User login
Children and COVID: New cases down slightly from record high
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.
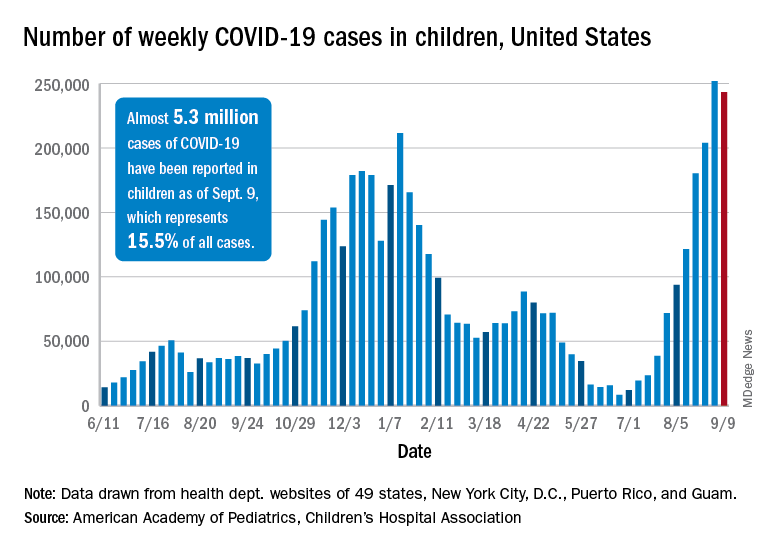
Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).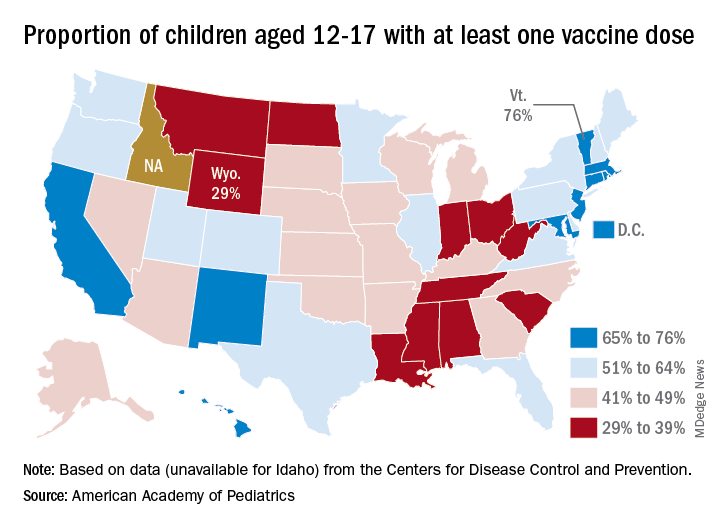
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.

Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.

Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
Man dies after 43 full ICUs turn him away
Ray Martin DeMonia, 73, of Cullman, Alabama, ran an antiques business for 40 years and served as an auctioneer at charity events, the obituary said.
He had a stroke in 2020 during the first months of the COVID pandemic and made sure to get vaccinated, his daughter, Raven DeMonia, told The Washington Post.
“He knew what the vaccine meant for his health and what it meant to staying alive,” she said. “He said, ‘I just want to get back to shaking hands with people, selling stuff, and talking antiques.’”
His daughter told the Post that her father went to Cullman Regional Medical Center on Aug. 23 with heart problems.
About 12 hours after he was admitted, her mother got a call from the hospital saying they’d called 43 hospitals and were unable to find a “specialized cardiac ICU bed” for him, Ms. DeMonia told the Post.
He was finally airlifted to Rush Foundation Hospital in Meridian, Mississippi, almost 200 miles from his home, but died there Sept. 1. His family decided to make a plea for increased vaccinations in his obituary.
“In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies,” the obit said. “Due to COVID 19, CRMC emergency staff contacted 43 hospitals in 3 states in search of a Cardiac ICU bed and finally located one in Meridian, MS. He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Mr. DeMonia is survived by his wife, daughter, grandson, and other family members.
The Alabama Hospital Association says state hospitals are still short of ICU beds. On Sept. 12, the AHA website said the state had 1,530 staffed ICU beds to accommodate 1,541 ICU patients.
The AHA said 83% of COVID patients in ICU had not been vaccinated against COVID, 4% were partially vaccinated, and 13% were fully vaccinated. Alabama trails other states in vaccination rates. Newsweek, citing CDC data, said 53.7% of people in Alabama were fully vaccinated. In comparison, 53.8% of all Americans nationally are fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Ray Martin DeMonia, 73, of Cullman, Alabama, ran an antiques business for 40 years and served as an auctioneer at charity events, the obituary said.
He had a stroke in 2020 during the first months of the COVID pandemic and made sure to get vaccinated, his daughter, Raven DeMonia, told The Washington Post.
“He knew what the vaccine meant for his health and what it meant to staying alive,” she said. “He said, ‘I just want to get back to shaking hands with people, selling stuff, and talking antiques.’”
His daughter told the Post that her father went to Cullman Regional Medical Center on Aug. 23 with heart problems.
About 12 hours after he was admitted, her mother got a call from the hospital saying they’d called 43 hospitals and were unable to find a “specialized cardiac ICU bed” for him, Ms. DeMonia told the Post.
He was finally airlifted to Rush Foundation Hospital in Meridian, Mississippi, almost 200 miles from his home, but died there Sept. 1. His family decided to make a plea for increased vaccinations in his obituary.
“In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies,” the obit said. “Due to COVID 19, CRMC emergency staff contacted 43 hospitals in 3 states in search of a Cardiac ICU bed and finally located one in Meridian, MS. He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Mr. DeMonia is survived by his wife, daughter, grandson, and other family members.
The Alabama Hospital Association says state hospitals are still short of ICU beds. On Sept. 12, the AHA website said the state had 1,530 staffed ICU beds to accommodate 1,541 ICU patients.
The AHA said 83% of COVID patients in ICU had not been vaccinated against COVID, 4% were partially vaccinated, and 13% were fully vaccinated. Alabama trails other states in vaccination rates. Newsweek, citing CDC data, said 53.7% of people in Alabama were fully vaccinated. In comparison, 53.8% of all Americans nationally are fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Ray Martin DeMonia, 73, of Cullman, Alabama, ran an antiques business for 40 years and served as an auctioneer at charity events, the obituary said.
He had a stroke in 2020 during the first months of the COVID pandemic and made sure to get vaccinated, his daughter, Raven DeMonia, told The Washington Post.
“He knew what the vaccine meant for his health and what it meant to staying alive,” she said. “He said, ‘I just want to get back to shaking hands with people, selling stuff, and talking antiques.’”
His daughter told the Post that her father went to Cullman Regional Medical Center on Aug. 23 with heart problems.
About 12 hours after he was admitted, her mother got a call from the hospital saying they’d called 43 hospitals and were unable to find a “specialized cardiac ICU bed” for him, Ms. DeMonia told the Post.
He was finally airlifted to Rush Foundation Hospital in Meridian, Mississippi, almost 200 miles from his home, but died there Sept. 1. His family decided to make a plea for increased vaccinations in his obituary.
“In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies,” the obit said. “Due to COVID 19, CRMC emergency staff contacted 43 hospitals in 3 states in search of a Cardiac ICU bed and finally located one in Meridian, MS. He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Mr. DeMonia is survived by his wife, daughter, grandson, and other family members.
The Alabama Hospital Association says state hospitals are still short of ICU beds. On Sept. 12, the AHA website said the state had 1,530 staffed ICU beds to accommodate 1,541 ICU patients.
The AHA said 83% of COVID patients in ICU had not been vaccinated against COVID, 4% were partially vaccinated, and 13% were fully vaccinated. Alabama trails other states in vaccination rates. Newsweek, citing CDC data, said 53.7% of people in Alabama were fully vaccinated. In comparison, 53.8% of all Americans nationally are fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
PRESERVED-HF: Dapagliflozin improves physical limitations in patients with HFpEF
The SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin scored a clear win in a randomized, controlled trial with more than 300 U.S. patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), showing a significant and clinically meaningful benefit for the primary endpoint, a KCCQ measure of symptoms and physical limitations, after 12 weeks of treatment.
These results in the PRESERVED-HF study follow closely on the heals of the initial report from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial that showed a benefit from a different sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, empagliflozin (Jardiance) in nearly 6,000 randomized patients for the primary endpoint of preventing cardiovascular death or hospitalizations for heart failure.
In PRESERVED-HF, patients with HFpEF who received a standard, once-daily dose of dapagliflozin (Farxiga) had an average 5.8-point improvement in their condition as measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire clinical summary score (KCCQ-CS), the study’s primary endpoint.
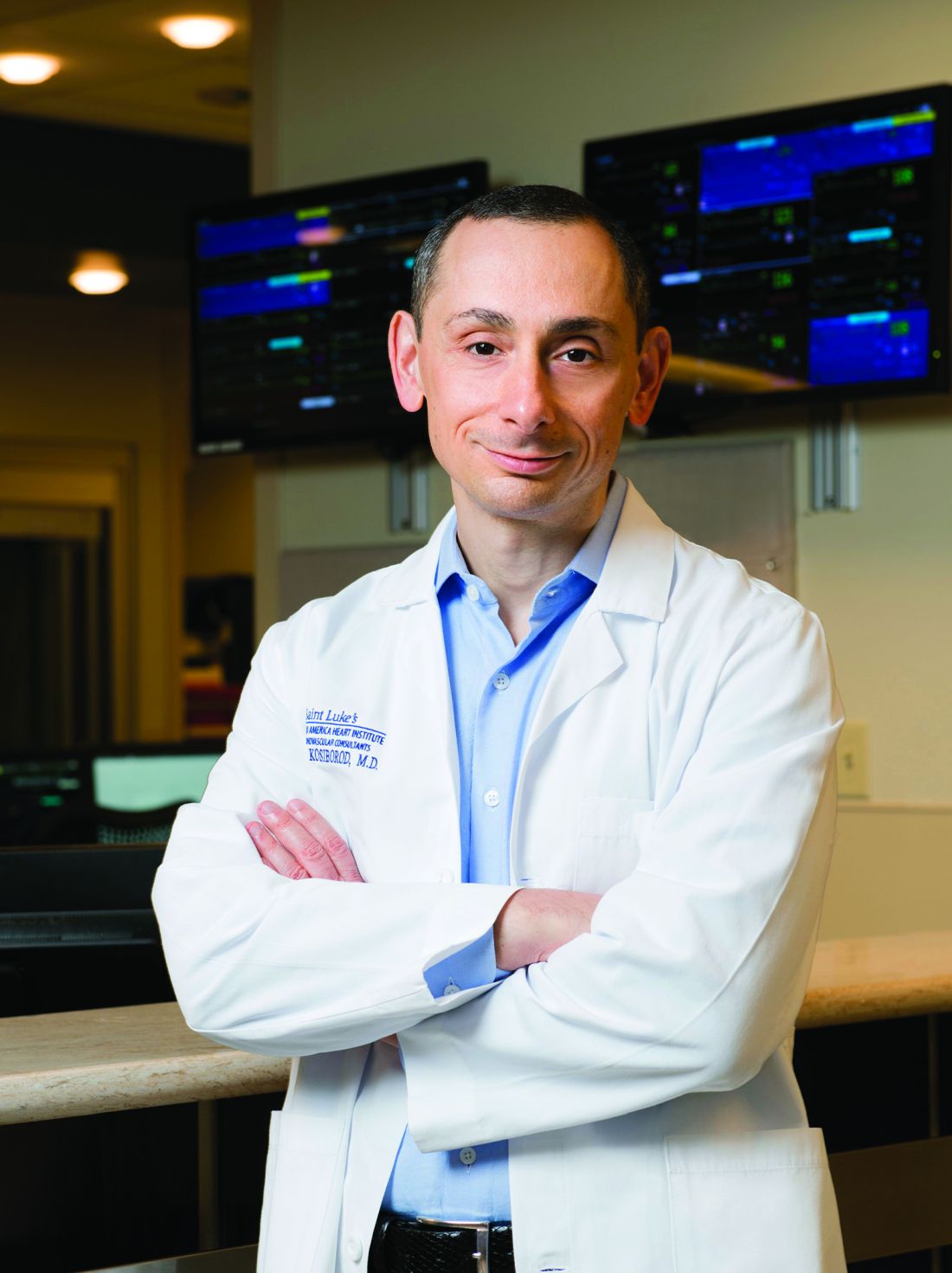
This is “the first study to demonstrate that an SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin significantly improves symptoms, physical limitations, and 6-minute walking distance in patients with HFpEF,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, reported at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America. The secondary endpoint of 6-minute walking distance “has been very difficult to improve in many previous studies of other treatments” tested in patients with HFpEF, noted Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist and codirector of the Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute.
The results are “highly complementary” to the findings from large outcome trials, such as the findings from EMPEROR-Preserved, he said, and collectively the recent findings from these studies of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with HFpEF identify drugs in this class as a “new treatment option” for patients with a disorder that until now had no treatment with unequivocally proven efficacy and safety.
‘Impressive and unprecedented’ findings
The findings are “really impressive and unprecedented,” said Milton Packer, MD, a cardiologist at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas who was not involved in the study. “This is the largest KCCQ benefit ever seen in either patients with HFpEF or in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction,” said Dr. Packer, one of the investigators who led the EMPEROR-Preserved trial.
PRESERVED-HF randomized 324 patients diagnosed with heart failure and with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 45% or higher at any of 26 U.S. centers, with 304 patients completing the planned final analysis after 12 weeks on treatment. Patients could be in New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class II-IV, they had to have a baseline N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level of at least 225 pg/mL (or higher if they also had atrial fibrillation), and they required at least one of three markers of established heart failure: recent hospitalization for heart failure or an urgent outpatient visit that required treatment with an IV diuretic, elevated filling pressure measured by left or right catheterization, or structural heart disease detected by echocardiography.
The average age of the enrolled patients was 70 years, and they had been diagnosed with heart failure for about 3 years; 57% were women, 30% were African American, and their median body mass index was 35 kg/m2. Roughly 42% had NYHA class III or IV disease, 56% had type 2 diabetes, their median estimated glomerular filtration rate was about 55 mL/min per 1.73m2, their median KCCQ-CS score at baseline was about 62, and their average 6-minute walk distance was 244 m.
These and other features of the enrolled population define a distinctly U.S. patient population, stressed Dr. Kosiborod, professor of medicine at the University of Missouri–Kansas City.
“The patients we enrolled are the patients we see in U.S. clinical practice,” he said in an interview. Importantly, the patient profile of a median BMI of 35 kg/m2, a median KCCQ-CS score of 62 – “quite low,” noted Dr. Kosiborod – and having more than 40% of patients in NYHA functional class III defines a study population with a substantially greater burden of obesity, symptoms, and functional impairment compared with those enrolled in prior trials involving patients with HFpEF such as EMPEROR-Preserved.
Results complement findings from larger trials
PRESERVED-HF was an investigator-initiated study designed to inform clinical practice, not as a pivotal trial like EMPEROR-Preserved, which aims to gather evidence to support a new indication for regulatory approval. (On Sept. 9, 2021, the Food and Drug Administration granted empagliflozin “breakthrough therapy” status for treating HFpEF based on the EMPEROR-Preserved results, which will fast-track the agency’s decision on this indication.)
Dr. Kosiborod noted that he and his associates designed PRESERVED-HF with adequate patient numbers to power a statistically valid assessment of effect on KCCQ-CS score. While the new findings will not by themselves lead to a new indication for dapagliflozin to treat patients with HFpEF, they will potentially complement the pending results of another trial, DELIVER, by showing efficacy and safety in a uniquely U.S. patient population. DELIVER is a pivotal, global trial of dapagliflozin in more than 6,000 patients with HFpEF that’s on track to report findings in 2022.
Dr. Kosiborod also stressed that dapagliflozin has U.S.-approved indications for treating patients with type 2 diabetes, and for patients with chronic kidney disease, and that a majority of patients enrolled in PRESERVED-HF had one or both of these conditions. That makes the new findings especially compelling for patients with either type 2 diabetes or chronic kidney disease and HFpEF who are not already receiving an SGLT2 inhibitor.
Other findings that he reported showed a range of benefits consistent with the primary endpoint, including the KCCQ overall summary score, which also showed a significant 4.5-point average increase over placebo after 12 weeks. Analysis by the percentage of patients achieving at least a 5-point improvement in the KCCQ clinical summary score (the threshold for a clinically meaningful improvement) showed that about 45% of patients treated with dapagliflozin reached this mark compared with roughly 35% of patients in the placebo arm, indicating a number needed to treat of nine to have one additional patient achieve this threshold after 12 weeks. Average improvement in 6-minute walk distance was about 20 m with dapagliflozin compared with placebo.
No heterogeneity of effect by baseline ejection fraction.
Subgroup analyses showed no heterogeneity of response across 12 different ways of subdividing the study population, including age, sex, race, diabetes status, and BMI. The median left ventricular ejection fraction among enrolled patients was 60%, and the findings showed identical KCCQ improvements among patients with ejection fractions less than the median and those with an ejection fraction above the median.
This last finding was especially relevant because the EMPEROR-Preserved results showed a possible signal of heterogeneity by ejection fraction and an attenuated effect among patients with HFpEF and an ejection fraction above the 60%-65% range, although the certainty of this finding is currently controversial.
The impact of empagliflozin on KCCQ clinical summary score in EMPEROR-Preserved showed an average incremental improvement of 1.32 points compared with placebo, a significant difference, but more modest than the increment from dapagliflozin treatment seen in PRESERVED-HF. Dr. Kosiborod hypothesized that this difference might be mostly because of the different patient populations enrolled in the two studies.
