User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
Daily Recap: Hospitalized COVID patients need MRIs; Americans vote for face masks
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
A new review outlined a three-stage classification of the impact of COVID-19 on the central nervous system and recommended all hospitalized patients with the virus undergo MRI to flag potential neurologic damage and inform postdischarge monitoring.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” said lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD. The review was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. Read more.
Topline results for novel intranasal med to treat opioid overdose
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release. Read more.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that such testing was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Read more.
Weight loss failures drive bariatric surgery regrets
Not all weight loss surgery patients “live happily ever after,” according to Daniel B. Jones, MD.
A 2014 study of 22 women who underwent weight loss surgery reported lower energy, worse quality of life, and persistent eating disorders.
Of gastric band patients, “almost 20% did not think they made the right decision,” he said. As for RYGP patients, 13% of patients at 1 year and 4 years reported that weight loss surgery caused “some” or “a lot” of negative effects. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
A new review outlined a three-stage classification of the impact of COVID-19 on the central nervous system and recommended all hospitalized patients with the virus undergo MRI to flag potential neurologic damage and inform postdischarge monitoring.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” said lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD. The review was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. Read more.
Topline results for novel intranasal med to treat opioid overdose
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release. Read more.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that such testing was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Read more.
Weight loss failures drive bariatric surgery regrets
Not all weight loss surgery patients “live happily ever after,” according to Daniel B. Jones, MD.
A 2014 study of 22 women who underwent weight loss surgery reported lower energy, worse quality of life, and persistent eating disorders.
Of gastric band patients, “almost 20% did not think they made the right decision,” he said. As for RYGP patients, 13% of patients at 1 year and 4 years reported that weight loss surgery caused “some” or “a lot” of negative effects. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
A new review outlined a three-stage classification of the impact of COVID-19 on the central nervous system and recommended all hospitalized patients with the virus undergo MRI to flag potential neurologic damage and inform postdischarge monitoring.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” said lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD. The review was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. Read more.
Topline results for novel intranasal med to treat opioid overdose
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release. Read more.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that such testing was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Read more.
Weight loss failures drive bariatric surgery regrets
Not all weight loss surgery patients “live happily ever after,” according to Daniel B. Jones, MD.
A 2014 study of 22 women who underwent weight loss surgery reported lower energy, worse quality of life, and persistent eating disorders.
Of gastric band patients, “almost 20% did not think they made the right decision,” he said. As for RYGP patients, 13% of patients at 1 year and 4 years reported that weight loss surgery caused “some” or “a lot” of negative effects. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
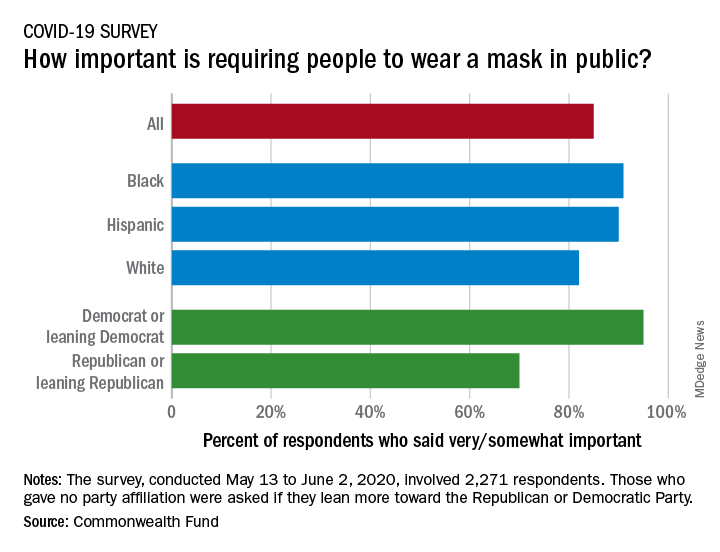
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.

Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.

Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center in McLean, Va., said.
“Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should have a neurological evaluation and ideally a brain MRI before leaving the hospital; and, if there are abnormalities, they should follow up with a neurologist in 3-4 months,” said Dr. Fotuhi, who is also affiliate staff at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
The review was published online June 8 in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Wreaks CNS havoc
It has become “increasingly evident” that SARS-CoV-2 can cause neurologic manifestations, including anosmia, seizures, stroke, confusion, encephalopathy, and total paralysis, the authors wrote.
They noted that SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, which facilitates the conversion of angiotensin II to angiotensin. After ACE2 has bound to respiratory epithelial cells and then to epithelial cells in blood vessels, SARS-CoV-2 triggers the formation of a “cytokine storm.”
These cytokines, in turn, increase vascular permeability, edema, and widespread inflammation, as well as triggering “hypercoagulation cascades,” which cause small and large blood clots that affect multiple organs.
If SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier, directly entering the brain, it can contribute to demyelination or neurodegeneration.
“We very thoroughly reviewed the literature published between Jan. 1 and May 1, 2020, about neurological issues [in COVID-19] and what I found interesting is that so many neurological things can happen due to a virus which is so small,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“This virus’ DNA has such limited information, and yet it can wreak havoc on our nervous system because it kicks off such a potent defense system in our body that damages our nervous system,” he said.
Three-stage classification
- Stage 1: The extent of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptors is limited to the nasal and gustatory epithelial cells, with the cytokine storm remaining “low and controlled.” During this stage, patients may experience smell or taste impairments, but often recover without any interventions.
- Stage 2: A “robust immune response” is activated by the virus, leading to inflammation in the blood vessels, increased hypercoagulability factors, and the formation of blood clots in cerebral arteries and veins. The patient may therefore experience either large or small strokes. Additional stage 2 symptoms include fatigue, hemiplegia, sensory loss, , tetraplegia, , or ataxia.
- Stage 3: The cytokine storm in the blood vessels is so severe that it causes an “explosive inflammatory response” and penetrates the blood-brain barrier, leading to the entry of cytokines, blood components, and viral particles into the brain parenchyma and causing neuronal cell death and encephalitis. This stage can be characterized by seizures, confusion, , coma, loss of consciousness, or death.
“Patients in stage 3 are more likely to have long-term consequences, because there is evidence that the virus particles have actually penetrated the brain, and we know that SARS-CoV-2 can remain dormant in neurons for many years,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“Studies of coronaviruses have shown a link between the viruses and the risk of multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease even decades later,” he added.
“Based on several reports in recent months, between 36% to 55% of patients with COVID-19 that are hospitalized have some neurological symptoms, but if you don’t look for them, you won’t see them,” Dr. Fotuhi noted.
As a result, patients should be monitored over time after discharge, as they may develop cognitive dysfunction down the road.
Additionally, “it is imperative for patients [hospitalized with COVID-19] to get a baseline MRI before leaving the hospital so that we have a starting point for future evaluation and treatment,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“The good news is that neurological manifestations of COVID-19 are treatable,” and “can improve with intensive training,” including lifestyle changes – such as a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress reduction, improved sleep, biofeedback, and brain rehabilitation, Dr. Fotuhi added.
Routine MRI not necessary
Kenneth Tyler, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, disagreed that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should routinely receive an MRI.
“Whenever you are using a piece of equipment on patients who are COVID-19 infected, you risk introducing the infection to uninfected patients,” he said. Instead, “the indication is in patients who develop unexplained neurological manifestations – altered mental status or focal seizures, for example – because in those cases, you do need to understand whether there are underlying structural abnormalities,” said Dr. Tyler, who was not involved in the review.
Also commenting on the review, Vanja Douglas, MD, associate professor of clinical neurology, University of California, San Francisco, described the review as “thorough” and suggested it may “help us understand how to design observational studies to test whether the associations are due to severe respiratory illness or are specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Dr. Douglas, who was not involved in the review, added that it is “helpful in giving us a sense of which neurologic syndromes have been observed in COVID-19 patients, and therefore which patients neurologists may want to screen more carefully during the pandemic.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Fotuhi disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor reported receiving consulting fees as a member of the scientific advisory board for Brainreader and reports royalties for expert witness consultation in conjunction with Neurevolution. Dr. Tyler and Dr. Douglas disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center in McLean, Va., said.
“Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should have a neurological evaluation and ideally a brain MRI before leaving the hospital; and, if there are abnormalities, they should follow up with a neurologist in 3-4 months,” said Dr. Fotuhi, who is also affiliate staff at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
The review was published online June 8 in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Wreaks CNS havoc
It has become “increasingly evident” that SARS-CoV-2 can cause neurologic manifestations, including anosmia, seizures, stroke, confusion, encephalopathy, and total paralysis, the authors wrote.
They noted that SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, which facilitates the conversion of angiotensin II to angiotensin. After ACE2 has bound to respiratory epithelial cells and then to epithelial cells in blood vessels, SARS-CoV-2 triggers the formation of a “cytokine storm.”
These cytokines, in turn, increase vascular permeability, edema, and widespread inflammation, as well as triggering “hypercoagulation cascades,” which cause small and large blood clots that affect multiple organs.
If SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier, directly entering the brain, it can contribute to demyelination or neurodegeneration.
“We very thoroughly reviewed the literature published between Jan. 1 and May 1, 2020, about neurological issues [in COVID-19] and what I found interesting is that so many neurological things can happen due to a virus which is so small,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“This virus’ DNA has such limited information, and yet it can wreak havoc on our nervous system because it kicks off such a potent defense system in our body that damages our nervous system,” he said.
Three-stage classification
- Stage 1: The extent of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptors is limited to the nasal and gustatory epithelial cells, with the cytokine storm remaining “low and controlled.” During this stage, patients may experience smell or taste impairments, but often recover without any interventions.
- Stage 2: A “robust immune response” is activated by the virus, leading to inflammation in the blood vessels, increased hypercoagulability factors, and the formation of blood clots in cerebral arteries and veins. The patient may therefore experience either large or small strokes. Additional stage 2 symptoms include fatigue, hemiplegia, sensory loss, , tetraplegia, , or ataxia.
- Stage 3: The cytokine storm in the blood vessels is so severe that it causes an “explosive inflammatory response” and penetrates the blood-brain barrier, leading to the entry of cytokines, blood components, and viral particles into the brain parenchyma and causing neuronal cell death and encephalitis. This stage can be characterized by seizures, confusion, , coma, loss of consciousness, or death.
“Patients in stage 3 are more likely to have long-term consequences, because there is evidence that the virus particles have actually penetrated the brain, and we know that SARS-CoV-2 can remain dormant in neurons for many years,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“Studies of coronaviruses have shown a link between the viruses and the risk of multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease even decades later,” he added.
“Based on several reports in recent months, between 36% to 55% of patients with COVID-19 that are hospitalized have some neurological symptoms, but if you don’t look for them, you won’t see them,” Dr. Fotuhi noted.
As a result, patients should be monitored over time after discharge, as they may develop cognitive dysfunction down the road.
Additionally, “it is imperative for patients [hospitalized with COVID-19] to get a baseline MRI before leaving the hospital so that we have a starting point for future evaluation and treatment,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“The good news is that neurological manifestations of COVID-19 are treatable,” and “can improve with intensive training,” including lifestyle changes – such as a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress reduction, improved sleep, biofeedback, and brain rehabilitation, Dr. Fotuhi added.
Routine MRI not necessary
Kenneth Tyler, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, disagreed that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should routinely receive an MRI.
“Whenever you are using a piece of equipment on patients who are COVID-19 infected, you risk introducing the infection to uninfected patients,” he said. Instead, “the indication is in patients who develop unexplained neurological manifestations – altered mental status or focal seizures, for example – because in those cases, you do need to understand whether there are underlying structural abnormalities,” said Dr. Tyler, who was not involved in the review.
Also commenting on the review, Vanja Douglas, MD, associate professor of clinical neurology, University of California, San Francisco, described the review as “thorough” and suggested it may “help us understand how to design observational studies to test whether the associations are due to severe respiratory illness or are specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Dr. Douglas, who was not involved in the review, added that it is “helpful in giving us a sense of which neurologic syndromes have been observed in COVID-19 patients, and therefore which patients neurologists may want to screen more carefully during the pandemic.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Fotuhi disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor reported receiving consulting fees as a member of the scientific advisory board for Brainreader and reports royalties for expert witness consultation in conjunction with Neurevolution. Dr. Tyler and Dr. Douglas disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center in McLean, Va., said.
“Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should have a neurological evaluation and ideally a brain MRI before leaving the hospital; and, if there are abnormalities, they should follow up with a neurologist in 3-4 months,” said Dr. Fotuhi, who is also affiliate staff at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
The review was published online June 8 in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Wreaks CNS havoc
It has become “increasingly evident” that SARS-CoV-2 can cause neurologic manifestations, including anosmia, seizures, stroke, confusion, encephalopathy, and total paralysis, the authors wrote.
They noted that SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, which facilitates the conversion of angiotensin II to angiotensin. After ACE2 has bound to respiratory epithelial cells and then to epithelial cells in blood vessels, SARS-CoV-2 triggers the formation of a “cytokine storm.”
These cytokines, in turn, increase vascular permeability, edema, and widespread inflammation, as well as triggering “hypercoagulation cascades,” which cause small and large blood clots that affect multiple organs.
If SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier, directly entering the brain, it can contribute to demyelination or neurodegeneration.
“We very thoroughly reviewed the literature published between Jan. 1 and May 1, 2020, about neurological issues [in COVID-19] and what I found interesting is that so many neurological things can happen due to a virus which is so small,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“This virus’ DNA has such limited information, and yet it can wreak havoc on our nervous system because it kicks off such a potent defense system in our body that damages our nervous system,” he said.
Three-stage classification
- Stage 1: The extent of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptors is limited to the nasal and gustatory epithelial cells, with the cytokine storm remaining “low and controlled.” During this stage, patients may experience smell or taste impairments, but often recover without any interventions.
- Stage 2: A “robust immune response” is activated by the virus, leading to inflammation in the blood vessels, increased hypercoagulability factors, and the formation of blood clots in cerebral arteries and veins. The patient may therefore experience either large or small strokes. Additional stage 2 symptoms include fatigue, hemiplegia, sensory loss, , tetraplegia, , or ataxia.
- Stage 3: The cytokine storm in the blood vessels is so severe that it causes an “explosive inflammatory response” and penetrates the blood-brain barrier, leading to the entry of cytokines, blood components, and viral particles into the brain parenchyma and causing neuronal cell death and encephalitis. This stage can be characterized by seizures, confusion, , coma, loss of consciousness, or death.
“Patients in stage 3 are more likely to have long-term consequences, because there is evidence that the virus particles have actually penetrated the brain, and we know that SARS-CoV-2 can remain dormant in neurons for many years,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“Studies of coronaviruses have shown a link between the viruses and the risk of multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease even decades later,” he added.
“Based on several reports in recent months, between 36% to 55% of patients with COVID-19 that are hospitalized have some neurological symptoms, but if you don’t look for them, you won’t see them,” Dr. Fotuhi noted.
As a result, patients should be monitored over time after discharge, as they may develop cognitive dysfunction down the road.
Additionally, “it is imperative for patients [hospitalized with COVID-19] to get a baseline MRI before leaving the hospital so that we have a starting point for future evaluation and treatment,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“The good news is that neurological manifestations of COVID-19 are treatable,” and “can improve with intensive training,” including lifestyle changes – such as a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress reduction, improved sleep, biofeedback, and brain rehabilitation, Dr. Fotuhi added.
Routine MRI not necessary
Kenneth Tyler, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, disagreed that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should routinely receive an MRI.
“Whenever you are using a piece of equipment on patients who are COVID-19 infected, you risk introducing the infection to uninfected patients,” he said. Instead, “the indication is in patients who develop unexplained neurological manifestations – altered mental status or focal seizures, for example – because in those cases, you do need to understand whether there are underlying structural abnormalities,” said Dr. Tyler, who was not involved in the review.
Also commenting on the review, Vanja Douglas, MD, associate professor of clinical neurology, University of California, San Francisco, described the review as “thorough” and suggested it may “help us understand how to design observational studies to test whether the associations are due to severe respiratory illness or are specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Dr. Douglas, who was not involved in the review, added that it is “helpful in giving us a sense of which neurologic syndromes have been observed in COVID-19 patients, and therefore which patients neurologists may want to screen more carefully during the pandemic.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Fotuhi disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor reported receiving consulting fees as a member of the scientific advisory board for Brainreader and reports royalties for expert witness consultation in conjunction with Neurevolution. Dr. Tyler and Dr. Douglas disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Topline results for novel intranasal med to treat opioid overdose
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced on June 30.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release.
“The need has also escalated due to the COVID-19 pandemic as the consequences of social distancing and economic weakness are expected to lead to a significant increase in mental health issues and substance use disorders,” Mr. Sørensen added.
Robert Rönn, vice president and head of research and development at Orexo, noted in the same release that the company will now be working with the Food and Drug Administration “to identify the optimal route to market.”
There were more than 31,000 fatalities from highly potent synthetic opioids in the United States in 2018, the manufacturer reported. “Like naloxone, nalmefene is an opioid antagonist that acts by blocking the effects of opioids at the opioid receptors.”
However, nalmefene has a longer half-life than naloxone. These longer-acting properties may be “of particular value to protect against renarcotization (second overdose), as the antagonist wears off,” according to an Orexo press release.
In addition to showing rapid absorption across all formulations studied, study results showed “good tolerability, supporting the viability” of the treatment as an opioid overdose rescue medication, the company said.
“This is not only a proof of concept for our wholly owned OX125 product, but also a demonstration of the value of our novel nasal technology platform,” Mr. Rönn said.
“Alongside OX124, our naloxone rescue project, OX125 will be an important lifesaving addition in our commitment to helping patients suffering from opioid addiction in all phases,” Mr. Sørensen added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced on June 30.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release.
“The need has also escalated due to the COVID-19 pandemic as the consequences of social distancing and economic weakness are expected to lead to a significant increase in mental health issues and substance use disorders,” Mr. Sørensen added.
Robert Rönn, vice president and head of research and development at Orexo, noted in the same release that the company will now be working with the Food and Drug Administration “to identify the optimal route to market.”
There were more than 31,000 fatalities from highly potent synthetic opioids in the United States in 2018, the manufacturer reported. “Like naloxone, nalmefene is an opioid antagonist that acts by blocking the effects of opioids at the opioid receptors.”
However, nalmefene has a longer half-life than naloxone. These longer-acting properties may be “of particular value to protect against renarcotization (second overdose), as the antagonist wears off,” according to an Orexo press release.
In addition to showing rapid absorption across all formulations studied, study results showed “good tolerability, supporting the viability” of the treatment as an opioid overdose rescue medication, the company said.
“This is not only a proof of concept for our wholly owned OX125 product, but also a demonstration of the value of our novel nasal technology platform,” Mr. Rönn said.
“Alongside OX124, our naloxone rescue project, OX125 will be an important lifesaving addition in our commitment to helping patients suffering from opioid addiction in all phases,” Mr. Sørensen added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced on June 30.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release.
“The need has also escalated due to the COVID-19 pandemic as the consequences of social distancing and economic weakness are expected to lead to a significant increase in mental health issues and substance use disorders,” Mr. Sørensen added.
Robert Rönn, vice president and head of research and development at Orexo, noted in the same release that the company will now be working with the Food and Drug Administration “to identify the optimal route to market.”
There were more than 31,000 fatalities from highly potent synthetic opioids in the United States in 2018, the manufacturer reported. “Like naloxone, nalmefene is an opioid antagonist that acts by blocking the effects of opioids at the opioid receptors.”
However, nalmefene has a longer half-life than naloxone. These longer-acting properties may be “of particular value to protect against renarcotization (second overdose), as the antagonist wears off,” according to an Orexo press release.
In addition to showing rapid absorption across all formulations studied, study results showed “good tolerability, supporting the viability” of the treatment as an opioid overdose rescue medication, the company said.
“This is not only a proof of concept for our wholly owned OX125 product, but also a demonstration of the value of our novel nasal technology platform,” Mr. Rönn said.
“Alongside OX124, our naloxone rescue project, OX125 will be an important lifesaving addition in our commitment to helping patients suffering from opioid addiction in all phases,” Mr. Sørensen added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Cognitive deficits complex in youths with type 2 diabetes
Teens and young adults with diabetes have cognitive deficits that vary by diabetes type and could negatively impact their medical literacy and self-care, an investigator reported at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Individuals with youth-onset type 1 or 2 diabetes all performed below average on tests that measure flexible thinking and problem solving, according to the investigator, who reported an analysis including 1,380 individuals enrolled in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study.
