1 credit.] Approval is valid for one year from the issue date of August 2016.
Article begins on next page >>
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that often goes undiagnosed initially. Timely detection of SLE is important, because prompt treatment can prevent its many major complications—notably, end organ damage. Here’s how to distinguish SLE from other illnesses with similar presentations and how to recognize the complications of undiagnosed SLE, which can progress rapidly and fatally.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that can involve multiple organ systems. The presence of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) is a common marker for this disease. In autoimmune diseases such as SLE, the immune system attacks the cells of healthy tissues throughout the body. Genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors (eg, ultraviolet light, infectious viruses, and even use of certain medications) have been implicated in the pathogenesis.1-3
It is estimated that 1.5 million people in the United States and up to 5 million people worldwide have SLE.4 It is nine to 10 times more prevalent in women—especially those of reproductive age—than menand occurs more frequently in African-American, Hispanic, and Asian women than in non-Hispanic Caucasian women.1,2,4-6 Siblings of SLE patients are 30 times more likely to develop the disease, compared to individuals without an affected relative.2 Increased mortality in persons with SLE is attributed to accelerated atherosclerosis, infection, malignancy, and target organ damage, particularly end-stage renal disease.3 Women ages 33 to 45 with SLE are at increased risk (50x greater) for myocardial infarction due to premature atherosclerosis than age-matched women in the general population.7 The life expectancy of SLE patients with renal damage is 23.7 years less than that of the general population.8
Increased awareness of SLE has led to drastic improvements in associated mortality over the past five decades. The survival rate in the 1950s was 50% at 2 years, while current rates are about 95% at 5 years and about 90% at 10 years.3,9 These improvements likely reflect earlier diagnosis and treatment on the part of well-informed clinicians, as well as more effective treatment.
SLE MANIFESTATIONS
SLE can affect any organ in the body with a broad spectrum of clinical manifestations, making it a devastatingly deceptive disease. Disease severity may vary by age, by organ involvement, and over time. Onset may be gradual and mild or rapidly progressive with severe organ involvement. Constitutional manifestations such as fatigue, weight loss, anorexia, and low-grade fever often serve as initial complaints. However, these features are common to a variety of infectious and inflammatory conditions, making early SLE easily overlooked and frequently misdiagnosed. 2
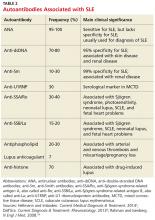
A mix of manifestations involving the joints, skin, mouth, kidneys, lungs, heart, and nervous system offers clues to the diagnosis of SLE (see Table 1). Arthritis is the most common symptom, occurring in 85% to 90% of SLE cases.1,10 It is typically nonerosive, inflammatory, symmetric or asymmetric, and polyarticular (involving five or more joints)and may be accompanied by constitutional symptoms.1,2,11 The joints most commonly affected are the proximal interphalangeals, metacarpophalangeals (MCP), knees, and wrists.2 Morning stiffness is a common complaint.1,11 Jaccoud arthropathy, which is characterized by reducible, nonerosive joint subluxations (eg, swan neck deformities, ulnar deviation, boutonniere deformities, and z-shaped thumbs), can be seen in SLE patients.3 When patients present with articular and constitutional symptoms but lack other typical manifestations of SLE, such as skin rash, appropriate measures—for example, arthrocentesis—should be taken to evaluate for infection.11
Cutaneous manifestations are the second most common feature at disease onset, with photosensitivity and malar rash being the most prevalent.10 Nearly all patients experience skin lesions at some point during the disease course.1 Diagnostic, or lupus-specific, lesions can be classified into three types: acute, subacute, and chronic.
Acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (ACLE) is almost always associated with SLE, while subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) is seen in about 50% of SLE patients.12 ACLE is usually precipitated by sunlight exposure and includes the classic erythematous, macular, “butterfly” rash located on the malar regions of the face, which may remain for days to weeks.2,12 Diffuse or discoid alopecia also may develop in ACLE, along with oral ulcers arising in purpuric necrotic lesions on the palate, buccal mucosa, or gums. Generalized erythematous, papular, or urticarial lesions may affect the face, arms, dorsa of the hands, or “V” of the neck.12
SCLE tends to be sudden in onset, with annular lesions or psoriasiform plaques on the upper trunk, arms, and dorsa of the hands that often coalesce into polycyclic lesions.12 These subacute rashes are often associated with anti-SSA/Ro antibodies.
Chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus is usually characterized by skin disease alone.12 Discoid lupus is the most common type, with circular scaly plaques with erythematous, hyperpigmented rims and atrophic hypopigmented centers that leave scars.2,12 It is commonly seen on the face, neck, and scalp.
During the course of SLE, mucous membrane involvement—typically painless oral or nasal ulcers—occurs in 25% to 45% of patients.2 Oral lesions are most commonly found on the hard palate and buccal mucosa.3,12
Lupus nephritis, perhaps the most dangerous manifestation of SLE, conveys high risk for organ failure, a higher mortality rate compared to patients without renal involvement, and lower life expectancy.8,11 Up to 60% of Asians, African Americans, and Hispanics develop renal disease during the course of their illness.8 The dominant feature is proteinuria, typically accompanied by microscopic hematuria.2
Neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) is a clinical manifestation that is poorly understood.13 An estimated 28% to 40% of NPSLE manifestations develop prior to or synchronous with the diagnosis, and 63% arise within the first year of diagnosis.13 Mild cognitive impairment is the most common manifestation,reported in up to 20% to 30% of SLE patients.2,13 Seizures and psychosis are reported in 7% to 10% of SLE patients, and psychosis—characterized by hallucinations or delusions—in 3.5%.2
Cardiac findings are common among SLE patients, with an estimated prevalence of 50%, but are rarely the presenting manifestation.14 Pericarditis with effusion is the most common cardiac manifestation, occurring in 25% of SLE patients.2 Advancing atherosclerosis due to chronic inflammation becomes a major cause of mortality in the later years for SLE patients.1 Compared to the general population, the incidence of myocardial infarction in SLE patients is increased fivefold.1 Pleuritis is the most common pleuropulmonary manifestation in SLE.11 Pleuritic chest pain with or without a pleural effusion occurs in 45% to 60% of SLE patients.2
Continue for differential diagnoses >>
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES
The differential diagnosis for SLE includes rheumatoid arthritis (RA), septic arthritis, mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), Sjögren syndrome, systemic sclerosis (SSc), polymyositis (PM), fibromyalgia, and drug-induced lupus. Symmetrical, inflammatory, polyarticular arthritis with a predilection for the wrist and MCP joints occurs in both RA and SLE.1,15 And, because the initial articular features of SLE are symmetric arthralgias, patients with SLE are frequently misdiagnosed with RA. The absence of destructive bony erosions on radiographs and large joint effusions, along with the joint reducibility in SLE, can help distinguish it from RA.16 Asymmetric arthritis, which can be a presenting feature in both RA and SLE, is more commonly seen in the latter. ANA and rheumatoid factor test results can be positive in both disorders, but antibodies to anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides, with a 95% specificity for RA but absent in SLE, distinguish RA from SLE.1,16
Patients with MCTD display an array of overlapping features of SLE, PM, and SSc, making the diagnosis difficult.17 Although MCTD can evolve into other connective tissue diseases, such as SLE, it is nonetheless considered a distinct entity.17 High titers of anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein (anti-U1RNP) antibodies are indicative of MCTD. Anti-U1RNP is rarely detected in SLE and almost never seen in other rheumatic diseases.17 Typical manifestations of MCTD are Raynaud phenomenon, swollen fingers (referred to as “sausage digits”), and protuberant polyarthritis.17
Anti-SSA/Ro and anti-SSB/La antibodies, although detectable in SLE patients, are more commonly associated with Sjögren syndrome. In addition, patients with Sjögren syndrome frequently demonstrate signs of keratoconjunctivitis sicca and xerostomia.16
The clinical features of fibromyalgia include diffuse musculoskeletal pain that readily mimics SLE arthralgias. The 2011 modification of the 2010 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia serves as a reliable tool for diagnosing patients with nonspecific, diffuse pain.18 This 2011 modification includes 19 pain locations and the six self-reported symptoms: fatigue, impaired sleep, headaches, depression, poor cognition, and abdominal pain.18
SSc, also known as scleroderma, is characterized by skin thickening and/or CREST syndrome (calcinosis, Raynaud phenomenon, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, telangiectasia). The presence of anti-Scl-70 and anti-centromere antibodies are noted as well.16
Finally, a suspicion of SLE mandates an evaluation for drug-induced lupus by assessing the patient’s exposure to culprit medications, such as hydralazine, procainamide, isoniazid, methyldopa, chlorpromazine, quinidine, minocycline, and tumor necrosis factor inhibitiors.1,11 Four key features point toward drug-induced lupus:
• The female-to-male ratio is nearly equivalent.
• Nephritis and central nervous system (CNS) manifestations are not commonly present.
• Anti–double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies and hypocomplementemia are absent.
• The clinical features and laboratory abnormalities return to baseline once the offending agent is removed.1
Anti-histone antibodies are present in approximately 75% of patients with drug-induced lupus but can also be seen in patients with SLE.11
Continue for laboratory work-up >>
LABORATORY WORK-UP
Laboratory abnormalities associated with SLE include anemia, leukopenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, hypocomplementemia, and proteinuria. A typical work-up includes a routine complete blood count (CBC) with differential, serum creatinine, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), urinalysis with microscopy, and serologic ANA titer.1,16,19 A CBC with differential may reveal hematologic abnormalities, such as anemia of chronic disease (most commonly) or autoimmune hemolytic anemia, as well as leukopenia and thrombocytopenia due to circulating autoantibodies.3 An elevated ESR and CRP indicate the severity of the systemic inflammation and/or infection. Urinalysis is effective for detecting lupus with renal diseaseand may reveal proteinuria due to renal dysfunction.2
A positive ANA titer indicates widespread activation of the immune system targeted against nuclear and cytoplasmic subparticles. The vast majority of patients with SLE will develop a positive ANA with a high titer at some point during the course of their disease.16 The ANA is highly sensitive for SLE (93% to 95%) but lacks specificity (57%).20The most common tests for ANA are enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA). ELISA is more sensitive in detecting ANA, while IFA is the gold standard due to its high specificity.21 Some laboratories may use immunoassay as a screening tool for ANA and then use IFA to confirm positive or equivocal results.21 Positive ANA results can be seen in patients with other rheumatologic diseases and in up to 15% of all healthy persons, but with low or borderline titers.22 For these reasons, ANA testing alone is a poor predictor of SLE.
When either the ANA test results are positive or are negative but a strong clinical suspicion for SLE remains, clinicians should order tests for antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens (ENA panel; see Table 2).3,16 Anti-dsDNA and anti-Smith (anti-Sm) antibodies are both specific for SLE, and levels of anti-dsDNA reflect disease activity in many patients.1,19 In contrast, anti-dsDNA antibodies are found in fewer than 0.5% of healthy individuals and patients with other autoimmune conditions.19 Among patients with high levels of anti-dsDNA antibodies and clinically inactive disease, 80% will have active disease within five years after elevated antibodies are detected.19
Autoantibodies, including ANA, anti-SSA/Ro, anti-SSB/La, and antiphospholipid antibodies, are usually detectable for many years prior to the onset of symptomatic SLE, while others, such as anti-Sm and anti-U1RNP, appear just months before the diagnosis.23 Patients with positive ANA results who do not meet criteria for SLE are still at risk for lupus and other autoimmune diseases, because complex autoimmune changes occur years before the diagnosis of SLE.23 These patients should be followed closely.
Continue for making the diagnosis >>
MAKING THE DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosing SLE may prove problematic because of the remarkable variety of relapsing and remitting clinical features, mimicry of similar conditions, and lack of a simple, definitive diagnostic test. Initial diagnosis of SLE depends on the disease manifestation, published criteria, and exclusion of alternative diagnoses. Confirmation requires careful clinical assessment, based on a thorough medical history and complete physical examination, along with specific laboratory testing.1,16 Biopsy results indicative of lupus nephritis in the presence of ANA or anti-dsDNA antibodies also confirm the diagnosis of SLE.24
Although created for research purposes, ACR classification criteria for SLE, published in 1982 and revised in 1997, have been used for more than 30 years to diagnose lupus (see www.rheumatology.org/Practice-Quality/Clinical-Support/Criteria/ACR-Endorsed-Criteria). In 2012, the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) group revised the 1997 ACR classification criteria to address major flaws and to improve clinical precision.24 According to SLICC, a definitive diagnosis requires the presence of at least four of 17 criteria, including at least one clinical and one immunologic criterion.24 The SLICC revisions have resulted in fewer misclassifications and provide greater sensitivity but lower specificity in the identification of SLE in comparison to the 1997 ACR criteria.24 To date, no one set of criteria allows for early diagnosis of SLE.
MANAGEMENT OPTIONS
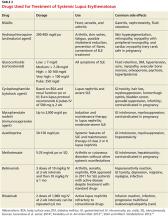
Treatment must be tailored to the patient’s specific organ system involvement. Effective therapy hinges on controlling symptoms and reducing underlying inflammation.25 Four classes of drugs are used: NSAIDs, antimalarial drugs, corticosteroids, and cytotoxic drugs (see Table 3). Most patients benefit from NSAIDs to alleviate minor arthritis and arthralgia symptoms, but the risk for peptic ulcers and nephrotoxicity should be addressed; this may require the concomitant use of gastroprotective agents such as proton pump inhibitors.25 Antimalarials are effective for musculoskeletal symptoms that do not respond to NSAIDs and for cutaneous rashes.1 The current antimalarial drug of choice is hydroxychloroquine (200 to 400 mg/d po), which has been shown to control SLE manifestations by reducing and preventing disease flares.1,11,26 It is well tolerated and can be used for the duration of treatment.11,26 Patients should be informed that this drug’s onset of action is one month.26 In rare cases, this drug can cause retinal toxicity; therefore, SLE patients receiving hydroxychloroquine should be referred to an ophthalmologist for a baseline eye examination and yearly assessments to monitor for this rare adverse effect.25,26
Low-dose corticosteroids, such as oral prednisolone or methylprednisolone, are employed when NSAIDs and antimalarials fail to control arthritis or cutaneous SLE eruptions.25 Major systemic manifestations that occur during a disease flare—such as severe arthritis, hemolytic anemia, glomerulonephritis, alveolar hemorrhage, pericarditis, pleurisy, or CNS involvement—necessitate high-dose IV corticosteroids in conjunction with immunosuppressive agents.1,11,25 These high-dose glucocorticoids should be gradually withdrawn as soon as remission is achieved.11 Long-term suppressive therapy with oral corticosteroids in addition to other agents is often needed to preserve organ function.25
The major adverse effects of long-term glucocorticoids are osteoporosis, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, glucose intolerance, and susceptibility to infection. It is recommended that patients taking prednisolone 7.5 mg/d or more undergo a bone mineral density scan every two years.25 Those with T scores below –2.5 should be prescribed bisphosphonates.25
Immunosuppressive agents, such as cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, and azathioprine, are used in conjunction with corticosteroids or when syndromes are resistant to corticosteroids.1 Collaboration between primary care, rheumatology, and nephrology is advisable for patients requiring immunosuppressive or disease-modifying pharmacologic agents.
Two new treatments for SLE are the immunologic agents belimumab and rituximab.7 Belimumab, a monoclonal human antibody, is the first medication in the past 50 years that has been approved by the FDA for antibody-positive SLE patients with active lupus unresponsive to standard treatment.7,27 Rituximab is an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, approved by the FDA for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and RA, and is now considered an option for SLE refractory to conventional treatment regimens.7,27 The efficacy of belimumab and rituximab, and the spectrum of indications for their use, are still under study, but these new therapeutic agents hold promise for the treatment of patients with refractory SLE.
Continue for helping patients live with SLE >>
HELPING PATIENTs LIVE WITH SLE
Patients with SLE have a higher mortality rate, as well as a lower quality of life, compared to the general population.28 The major contributors to a decreased quality of life are fatigue, mood disturbances (eg, depression), and chronic pain.28 Practitioners should advise SLE patients to participate in support groups and psychotherapy to alleviate the anxiety and depression associated with this chronic disease.
For patients with long-standing disease, accelerated atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease adds to morbidity and mortality. For this reason, obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and smoking are targets for intervention. Lifestyle modifications—such as exercise, smoking cessation, a healthy diet with low saturated fat, stress avoidance, and adequate rest—are recommended.26
Avoiding overexposure to sunlight, by using sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 and wearing sun-protective clothing, is essential for management of cutaneous lupus.25,26 Yearly influenza vaccination is appropriate, as are other immunizations (eg, pneumococcal vaccine).26
Advise women of childbearing age with SLE that lupus flares result in a high risk for miscarriage. All women should undergo yearly cervical cancer screening.26
Patients taking long-term glucocorticoids should adopt bone-protective behaviors, including quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, partaking in weight-bearing exercise, and consuming dietary calcium and vitamin D.25 Patients taking these drugs should avoid live virus vaccines. Those on immunosuppressive therapy should be warned about the hazardous adverse effects of glucocorticoids.
MONITORING AND FOLLOW-UP
Collaborative efforts between primary care providers and several types of specialty providers can facilitate coordinated interventions in the long-term management of lupus. Rheumatologists are experts in making therapeutic decisions for SLE.