Dr. Kosiborod noted that a report on the PRESERVED-HF results will soon appear in Nature Medicine.
PRESERVED-HF was funded by AstraZeneca, which markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga), but the trials’ design and conduct were independent of this funding source. Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant to AstraZeneca and numerous other companies, and he has received research funding from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Packer has had financial relationships with AstraZeneca and numerous other companies.
The SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin scored a clear win in a randomized, controlled trial with more than 300 U.S. patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), showing a significant and clinically meaningful benefit for the primary endpoint, a KCCQ measure of symptoms and physical limitations, after 12 weeks of treatment.
These results in the PRESERVED-HF study follow closely on the heals of the initial report from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial that showed a benefit from a different sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, empagliflozin (Jardiance) in nearly 6,000 randomized patients for the primary endpoint of preventing cardiovascular death or hospitalizations for heart failure.
In PRESERVED-HF, patients with HFpEF who received a standard, once-daily dose of dapagliflozin (Farxiga) had an average 5.8-point improvement in their condition as measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire clinical summary score (KCCQ-CS), the study’s primary endpoint.
This is “the first study to demonstrate that an SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin significantly improves symptoms, physical limitations, and 6-minute walking distance in patients with HFpEF,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, reported at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America. The secondary endpoint of 6-minute walking distance “has been very difficult to improve in many previous studies of other treatments” tested in patients with HFpEF, noted Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist and codirector of the Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute.
The results are “highly complementary” to the findings from large outcome trials, such as the findings from EMPEROR-Preserved, he said, and collectively the recent findings from these studies of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with HFpEF identify drugs in this class as a “new treatment option” for patients with a disorder that until now had no treatment with unequivocally proven efficacy and safety.
‘Impressive and unprecedented’ findings
The findings are “really impressive and unprecedented,” said Milton Packer, MD, a cardiologist at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas who was not involved in the study. “This is the largest KCCQ benefit ever seen in either patients with HFpEF or in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction,” said Dr. Packer, one of the investigators who led the EMPEROR-Preserved trial.
PRESERVED-HF randomized 324 patients diagnosed with heart failure and with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 45% or higher at any of 26 U.S. centers, with 304 patients completing the planned final analysis after 12 weeks on treatment. Patients could be in New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class II-IV, they had to have a baseline N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level of at least 225 pg/mL (or higher if they also had atrial fibrillation), and they required at least one of three markers of established heart failure: recent hospitalization for heart failure or an urgent outpatient visit that required treatment with an IV diuretic, elevated filling pressure measured by left or right catheterization, or structural heart disease detected by echocardiography.
The average age of the enrolled patients was 70 years, and they had been diagnosed with heart failure for about 3 years; 57% were women, 30% were African American, and their median body mass index was 35 kg/m2. Roughly 42% had NYHA class III or IV disease, 56% had type 2 diabetes, their median estimated glomerular filtration rate was about 55 mL/min per 1.73m2, their median KCCQ-CS score at baseline was about 62, and their average 6-minute walk distance was 244 m.
These and other features of the enrolled population define a distinctly U.S. patient population, stressed Dr. Kosiborod, professor of medicine at the University of Missouri–Kansas City.
“The patients we enrolled are the patients we see in U.S. clinical practice,” he said in an interview. Importantly, the patient profile of a median BMI of 35 kg/m2, a median KCCQ-CS score of 62 – “quite low,” noted Dr. Kosiborod – and having more than 40% of patients in NYHA functional class III defines a study population with a substantially greater burden of obesity, symptoms, and functional impairment compared with those enrolled in prior trials involving patients with HFpEF such as EMPEROR-Preserved.
Results complement findings from larger trials
PRESERVED-HF was an investigator-initiated study designed to inform clinical practice, not as a pivotal trial like EMPEROR-Preserved, which aims to gather evidence to support a new indication for regulatory approval. (On Sept. 9, 2021, the Food and Drug Administration granted empagliflozin “breakthrough therapy” status for treating HFpEF based on the EMPEROR-Preserved results, which will fast-track the agency’s decision on this indication.)
Dr. Kosiborod noted that he and his associates designed PRESERVED-HF with adequate patient numbers to power a statistically valid assessment of effect on KCCQ-CS score. While the new findings will not by themselves lead to a new indication for dapagliflozin to treat patients with HFpEF, they will potentially complement the pending results of another trial, DELIVER, by showing efficacy and safety in a uniquely U.S. patient population. DELIVER is a pivotal, global trial of dapagliflozin in more than 6,000 patients with HFpEF that’s on track to report findings in 2022.
Dr. Kosiborod also stressed that dapagliflozin has U.S.-approved indications for treating patients with type 2 diabetes, and for patients with chronic kidney disease, and that a majority of patients enrolled in PRESERVED-HF had one or both of these conditions. That makes the new findings especially compelling for patients with either type 2 diabetes or chronic kidney disease and HFpEF who are not already receiving an SGLT2 inhibitor.
Other findings that he reported showed a range of benefits consistent with the primary endpoint, including the KCCQ overall summary score, which also showed a significant 4.5-point average increase over placebo after 12 weeks. Analysis by the percentage of patients achieving at least a 5-point improvement in the KCCQ clinical summary score (the threshold for a clinically meaningful improvement) showed that about 45% of patients treated with dapagliflozin reached this mark compared with roughly 35% of patients in the placebo arm, indicating a number needed to treat of nine to have one additional patient achieve this threshold after 12 weeks. Average improvement in 6-minute walk distance was about 20 m with dapagliflozin compared with placebo.
No heterogeneity of effect by baseline ejection fraction.
Subgroup analyses showed no heterogeneity of response across 12 different ways of subdividing the study population, including age, sex, race, diabetes status, and BMI. The median left ventricular ejection fraction among enrolled patients was 60%, and the findings showed identical KCCQ improvements among patients with ejection fractions less than the median and those with an ejection fraction above the median.
This last finding was especially relevant because the EMPEROR-Preserved results showed a possible signal of heterogeneity by ejection fraction and an attenuated effect among patients with HFpEF and an ejection fraction above the 60%-65% range, although the certainty of this finding is currently controversial.
The impact of empagliflozin on KCCQ clinical summary score in EMPEROR-Preserved showed an average incremental improvement of 1.32 points compared with placebo, a significant difference, but more modest than the increment from dapagliflozin treatment seen in PRESERVED-HF. Dr. Kosiborod hypothesized that this difference might be mostly because of the different patient populations enrolled in the two studies.
Dr. Kosiborod noted that a report on the PRESERVED-HF results will soon appear in Nature Medicine.
PRESERVED-HF was funded by AstraZeneca, which markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga), but the trials’ design and conduct were independent of this funding source. Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant to AstraZeneca and numerous other companies, and he has received research funding from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Packer has had financial relationships with AstraZeneca and numerous other companies.
The SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin scored a clear win in a randomized, controlled trial with more than 300 U.S. patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), showing a significant and clinically meaningful benefit for the primary endpoint, a KCCQ measure of symptoms and physical limitations, after 12 weeks of treatment.
These results in the PRESERVED-HF study follow closely on the heals of the initial report from the EMPEROR-Preserved trial that showed a benefit from a different sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, empagliflozin (Jardiance) in nearly 6,000 randomized patients for the primary endpoint of preventing cardiovascular death or hospitalizations for heart failure.
In PRESERVED-HF, patients with HFpEF who received a standard, once-daily dose of dapagliflozin (Farxiga) had an average 5.8-point improvement in their condition as measured by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire clinical summary score (KCCQ-CS), the study’s primary endpoint.
This is “the first study to demonstrate that an SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin significantly improves symptoms, physical limitations, and 6-minute walking distance in patients with HFpEF,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, reported at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America. The secondary endpoint of 6-minute walking distance “has been very difficult to improve in many previous studies of other treatments” tested in patients with HFpEF, noted Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist and codirector of the Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute.
The results are “highly complementary” to the findings from large outcome trials, such as the findings from EMPEROR-Preserved, he said, and collectively the recent findings from these studies of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with HFpEF identify drugs in this class as a “new treatment option” for patients with a disorder that until now had no treatment with unequivocally proven efficacy and safety.
‘Impressive and unprecedented’ findings
The findings are “really impressive and unprecedented,” said Milton Packer, MD, a cardiologist at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas who was not involved in the study. “This is the largest KCCQ benefit ever seen in either patients with HFpEF or in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction,” said Dr. Packer, one of the investigators who led the EMPEROR-Preserved trial.
PRESERVED-HF randomized 324 patients diagnosed with heart failure and with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 45% or higher at any of 26 U.S. centers, with 304 patients completing the planned final analysis after 12 weeks on treatment. Patients could be in New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class II-IV, they had to have a baseline N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level of at least 225 pg/mL (or higher if they also had atrial fibrillation), and they required at least one of three markers of established heart failure: recent hospitalization for heart failure or an urgent outpatient visit that required treatment with an IV diuretic, elevated filling pressure measured by left or right catheterization, or structural heart disease detected by echocardiography.
The average age of the enrolled patients was 70 years, and they had been diagnosed with heart failure for about 3 years; 57% were women, 30% were African American, and their median body mass index was 35 kg/m2. Roughly 42% had NYHA class III or IV disease, 56% had type 2 diabetes, their median estimated glomerular filtration rate was about 55 mL/min per 1.73m2, their median KCCQ-CS score at baseline was about 62, and their average 6-minute walk distance was 244 m.
These and other features of the enrolled population define a distinctly U.S. patient population, stressed Dr. Kosiborod, professor of medicine at the University of Missouri–Kansas City.
“The patients we enrolled are the patients we see in U.S. clinical practice,” he said in an interview. Importantly, the patient profile of a median BMI of 35 kg/m2, a median KCCQ-CS score of 62 – “quite low,” noted Dr. Kosiborod – and having more than 40% of patients in NYHA functional class III defines a study population with a substantially greater burden of obesity, symptoms, and functional impairment compared with those enrolled in prior trials involving patients with HFpEF such as EMPEROR-Preserved.
Results complement findings from larger trials
PRESERVED-HF was an investigator-initiated study designed to inform clinical practice, not as a pivotal trial like EMPEROR-Preserved, which aims to gather evidence to support a new indication for regulatory approval. (On Sept. 9, 2021, the Food and Drug Administration granted empagliflozin “breakthrough therapy” status for treating HFpEF based on the EMPEROR-Preserved results, which will fast-track the agency’s decision on this indication.)
Dr. Kosiborod noted that he and his associates designed PRESERVED-HF with adequate patient numbers to power a statistically valid assessment of effect on KCCQ-CS score. While the new findings will not by themselves lead to a new indication for dapagliflozin to treat patients with HFpEF, they will potentially complement the pending results of another trial, DELIVER, by showing efficacy and safety in a uniquely U.S. patient population. DELIVER is a pivotal, global trial of dapagliflozin in more than 6,000 patients with HFpEF that’s on track to report findings in 2022.
Dr. Kosiborod also stressed that dapagliflozin has U.S.-approved indications for treating patients with type 2 diabetes, and for patients with chronic kidney disease, and that a majority of patients enrolled in PRESERVED-HF had one or both of these conditions. That makes the new findings especially compelling for patients with either type 2 diabetes or chronic kidney disease and HFpEF who are not already receiving an SGLT2 inhibitor.
Other findings that he reported showed a range of benefits consistent with the primary endpoint, including the KCCQ overall summary score, which also showed a significant 4.5-point average increase over placebo after 12 weeks. Analysis by the percentage of patients achieving at least a 5-point improvement in the KCCQ clinical summary score (the threshold for a clinically meaningful improvement) showed that about 45% of patients treated with dapagliflozin reached this mark compared with roughly 35% of patients in the placebo arm, indicating a number needed to treat of nine to have one additional patient achieve this threshold after 12 weeks. Average improvement in 6-minute walk distance was about 20 m with dapagliflozin compared with placebo.
No heterogeneity of effect by baseline ejection fraction.
Subgroup analyses showed no heterogeneity of response across 12 different ways of subdividing the study population, including age, sex, race, diabetes status, and BMI. The median left ventricular ejection fraction among enrolled patients was 60%, and the findings showed identical KCCQ improvements among patients with ejection fractions less than the median and those with an ejection fraction above the median.
This last finding was especially relevant because the EMPEROR-Preserved results showed a possible signal of heterogeneity by ejection fraction and an attenuated effect among patients with HFpEF and an ejection fraction above the 60%-65% range, although the certainty of this finding is currently controversial.
The impact of empagliflozin on KCCQ clinical summary score in EMPEROR-Preserved showed an average incremental improvement of 1.32 points compared with placebo, a significant difference, but more modest than the increment from dapagliflozin treatment seen in PRESERVED-HF. Dr. Kosiborod hypothesized that this difference might be mostly because of the different patient populations enrolled in the two studies.
Dr. Kosiborod noted that a report on the PRESERVED-HF results will soon appear in Nature Medicine.
PRESERVED-HF was funded by AstraZeneca, which markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga), but the trials’ design and conduct were independent of this funding source. Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant to AstraZeneca and numerous other companies, and he has received research funding from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Packer has had financial relationships with AstraZeneca and numerous other companies.
FROM HFSA 2021
Fewer inpatient work hours linked with worse patient outcomes
The number of physicians working part time in the United States has increased by nearly 11% since 1993, and as more physicians opt for part-time work, quality of care deserves further study, the investigators wrote in JAMA Internal Medicine. Most studies comparing outcomes for patients treated by full-timers and part-timers have focused on outpatient care settings, where mortality is low and the potential for confounding is high, according to the study authors Hirotaka Kato, PhD, of Keio University in Tokyo, and colleagues. The new study, in contrast, is based on data from nearly 400,000 hospitalizations.
The researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis on a 20% random sample of Medicare patients aged 65 years and older who were treated by a hospitalist for an emergency medical condition between 2011 and 2016. They examined associations between the number of days per year worked by hospitalists and they 30-day mortality rates among the patients they treated. The researchers analyzed a total of 392,797 hospitalizations in which patients were treated by 19,170 hospitalists. The mean age of the hospitalists was 41 years; 39% were female. Clinician work days were divided into quartiles.
Overall, the 30-day mortality was significantly higher among patients treated by clinicians in the bottom quartile with the fewest number of days worked, compared with those treated by clinicians in the top quartile with the most days worked (10.5% vs. 9.6%). The rates were similar in the second and third quartiles (10.0% and 9.5%).
The average number of days worked clinically per year was 57.6 in the lowest quartile versus 163.3 in the highest quartile, a 65% difference. No significant associations were noted between days worked and patient outcomes with regard to physician age, gender, or hospital teaching status.
Hospital 30-day readmission rates were examined as a secondary outcome, but there was no association between patient readmission and the number of days worked by the clinician. The adjusted 30-day readmission rate for clinicians in the bottom quartile of days worked, compared with those in the top quartile, was 15.3% versus 15.2% (P = .61).
The researchers found no difference in patients’ severity of illness (defined by expected mortality) or reason for admission between physicians in the different quartiles of days worked. They eliminated confounding from hospital-level differences by comparing outcomes of patients between physicians in the same hospital.
Possible explanations for worse patient outcomes
“As the number of physicians who engage in part-time clinical work continues to increase, these findings should lead to careful consideration by health systems to reevaluate preventive measures to address potential unintended patient harm,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers proposed several reasons for the association between fewer clinical work days and worse patient outcomes. First, physicians putting in less clinical time may be less updated on the latest guidelines, their skills may decline with less frequent patient care, and they may be less familiar with the nurses, medical assistants, and support staff, which may contribute to poor teamwork. The researchers also stated that some part-time physicians may need to balance nonclinical responsibilities, such as research or administrative tasks, concurrently with inpatient care. “It is also possible that physicians with less clinical knowledge or skills select to become part-time physicians, whereas physicians with higher clinical performance decide to work full time,” they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and potential for unmeasured confounding variables, and the results may not generalize to younger patients or surgical patients, the researchers noted. Also, the study did not include care by hospitalists that was not billed, days in which clinicians treated non-Medicare patients or patients not part of the Medicare sample, or information about the reasons for clinicians’ part-time work.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and suggest the need for better institutional support to maintain the clinical performance of physicians who may be balancing a range of obligations, they concluded.
Clinician work issues have renewed relevance
“The data in this paper are from 2016 and earlier, but it is possibly event more relevant today than then,” Eileen Barrett, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “The pandemic has exacerbated stressors being experienced by physicians and other health care workers, including higher clinical workloads and burnout, and spotlighted gendered effects on women in the workforce, which is likely to drive more physicians to part-time work.
“Reporting these findings now is so important so they can contribute to a shared mental model of the challenges physicians and hospitals face as we seek solutions to deliver high-quality and high-value care with an engaged, professionally fulfilled workforce,” she emphasized.
Dr. Barrett said she was surprised that the study did not show differences in readmission rates depending on the number of shifts worked, and also that the results were not different when considering expected mortality.
“However unpopular it may be to say so, physicians and administrators should assume these results apply to their practice unless they have examined their own data and know it does not,” Dr. Barrett said. “With that in mind, hospitals, administrators, and regulatory bodies have an urgent need to examine and reduce the forces driving physicians to part-time clinical work. Some of these factors include the absence of childcare, excessive paperwork, burnout, administrative duties, and valued experiences such as teaching, leadership, and research that keep clinicians from the bedside.
“Additionally, steps should be taken to reduce the administrative complexity that makes providing the best care to patients difficult and requires hospitalists to create ‘workarounds,’ because those who work fewer clinical hours may not know how to do these, nor how to advocate for their patients,” Dr. Barrett emphasized.
“Additional research is needed to determine how mortality varies by number of clinical shifts for pediatric and obstetric patients who are infrequently covered by Medicare, also how the pandemic and increasing administrative complexity since the time the data was obtained affect patient care,” Dr. Barrett noted.