That finding suggests that diabetes diagnosed before age 20 contributes to poor fluid cognitive function, which consists of skills that facilitate goal-directed behaviors, according to investigator Allison Shapiro, MPH, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
However, individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) performed even worse than those with type 1 diabetes (T1D) on the fluid cognitive function tests, even after adjustment for demographic factors and other confounders, Dr. Shapiro said in her presentation.
Further analysis revealed that individuals with T2D performed significantly worse on measures of crystallized cognition, a domain that includes skills such as vocabulary and language. That suggests the poor fluid cognitive abilities in youths with diabetes may in fact be a result of poor crystallized cognitive development, according to the investigator.
“Among adolescents and young adults with youth-onset type 2 diabetes specifically, intervention should focus on developing both fluid cognitive skills and crystallized cognitive skills,” Dr. Shapiro said.
Deficits in fluid cognitive function (such as reasoning or processing speed) can negatively affect diabetes self-care, thereby potentially increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications, while deficits in crystallized cognitive function (such as vocabulary and understanding of language) could impact medical literacy further compounding the self-care issues.
The study is believed to be one of the first to compare cognitive function deficits in youths with type 1 or 2 diabetes. Although studies in adults clearly show a detrimental relationship between diabetes and cognitive function, according to Dr. Shapiro, the bulk of the research in youths has focused on T1D.
“While limited work has been done in youth-onset type 2 diabetes, cognitive deficits are consistently observed, compared to youth without diabetes,” she said.
Results of this study emphasize the importance of dietary changes and other lifestyle interventions in young patients with diabetes, according to David Della-Morte, MD, PhD, associate professor of neurology at the University of Miami.
“Even the youngest patients may develop cognitive dysfunction,” Dr. Della-Morte said in an interview. “That means that lifestyle is very important, especially in obese patients that are prone to develop type 2 diabetes.”
The analysis by Dr. Shapiro and coinvestigators included 1,095 youths and young adults with T1D and 285 with T2D who had undergone a cognition assessment as part of a study visit. They were aged an average of 22 years, and had an average diabetes duration of 11 years.
The overall fluid cognition score was significantly lower in those individuals with T2D, compared with those with T1D, investigators found. Compared with the national average score of 100, the T2D group scored 84.7, or a full standard deviation below that average, said Dr. Shapiro, while those with T1D scored 95.5 (P < .001).
Participants with T2D also scored significantly lower in individual measures of fluid cognition, including processing speed, inhibitory control and attention, working memory, and episodic memory, she reported. At first glance, that suggested youth-onset T2D has a specific effect on fluid cognition; however, the story remains incomplete without looking at crystallized cognition markers such as vocabulary and language.
Toward that end, a picture vocabulary test conducted as part of the cognitive assessment showed a significant difference between those with T2D, who on average scored 91.5, and those with T1D, who scored 103.6 (P < .001). Accounting for those picture vocabulary scores attenuated the differences between groups in fluid cognitive scores, suggesting that differences in crystallized cognitive function underly the observed differences in fluid cognitive function between groups, Dr. Shapiro said.
Skills such as vocabulary and language are thought to be stable and not influenced by neurologic changes brought on by disease processes such as youth-onset diabetes, but rather, influenced by factors such as childcare and education, according to Dr. Shapiro.
“Crystallized cognition therefore provides a window into an individual’s cognitive functioning, independent of their disease or premorbid to the onset of their disease,” she said.
Dr. Shapiro said she had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Shapiro A et al. ADA 2020, Abstract 279-OR.
Teens and young adults with diabetes have cognitive deficits that vary by diabetes type and could negatively impact their medical literacy and self-care, an investigator reported at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Individuals with youth-onset type 1 or 2 diabetes all performed below average on tests that measure flexible thinking and problem solving, according to the investigator, who reported an analysis including 1,380 individuals enrolled in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study.
That finding suggests that diabetes diagnosed before age 20 contributes to poor fluid cognitive function, which consists of skills that facilitate goal-directed behaviors, according to investigator Allison Shapiro, MPH, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
However, individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) performed even worse than those with type 1 diabetes (T1D) on the fluid cognitive function tests, even after adjustment for demographic factors and other confounders, Dr. Shapiro said in her presentation.
Further analysis revealed that individuals with T2D performed significantly worse on measures of crystallized cognition, a domain that includes skills such as vocabulary and language. That suggests the poor fluid cognitive abilities in youths with diabetes may in fact be a result of poor crystallized cognitive development, according to the investigator.
“Among adolescents and young adults with youth-onset type 2 diabetes specifically, intervention should focus on developing both fluid cognitive skills and crystallized cognitive skills,” Dr. Shapiro said.
Deficits in fluid cognitive function (such as reasoning or processing speed) can negatively affect diabetes self-care, thereby potentially increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications, while deficits in crystallized cognitive function (such as vocabulary and understanding of language) could impact medical literacy further compounding the self-care issues.
The study is believed to be one of the first to compare cognitive function deficits in youths with type 1 or 2 diabetes. Although studies in adults clearly show a detrimental relationship between diabetes and cognitive function, according to Dr. Shapiro, the bulk of the research in youths has focused on T1D.
“While limited work has been done in youth-onset type 2 diabetes, cognitive deficits are consistently observed, compared to youth without diabetes,” she said.
Results of this study emphasize the importance of dietary changes and other lifestyle interventions in young patients with diabetes, according to David Della-Morte, MD, PhD, associate professor of neurology at the University of Miami.
“Even the youngest patients may develop cognitive dysfunction,” Dr. Della-Morte said in an interview. “That means that lifestyle is very important, especially in obese patients that are prone to develop type 2 diabetes.”
The analysis by Dr. Shapiro and coinvestigators included 1,095 youths and young adults with T1D and 285 with T2D who had undergone a cognition assessment as part of a study visit. They were aged an average of 22 years, and had an average diabetes duration of 11 years.
The overall fluid cognition score was significantly lower in those individuals with T2D, compared with those with T1D, investigators found. Compared with the national average score of 100, the T2D group scored 84.7, or a full standard deviation below that average, said Dr. Shapiro, while those with T1D scored 95.5 (P < .001).
Participants with T2D also scored significantly lower in individual measures of fluid cognition, including processing speed, inhibitory control and attention, working memory, and episodic memory, she reported. At first glance, that suggested youth-onset T2D has a specific effect on fluid cognition; however, the story remains incomplete without looking at crystallized cognition markers such as vocabulary and language.
Toward that end, a picture vocabulary test conducted as part of the cognitive assessment showed a significant difference between those with T2D, who on average scored 91.5, and those with T1D, who scored 103.6 (P < .001). Accounting for those picture vocabulary scores attenuated the differences between groups in fluid cognitive scores, suggesting that differences in crystallized cognitive function underly the observed differences in fluid cognitive function between groups, Dr. Shapiro said.
Skills such as vocabulary and language are thought to be stable and not influenced by neurologic changes brought on by disease processes such as youth-onset diabetes, but rather, influenced by factors such as childcare and education, according to Dr. Shapiro.
“Crystallized cognition therefore provides a window into an individual’s cognitive functioning, independent of their disease or premorbid to the onset of their disease,” she said.
Dr. Shapiro said she had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Shapiro A et al. ADA 2020, Abstract 279-OR.
Teens and young adults with diabetes have cognitive deficits that vary by diabetes type and could negatively impact their medical literacy and self-care, an investigator reported at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Individuals with youth-onset type 1 or 2 diabetes all performed below average on tests that measure flexible thinking and problem solving, according to the investigator, who reported an analysis including 1,380 individuals enrolled in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study.
That finding suggests that diabetes diagnosed before age 20 contributes to poor fluid cognitive function, which consists of skills that facilitate goal-directed behaviors, according to investigator Allison Shapiro, MPH, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
However, individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) performed even worse than those with type 1 diabetes (T1D) on the fluid cognitive function tests, even after adjustment for demographic factors and other confounders, Dr. Shapiro said in her presentation.
Further analysis revealed that individuals with T2D performed significantly worse on measures of crystallized cognition, a domain that includes skills such as vocabulary and language. That suggests the poor fluid cognitive abilities in youths with diabetes may in fact be a result of poor crystallized cognitive development, according to the investigator.
“Among adolescents and young adults with youth-onset type 2 diabetes specifically, intervention should focus on developing both fluid cognitive skills and crystallized cognitive skills,” Dr. Shapiro said.
Deficits in fluid cognitive function (such as reasoning or processing speed) can negatively affect diabetes self-care, thereby potentially increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications, while deficits in crystallized cognitive function (such as vocabulary and understanding of language) could impact medical literacy further compounding the self-care issues.
The study is believed to be one of the first to compare cognitive function deficits in youths with type 1 or 2 diabetes. Although studies in adults clearly show a detrimental relationship between diabetes and cognitive function, according to Dr. Shapiro, the bulk of the research in youths has focused on T1D.
“While limited work has been done in youth-onset type 2 diabetes, cognitive deficits are consistently observed, compared to youth without diabetes,” she said.
Results of this study emphasize the importance of dietary changes and other lifestyle interventions in young patients with diabetes, according to David Della-Morte, MD, PhD, associate professor of neurology at the University of Miami.
“Even the youngest patients may develop cognitive dysfunction,” Dr. Della-Morte said in an interview. “That means that lifestyle is very important, especially in obese patients that are prone to develop type 2 diabetes.”
The analysis by Dr. Shapiro and coinvestigators included 1,095 youths and young adults with T1D and 285 with T2D who had undergone a cognition assessment as part of a study visit. They were aged an average of 22 years, and had an average diabetes duration of 11 years.
The overall fluid cognition score was significantly lower in those individuals with T2D, compared with those with T1D, investigators found. Compared with the national average score of 100, the T2D group scored 84.7, or a full standard deviation below that average, said Dr. Shapiro, while those with T1D scored 95.5 (P < .001).
Participants with T2D also scored significantly lower in individual measures of fluid cognition, including processing speed, inhibitory control and attention, working memory, and episodic memory, she reported. At first glance, that suggested youth-onset T2D has a specific effect on fluid cognition; however, the story remains incomplete without looking at crystallized cognition markers such as vocabulary and language.
Toward that end, a picture vocabulary test conducted as part of the cognitive assessment showed a significant difference between those with T2D, who on average scored 91.5, and those with T1D, who scored 103.6 (P < .001). Accounting for those picture vocabulary scores attenuated the differences between groups in fluid cognitive scores, suggesting that differences in crystallized cognitive function underly the observed differences in fluid cognitive function between groups, Dr. Shapiro said.
Skills such as vocabulary and language are thought to be stable and not influenced by neurologic changes brought on by disease processes such as youth-onset diabetes, but rather, influenced by factors such as childcare and education, according to Dr. Shapiro.
“Crystallized cognition therefore provides a window into an individual’s cognitive functioning, independent of their disease or premorbid to the onset of their disease,” she said.
Dr. Shapiro said she had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Shapiro A et al. ADA 2020, Abstract 279-OR.
FROM ADA 2020
Psychiatric manifestations of sport-related concussion
Ms. J, age 19, is a Division I collegiate volleyball player who recently sustained her third sport-related concussion (SRC). She has no psychiatric history but does have a history of migraine, and her headaches have worsened since the most recent SRC. She has a family history of depression (mother and her sole sibling). Ms. J recently experienced the loss of her coach, someone she greatly admired, in a motor vehicle accident. She is referred to outpatient psychiatry for assessment of mood symptoms that are persisting 1 month after the SRC. Upon assessment, she is found to meet 8 of the 9 criteria for a major depressive episode, including suicidality with vague plans but no intent to end her life.
Although Ms. J does not have a history of psychiatric illness, her psychiatrist recognizes that she has factors that increase her risk of developing depression post-SRC, and of poor recovery from SRC. These include pre-existing symptoms, such as her history of migraine, which is common in patients after SRC. Additionally, a family history of psychiatric disorders and high life stressors (eg, recent loss of her coach) are risk factors for a poor SRC recovery.1 Due to these risk factors and the severity of Ms. J’s symptoms—which include suicidal ideation—the psychiatrist believes that her depressive symptoms might be unlikely to improve in the coming weeks, so he establishes a diagnosis of “depressive disorder due to another medical condition (concussion)” because the development of her depressive symptoms coincided with the SRC. If Ms. J had a pre-existing mood disorder, or if her depression had not developed until later in the post-injury period, it would have been more difficult to establish confidently that the depressive episode was a direct physiologic consequence of the SRC; if that had been the case, the diagnosis probably would have been unspecified or other specified depressive disorder.2
SRC is a traumatic brain injury (TBI) induced by biomechanical forces, typically resulting in short-lived impairment of neurologic function, although signs and symptoms may evolve over minutes to hours.3 It largely reflects functional, rather than structural, brain disturbances.3 SRC has been deemed a “neuropsychiatric syndrome” because psychiatric manifestations are common.4 There may be a myriad of biopsychosocial factors involved in the etiology of psychiatric symptoms in an individual who sustains an SRC. For example, SRC may have a direct physiologic cause of psychiatric symptoms based on the location and degree of injury to the brain. Additionally, pre-existing psychiatric symptoms might increase the likelihood of sustaining an SRC. Finally, as with any major injury, illness, or event, stressors associated with SRC may cause psychiatric symptoms.
Regardless of causal factors, psychiatrists should be comfortable with managing psychiatric symptoms that commonly accompany this condition. This article highlights possible psychiatric manifestations of SRC and delineates high-yield management considerations. Although it focuses on concussions that occur in the context of sport, much of the information applies to patients who experience concussions from other causes.
SRC and depression
Changes in mood, emotion, and behavior are common following SRC. On the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool 5 (SCAT5),5 which is a standardized tool used to evaluate athletes suspected of having sustained a concussion, most symptoms overlap with those attributable to anxiety and depression.4,6 These include5:
- feeling slowed down
- “not feeling right”
- difficulty concentrating
- fatigue or loss of energy
- feeling more emotional
- irritability
- sadness
- feeling nervous or anxious
- difficulty falling asleep.
A recent systematic review of mental health outcomes of SRC in athletes found that the most commonly described and studied psychiatric symptoms following SRC were depression, anxiety, and impulsivity.7 The most rigorous study included in this review found depressive symptoms in 20% of collegiate athletes following SRC (all tested within 41 days of the SRC) vs 5% in the control group.8 These researchers delineated factors that predicted depressive symptoms after SRC (Box 18). Data were insufficient to draw conclusions about the association between SRC and other psychiatric symptoms, such as anxiety.8
Box 1
- Baseline depressive symptoms
- Baseline “post-concussion” symptoms
- Lower estimated premorbid intelligence
- Nonwhite ethnicity
- Increased number of games missed following injury
- Age of first participation in organized sport (more depression in athletes with fewer years of experience)
Source: Reference 8
Psychiatric manifestations of concussion in retired athletes may shed light on the long-term impact of SRC on psychiatric disorders, particularly depression. Hutchison et al9 conducted a systematic review of mental health outcomes of SRC in retired athletes.Two of the included studies that measured clinically diagnosed disorders found positive associations between self-reported concussion and clinically diagnosed depression.10,11 Hutchison et al9 found insufficient data to draw conclusions about depression and a lifetime history of subconcussive impacts—a topic that is receiving growing attention.
Continue to: Regarding a dose-response relationship...
Regarding a dose-response relationship in retired athletes, Guskiewicz et al11 reported a 3-fold increased risk of depression among retired professional football players who had experienced ≥3 SRCs. Five years later, the same research group reported a 5.8-fold increased risk of depression in retired professional football players after 5 to 9 concussions.10 In sum, there is evidence to suggest that the more SRCs an athlete sustains, the more likely they are to develop depression. Moreover, depression may persist or develop long after an SRC occurs.
Suicide risk
While suicide among athletes, especially football players, who have experienced concussion has received relatively widespread media attention, the risk of suicide in former professional football players appears to be significantly lower than in the general population.12 A recent large systematic review and meta-analysis reported on 713,706 individuals diagnosed with concussion and/or mild TBI and 6,236,010 individuals with no such diagnoses.13 It found a 2-fold higher risk of suicide in individuals who experienced concussion and/or mild TBI, but because participants were not necessarily athletes, it is difficult to extrapolate these findings to the athlete population.
Other psychiatric symptoms associated with SRC
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Some athletes experience PTSD symptoms shortly after SRC, and these can be missed if clinicians do not specifically ask about them.14 For example, substantial proportions of athletes who have had an SRC report making efforts to avoid sport situations that are similar to how and where their SRC occurred (19%), having trouble keeping thoughts about sustaining the SRC out of their heads (18%), experiencing flashbacks of sustaining the SRC (13%), and having nightmares about sustaining the SRC (8%).14 Posttraumatic stress disorder may have a negative impact on an athlete’s performance because a fear of re-injury might lead them to avoid rehabilitation exercises and inhibit their effort.15-18
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is commonly comorbid with SRC.19,20 It is not known if pre-existing ADHD makes sustaining a concussion more likely (eg, because the athlete is distractible and thus does not notice when an opponent is about to hit them hard) and/or if a history of concussion makes ADHD more likely to develop (eg, because something about the concussed brain is changed in a way that leads to ADHD). Additionally, in some cases, ADHD has been associated with prolonged recovery from SRC.3,21
Immediate medical evaluation and cognitive assessment
Any patient in whom an SRC is suspected should undergo a medical evaluation immediately, whether in a physician’s office, emergency department, or on the sideline of a sports event. This medical evaluation should incorporate a clinical neurologic assessment, including evaluation of mental status/cognition, oculomotor function, gross sensorimotor, coordination, gait, vestibular function, and balance.3
Continue to: There is no single guideline...
There is no single guideline on how and when a neuropsychology referral is warranted.22 Insurance coverage for neurocognitive testing varies. Regardless of formal referral to neuropsychology, assessment of cognitive function is an important aspect of SRC management and is a factor in return-to-school and return-to-play decisions.3,22 Screening tools, such as the SCAT5, are useful in acute and subacute settings (ie, up to 3 to 5 days after injury); clinicians often use serial monitoring to track the resolution of symptoms.3 If pre-season baseline cognitive test results are available, clinicians may compare them to post-SRC results, but this should not be the sole basis of management decisions.3,22
Diagnosing psychiatric disorders in patients with SRC
Diagnosis of psychiatric symptoms and disorders associated with SRC can be challenging.7 There are no concussion-specific rating scales or diagnostic criteria for psychiatric disorders unique to patients who have sustained SRC. As a result, clinicians are left to use standard DSM-5 criteria for the diagnosis of psychiatric disorders in patients with SRC. Importantly, psychiatric symptoms must be distinguished from disorders. For example, Kontos et al23 reported significantly worse depressive symptoms following SRC, but not at the level to meet the criteria for major depressive disorder. This is an important distinction, because a psychiatrist might be less likely to initiate pharmacotherapy for a patient with SRC who has only a few depressive symptoms and is only 1 week post-SRC, vs for one who has had most symptoms of a major depressive episode for several weeks.
