User login
News and Views that Matter to the Ob.Gyn.
gambling
compulsive behaviors
ammunition
assault rifle
black jack
Boko Haram
bondage
child abuse
cocaine
Daech
drug paraphernalia
explosion
gun
human trafficking
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
slot machine
terrorism
terrorist
Texas hold 'em
UFC
substance abuse
abuseed
abuseer
abusees
abuseing
abusely
abuses
aeolus
aeolused
aeoluser
aeoluses
aeolusing
aeolusly
aeoluss
ahole
aholeed
aholeer
aholees
aholeing
aholely
aholes
alcohol
alcoholed
alcoholer
alcoholes
alcoholing
alcoholly
alcohols
allman
allmaned
allmaner
allmanes
allmaning
allmanly
allmans
alted
altes
alting
altly
alts
analed
analer
anales
analing
anally
analprobe
analprobeed
analprobeer
analprobees
analprobeing
analprobely
analprobes
anals
anilingus
anilingused
anilinguser
anilinguses
anilingusing
anilingusly
anilinguss
anus
anused
anuser
anuses
anusing
anusly
anuss
areola
areolaed
areolaer
areolaes
areolaing
areolaly
areolas
areole
areoleed
areoleer
areolees
areoleing
areolely
areoles
arian
arianed
arianer
arianes
arianing
arianly
arians
aryan
aryaned
aryaner
aryanes
aryaning
aryanly
aryans
asiaed
asiaer
asiaes
asiaing
asialy
asias
ass
ass hole
ass lick
ass licked
ass licker
ass lickes
ass licking
ass lickly
ass licks
assbang
assbanged
assbangeded
assbangeder
assbangedes
assbangeding
assbangedly
assbangeds
assbanger
assbanges
assbanging
assbangly
assbangs
assbangsed
assbangser
assbangses
assbangsing
assbangsly
assbangss
assed
asser
asses
assesed
asseser
asseses
assesing
assesly
assess
assfuck
assfucked
assfucker
assfuckered
assfuckerer
assfuckeres
assfuckering
assfuckerly
assfuckers
assfuckes
assfucking
assfuckly
assfucks
asshat
asshated
asshater
asshates
asshating
asshatly
asshats
assholeed
assholeer
assholees
assholeing
assholely
assholes
assholesed
assholeser
assholeses
assholesing
assholesly
assholess
assing
assly
assmaster
assmastered
assmasterer
assmasteres
assmastering
assmasterly
assmasters
assmunch
assmunched
assmuncher
assmunches
assmunching
assmunchly
assmunchs
asss
asswipe
asswipeed
asswipeer
asswipees
asswipeing
asswipely
asswipes
asswipesed
asswipeser
asswipeses
asswipesing
asswipesly
asswipess
azz
azzed
azzer
azzes
azzing
azzly
azzs
babeed
babeer
babees
babeing
babely
babes
babesed
babeser
babeses
babesing
babesly
babess
ballsac
ballsaced
ballsacer
ballsaces
ballsacing
ballsack
ballsacked
ballsacker
ballsackes
ballsacking
ballsackly
ballsacks
ballsacly
ballsacs
ballsed
ballser
ballses
ballsing
ballsly
ballss
barf
barfed
barfer
barfes
barfing
barfly
barfs
bastard
bastarded
bastarder
bastardes
bastarding
bastardly
bastards
bastardsed
bastardser
bastardses
bastardsing
bastardsly
bastardss
bawdy
bawdyed
bawdyer
bawdyes
bawdying
bawdyly
bawdys
beaner
beanered
beanerer
beaneres
beanering
beanerly
beaners
beardedclam
beardedclamed
beardedclamer
beardedclames
beardedclaming
beardedclamly
beardedclams
beastiality
beastialityed
beastialityer
beastialityes
beastialitying
beastialityly
beastialitys
beatch
beatched
beatcher
beatches
beatching
beatchly
beatchs
beater
beatered
beaterer
beateres
beatering
beaterly
beaters
beered
beerer
beeres
beering
beerly
beeyotch
beeyotched
beeyotcher
beeyotches
beeyotching
beeyotchly
beeyotchs
beotch
beotched
beotcher
beotches
beotching
beotchly
beotchs
biatch
biatched
biatcher
biatches
biatching
biatchly
biatchs
big tits
big titsed
big titser
big titses
big titsing
big titsly
big titss
bigtits
bigtitsed
bigtitser
bigtitses
bigtitsing
bigtitsly
bigtitss
bimbo
bimboed
bimboer
bimboes
bimboing
bimboly
bimbos
bisexualed
bisexualer
bisexuales
bisexualing
bisexually
bisexuals
bitch
bitched
bitcheded
bitcheder
bitchedes
bitcheding
bitchedly
bitcheds
bitcher
bitches
bitchesed
bitcheser
bitcheses
bitchesing
bitchesly
bitchess
bitching
bitchly
bitchs
bitchy
bitchyed
bitchyer
bitchyes
bitchying
bitchyly
bitchys
bleached
bleacher
bleaches
bleaching
bleachly
bleachs
blow job
blow jobed
blow jober
blow jobes
blow jobing
blow jobly
blow jobs
blowed
blower
blowes
blowing
blowjob
blowjobed
blowjober
blowjobes
blowjobing
blowjobly
blowjobs
blowjobsed
blowjobser
blowjobses
blowjobsing
blowjobsly
blowjobss
blowly
blows
boink
boinked
boinker
boinkes
boinking
boinkly
boinks
bollock
bollocked
bollocker
bollockes
bollocking
bollockly
bollocks
bollocksed
bollockser
bollockses
bollocksing
bollocksly
bollockss
bollok
bolloked
bolloker
bollokes
bolloking
bollokly
bolloks
boner
bonered
bonerer
boneres
bonering
bonerly
boners
bonersed
bonerser
bonerses
bonersing
bonersly
bonerss
bong
bonged
bonger
bonges
bonging
bongly
bongs
boob
boobed
boober
boobes
boobies
boobiesed
boobieser
boobieses
boobiesing
boobiesly
boobiess
boobing
boobly
boobs
boobsed
boobser
boobses
boobsing
boobsly
boobss
booby
boobyed
boobyer
boobyes
boobying
boobyly
boobys
booger
boogered
boogerer
boogeres
boogering
boogerly
boogers
bookie
bookieed
bookieer
bookiees
bookieing
bookiely
bookies
bootee
booteeed
booteeer
booteees
booteeing
booteely
bootees
bootie
bootieed
bootieer
bootiees
bootieing
bootiely
booties
booty
bootyed
bootyer
bootyes
bootying
bootyly
bootys
boozeed
boozeer
boozees
boozeing
boozely
boozer
boozered
boozerer
boozeres
boozering
boozerly
boozers
boozes
boozy
boozyed
boozyer
boozyes
boozying
boozyly
boozys
bosomed
bosomer
bosomes
bosoming
bosomly
bosoms
bosomy
bosomyed
bosomyer
bosomyes
bosomying
bosomyly
bosomys
bugger
buggered
buggerer
buggeres
buggering
buggerly
buggers
bukkake
bukkakeed
bukkakeer
bukkakees
bukkakeing
bukkakely
bukkakes
bull shit
bull shited
bull shiter
bull shites
bull shiting
bull shitly
bull shits
bullshit
bullshited
bullshiter
bullshites
bullshiting
bullshitly
bullshits
bullshitsed
bullshitser
bullshitses
bullshitsing
bullshitsly
bullshitss
bullshitted
bullshitteded
bullshitteder
bullshittedes
bullshitteding
bullshittedly
bullshitteds
bullturds
bullturdsed
bullturdser
bullturdses
bullturdsing
bullturdsly
bullturdss
bung
bunged
bunger
bunges
bunging
bungly
bungs
busty
bustyed
bustyer
bustyes
bustying
bustyly
bustys
butt
butt fuck
butt fucked
butt fucker
butt fuckes
butt fucking
butt fuckly
butt fucks
butted
buttes
buttfuck
buttfucked
buttfucker
buttfuckered
buttfuckerer
buttfuckeres
buttfuckering
buttfuckerly
buttfuckers
buttfuckes
buttfucking
buttfuckly
buttfucks
butting
buttly
buttplug
buttpluged
buttpluger
buttpluges
buttpluging
buttplugly
buttplugs
butts
caca
cacaed
cacaer
cacaes
cacaing
cacaly
cacas
cahone
cahoneed
cahoneer
cahonees
cahoneing
cahonely
cahones
cameltoe
cameltoeed
cameltoeer
cameltoees
cameltoeing
cameltoely
cameltoes
carpetmuncher
carpetmunchered
carpetmuncherer
carpetmuncheres
carpetmunchering
carpetmuncherly
carpetmunchers
cawk
cawked
cawker
cawkes
cawking
cawkly
cawks
chinc
chinced
chincer
chinces
chincing
chincly
chincs
chincsed
chincser
chincses
chincsing
chincsly
chincss
chink
chinked
chinker
chinkes
chinking
chinkly
chinks
chode
chodeed
chodeer
chodees
chodeing
chodely
chodes
chodesed
chodeser
chodeses
chodesing
chodesly
chodess
clit
clited
cliter
clites
cliting
clitly
clitoris
clitorised
clitoriser
clitorises
clitorising
clitorisly
clitoriss
clitorus
clitorused
clitoruser
clitoruses
clitorusing
clitorusly
clitoruss
clits
clitsed
clitser
clitses
clitsing
clitsly
clitss
clitty
clittyed
clittyer
clittyes
clittying
clittyly
clittys
cocain
cocaine
cocained
cocaineed
cocaineer
cocainees
cocaineing
cocainely
cocainer
cocaines
cocaining
cocainly
cocains
cock
cock sucker
cock suckered
cock suckerer
cock suckeres
cock suckering
cock suckerly
cock suckers
cockblock
cockblocked
cockblocker
cockblockes
cockblocking
cockblockly
cockblocks
cocked
cocker
cockes
cockholster
cockholstered
cockholsterer
cockholsteres
cockholstering
cockholsterly
cockholsters
cocking
cockknocker
cockknockered
cockknockerer
cockknockeres
cockknockering
cockknockerly
cockknockers
cockly
cocks
cocksed
cockser
cockses
cocksing
cocksly
cocksmoker
cocksmokered
cocksmokerer
cocksmokeres
cocksmokering
cocksmokerly
cocksmokers
cockss
cocksucker
cocksuckered
cocksuckerer
cocksuckeres
cocksuckering
cocksuckerly
cocksuckers
coital
coitaled
coitaler
coitales
coitaling
coitally
coitals
commie
commieed
commieer
commiees
commieing
commiely
commies
condomed
condomer
condomes
condoming
condomly
condoms
coon
cooned
cooner
coones
cooning
coonly
coons
coonsed
coonser
coonses
coonsing
coonsly
coonss
corksucker
corksuckered
corksuckerer
corksuckeres
corksuckering
corksuckerly
corksuckers
cracked
crackwhore
crackwhoreed
crackwhoreer
crackwhorees
crackwhoreing
crackwhorely
crackwhores
crap
craped
craper
crapes
craping
craply
crappy
crappyed
crappyer
crappyes
crappying
crappyly
crappys
cum
cumed
cumer
cumes
cuming
cumly
cummin
cummined
cumminer
cummines
cumming
cumminged
cumminger
cumminges
cumminging
cummingly
cummings
cummining
cumminly
cummins
cums
cumshot
cumshoted
cumshoter
cumshotes
cumshoting
cumshotly
cumshots
cumshotsed
cumshotser
cumshotses
cumshotsing
cumshotsly
cumshotss
cumslut
cumsluted
cumsluter
cumslutes
cumsluting
cumslutly
cumsluts
cumstain
cumstained
cumstainer
cumstaines
cumstaining
cumstainly
cumstains
cunilingus
cunilingused
cunilinguser
cunilinguses
cunilingusing
cunilingusly
cunilinguss
cunnilingus
cunnilingused
cunnilinguser
cunnilinguses
cunnilingusing
cunnilingusly
cunnilinguss
cunny
cunnyed
cunnyer
cunnyes
cunnying
cunnyly
cunnys
cunt
cunted
cunter
cuntes
cuntface
cuntfaceed
cuntfaceer
cuntfacees
cuntfaceing
cuntfacely
cuntfaces
cunthunter
cunthuntered
cunthunterer
cunthunteres
cunthuntering
cunthunterly
cunthunters
cunting
cuntlick
cuntlicked
cuntlicker
cuntlickered
cuntlickerer
cuntlickeres
cuntlickering
cuntlickerly
cuntlickers
cuntlickes
cuntlicking
cuntlickly
cuntlicks
cuntly
cunts
cuntsed
cuntser
cuntses
cuntsing
cuntsly
cuntss
dago
dagoed
dagoer
dagoes
dagoing
dagoly
dagos
dagosed
dagoser
dagoses
dagosing
dagosly
dagoss
dammit
dammited
dammiter
dammites
dammiting
dammitly
dammits
damn
damned
damneded
damneder
damnedes
damneding
damnedly
damneds
damner
damnes
damning
damnit
damnited
damniter
damnites
damniting
damnitly
damnits
damnly
damns
dick
dickbag
dickbaged
dickbager
dickbages
dickbaging
dickbagly
dickbags
dickdipper
dickdippered
dickdipperer
dickdipperes
dickdippering
dickdipperly
dickdippers
dicked
dicker
dickes
dickface
dickfaceed
dickfaceer
dickfacees
dickfaceing
dickfacely
dickfaces
dickflipper
dickflippered
dickflipperer
dickflipperes
dickflippering
dickflipperly
dickflippers
dickhead
dickheaded
dickheader
dickheades
dickheading
dickheadly
dickheads
dickheadsed
dickheadser
dickheadses
dickheadsing
dickheadsly
dickheadss
dicking
dickish
dickished
dickisher
dickishes
dickishing
dickishly
dickishs
dickly
dickripper
dickrippered
dickripperer
dickripperes
dickrippering
dickripperly
dickrippers
dicks
dicksipper
dicksippered
dicksipperer
dicksipperes
dicksippering
dicksipperly
dicksippers
dickweed
dickweeded
dickweeder
dickweedes
dickweeding
dickweedly
dickweeds
dickwhipper
dickwhippered
dickwhipperer
dickwhipperes
dickwhippering
dickwhipperly
dickwhippers
dickzipper
dickzippered
dickzipperer
dickzipperes
dickzippering
dickzipperly
dickzippers
diddle
diddleed
diddleer
diddlees
diddleing
diddlely
diddles
dike
dikeed
dikeer
dikees
dikeing
dikely
dikes
dildo
dildoed
dildoer
dildoes
dildoing
dildoly
dildos
dildosed
dildoser
dildoses
dildosing
dildosly
dildoss
diligaf
diligafed
diligafer
diligafes
diligafing
diligafly
diligafs
dillweed
dillweeded
dillweeder
dillweedes
dillweeding
dillweedly
dillweeds
dimwit
dimwited
dimwiter
dimwites
dimwiting
dimwitly
dimwits
dingle
dingleed
dingleer
dinglees
dingleing
dinglely
dingles
dipship
dipshiped
dipshiper
dipshipes
dipshiping
dipshiply
dipships
dizzyed
dizzyer
dizzyes
dizzying
dizzyly
dizzys
doggiestyleed
doggiestyleer
doggiestylees
doggiestyleing
doggiestylely
doggiestyles
doggystyleed
doggystyleer
doggystylees
doggystyleing
doggystylely
doggystyles
dong
donged
donger
donges
donging
dongly
dongs
doofus
doofused
doofuser
doofuses
doofusing
doofusly
doofuss
doosh
dooshed
doosher
dooshes
dooshing
dooshly
dooshs
dopeyed
dopeyer
dopeyes
dopeying
dopeyly
dopeys
douchebag
douchebaged
douchebager
douchebages
douchebaging
douchebagly
douchebags
douchebagsed
douchebagser
douchebagses
douchebagsing
douchebagsly
douchebagss
doucheed
doucheer
douchees
doucheing
douchely
douches
douchey
doucheyed
doucheyer
doucheyes
doucheying
doucheyly
doucheys
drunk
drunked
drunker
drunkes
drunking
drunkly
drunks
dumass
dumassed
dumasser
dumasses
dumassing
dumassly
dumasss
dumbass
dumbassed
dumbasser
dumbasses
dumbassesed
dumbasseser
dumbasseses
dumbassesing
dumbassesly
dumbassess
dumbassing
dumbassly
dumbasss
dummy
dummyed
dummyer
dummyes
dummying
dummyly
dummys
dyke
dykeed
dykeer
dykees
dykeing
dykely
dykes
dykesed
dykeser
dykeses
dykesing
dykesly
dykess
erotic
eroticed
eroticer
erotices
eroticing
eroticly
erotics
extacy
extacyed
extacyer
extacyes
extacying
extacyly
extacys
extasy
extasyed
extasyer
extasyes
extasying
extasyly
extasys
fack
facked
facker
fackes
facking
fackly
facks
fag
faged
fager
fages
fagg
fagged
faggeded
faggeder
faggedes
faggeding
faggedly
faggeds
fagger
fagges
fagging
faggit
faggited
faggiter
faggites
faggiting
faggitly
faggits
faggly
faggot
faggoted
faggoter
faggotes
faggoting
faggotly
faggots
faggs
faging
fagly
fagot
fagoted
fagoter
fagotes
fagoting
fagotly
fagots
fags
fagsed
fagser
fagses
fagsing
fagsly
fagss
faig
faiged
faiger
faiges
faiging
faigly
faigs
faigt
faigted
faigter
faigtes
faigting
faigtly
faigts
fannybandit
fannybandited
fannybanditer
fannybandites
fannybanditing
fannybanditly
fannybandits
farted
farter
fartes
farting
fartknocker
fartknockered
fartknockerer
fartknockeres
fartknockering
fartknockerly
fartknockers
fartly
farts
felch
felched
felcher
felchered
felcherer
felcheres
felchering
felcherly
felchers
felches
felching
felchinged
felchinger
felchinges
felchinging
felchingly
felchings
felchly
felchs
fellate
fellateed
fellateer
fellatees
fellateing
fellately
fellates
fellatio
fellatioed
fellatioer
fellatioes
fellatioing
fellatioly
fellatios
feltch
feltched
feltcher
feltchered
feltcherer
feltcheres
feltchering
feltcherly
feltchers
feltches
feltching
feltchly
feltchs
feom
feomed
feomer
feomes
feoming
feomly
feoms
fisted
fisteded
fisteder
fistedes
fisteding
fistedly
fisteds
fisting
fistinged
fistinger
fistinges
fistinging
fistingly
fistings
fisty
fistyed
fistyer
fistyes
fistying
fistyly
fistys
floozy
floozyed
floozyer
floozyes
floozying
floozyly
floozys
foad
foaded
foader
foades
foading
foadly
foads
fondleed
fondleer
fondlees
fondleing
fondlely
fondles
foobar
foobared
foobarer
foobares
foobaring
foobarly
foobars
freex
freexed
freexer
freexes
freexing
freexly
freexs
frigg
frigga
friggaed
friggaer
friggaes
friggaing
friggaly
friggas
frigged
frigger
frigges
frigging
friggly
friggs
fubar
fubared
fubarer
fubares
fubaring
fubarly
fubars
fuck
fuckass
fuckassed
fuckasser
fuckasses
fuckassing
fuckassly
fuckasss
fucked
fuckeded
fuckeder
fuckedes
fuckeding
fuckedly
fuckeds
fucker
fuckered
fuckerer
fuckeres
fuckering
fuckerly
fuckers
fuckes
fuckface
fuckfaceed
fuckfaceer
fuckfacees
fuckfaceing
fuckfacely
fuckfaces
fuckin
fuckined
fuckiner
fuckines
fucking
fuckinged
fuckinger
fuckinges
fuckinging
fuckingly
fuckings
fuckining
fuckinly
fuckins
fuckly
fucknugget
fucknuggeted
fucknuggeter
fucknuggetes
fucknuggeting
fucknuggetly
fucknuggets
fucknut
fucknuted
fucknuter
fucknutes
fucknuting
fucknutly
fucknuts
fuckoff
fuckoffed
fuckoffer
fuckoffes
fuckoffing
fuckoffly
fuckoffs
fucks
fucksed
fuckser
fuckses
fucksing
fucksly
fuckss
fucktard
fucktarded
fucktarder
fucktardes
fucktarding
fucktardly
fucktards
fuckup
fuckuped
fuckuper
fuckupes
fuckuping
fuckuply
fuckups
fuckwad
fuckwaded
fuckwader
fuckwades
fuckwading
fuckwadly
fuckwads
fuckwit
fuckwited
fuckwiter
fuckwites
fuckwiting
fuckwitly
fuckwits
fudgepacker
fudgepackered
fudgepackerer
fudgepackeres
fudgepackering
fudgepackerly
fudgepackers
fuk
fuked
fuker
fukes
fuking
fukly
fuks
fvck
fvcked
fvcker
fvckes
fvcking
fvckly
fvcks
fxck
fxcked
fxcker
fxckes
fxcking
fxckly
fxcks
gae
gaeed
gaeer
gaees
gaeing
gaely
gaes
gai
gaied
gaier
gaies
gaiing
gaily
gais
ganja
ganjaed
ganjaer
ganjaes
ganjaing
ganjaly
ganjas
gayed
gayer
gayes
gaying
gayly
gays
gaysed
gayser
gayses
gaysing
gaysly
gayss
gey
geyed
geyer
geyes
geying
geyly
geys
gfc
gfced
gfcer
gfces
gfcing
gfcly
gfcs
gfy
gfyed
gfyer
gfyes
gfying
gfyly
gfys
ghay
ghayed
ghayer
ghayes
ghaying
ghayly
ghays
ghey
gheyed
gheyer
gheyes
gheying
gheyly
gheys
gigolo
gigoloed
gigoloer
gigoloes
gigoloing
gigololy
gigolos
goatse
goatseed
goatseer
goatsees
goatseing
goatsely
goatses
godamn
godamned
godamner
godamnes
godamning
godamnit
godamnited
godamniter
godamnites
godamniting
godamnitly
godamnits
godamnly
godamns
goddam
goddamed
goddamer
goddames
goddaming
goddamly
goddammit
goddammited
goddammiter
goddammites
goddammiting
goddammitly
goddammits
goddamn
goddamned
goddamner
goddamnes
goddamning
goddamnly
goddamns
goddams
goldenshower
goldenshowered
goldenshowerer
goldenshoweres
goldenshowering
goldenshowerly
goldenshowers
gonad
gonaded
gonader
gonades
gonading
gonadly
gonads
gonadsed
gonadser
gonadses
gonadsing
gonadsly
gonadss
gook
gooked
gooker
gookes
gooking
gookly
gooks
gooksed
gookser
gookses
gooksing
gooksly
gookss
gringo
gringoed
gringoer
gringoes
gringoing
gringoly
gringos
gspot
gspoted
gspoter
gspotes
gspoting
gspotly
gspots
gtfo
gtfoed
gtfoer
gtfoes
gtfoing
gtfoly
gtfos
guido
guidoed
guidoer
guidoes
guidoing
guidoly
guidos
handjob
handjobed
handjober
handjobes
handjobing
handjobly
handjobs
hard on
hard oned
hard oner
hard ones
hard oning
hard only
hard ons
hardknight
hardknighted
hardknighter
hardknightes
hardknighting
hardknightly
hardknights
hebe
hebeed
hebeer
hebees
hebeing
hebely
hebes
heeb
heebed
heeber
heebes
heebing
heebly
heebs
hell
helled
heller
helles
helling
hellly
hells
hemp
hemped
hemper
hempes
hemping
hemply
hemps
heroined
heroiner
heroines
heroining
heroinly
heroins
herp
herped
herper
herpes
herpesed
herpeser
herpeses
herpesing
herpesly
herpess
herping
herply
herps
herpy
herpyed
herpyer
herpyes
herpying
herpyly
herpys
hitler
hitlered
hitlerer
hitleres
hitlering
hitlerly
hitlers
hived
hiver
hives
hiving
hivly
hivs
hobag
hobaged
hobager
hobages
hobaging
hobagly
hobags
homey
homeyed
homeyer
homeyes
homeying
homeyly
homeys
homo
homoed
homoer
homoes
homoey
homoeyed
homoeyer
homoeyes
homoeying
homoeyly
homoeys
homoing
homoly
homos
honky
honkyed
honkyer
honkyes
honkying
honkyly
honkys
hooch
hooched
hoocher
hooches
hooching
hoochly
hoochs
hookah
hookahed
hookaher
hookahes
hookahing
hookahly
hookahs
hooker
hookered
hookerer
hookeres
hookering
hookerly
hookers
hoor
hoored
hoorer
hoores
hooring
hoorly
hoors
hootch
hootched
hootcher
hootches
hootching
hootchly
hootchs
hooter
hootered
hooterer
hooteres
hootering
hooterly
hooters
hootersed
hooterser
hooterses
hootersing
hootersly
hooterss
horny
hornyed
hornyer
hornyes
hornying
hornyly
hornys
houstoned
houstoner
houstones
houstoning
houstonly
houstons
hump
humped
humpeded
humpeder
humpedes
humpeding
humpedly
humpeds
humper
humpes
humping
humpinged
humpinger
humpinges
humpinging
humpingly
humpings
humply
humps
husbanded
husbander
husbandes
husbanding
husbandly
husbands
hussy
hussyed
hussyer
hussyes
hussying
hussyly
hussys
hymened
hymener
hymenes
hymening
hymenly
hymens
inbred
inbreded
inbreder
inbredes
inbreding
inbredly
inbreds
incest
incested
incester
incestes
incesting
incestly
incests
injun
injuned
injuner
injunes
injuning
injunly
injuns
jackass
jackassed
jackasser
jackasses
jackassing
jackassly
jackasss
jackhole
jackholeed
jackholeer
jackholees
jackholeing
jackholely
jackholes
jackoff
jackoffed
jackoffer
jackoffes
jackoffing
jackoffly
jackoffs
jap
japed
japer
japes
japing
japly
japs
japsed
japser
japses
japsing
japsly
japss
jerkoff
jerkoffed
jerkoffer
jerkoffes
jerkoffing
jerkoffly
jerkoffs
jerks
jism
jismed
jismer
jismes
jisming
jismly
jisms
jiz
jized
jizer
jizes
jizing
jizly
jizm
jizmed
jizmer
jizmes
jizming
jizmly
jizms
jizs
jizz
jizzed
jizzeded
jizzeder
jizzedes
jizzeding
jizzedly
jizzeds
jizzer
jizzes
jizzing
jizzly
jizzs
junkie
junkieed
junkieer
junkiees
junkieing
junkiely
junkies
junky
junkyed
junkyer
junkyes
junkying
junkyly
junkys
kike
kikeed
kikeer
kikees
kikeing
kikely
kikes
kikesed
kikeser
kikeses
kikesing
kikesly
kikess
killed
killer
killes
killing
killly
kills
kinky
kinkyed
kinkyer
kinkyes
kinkying
kinkyly
kinkys
kkk
kkked
kkker
kkkes
kkking
kkkly
kkks
klan
klaned
klaner
klanes
klaning
klanly
klans
knobend
knobended
knobender
knobendes
knobending
knobendly
knobends
kooch
kooched
koocher
kooches
koochesed
koocheser
koocheses
koochesing
koochesly
koochess
kooching
koochly
koochs
kootch
kootched
kootcher
kootches
kootching
kootchly
kootchs
kraut
krauted
krauter
krautes
krauting
krautly
krauts
kyke
kykeed
kykeer
kykees
kykeing
kykely
kykes
lech
leched
lecher
leches
leching
lechly
lechs
leper
lepered
leperer
leperes
lepering
leperly
lepers
lesbiansed
lesbianser
lesbianses
lesbiansing
lesbiansly
lesbianss
lesbo
lesboed
lesboer
lesboes
lesboing
lesboly
lesbos
lesbosed
lesboser
lesboses
lesbosing
lesbosly
lesboss
lez
lezbianed
lezbianer
lezbianes
lezbianing
lezbianly
lezbians
lezbiansed
lezbianser
lezbianses
lezbiansing
lezbiansly
lezbianss
lezbo
lezboed
lezboer
lezboes
lezboing
lezboly
lezbos
lezbosed
lezboser
lezboses
lezbosing
lezbosly
lezboss
lezed
lezer
lezes
lezing
lezly
lezs
lezzie
lezzieed
lezzieer
lezziees
lezzieing
lezziely
lezzies
lezziesed
lezzieser
lezzieses
lezziesing
lezziesly
lezziess
lezzy
lezzyed
lezzyer
lezzyes
lezzying
lezzyly
lezzys
lmaoed
lmaoer
lmaoes
lmaoing
lmaoly
lmaos
lmfao
lmfaoed
lmfaoer
lmfaoes
lmfaoing
lmfaoly
lmfaos
loined
loiner
loines
loining
loinly
loins
loinsed
loinser
loinses
loinsing
loinsly
loinss
lubeed
lubeer
lubees
