User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'medstat-accordion-set article-series')]
Tendon Damage, Tenosynovitis Common But Not Limiting or Painful in Hand Osteoarthritis
TOPLINE:
Ultrasonography reveals tendon involvement in nearly 70% of the patients with hand osteoarthritis (OA), with no significant impact on hand function or pain. Tendon damage was more frequent in the flexor tendons, while tenosynovitis was more common in the extensor tendons.
METHODOLOGY:
- Tendon damage is commonly associated with radiographic damage in rheumatoid arthritis and is a typical finding in psoriatic arthritis; however, data on tendon involvement in hand OA are scarce.
- Researchers assessed tendon involvement, its impact on pain and hand function, and its association with radiographic features in hand OA.
- They conducted a cross-sectional, monocenter observational study including 86 patients with hand OA (mean age, 65.9 years; 87.2% women) and 23 age- and sex-matched control individuals without bony enlargement and hand pain at a tertiary center of rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease in Vienna.
- Clinical examination and ultrasonography were used to assess the extensor and flexor tendons of both hands for tenosynovitis and tendon damage.
- Participants completed the Modified Score for the Assessment and Quantification of Chronic Rheumatoid Affections of the Hands (M-SACRAH) questionnaire and the Moberg pickup test for the assessment of hand function, stiffness, and pain.
TAKEAWAY:
- Ultrasonography identified tendon involvement in a higher proportion of patients with hand OA than in control individuals (69.8% vs 8.7%; P < .01).
- In patients with hand OA, the flexor tendons were more commonly affected by tendon damage than the extensor tendons (2.1% vs 0.9%; P = .03), whereas tenosynovitis was more prevalent in the extensor tendons than in the flexor tendons (8.0% vs 0.6%; P < .001).
- No significant association was found between tendon involvement and hand function or self-reported pain.
- The sensitivity and specificity of clinical evaluation in identifying tendon involvement were 14.5% and 83.8%, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Physicians treating patients with hand OA should keep the high prevalence of tendon involvement in mind,” the authors wrote. “In case of clinical suspicion, a sonographic examination should be performed. If tenosynovitis or tendon damage is detected, treatment may be tailored accordingly.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Irina Gessl, MD, Department of Internal Medicine III, Medical University of Vienna in Austria, was published online on August 7, 2024, in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a standardized clinical examination and a preferred method for detecting tenosynovitis and tendon damage. The lack of a separate evaluation of clinical tenderness in individual joints may have hindered a more comprehensive assessment of pain. The M-SACRAH questionnaire is validated for assessing the overall hand function in patients with hand OA and rheumatoid arthritis but not tendon involvement.
DISCLOSURES:
The Medical Scientific Fund of the Mayor of the City of Vienna supported the study. Some authors reported receiving personal fees, grants, royalties, or licenses and being part of speakers bureau for various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Ultrasonography reveals tendon involvement in nearly 70% of the patients with hand osteoarthritis (OA), with no significant impact on hand function or pain. Tendon damage was more frequent in the flexor tendons, while tenosynovitis was more common in the extensor tendons.
METHODOLOGY:
- Tendon damage is commonly associated with radiographic damage in rheumatoid arthritis and is a typical finding in psoriatic arthritis; however, data on tendon involvement in hand OA are scarce.
- Researchers assessed tendon involvement, its impact on pain and hand function, and its association with radiographic features in hand OA.
- They conducted a cross-sectional, monocenter observational study including 86 patients with hand OA (mean age, 65.9 years; 87.2% women) and 23 age- and sex-matched control individuals without bony enlargement and hand pain at a tertiary center of rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease in Vienna.
- Clinical examination and ultrasonography were used to assess the extensor and flexor tendons of both hands for tenosynovitis and tendon damage.
- Participants completed the Modified Score for the Assessment and Quantification of Chronic Rheumatoid Affections of the Hands (M-SACRAH) questionnaire and the Moberg pickup test for the assessment of hand function, stiffness, and pain.
TAKEAWAY:
- Ultrasonography identified tendon involvement in a higher proportion of patients with hand OA than in control individuals (69.8% vs 8.7%; P < .01).
- In patients with hand OA, the flexor tendons were more commonly affected by tendon damage than the extensor tendons (2.1% vs 0.9%; P = .03), whereas tenosynovitis was more prevalent in the extensor tendons than in the flexor tendons (8.0% vs 0.6%; P < .001).
- No significant association was found between tendon involvement and hand function or self-reported pain.
- The sensitivity and specificity of clinical evaluation in identifying tendon involvement were 14.5% and 83.8%, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Physicians treating patients with hand OA should keep the high prevalence of tendon involvement in mind,” the authors wrote. “In case of clinical suspicion, a sonographic examination should be performed. If tenosynovitis or tendon damage is detected, treatment may be tailored accordingly.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Irina Gessl, MD, Department of Internal Medicine III, Medical University of Vienna in Austria, was published online on August 7, 2024, in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a standardized clinical examination and a preferred method for detecting tenosynovitis and tendon damage. The lack of a separate evaluation of clinical tenderness in individual joints may have hindered a more comprehensive assessment of pain. The M-SACRAH questionnaire is validated for assessing the overall hand function in patients with hand OA and rheumatoid arthritis but not tendon involvement.
