User login
FDA expands remdesivir use for all COVID-19 hospitalized patients
An EUA of remdesivir issued in May allowed the drug to be used only for patients with severe COVID-19, specifically, COVID-19 patients with low blood oxygen levels or who need oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
“Today, based on the Agency’s ongoing review of the EUA, including its review of the totality of scientific information now available, the FDA has determined that it is reasonable to believe Veklury may be effective for the treatment of suspected or laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 in all hospitalized adult and pediatric patients,” the FDA news release about the expanded EUA said. “The Agency’s review has also concluded that the known and potential benefits of Veklury outweigh the known and potential risks for these uses.”
‘Further evaluation’ needed
The EUA expansion is partially based on the results of a randomized, open-label trial that Gilead Sciences, remdesivir’s manufacturer, conducted at multiple sites.
The trial showed that a 5-day course of remdesivir was associated with statistically significant improvement among patients hospitalized with moderate COVID-19 in comparison with those receiving standard care. However, patients who were randomly assigned to a receive longer, 10-day remdesivir course had not improved significantly 11 days after treatment started, compared with those who received standard care.
Results with remdesivir in this trial and in two previously reported randomized trials varied, “raising the question of whether the discrepancies are artifacts of study design choices, including patient populations, or whether the drug is less efficacious than hoped,” wrote Erin K. McCreary, PharmD, and Derek C. Angus, MD, MPH, with the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, in an editorial that accompanied publication of the trials in JAMA.
Angus previously expressed concern that expanding remdesivir’s EUA could “interrupt or thwart efforts to execute the needed RCTs [randomized controlled trials].
“We think there really needs to be further evaluation of remdesivir in large-scale RCTs adequately powered to understand in which patients, at which dose, given at which point in the course of illness leads to what concrete and tangible improvement in clinical outcomes,” he told Medscape Medical News.
“At this point, remdesivir definitely holds promise, but given the cost to produce and distribute the drug, it seems crucial to know with more certainty how best to use it,” Angus said.
The EUA expansion is also partially based on results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that the National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases conducted. In that trial, there was a statistically significant reduction in median recovery time and higher odds of clinical improvement after 2 weeks for hospitalized patients who received remdesivir.
For hospitalized patients with mild to moderate disease, the results were consistent with the overall study results but were not statistically significant.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An EUA of remdesivir issued in May allowed the drug to be used only for patients with severe COVID-19, specifically, COVID-19 patients with low blood oxygen levels or who need oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
“Today, based on the Agency’s ongoing review of the EUA, including its review of the totality of scientific information now available, the FDA has determined that it is reasonable to believe Veklury may be effective for the treatment of suspected or laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 in all hospitalized adult and pediatric patients,” the FDA news release about the expanded EUA said. “The Agency’s review has also concluded that the known and potential benefits of Veklury outweigh the known and potential risks for these uses.”
‘Further evaluation’ needed
The EUA expansion is partially based on the results of a randomized, open-label trial that Gilead Sciences, remdesivir’s manufacturer, conducted at multiple sites.
The trial showed that a 5-day course of remdesivir was associated with statistically significant improvement among patients hospitalized with moderate COVID-19 in comparison with those receiving standard care. However, patients who were randomly assigned to a receive longer, 10-day remdesivir course had not improved significantly 11 days after treatment started, compared with those who received standard care.
Results with remdesivir in this trial and in two previously reported randomized trials varied, “raising the question of whether the discrepancies are artifacts of study design choices, including patient populations, or whether the drug is less efficacious than hoped,” wrote Erin K. McCreary, PharmD, and Derek C. Angus, MD, MPH, with the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, in an editorial that accompanied publication of the trials in JAMA.
Angus previously expressed concern that expanding remdesivir’s EUA could “interrupt or thwart efforts to execute the needed RCTs [randomized controlled trials].
“We think there really needs to be further evaluation of remdesivir in large-scale RCTs adequately powered to understand in which patients, at which dose, given at which point in the course of illness leads to what concrete and tangible improvement in clinical outcomes,” he told Medscape Medical News.
“At this point, remdesivir definitely holds promise, but given the cost to produce and distribute the drug, it seems crucial to know with more certainty how best to use it,” Angus said.
The EUA expansion is also partially based on results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that the National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases conducted. In that trial, there was a statistically significant reduction in median recovery time and higher odds of clinical improvement after 2 weeks for hospitalized patients who received remdesivir.
