User login
Suicide in America: The urban-rural divide
The gap in suicide rates between rural and urban areas has widened since 2000 for both males and females, according to a recent report from the National Center for Health Statistics.

After remaining stable from 2000 to 2007, the suicide rate for rural males rose 34% from 2007 to 2018, versus 17% among urban males over the same period. Suicide rates for females were significantly lower than those of men, but the changes were larger. For rural females, the rate increased 91% from 2000 to 2018, compared with 51% for urban females, Kristen Pettrone, MD, MPH, and Sally C. Curtin, MA, said in an NCHS Data Brief.
For 2018, the last year with available data, the age-adjusted rates look like this: 21.5 per 100,000 population for urban males, 30.7 for rural males, 5.9 per 100,000 for urban females, and 8.0 for rural females. The overall rate for the United States was 14.2 per 100,000, with combined male/female rates of 13.4 in urban areas and 19.4 in rural areas, the researchers said.
Methods of suicide also varied by sex and urban-rural status. Firearms were the leading method for males in both rural and urban areas, but females split between firearms in rural areas and suffocation (including hangings) in urban areas, said Dr. Pettrone of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Ms. Curtin of the NCHS.
Suffocation, however, was the fastest-growing method from 2000 to 2018, regardless of sex or location. Suffocation-related suicide rates more than quadrupled for rural females, and more than doubled for urban females and rural males, while rates rose 85% among males in urban areas, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
“Suicide has remained the 10th leading cause of death in the United States since 2008,” they wrote, and
SOURCE: Pettrone K, Curtin SC. 2020 Aug. NCHS Data Brief, No 373.
The gap in suicide rates between rural and urban areas has widened since 2000 for both males and females, according to a recent report from the National Center for Health Statistics.

After remaining stable from 2000 to 2007, the suicide rate for rural males rose 34% from 2007 to 2018, versus 17% among urban males over the same period. Suicide rates for females were significantly lower than those of men, but the changes were larger. For rural females, the rate increased 91% from 2000 to 2018, compared with 51% for urban females, Kristen Pettrone, MD, MPH, and Sally C. Curtin, MA, said in an NCHS Data Brief.
For 2018, the last year with available data, the age-adjusted rates look like this: 21.5 per 100,000 population for urban males, 30.7 for rural males, 5.9 per 100,000 for urban females, and 8.0 for rural females. The overall rate for the United States was 14.2 per 100,000, with combined male/female rates of 13.4 in urban areas and 19.4 in rural areas, the researchers said.
Methods of suicide also varied by sex and urban-rural status. Firearms were the leading method for males in both rural and urban areas, but females split between firearms in rural areas and suffocation (including hangings) in urban areas, said Dr. Pettrone of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Ms. Curtin of the NCHS.
Suffocation, however, was the fastest-growing method from 2000 to 2018, regardless of sex or location. Suffocation-related suicide rates more than quadrupled for rural females, and more than doubled for urban females and rural males, while rates rose 85% among males in urban areas, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
“Suicide has remained the 10th leading cause of death in the United States since 2008,” they wrote, and
SOURCE: Pettrone K, Curtin SC. 2020 Aug. NCHS Data Brief, No 373.
The gap in suicide rates between rural and urban areas has widened since 2000 for both males and females, according to a recent report from the National Center for Health Statistics.

After remaining stable from 2000 to 2007, the suicide rate for rural males rose 34% from 2007 to 2018, versus 17% among urban males over the same period. Suicide rates for females were significantly lower than those of men, but the changes were larger. For rural females, the rate increased 91% from 2000 to 2018, compared with 51% for urban females, Kristen Pettrone, MD, MPH, and Sally C. Curtin, MA, said in an NCHS Data Brief.
For 2018, the last year with available data, the age-adjusted rates look like this: 21.5 per 100,000 population for urban males, 30.7 for rural males, 5.9 per 100,000 for urban females, and 8.0 for rural females. The overall rate for the United States was 14.2 per 100,000, with combined male/female rates of 13.4 in urban areas and 19.4 in rural areas, the researchers said.
Methods of suicide also varied by sex and urban-rural status. Firearms were the leading method for males in both rural and urban areas, but females split between firearms in rural areas and suffocation (including hangings) in urban areas, said Dr. Pettrone of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Ms. Curtin of the NCHS.
Suffocation, however, was the fastest-growing method from 2000 to 2018, regardless of sex or location. Suffocation-related suicide rates more than quadrupled for rural females, and more than doubled for urban females and rural males, while rates rose 85% among males in urban areas, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
“Suicide has remained the 10th leading cause of death in the United States since 2008,” they wrote, and
SOURCE: Pettrone K, Curtin SC. 2020 Aug. NCHS Data Brief, No 373.
FDA adds polyarticular-course JIA to approved indications for tofacitinib
The Food and Drug Administration has (pJIA).
The approval, announced Sept. 28 by tofacitinib’s manufacturer, Pfizer, marks the first JAK inhibitor to be approved for the condition in the United States and is the fourth indication to be approved for the drug after approvals in adult patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis following methotrexate failure, active psoriatic arthritis after disease-modifying antirheumatic drug failure, and moderate to severe ulcerative colitis after failure on a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
The agency based its approval on a phase 3, multinational, randomized, double-blind, controlled withdrawal study that had an 18-week, open-label, run-in phase involving 225 patients who twice daily took either a 5-mg tablet or, in patients under 40 kg, a weight-based lower dose in the form of a 1 mg/mL oral solution, according to the company press release. A total of 173 patients from this phase met JIA American College of Rheumatology 30 response criteria, defined as 30% or greater improvement in three of six JIA core set variables and worsening in no more than one of the core set variables; they were then randomized in part 2 of the study to continue the same dose of tofacitinib or receive placebo until 44 weeks. By the end of this period, 31% who received tofacitinib had a disease flare, compared with 55% on placebo (P = .0007). Disease flare was defined as a 30% or greater worsening in at least three of the six variables of the JIA core set, with no more than one of the remaining JIA core response variables improving by 30% or more after randomization.
The types of adverse drug reactions in patients with pJIA were consistent with those seen in adult rheumatoid arthritis patients, according to Pfizer. Serious adverse drug reactions have most commonly been serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death, and most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants, such as methotrexate or corticosteroids. Common adverse drug reactions reported in 2% or more of patients during the first 3 months in controlled clinical trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis taking tofacitinib at 5 mg twice daily were upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, headache, and hypertension.
While the 5-mg tablet formulation is already available, Pfizer said it expects the oral solution to be available by the end of the first quarter in 2021.
Prescribing information can be found on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has (pJIA).
The approval, announced Sept. 28 by tofacitinib’s manufacturer, Pfizer, marks the first JAK inhibitor to be approved for the condition in the United States and is the fourth indication to be approved for the drug after approvals in adult patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis following methotrexate failure, active psoriatic arthritis after disease-modifying antirheumatic drug failure, and moderate to severe ulcerative colitis after failure on a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
The agency based its approval on a phase 3, multinational, randomized, double-blind, controlled withdrawal study that had an 18-week, open-label, run-in phase involving 225 patients who twice daily took either a 5-mg tablet or, in patients under 40 kg, a weight-based lower dose in the form of a 1 mg/mL oral solution, according to the company press release. A total of 173 patients from this phase met JIA American College of Rheumatology 30 response criteria, defined as 30% or greater improvement in three of six JIA core set variables and worsening in no more than one of the core set variables; they were then randomized in part 2 of the study to continue the same dose of tofacitinib or receive placebo until 44 weeks. By the end of this period, 31% who received tofacitinib had a disease flare, compared with 55% on placebo (P = .0007). Disease flare was defined as a 30% or greater worsening in at least three of the six variables of the JIA core set, with no more than one of the remaining JIA core response variables improving by 30% or more after randomization.