DISCLOSURES:
The Medical Scientific Fund of the Mayor of the City of Vienna supported the study. Some authors reported receiving personal fees, grants, royalties, or licenses and being part of speakers bureau for various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Ultrasonography reveals tendon involvement in nearly 70% of the patients with hand osteoarthritis (OA), with no significant impact on hand function or pain. Tendon damage was more frequent in the flexor tendons, while tenosynovitis was more common in the extensor tendons.
METHODOLOGY:
- Tendon damage is commonly associated with radiographic damage in rheumatoid arthritis and is a typical finding in psoriatic arthritis; however, data on tendon involvement in hand OA are scarce.
- Researchers assessed tendon involvement, its impact on pain and hand function, and its association with radiographic features in hand OA.
- They conducted a cross-sectional, monocenter observational study including 86 patients with hand OA (mean age, 65.9 years; 87.2% women) and 23 age- and sex-matched control individuals without bony enlargement and hand pain at a tertiary center of rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease in Vienna.
- Clinical examination and ultrasonography were used to assess the extensor and flexor tendons of both hands for tenosynovitis and tendon damage.
- Participants completed the Modified Score for the Assessment and Quantification of Chronic Rheumatoid Affections of the Hands (M-SACRAH) questionnaire and the Moberg pickup test for the assessment of hand function, stiffness, and pain.
TAKEAWAY:
- Ultrasonography identified tendon involvement in a higher proportion of patients with hand OA than in control individuals (69.8% vs 8.7%; P < .01).
- In patients with hand OA, the flexor tendons were more commonly affected by tendon damage than the extensor tendons (2.1% vs 0.9%; P = .03), whereas tenosynovitis was more prevalent in the extensor tendons than in the flexor tendons (8.0% vs 0.6%; P < .001).
- No significant association was found between tendon involvement and hand function or self-reported pain.
- The sensitivity and specificity of clinical evaluation in identifying tendon involvement were 14.5% and 83.8%, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“Physicians treating patients with hand OA should keep the high prevalence of tendon involvement in mind,” the authors wrote. “In case of clinical suspicion, a sonographic examination should be performed. If tenosynovitis or tendon damage is detected, treatment may be tailored accordingly.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Irina Gessl, MD, Department of Internal Medicine III, Medical University of Vienna in Austria, was published online on August 7, 2024, in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a standardized clinical examination and a preferred method for detecting tenosynovitis and tendon damage. The lack of a separate evaluation of clinical tenderness in individual joints may have hindered a more comprehensive assessment of pain. The M-SACRAH questionnaire is validated for assessing the overall hand function in patients with hand OA and rheumatoid arthritis but not tendon involvement.
DISCLOSURES:
The Medical Scientific Fund of the Mayor of the City of Vienna supported the study. Some authors reported receiving personal fees, grants, royalties, or licenses and being part of speakers bureau for various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mobile App Shows Promise in Managing Fibromyalgia Symptoms
TOPLINE:
A smartphone app that delivers acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), a type of cognitive behavioral therapy, improves overall well-being and reduces the severity of pain, fatigue, sleep issues, and depression to a greater extent than daily symptom tracking in patients with fibromyalgia.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted the phase 3 PROSPER-FM trial at 25 community sites in the United States to assess the efficacy and safety of digital ACT for patients with fibromyalgia.
- A total of 275 adult patients aged 22-75 years with fibromyalgia were randomly assigned to either the digital ACT group (n = 140) or the active control group (n = 135) for 12 weeks.
- Patients in the digital ACT group received a self-guided, smartphone-delivered program in which they learned and practiced the core ACT skills of acceptance, values, mindfulness, defusion, self as context, and willingness and committed action to build psychological flexibility, while the control group underwent daily symptom tracking and received educational materials.
- The primary endpoint was the response rate on the Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) at week 12, which is an indicator of patient well-being.
- The secondary endpoints included changes in the Revised Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ-R) total score and pain intensity, pain interference, and sleep interference scores.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, 71% of the patients in the digital ACT group responded with a minimally improved or better change in the PGIC response, compared with only 22% of the patients in the control group (P < .0001).
- The digital ACT group showed a significant reduction in the impact of fibromyalgia, with a between-group effect size of d = 0.65 (P < .0001) at week 12. The FIQ-R total score significantly improved within 3 weeks of using the self-guided digital ACT app.
- The use of digital ACT also demonstrated positive effects on the levels of weekly pain intensity (P = .001) and depression (P < .0001), compared with the control group.
- No serious adverse effects related to the app were reported, and both groups demonstrated high rates of adherence, with most (72%) participants in the digital ACT group completing at least 42 sessions.