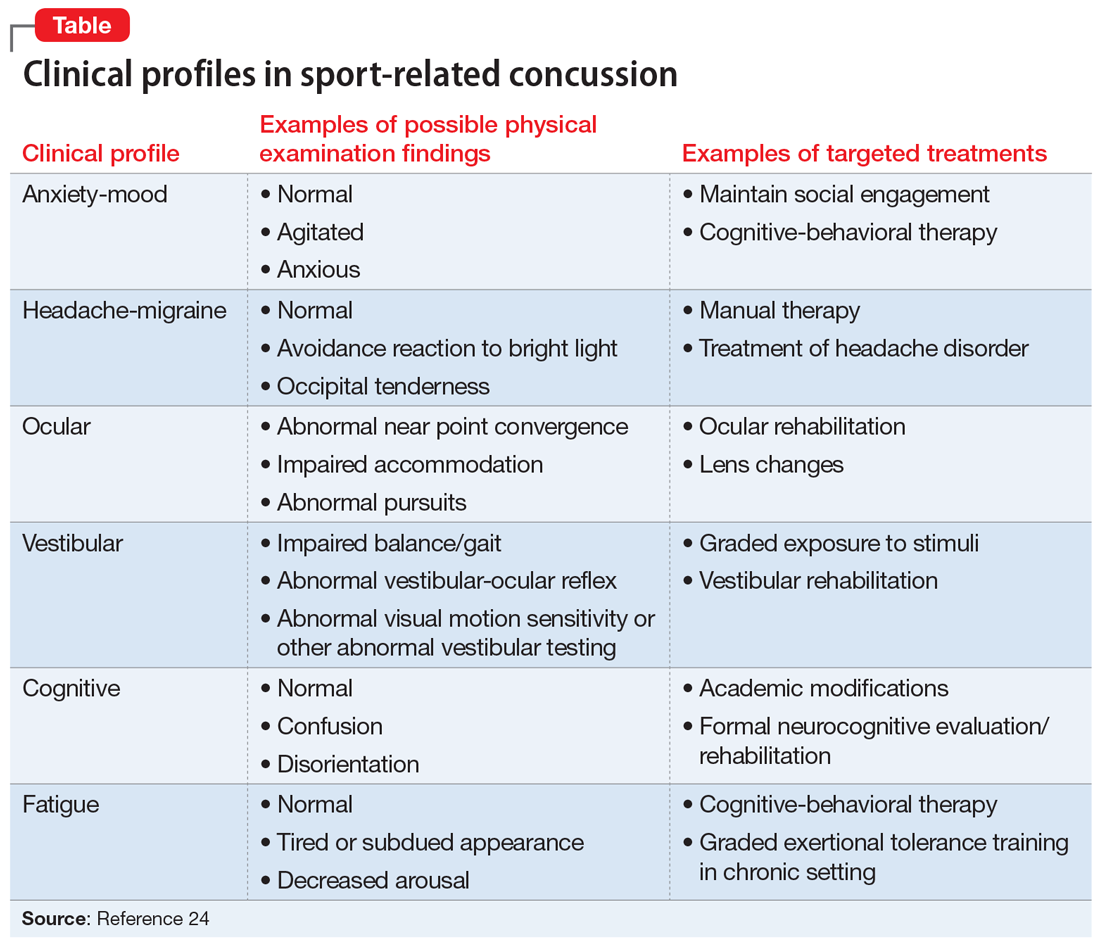
The American Medical Society for Sports Medicine has proposed 6 overlapping clinical profiles in patients with SRC (see the Table).24 Most patients with SRC have features of multiple clinical profiles.24 Anxiety/mood is one of these profiles. The impetus for developing these profiles was the recognition of heterogeneity among concussion presentations. Identification of the clinical profile(s) into which a patient’s symptoms fall might allow for more specific prognostication and targeted treatment.24 For example, referral to a psychiatrist obviously would be appropriate for a patient for whom anxiety/mood symptoms are prominent.
Treatment options for psychiatric sequelae of SRC
Both psychosocial and medical principles of management of psychiatric manifestations of SRC are important. Psychosocially, clinicians should address factors that may contribute to delayed SRC recovery (Box 225-30).
Box 2
- Recommend a progressive increase in exercise after a brief period of rest (often ameliorates psychiatric symptoms, as opposed to the historical approach of “cocoon therapy” in which the patient was to rest for prolonged periods of time in a darkened room so as to minimize brain stimulation)25
- Allow social activities, including team meetings (restriction of such activities has been associated with increased post-SRC depression)26
- Encourage members of the athlete’s “entourage” (team physicians, athletic trainers, coaches, teammates, and parents) to provide support27
- Educate coaches and teammates about how to make supportive statements because they often have trouble knowing how to do so27
- Recommend psychotherapy for mental and other physical symptoms of SRC that are moderate to severe or that persist longer than 4 weeks after the SRC28
- Recommend minimization of use of alcohol and other substances29,30
SRC: sport-related concussion
No medications are FDA-approved for SRC or associated psychiatric symptoms, and there is minimal evidence to support the use of specific medications.31 Most athletes with SRC recover quickly—typically within 2 weeks—and do not need medication.4,32 When medications are needed, start with low dosing and titrate slowly.33,34
Continue to: For patients with SRC who experience insomnia...
For patients with SRC who experience insomnia, clinicians should focus on sleep hygiene and, if needed, cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I).31 If medication is needed, melatonin may be a first-line agent.31,35,36 Trazodone may be a second option.32 Benzodiazepines typically are avoided because of their negative impact on cognition.31
For patients with SRC who have depression, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may simultaneously improve depressed mood31 and cognition.37 Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are sometimes used to treat headaches, depression, anxiety, and/or insomnia after SRC,32 but adverse effects such as sedation and weight gain may limit their use in athletes. Theoretically, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors might have some of the same benefits as TCAs with fewer adverse effects, but they have not been well studied in patients with SRC.
For patients with SRC who have cognitive dysfunction (eg, deficits in attention and processing speed), there is some evidence for treatment with stimulants.31,37 However, these medications are prohibited by many athletic governing organizations, including professional sports leagues, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA), and the World Anti-Doping Agency.4 If an athlete was receiving stimulants for ADHD before sustaining an SRC, there is no evidence that these medications should be stopped.
Consider interdisciplinary collaboration
Throughout the course of management, psychiatrists should consider if and when it is necessary to consult with other specialties such as primary care, sports medicine, neurology, and neuropsychology. As with many psychiatric symptoms and disorders, collaboration with an interdisciplinary team is recommended. Primary care, sports medicine, or neurology should be involved in the management of patients with SRC. Choice of which of those 3 specialties in particular will depend on comfort level and experience with managing SRC of the individual providers in question as well as availability of each provider type in a given community.
Additionally, psychiatrists may wonder if and when they should refer patients with SRC for neuroimaging. Because SRC is a functional, rather than structural, brain disturbance, neuroimaging is not typically pursued because results would be expected to be normal.3 However, when in doubt, consultation with the interdisciplinary team can guide this decision. Factors that may lead to a decision to obtain neuroimaging include:
- an abnormal neurologic examination
- prolonged loss of consciousness
- unexpected persistence of symptoms (eg, 6 to 12 weeks)
- worsening symptoms.22
Continue to: If imaging is deemed necessary...
If imaging is deemed necessary for a patient with an acute SRC, brain CT is typically the imaging modality of choice; however, if imaging is deemed necessary due to the persistence of symptoms, then MRI is often the preferred test because it provides more detailed information and does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation.22 While results are often normal, the ordering clinician should be prepared for the possibility of incidental findings, such as cysts or aneurysms, and the need for further consultation with other clinicians to weigh in on such findings.22
CASE CONTINUED
Ms. J is prescribed extended-release venlafaxine, 37.5 mg every morning for 5 days, and then is switched to 75 mg every morning. The psychiatrist hopes that venlafaxine might simultaneously offer benefit for Ms. J’s depression and migraine headaches. Venlafaxine is not FDA-approved for migraine, and there is more evidence supporting TCAs for preventing migraine. However, Ms. J is adamant that she does not want to take a medication, such as a TCA, that could cause weight gain or sedation, which could be problematic in her sport. The psychiatrist also tells Ms. J to avoid substances of abuse, and emphasizes the importance of good sleep hygiene. Finally, the psychiatrist communicates with the interdisciplinary medical team, which is helping Ms. J with gradual return-to-school and return-to-sport strategies and ensuring continued social involvement with the team even as she is held out from sport.
Ultimately, Ms. J’s extended-release venlafaxine is titrated to 150 mg every morning. After 2 months on this dose, her depressive symptoms remit. After her other symptoms remit, Ms. J has difficulty returning to certain practice drills that remind her of what she was doing when she sustained the SRC. She says that while participating in these drills, she has intrusive thoughts and images of the experience of her most recent concussion. She works with her psychiatrist on a gradual program of exposure therapy so she can return to all types of practice. Ms. J says she wishes to continue playing volleyball; however, together with her parents and treatment team, she decides that any additional SRCs might lead her to retire from the sport.
Bottom Line
Psychiatric symptoms are common after sport-related concussion (SRC). The nature of the relationship between concussion and mental health is not firmly established. Post-SRC psychiatric symptoms need to be carefully managed to avoid unnecessary treatment or restrictions.
Related Resources
- National Collegiate Athletic Association. Concussion. www.ncaa.org/sport-science-institute/concussion.
- American Academy of Neurology. Sports concussion resources. www.aan.com/tools-and-resources/practicing-neurologists-administrators/patient-resources/sports-concussion-resources. Published 2020.
Drug Brand Names
Trazodone • Desyrel
Venlafaxine • Effexor
1. Morgan CD, Zuckerman SL, Lee YM, et al. Predictors of postconcussion syndrome after sports-related concussion in young athletes: a matched case-control study. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015;15(6):589-598.
2. Jorge RE, Arciniegas DB. Mood disorders after TBI. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2014;37(1):13-29.
3. McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Dvor˘ák J, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport—the 5th International Conference on concussion in sport held in Berlin, October 2016. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(11):838-847.
4. Reardon CL, Hainline B, Aron CM, et al. Mental health in elite athletes: International Olympic Committee consensus statement (2019). Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(11):667-699.
5. Echemendia RJ, Meeuwisse W, McCrory P, et al. The sport concussion assessment tool 5th edition (SCAT5): background and rationale. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51:848-850.
6. Thompson E. Hamilton rating scale for anxiety (HAM-A). Occup Med. 2015;65(7):601.
7. Rice SM, Parker AG, Rosenbaum S, et al. Sport-related concussion outcomes in elite athletes: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2018;48(2):447-465.
8. Vargas G, Rabinowitz A, Meyer J, et al. Predictors and prevalence of postconcussion depression symptoms in collegiate athletes. J Athl Train. 2015;50(3):250-255.
9. Hutchison MG, Di Battista AP, McCoskey J, et al. Systematic review of mental health measures associated with concussive and subconcussive head trauma in former athletes. Int J Psychophysiol. 2018;132(Pt A):55-61.
10. Kerr GA, Stirling AE. Parents’ reflections on their child’s experiences of emotionally abusive coaching practices. J Appl Sport Psychol. 2012;24(2):191-206.
11. Guskiewicz KM, Marshall SW, Bailes J, et al. Recurrent concussion and risk of depression in retired professional football players. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(6):903-909.
12. Lehman EJ, Hein MJ, Gersic CM. Suicide mortality among retired National Football League players who played 5 or more seasons. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(10):2486-2491.
13. Fralick M, Sy E, Hassan A, et al. Association of concussion with the risk of suicide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2018;76(2):144-151.
14. Brassil HE, Salvatore AP. The frequency of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms in athletes with and without sports related concussion. Clin Transl Med. 2018;7:25.
15. Bateman A, Morgan KAD. The postinjury psychological sequelae of high-level Jamaican athletes: exploration of a posttraumatic stress disorder-self-efficacy conceptualization. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;28(2):144-152.
16. Brewer BW, Van Raalte JL, Cornelius AE, et al. Psychological factors, rehabilitation adherence, and rehabilitation outcome after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Rehabil Psychol. 2000;45(1):20-37.
17. Putukian M, Echemendia RJ. Psychological aspects of serious head injury in the competitive athlete. Clin Sports Med. 2003;22(33):617-630.
18. James LM, Strom TQ, Leskela J. Risk-taking behaviors and impulsivity among Veterans with and without PTSD and mild TBI. Mil Med. 2014;179(4):357-363.
19. Harmon KG, Drezner J, Gammons M, et al. American Medical Society for Sports Medicine position statement: concussion in sport. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;47(1):15-26.
20. Nelson LD, Guskiewicz KM, Marshall SW, et al. Multiple self-reported concussions are more prevalent in athletes with ADHD and learning disability. Clin J Sport Med. 2016;26(2):120-127.
21. Esfandiari A, Broshek DK, Freeman JR. Psychiatric and neuropsychological issues in sports medicine. Clin Sports Med. 2011;30(3):611-627.
22. Mahooti N. Sport-related concussion: acute management and chronic postconcussive issues. Chld Adolesc Psychiatric Clin N Am. 2018;27(1):93-108.
23. Kontos AP, Covassin T, Elbin RJ, et al. Depression and neurocognitive performance after concussion among male and female high school and collegiate athletes. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;93(10):1751-1756.
24. Harmon KG, Clugston JR, Dec K, et al. American Medical Society for Sports Medicine position statement on concussion in sport. Clin J Sport Med. 2019;29(2):87-100.
25. Leddy JJ, Willer B. Use of graded exercise testing in concussion and return-to-activity management. Current Sports Medicine Reports. 2013;12(6):370-376.
26. Schneider KJ, Iverson GL, Emery CA, et al. The effects of rest and treatment following sport-related concussion: a systematic review of the literature. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):304-307.
27. Wayment HA, Huffman AH. Psychosocial experiences of concussed collegiate athletes: the role of emotional support in the recovery process. J Am Coll Health. 2020;68(4):438-443.
28. Todd R, Bhalerao S, Vu MT, et al. Understanding the psychiatric effects of concussion on constructed identity in hockey players: implications for health professionals. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(2):e0192125.
29. Iverson GL, Silverberg ND, Mannix R, et al. Factors associated with concussion-like symptom reporting in high school athletes. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169(12):1132-1140.
30. Gaetz M. The multi-factorial origins of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) symptomatology in post-career athletes: the athlete post-career adjustment (AP-CA) model. Med Hypotheses. 2017;102:130-143.
31. Meehan WP. Medical therapies for concussion. Clin Sports Med. 2011;30(1):115-124.
32. Broglio SP, Collins MW, Williams RM, et al. Current and emerging rehabilitation for concussion: a review of the evidence. Clin Sports Med. 2015;34(2):213-231.
33. Arciniegas DB, Silver JM, McAllister TW. Stimulants and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of cognitive impairment after traumatic brain injury. Psychopharm Review. 2008;43(12):91-97.
34. Warden DL, Gordon B, McAllister TW, et al. Guidelines for the pharmacologic treatment of neurobehavioral sequelae of traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2006;23(10):1468-1501.
35. Maldonado MD, Murillo-Cabezas F, Terron MP, et al. The potential of melatonin in reducing morbidity/mortality after craniocerebral trauma. J Pineal Res. 2007;42(1):1-11.
36. Samantaray S, Das A, Thakore NP, et al. Therapeutic potential of melatonin in traumatic central nervous system injury. J Pineal Res. 2009;47(2):134-142.
37. Chew E, Zafonte RD. Pharmacological management of neurobehavioral disorders following traumatic brain injury—a state-of-the-art review. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2009;46(6):851-879.
Ms. J, age 19, is a Division I collegiate volleyball player who recently sustained her third sport-related concussion (SRC). She has no psychiatric history but does have a history of migraine, and her headaches have worsened since the most recent SRC. She has a family history of depression (mother and her sole sibling). Ms. J recently experienced the loss of her coach, someone she greatly admired, in a motor vehicle accident. She is referred to outpatient psychiatry for assessment of mood symptoms that are persisting 1 month after the SRC. Upon assessment, she is found to meet 8 of the 9 criteria for a major depressive episode, including suicidality with vague plans but no intent to end her life.
Although Ms. J does not have a history of psychiatric illness, her psychiatrist recognizes that she has factors that increase her risk of developing depression post-SRC, and of poor recovery from SRC. These include pre-existing symptoms, such as her history of migraine, which is common in patients after SRC. Additionally, a family history of psychiatric disorders and high life stressors (eg, recent loss of her coach) are risk factors for a poor SRC recovery.1 Due to these risk factors and the severity of Ms. J’s symptoms—which include suicidal ideation—the psychiatrist believes that her depressive symptoms might be unlikely to improve in the coming weeks, so he establishes a diagnosis of “depressive disorder due to another medical condition (concussion)” because the development of her depressive symptoms coincided with the SRC. If Ms. J had a pre-existing mood disorder, or if her depression had not developed until later in the post-injury period, it would have been more difficult to establish confidently that the depressive episode was a direct physiologic consequence of the SRC; if that had been the case, the diagnosis probably would have been unspecified or other specified depressive disorder.2
SRC is a traumatic brain injury (TBI) induced by biomechanical forces, typically resulting in short-lived impairment of neurologic function, although signs and symptoms may evolve over minutes to hours.3 It largely reflects functional, rather than structural, brain disturbances.3 SRC has been deemed a “neuropsychiatric syndrome” because psychiatric manifestations are common.4 There may be a myriad of biopsychosocial factors involved in the etiology of psychiatric symptoms in an individual who sustains an SRC. For example, SRC may have a direct physiologic cause of psychiatric symptoms based on the location and degree of injury to the brain. Additionally, pre-existing psychiatric symptoms might increase the likelihood of sustaining an SRC. Finally, as with any major injury, illness, or event, stressors associated with SRC may cause psychiatric symptoms.
Regardless of causal factors, psychiatrists should be comfortable with managing psychiatric symptoms that commonly accompany this condition. This article highlights possible psychiatric manifestations of SRC and delineates high-yield management considerations. Although it focuses on concussions that occur in the context of sport, much of the information applies to patients who experience concussions from other causes.
SRC and depression
Changes in mood, emotion, and behavior are common following SRC. On the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool 5 (SCAT5),5 which is a standardized tool used to evaluate athletes suspected of having sustained a concussion, most symptoms overlap with those attributable to anxiety and depression.4,6 These include5:
- feeling slowed down
- “not feeling right”
- difficulty concentrating
- fatigue or loss of energy
- feeling more emotional
- irritability
- sadness
- feeling nervous or anxious
- difficulty falling asleep.
A recent systematic review of mental health outcomes of SRC in athletes found that the most commonly described and studied psychiatric symptoms following SRC were depression, anxiety, and impulsivity.7 The most rigorous study included in this review found depressive symptoms in 20% of collegiate athletes following SRC (all tested within 41 days of the SRC) vs 5% in the control group.8 These researchers delineated factors that predicted depressive symptoms after SRC (Box 18). Data were insufficient to draw conclusions about the association between SRC and other psychiatric symptoms, such as anxiety.8
Box 1
- Baseline depressive symptoms
- Baseline “post-concussion” symptoms
- Lower estimated premorbid intelligence
- Nonwhite ethnicity
- Increased number of games missed following injury
- Age of first participation in organized sport (more depression in athletes with fewer years of experience)
Source: Reference 8
Psychiatric manifestations of concussion in retired athletes may shed light on the long-term impact of SRC on psychiatric disorders, particularly depression. Hutchison et al9 conducted a systematic review of mental health outcomes of SRC in retired athletes.Two of the included studies that measured clinically diagnosed disorders found positive associations between self-reported concussion and clinically diagnosed depression.10,11 Hutchison et al9 found insufficient data to draw conclusions about depression and a lifetime history of subconcussive impacts—a topic that is receiving growing attention.
Continue to: Regarding a dose-response relationship...
Regarding a dose-response relationship in retired athletes, Guskiewicz et al11 reported a 3-fold increased risk of depression among retired professional football players who had experienced ≥3 SRCs. Five years later, the same research group reported a 5.8-fold increased risk of depression in retired professional football players after 5 to 9 concussions.10 In sum, there is evidence to suggest that the more SRCs an athlete sustains, the more likely they are to develop depression. Moreover, depression may persist or develop long after an SRC occurs.
Suicide risk
While suicide among athletes, especially football players, who have experienced concussion has received relatively widespread media attention, the risk of suicide in former professional football players appears to be significantly lower than in the general population.12 A recent large systematic review and meta-analysis reported on 713,706 individuals diagnosed with concussion and/or mild TBI and 6,236,010 individuals with no such diagnoses.13 It found a 2-fold higher risk of suicide in individuals who experienced concussion and/or mild TBI, but because participants were not necessarily athletes, it is difficult to extrapolate these findings to the athlete population.
Other psychiatric symptoms associated with SRC
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Some athletes experience PTSD symptoms shortly after SRC, and these can be missed if clinicians do not specifically ask about them.14 For example, substantial proportions of athletes who have had an SRC report making efforts to avoid sport situations that are similar to how and where their SRC occurred (19%), having trouble keeping thoughts about sustaining the SRC out of their heads (18%), experiencing flashbacks of sustaining the SRC (13%), and having nightmares about sustaining the SRC (8%).14 Posttraumatic stress disorder may have a negative impact on an athlete’s performance because a fear of re-injury might lead them to avoid rehabilitation exercises and inhibit their effort.15-18
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is commonly comorbid with SRC.19,20 It is not known if pre-existing ADHD makes sustaining a concussion more likely (eg, because the athlete is distractible and thus does not notice when an opponent is about to hit them hard) and/or if a history of concussion makes ADHD more likely to develop (eg, because something about the concussed brain is changed in a way that leads to ADHD). Additionally, in some cases, ADHD has been associated with prolonged recovery from SRC.3,21
Immediate medical evaluation and cognitive assessment
Any patient in whom an SRC is suspected should undergo a medical evaluation immediately, whether in a physician’s office, emergency department, or on the sideline of a sports event. This medical evaluation should incorporate a clinical neurologic assessment, including evaluation of mental status/cognition, oculomotor function, gross sensorimotor, coordination, gait, vestibular function, and balance.3
Continue to: There is no single guideline...