The study was supported by a grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science to lead author Dr. Kato, who had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Barrett, who serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, had no financial conflicts.
The number of physicians working part time in the United States has increased by nearly 11% since 1993, and as more physicians opt for part-time work, quality of care deserves further study, the investigators wrote in JAMA Internal Medicine. Most studies comparing outcomes for patients treated by full-timers and part-timers have focused on outpatient care settings, where mortality is low and the potential for confounding is high, according to the study authors Hirotaka Kato, PhD, of Keio University in Tokyo, and colleagues. The new study, in contrast, is based on data from nearly 400,000 hospitalizations.
The researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis on a 20% random sample of Medicare patients aged 65 years and older who were treated by a hospitalist for an emergency medical condition between 2011 and 2016. They examined associations between the number of days per year worked by hospitalists and they 30-day mortality rates among the patients they treated. The researchers analyzed a total of 392,797 hospitalizations in which patients were treated by 19,170 hospitalists. The mean age of the hospitalists was 41 years; 39% were female. Clinician work days were divided into quartiles.
Overall, the 30-day mortality was significantly higher among patients treated by clinicians in the bottom quartile with the fewest number of days worked, compared with those treated by clinicians in the top quartile with the most days worked (10.5% vs. 9.6%). The rates were similar in the second and third quartiles (10.0% and 9.5%).
The average number of days worked clinically per year was 57.6 in the lowest quartile versus 163.3 in the highest quartile, a 65% difference. No significant associations were noted between days worked and patient outcomes with regard to physician age, gender, or hospital teaching status.
Hospital 30-day readmission rates were examined as a secondary outcome, but there was no association between patient readmission and the number of days worked by the clinician. The adjusted 30-day readmission rate for clinicians in the bottom quartile of days worked, compared with those in the top quartile, was 15.3% versus 15.2% (P = .61).
The researchers found no difference in patients’ severity of illness (defined by expected mortality) or reason for admission between physicians in the different quartiles of days worked. They eliminated confounding from hospital-level differences by comparing outcomes of patients between physicians in the same hospital.
Possible explanations for worse patient outcomes
“As the number of physicians who engage in part-time clinical work continues to increase, these findings should lead to careful consideration by health systems to reevaluate preventive measures to address potential unintended patient harm,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers proposed several reasons for the association between fewer clinical work days and worse patient outcomes. First, physicians putting in less clinical time may be less updated on the latest guidelines, their skills may decline with less frequent patient care, and they may be less familiar with the nurses, medical assistants, and support staff, which may contribute to poor teamwork. The researchers also stated that some part-time physicians may need to balance nonclinical responsibilities, such as research or administrative tasks, concurrently with inpatient care. “It is also possible that physicians with less clinical knowledge or skills select to become part-time physicians, whereas physicians with higher clinical performance decide to work full time,” they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and potential for unmeasured confounding variables, and the results may not generalize to younger patients or surgical patients, the researchers noted. Also, the study did not include care by hospitalists that was not billed, days in which clinicians treated non-Medicare patients or patients not part of the Medicare sample, or information about the reasons for clinicians’ part-time work.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and suggest the need for better institutional support to maintain the clinical performance of physicians who may be balancing a range of obligations, they concluded.
Clinician work issues have renewed relevance
“The data in this paper are from 2016 and earlier, but it is possibly event more relevant today than then,” Eileen Barrett, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “The pandemic has exacerbated stressors being experienced by physicians and other health care workers, including higher clinical workloads and burnout, and spotlighted gendered effects on women in the workforce, which is likely to drive more physicians to part-time work.
“Reporting these findings now is so important so they can contribute to a shared mental model of the challenges physicians and hospitals face as we seek solutions to deliver high-quality and high-value care with an engaged, professionally fulfilled workforce,” she emphasized.
Dr. Barrett said she was surprised that the study did not show differences in readmission rates depending on the number of shifts worked, and also that the results were not different when considering expected mortality.
“However unpopular it may be to say so, physicians and administrators should assume these results apply to their practice unless they have examined their own data and know it does not,” Dr. Barrett said. “With that in mind, hospitals, administrators, and regulatory bodies have an urgent need to examine and reduce the forces driving physicians to part-time clinical work. Some of these factors include the absence of childcare, excessive paperwork, burnout, administrative duties, and valued experiences such as teaching, leadership, and research that keep clinicians from the bedside.
“Additionally, steps should be taken to reduce the administrative complexity that makes providing the best care to patients difficult and requires hospitalists to create ‘workarounds,’ because those who work fewer clinical hours may not know how to do these, nor how to advocate for their patients,” Dr. Barrett emphasized.
“Additional research is needed to determine how mortality varies by number of clinical shifts for pediatric and obstetric patients who are infrequently covered by Medicare, also how the pandemic and increasing administrative complexity since the time the data was obtained affect patient care,” Dr. Barrett noted.
The study was supported by a grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science to lead author Dr. Kato, who had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Barrett, who serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, had no financial conflicts.
The number of physicians working part time in the United States has increased by nearly 11% since 1993, and as more physicians opt for part-time work, quality of care deserves further study, the investigators wrote in JAMA Internal Medicine. Most studies comparing outcomes for patients treated by full-timers and part-timers have focused on outpatient care settings, where mortality is low and the potential for confounding is high, according to the study authors Hirotaka Kato, PhD, of Keio University in Tokyo, and colleagues. The new study, in contrast, is based on data from nearly 400,000 hospitalizations.
The researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis on a 20% random sample of Medicare patients aged 65 years and older who were treated by a hospitalist for an emergency medical condition between 2011 and 2016. They examined associations between the number of days per year worked by hospitalists and they 30-day mortality rates among the patients they treated. The researchers analyzed a total of 392,797 hospitalizations in which patients were treated by 19,170 hospitalists. The mean age of the hospitalists was 41 years; 39% were female. Clinician work days were divided into quartiles.
Overall, the 30-day mortality was significantly higher among patients treated by clinicians in the bottom quartile with the fewest number of days worked, compared with those treated by clinicians in the top quartile with the most days worked (10.5% vs. 9.6%). The rates were similar in the second and third quartiles (10.0% and 9.5%).
The average number of days worked clinically per year was 57.6 in the lowest quartile versus 163.3 in the highest quartile, a 65% difference. No significant associations were noted between days worked and patient outcomes with regard to physician age, gender, or hospital teaching status.
Hospital 30-day readmission rates were examined as a secondary outcome, but there was no association between patient readmission and the number of days worked by the clinician. The adjusted 30-day readmission rate for clinicians in the bottom quartile of days worked, compared with those in the top quartile, was 15.3% versus 15.2% (P = .61).
The researchers found no difference in patients’ severity of illness (defined by expected mortality) or reason for admission between physicians in the different quartiles of days worked. They eliminated confounding from hospital-level differences by comparing outcomes of patients between physicians in the same hospital.
Possible explanations for worse patient outcomes
“As the number of physicians who engage in part-time clinical work continues to increase, these findings should lead to careful consideration by health systems to reevaluate preventive measures to address potential unintended patient harm,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers proposed several reasons for the association between fewer clinical work days and worse patient outcomes. First, physicians putting in less clinical time may be less updated on the latest guidelines, their skills may decline with less frequent patient care, and they may be less familiar with the nurses, medical assistants, and support staff, which may contribute to poor teamwork. The researchers also stated that some part-time physicians may need to balance nonclinical responsibilities, such as research or administrative tasks, concurrently with inpatient care. “It is also possible that physicians with less clinical knowledge or skills select to become part-time physicians, whereas physicians with higher clinical performance decide to work full time,” they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and potential for unmeasured confounding variables, and the results may not generalize to younger patients or surgical patients, the researchers noted. Also, the study did not include care by hospitalists that was not billed, days in which clinicians treated non-Medicare patients or patients not part of the Medicare sample, or information about the reasons for clinicians’ part-time work.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and suggest the need for better institutional support to maintain the clinical performance of physicians who may be balancing a range of obligations, they concluded.
Clinician work issues have renewed relevance
“The data in this paper are from 2016 and earlier, but it is possibly event more relevant today than then,” Eileen Barrett, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “The pandemic has exacerbated stressors being experienced by physicians and other health care workers, including higher clinical workloads and burnout, and spotlighted gendered effects on women in the workforce, which is likely to drive more physicians to part-time work.
“Reporting these findings now is so important so they can contribute to a shared mental model of the challenges physicians and hospitals face as we seek solutions to deliver high-quality and high-value care with an engaged, professionally fulfilled workforce,” she emphasized.
Dr. Barrett said she was surprised that the study did not show differences in readmission rates depending on the number of shifts worked, and also that the results were not different when considering expected mortality.
“However unpopular it may be to say so, physicians and administrators should assume these results apply to their practice unless they have examined their own data and know it does not,” Dr. Barrett said. “With that in mind, hospitals, administrators, and regulatory bodies have an urgent need to examine and reduce the forces driving physicians to part-time clinical work. Some of these factors include the absence of childcare, excessive paperwork, burnout, administrative duties, and valued experiences such as teaching, leadership, and research that keep clinicians from the bedside.
“Additionally, steps should be taken to reduce the administrative complexity that makes providing the best care to patients difficult and requires hospitalists to create ‘workarounds,’ because those who work fewer clinical hours may not know how to do these, nor how to advocate for their patients,” Dr. Barrett emphasized.
“Additional research is needed to determine how mortality varies by number of clinical shifts for pediatric and obstetric patients who are infrequently covered by Medicare, also how the pandemic and increasing administrative complexity since the time the data was obtained affect patient care,” Dr. Barrett noted.
The study was supported by a grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science to lead author Dr. Kato, who had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Barrett, who serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, had no financial conflicts.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
Study gives bleeding risk estimates for VTE patients on anticoagulants
The meta-analysis of data from 27 studies with 17,202 patients was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine. According to two of the paper’s coauthors, Faizan Khan, MSc, and Marc A. Rodger, MD, it “provides best available estimates of long-term bleeding risk with different anticoagulants in patients with unprovoked VTE,” including subgroups at increased risk.
Patients at increased risk for major bleeding include those who are older; those using antiplatelet therapy; and patients with kidney disease, a history of bleeding, or anemia, noted the coauthors, who work for the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
The researchers focused on randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and prospective cohort studies that reported major bleeding among patients with a first unprovoked or weakly provoked VTE who received oral anticoagulation for at least 6 months beyond an initial anticoagulant treatment course of at least 3 months.
The investigators analyzed data from 14 RCTs and 13 cohort studies. In all, 9,982 patients received a vitamin K antagonist (VKA), and 7,220 received a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC).
The incidence of major bleeding per 100 person-years was 1.7 events with VKAs, compared with 1.1 events with DOACs. The researchers estimated that the 5-year cumulative incidence of major bleeding with VKAs was 6.3%. The available data for DOACs were insufficient to estimate the incidence of major bleeding beyond 1 year.
“This information can help clinicians counsel patients and inform shared decision-making about extended therapy,” the researchers said.
Risks of serious bleeding ‘not trivial’
Margaret Fang, MD, with the University of California, San Francisco, agreed that the study can help clinicians and patients weigh the risks of extended anticoagulation for common types of VTE.
The study also “highlights that the risks of serious bleeding are not trivial” and points out gaps in the literature regarding the long-term use of DOACs for extended VTE therapy, Dr. Fang said.
Better ways to predict which patients will develop bleeding on anticoagulants are needed, Dr. Fang added. “It will also be important to establish which of the various therapies for preventing recurrent VTE – full dose versus lowered dose, or even aspirin – has the best balance of safety and efficacy,” she said.
‘Standardized approach’ for identifying high-risk patients lacking
Clinical practice guidelines recommend indefinite anticoagulation for an unprovoked VTE, except when patients are at high risk of bleeding, the authors noted. But clinicians lack a “standardized approach to identify patients at high risk of bleeding,” Mr. Khan and Dr. Rodger said. “Evidence from randomized trials on net long-term benefit of extended therapy is limited, and current guideline recommendations are largely based on expert consensus opinion. Major bleeding events are two to three times more likely to be fatal than recurrent VTE events, so extended therapy is not always associated with a net mortality benefit, particularly in patients at low risk of recurrent VTE or high risk of bleeding.”
The analysis indicates that there is “a clinically meaningful difference in long-term risk for anticoagulant-related major bleeding among patients with a first unprovoked VTE stratified according to presence or absence of the following risk factors: age older than 65 years, creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min, history of bleeding, concomitant use of antiplatelet therapy, and hemoglobin level less than 100 g/L,” the authors said.
For example, the researchers found that the incidence of major bleeding was higher among those older than 65 years, compared with younger patients (incidence rate ratio, 1.84 with VKAs and 2.92 with DOACs), and among those with creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min (IRR, 2.83 with VKAs and 3.71 with DOACs).
The case-fatality rate of major bleeding was 8.3% with VKAs and 9.7% with DOACs.
The study received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Some of the coauthors are employees of or have financial ties to pharmaceutical companies. Mr. Khan, Dr. Rodger, and Dr. Fang had no relevant disclosures.
The meta-analysis of data from 27 studies with 17,202 patients was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine. According to two of the paper’s coauthors, Faizan Khan, MSc, and Marc A. Rodger, MD, it “provides best available estimates of long-term bleeding risk with different anticoagulants in patients with unprovoked VTE,” including subgroups at increased risk.
Patients at increased risk for major bleeding include those who are older; those using antiplatelet therapy; and patients with kidney disease, a history of bleeding, or anemia, noted the coauthors, who work for the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
The researchers focused on randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and prospective cohort studies that reported major bleeding among patients with a first unprovoked or weakly provoked VTE who received oral anticoagulation for at least 6 months beyond an initial anticoagulant treatment course of at least 3 months.
The investigators analyzed data from 14 RCTs and 13 cohort studies. In all, 9,982 patients received a vitamin K antagonist (VKA), and 7,220 received a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC).
The incidence of major bleeding per 100 person-years was 1.7 events with VKAs, compared with 1.1 events with DOACs. The researchers estimated that the 5-year cumulative incidence of major bleeding with VKAs was 6.3%. The available data for DOACs were insufficient to estimate the incidence of major bleeding beyond 1 year.
“This information can help clinicians counsel patients and inform shared decision-making about extended therapy,” the researchers said.
Risks of serious bleeding ‘not trivial’
Margaret Fang, MD, with the University of California, San Francisco, agreed that the study can help clinicians and patients weigh the risks of extended anticoagulation for common types of VTE.
The study also “highlights that the risks of serious bleeding are not trivial” and points out gaps in the literature regarding the long-term use of DOACs for extended VTE therapy, Dr. Fang said.
Better ways to predict which patients will develop bleeding on anticoagulants are needed, Dr. Fang added. “It will also be important to establish which of the various therapies for preventing recurrent VTE – full dose versus lowered dose, or even aspirin – has the best balance of safety and efficacy,” she said.
‘Standardized approach’ for identifying high-risk patients lacking
Clinical practice guidelines recommend indefinite anticoagulation for an unprovoked VTE, except when patients are at high risk of bleeding, the authors noted. But clinicians lack a “standardized approach to identify patients at high risk of bleeding,” Mr. Khan and Dr. Rodger said. “Evidence from randomized trials on net long-term benefit of extended therapy is limited, and current guideline recommendations are largely based on expert consensus opinion. Major bleeding events are two to three times more likely to be fatal than recurrent VTE events, so extended therapy is not always associated with a net mortality benefit, particularly in patients at low risk of recurrent VTE or high risk of bleeding.”
The analysis indicates that there is “a clinically meaningful difference in long-term risk for anticoagulant-related major bleeding among patients with a first unprovoked VTE stratified according to presence or absence of the following risk factors: age older than 65 years, creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min, history of bleeding, concomitant use of antiplatelet therapy, and hemoglobin level less than 100 g/L,” the authors said.
For example, the researchers found that the incidence of major bleeding was higher among those older than 65 years, compared with younger patients (incidence rate ratio, 1.84 with VKAs and 2.92 with DOACs), and among those with creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min (IRR, 2.83 with VKAs and 3.71 with DOACs).
The case-fatality rate of major bleeding was 8.3% with VKAs and 9.7% with DOACs.
The study received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Some of the coauthors are employees of or have financial ties to pharmaceutical companies. Mr. Khan, Dr. Rodger, and Dr. Fang had no relevant disclosures.
The meta-analysis of data from 27 studies with 17,202 patients was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine. According to two of the paper’s coauthors, Faizan Khan, MSc, and Marc A. Rodger, MD, it “provides best available estimates of long-term bleeding risk with different anticoagulants in patients with unprovoked VTE,” including subgroups at increased risk.
Patients at increased risk for major bleeding include those who are older; those using antiplatelet therapy; and patients with kidney disease, a history of bleeding, or anemia, noted the coauthors, who work for the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
The researchers focused on randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and prospective cohort studies that reported major bleeding among patients with a first unprovoked or weakly provoked VTE who received oral anticoagulation for at least 6 months beyond an initial anticoagulant treatment course of at least 3 months.
The investigators analyzed data from 14 RCTs and 13 cohort studies. In all, 9,982 patients received a vitamin K antagonist (VKA), and 7,220 received a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC).
The incidence of major bleeding per 100 person-years was 1.7 events with VKAs, compared with 1.1 events with DOACs. The researchers estimated that the 5-year cumulative incidence of major bleeding with VKAs was 6.3%. The available data for DOACs were insufficient to estimate the incidence of major bleeding beyond 1 year.
“This information can help clinicians counsel patients and inform shared decision-making about extended therapy,” the researchers said.
Risks of serious bleeding ‘not trivial’
Margaret Fang, MD, with the University of California, San Francisco, agreed that the study can help clinicians and patients weigh the risks of extended anticoagulation for common types of VTE.