lubeing
lubely
lubes
lusty
lustyed
lustyer
lustyes
lustying
lustyly
lustys
massa
massaed
massaer
massaes
massaing
massaly
massas
masterbate
masterbateed
masterbateer
masterbatees
masterbateing
masterbately
masterbates
masterbating
masterbatinged
masterbatinger
masterbatinges
masterbatinging
masterbatingly
masterbatings
masterbation
masterbationed
masterbationer
masterbationes
masterbationing
masterbationly
masterbations
masturbate
masturbateed
masturbateer
masturbatees
masturbateing
masturbately
masturbates
masturbating
masturbatinged
masturbatinger
masturbatinges
masturbatinging
masturbatingly
masturbatings
masturbation
masturbationed
masturbationer
masturbationes
masturbationing
masturbationly
masturbations
methed
mether
methes
mething
methly
meths
militaryed
militaryer
militaryes
militarying
militaryly
militarys
mofo
mofoed
mofoer
mofoes
mofoing
mofoly
mofos
molest
molested
molester
molestes
molesting
molestly
molests
moolie
moolieed
moolieer
mooliees
moolieing
mooliely
moolies
moron
moroned
moroner
morones
moroning
moronly
morons
motherfucka
motherfuckaed
motherfuckaer
motherfuckaes
motherfuckaing
motherfuckaly
motherfuckas
motherfucker
motherfuckered
motherfuckerer
motherfuckeres
motherfuckering
motherfuckerly
motherfuckers
motherfucking
motherfuckinged
motherfuckinger
motherfuckinges
motherfuckinging
motherfuckingly
motherfuckings
mtherfucker
mtherfuckered
mtherfuckerer
mtherfuckeres
mtherfuckering
mtherfuckerly
mtherfuckers
mthrfucker
mthrfuckered
mthrfuckerer
mthrfuckeres
mthrfuckering
mthrfuckerly
mthrfuckers
mthrfucking
mthrfuckinged
mthrfuckinger
mthrfuckinges
mthrfuckinging
mthrfuckingly
mthrfuckings
muff
muffdiver
muffdivered
muffdiverer
muffdiveres
muffdivering
muffdiverly
muffdivers
muffed
muffer
muffes
muffing
muffly
muffs
murdered
murderer
murderes
murdering
murderly
murders
muthafuckaz
muthafuckazed
muthafuckazer
muthafuckazes
muthafuckazing
muthafuckazly
muthafuckazs
muthafucker
muthafuckered
muthafuckerer
muthafuckeres
muthafuckering
muthafuckerly
muthafuckers
mutherfucker
mutherfuckered
mutherfuckerer
mutherfuckeres
mutherfuckering
mutherfuckerly
mutherfuckers
mutherfucking
mutherfuckinged
mutherfuckinger
mutherfuckinges
mutherfuckinging
mutherfuckingly
mutherfuckings
muthrfucking
muthrfuckinged
muthrfuckinger
muthrfuckinges
muthrfuckinging
muthrfuckingly
muthrfuckings
nad
naded
nader
nades
nading
nadly
nads
nadsed
nadser
nadses
nadsing
nadsly
nadss
nakeded
nakeder
nakedes
nakeding
nakedly
nakeds
napalm
napalmed
napalmer
napalmes
napalming
napalmly
napalms
nappy
nappyed
nappyer
nappyes
nappying
nappyly
nappys
nazi
nazied
nazier
nazies
naziing
nazily
nazis
nazism
nazismed
nazismer
nazismes
nazisming
nazismly
nazisms
negro
negroed
negroer
negroes
negroing
negroly
negros
nigga
niggaed
niggaer
niggaes
niggah
niggahed
niggaher
niggahes
niggahing
niggahly
niggahs
niggaing
niggaly
niggas
niggased
niggaser
niggases
niggasing
niggasly
niggass
niggaz
niggazed
niggazer
niggazes
niggazing
niggazly
niggazs
nigger
niggered
niggerer
niggeres
niggering
niggerly
niggers
niggersed
niggerser
niggerses
niggersing
niggersly
niggerss
niggle
niggleed
niggleer
nigglees
niggleing
nigglely
niggles
niglet
nigleted
nigleter
nigletes
nigleting
nigletly
niglets
nimrod
nimroded
nimroder
nimrodes
nimroding
nimrodly
nimrods
ninny
ninnyed
ninnyer
ninnyes
ninnying
ninnyly
ninnys
nooky
nookyed
nookyer
nookyes
nookying
nookyly
nookys
nuccitelli
nuccitellied
nuccitellier
nuccitellies
nuccitelliing
nuccitellily
nuccitellis
nympho
nymphoed
nymphoer
nymphoes
nymphoing
nympholy
nymphos
opium
opiumed
opiumer
opiumes
opiuming
opiumly
opiums
orgies
orgiesed
orgieser
orgieses
orgiesing
orgiesly
orgiess
orgy
orgyed
orgyer
orgyes
orgying
orgyly
orgys
paddy
paddyed
paddyer
paddyes
paddying
paddyly
paddys
paki
pakied
pakier
pakies
pakiing
pakily
pakis
pantie
pantieed
pantieer
pantiees
pantieing
pantiely
panties
pantiesed
pantieser
pantieses
pantiesing
pantiesly
pantiess
panty
pantyed
pantyer
pantyes
pantying
pantyly
pantys
pastie
pastieed
pastieer
pastiees
pastieing
pastiely
pasties
pasty
pastyed
pastyer
pastyes
pastying
pastyly
pastys
pecker
peckered
peckerer
peckeres
peckering
peckerly
peckers
pedo
pedoed
pedoer
pedoes
pedoing
pedoly
pedophile
pedophileed
pedophileer
pedophilees
pedophileing
pedophilely
pedophiles
pedophilia
pedophiliac
pedophiliaced
pedophiliacer
pedophiliaces
pedophiliacing
pedophiliacly
pedophiliacs
pedophiliaed
pedophiliaer
pedophiliaes
pedophiliaing
pedophilialy
pedophilias
pedos
penial
penialed
penialer
peniales
penialing
penially
penials
penile
penileed
penileer
penilees
penileing
penilely
peniles
penis
penised
peniser
penises
penising
penisly
peniss
perversion
perversioned
perversioner
perversiones
perversioning
perversionly
perversions
peyote
peyoteed
peyoteer
peyotees
peyoteing
peyotely
peyotes
phuck
phucked
phucker
phuckes
phucking
phuckly
phucks
pillowbiter
pillowbitered
pillowbiterer
pillowbiteres
pillowbitering
pillowbiterly
pillowbiters
pimp
pimped
pimper
pimpes
pimping
pimply
pimps
pinko
pinkoed
pinkoer
pinkoes
pinkoing
pinkoly
pinkos
pissed
pisseded
pisseder
pissedes
pisseding
pissedly
pisseds
pisser
pisses
pissing
pissly
pissoff
pissoffed
pissoffer
pissoffes
pissoffing
pissoffly
pissoffs
pisss
polack
polacked
polacker
polackes
polacking
polackly
polacks
pollock
pollocked
pollocker
pollockes
pollocking
pollockly
pollocks
poon
pooned
pooner
poones
pooning
poonly
poons
poontang
poontanged
poontanger
poontanges
poontanging
poontangly
poontangs
porn
porned
porner
pornes
porning
pornly
porno
pornoed
pornoer
pornoes
pornography
pornographyed
pornographyer
pornographyes
pornographying
pornographyly
pornographys
pornoing
pornoly
pornos
porns
prick
pricked
pricker
prickes
pricking
prickly
pricks
prig
priged
priger
priges
priging
prigly
prigs
prostitute
prostituteed
prostituteer
prostitutees
prostituteing
prostitutely
prostitutes
prude
prudeed
prudeer
prudees
prudeing
prudely
prudes
punkass
punkassed
punkasser
punkasses
punkassing
punkassly
punkasss
punky
punkyed
punkyer
punkyes
punkying
punkyly
punkys
puss
pussed
pusser
pusses
pussies
pussiesed
pussieser
pussieses
pussiesing
pussiesly
pussiess
pussing
pussly
pusss
pussy
pussyed
pussyer
pussyes
pussying
pussyly
pussypounder
pussypoundered
pussypounderer
pussypounderes
pussypoundering
pussypounderly
pussypounders
pussys
puto
putoed
putoer
putoes
putoing
putoly
putos
queaf
queafed
queafer
queafes
queafing
queafly
queafs
queef
queefed
queefer
queefes
queefing
queefly
queefs
queer
queered
queerer
queeres
queering
queerly
queero
queeroed
queeroer
queeroes
queeroing
queeroly
queeros
queers
queersed
queerser
queerses
queersing
queersly
queerss
quicky
quickyed
quickyer
quickyes
quickying
quickyly
quickys
quim
quimed
quimer
quimes
quiming
quimly
quims
racy
racyed
racyer
racyes
racying
racyly
racys
rape
raped
rapeded
rapeder
rapedes
rapeding
rapedly
rapeds
rapeed
rapeer
rapees
rapeing
rapely
raper
rapered
raperer
raperes
rapering
raperly
rapers
rapes
rapist
rapisted
rapister
rapistes
rapisting
rapistly
rapists
raunch
raunched
rauncher
raunches
raunching
raunchly
raunchs
rectus
rectused
rectuser
rectuses
rectusing
rectusly
rectuss
reefer
reefered
reeferer
reeferes
reefering
reeferly
reefers
reetard
reetarded
reetarder
reetardes
reetarding
reetardly
reetards
reich
reiched
reicher
reiches
reiching
reichly
reichs
retard
retarded
retardeded
retardeder
retardedes
retardeding
retardedly
retardeds
retarder
retardes
retarding
retardly
retards
rimjob
rimjobed
rimjober
rimjobes
rimjobing
rimjobly
rimjobs
ritard
ritarded
ritarder
ritardes
ritarding
ritardly
ritards
rtard
rtarded
rtarder
rtardes
rtarding
rtardly
rtards
rum
rumed
rumer
rumes
ruming
rumly
rump
rumped
rumper
rumpes
rumping
rumply
rumprammer
rumprammered
rumprammerer
rumprammeres
rumprammering
rumprammerly
rumprammers
rumps
rums
ruski
ruskied
ruskier
ruskies
ruskiing
ruskily
ruskis
sadism
sadismed
sadismer
sadismes
sadisming
sadismly
sadisms
sadist
sadisted
sadister
sadistes
sadisting
sadistly
sadists
scag
scaged
scager
scages
scaging
scagly
scags
scantily
scantilyed
scantilyer
scantilyes
scantilying
scantilyly
scantilys
schlong
schlonged
schlonger
schlonges
schlonging
schlongly
schlongs
scrog
scroged
scroger
scroges
scroging
scrogly
scrogs
scrot
scrote
scroted
scroteed
scroteer
scrotees
scroteing
scrotely
scroter
scrotes
scroting
scrotly
scrots
scrotum
scrotumed
scrotumer
scrotumes
scrotuming
scrotumly
scrotums
scrud
scruded
scruder
scrudes
scruding
scrudly
scruds
scum
scumed
scumer
scumes
scuming
scumly
scums
seaman
seamaned
seamaner
seamanes
seamaning
seamanly
seamans
seamen
seamened
seamener
seamenes
seamening
seamenly
seamens
seduceed
seduceer
seducees
seduceing
seducely
seduces
semen
semened
semener
semenes
semening
semenly
semens
shamedame
shamedameed
shamedameer
shamedamees
shamedameing
shamedamely
shamedames
shit
shite
shiteater
shiteatered
shiteaterer
shiteateres
shiteatering
shiteaterly
shiteaters
shited
shiteed
shiteer
shitees
shiteing
shitely
shiter
shites
shitface
shitfaceed
shitfaceer
shitfacees
shitfaceing
shitfacely
shitfaces
shithead
shitheaded
shitheader
shitheades
shitheading
shitheadly
shitheads
shithole
shitholeed
shitholeer
shitholees
shitholeing
shitholely
shitholes
shithouse
shithouseed
shithouseer
shithousees
shithouseing
shithousely
shithouses
shiting
shitly
shits
shitsed
shitser
shitses
shitsing
shitsly
shitss
shitt
shitted
shitteded
shitteder
shittedes
shitteding
shittedly
shitteds
shitter
shittered
shitterer
shitteres
shittering
shitterly
shitters
shittes
shitting
shittly
shitts
shitty
shittyed
shittyer
shittyes
shittying
shittyly
shittys
shiz
shized
shizer
shizes
shizing
shizly
shizs
shooted
shooter
shootes
shooting
shootly
shoots
sissy
sissyed
sissyer
sissyes
sissying
sissyly
sissys
skag
skaged
skager
skages
skaging
skagly
skags
skank
skanked
skanker
skankes
skanking
skankly
skanks
slave
slaveed
slaveer
slavees
slaveing
slavely
slaves
sleaze
sleazeed
sleazeer
sleazees
sleazeing
sleazely
sleazes
sleazy
sleazyed
sleazyer
sleazyes
sleazying
sleazyly
sleazys
slut
slutdumper
slutdumpered
slutdumperer
slutdumperes
slutdumpering
slutdumperly
slutdumpers
sluted
sluter
slutes
sluting
slutkiss
slutkissed
slutkisser
slutkisses
slutkissing
slutkissly
slutkisss
slutly
sluts
slutsed
slutser
slutses
slutsing
slutsly
slutss
smegma
smegmaed
smegmaer
smegmaes
smegmaing
smegmaly
smegmas
smut
smuted
smuter
smutes
smuting
smutly
smuts
smutty
smuttyed
smuttyer
smuttyes
smuttying
smuttyly
smuttys
snatch
snatched
snatcher
snatches
snatching
snatchly
snatchs
sniper
snipered
sniperer
sniperes
snipering
sniperly
snipers
snort
snorted
snorter
snortes
snorting
snortly
snorts
snuff
snuffed
snuffer
snuffes
snuffing
snuffly
snuffs
sodom
sodomed
sodomer
sodomes
sodoming
sodomly
sodoms
spic
spiced
spicer
spices
spicing
spick
spicked
spicker
spickes
spicking
spickly
spicks
spicly
spics
spik
spoof
spoofed
spoofer
spoofes
spoofing
spoofly
spoofs
spooge
spoogeed
spoogeer
spoogees
spoogeing
spoogely
spooges
spunk
spunked
spunker
spunkes
spunking
spunkly
spunks
steamyed
steamyer
steamyes
steamying
steamyly
steamys
stfu
stfued
stfuer
stfues
stfuing
stfuly
stfus
stiffy
stiffyed
stiffyer
stiffyes
stiffying
stiffyly
stiffys
stoneded
stoneder
stonedes
stoneding
stonedly
stoneds
stupided
stupider
stupides
stupiding
stupidly
stupids
suckeded
suckeder
suckedes
suckeding
suckedly
suckeds
sucker
suckes
sucking
suckinged
suckinger
suckinges
suckinging
suckingly
suckings
suckly
sucks
sumofabiatch
sumofabiatched
sumofabiatcher
sumofabiatches
sumofabiatching
sumofabiatchly
sumofabiatchs
tard
tarded
tarder
tardes
tarding
tardly
tards
tawdry
tawdryed
tawdryer
tawdryes
tawdrying
tawdryly
tawdrys
teabagging
teabagginged
teabagginger
teabagginges
teabagginging
teabaggingly
teabaggings
terd
terded
terder
terdes
terding
terdly
terds
teste
testee
testeed
testeeed
testeeer
testeees
testeeing
testeely
testeer
testees
testeing
testely
testes
testesed
testeser
testeses
testesing
testesly
testess
testicle
testicleed
testicleer
testiclees
testicleing
testiclely
testicles
testis
testised
testiser
testises
testising
testisly
testiss
thrusted
thruster
thrustes
thrusting
thrustly
thrusts
thug
thuged
thuger
thuges
thuging
thugly
thugs
tinkle
tinkleed
tinkleer
tinklees
tinkleing
tinklely
tinkles
tit
tited
titer
tites
titfuck
titfucked
titfucker
titfuckes
titfucking
titfuckly
titfucks
titi
titied
titier
tities
titiing
titily
titing
titis
titly
tits
titsed
titser
titses
titsing
titsly
titss
tittiefucker
tittiefuckered
tittiefuckerer
tittiefuckeres
tittiefuckering
tittiefuckerly
tittiefuckers
titties
tittiesed
tittieser
tittieses
tittiesing
tittiesly
tittiess
titty
tittyed
tittyer
tittyes
tittyfuck
tittyfucked
tittyfucker
tittyfuckered
tittyfuckerer
tittyfuckeres
tittyfuckering
tittyfuckerly
tittyfuckers
tittyfuckes
tittyfucking
tittyfuckly
tittyfucks
tittying
tittyly
tittys
toke
tokeed
tokeer
tokees
tokeing
tokely
tokes
toots
tootsed
tootser
tootses
tootsing
tootsly
tootss
tramp
tramped
tramper
trampes
tramping
tramply
tramps
transsexualed
transsexualer
transsexuales
transsexualing
transsexually
transsexuals
trashy
trashyed
trashyer
trashyes
trashying
trashyly
trashys
tubgirl
tubgirled
tubgirler
tubgirles
tubgirling
tubgirlly
tubgirls
turd
turded
turder
turdes
turding
turdly
turds
tush
tushed
tusher
tushes
tushing
tushly
tushs
twat
twated
twater
twates
twating
twatly
twats
twatsed
twatser
twatses
twatsing
twatsly
twatss
undies
undiesed
undieser
undieses
undiesing
undiesly
undiess
unweded
unweder
unwedes
unweding
unwedly
unweds
uzi
uzied
uzier
uzies
uziing
uzily
uzis
vag
vaged
vager
vages
vaging
vagly
vags
valium
valiumed
valiumer
valiumes
valiuming
valiumly
valiums
venous
virgined
virginer
virgines
virgining
virginly
virgins
vixen
vixened
vixener
vixenes
vixening
vixenly
vixens
vodkaed
vodkaer
vodkaes
vodkaing
vodkaly
vodkas
voyeur
voyeured
voyeurer
voyeures
voyeuring
voyeurly
voyeurs
vulgar
vulgared
vulgarer
vulgares
vulgaring
vulgarly
vulgars
wang
wanged
wanger
wanges
wanging
wangly
wangs
wank
wanked
wanker
wankered
wankerer
wankeres
wankering
wankerly
wankers
wankes
wanking
wankly
wanks
wazoo
wazooed
wazooer
wazooes
wazooing
wazooly
wazoos
wedgie
wedgieed
wedgieer
wedgiees
wedgieing
wedgiely
wedgies
weeded
weeder
weedes
weeding
weedly
weeds
weenie
weenieed
weenieer
weeniees
weenieing
weeniely
weenies
weewee
weeweeed
weeweeer
weeweees
weeweeing
weeweely
weewees
weiner
weinered
weinerer
weineres
weinering
weinerly
weiners
weirdo
weirdoed
weirdoer
weirdoes
weirdoing
weirdoly
weirdos
wench
wenched
wencher
wenches
wenching
wenchly
wenchs
wetback
wetbacked
wetbacker
wetbackes
wetbacking
wetbackly
wetbacks
whitey
whiteyed
whiteyer
whiteyes
whiteying
whiteyly
whiteys
whiz
whized
whizer
whizes
whizing
whizly
whizs
whoralicious
whoralicioused
whoraliciouser
whoraliciouses
whoraliciousing
whoraliciously
whoraliciouss
whore
whorealicious
whorealicioused
whorealiciouser
whorealiciouses
whorealiciousing
whorealiciously
whorealiciouss
whored
whoreded
whoreder
whoredes
whoreding
whoredly
whoreds
whoreed
whoreer
whorees
whoreface
whorefaceed
whorefaceer
whorefacees
whorefaceing
whorefacely
whorefaces
whorehopper
whorehoppered
whorehopperer
whorehopperes
whorehoppering
whorehopperly
whorehoppers
whorehouse
whorehouseed
whorehouseer
whorehousees
whorehouseing
whorehousely
whorehouses
whoreing
whorely
whores
whoresed
whoreser
whoreses
whoresing
whoresly
whoress
whoring
whoringed
whoringer
whoringes
whoringing
whoringly
whorings
wigger
wiggered
wiggerer
wiggeres
wiggering
wiggerly
wiggers
woody
woodyed
woodyer
woodyes
woodying
woodyly
woodys
wop
woped
woper
wopes
woping
woply
wops
wtf
wtfed
wtfer
wtfes
wtfing
wtfly
wtfs
xxx
xxxed
xxxer
xxxes
xxxing
xxxly
xxxs
yeasty
yeastyed
yeastyer
yeastyes
yeastying
yeastyly
yeastys
yobbo
yobboed
yobboer
yobboes
yobboing
yobboly
yobbos
zoophile
zoophileed
zoophileer
zoophilees
zoophileing
zoophilely
zoophiles
anal
ass
ass lick
balls
ballsac
bisexual
bleach
causas
cheap
cost of miracles
cunt
display network stats
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gfc
humira AND expensive
illegal
madvocate
masturbation
nuccitelli
overdose
porn
shit
snort
texarkana
Doctors search for missing link between COVID-19 and ITP
Hospitalist Sarah Stone, MD, arrived for her day shift at Sharp Chula Vista one day in late December. The ICU and hospital wards were still overflowing with COVID-19 patients. But over the previous couple of months, she’d also seen more and more recovered patients presenting with a myriad of symptoms: pulmonary emboli, cardiomyopathy, a shocking case of aspergillosis, and those rare cases of “long COVID,” the patients who just can’t get better.
This morning it was a woman in her 30s. She felt fine, but 2 weeks after recovering from COVID-19, she had unexplained bruising on her arm, a petechiae rash on her legs, and her gums were bleeding. Once admitted to the emergency department, her platelet count of 5000/mm3 was a dead giveaway of immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP).
In Dr. Stone’s experience, new and otherwise unexplained symptoms so soon post COVID-19 can’t be written off as a coincidence without some additional consideration. But a quick preliminary search of the literature during her rounds came up almost empty. She found one report with three cases of post-COVID-19 ITP. But other online resources made no mention of it. Kenneth Johnson, MD, the hematologist/oncologist consulting on the new case, told Dr. Stone he’d seen one other case of post-COVID-19 ITP only earlier that month. Dr. Stone called a sister hospital. They’d seen one other case just weeks before.
“I was surprised to find just three cases in the literature when we had seen three among us in a matter of weeks,” Dr. Stone said in an interview. Something was missing.
A missing link
ITP is caused by an immune reaction against a patient’s own platelets.
“We know that infections like influenza can cause ITP, so in this light, [COVID-19-associated ITP] might not be surprising,” Gerard Jansen, MD, PhD, an internist and hematologist in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said in an interview.
Dr. Jansen and colleagues recorded three cases of post-COVID-19 ITP in May 2020 – the report Dr. Stone had found during her shift. Two patients developed ITP several weeks after COVID-19 and responded to treatment with corticosteroids and intravenous immunoglobulin G (IVIG). The third patient, however, died of intracerebral bleeding while still battling COVID-19. He was retrospectively diagnosed with COVID-19-associated ITP.
A deeper dive into the literature uncovers additional case reports from India, France, the United Kingdom, Turkey, and one from China as early as January 2020. A September 2020 review of ITP secondary to COVID-19 included 23 papers and a total of 45 patients. The review authors noted that more than 70% of cases occurred in patients who were aged over 50 years and 75% had had moderate to severe COVID-19 infections. However, the sample size of 45 is too small to definitively describe what’s happening in the overall population.
ITP’s link to COVID-19 gained a media spotlight after the Miami obstetrician, Gregory Michael, MD, developed ITP days after getting the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine. In early January, after 2 weeks in the ICU, Dr. Michael died of a hemorrhagic stroke caused by the low platelet count.
Pfizer said in a statement that the company is “actively investigating” the case, “but we don’t believe at this time that there is any direct connection to the vaccine.” Other experts have said the timing, particularly in a relatively young and healthy man, means a link to the vaccine is possible or even likely, but final results won›t be known until the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention finishes its investigation.
But “it is quite unusual to die from ITP,” San Diego hematologist Dr. Johnson said in an interview. In his more than 20 years of practice, he has never had a patient die from the condition.
For his part, Dr. Jansen, the hematologist in Rotterdam, said that at this point we just don’t know if there’s a link between the vaccine and ITP. Both infection and drugs are well established causes of ITP, so with that general mechanism or pathology in mind it makes sense that COVID-19 and the vaccine could instigate ITP. But it would be very difficult to prove in just one instance, he said. And considering the millions who have thus far received the vaccine without incident, and the known risks and dangers of COVID-19, “we still advise to vaccinate,” he said.
The number of cases is underestimated
Since his original case report in May, Dr. Jansen has seen five or so additional cases. But the causal link between the coronavirus and the hematologic symptoms is still undefined. “We don’t know much about platelet counts in COVID-19 at all,” he said. It could be that COVID-19 somehow inhibits platelet production or that it kills existing platelets. Whatever the exact relationship to the virus, Dr. Jansen expects that the true number of COVID-19-related ITP cases is higher than current estimates suggest.
One reason it isn’t coming up more often, Dr. Jansen said, may be that the cause of ITP in COVID-19 patients is hard to pin down. In the case report from May, Dr. Jansen and colleagues wrote: “And there are numerous other factors that can cause thrombocytopenia where COVID is concerned. For instance the coagulation activation by COVID‐19 infection leading to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and subsequent thrombocytopenia. Also, treatments for COVID‐19, including heparin, azithromycin and hydroxychloroquine, may lead to thrombocytopenia.”