There is no single guideline on how and when a neuropsychology referral is warranted.22 Insurance coverage for neurocognitive testing varies. Regardless of formal referral to neuropsychology, assessment of cognitive function is an important aspect of SRC management and is a factor in return-to-school and return-to-play decisions.3,22 Screening tools, such as the SCAT5, are useful in acute and subacute settings (ie, up to 3 to 5 days after injury); clinicians often use serial monitoring to track the resolution of symptoms.3 If pre-season baseline cognitive test results are available, clinicians may compare them to post-SRC results, but this should not be the sole basis of management decisions.3,22
Diagnosing psychiatric disorders in patients with SRC
Diagnosis of psychiatric symptoms and disorders associated with SRC can be challenging.7 There are no concussion-specific rating scales or diagnostic criteria for psychiatric disorders unique to patients who have sustained SRC. As a result, clinicians are left to use standard DSM-5 criteria for the diagnosis of psychiatric disorders in patients with SRC. Importantly, psychiatric symptoms must be distinguished from disorders. For example, Kontos et al23 reported significantly worse depressive symptoms following SRC, but not at the level to meet the criteria for major depressive disorder. This is an important distinction, because a psychiatrist might be less likely to initiate pharmacotherapy for a patient with SRC who has only a few depressive symptoms and is only 1 week post-SRC, vs for one who has had most symptoms of a major depressive episode for several weeks.
The American Medical Society for Sports Medicine has proposed 6 overlapping clinical profiles in patients with SRC (see the Table).24 Most patients with SRC have features of multiple clinical profiles.24 Anxiety/mood is one of these profiles. The impetus for developing these profiles was the recognition of heterogeneity among concussion presentations. Identification of the clinical profile(s) into which a patient’s symptoms fall might allow for more specific prognostication and targeted treatment.24 For example, referral to a psychiatrist obviously would be appropriate for a patient for whom anxiety/mood symptoms are prominent.

Treatment options for psychiatric sequelae of SRC
Both psychosocial and medical principles of management of psychiatric manifestations of SRC are important. Psychosocially, clinicians should address factors that may contribute to delayed SRC recovery (Box 225-30).
Box 2
- Recommend a progressive increase in exercise after a brief period of rest (often ameliorates psychiatric symptoms, as opposed to the historical approach of “cocoon therapy” in which the patient was to rest for prolonged periods of time in a darkened room so as to minimize brain stimulation)25
- Allow social activities, including team meetings (restriction of such activities has been associated with increased post-SRC depression)26
- Encourage members of the athlete’s “entourage” (team physicians, athletic trainers, coaches, teammates, and parents) to provide support27
- Educate coaches and teammates about how to make supportive statements because they often have trouble knowing how to do so27
- Recommend psychotherapy for mental and other physical symptoms of SRC that are moderate to severe or that persist longer than 4 weeks after the SRC28
- Recommend minimization of use of alcohol and other substances29,30
SRC: sport-related concussion
No medications are FDA-approved for SRC or associated psychiatric symptoms, and there is minimal evidence to support the use of specific medications.31 Most athletes with SRC recover quickly—typically within 2 weeks—and do not need medication.4,32 When medications are needed, start with low dosing and titrate slowly.33,34
Continue to: For patients with SRC who experience insomnia...
For patients with SRC who experience insomnia, clinicians should focus on sleep hygiene and, if needed, cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I).31 If medication is needed, melatonin may be a first-line agent.31,35,36 Trazodone may be a second option.32 Benzodiazepines typically are avoided because of their negative impact on cognition.31
For patients with SRC who have depression, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may simultaneously improve depressed mood31 and cognition.37 Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are sometimes used to treat headaches, depression, anxiety, and/or insomnia after SRC,32 but adverse effects such as sedation and weight gain may limit their use in athletes. Theoretically, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors might have some of the same benefits as TCAs with fewer adverse effects, but they have not been well studied in patients with SRC.
For patients with SRC who have cognitive dysfunction (eg, deficits in attention and processing speed), there is some evidence for treatment with stimulants.31,37 However, these medications are prohibited by many athletic governing organizations, including professional sports leagues, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA), and the World Anti-Doping Agency.4 If an athlete was receiving stimulants for ADHD before sustaining an SRC, there is no evidence that these medications should be stopped.
Consider interdisciplinary collaboration
Throughout the course of management, psychiatrists should consider if and when it is necessary to consult with other specialties such as primary care, sports medicine, neurology, and neuropsychology. As with many psychiatric symptoms and disorders, collaboration with an interdisciplinary team is recommended. Primary care, sports medicine, or neurology should be involved in the management of patients with SRC. Choice of which of those 3 specialties in particular will depend on comfort level and experience with managing SRC of the individual providers in question as well as availability of each provider type in a given community.
Additionally, psychiatrists may wonder if and when they should refer patients with SRC for neuroimaging. Because SRC is a functional, rather than structural, brain disturbance, neuroimaging is not typically pursued because results would be expected to be normal.3 However, when in doubt, consultation with the interdisciplinary team can guide this decision. Factors that may lead to a decision to obtain neuroimaging include:
- an abnormal neurologic examination
- prolonged loss of consciousness
- unexpected persistence of symptoms (eg, 6 to 12 weeks)
- worsening symptoms.22
Continue to: If imaging is deemed necessary...
If imaging is deemed necessary for a patient with an acute SRC, brain CT is typically the imaging modality of choice; however, if imaging is deemed necessary due to the persistence of symptoms, then MRI is often the preferred test because it provides more detailed information and does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation.22 While results are often normal, the ordering clinician should be prepared for the possibility of incidental findings, such as cysts or aneurysms, and the need for further consultation with other clinicians to weigh in on such findings.22
CASE CONTINUED
Ms. J is prescribed extended-release venlafaxine, 37.5 mg every morning for 5 days, and then is switched to 75 mg every morning. The psychiatrist hopes that venlafaxine might simultaneously offer benefit for Ms. J’s depression and migraine headaches. Venlafaxine is not FDA-approved for migraine, and there is more evidence supporting TCAs for preventing migraine. However, Ms. J is adamant that she does not want to take a medication, such as a TCA, that could cause weight gain or sedation, which could be problematic in her sport. The psychiatrist also tells Ms. J to avoid substances of abuse, and emphasizes the importance of good sleep hygiene. Finally, the psychiatrist communicates with the interdisciplinary medical team, which is helping Ms. J with gradual return-to-school and return-to-sport strategies and ensuring continued social involvement with the team even as she is held out from sport.
Ultimately, Ms. J’s extended-release venlafaxine is titrated to 150 mg every morning. After 2 months on this dose, her depressive symptoms remit. After her other symptoms remit, Ms. J has difficulty returning to certain practice drills that remind her of what she was doing when she sustained the SRC. She says that while participating in these drills, she has intrusive thoughts and images of the experience of her most recent concussion. She works with her psychiatrist on a gradual program of exposure therapy so she can return to all types of practice. Ms. J says she wishes to continue playing volleyball; however, together with her parents and treatment team, she decides that any additional SRCs might lead her to retire from the sport.
Bottom Line
Psychiatric symptoms are common after sport-related concussion (SRC). The nature of the relationship between concussion and mental health is not firmly established. Post-SRC psychiatric symptoms need to be carefully managed to avoid unnecessary treatment or restrictions.
Related Resources
- National Collegiate Athletic Association. Concussion. www.ncaa.org/sport-science-institute/concussion.
- American Academy of Neurology. Sports concussion resources. www.aan.com/tools-and-resources/practicing-neurologists-administrators/patient-resources/sports-concussion-resources. Published 2020.
Drug Brand Names
Trazodone • Desyrel
Venlafaxine • Effexor
Ms. J, age 19, is a Division I collegiate volleyball player who recently sustained her third sport-related concussion (SRC). She has no psychiatric history but does have a history of migraine, and her headaches have worsened since the most recent SRC. She has a family history of depression (mother and her sole sibling). Ms. J recently experienced the loss of her coach, someone she greatly admired, in a motor vehicle accident. She is referred to outpatient psychiatry for assessment of mood symptoms that are persisting 1 month after the SRC. Upon assessment, she is found to meet 8 of the 9 criteria for a major depressive episode, including suicidality with vague plans but no intent to end her life.
Although Ms. J does not have a history of psychiatric illness, her psychiatrist recognizes that she has factors that increase her risk of developing depression post-SRC, and of poor recovery from SRC. These include pre-existing symptoms, such as her history of migraine, which is common in patients after SRC. Additionally, a family history of psychiatric disorders and high life stressors (eg, recent loss of her coach) are risk factors for a poor SRC recovery.1 Due to these risk factors and the severity of Ms. J’s symptoms—which include suicidal ideation—the psychiatrist believes that her depressive symptoms might be unlikely to improve in the coming weeks, so he establishes a diagnosis of “depressive disorder due to another medical condition (concussion)” because the development of her depressive symptoms coincided with the SRC. If Ms. J had a pre-existing mood disorder, or if her depression had not developed until later in the post-injury period, it would have been more difficult to establish confidently that the depressive episode was a direct physiologic consequence of the SRC; if that had been the case, the diagnosis probably would have been unspecified or other specified depressive disorder.2
SRC is a traumatic brain injury (TBI) induced by biomechanical forces, typically resulting in short-lived impairment of neurologic function, although signs and symptoms may evolve over minutes to hours.3 It largely reflects functional, rather than structural, brain disturbances.3 SRC has been deemed a “neuropsychiatric syndrome” because psychiatric manifestations are common.4 There may be a myriad of biopsychosocial factors involved in the etiology of psychiatric symptoms in an individual who sustains an SRC. For example, SRC may have a direct physiologic cause of psychiatric symptoms based on the location and degree of injury to the brain. Additionally, pre-existing psychiatric symptoms might increase the likelihood of sustaining an SRC. Finally, as with any major injury, illness, or event, stressors associated with SRC may cause psychiatric symptoms.
Regardless of causal factors, psychiatrists should be comfortable with managing psychiatric symptoms that commonly accompany this condition. This article highlights possible psychiatric manifestations of SRC and delineates high-yield management considerations. Although it focuses on concussions that occur in the context of sport, much of the information applies to patients who experience concussions from other causes.
SRC and depression
Changes in mood, emotion, and behavior are common following SRC. On the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool 5 (SCAT5),5 which is a standardized tool used to evaluate athletes suspected of having sustained a concussion, most symptoms overlap with those attributable to anxiety and depression.4,6 These include5:
- feeling slowed down
- “not feeling right”
- difficulty concentrating
- fatigue or loss of energy
- feeling more emotional
- irritability
- sadness
- feeling nervous or anxious
- difficulty falling asleep.
A recent systematic review of mental health outcomes of SRC in athletes found that the most commonly described and studied psychiatric symptoms following SRC were depression, anxiety, and impulsivity.7 The most rigorous study included in this review found depressive symptoms in 20% of collegiate athletes following SRC (all tested within 41 days of the SRC) vs 5% in the control group.8 These researchers delineated factors that predicted depressive symptoms after SRC (Box 18). Data were insufficient to draw conclusions about the association between SRC and other psychiatric symptoms, such as anxiety.8
Box 1
- Baseline depressive symptoms
- Baseline “post-concussion” symptoms
- Lower estimated premorbid intelligence
- Nonwhite ethnicity
- Increased number of games missed following injury
- Age of first participation in organized sport (more depression in athletes with fewer years of experience)
Source: Reference 8
Psychiatric manifestations of concussion in retired athletes may shed light on the long-term impact of SRC on psychiatric disorders, particularly depression. Hutchison et al9 conducted a systematic review of mental health outcomes of SRC in retired athletes.Two of the included studies that measured clinically diagnosed disorders found positive associations between self-reported concussion and clinically diagnosed depression.10,11 Hutchison et al9 found insufficient data to draw conclusions about depression and a lifetime history of subconcussive impacts—a topic that is receiving growing attention.
Continue to: Regarding a dose-response relationship...
Regarding a dose-response relationship in retired athletes, Guskiewicz et al11 reported a 3-fold increased risk of depression among retired professional football players who had experienced ≥3 SRCs. Five years later, the same research group reported a 5.8-fold increased risk of depression in retired professional football players after 5 to 9 concussions.10 In sum, there is evidence to suggest that the more SRCs an athlete sustains, the more likely they are to develop depression. Moreover, depression may persist or develop long after an SRC occurs.
Suicide risk
While suicide among athletes, especially football players, who have experienced concussion has received relatively widespread media attention, the risk of suicide in former professional football players appears to be significantly lower than in the general population.12 A recent large systematic review and meta-analysis reported on 713,706 individuals diagnosed with concussion and/or mild TBI and 6,236,010 individuals with no such diagnoses.13 It found a 2-fold higher risk of suicide in individuals who experienced concussion and/or mild TBI, but because participants were not necessarily athletes, it is difficult to extrapolate these findings to the athlete population.
Other psychiatric symptoms associated with SRC
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Some athletes experience PTSD symptoms shortly after SRC, and these can be missed if clinicians do not specifically ask about them.14 For example, substantial proportions of athletes who have had an SRC report making efforts to avoid sport situations that are similar to how and where their SRC occurred (19%), having trouble keeping thoughts about sustaining the SRC out of their heads (18%), experiencing flashbacks of sustaining the SRC (13%), and having nightmares about sustaining the SRC (8%).14 Posttraumatic stress disorder may have a negative impact on an athlete’s performance because a fear of re-injury might lead them to avoid rehabilitation exercises and inhibit their effort.15-18
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is commonly comorbid with SRC.19,20 It is not known if pre-existing ADHD makes sustaining a concussion more likely (eg, because the athlete is distractible and thus does not notice when an opponent is about to hit them hard) and/or if a history of concussion makes ADHD more likely to develop (eg, because something about the concussed brain is changed in a way that leads to ADHD). Additionally, in some cases, ADHD has been associated with prolonged recovery from SRC.3,21
Immediate medical evaluation and cognitive assessment
Any patient in whom an SRC is suspected should undergo a medical evaluation immediately, whether in a physician’s office, emergency department, or on the sideline of a sports event. This medical evaluation should incorporate a clinical neurologic assessment, including evaluation of mental status/cognition, oculomotor function, gross sensorimotor, coordination, gait, vestibular function, and balance.3
Continue to: There is no single guideline...
There is no single guideline on how and when a neuropsychology referral is warranted.22 Insurance coverage for neurocognitive testing varies. Regardless of formal referral to neuropsychology, assessment of cognitive function is an important aspect of SRC management and is a factor in return-to-school and return-to-play decisions.3,22 Screening tools, such as the SCAT5, are useful in acute and subacute settings (ie, up to 3 to 5 days after injury); clinicians often use serial monitoring to track the resolution of symptoms.3 If pre-season baseline cognitive test results are available, clinicians may compare them to post-SRC results, but this should not be the sole basis of management decisions.3,22
Diagnosing psychiatric disorders in patients with SRC
Diagnosis of psychiatric symptoms and disorders associated with SRC can be challenging.7 There are no concussion-specific rating scales or diagnostic criteria for psychiatric disorders unique to patients who have sustained SRC. As a result, clinicians are left to use standard DSM-5 criteria for the diagnosis of psychiatric disorders in patients with SRC. Importantly, psychiatric symptoms must be distinguished from disorders. For example, Kontos et al23 reported significantly worse depressive symptoms following SRC, but not at the level to meet the criteria for major depressive disorder. This is an important distinction, because a psychiatrist might be less likely to initiate pharmacotherapy for a patient with SRC who has only a few depressive symptoms and is only 1 week post-SRC, vs for one who has had most symptoms of a major depressive episode for several weeks.
The American Medical Society for Sports Medicine has proposed 6 overlapping clinical profiles in patients with SRC (see the Table).24 Most patients with SRC have features of multiple clinical profiles.24 Anxiety/mood is one of these profiles. The impetus for developing these profiles was the recognition of heterogeneity among concussion presentations. Identification of the clinical profile(s) into which a patient’s symptoms fall might allow for more specific prognostication and targeted treatment.24 For example, referral to a psychiatrist obviously would be appropriate for a patient for whom anxiety/mood symptoms are prominent.

Treatment options for psychiatric sequelae of SRC
Both psychosocial and medical principles of management of psychiatric manifestations of SRC are important. Psychosocially, clinicians should address factors that may contribute to delayed SRC recovery (Box 225-30).
Box 2
- Recommend a progressive increase in exercise after a brief period of rest (often ameliorates psychiatric symptoms, as opposed to the historical approach of “cocoon therapy” in which the patient was to rest for prolonged periods of time in a darkened room so as to minimize brain stimulation)25
- Allow social activities, including team meetings (restriction of such activities has been associated with increased post-SRC depression)26
- Encourage members of the athlete’s “entourage” (team physicians, athletic trainers, coaches, teammates, and parents) to provide support27
- Educate coaches and teammates about how to make supportive statements because they often have trouble knowing how to do so27
- Recommend psychotherapy for mental and other physical symptoms of SRC that are moderate to severe or that persist longer than 4 weeks after the SRC28
- Recommend minimization of use of alcohol and other substances29,30
SRC: sport-related concussion
No medications are FDA-approved for SRC or associated psychiatric symptoms, and there is minimal evidence to support the use of specific medications.31 Most athletes with SRC recover quickly—typically within 2 weeks—and do not need medication.4,32 When medications are needed, start with low dosing and titrate slowly.33,34
Continue to: For patients with SRC who experience insomnia...
For patients with SRC who experience insomnia, clinicians should focus on sleep hygiene and, if needed, cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I).31 If medication is needed, melatonin may be a first-line agent.31,35,36 Trazodone may be a second option.32 Benzodiazepines typically are avoided because of their negative impact on cognition.31
For patients with SRC who have depression, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may simultaneously improve depressed mood31 and cognition.37 Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are sometimes used to treat headaches, depression, anxiety, and/or insomnia after SRC,32 but adverse effects such as sedation and weight gain may limit their use in athletes. Theoretically, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors might have some of the same benefits as TCAs with fewer adverse effects, but they have not been well studied in patients with SRC.
For patients with SRC who have cognitive dysfunction (eg, deficits in attention and processing speed), there is some evidence for treatment with stimulants.31,37 However, these medications are prohibited by many athletic governing organizations, including professional sports leagues, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA), and the World Anti-Doping Agency.4 If an athlete was receiving stimulants for ADHD before sustaining an SRC, there is no evidence that these medications should be stopped.
Consider interdisciplinary collaboration
Throughout the course of management, psychiatrists should consider if and when it is necessary to consult with other specialties such as primary care, sports medicine, neurology, and neuropsychology. As with many psychiatric symptoms and disorders, collaboration with an interdisciplinary team is recommended. Primary care, sports medicine, or neurology should be involved in the management of patients with SRC. Choice of which of those 3 specialties in particular will depend on comfort level and experience with managing SRC of the individual providers in question as well as availability of each provider type in a given community.
Additionally, psychiatrists may wonder if and when they should refer patients with SRC for neuroimaging. Because SRC is a functional, rather than structural, brain disturbance, neuroimaging is not typically pursued because results would be expected to be normal.3 However, when in doubt, consultation with the interdisciplinary team can guide this decision. Factors that may lead to a decision to obtain neuroimaging include:
- an abnormal neurologic examination
- prolonged loss of consciousness
- unexpected persistence of symptoms (eg, 6 to 12 weeks)
- worsening symptoms.22
Continue to: If imaging is deemed necessary...
If imaging is deemed necessary for a patient with an acute SRC, brain CT is typically the imaging modality of choice; however, if imaging is deemed necessary due to the persistence of symptoms, then MRI is often the preferred test because it provides more detailed information and does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation.22 While results are often normal, the ordering clinician should be prepared for the possibility of incidental findings, such as cysts or aneurysms, and the need for further consultation with other clinicians to weigh in on such findings.22
CASE CONTINUED
Ms. J is prescribed extended-release venlafaxine, 37.5 mg every morning for 5 days, and then is switched to 75 mg every morning. The psychiatrist hopes that venlafaxine might simultaneously offer benefit for Ms. J’s depression and migraine headaches. Venlafaxine is not FDA-approved for migraine, and there is more evidence supporting TCAs for preventing migraine. However, Ms. J is adamant that she does not want to take a medication, such as a TCA, that could cause weight gain or sedation, which could be problematic in her sport. The psychiatrist also tells Ms. J to avoid substances of abuse, and emphasizes the importance of good sleep hygiene. Finally, the psychiatrist communicates with the interdisciplinary medical team, which is helping Ms. J with gradual return-to-school and return-to-sport strategies and ensuring continued social involvement with the team even as she is held out from sport.