Patients being treated for SLE require routine monitoring to assess disease activity and detect flares. The European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) guidelines recommend that monitoring include assessment for new clinical manifestations, routine laboratory tests, and immunologic assays, chiefly anti-dsDNA, anti-Sm, and serum complement levels, coupled with one of the validated global activity indices, such as the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI).29
A routine office visit with a physical examination and laboratory testing for CBC with differential, basic metabolic panel, and urinalysis every three months is recommended for patients with stable disease; patients with uncontrolled SLE may require weekly visits.11,29 Patients taking immunosuppressive drugs should be provided with adverse-effect profiles alerting them to toxicity symptoms and require frequent laboratory monitoring for potential toxicity.11
CONCLUSION
Advances in immunologically targeted serologic tests have shed more light on the underlying pathogenesis of SLE, which in turn has led to improvements in disease detection and monitoring of complications, as well as advances in therapy. Although SLE cannot be cured, emerging therapies targeting different mechanisms of SLE offer hope for patients diagnosed with this complex disease.
1. Hellmann DB, Imboden JB. Rheumatologic & immunologic disorders. In: Papadakis M, McPhee SJ, Rabow MW, eds. Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment. 53rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2014:786-836.
2. Bertsias G, Cervera R, Boumpas DT. Systemic lupus erythematosus: pathogenesis and clinical features. In: Bijlsma JWJ, ed. EULAR Textbook on Rheumatic Diseases. London: BMJ Group; 2012:476-505.
3. Dall’Era M. Chapter 21. Systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Imboden JB, Hellmann DB, Stone JH, eds. Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Rheumatology. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013.
4. Lupus Foundation of America. What is lupus? www.lupus.org/answers/entry/what-is-lupus. Accessed July 19, 2016.
5. Furst DE, Clarke AE, Fernandes AW, et al. Incidence and prevalence of adult systemic lupus erythematosus in a large US managed-care population. Lupus. 2012;22(1):99-105.
6. Pons-Estel GL, Alarcón GS, Scofield L, et al. Understanding the epidemiology and progression of systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010;39(4):257-268.
7. Lisnevskaia L, Murphy G, Isenberg D. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 2014;384(9957):1878-1888.
8. Mok CC, Kwok RC, Yip PS. Effect of renal disease on the standardized mortality ratio and life expectancy of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(8):2154-2160.
9. Merola JF, Bermas B, Lu B, et al. Clinical manifestations and survival among adults with SLE according to age at diagnosis. Lupus. 2014;23(8):778-784.
10. Font J, Cervera R, Ramos-Casals M, et al. Clusters of clinical and immunologic features in systemic lupus erythematosus: analysis of 600 patients from a single center. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004;33(4):217-230.
11. Kiriakidou M, Cotton D, Taichman D, Williams S. Systemic lupus erythematosus.Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(7):2-16.
12. Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra A. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:334-342.
13. Popescu A, Kao AH. Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011;9(3):449-457.
14. Chen PY, Chang CH, Hsu CC, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus presenting with cardiac symptoms. Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32(9):1117-1119.
15. Hahn BHH. Chapter 378: Systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, et al, eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2015.
16. Wallace DJ. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. UpToDate. www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnosis-and-differential-diagnosis-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-in-adults. Accessed July 19, 2016.
17. Cappelli S, Bellando Randone S, Martinovic D, et al. “To be or not to be,” ten years after: evidence for mixed connective tissue disease as a distinct entity. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;41(4):589-598.
18. Bennett RM, Friend R, Marcus D, et al. Criteria for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia: validation of the modified 2010 preliminary American College of Rheumatology criteria and the development of alternative criteria. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014;66(9):1364-1373.
19. Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(9):929-939.
20. Magrey M, Abelson A. Laboratory evaluation of rheumatic diseases. Cleveland Clinic Center for Continuing Education 2010. www.cleveland clinicmeded.com/medicalpubs/diseasemanagement/rheumatology/laboratory-evaluation-rheumatic-diseases/. Accessed July 19, 2016.
21. Copple SS, Sawitzke AD, Wilson AM, et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay screening then indirect immunofluorescence confirmation of antinuclear antibodies: a statistical analysis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;135(5):678-684.
22. Von Feld JM; American College of Rheumatology. Antinuclear antibodies (ANA). 2015. www.rheumatology.org/I-Am-A/Patient-Caregiver/Diseases-Conditions/Antinuclear-Antibodies-ANA. Accessed July 19, 2016.
23. Arbuckle MR, McClain MT, Rubertone MV, et al. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(16):1526-1533.
24. Petri M, Orbai A, Alarcón G, et al. Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(8):2677-2686.
25. Ioannou Y, Isenberg DA. Current concepts for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus in adults: a therapeutic challenge. Postgrad Med J. 2002;78:599-606.
26. Dall’Era M, Wofsy D. Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Imboden JB, Hellmann DB, Stone JH, eds. Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Rheumatology. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013.
27. Stohl W, Hilbert DM. The discovery and development of belimumab: the anti-BLyS–lupus connection. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(1):69-77.
28. Lateef A, Petri M. Unmet medical needs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Research & Ther. 2012;14(suppl 4):S4.
29. Bertsias G, Ioannidis JP, Boletis J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Report of a task force of the EULAR standing committee for international clinical studies including therapeutics. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(2):195-205.
CE/CME No: CR-1608
PROGRAM OVERVIEW
Earn credit by reading this article and successfully completing the posttest and evaluation. Successful completion is defined as a cumulative score of at least 70% correct.
EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES
• Describe the pathophysiology and explain the various clinical manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
• Define the differential diagnosis for SLE.
• List the elements of the laboratory work-up used in the diagnosis of lupus.
• Describe the therapeutic options for patients with SLE.
FACULTY
Michael Felz is an Assistant Professor at Augusta University (formerly Georgia Regents University) in Augusta, Georgia. Mary Bailey Wickham is a PA student in her final year at Augusta University.
The authors have no financial relationships to disclose.
ACCREDITATION STATEMENT
This program has been reviewed and is approved for a maximum of 1.0 hour of American Academy of Physician Assistants (AAPA) Category 1 CME credit by the Physician Assistant Review Panel. [NPs: Both ANCC and the AANP Certification Program recognize AAPA as an approved provider of Category 1 credit.] Approval is valid for one year from the issue date of August 2016.
Article begins on next page >>
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that often goes undiagnosed initially. Timely detection of SLE is important, because prompt treatment can prevent its many major complications—notably, end organ damage. Here’s how to distinguish SLE from other illnesses with similar presentations and how to recognize the complications of undiagnosed SLE, which can progress rapidly and fatally.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that can involve multiple organ systems. The presence of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) is a common marker for this disease. In autoimmune diseases such as SLE, the immune system attacks the cells of healthy tissues throughout the body. Genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors (eg, ultraviolet light, infectious viruses, and even use of certain medications) have been implicated in the pathogenesis.1-3
It is estimated that 1.5 million people in the United States and up to 5 million people worldwide have SLE.4 It is nine to 10 times more prevalent in women—especially those of reproductive age—than menand occurs more frequently in African-American, Hispanic, and Asian women than in non-Hispanic Caucasian women.1,2,4-6 Siblings of SLE patients are 30 times more likely to develop the disease, compared to individuals without an affected relative.2 Increased mortality in persons with SLE is attributed to accelerated atherosclerosis, infection, malignancy, and target organ damage, particularly end-stage renal disease.3 Women ages 33 to 45 with SLE are at increased risk (50x greater) for myocardial infarction due to premature atherosclerosis than age-matched women in the general population.7 The life expectancy of SLE patients with renal damage is 23.7 years less than that of the general population.8
Increased awareness of SLE has led to drastic improvements in associated mortality over the past five decades. The survival rate in the 1950s was 50% at 2 years, while current rates are about 95% at 5 years and about 90% at 10 years.3,9 These improvements likely reflect earlier diagnosis and treatment on the part of well-informed clinicians, as well as more effective treatment.
SLE MANIFESTATIONS
SLE can affect any organ in the body with a broad spectrum of clinical manifestations, making it a devastatingly deceptive disease. Disease severity may vary by age, by organ involvement, and over time. Onset may be gradual and mild or rapidly progressive with severe organ involvement. Constitutional manifestations such as fatigue, weight loss, anorexia, and low-grade fever often serve as initial complaints. However, these features are common to a variety of infectious and inflammatory conditions, making early SLE easily overlooked and frequently misdiagnosed. 2
A mix of manifestations involving the joints, skin, mouth, kidneys, lungs, heart, and nervous system offers clues to the diagnosis of SLE (see Table 1). Arthritis is the most common symptom, occurring in 85% to 90% of SLE cases.1,10 It is typically nonerosive, inflammatory, symmetric or asymmetric, and polyarticular (involving five or more joints)and may be accompanied by constitutional symptoms.1,2,11 The joints most commonly affected are the proximal interphalangeals, metacarpophalangeals (MCP), knees, and wrists.2 Morning stiffness is a common complaint.1,11 Jaccoud arthropathy, which is characterized by reducible, nonerosive joint subluxations (eg, swan neck deformities, ulnar deviation, boutonniere deformities, and z-shaped thumbs), can be seen in SLE patients.3 When patients present with articular and constitutional symptoms but lack other typical manifestations of SLE, such as skin rash, appropriate measures—for example, arthrocentesis—should be taken to evaluate for infection.11
Cutaneous manifestations are the second most common feature at disease onset, with photosensitivity and malar rash being the most prevalent.10 Nearly all patients experience skin lesions at some point during the disease course.1 Diagnostic, or lupus-specific, lesions can be classified into three types: acute, subacute, and chronic.
Acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (ACLE) is almost always associated with SLE, while subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) is seen in about 50% of SLE patients.12 ACLE is usually precipitated by sunlight exposure and includes the classic erythematous, macular, “butterfly” rash located on the malar regions of the face, which may remain for days to weeks.2,12 Diffuse or discoid alopecia also may develop in ACLE, along with oral ulcers arising in purpuric necrotic lesions on the palate, buccal mucosa, or gums. Generalized erythematous, papular, or urticarial lesions may affect the face, arms, dorsa of the hands, or “V” of the neck.12
SCLE tends to be sudden in onset, with annular lesions or psoriasiform plaques on the upper trunk, arms, and dorsa of the hands that often coalesce into polycyclic lesions.12 These subacute rashes are often associated with anti-SSA/Ro antibodies.
Chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus is usually characterized by skin disease alone.12 Discoid lupus is the most common type, with circular scaly plaques with erythematous, hyperpigmented rims and atrophic hypopigmented centers that leave scars.2,12 It is commonly seen on the face, neck, and scalp.
During the course of SLE, mucous membrane involvement—typically painless oral or nasal ulcers—occurs in 25% to 45% of patients.2 Oral lesions are most commonly found on the hard palate and buccal mucosa.3,12
Lupus nephritis, perhaps the most dangerous manifestation of SLE, conveys high risk for organ failure, a higher mortality rate compared to patients without renal involvement, and lower life expectancy.8,11 Up to 60% of Asians, African Americans, and Hispanics develop renal disease during the course of their illness.8 The dominant feature is proteinuria, typically accompanied by microscopic hematuria.2
Neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) is a clinical manifestation that is poorly understood.13 An estimated 28% to 40% of NPSLE manifestations develop prior to or synchronous with the diagnosis, and 63% arise within the first year of diagnosis.13 Mild cognitive impairment is the most common manifestation,reported in up to 20% to 30% of SLE patients.2,13 Seizures and psychosis are reported in 7% to 10% of SLE patients, and psychosis—characterized by hallucinations or delusions—in 3.5%.2
Cardiac findings are common among SLE patients, with an estimated prevalence of 50%, but are rarely the presenting manifestation.14 Pericarditis with effusion is the most common cardiac manifestation, occurring in 25% of SLE patients.2 Advancing atherosclerosis due to chronic inflammation becomes a major cause of mortality in the later years for SLE patients.1 Compared to the general population, the incidence of myocardial infarction in SLE patients is increased fivefold.1 Pleuritis is the most common pleuropulmonary manifestation in SLE.11 Pleuritic chest pain with or without a pleural effusion occurs in 45% to 60% of SLE patients.2
Continue for differential diagnoses >>
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES
The differential diagnosis for SLE includes rheumatoid arthritis (RA), septic arthritis, mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), Sjögren syndrome, systemic sclerosis (SSc), polymyositis (PM), fibromyalgia, and drug-induced lupus. Symmetrical, inflammatory, polyarticular arthritis with a predilection for the wrist and MCP joints occurs in both RA and SLE.1,15 And, because the initial articular features of SLE are symmetric arthralgias, patients with SLE are frequently misdiagnosed with RA. The absence of destructive bony erosions on radiographs and large joint effusions, along with the joint reducibility in SLE, can help distinguish it from RA.16 Asymmetric arthritis, which can be a presenting feature in both RA and SLE, is more commonly seen in the latter. ANA and rheumatoid factor test results can be positive in both disorders, but antibodies to anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides, with a 95% specificity for RA but absent in SLE, distinguish RA from SLE.1,16
Patients with MCTD display an array of overlapping features of SLE, PM, and SSc, making the diagnosis difficult.17 Although MCTD can evolve into other connective tissue diseases, such as SLE, it is nonetheless considered a distinct entity.17 High titers of anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein (anti-U1RNP) antibodies are indicative of MCTD. Anti-U1RNP is rarely detected in SLE and almost never seen in other rheumatic diseases.17 Typical manifestations of MCTD are Raynaud phenomenon, swollen fingers (referred to as “sausage digits”), and protuberant polyarthritis.17
Anti-SSA/Ro and anti-SSB/La antibodies, although detectable in SLE patients, are more commonly associated with Sjögren syndrome. In addition, patients with Sjögren syndrome frequently demonstrate signs of keratoconjunctivitis sicca and xerostomia.16
The clinical features of fibromyalgia include diffuse musculoskeletal pain that readily mimics SLE arthralgias. The 2011 modification of the 2010 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia serves as a reliable tool for diagnosing patients with nonspecific, diffuse pain.18 This 2011 modification includes 19 pain locations and the six self-reported symptoms: fatigue, impaired sleep, headaches, depression, poor cognition, and abdominal pain.18
SSc, also known as scleroderma, is characterized by skin thickening and/or CREST syndrome (calcinosis, Raynaud phenomenon, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, telangiectasia). The presence of anti-Scl-70 and anti-centromere antibodies are noted as well.16
Finally, a suspicion of SLE mandates an evaluation for drug-induced lupus by assessing the patient’s exposure to culprit medications, such as hydralazine, procainamide, isoniazid, methyldopa, chlorpromazine, quinidine, minocycline, and tumor necrosis factor inhibitiors.1,11 Four key features point toward drug-induced lupus:
• The female-to-male ratio is nearly equivalent.
• Nephritis and central nervous system (CNS) manifestations are not commonly present.
• Anti–double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies and hypocomplementemia are absent.
• The clinical features and laboratory abnormalities return to baseline once the offending agent is removed.1
Anti-histone antibodies are present in approximately 75% of patients with drug-induced lupus but can also be seen in patients with SLE.11
Continue for laboratory work-up >>
LABORATORY WORK-UP
Laboratory abnormalities associated with SLE include anemia, leukopenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, hypocomplementemia, and proteinuria. A typical work-up includes a routine complete blood count (CBC) with differential, serum creatinine, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), urinalysis with microscopy, and serologic ANA titer.1,16,19 A CBC with differential may reveal hematologic abnormalities, such as anemia of chronic disease (most commonly) or autoimmune hemolytic anemia, as well as leukopenia and thrombocytopenia due to circulating autoantibodies.3 An elevated ESR and CRP indicate the severity of the systemic inflammation and/or infection. Urinalysis is effective for detecting lupus with renal diseaseand may reveal proteinuria due to renal dysfunction.2
A positive ANA titer indicates widespread activation of the immune system targeted against nuclear and cytoplasmic subparticles. The vast majority of patients with SLE will develop a positive ANA with a high titer at some point during the course of their disease.16 The ANA is highly sensitive for SLE (93% to 95%) but lacks specificity (57%).20The most common tests for ANA are enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA). ELISA is more sensitive in detecting ANA, while IFA is the gold standard due to its high specificity.21 Some laboratories may use immunoassay as a screening tool for ANA and then use IFA to confirm positive or equivocal results.21 Positive ANA results can be seen in patients with other rheumatologic diseases and in up to 15% of all healthy persons, but with low or borderline titers.22 For these reasons, ANA testing alone is a poor predictor of SLE.
When either the ANA test results are positive or are negative but a strong clinical suspicion for SLE remains, clinicians should order tests for antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens (ENA panel; see Table 2).3,16 Anti-dsDNA and anti-Smith (anti-Sm) antibodies are both specific for SLE, and levels of anti-dsDNA reflect disease activity in many patients.1,19 In contrast, anti-dsDNA antibodies are found in fewer than 0.5% of healthy individuals and patients with other autoimmune conditions.19 Among patients with high levels of anti-dsDNA antibodies and clinically inactive disease, 80% will have active disease within five years after elevated antibodies are detected.19
Autoantibodies, including ANA, anti-SSA/Ro, anti-SSB/La, and antiphospholipid antibodies, are usually detectable for many years prior to the onset of symptomatic SLE, while others, such as anti-Sm and anti-U1RNP, appear just months before the diagnosis.23 Patients with positive ANA results who do not meet criteria for SLE are still at risk for lupus and other autoimmune diseases, because complex autoimmune changes occur years before the diagnosis of SLE.23 These patients should be followed closely.
Continue for making the diagnosis >>
MAKING THE DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosing SLE may prove problematic because of the remarkable variety of relapsing and remitting clinical features, mimicry of similar conditions, and lack of a simple, definitive diagnostic test. Initial diagnosis of SLE depends on the disease manifestation, published criteria, and exclusion of alternative diagnoses. Confirmation requires careful clinical assessment, based on a thorough medical history and complete physical examination, along with specific laboratory testing.1,16 Biopsy results indicative of lupus nephritis in the presence of ANA or anti-dsDNA antibodies also confirm the diagnosis of SLE.24
Although created for research purposes, ACR classification criteria for SLE, published in 1982 and revised in 1997, have been used for more than 30 years to diagnose lupus (see www.rheumatology.org/Practice-Quality/Clinical-Support/Criteria/ACR-Endorsed-Criteria). In 2012, the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) group revised the 1997 ACR classification criteria to address major flaws and to improve clinical precision.24 According to SLICC, a definitive diagnosis requires the presence of at least four of 17 criteria, including at least one clinical and one immunologic criterion.24 The SLICC revisions have resulted in fewer misclassifications and provide greater sensitivity but lower specificity in the identification of SLE in comparison to the 1997 ACR criteria.24 To date, no one set of criteria allows for early diagnosis of SLE.