Tracking and understanding COVID-19-associated ITP first requires the extensive process of elimination needed to diagnose it.
In addition, drugs used to treat COVID-19 could be masking COVID-19-related ITP. “Dexamethasone is a mainstay of COVID treatment. And it’s how we treat ITP,” Dr. Johnson said, which means physicians may be treating ITP without even registering it. And that’s one hypothesis for why Dr. Stone and Dr. Johnson didn’t see a case until 9 months into the pandemic.
Treating COVID-19-associated ITP also has its challenges, particularly in patients who develop it during an acute COVID-19 infection and are at risk for both internal bleeding and thrombosis. This was the case for the third patient in Dr. Jansen’s case report. The patient developed a pulmonary embolism and had a falling platelet count. He was given a platelet infusion and then an anticoagulant for the thrombosis. But a retrospective look at the case revealed the transfusion “did not increase numbers at all – which suggests ITP,” Dr. Jansen said. Intracerebral bleeding was the cause of death.
That’s why “it’s important to be aware of this phenomenon,” Dr. Jansen said of COVID-19-associated ITP. If a transfusion is unsuccessful, consider that the patient may have ITP and adjust. Dr. Johnson hasn’t had to treat a patient battling both complications simultaneously but says the ideal course of action would be to raise platelets with steroids and IVIG and then give the anticoagulant once the platelet count is higher. But reality is rarely ideal. Often these two treatments will have to be given concurrently since the patient faces two life-threatening risks, he said. “It’s a very challenging situation,” he said.
The good news is that standard treatments for ITP seem to work for COVID-19-associated ITP. The 30-year-old patient of Dr. Stone and Dr. Johnson responded so well to intravenous steroids that IVIG was unnecessary. She’s now on a slow prednisone taper and maintains platelet counts at 114,000/mm3 at her weekly follow-up appointments with Dr. Johnson.
Meanwhile, Dr. Jansen’s two other patients, now nearly a year out of treatment, require no additional medication. One of the patients is fully recovered and, though the other still has lower than normal platelet counts, she has no bleeding symptoms and her platelet counts remain stable. Still, Dr. Jansen is anxious for more data looking at the platelet counts in every COVID-19 patient and to combine findings from existing COVID-19-associated ITP patients.
For Dr. Stone, she says she’s added one COVID-19-associated complication to her belt. One less aftereffect will catch her off guard. And she wants others to have the same information.
“It’s just a little bit daunting. We don’t know how bad post-COVID will be,” she said. “There’s so many levels to this disease. Some people deal with it for so long and some people just get better and move on – we think ... so far.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitalist Sarah Stone, MD, arrived for her day shift at Sharp Chula Vista one day in late December. The ICU and hospital wards were still overflowing with COVID-19 patients. But over the previous couple of months, she’d also seen more and more recovered patients presenting with a myriad of symptoms: pulmonary emboli, cardiomyopathy, a shocking case of aspergillosis, and those rare cases of “long COVID,” the patients who just can’t get better.
This morning it was a woman in her 30s. She felt fine, but 2 weeks after recovering from COVID-19, she had unexplained bruising on her arm, a petechiae rash on her legs, and her gums were bleeding. Once admitted to the emergency department, her platelet count of 5000/mm3 was a dead giveaway of immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP).
In Dr. Stone’s experience, new and otherwise unexplained symptoms so soon post COVID-19 can’t be written off as a coincidence without some additional consideration. But a quick preliminary search of the literature during her rounds came up almost empty. She found one report with three cases of post-COVID-19 ITP. But other online resources made no mention of it. Kenneth Johnson, MD, the hematologist/oncologist consulting on the new case, told Dr. Stone he’d seen one other case of post-COVID-19 ITP only earlier that month. Dr. Stone called a sister hospital. They’d seen one other case just weeks before.
“I was surprised to find just three cases in the literature when we had seen three among us in a matter of weeks,” Dr. Stone said in an interview. Something was missing.
A missing link
ITP is caused by an immune reaction against a patient’s own platelets.
“We know that infections like influenza can cause ITP, so in this light, [COVID-19-associated ITP] might not be surprising,” Gerard Jansen, MD, PhD, an internist and hematologist in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said in an interview.
Dr. Jansen and colleagues recorded three cases of post-COVID-19 ITP in May 2020 – the report Dr. Stone had found during her shift. Two patients developed ITP several weeks after COVID-19 and responded to treatment with corticosteroids and intravenous immunoglobulin G (IVIG). The third patient, however, died of intracerebral bleeding while still battling COVID-19. He was retrospectively diagnosed with COVID-19-associated ITP.
A deeper dive into the literature uncovers additional case reports from India, France, the United Kingdom, Turkey, and one from China as early as January 2020. A September 2020 review of ITP secondary to COVID-19 included 23 papers and a total of 45 patients. The review authors noted that more than 70% of cases occurred in patients who were aged over 50 years and 75% had had moderate to severe COVID-19 infections. However, the sample size of 45 is too small to definitively describe what’s happening in the overall population.
ITP’s link to COVID-19 gained a media spotlight after the Miami obstetrician, Gregory Michael, MD, developed ITP days after getting the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine. In early January, after 2 weeks in the ICU, Dr. Michael died of a hemorrhagic stroke caused by the low platelet count.
Pfizer said in a statement that the company is “actively investigating” the case, “but we don’t believe at this time that there is any direct connection to the vaccine.” Other experts have said the timing, particularly in a relatively young and healthy man, means a link to the vaccine is possible or even likely, but final results won›t be known until the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention finishes its investigation.
But “it is quite unusual to die from ITP,” San Diego hematologist Dr. Johnson said in an interview. In his more than 20 years of practice, he has never had a patient die from the condition.
For his part, Dr. Jansen, the hematologist in Rotterdam, said that at this point we just don’t know if there’s a link between the vaccine and ITP. Both infection and drugs are well established causes of ITP, so with that general mechanism or pathology in mind it makes sense that COVID-19 and the vaccine could instigate ITP. But it would be very difficult to prove in just one instance, he said. And considering the millions who have thus far received the vaccine without incident, and the known risks and dangers of COVID-19, “we still advise to vaccinate,” he said.
The number of cases is underestimated
Since his original case report in May, Dr. Jansen has seen five or so additional cases. But the causal link between the coronavirus and the hematologic symptoms is still undefined. “We don’t know much about platelet counts in COVID-19 at all,” he said. It could be that COVID-19 somehow inhibits platelet production or that it kills existing platelets. Whatever the exact relationship to the virus, Dr. Jansen expects that the true number of COVID-19-related ITP cases is higher than current estimates suggest.
One reason it isn’t coming up more often, Dr. Jansen said, may be that the cause of ITP in COVID-19 patients is hard to pin down. In the case report from May, Dr. Jansen and colleagues wrote: “And there are numerous other factors that can cause thrombocytopenia where COVID is concerned. For instance the coagulation activation by COVID‐19 infection leading to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and subsequent thrombocytopenia. Also, treatments for COVID‐19, including heparin, azithromycin and hydroxychloroquine, may lead to thrombocytopenia.”
Tracking and understanding COVID-19-associated ITP first requires the extensive process of elimination needed to diagnose it.
In addition, drugs used to treat COVID-19 could be masking COVID-19-related ITP. “Dexamethasone is a mainstay of COVID treatment. And it’s how we treat ITP,” Dr. Johnson said, which means physicians may be treating ITP without even registering it. And that’s one hypothesis for why Dr. Stone and Dr. Johnson didn’t see a case until 9 months into the pandemic.
Treating COVID-19-associated ITP also has its challenges, particularly in patients who develop it during an acute COVID-19 infection and are at risk for both internal bleeding and thrombosis. This was the case for the third patient in Dr. Jansen’s case report. The patient developed a pulmonary embolism and had a falling platelet count. He was given a platelet infusion and then an anticoagulant for the thrombosis. But a retrospective look at the case revealed the transfusion “did not increase numbers at all – which suggests ITP,” Dr. Jansen said. Intracerebral bleeding was the cause of death.
That’s why “it’s important to be aware of this phenomenon,” Dr. Jansen said of COVID-19-associated ITP. If a transfusion is unsuccessful, consider that the patient may have ITP and adjust. Dr. Johnson hasn’t had to treat a patient battling both complications simultaneously but says the ideal course of action would be to raise platelets with steroids and IVIG and then give the anticoagulant once the platelet count is higher. But reality is rarely ideal. Often these two treatments will have to be given concurrently since the patient faces two life-threatening risks, he said. “It’s a very challenging situation,” he said.
The good news is that standard treatments for ITP seem to work for COVID-19-associated ITP. The 30-year-old patient of Dr. Stone and Dr. Johnson responded so well to intravenous steroids that IVIG was unnecessary. She’s now on a slow prednisone taper and maintains platelet counts at 114,000/mm3 at her weekly follow-up appointments with Dr. Johnson.
Meanwhile, Dr. Jansen’s two other patients, now nearly a year out of treatment, require no additional medication. One of the patients is fully recovered and, though the other still has lower than normal platelet counts, she has no bleeding symptoms and her platelet counts remain stable. Still, Dr. Jansen is anxious for more data looking at the platelet counts in every COVID-19 patient and to combine findings from existing COVID-19-associated ITP patients.
For Dr. Stone, she says she’s added one COVID-19-associated complication to her belt. One less aftereffect will catch her off guard. And she wants others to have the same information.
“It’s just a little bit daunting. We don’t know how bad post-COVID will be,” she said. “There’s so many levels to this disease. Some people deal with it for so long and some people just get better and move on – we think ... so far.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitalist Sarah Stone, MD, arrived for her day shift at Sharp Chula Vista one day in late December. The ICU and hospital wards were still overflowing with COVID-19 patients. But over the previous couple of months, she’d also seen more and more recovered patients presenting with a myriad of symptoms: pulmonary emboli, cardiomyopathy, a shocking case of aspergillosis, and those rare cases of “long COVID,” the patients who just can’t get better.
This morning it was a woman in her 30s. She felt fine, but 2 weeks after recovering from COVID-19, she had unexplained bruising on her arm, a petechiae rash on her legs, and her gums were bleeding. Once admitted to the emergency department, her platelet count of 5000/mm3 was a dead giveaway of immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP).
In Dr. Stone’s experience, new and otherwise unexplained symptoms so soon post COVID-19 can’t be written off as a coincidence without some additional consideration. But a quick preliminary search of the literature during her rounds came up almost empty. She found one report with three cases of post-COVID-19 ITP. But other online resources made no mention of it. Kenneth Johnson, MD, the hematologist/oncologist consulting on the new case, told Dr. Stone he’d seen one other case of post-COVID-19 ITP only earlier that month. Dr. Stone called a sister hospital. They’d seen one other case just weeks before.
“I was surprised to find just three cases in the literature when we had seen three among us in a matter of weeks,” Dr. Stone said in an interview. Something was missing.
A missing link
ITP is caused by an immune reaction against a patient’s own platelets.
“We know that infections like influenza can cause ITP, so in this light, [COVID-19-associated ITP] might not be surprising,” Gerard Jansen, MD, PhD, an internist and hematologist in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said in an interview.
Dr. Jansen and colleagues recorded three cases of post-COVID-19 ITP in May 2020 – the report Dr. Stone had found during her shift. Two patients developed ITP several weeks after COVID-19 and responded to treatment with corticosteroids and intravenous immunoglobulin G (IVIG). The third patient, however, died of intracerebral bleeding while still battling COVID-19. He was retrospectively diagnosed with COVID-19-associated ITP.
A deeper dive into the literature uncovers additional case reports from India, France, the United Kingdom, Turkey, and one from China as early as January 2020. A September 2020 review of ITP secondary to COVID-19 included 23 papers and a total of 45 patients. The review authors noted that more than 70% of cases occurred in patients who were aged over 50 years and 75% had had moderate to severe COVID-19 infections. However, the sample size of 45 is too small to definitively describe what’s happening in the overall population.
ITP’s link to COVID-19 gained a media spotlight after the Miami obstetrician, Gregory Michael, MD, developed ITP days after getting the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine. In early January, after 2 weeks in the ICU, Dr. Michael died of a hemorrhagic stroke caused by the low platelet count.
Pfizer said in a statement that the company is “actively investigating” the case, “but we don’t believe at this time that there is any direct connection to the vaccine.” Other experts have said the timing, particularly in a relatively young and healthy man, means a link to the vaccine is possible or even likely, but final results won›t be known until the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention finishes its investigation.
But “it is quite unusual to die from ITP,” San Diego hematologist Dr. Johnson said in an interview. In his more than 20 years of practice, he has never had a patient die from the condition.
For his part, Dr. Jansen, the hematologist in Rotterdam, said that at this point we just don’t know if there’s a link between the vaccine and ITP. Both infection and drugs are well established causes of ITP, so with that general mechanism or pathology in mind it makes sense that COVID-19 and the vaccine could instigate ITP. But it would be very difficult to prove in just one instance, he said. And considering the millions who have thus far received the vaccine without incident, and the known risks and dangers of COVID-19, “we still advise to vaccinate,” he said.
The number of cases is underestimated
Since his original case report in May, Dr. Jansen has seen five or so additional cases. But the causal link between the coronavirus and the hematologic symptoms is still undefined. “We don’t know much about platelet counts in COVID-19 at all,” he said. It could be that COVID-19 somehow inhibits platelet production or that it kills existing platelets. Whatever the exact relationship to the virus, Dr. Jansen expects that the true number of COVID-19-related ITP cases is higher than current estimates suggest.
One reason it isn’t coming up more often, Dr. Jansen said, may be that the cause of ITP in COVID-19 patients is hard to pin down. In the case report from May, Dr. Jansen and colleagues wrote: “And there are numerous other factors that can cause thrombocytopenia where COVID is concerned. For instance the coagulation activation by COVID‐19 infection leading to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and subsequent thrombocytopenia. Also, treatments for COVID‐19, including heparin, azithromycin and hydroxychloroquine, may lead to thrombocytopenia.”
Tracking and understanding COVID-19-associated ITP first requires the extensive process of elimination needed to diagnose it.
In addition, drugs used to treat COVID-19 could be masking COVID-19-related ITP. “Dexamethasone is a mainstay of COVID treatment. And it’s how we treat ITP,” Dr. Johnson said, which means physicians may be treating ITP without even registering it. And that’s one hypothesis for why Dr. Stone and Dr. Johnson didn’t see a case until 9 months into the pandemic.
Treating COVID-19-associated ITP also has its challenges, particularly in patients who develop it during an acute COVID-19 infection and are at risk for both internal bleeding and thrombosis. This was the case for the third patient in Dr. Jansen’s case report. The patient developed a pulmonary embolism and had a falling platelet count. He was given a platelet infusion and then an anticoagulant for the thrombosis. But a retrospective look at the case revealed the transfusion “did not increase numbers at all – which suggests ITP,” Dr. Jansen said. Intracerebral bleeding was the cause of death.
That’s why “it’s important to be aware of this phenomenon,” Dr. Jansen said of COVID-19-associated ITP. If a transfusion is unsuccessful, consider that the patient may have ITP and adjust. Dr. Johnson hasn’t had to treat a patient battling both complications simultaneously but says the ideal course of action would be to raise platelets with steroids and IVIG and then give the anticoagulant once the platelet count is higher. But reality is rarely ideal. Often these two treatments will have to be given concurrently since the patient faces two life-threatening risks, he said. “It’s a very challenging situation,” he said.
The good news is that standard treatments for ITP seem to work for COVID-19-associated ITP. The 30-year-old patient of Dr. Stone and Dr. Johnson responded so well to intravenous steroids that IVIG was unnecessary. She’s now on a slow prednisone taper and maintains platelet counts at 114,000/mm3 at her weekly follow-up appointments with Dr. Johnson.
Meanwhile, Dr. Jansen’s two other patients, now nearly a year out of treatment, require no additional medication. One of the patients is fully recovered and, though the other still has lower than normal platelet counts, she has no bleeding symptoms and her platelet counts remain stable. Still, Dr. Jansen is anxious for more data looking at the platelet counts in every COVID-19 patient and to combine findings from existing COVID-19-associated ITP patients.
For Dr. Stone, she says she’s added one COVID-19-associated complication to her belt. One less aftereffect will catch her off guard. And she wants others to have the same information.
“It’s just a little bit daunting. We don’t know how bad post-COVID will be,” she said. “There’s so many levels to this disease. Some people deal with it for so long and some people just get better and move on – we think ... so far.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe maternal morbidity promotes long-term mortality
Women who experienced severe complications during pregnancy were more than twice as likely to die at any time after their last pregnancy, including post partum and beyond, based on data from more than 1 million women.
“Current data suggest that up to 88% of maternal deaths are preceded by severe maternal morbidity,” but the long-term risk of mortality and the effect of severe maternal morbidity has not been well studied, wrote U. Vivian Ukah, MPH, PhD, of McGill University, Montreal, and colleagues.
In a longitudinal cohort study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers identified 1,229,306 pregnant women who delivered in Quebec between 1989 and 2016.
The primary outcome of in-hospital mortality after the last pregnancy, either post partum (within 42 days of delivery) or long term (43 days to 29 years after delivery).
Overall, 2.9% of the study population experienced severe maternal morbidity, with an associated mortality rate of 0.86 per 1,000 person-years versus 0.41 per 1,000 person-years in women without severe maternal morbidity. The median time to death for women with severe maternal mortality was 6.8 years, compared with 151 years for those without severe maternal morbidity.
The death rate at any time after delivery, post partum and beyond, was twice as high among women with severe maternal morbidity. The morbidities most often associated with long-term mortality after 42 days were severe cardiac complications (hazard ratio, 7.00), acute renal failure (HR, 4.35), and cerebrovascular accidents (HR, 4.03).
However, the mortality risk following severe maternal morbidity decreased over time, the researchers noted. Severe maternal morbidity was associated with 6.73 times the mortality risk, compared with no morbidity, during the period from 43 days to 11 months, but this difference dropped to 1.91, 1.77, and 1.18 times the risk, compared with no comorbidity, at 1-4 years, 5-9 years, and 10-29 years, respectively.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to prove causality, the use of only in-hospital mortality data, and the potential for missed cases that fell outside the Canadian Perinatal Surveillance System definition of severe maternal morbidity, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that identifying severe maternal morbidity may help identify women at risk for postpartum and long-term premature mortality. “Women with severe maternal morbidity may benefit from continued surveillance and preventative interventions to reduce the risk of premature mortality,” they concluded.
Increased morbidity rates drive need for research
“In this retrospective longitudinal cohort study of over 1.2 million women delivering in Quebec between 1989 and 2016, Dr. Ukah and her colleagues demonstrated the association between severe maternal morbidity [SMM] and an accelerated risk of mortality beyond the postpartum period, compared with women who do not experience SMM,” Rachel Humphrey, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Advent Health in Orlando, said in an interview. “This study is important as there has been a steady increase in SMM in recent years. In the United States, the CDC reports that SMM affected more than 50,000 women in 2014 alone. Across multiple countries the decline in overall health of women giving birth is felt to contribute to SMM. As the rates of preexisting conditions such as maternal obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and advanced age increases, we can assume that SMM will increase as well. This study clearly depicts the association between SMM and maternal death at 43 days to years after the complicated delivery. We can assume that, as SMM increases, so will the risk of mortality beyond the postpartum period for these women who initially survive their serious pregnancy complication.”
Dr. Humphrey said that, in some respects, the study results are to be expected. “It is logical to assume that a patient with a life-threatening issue at delivery such as severe cardiac complications, acute renal failure and cerebrovascular accident would be at higher risk for long-term morbidity and mortality. This study also adds to the large body of evidence linking socioeconomic deprivation with SMM. But there were unexpected findings in this study. I did not expect certain types of SMM to be associated with an increased risk of death years after the event.For example, hysterectomy at delivery carried a hazard ratio of 3.54 for death at 5-9 years after the event. The association between severe hemorrhage and fully adjusted hazard ratio was similarly increased at 2.96 [2.37-3.71].”
More screening and prospective studies needed
“Recognizing the association between SMM and accelerated long-term risk of mortality is a first step in determining what interventions might improve health and longevity in women who experience SMM,” said Dr. Humphrey. “With the absence of prospective studies, it still is logical to assume that close medical follow-up and lifestyle interventions are appropriate in this population. Screening for and actively managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension seems appropriate for these patients.”
As for further research, “I am interested to know through prospective clinical trials if specific health maintenance screens and interventions would have a positive impact on the life expectancy of survivors of SMM,” said Dr. Humphrey. “I applaud this team for providing data up to 27 years after an obstetric complication, and I am interested to see if Dr. Ukah and her team will continue their research to determine if there is a ‘second peak’ in mortality in the survivors of SMM when they are elderly. Finally, I would be interested to see more detailed data from this team on the associations between socioeconomic deprivation and short- and long-term mortality for women in their study. This information may help further fuel the movement toward social changes to maximize the health of the women and families we serve.”
The study was supported by the Heart & Stroke Foundation of Canada and awards to the lead author and others from the Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé. The researchers and Dr. Humphrey had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Women who experienced severe complications during pregnancy were more than twice as likely to die at any time after their last pregnancy, including post partum and beyond, based on data from more than 1 million women.
“Current data suggest that up to 88% of maternal deaths are preceded by severe maternal morbidity,” but the long-term risk of mortality and the effect of severe maternal morbidity has not been well studied, wrote U. Vivian Ukah, MPH, PhD, of McGill University, Montreal, and colleagues.
In a longitudinal cohort study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers identified 1,229,306 pregnant women who delivered in Quebec between 1989 and 2016.
The primary outcome of in-hospital mortality after the last pregnancy, either post partum (within 42 days of delivery) or long term (43 days to 29 years after delivery).
Overall, 2.9% of the study population experienced severe maternal morbidity, with an associated mortality rate of 0.86 per 1,000 person-years versus 0.41 per 1,000 person-years in women without severe maternal morbidity. The median time to death for women with severe maternal mortality was 6.8 years, compared with 151 years for those without severe maternal morbidity.
The death rate at any time after delivery, post partum and beyond, was twice as high among women with severe maternal morbidity. The morbidities most often associated with long-term mortality after 42 days were severe cardiac complications (hazard ratio, 7.00), acute renal failure (HR, 4.35), and cerebrovascular accidents (HR, 4.03).
However, the mortality risk following severe maternal morbidity decreased over time, the researchers noted. Severe maternal morbidity was associated with 6.73 times the mortality risk, compared with no morbidity, during the period from 43 days to 11 months, but this difference dropped to 1.91, 1.77, and 1.18 times the risk, compared with no comorbidity, at 1-4 years, 5-9 years, and 10-29 years, respectively.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to prove causality, the use of only in-hospital mortality data, and the potential for missed cases that fell outside the Canadian Perinatal Surveillance System definition of severe maternal morbidity, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that identifying severe maternal morbidity may help identify women at risk for postpartum and long-term premature mortality. “Women with severe maternal morbidity may benefit from continued surveillance and preventative interventions to reduce the risk of premature mortality,” they concluded.
Increased morbidity rates drive need for research
“In this retrospective longitudinal cohort study of over 1.2 million women delivering in Quebec between 1989 and 2016, Dr. Ukah and her colleagues demonstrated the association between severe maternal morbidity [SMM] and an accelerated risk of mortality beyond the postpartum period, compared with women who do not experience SMM,” Rachel Humphrey, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Advent Health in Orlando, said in an interview. “This study is important as there has been a steady increase in SMM in recent years. In the United States, the CDC reports that SMM affected more than 50,000 women in 2014 alone. Across multiple countries the decline in overall health of women giving birth is felt to contribute to SMM. As the rates of preexisting conditions such as maternal obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and advanced age increases, we can assume that SMM will increase as well. This study clearly depicts the association between SMM and maternal death at 43 days to years after the complicated delivery. We can assume that, as SMM increases, so will the risk of mortality beyond the postpartum period for these women who initially survive their serious pregnancy complication.”
Dr. Humphrey said that, in some respects, the study results are to be expected. “It is logical to assume that a patient with a life-threatening issue at delivery such as severe cardiac complications, acute renal failure and cerebrovascular accident would be at higher risk for long-term morbidity and mortality. This study also adds to the large body of evidence linking socioeconomic deprivation with SMM. But there were unexpected findings in this study. I did not expect certain types of SMM to be associated with an increased risk of death years after the event.For example, hysterectomy at delivery carried a hazard ratio of 3.54 for death at 5-9 years after the event. The association between severe hemorrhage and fully adjusted hazard ratio was similarly increased at 2.96 [2.37-3.71].”
More screening and prospective studies needed
“Recognizing the association between SMM and accelerated long-term risk of mortality is a first step in determining what interventions might improve health and longevity in women who experience SMM,” said Dr. Humphrey. “With the absence of prospective studies, it still is logical to assume that close medical follow-up and lifestyle interventions are appropriate in this population. Screening for and actively managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension seems appropriate for these patients.”
As for further research, “I am interested to know through prospective clinical trials if specific health maintenance screens and interventions would have a positive impact on the life expectancy of survivors of SMM,” said Dr. Humphrey. “I applaud this team for providing data up to 27 years after an obstetric complication, and I am interested to see if Dr. Ukah and her team will continue their research to determine if there is a ‘second peak’ in mortality in the survivors of SMM when they are elderly. Finally, I would be interested to see more detailed data from this team on the associations between socioeconomic deprivation and short- and long-term mortality for women in their study. This information may help further fuel the movement toward social changes to maximize the health of the women and families we serve.”
The study was supported by the Heart & Stroke Foundation of Canada and awards to the lead author and others from the Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé. The researchers and Dr. Humphrey had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Women who experienced severe complications during pregnancy were more than twice as likely to die at any time after their last pregnancy, including post partum and beyond, based on data from more than 1 million women.
“Current data suggest that up to 88% of maternal deaths are preceded by severe maternal morbidity,” but the long-term risk of mortality and the effect of severe maternal morbidity has not been well studied, wrote U. Vivian Ukah, MPH, PhD, of McGill University, Montreal, and colleagues.
In a longitudinal cohort study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers identified 1,229,306 pregnant women who delivered in Quebec between 1989 and 2016.
The primary outcome of in-hospital mortality after the last pregnancy, either post partum (within 42 days of delivery) or long term (43 days to 29 years after delivery).
Overall, 2.9% of the study population experienced severe maternal morbidity, with an associated mortality rate of 0.86 per 1,000 person-years versus 0.41 per 1,000 person-years in women without severe maternal morbidity. The median time to death for women with severe maternal mortality was 6.8 years, compared with 151 years for those without severe maternal morbidity.
The death rate at any time after delivery, post partum and beyond, was twice as high among women with severe maternal morbidity. The morbidities most often associated with long-term mortality after 42 days were severe cardiac complications (hazard ratio, 7.00), acute renal failure (HR, 4.35), and cerebrovascular accidents (HR, 4.03).