The types of adverse drug reactions in patients with pJIA were consistent with those seen in adult rheumatoid arthritis patients, according to Pfizer. Serious adverse drug reactions have most commonly been serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death, and most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants, such as methotrexate or corticosteroids. Common adverse drug reactions reported in 2% or more of patients during the first 3 months in controlled clinical trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis taking tofacitinib at 5 mg twice daily were upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, headache, and hypertension.
While the 5-mg tablet formulation is already available, Pfizer said it expects the oral solution to be available by the end of the first quarter in 2021.
Prescribing information can be found on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has (pJIA).
The approval, announced Sept. 28 by tofacitinib’s manufacturer, Pfizer, marks the first JAK inhibitor to be approved for the condition in the United States and is the fourth indication to be approved for the drug after approvals in adult patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis following methotrexate failure, active psoriatic arthritis after disease-modifying antirheumatic drug failure, and moderate to severe ulcerative colitis after failure on a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
The agency based its approval on a phase 3, multinational, randomized, double-blind, controlled withdrawal study that had an 18-week, open-label, run-in phase involving 225 patients who twice daily took either a 5-mg tablet or, in patients under 40 kg, a weight-based lower dose in the form of a 1 mg/mL oral solution, according to the company press release. A total of 173 patients from this phase met JIA American College of Rheumatology 30 response criteria, defined as 30% or greater improvement in three of six JIA core set variables and worsening in no more than one of the core set variables; they were then randomized in part 2 of the study to continue the same dose of tofacitinib or receive placebo until 44 weeks. By the end of this period, 31% who received tofacitinib had a disease flare, compared with 55% on placebo (P = .0007). Disease flare was defined as a 30% or greater worsening in at least three of the six variables of the JIA core set, with no more than one of the remaining JIA core response variables improving by 30% or more after randomization.
The types of adverse drug reactions in patients with pJIA were consistent with those seen in adult rheumatoid arthritis patients, according to Pfizer. Serious adverse drug reactions have most commonly been serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death, and most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants, such as methotrexate or corticosteroids. Common adverse drug reactions reported in 2% or more of patients during the first 3 months in controlled clinical trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis taking tofacitinib at 5 mg twice daily were upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, headache, and hypertension.
While the 5-mg tablet formulation is already available, Pfizer said it expects the oral solution to be available by the end of the first quarter in 2021.
Prescribing information can be found on the FDA website.
High schoolers send mixed signals on contraceptive use
according to data from the Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS).
Nonuse of birth control in this population dropped to 11.9% in 2019, but the overall trend is one of no significant change since 2003. Meanwhile, the use of birth control pills has taken a different path, with prevalence rising significantly from 16.0% in 2007 to 23.0% in 2019, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
The prevalence of condom use among sexually active students was 54.3% in 2019, up from 53.8% in 2017 – the survey is conducted every 2 years – but down from a high of 63.0% in 2003, the YRBS data show.
Condoms were the most prevalent method of contraception, but the finding that “only approximately half of sexually active students reported any condom use at last sexual intercourse … is concerning given the high risk for STDs among this population,” Leigh E. Szucs, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In 2019, White (55.8%) and Hispanic (56.2%) students were more likely than Blacks (48.2%) to have used a condom during their last sexual intercourse, but use of birth control pills was much higher among Whites (29.1%) than Hispanics (15.4%) or Blacks (12.9%).The Black respondents were much more likely (23.0%) to use no contraceptive method, compared with Whites (8.4%) or Hispanics (13.3%), they said.
“Meeting the unintended pregnancy and STD/HIV prevention needs of black and Hispanic youths is vital,” wrote Dr. Szucs of the CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention and associates. “Understanding and addressing structural barriers that might contribute to the observed differences are important next steps.”
The high school students taking the YRBS were considered sexually active if they had intercourse with at least one person in the previous 3 months. Overall, 3,226 (27.4%) of respondents in 2019 reported being sexually active: 52.2% were female and 47.8% were male, the CDC said.
SOURCE: Szucs LE et al. MMWR. 2019 Aug 21;69(SS-01)11-8.
according to data from the Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS).
Nonuse of birth control in this population dropped to 11.9% in 2019, but the overall trend is one of no significant change since 2003. Meanwhile, the use of birth control pills has taken a different path, with prevalence rising significantly from 16.0% in 2007 to 23.0% in 2019, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
The prevalence of condom use among sexually active students was 54.3% in 2019, up from 53.8% in 2017 – the survey is conducted every 2 years – but down from a high of 63.0% in 2003, the YRBS data show.
Condoms were the most prevalent method of contraception, but the finding that “only approximately half of sexually active students reported any condom use at last sexual intercourse … is concerning given the high risk for STDs among this population,” Leigh E. Szucs, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In 2019, White (55.8%) and Hispanic (56.2%) students were more likely than Blacks (48.2%) to have used a condom during their last sexual intercourse, but use of birth control pills was much higher among Whites (29.1%) than Hispanics (15.4%) or Blacks (12.9%).The Black respondents were much more likely (23.0%) to use no contraceptive method, compared with Whites (8.4%) or Hispanics (13.3%), they said.
“Meeting the unintended pregnancy and STD/HIV prevention needs of black and Hispanic youths is vital,” wrote Dr. Szucs of the CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention and associates. “Understanding and addressing structural barriers that might contribute to the observed differences are important next steps.”
The high school students taking the YRBS were considered sexually active if they had intercourse with at least one person in the previous 3 months. Overall, 3,226 (27.4%) of respondents in 2019 reported being sexually active: 52.2% were female and 47.8% were male, the CDC said.
SOURCE: Szucs LE et al. MMWR. 2019 Aug 21;69(SS-01)11-8.
according to data from the Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS).
Nonuse of birth control in this population dropped to 11.9% in 2019, but the overall trend is one of no significant change since 2003. Meanwhile, the use of birth control pills has taken a different path, with prevalence rising significantly from 16.0% in 2007 to 23.0% in 2019, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
The prevalence of condom use among sexually active students was 54.3% in 2019, up from 53.8% in 2017 – the survey is conducted every 2 years – but down from a high of 63.0% in 2003, the YRBS data show.
Condoms were the most prevalent method of contraception, but the finding that “only approximately half of sexually active students reported any condom use at last sexual intercourse … is concerning given the high risk for STDs among this population,” Leigh E. Szucs, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In 2019, White (55.8%) and Hispanic (56.2%) students were more likely than Blacks (48.2%) to have used a condom during their last sexual intercourse, but use of birth control pills was much higher among Whites (29.1%) than Hispanics (15.4%) or Blacks (12.9%).The Black respondents were much more likely (23.0%) to use no contraceptive method, compared with Whites (8.4%) or Hispanics (13.3%), they said.
“Meeting the unintended pregnancy and STD/HIV prevention needs of black and Hispanic youths is vital,” wrote Dr. Szucs of the CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention and associates. “Understanding and addressing structural barriers that might contribute to the observed differences are important next steps.”
The high school students taking the YRBS were considered sexually active if they had intercourse with at least one person in the previous 3 months. Overall, 3,226 (27.4%) of respondents in 2019 reported being sexually active: 52.2% were female and 47.8% were male, the CDC said.
SOURCE: Szucs LE et al. MMWR. 2019 Aug 21;69(SS-01)11-8.