MANAGEMENT OPTIONS
Treatment must be tailored to the patient’s specific organ system involvement. Effective therapy hinges on controlling symptoms and reducing underlying inflammation.25 Four classes of drugs are used: NSAIDs, antimalarial drugs, corticosteroids, and cytotoxic drugs (see Table 3). Most patients benefit from NSAIDs to alleviate minor arthritis and arthralgia symptoms, but the risk for peptic ulcers and nephrotoxicity should be addressed; this may require the concomitant use of gastroprotective agents such as proton pump inhibitors.25 Antimalarials are effective for musculoskeletal symptoms that do not respond to NSAIDs and for cutaneous rashes.1 The current antimalarial drug of choice is hydroxychloroquine (200 to 400 mg/d po), which has been shown to control SLE manifestations by reducing and preventing disease flares.1,11,26 It is well tolerated and can be used for the duration of treatment.11,26 Patients should be informed that this drug’s onset of action is one month.26 In rare cases, this drug can cause retinal toxicity; therefore, SLE patients receiving hydroxychloroquine should be referred to an ophthalmologist for a baseline eye examination and yearly assessments to monitor for this rare adverse effect.25,26
Low-dose corticosteroids, such as oral prednisolone or methylprednisolone, are employed when NSAIDs and antimalarials fail to control arthritis or cutaneous SLE eruptions.25 Major systemic manifestations that occur during a disease flare—such as severe arthritis, hemolytic anemia, glomerulonephritis, alveolar hemorrhage, pericarditis, pleurisy, or CNS involvement—necessitate high-dose IV corticosteroids in conjunction with immunosuppressive agents.1,11,25 These high-dose glucocorticoids should be gradually withdrawn as soon as remission is achieved.11 Long-term suppressive therapy with oral corticosteroids in addition to other agents is often needed to preserve organ function.25
The major adverse effects of long-term glucocorticoids are osteoporosis, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, glucose intolerance, and susceptibility to infection. It is recommended that patients taking prednisolone 7.5 mg/d or more undergo a bone mineral density scan every two years.25 Those with T scores below –2.5 should be prescribed bisphosphonates.25
Immunosuppressive agents, such as cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, and azathioprine, are used in conjunction with corticosteroids or when syndromes are resistant to corticosteroids.1 Collaboration between primary care, rheumatology, and nephrology is advisable for patients requiring immunosuppressive or disease-modifying pharmacologic agents.
Two new treatments for SLE are the immunologic agents belimumab and rituximab.7 Belimumab, a monoclonal human antibody, is the first medication in the past 50 years that has been approved by the FDA for antibody-positive SLE patients with active lupus unresponsive to standard treatment.7,27 Rituximab is an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, approved by the FDA for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and RA, and is now considered an option for SLE refractory to conventional treatment regimens.7,27 The efficacy of belimumab and rituximab, and the spectrum of indications for their use, are still under study, but these new therapeutic agents hold promise for the treatment of patients with refractory SLE.
Continue for helping patients live with SLE >>
HELPING PATIENTs LIVE WITH SLE
Patients with SLE have a higher mortality rate, as well as a lower quality of life, compared to the general population.28 The major contributors to a decreased quality of life are fatigue, mood disturbances (eg, depression), and chronic pain.28 Practitioners should advise SLE patients to participate in support groups and psychotherapy to alleviate the anxiety and depression associated with this chronic disease.
For patients with long-standing disease, accelerated atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease adds to morbidity and mortality. For this reason, obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and smoking are targets for intervention. Lifestyle modifications—such as exercise, smoking cessation, a healthy diet with low saturated fat, stress avoidance, and adequate rest—are recommended.26
Avoiding overexposure to sunlight, by using sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 and wearing sun-protective clothing, is essential for management of cutaneous lupus.25,26 Yearly influenza vaccination is appropriate, as are other immunizations (eg, pneumococcal vaccine).26
Advise women of childbearing age with SLE that lupus flares result in a high risk for miscarriage. All women should undergo yearly cervical cancer screening.26
Patients taking long-term glucocorticoids should adopt bone-protective behaviors, including quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, partaking in weight-bearing exercise, and consuming dietary calcium and vitamin D.25 Patients taking these drugs should avoid live virus vaccines. Those on immunosuppressive therapy should be warned about the hazardous adverse effects of glucocorticoids.
MONITORING AND FOLLOW-UP
Collaborative efforts between primary care providers and several types of specialty providers can facilitate coordinated interventions in the long-term management of lupus. Rheumatologists are experts in making therapeutic decisions for SLE.
Patients being treated for SLE require routine monitoring to assess disease activity and detect flares. The European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) guidelines recommend that monitoring include assessment for new clinical manifestations, routine laboratory tests, and immunologic assays, chiefly anti-dsDNA, anti-Sm, and serum complement levels, coupled with one of the validated global activity indices, such as the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI).29
A routine office visit with a physical examination and laboratory testing for CBC with differential, basic metabolic panel, and urinalysis every three months is recommended for patients with stable disease; patients with uncontrolled SLE may require weekly visits.11,29 Patients taking immunosuppressive drugs should be provided with adverse-effect profiles alerting them to toxicity symptoms and require frequent laboratory monitoring for potential toxicity.11
CONCLUSION
Advances in immunologically targeted serologic tests have shed more light on the underlying pathogenesis of SLE, which in turn has led to improvements in disease detection and monitoring of complications, as well as advances in therapy. Although SLE cannot be cured, emerging therapies targeting different mechanisms of SLE offer hope for patients diagnosed with this complex disease.
CE/CME No: CR-1608
PROGRAM OVERVIEW
Earn credit by reading this article and successfully completing the posttest and evaluation. Successful completion is defined as a cumulative score of at least 70% correct.
EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES
• Describe the pathophysiology and explain the various clinical manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
• Define the differential diagnosis for SLE.
• List the elements of the laboratory work-up used in the diagnosis of lupus.
• Describe the therapeutic options for patients with SLE.
FACULTY
Michael Felz is an Assistant Professor at Augusta University (formerly Georgia Regents University) in Augusta, Georgia. Mary Bailey Wickham is a PA student in her final year at Augusta University.
The authors have no financial relationships to disclose.
ACCREDITATION STATEMENT
This program has been reviewed and is approved for a maximum of 1.0 hour of American Academy of Physician Assistants (AAPA) Category 1 CME credit by the Physician Assistant Review Panel. [NPs: Both ANCC and the AANP Certification Program recognize AAPA as an approved provider of Category 1 credit.] Approval is valid for one year from the issue date of August 2016.
Article begins on next page >>
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that often goes undiagnosed initially. Timely detection of SLE is important, because prompt treatment can prevent its many major complications—notably, end organ damage. Here’s how to distinguish SLE from other illnesses with similar presentations and how to recognize the complications of undiagnosed SLE, which can progress rapidly and fatally.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that can involve multiple organ systems. The presence of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) is a common marker for this disease. In autoimmune diseases such as SLE, the immune system attacks the cells of healthy tissues throughout the body. Genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors (eg, ultraviolet light, infectious viruses, and even use of certain medications) have been implicated in the pathogenesis.1-3
It is estimated that 1.5 million people in the United States and up to 5 million people worldwide have SLE.4 It is nine to 10 times more prevalent in women—especially those of reproductive age—than menand occurs more frequently in African-American, Hispanic, and Asian women than in non-Hispanic Caucasian women.1,2,4-6 Siblings of SLE patients are 30 times more likely to develop the disease, compared to individuals without an affected relative.2 Increased mortality in persons with SLE is attributed to accelerated atherosclerosis, infection, malignancy, and target organ damage, particularly end-stage renal disease.3 Women ages 33 to 45 with SLE are at increased risk (50x greater) for myocardial infarction due to premature atherosclerosis than age-matched women in the general population.7 The life expectancy of SLE patients with renal damage is 23.7 years less than that of the general population.8
Increased awareness of SLE has led to drastic improvements in associated mortality over the past five decades. The survival rate in the 1950s was 50% at 2 years, while current rates are about 95% at 5 years and about 90% at 10 years.3,9 These improvements likely reflect earlier diagnosis and treatment on the part of well-informed clinicians, as well as more effective treatment.
SLE MANIFESTATIONS
SLE can affect any organ in the body with a broad spectrum of clinical manifestations, making it a devastatingly deceptive disease. Disease severity may vary by age, by organ involvement, and over time. Onset may be gradual and mild or rapidly progressive with severe organ involvement. Constitutional manifestations such as fatigue, weight loss, anorexia, and low-grade fever often serve as initial complaints. However, these features are common to a variety of infectious and inflammatory conditions, making early SLE easily overlooked and frequently misdiagnosed. 2
A mix of manifestations involving the joints, skin, mouth, kidneys, lungs, heart, and nervous system offers clues to the diagnosis of SLE (see Table 1). Arthritis is the most common symptom, occurring in 85% to 90% of SLE cases.1,10 It is typically nonerosive, inflammatory, symmetric or asymmetric, and polyarticular (involving five or more joints)and may be accompanied by constitutional symptoms.1,2,11 The joints most commonly affected are the proximal interphalangeals, metacarpophalangeals (MCP), knees, and wrists.2 Morning stiffness is a common complaint.1,11 Jaccoud arthropathy, which is characterized by reducible, nonerosive joint subluxations (eg, swan neck deformities, ulnar deviation, boutonniere deformities, and z-shaped thumbs), can be seen in SLE patients.3 When patients present with articular and constitutional symptoms but lack other typical manifestations of SLE, such as skin rash, appropriate measures—for example, arthrocentesis—should be taken to evaluate for infection.11
Cutaneous manifestations are the second most common feature at disease onset, with photosensitivity and malar rash being the most prevalent.10 Nearly all patients experience skin lesions at some point during the disease course.1 Diagnostic, or lupus-specific, lesions can be classified into three types: acute, subacute, and chronic.
Acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (ACLE) is almost always associated with SLE, while subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) is seen in about 50% of SLE patients.12 ACLE is usually precipitated by sunlight exposure and includes the classic erythematous, macular, “butterfly” rash located on the malar regions of the face, which may remain for days to weeks.2,12 Diffuse or discoid alopecia also may develop in ACLE, along with oral ulcers arising in purpuric necrotic lesions on the palate, buccal mucosa, or gums. Generalized erythematous, papular, or urticarial lesions may affect the face, arms, dorsa of the hands, or “V” of the neck.12
SCLE tends to be sudden in onset, with annular lesions or psoriasiform plaques on the upper trunk, arms, and dorsa of the hands that often coalesce into polycyclic lesions.12 These subacute rashes are often associated with anti-SSA/Ro antibodies.
Chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus is usually characterized by skin disease alone.12 Discoid lupus is the most common type, with circular scaly plaques with erythematous, hyperpigmented rims and atrophic hypopigmented centers that leave scars.2,12 It is commonly seen on the face, neck, and scalp.
During the course of SLE, mucous membrane involvement—typically painless oral or nasal ulcers—occurs in 25% to 45% of patients.2 Oral lesions are most commonly found on the hard palate and buccal mucosa.3,12
Lupus nephritis, perhaps the most dangerous manifestation of SLE, conveys high risk for organ failure, a higher mortality rate compared to patients without renal involvement, and lower life expectancy.8,11 Up to 60% of Asians, African Americans, and Hispanics develop renal disease during the course of their illness.8 The dominant feature is proteinuria, typically accompanied by microscopic hematuria.2
Neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) is a clinical manifestation that is poorly understood.13 An estimated 28% to 40% of NPSLE manifestations develop prior to or synchronous with the diagnosis, and 63% arise within the first year of diagnosis.13 Mild cognitive impairment is the most common manifestation,reported in up to 20% to 30% of SLE patients.2,13 Seizures and psychosis are reported in 7% to 10% of SLE patients, and psychosis—characterized by hallucinations or delusions—in 3.5%.2
Cardiac findings are common among SLE patients, with an estimated prevalence of 50%, but are rarely the presenting manifestation.14 Pericarditis with effusion is the most common cardiac manifestation, occurring in 25% of SLE patients.2 Advancing atherosclerosis due to chronic inflammation becomes a major cause of mortality in the later years for SLE patients.1 Compared to the general population, the incidence of myocardial infarction in SLE patients is increased fivefold.1 Pleuritis is the most common pleuropulmonary manifestation in SLE.11 Pleuritic chest pain with or without a pleural effusion occurs in 45% to 60% of SLE patients.2
Continue for differential diagnoses >>
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES
The differential diagnosis for SLE includes rheumatoid arthritis (RA), septic arthritis, mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), Sjögren syndrome, systemic sclerosis (SSc), polymyositis (PM), fibromyalgia, and drug-induced lupus. Symmetrical, inflammatory, polyarticular arthritis with a predilection for the wrist and MCP joints occurs in both RA and SLE.1,15 And, because the initial articular features of SLE are symmetric arthralgias, patients with SLE are frequently misdiagnosed with RA. The absence of destructive bony erosions on radiographs and large joint effusions, along with the joint reducibility in SLE, can help distinguish it from RA.16 Asymmetric arthritis, which can be a presenting feature in both RA and SLE, is more commonly seen in the latter. ANA and rheumatoid factor test results can be positive in both disorders, but antibodies to anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides, with a 95% specificity for RA but absent in SLE, distinguish RA from SLE.1,16
Patients with MCTD display an array of overlapping features of SLE, PM, and SSc, making the diagnosis difficult.17 Although MCTD can evolve into other connective tissue diseases, such as SLE, it is nonetheless considered a distinct entity.17 High titers of anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein (anti-U1RNP) antibodies are indicative of MCTD. Anti-U1RNP is rarely detected in SLE and almost never seen in other rheumatic diseases.17 Typical manifestations of MCTD are Raynaud phenomenon, swollen fingers (referred to as “sausage digits”), and protuberant polyarthritis.17
Anti-SSA/Ro and anti-SSB/La antibodies, although detectable in SLE patients, are more commonly associated with Sjögren syndrome. In addition, patients with Sjögren syndrome frequently demonstrate signs of keratoconjunctivitis sicca and xerostomia.16
The clinical features of fibromyalgia include diffuse musculoskeletal pain that readily mimics SLE arthralgias. The 2011 modification of the 2010 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia serves as a reliable tool for diagnosing patients with nonspecific, diffuse pain.18 This 2011 modification includes 19 pain locations and the six self-reported symptoms: fatigue, impaired sleep, headaches, depression, poor cognition, and abdominal pain.18
SSc, also known as scleroderma, is characterized by skin thickening and/or CREST syndrome (calcinosis, Raynaud phenomenon, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, telangiectasia). The presence of anti-Scl-70 and anti-centromere antibodies are noted as well.16
Finally, a suspicion of SLE mandates an evaluation for drug-induced lupus by assessing the patient’s exposure to culprit medications, such as hydralazine, procainamide, isoniazid, methyldopa, chlorpromazine, quinidine, minocycline, and tumor necrosis factor inhibitiors.1,11 Four key features point toward drug-induced lupus:
• The female-to-male ratio is nearly equivalent.
• Nephritis and central nervous system (CNS) manifestations are not commonly present.
• Anti–double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies and hypocomplementemia are absent.
• The clinical features and laboratory abnormalities return to baseline once the offending agent is removed.1
Anti-histone antibodies are present in approximately 75% of patients with drug-induced lupus but can also be seen in patients with SLE.11
Continue for laboratory work-up >>
LABORATORY WORK-UP
Laboratory abnormalities associated with SLE include anemia, leukopenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, hypocomplementemia, and proteinuria. A typical work-up includes a routine complete blood count (CBC) with differential, serum creatinine, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), urinalysis with microscopy, and serologic ANA titer.1,16,19 A CBC with differential may reveal hematologic abnormalities, such as anemia of chronic disease (most commonly) or autoimmune hemolytic anemia, as well as leukopenia and thrombocytopenia due to circulating autoantibodies.3 An elevated ESR and CRP indicate the severity of the systemic inflammation and/or infection. Urinalysis is effective for detecting lupus with renal diseaseand may reveal proteinuria due to renal dysfunction.2
A positive ANA titer indicates widespread activation of the immune system targeted against nuclear and cytoplasmic subparticles. The vast majority of patients with SLE will develop a positive ANA with a high titer at some point during the course of their disease.16 The ANA is highly sensitive for SLE (93% to 95%) but lacks specificity (57%).20The most common tests for ANA are enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA). ELISA is more sensitive in detecting ANA, while IFA is the gold standard due to its high specificity.21 Some laboratories may use immunoassay as a screening tool for ANA and then use IFA to confirm positive or equivocal results.21 Positive ANA results can be seen in patients with other rheumatologic diseases and in up to 15% of all healthy persons, but with low or borderline titers.22 For these reasons, ANA testing alone is a poor predictor of SLE.