Ultimately, Ms. J’s extended-release venlafaxine is titrated to 150 mg every morning. After 2 months on this dose, her depressive symptoms remit. After her other symptoms remit, Ms. J has difficulty returning to certain practice drills that remind her of what she was doing when she sustained the SRC. She says that while participating in these drills, she has intrusive thoughts and images of the experience of her most recent concussion. She works with her psychiatrist on a gradual program of exposure therapy so she can return to all types of practice. Ms. J says she wishes to continue playing volleyball; however, together with her parents and treatment team, she decides that any additional SRCs might lead her to retire from the sport.
Bottom Line
Psychiatric symptoms are common after sport-related concussion (SRC). The nature of the relationship between concussion and mental health is not firmly established. Post-SRC psychiatric symptoms need to be carefully managed to avoid unnecessary treatment or restrictions.
Related Resources
- National Collegiate Athletic Association. Concussion. www.ncaa.org/sport-science-institute/concussion.
- American Academy of Neurology. Sports concussion resources. www.aan.com/tools-and-resources/practicing-neurologists-administrators/patient-resources/sports-concussion-resources. Published 2020.
Drug Brand Names
Trazodone • Desyrel
Venlafaxine • Effexor
1. Morgan CD, Zuckerman SL, Lee YM, et al. Predictors of postconcussion syndrome after sports-related concussion in young athletes: a matched case-control study. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015;15(6):589-598.
2. Jorge RE, Arciniegas DB. Mood disorders after TBI. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2014;37(1):13-29.
3. McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Dvor˘ák J, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport—the 5th International Conference on concussion in sport held in Berlin, October 2016. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(11):838-847.
4. Reardon CL, Hainline B, Aron CM, et al. Mental health in elite athletes: International Olympic Committee consensus statement (2019). Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(11):667-699.
5. Echemendia RJ, Meeuwisse W, McCrory P, et al. The sport concussion assessment tool 5th edition (SCAT5): background and rationale. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51:848-850.
6. Thompson E. Hamilton rating scale for anxiety (HAM-A). Occup Med. 2015;65(7):601.
7. Rice SM, Parker AG, Rosenbaum S, et al. Sport-related concussion outcomes in elite athletes: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2018;48(2):447-465.
8. Vargas G, Rabinowitz A, Meyer J, et al. Predictors and prevalence of postconcussion depression symptoms in collegiate athletes. J Athl Train. 2015;50(3):250-255.
9. Hutchison MG, Di Battista AP, McCoskey J, et al. Systematic review of mental health measures associated with concussive and subconcussive head trauma in former athletes. Int J Psychophysiol. 2018;132(Pt A):55-61.
10. Kerr GA, Stirling AE. Parents’ reflections on their child’s experiences of emotionally abusive coaching practices. J Appl Sport Psychol. 2012;24(2):191-206.
11. Guskiewicz KM, Marshall SW, Bailes J, et al. Recurrent concussion and risk of depression in retired professional football players. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(6):903-909.
12. Lehman EJ, Hein MJ, Gersic CM. Suicide mortality among retired National Football League players who played 5 or more seasons. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(10):2486-2491.
13. Fralick M, Sy E, Hassan A, et al. Association of concussion with the risk of suicide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2018;76(2):144-151.
14. Brassil HE, Salvatore AP. The frequency of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms in athletes with and without sports related concussion. Clin Transl Med. 2018;7:25.
15. Bateman A, Morgan KAD. The postinjury psychological sequelae of high-level Jamaican athletes: exploration of a posttraumatic stress disorder-self-efficacy conceptualization. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;28(2):144-152.
16. Brewer BW, Van Raalte JL, Cornelius AE, et al. Psychological factors, rehabilitation adherence, and rehabilitation outcome after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Rehabil Psychol. 2000;45(1):20-37.
17. Putukian M, Echemendia RJ. Psychological aspects of serious head injury in the competitive athlete. Clin Sports Med. 2003;22(33):617-630.
18. James LM, Strom TQ, Leskela J. Risk-taking behaviors and impulsivity among Veterans with and without PTSD and mild TBI. Mil Med. 2014;179(4):357-363.
19. Harmon KG, Drezner J, Gammons M, et al. American Medical Society for Sports Medicine position statement: concussion in sport. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;47(1):15-26.
20. Nelson LD, Guskiewicz KM, Marshall SW, et al. Multiple self-reported concussions are more prevalent in athletes with ADHD and learning disability. Clin J Sport Med. 2016;26(2):120-127.
21. Esfandiari A, Broshek DK, Freeman JR. Psychiatric and neuropsychological issues in sports medicine. Clin Sports Med. 2011;30(3):611-627.
22. Mahooti N. Sport-related concussion: acute management and chronic postconcussive issues. Chld Adolesc Psychiatric Clin N Am. 2018;27(1):93-108.
23. Kontos AP, Covassin T, Elbin RJ, et al. Depression and neurocognitive performance after concussion among male and female high school and collegiate athletes. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;93(10):1751-1756.
24. Harmon KG, Clugston JR, Dec K, et al. American Medical Society for Sports Medicine position statement on concussion in sport. Clin J Sport Med. 2019;29(2):87-100.
25. Leddy JJ, Willer B. Use of graded exercise testing in concussion and return-to-activity management. Current Sports Medicine Reports. 2013;12(6):370-376.
26. Schneider KJ, Iverson GL, Emery CA, et al. The effects of rest and treatment following sport-related concussion: a systematic review of the literature. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):304-307.
27. Wayment HA, Huffman AH. Psychosocial experiences of concussed collegiate athletes: the role of emotional support in the recovery process. J Am Coll Health. 2020;68(4):438-443.
28. Todd R, Bhalerao S, Vu MT, et al. Understanding the psychiatric effects of concussion on constructed identity in hockey players: implications for health professionals. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(2):e0192125.
29. Iverson GL, Silverberg ND, Mannix R, et al. Factors associated with concussion-like symptom reporting in high school athletes. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169(12):1132-1140.
30. Gaetz M. The multi-factorial origins of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) symptomatology in post-career athletes: the athlete post-career adjustment (AP-CA) model. Med Hypotheses. 2017;102:130-143.
31. Meehan WP. Medical therapies for concussion. Clin Sports Med. 2011;30(1):115-124.
32. Broglio SP, Collins MW, Williams RM, et al. Current and emerging rehabilitation for concussion: a review of the evidence. Clin Sports Med. 2015;34(2):213-231.
33. Arciniegas DB, Silver JM, McAllister TW. Stimulants and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of cognitive impairment after traumatic brain injury. Psychopharm Review. 2008;43(12):91-97.
34. Warden DL, Gordon B, McAllister TW, et al. Guidelines for the pharmacologic treatment of neurobehavioral sequelae of traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2006;23(10):1468-1501.
35. Maldonado MD, Murillo-Cabezas F, Terron MP, et al. The potential of melatonin in reducing morbidity/mortality after craniocerebral trauma. J Pineal Res. 2007;42(1):1-11.
36. Samantaray S, Das A, Thakore NP, et al. Therapeutic potential of melatonin in traumatic central nervous system injury. J Pineal Res. 2009;47(2):134-142.
37. Chew E, Zafonte RD. Pharmacological management of neurobehavioral disorders following traumatic brain injury—a state-of-the-art review. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2009;46(6):851-879.
1. Morgan CD, Zuckerman SL, Lee YM, et al. Predictors of postconcussion syndrome after sports-related concussion in young athletes: a matched case-control study. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015;15(6):589-598.
2. Jorge RE, Arciniegas DB. Mood disorders after TBI. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2014;37(1):13-29.
3. McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Dvor˘ák J, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport—the 5th International Conference on concussion in sport held in Berlin, October 2016. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(11):838-847.
4. Reardon CL, Hainline B, Aron CM, et al. Mental health in elite athletes: International Olympic Committee consensus statement (2019). Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(11):667-699.
5. Echemendia RJ, Meeuwisse W, McCrory P, et al. The sport concussion assessment tool 5th edition (SCAT5): background and rationale. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51:848-850.
6. Thompson E. Hamilton rating scale for anxiety (HAM-A). Occup Med. 2015;65(7):601.
7. Rice SM, Parker AG, Rosenbaum S, et al. Sport-related concussion outcomes in elite athletes: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2018;48(2):447-465.
8. Vargas G, Rabinowitz A, Meyer J, et al. Predictors and prevalence of postconcussion depression symptoms in collegiate athletes. J Athl Train. 2015;50(3):250-255.
9. Hutchison MG, Di Battista AP, McCoskey J, et al. Systematic review of mental health measures associated with concussive and subconcussive head trauma in former athletes. Int J Psychophysiol. 2018;132(Pt A):55-61.
10. Kerr GA, Stirling AE. Parents’ reflections on their child’s experiences of emotionally abusive coaching practices. J Appl Sport Psychol. 2012;24(2):191-206.
11. Guskiewicz KM, Marshall SW, Bailes J, et al. Recurrent concussion and risk of depression in retired professional football players. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(6):903-909.
12. Lehman EJ, Hein MJ, Gersic CM. Suicide mortality among retired National Football League players who played 5 or more seasons. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(10):2486-2491.
13. Fralick M, Sy E, Hassan A, et al. Association of concussion with the risk of suicide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2018;76(2):144-151.
14. Brassil HE, Salvatore AP. The frequency of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms in athletes with and without sports related concussion. Clin Transl Med. 2018;7:25.
15. Bateman A, Morgan KAD. The postinjury psychological sequelae of high-level Jamaican athletes: exploration of a posttraumatic stress disorder-self-efficacy conceptualization. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;28(2):144-152.
16. Brewer BW, Van Raalte JL, Cornelius AE, et al. Psychological factors, rehabilitation adherence, and rehabilitation outcome after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Rehabil Psychol. 2000;45(1):20-37.
17. Putukian M, Echemendia RJ. Psychological aspects of serious head injury in the competitive athlete. Clin Sports Med. 2003;22(33):617-630.
18. James LM, Strom TQ, Leskela J. Risk-taking behaviors and impulsivity among Veterans with and without PTSD and mild TBI. Mil Med. 2014;179(4):357-363.
19. Harmon KG, Drezner J, Gammons M, et al. American Medical Society for Sports Medicine position statement: concussion in sport. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;47(1):15-26.
20. Nelson LD, Guskiewicz KM, Marshall SW, et al. Multiple self-reported concussions are more prevalent in athletes with ADHD and learning disability. Clin J Sport Med. 2016;26(2):120-127.
21. Esfandiari A, Broshek DK, Freeman JR. Psychiatric and neuropsychological issues in sports medicine. Clin Sports Med. 2011;30(3):611-627.
22. Mahooti N. Sport-related concussion: acute management and chronic postconcussive issues. Chld Adolesc Psychiatric Clin N Am. 2018;27(1):93-108.
23. Kontos AP, Covassin T, Elbin RJ, et al. Depression and neurocognitive performance after concussion among male and female high school and collegiate athletes. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;93(10):1751-1756.
24. Harmon KG, Clugston JR, Dec K, et al. American Medical Society for Sports Medicine position statement on concussion in sport. Clin J Sport Med. 2019;29(2):87-100.
25. Leddy JJ, Willer B. Use of graded exercise testing in concussion and return-to-activity management. Current Sports Medicine Reports. 2013;12(6):370-376.
26. Schneider KJ, Iverson GL, Emery CA, et al. The effects of rest and treatment following sport-related concussion: a systematic review of the literature. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):304-307.
27. Wayment HA, Huffman AH. Psychosocial experiences of concussed collegiate athletes: the role of emotional support in the recovery process. J Am Coll Health. 2020;68(4):438-443.
28. Todd R, Bhalerao S, Vu MT, et al. Understanding the psychiatric effects of concussion on constructed identity in hockey players: implications for health professionals. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(2):e0192125.
29. Iverson GL, Silverberg ND, Mannix R, et al. Factors associated with concussion-like symptom reporting in high school athletes. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169(12):1132-1140.
30. Gaetz M. The multi-factorial origins of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) symptomatology in post-career athletes: the athlete post-career adjustment (AP-CA) model. Med Hypotheses. 2017;102:130-143.
31. Meehan WP. Medical therapies for concussion. Clin Sports Med. 2011;30(1):115-124.
32. Broglio SP, Collins MW, Williams RM, et al. Current and emerging rehabilitation for concussion: a review of the evidence. Clin Sports Med. 2015;34(2):213-231.
33. Arciniegas DB, Silver JM, McAllister TW. Stimulants and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of cognitive impairment after traumatic brain injury. Psychopharm Review. 2008;43(12):91-97.
34. Warden DL, Gordon B, McAllister TW, et al. Guidelines for the pharmacologic treatment of neurobehavioral sequelae of traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2006;23(10):1468-1501.
35. Maldonado MD, Murillo-Cabezas F, Terron MP, et al. The potential of melatonin in reducing morbidity/mortality after craniocerebral trauma. J Pineal Res. 2007;42(1):1-11.
36. Samantaray S, Das A, Thakore NP, et al. Therapeutic potential of melatonin in traumatic central nervous system injury. J Pineal Res. 2009;47(2):134-142.
37. Chew E, Zafonte RD. Pharmacological management of neurobehavioral disorders following traumatic brain injury—a state-of-the-art review. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2009;46(6):851-879.
COVID-19’s effects on emergency psychiatry
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is affecting every aspect of medical care. Much has been written about overwhelmed hospital settings, the financial devastation to outpatient treatment centers, and an impending pandemic of mental illness that the existing underfunded and fragmented mental health system would not be prepared to weather. Although COVID-19 has undeniably affected the practice of emergency psychiatry, its impact has been surprising and complex. In this article, I describe the effects COVID-19 has had on our psychiatric emergency service, and how the pandemic has affected me personally.
How the pandemic affected our psychiatric ED
The Comprehensive Psychiatric Emergency Program (CPEP) in Buffalo, New York, is part of the emergency department (ED) in the local county hospital and is staffed by faculty from the Department of Psychiatry at the University at Buffalo. It was developed to provide evaluations of acutely psychiatrically ill individuals, to determine their treatment needs and facilitate access to the appropriate level of care.
Before COVID-19, as the only fully staffed psychiatric emergency service in the region, CPEP would routinely be called upon to serve many functions for which it was not designed. For example, people who had difficulty accessing psychiatric care in the community might come to CPEP expecting treatment for chronic conditions. Additionally, due to systemic deficiencies and limited resources, police and other community agencies refer individuals to CPEP who either have illnesses unrelated to current circumstances or who are not psychiatrically ill but unmanageable because of aggression or otherwise unresolvable social challenges such as homelessness, criminal behavior, poor parenting and other family strains, or general dissatisfaction with life. Parents unable to set limits with bored or defiant children might leave them in CPEP, hoping to transfer the parenting role, just as law enforcement officers who feel impotent to apply meaningful sanctions to non-felonious offenders might bring them to CPEP seeking containment. Labeling these problems as psychiatric emergencies has made it more palatable to leave these individuals in our care. These types of visits have contributed to the substantial growth of CPEP in recent years, in terms of annual patient visits, number of children abandoned and their lengths of stay in the CPEP, among other metrics.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on an emergency psychiatry service that is expected to be all things to all people has been interesting. For the first few weeks of the societal shutdown, the patient flow was unchanged. However, during this time, the usual overcrowding created a feeling of vulnerability to contagion that sparked an urgency to minimize the census. Superhuman efforts were fueled by an unspoken sense of impending doom, and wait times dropped from approximately 17 hours to 3 or 4 hours. This state of hypervigilance was impossible to sustain indefinitely, and inevitably those efforts were exhausted. As adrenaline waned, the focus turned toward family and self-preservation. Nursing and social work staff began cancelling shifts, as did part-time physicians who contracted services with our department. Others, however, were drawn to join the front-line fight.
Trends in psychiatric ED usage during the pandemic
As COVID-19 spread, local media reported the paucity of personal protective equipment (PPE) and created the sense that no one would receive hospital treatment unless they were on the brink of death. Consequently, total visits to the ED began to slow. During April, CPEP saw 25% fewer visits than average. This reduction was partly attributable to cohorting patients with any suspicion of infection in a designated area within the medical ED, with access to remote evaluation by CPEP psychiatrists via telemedicine. In addition, the characteristics and circumstances of patients presenting to CPEP began to change (Table).
Children/adolescents. In the months before COVID-19’s spread to the United States, there had been an exponential surge in child visits to CPEP, with >200 such visits in January 2020. When schools closed on March 13, school-related stress abruptly abated, and during April, child visits dropped to 89. This reduction might have been due in part to increased access to outpatient treatment via telemedicine or telephone appointments. In our affiliated clinics, both new patient visits and remote attendance to appointments by established patients increased substantially, likely contributing to a decreased reliance on the CPEP for treatment. Limited Family Court operations, though, left already-frustrated police without much recourse when called to intervene with adolescent offenders. CPEP once again served an untraditional role, facilitating the removal of these disruptive individuals from potentially dangerous circumstances, under the guise of behavioral emergencies.
Suicidality. While nonemergent visits declined, presentations related to suicidality persisted. In the United States, suicide rates have increased annually for decades. This trend has also been observed locally, with early evidence suggesting that the changes inflicted by COVID-19 perpetuated the surge in suicidal thinking and behavior, but with a change in character. Some of this is likely related to financial stress and social disruption, though job loss seems more likely to result in increased substance use than suicidality. Even more distressing to those coming to CPEP was anxiety about the illness itself, social isolation, and loss. The death of a loved one is painful enough, but disrupting the grief process by preventing people from visiting family members dying in hospitals or gathering for funerals has been devastating. Reports of increased gun sales undoubtedly associated with fears of social decay caused by the pandemic are concerning with regard to patients with suicidality, because shooting has emerged as the means most likely to result in completed suicide.1 The imposition of social distancing directly isolated some individuals, increasing suicidality. Limitations on gathering in groups disrupted other sources of social support as well, such as religious services, clubhouses, and meetings of 12-step programs such as Alcoholics Anonymous. This could increase suicidality, either directly for more vulnerable patients or indirectly by compromising sobriety and thereby adding to the risk for suicide.
Continue to: Substance use disorders (SUDs)
Substance use disorders (SUDs). Presentations to CPEP by patients with SUDs surged, but the patient profile changed, undoubtedly influenced by the pandemic. Requests for detoxification became less frequent because people who were not in severe distress avoided the hospital. At the same time, alcohol-dependent individuals who might typically avoid clinical attention were requiring emergent medical attention for delirium. This is attributable to a combination of factors, including nutritional depletion, and a lack of access to alcohol leading to abrupt withdrawal or consumption of unconventional sources of alcohol, such as hand sanitizer, or hard liquor (over beer). Amphetamine use appears to have increased, although the observed surge may simply be related to the conspicuousness of stimulant intoxication for someone who is sheltering in place. There was a noticeable uptick in overdoses (primarily with opioids) requiring CPEP evaluation, which was possibly related to a reduction of available beds in inpatient rehabilitation facilities as a result of social distancing rules.
Patients with chronic mental illness. Many experts anticipated an increase in hospital visits by individuals with chronic mental illness expected to decompensate as a result of reduced access to community treatment resources.2 Closing courts did not prevent remote sessions for inpatient retention and treatment over objection, but did result in the expiration of many Assisted Outpatient Treatment orders by restricting renewal hearings, which is circuitously beginning to fulfill this prediction. On the other hand, an impressive community response has managed to continue meeting the needs of most of these patients. Dedicated mental health clinics have recruited mobile teams or developed carefully scheduled, nursing-run “shot clinics” to ensure that patients who require long-acting injectable medications or medication-assisted treatment for SUDs continue to receive treatment.
New-onset psychosis. A new population of patients with acute mania and psychosis also seems to have surfaced during this pandemic. Previously high-functioning individuals in their 30s, 40s, and 50s without a history of mental illness were presenting with new-onset psychotic symptoms. These are individuals who may have been characteristically anxious, or had a “Type A personality,” but were social and employed. The cause is unclear, but given the extreme uncertainty and the political climate COVID-19 brings, it is possible that the pandemic may have triggered these episodes. These individuals and their families now have the stress of learning to navigate the mental health system added to the anxiety COVID-19 brings to most households.
Homelessness. Limitations on occupancy have reduced the availability of beds in shelters and residences, resulting in increased homelessness. Locally, authorities estimated that the homeless population has grown nearly threefold as a result of bussing in from neighboring counties with fewer resources, flight from New York City, and the urgent release from jail of nonviolent offenders, many of whom had no place to go for shelter. New emergency shelter beds have not fully compensated for the relative shortage, leading individuals who had been avoiding the hospital due to fear of infection to CPEP looking for a place to stay.