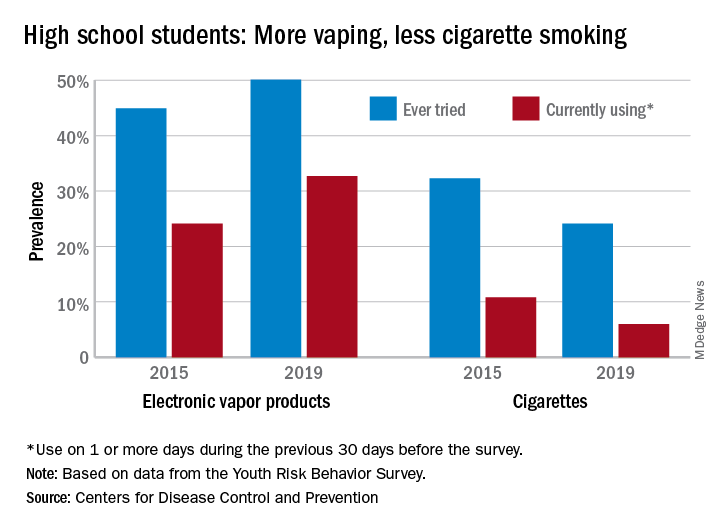
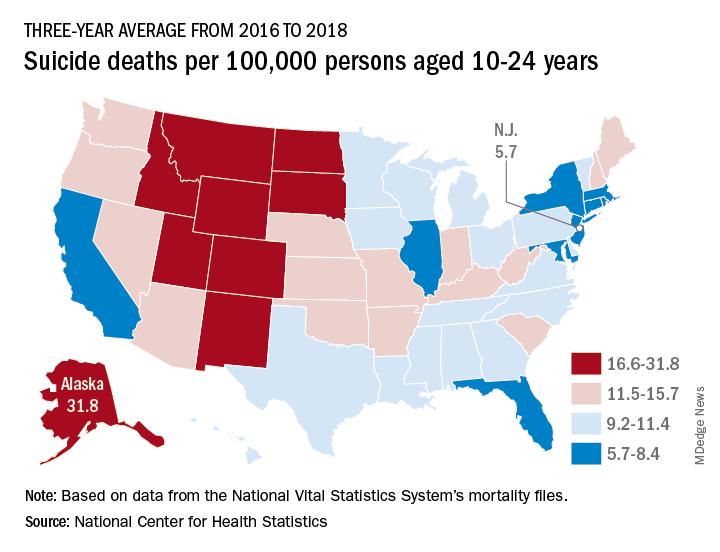
Suicide rates up significantly among adolescents, young adults
Suicide rates in young people aged 10-24 years increased significantly in 42 states from 2007-2009 to 2016-2018, according to a recent analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.
Nationally, the suicide rate jumped 47%, based on the averages for the two 3-year periods, rising from 7.0 per 100,000 persons aged 10-24 years to 10.3 per 100,000. For all ages, the corresponding increase was 47%, Sally C. Curtin, MA, of the NCHS, said in a National Vital Statistics Report.
There was no state with a decrease in suicide rates for adolescents and young adults, as the other eight all had nonsignificant increases, the smallest being 14% in South Dakota. Three-year averages were used to increase statistical power for states with relatively small numbers of deaths but were still not enough to show significance for some large increases, such as the 48% rise in Delaware, Ms. Curtin noted.
In 2016-2018, Alaska’s suicide rate of 31.8 per 100,000 persons aged 10-24 years was the highest in the country, followed by South Dakota (23.6), Montana (23.2), and Wyoming (20.5). New Jersey had the lowest rate at 5.7 per 100,000, with New York and Rhode Island both slightly higher at 5.9 and Connecticut at 6.3, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
Even the low numbers, however, hide some large changes, as New Jersey (up by 39%) and New York (up by 44%) were among the 42 states with statistically significant increases, which ranged from 21.7% in Maryland to 110% in New Hampshire, Ms. Curtin said in the report. The increases seen in this analysis contrast with data from the preceding time period, as “the suicide rate among persons aged 10-24 was statistically stable from 2000 to 2007.”
SOURCE: Curtin SC. National Vital Statistics Reports. 2020;69(11)1-9.
Suicide rates in young people aged 10-24 years increased significantly in 42 states from 2007-2009 to 2016-2018, according to a recent analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.

Nationally, the suicide rate jumped 47%, based on the averages for the two 3-year periods, rising from 7.0 per 100,000 persons aged 10-24 years to 10.3 per 100,000. For all ages, the corresponding increase was 47%, Sally C. Curtin, MA, of the NCHS, said in a National Vital Statistics Report.
There was no state with a decrease in suicide rates for adolescents and young adults, as the other eight all had nonsignificant increases, the smallest being 14% in South Dakota. Three-year averages were used to increase statistical power for states with relatively small numbers of deaths but were still not enough to show significance for some large increases, such as the 48% rise in Delaware, Ms. Curtin noted.
In 2016-2018, Alaska’s suicide rate of 31.8 per 100,000 persons aged 10-24 years was the highest in the country, followed by South Dakota (23.6), Montana (23.2), and Wyoming (20.5). New Jersey had the lowest rate at 5.7 per 100,000, with New York and Rhode Island both slightly higher at 5.9 and Connecticut at 6.3, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
Even the low numbers, however, hide some large changes, as New Jersey (up by 39%) and New York (up by 44%) were among the 42 states with statistically significant increases, which ranged from 21.7% in Maryland to 110% in New Hampshire, Ms. Curtin said in the report. The increases seen in this analysis contrast with data from the preceding time period, as “the suicide rate among persons aged 10-24 was statistically stable from 2000 to 2007.”
SOURCE: Curtin SC. National Vital Statistics Reports. 2020;69(11)1-9.
Suicide rates in young people aged 10-24 years increased significantly in 42 states from 2007-2009 to 2016-2018, according to a recent analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.

Nationally, the suicide rate jumped 47%, based on the averages for the two 3-year periods, rising from 7.0 per 100,000 persons aged 10-24 years to 10.3 per 100,000. For all ages, the corresponding increase was 47%, Sally C. Curtin, MA, of the NCHS, said in a National Vital Statistics Report.
There was no state with a decrease in suicide rates for adolescents and young adults, as the other eight all had nonsignificant increases, the smallest being 14% in South Dakota. Three-year averages were used to increase statistical power for states with relatively small numbers of deaths but were still not enough to show significance for some large increases, such as the 48% rise in Delaware, Ms. Curtin noted.
In 2016-2018, Alaska’s suicide rate of 31.8 per 100,000 persons aged 10-24 years was the highest in the country, followed by South Dakota (23.6), Montana (23.2), and Wyoming (20.5). New Jersey had the lowest rate at 5.7 per 100,000, with New York and Rhode Island both slightly higher at 5.9 and Connecticut at 6.3, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
Even the low numbers, however, hide some large changes, as New Jersey (up by 39%) and New York (up by 44%) were among the 42 states with statistically significant increases, which ranged from 21.7% in Maryland to 110% in New Hampshire, Ms. Curtin said in the report. The increases seen in this analysis contrast with data from the preceding time period, as “the suicide rate among persons aged 10-24 was statistically stable from 2000 to 2007.”
SOURCE: Curtin SC. National Vital Statistics Reports. 2020;69(11)1-9.
Disparities seen in COVID-19–related avoidance of care
In the early weeks and months of the COVID-19 pandemic, many people were trying to avoid the coronavirus by staying away from emergency rooms and medical offices. But how many people is “many”?
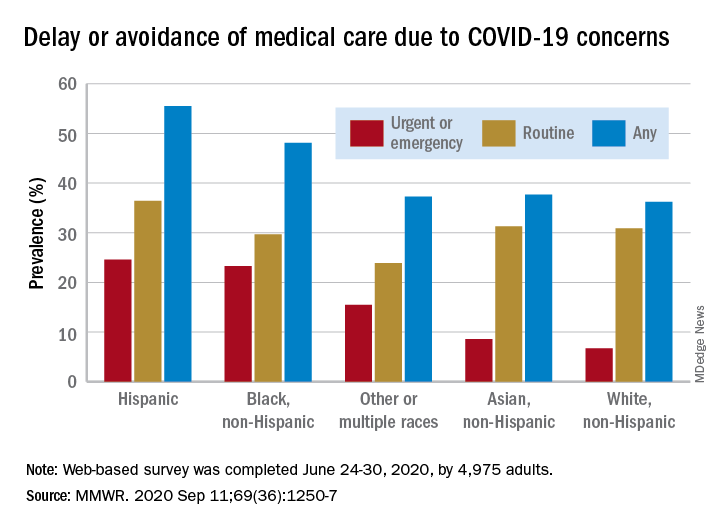
Turns out almost 41% of Americans delayed or avoided some form of medical care because of concerns about COVID-19, according to the results of a survey conducted June 24-30 by commercial survey company Qualtrics.