When either the ANA test results are positive or are negative but a strong clinical suspicion for SLE remains, clinicians should order tests for antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens (ENA panel; see Table 2).3,16 Anti-dsDNA and anti-Smith (anti-Sm) antibodies are both specific for SLE, and levels of anti-dsDNA reflect disease activity in many patients.1,19 In contrast, anti-dsDNA antibodies are found in fewer than 0.5% of healthy individuals and patients with other autoimmune conditions.19 Among patients with high levels of anti-dsDNA antibodies and clinically inactive disease, 80% will have active disease within five years after elevated antibodies are detected.19
Autoantibodies, including ANA, anti-SSA/Ro, anti-SSB/La, and antiphospholipid antibodies, are usually detectable for many years prior to the onset of symptomatic SLE, while others, such as anti-Sm and anti-U1RNP, appear just months before the diagnosis.23 Patients with positive ANA results who do not meet criteria for SLE are still at risk for lupus and other autoimmune diseases, because complex autoimmune changes occur years before the diagnosis of SLE.23 These patients should be followed closely.
Continue for making the diagnosis >>
MAKING THE DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosing SLE may prove problematic because of the remarkable variety of relapsing and remitting clinical features, mimicry of similar conditions, and lack of a simple, definitive diagnostic test. Initial diagnosis of SLE depends on the disease manifestation, published criteria, and exclusion of alternative diagnoses. Confirmation requires careful clinical assessment, based on a thorough medical history and complete physical examination, along with specific laboratory testing.1,16 Biopsy results indicative of lupus nephritis in the presence of ANA or anti-dsDNA antibodies also confirm the diagnosis of SLE.24
Although created for research purposes, ACR classification criteria for SLE, published in 1982 and revised in 1997, have been used for more than 30 years to diagnose lupus (see www.rheumatology.org/Practice-Quality/Clinical-Support/Criteria/ACR-Endorsed-Criteria). In 2012, the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) group revised the 1997 ACR classification criteria to address major flaws and to improve clinical precision.24 According to SLICC, a definitive diagnosis requires the presence of at least four of 17 criteria, including at least one clinical and one immunologic criterion.24 The SLICC revisions have resulted in fewer misclassifications and provide greater sensitivity but lower specificity in the identification of SLE in comparison to the 1997 ACR criteria.24 To date, no one set of criteria allows for early diagnosis of SLE.
MANAGEMENT OPTIONS
Treatment must be tailored to the patient’s specific organ system involvement. Effective therapy hinges on controlling symptoms and reducing underlying inflammation.25 Four classes of drugs are used: NSAIDs, antimalarial drugs, corticosteroids, and cytotoxic drugs (see Table 3). Most patients benefit from NSAIDs to alleviate minor arthritis and arthralgia symptoms, but the risk for peptic ulcers and nephrotoxicity should be addressed; this may require the concomitant use of gastroprotective agents such as proton pump inhibitors.25 Antimalarials are effective for musculoskeletal symptoms that do not respond to NSAIDs and for cutaneous rashes.1 The current antimalarial drug of choice is hydroxychloroquine (200 to 400 mg/d po), which has been shown to control SLE manifestations by reducing and preventing disease flares.1,11,26 It is well tolerated and can be used for the duration of treatment.11,26 Patients should be informed that this drug’s onset of action is one month.26 In rare cases, this drug can cause retinal toxicity; therefore, SLE patients receiving hydroxychloroquine should be referred to an ophthalmologist for a baseline eye examination and yearly assessments to monitor for this rare adverse effect.25,26
Low-dose corticosteroids, such as oral prednisolone or methylprednisolone, are employed when NSAIDs and antimalarials fail to control arthritis or cutaneous SLE eruptions.25 Major systemic manifestations that occur during a disease flare—such as severe arthritis, hemolytic anemia, glomerulonephritis, alveolar hemorrhage, pericarditis, pleurisy, or CNS involvement—necessitate high-dose IV corticosteroids in conjunction with immunosuppressive agents.1,11,25 These high-dose glucocorticoids should be gradually withdrawn as soon as remission is achieved.11 Long-term suppressive therapy with oral corticosteroids in addition to other agents is often needed to preserve organ function.25
The major adverse effects of long-term glucocorticoids are osteoporosis, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, glucose intolerance, and susceptibility to infection. It is recommended that patients taking prednisolone 7.5 mg/d or more undergo a bone mineral density scan every two years.25 Those with T scores below –2.5 should be prescribed bisphosphonates.25
Immunosuppressive agents, such as cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, and azathioprine, are used in conjunction with corticosteroids or when syndromes are resistant to corticosteroids.1 Collaboration between primary care, rheumatology, and nephrology is advisable for patients requiring immunosuppressive or disease-modifying pharmacologic agents.
Two new treatments for SLE are the immunologic agents belimumab and rituximab.7 Belimumab, a monoclonal human antibody, is the first medication in the past 50 years that has been approved by the FDA for antibody-positive SLE patients with active lupus unresponsive to standard treatment.7,27 Rituximab is an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, approved by the FDA for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and RA, and is now considered an option for SLE refractory to conventional treatment regimens.7,27 The efficacy of belimumab and rituximab, and the spectrum of indications for their use, are still under study, but these new therapeutic agents hold promise for the treatment of patients with refractory SLE.
Continue for helping patients live with SLE >>
HELPING PATIENTs LIVE WITH SLE
Patients with SLE have a higher mortality rate, as well as a lower quality of life, compared to the general population.28 The major contributors to a decreased quality of life are fatigue, mood disturbances (eg, depression), and chronic pain.28 Practitioners should advise SLE patients to participate in support groups and psychotherapy to alleviate the anxiety and depression associated with this chronic disease.
For patients with long-standing disease, accelerated atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease adds to morbidity and mortality. For this reason, obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and smoking are targets for intervention. Lifestyle modifications—such as exercise, smoking cessation, a healthy diet with low saturated fat, stress avoidance, and adequate rest—are recommended.26
Avoiding overexposure to sunlight, by using sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 and wearing sun-protective clothing, is essential for management of cutaneous lupus.25,26 Yearly influenza vaccination is appropriate, as are other immunizations (eg, pneumococcal vaccine).26
Advise women of childbearing age with SLE that lupus flares result in a high risk for miscarriage. All women should undergo yearly cervical cancer screening.26
Patients taking long-term glucocorticoids should adopt bone-protective behaviors, including quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, partaking in weight-bearing exercise, and consuming dietary calcium and vitamin D.25 Patients taking these drugs should avoid live virus vaccines. Those on immunosuppressive therapy should be warned about the hazardous adverse effects of glucocorticoids.
MONITORING AND FOLLOW-UP
Collaborative efforts between primary care providers and several types of specialty providers can facilitate coordinated interventions in the long-term management of lupus. Rheumatologists are experts in making therapeutic decisions for SLE.
Patients being treated for SLE require routine monitoring to assess disease activity and detect flares. The European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) guidelines recommend that monitoring include assessment for new clinical manifestations, routine laboratory tests, and immunologic assays, chiefly anti-dsDNA, anti-Sm, and serum complement levels, coupled with one of the validated global activity indices, such as the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI).29
A routine office visit with a physical examination and laboratory testing for CBC with differential, basic metabolic panel, and urinalysis every three months is recommended for patients with stable disease; patients with uncontrolled SLE may require weekly visits.11,29 Patients taking immunosuppressive drugs should be provided with adverse-effect profiles alerting them to toxicity symptoms and require frequent laboratory monitoring for potential toxicity.11
CONCLUSION
Advances in immunologically targeted serologic tests have shed more light on the underlying pathogenesis of SLE, which in turn has led to improvements in disease detection and monitoring of complications, as well as advances in therapy. Although SLE cannot be cured, emerging therapies targeting different mechanisms of SLE offer hope for patients diagnosed with this complex disease.
1. Hellmann DB, Imboden JB. Rheumatologic & immunologic disorders. In: Papadakis M, McPhee SJ, Rabow MW, eds. Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment. 53rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2014:786-836.
2. Bertsias G, Cervera R, Boumpas DT. Systemic lupus erythematosus: pathogenesis and clinical features. In: Bijlsma JWJ, ed. EULAR Textbook on Rheumatic Diseases. London: BMJ Group; 2012:476-505.
3. Dall’Era M. Chapter 21. Systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Imboden JB, Hellmann DB, Stone JH, eds. Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Rheumatology. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013.
4. Lupus Foundation of America. What is lupus? www.lupus.org/answers/entry/what-is-lupus. Accessed July 19, 2016.
5. Furst DE, Clarke AE, Fernandes AW, et al. Incidence and prevalence of adult systemic lupus erythematosus in a large US managed-care population. Lupus. 2012;22(1):99-105.
6. Pons-Estel GL, Alarcón GS, Scofield L, et al. Understanding the epidemiology and progression of systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010;39(4):257-268.
7. Lisnevskaia L, Murphy G, Isenberg D. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 2014;384(9957):1878-1888.
8. Mok CC, Kwok RC, Yip PS. Effect of renal disease on the standardized mortality ratio and life expectancy of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(8):2154-2160.
9. Merola JF, Bermas B, Lu B, et al. Clinical manifestations and survival among adults with SLE according to age at diagnosis. Lupus. 2014;23(8):778-784.
10. Font J, Cervera R, Ramos-Casals M, et al. Clusters of clinical and immunologic features in systemic lupus erythematosus: analysis of 600 patients from a single center. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004;33(4):217-230.
11. Kiriakidou M, Cotton D, Taichman D, Williams S. Systemic lupus erythematosus.Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(7):2-16.
12. Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra A. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:334-342.
13. Popescu A, Kao AH. Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011;9(3):449-457.
14. Chen PY, Chang CH, Hsu CC, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus presenting with cardiac symptoms. Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32(9):1117-1119.
15. Hahn BHH. Chapter 378: Systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, et al, eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2015.
16. Wallace DJ. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. UpToDate. www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnosis-and-differential-diagnosis-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-in-adults. Accessed July 19, 2016.
17. Cappelli S, Bellando Randone S, Martinovic D, et al. “To be or not to be,” ten years after: evidence for mixed connective tissue disease as a distinct entity. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;41(4):589-598.
18. Bennett RM, Friend R, Marcus D, et al. Criteria for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia: validation of the modified 2010 preliminary American College of Rheumatology criteria and the development of alternative criteria. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014;66(9):1364-1373.
19. Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(9):929-939.
20. Magrey M, Abelson A. Laboratory evaluation of rheumatic diseases. Cleveland Clinic Center for Continuing Education 2010. www.cleveland clinicmeded.com/medicalpubs/diseasemanagement/rheumatology/laboratory-evaluation-rheumatic-diseases/. Accessed July 19, 2016.
21. Copple SS, Sawitzke AD, Wilson AM, et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay screening then indirect immunofluorescence confirmation of antinuclear antibodies: a statistical analysis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;135(5):678-684.
22. Von Feld JM; American College of Rheumatology. Antinuclear antibodies (ANA). 2015. www.rheumatology.org/I-Am-A/Patient-Caregiver/Diseases-Conditions/Antinuclear-Antibodies-ANA. Accessed July 19, 2016.
23. Arbuckle MR, McClain MT, Rubertone MV, et al. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(16):1526-1533.
24. Petri M, Orbai A, Alarcón G, et al. Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(8):2677-2686.
25. Ioannou Y, Isenberg DA. Current concepts for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus in adults: a therapeutic challenge. Postgrad Med J. 2002;78:599-606.
26. Dall’Era M, Wofsy D. Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Imboden JB, Hellmann DB, Stone JH, eds. Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Rheumatology. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013.
27. Stohl W, Hilbert DM. The discovery and development of belimumab: the anti-BLyS–lupus connection. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(1):69-77.
28. Lateef A, Petri M. Unmet medical needs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Research & Ther. 2012;14(suppl 4):S4.
29. Bertsias G, Ioannidis JP, Boletis J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Report of a task force of the EULAR standing committee for international clinical studies including therapeutics. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(2):195-205.
1. Hellmann DB, Imboden JB. Rheumatologic & immunologic disorders. In: Papadakis M, McPhee SJ, Rabow MW, eds. Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment. 53rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2014:786-836.
2. Bertsias G, Cervera R, Boumpas DT. Systemic lupus erythematosus: pathogenesis and clinical features. In: Bijlsma JWJ, ed. EULAR Textbook on Rheumatic Diseases. London: BMJ Group; 2012:476-505.
3. Dall’Era M. Chapter 21. Systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Imboden JB, Hellmann DB, Stone JH, eds. Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Rheumatology. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013.
4. Lupus Foundation of America. What is lupus? www.lupus.org/answers/entry/what-is-lupus. Accessed July 19, 2016.
5. Furst DE, Clarke AE, Fernandes AW, et al. Incidence and prevalence of adult systemic lupus erythematosus in a large US managed-care population. Lupus. 2012;22(1):99-105.
6. Pons-Estel GL, Alarcón GS, Scofield L, et al. Understanding the epidemiology and progression of systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010;39(4):257-268.
7. Lisnevskaia L, Murphy G, Isenberg D. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 2014;384(9957):1878-1888.
8. Mok CC, Kwok RC, Yip PS. Effect of renal disease on the standardized mortality ratio and life expectancy of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(8):2154-2160.
9. Merola JF, Bermas B, Lu B, et al. Clinical manifestations and survival among adults with SLE according to age at diagnosis. Lupus. 2014;23(8):778-784.
10. Font J, Cervera R, Ramos-Casals M, et al. Clusters of clinical and immunologic features in systemic lupus erythematosus: analysis of 600 patients from a single center. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004;33(4):217-230.
11. Kiriakidou M, Cotton D, Taichman D, Williams S. Systemic lupus erythematosus.Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(7):2-16.
12. Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra A. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:334-342.
13. Popescu A, Kao AH. Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011;9(3):449-457.
14. Chen PY, Chang CH, Hsu CC, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus presenting with cardiac symptoms. Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32(9):1117-1119.
15. Hahn BHH. Chapter 378: Systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, et al, eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2015.
16. Wallace DJ. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. UpToDate. www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnosis-and-differential-diagnosis-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-in-adults. Accessed July 19, 2016.
17. Cappelli S, Bellando Randone S, Martinovic D, et al. “To be or not to be,” ten years after: evidence for mixed connective tissue disease as a distinct entity. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;41(4):589-598.
18. Bennett RM, Friend R, Marcus D, et al. Criteria for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia: validation of the modified 2010 preliminary American College of Rheumatology criteria and the development of alternative criteria. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014;66(9):1364-1373.
19. Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(9):929-939.
20. Magrey M, Abelson A. Laboratory evaluation of rheumatic diseases. Cleveland Clinic Center for Continuing Education 2010. www.cleveland clinicmeded.com/medicalpubs/diseasemanagement/rheumatology/laboratory-evaluation-rheumatic-diseases/. Accessed July 19, 2016.
21. Copple SS, Sawitzke AD, Wilson AM, et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay screening then indirect immunofluorescence confirmation of antinuclear antibodies: a statistical analysis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;135(5):678-684.
22. Von Feld JM; American College of Rheumatology. Antinuclear antibodies (ANA). 2015. www.rheumatology.org/I-Am-A/Patient-Caregiver/Diseases-Conditions/Antinuclear-Antibodies-ANA. Accessed July 19, 2016.
23. Arbuckle MR, McClain MT, Rubertone MV, et al. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(16):1526-1533.
24. Petri M, Orbai A, Alarcón G, et al. Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(8):2677-2686.
25. Ioannou Y, Isenberg DA. Current concepts for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus in adults: a therapeutic challenge. Postgrad Med J. 2002;78:599-606.
26. Dall’Era M, Wofsy D. Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Imboden JB, Hellmann DB, Stone JH, eds. Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Rheumatology. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013.
27. Stohl W, Hilbert DM. The discovery and development of belimumab: the anti-BLyS–lupus connection. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(1):69-77.
28. Lateef A, Petri M. Unmet medical needs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Research & Ther. 2012;14(suppl 4):S4.
29. Bertsias G, Ioannidis JP, Boletis J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Report of a task force of the EULAR standing committee for international clinical studies including therapeutics. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(2):195-205.
Light Therapy For Nonseasonal Major Depressive Disorder?
PRACTICE CHANGER
Consider treatment with bright light therapy, alone or in combination with fluoxetine, for patients with nonseasonal major depressive disorder.1
Strength of Recommendation
B: Based on a single moderate-quality randomized controlled trial.1
A 38-year-old woman recently diagnosed with major depressive disorder (MDD) without a seasonal pattern presents to discuss treatment options. Her Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D) score is 22, and she is not suicidal. Should you consider bright light therapy in addition to pharmacotherapy?
MDD is one of the most common psychiatric illnesses in the United States, affecting approximately one in five adults at some point in their lives.2 Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are considered effective firstline pharmacotherapy options for MDD.2,3 Despite their effectiveness, however, studies have shown that only about 40% of patients with MDD achieve remission with firstline or secondline drugs.2 In addition, pharmacologic agents have a higher frequency of treatment-associated adverse effects than fluorescent light therapy.4
A Cochrane systematic review of 20 studies (N = 620) demonstrated the effectiveness of combined light therapy and pharmacotherapy in treating nonseasonal MDD but found no benefit to light used as monotherapy.5 However, the majority of the studies were of poor quality, occurred in the inpatient setting, and lasted less than four weeks.
In a five-week, controlled, double-blind trial not included in the Cochrane review, 102 patients with nonseasonal MDD were randomized to receive either active treatment (bright light therapy) plus sertraline (50 mg/d) or sham light treatment (using a dim red light) plus sertraline (50 mg/d). The investigators found a statistically significant reduction in depression score in the active treatment group compared to the sham light group, based on the HAM-D, the Hamilton 6-Item Subscale, the Melancholia Scale, and the seven atypical items from the Structured Interview Guide for the Seasonal Affective Disorder version of the HAM-D.6,7
Continue for the study summary >>
STUDY SUMMARY
Light therapy improves nonseasonal depression
This latest study was an eight-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and sham-controlled clinical trial evaluating the benefit of light therapy with and without pharmacotherapy for nonseasonal MDD.1 The investigators enrolled 122 adult patients (ages 19 to 60) from outpatient psychiatry clinics who had a diagnosis of MDD (diagnosed by a psychiatrist) and a HAM-D8 score of at least 20. Subjects had to be off psychotropic medication for at least two weeks prior to the first visit; they were subsequently monitored for one week to identify spontaneous responders and give patients time to better regulate their sleep-wake cycle (with the goal of sleeping only between 10 PM and 8 AM daily).