For hospitalized patients with mild to moderate disease, the results were consistent with the overall study results but were not statistically significant.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An EUA of remdesivir issued in May allowed the drug to be used only for patients with severe COVID-19, specifically, COVID-19 patients with low blood oxygen levels or who need oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
“Today, based on the Agency’s ongoing review of the EUA, including its review of the totality of scientific information now available, the FDA has determined that it is reasonable to believe Veklury may be effective for the treatment of suspected or laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 in all hospitalized adult and pediatric patients,” the FDA news release about the expanded EUA said. “The Agency’s review has also concluded that the known and potential benefits of Veklury outweigh the known and potential risks for these uses.”
‘Further evaluation’ needed
The EUA expansion is partially based on the results of a randomized, open-label trial that Gilead Sciences, remdesivir’s manufacturer, conducted at multiple sites.
The trial showed that a 5-day course of remdesivir was associated with statistically significant improvement among patients hospitalized with moderate COVID-19 in comparison with those receiving standard care. However, patients who were randomly assigned to a receive longer, 10-day remdesivir course had not improved significantly 11 days after treatment started, compared with those who received standard care.
Results with remdesivir in this trial and in two previously reported randomized trials varied, “raising the question of whether the discrepancies are artifacts of study design choices, including patient populations, or whether the drug is less efficacious than hoped,” wrote Erin K. McCreary, PharmD, and Derek C. Angus, MD, MPH, with the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, in an editorial that accompanied publication of the trials in JAMA.
Angus previously expressed concern that expanding remdesivir’s EUA could “interrupt or thwart efforts to execute the needed RCTs [randomized controlled trials].
“We think there really needs to be further evaluation of remdesivir in large-scale RCTs adequately powered to understand in which patients, at which dose, given at which point in the course of illness leads to what concrete and tangible improvement in clinical outcomes,” he told Medscape Medical News.
“At this point, remdesivir definitely holds promise, but given the cost to produce and distribute the drug, it seems crucial to know with more certainty how best to use it,” Angus said.
The EUA expansion is also partially based on results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that the National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases conducted. In that trial, there was a statistically significant reduction in median recovery time and higher odds of clinical improvement after 2 weeks for hospitalized patients who received remdesivir.
For hospitalized patients with mild to moderate disease, the results were consistent with the overall study results but were not statistically significant.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves point-of-care COVID-19 antigen test
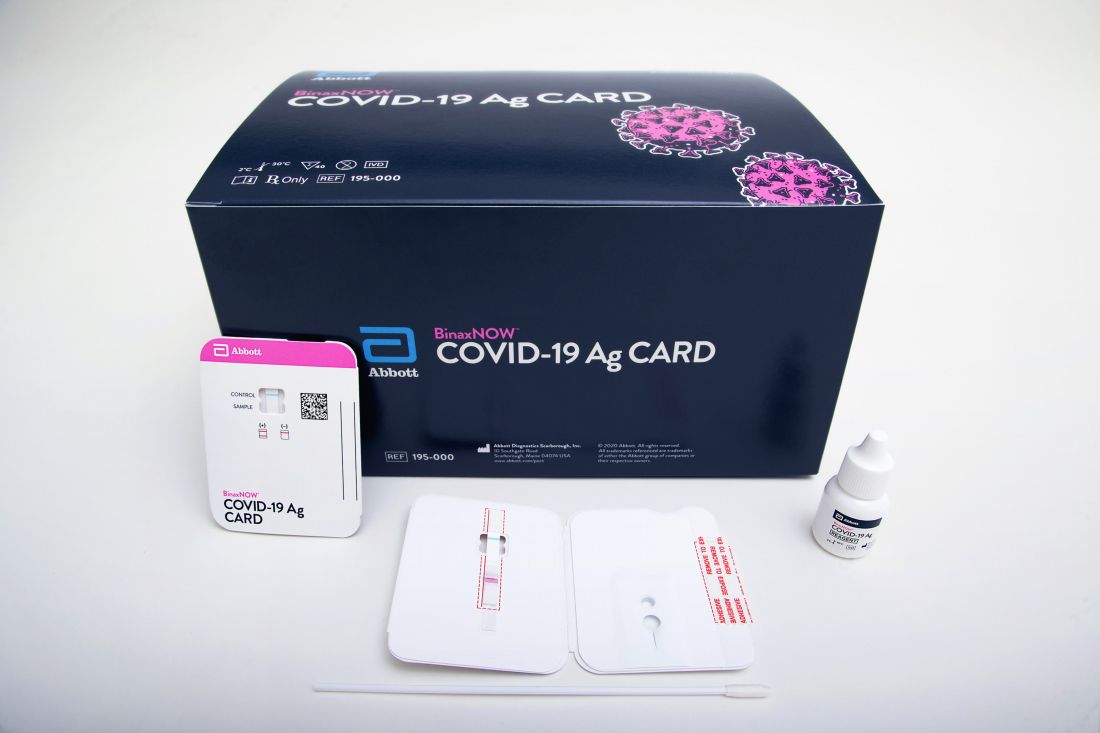
The BinaxNOW COVID-19 Ag Card (Abbott) is similar in some ways to a home pregnancy test. Clinicians read results on a card – one line for a negative result, two lines for positive.