More specifically, the avoidance looks like this: 31.5% of the 4,975 adult respondents had avoided routine care and 12.0% had avoided urgent or emergency care, Mark E. Czeisler and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. The two categories were not mutually exclusive since respondents could select both routine care and urgent/emergency care.
There were, however, a number of significant disparities hidden among those numbers for the overall population. Blacks and Hispanics, with respective prevalences of 23.3% and 24.6%, were significantly more likely to delay or avoid urgent/emergency care than were Whites (6.7%), said Mr. Czeisler, a graduate student at Monash University, Melbourne, and associates.
Those differences “are especially concerning given increased COVID-19–associated mortality among Black adults and Hispanic adults,” they noted, adding that “age-adjusted COVID-19 hospitalization rates are approximately five times higher among Black persons and four times higher among Hispanic persons than” among Whites.
Other significant disparities in urgent/emergency care avoidance included the following:
- Unpaid caregivers for adults (29.8%) vs. noncaregivers (5.4%).
- Adults with two or more underlying conditions (22.7%) vs. those without such conditions (8.2%).
- Those with a disability (22.8%) vs. those without (8.9%).
- Those with health insurance (12.4%) vs. those without (7.8%).
The highest prevalence for all types of COVID-19–related delay and avoidance came from the adult caregivers (64.3%), followed by those with a disability (60.3%) and adults aged 18-24 years (57.2%). The lowest prevalence numbers were for adults with health insurance (24.8%) and those who were not caregivers for adults (32.2%), Mr. Czeisler and associates reported.
These reports of delayed and avoided care “might reflect adherence to community mitigation efforts such as stay-at-home orders, temporary closures of health facilities, or additional factors. However, if routine care avoidance were to be sustained, adults could miss opportunities for management of chronic conditions, receipt of routine vaccinations, or early detection of new conditions, which might worsen outcomes,” they wrote.
SOURCE: Czeisler ME et al. MMWR. 2020 Sep 11;69(36):1250-7.
In the early weeks and months of the COVID-19 pandemic, many people were trying to avoid the coronavirus by staying away from emergency rooms and medical offices. But how many people is “many”?

Turns out almost 41% of Americans delayed or avoided some form of medical care because of concerns about COVID-19, according to the results of a survey conducted June 24-30 by commercial survey company Qualtrics.
More specifically, the avoidance looks like this: 31.5% of the 4,975 adult respondents had avoided routine care and 12.0% had avoided urgent or emergency care, Mark E. Czeisler and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. The two categories were not mutually exclusive since respondents could select both routine care and urgent/emergency care.
There were, however, a number of significant disparities hidden among those numbers for the overall population. Blacks and Hispanics, with respective prevalences of 23.3% and 24.6%, were significantly more likely to delay or avoid urgent/emergency care than were Whites (6.7%), said Mr. Czeisler, a graduate student at Monash University, Melbourne, and associates.
Those differences “are especially concerning given increased COVID-19–associated mortality among Black adults and Hispanic adults,” they noted, adding that “age-adjusted COVID-19 hospitalization rates are approximately five times higher among Black persons and four times higher among Hispanic persons than” among Whites.
Other significant disparities in urgent/emergency care avoidance included the following:
- Unpaid caregivers for adults (29.8%) vs. noncaregivers (5.4%).
- Adults with two or more underlying conditions (22.7%) vs. those without such conditions (8.2%).
- Those with a disability (22.8%) vs. those without (8.9%).
- Those with health insurance (12.4%) vs. those without (7.8%).
The highest prevalence for all types of COVID-19–related delay and avoidance came from the adult caregivers (64.3%), followed by those with a disability (60.3%) and adults aged 18-24 years (57.2%). The lowest prevalence numbers were for adults with health insurance (24.8%) and those who were not caregivers for adults (32.2%), Mr. Czeisler and associates reported.
These reports of delayed and avoided care “might reflect adherence to community mitigation efforts such as stay-at-home orders, temporary closures of health facilities, or additional factors. However, if routine care avoidance were to be sustained, adults could miss opportunities for management of chronic conditions, receipt of routine vaccinations, or early detection of new conditions, which might worsen outcomes,” they wrote.
SOURCE: Czeisler ME et al. MMWR. 2020 Sep 11;69(36):1250-7.
In the early weeks and months of the COVID-19 pandemic, many people were trying to avoid the coronavirus by staying away from emergency rooms and medical offices. But how many people is “many”?

Turns out almost 41% of Americans delayed or avoided some form of medical care because of concerns about COVID-19, according to the results of a survey conducted June 24-30 by commercial survey company Qualtrics.
More specifically, the avoidance looks like this: 31.5% of the 4,975 adult respondents had avoided routine care and 12.0% had avoided urgent or emergency care, Mark E. Czeisler and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. The two categories were not mutually exclusive since respondents could select both routine care and urgent/emergency care.
There were, however, a number of significant disparities hidden among those numbers for the overall population. Blacks and Hispanics, with respective prevalences of 23.3% and 24.6%, were significantly more likely to delay or avoid urgent/emergency care than were Whites (6.7%), said Mr. Czeisler, a graduate student at Monash University, Melbourne, and associates.
Those differences “are especially concerning given increased COVID-19–associated mortality among Black adults and Hispanic adults,” they noted, adding that “age-adjusted COVID-19 hospitalization rates are approximately five times higher among Black persons and four times higher among Hispanic persons than” among Whites.
Other significant disparities in urgent/emergency care avoidance included the following:
- Unpaid caregivers for adults (29.8%) vs. noncaregivers (5.4%).
- Adults with two or more underlying conditions (22.7%) vs. those without such conditions (8.2%).
- Those with a disability (22.8%) vs. those without (8.9%).
- Those with health insurance (12.4%) vs. those without (7.8%).
The highest prevalence for all types of COVID-19–related delay and avoidance came from the adult caregivers (64.3%), followed by those with a disability (60.3%) and adults aged 18-24 years (57.2%). The lowest prevalence numbers were for adults with health insurance (24.8%) and those who were not caregivers for adults (32.2%), Mr. Czeisler and associates reported.
These reports of delayed and avoided care “might reflect adherence to community mitigation efforts such as stay-at-home orders, temporary closures of health facilities, or additional factors. However, if routine care avoidance were to be sustained, adults could miss opportunities for management of chronic conditions, receipt of routine vaccinations, or early detection of new conditions, which might worsen outcomes,” they wrote.
SOURCE: Czeisler ME et al. MMWR. 2020 Sep 11;69(36):1250-7.
One in seven high schoolers is misusing opioids
according to an analysis from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
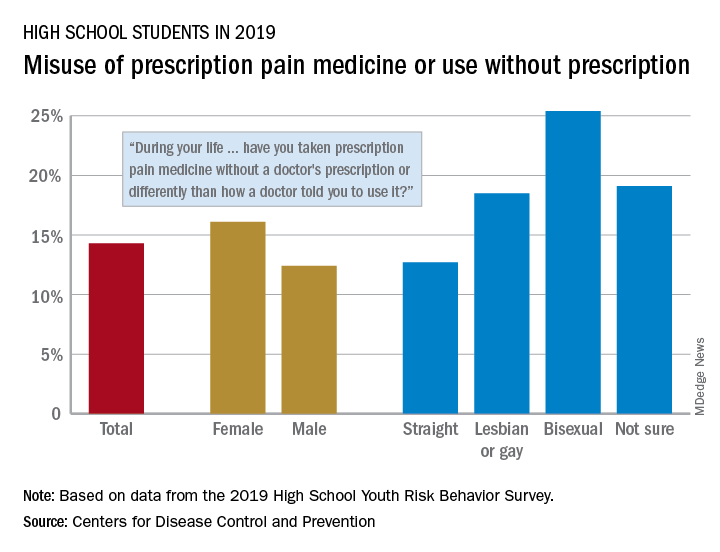
That type of opioid use/misuse, reported by 14.3% of respondents to the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, was more common among females (16.1%) than males (12.4%) and even more prevalent among nonheterosexuals and those who are unsure about their sexual identity, Christopher M. Jones, PharmD, DrPH, and associates at the CDC said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The YRBS data show that 18.5% of gay or lesbian students had, at some point in their lives, used a prescription opioid differently than a physician had told them to or taken one without a prescription. That figure was slightly higher (19.1%) for those unsure of their sexual identity, considerably higher (25.4%) for bisexuals, and lower for heterosexuals (12.7%), they reported.