IN PRACTICE:
“The results found in the study are essential for professionals who care for patients with fibromyalgia as they present a new viable treatment alternative,” Guilherme Torres Vilarino, PhD, Santa Catarina State University, Florianópolis, Brazil, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
This study was led by R. Michael Gendreau, MD, PhD, Gendreau Consulting, Poway, California. It was published online in The Lancet.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population predominantly consisted of women and White individuals, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to more diverse populations. Additionally, the study was conducted in the United States, and the results may thus not be applicable to other countries with different racial, ethnic, educational, and economic characteristics. The study duration was 12 weeks, and the long-term benefits of digital ACT have not yet been shown.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Swing Therapeutics. Seven authors declared having stock options and/or receiving salary from Swing Therapeutics. Other authors reported having many ties with several sources, including Swing Therapeutics.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A smartphone app that delivers acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), a type of cognitive behavioral therapy, improves overall well-being and reduces the severity of pain, fatigue, sleep issues, and depression to a greater extent than daily symptom tracking in patients with fibromyalgia.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted the phase 3 PROSPER-FM trial at 25 community sites in the United States to assess the efficacy and safety of digital ACT for patients with fibromyalgia.
- A total of 275 adult patients aged 22-75 years with fibromyalgia were randomly assigned to either the digital ACT group (n = 140) or the active control group (n = 135) for 12 weeks.
- Patients in the digital ACT group received a self-guided, smartphone-delivered program in which they learned and practiced the core ACT skills of acceptance, values, mindfulness, defusion, self as context, and willingness and committed action to build psychological flexibility, while the control group underwent daily symptom tracking and received educational materials.
- The primary endpoint was the response rate on the Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) at week 12, which is an indicator of patient well-being.
- The secondary endpoints included changes in the Revised Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ-R) total score and pain intensity, pain interference, and sleep interference scores.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, 71% of the patients in the digital ACT group responded with a minimally improved or better change in the PGIC response, compared with only 22% of the patients in the control group (P < .0001).
- The digital ACT group showed a significant reduction in the impact of fibromyalgia, with a between-group effect size of d = 0.65 (P < .0001) at week 12. The FIQ-R total score significantly improved within 3 weeks of using the self-guided digital ACT app.
- The use of digital ACT also demonstrated positive effects on the levels of weekly pain intensity (P = .001) and depression (P < .0001), compared with the control group.
- No serious adverse effects related to the app were reported, and both groups demonstrated high rates of adherence, with most (72%) participants in the digital ACT group completing at least 42 sessions.
IN PRACTICE:
“The results found in the study are essential for professionals who care for patients with fibromyalgia as they present a new viable treatment alternative,” Guilherme Torres Vilarino, PhD, Santa Catarina State University, Florianópolis, Brazil, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
This study was led by R. Michael Gendreau, MD, PhD, Gendreau Consulting, Poway, California. It was published online in The Lancet.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population predominantly consisted of women and White individuals, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to more diverse populations. Additionally, the study was conducted in the United States, and the results may thus not be applicable to other countries with different racial, ethnic, educational, and economic characteristics. The study duration was 12 weeks, and the long-term benefits of digital ACT have not yet been shown.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Swing Therapeutics. Seven authors declared having stock options and/or receiving salary from Swing Therapeutics. Other authors reported having many ties with several sources, including Swing Therapeutics.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A smartphone app that delivers acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), a type of cognitive behavioral therapy, improves overall well-being and reduces the severity of pain, fatigue, sleep issues, and depression to a greater extent than daily symptom tracking in patients with fibromyalgia.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted the phase 3 PROSPER-FM trial at 25 community sites in the United States to assess the efficacy and safety of digital ACT for patients with fibromyalgia.
- A total of 275 adult patients aged 22-75 years with fibromyalgia were randomly assigned to either the digital ACT group (n = 140) or the active control group (n = 135) for 12 weeks.
- Patients in the digital ACT group received a self-guided, smartphone-delivered program in which they learned and practiced the core ACT skills of acceptance, values, mindfulness, defusion, self as context, and willingness and committed action to build psychological flexibility, while the control group underwent daily symptom tracking and received educational materials.
- The primary endpoint was the response rate on the Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) at week 12, which is an indicator of patient well-being.
- The secondary endpoints included changes in the Revised Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ-R) total score and pain intensity, pain interference, and sleep interference scores.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, 71% of the patients in the digital ACT group responded with a minimally improved or better change in the PGIC response, compared with only 22% of the patients in the control group (P < .0001).
- The digital ACT group showed a significant reduction in the impact of fibromyalgia, with a between-group effect size of d = 0.65 (P < .0001) at week 12. The FIQ-R total score significantly improved within 3 weeks of using the self-guided digital ACT app.
- The use of digital ACT also demonstrated positive effects on the levels of weekly pain intensity (P = .001) and depression (P < .0001), compared with the control group.
- No serious adverse effects related to the app were reported, and both groups demonstrated high rates of adherence, with most (72%) participants in the digital ACT group completing at least 42 sessions.