The investigators randomly assigned patients to one of four treatment groups:
• Active light monotherapy (10,000-lux fluorescent white light for 30 min/d early in the morning) plus a placebo pill
• Fluoxetine (20 mg/d) plus sham light therapy
• Placebo pills with sham light therapy; or
• Combined active light therapy with fluoxetine (20 mg/d).
Sham light therapy consisted of the use of an inactivated negative ion generator, used in the same fashion as a light box. All patients were analyzed based on modified intention to treat. Adherence was assessed through review of patients’ daily logs of device treatment times and through pill counts.
The primary outcome at eight weeks was the change from baseline in the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS), a 10-item questionnaire with a worst score of 60.9 Secondary outcomes were treatment response (≥ 50% reduction in MADRS score) and remission (MADRS score ≤ 10) at the final eighth-week visit. MADRS scoring was used because of its sensitivity to treatment-induced changes and its high correlation with the HAM-D scale.
At the end of eight weeks, the mean changes in MADRS scores from baseline were: light monotherapy, 13.4; fluoxetine monotherapy, 8.8; combination therapy, 16.9; and placebo, 6.5. The improvement was significant in the light monotherapy treatment group and in the combination therapy group, compared with the placebo group, and in the combination group, compared with the fluoxetine treatment group; improvement was not significant for the fluoxetine treatment group compared with the placebo group, however.
The treatment response (≥ 50% MADRS improvement) rate was highest in the combination treatment group (75.9%), followed by light monotherapy (50%), placebo (33.3%), and fluoxetine monotherapy (29%). There was a significant response effect for the combination versus placebo treatment group.
Similarly, there was a higher remission rate in the combination treatment group (58.6%) than in the placebo, light monotherapy, or fluoxetine treatment groups (30%, 43.8%, and 19.4%, respectively). Combination therapy was superior to placebo in treatment response (≥ 50% reduction in the MADRS score) and remission (MADRS ≤ 10), with numbers needed to treat of 2.4 and 3.5, respectively.
By the end of the eight-week study period, 16 of 122 patients had dropped out. Two reported lack of efficacy, five reported adverse effects, and the remainder cited administrative reasons, were lost to follow-up, or withdrew consent.
WHAT’S NEW
New evidence on a not-so-new treatment
We now have evidence that bright light therapy, either alone or in combination with fluoxetine, is efficacious for increasing the remission rate of nonseasonal MDD.
Continue for caveats >>
CAVEATS
Variables may have affected results
Among the study’s limitations: use of a single SSRI (other, more potent SSRIs might work better); location (southern Canada; benefits may differ in regions farther south); and exclusion of pregnant and breastfeeding women from the study population.
Furthermore, the trial duration was relatively short, and the investigators did not attain their preplanned sample size for the study. This limited the power to detect clinically significant seasonal treatment effects and differences between the fluoxetine and placebo groups, regardless of whether they received active phototherapy.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Commercial insurance doesn’t usually cover light therapy
Bright light therapy is fairly safe, and some evidence exists supporting its use in the treatment of nonseasonal MDD; however, the data for its use in this area are limited.10 Since few studies have tested light therapy for nonseasonal MDD, uncertainty remains about patient selection, as well as optimal dose, timing, and duration in the management of nonseasonal MDD.11 Although the associated risks are minimal, bright light therapy can lead to mania or hypomania; clinicians need to monitor for such effects when initiating therapy.3
Lastly, commercial insurance does not usually cover light therapy. The average price of the bright light devices, which are available in medical supply stores and online, ranges from $118 to $237.4,11 However, such devices are reusable, making the amortized cost almost negligible and perhaps negating this concern.12
REFERENCES
1. Lam RW, Levitt AJ, Levitan RD, et al. Efficacy of bright light treatment, fluoxetine, and the combination in patients with nonseasonal major depressive disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73:56-63.
2. Weihs K, Wert JM. A primary care focus on the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder. Am J Med Sci. 2011;342:324-330.
3. Gelenberg AJ, Freeman CMP, Markowitz JC, et al. American Psychiatric Association practice guideline for the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder. 3rd ed. 2010. http://psychiatryonline.org/pb/assets/raw/sitewide/practice_guidelines/guidelines/mdd.pdf. Accessed July 5, 2016.
4. Lam RW, Tam EM. A Clinician’s Guide to Using Light Therapy. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2009. www.ubcmood.ca/sad/SAD%20resources%20package%202009.pdf. Accessed July 5, 2016.
5. Tuunainen A, Kripke DF, Endo T. Light therapy for non-seasonal depression. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;2:CD004050.
6. Martiny K. Adjunctive bright light in non-seasonal major depression. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2004;425:7-28.
7. Martiny K, Lunde M, Unden M, et al. Adjunctive bright light in non-seasonal major depression: results from clinician-rated depression scales. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2005;112:117-125.
8. Hamilton M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1960;23:56-62.
9. Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. Br J Psychiatry. 1979;134:382-389.
10. Oldham MA, Ciraulo DA. Use of bright light therapy among psychiatrists in Massachusetts: an e-mail survey. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2014;16(3). Epub 2014 Jun 26.
11. Sloane PD, Figueiro M, Cohen L. Light as therapy for sleep disorders and depression in older adults. Clin Geriatr. 2008;16:25-31.
12. Kripke DF. A breakthrough treatment for major depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76:e660-e661.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
Copyright © 2016. The Family Physicians Inquiries Network. All rights reserved.
Reprinted with permission from the Family Physicians Inquiries Network and The Journal of Family Practice. 2016;65(7):486-488.
PRACTICE CHANGER
Consider treatment with bright light therapy, alone or in combination with fluoxetine, for patients with nonseasonal major depressive disorder.1
Strength of Recommendation
B: Based on a single moderate-quality randomized controlled trial.1
A 38-year-old woman recently diagnosed with major depressive disorder (MDD) without a seasonal pattern presents to discuss treatment options. Her Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D) score is 22, and she is not suicidal. Should you consider bright light therapy in addition to pharmacotherapy?
MDD is one of the most common psychiatric illnesses in the United States, affecting approximately one in five adults at some point in their lives.2 Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are considered effective firstline pharmacotherapy options for MDD.2,3 Despite their effectiveness, however, studies have shown that only about 40% of patients with MDD achieve remission with firstline or secondline drugs.2 In addition, pharmacologic agents have a higher frequency of treatment-associated adverse effects than fluorescent light therapy.4
A Cochrane systematic review of 20 studies (N = 620) demonstrated the effectiveness of combined light therapy and pharmacotherapy in treating nonseasonal MDD but found no benefit to light used as monotherapy.5 However, the majority of the studies were of poor quality, occurred in the inpatient setting, and lasted less than four weeks.
In a five-week, controlled, double-blind trial not included in the Cochrane review, 102 patients with nonseasonal MDD were randomized to receive either active treatment (bright light therapy) plus sertraline (50 mg/d) or sham light treatment (using a dim red light) plus sertraline (50 mg/d). The investigators found a statistically significant reduction in depression score in the active treatment group compared to the sham light group, based on the HAM-D, the Hamilton 6-Item Subscale, the Melancholia Scale, and the seven atypical items from the Structured Interview Guide for the Seasonal Affective Disorder version of the HAM-D.6,7
Continue for the study summary >>
STUDY SUMMARY
Light therapy improves nonseasonal depression
This latest study was an eight-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and sham-controlled clinical trial evaluating the benefit of light therapy with and without pharmacotherapy for nonseasonal MDD.1 The investigators enrolled 122 adult patients (ages 19 to 60) from outpatient psychiatry clinics who had a diagnosis of MDD (diagnosed by a psychiatrist) and a HAM-D8 score of at least 20. Subjects had to be off psychotropic medication for at least two weeks prior to the first visit; they were subsequently monitored for one week to identify spontaneous responders and give patients time to better regulate their sleep-wake cycle (with the goal of sleeping only between 10 PM and 8 AM daily).
The investigators randomly assigned patients to one of four treatment groups:
• Active light monotherapy (10,000-lux fluorescent white light for 30 min/d early in the morning) plus a placebo pill
• Fluoxetine (20 mg/d) plus sham light therapy
• Placebo pills with sham light therapy; or
• Combined active light therapy with fluoxetine (20 mg/d).
Sham light therapy consisted of the use of an inactivated negative ion generator, used in the same fashion as a light box. All patients were analyzed based on modified intention to treat. Adherence was assessed through review of patients’ daily logs of device treatment times and through pill counts.
The primary outcome at eight weeks was the change from baseline in the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS), a 10-item questionnaire with a worst score of 60.9 Secondary outcomes were treatment response (≥ 50% reduction in MADRS score) and remission (MADRS score ≤ 10) at the final eighth-week visit. MADRS scoring was used because of its sensitivity to treatment-induced changes and its high correlation with the HAM-D scale.
At the end of eight weeks, the mean changes in MADRS scores from baseline were: light monotherapy, 13.4; fluoxetine monotherapy, 8.8; combination therapy, 16.9; and placebo, 6.5. The improvement was significant in the light monotherapy treatment group and in the combination therapy group, compared with the placebo group, and in the combination group, compared with the fluoxetine treatment group; improvement was not significant for the fluoxetine treatment group compared with the placebo group, however.
The treatment response (≥ 50% MADRS improvement) rate was highest in the combination treatment group (75.9%), followed by light monotherapy (50%), placebo (33.3%), and fluoxetine monotherapy (29%). There was a significant response effect for the combination versus placebo treatment group.
Similarly, there was a higher remission rate in the combination treatment group (58.6%) than in the placebo, light monotherapy, or fluoxetine treatment groups (30%, 43.8%, and 19.4%, respectively). Combination therapy was superior to placebo in treatment response (≥ 50% reduction in the MADRS score) and remission (MADRS ≤ 10), with numbers needed to treat of 2.4 and 3.5, respectively.
By the end of the eight-week study period, 16 of 122 patients had dropped out. Two reported lack of efficacy, five reported adverse effects, and the remainder cited administrative reasons, were lost to follow-up, or withdrew consent.
WHAT’S NEW
New evidence on a not-so-new treatment
We now have evidence that bright light therapy, either alone or in combination with fluoxetine, is efficacious for increasing the remission rate of nonseasonal MDD.
Continue for caveats >>
CAVEATS
Variables may have affected results
Among the study’s limitations: use of a single SSRI (other, more potent SSRIs might work better); location (southern Canada; benefits may differ in regions farther south); and exclusion of pregnant and breastfeeding women from the study population.
Furthermore, the trial duration was relatively short, and the investigators did not attain their preplanned sample size for the study. This limited the power to detect clinically significant seasonal treatment effects and differences between the fluoxetine and placebo groups, regardless of whether they received active phototherapy.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Commercial insurance doesn’t usually cover light therapy
Bright light therapy is fairly safe, and some evidence exists supporting its use in the treatment of nonseasonal MDD; however, the data for its use in this area are limited.10 Since few studies have tested light therapy for nonseasonal MDD, uncertainty remains about patient selection, as well as optimal dose, timing, and duration in the management of nonseasonal MDD.11 Although the associated risks are minimal, bright light therapy can lead to mania or hypomania; clinicians need to monitor for such effects when initiating therapy.3
Lastly, commercial insurance does not usually cover light therapy. The average price of the bright light devices, which are available in medical supply stores and online, ranges from $118 to $237.4,11 However, such devices are reusable, making the amortized cost almost negligible and perhaps negating this concern.12
REFERENCES
1. Lam RW, Levitt AJ, Levitan RD, et al. Efficacy of bright light treatment, fluoxetine, and the combination in patients with nonseasonal major depressive disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73:56-63.
2. Weihs K, Wert JM. A primary care focus on the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder. Am J Med Sci. 2011;342:324-330.
3. Gelenberg AJ, Freeman CMP, Markowitz JC, et al. American Psychiatric Association practice guideline for the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder. 3rd ed. 2010. http://psychiatryonline.org/pb/assets/raw/sitewide/practice_guidelines/guidelines/mdd.pdf. Accessed July 5, 2016.
4. Lam RW, Tam EM. A Clinician’s Guide to Using Light Therapy. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2009. www.ubcmood.ca/sad/SAD%20resources%20package%202009.pdf. Accessed July 5, 2016.
5. Tuunainen A, Kripke DF, Endo T. Light therapy for non-seasonal depression. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;2:CD004050.
6. Martiny K. Adjunctive bright light in non-seasonal major depression. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2004;425:7-28.
7. Martiny K, Lunde M, Unden M, et al. Adjunctive bright light in non-seasonal major depression: results from clinician-rated depression scales. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2005;112:117-125.
8. Hamilton M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1960;23:56-62.
9. Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. Br J Psychiatry. 1979;134:382-389.
10. Oldham MA, Ciraulo DA. Use of bright light therapy among psychiatrists in Massachusetts: an e-mail survey. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2014;16(3). Epub 2014 Jun 26.
11. Sloane PD, Figueiro M, Cohen L. Light as therapy for sleep disorders and depression in older adults. Clin Geriatr. 2008;16:25-31.
12. Kripke DF. A breakthrough treatment for major depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76:e660-e661.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
Copyright © 2016. The Family Physicians Inquiries Network. All rights reserved.
Reprinted with permission from the Family Physicians Inquiries Network and The Journal of Family Practice. 2016;65(7):486-488.
PRACTICE CHANGER
Consider treatment with bright light therapy, alone or in combination with fluoxetine, for patients with nonseasonal major depressive disorder.1
Strength of Recommendation
B: Based on a single moderate-quality randomized controlled trial.1
A 38-year-old woman recently diagnosed with major depressive disorder (MDD) without a seasonal pattern presents to discuss treatment options. Her Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D) score is 22, and she is not suicidal. Should you consider bright light therapy in addition to pharmacotherapy?
MDD is one of the most common psychiatric illnesses in the United States, affecting approximately one in five adults at some point in their lives.2 Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are considered effective firstline pharmacotherapy options for MDD.2,3 Despite their effectiveness, however, studies have shown that only about 40% of patients with MDD achieve remission with firstline or secondline drugs.2 In addition, pharmacologic agents have a higher frequency of treatment-associated adverse effects than fluorescent light therapy.4
A Cochrane systematic review of 20 studies (N = 620) demonstrated the effectiveness of combined light therapy and pharmacotherapy in treating nonseasonal MDD but found no benefit to light used as monotherapy.5 However, the majority of the studies were of poor quality, occurred in the inpatient setting, and lasted less than four weeks.
In a five-week, controlled, double-blind trial not included in the Cochrane review, 102 patients with nonseasonal MDD were randomized to receive either active treatment (bright light therapy) plus sertraline (50 mg/d) or sham light treatment (using a dim red light) plus sertraline (50 mg/d). The investigators found a statistically significant reduction in depression score in the active treatment group compared to the sham light group, based on the HAM-D, the Hamilton 6-Item Subscale, the Melancholia Scale, and the seven atypical items from the Structured Interview Guide for the Seasonal Affective Disorder version of the HAM-D.6,7
Continue for the study summary >>
STUDY SUMMARY
Light therapy improves nonseasonal depression
This latest study was an eight-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and sham-controlled clinical trial evaluating the benefit of light therapy with and without pharmacotherapy for nonseasonal MDD.1 The investigators enrolled 122 adult patients (ages 19 to 60) from outpatient psychiatry clinics who had a diagnosis of MDD (diagnosed by a psychiatrist) and a HAM-D8 score of at least 20. Subjects had to be off psychotropic medication for at least two weeks prior to the first visit; they were subsequently monitored for one week to identify spontaneous responders and give patients time to better regulate their sleep-wake cycle (with the goal of sleeping only between 10 PM and 8 AM daily).
The investigators randomly assigned patients to one of four treatment groups:
• Active light monotherapy (10,000-lux fluorescent white light for 30 min/d early in the morning) plus a placebo pill
• Fluoxetine (20 mg/d) plus sham light therapy
• Placebo pills with sham light therapy; or
• Combined active light therapy with fluoxetine (20 mg/d).
Sham light therapy consisted of the use of an inactivated negative ion generator, used in the same fashion as a light box. All patients were analyzed based on modified intention to treat. Adherence was assessed through review of patients’ daily logs of device treatment times and through pill counts.
The primary outcome at eight weeks was the change from baseline in the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS), a 10-item questionnaire with a worst score of 60.9 Secondary outcomes were treatment response (≥ 50% reduction in MADRS score) and remission (MADRS score ≤ 10) at the final eighth-week visit. MADRS scoring was used because of its sensitivity to treatment-induced changes and its high correlation with the HAM-D scale.
At the end of eight weeks, the mean changes in MADRS scores from baseline were: light monotherapy, 13.4; fluoxetine monotherapy, 8.8; combination therapy, 16.9; and placebo, 6.5. The improvement was significant in the light monotherapy treatment group and in the combination therapy group, compared with the placebo group, and in the combination group, compared with the fluoxetine treatment group; improvement was not significant for the fluoxetine treatment group compared with the placebo group, however.
The treatment response (≥ 50% MADRS improvement) rate was highest in the combination treatment group (75.9%), followed by light monotherapy (50%), placebo (33.3%), and fluoxetine monotherapy (29%). There was a significant response effect for the combination versus placebo treatment group.
Similarly, there was a higher remission rate in the combination treatment group (58.6%) than in the placebo, light monotherapy, or fluoxetine treatment groups (30%, 43.8%, and 19.4%, respectively). Combination therapy was superior to placebo in treatment response (≥ 50% reduction in the MADRS score) and remission (MADRS ≤ 10), with numbers needed to treat of 2.4 and 3.5, respectively.