The pattern for current use/misuse of opioids, defined as use one or more times in the 30 days before the survey, was similar to ever use but somewhat less pronounced in 2019. Prevalence was 7.2% for all students in grades 9-12, 8.3% for females, and 6.1% for males. By sexual identity, prevalence was 6.4% for heterosexuals, 7.6% for gays or lesbians, 11.5% for those unsure about their sexual identity, and 13.1% for bisexuals, based on the YRBS data.
This increased misuse of opioids among sexual minority youths, “even after controlling for other demographic and substance use characteristics ... emphasizes the importance of identifying tailored prevention strategies to address disparities among this vulnerable population,” the CDC researchers wrote.
SOURCE: Jones CM et al. MMWR Suppl. 2020 Aug 21;69(1):38-46.
according to an analysis from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

That type of opioid use/misuse, reported by 14.3% of respondents to the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, was more common among females (16.1%) than males (12.4%) and even more prevalent among nonheterosexuals and those who are unsure about their sexual identity, Christopher M. Jones, PharmD, DrPH, and associates at the CDC said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The YRBS data show that 18.5% of gay or lesbian students had, at some point in their lives, used a prescription opioid differently than a physician had told them to or taken one without a prescription. That figure was slightly higher (19.1%) for those unsure of their sexual identity, considerably higher (25.4%) for bisexuals, and lower for heterosexuals (12.7%), they reported.
The pattern for current use/misuse of opioids, defined as use one or more times in the 30 days before the survey, was similar to ever use but somewhat less pronounced in 2019. Prevalence was 7.2% for all students in grades 9-12, 8.3% for females, and 6.1% for males. By sexual identity, prevalence was 6.4% for heterosexuals, 7.6% for gays or lesbians, 11.5% for those unsure about their sexual identity, and 13.1% for bisexuals, based on the YRBS data.
This increased misuse of opioids among sexual minority youths, “even after controlling for other demographic and substance use characteristics ... emphasizes the importance of identifying tailored prevention strategies to address disparities among this vulnerable population,” the CDC researchers wrote.
SOURCE: Jones CM et al. MMWR Suppl. 2020 Aug 21;69(1):38-46.
according to an analysis from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

That type of opioid use/misuse, reported by 14.3% of respondents to the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, was more common among females (16.1%) than males (12.4%) and even more prevalent among nonheterosexuals and those who are unsure about their sexual identity, Christopher M. Jones, PharmD, DrPH, and associates at the CDC said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The YRBS data show that 18.5% of gay or lesbian students had, at some point in their lives, used a prescription opioid differently than a physician had told them to or taken one without a prescription. That figure was slightly higher (19.1%) for those unsure of their sexual identity, considerably higher (25.4%) for bisexuals, and lower for heterosexuals (12.7%), they reported.
The pattern for current use/misuse of opioids, defined as use one or more times in the 30 days before the survey, was similar to ever use but somewhat less pronounced in 2019. Prevalence was 7.2% for all students in grades 9-12, 8.3% for females, and 6.1% for males. By sexual identity, prevalence was 6.4% for heterosexuals, 7.6% for gays or lesbians, 11.5% for those unsure about their sexual identity, and 13.1% for bisexuals, based on the YRBS data.
This increased misuse of opioids among sexual minority youths, “even after controlling for other demographic and substance use characteristics ... emphasizes the importance of identifying tailored prevention strategies to address disparities among this vulnerable population,” the CDC researchers wrote.
SOURCE: Jones CM et al. MMWR Suppl. 2020 Aug 21;69(1):38-46.
FROM MMWR
Atezolizumab TNBC indication ‘in jeopardy’ because of phase 3 results
The FDA said the phase 3 IMpassion131 trial showed that atezolizumab plus paclitaxel did not significantly reduce the risk of cancer progression and death, when compared with paclitaxel plus placebo, in programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1)–positive patients.
“Additionally, interim overall survival results favored paclitaxel plus placebo over paclitaxel plus atezolizumab in both the PD-L1-positive population and total population,” the FDA noted.
As a result, “health care professionals should not replace paclitaxel protein-bound (Abraxane) with paclitaxel in clinical practice,” the FDA advised.
Atezolizumab is approved for use in combination with protein-bound paclitaxel, also known as nanoparticle albumin–bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel), to treat patients with unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic TNBC whose tumors express PD-L1, as detected by an FDA-approved test. The combination was granted accelerated approval for this indication last year.
Atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel is the combination most often used in PD-L1-positive TNBC, as opposed to atezolizumab and unbound paclitaxel, said Melinda L. Telli, MD, an associate professor of medicine and director of the Stanford Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Program at Stanford (Calif.) University.
However, as the FDA noted, “continued approval of atezolizumab in combination with [nab-paclitaxel] may be contingent on proven benefit of the treatment in additional trials.”
Dr. Telli explained that atezolizumab was granted accelerated approval for the treatment of PD-L1-positive TNBC based on results of the phase 3 IMpassion130 trial, which compared nab-paclitaxel plus atezolizumab with nab-paclitaxel plus placebo.
“Additional data from IMpassion131 was hoped to be used to support the conversion of the accelerated approval to a full approval. Since IMpassion131 was negative, it unfortunately places the status of atezolizumab in [TNBC] in jeopardy as the benefits were not corroborated. The FDA may move to revoke the approval of atezolizumab for [TNBC],” Dr. Telli said.
In its alert, the FDA stated that it “will review the findings of IMpassion131 and will communicate new information regarding the IMpassion131 results and any potential changes to prescribing information.”
“We need to wait for full presentation and publication of the study results, but, in my assessment, the negative results in IMpassion131 are most likely due to differences in patient selection [from IMpassion130],” Dr. Telli said.
Results from IMpassion131 are scheduled to be presented at the ESMO Virtual Congress 2020.
The IMpassion trials were funded by Roche, maker of atezolizumab. Dr. Telli disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Merck, PharmaMar, Pfizer, and Tesaro.
The FDA said the phase 3 IMpassion131 trial showed that atezolizumab plus paclitaxel did not significantly reduce the risk of cancer progression and death, when compared with paclitaxel plus placebo, in programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1)–positive patients.
“Additionally, interim overall survival results favored paclitaxel plus placebo over paclitaxel plus atezolizumab in both the PD-L1-positive population and total population,” the FDA noted.
As a result, “health care professionals should not replace paclitaxel protein-bound (Abraxane) with paclitaxel in clinical practice,” the FDA advised.
Atezolizumab is approved for use in combination with protein-bound paclitaxel, also known as nanoparticle albumin–bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel), to treat patients with unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic TNBC whose tumors express PD-L1, as detected by an FDA-approved test. The combination was granted accelerated approval for this indication last year.
Atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel is the combination most often used in PD-L1-positive TNBC, as opposed to atezolizumab and unbound paclitaxel, said Melinda L. Telli, MD, an associate professor of medicine and director of the Stanford Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Program at Stanford (Calif.) University.
However, as the FDA noted, “continued approval of atezolizumab in combination with [nab-paclitaxel] may be contingent on proven benefit of the treatment in additional trials.”
Dr. Telli explained that atezolizumab was granted accelerated approval for the treatment of PD-L1-positive TNBC based on results of the phase 3 IMpassion130 trial, which compared nab-paclitaxel plus atezolizumab with nab-paclitaxel plus placebo.