Home stressors. Whereas CPEP visits by children initially decreased, after 6 weeks, the relief from school pressures appears to have been replaced by weariness from stresses at home, and the number of children presenting with depression, SUDs, and behavioral disruptions has increased. Domestic violence involving children and adults increased. Factors that might be contributing to this include the forced proximity of family members who would typically need intermittent interpersonal distance, and an obligation to care for children who would normally be in school or for disabled loved ones now unable to attend day programs or respite services. After months of enduring the pressure of these conflicts and the resulting emotional strain, patient volumes in CPEP have begun slowly returning toward the expected average, particularly since the perceived threat of coming to the hospital has attenuated.
Continue to: Personal challenges
Personal challenges
For me, COVID-19 has brought the chance to grow and learn, fumbling at times to provide the best care when crisis abounds and when not much can be said to ease the appropriate emotional distress our patients experience. The lines between what is pathological anxiety, what level of anxiety causes functional impairment, and what can realistically be expected to respond to psychiatric treatment have become blurred. At the same time, I have come across some of the sickest patients I have ever encountered.
In some ways, my passion for psychiatry has been rekindled by COVID-19, sparking an enthusiasm to teach and inspire students to pursue careers in this wonderful field of medicine. Helping to care for patients in the absence of a cure can necessitate the application of creativity and thoughtfulness to relieve suffering, thereby teaching the art of healing above offering treatment alone. Unfortunately, replacing actual patient contact with remote learning deprives students of this unique educational opportunity. Residents who attempt to continue training while limiting exposure to patients may mitigate their own risk but could also be missing an opportunity to learn how to balance their needs with making their patients’ well-being a priority. This raises the question of how the next generation of medical students and residents will learn to navigate future crises. Gruesome media depictions of haunting experiences witnessed by medical professionals exposed to an enormity of loss and death, magnified by the suicide deaths of 2 front-line workers in New York City, undoubtedly contribute to the instinct driving the protection of students and residents in this way.
The gratitude the public expresses toward me for simply continuing to do my job brings an expectation of heroism I did not seek, and with which I am uncomfortable. For me, exceptionally poised to analyze and over-analyze myriad aspects of an internal conflict that is exhausting to balance, it all generates frustration and guilt more than anything.
I am theoretically at lower risk than intubating anesthesiologists, emergency medicine physicians, and emergency medical technicians who face patients with active COVID-19. Nevertheless, daily proximity to so many patients naturally generates fear. I convince myself that performing video consultations to the medical ED is an adaptation necessary to preserve PPE, to keep me healthy through reduced exposure, to be available to patients longer, and to support the emotional health of the medical staff who are handing over that headset to patients “under investigation.” At the same time, I am secretly relieved to avoid entering those rooms and taunting death, or even worse, risking exposing my family to the virus. The threat of COVID-19 can be so consuming that it becomes easy to forget that most individuals infected are asymptomatic and therefore difficult to quickly identify.
So I continue to sit with patients face-to-face all day. Many of them are not capable of following masking and distancing recommendations, and are more prone to spitting and biting than their counterparts in the medical ED. I must ignore this threat and convince myself I am safe to be able to place my responsibility to patient care above my own needs and do my job.
Continue to: Most of my colleagues exhibit...
Most of my colleagues exhibit an effortless bravery, even if we all naturally waver briefly at times. I am proud to stand shoulder-to-shoulder every day with these clinicians, and other staff, from police to custodians, as we continue to care for the people of this community. Despite the lower clinical burden, each day we expend significant emotional energy struggling with unexpected and unique challenges, including the burden of facing the unknown. Everyone is under stress right now. For most, the effects will be transient. For some, the damage might be permanent. For others, this stress has brought out the best in us. But knowing that physicians are particularly prone to burnout, how long can the current state of hypervigilance be maintained?
What will the future hold?
The COVID-19 era has brought fewer patients through the door of my psychiatric ED; however, just like everywhere else in the world, everything has changed. The only thing that is certain is that further change is inevitable, and we must adapt to the challenge and learn from it. As unsettling as disruptions to the status quo can be, human behavior dictates that we have the option to seize opportunities created by instability to produce superior outcomes, which can be accomplished only by looking at things anew. The question is whether we will revert to the pre-COVID-19 dysfunctional use of psychiatric emergency services, or can we use what we have learned—particularly about the value of telepsychiatry—to pursue a more effective system based on an improved understanding of the mental health treatment needs of our community. While technology is proving that social distancing requires only space between people, and not necessarily social separation, there is a risk that excessive use of remote treatment could compromise the therapeutic relationship with our patients. Despite emerging opportunities, it is difficult to direct change in a productive way when the future is uncertain.
The continuous outpouring of respect for clinicians is morale-boosting. Behind closed doors, however, news that this county hospital failed to qualify for any of the second round of federal support funding because the management of COVID-19 patients has been too effective brought a new layer of unanticipated stress. This is the only hospital in 7 counties operating a psychiatric emergency service. The mandatory, “voluntary” furloughs expected of nursing and social work staff are only now being scheduled to occur over the next couple of months. And just in time for patient volumes to return to normal. How can we continue to provide quality care, let alone build changes into practice, with reduced nursing and support staff?
It is promising, however, that in the midst of social distancing, the shared experience of endeavoring to overcome COVID-19 has promoted a connectedness among individuals who might otherwise never cross paths. This observation has bolstered my confidence in the capacity for resilience of the mental health system and the individuals within it. The reality is that we are all in this together. Differences should matter less in the face of altered perceptions of mortality. Despite the stress, suicide becomes a less reasonable choice when the value of life is magnified by pandemic circumstances. Maybe there will be even less of a need for psychiatric emergency services in the wake of COVID-19, rather than the anticipated wave of mental health crises. Until we know for sure, it is only through fellowship and continued dedication to healing that the ED experience will continue to be a positive one.
Bottom Line
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) led to changes in the characteristics and circumstances of patients presenting to our psychiatric emergency service. Despite a lower clinical burden, each day we expended significant emotional energy struggling with unexpected and unique challenges. We can use what we have learned from COVID-19 to pursue a more effective system based on an improved understanding of the mental health treatment needs of our community.
Related Resource
- American Association for Emergency Psychiatry, American College of Emergency Physicians, American Psychiatric Association, Coalition on Psychiatric Emergencies, Crisis Residential Association, and the Emergency Nurses Association. Joint statement for care of patients with behavioral health emergencies and suspected or confirmed COVID-19. https://aaep.memberclicks.net/assets/joint-statement-covid-behavioral-health.pdf.
1. Wang J, Sumner SA, Simon TR, et al. Trends in the incidence and lethality of suicidal acts in the United States, 2006-2015 [published online April 22, 2020]. JAMA Psychiatry. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.0596.
2. Reger MA, Stanley IH, Joiner TE. Suicide mortality and coronavirus disease 2019--a perfect storm? [published online April 10, 2020]. JAMA Psychiatry. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.1060.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is affecting every aspect of medical care. Much has been written about overwhelmed hospital settings, the financial devastation to outpatient treatment centers, and an impending pandemic of mental illness that the existing underfunded and fragmented mental health system would not be prepared to weather. Although COVID-19 has undeniably affected the practice of emergency psychiatry, its impact has been surprising and complex. In this article, I describe the effects COVID-19 has had on our psychiatric emergency service, and how the pandemic has affected me personally.
How the pandemic affected our psychiatric ED
The Comprehensive Psychiatric Emergency Program (CPEP) in Buffalo, New York, is part of the emergency department (ED) in the local county hospital and is staffed by faculty from the Department of Psychiatry at the University at Buffalo. It was developed to provide evaluations of acutely psychiatrically ill individuals, to determine their treatment needs and facilitate access to the appropriate level of care.
Before COVID-19, as the only fully staffed psychiatric emergency service in the region, CPEP would routinely be called upon to serve many functions for which it was not designed. For example, people who had difficulty accessing psychiatric care in the community might come to CPEP expecting treatment for chronic conditions. Additionally, due to systemic deficiencies and limited resources, police and other community agencies refer individuals to CPEP who either have illnesses unrelated to current circumstances or who are not psychiatrically ill but unmanageable because of aggression or otherwise unresolvable social challenges such as homelessness, criminal behavior, poor parenting and other family strains, or general dissatisfaction with life. Parents unable to set limits with bored or defiant children might leave them in CPEP, hoping to transfer the parenting role, just as law enforcement officers who feel impotent to apply meaningful sanctions to non-felonious offenders might bring them to CPEP seeking containment. Labeling these problems as psychiatric emergencies has made it more palatable to leave these individuals in our care. These types of visits have contributed to the substantial growth of CPEP in recent years, in terms of annual patient visits, number of children abandoned and their lengths of stay in the CPEP, among other metrics.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on an emergency psychiatry service that is expected to be all things to all people has been interesting. For the first few weeks of the societal shutdown, the patient flow was unchanged. However, during this time, the usual overcrowding created a feeling of vulnerability to contagion that sparked an urgency to minimize the census. Superhuman efforts were fueled by an unspoken sense of impending doom, and wait times dropped from approximately 17 hours to 3 or 4 hours. This state of hypervigilance was impossible to sustain indefinitely, and inevitably those efforts were exhausted. As adrenaline waned, the focus turned toward family and self-preservation. Nursing and social work staff began cancelling shifts, as did part-time physicians who contracted services with our department. Others, however, were drawn to join the front-line fight.
Trends in psychiatric ED usage during the pandemic
As COVID-19 spread, local media reported the paucity of personal protective equipment (PPE) and created the sense that no one would receive hospital treatment unless they were on the brink of death. Consequently, total visits to the ED began to slow. During April, CPEP saw 25% fewer visits than average. This reduction was partly attributable to cohorting patients with any suspicion of infection in a designated area within the medical ED, with access to remote evaluation by CPEP psychiatrists via telemedicine. In addition, the characteristics and circumstances of patients presenting to CPEP began to change (Table).

Children/adolescents. In the months before COVID-19’s spread to the United States, there had been an exponential surge in child visits to CPEP, with >200 such visits in January 2020. When schools closed on March 13, school-related stress abruptly abated, and during April, child visits dropped to 89. This reduction might have been due in part to increased access to outpatient treatment via telemedicine or telephone appointments. In our affiliated clinics, both new patient visits and remote attendance to appointments by established patients increased substantially, likely contributing to a decreased reliance on the CPEP for treatment. Limited Family Court operations, though, left already-frustrated police without much recourse when called to intervene with adolescent offenders. CPEP once again served an untraditional role, facilitating the removal of these disruptive individuals from potentially dangerous circumstances, under the guise of behavioral emergencies.
Suicidality. While nonemergent visits declined, presentations related to suicidality persisted. In the United States, suicide rates have increased annually for decades. This trend has also been observed locally, with early evidence suggesting that the changes inflicted by COVID-19 perpetuated the surge in suicidal thinking and behavior, but with a change in character. Some of this is likely related to financial stress and social disruption, though job loss seems more likely to result in increased substance use than suicidality. Even more distressing to those coming to CPEP was anxiety about the illness itself, social isolation, and loss. The death of a loved one is painful enough, but disrupting the grief process by preventing people from visiting family members dying in hospitals or gathering for funerals has been devastating. Reports of increased gun sales undoubtedly associated with fears of social decay caused by the pandemic are concerning with regard to patients with suicidality, because shooting has emerged as the means most likely to result in completed suicide.1 The imposition of social distancing directly isolated some individuals, increasing suicidality. Limitations on gathering in groups disrupted other sources of social support as well, such as religious services, clubhouses, and meetings of 12-step programs such as Alcoholics Anonymous. This could increase suicidality, either directly for more vulnerable patients or indirectly by compromising sobriety and thereby adding to the risk for suicide.
Continue to: Substance use disorders (SUDs)
Substance use disorders (SUDs). Presentations to CPEP by patients with SUDs surged, but the patient profile changed, undoubtedly influenced by the pandemic. Requests for detoxification became less frequent because people who were not in severe distress avoided the hospital. At the same time, alcohol-dependent individuals who might typically avoid clinical attention were requiring emergent medical attention for delirium. This is attributable to a combination of factors, including nutritional depletion, and a lack of access to alcohol leading to abrupt withdrawal or consumption of unconventional sources of alcohol, such as hand sanitizer, or hard liquor (over beer). Amphetamine use appears to have increased, although the observed surge may simply be related to the conspicuousness of stimulant intoxication for someone who is sheltering in place. There was a noticeable uptick in overdoses (primarily with opioids) requiring CPEP evaluation, which was possibly related to a reduction of available beds in inpatient rehabilitation facilities as a result of social distancing rules.
Patients with chronic mental illness. Many experts anticipated an increase in hospital visits by individuals with chronic mental illness expected to decompensate as a result of reduced access to community treatment resources.2 Closing courts did not prevent remote sessions for inpatient retention and treatment over objection, but did result in the expiration of many Assisted Outpatient Treatment orders by restricting renewal hearings, which is circuitously beginning to fulfill this prediction. On the other hand, an impressive community response has managed to continue meeting the needs of most of these patients. Dedicated mental health clinics have recruited mobile teams or developed carefully scheduled, nursing-run “shot clinics” to ensure that patients who require long-acting injectable medications or medication-assisted treatment for SUDs continue to receive treatment.
New-onset psychosis. A new population of patients with acute mania and psychosis also seems to have surfaced during this pandemic. Previously high-functioning individuals in their 30s, 40s, and 50s without a history of mental illness were presenting with new-onset psychotic symptoms. These are individuals who may have been characteristically anxious, or had a “Type A personality,” but were social and employed. The cause is unclear, but given the extreme uncertainty and the political climate COVID-19 brings, it is possible that the pandemic may have triggered these episodes. These individuals and their families now have the stress of learning to navigate the mental health system added to the anxiety COVID-19 brings to most households.
Homelessness. Limitations on occupancy have reduced the availability of beds in shelters and residences, resulting in increased homelessness. Locally, authorities estimated that the homeless population has grown nearly threefold as a result of bussing in from neighboring counties with fewer resources, flight from New York City, and the urgent release from jail of nonviolent offenders, many of whom had no place to go for shelter. New emergency shelter beds have not fully compensated for the relative shortage, leading individuals who had been avoiding the hospital due to fear of infection to CPEP looking for a place to stay.
Home stressors. Whereas CPEP visits by children initially decreased, after 6 weeks, the relief from school pressures appears to have been replaced by weariness from stresses at home, and the number of children presenting with depression, SUDs, and behavioral disruptions has increased. Domestic violence involving children and adults increased. Factors that might be contributing to this include the forced proximity of family members who would typically need intermittent interpersonal distance, and an obligation to care for children who would normally be in school or for disabled loved ones now unable to attend day programs or respite services. After months of enduring the pressure of these conflicts and the resulting emotional strain, patient volumes in CPEP have begun slowly returning toward the expected average, particularly since the perceived threat of coming to the hospital has attenuated.
Continue to: Personal challenges
Personal challenges
For me, COVID-19 has brought the chance to grow and learn, fumbling at times to provide the best care when crisis abounds and when not much can be said to ease the appropriate emotional distress our patients experience. The lines between what is pathological anxiety, what level of anxiety causes functional impairment, and what can realistically be expected to respond to psychiatric treatment have become blurred. At the same time, I have come across some of the sickest patients I have ever encountered.
In some ways, my passion for psychiatry has been rekindled by COVID-19, sparking an enthusiasm to teach and inspire students to pursue careers in this wonderful field of medicine. Helping to care for patients in the absence of a cure can necessitate the application of creativity and thoughtfulness to relieve suffering, thereby teaching the art of healing above offering treatment alone. Unfortunately, replacing actual patient contact with remote learning deprives students of this unique educational opportunity. Residents who attempt to continue training while limiting exposure to patients may mitigate their own risk but could also be missing an opportunity to learn how to balance their needs with making their patients’ well-being a priority. This raises the question of how the next generation of medical students and residents will learn to navigate future crises. Gruesome media depictions of haunting experiences witnessed by medical professionals exposed to an enormity of loss and death, magnified by the suicide deaths of 2 front-line workers in New York City, undoubtedly contribute to the instinct driving the protection of students and residents in this way.
The gratitude the public expresses toward me for simply continuing to do my job brings an expectation of heroism I did not seek, and with which I am uncomfortable. For me, exceptionally poised to analyze and over-analyze myriad aspects of an internal conflict that is exhausting to balance, it all generates frustration and guilt more than anything.
I am theoretically at lower risk than intubating anesthesiologists, emergency medicine physicians, and emergency medical technicians who face patients with active COVID-19. Nevertheless, daily proximity to so many patients naturally generates fear. I convince myself that performing video consultations to the medical ED is an adaptation necessary to preserve PPE, to keep me healthy through reduced exposure, to be available to patients longer, and to support the emotional health of the medical staff who are handing over that headset to patients “under investigation.” At the same time, I am secretly relieved to avoid entering those rooms and taunting death, or even worse, risking exposing my family to the virus. The threat of COVID-19 can be so consuming that it becomes easy to forget that most individuals infected are asymptomatic and therefore difficult to quickly identify.
So I continue to sit with patients face-to-face all day. Many of them are not capable of following masking and distancing recommendations, and are more prone to spitting and biting than their counterparts in the medical ED. I must ignore this threat and convince myself I am safe to be able to place my responsibility to patient care above my own needs and do my job.
Continue to: Most of my colleagues exhibit...
Most of my colleagues exhibit an effortless bravery, even if we all naturally waver briefly at times. I am proud to stand shoulder-to-shoulder every day with these clinicians, and other staff, from police to custodians, as we continue to care for the people of this community. Despite the lower clinical burden, each day we expend significant emotional energy struggling with unexpected and unique challenges, including the burden of facing the unknown. Everyone is under stress right now. For most, the effects will be transient. For some, the damage might be permanent. For others, this stress has brought out the best in us. But knowing that physicians are particularly prone to burnout, how long can the current state of hypervigilance be maintained?
What will the future hold?
The COVID-19 era has brought fewer patients through the door of my psychiatric ED; however, just like everywhere else in the world, everything has changed. The only thing that is certain is that further change is inevitable, and we must adapt to the challenge and learn from it. As unsettling as disruptions to the status quo can be, human behavior dictates that we have the option to seize opportunities created by instability to produce superior outcomes, which can be accomplished only by looking at things anew. The question is whether we will revert to the pre-COVID-19 dysfunctional use of psychiatric emergency services, or can we use what we have learned—particularly about the value of telepsychiatry—to pursue a more effective system based on an improved understanding of the mental health treatment needs of our community. While technology is proving that social distancing requires only space between people, and not necessarily social separation, there is a risk that excessive use of remote treatment could compromise the therapeutic relationship with our patients. Despite emerging opportunities, it is difficult to direct change in a productive way when the future is uncertain.
The continuous outpouring of respect for clinicians is morale-boosting. Behind closed doors, however, news that this county hospital failed to qualify for any of the second round of federal support funding because the management of COVID-19 patients has been too effective brought a new layer of unanticipated stress. This is the only hospital in 7 counties operating a psychiatric emergency service. The mandatory, “voluntary” furloughs expected of nursing and social work staff are only now being scheduled to occur over the next couple of months. And just in time for patient volumes to return to normal. How can we continue to provide quality care, let alone build changes into practice, with reduced nursing and support staff?
It is promising, however, that in the midst of social distancing, the shared experience of endeavoring to overcome COVID-19 has promoted a connectedness among individuals who might otherwise never cross paths. This observation has bolstered my confidence in the capacity for resilience of the mental health system and the individuals within it. The reality is that we are all in this together. Differences should matter less in the face of altered perceptions of mortality. Despite the stress, suicide becomes a less reasonable choice when the value of life is magnified by pandemic circumstances. Maybe there will be even less of a need for psychiatric emergency services in the wake of COVID-19, rather than the anticipated wave of mental health crises. Until we know for sure, it is only through fellowship and continued dedication to healing that the ED experience will continue to be a positive one.
Bottom Line
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) led to changes in the characteristics and circumstances of patients presenting to our psychiatric emergency service. Despite a lower clinical burden, each day we expended significant emotional energy struggling with unexpected and unique challenges. We can use what we have learned from COVID-19 to pursue a more effective system based on an improved understanding of the mental health treatment needs of our community.