IN PRACTICE:
“The results found in the study are essential for professionals who care for patients with fibromyalgia as they present a new viable treatment alternative,” Guilherme Torres Vilarino, PhD, Santa Catarina State University, Florianópolis, Brazil, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
This study was led by R. Michael Gendreau, MD, PhD, Gendreau Consulting, Poway, California. It was published online in The Lancet.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population predominantly consisted of women and White individuals, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to more diverse populations. Additionally, the study was conducted in the United States, and the results may thus not be applicable to other countries with different racial, ethnic, educational, and economic characteristics. The study duration was 12 weeks, and the long-term benefits of digital ACT have not yet been shown.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Swing Therapeutics. Seven authors declared having stock options and/or receiving salary from Swing Therapeutics. Other authors reported having many ties with several sources, including Swing Therapeutics.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Do You Have Patients With JAKne — JAK Inhibitor–Associated Acne? Here’s What to Know
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
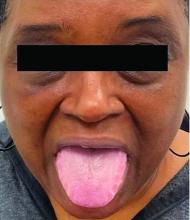
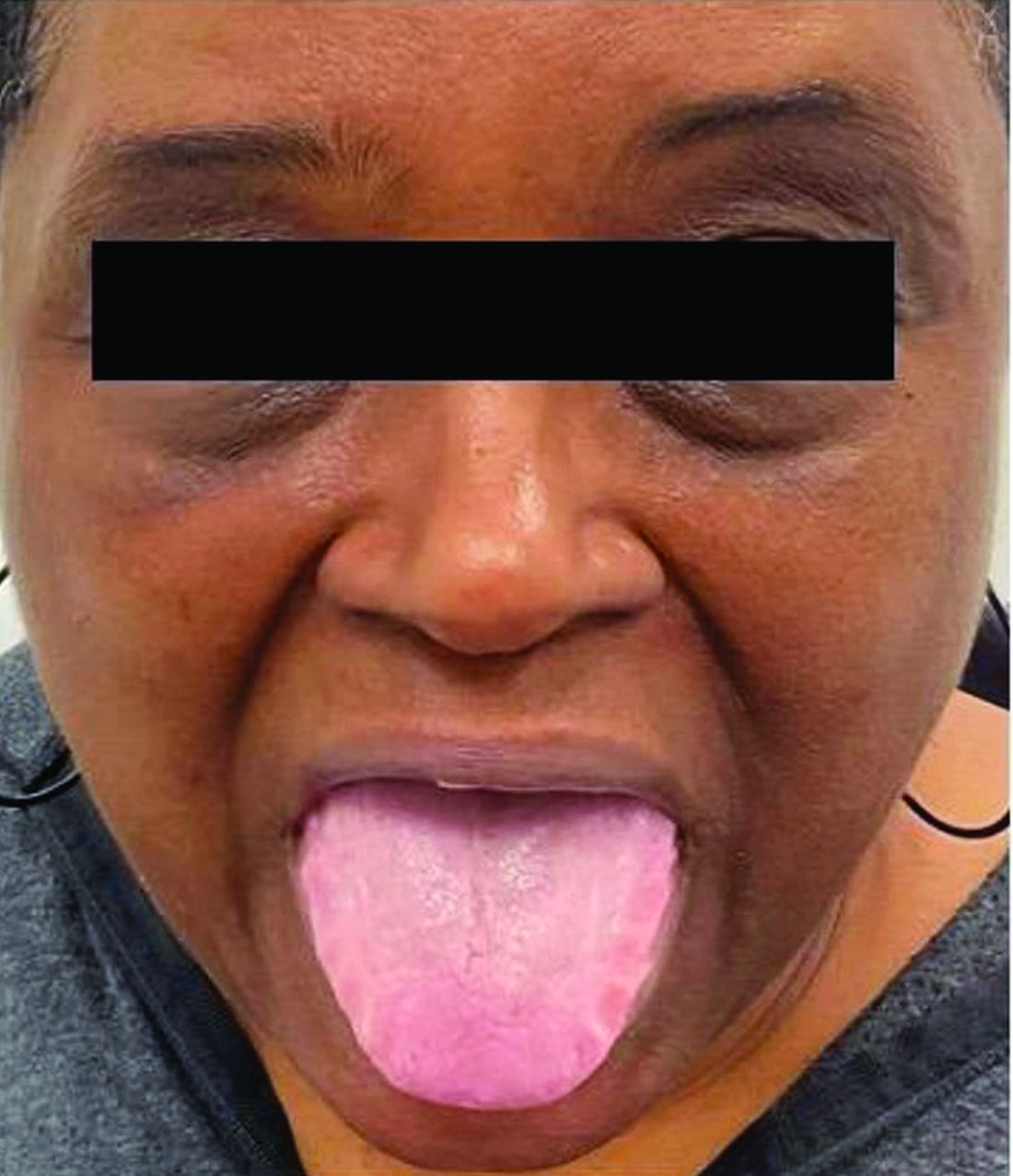
A 62-year-old Black female presented with an epidermal inclusion cyst on her left upper back
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
Doctors Are Seeking Professional Coaches More Often. Here’s Why
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fillers, Hyaluronidase Relieve Orofacial Changes in Patients with Scleroderma
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — In 2003, researchers asked 303 patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) what bothered them most about their disease from an aesthetic standpoint: Orofacial features, such as thin lips and mouth furrows, or non-facial features, such as fingertip ulceration and waxy changes to the skin.