The study also “highlights that the risks of serious bleeding are not trivial” and points out gaps in the literature regarding the long-term use of DOACs for extended VTE therapy, Dr. Fang said.
Better ways to predict which patients will develop bleeding on anticoagulants are needed, Dr. Fang added. “It will also be important to establish which of the various therapies for preventing recurrent VTE – full dose versus lowered dose, or even aspirin – has the best balance of safety and efficacy,” she said.
‘Standardized approach’ for identifying high-risk patients lacking
Clinical practice guidelines recommend indefinite anticoagulation for an unprovoked VTE, except when patients are at high risk of bleeding, the authors noted. But clinicians lack a “standardized approach to identify patients at high risk of bleeding,” Mr. Khan and Dr. Rodger said. “Evidence from randomized trials on net long-term benefit of extended therapy is limited, and current guideline recommendations are largely based on expert consensus opinion. Major bleeding events are two to three times more likely to be fatal than recurrent VTE events, so extended therapy is not always associated with a net mortality benefit, particularly in patients at low risk of recurrent VTE or high risk of bleeding.”
The analysis indicates that there is “a clinically meaningful difference in long-term risk for anticoagulant-related major bleeding among patients with a first unprovoked VTE stratified according to presence or absence of the following risk factors: age older than 65 years, creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min, history of bleeding, concomitant use of antiplatelet therapy, and hemoglobin level less than 100 g/L,” the authors said.
For example, the researchers found that the incidence of major bleeding was higher among those older than 65 years, compared with younger patients (incidence rate ratio, 1.84 with VKAs and 2.92 with DOACs), and among those with creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min (IRR, 2.83 with VKAs and 3.71 with DOACs).
The case-fatality rate of major bleeding was 8.3% with VKAs and 9.7% with DOACs.
The study received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Some of the coauthors are employees of or have financial ties to pharmaceutical companies. Mr. Khan, Dr. Rodger, and Dr. Fang had no relevant disclosures.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
At 18 months, much still unknown about diabetes and COVID-19
At 18 months into the COVID-19 pandemic, many of the direct and indirect effects of SARS-CoV-2 on people with diabetes have become clearer, but knowledge gaps remain, say epidemiologists.
“COVID-19 has had a devastating effect on the population with diabetes, and conversely, the high prevalence of diabetes and uncontrolled diabetes has exacerbated the problem,” Edward W. Gregg, PhD, Imperial College London, lead author of a new literature review, told this news organization.
“As it becomes clear that the COVID-19 pandemic will be with us in different forms for the foreseeable future, the emphasis for people with diabetes needs to be continued primary care, glycemic management, and vaccination to reduce the long-term impact of COVID-19 in this population,” he added.
In data, mostly from case series, the review shows that more than one-third of people hospitalized with COVID-19 have diabetes. It is published in the September issue of Diabetes Care.
People with diabetes are more than three times as likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than those without diabetes, even after adjustment for age, sex, and other underlying conditions. Diabetes also accounts for 30%-40% of severe COVID-19 cases and deaths. Among those with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19, 21%-43% require intensive care, and the case fatality rate is about 25%.
In one of the few multivariate analyses that examined type 1 and type 2 diabetes separately, conducted in the U.K., the odds of in-hospital COVID-19–related deaths, compared with people without diabetes, were almost three times higher (odds ratio, 2.9) for individuals with type 1 diabetes and almost twice as high (OR, 1.8) for those with type 2, after adjustment for comorbidities.
The causes of death appear to be a combination of factors specific to the SARS-CoV-2 infection and to diabetes-related factors, Dr. Gregg said in an interview.
“Much of the increased risk is due to the fact that people with diabetes have more comorbid factors, but there are many other mechanisms that appear to further increase risk, including the inflammatory and immune responses of people with diabetes, and hyperglycemia appears to have an exacerbating effect by itself.”
Elevated glucose is clear risk factor for COVID-19 severity
Elevated A1c was identified among several other overall predictors of poor COVID-19 outcomes, including obesity as well as comorbid kidney and cardiovascular disease.
High blood glucose levels at the time of admission in people with previously diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes emerged as a clear predictor of worse outcomes. For example, among 605 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in China, those with fasting plasma glucose 6.1-6.9 mmol/L (110-125 mg/dL) and ≥7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) had odds ratios of poor outcomes within 28 days of 2.6 and 4.0 compared with FPG <6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL).
Population-based studies in the U.K. found that A1c levels measured months before COVID-19 hospitalization were associated with risk for intensive care unit admission and/or death, particularly among those with type 1 diabetes. Overall, the death rate was 36% higher for those with A1c of 9%-9.9% versus 6.5%-7%.
Despite the link between high A1c and death, there is as yet no clear evidence that normalizing blood glucose levels minimizes COVID-19 severity, Dr. Gregg said.
“There are data that suggest poor glycemic control is associated with higher risk of poor outcomes. This is indirect evidence that managing blood sugar will help, but more direct evidence is needed.”
Evidence gaps identified
Dr. Gregg and co-authors Marisa Sophiea, PhD, MSc, and Misghina Weldegiorgis, PhD, BSc, also from Imperial College London, identify three areas in which more data are needed.
First, more information is needed to determine whether exposure, infection, and hospitalization risks differ by diabetes status and how those factors affect outcomes. The same studies would also be important to identify how factors such as behavior, masking, and lockdown policies, risk factor control, and household/community environments affect risk in people with diabetes.
Second, studies are needed to better understand indirect effects of the pandemic, such as care and management factors. Some of these, such as the advent of telehealth, may turn out to be beneficial in the long run, they note.
Finally, the pandemic has “brought a wealth of natural experiments,” such as how vaccination programs and other interventions are affecting people with diabetes specifically. Finally, population studies are needed in many parts of the world beyond the U.S. and the U.K., where most of that work has been done thus far.
“Many of the most important unanswered questions lie in the potential indirect and long-term impact of the pandemic that require population-based studies,” Dr. Gregg said. “Most of our knowledge so far is from case series, which only assess patients from the time of hospitalization.”
Indeed, very little data are available for people with diabetes who get COVID-19 but are not hospitalized, so it’s not known whether they have a longer duration of illness or are at greater risk for “long COVID” than those without diabetes who experience COVID-19 at home.
“I have not seen published data on this yet, and it’s an important unanswered question,” Dr. Gregg said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At 18 months into the COVID-19 pandemic, many of the direct and indirect effects of SARS-CoV-2 on people with diabetes have become clearer, but knowledge gaps remain, say epidemiologists.
“COVID-19 has had a devastating effect on the population with diabetes, and conversely, the high prevalence of diabetes and uncontrolled diabetes has exacerbated the problem,” Edward W. Gregg, PhD, Imperial College London, lead author of a new literature review, told this news organization.
“As it becomes clear that the COVID-19 pandemic will be with us in different forms for the foreseeable future, the emphasis for people with diabetes needs to be continued primary care, glycemic management, and vaccination to reduce the long-term impact of COVID-19 in this population,” he added.
In data, mostly from case series, the review shows that more than one-third of people hospitalized with COVID-19 have diabetes. It is published in the September issue of Diabetes Care.
People with diabetes are more than three times as likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than those without diabetes, even after adjustment for age, sex, and other underlying conditions. Diabetes also accounts for 30%-40% of severe COVID-19 cases and deaths. Among those with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19, 21%-43% require intensive care, and the case fatality rate is about 25%.
In one of the few multivariate analyses that examined type 1 and type 2 diabetes separately, conducted in the U.K., the odds of in-hospital COVID-19–related deaths, compared with people without diabetes, were almost three times higher (odds ratio, 2.9) for individuals with type 1 diabetes and almost twice as high (OR, 1.8) for those with type 2, after adjustment for comorbidities.
The causes of death appear to be a combination of factors specific to the SARS-CoV-2 infection and to diabetes-related factors, Dr. Gregg said in an interview.
“Much of the increased risk is due to the fact that people with diabetes have more comorbid factors, but there are many other mechanisms that appear to further increase risk, including the inflammatory and immune responses of people with diabetes, and hyperglycemia appears to have an exacerbating effect by itself.”
Elevated glucose is clear risk factor for COVID-19 severity
Elevated A1c was identified among several other overall predictors of poor COVID-19 outcomes, including obesity as well as comorbid kidney and cardiovascular disease.
High blood glucose levels at the time of admission in people with previously diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes emerged as a clear predictor of worse outcomes. For example, among 605 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in China, those with fasting plasma glucose 6.1-6.9 mmol/L (110-125 mg/dL) and ≥7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) had odds ratios of poor outcomes within 28 days of 2.6 and 4.0 compared with FPG <6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL).
Population-based studies in the U.K. found that A1c levels measured months before COVID-19 hospitalization were associated with risk for intensive care unit admission and/or death, particularly among those with type 1 diabetes. Overall, the death rate was 36% higher for those with A1c of 9%-9.9% versus 6.5%-7%.
Despite the link between high A1c and death, there is as yet no clear evidence that normalizing blood glucose levels minimizes COVID-19 severity, Dr. Gregg said.
“There are data that suggest poor glycemic control is associated with higher risk of poor outcomes. This is indirect evidence that managing blood sugar will help, but more direct evidence is needed.”
Evidence gaps identified
Dr. Gregg and co-authors Marisa Sophiea, PhD, MSc, and Misghina Weldegiorgis, PhD, BSc, also from Imperial College London, identify three areas in which more data are needed.
First, more information is needed to determine whether exposure, infection, and hospitalization risks differ by diabetes status and how those factors affect outcomes. The same studies would also be important to identify how factors such as behavior, masking, and lockdown policies, risk factor control, and household/community environments affect risk in people with diabetes.
Second, studies are needed to better understand indirect effects of the pandemic, such as care and management factors. Some of these, such as the advent of telehealth, may turn out to be beneficial in the long run, they note.
Finally, the pandemic has “brought a wealth of natural experiments,” such as how vaccination programs and other interventions are affecting people with diabetes specifically. Finally, population studies are needed in many parts of the world beyond the U.S. and the U.K., where most of that work has been done thus far.
“Many of the most important unanswered questions lie in the potential indirect and long-term impact of the pandemic that require population-based studies,” Dr. Gregg said. “Most of our knowledge so far is from case series, which only assess patients from the time of hospitalization.”
Indeed, very little data are available for people with diabetes who get COVID-19 but are not hospitalized, so it’s not known whether they have a longer duration of illness or are at greater risk for “long COVID” than those without diabetes who experience COVID-19 at home.
“I have not seen published data on this yet, and it’s an important unanswered question,” Dr. Gregg said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At 18 months into the COVID-19 pandemic, many of the direct and indirect effects of SARS-CoV-2 on people with diabetes have become clearer, but knowledge gaps remain, say epidemiologists.
“COVID-19 has had a devastating effect on the population with diabetes, and conversely, the high prevalence of diabetes and uncontrolled diabetes has exacerbated the problem,” Edward W. Gregg, PhD, Imperial College London, lead author of a new literature review, told this news organization.
“As it becomes clear that the COVID-19 pandemic will be with us in different forms for the foreseeable future, the emphasis for people with diabetes needs to be continued primary care, glycemic management, and vaccination to reduce the long-term impact of COVID-19 in this population,” he added.
In data, mostly from case series, the review shows that more than one-third of people hospitalized with COVID-19 have diabetes. It is published in the September issue of Diabetes Care.
People with diabetes are more than three times as likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19 than those without diabetes, even after adjustment for age, sex, and other underlying conditions. Diabetes also accounts for 30%-40% of severe COVID-19 cases and deaths. Among those with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19, 21%-43% require intensive care, and the case fatality rate is about 25%.
In one of the few multivariate analyses that examined type 1 and type 2 diabetes separately, conducted in the U.K., the odds of in-hospital COVID-19–related deaths, compared with people without diabetes, were almost three times higher (odds ratio, 2.9) for individuals with type 1 diabetes and almost twice as high (OR, 1.8) for those with type 2, after adjustment for comorbidities.
The causes of death appear to be a combination of factors specific to the SARS-CoV-2 infection and to diabetes-related factors, Dr. Gregg said in an interview.
“Much of the increased risk is due to the fact that people with diabetes have more comorbid factors, but there are many other mechanisms that appear to further increase risk, including the inflammatory and immune responses of people with diabetes, and hyperglycemia appears to have an exacerbating effect by itself.”
Elevated glucose is clear risk factor for COVID-19 severity
Elevated A1c was identified among several other overall predictors of poor COVID-19 outcomes, including obesity as well as comorbid kidney and cardiovascular disease.
High blood glucose levels at the time of admission in people with previously diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes emerged as a clear predictor of worse outcomes. For example, among 605 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in China, those with fasting plasma glucose 6.1-6.9 mmol/L (110-125 mg/dL) and ≥7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) had odds ratios of poor outcomes within 28 days of 2.6 and 4.0 compared with FPG <6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL).
Population-based studies in the U.K. found that A1c levels measured months before COVID-19 hospitalization were associated with risk for intensive care unit admission and/or death, particularly among those with type 1 diabetes. Overall, the death rate was 36% higher for those with A1c of 9%-9.9% versus 6.5%-7%.
Despite the link between high A1c and death, there is as yet no clear evidence that normalizing blood glucose levels minimizes COVID-19 severity, Dr. Gregg said.
“There are data that suggest poor glycemic control is associated with higher risk of poor outcomes. This is indirect evidence that managing blood sugar will help, but more direct evidence is needed.”
Evidence gaps identified
Dr. Gregg and co-authors Marisa Sophiea, PhD, MSc, and Misghina Weldegiorgis, PhD, BSc, also from Imperial College London, identify three areas in which more data are needed.
First, more information is needed to determine whether exposure, infection, and hospitalization risks differ by diabetes status and how those factors affect outcomes. The same studies would also be important to identify how factors such as behavior, masking, and lockdown policies, risk factor control, and household/community environments affect risk in people with diabetes.
Second, studies are needed to better understand indirect effects of the pandemic, such as care and management factors. Some of these, such as the advent of telehealth, may turn out to be beneficial in the long run, they note.
Finally, the pandemic has “brought a wealth of natural experiments,” such as how vaccination programs and other interventions are affecting people with diabetes specifically. Finally, population studies are needed in many parts of the world beyond the U.S. and the U.K., where most of that work has been done thus far.
“Many of the most important unanswered questions lie in the potential indirect and long-term impact of the pandemic that require population-based studies,” Dr. Gregg said. “Most of our knowledge so far is from case series, which only assess patients from the time of hospitalization.”
Indeed, very little data are available for people with diabetes who get COVID-19 but are not hospitalized, so it’s not known whether they have a longer duration of illness or are at greater risk for “long COVID” than those without diabetes who experience COVID-19 at home.
“I have not seen published data on this yet, and it’s an important unanswered question,” Dr. Gregg said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How an ‘ad hoc’ hospitalist model evolved during India’s COVID surge
Hospital administrators recognize the efficiencies
A year after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, as the United States was getting a reprieve in new cases from its winter surge, the opposite was happening in the rest of the world. In India, a deadly second wave hit, crippling the health care system in the country for months.
Yugandhar Bhatt, MBBS, MD, a consultant pulmonologist with Yashoda Hospital–Malakpet in Hyderabad, India, told this news organization that someone looking at his hospital before the pandemic – a 400-bed multispecialty care unit – would see patients being treated for respiratory failure secondary to exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma, community-acquired pneumonia, and heart failure. About 30-40 patients per day were treated on an outpatient basis, and more than 30 people were admitted as inpatients.
“After [the] COVID-19 surge, our hospital totally divided into COVID and non-COVID [wards], in which COVID patients occupied 70% of [the] total,” he said. About half of COVID-19 patients were in the ICU, with half of those patients requiring supplemental oxygen.
During the first wave in India, which lasted from May to December 2020, 50% of patients who were intubated were discharged. The percentage of extubated patients decreased to 20% in the second wave, Dr. Bhatt said.
The death toll during the second wave of COVID-19 cases was unlike anything India has seen previously. Between March 1 and June 29, 2021, an estimated 19.24 million individuals were newly infected with COVID-19 and 241,206 patients died, according to Our World in Data, a project of the Global Change Data Lab. When the second wave peaked on May 22, more than 4,000 people were dying each day.
“All hospitals [in India] were treating COVID-19 more than any other acute or chronic disease,” Ramesh Adhikari, MD, MS, SFHM, a hospitalist with Franciscan Health in Lafayette, Ind., said in an interview.
Challenges arose in treating COVID-19 in India that ran counter to how medicine was usually performed. Physicians were seeing more inpatient cases than usual – and more patients in general. The change, Dr. Adhikari said, forced health care providers to think outside the box.
An ‘on-the-fly’ hospitalist model
Patients in India access health care by visiting a hospital or primary health center and then are referred out to consultants – specialist doctors – if needed. While India has universal health coverage, it is a multi-payer system that includes approximately 37% of the population covered under the government plan, a large number of private health care facilities and no caps on cost-sharing for the patient. Initiatives like Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana in 2008 and Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana in 2018 have attempted to close the gap and raise the number of lower-income individuals in India covered under the government plan and reduce out-of-pocket spending. Out-of-pocket payments still consist of about 70% of total health expenditures, according to the Commonwealth Fund.
“There is not much scope for a hospitalist because it’s so cash driven,” Shyam Odeti, MD, SFHM, section chief, hospital medicine, at the Carilion Clinic in Roanoke, Va., said in an interview. “For a hospitalist, there is no urgency in getting them out of the hospital. There was no need for much efficiency before.”