A health care provider swabs a symptomatic patient’s nose, twirls the sample on a test card with a reagent, and waits approximately 15 minutes for results. No additional equipment is required.
Abbott expects the test to cost about $5.00, the company announced.
Office-based physicians, ED physicians, and school nurses could potentially use the product as a point-of-care test. The FDA granted the test emergency use authorization. It is approved for people suspected of having COVID-19 who are within 7 days of symptom onset.
“This new COVID-19 antigen test is an important addition to available tests because the results can be read in minutes, right off the testing card,” Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, wrote in a news release. “This means people will know if they have the virus in almost real time.”
“This fits into the testing landscape as a simple, inexpensive test that does not require additional equipment,” Marcus Lynch, PhD, assistant manager of the Health Care Horizon Scanning program at ECRI, told Medscape Medical News when asked to comment. ECRI is an independent, nonprofit organization that reviews and analyses COVID-19 therapeutics and diagnostics.
The test could help with early triage of patients who test positive, perhaps alerting physicians to the need to start COVID-19 therapy, added Lynch, who specializes in immunology and vaccine development. The test also could be useful in low-resource settings.
The FDA included a caveat: antigen tests are generally less sensitive than molecular assays. “Due to the potential for decreased sensitivity compared to molecular assays, negative results from an antigen test may need to be confirmed with a molecular test prior to making treatment decisions,” the agency noted.
Lynch agreed and said that when a patient tests negative, physicians still need to use their clinical judgment on the basis of symptoms and other factors. The test is not designed for population-based screening of asymptomatic people, he added.
Abbott announced plans to make up to 50 million tests available per month in the United States starting in October. The product comes with a free smartphone app that people can use to share results with an employer or with others as needed.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.

The BinaxNOW COVID-19 Ag Card (Abbott) is similar in some ways to a home pregnancy test. Clinicians read results on a card – one line for a negative result, two lines for positive.
A health care provider swabs a symptomatic patient’s nose, twirls the sample on a test card with a reagent, and waits approximately 15 minutes for results. No additional equipment is required.
Abbott expects the test to cost about $5.00, the company announced.
Office-based physicians, ED physicians, and school nurses could potentially use the product as a point-of-care test. The FDA granted the test emergency use authorization. It is approved for people suspected of having COVID-19 who are within 7 days of symptom onset.
“This new COVID-19 antigen test is an important addition to available tests because the results can be read in minutes, right off the testing card,” Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, wrote in a news release. “This means people will know if they have the virus in almost real time.”
“This fits into the testing landscape as a simple, inexpensive test that does not require additional equipment,” Marcus Lynch, PhD, assistant manager of the Health Care Horizon Scanning program at ECRI, told Medscape Medical News when asked to comment. ECRI is an independent, nonprofit organization that reviews and analyses COVID-19 therapeutics and diagnostics.
The test could help with early triage of patients who test positive, perhaps alerting physicians to the need to start COVID-19 therapy, added Lynch, who specializes in immunology and vaccine development. The test also could be useful in low-resource settings.
The FDA included a caveat: antigen tests are generally less sensitive than molecular assays. “Due to the potential for decreased sensitivity compared to molecular assays, negative results from an antigen test may need to be confirmed with a molecular test prior to making treatment decisions,” the agency noted.
Lynch agreed and said that when a patient tests negative, physicians still need to use their clinical judgment on the basis of symptoms and other factors. The test is not designed for population-based screening of asymptomatic people, he added.