Respondents expressed significant concern about specific orofacial features, including thin lips (73%), mouth furrows (80%), loss of facial lines (68%), and a smaller, tighter mouth (77%).
“Patients with systemic sclerosis may have loss of vermilion lip, microstomia, and perioral rhytids,” Kathleen Cook Suozzi, MD, who directs the Aesthetic Dermatology Program at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “How can we address these changes for our patients?”
Recent research has shown that hyaluronidase injections can help improve orofacial changes commonly experienced by patients with scleroderma. In 2019, researchers in Alabama reported the case of a 53-year-old woman treated with hyaluronidase for scleroderma-induced microstomia. After four visits over 7 months and a total hyaluronidase dose of 470 IU, the patient reported an improved Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis (MHISS) score (38 of 48); subjective improvement of symptoms, including greater ease in eating and undergoing dental treatment; and improved mouth closure.
In 2023, researchers published a cohort study of four women between the ages of 43 and 61 with autoimmune sclerosing conditions that resulted in oral microstomia. Following hyaluronidase injections, all improved in mouth opening capacity and MHISS, with change stabilizing between three and five treatments. More recently, in a study pending publication in JAAD Case Reports, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues retrospectively evaluated 12 women with scleroderma who received between 150 and 300 units of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler for microstomia between 2020 and 2023. Of the 12 women, 58% had diffuse disease, and 42% had limited disease. Overall, oral aperture width increased by 0.65 cm (P = .0027) and oral aperture height increased by 0.88 cm (P < .0001). “In general, patients needed three to four treatments to reach peak effect, and then they reached a plateau,” Dr. Suozzi said. “It wasn’t that the treatment wasn’t working anymore, but it was because their oral aperture had gotten to a size of around 5 cm, which is clinically normal. Interestingly, we found that if the patient’s disease flared and their microstomia started to return, when you rechallenged them, they continued to respond. So, patients can continue to use this treatment over time.”
In a separate case series of seven patients, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues prospectively evaluated the effect of HA soft tissue filler with Restylane Silk for lip augmentation. Study participants experienced statistically significant increases in the difference between pre- and postinjection fullness in both upper and lower lips. Also, the mean posttreatment score fell between “much improved” (2) and “improved” (3) on both the Investigator Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale and the Subject Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale.
Dr. Suozzi recommends using nerve blocks for injecting HA filler or hyaluronidase in patients with scleroderma and minimizing the injection points. “Initially, we were using 30% lidocaine preparations around the mouth for an hour before the procedure, and patients were still having pain, so now we use nerve blocks,” she said. “For hyaluronidase, we do perform a test dose of 75-100 units, usually in the commissure. It’s amazing how well it works; people will usually come back after their test dose and have improvements in their measurements. This is a really easy treatment to perform, and I think it can be done in the office of a general dermatologist. There is concern about cross-reactivity with bee venom, so you want to ask patients about that.”
Dr. Suozzi reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — In 2003, researchers asked 303 patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) what bothered them most about their disease from an aesthetic standpoint: Orofacial features, such as thin lips and mouth furrows, or non-facial features, such as fingertip ulceration and waxy changes to the skin.
Respondents expressed significant concern about specific orofacial features, including thin lips (73%), mouth furrows (80%), loss of facial lines (68%), and a smaller, tighter mouth (77%).
“Patients with systemic sclerosis may have loss of vermilion lip, microstomia, and perioral rhytids,” Kathleen Cook Suozzi, MD, who directs the Aesthetic Dermatology Program at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “How can we address these changes for our patients?”
Recent research has shown that hyaluronidase injections can help improve orofacial changes commonly experienced by patients with scleroderma. In 2019, researchers in Alabama reported the case of a 53-year-old woman treated with hyaluronidase for scleroderma-induced microstomia. After four visits over 7 months and a total hyaluronidase dose of 470 IU, the patient reported an improved Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis (MHISS) score (38 of 48); subjective improvement of symptoms, including greater ease in eating and undergoing dental treatment; and improved mouth closure.
In 2023, researchers published a cohort study of four women between the ages of 43 and 61 with autoimmune sclerosing conditions that resulted in oral microstomia. Following hyaluronidase injections, all improved in mouth opening capacity and MHISS, with change stabilizing between three and five treatments. More recently, in a study pending publication in JAAD Case Reports, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues retrospectively evaluated 12 women with scleroderma who received between 150 and 300 units of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler for microstomia between 2020 and 2023. Of the 12 women, 58% had diffuse disease, and 42% had limited disease. Overall, oral aperture width increased by 0.65 cm (P = .0027) and oral aperture height increased by 0.88 cm (P < .0001). “In general, patients needed three to four treatments to reach peak effect, and then they reached a plateau,” Dr. Suozzi said. “It wasn’t that the treatment wasn’t working anymore, but it was because their oral aperture had gotten to a size of around 5 cm, which is clinically normal. Interestingly, we found that if the patient’s disease flared and their microstomia started to return, when you rechallenged them, they continued to respond. So, patients can continue to use this treatment over time.”