“Additional data from IMpassion131 was hoped to be used to support the conversion of the accelerated approval to a full approval. Since IMpassion131 was negative, it unfortunately places the status of atezolizumab in [TNBC] in jeopardy as the benefits were not corroborated. The FDA may move to revoke the approval of atezolizumab for [TNBC],” Dr. Telli said.
In its alert, the FDA stated that it “will review the findings of IMpassion131 and will communicate new information regarding the IMpassion131 results and any potential changes to prescribing information.”
“We need to wait for full presentation and publication of the study results, but, in my assessment, the negative results in IMpassion131 are most likely due to differences in patient selection [from IMpassion130],” Dr. Telli said.
Results from IMpassion131 are scheduled to be presented at the ESMO Virtual Congress 2020.
The IMpassion trials were funded by Roche, maker of atezolizumab. Dr. Telli disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Merck, PharmaMar, Pfizer, and Tesaro.
The FDA said the phase 3 IMpassion131 trial showed that atezolizumab plus paclitaxel did not significantly reduce the risk of cancer progression and death, when compared with paclitaxel plus placebo, in programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1)–positive patients.
“Additionally, interim overall survival results favored paclitaxel plus placebo over paclitaxel plus atezolizumab in both the PD-L1-positive population and total population,” the FDA noted.
As a result, “health care professionals should not replace paclitaxel protein-bound (Abraxane) with paclitaxel in clinical practice,” the FDA advised.
Atezolizumab is approved for use in combination with protein-bound paclitaxel, also known as nanoparticle albumin–bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel), to treat patients with unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic TNBC whose tumors express PD-L1, as detected by an FDA-approved test. The combination was granted accelerated approval for this indication last year.
Atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel is the combination most often used in PD-L1-positive TNBC, as opposed to atezolizumab and unbound paclitaxel, said Melinda L. Telli, MD, an associate professor of medicine and director of the Stanford Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Program at Stanford (Calif.) University.
However, as the FDA noted, “continued approval of atezolizumab in combination with [nab-paclitaxel] may be contingent on proven benefit of the treatment in additional trials.”
Dr. Telli explained that atezolizumab was granted accelerated approval for the treatment of PD-L1-positive TNBC based on results of the phase 3 IMpassion130 trial, which compared nab-paclitaxel plus atezolizumab with nab-paclitaxel plus placebo.
“Additional data from IMpassion131 was hoped to be used to support the conversion of the accelerated approval to a full approval. Since IMpassion131 was negative, it unfortunately places the status of atezolizumab in [TNBC] in jeopardy as the benefits were not corroborated. The FDA may move to revoke the approval of atezolizumab for [TNBC],” Dr. Telli said.
In its alert, the FDA stated that it “will review the findings of IMpassion131 and will communicate new information regarding the IMpassion131 results and any potential changes to prescribing information.”
“We need to wait for full presentation and publication of the study results, but, in my assessment, the negative results in IMpassion131 are most likely due to differences in patient selection [from IMpassion130],” Dr. Telli said.
Results from IMpassion131 are scheduled to be presented at the ESMO Virtual Congress 2020.
The IMpassion trials were funded by Roche, maker of atezolizumab. Dr. Telli disclosed relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Merck, PharmaMar, Pfizer, and Tesaro.
Pralsetinib: Second drug for RET+ NSCLC approved in U.S.
A second drug is now available in the United States for use in the treatment of patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that tests positive for rearranged during transfection (RET) fusions.
The new drug is pralsetinib (Gavreto). The Food and Drug Administration granted it an accelerated approval for this indication on the basis of response rate data. Continued approval for this indication depends on clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Pralsetinib joins selpercatinib (Retevmo), which was approved in the United States in May 2020 as the first RET-targeted therapy. Selpercatinib is also indicated for use in RET+ NSCLC and was approved for use in RET+ medullary thyroid cancer and RET+ thyroid cancer.
Pralsetinib is still awaiting approval for these thyroid cancer indications.
Both drugs are taken orally; pralsetinib is taken once daily, and selpercatinib is taken twice daily.
For both drugs, before treatment is initiated, laboratory testing is needed to show that a RET gene alteration is present in the tumor.
RET fusions are found in approximately 1%-2% of patients with NSCLC.
They are the latest of a number of tumor-specific gene alterations found in NSCLC that are targeted with an approved drug.
“Targeted therapies have dramatically improved care for patients with non–small cell lung cancer driven by oncogenes, including EGFR and ALK, and the approval of the selective RET inhibitor pralsetinib, or Gavreto, marks another milestone in a paradigm shift toward precision medicine,” Vivek Subbiah, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a press release.
Dr. Subbiah was an investigator of the phase 1/2 clinical trial known as ARROW, which provided the data on which the accelerated approval was based. In this trial, patients with RET+ NSCLC were found by testing with next-generation sequencing, FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization), or other methods.
The ARROW trial involved one cohort of 87 patients who had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. In these patients, the overall response rate (ORR) was 57%, the complete response (CR) rate was 5.7%, and the median duration of response (DOR) was not estimable, according to the manufacturer, Blueprint Medicines.
The trial also involved 27 treatment-naive patients who were ineligible for platinum-based chemotherapy per the study protocol. In this group, the ORR was 70%, and the CR rate was 11%. The median DOR was 9.0 months.
“Patients treated with [pralsetinib] had durable clinical responses, with a subset achieving complete responses characterized by the resolution of all target lesions, an uncommon outcome in metastatic lung cancer,” Dr. Subbiah commented.
“We observed this activity with or without prior therapy and regardless of RET fusion partner or the presence of brain metastases. This approval represents an important advance with the potential to change standards of care for patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC, who have historically had limited treatment options,” Dr. Subbiah added.
Product information for pralsetinib has warnings and precautions of interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, hypertension, hepatotoxicity, hemorrhagic events, risk for impaired wound healing, and risk for embryo-fetal toxicity.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A second drug is now available in the United States for use in the treatment of patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that tests positive for rearranged during transfection (RET) fusions.
The new drug is pralsetinib (Gavreto). The Food and Drug Administration granted it an accelerated approval for this indication on the basis of response rate data. Continued approval for this indication depends on clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Pralsetinib joins selpercatinib (Retevmo), which was approved in the United States in May 2020 as the first RET-targeted therapy. Selpercatinib is also indicated for use in RET+ NSCLC and was approved for use in RET+ medullary thyroid cancer and RET+ thyroid cancer.
Pralsetinib is still awaiting approval for these thyroid cancer indications.
Both drugs are taken orally; pralsetinib is taken once daily, and selpercatinib is taken twice daily.
For both drugs, before treatment is initiated, laboratory testing is needed to show that a RET gene alteration is present in the tumor.
RET fusions are found in approximately 1%-2% of patients with NSCLC.
They are the latest of a number of tumor-specific gene alterations found in NSCLC that are targeted with an approved drug.
“Targeted therapies have dramatically improved care for patients with non–small cell lung cancer driven by oncogenes, including EGFR and ALK, and the approval of the selective RET inhibitor pralsetinib, or Gavreto, marks another milestone in a paradigm shift toward precision medicine,” Vivek Subbiah, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a press release.
Dr. Subbiah was an investigator of the phase 1/2 clinical trial known as ARROW, which provided the data on which the accelerated approval was based. In this trial, patients with RET+ NSCLC were found by testing with next-generation sequencing, FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization), or other methods.
The ARROW trial involved one cohort of 87 patients who had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. In these patients, the overall response rate (ORR) was 57%, the complete response (CR) rate was 5.7%, and the median duration of response (DOR) was not estimable, according to the manufacturer, Blueprint Medicines.
The trial also involved 27 treatment-naive patients who were ineligible for platinum-based chemotherapy per the study protocol. In this group, the ORR was 70%, and the CR rate was 11%. The median DOR was 9.0 months.
“Patients treated with [pralsetinib] had durable clinical responses, with a subset achieving complete responses characterized by the resolution of all target lesions, an uncommon outcome in metastatic lung cancer,” Dr. Subbiah commented.