Abbott announced plans to make up to 50 million tests available per month in the United States starting in October. The product comes with a free smartphone app that people can use to share results with an employer or with others as needed.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.

The BinaxNOW COVID-19 Ag Card (Abbott) is similar in some ways to a home pregnancy test. Clinicians read results on a card – one line for a negative result, two lines for positive.
A health care provider swabs a symptomatic patient’s nose, twirls the sample on a test card with a reagent, and waits approximately 15 minutes for results. No additional equipment is required.
Abbott expects the test to cost about $5.00, the company announced.
Office-based physicians, ED physicians, and school nurses could potentially use the product as a point-of-care test. The FDA granted the test emergency use authorization. It is approved for people suspected of having COVID-19 who are within 7 days of symptom onset.
“This new COVID-19 antigen test is an important addition to available tests because the results can be read in minutes, right off the testing card,” Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, wrote in a news release. “This means people will know if they have the virus in almost real time.”
“This fits into the testing landscape as a simple, inexpensive test that does not require additional equipment,” Marcus Lynch, PhD, assistant manager of the Health Care Horizon Scanning program at ECRI, told Medscape Medical News when asked to comment. ECRI is an independent, nonprofit organization that reviews and analyses COVID-19 therapeutics and diagnostics.
The test could help with early triage of patients who test positive, perhaps alerting physicians to the need to start COVID-19 therapy, added Lynch, who specializes in immunology and vaccine development. The test also could be useful in low-resource settings.
The FDA included a caveat: antigen tests are generally less sensitive than molecular assays. “Due to the potential for decreased sensitivity compared to molecular assays, negative results from an antigen test may need to be confirmed with a molecular test prior to making treatment decisions,” the agency noted.
Lynch agreed and said that when a patient tests negative, physicians still need to use their clinical judgment on the basis of symptoms and other factors. The test is not designed for population-based screening of asymptomatic people, he added.
Abbott announced plans to make up to 50 million tests available per month in the United States starting in October. The product comes with a free smartphone app that people can use to share results with an employer or with others as needed.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves clinical trials for cannabinoid drug designed to reduce COVID-19 lung inflammation
The US Food and Drug Administration has approved phase one clinical trials for a synthetic cannabinoid drug designed to treat acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a life-threatening lung condition which may occur in severe cases of the novel coronavirus, Forbes reported.
ARDS can be triggered by over-creation of cytokines, proteins which tell the body to produce more inflammation, Forbes said.
The drug going to clinical trials, ARDS-003, would “dampen the cytokine release” and prevent development of ARDS, Tetra Bio-Pharma company CEO and chief regulatory officer Guy Chamberland, MD, said in a news release.
Consequences of ARDS include scarring of the lungs and organ injury caused by the decrease in blood to the tissue, the release said.
“The FDA repeatedly stated that they want clinical trials for COVID-19 to begin as soon as possible, as long as they meet regulatory requirements,” the news release said. “The medical community is in urgent need of drugs that can reduce the strength and duration of the severe inflammation. It is anticipated that this type of new drug would favorably impact health care and possibly reduce the negative health outcomes post infection.”
ARDS-003 works by binding to CB2 receptors, one of two main receptors in the endocannabinoid system which modulate inflammation and cytokine activity, Forbes said. CB2 receptors don’t bring on a psychoactive high.
Phase one clinical trials would begin enrolling participants in December to determine if the drug is safe, Chamberland said, according to Forbes.
If phase one is successful, phase two would test the drug on a larger group in the second quarter of 2021 to assess safety and tolerability for people who have COVID-19.
If phase two is successful, the company may seek emergency authorization through the FDA, Chamberland said. Phase three would start at the end of 2021.
Tetra Bio-Pharma says it has already contracted with Dalton Pharma Services to manufacture the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), HU-308, and the finished drug product ARDS-003.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration has approved phase one clinical trials for a synthetic cannabinoid drug designed to treat acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a life-threatening lung condition which may occur in severe cases of the novel coronavirus, Forbes reported.
ARDS can be triggered by over-creation of cytokines, proteins which tell the body to produce more inflammation, Forbes said.
The drug going to clinical trials, ARDS-003, would “dampen the cytokine release” and prevent development of ARDS, Tetra Bio-Pharma company CEO and chief regulatory officer Guy Chamberland, MD, said in a news release.
Consequences of ARDS include scarring of the lungs and organ injury caused by the decrease in blood to the tissue, the release said.