In a separate case series of seven patients, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues prospectively evaluated the effect of HA soft tissue filler with Restylane Silk for lip augmentation. Study participants experienced statistically significant increases in the difference between pre- and postinjection fullness in both upper and lower lips. Also, the mean posttreatment score fell between “much improved” (2) and “improved” (3) on both the Investigator Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale and the Subject Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale.
Dr. Suozzi recommends using nerve blocks for injecting HA filler or hyaluronidase in patients with scleroderma and minimizing the injection points. “Initially, we were using 30% lidocaine preparations around the mouth for an hour before the procedure, and patients were still having pain, so now we use nerve blocks,” she said. “For hyaluronidase, we do perform a test dose of 75-100 units, usually in the commissure. It’s amazing how well it works; people will usually come back after their test dose and have improvements in their measurements. This is a really easy treatment to perform, and I think it can be done in the office of a general dermatologist. There is concern about cross-reactivity with bee venom, so you want to ask patients about that.”
Dr. Suozzi reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIFORNIA — In 2003, researchers asked 303 patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) what bothered them most about their disease from an aesthetic standpoint: Orofacial features, such as thin lips and mouth furrows, or non-facial features, such as fingertip ulceration and waxy changes to the skin.
Respondents expressed significant concern about specific orofacial features, including thin lips (73%), mouth furrows (80%), loss of facial lines (68%), and a smaller, tighter mouth (77%).
“Patients with systemic sclerosis may have loss of vermilion lip, microstomia, and perioral rhytids,” Kathleen Cook Suozzi, MD, who directs the Aesthetic Dermatology Program at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said at the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “How can we address these changes for our patients?”
Recent research has shown that hyaluronidase injections can help improve orofacial changes commonly experienced by patients with scleroderma. In 2019, researchers in Alabama reported the case of a 53-year-old woman treated with hyaluronidase for scleroderma-induced microstomia. After four visits over 7 months and a total hyaluronidase dose of 470 IU, the patient reported an improved Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis (MHISS) score (38 of 48); subjective improvement of symptoms, including greater ease in eating and undergoing dental treatment; and improved mouth closure.
In 2023, researchers published a cohort study of four women between the ages of 43 and 61 with autoimmune sclerosing conditions that resulted in oral microstomia. Following hyaluronidase injections, all improved in mouth opening capacity and MHISS, with change stabilizing between three and five treatments. More recently, in a study pending publication in JAAD Case Reports, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues retrospectively evaluated 12 women with scleroderma who received between 150 and 300 units of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler for microstomia between 2020 and 2023. Of the 12 women, 58% had diffuse disease, and 42% had limited disease. Overall, oral aperture width increased by 0.65 cm (P = .0027) and oral aperture height increased by 0.88 cm (P < .0001). “In general, patients needed three to four treatments to reach peak effect, and then they reached a plateau,” Dr. Suozzi said. “It wasn’t that the treatment wasn’t working anymore, but it was because their oral aperture had gotten to a size of around 5 cm, which is clinically normal. Interestingly, we found that if the patient’s disease flared and their microstomia started to return, when you rechallenged them, they continued to respond. So, patients can continue to use this treatment over time.”
In a separate case series of seven patients, Dr. Suozzi and colleagues prospectively evaluated the effect of HA soft tissue filler with Restylane Silk for lip augmentation. Study participants experienced statistically significant increases in the difference between pre- and postinjection fullness in both upper and lower lips. Also, the mean posttreatment score fell between “much improved” (2) and “improved” (3) on both the Investigator Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale and the Subject Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale.
Dr. Suozzi recommends using nerve blocks for injecting HA filler or hyaluronidase in patients with scleroderma and minimizing the injection points. “Initially, we were using 30% lidocaine preparations around the mouth for an hour before the procedure, and patients were still having pain, so now we use nerve blocks,” she said. “For hyaluronidase, we do perform a test dose of 75-100 units, usually in the commissure. It’s amazing how well it works; people will usually come back after their test dose and have improvements in their measurements. This is a really easy treatment to perform, and I think it can be done in the office of a general dermatologist. There is concern about cross-reactivity with bee venom, so you want to ask patients about that.”
Dr. Suozzi reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Genetic Study Reveals Increased Mutual Risk Between PsA and Ulcerative Colitis
Key clinical point: A Mendelian randomization analysis revealed that psoriatic arthritis (PsA) was a significant risk factor for ulcerative colitis (UC) and vice versa.
Major finding: UC was associated with a 45.8% increased risk for PsA (odds ratio [OR] 1.458; P = .0013); conversely, PsA was associated with a 32.9% increased risk for UC (OR 1.329; P < .001).