However, the mortality risk following severe maternal morbidity decreased over time, the researchers noted. Severe maternal morbidity was associated with 6.73 times the mortality risk, compared with no morbidity, during the period from 43 days to 11 months, but this difference dropped to 1.91, 1.77, and 1.18 times the risk, compared with no comorbidity, at 1-4 years, 5-9 years, and 10-29 years, respectively.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to prove causality, the use of only in-hospital mortality data, and the potential for missed cases that fell outside the Canadian Perinatal Surveillance System definition of severe maternal morbidity, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that identifying severe maternal morbidity may help identify women at risk for postpartum and long-term premature mortality. “Women with severe maternal morbidity may benefit from continued surveillance and preventative interventions to reduce the risk of premature mortality,” they concluded.
Increased morbidity rates drive need for research
“In this retrospective longitudinal cohort study of over 1.2 million women delivering in Quebec between 1989 and 2016, Dr. Ukah and her colleagues demonstrated the association between severe maternal morbidity [SMM] and an accelerated risk of mortality beyond the postpartum period, compared with women who do not experience SMM,” Rachel Humphrey, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Advent Health in Orlando, said in an interview. “This study is important as there has been a steady increase in SMM in recent years. In the United States, the CDC reports that SMM affected more than 50,000 women in 2014 alone. Across multiple countries the decline in overall health of women giving birth is felt to contribute to SMM. As the rates of preexisting conditions such as maternal obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and advanced age increases, we can assume that SMM will increase as well. This study clearly depicts the association between SMM and maternal death at 43 days to years after the complicated delivery. We can assume that, as SMM increases, so will the risk of mortality beyond the postpartum period for these women who initially survive their serious pregnancy complication.”
Dr. Humphrey said that, in some respects, the study results are to be expected. “It is logical to assume that a patient with a life-threatening issue at delivery such as severe cardiac complications, acute renal failure and cerebrovascular accident would be at higher risk for long-term morbidity and mortality. This study also adds to the large body of evidence linking socioeconomic deprivation with SMM. But there were unexpected findings in this study. I did not expect certain types of SMM to be associated with an increased risk of death years after the event.For example, hysterectomy at delivery carried a hazard ratio of 3.54 for death at 5-9 years after the event. The association between severe hemorrhage and fully adjusted hazard ratio was similarly increased at 2.96 [2.37-3.71].”
More screening and prospective studies needed
“Recognizing the association between SMM and accelerated long-term risk of mortality is a first step in determining what interventions might improve health and longevity in women who experience SMM,” said Dr. Humphrey. “With the absence of prospective studies, it still is logical to assume that close medical follow-up and lifestyle interventions are appropriate in this population. Screening for and actively managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension seems appropriate for these patients.”
As for further research, “I am interested to know through prospective clinical trials if specific health maintenance screens and interventions would have a positive impact on the life expectancy of survivors of SMM,” said Dr. Humphrey. “I applaud this team for providing data up to 27 years after an obstetric complication, and I am interested to see if Dr. Ukah and her team will continue their research to determine if there is a ‘second peak’ in mortality in the survivors of SMM when they are elderly. Finally, I would be interested to see more detailed data from this team on the associations between socioeconomic deprivation and short- and long-term mortality for women in their study. This information may help further fuel the movement toward social changes to maximize the health of the women and families we serve.”
The study was supported by the Heart & Stroke Foundation of Canada and awards to the lead author and others from the Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé. The researchers and Dr. Humphrey had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
CDC panel: No COVID-19 vaccine safety surprises
The United States is nearly 6 weeks into its historic campaign to vaccinate Americans against the virus that causes COVID-19, and so far, the two vaccines in use look remarkably low risk, according to new data presented today at a meeting of vaccine experts that advise the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
With 23.5 million doses of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines now given, there have been very few serious side effects. In addition, deaths reported after people got the vaccine do not seem to be related to it.
The most common symptoms reported after vaccination were pain where people got the shot, fatigue, headache, and muscle soreness. These were more common after the second dose. In addition, about one in four people reported fever and chills after the second shot.
“On the whole, I thought it was very reassuring,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert with Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who listened to the presentations.
The CDC is collecting safety information through multiple channels. These include a new smartphone-based app called V-Safe, which collects daily information from people who’ve been vaccinated; the federal Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, which accepts reports from anyone; and the Vaccine Safety Datalink, which is a collaboration between the CDC and nine major hospital systems. There’s also the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project, a collaboration between the CDC and vaccine safety experts.
After surveying these systems, experts heading the safety committee for the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices said there have been few serious side effects reported.
Very rarely, severe allergic reactions – called anaphylaxis – have occurred after vaccination. There have been 50 of these cases reported after the Pfizer vaccine and 21 cases reported after the Moderna vaccine to date. Nearly all of them – 94% of the anaphylaxis cases after Pfizer vaccines and 100% of those after Moderna’s vaccine – have been in women, though it’s not clear why.
That translates to a rate of about five cases of anaphylaxis for every million doses of the Pfizer vaccine and about three for every million doses of the Moderna vaccine. Most of these occur within 15 minutes after getting a vaccine dose, with one reported as long as 20 hours after the shot.
The CDC suspects these may be related to an ingredient called polyethylene glycol (PEG). PEG is a part of the particles that slip the vaccines’ mRNA into cells with instructions to make the spike protein of the virus. Cells then express these spikes on their surfaces so the immune system can learn to recognize them and make defenses against them. PEG is a common ingredient in many drugs and occasionally triggers anaphylaxis.
Reported deaths seem unrelated to vaccines
Through Jan. 18, 196 people have died after getting a vaccine.
Most of these deaths (129) were in patients in long term care facilities. These deaths are still being investigated, but when they were compared with the number of deaths that might be expected over the same period because of natural causes, they seemed to be coincidental and not caused by the vaccine, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, deputy director of the Immunization Safety Office at the CDC, who studied the data.
In fact, death rates were lower among vaccinated nursing home residents, compared with those who had not been vaccinated.
“These findings suggest that short-term mortality rates appear unrelated to vaccination for COVID-19,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
This also appeared to be true for younger adults who died after their shots.
There were 28 people aged under 65 years who died after being vaccinated. Most of these deaths were heart related, according to autopsy reports. When investigators compared the number of sudden cardiac deaths expected to occur in this population naturally, they found people who were vaccinated had a lower rate than would have been expected without vaccination. This suggests that these deaths were also unrelated to the vaccine.
More vaccines on the horizon
The panel also heard an update from drug company AstraZeneca on its vaccine. It’s being used in 18 countries but has not yet been authorized in the United States.
That vaccine is currently in phase 3 of its U.S. clinical trials, and more than 26,000 people who have volunteered to get the shot had received their second dose as of Jan. 21, the company said.
The Food and Drug Administration requires at least 2 months of follow-up before it will evaluate a vaccine for an emergency-use authorization, which means the company would be ready to submit by the end of March, with a possible approval by April.
The AstraZeneca vaccine uses a more traditional method to create immunity, slipping a key part of the virus that causes COVID-19 into the shell of an adenovirus – a virus that causes cold-like symptoms – that normally infects monkeys. When the immune system sees the virus, it generates protective defenses against it.
The two-dose vaccine can be stored in a regular refrigerator for up to 6 months, which makes it easier to handle than the mRNA vaccines, which require much colder storage. Another advantage appears to be that it’s less likely to trigger severe allergic reactions. So far, there have been no cases of anaphylaxis reported after this shot.
In total, four serious side effects have been reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine, including two cases of transverse myelitis, a serious condition that causes swelling of the spinal cord, leading to pain, muscle weakness, and paralysis. One of these was in the group that got the placebo. The reports paused the trial, but it was allowed to continue after a safety review.
This vaccine also appears to be less effective than the mRNA shots. Data presented to the panel show it appears to cut the risk of developing a COVID infection that has symptoms by 62%. That’s over the 50% threshold the FDA set for approval but less than seen with the mRNA vaccines, which are more than 90% effective at preventing infections.
“Is the average person going to want to take the AstraZeneca shot? What role is this going to play in our vaccination program?” Dr. Schaffner said.
Johnson & Johnson will have enough data from its clinical trials to submit it to the FDA within the next week, the company said in a call with shareholders on Tuesday. So far, its one-dose shots looks to be about as effective as both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
“It could be that we wind up with four vaccines: Three that can run very fast, and one that’s not so fast,” Dr. Schaffner said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States is nearly 6 weeks into its historic campaign to vaccinate Americans against the virus that causes COVID-19, and so far, the two vaccines in use look remarkably low risk, according to new data presented today at a meeting of vaccine experts that advise the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
With 23.5 million doses of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines now given, there have been very few serious side effects. In addition, deaths reported after people got the vaccine do not seem to be related to it.
The most common symptoms reported after vaccination were pain where people got the shot, fatigue, headache, and muscle soreness. These were more common after the second dose. In addition, about one in four people reported fever and chills after the second shot.
“On the whole, I thought it was very reassuring,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert with Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who listened to the presentations.
The CDC is collecting safety information through multiple channels. These include a new smartphone-based app called V-Safe, which collects daily information from people who’ve been vaccinated; the federal Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, which accepts reports from anyone; and the Vaccine Safety Datalink, which is a collaboration between the CDC and nine major hospital systems. There’s also the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project, a collaboration between the CDC and vaccine safety experts.
After surveying these systems, experts heading the safety committee for the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices said there have been few serious side effects reported.
Very rarely, severe allergic reactions – called anaphylaxis – have occurred after vaccination. There have been 50 of these cases reported after the Pfizer vaccine and 21 cases reported after the Moderna vaccine to date. Nearly all of them – 94% of the anaphylaxis cases after Pfizer vaccines and 100% of those after Moderna’s vaccine – have been in women, though it’s not clear why.
That translates to a rate of about five cases of anaphylaxis for every million doses of the Pfizer vaccine and about three for every million doses of the Moderna vaccine. Most of these occur within 15 minutes after getting a vaccine dose, with one reported as long as 20 hours after the shot.
The CDC suspects these may be related to an ingredient called polyethylene glycol (PEG). PEG is a part of the particles that slip the vaccines’ mRNA into cells with instructions to make the spike protein of the virus. Cells then express these spikes on their surfaces so the immune system can learn to recognize them and make defenses against them. PEG is a common ingredient in many drugs and occasionally triggers anaphylaxis.
Reported deaths seem unrelated to vaccines
Through Jan. 18, 196 people have died after getting a vaccine.
Most of these deaths (129) were in patients in long term care facilities. These deaths are still being investigated, but when they were compared with the number of deaths that might be expected over the same period because of natural causes, they seemed to be coincidental and not caused by the vaccine, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, deputy director of the Immunization Safety Office at the CDC, who studied the data.
In fact, death rates were lower among vaccinated nursing home residents, compared with those who had not been vaccinated.
“These findings suggest that short-term mortality rates appear unrelated to vaccination for COVID-19,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
This also appeared to be true for younger adults who died after their shots.
There were 28 people aged under 65 years who died after being vaccinated. Most of these deaths were heart related, according to autopsy reports. When investigators compared the number of sudden cardiac deaths expected to occur in this population naturally, they found people who were vaccinated had a lower rate than would have been expected without vaccination. This suggests that these deaths were also unrelated to the vaccine.
More vaccines on the horizon
The panel also heard an update from drug company AstraZeneca on its vaccine. It’s being used in 18 countries but has not yet been authorized in the United States.
That vaccine is currently in phase 3 of its U.S. clinical trials, and more than 26,000 people who have volunteered to get the shot had received their second dose as of Jan. 21, the company said.
The Food and Drug Administration requires at least 2 months of follow-up before it will evaluate a vaccine for an emergency-use authorization, which means the company would be ready to submit by the end of March, with a possible approval by April.
The AstraZeneca vaccine uses a more traditional method to create immunity, slipping a key part of the virus that causes COVID-19 into the shell of an adenovirus – a virus that causes cold-like symptoms – that normally infects monkeys. When the immune system sees the virus, it generates protective defenses against it.
The two-dose vaccine can be stored in a regular refrigerator for up to 6 months, which makes it easier to handle than the mRNA vaccines, which require much colder storage. Another advantage appears to be that it’s less likely to trigger severe allergic reactions. So far, there have been no cases of anaphylaxis reported after this shot.
In total, four serious side effects have been reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine, including two cases of transverse myelitis, a serious condition that causes swelling of the spinal cord, leading to pain, muscle weakness, and paralysis. One of these was in the group that got the placebo. The reports paused the trial, but it was allowed to continue after a safety review.
This vaccine also appears to be less effective than the mRNA shots. Data presented to the panel show it appears to cut the risk of developing a COVID infection that has symptoms by 62%. That’s over the 50% threshold the FDA set for approval but less than seen with the mRNA vaccines, which are more than 90% effective at preventing infections.
“Is the average person going to want to take the AstraZeneca shot? What role is this going to play in our vaccination program?” Dr. Schaffner said.
Johnson & Johnson will have enough data from its clinical trials to submit it to the FDA within the next week, the company said in a call with shareholders on Tuesday. So far, its one-dose shots looks to be about as effective as both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
“It could be that we wind up with four vaccines: Three that can run very fast, and one that’s not so fast,” Dr. Schaffner said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States is nearly 6 weeks into its historic campaign to vaccinate Americans against the virus that causes COVID-19, and so far, the two vaccines in use look remarkably low risk, according to new data presented today at a meeting of vaccine experts that advise the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
With 23.5 million doses of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines now given, there have been very few serious side effects. In addition, deaths reported after people got the vaccine do not seem to be related to it.
The most common symptoms reported after vaccination were pain where people got the shot, fatigue, headache, and muscle soreness. These were more common after the second dose. In addition, about one in four people reported fever and chills after the second shot.
“On the whole, I thought it was very reassuring,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert with Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who listened to the presentations.
The CDC is collecting safety information through multiple channels. These include a new smartphone-based app called V-Safe, which collects daily information from people who’ve been vaccinated; the federal Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, which accepts reports from anyone; and the Vaccine Safety Datalink, which is a collaboration between the CDC and nine major hospital systems. There’s also the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project, a collaboration between the CDC and vaccine safety experts.
After surveying these systems, experts heading the safety committee for the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices said there have been few serious side effects reported.
Very rarely, severe allergic reactions – called anaphylaxis – have occurred after vaccination. There have been 50 of these cases reported after the Pfizer vaccine and 21 cases reported after the Moderna vaccine to date. Nearly all of them – 94% of the anaphylaxis cases after Pfizer vaccines and 100% of those after Moderna’s vaccine – have been in women, though it’s not clear why.
That translates to a rate of about five cases of anaphylaxis for every million doses of the Pfizer vaccine and about three for every million doses of the Moderna vaccine. Most of these occur within 15 minutes after getting a vaccine dose, with one reported as long as 20 hours after the shot.
The CDC suspects these may be related to an ingredient called polyethylene glycol (PEG). PEG is a part of the particles that slip the vaccines’ mRNA into cells with instructions to make the spike protein of the virus. Cells then express these spikes on their surfaces so the immune system can learn to recognize them and make defenses against them. PEG is a common ingredient in many drugs and occasionally triggers anaphylaxis.
Reported deaths seem unrelated to vaccines
Through Jan. 18, 196 people have died after getting a vaccine.
Most of these deaths (129) were in patients in long term care facilities. These deaths are still being investigated, but when they were compared with the number of deaths that might be expected over the same period because of natural causes, they seemed to be coincidental and not caused by the vaccine, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, deputy director of the Immunization Safety Office at the CDC, who studied the data.
In fact, death rates were lower among vaccinated nursing home residents, compared with those who had not been vaccinated.
“These findings suggest that short-term mortality rates appear unrelated to vaccination for COVID-19,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
This also appeared to be true for younger adults who died after their shots.
There were 28 people aged under 65 years who died after being vaccinated. Most of these deaths were heart related, according to autopsy reports. When investigators compared the number of sudden cardiac deaths expected to occur in this population naturally, they found people who were vaccinated had a lower rate than would have been expected without vaccination. This suggests that these deaths were also unrelated to the vaccine.
More vaccines on the horizon
The panel also heard an update from drug company AstraZeneca on its vaccine. It’s being used in 18 countries but has not yet been authorized in the United States.
That vaccine is currently in phase 3 of its U.S. clinical trials, and more than 26,000 people who have volunteered to get the shot had received their second dose as of Jan. 21, the company said.
The Food and Drug Administration requires at least 2 months of follow-up before it will evaluate a vaccine for an emergency-use authorization, which means the company would be ready to submit by the end of March, with a possible approval by April.
The AstraZeneca vaccine uses a more traditional method to create immunity, slipping a key part of the virus that causes COVID-19 into the shell of an adenovirus – a virus that causes cold-like symptoms – that normally infects monkeys. When the immune system sees the virus, it generates protective defenses against it.
The two-dose vaccine can be stored in a regular refrigerator for up to 6 months, which makes it easier to handle than the mRNA vaccines, which require much colder storage. Another advantage appears to be that it’s less likely to trigger severe allergic reactions. So far, there have been no cases of anaphylaxis reported after this shot.
In total, four serious side effects have been reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine, including two cases of transverse myelitis, a serious condition that causes swelling of the spinal cord, leading to pain, muscle weakness, and paralysis. One of these was in the group that got the placebo. The reports paused the trial, but it was allowed to continue after a safety review.
This vaccine also appears to be less effective than the mRNA shots. Data presented to the panel show it appears to cut the risk of developing a COVID infection that has symptoms by 62%. That’s over the 50% threshold the FDA set for approval but less than seen with the mRNA vaccines, which are more than 90% effective at preventing infections.
“Is the average person going to want to take the AstraZeneca shot? What role is this going to play in our vaccination program?” Dr. Schaffner said.
Johnson & Johnson will have enough data from its clinical trials to submit it to the FDA within the next week, the company said in a call with shareholders on Tuesday. So far, its one-dose shots looks to be about as effective as both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
“It could be that we wind up with four vaccines: Three that can run very fast, and one that’s not so fast,” Dr. Schaffner said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Are there COVID-19–related ‘long-haul’ skin issues?
– as a result of infection with or exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, but some dermatologists question if the skin signs and symptoms are truly related.
In their commentary in the Lancet Infectious Diseases, Esther P. Freeman, MD, PhD, and colleagues who lead and participate in the American Academy of Dermatology’s international registry said their analysis “revealed a previously unreported subset of patients who experience long-haul symptoms in dermatology-dominant COVID-19.”
Some of the data was presented at the 29th European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology in late October 2020, but has since been updated with more cases.
Dermatologists who spoke with this news organization said it has not been settled that some skin manifestations – such as pernio/chilblains rashes, seen primarily in nonhospitalized patients, and described in the registry – are definitively caused by COVID. They also noted that in some cases, patients who initially test negative for COVID-19 by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) sometimes do not ever develop antibodies, which could mean they were never actually exposed to SARS-CoV-2.
“I still question whether the perniosis is directly related to infection with SARS-CoV-2 or not,” said Anthony Fernandez, MD, PhD, director of medical and inpatient dermatology and assistant professor of dermatopathology at the Cleveland Clinic. His uncertainty is driven by the lack of seroconversion and that few cases were seen over the summer in the United States – suggesting that it may still be a result of cold temperatures.
“I’m not sure there is a definitive correct answer, definitely not that everyone would agree on,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Freeman, however, believed that pernio and especially persistent lesions are caused by an immune response to COVID.
In an interview, she noted the multiple cases of patients in the registry who did seroconvert and that, while a registry is not a perfect means of getting an answer, it is good for generating questions. Taken collectively, the cases in the registry can “tell a story for further hypotheses,” said Dr. Freeman, who is director of global health dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital and assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard University, both in Boston.
“We were noticing this signal across the world” that patients “developed these toe lesions and they never got better,” said Dr. Freeman. Generally, people who experience pernio, also described as COVID toes or “COVID fingers,” recover in 4-8 weeks. But in the registry, “we did have this subset of patients who really were experiencing these very longstanding symptoms,” she added.
Two patients with lab-confirmed COVID have had long-lasting pernio of 133 days and 150 days. “I’m caring for a cohort in Boston who have had long COVID of the skin and symptoms for over 10 months,” Dr. Freeman said.
Pernio dominates
The registry – a collaboration between the AAD and the International League of Dermatological Societies – was launched in April 2020. Any medical professional can enter case information. From April to October, 1,030 total cases and 331 laboratory-confirmed or suspected COVID-19 cases with dermatological manifestations were entered from 41 countries.
Most of the cases were just recorded at a single time point, which is an acknowledged limitation of the study.
Dr. Freeman and colleagues reached out to registry participants in June and August to get updates on COVID lab test results and sign and symptom duration. Overall, 234 total and 96 lab-confirmed COVID infections had more lengthy data about sign and symptom duration.
Pernio lasted a median of 15 days in patients with suspected disease and 12 days for those with lab-confirmed COVID, compared with a median of 7 days for morbilliform eruptions, 4 days for urticarial eruptions, and 20 days for papulosquamous eruptions – all in patients with lab-confirmed disease.
Of the 103 cases of pernio, 7 had symptoms lasting more than 60 days. Only two of those seven patients had lab-confirmed COVID. Initially, the one patient tested negative with nasopharyngeal PCR, and serum IgM and IgG. Six weeks after pernio onset, the patient – still experiencing fatigue and pernio – seroconverted to anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgM positivity.
The other long-haul patient, after a negative PCR, tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 serum IgG 1 month after pernio onset.
Robust immune response?
Dr. Freeman said these patients might have a very high interferon response initially to the virus, which makes for a mild to nonexistent disease, but could create inflammation elsewhere. “I almost view the toes as an innocent bystander of a robust immune response to SARS-CoV-2.”
Although he has not seen extended pernio or other skin manifestations in his patients, Dr. Fernandez said the interferon hypothesis is “fair,” and “the best that’s out there.” Dr. Fernandez is currently studying cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 as a principal investigator of a trial sponsored by the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative of Cleveland.
Dr. Ko said in an interview that she has not observed long-haul skin issues in her patients, but Yale colleagues have.
In a study, she and Yale colleagues published in September, SARS-CoV-2 spike protein was detected in perniotic lesions, but not nuclear protein or viral RNA. The test they used – immunohistochemistry – can be nonspecific, which muddied results.
She does not think there is replicating virus in the skin or the lesions. Instead, said Dr. Ko, “either there is viral spike protein that has somehow become disassociated from actively replicating virus that somehow got deposited in endothelial cells,” or the staining “was spurious,” or some other protein is cross-reacting. “And the people who are unlucky enough to have that protein in their endothelial cells can manifest this COVID-toe, COVID-finger phenomenon.”
To her, it’s an unsolved mystery. “The weird thing is, we’ve never before had this much perniosis,” Dr. Ko said.
Dr. Fernandez is not convinced yet, noting that, in Cleveland, more pernio cases were observed in March and April than in the summer. “If it is a manifestation of the infection then you also need the right environment, the cold weather for this manifestation to present,” he said. “Or, it really isn’t a direct manifestation of COVID-19 but may be more related to other factors,” such as lifestyle changes related to limitations implemented to help mitigate the spread of the disease.
“To me the jury is still out whether or not the perniotic lesions really can tell us something about a patient’s exposure and infection with SARS-CoV-2,” he said.
Dr. Freeman reported receiving a grant from the International League of Dermatological Societies and nonfinancial support from the AAD for the study. Dr. Ko reported no conflicts. Dr. Fernadnez had no disclosures.
– as a result of infection with or exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, but some dermatologists question if the skin signs and symptoms are truly related.
In their commentary in the Lancet Infectious Diseases, Esther P. Freeman, MD, PhD, and colleagues who lead and participate in the American Academy of Dermatology’s international registry said their analysis “revealed a previously unreported subset of patients who experience long-haul symptoms in dermatology-dominant COVID-19.”
Some of the data was presented at the 29th European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology in late October 2020, but has since been updated with more cases.
Dermatologists who spoke with this news organization said it has not been settled that some skin manifestations – such as pernio/chilblains rashes, seen primarily in nonhospitalized patients, and described in the registry – are definitively caused by COVID. They also noted that in some cases, patients who initially test negative for COVID-19 by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) sometimes do not ever develop antibodies, which could mean they were never actually exposed to SARS-CoV-2.
“I still question whether the perniosis is directly related to infection with SARS-CoV-2 or not,” said Anthony Fernandez, MD, PhD, director of medical and inpatient dermatology and assistant professor of dermatopathology at the Cleveland Clinic. His uncertainty is driven by the lack of seroconversion and that few cases were seen over the summer in the United States – suggesting that it may still be a result of cold temperatures.
“I’m not sure there is a definitive correct answer, definitely not that everyone would agree on,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Freeman, however, believed that pernio and especially persistent lesions are caused by an immune response to COVID.
In an interview, she noted the multiple cases of patients in the registry who did seroconvert and that, while a registry is not a perfect means of getting an answer, it is good for generating questions. Taken collectively, the cases in the registry can “tell a story for further hypotheses,” said Dr. Freeman, who is director of global health dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital and assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard University, both in Boston.
“We were noticing this signal across the world” that patients “developed these toe lesions and they never got better,” said Dr. Freeman. Generally, people who experience pernio, also described as COVID toes or “COVID fingers,” recover in 4-8 weeks. But in the registry, “we did have this subset of patients who really were experiencing these very longstanding symptoms,” she added.
Two patients with lab-confirmed COVID have had long-lasting pernio of 133 days and 150 days. “I’m caring for a cohort in Boston who have had long COVID of the skin and symptoms for over 10 months,” Dr. Freeman said.
Pernio dominates
The registry – a collaboration between the AAD and the International League of Dermatological Societies – was launched in April 2020. Any medical professional can enter case information. From April to October, 1,030 total cases and 331 laboratory-confirmed or suspected COVID-19 cases with dermatological manifestations were entered from 41 countries.
Most of the cases were just recorded at a single time point, which is an acknowledged limitation of the study.
Dr. Freeman and colleagues reached out to registry participants in June and August to get updates on COVID lab test results and sign and symptom duration. Overall, 234 total and 96 lab-confirmed COVID infections had more lengthy data about sign and symptom duration.
Pernio lasted a median of 15 days in patients with suspected disease and 12 days for those with lab-confirmed COVID, compared with a median of 7 days for morbilliform eruptions, 4 days for urticarial eruptions, and 20 days for papulosquamous eruptions – all in patients with lab-confirmed disease.
Of the 103 cases of pernio, 7 had symptoms lasting more than 60 days. Only two of those seven patients had lab-confirmed COVID. Initially, the one patient tested negative with nasopharyngeal PCR, and serum IgM and IgG. Six weeks after pernio onset, the patient – still experiencing fatigue and pernio – seroconverted to anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgM positivity.
The other long-haul patient, after a negative PCR, tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 serum IgG 1 month after pernio onset.
Robust immune response?
Dr. Freeman said these patients might have a very high interferon response initially to the virus, which makes for a mild to nonexistent disease, but could create inflammation elsewhere. “I almost view the toes as an innocent bystander of a robust immune response to SARS-CoV-2.”
Although he has not seen extended pernio or other skin manifestations in his patients, Dr. Fernandez said the interferon hypothesis is “fair,” and “the best that’s out there.” Dr. Fernandez is currently studying cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 as a principal investigator of a trial sponsored by the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative of Cleveland.