“The FDA repeatedly stated that they want clinical trials for COVID-19 to begin as soon as possible, as long as they meet regulatory requirements,” the news release said. “The medical community is in urgent need of drugs that can reduce the strength and duration of the severe inflammation. It is anticipated that this type of new drug would favorably impact health care and possibly reduce the negative health outcomes post infection.”
ARDS-003 works by binding to CB2 receptors, one of two main receptors in the endocannabinoid system which modulate inflammation and cytokine activity, Forbes said. CB2 receptors don’t bring on a psychoactive high.
Phase one clinical trials would begin enrolling participants in December to determine if the drug is safe, Chamberland said, according to Forbes.
If phase one is successful, phase two would test the drug on a larger group in the second quarter of 2021 to assess safety and tolerability for people who have COVID-19.
If phase two is successful, the company may seek emergency authorization through the FDA, Chamberland said. Phase three would start at the end of 2021.
Tetra Bio-Pharma says it has already contracted with Dalton Pharma Services to manufacture the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), HU-308, and the finished drug product ARDS-003.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration has approved phase one clinical trials for a synthetic cannabinoid drug designed to treat acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a life-threatening lung condition which may occur in severe cases of the novel coronavirus, Forbes reported.
ARDS can be triggered by over-creation of cytokines, proteins which tell the body to produce more inflammation, Forbes said.
The drug going to clinical trials, ARDS-003, would “dampen the cytokine release” and prevent development of ARDS, Tetra Bio-Pharma company CEO and chief regulatory officer Guy Chamberland, MD, said in a news release.
Consequences of ARDS include scarring of the lungs and organ injury caused by the decrease in blood to the tissue, the release said.
“The FDA repeatedly stated that they want clinical trials for COVID-19 to begin as soon as possible, as long as they meet regulatory requirements,” the news release said. “The medical community is in urgent need of drugs that can reduce the strength and duration of the severe inflammation. It is anticipated that this type of new drug would favorably impact health care and possibly reduce the negative health outcomes post infection.”
ARDS-003 works by binding to CB2 receptors, one of two main receptors in the endocannabinoid system which modulate inflammation and cytokine activity, Forbes said. CB2 receptors don’t bring on a psychoactive high.
Phase one clinical trials would begin enrolling participants in December to determine if the drug is safe, Chamberland said, according to Forbes.
If phase one is successful, phase two would test the drug on a larger group in the second quarter of 2021 to assess safety and tolerability for people who have COVID-19.
If phase two is successful, the company may seek emergency authorization through the FDA, Chamberland said. Phase three would start at the end of 2021.
Tetra Bio-Pharma says it has already contracted with Dalton Pharma Services to manufacture the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), HU-308, and the finished drug product ARDS-003.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA updates hydrochlorothiazide label to include nonmelanoma skin cancer risk
and undergo regular skin cancer screening, according to updates to the medication’s label.
The skin cancer risk is small, however, and patients should continue taking HCTZ, a commonly used diuretic and antihypertensive drug, unless their doctor says otherwise, according to a U.S. Food and Drug Administration announcement about the labeling changes, which the agency approved on Aug. 20.
HCTZ, first approved in 1959, is associated with photosensitivity. Researchers identified a relationship between HCTZ and nonmelanoma skin cancer in postmarketing studies. Investigators have described dose-response patterns for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
An FDA analysis found that the risk mostly was increased for SCC. The drug was associated with approximately one additional case of SCC per 16,000 patients per year. For white patients who received a cumulative dose of 50,000 mg or more, the risk was greater. In this patient population, HCTZ was associated with about one additional case of SCC per 6,700 patients per year, according to the label.
Reliably estimating the frequency of nonmelanoma skin cancer and establishing a causal relationship to drug exposure is not possible with the available postmarketing data, the label notes
“Treatment for nonmelanoma skin cancer is typically local and successful, with very low rates of death,” the FDA said. “Meanwhile, the risks of uncontrolled blood pressure can be severe and include life-threatening heart attacks or stroke. Given this information, patients should continue to use HCTZ and take protective skin care measures to reduce their risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer, unless directed otherwise from their health care provider.”
Patients can reduce sun exposure by using broad-spectrum sunscreens with a sun protection factor value of at least 15, limiting time in the sun, and wearing protective clothing, the agency advised.
and undergo regular skin cancer screening, according to updates to the medication’s label.