“We observed this activity with or without prior therapy and regardless of RET fusion partner or the presence of brain metastases. This approval represents an important advance with the potential to change standards of care for patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC, who have historically had limited treatment options,” Dr. Subbiah added.
Product information for pralsetinib has warnings and precautions of interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, hypertension, hepatotoxicity, hemorrhagic events, risk for impaired wound healing, and risk for embryo-fetal toxicity.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A second drug is now available in the United States for use in the treatment of patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that tests positive for rearranged during transfection (RET) fusions.
The new drug is pralsetinib (Gavreto). The Food and Drug Administration granted it an accelerated approval for this indication on the basis of response rate data. Continued approval for this indication depends on clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Pralsetinib joins selpercatinib (Retevmo), which was approved in the United States in May 2020 as the first RET-targeted therapy. Selpercatinib is also indicated for use in RET+ NSCLC and was approved for use in RET+ medullary thyroid cancer and RET+ thyroid cancer.
Pralsetinib is still awaiting approval for these thyroid cancer indications.
Both drugs are taken orally; pralsetinib is taken once daily, and selpercatinib is taken twice daily.
For both drugs, before treatment is initiated, laboratory testing is needed to show that a RET gene alteration is present in the tumor.
RET fusions are found in approximately 1%-2% of patients with NSCLC.
They are the latest of a number of tumor-specific gene alterations found in NSCLC that are targeted with an approved drug.
“Targeted therapies have dramatically improved care for patients with non–small cell lung cancer driven by oncogenes, including EGFR and ALK, and the approval of the selective RET inhibitor pralsetinib, or Gavreto, marks another milestone in a paradigm shift toward precision medicine,” Vivek Subbiah, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a press release.
Dr. Subbiah was an investigator of the phase 1/2 clinical trial known as ARROW, which provided the data on which the accelerated approval was based. In this trial, patients with RET+ NSCLC were found by testing with next-generation sequencing, FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization), or other methods.
The ARROW trial involved one cohort of 87 patients who had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. In these patients, the overall response rate (ORR) was 57%, the complete response (CR) rate was 5.7%, and the median duration of response (DOR) was not estimable, according to the manufacturer, Blueprint Medicines.
The trial also involved 27 treatment-naive patients who were ineligible for platinum-based chemotherapy per the study protocol. In this group, the ORR was 70%, and the CR rate was 11%. The median DOR was 9.0 months.
“Patients treated with [pralsetinib] had durable clinical responses, with a subset achieving complete responses characterized by the resolution of all target lesions, an uncommon outcome in metastatic lung cancer,” Dr. Subbiah commented.
“We observed this activity with or without prior therapy and regardless of RET fusion partner or the presence of brain metastases. This approval represents an important advance with the potential to change standards of care for patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC, who have historically had limited treatment options,” Dr. Subbiah added.
Product information for pralsetinib has warnings and precautions of interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, hypertension, hepatotoxicity, hemorrhagic events, risk for impaired wound healing, and risk for embryo-fetal toxicity.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antidepressant use shows gender, racial disparities
Women are more than twice as likely as men to use antidepressants, and use among White women is at least double that of other races/ethnicities, according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.
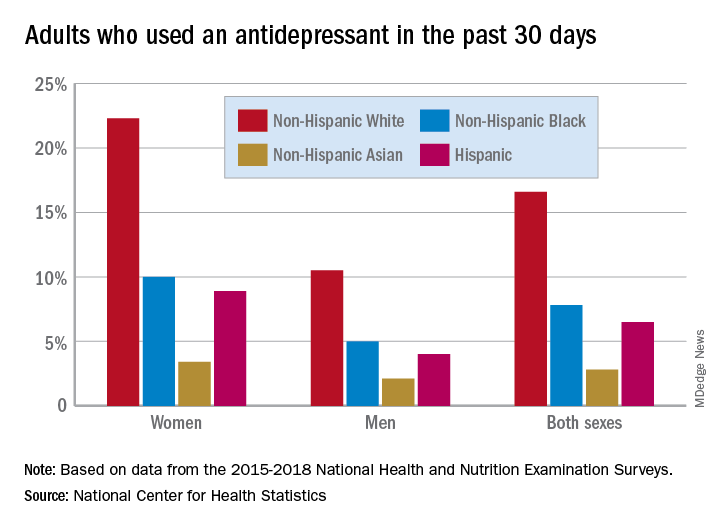
Here are the actual numbers: 17.7% of women and 8.4% of men used an antidepressant in the 30 days before being interviewed for the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Put them together, and it works out to 13.2% of all adults over the 4-year period from 2015 to 2018, Debra J. Brody, MPH, and Qiuping Gu, MD, PhD, said Sept. 4 in an NCHS data brief.
Non-Hispanic White women had a past-30-day prevalence of 22.3%, compared with 10.0% for non-Hispanic Black women, 3.4% for non-Hispanic Asian women, and 8.9% for Hispanic women, based on the NHANES data.
The order was the same for men, but the numbers are lower. Non-Hispanic Whites had the highest antidepressant use at 10.5%, followed by non-Hispanic Blacks (5.0%), non-Hispanic Asians (2.1%), and Hispanics (4.0%). All of the differences between Whites and non-Whites were significant for both women and men, the researchers noted.
A look at trends over time shows that the gap between men and women has widened in the last 10 years. Past-30-day use among women went from 13.8% in 2009-2010 to 18.6% in 2017-2018, with a corresponding increase from 7.1% to 8.7% in men. For women, that change was significant; for men, it was not, Ms. Brody and Dr. Gu said.
The sample size averaged just over 6,000 for each of the five 2-year NHANES cycles included in the analysis. The survey includes a household interview and a physical examination at a mobile exam center.
Women are more than twice as likely as men to use antidepressants, and use among White women is at least double that of other races/ethnicities, according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.

Here are the actual numbers: 17.7% of women and 8.4% of men used an antidepressant in the 30 days before being interviewed for the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Put them together, and it works out to 13.2% of all adults over the 4-year period from 2015 to 2018, Debra J. Brody, MPH, and Qiuping Gu, MD, PhD, said Sept. 4 in an NCHS data brief.
Non-Hispanic White women had a past-30-day prevalence of 22.3%, compared with 10.0% for non-Hispanic Black women, 3.4% for non-Hispanic Asian women, and 8.9% for Hispanic women, based on the NHANES data.
The order was the same for men, but the numbers are lower. Non-Hispanic Whites had the highest antidepressant use at 10.5%, followed by non-Hispanic Blacks (5.0%), non-Hispanic Asians (2.1%), and Hispanics (4.0%). All of the differences between Whites and non-Whites were significant for both women and men, the researchers noted.
A look at trends over time shows that the gap between men and women has widened in the last 10 years. Past-30-day use among women went from 13.8% in 2009-2010 to 18.6% in 2017-2018, with a corresponding increase from 7.1% to 8.7% in men. For women, that change was significant; for men, it was not, Ms. Brody and Dr. Gu said.
The sample size averaged just over 6,000 for each of the five 2-year NHANES cycles included in the analysis. The survey includes a household interview and a physical examination at a mobile exam center.
Women are more than twice as likely as men to use antidepressants, and use among White women is at least double that of other races/ethnicities, according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.

Here are the actual numbers: 17.7% of women and 8.4% of men used an antidepressant in the 30 days before being interviewed for the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Put them together, and it works out to 13.2% of all adults over the 4-year period from 2015 to 2018, Debra J. Brody, MPH, and Qiuping Gu, MD, PhD, said Sept. 4 in an NCHS data brief.
Non-Hispanic White women had a past-30-day prevalence of 22.3%, compared with 10.0% for non-Hispanic Black women, 3.4% for non-Hispanic Asian women, and 8.9% for Hispanic women, based on the NHANES data.
The order was the same for men, but the numbers are lower. Non-Hispanic Whites had the highest antidepressant use at 10.5%, followed by non-Hispanic Blacks (5.0%), non-Hispanic Asians (2.1%), and Hispanics (4.0%). All of the differences between Whites and non-Whites were significant for both women and men, the researchers noted.