The first issue during the second wave was figuring out which consultants would care for COVID-19 patients. As there is no dedicated specialty for infectious disease in India, the responsibilities fell to internists and critical care medicine consultants who volunteered. Both are considered small specialties in India. They became “makeshift hospitalists” who learned as they went and became the experts in COVID-19 care, treating their own patients while making themselves available for consultations, Dr. Odeti said.
While no official hospital medicine model in India exists like in the United States, the second COVID-19 surge caused these consultants to begin thinking like hospitalists. Tenets of hospital medicine – like team-based treatment across specialties – arose out of necessity during the crisis. “They were trying to implement a hospitalist model because that’s the only way they could treat COVID-19,” said Dr. Adhikari, an editorial advisory board member for the Hospitalist.
“Even in the U.S. when we started the hospitalist model, it started out of necessity. It’s a combination of creating efficiencies and improving quality,” Dr. Odeti said. “It’s the same thing in India. It’s borne of necessity, but it was [done] at a rapid pace.”
Problems with patient flow
The next issue was triaging patients in the hospital based on COVID-19 severity. When the second wave began, hospitals in India ran out of beds and experienced staff shortages like in many countries. But this situation “was unusual for the health system,” according to Dr. Odeti, who is also an editorial board member for the Hospitalist.
“We never had that issue. There were so many patients wanting to come to the hospital, and so there was this rush.” There was no process to triage patients to determine who needed to stay. “Everybody got put into the hospital,” he said.
Once it was determined who would take care of patients with COVID-19, access to supplies became the primary problem, Dr. Adhikari explained. Lack of oxygen, ventilators, and critical medicines like the antiviral drug remdesivir were and continue to be in short supply. “I had friends who [said] they could not admit patients because they were worried if their oxygen supply [went] low in the middle of the night. They will treat the patients who were already admitted versus taking new patients. That had caused problems for the administrators,” Dr. Adhikari added.
It is also a source of additional stress for the physicians. Where patients flow through a hospital medicine model in the United States, a system that might include case managers, social workers, pharmacists, physician advocates, and other professionals to keep a patient’s care on track, the physician is the go-to person in India for patient care. While physicians provide access to medications and remain available to a patient’s family, those duties become much harder when caring for a greater number of patients during the pandemic. “That has led to some unrealistic expectations among the patients,” Dr. Adhikari said.
Dr. Bhatt said “more than half” of a physician’s time in India is spent counseling patients on concerns about COVID-19. “Awareness about the disease is limited from the patient and patient’s family perspective, as [there is] too much apprehension toward the nature of [the] disease,” he added. “Theoretical discussions collected from social media” obstruct the physician from executing his or her duties.
Physicians in India have had to contend with physical violence from patients and individuals on the street, Dr. Adhikari added. Workplace violence was already a concern – for years, the Indian Medical Association has cited a statistic that 75% of doctors in India have experienced violence at work (Indian J Psychiatry. 2019 Apr;61[Suppl 4]:S782-5). But the threat of violence against physicians has sharply increased during the COVID-19 pandemic. Disruptions to daily life through lockdowns “made people fearful, anxious, and sometimes they have found it difficult to access emergency treatment,” according to a letter published by Karthikeyan Iyengar and colleagues in the Postgraduate Medical Journal. In response to the restlessness, irritation, and despair resulting from hospitals closing their doors, “people have shown their frustration by verbally abusing and threatening to physically assault doctors and other health care workers,” the authors wrote.
A telemedicine boon in India
Back in the United States, hospitalists with family and friends in India were trying to figure out how to help. Some were working through the day, only to answer calls and WhatsApp messages from loved ones at night. “Everyone knows a physician or someone who’s your colleague, who owns a hospital or runs a hospital, or one of the family members is sick,” Dr. Adhikari said.
These U.S.-based hospitalists were burning the candle at both ends, helping with the pandemic in both countries. Physicians in India were posing questions to U.S. colleagues who they saw as having the most recent evidence for COVID-19 treatment. Out of the 180 physicians he trained with in India, Dr. Odeti said 110 of the physicians were in a large WhatsApp group chat that was constantly exchanging messages and serving as “kind of a friendly support group.”
In Dr. Odeti’s group chat, physicians helped one another find hospital beds for patients who reached out to them. “The first couple of weeks, there was no proper way for people to know where [patients] were based. There was no way to find if this hospital had a bed, so they reached out to any doctors they knew,” he said.
While he said it was emotionally draining, “at the same time, we felt a responsibility toward colleagues in India,” Dr. Odeti said, noting that as COVID-19 cases have decreased in India, the requests have been less frequent.
Because of concerns about traveling to India during the pandemic while on a J-1, H-1B, or other visa with the United States, directly helping friends and family in India seemed out of reach. But many hospitalists of Indian origin instead turned to telemedicine to help their colleagues. Telemedicine had already been steadily growing in India, but was accelerated by the pandemic. The current ratio of doctors to patients in India is 0.62 to 1,000 – lower than recommendations from the World Health Organization. That makes telemedicine a unique opportunity for one physician in India to reach many patients regardless of location.
Dr. Adhikari said he helped out his colleagues in India by performing consults for their patients. “They were just worried because they did not ‘know where to go, or what to get,” he said. “I was treating more patients in India than I was actually treating here.”
In March 2020, the Indian Ministry of Health and Family Welfare released telemedicine practice guidelines for the country, which relaxed regulations on privacy requirements and has been credited in part for giving telemedicine an additional boost during the pandemic. “That makes it easy for people to reach out but also has its own problems,” Dr. Adhikari said.
Monitoring of milder COVID-19 cases that don’t require hospitalization can be performed by a nurse who calls every few hours to check on a patient, make recommendations, and text treatment plans. “The telemedicine platforms are being adopted really fast,” Dr. Adhikari said. “The platforms were built in no time.”
According to NewZoo, a games market data analytics company, India has 345.9 million smartphone users as of 2019 – the second highest number of users in the world after China. Dr. Odeti said he believes telemedicine will be widely adopted.
“In India, they are very proactive in accepting these kinds of methods, so I’m sure they will,” he said. “Governments were trying to do it before the pandemic, because access to care is a problem in India. There are villages which are very, very remote.”
Reversion to old systems
After the peak in late May, new COVID-19 cases in India began to decrease, and the second wave waned on a national level. Hospitals began to get the supplies they needed, beds are available, and patients aren’t as sick as before, according to Dr. Adhikari. The federal government has begun issuing supplies to patients in each state, including COVID-19 vaccines. “The peak for the second wave is gone,” he said.
What remains is a group of physicians trained in how to triage patients and create efficiencies in a hospital setting. Could those skills be put to use elsewhere in India after the pandemic?
According to Dr. Bhatt, the patient care model is likely to revert to the system that existed before. “Whatever the changes, interims of bed occupancy, cost of ICU will be temporary [and] will change to normal,” he said. “But awareness about masks [and] sanitizing methods will be permanent.”
Dr. Adhikari believes that not utilizing the skills of newly minted hospitalists in India would be a missed opportunity. “This is a silver lining from COVID-19, that hospital medicine plays a vital role in the sickest patients, whether it is in India or the U.S. or anywhere,” he said. “I think the model of hospital medicine should be adopted. It’s not: ‘Should it really be adopted or not?’ It should be. There is a huge potential in doing inpatient coordinated [care], having people dedicated in the hospital.”
There are tangible benefits to creating efficiencies in India’s health system, Dr. Odeti said. Length of stay for sicker patients “was much longer” at 10-14 days during the second wave, compared with the United States, before lowering to around 5 days. “These hospitals right now are learning the efficient ways of doing it: when to send [patients] out, how to send them out, how to [perform] service-based practices, creating processes which were nonexistent before.”
While he doesn’t personally believe physicians will adopt a full-fledged hospitalist model unless the payer structure in India changes, “these people are at an advantage with this extra set of skills,” he said. “I think all the knowledge that these people have are going to come in handy.”
Opportunities for growth
Dr. Odeti sees the potential for the hospitalist model to grow in India – if not into its own specialty, then in how critical care consultants handle sicker patients and handoffs.
“The critical care clinician cannot keep the patient from the time they are admitted to the ICU until the discharge, so there will be a need for the transition,” Dr. Odeti said. “In the past, there were not many capabilities in Indian health systems to take care of these extremely sick patients, and now it is evolving. I think that is one more thing that will help.”
Dr. Adhikari said hospital systems in India are beginning to realize how having dedicated hospital physicians could benefit them. In India, “if you’re sick, you go to your doctor, you get treated and you disappear,” he said. The next time, you may see the same doctor or a completely different doctor. “There’s no system there, so it’s really hard for hospital medicine as such because patients, when they are very sick, they just come to the ER. They’re not followed by their primary care.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Odeti sees patients already adapting to having access to a physician for asking questions normally answered by primary care physicians. “I think primary care will come into play,” he said. “When I was doing a Zoom call for patients, they were asking me questions about sciatica. I think they are getting comfortable with this technology.”
A hospitalist model could even be applied to specific diseases with a large population of patients. Hospital administrators “have seen this for the first time, how efficient it could be if they had their own hospitalists and actually run it. So that’s the part that has crossed their minds,” Dr. Adhikari said. “How they will apply it going forward, other than during the COVID-19 pandemic, depends on the size of the hospital and the volume of the patients for a particular disease.”
“You can see in certain areas there is large growth for hospital medicine. But to rise to the level of the United States and how we do it, India needs bigger health systems to adopt the model,” Dr. Adhikari said.
Hospital administrators recognize the efficiencies
Hospital administrators recognize the efficiencies
A year after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, as the United States was getting a reprieve in new cases from its winter surge, the opposite was happening in the rest of the world. In India, a deadly second wave hit, crippling the health care system in the country for months.
Yugandhar Bhatt, MBBS, MD, a consultant pulmonologist with Yashoda Hospital–Malakpet in Hyderabad, India, told this news organization that someone looking at his hospital before the pandemic – a 400-bed multispecialty care unit – would see patients being treated for respiratory failure secondary to exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma, community-acquired pneumonia, and heart failure. About 30-40 patients per day were treated on an outpatient basis, and more than 30 people were admitted as inpatients.
“After [the] COVID-19 surge, our hospital totally divided into COVID and non-COVID [wards], in which COVID patients occupied 70% of [the] total,” he said. About half of COVID-19 patients were in the ICU, with half of those patients requiring supplemental oxygen.
During the first wave in India, which lasted from May to December 2020, 50% of patients who were intubated were discharged. The percentage of extubated patients decreased to 20% in the second wave, Dr. Bhatt said.
The death toll during the second wave of COVID-19 cases was unlike anything India has seen previously. Between March 1 and June 29, 2021, an estimated 19.24 million individuals were newly infected with COVID-19 and 241,206 patients died, according to Our World in Data, a project of the Global Change Data Lab. When the second wave peaked on May 22, more than 4,000 people were dying each day.
“All hospitals [in India] were treating COVID-19 more than any other acute or chronic disease,” Ramesh Adhikari, MD, MS, SFHM, a hospitalist with Franciscan Health in Lafayette, Ind., said in an interview.
Challenges arose in treating COVID-19 in India that ran counter to how medicine was usually performed. Physicians were seeing more inpatient cases than usual – and more patients in general. The change, Dr. Adhikari said, forced health care providers to think outside the box.
An ‘on-the-fly’ hospitalist model
Patients in India access health care by visiting a hospital or primary health center and then are referred out to consultants – specialist doctors – if needed. While India has universal health coverage, it is a multi-payer system that includes approximately 37% of the population covered under the government plan, a large number of private health care facilities and no caps on cost-sharing for the patient. Initiatives like Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana in 2008 and Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana in 2018 have attempted to close the gap and raise the number of lower-income individuals in India covered under the government plan and reduce out-of-pocket spending. Out-of-pocket payments still consist of about 70% of total health expenditures, according to the Commonwealth Fund.
“There is not much scope for a hospitalist because it’s so cash driven,” Shyam Odeti, MD, SFHM, section chief, hospital medicine, at the Carilion Clinic in Roanoke, Va., said in an interview. “For a hospitalist, there is no urgency in getting them out of the hospital. There was no need for much efficiency before.”
The first issue during the second wave was figuring out which consultants would care for COVID-19 patients. As there is no dedicated specialty for infectious disease in India, the responsibilities fell to internists and critical care medicine consultants who volunteered. Both are considered small specialties in India. They became “makeshift hospitalists” who learned as they went and became the experts in COVID-19 care, treating their own patients while making themselves available for consultations, Dr. Odeti said.
While no official hospital medicine model in India exists like in the United States, the second COVID-19 surge caused these consultants to begin thinking like hospitalists. Tenets of hospital medicine – like team-based treatment across specialties – arose out of necessity during the crisis. “They were trying to implement a hospitalist model because that’s the only way they could treat COVID-19,” said Dr. Adhikari, an editorial advisory board member for the Hospitalist.
“Even in the U.S. when we started the hospitalist model, it started out of necessity. It’s a combination of creating efficiencies and improving quality,” Dr. Odeti said. “It’s the same thing in India. It’s borne of necessity, but it was [done] at a rapid pace.”
Problems with patient flow
The next issue was triaging patients in the hospital based on COVID-19 severity. When the second wave began, hospitals in India ran out of beds and experienced staff shortages like in many countries. But this situation “was unusual for the health system,” according to Dr. Odeti, who is also an editorial board member for the Hospitalist.
“We never had that issue. There were so many patients wanting to come to the hospital, and so there was this rush.” There was no process to triage patients to determine who needed to stay. “Everybody got put into the hospital,” he said.
Once it was determined who would take care of patients with COVID-19, access to supplies became the primary problem, Dr. Adhikari explained. Lack of oxygen, ventilators, and critical medicines like the antiviral drug remdesivir were and continue to be in short supply. “I had friends who [said] they could not admit patients because they were worried if their oxygen supply [went] low in the middle of the night. They will treat the patients who were already admitted versus taking new patients. That had caused problems for the administrators,” Dr. Adhikari added.
It is also a source of additional stress for the physicians. Where patients flow through a hospital medicine model in the United States, a system that might include case managers, social workers, pharmacists, physician advocates, and other professionals to keep a patient’s care on track, the physician is the go-to person in India for patient care. While physicians provide access to medications and remain available to a patient’s family, those duties become much harder when caring for a greater number of patients during the pandemic. “That has led to some unrealistic expectations among the patients,” Dr. Adhikari said.
Dr. Bhatt said “more than half” of a physician’s time in India is spent counseling patients on concerns about COVID-19. “Awareness about the disease is limited from the patient and patient’s family perspective, as [there is] too much apprehension toward the nature of [the] disease,” he added. “Theoretical discussions collected from social media” obstruct the physician from executing his or her duties.
Physicians in India have had to contend with physical violence from patients and individuals on the street, Dr. Adhikari added. Workplace violence was already a concern – for years, the Indian Medical Association has cited a statistic that 75% of doctors in India have experienced violence at work (Indian J Psychiatry. 2019 Apr;61[Suppl 4]:S782-5). But the threat of violence against physicians has sharply increased during the COVID-19 pandemic. Disruptions to daily life through lockdowns “made people fearful, anxious, and sometimes they have found it difficult to access emergency treatment,” according to a letter published by Karthikeyan Iyengar and colleagues in the Postgraduate Medical Journal. In response to the restlessness, irritation, and despair resulting from hospitals closing their doors, “people have shown their frustration by verbally abusing and threatening to physically assault doctors and other health care workers,” the authors wrote.
A telemedicine boon in India
Back in the United States, hospitalists with family and friends in India were trying to figure out how to help. Some were working through the day, only to answer calls and WhatsApp messages from loved ones at night. “Everyone knows a physician or someone who’s your colleague, who owns a hospital or runs a hospital, or one of the family members is sick,” Dr. Adhikari said.
These U.S.-based hospitalists were burning the candle at both ends, helping with the pandemic in both countries. Physicians in India were posing questions to U.S. colleagues who they saw as having the most recent evidence for COVID-19 treatment. Out of the 180 physicians he trained with in India, Dr. Odeti said 110 of the physicians were in a large WhatsApp group chat that was constantly exchanging messages and serving as “kind of a friendly support group.”
In Dr. Odeti’s group chat, physicians helped one another find hospital beds for patients who reached out to them. “The first couple of weeks, there was no proper way for people to know where [patients] were based. There was no way to find if this hospital had a bed, so they reached out to any doctors they knew,” he said.
While he said it was emotionally draining, “at the same time, we felt a responsibility toward colleagues in India,” Dr. Odeti said, noting that as COVID-19 cases have decreased in India, the requests have been less frequent.
Because of concerns about traveling to India during the pandemic while on a J-1, H-1B, or other visa with the United States, directly helping friends and family in India seemed out of reach. But many hospitalists of Indian origin instead turned to telemedicine to help their colleagues. Telemedicine had already been steadily growing in India, but was accelerated by the pandemic. The current ratio of doctors to patients in India is 0.62 to 1,000 – lower than recommendations from the World Health Organization. That makes telemedicine a unique opportunity for one physician in India to reach many patients regardless of location.
Dr. Adhikari said he helped out his colleagues in India by performing consults for their patients. “They were just worried because they did not ‘know where to go, or what to get,” he said. “I was treating more patients in India than I was actually treating here.”
In March 2020, the Indian Ministry of Health and Family Welfare released telemedicine practice guidelines for the country, which relaxed regulations on privacy requirements and has been credited in part for giving telemedicine an additional boost during the pandemic. “That makes it easy for people to reach out but also has its own problems,” Dr. Adhikari said.
Monitoring of milder COVID-19 cases that don’t require hospitalization can be performed by a nurse who calls every few hours to check on a patient, make recommendations, and text treatment plans. “The telemedicine platforms are being adopted really fast,” Dr. Adhikari said. “The platforms were built in no time.”
According to NewZoo, a games market data analytics company, India has 345.9 million smartphone users as of 2019 – the second highest number of users in the world after China. Dr. Odeti said he believes telemedicine will be widely adopted.