Study details: This Mendelian randomization study evaluated the causal association between PsA, UC, and psoriasis using 123 single nucleotide polymorphisms from genome-wide association studies as genetic instrumental variables.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Pan J, Lv Y, Wang L, et al. Mendelian randomization analysis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis associated with risks of ulcerative colitis. Skin Res Technol. 2024;30:e13795 (Jul 12). Doi: 10.3390/jcm13154567 Source
Key clinical point: A Mendelian randomization analysis revealed that psoriatic arthritis (PsA) was a significant risk factor for ulcerative colitis (UC) and vice versa.
Major finding: UC was associated with a 45.8% increased risk for PsA (odds ratio [OR] 1.458; P = .0013); conversely, PsA was associated with a 32.9% increased risk for UC (OR 1.329; P < .001).
Study details: This Mendelian randomization study evaluated the causal association between PsA, UC, and psoriasis using 123 single nucleotide polymorphisms from genome-wide association studies as genetic instrumental variables.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Pan J, Lv Y, Wang L, et al. Mendelian randomization analysis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis associated with risks of ulcerative colitis. Skin Res Technol. 2024;30:e13795 (Jul 12). Doi: 10.3390/jcm13154567 Source
Key clinical point: A Mendelian randomization analysis revealed that psoriatic arthritis (PsA) was a significant risk factor for ulcerative colitis (UC) and vice versa.
Major finding: UC was associated with a 45.8% increased risk for PsA (odds ratio [OR] 1.458; P = .0013); conversely, PsA was associated with a 32.9% increased risk for UC (OR 1.329; P < .001).
Study details: This Mendelian randomization study evaluated the causal association between PsA, UC, and psoriasis using 123 single nucleotide polymorphisms from genome-wide association studies as genetic instrumental variables.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Pan J, Lv Y, Wang L, et al. Mendelian randomization analysis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis associated with risks of ulcerative colitis. Skin Res Technol. 2024;30:e13795 (Jul 12). Doi: 10.3390/jcm13154567 Source
Ultrasound Can Detect Disease Activity in PsA Patients Apparently Within Treatment Target
Key clinical point: Ultrasound detected active enthesitis and synovitis in a non-negligible proportion of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who achieved remission or low disease activity with biological or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARD).
Major finding: Despite achieving the Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA) treatment target, 21.6% patients had at least one painful enthesis on clinical examination. Ultrasound showed evidence of active enthesitis in 19.6% and active synovitis in 15.7% patients.
Study details: This cross-sectional study included 51 patients with PsA who met the DAPSA treatment target after at least 6 months of therapy with b/tsDMARD and underwent bilateral ultrasound and clinical examination of entheses and joints.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interests.
Source: Agache M, Popescu CC, Enache L, et al. Additional value of ultrasound in patients with psoriatic arthritis within treatment target. J Clin Med. 2024;13(5):4567 (Aug 5). Doi: 10.3390/jcm13154567 Source
Key clinical point: Ultrasound detected active enthesitis and synovitis in a non-negligible proportion of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who achieved remission or low disease activity with biological or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARD).
Major finding: Despite achieving the Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA) treatment target, 21.6% patients had at least one painful enthesis on clinical examination. Ultrasound showed evidence of active enthesitis in 19.6% and active synovitis in 15.7% patients.
Study details: This cross-sectional study included 51 patients with PsA who met the DAPSA treatment target after at least 6 months of therapy with b/tsDMARD and underwent bilateral ultrasound and clinical examination of entheses and joints.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interests.
Source: Agache M, Popescu CC, Enache L, et al. Additional value of ultrasound in patients with psoriatic arthritis within treatment target. J Clin Med. 2024;13(5):4567 (Aug 5). Doi: 10.3390/jcm13154567 Source
Key clinical point: Ultrasound detected active enthesitis and synovitis in a non-negligible proportion of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who achieved remission or low disease activity with biological or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARD).
Major finding: Despite achieving the Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA) treatment target, 21.6% patients had at least one painful enthesis on clinical examination. Ultrasound showed evidence of active enthesitis in 19.6% and active synovitis in 15.7% patients.
Study details: This cross-sectional study included 51 patients with PsA who met the DAPSA treatment target after at least 6 months of therapy with b/tsDMARD and underwent bilateral ultrasound and clinical examination of entheses and joints.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interests.
Source: Agache M, Popescu CC, Enache L, et al. Additional value of ultrasound in patients with psoriatic arthritis within treatment target. J Clin Med. 2024;13(5):4567 (Aug 5). Doi: 10.3390/jcm13154567 Source
Exercise and Mediterranean Diet Benefit Skin and Joints in PsA
Key clinical point: Exercise and a Mediterranean diet improved disease activity outcomes pertaining to skin and joints in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), indicating that combining lifestyle changes with conventional medical treatment can benefit patients with PsA.
Major finding: High vs low levels of exercise were associated with lower median values of Disease Activity in PsA Score (10.6 vs 28.5; P = .004), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (9 vs 16; P = .001), and fewer tender (1.5 vs 10; P = .003) and swollen (1.5 vs 9; P = .016) joints. Similarly, high vs low adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with a lower Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (0.9 vs 1.5; P = .001) and body surface area (1 vs 2; P = .009).