A look at trends over time shows that the gap between men and women has widened in the last 10 years. Past-30-day use among women went from 13.8% in 2009-2010 to 18.6% in 2017-2018, with a corresponding increase from 7.1% to 8.7% in men. For women, that change was significant; for men, it was not, Ms. Brody and Dr. Gu said.
The sample size averaged just over 6,000 for each of the five 2-year NHANES cycles included in the analysis. The survey includes a household interview and a physical examination at a mobile exam center.
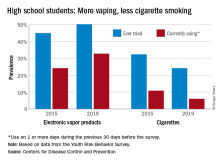
High schoolers prefer tobacco as vapor, not smoke
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
From 2015 to 2019, current use of electronic vapor products among students in grades 9-12 rose from 24.1% to 32.7%, while the same level of cigarette use – on 1 or more days in the previous 30 – dropped from 10.8% to 6.0%, based on data from the Youth Risk Behavior Survey.
Among the survey respondents, 50.1% had at least tried an electronic vapor product by 2019, up from 44.9% in 2015. Cigarettes again showed a decline, as ever use fell from 32.3% to 24.1%, or less than half of the e-product prevalence. Everyday use of vaping products was 7.2% in 2019 (up from 2.0% in 2015), compared with 1.1% for cigarettes (down from 2.3%), the YRBS data show.
“The dramatic increase in electronic vapor product use among high school students has led to increases in overall tobacco product use among U.S. youths, erasing gains made in previous years and leading the U.S. Surgeon General to declare youth e-cigarette use an epidemic in the United States,” MeLisa R. Creamer, PhD, and associates at the CDC wrote in the MMWR.
Electronic vapor products, as defined by the survey, “include e-cigarettes, vapes, vape pens, e-cigars, e-hookahs, hookah pens, and mods.”
Current use of cigarettes among high school students, as measured by the YRBS, has been declining since reaching a high of 36.4% in 1997; the prevalence of everyday use peaked at 12.8% in 1999. Current use of cigars declined as well, falling from 17.7% in 1999 to 5.7% in 2019, according to YRBS data.
“In 2019, a total of 36.5% of high school students currently used any tobacco product, with electronic vapor products being the most commonly used product,” Dr. Creamer and associates wrote in their recent analysis of the YRBS data (MMWR Supp. 2020 Aug 21;69[1]:56-63).
For the first time since the use of electronic vapor products was included in the every-other-year survey in 2015, females were more likely than males to be current users of vaping products last year, 33.5% to 32.0%. Males were heavier users of cigarettes by a margin of 6.9% to 4.9%, the CDC reported.
Geographically speaking, use of both electronic vapor products and cigarettes varied considerably among the 43 states with available data. Current use of electronic products ranged from a low of 9.7% in Utah to a high of 35.7% in West Virginia, with the two states in the same positions regarding current cigarette use: Utah (2.2%) lowest and West Virginia (13.5%) highest, based on the 2019 YRBS data.
“Tobacco product usage has evolved, and the increasing prevalence of electronic vapor product use among youths during recent years is concerning,” Dr. Creamer and associates wrote.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
From 2015 to 2019, current use of electronic vapor products among students in grades 9-12 rose from 24.1% to 32.7%, while the same level of cigarette use – on 1 or more days in the previous 30 – dropped from 10.8% to 6.0%, based on data from the Youth Risk Behavior Survey.
Among the survey respondents, 50.1% had at least tried an electronic vapor product by 2019, up from 44.9% in 2015. Cigarettes again showed a decline, as ever use fell from 32.3% to 24.1%, or less than half of the e-product prevalence. Everyday use of vaping products was 7.2% in 2019 (up from 2.0% in 2015), compared with 1.1% for cigarettes (down from 2.3%), the YRBS data show.
“The dramatic increase in electronic vapor product use among high school students has led to increases in overall tobacco product use among U.S. youths, erasing gains made in previous years and leading the U.S. Surgeon General to declare youth e-cigarette use an epidemic in the United States,” MeLisa R. Creamer, PhD, and associates at the CDC wrote in the MMWR.
Electronic vapor products, as defined by the survey, “include e-cigarettes, vapes, vape pens, e-cigars, e-hookahs, hookah pens, and mods.”
Current use of cigarettes among high school students, as measured by the YRBS, has been declining since reaching a high of 36.4% in 1997; the prevalence of everyday use peaked at 12.8% in 1999. Current use of cigars declined as well, falling from 17.7% in 1999 to 5.7% in 2019, according to YRBS data.
“In 2019, a total of 36.5% of high school students currently used any tobacco product, with electronic vapor products being the most commonly used product,” Dr. Creamer and associates wrote in their recent analysis of the YRBS data (MMWR Supp. 2020 Aug 21;69[1]:56-63).
For the first time since the use of electronic vapor products was included in the every-other-year survey in 2015, females were more likely than males to be current users of vaping products last year, 33.5% to 32.0%. Males were heavier users of cigarettes by a margin of 6.9% to 4.9%, the CDC reported.
Geographically speaking, use of both electronic vapor products and cigarettes varied considerably among the 43 states with available data. Current use of electronic products ranged from a low of 9.7% in Utah to a high of 35.7% in West Virginia, with the two states in the same positions regarding current cigarette use: Utah (2.2%) lowest and West Virginia (13.5%) highest, based on the 2019 YRBS data.
“Tobacco product usage has evolved, and the increasing prevalence of electronic vapor product use among youths during recent years is concerning,” Dr. Creamer and associates wrote.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
From 2015 to 2019, current use of electronic vapor products among students in grades 9-12 rose from 24.1% to 32.7%, while the same level of cigarette use – on 1 or more days in the previous 30 – dropped from 10.8% to 6.0%, based on data from the Youth Risk Behavior Survey.
Among the survey respondents, 50.1% had at least tried an electronic vapor product by 2019, up from 44.9% in 2015. Cigarettes again showed a decline, as ever use fell from 32.3% to 24.1%, or less than half of the e-product prevalence. Everyday use of vaping products was 7.2% in 2019 (up from 2.0% in 2015), compared with 1.1% for cigarettes (down from 2.3%), the YRBS data show.
“The dramatic increase in electronic vapor product use among high school students has led to increases in overall tobacco product use among U.S. youths, erasing gains made in previous years and leading the U.S. Surgeon General to declare youth e-cigarette use an epidemic in the United States,” MeLisa R. Creamer, PhD, and associates at the CDC wrote in the MMWR.
Electronic vapor products, as defined by the survey, “include e-cigarettes, vapes, vape pens, e-cigars, e-hookahs, hookah pens, and mods.”
Current use of cigarettes among high school students, as measured by the YRBS, has been declining since reaching a high of 36.4% in 1997; the prevalence of everyday use peaked at 12.8% in 1999. Current use of cigars declined as well, falling from 17.7% in 1999 to 5.7% in 2019, according to YRBS data.
“In 2019, a total of 36.5% of high school students currently used any tobacco product, with electronic vapor products being the most commonly used product,” Dr. Creamer and associates wrote in their recent analysis of the YRBS data (MMWR Supp. 2020 Aug 21;69[1]:56-63).
For the first time since the use of electronic vapor products was included in the every-other-year survey in 2015, females were more likely than males to be current users of vaping products last year, 33.5% to 32.0%. Males were heavier users of cigarettes by a margin of 6.9% to 4.9%, the CDC reported.
Geographically speaking, use of both electronic vapor products and cigarettes varied considerably among the 43 states with available data. Current use of electronic products ranged from a low of 9.7% in Utah to a high of 35.7% in West Virginia, with the two states in the same positions regarding current cigarette use: Utah (2.2%) lowest and West Virginia (13.5%) highest, based on the 2019 YRBS data.
“Tobacco product usage has evolved, and the increasing prevalence of electronic vapor product use among youths during recent years is concerning,” Dr. Creamer and associates wrote.