“In India, they are very proactive in accepting these kinds of methods, so I’m sure they will,” he said. “Governments were trying to do it before the pandemic, because access to care is a problem in India. There are villages which are very, very remote.”
Reversion to old systems
After the peak in late May, new COVID-19 cases in India began to decrease, and the second wave waned on a national level. Hospitals began to get the supplies they needed, beds are available, and patients aren’t as sick as before, according to Dr. Adhikari. The federal government has begun issuing supplies to patients in each state, including COVID-19 vaccines. “The peak for the second wave is gone,” he said.
What remains is a group of physicians trained in how to triage patients and create efficiencies in a hospital setting. Could those skills be put to use elsewhere in India after the pandemic?
According to Dr. Bhatt, the patient care model is likely to revert to the system that existed before. “Whatever the changes, interims of bed occupancy, cost of ICU will be temporary [and] will change to normal,” he said. “But awareness about masks [and] sanitizing methods will be permanent.”
Dr. Adhikari believes that not utilizing the skills of newly minted hospitalists in India would be a missed opportunity. “This is a silver lining from COVID-19, that hospital medicine plays a vital role in the sickest patients, whether it is in India or the U.S. or anywhere,” he said. “I think the model of hospital medicine should be adopted. It’s not: ‘Should it really be adopted or not?’ It should be. There is a huge potential in doing inpatient coordinated [care], having people dedicated in the hospital.”
There are tangible benefits to creating efficiencies in India’s health system, Dr. Odeti said. Length of stay for sicker patients “was much longer” at 10-14 days during the second wave, compared with the United States, before lowering to around 5 days. “These hospitals right now are learning the efficient ways of doing it: when to send [patients] out, how to send them out, how to [perform] service-based practices, creating processes which were nonexistent before.”
While he doesn’t personally believe physicians will adopt a full-fledged hospitalist model unless the payer structure in India changes, “these people are at an advantage with this extra set of skills,” he said. “I think all the knowledge that these people have are going to come in handy.”
Opportunities for growth
Dr. Odeti sees the potential for the hospitalist model to grow in India – if not into its own specialty, then in how critical care consultants handle sicker patients and handoffs.
“The critical care clinician cannot keep the patient from the time they are admitted to the ICU until the discharge, so there will be a need for the transition,” Dr. Odeti said. “In the past, there were not many capabilities in Indian health systems to take care of these extremely sick patients, and now it is evolving. I think that is one more thing that will help.”
Dr. Adhikari said hospital systems in India are beginning to realize how having dedicated hospital physicians could benefit them. In India, “if you’re sick, you go to your doctor, you get treated and you disappear,” he said. The next time, you may see the same doctor or a completely different doctor. “There’s no system there, so it’s really hard for hospital medicine as such because patients, when they are very sick, they just come to the ER. They’re not followed by their primary care.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Odeti sees patients already adapting to having access to a physician for asking questions normally answered by primary care physicians. “I think primary care will come into play,” he said. “When I was doing a Zoom call for patients, they were asking me questions about sciatica. I think they are getting comfortable with this technology.”
A hospitalist model could even be applied to specific diseases with a large population of patients. Hospital administrators “have seen this for the first time, how efficient it could be if they had their own hospitalists and actually run it. So that’s the part that has crossed their minds,” Dr. Adhikari said. “How they will apply it going forward, other than during the COVID-19 pandemic, depends on the size of the hospital and the volume of the patients for a particular disease.”
“You can see in certain areas there is large growth for hospital medicine. But to rise to the level of the United States and how we do it, India needs bigger health systems to adopt the model,” Dr. Adhikari said.
A year after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, as the United States was getting a reprieve in new cases from its winter surge, the opposite was happening in the rest of the world. In India, a deadly second wave hit, crippling the health care system in the country for months.
Yugandhar Bhatt, MBBS, MD, a consultant pulmonologist with Yashoda Hospital–Malakpet in Hyderabad, India, told this news organization that someone looking at his hospital before the pandemic – a 400-bed multispecialty care unit – would see patients being treated for respiratory failure secondary to exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma, community-acquired pneumonia, and heart failure. About 30-40 patients per day were treated on an outpatient basis, and more than 30 people were admitted as inpatients.
“After [the] COVID-19 surge, our hospital totally divided into COVID and non-COVID [wards], in which COVID patients occupied 70% of [the] total,” he said. About half of COVID-19 patients were in the ICU, with half of those patients requiring supplemental oxygen.
During the first wave in India, which lasted from May to December 2020, 50% of patients who were intubated were discharged. The percentage of extubated patients decreased to 20% in the second wave, Dr. Bhatt said.
The death toll during the second wave of COVID-19 cases was unlike anything India has seen previously. Between March 1 and June 29, 2021, an estimated 19.24 million individuals were newly infected with COVID-19 and 241,206 patients died, according to Our World in Data, a project of the Global Change Data Lab. When the second wave peaked on May 22, more than 4,000 people were dying each day.
“All hospitals [in India] were treating COVID-19 more than any other acute or chronic disease,” Ramesh Adhikari, MD, MS, SFHM, a hospitalist with Franciscan Health in Lafayette, Ind., said in an interview.
Challenges arose in treating COVID-19 in India that ran counter to how medicine was usually performed. Physicians were seeing more inpatient cases than usual – and more patients in general. The change, Dr. Adhikari said, forced health care providers to think outside the box.
An ‘on-the-fly’ hospitalist model
Patients in India access health care by visiting a hospital or primary health center and then are referred out to consultants – specialist doctors – if needed. While India has universal health coverage, it is a multi-payer system that includes approximately 37% of the population covered under the government plan, a large number of private health care facilities and no caps on cost-sharing for the patient. Initiatives like Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana in 2008 and Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana in 2018 have attempted to close the gap and raise the number of lower-income individuals in India covered under the government plan and reduce out-of-pocket spending. Out-of-pocket payments still consist of about 70% of total health expenditures, according to the Commonwealth Fund.
“There is not much scope for a hospitalist because it’s so cash driven,” Shyam Odeti, MD, SFHM, section chief, hospital medicine, at the Carilion Clinic in Roanoke, Va., said in an interview. “For a hospitalist, there is no urgency in getting them out of the hospital. There was no need for much efficiency before.”
The first issue during the second wave was figuring out which consultants would care for COVID-19 patients. As there is no dedicated specialty for infectious disease in India, the responsibilities fell to internists and critical care medicine consultants who volunteered. Both are considered small specialties in India. They became “makeshift hospitalists” who learned as they went and became the experts in COVID-19 care, treating their own patients while making themselves available for consultations, Dr. Odeti said.
While no official hospital medicine model in India exists like in the United States, the second COVID-19 surge caused these consultants to begin thinking like hospitalists. Tenets of hospital medicine – like team-based treatment across specialties – arose out of necessity during the crisis. “They were trying to implement a hospitalist model because that’s the only way they could treat COVID-19,” said Dr. Adhikari, an editorial advisory board member for the Hospitalist.
“Even in the U.S. when we started the hospitalist model, it started out of necessity. It’s a combination of creating efficiencies and improving quality,” Dr. Odeti said. “It’s the same thing in India. It’s borne of necessity, but it was [done] at a rapid pace.”
Problems with patient flow
The next issue was triaging patients in the hospital based on COVID-19 severity. When the second wave began, hospitals in India ran out of beds and experienced staff shortages like in many countries. But this situation “was unusual for the health system,” according to Dr. Odeti, who is also an editorial board member for the Hospitalist.
“We never had that issue. There were so many patients wanting to come to the hospital, and so there was this rush.” There was no process to triage patients to determine who needed to stay. “Everybody got put into the hospital,” he said.
Once it was determined who would take care of patients with COVID-19, access to supplies became the primary problem, Dr. Adhikari explained. Lack of oxygen, ventilators, and critical medicines like the antiviral drug remdesivir were and continue to be in short supply. “I had friends who [said] they could not admit patients because they were worried if their oxygen supply [went] low in the middle of the night. They will treat the patients who were already admitted versus taking new patients. That had caused problems for the administrators,” Dr. Adhikari added.
It is also a source of additional stress for the physicians. Where patients flow through a hospital medicine model in the United States, a system that might include case managers, social workers, pharmacists, physician advocates, and other professionals to keep a patient’s care on track, the physician is the go-to person in India for patient care. While physicians provide access to medications and remain available to a patient’s family, those duties become much harder when caring for a greater number of patients during the pandemic. “That has led to some unrealistic expectations among the patients,” Dr. Adhikari said.
Dr. Bhatt said “more than half” of a physician’s time in India is spent counseling patients on concerns about COVID-19. “Awareness about the disease is limited from the patient and patient’s family perspective, as [there is] too much apprehension toward the nature of [the] disease,” he added. “Theoretical discussions collected from social media” obstruct the physician from executing his or her duties.
Physicians in India have had to contend with physical violence from patients and individuals on the street, Dr. Adhikari added. Workplace violence was already a concern – for years, the Indian Medical Association has cited a statistic that 75% of doctors in India have experienced violence at work (Indian J Psychiatry. 2019 Apr;61[Suppl 4]:S782-5). But the threat of violence against physicians has sharply increased during the COVID-19 pandemic. Disruptions to daily life through lockdowns “made people fearful, anxious, and sometimes they have found it difficult to access emergency treatment,” according to a letter published by Karthikeyan Iyengar and colleagues in the Postgraduate Medical Journal. In response to the restlessness, irritation, and despair resulting from hospitals closing their doors, “people have shown their frustration by verbally abusing and threatening to physically assault doctors and other health care workers,” the authors wrote.
A telemedicine boon in India
Back in the United States, hospitalists with family and friends in India were trying to figure out how to help. Some were working through the day, only to answer calls and WhatsApp messages from loved ones at night. “Everyone knows a physician or someone who’s your colleague, who owns a hospital or runs a hospital, or one of the family members is sick,” Dr. Adhikari said.
These U.S.-based hospitalists were burning the candle at both ends, helping with the pandemic in both countries. Physicians in India were posing questions to U.S. colleagues who they saw as having the most recent evidence for COVID-19 treatment. Out of the 180 physicians he trained with in India, Dr. Odeti said 110 of the physicians were in a large WhatsApp group chat that was constantly exchanging messages and serving as “kind of a friendly support group.”
In Dr. Odeti’s group chat, physicians helped one another find hospital beds for patients who reached out to them. “The first couple of weeks, there was no proper way for people to know where [patients] were based. There was no way to find if this hospital had a bed, so they reached out to any doctors they knew,” he said.
While he said it was emotionally draining, “at the same time, we felt a responsibility toward colleagues in India,” Dr. Odeti said, noting that as COVID-19 cases have decreased in India, the requests have been less frequent.
Because of concerns about traveling to India during the pandemic while on a J-1, H-1B, or other visa with the United States, directly helping friends and family in India seemed out of reach. But many hospitalists of Indian origin instead turned to telemedicine to help their colleagues. Telemedicine had already been steadily growing in India, but was accelerated by the pandemic. The current ratio of doctors to patients in India is 0.62 to 1,000 – lower than recommendations from the World Health Organization. That makes telemedicine a unique opportunity for one physician in India to reach many patients regardless of location.
Dr. Adhikari said he helped out his colleagues in India by performing consults for their patients. “They were just worried because they did not ‘know where to go, or what to get,” he said. “I was treating more patients in India than I was actually treating here.”
In March 2020, the Indian Ministry of Health and Family Welfare released telemedicine practice guidelines for the country, which relaxed regulations on privacy requirements and has been credited in part for giving telemedicine an additional boost during the pandemic. “That makes it easy for people to reach out but also has its own problems,” Dr. Adhikari said.
Monitoring of milder COVID-19 cases that don’t require hospitalization can be performed by a nurse who calls every few hours to check on a patient, make recommendations, and text treatment plans. “The telemedicine platforms are being adopted really fast,” Dr. Adhikari said. “The platforms were built in no time.”
According to NewZoo, a games market data analytics company, India has 345.9 million smartphone users as of 2019 – the second highest number of users in the world after China. Dr. Odeti said he believes telemedicine will be widely adopted.
“In India, they are very proactive in accepting these kinds of methods, so I’m sure they will,” he said. “Governments were trying to do it before the pandemic, because access to care is a problem in India. There are villages which are very, very remote.”
Reversion to old systems
After the peak in late May, new COVID-19 cases in India began to decrease, and the second wave waned on a national level. Hospitals began to get the supplies they needed, beds are available, and patients aren’t as sick as before, according to Dr. Adhikari. The federal government has begun issuing supplies to patients in each state, including COVID-19 vaccines. “The peak for the second wave is gone,” he said.
What remains is a group of physicians trained in how to triage patients and create efficiencies in a hospital setting. Could those skills be put to use elsewhere in India after the pandemic?
According to Dr. Bhatt, the patient care model is likely to revert to the system that existed before. “Whatever the changes, interims of bed occupancy, cost of ICU will be temporary [and] will change to normal,” he said. “But awareness about masks [and] sanitizing methods will be permanent.”
Dr. Adhikari believes that not utilizing the skills of newly minted hospitalists in India would be a missed opportunity. “This is a silver lining from COVID-19, that hospital medicine plays a vital role in the sickest patients, whether it is in India or the U.S. or anywhere,” he said. “I think the model of hospital medicine should be adopted. It’s not: ‘Should it really be adopted or not?’ It should be. There is a huge potential in doing inpatient coordinated [care], having people dedicated in the hospital.”
There are tangible benefits to creating efficiencies in India’s health system, Dr. Odeti said. Length of stay for sicker patients “was much longer” at 10-14 days during the second wave, compared with the United States, before lowering to around 5 days. “These hospitals right now are learning the efficient ways of doing it: when to send [patients] out, how to send them out, how to [perform] service-based practices, creating processes which were nonexistent before.”
While he doesn’t personally believe physicians will adopt a full-fledged hospitalist model unless the payer structure in India changes, “these people are at an advantage with this extra set of skills,” he said. “I think all the knowledge that these people have are going to come in handy.”
Opportunities for growth
Dr. Odeti sees the potential for the hospitalist model to grow in India – if not into its own specialty, then in how critical care consultants handle sicker patients and handoffs.
“The critical care clinician cannot keep the patient from the time they are admitted to the ICU until the discharge, so there will be a need for the transition,” Dr. Odeti said. “In the past, there were not many capabilities in Indian health systems to take care of these extremely sick patients, and now it is evolving. I think that is one more thing that will help.”
Dr. Adhikari said hospital systems in India are beginning to realize how having dedicated hospital physicians could benefit them. In India, “if you’re sick, you go to your doctor, you get treated and you disappear,” he said. The next time, you may see the same doctor or a completely different doctor. “There’s no system there, so it’s really hard for hospital medicine as such because patients, when they are very sick, they just come to the ER. They’re not followed by their primary care.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Odeti sees patients already adapting to having access to a physician for asking questions normally answered by primary care physicians. “I think primary care will come into play,” he said. “When I was doing a Zoom call for patients, they were asking me questions about sciatica. I think they are getting comfortable with this technology.”
A hospitalist model could even be applied to specific diseases with a large population of patients. Hospital administrators “have seen this for the first time, how efficient it could be if they had their own hospitalists and actually run it. So that’s the part that has crossed their minds,” Dr. Adhikari said. “How they will apply it going forward, other than during the COVID-19 pandemic, depends on the size of the hospital and the volume of the patients for a particular disease.”
“You can see in certain areas there is large growth for hospital medicine. But to rise to the level of the United States and how we do it, India needs bigger health systems to adopt the model,” Dr. Adhikari said.
COVID-19 spares lung function in young adults
Here’s some encouraging news for once regarding SARS-CoV-2 infections: A study of young adults for whom prepandemic spirometry data were available showed that COVID-19 did not have a significant impact on lung function, even among patients with asthma.
Among 853 Swedish men and women (mean age, 22 years) who were part of a birth cohort study, there were no significant differences in either forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) or in the ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity, reported Ida Mogensen, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
“We found no effect of COVID-19 on spirometric lung function in generally healthy adults,” she said in an oral abstract presented at the European Respiratory Society 2021 International Congress.
The findings echo those of a small study that involved 73 children and adolescents with COVID-19 and 45 uninfected control persons. The investigators in that study, which was also presented at ERS 2021, found that there were no significant differences in the frequency of abnormal pulmonary function measures between case patients and control patients (abstract OA1303).
“The findings from these two studies provide important reassurance about the impact of COVID infection on lung function in children and young adults,” commented Anita Simonds, MD, an honorary consultant in respiratory and sleep medicine at the Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
“We know already that this group is less likely to suffer severe illness if they contract the virus, and these studies, which importantly include comparator groups without COVID-19, show that they are also less likely to suffer long-term consequences with respect to lung function,” she said. Dr. Simonds was not involved in either study.
Young adult study
Dr. Mogenson and colleagues assessed data on 853 participants in the BAMSE Project, a prospective birth cohort study that included 4,089 children born in Stockholm from 1994 to 1996. Of the participants, 147 had asthma. They have been regularly followed with questionnaires on respiratory symptoms and medications. In addition, at 8 and 16 years’ follow-up, spirometry measures and fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) levels were assessed, allergic sensitization tests were administered, and blood eosinophil levels were measured.
In 2020 and 2021, during the pandemic, the participants underwent spirometry testing and were assessed for antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, and they self-reported use of inhaled corticosteroids.
The investigators defined asthma as any physician diagnosis and asthma symptoms and/or asthma medication use within the previous year. Participants were determined to be COVID-19 seropositive if they had IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike greater than 25.09 AU/mL, IgM antibodies greater than 14.42 AU/mL, or IgA antibodies greater than 2.61 AU/mL, as measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Participants who had been vaccinated against COVID-19 were excluded.