Study details: This cross-sectional study enrolled 355 patients with psoriatic disease (age > 18 years), including 279 patients with PsA and 76 patients with psoriasis.
Disclosures: No funding sources were declared for this study. The authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
Source: Katsimbri P, Grivas A, Papadavid E, et al. Mediterranean diet and exercise are associated with better disease control in psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2024 (Jul 25). Doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07080-6 Source
Key clinical point: Exercise and a Mediterranean diet improved disease activity outcomes pertaining to skin and joints in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), indicating that combining lifestyle changes with conventional medical treatment can benefit patients with PsA.
Major finding: High vs low levels of exercise were associated with lower median values of Disease Activity in PsA Score (10.6 vs 28.5; P = .004), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (9 vs 16; P = .001), and fewer tender (1.5 vs 10; P = .003) and swollen (1.5 vs 9; P = .016) joints. Similarly, high vs low adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with a lower Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (0.9 vs 1.5; P = .001) and body surface area (1 vs 2; P = .009).
Study details: This cross-sectional study enrolled 355 patients with psoriatic disease (age > 18 years), including 279 patients with PsA and 76 patients with psoriasis.
Disclosures: No funding sources were declared for this study. The authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
Source: Katsimbri P, Grivas A, Papadavid E, et al. Mediterranean diet and exercise are associated with better disease control in psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2024 (Jul 25). Doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07080-6 Source
Key clinical point: Exercise and a Mediterranean diet improved disease activity outcomes pertaining to skin and joints in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), indicating that combining lifestyle changes with conventional medical treatment can benefit patients with PsA.
Major finding: High vs low levels of exercise were associated with lower median values of Disease Activity in PsA Score (10.6 vs 28.5; P = .004), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (9 vs 16; P = .001), and fewer tender (1.5 vs 10; P = .003) and swollen (1.5 vs 9; P = .016) joints. Similarly, high vs low adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with a lower Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (0.9 vs 1.5; P = .001) and body surface area (1 vs 2; P = .009).
Study details: This cross-sectional study enrolled 355 patients with psoriatic disease (age > 18 years), including 279 patients with PsA and 76 patients with psoriasis.
Disclosures: No funding sources were declared for this study. The authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
Source: Katsimbri P, Grivas A, Papadavid E, et al. Mediterranean diet and exercise are associated with better disease control in psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2024 (Jul 25). Doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07080-6 Source
Autoimmune Diseases Increase PsA Risk
Key clinical point: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and certain other autoimmune diseases (AID) may have an increased risk of developing psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: The risk factors for PsA included RA (inverse variance weighting odds ratio [ORIVW] 1.11; P = .0205), SLE (ORIVW 1.04; P = .0107), AS (ORIVW 2.18; P = .000155), Crohn's disease (CD; ORIVW 1.07; P = .01), Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT; ORIVW 1.23; P = .00143), and vitiligo (ORIVW 1.27; P = .0000267). However, PsA did not increase the risk for these AID.
Study details: This bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study used genome-wide association data for PsA (3186 cases and 240,862 control individuals and an additional 5065 cases and 21,286 control individuals), psoriasis, and AID.
Disclosures: This study was supported by two research projects from China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Duan K, Wang J, Chen S, et al. Causal associations between both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis and multiple autoimmune diseases: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2024;15:1422626 (Jul 24). Doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1422626 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and certain other autoimmune diseases (AID) may have an increased risk of developing psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: The risk factors for PsA included RA (inverse variance weighting odds ratio [ORIVW] 1.11; P = .0205), SLE (ORIVW 1.04; P = .0107), AS (ORIVW 2.18; P = .000155), Crohn's disease (CD; ORIVW 1.07; P = .01), Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT; ORIVW 1.23; P = .00143), and vitiligo (ORIVW 1.27; P = .0000267). However, PsA did not increase the risk for these AID.
Study details: This bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study used genome-wide association data for PsA (3186 cases and 240,862 control individuals and an additional 5065 cases and 21,286 control individuals), psoriasis, and AID.
Disclosures: This study was supported by two research projects from China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Duan K, Wang J, Chen S, et al. Causal associations between both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis and multiple autoimmune diseases: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2024;15:1422626 (Jul 24). Doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1422626 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and certain other autoimmune diseases (AID) may have an increased risk of developing psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: The risk factors for PsA included RA (inverse variance weighting odds ratio [ORIVW] 1.11; P = .0205), SLE (ORIVW 1.04; P = .0107), AS (ORIVW 2.18; P = .000155), Crohn's disease (CD; ORIVW 1.07; P = .01), Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT; ORIVW 1.23; P = .00143), and vitiligo (ORIVW 1.27; P = .0000267). However, PsA did not increase the risk for these AID.
Study details: This bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study used genome-wide association data for PsA (3186 cases and 240,862 control individuals and an additional 5065 cases and 21,286 control individuals), psoriasis, and AID.
Disclosures: This study was supported by two research projects from China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Duan K, Wang J, Chen S, et al. Causal associations between both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis and multiple autoimmune diseases: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2024;15:1422626 (Jul 24). Doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1422626 Source