Dr. Ko said in an interview that she has not observed long-haul skin issues in her patients, but Yale colleagues have.
In a study, she and Yale colleagues published in September, SARS-CoV-2 spike protein was detected in perniotic lesions, but not nuclear protein or viral RNA. The test they used – immunohistochemistry – can be nonspecific, which muddied results.
She does not think there is replicating virus in the skin or the lesions. Instead, said Dr. Ko, “either there is viral spike protein that has somehow become disassociated from actively replicating virus that somehow got deposited in endothelial cells,” or the staining “was spurious,” or some other protein is cross-reacting. “And the people who are unlucky enough to have that protein in their endothelial cells can manifest this COVID-toe, COVID-finger phenomenon.”
To her, it’s an unsolved mystery. “The weird thing is, we’ve never before had this much perniosis,” Dr. Ko said.
Dr. Fernandez is not convinced yet, noting that, in Cleveland, more pernio cases were observed in March and April than in the summer. “If it is a manifestation of the infection then you also need the right environment, the cold weather for this manifestation to present,” he said. “Or, it really isn’t a direct manifestation of COVID-19 but may be more related to other factors,” such as lifestyle changes related to limitations implemented to help mitigate the spread of the disease.
“To me the jury is still out whether or not the perniotic lesions really can tell us something about a patient’s exposure and infection with SARS-CoV-2,” he said.
Dr. Freeman reported receiving a grant from the International League of Dermatological Societies and nonfinancial support from the AAD for the study. Dr. Ko reported no conflicts. Dr. Fernadnez had no disclosures.
– as a result of infection with or exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, but some dermatologists question if the skin signs and symptoms are truly related.
In their commentary in the Lancet Infectious Diseases, Esther P. Freeman, MD, PhD, and colleagues who lead and participate in the American Academy of Dermatology’s international registry said their analysis “revealed a previously unreported subset of patients who experience long-haul symptoms in dermatology-dominant COVID-19.”
Some of the data was presented at the 29th European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology in late October 2020, but has since been updated with more cases.
Dermatologists who spoke with this news organization said it has not been settled that some skin manifestations – such as pernio/chilblains rashes, seen primarily in nonhospitalized patients, and described in the registry – are definitively caused by COVID. They also noted that in some cases, patients who initially test negative for COVID-19 by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) sometimes do not ever develop antibodies, which could mean they were never actually exposed to SARS-CoV-2.
“I still question whether the perniosis is directly related to infection with SARS-CoV-2 or not,” said Anthony Fernandez, MD, PhD, director of medical and inpatient dermatology and assistant professor of dermatopathology at the Cleveland Clinic. His uncertainty is driven by the lack of seroconversion and that few cases were seen over the summer in the United States – suggesting that it may still be a result of cold temperatures.
“I’m not sure there is a definitive correct answer, definitely not that everyone would agree on,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Freeman, however, believed that pernio and especially persistent lesions are caused by an immune response to COVID.
In an interview, she noted the multiple cases of patients in the registry who did seroconvert and that, while a registry is not a perfect means of getting an answer, it is good for generating questions. Taken collectively, the cases in the registry can “tell a story for further hypotheses,” said Dr. Freeman, who is director of global health dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital and assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard University, both in Boston.
“We were noticing this signal across the world” that patients “developed these toe lesions and they never got better,” said Dr. Freeman. Generally, people who experience pernio, also described as COVID toes or “COVID fingers,” recover in 4-8 weeks. But in the registry, “we did have this subset of patients who really were experiencing these very longstanding symptoms,” she added.
Two patients with lab-confirmed COVID have had long-lasting pernio of 133 days and 150 days. “I’m caring for a cohort in Boston who have had long COVID of the skin and symptoms for over 10 months,” Dr. Freeman said.
Pernio dominates
The registry – a collaboration between the AAD and the International League of Dermatological Societies – was launched in April 2020. Any medical professional can enter case information. From April to October, 1,030 total cases and 331 laboratory-confirmed or suspected COVID-19 cases with dermatological manifestations were entered from 41 countries.
Most of the cases were just recorded at a single time point, which is an acknowledged limitation of the study.
Dr. Freeman and colleagues reached out to registry participants in June and August to get updates on COVID lab test results and sign and symptom duration. Overall, 234 total and 96 lab-confirmed COVID infections had more lengthy data about sign and symptom duration.
Pernio lasted a median of 15 days in patients with suspected disease and 12 days for those with lab-confirmed COVID, compared with a median of 7 days for morbilliform eruptions, 4 days for urticarial eruptions, and 20 days for papulosquamous eruptions – all in patients with lab-confirmed disease.
Of the 103 cases of pernio, 7 had symptoms lasting more than 60 days. Only two of those seven patients had lab-confirmed COVID. Initially, the one patient tested negative with nasopharyngeal PCR, and serum IgM and IgG. Six weeks after pernio onset, the patient – still experiencing fatigue and pernio – seroconverted to anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgM positivity.
The other long-haul patient, after a negative PCR, tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 serum IgG 1 month after pernio onset.
Robust immune response?
Dr. Freeman said these patients might have a very high interferon response initially to the virus, which makes for a mild to nonexistent disease, but could create inflammation elsewhere. “I almost view the toes as an innocent bystander of a robust immune response to SARS-CoV-2.”
Although he has not seen extended pernio or other skin manifestations in his patients, Dr. Fernandez said the interferon hypothesis is “fair,” and “the best that’s out there.” Dr. Fernandez is currently studying cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 as a principal investigator of a trial sponsored by the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative of Cleveland.
Dr. Ko said in an interview that she has not observed long-haul skin issues in her patients, but Yale colleagues have.
In a study, she and Yale colleagues published in September, SARS-CoV-2 spike protein was detected in perniotic lesions, but not nuclear protein or viral RNA. The test they used – immunohistochemistry – can be nonspecific, which muddied results.
She does not think there is replicating virus in the skin or the lesions. Instead, said Dr. Ko, “either there is viral spike protein that has somehow become disassociated from actively replicating virus that somehow got deposited in endothelial cells,” or the staining “was spurious,” or some other protein is cross-reacting. “And the people who are unlucky enough to have that protein in their endothelial cells can manifest this COVID-toe, COVID-finger phenomenon.”
To her, it’s an unsolved mystery. “The weird thing is, we’ve never before had this much perniosis,” Dr. Ko said.
Dr. Fernandez is not convinced yet, noting that, in Cleveland, more pernio cases were observed in March and April than in the summer. “If it is a manifestation of the infection then you also need the right environment, the cold weather for this manifestation to present,” he said. “Or, it really isn’t a direct manifestation of COVID-19 but may be more related to other factors,” such as lifestyle changes related to limitations implemented to help mitigate the spread of the disease.
“To me the jury is still out whether or not the perniotic lesions really can tell us something about a patient’s exposure and infection with SARS-CoV-2,” he said.
Dr. Freeman reported receiving a grant from the International League of Dermatological Societies and nonfinancial support from the AAD for the study. Dr. Ko reported no conflicts. Dr. Fernadnez had no disclosures.
FROM THE LANCET INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Menopause, not aging, may influence brain volume
Postmenopausal women not only have larger brain volume than women who are premenopausal, but they also experience larger reductions in brain volume over time, reported Ananthan Ambikairajah of the Centre for Research on Ageing, Health and Wellbeing, Australian National University, Canberra, and associates. Their report was published in Menopause.
In this large population-based cohort of 5,072 women aged 37-73 years, the goal of the study was to look at links between brain volume and measures of menstruation history, such as menopausal status, age at menopause, age at menarche, and the duration of a woman’s reproductive stage, but to do so within the context of how it relates to dementia prevalence. Citing a study in The Lancet Neurology, the authors noted that the age-standardized prevalence for dementia is 17% higher in women than in men, and they speculated that it may be important to look beyond age for answers.
What about menstrual history and Alzheimer’s disease?
According to the Framingham Study in Neurology, the remaining lifetime risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is nearly double for a 65-year-old woman (12%) compared with a 65-year-old man (6.3%), leading Mr. Ambikairajah and associates to conclude that “menstruation history may also be particularly relevant, given that it is unique to female aging.” They further speculated, citing several related studies, that because AD pathology is initiated decades prior to the onset of clinical signs, menstruation history and its effects on brain health may, in fact, be reflected in brain volume.
Postmenopausal women had 0.82% and 1.33% larger total brain and hippocampal volume, respectively, compared with premenopausal women. Postmenopausal women had a 23% greater decrease in total brain volume but not in hippocampal volume over time, compared with premenopausal women.
As Braak and Braak illustrated in Acta Neuropathologica, chronic inflammation has been linked to brain shrinkage “consistent with the pattern of results in the present study,” Mr. Ambikairajah and colleagues noted, adding that longitudinal neuroimaging/biomarker studies are needed to explore this further.
What made this study unique was its ability to match pre- and postmenopausal women for age, a critically important attribute “given that aging and menopause both progress concurrently, which can make it difficult to determine the individual contribution of each for measures of brain health,” the authors explained.
In an interview, Constance Bohon, MD, an ob.gyn. in private practice and assistant clinical professor, George Washington University, Washington, observed: “The conclusion [in this study] is that an early age of menarche, delayed age of menopause and increased duration of the reproductive stage is negatively associated with brain volume.”
What of the neuroprotective effects of endogenous estrogen?
“Their findings are not consistent with a neuroprotective effect of endogenous estrogen exposure on brain volume,” she noted, adding that the study “did not assess the effect of exogenous estrogen on brain volume. Neither was the effect of exogenous or endogenous estrogen on cerebral blood flow assessed. In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the conclusion was that oophorectomy before the age of natural menopause is associated with a decrease in cognitive impairment and dementia. There was no assessment of brain volume or cerebral blood flow. Likewise in a report published in Neurobiology of Aging, Maki P and Resnick S M. concluded that estrogen helps maintain hippocampal and prefrontal function as women age,” observed Dr. Bohon, noting that the study did not assess brain volume.
“It is unclear whether the most predictive assessment for worsening cognition and dementia is the finding of decreased total brain volume, decreased hippocampal volume, or decreased cerebral blood flow. The effect of both endogenous and exogenous estrogen on the risk for dementia needs further evaluation,” she cautioned.
Mr. Ambikairajah cited one financial disclosure; the remaining contributors had no relevant disclosures.
Postmenopausal women not only have larger brain volume than women who are premenopausal, but they also experience larger reductions in brain volume over time, reported Ananthan Ambikairajah of the Centre for Research on Ageing, Health and Wellbeing, Australian National University, Canberra, and associates. Their report was published in Menopause.
In this large population-based cohort of 5,072 women aged 37-73 years, the goal of the study was to look at links between brain volume and measures of menstruation history, such as menopausal status, age at menopause, age at menarche, and the duration of a woman’s reproductive stage, but to do so within the context of how it relates to dementia prevalence. Citing a study in The Lancet Neurology, the authors noted that the age-standardized prevalence for dementia is 17% higher in women than in men, and they speculated that it may be important to look beyond age for answers.
What about menstrual history and Alzheimer’s disease?
According to the Framingham Study in Neurology, the remaining lifetime risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is nearly double for a 65-year-old woman (12%) compared with a 65-year-old man (6.3%), leading Mr. Ambikairajah and associates to conclude that “menstruation history may also be particularly relevant, given that it is unique to female aging.” They further speculated, citing several related studies, that because AD pathology is initiated decades prior to the onset of clinical signs, menstruation history and its effects on brain health may, in fact, be reflected in brain volume.
Postmenopausal women had 0.82% and 1.33% larger total brain and hippocampal volume, respectively, compared with premenopausal women. Postmenopausal women had a 23% greater decrease in total brain volume but not in hippocampal volume over time, compared with premenopausal women.
As Braak and Braak illustrated in Acta Neuropathologica, chronic inflammation has been linked to brain shrinkage “consistent with the pattern of results in the present study,” Mr. Ambikairajah and colleagues noted, adding that longitudinal neuroimaging/biomarker studies are needed to explore this further.
What made this study unique was its ability to match pre- and postmenopausal women for age, a critically important attribute “given that aging and menopause both progress concurrently, which can make it difficult to determine the individual contribution of each for measures of brain health,” the authors explained.
In an interview, Constance Bohon, MD, an ob.gyn. in private practice and assistant clinical professor, George Washington University, Washington, observed: “The conclusion [in this study] is that an early age of menarche, delayed age of menopause and increased duration of the reproductive stage is negatively associated with brain volume.”
What of the neuroprotective effects of endogenous estrogen?
“Their findings are not consistent with a neuroprotective effect of endogenous estrogen exposure on brain volume,” she noted, adding that the study “did not assess the effect of exogenous estrogen on brain volume. Neither was the effect of exogenous or endogenous estrogen on cerebral blood flow assessed. In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the conclusion was that oophorectomy before the age of natural menopause is associated with a decrease in cognitive impairment and dementia. There was no assessment of brain volume or cerebral blood flow. Likewise in a report published in Neurobiology of Aging, Maki P and Resnick S M. concluded that estrogen helps maintain hippocampal and prefrontal function as women age,” observed Dr. Bohon, noting that the study did not assess brain volume.
“It is unclear whether the most predictive assessment for worsening cognition and dementia is the finding of decreased total brain volume, decreased hippocampal volume, or decreased cerebral blood flow. The effect of both endogenous and exogenous estrogen on the risk for dementia needs further evaluation,” she cautioned.
Mr. Ambikairajah cited one financial disclosure; the remaining contributors had no relevant disclosures.
Postmenopausal women not only have larger brain volume than women who are premenopausal, but they also experience larger reductions in brain volume over time, reported Ananthan Ambikairajah of the Centre for Research on Ageing, Health and Wellbeing, Australian National University, Canberra, and associates. Their report was published in Menopause.
In this large population-based cohort of 5,072 women aged 37-73 years, the goal of the study was to look at links between brain volume and measures of menstruation history, such as menopausal status, age at menopause, age at menarche, and the duration of a woman’s reproductive stage, but to do so within the context of how it relates to dementia prevalence. Citing a study in The Lancet Neurology, the authors noted that the age-standardized prevalence for dementia is 17% higher in women than in men, and they speculated that it may be important to look beyond age for answers.
What about menstrual history and Alzheimer’s disease?
According to the Framingham Study in Neurology, the remaining lifetime risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is nearly double for a 65-year-old woman (12%) compared with a 65-year-old man (6.3%), leading Mr. Ambikairajah and associates to conclude that “menstruation history may also be particularly relevant, given that it is unique to female aging.” They further speculated, citing several related studies, that because AD pathology is initiated decades prior to the onset of clinical signs, menstruation history and its effects on brain health may, in fact, be reflected in brain volume.
Postmenopausal women had 0.82% and 1.33% larger total brain and hippocampal volume, respectively, compared with premenopausal women. Postmenopausal women had a 23% greater decrease in total brain volume but not in hippocampal volume over time, compared with premenopausal women.
As Braak and Braak illustrated in Acta Neuropathologica, chronic inflammation has been linked to brain shrinkage “consistent with the pattern of results in the present study,” Mr. Ambikairajah and colleagues noted, adding that longitudinal neuroimaging/biomarker studies are needed to explore this further.
What made this study unique was its ability to match pre- and postmenopausal women for age, a critically important attribute “given that aging and menopause both progress concurrently, which can make it difficult to determine the individual contribution of each for measures of brain health,” the authors explained.
In an interview, Constance Bohon, MD, an ob.gyn. in private practice and assistant clinical professor, George Washington University, Washington, observed: “The conclusion [in this study] is that an early age of menarche, delayed age of menopause and increased duration of the reproductive stage is negatively associated with brain volume.”
What of the neuroprotective effects of endogenous estrogen?
“Their findings are not consistent with a neuroprotective effect of endogenous estrogen exposure on brain volume,” she noted, adding that the study “did not assess the effect of exogenous estrogen on brain volume. Neither was the effect of exogenous or endogenous estrogen on cerebral blood flow assessed. In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the conclusion was that oophorectomy before the age of natural menopause is associated with a decrease in cognitive impairment and dementia. There was no assessment of brain volume or cerebral blood flow. Likewise in a report published in Neurobiology of Aging, Maki P and Resnick S M. concluded that estrogen helps maintain hippocampal and prefrontal function as women age,” observed Dr. Bohon, noting that the study did not assess brain volume.
“It is unclear whether the most predictive assessment for worsening cognition and dementia is the finding of decreased total brain volume, decreased hippocampal volume, or decreased cerebral blood flow. The effect of both endogenous and exogenous estrogen on the risk for dementia needs further evaluation,” she cautioned.
Mr. Ambikairajah cited one financial disclosure; the remaining contributors had no relevant disclosures.
FROM MENOPAUSE
CDC: 20% of people in the U.S. are infected with an STD
Among the more than 320 million people in the United States, there was a prevalence estimate of 67.6 million sexually transmitted infections at the time of assessment in 2018, according to the results of an epidemiologic study using multiple data sources, including the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
In addition, almost half of the incident STIs occurred in the 15- to 24-year age bracket, according to a report published online in Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Researchers estimated the combined number of prevalent and incident infections of eight STIs in the United States in 2018: chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, syphilis, genital herpes (caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 [HSV-2]), human papillomavirus (HPV), sexually transmitted hepatitis B virus (HBV), and sexually transmitted HIV.
The estimated incidences of these STIs in this update, the first since 2008, were made using more recent data and improved estimation methods to provide updated STI prevalence and incidence estimates for 2018, both overall and by disease. “Having a combined estimate is crucial for policy purposes to illustrate the importance of STIs in the United States,” according to Kristen M. Kreisel, PhD, an epidemiologist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, division of STD prevention, and colleagues.
The number of prevalent and incident infections were obtained by multiplying each STI’s updated per capita estimates by the 2018 full resident population estimates from the American Community Survey.
Detailed results
Chlamydia. The prevalence of chlamydia was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. There were an estimated 2.4 million prevalent urogenital chlamydial infections among persons aged 15-39 years in 2018; 1.1 and 1.3 million infections among men and women, respectively. Individuals aged 15-24 years comprised 56.7% and 75.8% of all infections in men and women respectively.
Gonorrhea. The prevalence of gonorrhea was estimated using ordinary differential equation based modeling. The number of prevalent urogenital gonococcal infections in 2018 among 15- to 39-year-olds was 209,000 overall; 50,000 in men and 155,000 in women. Of these, 113,000 (54.1%) occurred in 15- to 24-year-olds.
Trichomoniasis. The prevalence of trichomoniasis was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. The number of prevalent Trichomonas infections among 15- to 59-year-olds was 2.6 million, with 470,000 in men and 2.1 million in women. Persons aged 15-24 years comprised 15.6% of all prevalent infections, according to the authors.
Syphilis. The number of estimated prevalent syphilitic infections (all stages) among 14- to 49-year-old persons in 2018 was 156,000, with infections in men comprising 71.8% of all infections. Infections in both men and women aged 14-24 years accounted for about 25% of all infections, with 36,000 total prevalent syphilitic infections among 14- to 24-year-olds in 2018.
Genital herpes. The prevalence of genital herpes (caused by HSV-2) was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, according to the authors. In persons aged 15-49 years in 2018, there were 18.6 million prevalent HSV-2 infections; 6.4 million among men and 12.2 million among women. Infections in 15- to 24-year-olds comprised 7.1% of all prevalent HSV-2 infections.
HPV. The prevalence of HPV was estimated using 2013-2016 NHANES data, which was assumed to reflect stable prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. Among 15- to 59-year-olds, the estimated number of persons, men, and women infected with one or more disease-associated HPV types in 2018 was 42.5, 23.4, and 19.2 million, respectively, with an estimated 9.0 million (21%) 15- to 24-year-olds infected,
HBV. NHANES 2013-2018 data were used to estimate the prevalence of sexually transmitted chronic HBV infections in 2018, according to the authors. The estimated number of infections among persons aged 15 years and older in 2018 was 103,000 (51,000 men and 52,000 women). There small sample size of individuals aged 15-24 years in the NHANES database made it impossible to obtain an accurate estimate for this group, according to the authors.
HIV. Data from the National HIV Surveillance System were used to estimate the prevalence and incidence of sexually transmitted HIV infections for persons aged 13 years and older in 2018. A total of 984,000 individuals aged 13 years and older were estimated to be living with sexually transmitted HIV at the end of 2018, according to the authors. Nearly 80% were men. In the 13- to 24-year-old age bracket, there were an estimated 45,400 living with sexually transmitted HIV.
Billions in costs
Commenting on the study by the CDC researchers, Raul Romaguera, acting director for CDC’s division of STD prevention, stated in a press release: “There are significant human and financial costs associated with these infections, and we know from other studies that cuts in STI prevention efforts result in higher costs down the road. Preventing STIs could save billions in medical costs, but more importantly, prevention would improve the health and lives of millions of people.”
“About 20% of the total U.S. population had an STI at a given point in 2018, while nearly half of all incident infections occurred in people aged 15-24 years. Focusing STI prevention efforts on the 15- to 24-year-old population may be key to lowering the STI burden in the U.S.,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
Among the more than 320 million people in the United States, there was a prevalence estimate of 67.6 million sexually transmitted infections at the time of assessment in 2018, according to the results of an epidemiologic study using multiple data sources, including the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
In addition, almost half of the incident STIs occurred in the 15- to 24-year age bracket, according to a report published online in Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Researchers estimated the combined number of prevalent and incident infections of eight STIs in the United States in 2018: chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, syphilis, genital herpes (caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 [HSV-2]), human papillomavirus (HPV), sexually transmitted hepatitis B virus (HBV), and sexually transmitted HIV.
The estimated incidences of these STIs in this update, the first since 2008, were made using more recent data and improved estimation methods to provide updated STI prevalence and incidence estimates for 2018, both overall and by disease. “Having a combined estimate is crucial for policy purposes to illustrate the importance of STIs in the United States,” according to Kristen M. Kreisel, PhD, an epidemiologist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, division of STD prevention, and colleagues.
The number of prevalent and incident infections were obtained by multiplying each STI’s updated per capita estimates by the 2018 full resident population estimates from the American Community Survey.
Detailed results
Chlamydia. The prevalence of chlamydia was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. There were an estimated 2.4 million prevalent urogenital chlamydial infections among persons aged 15-39 years in 2018; 1.1 and 1.3 million infections among men and women, respectively. Individuals aged 15-24 years comprised 56.7% and 75.8% of all infections in men and women respectively.
Gonorrhea. The prevalence of gonorrhea was estimated using ordinary differential equation based modeling. The number of prevalent urogenital gonococcal infections in 2018 among 15- to 39-year-olds was 209,000 overall; 50,000 in men and 155,000 in women. Of these, 113,000 (54.1%) occurred in 15- to 24-year-olds.
Trichomoniasis. The prevalence of trichomoniasis was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. The number of prevalent Trichomonas infections among 15- to 59-year-olds was 2.6 million, with 470,000 in men and 2.1 million in women. Persons aged 15-24 years comprised 15.6% of all prevalent infections, according to the authors.
Syphilis. The number of estimated prevalent syphilitic infections (all stages) among 14- to 49-year-old persons in 2018 was 156,000, with infections in men comprising 71.8% of all infections. Infections in both men and women aged 14-24 years accounted for about 25% of all infections, with 36,000 total prevalent syphilitic infections among 14- to 24-year-olds in 2018.
Genital herpes. The prevalence of genital herpes (caused by HSV-2) was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, according to the authors. In persons aged 15-49 years in 2018, there were 18.6 million prevalent HSV-2 infections; 6.4 million among men and 12.2 million among women. Infections in 15- to 24-year-olds comprised 7.1% of all prevalent HSV-2 infections.
HPV. The prevalence of HPV was estimated using 2013-2016 NHANES data, which was assumed to reflect stable prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. Among 15- to 59-year-olds, the estimated number of persons, men, and women infected with one or more disease-associated HPV types in 2018 was 42.5, 23.4, and 19.2 million, respectively, with an estimated 9.0 million (21%) 15- to 24-year-olds infected,
HBV. NHANES 2013-2018 data were used to estimate the prevalence of sexually transmitted chronic HBV infections in 2018, according to the authors. The estimated number of infections among persons aged 15 years and older in 2018 was 103,000 (51,000 men and 52,000 women). There small sample size of individuals aged 15-24 years in the NHANES database made it impossible to obtain an accurate estimate for this group, according to the authors.
HIV. Data from the National HIV Surveillance System were used to estimate the prevalence and incidence of sexually transmitted HIV infections for persons aged 13 years and older in 2018. A total of 984,000 individuals aged 13 years and older were estimated to be living with sexually transmitted HIV at the end of 2018, according to the authors. Nearly 80% were men. In the 13- to 24-year-old age bracket, there were an estimated 45,400 living with sexually transmitted HIV.
Billions in costs
Commenting on the study by the CDC researchers, Raul Romaguera, acting director for CDC’s division of STD prevention, stated in a press release: “There are significant human and financial costs associated with these infections, and we know from other studies that cuts in STI prevention efforts result in higher costs down the road. Preventing STIs could save billions in medical costs, but more importantly, prevention would improve the health and lives of millions of people.”
“About 20% of the total U.S. population had an STI at a given point in 2018, while nearly half of all incident infections occurred in people aged 15-24 years. Focusing STI prevention efforts on the 15- to 24-year-old population may be key to lowering the STI burden in the U.S.,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
Among the more than 320 million people in the United States, there was a prevalence estimate of 67.6 million sexually transmitted infections at the time of assessment in 2018, according to the results of an epidemiologic study using multiple data sources, including the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
In addition, almost half of the incident STIs occurred in the 15- to 24-year age bracket, according to a report published online in Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Researchers estimated the combined number of prevalent and incident infections of eight STIs in the United States in 2018: chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, syphilis, genital herpes (caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 [HSV-2]), human papillomavirus (HPV), sexually transmitted hepatitis B virus (HBV), and sexually transmitted HIV.
The estimated incidences of these STIs in this update, the first since 2008, were made using more recent data and improved estimation methods to provide updated STI prevalence and incidence estimates for 2018, both overall and by disease. “Having a combined estimate is crucial for policy purposes to illustrate the importance of STIs in the United States,” according to Kristen M. Kreisel, PhD, an epidemiologist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, division of STD prevention, and colleagues.
The number of prevalent and incident infections were obtained by multiplying each STI’s updated per capita estimates by the 2018 full resident population estimates from the American Community Survey.
Detailed results
Chlamydia. The prevalence of chlamydia was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. There were an estimated 2.4 million prevalent urogenital chlamydial infections among persons aged 15-39 years in 2018; 1.1 and 1.3 million infections among men and women, respectively. Individuals aged 15-24 years comprised 56.7% and 75.8% of all infections in men and women respectively.
Gonorrhea. The prevalence of gonorrhea was estimated using ordinary differential equation based modeling. The number of prevalent urogenital gonococcal infections in 2018 among 15- to 39-year-olds was 209,000 overall; 50,000 in men and 155,000 in women. Of these, 113,000 (54.1%) occurred in 15- to 24-year-olds.