By the end of the eight-week study period, 16 of 122 patients had dropped out. Two reported lack of efficacy, five reported adverse effects, and the remainder cited administrative reasons, were lost to follow-up, or withdrew consent.
WHAT’S NEW
New evidence on a not-so-new treatment
We now have evidence that bright light therapy, either alone or in combination with fluoxetine, is efficacious for increasing the remission rate of nonseasonal MDD.
Continue for caveats >>
CAVEATS
Variables may have affected results
Among the study’s limitations: use of a single SSRI (other, more potent SSRIs might work better); location (southern Canada; benefits may differ in regions farther south); and exclusion of pregnant and breastfeeding women from the study population.
Furthermore, the trial duration was relatively short, and the investigators did not attain their preplanned sample size for the study. This limited the power to detect clinically significant seasonal treatment effects and differences between the fluoxetine and placebo groups, regardless of whether they received active phototherapy.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
Commercial insurance doesn’t usually cover light therapy
Bright light therapy is fairly safe, and some evidence exists supporting its use in the treatment of nonseasonal MDD; however, the data for its use in this area are limited.10 Since few studies have tested light therapy for nonseasonal MDD, uncertainty remains about patient selection, as well as optimal dose, timing, and duration in the management of nonseasonal MDD.11 Although the associated risks are minimal, bright light therapy can lead to mania or hypomania; clinicians need to monitor for such effects when initiating therapy.3
Lastly, commercial insurance does not usually cover light therapy. The average price of the bright light devices, which are available in medical supply stores and online, ranges from $118 to $237.4,11 However, such devices are reusable, making the amortized cost almost negligible and perhaps negating this concern.12
REFERENCES
1. Lam RW, Levitt AJ, Levitan RD, et al. Efficacy of bright light treatment, fluoxetine, and the combination in patients with nonseasonal major depressive disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73:56-63.
2. Weihs K, Wert JM. A primary care focus on the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder. Am J Med Sci. 2011;342:324-330.
3. Gelenberg AJ, Freeman CMP, Markowitz JC, et al. American Psychiatric Association practice guideline for the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder. 3rd ed. 2010. http://psychiatryonline.org/pb/assets/raw/sitewide/practice_guidelines/guidelines/mdd.pdf. Accessed July 5, 2016.
4. Lam RW, Tam EM. A Clinician’s Guide to Using Light Therapy. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2009. www.ubcmood.ca/sad/SAD%20resources%20package%202009.pdf. Accessed July 5, 2016.
5. Tuunainen A, Kripke DF, Endo T. Light therapy for non-seasonal depression. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;2:CD004050.
6. Martiny K. Adjunctive bright light in non-seasonal major depression. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2004;425:7-28.
7. Martiny K, Lunde M, Unden M, et al. Adjunctive bright light in non-seasonal major depression: results from clinician-rated depression scales. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2005;112:117-125.
8. Hamilton M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1960;23:56-62.
9. Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. Br J Psychiatry. 1979;134:382-389.
10. Oldham MA, Ciraulo DA. Use of bright light therapy among psychiatrists in Massachusetts: an e-mail survey. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2014;16(3). Epub 2014 Jun 26.
11. Sloane PD, Figueiro M, Cohen L. Light as therapy for sleep disorders and depression in older adults. Clin Geriatr. 2008;16:25-31.
12. Kripke DF. A breakthrough treatment for major depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76:e660-e661.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
Copyright © 2016. The Family Physicians Inquiries Network. All rights reserved.
Reprinted with permission from the Family Physicians Inquiries Network and The Journal of Family Practice. 2016;65(7):486-488.
Did Somebody Say “Precepting”?
But First, a Word About Vaping …
As advocates for tobacco control, my colleagues and I took great interest in Randy D. Danielsen’s editorial, “Vaping: Are Its ‘Benefits’ a Lot of Hot Air?” (Clinician Reviews. 2016;26[6]:15-16). Our practice offers evidence-based cessation treatment for individuals with nicotine addiction through counseling, pharmacotherapy, and the use of nicotine replacement products.
At our center, we often interact with clients who have had multiple quit attempts. Many of our clients state that they have been unsuccessful using an e-cigarette as a smoking cessation strategy. More often than not, they report smoking a cigarette “here and there” along with “vaping,” until they eventually relapse to their usual smoking pattern. Some report that they smoke even more than before they tried to quit. We have concerns about how vaping may renormalize the behaviors associated with smoking. Our clients say that when they vape, it reminds them of the “social” aspects of smoking— “being part of a group” and participating in an activity that keeps their hands busy.
Recent literature suggests that curiosity is the primary reason adolescents engage in e-cigarette use. While the newly implemented FDA regulations on e-cigarettes may keep these products out of the hands of some adolescents by prohibiting sales to those younger than 18, there is much more to consider. Along with exposure to nicotine, these devices offer a variety of kid-friendly flavorings that make these products attractive to middle and high school youth. Flavorings will not be regulated at this point in time.
According to researchers, this is a major concern. Findings from studies report that when inhaled, certain flavors are more harmful than others. For example, very high—even toxic—levels of benzaldehyde are inhaled by the user when cherry-flavored e-liquid is heated at high temperatures. The chemical diacetyl, a respiratory irritant known to be associated with bronchiolitis obliterans (popcorn lung), is produced by the aerosol vapors from buttered popcorn and certain fruit-flavored e-cigarette liquids.
As public health advocates, we must provide research to the FDA about the health hazards of the flavoring added to e-cigarettes and continue to fight for this regulation. We must support evidence-based tobacco control interventions, such as hard-hitting media campaigns and tobacco excise taxes, and promote access to cessation treatment, smoke-free policies, and statewide funding. Elimination of tobacco products will reduce the public health burden of tobacco-related illness.
Andrea Spatarella, DNP, RN, FNP-BC, Christine Fardellone, DNP, RN, Raisa Abramova, FNP-BC, RN
Great Neck, NY
Continue for Precepting & E-Quality of Care >>
Precepting & E-Quality of Care
As a woman of the baby-boomer generation, I was raised in an era when feminism was a focus for many. There was a great deal being written and discussed to encourage women to attain equal pay for equal work. Because nursing was (and still is) a profession dominated by women, this was a frequent topic in the classroom. We were repeatedly told, “Don’t give away your knowledge for free” and “You deserve to be paid what you’re worth, don’t discount yourself.”
I find it very telling that the same female-dominated academic programs that encouraged me to seek proper payment are now taking advantage of my free labor. I am somewhat offended by this attitude and consider it a step backward. Each time NPs are guilted or browbeaten into teaching without proper compensation, the profession is devalued. To continue to participate is to enable a problematic, if not broken, system.
NP education is in need of major reform. The precepting issue is the weak link in becoming a qualified professional who is able to meet the demands and responsibilities that academics and politicos are pushing harder and harder for. Our physician and PA colleagues can rightly argue that their clinical education is superior to ours—and I cannot fault our colleagues for expressing concern about quality of care. If nursing really wants an equal place at the table, this weakness must be improved, or the naysayers will have plenty of evidence that they were correct in the years to come.
Rebecca Shively, MSN, RN, FNP-BC
San Marcos, TX
Continue for NP Schools & Their Rigid Rules >>
NP Schools & Their Rigid Rules
I have been a preceptor for at least a dozen NP students and have yet to be offered compensation. Preceptors take the place of a paid instructor, giving away free advice and experiences. I don’t mind doing this, but at times it can be a struggle. Some students, for example, have never done a pelvic exam. Letting an inexperienced NP student practice a pelvic exam on a patient who made an appointment to see an experienced provider is unjust and unfair to the patient—I won’t do it. These schools need to provide practice sessions on paid patients so their students can learn these skills.
I have my beef with the institutes of higher learning, not the students. It feels like a one-way street. You fill out the forms they require in order to precept, which takes up valuable work time. You equip their students with the skills they need to practice safely and correctly, and then try to fill out their evaluation sheets on things that students are not licensed to do.
Schools present their contracts and won’t adapt them to match what your employer wants. We are doing them a service, yet they dictate how we do it. My practice no longer takes students from certain schools, simply because we do not agree with their contracts. These poor students are thrown out without a life raft to find their preceptors! Aren’t their schools getting paid to do something?
Carol Glascock, WHNP-BC
Columbia, MO
Continue for Teaching & Precepting: Two Sides of the Same Coin >>
Teaching & Precepting: Two Sides of the Same Coin
I am a 64-year-old NP who has been precepting in Montana for the past four years. The students I precept are responsible for finding their own preceptors, just as I was 20+ years ago. However, preceptors are hard to find here, as the population is widely scattered; this places an emotional burden on students. They cannot be picky in choosing where they go. Thus, students may not be familiar with the preceptor’s practice or ability to teach.
The students I precept are in doctorate programs. My experience has shown that these students have very little understanding of practical application and instead have an overabundance of theoretical knowledge that does not always apply to seeing and treating patients. I believe that this, and the suggested “lack of preparedness,” is the fault of the program—not of the student.
Regardless of program faults, students are looking to learn from our experience. Teaching is part of being a preceptor; if you do not want to teach, being a preceptor is not for you. If you want to share your experience and knowledge with those following you (mindful that they may treat you in the future), precepting is an enjoyable experience. But—a good practitioner does not always make a good teacher.
Before becoming a preceptor, you must consider your time constraints, as well as your staff’s. You also must consider how your patients will react to seeing a student in your place.
Preceptors need to have a relationship with the student’s university apart from signing a paper saying they, the NP, will be the student’s preceptor. The university needs to be more proactive, as medical schools are, when finding preceptors willing to take students.
Compensation is another consideration that is rarely mentioned or discussed. Compensation would eliminate some of the negative reactions and might get more preceptors to sign on.
Harold W. Bruce, MSN, FNP-BC
Butte, MT
Continue for Collision of Causes for Precepting Hurdles >>
Collision of Causes for Precepting Hurdles
I am a family NP practicing in a large internal medicine practice owned by a university-based health care system. I precept NP students because I feel an obligation to my profession. However, the stress and additional workload that precepting places on me will probably lead me to stop sooner than I would like.
The inability to locate enough quality preceptors is a multifaceted issue. Too many students in too many programs, as mentioned in the editorial, is one contributing problem. I have been told by nursing professors that universities profit from their NP programs. They have an incentive to admit a large quantity of students and push them through. We could learn from our MD colleagues, who recognize the value of limiting student numbers.
The rise in NP students has led to a high number of poorly prepared students who enter their programs with no experience as RNs. Preceptors should not teach the basics, and professors should not expect preceptors to do so. Likewise, professors should not expect employers to fill in the gaps for new NPs they hire.
Many NP students have no “real-life” clinical experience to supplement their knowledge and skills. A strong foundation that combines nursing and medical knowledge, clinical experiences, basic assessment skills, and an understanding of human nature and human responses is crucial to being a successful NP. The latter is only developed through experience with patients. Students cannot develop these skills when their professors push them to immediately enroll in NP or DNP programs upon graduation from their BSN or basic non-NP MSN programs.
Our programs would do well to provide all the didactic classroom hours prior to the start of clinical rotations. Thus, the limited clinical hours can be used to hone clinical skills, instead of the current practice of students learning basics while also trying to incorporate knowledge with practice. It is a disservice to our NP students not to have completed classroom learning before starting their limited clinical rotations.
Preceptor overload and “burnout” occurs when very busy NPs are expected to fit precepting into their usual clinical sessions. There are strict mandates that dictate the number of residents a physician can precept. Those rules also allot physicians time reserved just for precepting. Why are NPs expected to precept during their already overworked day? Why haven’t our Boards of Nursing and nursing educators demanded this?
Precepting puts us behind during our clinical sessions. In some cases, it can impact our relative value units or patient numbers and salaries. We are teaching on our own time, with no incentives or monetary gain, yet we are expected to devote time and resources to our students.
Most of us do not receive merit-based financial rewards for the extra work. When did it become wrong to expect to be paid for our work? No other profession has this sense of guilt or self-recrimination when asking to be paid for services.
Preceptor training is another issue. Unlike physicians, we are not acculturated in the “see one, do one, teach one” manner. In nursing, we are trained that we must be taught, observed, and tested before being allowed to do anything new. We have a need to be taught everything, including how to precept. That being said, precepting is both an art and a science that involves grasping the basic tenets of learning and mentoring. These are skills that should be taught through observation or in classes so that we can pass on our knowledge. If our NP programs were longer and more step-by-step—in terms of first acquiring knowledge, then incorporating clinical skills with practice—we might learn the skills of teaching and mentoring without feeling we need additional “education” in precepting.
I have been in nursing for more than 40 years and love my profession. There are challenges ahead of us that we can only meet if we are brave enough to look clearly at the way we teach younger nurses, create improved ways of teaching those who will replace us, and actually recognize the value and efforts of those we ask to precept the next generation.
Theresa Dippolito, MSN, NP-C, CRNP, APN, CCM
Levittown, PA
Continue for Raising the Bar >>
Raising the Bar
I no longer want to be involved in precepting. I, too, find the students to be poorly prepared, and I was flabbergasted when I read a recent post on Facebook—a student offered to pay her preceptor to sign off on her clinicals!
I graduated from an FNP program in 1998 and also felt unprepared at first. My class thought like nurses, in that we expected things to be presented to us. Very few of us were aware that we should prepare ourselves, and the program I went through did nothing to inform us of this. It was a rude awakening.
NP programs should have improved since then, but they certainly have not. I have precepted multiple students who did not know how to do a proper physical exam, despite having passed their related courses. I have also precepted students who thought they knew everything and felt I should let them practice solo. Sadly, the majority were simultaneously in both groups.
There is still the stigma that we should remain within a nursing philosophy when we practice, when the reality is that we practice side by side with the doctors. We need to think critically, as they do, and have our programs teach such thinking via competent instructors.
My suggestions include a competency exam for NP instructors so that we can assure a higher, more standardized level of teaching. There should also be a prep course for potential NP students on how to think, including an explanation that it will be their responsibility to go after knowledge as well. Finally, we need to stray from the nursing philosophy-type teaching in NP programs and instead focus on stronger clinical knowledge and competence.
Nikki Knight, MSN, FNP-C
San Francisco, CA
But First, a Word About Vaping …
As advocates for tobacco control, my colleagues and I took great interest in Randy D. Danielsen’s editorial, “Vaping: Are Its ‘Benefits’ a Lot of Hot Air?” (Clinician Reviews. 2016;26[6]:15-16). Our practice offers evidence-based cessation treatment for individuals with nicotine addiction through counseling, pharmacotherapy, and the use of nicotine replacement products.
At our center, we often interact with clients who have had multiple quit attempts. Many of our clients state that they have been unsuccessful using an e-cigarette as a smoking cessation strategy. More often than not, they report smoking a cigarette “here and there” along with “vaping,” until they eventually relapse to their usual smoking pattern. Some report that they smoke even more than before they tried to quit. We have concerns about how vaping may renormalize the behaviors associated with smoking. Our clients say that when they vape, it reminds them of the “social” aspects of smoking— “being part of a group” and participating in an activity that keeps their hands busy.
Recent literature suggests that curiosity is the primary reason adolescents engage in e-cigarette use. While the newly implemented FDA regulations on e-cigarettes may keep these products out of the hands of some adolescents by prohibiting sales to those younger than 18, there is much more to consider. Along with exposure to nicotine, these devices offer a variety of kid-friendly flavorings that make these products attractive to middle and high school youth. Flavorings will not be regulated at this point in time.
According to researchers, this is a major concern. Findings from studies report that when inhaled, certain flavors are more harmful than others. For example, very high—even toxic—levels of benzaldehyde are inhaled by the user when cherry-flavored e-liquid is heated at high temperatures. The chemical diacetyl, a respiratory irritant known to be associated with bronchiolitis obliterans (popcorn lung), is produced by the aerosol vapors from buttered popcorn and certain fruit-flavored e-cigarette liquids.
As public health advocates, we must provide research to the FDA about the health hazards of the flavoring added to e-cigarettes and continue to fight for this regulation. We must support evidence-based tobacco control interventions, such as hard-hitting media campaigns and tobacco excise taxes, and promote access to cessation treatment, smoke-free policies, and statewide funding. Elimination of tobacco products will reduce the public health burden of tobacco-related illness.
Andrea Spatarella, DNP, RN, FNP-BC, Christine Fardellone, DNP, RN, Raisa Abramova, FNP-BC, RN
Great Neck, NY
Continue for Precepting & E-Quality of Care >>
Precepting & E-Quality of Care
As a woman of the baby-boomer generation, I was raised in an era when feminism was a focus for many. There was a great deal being written and discussed to encourage women to attain equal pay for equal work. Because nursing was (and still is) a profession dominated by women, this was a frequent topic in the classroom. We were repeatedly told, “Don’t give away your knowledge for free” and “You deserve to be paid what you’re worth, don’t discount yourself.”
I find it very telling that the same female-dominated academic programs that encouraged me to seek proper payment are now taking advantage of my free labor. I am somewhat offended by this attitude and consider it a step backward. Each time NPs are guilted or browbeaten into teaching without proper compensation, the profession is devalued. To continue to participate is to enable a problematic, if not broken, system.
NP education is in need of major reform. The precepting issue is the weak link in becoming a qualified professional who is able to meet the demands and responsibilities that academics and politicos are pushing harder and harder for. Our physician and PA colleagues can rightly argue that their clinical education is superior to ours—and I cannot fault our colleagues for expressing concern about quality of care. If nursing really wants an equal place at the table, this weakness must be improved, or the naysayers will have plenty of evidence that they were correct in the years to come.