The skin cancer risk is small, however, and patients should continue taking HCTZ, a commonly used diuretic and antihypertensive drug, unless their doctor says otherwise, according to a U.S. Food and Drug Administration announcement about the labeling changes, which the agency approved on Aug. 20.
HCTZ, first approved in 1959, is associated with photosensitivity. Researchers identified a relationship between HCTZ and nonmelanoma skin cancer in postmarketing studies. Investigators have described dose-response patterns for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
An FDA analysis found that the risk mostly was increased for SCC. The drug was associated with approximately one additional case of SCC per 16,000 patients per year. For white patients who received a cumulative dose of 50,000 mg or more, the risk was greater. In this patient population, HCTZ was associated with about one additional case of SCC per 6,700 patients per year, according to the label.
Reliably estimating the frequency of nonmelanoma skin cancer and establishing a causal relationship to drug exposure is not possible with the available postmarketing data, the label notes
“Treatment for nonmelanoma skin cancer is typically local and successful, with very low rates of death,” the FDA said. “Meanwhile, the risks of uncontrolled blood pressure can be severe and include life-threatening heart attacks or stroke. Given this information, patients should continue to use HCTZ and take protective skin care measures to reduce their risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer, unless directed otherwise from their health care provider.”
Patients can reduce sun exposure by using broad-spectrum sunscreens with a sun protection factor value of at least 15, limiting time in the sun, and wearing protective clothing, the agency advised.
and undergo regular skin cancer screening, according to updates to the medication’s label.
The skin cancer risk is small, however, and patients should continue taking HCTZ, a commonly used diuretic and antihypertensive drug, unless their doctor says otherwise, according to a U.S. Food and Drug Administration announcement about the labeling changes, which the agency approved on Aug. 20.
HCTZ, first approved in 1959, is associated with photosensitivity. Researchers identified a relationship between HCTZ and nonmelanoma skin cancer in postmarketing studies. Investigators have described dose-response patterns for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
An FDA analysis found that the risk mostly was increased for SCC. The drug was associated with approximately one additional case of SCC per 16,000 patients per year. For white patients who received a cumulative dose of 50,000 mg or more, the risk was greater. In this patient population, HCTZ was associated with about one additional case of SCC per 6,700 patients per year, according to the label.
Reliably estimating the frequency of nonmelanoma skin cancer and establishing a causal relationship to drug exposure is not possible with the available postmarketing data, the label notes
“Treatment for nonmelanoma skin cancer is typically local and successful, with very low rates of death,” the FDA said. “Meanwhile, the risks of uncontrolled blood pressure can be severe and include life-threatening heart attacks or stroke. Given this information, patients should continue to use HCTZ and take protective skin care measures to reduce their risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer, unless directed otherwise from their health care provider.”
Patients can reduce sun exposure by using broad-spectrum sunscreens with a sun protection factor value of at least 15, limiting time in the sun, and wearing protective clothing, the agency advised.
FDA clamps down on compliance for gluten-free products
To retain the label of “gluten free,” manufacturers of foods that are fermented and hydrolyzed, or that contain fermented or hydrolyzed ingredients, must make and keep detailed records of the manufacturing and production process, according to a final rule issued by the Food and Drug Administration.
In an announcement released on Aug. 12, the FDA stated that manufacturers must confirm that food products such as soy sauce, yogurt, sauerkraut, pickles, cheese, and green olives, as well as distilled foods such as vinegar, meet the definition of gluten free before the fermentation or hydrolysis process. In addition, the rule states that “the manufacturer has adequately evaluated the potential for cross-contact with gluten during the manufacturing process; and if necessary, measures are in place to prevent the introduction of gluten into the food during the manufacturing process,” according to the FDA.
Gluten breaks down during fermentation and hydrolysis, and the gluten-free status of products manufactured in this way can’t be confirmed after the process using currently available methods, according to the FDA.
The new rule is designed to ensure that products labeled as gluten-free meet the definition of gluten free, which remains unchanged from the FDA guidance in 2013.
“The FDA continues to work to protect people with celiac disease, which impacts at least 3 million Americans,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a statement.
“The agency has taken a number of steps on this front by first establishing a standardized definition of gluten free, and now by continuing to work to ensure manufacturers are keeping the products that are labeled with this claim gluten free,” he emphasized.
The final rule states that manufacturers will not need to keep such records if and when other analytical methods are developed, but in the meantime products that do not meet the definition will be deemed misbranded, according to the FDA.