No significant decreases
A total of 243 participants, including 38 with asthma, were seropositive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The mean change in lung function from before the pandemic to the study end date during the pandemic were not significantly different between seropositive participants and seronegative participants or IgM-positive participants and seronegative participants.
Similarly, there were no significant differences in lung function between seropositive and seronegative participants in an analysis that was adjusted for sex, body mass index, smoking status, or prepandemic lung function.
Although there was a trend toward slightly lower function among seropositive participants with asthma in comparison with seronegative patients with asthma, it was not statistically significant, Dr. Mogenson said.
There were also no significant decreases in lung function from the prepandemic measure to the present in any of the inflammatory parameters, including blood eosinophil levels, FeNO, allergic sensitization, or inhaled corticosteroid use.
Potential misclassification
In the question-and-answer period that followed the presentation, session comoderator Sam Bayat, MD, PhD, from the University of Grenoble (France), who was not involved in the study, noted that “some subjects can have positive serology without any symptoms, while others can have symptomatic disease and a couple of months later they have negative serology.”
He asked Dr. Mogenson whether they had included in their study participants with symptomatic COVID-19 and whether that would change the findings.
“We did not have access to RNA testing, so we only had serology, and of course some participants could be wrongly classified to have disease – probably around 15%,” she acknowledged.
She noted that there were no significant changes in lung function among patients who reported having respiratory symptoms.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Karolinska Institutet, Formas, the European Research Council, and Region Stockholm. Dr. Mogenson, Dr. Simonds, and Dr. Bayat disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Here’s some encouraging news for once regarding SARS-CoV-2 infections: A study of young adults for whom prepandemic spirometry data were available showed that COVID-19 did not have a significant impact on lung function, even among patients with asthma.
Among 853 Swedish men and women (mean age, 22 years) who were part of a birth cohort study, there were no significant differences in either forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) or in the ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity, reported Ida Mogensen, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
“We found no effect of COVID-19 on spirometric lung function in generally healthy adults,” she said in an oral abstract presented at the European Respiratory Society 2021 International Congress.
The findings echo those of a small study that involved 73 children and adolescents with COVID-19 and 45 uninfected control persons. The investigators in that study, which was also presented at ERS 2021, found that there were no significant differences in the frequency of abnormal pulmonary function measures between case patients and control patients (abstract OA1303).
“The findings from these two studies provide important reassurance about the impact of COVID infection on lung function in children and young adults,” commented Anita Simonds, MD, an honorary consultant in respiratory and sleep medicine at the Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
“We know already that this group is less likely to suffer severe illness if they contract the virus, and these studies, which importantly include comparator groups without COVID-19, show that they are also less likely to suffer long-term consequences with respect to lung function,” she said. Dr. Simonds was not involved in either study.
Young adult study
Dr. Mogenson and colleagues assessed data on 853 participants in the BAMSE Project, a prospective birth cohort study that included 4,089 children born in Stockholm from 1994 to 1996. Of the participants, 147 had asthma. They have been regularly followed with questionnaires on respiratory symptoms and medications. In addition, at 8 and 16 years’ follow-up, spirometry measures and fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) levels were assessed, allergic sensitization tests were administered, and blood eosinophil levels were measured.
In 2020 and 2021, during the pandemic, the participants underwent spirometry testing and were assessed for antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, and they self-reported use of inhaled corticosteroids.
The investigators defined asthma as any physician diagnosis and asthma symptoms and/or asthma medication use within the previous year. Participants were determined to be COVID-19 seropositive if they had IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike greater than 25.09 AU/mL, IgM antibodies greater than 14.42 AU/mL, or IgA antibodies greater than 2.61 AU/mL, as measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Participants who had been vaccinated against COVID-19 were excluded.
No significant decreases
A total of 243 participants, including 38 with asthma, were seropositive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The mean change in lung function from before the pandemic to the study end date during the pandemic were not significantly different between seropositive participants and seronegative participants or IgM-positive participants and seronegative participants.
Similarly, there were no significant differences in lung function between seropositive and seronegative participants in an analysis that was adjusted for sex, body mass index, smoking status, or prepandemic lung function.
Although there was a trend toward slightly lower function among seropositive participants with asthma in comparison with seronegative patients with asthma, it was not statistically significant, Dr. Mogenson said.
There were also no significant decreases in lung function from the prepandemic measure to the present in any of the inflammatory parameters, including blood eosinophil levels, FeNO, allergic sensitization, or inhaled corticosteroid use.
Potential misclassification
In the question-and-answer period that followed the presentation, session comoderator Sam Bayat, MD, PhD, from the University of Grenoble (France), who was not involved in the study, noted that “some subjects can have positive serology without any symptoms, while others can have symptomatic disease and a couple of months later they have negative serology.”
He asked Dr. Mogenson whether they had included in their study participants with symptomatic COVID-19 and whether that would change the findings.
“We did not have access to RNA testing, so we only had serology, and of course some participants could be wrongly classified to have disease – probably around 15%,” she acknowledged.
She noted that there were no significant changes in lung function among patients who reported having respiratory symptoms.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Karolinska Institutet, Formas, the European Research Council, and Region Stockholm. Dr. Mogenson, Dr. Simonds, and Dr. Bayat disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Here’s some encouraging news for once regarding SARS-CoV-2 infections: A study of young adults for whom prepandemic spirometry data were available showed that COVID-19 did not have a significant impact on lung function, even among patients with asthma.
Among 853 Swedish men and women (mean age, 22 years) who were part of a birth cohort study, there were no significant differences in either forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) or in the ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity, reported Ida Mogensen, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
“We found no effect of COVID-19 on spirometric lung function in generally healthy adults,” she said in an oral abstract presented at the European Respiratory Society 2021 International Congress.
The findings echo those of a small study that involved 73 children and adolescents with COVID-19 and 45 uninfected control persons. The investigators in that study, which was also presented at ERS 2021, found that there were no significant differences in the frequency of abnormal pulmonary function measures between case patients and control patients (abstract OA1303).
“The findings from these two studies provide important reassurance about the impact of COVID infection on lung function in children and young adults,” commented Anita Simonds, MD, an honorary consultant in respiratory and sleep medicine at the Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
“We know already that this group is less likely to suffer severe illness if they contract the virus, and these studies, which importantly include comparator groups without COVID-19, show that they are also less likely to suffer long-term consequences with respect to lung function,” she said. Dr. Simonds was not involved in either study.
Young adult study
Dr. Mogenson and colleagues assessed data on 853 participants in the BAMSE Project, a prospective birth cohort study that included 4,089 children born in Stockholm from 1994 to 1996. Of the participants, 147 had asthma. They have been regularly followed with questionnaires on respiratory symptoms and medications. In addition, at 8 and 16 years’ follow-up, spirometry measures and fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) levels were assessed, allergic sensitization tests were administered, and blood eosinophil levels were measured.
In 2020 and 2021, during the pandemic, the participants underwent spirometry testing and were assessed for antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, and they self-reported use of inhaled corticosteroids.
The investigators defined asthma as any physician diagnosis and asthma symptoms and/or asthma medication use within the previous year. Participants were determined to be COVID-19 seropositive if they had IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike greater than 25.09 AU/mL, IgM antibodies greater than 14.42 AU/mL, or IgA antibodies greater than 2.61 AU/mL, as measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Participants who had been vaccinated against COVID-19 were excluded.
No significant decreases
A total of 243 participants, including 38 with asthma, were seropositive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The mean change in lung function from before the pandemic to the study end date during the pandemic were not significantly different between seropositive participants and seronegative participants or IgM-positive participants and seronegative participants.
Similarly, there were no significant differences in lung function between seropositive and seronegative participants in an analysis that was adjusted for sex, body mass index, smoking status, or prepandemic lung function.
Although there was a trend toward slightly lower function among seropositive participants with asthma in comparison with seronegative patients with asthma, it was not statistically significant, Dr. Mogenson said.
There were also no significant decreases in lung function from the prepandemic measure to the present in any of the inflammatory parameters, including blood eosinophil levels, FeNO, allergic sensitization, or inhaled corticosteroid use.
Potential misclassification
In the question-and-answer period that followed the presentation, session comoderator Sam Bayat, MD, PhD, from the University of Grenoble (France), who was not involved in the study, noted that “some subjects can have positive serology without any symptoms, while others can have symptomatic disease and a couple of months later they have negative serology.”
He asked Dr. Mogenson whether they had included in their study participants with symptomatic COVID-19 and whether that would change the findings.
“We did not have access to RNA testing, so we only had serology, and of course some participants could be wrongly classified to have disease – probably around 15%,” she acknowledged.
She noted that there were no significant changes in lung function among patients who reported having respiratory symptoms.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Karolinska Institutet, Formas, the European Research Council, and Region Stockholm. Dr. Mogenson, Dr. Simonds, and Dr. Bayat disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Growing proportion of cardiac arrests in U.S. considered opioid related
Observational data indicate that the number of hospitalizations for cardiac arrests linked to opioid use roughly doubled from 2012 to 2018.
“This was an observational study, so we cannot conclude that all of the arrests were caused by opioids, but the findings do suggest the opioid epidemic is a contributor to increasing rates,” Senada S. Malik, of the University of New England, Portland, Maine, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The data were drawn from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2012 to 2018, the most recent period available. Cardiac arrests were considered opioid related if there was a secondary diagnosis of opioid disease. The rates of opioid-associated hospitalizations for these types of cardiac arrests climbed from about 800 per year in 2012 to 1,500 per year in 2018, a trend that was statistically significant (P < .05).
The profile of patients with an opioid-associated cardiac arrest was different from those without secondary diagnosis of opioid disease. This included a younger age and lower rates of comorbidities: heart failure (21.2% vs. 40.6%; P < .05), renal failure (14.3% vs. 30.2%; P < .05), diabetes (19.5% vs. 35.4%; P < .05), and hypertension (43.4% vs. 64.9%; P < .05).
Mortality from opioid-associated cardiac arrest is lower
These features might explain the lower rate of in-hospital mortality for opioid-associated cardiac arrests (56.7% vs. 61.2%), according to Ms. Malik, who performed this research in collaboration with Wilbert S. Aronow, MD, director of cardiology research, Westchester Medical Center, Valhalla, N.Y.
When compared to those without a history of opioid use on admission, those with opioid-associated cardiac arrest were more likely to be depressed (18.8% vs. 9.0%), to smoke (37.0% vs. 21.8%) and to abuse alcohol (16.9% vs. 7.1%), according to the NIS data.
While these findings are based on cardiac arrests brought to a hospital, some opioid-induced cardiac arrests never result in hospital admission, according to data included in a recently issued scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
Rate of opioid-associated cardiac arrests underestimated
In that statement, which was focused on opioid-associated out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OA-OHCA), numerous studies were cited to support the conclusion that these events are common and underestimated. One problem is that opioid-induced cardiac arrests are not always accurately differentiated from cardiac arrests induced by use of other substances, such as barbiturates, cocaine, or alcohol.
For this and other reasons, the data are inconsistent. One study based on emergency medical service (EMS) response data concluded that 9% of all out-of-hospital cardiac arrests are opioid associated.
In another study using potentially more accurate autopsy data, 60% of the non–cardiac-associated cardiac arrests were found to occur in individuals with potentially lethal serum concentrations of opioids. As 40% of out-of-hospital cardiac arrests were considered non–cardiac related, this suggested that 15% of all out-of-hospital cardiac arrests are opioid related.
In the NIS data, the incident curves of opioid-related cardiac arrests appeared to be flattening in 2018, the last year of data collection, but there was no indication they were declining.
Patterns of opioid-induced cardiac arrests evolving
The patterns of opioid-induced cardiac arrest have changed and are likely to continue to change in response to the evolving opioid epidemic, according to the AHA scientific statement. The authors described three waves of opioid abuse. The first, which was related to the promotion of prescription opioids to treat chronic pain that ultimately led to high rates of opioid addiction, peaked in 2012 when rates of these prescriptions began to fall. At that time a second wave, attributed to patients switching to less expensive nonprescription heroin, was already underway. A third wave, attributed to growth in the use of synthetic opioids, such as fentanyl, began in 2013 and is ongoing, according to data cited in the AHA statement.
Recognizing the role of opioids in rising rates of cardiac arrest is important for promoting strategies of effective treatment and prevention, according to Cameron Dezfulian, MD, medical director of the adult congenital heart disease program at Texas Children’s Hospital, Houston. Dr. Dezfulian was vice chair and leader of the writing committee for the AHA scientific statement on OA-OHCA. He said there are plenty of data to support the need for greater attention to the role of opioids in cardiac arrest.
“The recent data affirms the trends many of us have observed without our emergency rooms and ICUs: a steady increase in the proportion of OA-OHCA, primarily in young and otherwise healthy individuals,” he said.
He calls not only for more awareness at the front lines of health are but also for a more comprehensive approach.
“Public health policies and community- and hospital-based interventions are needed to reduce the mortality due to OA-OHCA, which is distinct from the traditional cardiac etiology,” Dr. Dezfulian said.
In opioid-induced cardiac arrest, as in other types of cardiac arrest, prompt initiation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation is essential, but early administration of the opioid antagonist naloxone can also be lifesaving, according to treatment strategies outlined in the AHA scientific statement. The fact that OA-OHCA typically occur in patients with structurally and electrophysiologically normal hearts is emphasized in the AHA statement. So is the enormous public health toll of OA-OHCA.
Death due to opioid overdose, which includes cardiac arrests, is now the leading cause of mortality in the U.S. among individuals between the ages of 25 and 64 years, according to the statement.
Ms. Malik reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Dezfulian reports a financial relationship with Mallinckrodt.
Observational data indicate that the number of hospitalizations for cardiac arrests linked to opioid use roughly doubled from 2012 to 2018.
“This was an observational study, so we cannot conclude that all of the arrests were caused by opioids, but the findings do suggest the opioid epidemic is a contributor to increasing rates,” Senada S. Malik, of the University of New England, Portland, Maine, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The data were drawn from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2012 to 2018, the most recent period available. Cardiac arrests were considered opioid related if there was a secondary diagnosis of opioid disease. The rates of opioid-associated hospitalizations for these types of cardiac arrests climbed from about 800 per year in 2012 to 1,500 per year in 2018, a trend that was statistically significant (P < .05).
The profile of patients with an opioid-associated cardiac arrest was different from those without secondary diagnosis of opioid disease. This included a younger age and lower rates of comorbidities: heart failure (21.2% vs. 40.6%; P < .05), renal failure (14.3% vs. 30.2%; P < .05), diabetes (19.5% vs. 35.4%; P < .05), and hypertension (43.4% vs. 64.9%; P < .05).
Mortality from opioid-associated cardiac arrest is lower
These features might explain the lower rate of in-hospital mortality for opioid-associated cardiac arrests (56.7% vs. 61.2%), according to Ms. Malik, who performed this research in collaboration with Wilbert S. Aronow, MD, director of cardiology research, Westchester Medical Center, Valhalla, N.Y.
When compared to those without a history of opioid use on admission, those with opioid-associated cardiac arrest were more likely to be depressed (18.8% vs. 9.0%), to smoke (37.0% vs. 21.8%) and to abuse alcohol (16.9% vs. 7.1%), according to the NIS data.
While these findings are based on cardiac arrests brought to a hospital, some opioid-induced cardiac arrests never result in hospital admission, according to data included in a recently issued scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
Rate of opioid-associated cardiac arrests underestimated
In that statement, which was focused on opioid-associated out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OA-OHCA), numerous studies were cited to support the conclusion that these events are common and underestimated. One problem is that opioid-induced cardiac arrests are not always accurately differentiated from cardiac arrests induced by use of other substances, such as barbiturates, cocaine, or alcohol.
For this and other reasons, the data are inconsistent. One study based on emergency medical service (EMS) response data concluded that 9% of all out-of-hospital cardiac arrests are opioid associated.
In another study using potentially more accurate autopsy data, 60% of the non–cardiac-associated cardiac arrests were found to occur in individuals with potentially lethal serum concentrations of opioids. As 40% of out-of-hospital cardiac arrests were considered non–cardiac related, this suggested that 15% of all out-of-hospital cardiac arrests are opioid related.
In the NIS data, the incident curves of opioid-related cardiac arrests appeared to be flattening in 2018, the last year of data collection, but there was no indication they were declining.
Patterns of opioid-induced cardiac arrests evolving
The patterns of opioid-induced cardiac arrest have changed and are likely to continue to change in response to the evolving opioid epidemic, according to the AHA scientific statement. The authors described three waves of opioid abuse. The first, which was related to the promotion of prescription opioids to treat chronic pain that ultimately led to high rates of opioid addiction, peaked in 2012 when rates of these prescriptions began to fall. At that time a second wave, attributed to patients switching to less expensive nonprescription heroin, was already underway. A third wave, attributed to growth in the use of synthetic opioids, such as fentanyl, began in 2013 and is ongoing, according to data cited in the AHA statement.
Recognizing the role of opioids in rising rates of cardiac arrest is important for promoting strategies of effective treatment and prevention, according to Cameron Dezfulian, MD, medical director of the adult congenital heart disease program at Texas Children’s Hospital, Houston. Dr. Dezfulian was vice chair and leader of the writing committee for the AHA scientific statement on OA-OHCA. He said there are plenty of data to support the need for greater attention to the role of opioids in cardiac arrest.
“The recent data affirms the trends many of us have observed without our emergency rooms and ICUs: a steady increase in the proportion of OA-OHCA, primarily in young and otherwise healthy individuals,” he said.
He calls not only for more awareness at the front lines of health are but also for a more comprehensive approach.
“Public health policies and community- and hospital-based interventions are needed to reduce the mortality due to OA-OHCA, which is distinct from the traditional cardiac etiology,” Dr. Dezfulian said.