Rebecca Shively, MSN, RN, FNP-BC
San Marcos, TX
Continue for NP Schools & Their Rigid Rules >>
NP Schools & Their Rigid Rules
I have been a preceptor for at least a dozen NP students and have yet to be offered compensation. Preceptors take the place of a paid instructor, giving away free advice and experiences. I don’t mind doing this, but at times it can be a struggle. Some students, for example, have never done a pelvic exam. Letting an inexperienced NP student practice a pelvic exam on a patient who made an appointment to see an experienced provider is unjust and unfair to the patient—I won’t do it. These schools need to provide practice sessions on paid patients so their students can learn these skills.
I have my beef with the institutes of higher learning, not the students. It feels like a one-way street. You fill out the forms they require in order to precept, which takes up valuable work time. You equip their students with the skills they need to practice safely and correctly, and then try to fill out their evaluation sheets on things that students are not licensed to do.
Schools present their contracts and won’t adapt them to match what your employer wants. We are doing them a service, yet they dictate how we do it. My practice no longer takes students from certain schools, simply because we do not agree with their contracts. These poor students are thrown out without a life raft to find their preceptors! Aren’t their schools getting paid to do something?
Carol Glascock, WHNP-BC
Columbia, MO
Continue for Teaching & Precepting: Two Sides of the Same Coin >>
Teaching & Precepting: Two Sides of the Same Coin
I am a 64-year-old NP who has been precepting in Montana for the past four years. The students I precept are responsible for finding their own preceptors, just as I was 20+ years ago. However, preceptors are hard to find here, as the population is widely scattered; this places an emotional burden on students. They cannot be picky in choosing where they go. Thus, students may not be familiar with the preceptor’s practice or ability to teach.
The students I precept are in doctorate programs. My experience has shown that these students have very little understanding of practical application and instead have an overabundance of theoretical knowledge that does not always apply to seeing and treating patients. I believe that this, and the suggested “lack of preparedness,” is the fault of the program—not of the student.
Regardless of program faults, students are looking to learn from our experience. Teaching is part of being a preceptor; if you do not want to teach, being a preceptor is not for you. If you want to share your experience and knowledge with those following you (mindful that they may treat you in the future), precepting is an enjoyable experience. But—a good practitioner does not always make a good teacher.
Before becoming a preceptor, you must consider your time constraints, as well as your staff’s. You also must consider how your patients will react to seeing a student in your place.
Preceptors need to have a relationship with the student’s university apart from signing a paper saying they, the NP, will be the student’s preceptor. The university needs to be more proactive, as medical schools are, when finding preceptors willing to take students.
Compensation is another consideration that is rarely mentioned or discussed. Compensation would eliminate some of the negative reactions and might get more preceptors to sign on.
Harold W. Bruce, MSN, FNP-BC
Butte, MT
Continue for Collision of Causes for Precepting Hurdles >>
Collision of Causes for Precepting Hurdles
I am a family NP practicing in a large internal medicine practice owned by a university-based health care system. I precept NP students because I feel an obligation to my profession. However, the stress and additional workload that precepting places on me will probably lead me to stop sooner than I would like.
The inability to locate enough quality preceptors is a multifaceted issue. Too many students in too many programs, as mentioned in the editorial, is one contributing problem. I have been told by nursing professors that universities profit from their NP programs. They have an incentive to admit a large quantity of students and push them through. We could learn from our MD colleagues, who recognize the value of limiting student numbers.
The rise in NP students has led to a high number of poorly prepared students who enter their programs with no experience as RNs. Preceptors should not teach the basics, and professors should not expect preceptors to do so. Likewise, professors should not expect employers to fill in the gaps for new NPs they hire.
Many NP students have no “real-life” clinical experience to supplement their knowledge and skills. A strong foundation that combines nursing and medical knowledge, clinical experiences, basic assessment skills, and an understanding of human nature and human responses is crucial to being a successful NP. The latter is only developed through experience with patients. Students cannot develop these skills when their professors push them to immediately enroll in NP or DNP programs upon graduation from their BSN or basic non-NP MSN programs.
Our programs would do well to provide all the didactic classroom hours prior to the start of clinical rotations. Thus, the limited clinical hours can be used to hone clinical skills, instead of the current practice of students learning basics while also trying to incorporate knowledge with practice. It is a disservice to our NP students not to have completed classroom learning before starting their limited clinical rotations.
Preceptor overload and “burnout” occurs when very busy NPs are expected to fit precepting into their usual clinical sessions. There are strict mandates that dictate the number of residents a physician can precept. Those rules also allot physicians time reserved just for precepting. Why are NPs expected to precept during their already overworked day? Why haven’t our Boards of Nursing and nursing educators demanded this?
Precepting puts us behind during our clinical sessions. In some cases, it can impact our relative value units or patient numbers and salaries. We are teaching on our own time, with no incentives or monetary gain, yet we are expected to devote time and resources to our students.
Most of us do not receive merit-based financial rewards for the extra work. When did it become wrong to expect to be paid for our work? No other profession has this sense of guilt or self-recrimination when asking to be paid for services.
Preceptor training is another issue. Unlike physicians, we are not acculturated in the “see one, do one, teach one” manner. In nursing, we are trained that we must be taught, observed, and tested before being allowed to do anything new. We have a need to be taught everything, including how to precept. That being said, precepting is both an art and a science that involves grasping the basic tenets of learning and mentoring. These are skills that should be taught through observation or in classes so that we can pass on our knowledge. If our NP programs were longer and more step-by-step—in terms of first acquiring knowledge, then incorporating clinical skills with practice—we might learn the skills of teaching and mentoring without feeling we need additional “education” in precepting.
I have been in nursing for more than 40 years and love my profession. There are challenges ahead of us that we can only meet if we are brave enough to look clearly at the way we teach younger nurses, create improved ways of teaching those who will replace us, and actually recognize the value and efforts of those we ask to precept the next generation.
Theresa Dippolito, MSN, NP-C, CRNP, APN, CCM
Levittown, PA
Continue for Raising the Bar >>
Raising the Bar
I no longer want to be involved in precepting. I, too, find the students to be poorly prepared, and I was flabbergasted when I read a recent post on Facebook—a student offered to pay her preceptor to sign off on her clinicals!
I graduated from an FNP program in 1998 and also felt unprepared at first. My class thought like nurses, in that we expected things to be presented to us. Very few of us were aware that we should prepare ourselves, and the program I went through did nothing to inform us of this. It was a rude awakening.
NP programs should have improved since then, but they certainly have not. I have precepted multiple students who did not know how to do a proper physical exam, despite having passed their related courses. I have also precepted students who thought they knew everything and felt I should let them practice solo. Sadly, the majority were simultaneously in both groups.
There is still the stigma that we should remain within a nursing philosophy when we practice, when the reality is that we practice side by side with the doctors. We need to think critically, as they do, and have our programs teach such thinking via competent instructors.
My suggestions include a competency exam for NP instructors so that we can assure a higher, more standardized level of teaching. There should also be a prep course for potential NP students on how to think, including an explanation that it will be their responsibility to go after knowledge as well. Finally, we need to stray from the nursing philosophy-type teaching in NP programs and instead focus on stronger clinical knowledge and competence.
Nikki Knight, MSN, FNP-C
San Francisco, CA
But First, a Word About Vaping …
As advocates for tobacco control, my colleagues and I took great interest in Randy D. Danielsen’s editorial, “Vaping: Are Its ‘Benefits’ a Lot of Hot Air?” (Clinician Reviews. 2016;26[6]:15-16). Our practice offers evidence-based cessation treatment for individuals with nicotine addiction through counseling, pharmacotherapy, and the use of nicotine replacement products.
At our center, we often interact with clients who have had multiple quit attempts. Many of our clients state that they have been unsuccessful using an e-cigarette as a smoking cessation strategy. More often than not, they report smoking a cigarette “here and there” along with “vaping,” until they eventually relapse to their usual smoking pattern. Some report that they smoke even more than before they tried to quit. We have concerns about how vaping may renormalize the behaviors associated with smoking. Our clients say that when they vape, it reminds them of the “social” aspects of smoking— “being part of a group” and participating in an activity that keeps their hands busy.
Recent literature suggests that curiosity is the primary reason adolescents engage in e-cigarette use. While the newly implemented FDA regulations on e-cigarettes may keep these products out of the hands of some adolescents by prohibiting sales to those younger than 18, there is much more to consider. Along with exposure to nicotine, these devices offer a variety of kid-friendly flavorings that make these products attractive to middle and high school youth. Flavorings will not be regulated at this point in time.
According to researchers, this is a major concern. Findings from studies report that when inhaled, certain flavors are more harmful than others. For example, very high—even toxic—levels of benzaldehyde are inhaled by the user when cherry-flavored e-liquid is heated at high temperatures. The chemical diacetyl, a respiratory irritant known to be associated with bronchiolitis obliterans (popcorn lung), is produced by the aerosol vapors from buttered popcorn and certain fruit-flavored e-cigarette liquids.
As public health advocates, we must provide research to the FDA about the health hazards of the flavoring added to e-cigarettes and continue to fight for this regulation. We must support evidence-based tobacco control interventions, such as hard-hitting media campaigns and tobacco excise taxes, and promote access to cessation treatment, smoke-free policies, and statewide funding. Elimination of tobacco products will reduce the public health burden of tobacco-related illness.
Andrea Spatarella, DNP, RN, FNP-BC, Christine Fardellone, DNP, RN, Raisa Abramova, FNP-BC, RN
Great Neck, NY
Continue for Precepting & E-Quality of Care >>
Precepting & E-Quality of Care
As a woman of the baby-boomer generation, I was raised in an era when feminism was a focus for many. There was a great deal being written and discussed to encourage women to attain equal pay for equal work. Because nursing was (and still is) a profession dominated by women, this was a frequent topic in the classroom. We were repeatedly told, “Don’t give away your knowledge for free” and “You deserve to be paid what you’re worth, don’t discount yourself.”
I find it very telling that the same female-dominated academic programs that encouraged me to seek proper payment are now taking advantage of my free labor. I am somewhat offended by this attitude and consider it a step backward. Each time NPs are guilted or browbeaten into teaching without proper compensation, the profession is devalued. To continue to participate is to enable a problematic, if not broken, system.
NP education is in need of major reform. The precepting issue is the weak link in becoming a qualified professional who is able to meet the demands and responsibilities that academics and politicos are pushing harder and harder for. Our physician and PA colleagues can rightly argue that their clinical education is superior to ours—and I cannot fault our colleagues for expressing concern about quality of care. If nursing really wants an equal place at the table, this weakness must be improved, or the naysayers will have plenty of evidence that they were correct in the years to come.
Rebecca Shively, MSN, RN, FNP-BC
San Marcos, TX
Continue for NP Schools & Their Rigid Rules >>
NP Schools & Their Rigid Rules
I have been a preceptor for at least a dozen NP students and have yet to be offered compensation. Preceptors take the place of a paid instructor, giving away free advice and experiences. I don’t mind doing this, but at times it can be a struggle. Some students, for example, have never done a pelvic exam. Letting an inexperienced NP student practice a pelvic exam on a patient who made an appointment to see an experienced provider is unjust and unfair to the patient—I won’t do it. These schools need to provide practice sessions on paid patients so their students can learn these skills.
I have my beef with the institutes of higher learning, not the students. It feels like a one-way street. You fill out the forms they require in order to precept, which takes up valuable work time. You equip their students with the skills they need to practice safely and correctly, and then try to fill out their evaluation sheets on things that students are not licensed to do.
Schools present their contracts and won’t adapt them to match what your employer wants. We are doing them a service, yet they dictate how we do it. My practice no longer takes students from certain schools, simply because we do not agree with their contracts. These poor students are thrown out without a life raft to find their preceptors! Aren’t their schools getting paid to do something?
Carol Glascock, WHNP-BC
Columbia, MO
Continue for Teaching & Precepting: Two Sides of the Same Coin >>
Teaching & Precepting: Two Sides of the Same Coin
I am a 64-year-old NP who has been precepting in Montana for the past four years. The students I precept are responsible for finding their own preceptors, just as I was 20+ years ago. However, preceptors are hard to find here, as the population is widely scattered; this places an emotional burden on students. They cannot be picky in choosing where they go. Thus, students may not be familiar with the preceptor’s practice or ability to teach.
The students I precept are in doctorate programs. My experience has shown that these students have very little understanding of practical application and instead have an overabundance of theoretical knowledge that does not always apply to seeing and treating patients. I believe that this, and the suggested “lack of preparedness,” is the fault of the program—not of the student.
Regardless of program faults, students are looking to learn from our experience. Teaching is part of being a preceptor; if you do not want to teach, being a preceptor is not for you. If you want to share your experience and knowledge with those following you (mindful that they may treat you in the future), precepting is an enjoyable experience. But—a good practitioner does not always make a good teacher.
Before becoming a preceptor, you must consider your time constraints, as well as your staff’s. You also must consider how your patients will react to seeing a student in your place.
Preceptors need to have a relationship with the student’s university apart from signing a paper saying they, the NP, will be the student’s preceptor. The university needs to be more proactive, as medical schools are, when finding preceptors willing to take students.
Compensation is another consideration that is rarely mentioned or discussed. Compensation would eliminate some of the negative reactions and might get more preceptors to sign on.
Harold W. Bruce, MSN, FNP-BC
Butte, MT
Continue for Collision of Causes for Precepting Hurdles >>
Collision of Causes for Precepting Hurdles
I am a family NP practicing in a large internal medicine practice owned by a university-based health care system. I precept NP students because I feel an obligation to my profession. However, the stress and additional workload that precepting places on me will probably lead me to stop sooner than I would like.
The inability to locate enough quality preceptors is a multifaceted issue. Too many students in too many programs, as mentioned in the editorial, is one contributing problem. I have been told by nursing professors that universities profit from their NP programs. They have an incentive to admit a large quantity of students and push them through. We could learn from our MD colleagues, who recognize the value of limiting student numbers.
The rise in NP students has led to a high number of poorly prepared students who enter their programs with no experience as RNs. Preceptors should not teach the basics, and professors should not expect preceptors to do so. Likewise, professors should not expect employers to fill in the gaps for new NPs they hire.
Many NP students have no “real-life” clinical experience to supplement their knowledge and skills. A strong foundation that combines nursing and medical knowledge, clinical experiences, basic assessment skills, and an understanding of human nature and human responses is crucial to being a successful NP. The latter is only developed through experience with patients. Students cannot develop these skills when their professors push them to immediately enroll in NP or DNP programs upon graduation from their BSN or basic non-NP MSN programs.
Our programs would do well to provide all the didactic classroom hours prior to the start of clinical rotations. Thus, the limited clinical hours can be used to hone clinical skills, instead of the current practice of students learning basics while also trying to incorporate knowledge with practice. It is a disservice to our NP students not to have completed classroom learning before starting their limited clinical rotations.
Preceptor overload and “burnout” occurs when very busy NPs are expected to fit precepting into their usual clinical sessions. There are strict mandates that dictate the number of residents a physician can precept. Those rules also allot physicians time reserved just for precepting. Why are NPs expected to precept during their already overworked day? Why haven’t our Boards of Nursing and nursing educators demanded this?
Precepting puts us behind during our clinical sessions. In some cases, it can impact our relative value units or patient numbers and salaries. We are teaching on our own time, with no incentives or monetary gain, yet we are expected to devote time and resources to our students.
Most of us do not receive merit-based financial rewards for the extra work. When did it become wrong to expect to be paid for our work? No other profession has this sense of guilt or self-recrimination when asking to be paid for services.
Preceptor training is another issue. Unlike physicians, we are not acculturated in the “see one, do one, teach one” manner. In nursing, we are trained that we must be taught, observed, and tested before being allowed to do anything new. We have a need to be taught everything, including how to precept. That being said, precepting is both an art and a science that involves grasping the basic tenets of learning and mentoring. These are skills that should be taught through observation or in classes so that we can pass on our knowledge. If our NP programs were longer and more step-by-step—in terms of first acquiring knowledge, then incorporating clinical skills with practice—we might learn the skills of teaching and mentoring without feeling we need additional “education” in precepting.
I have been in nursing for more than 40 years and love my profession. There are challenges ahead of us that we can only meet if we are brave enough to look clearly at the way we teach younger nurses, create improved ways of teaching those who will replace us, and actually recognize the value and efforts of those we ask to precept the next generation.
Theresa Dippolito, MSN, NP-C, CRNP, APN, CCM
Levittown, PA
Continue for Raising the Bar >>
Raising the Bar
I no longer want to be involved in precepting. I, too, find the students to be poorly prepared, and I was flabbergasted when I read a recent post on Facebook—a student offered to pay her preceptor to sign off on her clinicals!
I graduated from an FNP program in 1998 and also felt unprepared at first. My class thought like nurses, in that we expected things to be presented to us. Very few of us were aware that we should prepare ourselves, and the program I went through did nothing to inform us of this. It was a rude awakening.
NP programs should have improved since then, but they certainly have not. I have precepted multiple students who did not know how to do a proper physical exam, despite having passed their related courses. I have also precepted students who thought they knew everything and felt I should let them practice solo. Sadly, the majority were simultaneously in both groups.
There is still the stigma that we should remain within a nursing philosophy when we practice, when the reality is that we practice side by side with the doctors. We need to think critically, as they do, and have our programs teach such thinking via competent instructors.
My suggestions include a competency exam for NP instructors so that we can assure a higher, more standardized level of teaching. There should also be a prep course for potential NP students on how to think, including an explanation that it will be their responsibility to go after knowledge as well. Finally, we need to stray from the nursing philosophy-type teaching in NP programs and instead focus on stronger clinical knowledge and competence.
Nikki Knight, MSN, FNP-C
San Francisco, CA
To Cut Zika Microcephaly Risk, Delay Pregnancy More Than 9 Months
Women and couples planning to get pregnant may want to delay that pregnancy more than 9 months if there is an ongoing outbreak of the Zika virus in their area of residence, although that measure alone is not powerful enough to make a significant dent in stopping the Zika virus from spreading.