Trichomoniasis. The prevalence of trichomoniasis was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. The number of prevalent Trichomonas infections among 15- to 59-year-olds was 2.6 million, with 470,000 in men and 2.1 million in women. Persons aged 15-24 years comprised 15.6% of all prevalent infections, according to the authors.
Syphilis. The number of estimated prevalent syphilitic infections (all stages) among 14- to 49-year-old persons in 2018 was 156,000, with infections in men comprising 71.8% of all infections. Infections in both men and women aged 14-24 years accounted for about 25% of all infections, with 36,000 total prevalent syphilitic infections among 14- to 24-year-olds in 2018.
Genital herpes. The prevalence of genital herpes (caused by HSV-2) was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, according to the authors. In persons aged 15-49 years in 2018, there were 18.6 million prevalent HSV-2 infections; 6.4 million among men and 12.2 million among women. Infections in 15- to 24-year-olds comprised 7.1% of all prevalent HSV-2 infections.
HPV. The prevalence of HPV was estimated using 2013-2016 NHANES data, which was assumed to reflect stable prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. Among 15- to 59-year-olds, the estimated number of persons, men, and women infected with one or more disease-associated HPV types in 2018 was 42.5, 23.4, and 19.2 million, respectively, with an estimated 9.0 million (21%) 15- to 24-year-olds infected,
HBV. NHANES 2013-2018 data were used to estimate the prevalence of sexually transmitted chronic HBV infections in 2018, according to the authors. The estimated number of infections among persons aged 15 years and older in 2018 was 103,000 (51,000 men and 52,000 women). There small sample size of individuals aged 15-24 years in the NHANES database made it impossible to obtain an accurate estimate for this group, according to the authors.
HIV. Data from the National HIV Surveillance System were used to estimate the prevalence and incidence of sexually transmitted HIV infections for persons aged 13 years and older in 2018. A total of 984,000 individuals aged 13 years and older were estimated to be living with sexually transmitted HIV at the end of 2018, according to the authors. Nearly 80% were men. In the 13- to 24-year-old age bracket, there were an estimated 45,400 living with sexually transmitted HIV.
Billions in costs
Commenting on the study by the CDC researchers, Raul Romaguera, acting director for CDC’s division of STD prevention, stated in a press release: “There are significant human and financial costs associated with these infections, and we know from other studies that cuts in STI prevention efforts result in higher costs down the road. Preventing STIs could save billions in medical costs, but more importantly, prevention would improve the health and lives of millions of people.”
“About 20% of the total U.S. population had an STI at a given point in 2018, while nearly half of all incident infections occurred in people aged 15-24 years. Focusing STI prevention efforts on the 15- to 24-year-old population may be key to lowering the STI burden in the U.S.,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
FROM SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
Intraoperative rupture of ovarian cancer: Does it worsen outcomes?
Intact removal of an ovarian cyst is a well-established gynecologic surgical principle because ovarian cancer is definitively diagnosed only in retrospect (after ovarian extraction) and intraoperative cyst rupture upstages an otherwise nonmetastatic cancer to stage IC. This lumps cancers that are ruptured during surgical extraction together with those that have spontaneously ruptured or have surface excrescences. The theoretical rationale for this “lumping” is that contact between malignant cells from the ruptured cyst may take hold on peritoneal surfaces resulting in development of metastases. To offset this theoretical risk, it has been recommended that all stage IC ovarian cancer is treated with chemotherapy, whereas low-grade stage IA and IB cancers generally are not. No conscientious surgeon wants their surgical intervention to be the cause of a patient needing toxic chemotherapy. But is the contact between malignant cyst fluid and the peritoneum truly as bad as a spontaneous breach of the surface of the tumor? Or is cyst rupture a confounder for other adverse prognostic features, such as histologic cell type and dense pelvic attachments? If ovarian cyst rupture is an independent risk factor for patients with stage I ovarian cancer, strategies should be employed to avoid this occurrence, and we should understand how to counsel and treat patients in whom this has occurred.
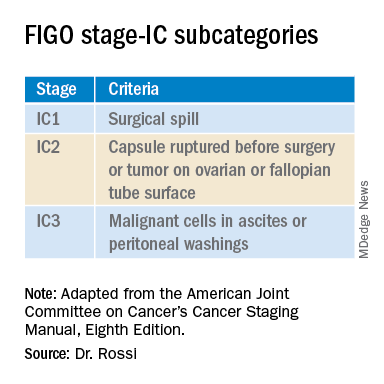
In 2017 the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) staging of epithelial ovarian cancer subcategorized stage IC. This group encompasses women with contact between malignant cells and the peritoneum in the absence of other extraovarian disease. The table includes these distinct groupings. Stage IC1 includes patients in whom intraoperative spill occurred. Stage IC2 includes women with preoperative cyst rupture, and or microscopic or macroscopic surface involvement because the data support that these cases carry a poorer prognosis, compared with those with intraoperative rupture (IC1).1 The final subcategory, IC3, includes women who have washings (obtained at the onset of surgery, prior to manipulation of the tumor) that were positive for malignant cells, denoting preexisting contact between the tumor and peritoneum and a phenotypically more aggressive tumor.
The clinical significance of ovarian cancer capsule rupture has been evaluated in multiple studies with some mixed results.1 Consistently, it is reported that preoperative rupture, surface or capsular involvement, and preexisting peritoneal circulation of metastatic cells all portend a poorer prognosis; however, it is less clear that iatrogenic surgical rupture has the same deleterious association. In a large retrospective series from Japan, the authors evaluated 15,163 cases of stage I ovarian cancer and identified 7,227 cases of iatrogenic (intraoperative) cyst rupture.2 These cases were significantly more likely to occur among clear cell cancers, and were more likely to occur in younger patients. Worse prognosis was associated with cell type (clear cell cancers), but non–clear cell cancers (such as serous, mucinous, and endometrioid) did not have a higher hazard ratio for death when intraoperative rupture occurred. But why would intraoperative cyst rupture result in worse prognosis for only one histologic cell type? The authors hypothesized that perhaps rupture was more likely to occur during extraction of these clear cell tumors because they were associated with dense adhesions from associated endometriosis, and perhaps an adverse biologic phenomenon associated with infiltrative endometriosis is driving the behavior of this cancer.
The Japanese study also looked at the effect of chemotherapy on these same patients’ outcomes. Interestingly, the addition of chemotherapy did not improve survival for the patients with stage IC1 cancers, which was in contrast to the improved survival seen when chemotherapy was given to those with spontaneous rupture or ovarian surface involvement (IC2, IC3). These data support differentiating the subgroups of stage IC cancer in treatment decision-making, and suggest that adjuvant chemotherapy might be avoided for patients with nonclear cell stage IC1 ovarian cancer. While the outcomes are worse for patients with ruptured clear cell cancers, current therapeutic options for clear cell cancers are limited because of their known resistance to traditional agents, and outcomes for women with clear cell cancer can be worse across all stages.
While cyst rupture may not always negatively affect prognosis, the goal of surgery remains an intact removal, which influences decisions regarding surgical approach. Most adnexal masses are removed via minimally invasive surgery (MIS). MIS is associated with benefits of morbidity and cost, and therefore should be considered wherever feasible. However, MIS is associated with an increased risk of ovarian cyst rupture, likely because of the rigid instrumentation used when approaching a curved structure, in addition to the disparity in size of the pathology, compared with the extraction site incision.3 When weighing the benefits and risks of different surgical approaches, it is important to gauge the probability of malignancy. Not all complex ovarian masses associated with elevations in tumor markers are malignant, and certainly most that are associated with normal tumor markers are not. If the preoperative clinical data suggest that the mass is more likely to be malignant (e.g., mostly solid, vascular tumors with very elevated tumor markers), consideration might be made to abandoning a purely minimally invasive approach to a hand-assisted MIS or laparotomy approach. However, it would seem that abandoning an MIS approach to remove every ovarian cyst is unwise given that there is clear patient benefit with MIS and, as discussed above, most cases of iatrogenic malignant cyst rupture are unavoidable even with laparotomy, and do not necessarily independently portend poorer survival or mandate chemotherapy.
Surgeons should be both nuanced and flexible and apply some basic rules of thumb when approaching the diagnostically uncertain adnexal mass. Peritoneal washings should be obtained at the commencement of the case to discriminate those cases of true stage IC3. The peritoneum parallel to the ovarian vessel should be extensively opened to a level above the pelvic brim. In order to do this, the physiological attachments between the sigmoid colon or cecum and the suspensory ligament of the ovary may need to be carefully mobilized. This allows for retroperitoneal identification of the ureter and skeletonization of the ovarian vessels at least 2 cm proximal to their insertion into the ovary and avoidance of contact with the ovary itself (which may have a fragile capsule) or incomplete ovarian resection. If the ovary remains invested close to the sidewall or colonic structures and the appropriate peritoneal and retroperitoneal mobilization has not occurred, the surgeon may unavoidably rupture the ovarian cyst as they try to “hug” the ovary with their bites of tissue in an attempt to avoid visceral injury. There is little role for an ovarian cystectomy in a postmenopausal woman undergoing surgery for a complex adnexal mass, particularly if she has elevated tumor markers, because the process of performing ovarian cystectomy commonly invokes cyst rupture or fragmentation. Ovarian cystectomy should be reserved for premenopausal women with adnexal masses at low suspicion for malignancy. If the adnexa appears densely adherent to adjacent structures – for example, associated with infiltrative endometriosis – consideration for laparotomy or a hand-assisted approach may be necessary; in such cases, even open surgery can result in cyst rupture, and the morbidity of conversion to laparotomy should be weighed for individual cases.
Finally, retrieval of the ovarian specimen should occur intact without morcellation. There should be no uncontained morcellation of adnexal structures during retrieval of even normal-appearing ovaries. The preferred retrieval method is to place the adnexa in an appropriately sized retrieval bag, after which contained morcellation or drainage can occur to facilitate removal through a laparoscopic incision. Contained morcellation is very difficult for large solid masses through a laparoscopic port site; in these cases, extension of the incision may be necessary.
While operative spill of an ovarian cancer does upstage nonmetastatic ovarian cancer, it is unclear that, in most cases, this is independently associated with worse prognosis, and chemotherapy may not always be of added value. However, best surgical practice should always include strategies to minimize the chance of rupture when approaching adnexal masses, particularly those at highest likelihood of malignancy.
References
1. Kim HS et al. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2013 Mar 39(3):279-89.
2. Matsuo K et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Nov;134(5):1017-26.
3. Matsuo K et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jul 1;6(7):1110-3.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Intact removal of an ovarian cyst is a well-established gynecologic surgical principle because ovarian cancer is definitively diagnosed only in retrospect (after ovarian extraction) and intraoperative cyst rupture upstages an otherwise nonmetastatic cancer to stage IC. This lumps cancers that are ruptured during surgical extraction together with those that have spontaneously ruptured or have surface excrescences. The theoretical rationale for this “lumping” is that contact between malignant cells from the ruptured cyst may take hold on peritoneal surfaces resulting in development of metastases. To offset this theoretical risk, it has been recommended that all stage IC ovarian cancer is treated with chemotherapy, whereas low-grade stage IA and IB cancers generally are not. No conscientious surgeon wants their surgical intervention to be the cause of a patient needing toxic chemotherapy. But is the contact between malignant cyst fluid and the peritoneum truly as bad as a spontaneous breach of the surface of the tumor? Or is cyst rupture a confounder for other adverse prognostic features, such as histologic cell type and dense pelvic attachments? If ovarian cyst rupture is an independent risk factor for patients with stage I ovarian cancer, strategies should be employed to avoid this occurrence, and we should understand how to counsel and treat patients in whom this has occurred.

In 2017 the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) staging of epithelial ovarian cancer subcategorized stage IC. This group encompasses women with contact between malignant cells and the peritoneum in the absence of other extraovarian disease. The table includes these distinct groupings. Stage IC1 includes patients in whom intraoperative spill occurred. Stage IC2 includes women with preoperative cyst rupture, and or microscopic or macroscopic surface involvement because the data support that these cases carry a poorer prognosis, compared with those with intraoperative rupture (IC1).1 The final subcategory, IC3, includes women who have washings (obtained at the onset of surgery, prior to manipulation of the tumor) that were positive for malignant cells, denoting preexisting contact between the tumor and peritoneum and a phenotypically more aggressive tumor.
The clinical significance of ovarian cancer capsule rupture has been evaluated in multiple studies with some mixed results.1 Consistently, it is reported that preoperative rupture, surface or capsular involvement, and preexisting peritoneal circulation of metastatic cells all portend a poorer prognosis; however, it is less clear that iatrogenic surgical rupture has the same deleterious association. In a large retrospective series from Japan, the authors evaluated 15,163 cases of stage I ovarian cancer and identified 7,227 cases of iatrogenic (intraoperative) cyst rupture.2 These cases were significantly more likely to occur among clear cell cancers, and were more likely to occur in younger patients. Worse prognosis was associated with cell type (clear cell cancers), but non–clear cell cancers (such as serous, mucinous, and endometrioid) did not have a higher hazard ratio for death when intraoperative rupture occurred. But why would intraoperative cyst rupture result in worse prognosis for only one histologic cell type? The authors hypothesized that perhaps rupture was more likely to occur during extraction of these clear cell tumors because they were associated with dense adhesions from associated endometriosis, and perhaps an adverse biologic phenomenon associated with infiltrative endometriosis is driving the behavior of this cancer.
The Japanese study also looked at the effect of chemotherapy on these same patients’ outcomes. Interestingly, the addition of chemotherapy did not improve survival for the patients with stage IC1 cancers, which was in contrast to the improved survival seen when chemotherapy was given to those with spontaneous rupture or ovarian surface involvement (IC2, IC3). These data support differentiating the subgroups of stage IC cancer in treatment decision-making, and suggest that adjuvant chemotherapy might be avoided for patients with nonclear cell stage IC1 ovarian cancer. While the outcomes are worse for patients with ruptured clear cell cancers, current therapeutic options for clear cell cancers are limited because of their known resistance to traditional agents, and outcomes for women with clear cell cancer can be worse across all stages.
While cyst rupture may not always negatively affect prognosis, the goal of surgery remains an intact removal, which influences decisions regarding surgical approach. Most adnexal masses are removed via minimally invasive surgery (MIS). MIS is associated with benefits of morbidity and cost, and therefore should be considered wherever feasible. However, MIS is associated with an increased risk of ovarian cyst rupture, likely because of the rigid instrumentation used when approaching a curved structure, in addition to the disparity in size of the pathology, compared with the extraction site incision.3 When weighing the benefits and risks of different surgical approaches, it is important to gauge the probability of malignancy. Not all complex ovarian masses associated with elevations in tumor markers are malignant, and certainly most that are associated with normal tumor markers are not. If the preoperative clinical data suggest that the mass is more likely to be malignant (e.g., mostly solid, vascular tumors with very elevated tumor markers), consideration might be made to abandoning a purely minimally invasive approach to a hand-assisted MIS or laparotomy approach. However, it would seem that abandoning an MIS approach to remove every ovarian cyst is unwise given that there is clear patient benefit with MIS and, as discussed above, most cases of iatrogenic malignant cyst rupture are unavoidable even with laparotomy, and do not necessarily independently portend poorer survival or mandate chemotherapy.
Surgeons should be both nuanced and flexible and apply some basic rules of thumb when approaching the diagnostically uncertain adnexal mass. Peritoneal washings should be obtained at the commencement of the case to discriminate those cases of true stage IC3. The peritoneum parallel to the ovarian vessel should be extensively opened to a level above the pelvic brim. In order to do this, the physiological attachments between the sigmoid colon or cecum and the suspensory ligament of the ovary may need to be carefully mobilized. This allows for retroperitoneal identification of the ureter and skeletonization of the ovarian vessels at least 2 cm proximal to their insertion into the ovary and avoidance of contact with the ovary itself (which may have a fragile capsule) or incomplete ovarian resection. If the ovary remains invested close to the sidewall or colonic structures and the appropriate peritoneal and retroperitoneal mobilization has not occurred, the surgeon may unavoidably rupture the ovarian cyst as they try to “hug” the ovary with their bites of tissue in an attempt to avoid visceral injury. There is little role for an ovarian cystectomy in a postmenopausal woman undergoing surgery for a complex adnexal mass, particularly if she has elevated tumor markers, because the process of performing ovarian cystectomy commonly invokes cyst rupture or fragmentation. Ovarian cystectomy should be reserved for premenopausal women with adnexal masses at low suspicion for malignancy. If the adnexa appears densely adherent to adjacent structures – for example, associated with infiltrative endometriosis – consideration for laparotomy or a hand-assisted approach may be necessary; in such cases, even open surgery can result in cyst rupture, and the morbidity of conversion to laparotomy should be weighed for individual cases.
Finally, retrieval of the ovarian specimen should occur intact without morcellation. There should be no uncontained morcellation of adnexal structures during retrieval of even normal-appearing ovaries. The preferred retrieval method is to place the adnexa in an appropriately sized retrieval bag, after which contained morcellation or drainage can occur to facilitate removal through a laparoscopic incision. Contained morcellation is very difficult for large solid masses through a laparoscopic port site; in these cases, extension of the incision may be necessary.
While operative spill of an ovarian cancer does upstage nonmetastatic ovarian cancer, it is unclear that, in most cases, this is independently associated with worse prognosis, and chemotherapy may not always be of added value. However, best surgical practice should always include strategies to minimize the chance of rupture when approaching adnexal masses, particularly those at highest likelihood of malignancy.
References
1. Kim HS et al. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2013 Mar 39(3):279-89.
2. Matsuo K et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Nov;134(5):1017-26.
3. Matsuo K et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jul 1;6(7):1110-3.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Intact removal of an ovarian cyst is a well-established gynecologic surgical principle because ovarian cancer is definitively diagnosed only in retrospect (after ovarian extraction) and intraoperative cyst rupture upstages an otherwise nonmetastatic cancer to stage IC. This lumps cancers that are ruptured during surgical extraction together with those that have spontaneously ruptured or have surface excrescences. The theoretical rationale for this “lumping” is that contact between malignant cells from the ruptured cyst may take hold on peritoneal surfaces resulting in development of metastases. To offset this theoretical risk, it has been recommended that all stage IC ovarian cancer is treated with chemotherapy, whereas low-grade stage IA and IB cancers generally are not. No conscientious surgeon wants their surgical intervention to be the cause of a patient needing toxic chemotherapy. But is the contact between malignant cyst fluid and the peritoneum truly as bad as a spontaneous breach of the surface of the tumor? Or is cyst rupture a confounder for other adverse prognostic features, such as histologic cell type and dense pelvic attachments? If ovarian cyst rupture is an independent risk factor for patients with stage I ovarian cancer, strategies should be employed to avoid this occurrence, and we should understand how to counsel and treat patients in whom this has occurred.

In 2017 the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) staging of epithelial ovarian cancer subcategorized stage IC. This group encompasses women with contact between malignant cells and the peritoneum in the absence of other extraovarian disease. The table includes these distinct groupings. Stage IC1 includes patients in whom intraoperative spill occurred. Stage IC2 includes women with preoperative cyst rupture, and or microscopic or macroscopic surface involvement because the data support that these cases carry a poorer prognosis, compared with those with intraoperative rupture (IC1).1 The final subcategory, IC3, includes women who have washings (obtained at the onset of surgery, prior to manipulation of the tumor) that were positive for malignant cells, denoting preexisting contact between the tumor and peritoneum and a phenotypically more aggressive tumor.
The clinical significance of ovarian cancer capsule rupture has been evaluated in multiple studies with some mixed results.1 Consistently, it is reported that preoperative rupture, surface or capsular involvement, and preexisting peritoneal circulation of metastatic cells all portend a poorer prognosis; however, it is less clear that iatrogenic surgical rupture has the same deleterious association. In a large retrospective series from Japan, the authors evaluated 15,163 cases of stage I ovarian cancer and identified 7,227 cases of iatrogenic (intraoperative) cyst rupture.2 These cases were significantly more likely to occur among clear cell cancers, and were more likely to occur in younger patients. Worse prognosis was associated with cell type (clear cell cancers), but non–clear cell cancers (such as serous, mucinous, and endometrioid) did not have a higher hazard ratio for death when intraoperative rupture occurred. But why would intraoperative cyst rupture result in worse prognosis for only one histologic cell type? The authors hypothesized that perhaps rupture was more likely to occur during extraction of these clear cell tumors because they were associated with dense adhesions from associated endometriosis, and perhaps an adverse biologic phenomenon associated with infiltrative endometriosis is driving the behavior of this cancer.
The Japanese study also looked at the effect of chemotherapy on these same patients’ outcomes. Interestingly, the addition of chemotherapy did not improve survival for the patients with stage IC1 cancers, which was in contrast to the improved survival seen when chemotherapy was given to those with spontaneous rupture or ovarian surface involvement (IC2, IC3). These data support differentiating the subgroups of stage IC cancer in treatment decision-making, and suggest that adjuvant chemotherapy might be avoided for patients with nonclear cell stage IC1 ovarian cancer. While the outcomes are worse for patients with ruptured clear cell cancers, current therapeutic options for clear cell cancers are limited because of their known resistance to traditional agents, and outcomes for women with clear cell cancer can be worse across all stages.
While cyst rupture may not always negatively affect prognosis, the goal of surgery remains an intact removal, which influences decisions regarding surgical approach. Most adnexal masses are removed via minimally invasive surgery (MIS). MIS is associated with benefits of morbidity and cost, and therefore should be considered wherever feasible. However, MIS is associated with an increased risk of ovarian cyst rupture, likely because of the rigid instrumentation used when approaching a curved structure, in addition to the disparity in size of the pathology, compared with the extraction site incision.3 When weighing the benefits and risks of different surgical approaches, it is important to gauge the probability of malignancy. Not all complex ovarian masses associated with elevations in tumor markers are malignant, and certainly most that are associated with normal tumor markers are not. If the preoperative clinical data suggest that the mass is more likely to be malignant (e.g., mostly solid, vascular tumors with very elevated tumor markers), consideration might be made to abandoning a purely minimally invasive approach to a hand-assisted MIS or laparotomy approach. However, it would seem that abandoning an MIS approach to remove every ovarian cyst is unwise given that there is clear patient benefit with MIS and, as discussed above, most cases of iatrogenic malignant cyst rupture are unavoidable even with laparotomy, and do not necessarily independently portend poorer survival or mandate chemotherapy.
Surgeons should be both nuanced and flexible and apply some basic rules of thumb when approaching the diagnostically uncertain adnexal mass. Peritoneal washings should be obtained at the commencement of the case to discriminate those cases of true stage IC3. The peritoneum parallel to the ovarian vessel should be extensively opened to a level above the pelvic brim. In order to do this, the physiological attachments between the sigmoid colon or cecum and the suspensory ligament of the ovary may need to be carefully mobilized. This allows for retroperitoneal identification of the ureter and skeletonization of the ovarian vessels at least 2 cm proximal to their insertion into the ovary and avoidance of contact with the ovary itself (which may have a fragile capsule) or incomplete ovarian resection. If the ovary remains invested close to the sidewall or colonic structures and the appropriate peritoneal and retroperitoneal mobilization has not occurred, the surgeon may unavoidably rupture the ovarian cyst as they try to “hug” the ovary with their bites of tissue in an attempt to avoid visceral injury. There is little role for an ovarian cystectomy in a postmenopausal woman undergoing surgery for a complex adnexal mass, particularly if she has elevated tumor markers, because the process of performing ovarian cystectomy commonly invokes cyst rupture or fragmentation. Ovarian cystectomy should be reserved for premenopausal women with adnexal masses at low suspicion for malignancy. If the adnexa appears densely adherent to adjacent structures – for example, associated with infiltrative endometriosis – consideration for laparotomy or a hand-assisted approach may be necessary; in such cases, even open surgery can result in cyst rupture, and the morbidity of conversion to laparotomy should be weighed for individual cases.
Finally, retrieval of the ovarian specimen should occur intact without morcellation. There should be no uncontained morcellation of adnexal structures during retrieval of even normal-appearing ovaries. The preferred retrieval method is to place the adnexa in an appropriately sized retrieval bag, after which contained morcellation or drainage can occur to facilitate removal through a laparoscopic incision. Contained morcellation is very difficult for large solid masses through a laparoscopic port site; in these cases, extension of the incision may be necessary.
While operative spill of an ovarian cancer does upstage nonmetastatic ovarian cancer, it is unclear that, in most cases, this is independently associated with worse prognosis, and chemotherapy may not always be of added value. However, best surgical practice should always include strategies to minimize the chance of rupture when approaching adnexal masses, particularly those at highest likelihood of malignancy.
References
1. Kim HS et al. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2013 Mar 39(3):279-89.
2. Matsuo K et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Nov;134(5):1017-26.
3. Matsuo K et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jul 1;6(7):1110-3.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
USMLE stuns again: Clinical skills test permanently ended
The Step 2 Clinical Skills (CS) test for medical school students and graduates has been permanently canceled, cosponsors of the U.S. Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) announced in a press release this afternoon.
As previously reported by this news organization, the USMLE cosponsors, the Federation of State Medical Boards and the National Board of Medical Examiners, had announced in May that they would take the following 12-18 months to revamp the required test.
COVID-19 had forced a suspension of the all-day test, which requires test takers to have physical contact with standardized patients. It’s designed to gauge how soon-to-be doctors gather information from patients, perform physical exams, and communicate their findings to patients and colleagues.
However, the cosponsors said today, “we have no plans to bring back Step 2 CS, but we intend to take this opportunity to focus on working with our colleagues in medical education and at the state medical boards to determine innovative ways to assess clinical skills.”
David Johnson, FSMB’s chief assessment officer, said in an interview that, after months of study, “it became clear that the relaunch of a modified Step 2 CS exam would not meet our expectations to be appreciably better than the prior exam.”
Only weeks ago, NBME was hiring for the revamp
The news came as a huge surprise. Just weeks earlier, NBME was advertising for a position key to modifying the exam. The description for the position read: “This role will focus on operational planning and coordination both within the NBME and with ECFMG [Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates] to effectively deliver a modified Step 2 Clinical Skills exam.”
Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, an assistant professor at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, noted in a Jan. 15 tweet that the position requires extensive information technology experience, “suggesting plans for a virtual test remain intact.”
Dr. Johnson said that, although the opportunities for helping lead the revamp of the test were posted until the announcement, no one had been hired for the position.
Today’s announcement stated that the USMLE still believes independent standardized tests for medical knowledge and clinical skills are important; however, it now feels clinical reasoning and communication skills will be able to be assessed in other steps.
“Computer-based case simulations in Step 3 and communication content recently bolstered in Step 1 are examples of these efforts that will continue,” the press release stated. “While not a replacement for Step 2 CS, these formats continue to contribute positively, e.g., measuring critical knowledge of medical communication.”
Critics ‘thrilled’ by test termination
Lydia Flier, MD, from the department of internal medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston – who wrote an editorial for this news organization in August 2020 advocating that Step 2 CS be changed completely or ended entirely – said in an interview that she was “surprised and thrilled” by the announcement.