Related Resource
- American Association for Emergency Psychiatry, American College of Emergency Physicians, American Psychiatric Association, Coalition on Psychiatric Emergencies, Crisis Residential Association, and the Emergency Nurses Association. Joint statement for care of patients with behavioral health emergencies and suspected or confirmed COVID-19. https://aaep.memberclicks.net/assets/joint-statement-covid-behavioral-health.pdf.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is affecting every aspect of medical care. Much has been written about overwhelmed hospital settings, the financial devastation to outpatient treatment centers, and an impending pandemic of mental illness that the existing underfunded and fragmented mental health system would not be prepared to weather. Although COVID-19 has undeniably affected the practice of emergency psychiatry, its impact has been surprising and complex. In this article, I describe the effects COVID-19 has had on our psychiatric emergency service, and how the pandemic has affected me personally.
How the pandemic affected our psychiatric ED
The Comprehensive Psychiatric Emergency Program (CPEP) in Buffalo, New York, is part of the emergency department (ED) in the local county hospital and is staffed by faculty from the Department of Psychiatry at the University at Buffalo. It was developed to provide evaluations of acutely psychiatrically ill individuals, to determine their treatment needs and facilitate access to the appropriate level of care.
Before COVID-19, as the only fully staffed psychiatric emergency service in the region, CPEP would routinely be called upon to serve many functions for which it was not designed. For example, people who had difficulty accessing psychiatric care in the community might come to CPEP expecting treatment for chronic conditions. Additionally, due to systemic deficiencies and limited resources, police and other community agencies refer individuals to CPEP who either have illnesses unrelated to current circumstances or who are not psychiatrically ill but unmanageable because of aggression or otherwise unresolvable social challenges such as homelessness, criminal behavior, poor parenting and other family strains, or general dissatisfaction with life. Parents unable to set limits with bored or defiant children might leave them in CPEP, hoping to transfer the parenting role, just as law enforcement officers who feel impotent to apply meaningful sanctions to non-felonious offenders might bring them to CPEP seeking containment. Labeling these problems as psychiatric emergencies has made it more palatable to leave these individuals in our care. These types of visits have contributed to the substantial growth of CPEP in recent years, in terms of annual patient visits, number of children abandoned and their lengths of stay in the CPEP, among other metrics.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on an emergency psychiatry service that is expected to be all things to all people has been interesting. For the first few weeks of the societal shutdown, the patient flow was unchanged. However, during this time, the usual overcrowding created a feeling of vulnerability to contagion that sparked an urgency to minimize the census. Superhuman efforts were fueled by an unspoken sense of impending doom, and wait times dropped from approximately 17 hours to 3 or 4 hours. This state of hypervigilance was impossible to sustain indefinitely, and inevitably those efforts were exhausted. As adrenaline waned, the focus turned toward family and self-preservation. Nursing and social work staff began cancelling shifts, as did part-time physicians who contracted services with our department. Others, however, were drawn to join the front-line fight.
Trends in psychiatric ED usage during the pandemic
As COVID-19 spread, local media reported the paucity of personal protective equipment (PPE) and created the sense that no one would receive hospital treatment unless they were on the brink of death. Consequently, total visits to the ED began to slow. During April, CPEP saw 25% fewer visits than average. This reduction was partly attributable to cohorting patients with any suspicion of infection in a designated area within the medical ED, with access to remote evaluation by CPEP psychiatrists via telemedicine. In addition, the characteristics and circumstances of patients presenting to CPEP began to change (Table).

Children/adolescents. In the months before COVID-19’s spread to the United States, there had been an exponential surge in child visits to CPEP, with >200 such visits in January 2020. When schools closed on March 13, school-related stress abruptly abated, and during April, child visits dropped to 89. This reduction might have been due in part to increased access to outpatient treatment via telemedicine or telephone appointments. In our affiliated clinics, both new patient visits and remote attendance to appointments by established patients increased substantially, likely contributing to a decreased reliance on the CPEP for treatment. Limited Family Court operations, though, left already-frustrated police without much recourse when called to intervene with adolescent offenders. CPEP once again served an untraditional role, facilitating the removal of these disruptive individuals from potentially dangerous circumstances, under the guise of behavioral emergencies.
Suicidality. While nonemergent visits declined, presentations related to suicidality persisted. In the United States, suicide rates have increased annually for decades. This trend has also been observed locally, with early evidence suggesting that the changes inflicted by COVID-19 perpetuated the surge in suicidal thinking and behavior, but with a change in character. Some of this is likely related to financial stress and social disruption, though job loss seems more likely to result in increased substance use than suicidality. Even more distressing to those coming to CPEP was anxiety about the illness itself, social isolation, and loss. The death of a loved one is painful enough, but disrupting the grief process by preventing people from visiting family members dying in hospitals or gathering for funerals has been devastating. Reports of increased gun sales undoubtedly associated with fears of social decay caused by the pandemic are concerning with regard to patients with suicidality, because shooting has emerged as the means most likely to result in completed suicide.1 The imposition of social distancing directly isolated some individuals, increasing suicidality. Limitations on gathering in groups disrupted other sources of social support as well, such as religious services, clubhouses, and meetings of 12-step programs such as Alcoholics Anonymous. This could increase suicidality, either directly for more vulnerable patients or indirectly by compromising sobriety and thereby adding to the risk for suicide.
Continue to: Substance use disorders (SUDs)
Substance use disorders (SUDs). Presentations to CPEP by patients with SUDs surged, but the patient profile changed, undoubtedly influenced by the pandemic. Requests for detoxification became less frequent because people who were not in severe distress avoided the hospital. At the same time, alcohol-dependent individuals who might typically avoid clinical attention were requiring emergent medical attention for delirium. This is attributable to a combination of factors, including nutritional depletion, and a lack of access to alcohol leading to abrupt withdrawal or consumption of unconventional sources of alcohol, such as hand sanitizer, or hard liquor (over beer). Amphetamine use appears to have increased, although the observed surge may simply be related to the conspicuousness of stimulant intoxication for someone who is sheltering in place. There was a noticeable uptick in overdoses (primarily with opioids) requiring CPEP evaluation, which was possibly related to a reduction of available beds in inpatient rehabilitation facilities as a result of social distancing rules.
Patients with chronic mental illness. Many experts anticipated an increase in hospital visits by individuals with chronic mental illness expected to decompensate as a result of reduced access to community treatment resources.2 Closing courts did not prevent remote sessions for inpatient retention and treatment over objection, but did result in the expiration of many Assisted Outpatient Treatment orders by restricting renewal hearings, which is circuitously beginning to fulfill this prediction. On the other hand, an impressive community response has managed to continue meeting the needs of most of these patients. Dedicated mental health clinics have recruited mobile teams or developed carefully scheduled, nursing-run “shot clinics” to ensure that patients who require long-acting injectable medications or medication-assisted treatment for SUDs continue to receive treatment.
New-onset psychosis. A new population of patients with acute mania and psychosis also seems to have surfaced during this pandemic. Previously high-functioning individuals in their 30s, 40s, and 50s without a history of mental illness were presenting with new-onset psychotic symptoms. These are individuals who may have been characteristically anxious, or had a “Type A personality,” but were social and employed. The cause is unclear, but given the extreme uncertainty and the political climate COVID-19 brings, it is possible that the pandemic may have triggered these episodes. These individuals and their families now have the stress of learning to navigate the mental health system added to the anxiety COVID-19 brings to most households.
Homelessness. Limitations on occupancy have reduced the availability of beds in shelters and residences, resulting in increased homelessness. Locally, authorities estimated that the homeless population has grown nearly threefold as a result of bussing in from neighboring counties with fewer resources, flight from New York City, and the urgent release from jail of nonviolent offenders, many of whom had no place to go for shelter. New emergency shelter beds have not fully compensated for the relative shortage, leading individuals who had been avoiding the hospital due to fear of infection to CPEP looking for a place to stay.
Home stressors. Whereas CPEP visits by children initially decreased, after 6 weeks, the relief from school pressures appears to have been replaced by weariness from stresses at home, and the number of children presenting with depression, SUDs, and behavioral disruptions has increased. Domestic violence involving children and adults increased. Factors that might be contributing to this include the forced proximity of family members who would typically need intermittent interpersonal distance, and an obligation to care for children who would normally be in school or for disabled loved ones now unable to attend day programs or respite services. After months of enduring the pressure of these conflicts and the resulting emotional strain, patient volumes in CPEP have begun slowly returning toward the expected average, particularly since the perceived threat of coming to the hospital has attenuated.
Continue to: Personal challenges
Personal challenges
For me, COVID-19 has brought the chance to grow and learn, fumbling at times to provide the best care when crisis abounds and when not much can be said to ease the appropriate emotional distress our patients experience. The lines between what is pathological anxiety, what level of anxiety causes functional impairment, and what can realistically be expected to respond to psychiatric treatment have become blurred. At the same time, I have come across some of the sickest patients I have ever encountered.
In some ways, my passion for psychiatry has been rekindled by COVID-19, sparking an enthusiasm to teach and inspire students to pursue careers in this wonderful field of medicine. Helping to care for patients in the absence of a cure can necessitate the application of creativity and thoughtfulness to relieve suffering, thereby teaching the art of healing above offering treatment alone. Unfortunately, replacing actual patient contact with remote learning deprives students of this unique educational opportunity. Residents who attempt to continue training while limiting exposure to patients may mitigate their own risk but could also be missing an opportunity to learn how to balance their needs with making their patients’ well-being a priority. This raises the question of how the next generation of medical students and residents will learn to navigate future crises. Gruesome media depictions of haunting experiences witnessed by medical professionals exposed to an enormity of loss and death, magnified by the suicide deaths of 2 front-line workers in New York City, undoubtedly contribute to the instinct driving the protection of students and residents in this way.
The gratitude the public expresses toward me for simply continuing to do my job brings an expectation of heroism I did not seek, and with which I am uncomfortable. For me, exceptionally poised to analyze and over-analyze myriad aspects of an internal conflict that is exhausting to balance, it all generates frustration and guilt more than anything.
I am theoretically at lower risk than intubating anesthesiologists, emergency medicine physicians, and emergency medical technicians who face patients with active COVID-19. Nevertheless, daily proximity to so many patients naturally generates fear. I convince myself that performing video consultations to the medical ED is an adaptation necessary to preserve PPE, to keep me healthy through reduced exposure, to be available to patients longer, and to support the emotional health of the medical staff who are handing over that headset to patients “under investigation.” At the same time, I am secretly relieved to avoid entering those rooms and taunting death, or even worse, risking exposing my family to the virus. The threat of COVID-19 can be so consuming that it becomes easy to forget that most individuals infected are asymptomatic and therefore difficult to quickly identify.
So I continue to sit with patients face-to-face all day. Many of them are not capable of following masking and distancing recommendations, and are more prone to spitting and biting than their counterparts in the medical ED. I must ignore this threat and convince myself I am safe to be able to place my responsibility to patient care above my own needs and do my job.
Continue to: Most of my colleagues exhibit...
Most of my colleagues exhibit an effortless bravery, even if we all naturally waver briefly at times. I am proud to stand shoulder-to-shoulder every day with these clinicians, and other staff, from police to custodians, as we continue to care for the people of this community. Despite the lower clinical burden, each day we expend significant emotional energy struggling with unexpected and unique challenges, including the burden of facing the unknown. Everyone is under stress right now. For most, the effects will be transient. For some, the damage might be permanent. For others, this stress has brought out the best in us. But knowing that physicians are particularly prone to burnout, how long can the current state of hypervigilance be maintained?
What will the future hold?
The COVID-19 era has brought fewer patients through the door of my psychiatric ED; however, just like everywhere else in the world, everything has changed. The only thing that is certain is that further change is inevitable, and we must adapt to the challenge and learn from it. As unsettling as disruptions to the status quo can be, human behavior dictates that we have the option to seize opportunities created by instability to produce superior outcomes, which can be accomplished only by looking at things anew. The question is whether we will revert to the pre-COVID-19 dysfunctional use of psychiatric emergency services, or can we use what we have learned—particularly about the value of telepsychiatry—to pursue a more effective system based on an improved understanding of the mental health treatment needs of our community. While technology is proving that social distancing requires only space between people, and not necessarily social separation, there is a risk that excessive use of remote treatment could compromise the therapeutic relationship with our patients. Despite emerging opportunities, it is difficult to direct change in a productive way when the future is uncertain.
The continuous outpouring of respect for clinicians is morale-boosting. Behind closed doors, however, news that this county hospital failed to qualify for any of the second round of federal support funding because the management of COVID-19 patients has been too effective brought a new layer of unanticipated stress. This is the only hospital in 7 counties operating a psychiatric emergency service. The mandatory, “voluntary” furloughs expected of nursing and social work staff are only now being scheduled to occur over the next couple of months. And just in time for patient volumes to return to normal. How can we continue to provide quality care, let alone build changes into practice, with reduced nursing and support staff?
It is promising, however, that in the midst of social distancing, the shared experience of endeavoring to overcome COVID-19 has promoted a connectedness among individuals who might otherwise never cross paths. This observation has bolstered my confidence in the capacity for resilience of the mental health system and the individuals within it. The reality is that we are all in this together. Differences should matter less in the face of altered perceptions of mortality. Despite the stress, suicide becomes a less reasonable choice when the value of life is magnified by pandemic circumstances. Maybe there will be even less of a need for psychiatric emergency services in the wake of COVID-19, rather than the anticipated wave of mental health crises. Until we know for sure, it is only through fellowship and continued dedication to healing that the ED experience will continue to be a positive one.
Bottom Line
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) led to changes in the characteristics and circumstances of patients presenting to our psychiatric emergency service. Despite a lower clinical burden, each day we expended significant emotional energy struggling with unexpected and unique challenges. We can use what we have learned from COVID-19 to pursue a more effective system based on an improved understanding of the mental health treatment needs of our community.
Related Resource
- American Association for Emergency Psychiatry, American College of Emergency Physicians, American Psychiatric Association, Coalition on Psychiatric Emergencies, Crisis Residential Association, and the Emergency Nurses Association. Joint statement for care of patients with behavioral health emergencies and suspected or confirmed COVID-19. https://aaep.memberclicks.net/assets/joint-statement-covid-behavioral-health.pdf.
1. Wang J, Sumner SA, Simon TR, et al. Trends in the incidence and lethality of suicidal acts in the United States, 2006-2015 [published online April 22, 2020]. JAMA Psychiatry. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.0596.
2. Reger MA, Stanley IH, Joiner TE. Suicide mortality and coronavirus disease 2019--a perfect storm? [published online April 10, 2020]. JAMA Psychiatry. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.1060.
1. Wang J, Sumner SA, Simon TR, et al. Trends in the incidence and lethality of suicidal acts in the United States, 2006-2015 [published online April 22, 2020]. JAMA Psychiatry. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.0596.
2. Reger MA, Stanley IH, Joiner TE. Suicide mortality and coronavirus disease 2019--a perfect storm? [published online April 10, 2020]. JAMA Psychiatry. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.1060.
The hidden dangers of supplements: A case of substance-induced psychosis
“You are what you eat,” my mother always said, and structured our dinner plates according to the USDA food pyramid. We dutifully consumed leafy greens, and prior to medical school I invested time and money into healthy diet choices. I drank green smoothies, pureed baby food for my children, read up on the pH balancing diet, grew sprouts on windowsills, bought organic.
With the stressors and time constraints of managing medical school and a family, nutrition tumbled down the ladder of priorities until eventually my family was subsisting on chicken nuggets, pizza, and peanut butter. Intern year has only added the occasional candy bar from the doctors’ lounge. I experienced a vague sense of loss for something I had once valued, but simultaneously felt dismissive of trendy topics such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants in the face of myocardial infarctions and liver failure. A biochemistry professor once scoffed at “the laypeople’s obsession with toxins,” and nutrition received zero attention in our medical school curriculum or board exams.
However, a clinical experience on the inpatient psychiatric unit made me reevaluate the importance nutrition should have in both our personal lives and the practice of medicine. This is the case of an otherwise healthy young man with no psychiatric history who suffered a psychotic break after ingesting an excess of a supplement he purchased online with the purpose of improving his performance at a high-stress job.
CASE REPORT
Mr. K, a 28-year-old computer programmer, was voluntarily admitted to the inpatient psychiatry unit for paranoia and persecutory delusions along with auditory hallucinations. His father reported that Mr. K had been behaving erratically for several days prior to admission and was subsequently found wandering in the street.
On admission, Mr. K was not oriented to place or situation. He was unkempt and guarded, and claimed people were following him. His urine toxicology screen and blood alcohol levels were negative.
While hospitalized, Mr. K was hyperverbal and delusional. He related that at work he had been developing programs to make slaves in the computer, “algorithms for orchestration,” and that he was uncomfortable with the ethical implications. He eventually endorsed having purchased the supplement phenylethylamine (PEA) to improve his focus, and ingesting “two substantial scoops of the crystalline substance.”
We did not initiate any psychiatric medications. On the third day of his hospitalization, Mr. K was alert, oriented, euthymic, relaxed, and had a full range of affect; upon discharge we advised him to discard the PEA and avoid stimulants. He complied, quit his high-stress job, and had no subsequent psychotic symptoms in the 7 months since discharge.
Continue to: Dietary supplements carry risks
Dietary supplements carry risks
According to the FDA, dietary supplements are regulated as food, but many have strong biologic effects or may even contain drugs.1 More than 18% of Americans use herbal or nutritional therapies as part of their health regimen.2 However, many over-the-counter remedies have been found to exhibit psychotropic effects,3 and many more are purported to impact mental and physical health with little to no scientific research into these claims or potential adverse effects.
Phenylethylamine is sold as a nutritional supplement and marketed for its purported beneficial effects on weight loss, mood, and focus.4 However, PEA is known to act as a natural amphetamine and to play a role in the development of neuropsychiatric disorders.5 It is an endogenous psychotogenic molecule that has been previously theorized as a cause for primary psychosis.6 Phenylethylamine interacts with the same receptor ligand that responds to amphetamine and related compounds (such as methamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine [MDMA]), the genetic coding for which is located in an area of DNA associated with schizophrenia: chromosome 6q23.2.7 While the mechanisms and details of these interactions remain poorly understood, this case of PEA-induced psychosis represents a glimpse into the potential psychoactive properties of this readily available nutritional supplement.
This patient’s cautionary tale has given me pause regarding both my family’s nutrition and the oft-neglected dietary portion of the social history. Also, several subsequent patient experiences hearken back to my mother’s words regarding the importance of healthy eating. A patient with phenylketonuria presented with psychosis after running out of her formula and consuming junk food. Another patient with severely elevated blood glucose levels presented with confusion. I have come to realize that ingestion impacts presentation, or, in other words, you are what you eat.
1. US Food and Drug Administration. Dietary supplements. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/dietary-supplements. Accessed December 11, 2019.
2. Tindle H, Davis R, Philips R, et al. Trends in use of complementary and alternative medicine by US adults: 1997-2002. Altern Ther Health Med. 2005;11(1):42-49.
3. Sarris J. Herbal medicines in the treatment of psychiatric disorders: 10-year updated review. Phytotherapy Research. 2018;32(7):1147-1162.
4. Irsfeld M, Spadafore M, Prüß BM. β-phenylethylamine, a small molecule with a large impact. WebmedCentral. 2013;4(9):4409.
5. Wolf M, Mosnaim A. Phenylethylamine in neuropsychiatric disorders. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(4):385-390.
6. Janssen P, Leysen J, Megens A, et al. Does phenylethylamine act as an endogenous amphetamine in some patients? In J Neuropsychopharmacol. 1999;2(3):229-240.
7. Zucchi R, Chiellini G, Scanlan TS, et al. Trace amine-associated receptors and their ligands. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;149(8):967-978.
“You are what you eat,” my mother always said, and structured our dinner plates according to the USDA food pyramid. We dutifully consumed leafy greens, and prior to medical school I invested time and money into healthy diet choices. I drank green smoothies, pureed baby food for my children, read up on the pH balancing diet, grew sprouts on windowsills, bought organic.
With the stressors and time constraints of managing medical school and a family, nutrition tumbled down the ladder of priorities until eventually my family was subsisting on chicken nuggets, pizza, and peanut butter. Intern year has only added the occasional candy bar from the doctors’ lounge. I experienced a vague sense of loss for something I had once valued, but simultaneously felt dismissive of trendy topics such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants in the face of myocardial infarctions and liver failure. A biochemistry professor once scoffed at “the laypeople’s obsession with toxins,” and nutrition received zero attention in our medical school curriculum or board exams.
However, a clinical experience on the inpatient psychiatric unit made me reevaluate the importance nutrition should have in both our personal lives and the practice of medicine. This is the case of an otherwise healthy young man with no psychiatric history who suffered a psychotic break after ingesting an excess of a supplement he purchased online with the purpose of improving his performance at a high-stress job.