That is according to a new study in which investigators examined epidemiological data from Colombian Zika virus cases to determine if delaying pregnancies – which has been advised by a number of Central and South American health ministries – would be an effective course of action against the disease and its effects on both pregnant mothers and their fetuses (Ann Intern Med. 2016 Jul 26. doi: 10.7326/M16-0919).
“We developed a data-driven Zika virus transmission model to evaluate the effect of a mass pregnancy delay strategy in which women of reproductive age avoid pregnancy for the recommended duration, at varying degrees of adherence,” wrote Martial L. Ndeffo-Mbah, PhD, of Yale University in New Haven, Conn., and his coauthors.
Cases included were reported to Colombia’s National Institute of Health between Oct. 11, 2015, and May 8, 2016. Investigators classified cases as “suspected cases” of Zika virus infection if the patient presented to a hospital or clinic with “rash, fever (temperature higher than 37.2 degrees C), and at least one of the following symptoms within 5 days of symptom onset that could not be explained by other medical conditions: nonpurulent conjunctivitis or conjunctival hyperemia, arthralgia, myalgia, headache, or malaise.”
Modeling was used to project incidence rates of Zika virus infections, based on a 50% adherence rate to the recommendations.
Among those women who would delay getting pregnant by 6 months or less after possible exposure to Zika virus, prenatal Zika virus infections would decrease by 2%-7%. However, that number would decrease substantially, by 7%-44%, for those who delayed their pregnancy by as much as 9-24 months after exposure.
“Because the incidence peak of the epidemic occurs around 8 months into the outbreak, a strategy to delay pregnancy by more than 9 months, initiated at the onset of the epidemic, would allow women of reproductive age to avoid being pregnant during the incidence peak, when risk for exposure to Zika virus is highest,” Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors noted.
While delaying pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of birth defects in infants, the authors noted, it won’t have the same effect on reducing the overall spread of Zika virus in an affected region.
“Our results indicate that delays in pregnancy alone will probably be insufficient to curtail Zika-related birth abnormalities,” the authors concluded. “In the absence of a vaccine or therapeutic drugs for Zika virus infection, a combination of mass and individual pregnancy-delay strategies with effective vector-control measures is needed to curtail the spread and burden of the ongoing outbreak in the Americas.”
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Women and couples planning to get pregnant may want to delay that pregnancy more than 9 months if there is an ongoing outbreak of the Zika virus in their area of residence, although that measure alone is not powerful enough to make a significant dent in stopping the Zika virus from spreading.
That is according to a new study in which investigators examined epidemiological data from Colombian Zika virus cases to determine if delaying pregnancies – which has been advised by a number of Central and South American health ministries – would be an effective course of action against the disease and its effects on both pregnant mothers and their fetuses (Ann Intern Med. 2016 Jul 26. doi: 10.7326/M16-0919).
“We developed a data-driven Zika virus transmission model to evaluate the effect of a mass pregnancy delay strategy in which women of reproductive age avoid pregnancy for the recommended duration, at varying degrees of adherence,” wrote Martial L. Ndeffo-Mbah, PhD, of Yale University in New Haven, Conn., and his coauthors.
Cases included were reported to Colombia’s National Institute of Health between Oct. 11, 2015, and May 8, 2016. Investigators classified cases as “suspected cases” of Zika virus infection if the patient presented to a hospital or clinic with “rash, fever (temperature higher than 37.2 degrees C), and at least one of the following symptoms within 5 days of symptom onset that could not be explained by other medical conditions: nonpurulent conjunctivitis or conjunctival hyperemia, arthralgia, myalgia, headache, or malaise.”
Modeling was used to project incidence rates of Zika virus infections, based on a 50% adherence rate to the recommendations.
Among those women who would delay getting pregnant by 6 months or less after possible exposure to Zika virus, prenatal Zika virus infections would decrease by 2%-7%. However, that number would decrease substantially, by 7%-44%, for those who delayed their pregnancy by as much as 9-24 months after exposure.
“Because the incidence peak of the epidemic occurs around 8 months into the outbreak, a strategy to delay pregnancy by more than 9 months, initiated at the onset of the epidemic, would allow women of reproductive age to avoid being pregnant during the incidence peak, when risk for exposure to Zika virus is highest,” Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors noted.
While delaying pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of birth defects in infants, the authors noted, it won’t have the same effect on reducing the overall spread of Zika virus in an affected region.
“Our results indicate that delays in pregnancy alone will probably be insufficient to curtail Zika-related birth abnormalities,” the authors concluded. “In the absence of a vaccine or therapeutic drugs for Zika virus infection, a combination of mass and individual pregnancy-delay strategies with effective vector-control measures is needed to curtail the spread and burden of the ongoing outbreak in the Americas.”
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Women and couples planning to get pregnant may want to delay that pregnancy more than 9 months if there is an ongoing outbreak of the Zika virus in their area of residence, although that measure alone is not powerful enough to make a significant dent in stopping the Zika virus from spreading.
That is according to a new study in which investigators examined epidemiological data from Colombian Zika virus cases to determine if delaying pregnancies – which has been advised by a number of Central and South American health ministries – would be an effective course of action against the disease and its effects on both pregnant mothers and their fetuses (Ann Intern Med. 2016 Jul 26. doi: 10.7326/M16-0919).
“We developed a data-driven Zika virus transmission model to evaluate the effect of a mass pregnancy delay strategy in which women of reproductive age avoid pregnancy for the recommended duration, at varying degrees of adherence,” wrote Martial L. Ndeffo-Mbah, PhD, of Yale University in New Haven, Conn., and his coauthors.
Cases included were reported to Colombia’s National Institute of Health between Oct. 11, 2015, and May 8, 2016. Investigators classified cases as “suspected cases” of Zika virus infection if the patient presented to a hospital or clinic with “rash, fever (temperature higher than 37.2 degrees C), and at least one of the following symptoms within 5 days of symptom onset that could not be explained by other medical conditions: nonpurulent conjunctivitis or conjunctival hyperemia, arthralgia, myalgia, headache, or malaise.”
Modeling was used to project incidence rates of Zika virus infections, based on a 50% adherence rate to the recommendations.
Among those women who would delay getting pregnant by 6 months or less after possible exposure to Zika virus, prenatal Zika virus infections would decrease by 2%-7%. However, that number would decrease substantially, by 7%-44%, for those who delayed their pregnancy by as much as 9-24 months after exposure.
“Because the incidence peak of the epidemic occurs around 8 months into the outbreak, a strategy to delay pregnancy by more than 9 months, initiated at the onset of the epidemic, would allow women of reproductive age to avoid being pregnant during the incidence peak, when risk for exposure to Zika virus is highest,” Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors noted.
While delaying pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of birth defects in infants, the authors noted, it won’t have the same effect on reducing the overall spread of Zika virus in an affected region.
“Our results indicate that delays in pregnancy alone will probably be insufficient to curtail Zika-related birth abnormalities,” the authors concluded. “In the absence of a vaccine or therapeutic drugs for Zika virus infection, a combination of mass and individual pregnancy-delay strategies with effective vector-control measures is needed to curtail the spread and burden of the ongoing outbreak in the Americas.”
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM THE ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
To cut Zika microcephaly risk, delay pregnancy more than 9 months
Women and couples planning to get pregnant may want to delay that pregnancy more than 9 months if there is an ongoing outbreak of the Zika virus in their area of residence, although that measure alone is not powerful enough to make a significant dent in stopping the Zika virus from spreading.
That is according to a new study in which investigators examined epidemiological data from Colombian Zika virus cases to determine if delaying pregnancies – which has been advised by a number of Central and South American health ministries – would be an effective course of action against the disease and its effects on both pregnant mothers and their fetuses (Ann Intern Med. 2016 Jul 26. doi: 10.7326/M16-0919).
“We developed a data-driven Zika virus transmission model to evaluate the effect of a mass pregnancy delay strategy in which women of reproductive age avoid pregnancy for the recommended duration, at varying degrees of adherence,” wrote Martial L. Ndeffo-Mbah, PhD, of Yale University in New Haven, Conn., and his coauthors.
Cases included were reported to Colombia’s National Institute of Health between Oct. 11, 2015, and May 8, 2016. Investigators classified cases as “suspected cases” of Zika virus infection if the patient presented to a hospital or clinic with “rash, fever (temperature higher than 37.2 degrees C), and at least one of the following symptoms within 5 days of symptom onset that could not be explained by other medical conditions: nonpurulent conjunctivitis or conjunctival hyperemia, arthralgia, myalgia, headache, or malaise.”
Modeling was used to project incidence rates of Zika virus infections, based on a 50% adherence rate to the recommendations.
Among those women who would delay getting pregnant by 6 months or less after possible exposure to Zika virus, prenatal Zika virus infections would decrease by 2%-7%. However, that number would decrease substantially, by 7%-44%, for those who delayed their pregnancy by as much as 9-24 months after exposure.
“Because the incidence peak of the epidemic occurs around 8 months into the outbreak, a strategy to delay pregnancy by more than 9 months, initiated at the onset of the epidemic, would allow women of reproductive age to avoid being pregnant during the incidence peak, when risk for exposure to Zika virus is highest,” Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors noted.
While delaying pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of birth defects in infants, the authors noted, it won’t have the same effect on reducing the overall spread of Zika virus in an affected region.
“Our results indicate that delays in pregnancy alone will probably be insufficient to curtail Zika-related birth abnormalities,” the authors concluded. “In the absence of a vaccine or therapeutic drugs for Zika virus infection, a combination of mass and individual pregnancy-delay strategies with effective vector-control measures is needed to curtail the spread and burden of the ongoing outbreak in the Americas.”
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Women and couples planning to get pregnant may want to delay that pregnancy more than 9 months if there is an ongoing outbreak of the Zika virus in their area of residence, although that measure alone is not powerful enough to make a significant dent in stopping the Zika virus from spreading.
That is according to a new study in which investigators examined epidemiological data from Colombian Zika virus cases to determine if delaying pregnancies – which has been advised by a number of Central and South American health ministries – would be an effective course of action against the disease and its effects on both pregnant mothers and their fetuses (Ann Intern Med. 2016 Jul 26. doi: 10.7326/M16-0919).
“We developed a data-driven Zika virus transmission model to evaluate the effect of a mass pregnancy delay strategy in which women of reproductive age avoid pregnancy for the recommended duration, at varying degrees of adherence,” wrote Martial L. Ndeffo-Mbah, PhD, of Yale University in New Haven, Conn., and his coauthors.
Cases included were reported to Colombia’s National Institute of Health between Oct. 11, 2015, and May 8, 2016. Investigators classified cases as “suspected cases” of Zika virus infection if the patient presented to a hospital or clinic with “rash, fever (temperature higher than 37.2 degrees C), and at least one of the following symptoms within 5 days of symptom onset that could not be explained by other medical conditions: nonpurulent conjunctivitis or conjunctival hyperemia, arthralgia, myalgia, headache, or malaise.”
Modeling was used to project incidence rates of Zika virus infections, based on a 50% adherence rate to the recommendations.
Among those women who would delay getting pregnant by 6 months or less after possible exposure to Zika virus, prenatal Zika virus infections would decrease by 2%-7%. However, that number would decrease substantially, by 7%-44%, for those who delayed their pregnancy by as much as 9-24 months after exposure.
“Because the incidence peak of the epidemic occurs around 8 months into the outbreak, a strategy to delay pregnancy by more than 9 months, initiated at the onset of the epidemic, would allow women of reproductive age to avoid being pregnant during the incidence peak, when risk for exposure to Zika virus is highest,” Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors noted.
While delaying pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of birth defects in infants, the authors noted, it won’t have the same effect on reducing the overall spread of Zika virus in an affected region.
“Our results indicate that delays in pregnancy alone will probably be insufficient to curtail Zika-related birth abnormalities,” the authors concluded. “In the absence of a vaccine or therapeutic drugs for Zika virus infection, a combination of mass and individual pregnancy-delay strategies with effective vector-control measures is needed to curtail the spread and burden of the ongoing outbreak in the Americas.”
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Women and couples planning to get pregnant may want to delay that pregnancy more than 9 months if there is an ongoing outbreak of the Zika virus in their area of residence, although that measure alone is not powerful enough to make a significant dent in stopping the Zika virus from spreading.
That is according to a new study in which investigators examined epidemiological data from Colombian Zika virus cases to determine if delaying pregnancies – which has been advised by a number of Central and South American health ministries – would be an effective course of action against the disease and its effects on both pregnant mothers and their fetuses (Ann Intern Med. 2016 Jul 26. doi: 10.7326/M16-0919).
“We developed a data-driven Zika virus transmission model to evaluate the effect of a mass pregnancy delay strategy in which women of reproductive age avoid pregnancy for the recommended duration, at varying degrees of adherence,” wrote Martial L. Ndeffo-Mbah, PhD, of Yale University in New Haven, Conn., and his coauthors.
Cases included were reported to Colombia’s National Institute of Health between Oct. 11, 2015, and May 8, 2016. Investigators classified cases as “suspected cases” of Zika virus infection if the patient presented to a hospital or clinic with “rash, fever (temperature higher than 37.2 degrees C), and at least one of the following symptoms within 5 days of symptom onset that could not be explained by other medical conditions: nonpurulent conjunctivitis or conjunctival hyperemia, arthralgia, myalgia, headache, or malaise.”
Modeling was used to project incidence rates of Zika virus infections, based on a 50% adherence rate to the recommendations.
Among those women who would delay getting pregnant by 6 months or less after possible exposure to Zika virus, prenatal Zika virus infections would decrease by 2%-7%. However, that number would decrease substantially, by 7%-44%, for those who delayed their pregnancy by as much as 9-24 months after exposure.
“Because the incidence peak of the epidemic occurs around 8 months into the outbreak, a strategy to delay pregnancy by more than 9 months, initiated at the onset of the epidemic, would allow women of reproductive age to avoid being pregnant during the incidence peak, when risk for exposure to Zika virus is highest,” Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors noted.
While delaying pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of birth defects in infants, the authors noted, it won’t have the same effect on reducing the overall spread of Zika virus in an affected region.
“Our results indicate that delays in pregnancy alone will probably be insufficient to curtail Zika-related birth abnormalities,” the authors concluded. “In the absence of a vaccine or therapeutic drugs for Zika virus infection, a combination of mass and individual pregnancy-delay strategies with effective vector-control measures is needed to curtail the spread and burden of the ongoing outbreak in the Americas.”
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM THE ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Key clinical point: Delaying pregnancy after a Zika outbreak can reduce the risk of having a child with microcephaly, but it is only a small part in what must be a larger effort to prevent the spread of Zika virus.
Major finding: Pregnancies delayed by 6 months after a local Zika outbreak could decrease prenatal Zika infections 2%-7%, but delaying pregnancies 9-24 months could decrease infections by 17%-44%.
Data source: A vector-borne Zika virus transmission model of data on Colombian Zika virus infections in 2015-2016.
Disclosures: The National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Ndeffo-Mbah and his coauthors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
VIDEO: Proposed Alzheimer’s funding boost could mean wider research scope
TORONTO – In 2011, President Barack Obama signed into law the National Alzheimer’s Project Act, with the lofty goal of preventing or effectively treating Alzheimer’s disease by 2025. A year later, a panel of leading researchers translated that goal into harsh reality: Reaching it would cost at least $2 billion each year. That level of funding would put Alzheimer’s research on the same footing as research on cancer, heart disease, and HIV – areas that have experienced rapid and sustained clinical progress.
But securing federal funding support has been a slow go. At the end of 2016, even with historic funding increases, the total allocation still fell short of $1 billion. That’s about to change for the better. The proposed 2017 budget, if approved, will boost the allocation to $1.4 billion.
What will that new money mean to researchers who’ve struggled for years to get grants? And what could it mean to doctors, patients, and families who still face a devastating disease with no cure, no prevention, and no effective treatments? Robert J. Egge, chief public policy officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, breaks it down in this video interview at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference 2016.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
On Twitter @alz_gal
TORONTO – In 2011, President Barack Obama signed into law the National Alzheimer’s Project Act, with the lofty goal of preventing or effectively treating Alzheimer’s disease by 2025. A year later, a panel of leading researchers translated that goal into harsh reality: Reaching it would cost at least $2 billion each year. That level of funding would put Alzheimer’s research on the same footing as research on cancer, heart disease, and HIV – areas that have experienced rapid and sustained clinical progress.
But securing federal funding support has been a slow go. At the end of 2016, even with historic funding increases, the total allocation still fell short of $1 billion. That’s about to change for the better. The proposed 2017 budget, if approved, will boost the allocation to $1.4 billion.
What will that new money mean to researchers who’ve struggled for years to get grants? And what could it mean to doctors, patients, and families who still face a devastating disease with no cure, no prevention, and no effective treatments? Robert J. Egge, chief public policy officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, breaks it down in this video interview at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference 2016.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
On Twitter @alz_gal
TORONTO – In 2011, President Barack Obama signed into law the National Alzheimer’s Project Act, with the lofty goal of preventing or effectively treating Alzheimer’s disease by 2025. A year later, a panel of leading researchers translated that goal into harsh reality: Reaching it would cost at least $2 billion each year. That level of funding would put Alzheimer’s research on the same footing as research on cancer, heart disease, and HIV – areas that have experienced rapid and sustained clinical progress.
But securing federal funding support has been a slow go. At the end of 2016, even with historic funding increases, the total allocation still fell short of $1 billion. That’s about to change for the better. The proposed 2017 budget, if approved, will boost the allocation to $1.4 billion.
What will that new money mean to researchers who’ve struggled for years to get grants? And what could it mean to doctors, patients, and families who still face a devastating disease with no cure, no prevention, and no effective treatments? Robert J. Egge, chief public policy officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, breaks it down in this video interview at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference 2016.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
On Twitter @alz_gal
AT AAIC 2016