She said the cosponsors hadn’t initially appeared to agree with the growing sentiment that disruption from the pandemic had “proven the test was unnecessary and it looked like they really were going to try and keep it.”
“I’m thrilled for future generations,” she said. “It is proof of what many people have known all along, which is that the test is a no-value-add proposition that did not actually help determine people’s clinical skills.”
The test “met a breaking point” during the pandemic, she said, “from which CS could not recover.”
She noted in her editorial that the test costs $1,300 plus travel fees, as the test had been offered at only five sites. She agreed that the skills assessed by the Step 2 CS are already covered in medical school and through other Steps.
“It seems as though they could not justify it anymore. It’s the obvious right answer,” said Dr. Flier, who in 2016 cofounded #EndStep2CS, a nationwide movement demanding an end to the exam.
Another cofounder in that movement, Christopher Henderson, MD, a staff physician with Kaiser Permanente in Seattle, said in an interview that “this decision represents tremendous progress in the fight to reduce unnecessary costs in medical education, and is a win for future students. Credit goes to the many women and men who organized and voiced their desire for change.” He added that his views are his own and “do not reflect or imply the views of my organization.”
For the FSMB’s part, Dr. Johnson acknowledged that “the consideration of cost and value were two of many important factors for the Step 2 CS revitalization work.”
Dr. Johnson, Dr. Flier, and Dr. Henderson have declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Step 2 Clinical Skills (CS) test for medical school students and graduates has been permanently canceled, cosponsors of the U.S. Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) announced in a press release this afternoon.
As previously reported by this news organization, the USMLE cosponsors, the Federation of State Medical Boards and the National Board of Medical Examiners, had announced in May that they would take the following 12-18 months to revamp the required test.
COVID-19 had forced a suspension of the all-day test, which requires test takers to have physical contact with standardized patients. It’s designed to gauge how soon-to-be doctors gather information from patients, perform physical exams, and communicate their findings to patients and colleagues.
However, the cosponsors said today, “we have no plans to bring back Step 2 CS, but we intend to take this opportunity to focus on working with our colleagues in medical education and at the state medical boards to determine innovative ways to assess clinical skills.”
David Johnson, FSMB’s chief assessment officer, said in an interview that, after months of study, “it became clear that the relaunch of a modified Step 2 CS exam would not meet our expectations to be appreciably better than the prior exam.”
Only weeks ago, NBME was hiring for the revamp
The news came as a huge surprise. Just weeks earlier, NBME was advertising for a position key to modifying the exam. The description for the position read: “This role will focus on operational planning and coordination both within the NBME and with ECFMG [Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates] to effectively deliver a modified Step 2 Clinical Skills exam.”
Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, an assistant professor at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, noted in a Jan. 15 tweet that the position requires extensive information technology experience, “suggesting plans for a virtual test remain intact.”
Dr. Johnson said that, although the opportunities for helping lead the revamp of the test were posted until the announcement, no one had been hired for the position.
Today’s announcement stated that the USMLE still believes independent standardized tests for medical knowledge and clinical skills are important; however, it now feels clinical reasoning and communication skills will be able to be assessed in other steps.
“Computer-based case simulations in Step 3 and communication content recently bolstered in Step 1 are examples of these efforts that will continue,” the press release stated. “While not a replacement for Step 2 CS, these formats continue to contribute positively, e.g., measuring critical knowledge of medical communication.”
Critics ‘thrilled’ by test termination
Lydia Flier, MD, from the department of internal medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston – who wrote an editorial for this news organization in August 2020 advocating that Step 2 CS be changed completely or ended entirely – said in an interview that she was “surprised and thrilled” by the announcement.
She said the cosponsors hadn’t initially appeared to agree with the growing sentiment that disruption from the pandemic had “proven the test was unnecessary and it looked like they really were going to try and keep it.”
“I’m thrilled for future generations,” she said. “It is proof of what many people have known all along, which is that the test is a no-value-add proposition that did not actually help determine people’s clinical skills.”
The test “met a breaking point” during the pandemic, she said, “from which CS could not recover.”
She noted in her editorial that the test costs $1,300 plus travel fees, as the test had been offered at only five sites. She agreed that the skills assessed by the Step 2 CS are already covered in medical school and through other Steps.
“It seems as though they could not justify it anymore. It’s the obvious right answer,” said Dr. Flier, who in 2016 cofounded #EndStep2CS, a nationwide movement demanding an end to the exam.
Another cofounder in that movement, Christopher Henderson, MD, a staff physician with Kaiser Permanente in Seattle, said in an interview that “this decision represents tremendous progress in the fight to reduce unnecessary costs in medical education, and is a win for future students. Credit goes to the many women and men who organized and voiced their desire for change.” He added that his views are his own and “do not reflect or imply the views of my organization.”
For the FSMB’s part, Dr. Johnson acknowledged that “the consideration of cost and value were two of many important factors for the Step 2 CS revitalization work.”
Dr. Johnson, Dr. Flier, and Dr. Henderson have declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Step 2 Clinical Skills (CS) test for medical school students and graduates has been permanently canceled, cosponsors of the U.S. Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) announced in a press release this afternoon.
As previously reported by this news organization, the USMLE cosponsors, the Federation of State Medical Boards and the National Board of Medical Examiners, had announced in May that they would take the following 12-18 months to revamp the required test.
COVID-19 had forced a suspension of the all-day test, which requires test takers to have physical contact with standardized patients. It’s designed to gauge how soon-to-be doctors gather information from patients, perform physical exams, and communicate their findings to patients and colleagues.
However, the cosponsors said today, “we have no plans to bring back Step 2 CS, but we intend to take this opportunity to focus on working with our colleagues in medical education and at the state medical boards to determine innovative ways to assess clinical skills.”
David Johnson, FSMB’s chief assessment officer, said in an interview that, after months of study, “it became clear that the relaunch of a modified Step 2 CS exam would not meet our expectations to be appreciably better than the prior exam.”
Only weeks ago, NBME was hiring for the revamp
The news came as a huge surprise. Just weeks earlier, NBME was advertising for a position key to modifying the exam. The description for the position read: “This role will focus on operational planning and coordination both within the NBME and with ECFMG [Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates] to effectively deliver a modified Step 2 Clinical Skills exam.”
Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, an assistant professor at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, noted in a Jan. 15 tweet that the position requires extensive information technology experience, “suggesting plans for a virtual test remain intact.”
Dr. Johnson said that, although the opportunities for helping lead the revamp of the test were posted until the announcement, no one had been hired for the position.
Today’s announcement stated that the USMLE still believes independent standardized tests for medical knowledge and clinical skills are important; however, it now feels clinical reasoning and communication skills will be able to be assessed in other steps.
“Computer-based case simulations in Step 3 and communication content recently bolstered in Step 1 are examples of these efforts that will continue,” the press release stated. “While not a replacement for Step 2 CS, these formats continue to contribute positively, e.g., measuring critical knowledge of medical communication.”
Critics ‘thrilled’ by test termination
Lydia Flier, MD, from the department of internal medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston – who wrote an editorial for this news organization in August 2020 advocating that Step 2 CS be changed completely or ended entirely – said in an interview that she was “surprised and thrilled” by the announcement.
She said the cosponsors hadn’t initially appeared to agree with the growing sentiment that disruption from the pandemic had “proven the test was unnecessary and it looked like they really were going to try and keep it.”
“I’m thrilled for future generations,” she said. “It is proof of what many people have known all along, which is that the test is a no-value-add proposition that did not actually help determine people’s clinical skills.”
The test “met a breaking point” during the pandemic, she said, “from which CS could not recover.”
She noted in her editorial that the test costs $1,300 plus travel fees, as the test had been offered at only five sites. She agreed that the skills assessed by the Step 2 CS are already covered in medical school and through other Steps.
“It seems as though they could not justify it anymore. It’s the obvious right answer,” said Dr. Flier, who in 2016 cofounded #EndStep2CS, a nationwide movement demanding an end to the exam.
Another cofounder in that movement, Christopher Henderson, MD, a staff physician with Kaiser Permanente in Seattle, said in an interview that “this decision represents tremendous progress in the fight to reduce unnecessary costs in medical education, and is a win for future students. Credit goes to the many women and men who organized and voiced their desire for change.” He added that his views are his own and “do not reflect or imply the views of my organization.”
For the FSMB’s part, Dr. Johnson acknowledged that “the consideration of cost and value were two of many important factors for the Step 2 CS revitalization work.”
Dr. Johnson, Dr. Flier, and Dr. Henderson have declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.K. variant spreading in the U.S. as COVID mutations raise stakes
The U.K.’s B117 variant is circulating in at least 24 states, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19 variant surveillance. The CDC projects that the U.K. variant will become the dominant strain in the United States by March.
From any vantage point, the United Kingdom appears to be in the crosshairs of COVID-19: Weeks after a new, highly contagious variant emerged that fueled a surge in cases and fresh lockdowns, the United Kingdom was revealed to have the world’s highest coronavirus death rate.
But the United Kingdom also has a not-so-secret weapon of its own: A genomic sequencing program widely believed to be the most coordinated and advanced any nation has forged. In the vise grip of the virus, the Brits have gleaned key insights into the behavior and consequences of SARS-CoV-2.
But B117 is also notable for what it is missing: In this case, producing a negative result on certain polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests in the spike protein, or S-gene.
One of the S-gene mutations specific to the variant deletes two amino acids, causing that portion of the PCR test to show up negative. The coincidental finding known as an S-gene target failure has become an integral proxy to help track where and when the variant is spreading in the United Kingdom, where about 5% of samples from COVID-19–infected patients are sequenced, said Sharon Peacock, PhD, executive director and chair of the COVID-19 Genomics U.K. Consortium.
That same tactic could prove valuable to clinicians similarly overwhelmed with cases and deaths but lacking high-level sequencing information on the virus, Dr. Peacock said in an interview. A British report released Friday stated that there is a “realistic possibility” that the variant has a higher death rate than other cases of SARS-CoV-2.
“In this particular variant, a deletion in the genome leads to one part of the diagnostic test failing,” Dr. Peacock explained. “Several targets are positive, but this is negative. In the U.K., this has been used as a surrogate marker.”
Targeting an invisible adversary
B117 is not the only variant that produces this result, Dr. Peacock cautioned, “but in screening for it, you can have this in mind.”
“Since the U.K. is sequencing about 5% of the cases they detect, this gives them really important clues about what’s happening there,” said Anderson Brito, PhD, a virologist and postdoctoral researcher at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., where investigators are creating custom PCR tests to detect the B117 variant.
Dr. Brito, who lived in the United Kingdom for 4 years while studying for his doctorate at Imperial College London, said a “major advantage” is the more unified process to collect and sequence samples. Crucial information – including the date and place of collection – comes with each sample, which fuels not only sequencing, but an epidemiologic perspective.
“They’re not in the dark at all,” Dr. Brito said in an interview. “I think no other country in the world knows better which virus lineages are circulating.”
The CDC launched the SPHERES consortium in May 2020 to coordinate the sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 genomes across the United States.
But American genomic efforts are “not as centralized,” said Dr. Brito, whose lab detected the first two cases of the U.K. variant in Connecticut on Jan. 6. “We struggle to get samples, because they’re decentralized to a level where there’s little coordination between hospitals and research centers. They’re not as connected as in the U.K. If we just get a sample and it has no date of collection and no origin information, for example, it’s basically useless.”
Global genomic collaborations include GISAID, an international database where researchers share new genomes from various coronaviruses. As of mid-January, the United States had submitted about 68,000 sequences to GISAID, adding about 3,000 new samples every week and expecting even more from commercial labs in coming days, according to the CDC.
“The U.K. is definitely much more on top of looking for variants as they pop up,” said Gigi Gronvall, PhD, an immunologist and senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in Baltimore. “The U.S. has now turned that up.”
Warning from British scientists to the world
Despite these genomic accomplishments, some British scientists said they have regrets too, wishing they’d known just how rapidly SARS-CoV-2 was actually spreading a year ago, when it hit western Europe.
That information was crucial not only for preventive efforts, but because viruses inevitably mutate faster the more people who are infected, said Igor Rudan, MD, PhD, director of the Center for Global Health Research at University of Edinburgh.
“Italy showed us just how fast it was spreading and how deadly it is for the very old and people with multiple comorbidities,” said Dr. Rudan, who also editor in chief of the Journal of Global Health. “We wish we knew it was spreading so fast, and we wish we knew the threshold of cases we could allow to be infected before the virus would mutate.”
More mutations mean more new strains of SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Rudan said in an interview. “We’ve reached that threshold now and will see more of these mutations.”
Despite its current struggles, the United Kingdom is reaching beyond tracking its new variant’s spread and trying to identify new mutations that might change the way the virus behaves.
Three features of any emerging variant are particularly important, Dr. Peacock explained: Is it more transmissible? Is it more lethal? And does it cut the ability of natural- or vaccine-induced immunity to protect people from infection?
“We need to sequence people coming to the hospital who are sicker,” said Dr. Peacock, also a professor of public health and microbiology at the University of Cambridge (England). “Also, if anyone has the infection after they’ve already been sick or had the vaccine, we really want to know what that looks like” genomically.
SARS-CoV-2 has already logged more than 4,000 mutations, Dr. Peacock said. But “knowing that viruses mutate all the time is not sufficient reason not to look. We really want to know if mutations lead to changes in amino acids, and if that can lead to changes in functionality.”
For the moment, however, experts say they’re relieved that the U.K. strain doesn’t seem able to evade COVID-19 vaccines or render them less effective.
“Even though mutations are common, those able to change the viral coding are rare,” Dr. Brito explained. If necessary, vaccines could be tweaked to replace the spike gene sequence “within a matter of weeks. We already do this for flu vaccines. Every year, we have to monitor variants of the virus circulating to develop a vaccine that covers most of them. If we end up having to do it for SARS-CoV-2, I would not be surprised.”
But variant-fueled increases in infections will require more people to be vaccinated before herd immunity can be achieved, Dr. Rudan warned. “If it spreads faster, we’ll need to vaccinate probably 85% of people versus 70% to reach herd immunity.”
One lesson the COVID-19 pandemic has driven home “is to always be on your guard about what happens next,” Dr. Peacock said. Although confident about the genomic efforts in the United Kingdom to date, she and her colleagues feel they’re still reaching for a complete understanding of the evolutionary changes of the virus.
“We’re ahead of the curve right now, but we want to get in front of the curve,” Dr. Peacock said. “It’s essential to get ahead of what might be around the corner because we don’t know how the virus is going to evolve.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.K.’s B117 variant is circulating in at least 24 states, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19 variant surveillance. The CDC projects that the U.K. variant will become the dominant strain in the United States by March.
From any vantage point, the United Kingdom appears to be in the crosshairs of COVID-19: Weeks after a new, highly contagious variant emerged that fueled a surge in cases and fresh lockdowns, the United Kingdom was revealed to have the world’s highest coronavirus death rate.
But the United Kingdom also has a not-so-secret weapon of its own: A genomic sequencing program widely believed to be the most coordinated and advanced any nation has forged. In the vise grip of the virus, the Brits have gleaned key insights into the behavior and consequences of SARS-CoV-2.
But B117 is also notable for what it is missing: In this case, producing a negative result on certain polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests in the spike protein, or S-gene.
One of the S-gene mutations specific to the variant deletes two amino acids, causing that portion of the PCR test to show up negative. The coincidental finding known as an S-gene target failure has become an integral proxy to help track where and when the variant is spreading in the United Kingdom, where about 5% of samples from COVID-19–infected patients are sequenced, said Sharon Peacock, PhD, executive director and chair of the COVID-19 Genomics U.K. Consortium.
That same tactic could prove valuable to clinicians similarly overwhelmed with cases and deaths but lacking high-level sequencing information on the virus, Dr. Peacock said in an interview. A British report released Friday stated that there is a “realistic possibility” that the variant has a higher death rate than other cases of SARS-CoV-2.
“In this particular variant, a deletion in the genome leads to one part of the diagnostic test failing,” Dr. Peacock explained. “Several targets are positive, but this is negative. In the U.K., this has been used as a surrogate marker.”
Targeting an invisible adversary
B117 is not the only variant that produces this result, Dr. Peacock cautioned, “but in screening for it, you can have this in mind.”
“Since the U.K. is sequencing about 5% of the cases they detect, this gives them really important clues about what’s happening there,” said Anderson Brito, PhD, a virologist and postdoctoral researcher at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., where investigators are creating custom PCR tests to detect the B117 variant.
Dr. Brito, who lived in the United Kingdom for 4 years while studying for his doctorate at Imperial College London, said a “major advantage” is the more unified process to collect and sequence samples. Crucial information – including the date and place of collection – comes with each sample, which fuels not only sequencing, but an epidemiologic perspective.
“They’re not in the dark at all,” Dr. Brito said in an interview. “I think no other country in the world knows better which virus lineages are circulating.”
The CDC launched the SPHERES consortium in May 2020 to coordinate the sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 genomes across the United States.
But American genomic efforts are “not as centralized,” said Dr. Brito, whose lab detected the first two cases of the U.K. variant in Connecticut on Jan. 6. “We struggle to get samples, because they’re decentralized to a level where there’s little coordination between hospitals and research centers. They’re not as connected as in the U.K. If we just get a sample and it has no date of collection and no origin information, for example, it’s basically useless.”
Global genomic collaborations include GISAID, an international database where researchers share new genomes from various coronaviruses. As of mid-January, the United States had submitted about 68,000 sequences to GISAID, adding about 3,000 new samples every week and expecting even more from commercial labs in coming days, according to the CDC.
“The U.K. is definitely much more on top of looking for variants as they pop up,” said Gigi Gronvall, PhD, an immunologist and senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in Baltimore. “The U.S. has now turned that up.”
Warning from British scientists to the world
Despite these genomic accomplishments, some British scientists said they have regrets too, wishing they’d known just how rapidly SARS-CoV-2 was actually spreading a year ago, when it hit western Europe.
That information was crucial not only for preventive efforts, but because viruses inevitably mutate faster the more people who are infected, said Igor Rudan, MD, PhD, director of the Center for Global Health Research at University of Edinburgh.
“Italy showed us just how fast it was spreading and how deadly it is for the very old and people with multiple comorbidities,” said Dr. Rudan, who also editor in chief of the Journal of Global Health. “We wish we knew it was spreading so fast, and we wish we knew the threshold of cases we could allow to be infected before the virus would mutate.”
More mutations mean more new strains of SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Rudan said in an interview. “We’ve reached that threshold now and will see more of these mutations.”
Despite its current struggles, the United Kingdom is reaching beyond tracking its new variant’s spread and trying to identify new mutations that might change the way the virus behaves.
Three features of any emerging variant are particularly important, Dr. Peacock explained: Is it more transmissible? Is it more lethal? And does it cut the ability of natural- or vaccine-induced immunity to protect people from infection?
“We need to sequence people coming to the hospital who are sicker,” said Dr. Peacock, also a professor of public health and microbiology at the University of Cambridge (England). “Also, if anyone has the infection after they’ve already been sick or had the vaccine, we really want to know what that looks like” genomically.
SARS-CoV-2 has already logged more than 4,000 mutations, Dr. Peacock said. But “knowing that viruses mutate all the time is not sufficient reason not to look. We really want to know if mutations lead to changes in amino acids, and if that can lead to changes in functionality.”
For the moment, however, experts say they’re relieved that the U.K. strain doesn’t seem able to evade COVID-19 vaccines or render them less effective.
“Even though mutations are common, those able to change the viral coding are rare,” Dr. Brito explained. If necessary, vaccines could be tweaked to replace the spike gene sequence “within a matter of weeks. We already do this for flu vaccines. Every year, we have to monitor variants of the virus circulating to develop a vaccine that covers most of them. If we end up having to do it for SARS-CoV-2, I would not be surprised.”
But variant-fueled increases in infections will require more people to be vaccinated before herd immunity can be achieved, Dr. Rudan warned. “If it spreads faster, we’ll need to vaccinate probably 85% of people versus 70% to reach herd immunity.”
One lesson the COVID-19 pandemic has driven home “is to always be on your guard about what happens next,” Dr. Peacock said. Although confident about the genomic efforts in the United Kingdom to date, she and her colleagues feel they’re still reaching for a complete understanding of the evolutionary changes of the virus.
“We’re ahead of the curve right now, but we want to get in front of the curve,” Dr. Peacock said. “It’s essential to get ahead of what might be around the corner because we don’t know how the virus is going to evolve.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.K.’s B117 variant is circulating in at least 24 states, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19 variant surveillance. The CDC projects that the U.K. variant will become the dominant strain in the United States by March.
From any vantage point, the United Kingdom appears to be in the crosshairs of COVID-19: Weeks after a new, highly contagious variant emerged that fueled a surge in cases and fresh lockdowns, the United Kingdom was revealed to have the world’s highest coronavirus death rate.
But the United Kingdom also has a not-so-secret weapon of its own: A genomic sequencing program widely believed to be the most coordinated and advanced any nation has forged. In the vise grip of the virus, the Brits have gleaned key insights into the behavior and consequences of SARS-CoV-2.
But B117 is also notable for what it is missing: In this case, producing a negative result on certain polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests in the spike protein, or S-gene.
One of the S-gene mutations specific to the variant deletes two amino acids, causing that portion of the PCR test to show up negative. The coincidental finding known as an S-gene target failure has become an integral proxy to help track where and when the variant is spreading in the United Kingdom, where about 5% of samples from COVID-19–infected patients are sequenced, said Sharon Peacock, PhD, executive director and chair of the COVID-19 Genomics U.K. Consortium.
That same tactic could prove valuable to clinicians similarly overwhelmed with cases and deaths but lacking high-level sequencing information on the virus, Dr. Peacock said in an interview. A British report released Friday stated that there is a “realistic possibility” that the variant has a higher death rate than other cases of SARS-CoV-2.
“In this particular variant, a deletion in the genome leads to one part of the diagnostic test failing,” Dr. Peacock explained. “Several targets are positive, but this is negative. In the U.K., this has been used as a surrogate marker.”
Targeting an invisible adversary
B117 is not the only variant that produces this result, Dr. Peacock cautioned, “but in screening for it, you can have this in mind.”
“Since the U.K. is sequencing about 5% of the cases they detect, this gives them really important clues about what’s happening there,” said Anderson Brito, PhD, a virologist and postdoctoral researcher at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., where investigators are creating custom PCR tests to detect the B117 variant.
Dr. Brito, who lived in the United Kingdom for 4 years while studying for his doctorate at Imperial College London, said a “major advantage” is the more unified process to collect and sequence samples. Crucial information – including the date and place of collection – comes with each sample, which fuels not only sequencing, but an epidemiologic perspective.
“They’re not in the dark at all,” Dr. Brito said in an interview. “I think no other country in the world knows better which virus lineages are circulating.”
The CDC launched the SPHERES consortium in May 2020 to coordinate the sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 genomes across the United States.
But American genomic efforts are “not as centralized,” said Dr. Brito, whose lab detected the first two cases of the U.K. variant in Connecticut on Jan. 6. “We struggle to get samples, because they’re decentralized to a level where there’s little coordination between hospitals and research centers. They’re not as connected as in the U.K. If we just get a sample and it has no date of collection and no origin information, for example, it’s basically useless.”
Global genomic collaborations include GISAID, an international database where researchers share new genomes from various coronaviruses. As of mid-January, the United States had submitted about 68,000 sequences to GISAID, adding about 3,000 new samples every week and expecting even more from commercial labs in coming days, according to the CDC.
“The U.K. is definitely much more on top of looking for variants as they pop up,” said Gigi Gronvall, PhD, an immunologist and senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in Baltimore. “The U.S. has now turned that up.”
Warning from British scientists to the world
Despite these genomic accomplishments, some British scientists said they have regrets too, wishing they’d known just how rapidly SARS-CoV-2 was actually spreading a year ago, when it hit western Europe.
That information was crucial not only for preventive efforts, but because viruses inevitably mutate faster the more people who are infected, said Igor Rudan, MD, PhD, director of the Center for Global Health Research at University of Edinburgh.
“Italy showed us just how fast it was spreading and how deadly it is for the very old and people with multiple comorbidities,” said Dr. Rudan, who also editor in chief of the Journal of Global Health. “We wish we knew it was spreading so fast, and we wish we knew the threshold of cases we could allow to be infected before the virus would mutate.”
More mutations mean more new strains of SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Rudan said in an interview. “We’ve reached that threshold now and will see more of these mutations.”
Despite its current struggles, the United Kingdom is reaching beyond tracking its new variant’s spread and trying to identify new mutations that might change the way the virus behaves.
Three features of any emerging variant are particularly important, Dr. Peacock explained: Is it more transmissible? Is it more lethal? And does it cut the ability of natural- or vaccine-induced immunity to protect people from infection?
“We need to sequence people coming to the hospital who are sicker,” said Dr. Peacock, also a professor of public health and microbiology at the University of Cambridge (England). “Also, if anyone has the infection after they’ve already been sick or had the vaccine, we really want to know what that looks like” genomically.
SARS-CoV-2 has already logged more than 4,000 mutations, Dr. Peacock said. But “knowing that viruses mutate all the time is not sufficient reason not to look. We really want to know if mutations lead to changes in amino acids, and if that can lead to changes in functionality.”
For the moment, however, experts say they’re relieved that the U.K. strain doesn’t seem able to evade COVID-19 vaccines or render them less effective.
“Even though mutations are common, those able to change the viral coding are rare,” Dr. Brito explained. If necessary, vaccines could be tweaked to replace the spike gene sequence “within a matter of weeks. We already do this for flu vaccines. Every year, we have to monitor variants of the virus circulating to develop a vaccine that covers most of them. If we end up having to do it for SARS-CoV-2, I would not be surprised.”
But variant-fueled increases in infections will require more people to be vaccinated before herd immunity can be achieved, Dr. Rudan warned. “If it spreads faster, we’ll need to vaccinate probably 85% of people versus 70% to reach herd immunity.”
One lesson the COVID-19 pandemic has driven home “is to always be on your guard about what happens next,” Dr. Peacock said. Although confident about the genomic efforts in the United Kingdom to date, she and her colleagues feel they’re still reaching for a complete understanding of the evolutionary changes of the virus.
“We’re ahead of the curve right now, but we want to get in front of the curve,” Dr. Peacock said. “It’s essential to get ahead of what might be around the corner because we don’t know how the virus is going to evolve.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Brazilian researchers tracking reinfection by new virus variant
Just as Brazil surpassed 200,000 deaths from COVID-19 on Jan. 7, news from Bahia added another layer of concern: A platform case report in a preprint detailed the first case of reinfection in that state, apparently caused by a new strain, one having the E484K mutation.
That variant, now called Brazil P.1, has migrated to the United States. The Minnesota Department of Health announced on Jan. 25 the nation’s first known COVID-19 case associated with it.
The mutation is located in the protein gene of the virus’ spike, which forms the crown structure of coronaviruses and is responsible for the virus’ binding to human cells. The E484K mutation is now the focus because it’s associated with mutations that escape the immune system’s neutralizing antibodies.