AGA offers guidance on a gluten free diet for patients with celiac disease in the AGA GI Patient Center at http://ow.ly/Wu8F30r4phT.
To retain the label of “gluten free,” manufacturers of foods that are fermented and hydrolyzed, or that contain fermented or hydrolyzed ingredients, must make and keep detailed records of the manufacturing and production process, according to a final rule issued by the Food and Drug Administration.
In an announcement released on Aug. 12, the FDA stated that manufacturers must confirm that food products such as soy sauce, yogurt, sauerkraut, pickles, cheese, and green olives, as well as distilled foods such as vinegar, meet the definition of gluten free before the fermentation or hydrolysis process. In addition, the rule states that “the manufacturer has adequately evaluated the potential for cross-contact with gluten during the manufacturing process; and if necessary, measures are in place to prevent the introduction of gluten into the food during the manufacturing process,” according to the FDA.
Gluten breaks down during fermentation and hydrolysis, and the gluten-free status of products manufactured in this way can’t be confirmed after the process using currently available methods, according to the FDA.
The new rule is designed to ensure that products labeled as gluten-free meet the definition of gluten free, which remains unchanged from the FDA guidance in 2013.
“The FDA continues to work to protect people with celiac disease, which impacts at least 3 million Americans,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a statement.
“The agency has taken a number of steps on this front by first establishing a standardized definition of gluten free, and now by continuing to work to ensure manufacturers are keeping the products that are labeled with this claim gluten free,” he emphasized.
The final rule states that manufacturers will not need to keep such records if and when other analytical methods are developed, but in the meantime products that do not meet the definition will be deemed misbranded, according to the FDA.
AGA offers guidance on a gluten free diet for patients with celiac disease in the AGA GI Patient Center at http://ow.ly/Wu8F30r4phT.
To retain the label of “gluten free,” manufacturers of foods that are fermented and hydrolyzed, or that contain fermented or hydrolyzed ingredients, must make and keep detailed records of the manufacturing and production process, according to a final rule issued by the Food and Drug Administration.
In an announcement released on Aug. 12, the FDA stated that manufacturers must confirm that food products such as soy sauce, yogurt, sauerkraut, pickles, cheese, and green olives, as well as distilled foods such as vinegar, meet the definition of gluten free before the fermentation or hydrolysis process. In addition, the rule states that “the manufacturer has adequately evaluated the potential for cross-contact with gluten during the manufacturing process; and if necessary, measures are in place to prevent the introduction of gluten into the food during the manufacturing process,” according to the FDA.
Gluten breaks down during fermentation and hydrolysis, and the gluten-free status of products manufactured in this way can’t be confirmed after the process using currently available methods, according to the FDA.
The new rule is designed to ensure that products labeled as gluten-free meet the definition of gluten free, which remains unchanged from the FDA guidance in 2013.
“The FDA continues to work to protect people with celiac disease, which impacts at least 3 million Americans,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a statement.
“The agency has taken a number of steps on this front by first establishing a standardized definition of gluten free, and now by continuing to work to ensure manufacturers are keeping the products that are labeled with this claim gluten free,” he emphasized.
The final rule states that manufacturers will not need to keep such records if and when other analytical methods are developed, but in the meantime products that do not meet the definition will be deemed misbranded, according to the FDA.
AGA offers guidance on a gluten free diet for patients with celiac disease in the AGA GI Patient Center at http://ow.ly/Wu8F30r4phT.
FDA approves first liquid biopsy/NGS test for lung cancer
A new test, the first to combine liquid biopsy and next-generation sequencing (NGS), has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) to identify tumors with specific mutation types of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene.
The Guardant360 CDx assay (Guardant Health) is the first to combine the two technologies into a diagnostic test to guide treatment decisions.
Liquid biopsy offers the advantage of obtaining genetic information on a tumor from a simple blood draw instead of a tissue biopsy, which requires fine-needle aspiration of the lung. “ It is less invasive and more easily repeatable in comparison to standard tissue biopsies ... and can be used in cases in which standard tissue biopsies are not feasible, for instance, due to the location of the tumor,” the FDA commented.
NGS offers the advantage of simultaneously detecting mutations in 55 tumor genes, as opposed to conducting a separate test for each gene.
However, although the assay can provide information on multiple solid tumor biomarkers, the approval is specific only to identifying EGFR mutations in patients who will benefit from treatment with osimertinib (Tagrisso, AstraZeneca).