In opioid-induced cardiac arrest, as in other types of cardiac arrest, prompt initiation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation is essential, but early administration of the opioid antagonist naloxone can also be lifesaving, according to treatment strategies outlined in the AHA scientific statement. The fact that OA-OHCA typically occur in patients with structurally and electrophysiologically normal hearts is emphasized in the AHA statement. So is the enormous public health toll of OA-OHCA.
Death due to opioid overdose, which includes cardiac arrests, is now the leading cause of mortality in the U.S. among individuals between the ages of 25 and 64 years, according to the statement.
Ms. Malik reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Dezfulian reports a financial relationship with Mallinckrodt.
Observational data indicate that the number of hospitalizations for cardiac arrests linked to opioid use roughly doubled from 2012 to 2018.
“This was an observational study, so we cannot conclude that all of the arrests were caused by opioids, but the findings do suggest the opioid epidemic is a contributor to increasing rates,” Senada S. Malik, of the University of New England, Portland, Maine, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The data were drawn from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2012 to 2018, the most recent period available. Cardiac arrests were considered opioid related if there was a secondary diagnosis of opioid disease. The rates of opioid-associated hospitalizations for these types of cardiac arrests climbed from about 800 per year in 2012 to 1,500 per year in 2018, a trend that was statistically significant (P < .05).
The profile of patients with an opioid-associated cardiac arrest was different from those without secondary diagnosis of opioid disease. This included a younger age and lower rates of comorbidities: heart failure (21.2% vs. 40.6%; P < .05), renal failure (14.3% vs. 30.2%; P < .05), diabetes (19.5% vs. 35.4%; P < .05), and hypertension (43.4% vs. 64.9%; P < .05).
Mortality from opioid-associated cardiac arrest is lower
These features might explain the lower rate of in-hospital mortality for opioid-associated cardiac arrests (56.7% vs. 61.2%), according to Ms. Malik, who performed this research in collaboration with Wilbert S. Aronow, MD, director of cardiology research, Westchester Medical Center, Valhalla, N.Y.
When compared to those without a history of opioid use on admission, those with opioid-associated cardiac arrest were more likely to be depressed (18.8% vs. 9.0%), to smoke (37.0% vs. 21.8%) and to abuse alcohol (16.9% vs. 7.1%), according to the NIS data.
While these findings are based on cardiac arrests brought to a hospital, some opioid-induced cardiac arrests never result in hospital admission, according to data included in a recently issued scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
Rate of opioid-associated cardiac arrests underestimated
In that statement, which was focused on opioid-associated out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OA-OHCA), numerous studies were cited to support the conclusion that these events are common and underestimated. One problem is that opioid-induced cardiac arrests are not always accurately differentiated from cardiac arrests induced by use of other substances, such as barbiturates, cocaine, or alcohol.
For this and other reasons, the data are inconsistent. One study based on emergency medical service (EMS) response data concluded that 9% of all out-of-hospital cardiac arrests are opioid associated.
In another study using potentially more accurate autopsy data, 60% of the non–cardiac-associated cardiac arrests were found to occur in individuals with potentially lethal serum concentrations of opioids. As 40% of out-of-hospital cardiac arrests were considered non–cardiac related, this suggested that 15% of all out-of-hospital cardiac arrests are opioid related.
In the NIS data, the incident curves of opioid-related cardiac arrests appeared to be flattening in 2018, the last year of data collection, but there was no indication they were declining.
Patterns of opioid-induced cardiac arrests evolving
The patterns of opioid-induced cardiac arrest have changed and are likely to continue to change in response to the evolving opioid epidemic, according to the AHA scientific statement. The authors described three waves of opioid abuse. The first, which was related to the promotion of prescription opioids to treat chronic pain that ultimately led to high rates of opioid addiction, peaked in 2012 when rates of these prescriptions began to fall. At that time a second wave, attributed to patients switching to less expensive nonprescription heroin, was already underway. A third wave, attributed to growth in the use of synthetic opioids, such as fentanyl, began in 2013 and is ongoing, according to data cited in the AHA statement.
Recognizing the role of opioids in rising rates of cardiac arrest is important for promoting strategies of effective treatment and prevention, according to Cameron Dezfulian, MD, medical director of the adult congenital heart disease program at Texas Children’s Hospital, Houston. Dr. Dezfulian was vice chair and leader of the writing committee for the AHA scientific statement on OA-OHCA. He said there are plenty of data to support the need for greater attention to the role of opioids in cardiac arrest.
“The recent data affirms the trends many of us have observed without our emergency rooms and ICUs: a steady increase in the proportion of OA-OHCA, primarily in young and otherwise healthy individuals,” he said.
He calls not only for more awareness at the front lines of health are but also for a more comprehensive approach.
“Public health policies and community- and hospital-based interventions are needed to reduce the mortality due to OA-OHCA, which is distinct from the traditional cardiac etiology,” Dr. Dezfulian said.
In opioid-induced cardiac arrest, as in other types of cardiac arrest, prompt initiation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation is essential, but early administration of the opioid antagonist naloxone can also be lifesaving, according to treatment strategies outlined in the AHA scientific statement. The fact that OA-OHCA typically occur in patients with structurally and electrophysiologically normal hearts is emphasized in the AHA statement. So is the enormous public health toll of OA-OHCA.
Death due to opioid overdose, which includes cardiac arrests, is now the leading cause of mortality in the U.S. among individuals between the ages of 25 and 64 years, according to the statement.
Ms. Malik reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Dezfulian reports a financial relationship with Mallinckrodt.
FROM ESC 2021
Sweeping new vaccine mandates will impact most U.S. workers
, including sweeping vaccine mandates that will affect 100 million American workers, nearly two-thirds of the country’s workforce.
“As your president, I’m announcing tonight a new plan to get more Americans vaccinated to combat those blocking public health,” he said Sept. 9.
As part of a six-part plan unveiled in a speech from the State Dining Room of the White House, President Biden said he would require vaccinations for nearly 4 million federal workers and the employees of companies that contract with the federal government.
He has also directed the Occupational Safety and Health Administration to develop a rule that will require large employers -- those with at least 100 employees -- to ensure their workers are vaccinated or tested weekly.
Nearly 17 million health care workers will face new vaccine mandates as part of the conditions of participation in the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
President Biden said the federal government will require staff at federally funded Head Start programs and schools to be vaccinated. He’s also calling on all states to mandate vaccines for teachers.
“A distinct minority of Americans, supported by a distinct minority of elected officials, are keeping us from turning the corner,” PresidentBiden said. “These pandemic politics, as I refer to them, are making people sick, causing unvaccinated people to die.”
One public health official said he was glad to see the president’s bold action.
“What I saw today was the federal government trying to use its powers to create greater safety in the American population,” said Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the school of public health at Brown University, Providence, R.I., in a call with reporters after the speech.
National Nurses United, the largest union of registered nurses in the United States, issued a statement in support of President Biden’s new vaccination requirements, but pushed back on his language.
“…as advocates for public health, registered nurses want to be extremely clear: There is no such thing as a pandemic of only the unvaccinated. The science of epidemiology tells us there is just one deadly, global pandemic that has not yet ended, and we are all in it together. To get out of it, we must act together. All of us,” the statement says.
A host of other professional groups, including the American Medical Association and the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, also issued statements of support for President Biden’s plan.
But the plan was not well received by all.
“I will pursue every legal option available to the state of Georgia to stop this blatantly unlawful overreach by the Biden Administration,” said Georgia Governor Brian Kemp, a Republican, in a Tweet.
The National Council for Occupational Safety and Health called the plan “a missed opportunity” because it failed to include workplace protections for essential workers such as grocery, postal, and transit workers.
“Social distancing, improved ventilation, shift rotation, and protective equipment to reduce exposure are important components of an overall plan to reduce risk and stop the virus. These tools are missing from the new steps President Biden announced today,” said Jessica Martinez, co-executive director of the group.
In addition to the new vaccination requirements, President Biden said extra doses would be on the way for people who have already been fully vaccinated in order to protect against waning immunity, starting on Sept. 20. But he noted that those plans would be contingent on the Food and Drug Administration’s approval for third doses and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation of the shots.
President Biden pledged to use the Defense Production Act to ramp up production of at-home tests, which have been selling out across the nation as the Delta variant spreads.
He also announced plans to expand access to COVID-19 testing, including offering testing for free at thousands of pharmacies nationwide and getting major retailers to sell at-home COVID-19 tests at cost.
The BinaxNow test kit, which currently retails for $23.99, will now cost about $15 for two tests at Kroger, Amazon, and Walmart, according to the White House. Food banks and community health centers will get free tests, too.
He called on states to set up COVID-19 testing programs at all schools.
Jha said that in his view, the big, game-changing news out of the president’s speech was the expansion of testing.
“Our country has failed to deploy tests in a way that can really bring this pandemic under control,” Jha said. “There are plenty of reasons, data, experience to indicate that if these were widely available, it would make a dramatic difference in reducing infection numbers across our country.”.
Dr. Jha said the private market had not worked effectively to make testing more widely available, so it was “absolutely a requirement of the federal government to step in and make testing more widely available,” he said.
President Biden also announced new economic stimulus programs, saying he’s expanding loan programs to small businesses and streamlining the loan forgiveness process.
President Biden said he’s boosting help for overburdened hospitals, doubling the number of federal surge response teams sent to hard-hit areas to reduce the strain on local health care workers. He said he would increase the pace of antibody treatments to states by 50%.
“We made so much progress during the past 7 months of this pandemic. Even so, we remain at a critical moment, a critical time,” he said. “We have the tools. Now, we just have to finish the job with truth, with science, with confidence and together as one nation.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, including sweeping vaccine mandates that will affect 100 million American workers, nearly two-thirds of the country’s workforce.
“As your president, I’m announcing tonight a new plan to get more Americans vaccinated to combat those blocking public health,” he said Sept. 9.
As part of a six-part plan unveiled in a speech from the State Dining Room of the White House, President Biden said he would require vaccinations for nearly 4 million federal workers and the employees of companies that contract with the federal government.
He has also directed the Occupational Safety and Health Administration to develop a rule that will require large employers -- those with at least 100 employees -- to ensure their workers are vaccinated or tested weekly.
Nearly 17 million health care workers will face new vaccine mandates as part of the conditions of participation in the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
President Biden said the federal government will require staff at federally funded Head Start programs and schools to be vaccinated. He’s also calling on all states to mandate vaccines for teachers.
“A distinct minority of Americans, supported by a distinct minority of elected officials, are keeping us from turning the corner,” PresidentBiden said. “These pandemic politics, as I refer to them, are making people sick, causing unvaccinated people to die.”
One public health official said he was glad to see the president’s bold action.
“What I saw today was the federal government trying to use its powers to create greater safety in the American population,” said Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the school of public health at Brown University, Providence, R.I., in a call with reporters after the speech.
National Nurses United, the largest union of registered nurses in the United States, issued a statement in support of President Biden’s new vaccination requirements, but pushed back on his language.
“…as advocates for public health, registered nurses want to be extremely clear: There is no such thing as a pandemic of only the unvaccinated. The science of epidemiology tells us there is just one deadly, global pandemic that has not yet ended, and we are all in it together. To get out of it, we must act together. All of us,” the statement says.
A host of other professional groups, including the American Medical Association and the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, also issued statements of support for President Biden’s plan.
But the plan was not well received by all.
“I will pursue every legal option available to the state of Georgia to stop this blatantly unlawful overreach by the Biden Administration,” said Georgia Governor Brian Kemp, a Republican, in a Tweet.
The National Council for Occupational Safety and Health called the plan “a missed opportunity” because it failed to include workplace protections for essential workers such as grocery, postal, and transit workers.
“Social distancing, improved ventilation, shift rotation, and protective equipment to reduce exposure are important components of an overall plan to reduce risk and stop the virus. These tools are missing from the new steps President Biden announced today,” said Jessica Martinez, co-executive director of the group.
In addition to the new vaccination requirements, President Biden said extra doses would be on the way for people who have already been fully vaccinated in order to protect against waning immunity, starting on Sept. 20. But he noted that those plans would be contingent on the Food and Drug Administration’s approval for third doses and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation of the shots.
President Biden pledged to use the Defense Production Act to ramp up production of at-home tests, which have been selling out across the nation as the Delta variant spreads.
He also announced plans to expand access to COVID-19 testing, including offering testing for free at thousands of pharmacies nationwide and getting major retailers to sell at-home COVID-19 tests at cost.
The BinaxNow test kit, which currently retails for $23.99, will now cost about $15 for two tests at Kroger, Amazon, and Walmart, according to the White House. Food banks and community health centers will get free tests, too.
He called on states to set up COVID-19 testing programs at all schools.
Jha said that in his view, the big, game-changing news out of the president’s speech was the expansion of testing.
“Our country has failed to deploy tests in a way that can really bring this pandemic under control,” Jha said. “There are plenty of reasons, data, experience to indicate that if these were widely available, it would make a dramatic difference in reducing infection numbers across our country.”.
Dr. Jha said the private market had not worked effectively to make testing more widely available, so it was “absolutely a requirement of the federal government to step in and make testing more widely available,” he said.
President Biden also announced new economic stimulus programs, saying he’s expanding loan programs to small businesses and streamlining the loan forgiveness process.
President Biden said he’s boosting help for overburdened hospitals, doubling the number of federal surge response teams sent to hard-hit areas to reduce the strain on local health care workers. He said he would increase the pace of antibody treatments to states by 50%.
“We made so much progress during the past 7 months of this pandemic. Even so, we remain at a critical moment, a critical time,” he said. “We have the tools. Now, we just have to finish the job with truth, with science, with confidence and together as one nation.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, including sweeping vaccine mandates that will affect 100 million American workers, nearly two-thirds of the country’s workforce.
“As your president, I’m announcing tonight a new plan to get more Americans vaccinated to combat those blocking public health,” he said Sept. 9.
As part of a six-part plan unveiled in a speech from the State Dining Room of the White House, President Biden said he would require vaccinations for nearly 4 million federal workers and the employees of companies that contract with the federal government.
He has also directed the Occupational Safety and Health Administration to develop a rule that will require large employers -- those with at least 100 employees -- to ensure their workers are vaccinated or tested weekly.
Nearly 17 million health care workers will face new vaccine mandates as part of the conditions of participation in the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
President Biden said the federal government will require staff at federally funded Head Start programs and schools to be vaccinated. He’s also calling on all states to mandate vaccines for teachers.
“A distinct minority of Americans, supported by a distinct minority of elected officials, are keeping us from turning the corner,” PresidentBiden said. “These pandemic politics, as I refer to them, are making people sick, causing unvaccinated people to die.”
One public health official said he was glad to see the president’s bold action.
“What I saw today was the federal government trying to use its powers to create greater safety in the American population,” said Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the school of public health at Brown University, Providence, R.I., in a call with reporters after the speech.
National Nurses United, the largest union of registered nurses in the United States, issued a statement in support of President Biden’s new vaccination requirements, but pushed back on his language.
“…as advocates for public health, registered nurses want to be extremely clear: There is no such thing as a pandemic of only the unvaccinated. The science of epidemiology tells us there is just one deadly, global pandemic that has not yet ended, and we are all in it together. To get out of it, we must act together. All of us,” the statement says.
A host of other professional groups, including the American Medical Association and the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, also issued statements of support for President Biden’s plan.
But the plan was not well received by all.
“I will pursue every legal option available to the state of Georgia to stop this blatantly unlawful overreach by the Biden Administration,” said Georgia Governor Brian Kemp, a Republican, in a Tweet.
The National Council for Occupational Safety and Health called the plan “a missed opportunity” because it failed to include workplace protections for essential workers such as grocery, postal, and transit workers.
“Social distancing, improved ventilation, shift rotation, and protective equipment to reduce exposure are important components of an overall plan to reduce risk and stop the virus. These tools are missing from the new steps President Biden announced today,” said Jessica Martinez, co-executive director of the group.
In addition to the new vaccination requirements, President Biden said extra doses would be on the way for people who have already been fully vaccinated in order to protect against waning immunity, starting on Sept. 20. But he noted that those plans would be contingent on the Food and Drug Administration’s approval for third doses and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation of the shots.
President Biden pledged to use the Defense Production Act to ramp up production of at-home tests, which have been selling out across the nation as the Delta variant spreads.
He also announced plans to expand access to COVID-19 testing, including offering testing for free at thousands of pharmacies nationwide and getting major retailers to sell at-home COVID-19 tests at cost.
The BinaxNow test kit, which currently retails for $23.99, will now cost about $15 for two tests at Kroger, Amazon, and Walmart, according to the White House. Food banks and community health centers will get free tests, too.
He called on states to set up COVID-19 testing programs at all schools.
Jha said that in his view, the big, game-changing news out of the president’s speech was the expansion of testing.
“Our country has failed to deploy tests in a way that can really bring this pandemic under control,” Jha said. “There are plenty of reasons, data, experience to indicate that if these were widely available, it would make a dramatic difference in reducing infection numbers across our country.”.
Dr. Jha said the private market had not worked effectively to make testing more widely available, so it was “absolutely a requirement of the federal government to step in and make testing more widely available,” he said.
President Biden also announced new economic stimulus programs, saying he’s expanding loan programs to small businesses and streamlining the loan forgiveness process.
President Biden said he’s boosting help for overburdened hospitals, doubling the number of federal surge response teams sent to hard-hit areas to reduce the strain on local health care workers. He said he would increase the pace of antibody treatments to states by 50%.
“We made so much progress during the past 7 months of this pandemic. Even so, we remain at a critical moment, a critical time,” he said. “We have the tools. Now, we just have to finish the job with truth, with science, with confidence and together as one nation.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.