“This mutation is at the center of worldwide concern, and it is the first time that it has appeared in a reinfection,” the study’s first author, Bruno Solano de Freitas Souza, MD, a researcher at the Salvador regional unit of Instituto D’Or of Teaching and Research, based at Hospital São Rafael, Salvador, Brazil, explained in an interview.
“We will wait for the sample from Bahia to confirm the case from the perspective of the Ministry of Health’s surveillance network,” said Fernando Motta, PhD, deputy head of the Laboratory for Respiratory Virus and Measles at the Oswaldo Cruz Institute in Rio de Janeiro, which acts as a national reference center for respiratory viruses with the Brazilian Ministry of Health (MS) and as a reference for the World Health Organization.
A case of reinfection
The case patient that led to the alarm was a 45-year-old woman who is a health care executive. She had no comorbidities. The team had been following health care professionals and patients who had tested positive on reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing more than once to understand whether they represented cases of prolonged viral persistence or new infections.
The woman had symptoms of viral infection on two occasions (May 26 and Oct. 26). On both occasions, results of RT-PCR testing for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal samples were positive. In the first episode, the patient had diarrhea, myalgia, asthenia, and odynophagia for about 7 days. She returned to activities 21 days later. In the second episode, she had more severe symptoms that lasted longer, but she still did not require hospitalization.
“It was the first confirmed case of reinfection in Bahia, and in the second episode, we observed a mutation that could have an impact on the ability of antibodies to neutralize the virus,” Dr. Souza said. “The research continues with the investigation of cases in which the patient has a positive SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR more than once in an interval greater than 45 days, to have a higher level of evidence.”
He stressed that “it is very important to reinforce measures to control the pandemic, social distance, use of masks, and speed up vaccination to be able to control the circulation of the virus, while monitoring the evolution of it.”
On alert for more cases
A person who twice tests positive for SARS-CoV-2 on real-time RT-PCR is suspected of having been reinfected, provided 90 or more days have elapsed between the two episodes, regardless of the condition observed. To confirm the suspected case, the samples must be sent to reference laboratories according to a plan established by the Ministry of Health in Brazil.
A health professional living in the Brazilian city of Natal represented the first confirmed case of reinfection by the new coronavirus in Brazil. That case was announced on Dec. 10, 2020.
“We communicated this case of reinfection to the MS in early December 2020. And the second sample already had the E484K mutation on the spike, as in the case of Bahia,” said Dr. Motta.
The first step in differentiating reinfection from persistence is to observe differences in the genotyping of the virus. For the technique to be successful, Dr. Souza said, researchers need a large amount of viral genetic material, which usually cannot be obtained.
“That is why there are many more suspected than confirmed cases,” Dr. Souza explained. He admitted that, although there are few cases, “it is increasingly clear that reinfection is a reality.”
Markers of mutations
What worried the researchers most was not only the possibility of reinfection but also the fact that preliminary analyses showed a specific mutation.
“The E484K mutation is present in a group of variants identified in South Africa that have been associated with increased infectivity and has been observed in a strain recently described in Brazil,” Dr. Souza said.
Mutations are expected, appear spontaneously, and in most cases have no effects on transmission or clinical outcome – they are simply used as markers and are useful for contact tracing or studying transmission routes. But some mutations can last because they provide an advantage for the pathogen, even if only momentary. In the case of SARS-CoV-2, mutations in the protein spike gene (S) are relevant because they may give clues to that advantage – as well as to changes in infectivity, transmission potential, antibodies, and response to vaccines.
A variant of the virus that has eight changes that affect the protein S gene – and several others in different genes – is behind the increase in the number of cases in London and southeastern England. Researchers from the University of São Paulo identified one of the factors that made this new variant – classified as B.1.1.7 – more infectious.
With bioinformatics tools, they found that the protein S gene in the new viral strain has a stronger molecular interaction with the ACE2 receptor, which is on the surface of human cells and to which the virus binds, making infection possible. The variant has already spread to the rest of the world, and the first two cases have been confirmed in Brazil by the Adolf Lutz Institute.
The alert for a new variant in Africa – similar to B.1.1.7 in the United Kingdom in that it carries nine changes in protein S at position 501 – was made by the Brazilian virologist Tulio de Oliveira, PhD.
“We found that this strain seems to be spreading much faster,” Dr. Oliveira, who is with the University of KwaZulu Natal, told the journal Science. His work first alerted British scientists to the importance of the position N501Y.
“The new variants just described in the United Kingdom and South Africa are slightly more transmissible and have already been identified in cases imported into Brazil,” Dr. Motta said. “Unfortunately, we believe it is only a matter of time before it becomes indigenous.”
The viral family grows
Viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 are classified into strains on the basis of small differences in their genetic material. Since Dec. 26, 2020, in addition to the British and South African variants, it appears the Carioca lineage also is a player.
In a preprint article, researchers analyzed the evolution of the epidemic in Rio de Janeiro from April 2020 until just before the new increase in incidence in December. They compared the complete sequences of the viral genome of 180 patients from different municipalities. The study, which is being jointly conducted by members of the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro and the National Laboratory for Scientific Computing, identified a new variant of SARS-CoV-2 that has five unique mutations (from one of the predominant strains). Concern arose because, in addition to those five genetic changes, many of the samples had a sixth – the well-known E484K mutation.
“The three lines – the U.K., South Africa, and Brazil – were almost synchronous publications, but there is no clear evidence that they have any kind of common ancestry,” Carolina M. Voloch, PhD, the article’s first author and a biologist and researcher at the Molecular Virology Laboratory and associate professor in the department of genetics at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, said in an interview.
Dr. Voloch’s research focuses on the use of bioinformatics tools to study the molecular, phylogenetic, and genomic evolution of viruses.
“The emergence of new strains is common for viruses,” she said. “It can be happening anywhere in the world at any time.”
She stressed that identifying when mutations emerge will help to define the new Brazilian lineage. Researchers are working to determine whether the neutralizing antibodies of patients who have been infected with other strains respond to this Rio de Janeiro strain.
“We hope to soon be sharing these results,” Dr. Voloch said.
The article’s authors estimated that the new strain likely appeared in early July. They say more analysis is needed to predict whether the changes have a major effect on viral infectivity, the host’s immune response, or the severity of the disease. Asked about the lineage that caused the reinfection in Bahia, Dr. Voloch said she hadn’t yet contacted the authors to conduct a joint analysis but added that the data disclosed in the preprint would not represent the same variant.
“There are only two of the five mutations that characterize the Rio de Janeiro lineage. However, it has the E484K mutation that is present in more than 94% of the samples of the new variant of Rio,” she said.
She added that there’s a possibility of reinfection by the lineage that’s circulating in Rio de Janeiro and in other states, as well as countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Japan.
“The Carioca virus is being exported to the rest of the world,” Dr. Voloch said.
Virus’ diversity still unknown
Researchers now know that SARS-CoV-2 probably circulated silently in Brazil as early as February 2020 and reached all the nation’s regions before air travel was restricted. Since the first half of 2020, there have been two predominant strains.
“More than a dozen strains have been identified in Brazil, but more important than counting strains to identify the speed with which they arise – which is directly associated with the rate of infection, which is very high in the country,” said Dr. Motta.
The so-called variant of Rio de Janeiro, he said, has also been detected in other states in four regions of Brazil. The key to documenting variants is to get a more representative sample with genomes from other parts of the country.
As of Jan. 10, a total of 347,000 complete genome sequences had been shared globally through open databases since SARS-CoV-2 was first identified, but the contribution of countries is uneven. Although the cost and complexity of genetic sequencing has dropped significantly over time, effective sequencing programs still require substantial investments in personnel, equipment, reagents, and bioinformatics infrastructure.
According to Dr. Voloch, it will only be possible to combat the new coronavirus by knowing its diversity and understanding how it evolves. The Fiocruz Genomic Network has made an infographic available so researchers can track the strains circulating in Brazil. It›s the result of collaboration between researchers from Fiocruz and the GISAID Initiative, an international partnership that promotes rapid data sharing.
As of Jan. 5, researchers in Brazil had studied 1,897 genomes – not nearly enough.
“In Brazil, there is little testing and even less sequencing,” lamented Dr. Souza.
“In the U.K., 1 in 600 cases is sequenced. In Brazil it is less than 1 in 10 million cases,” Dr. Voloch added.
So far, no decisive factors for public health, such as greater virulence or greater transmissibility, have been identified in any of the strains established in Brazil. The million-dollar question is whether the emergence of new strains could have an impact on the effectiveness of vaccines being administered today.
“In one way or another, the vaccine is our best bet ever, even if in the future we identify escapist mutants and have to modify it,” Dr. Motta said. “It is what we do annually with influenza.”
Dr. Voloch, Dr. Motta, and Dr. Souza disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on the Portuguese edition of Medscape.com.
Just as Brazil surpassed 200,000 deaths from COVID-19 on Jan. 7, news from Bahia added another layer of concern: A platform case report in a preprint detailed the first case of reinfection in that state, apparently caused by a new strain, one having the E484K mutation.
That variant, now called Brazil P.1, has migrated to the United States. The Minnesota Department of Health announced on Jan. 25 the nation’s first known COVID-19 case associated with it.
The mutation is located in the protein gene of the virus’ spike, which forms the crown structure of coronaviruses and is responsible for the virus’ binding to human cells. The E484K mutation is now the focus because it’s associated with mutations that escape the immune system’s neutralizing antibodies.
“This mutation is at the center of worldwide concern, and it is the first time that it has appeared in a reinfection,” the study’s first author, Bruno Solano de Freitas Souza, MD, a researcher at the Salvador regional unit of Instituto D’Or of Teaching and Research, based at Hospital São Rafael, Salvador, Brazil, explained in an interview.
“We will wait for the sample from Bahia to confirm the case from the perspective of the Ministry of Health’s surveillance network,” said Fernando Motta, PhD, deputy head of the Laboratory for Respiratory Virus and Measles at the Oswaldo Cruz Institute in Rio de Janeiro, which acts as a national reference center for respiratory viruses with the Brazilian Ministry of Health (MS) and as a reference for the World Health Organization.
A case of reinfection
The case patient that led to the alarm was a 45-year-old woman who is a health care executive. She had no comorbidities. The team had been following health care professionals and patients who had tested positive on reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing more than once to understand whether they represented cases of prolonged viral persistence or new infections.
The woman had symptoms of viral infection on two occasions (May 26 and Oct. 26). On both occasions, results of RT-PCR testing for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal samples were positive. In the first episode, the patient had diarrhea, myalgia, asthenia, and odynophagia for about 7 days. She returned to activities 21 days later. In the second episode, she had more severe symptoms that lasted longer, but she still did not require hospitalization.
“It was the first confirmed case of reinfection in Bahia, and in the second episode, we observed a mutation that could have an impact on the ability of antibodies to neutralize the virus,” Dr. Souza said. “The research continues with the investigation of cases in which the patient has a positive SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR more than once in an interval greater than 45 days, to have a higher level of evidence.”
He stressed that “it is very important to reinforce measures to control the pandemic, social distance, use of masks, and speed up vaccination to be able to control the circulation of the virus, while monitoring the evolution of it.”
On alert for more cases
A person who twice tests positive for SARS-CoV-2 on real-time RT-PCR is suspected of having been reinfected, provided 90 or more days have elapsed between the two episodes, regardless of the condition observed. To confirm the suspected case, the samples must be sent to reference laboratories according to a plan established by the Ministry of Health in Brazil.
A health professional living in the Brazilian city of Natal represented the first confirmed case of reinfection by the new coronavirus in Brazil. That case was announced on Dec. 10, 2020.
“We communicated this case of reinfection to the MS in early December 2020. And the second sample already had the E484K mutation on the spike, as in the case of Bahia,” said Dr. Motta.
The first step in differentiating reinfection from persistence is to observe differences in the genotyping of the virus. For the technique to be successful, Dr. Souza said, researchers need a large amount of viral genetic material, which usually cannot be obtained.
“That is why there are many more suspected than confirmed cases,” Dr. Souza explained. He admitted that, although there are few cases, “it is increasingly clear that reinfection is a reality.”
Markers of mutations
What worried the researchers most was not only the possibility of reinfection but also the fact that preliminary analyses showed a specific mutation.
“The E484K mutation is present in a group of variants identified in South Africa that have been associated with increased infectivity and has been observed in a strain recently described in Brazil,” Dr. Souza said.
Mutations are expected, appear spontaneously, and in most cases have no effects on transmission or clinical outcome – they are simply used as markers and are useful for contact tracing or studying transmission routes. But some mutations can last because they provide an advantage for the pathogen, even if only momentary. In the case of SARS-CoV-2, mutations in the protein spike gene (S) are relevant because they may give clues to that advantage – as well as to changes in infectivity, transmission potential, antibodies, and response to vaccines.
A variant of the virus that has eight changes that affect the protein S gene – and several others in different genes – is behind the increase in the number of cases in London and southeastern England. Researchers from the University of São Paulo identified one of the factors that made this new variant – classified as B.1.1.7 – more infectious.
With bioinformatics tools, they found that the protein S gene in the new viral strain has a stronger molecular interaction with the ACE2 receptor, which is on the surface of human cells and to which the virus binds, making infection possible. The variant has already spread to the rest of the world, and the first two cases have been confirmed in Brazil by the Adolf Lutz Institute.
The alert for a new variant in Africa – similar to B.1.1.7 in the United Kingdom in that it carries nine changes in protein S at position 501 – was made by the Brazilian virologist Tulio de Oliveira, PhD.
“We found that this strain seems to be spreading much faster,” Dr. Oliveira, who is with the University of KwaZulu Natal, told the journal Science. His work first alerted British scientists to the importance of the position N501Y.
“The new variants just described in the United Kingdom and South Africa are slightly more transmissible and have already been identified in cases imported into Brazil,” Dr. Motta said. “Unfortunately, we believe it is only a matter of time before it becomes indigenous.”
The viral family grows
Viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 are classified into strains on the basis of small differences in their genetic material. Since Dec. 26, 2020, in addition to the British and South African variants, it appears the Carioca lineage also is a player.
In a preprint article, researchers analyzed the evolution of the epidemic in Rio de Janeiro from April 2020 until just before the new increase in incidence in December. They compared the complete sequences of the viral genome of 180 patients from different municipalities. The study, which is being jointly conducted by members of the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro and the National Laboratory for Scientific Computing, identified a new variant of SARS-CoV-2 that has five unique mutations (from one of the predominant strains). Concern arose because, in addition to those five genetic changes, many of the samples had a sixth – the well-known E484K mutation.
“The three lines – the U.K., South Africa, and Brazil – were almost synchronous publications, but there is no clear evidence that they have any kind of common ancestry,” Carolina M. Voloch, PhD, the article’s first author and a biologist and researcher at the Molecular Virology Laboratory and associate professor in the department of genetics at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, said in an interview.
Dr. Voloch’s research focuses on the use of bioinformatics tools to study the molecular, phylogenetic, and genomic evolution of viruses.
“The emergence of new strains is common for viruses,” she said. “It can be happening anywhere in the world at any time.”
She stressed that identifying when mutations emerge will help to define the new Brazilian lineage. Researchers are working to determine whether the neutralizing antibodies of patients who have been infected with other strains respond to this Rio de Janeiro strain.
“We hope to soon be sharing these results,” Dr. Voloch said.
The article’s authors estimated that the new strain likely appeared in early July. They say more analysis is needed to predict whether the changes have a major effect on viral infectivity, the host’s immune response, or the severity of the disease. Asked about the lineage that caused the reinfection in Bahia, Dr. Voloch said she hadn’t yet contacted the authors to conduct a joint analysis but added that the data disclosed in the preprint would not represent the same variant.
“There are only two of the five mutations that characterize the Rio de Janeiro lineage. However, it has the E484K mutation that is present in more than 94% of the samples of the new variant of Rio,” she said.
She added that there’s a possibility of reinfection by the lineage that’s circulating in Rio de Janeiro and in other states, as well as countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Japan.
“The Carioca virus is being exported to the rest of the world,” Dr. Voloch said.
Virus’ diversity still unknown
Researchers now know that SARS-CoV-2 probably circulated silently in Brazil as early as February 2020 and reached all the nation’s regions before air travel was restricted. Since the first half of 2020, there have been two predominant strains.
“More than a dozen strains have been identified in Brazil, but more important than counting strains to identify the speed with which they arise – which is directly associated with the rate of infection, which is very high in the country,” said Dr. Motta.
The so-called variant of Rio de Janeiro, he said, has also been detected in other states in four regions of Brazil. The key to documenting variants is to get a more representative sample with genomes from other parts of the country.
As of Jan. 10, a total of 347,000 complete genome sequences had been shared globally through open databases since SARS-CoV-2 was first identified, but the contribution of countries is uneven. Although the cost and complexity of genetic sequencing has dropped significantly over time, effective sequencing programs still require substantial investments in personnel, equipment, reagents, and bioinformatics infrastructure.
According to Dr. Voloch, it will only be possible to combat the new coronavirus by knowing its diversity and understanding how it evolves. The Fiocruz Genomic Network has made an infographic available so researchers can track the strains circulating in Brazil. It›s the result of collaboration between researchers from Fiocruz and the GISAID Initiative, an international partnership that promotes rapid data sharing.
As of Jan. 5, researchers in Brazil had studied 1,897 genomes – not nearly enough.
“In Brazil, there is little testing and even less sequencing,” lamented Dr. Souza.
“In the U.K., 1 in 600 cases is sequenced. In Brazil it is less than 1 in 10 million cases,” Dr. Voloch added.
So far, no decisive factors for public health, such as greater virulence or greater transmissibility, have been identified in any of the strains established in Brazil. The million-dollar question is whether the emergence of new strains could have an impact on the effectiveness of vaccines being administered today.
“In one way or another, the vaccine is our best bet ever, even if in the future we identify escapist mutants and have to modify it,” Dr. Motta said. “It is what we do annually with influenza.”
Dr. Voloch, Dr. Motta, and Dr. Souza disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on the Portuguese edition of Medscape.com.
Just as Brazil surpassed 200,000 deaths from COVID-19 on Jan. 7, news from Bahia added another layer of concern: A platform case report in a preprint detailed the first case of reinfection in that state, apparently caused by a new strain, one having the E484K mutation.
That variant, now called Brazil P.1, has migrated to the United States. The Minnesota Department of Health announced on Jan. 25 the nation’s first known COVID-19 case associated with it.
The mutation is located in the protein gene of the virus’ spike, which forms the crown structure of coronaviruses and is responsible for the virus’ binding to human cells. The E484K mutation is now the focus because it’s associated with mutations that escape the immune system’s neutralizing antibodies.
“This mutation is at the center of worldwide concern, and it is the first time that it has appeared in a reinfection,” the study’s first author, Bruno Solano de Freitas Souza, MD, a researcher at the Salvador regional unit of Instituto D’Or of Teaching and Research, based at Hospital São Rafael, Salvador, Brazil, explained in an interview.
“We will wait for the sample from Bahia to confirm the case from the perspective of the Ministry of Health’s surveillance network,” said Fernando Motta, PhD, deputy head of the Laboratory for Respiratory Virus and Measles at the Oswaldo Cruz Institute in Rio de Janeiro, which acts as a national reference center for respiratory viruses with the Brazilian Ministry of Health (MS) and as a reference for the World Health Organization.
A case of reinfection
The case patient that led to the alarm was a 45-year-old woman who is a health care executive. She had no comorbidities. The team had been following health care professionals and patients who had tested positive on reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing more than once to understand whether they represented cases of prolonged viral persistence or new infections.
The woman had symptoms of viral infection on two occasions (May 26 and Oct. 26). On both occasions, results of RT-PCR testing for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal samples were positive. In the first episode, the patient had diarrhea, myalgia, asthenia, and odynophagia for about 7 days. She returned to activities 21 days later. In the second episode, she had more severe symptoms that lasted longer, but she still did not require hospitalization.
“It was the first confirmed case of reinfection in Bahia, and in the second episode, we observed a mutation that could have an impact on the ability of antibodies to neutralize the virus,” Dr. Souza said. “The research continues with the investigation of cases in which the patient has a positive SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR more than once in an interval greater than 45 days, to have a higher level of evidence.”
He stressed that “it is very important to reinforce measures to control the pandemic, social distance, use of masks, and speed up vaccination to be able to control the circulation of the virus, while monitoring the evolution of it.”
On alert for more cases
A person who twice tests positive for SARS-CoV-2 on real-time RT-PCR is suspected of having been reinfected, provided 90 or more days have elapsed between the two episodes, regardless of the condition observed. To confirm the suspected case, the samples must be sent to reference laboratories according to a plan established by the Ministry of Health in Brazil.
A health professional living in the Brazilian city of Natal represented the first confirmed case of reinfection by the new coronavirus in Brazil. That case was announced on Dec. 10, 2020.
“We communicated this case of reinfection to the MS in early December 2020. And the second sample already had the E484K mutation on the spike, as in the case of Bahia,” said Dr. Motta.
The first step in differentiating reinfection from persistence is to observe differences in the genotyping of the virus. For the technique to be successful, Dr. Souza said, researchers need a large amount of viral genetic material, which usually cannot be obtained.
“That is why there are many more suspected than confirmed cases,” Dr. Souza explained. He admitted that, although there are few cases, “it is increasingly clear that reinfection is a reality.”
Markers of mutations
What worried the researchers most was not only the possibility of reinfection but also the fact that preliminary analyses showed a specific mutation.
“The E484K mutation is present in a group of variants identified in South Africa that have been associated with increased infectivity and has been observed in a strain recently described in Brazil,” Dr. Souza said.
Mutations are expected, appear spontaneously, and in most cases have no effects on transmission or clinical outcome – they are simply used as markers and are useful for contact tracing or studying transmission routes. But some mutations can last because they provide an advantage for the pathogen, even if only momentary. In the case of SARS-CoV-2, mutations in the protein spike gene (S) are relevant because they may give clues to that advantage – as well as to changes in infectivity, transmission potential, antibodies, and response to vaccines.
A variant of the virus that has eight changes that affect the protein S gene – and several others in different genes – is behind the increase in the number of cases in London and southeastern England. Researchers from the University of São Paulo identified one of the factors that made this new variant – classified as B.1.1.7 – more infectious.
With bioinformatics tools, they found that the protein S gene in the new viral strain has a stronger molecular interaction with the ACE2 receptor, which is on the surface of human cells and to which the virus binds, making infection possible. The variant has already spread to the rest of the world, and the first two cases have been confirmed in Brazil by the Adolf Lutz Institute.
The alert for a new variant in Africa – similar to B.1.1.7 in the United Kingdom in that it carries nine changes in protein S at position 501 – was made by the Brazilian virologist Tulio de Oliveira, PhD.
“We found that this strain seems to be spreading much faster,” Dr. Oliveira, who is with the University of KwaZulu Natal, told the journal Science. His work first alerted British scientists to the importance of the position N501Y.
“The new variants just described in the United Kingdom and South Africa are slightly more transmissible and have already been identified in cases imported into Brazil,” Dr. Motta said. “Unfortunately, we believe it is only a matter of time before it becomes indigenous.”
The viral family grows
Viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 are classified into strains on the basis of small differences in their genetic material. Since Dec. 26, 2020, in addition to the British and South African variants, it appears the Carioca lineage also is a player.
In a preprint article, researchers analyzed the evolution of the epidemic in Rio de Janeiro from April 2020 until just before the new increase in incidence in December. They compared the complete sequences of the viral genome of 180 patients from different municipalities. The study, which is being jointly conducted by members of the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro and the National Laboratory for Scientific Computing, identified a new variant of SARS-CoV-2 that has five unique mutations (from one of the predominant strains). Concern arose because, in addition to those five genetic changes, many of the samples had a sixth – the well-known E484K mutation.
“The three lines – the U.K., South Africa, and Brazil – were almost synchronous publications, but there is no clear evidence that they have any kind of common ancestry,” Carolina M. Voloch, PhD, the article’s first author and a biologist and researcher at the Molecular Virology Laboratory and associate professor in the department of genetics at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, said in an interview.
Dr. Voloch’s research focuses on the use of bioinformatics tools to study the molecular, phylogenetic, and genomic evolution of viruses.
“The emergence of new strains is common for viruses,” she said. “It can be happening anywhere in the world at any time.”
She stressed that identifying when mutations emerge will help to define the new Brazilian lineage. Researchers are working to determine whether the neutralizing antibodies of patients who have been infected with other strains respond to this Rio de Janeiro strain.
“We hope to soon be sharing these results,” Dr. Voloch said.
The article’s authors estimated that the new strain likely appeared in early July. They say more analysis is needed to predict whether the changes have a major effect on viral infectivity, the host’s immune response, or the severity of the disease. Asked about the lineage that caused the reinfection in Bahia, Dr. Voloch said she hadn’t yet contacted the authors to conduct a joint analysis but added that the data disclosed in the preprint would not represent the same variant.
“There are only two of the five mutations that characterize the Rio de Janeiro lineage. However, it has the E484K mutation that is present in more than 94% of the samples of the new variant of Rio,” she said.
She added that there’s a possibility of reinfection by the lineage that’s circulating in Rio de Janeiro and in other states, as well as countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Japan.
“The Carioca virus is being exported to the rest of the world,” Dr. Voloch said.
Virus’ diversity still unknown
Researchers now know that SARS-CoV-2 probably circulated silently in Brazil as early as February 2020 and reached all the nation’s regions before air travel was restricted. Since the first half of 2020, there have been two predominant strains.
“More than a dozen strains have been identified in Brazil, but more important than counting strains to identify the speed with which they arise – which is directly associated with the rate of infection, which is very high in the country,” said Dr. Motta.
The so-called variant of Rio de Janeiro, he said, has also been detected in other states in four regions of Brazil. The key to documenting variants is to get a more representative sample with genomes from other parts of the country.
As of Jan. 10, a total of 347,000 complete genome sequences had been shared globally through open databases since SARS-CoV-2 was first identified, but the contribution of countries is uneven. Although the cost and complexity of genetic sequencing has dropped significantly over time, effective sequencing programs still require substantial investments in personnel, equipment, reagents, and bioinformatics infrastructure.
According to Dr. Voloch, it will only be possible to combat the new coronavirus by knowing its diversity and understanding how it evolves. The Fiocruz Genomic Network has made an infographic available so researchers can track the strains circulating in Brazil. It›s the result of collaboration between researchers from Fiocruz and the GISAID Initiative, an international partnership that promotes rapid data sharing.
As of Jan. 5, researchers in Brazil had studied 1,897 genomes – not nearly enough.
“In Brazil, there is little testing and even less sequencing,” lamented Dr. Souza.
“In the U.K., 1 in 600 cases is sequenced. In Brazil it is less than 1 in 10 million cases,” Dr. Voloch added.
So far, no decisive factors for public health, such as greater virulence or greater transmissibility, have been identified in any of the strains established in Brazil. The million-dollar question is whether the emergence of new strains could have an impact on the effectiveness of vaccines being administered today.
“In one way or another, the vaccine is our best bet ever, even if in the future we identify escapist mutants and have to modify it,” Dr. Motta said. “It is what we do annually with influenza.”
Dr. Voloch, Dr. Motta, and Dr. Souza disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on the Portuguese edition of Medscape.com.