CASE REPORT
Mr. K, a 28-year-old computer programmer, was voluntarily admitted to the inpatient psychiatry unit for paranoia and persecutory delusions along with auditory hallucinations. His father reported that Mr. K had been behaving erratically for several days prior to admission and was subsequently found wandering in the street.
On admission, Mr. K was not oriented to place or situation. He was unkempt and guarded, and claimed people were following him. His urine toxicology screen and blood alcohol levels were negative.
While hospitalized, Mr. K was hyperverbal and delusional. He related that at work he had been developing programs to make slaves in the computer, “algorithms for orchestration,” and that he was uncomfortable with the ethical implications. He eventually endorsed having purchased the supplement phenylethylamine (PEA) to improve his focus, and ingesting “two substantial scoops of the crystalline substance.”
We did not initiate any psychiatric medications. On the third day of his hospitalization, Mr. K was alert, oriented, euthymic, relaxed, and had a full range of affect; upon discharge we advised him to discard the PEA and avoid stimulants. He complied, quit his high-stress job, and had no subsequent psychotic symptoms in the 7 months since discharge.
Continue to: Dietary supplements carry risks
Dietary supplements carry risks
According to the FDA, dietary supplements are regulated as food, but many have strong biologic effects or may even contain drugs.1 More than 18% of Americans use herbal or nutritional therapies as part of their health regimen.2 However, many over-the-counter remedies have been found to exhibit psychotropic effects,3 and many more are purported to impact mental and physical health with little to no scientific research into these claims or potential adverse effects.
Phenylethylamine is sold as a nutritional supplement and marketed for its purported beneficial effects on weight loss, mood, and focus.4 However, PEA is known to act as a natural amphetamine and to play a role in the development of neuropsychiatric disorders.5 It is an endogenous psychotogenic molecule that has been previously theorized as a cause for primary psychosis.6 Phenylethylamine interacts with the same receptor ligand that responds to amphetamine and related compounds (such as methamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine [MDMA]), the genetic coding for which is located in an area of DNA associated with schizophrenia: chromosome 6q23.2.7 While the mechanisms and details of these interactions remain poorly understood, this case of PEA-induced psychosis represents a glimpse into the potential psychoactive properties of this readily available nutritional supplement.
This patient’s cautionary tale has given me pause regarding both my family’s nutrition and the oft-neglected dietary portion of the social history. Also, several subsequent patient experiences hearken back to my mother’s words regarding the importance of healthy eating. A patient with phenylketonuria presented with psychosis after running out of her formula and consuming junk food. Another patient with severely elevated blood glucose levels presented with confusion. I have come to realize that ingestion impacts presentation, or, in other words, you are what you eat.
“You are what you eat,” my mother always said, and structured our dinner plates according to the USDA food pyramid. We dutifully consumed leafy greens, and prior to medical school I invested time and money into healthy diet choices. I drank green smoothies, pureed baby food for my children, read up on the pH balancing diet, grew sprouts on windowsills, bought organic.
With the stressors and time constraints of managing medical school and a family, nutrition tumbled down the ladder of priorities until eventually my family was subsisting on chicken nuggets, pizza, and peanut butter. Intern year has only added the occasional candy bar from the doctors’ lounge. I experienced a vague sense of loss for something I had once valued, but simultaneously felt dismissive of trendy topics such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants in the face of myocardial infarctions and liver failure. A biochemistry professor once scoffed at “the laypeople’s obsession with toxins,” and nutrition received zero attention in our medical school curriculum or board exams.
However, a clinical experience on the inpatient psychiatric unit made me reevaluate the importance nutrition should have in both our personal lives and the practice of medicine. This is the case of an otherwise healthy young man with no psychiatric history who suffered a psychotic break after ingesting an excess of a supplement he purchased online with the purpose of improving his performance at a high-stress job.
CASE REPORT
Mr. K, a 28-year-old computer programmer, was voluntarily admitted to the inpatient psychiatry unit for paranoia and persecutory delusions along with auditory hallucinations. His father reported that Mr. K had been behaving erratically for several days prior to admission and was subsequently found wandering in the street.
On admission, Mr. K was not oriented to place or situation. He was unkempt and guarded, and claimed people were following him. His urine toxicology screen and blood alcohol levels were negative.
While hospitalized, Mr. K was hyperverbal and delusional. He related that at work he had been developing programs to make slaves in the computer, “algorithms for orchestration,” and that he was uncomfortable with the ethical implications. He eventually endorsed having purchased the supplement phenylethylamine (PEA) to improve his focus, and ingesting “two substantial scoops of the crystalline substance.”
We did not initiate any psychiatric medications. On the third day of his hospitalization, Mr. K was alert, oriented, euthymic, relaxed, and had a full range of affect; upon discharge we advised him to discard the PEA and avoid stimulants. He complied, quit his high-stress job, and had no subsequent psychotic symptoms in the 7 months since discharge.
Continue to: Dietary supplements carry risks
Dietary supplements carry risks
According to the FDA, dietary supplements are regulated as food, but many have strong biologic effects or may even contain drugs.1 More than 18% of Americans use herbal or nutritional therapies as part of their health regimen.2 However, many over-the-counter remedies have been found to exhibit psychotropic effects,3 and many more are purported to impact mental and physical health with little to no scientific research into these claims or potential adverse effects.
Phenylethylamine is sold as a nutritional supplement and marketed for its purported beneficial effects on weight loss, mood, and focus.4 However, PEA is known to act as a natural amphetamine and to play a role in the development of neuropsychiatric disorders.5 It is an endogenous psychotogenic molecule that has been previously theorized as a cause for primary psychosis.6 Phenylethylamine interacts with the same receptor ligand that responds to amphetamine and related compounds (such as methamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine [MDMA]), the genetic coding for which is located in an area of DNA associated with schizophrenia: chromosome 6q23.2.7 While the mechanisms and details of these interactions remain poorly understood, this case of PEA-induced psychosis represents a glimpse into the potential psychoactive properties of this readily available nutritional supplement.
This patient’s cautionary tale has given me pause regarding both my family’s nutrition and the oft-neglected dietary portion of the social history. Also, several subsequent patient experiences hearken back to my mother’s words regarding the importance of healthy eating. A patient with phenylketonuria presented with psychosis after running out of her formula and consuming junk food. Another patient with severely elevated blood glucose levels presented with confusion. I have come to realize that ingestion impacts presentation, or, in other words, you are what you eat.
1. US Food and Drug Administration. Dietary supplements. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/dietary-supplements. Accessed December 11, 2019.
2. Tindle H, Davis R, Philips R, et al. Trends in use of complementary and alternative medicine by US adults: 1997-2002. Altern Ther Health Med. 2005;11(1):42-49.
3. Sarris J. Herbal medicines in the treatment of psychiatric disorders: 10-year updated review. Phytotherapy Research. 2018;32(7):1147-1162.
4. Irsfeld M, Spadafore M, Prüß BM. β-phenylethylamine, a small molecule with a large impact. WebmedCentral. 2013;4(9):4409.
5. Wolf M, Mosnaim A. Phenylethylamine in neuropsychiatric disorders. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(4):385-390.
6. Janssen P, Leysen J, Megens A, et al. Does phenylethylamine act as an endogenous amphetamine in some patients? In J Neuropsychopharmacol. 1999;2(3):229-240.
7. Zucchi R, Chiellini G, Scanlan TS, et al. Trace amine-associated receptors and their ligands. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;149(8):967-978.
1. US Food and Drug Administration. Dietary supplements. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/dietary-supplements. Accessed December 11, 2019.
2. Tindle H, Davis R, Philips R, et al. Trends in use of complementary and alternative medicine by US adults: 1997-2002. Altern Ther Health Med. 2005;11(1):42-49.
3. Sarris J. Herbal medicines in the treatment of psychiatric disorders: 10-year updated review. Phytotherapy Research. 2018;32(7):1147-1162.
4. Irsfeld M, Spadafore M, Prüß BM. β-phenylethylamine, a small molecule with a large impact. WebmedCentral. 2013;4(9):4409.
5. Wolf M, Mosnaim A. Phenylethylamine in neuropsychiatric disorders. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(4):385-390.
6. Janssen P, Leysen J, Megens A, et al. Does phenylethylamine act as an endogenous amphetamine in some patients? In J Neuropsychopharmacol. 1999;2(3):229-240.
7. Zucchi R, Chiellini G, Scanlan TS, et al. Trace amine-associated receptors and their ligands. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;149(8):967-978.
Rethinking the language of substance abuse
In December 2019, Seattle Seahawks wide receiver Josh Gordon was suspended indefinitely from the NFL for violation of the league’s substance abuse policy. Gordon, once known as one of the most promising wide receivers of the last few decades, had a tumultuous relationship with the NFL as a result of his struggles with substance use. However, the headlines from major sports and news outlets often describe Gordon and other professional and collegiate athletes who struggle with substance use as “violating policies of abuse.” Media coverage of such athletes frequently imposes labels such as “violation” and “abuse,” implying a greater level of personal responsibility and willful misconduct than the biological process of addiction would typically allow. Gordon’s story brought attention not only to the adversity and impairments of substance use, but also the stigmatizing language that often accompanies it.
Shifting to less stigmatizing terminology
In DMS-5, use of the terminology substance use disorder fosters a more biologically-based model of behavior, and encourages recovery-oriented terminology.1 However, for most collegiate and professional sports leagues, the policies regarding substance use often use the term substance abuse, which can perpetuate stigma and a misunderstanding of the underpinnings of substance use, insinuating a sense of personal responsibility, deliberate misconduct, and criminality. When an individual is referred to as an “abuser” of substances, this might suggest that they are willful perpetrators of the disease on themselves, and thus may be undeserving of care.2 Individuals referred to as “substance abusers” rather than having a substance use disorder are more likely to be subjected to negative perceptions and evaluations of their behaviors, particularly by clinicians.
Individuals with substance use disorders are often viewed more negatively than individuals with physical or other psychiatric disorders, and are among the most stigmatized and marginalized groups in health care.4,5 Today, lawmakers, advocates, and health care professionals across the country are working to integrate destigmatizing language into media, policy, and educational settings in order to characterize substance use as a neurobiological process rather than a moral fault.6 For example, legislation in Maine passed in 2018 removed references to stigmatizing terms in policies related to substance use, replacing substance abuse and drug addict with recovery-oriented terminology such as substance use disorder and person with a substance use disorder.7
Individuals with substance use disorders often fear judgment and stigma during clinical encounters, and commonly cite this as a reason to avoid seeking care.8 Words matter, and if we are not careful, the language we use can convey meaning and attitudes that perpetuate the stigma that prevents so many from accessing treatment.9,10 Individuals with a substance use disorder should feel institutionally supported, and the language of policies and the clinicians who treat these patients should reflect this as well.
1. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Wakeman SE. Language and addiction: choosing words wisely. Am J Public Health. 2013;103(4):e1‐e2.
3. Kelly JF, Westerhoff CM. Does it matter how we refer to individuals with substance-related conditions? A randomized study of two commonly used terms. Int J Drug Policy. 2010;21(3):202‐207.
4. Corrigan PW, Kuwabara SA, O’Shaughnessy J. The public stigma of mental illness and drug addiction: findings from a stratified random sample. Journal of Social Work. 2009;9(2):139-147.
5. Barry CL, McGinty EE, Pescosolido BA, et al. Stigma, discrimination, treatment effectiveness, and policy: public views about drug addiction and mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2014;65(10):1269‐1272.
6. Office of National Drug Control Policy. Changing the language of addiction. https://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/whitehouse.gov/files/images/Memo%20-%20Changing%20Federal%20Terminology%20Regrading%20Substance%20Use%20and%20Substance%20Use%20Disorders.pdf. Published January 9, 2017. Accessed June 8, 2020.
7. Flaherty N. Why language matters when describing substance use disorder in Maine. http://www.mainepublic.org/post/why-language-matters-when-describing-substance-use-disorder-maine. Published May 16, 2018. Accessed June 8, 2020.
8. Merrill JO, Rhodes LA, Deyo RA, et al. Mutual mistrust in the medical care of drug users: the keys to the “narc” cabinet. J Gen Intern Med. 2002;17(5):327‐333.
9. Yang LH, Wong LY, Grivel MM, et al. Stigma and substance use disorders: an international phenomenon. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2017;30(5):378‐388.
10. Broyles LM, Binswanger IA, Jenkins JA, et al. Confronting inadvertent stigma and pejorative language in addiction scholarship: a recognition and response. Subst Abus. 2014;35(3):217‐221.
In December 2019, Seattle Seahawks wide receiver Josh Gordon was suspended indefinitely from the NFL for violation of the league’s substance abuse policy. Gordon, once known as one of the most promising wide receivers of the last few decades, had a tumultuous relationship with the NFL as a result of his struggles with substance use. However, the headlines from major sports and news outlets often describe Gordon and other professional and collegiate athletes who struggle with substance use as “violating policies of abuse.” Media coverage of such athletes frequently imposes labels such as “violation” and “abuse,” implying a greater level of personal responsibility and willful misconduct than the biological process of addiction would typically allow. Gordon’s story brought attention not only to the adversity and impairments of substance use, but also the stigmatizing language that often accompanies it.
Shifting to less stigmatizing terminology
In DMS-5, use of the terminology substance use disorder fosters a more biologically-based model of behavior, and encourages recovery-oriented terminology.1 However, for most collegiate and professional sports leagues, the policies regarding substance use often use the term substance abuse, which can perpetuate stigma and a misunderstanding of the underpinnings of substance use, insinuating a sense of personal responsibility, deliberate misconduct, and criminality. When an individual is referred to as an “abuser” of substances, this might suggest that they are willful perpetrators of the disease on themselves, and thus may be undeserving of care.2 Individuals referred to as “substance abusers” rather than having a substance use disorder are more likely to be subjected to negative perceptions and evaluations of their behaviors, particularly by clinicians.
Individuals with substance use disorders are often viewed more negatively than individuals with physical or other psychiatric disorders, and are among the most stigmatized and marginalized groups in health care.4,5 Today, lawmakers, advocates, and health care professionals across the country are working to integrate destigmatizing language into media, policy, and educational settings in order to characterize substance use as a neurobiological process rather than a moral fault.6 For example, legislation in Maine passed in 2018 removed references to stigmatizing terms in policies related to substance use, replacing substance abuse and drug addict with recovery-oriented terminology such as substance use disorder and person with a substance use disorder.7
Individuals with substance use disorders often fear judgment and stigma during clinical encounters, and commonly cite this as a reason to avoid seeking care.8 Words matter, and if we are not careful, the language we use can convey meaning and attitudes that perpetuate the stigma that prevents so many from accessing treatment.9,10 Individuals with a substance use disorder should feel institutionally supported, and the language of policies and the clinicians who treat these patients should reflect this as well.
In December 2019, Seattle Seahawks wide receiver Josh Gordon was suspended indefinitely from the NFL for violation of the league’s substance abuse policy. Gordon, once known as one of the most promising wide receivers of the last few decades, had a tumultuous relationship with the NFL as a result of his struggles with substance use. However, the headlines from major sports and news outlets often describe Gordon and other professional and collegiate athletes who struggle with substance use as “violating policies of abuse.” Media coverage of such athletes frequently imposes labels such as “violation” and “abuse,” implying a greater level of personal responsibility and willful misconduct than the biological process of addiction would typically allow. Gordon’s story brought attention not only to the adversity and impairments of substance use, but also the stigmatizing language that often accompanies it.
Shifting to less stigmatizing terminology
In DMS-5, use of the terminology substance use disorder fosters a more biologically-based model of behavior, and encourages recovery-oriented terminology.1 However, for most collegiate and professional sports leagues, the policies regarding substance use often use the term substance abuse, which can perpetuate stigma and a misunderstanding of the underpinnings of substance use, insinuating a sense of personal responsibility, deliberate misconduct, and criminality. When an individual is referred to as an “abuser” of substances, this might suggest that they are willful perpetrators of the disease on themselves, and thus may be undeserving of care.2 Individuals referred to as “substance abusers” rather than having a substance use disorder are more likely to be subjected to negative perceptions and evaluations of their behaviors, particularly by clinicians.
Individuals with substance use disorders are often viewed more negatively than individuals with physical or other psychiatric disorders, and are among the most stigmatized and marginalized groups in health care.4,5 Today, lawmakers, advocates, and health care professionals across the country are working to integrate destigmatizing language into media, policy, and educational settings in order to characterize substance use as a neurobiological process rather than a moral fault.6 For example, legislation in Maine passed in 2018 removed references to stigmatizing terms in policies related to substance use, replacing substance abuse and drug addict with recovery-oriented terminology such as substance use disorder and person with a substance use disorder.7
Individuals with substance use disorders often fear judgment and stigma during clinical encounters, and commonly cite this as a reason to avoid seeking care.8 Words matter, and if we are not careful, the language we use can convey meaning and attitudes that perpetuate the stigma that prevents so many from accessing treatment.9,10 Individuals with a substance use disorder should feel institutionally supported, and the language of policies and the clinicians who treat these patients should reflect this as well.
1. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Wakeman SE. Language and addiction: choosing words wisely. Am J Public Health. 2013;103(4):e1‐e2.
3. Kelly JF, Westerhoff CM. Does it matter how we refer to individuals with substance-related conditions? A randomized study of two commonly used terms. Int J Drug Policy. 2010;21(3):202‐207.
4. Corrigan PW, Kuwabara SA, O’Shaughnessy J. The public stigma of mental illness and drug addiction: findings from a stratified random sample. Journal of Social Work. 2009;9(2):139-147.
5. Barry CL, McGinty EE, Pescosolido BA, et al. Stigma, discrimination, treatment effectiveness, and policy: public views about drug addiction and mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2014;65(10):1269‐1272.
6. Office of National Drug Control Policy. Changing the language of addiction. https://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/whitehouse.gov/files/images/Memo%20-%20Changing%20Federal%20Terminology%20Regrading%20Substance%20Use%20and%20Substance%20Use%20Disorders.pdf. Published January 9, 2017. Accessed June 8, 2020.
7. Flaherty N. Why language matters when describing substance use disorder in Maine. http://www.mainepublic.org/post/why-language-matters-when-describing-substance-use-disorder-maine. Published May 16, 2018. Accessed June 8, 2020.
8. Merrill JO, Rhodes LA, Deyo RA, et al. Mutual mistrust in the medical care of drug users: the keys to the “narc” cabinet. J Gen Intern Med. 2002;17(5):327‐333.
9. Yang LH, Wong LY, Grivel MM, et al. Stigma and substance use disorders: an international phenomenon. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2017;30(5):378‐388.
10. Broyles LM, Binswanger IA, Jenkins JA, et al. Confronting inadvertent stigma and pejorative language in addiction scholarship: a recognition and response. Subst Abus. 2014;35(3):217‐221.
1. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Wakeman SE. Language and addiction: choosing words wisely. Am J Public Health. 2013;103(4):e1‐e2.
3. Kelly JF, Westerhoff CM. Does it matter how we refer to individuals with substance-related conditions? A randomized study of two commonly used terms. Int J Drug Policy. 2010;21(3):202‐207.
4. Corrigan PW, Kuwabara SA, O’Shaughnessy J. The public stigma of mental illness and drug addiction: findings from a stratified random sample. Journal of Social Work. 2009;9(2):139-147.
5. Barry CL, McGinty EE, Pescosolido BA, et al. Stigma, discrimination, treatment effectiveness, and policy: public views about drug addiction and mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2014;65(10):1269‐1272.
6. Office of National Drug Control Policy. Changing the language of addiction. https://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/whitehouse.gov/files/images/Memo%20-%20Changing%20Federal%20Terminology%20Regrading%20Substance%20Use%20and%20Substance%20Use%20Disorders.pdf. Published January 9, 2017. Accessed June 8, 2020.
7. Flaherty N. Why language matters when describing substance use disorder in Maine. http://www.mainepublic.org/post/why-language-matters-when-describing-substance-use-disorder-maine. Published May 16, 2018. Accessed June 8, 2020.
8. Merrill JO, Rhodes LA, Deyo RA, et al. Mutual mistrust in the medical care of drug users: the keys to the “narc” cabinet. J Gen Intern Med. 2002;17(5):327‐333.
9. Yang LH, Wong LY, Grivel MM, et al. Stigma and substance use disorders: an international phenomenon. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2017;30(5):378‐388.
10. Broyles LM, Binswanger IA, Jenkins JA, et al. Confronting inadvertent stigma and pejorative language in addiction scholarship: a recognition and response. Subst Abus. 2014;35(3):217‐221.