The approval does not validate the test for use in detecting other biomarkers, the FDA noted.
As previously reported, the assay has a comprehensive NGS panel that identifies seven guideline-recommended predictive biomarkers (EGFR, ALK, ROS1, BRAF, RET, MET, ERBB2) — known as the G7 biomarkers — and one prognostic marker (KRAS).
But the FDA noted that “genomic findings for other biomarkers evaluated are not validated for choosing a particular corresponding treatment with this approval.
“If the specific NSCLC mutations associated with today’s approval are not detected in the blood, then a tumor biopsy should be performed to determine if the NSCLC mutations are present,” the agency emphasized.
Nevertheless, the FDA announcement highlights the potential of the test to identify these other biomarkers.
“Approval of a companion diagnostic that uses a liquid biopsy and leverages next-generation sequencing marks a new era for mutation testing,” Tim Stenzel, MD, PhD, director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostics and Radiological Health in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, commented in a statement.
“In addition to benefiting from less invasive testing, patients are provided with a simultaneous mapping of multiple biomarkers of genomic alterations, rather than one biomarker at a time, which can translate to decreased wait times for starting treatment and provide insight into possible resistance mechanisms,” he noted.
The manufacturer also highlighted this potential. “We are confident that our FDA approval will help accelerate wider adoption of guideline-recommended genomic profiling, increase the number of advanced cancer patients who receive potentially life-changing treatments, and pave the way for new companion diagnostic developments for the Guardant360 CDx,” Helmy Eltoukhy, PhD, CEO of Guardant Health, said in a statement.
NILE Study
The FDA did not cite any specific trial of the assay in its announcement of the approval, but Medscape Medical News has previously reported results from the NILE study presented at the 2019 Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
The NILE trial was conducted in 282 patients with untreated nonsquamous NSCLC who underwent standard-of-care tissue genotyping and had a pretreatment blood sample for cell-free DNA (cfDNA) analysis.
Results showed that a G7 biomarker was identified in a significantly higher proportion of liquid biopsies compared with tissue genotyping (27.3% vs 21.3%; P < .0001).
The lower frequency of G7 biomarkers in tissue genotyping was due to insufficient tissue for sequential sequencing, the authors reported at that time.
Liquid biopsy improved G7 detection frequency by 48%, from 60 to 89 patients, which included samples that were negative by tissue testing (7), not tested (16), or lacked sufficient sample for a tissue-based test (6).
Of 193 patients without a G7 biomarker by tissue or cfDNA, 24 patients (12.4%) had an activating KRAS mutation identified in the tissue alone, and with cfDNA, KRAS-positivity increased from 24 to 92 patients.
The Guardant360 CDx assay has been granted a breakthrough device designation, whereby the FDA provides intensive interaction and guidance on efficient device development to the company.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new test, the first to combine liquid biopsy and next-generation sequencing (NGS), has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) to identify tumors with specific mutation types of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene.
The Guardant360 CDx assay (Guardant Health) is the first to combine the two technologies into a diagnostic test to guide treatment decisions.
Liquid biopsy offers the advantage of obtaining genetic information on a tumor from a simple blood draw instead of a tissue biopsy, which requires fine-needle aspiration of the lung. “ It is less invasive and more easily repeatable in comparison to standard tissue biopsies ... and can be used in cases in which standard tissue biopsies are not feasible, for instance, due to the location of the tumor,” the FDA commented.
NGS offers the advantage of simultaneously detecting mutations in 55 tumor genes, as opposed to conducting a separate test for each gene.
However, although the assay can provide information on multiple solid tumor biomarkers, the approval is specific only to identifying EGFR mutations in patients who will benefit from treatment with osimertinib (Tagrisso, AstraZeneca).
The approval does not validate the test for use in detecting other biomarkers, the FDA noted.
As previously reported, the assay has a comprehensive NGS panel that identifies seven guideline-recommended predictive biomarkers (EGFR, ALK, ROS1, BRAF, RET, MET, ERBB2) — known as the G7 biomarkers — and one prognostic marker (KRAS).
But the FDA noted that “genomic findings for other biomarkers evaluated are not validated for choosing a particular corresponding treatment with this approval.
“If the specific NSCLC mutations associated with today’s approval are not detected in the blood, then a tumor biopsy should be performed to determine if the NSCLC mutations are present,” the agency emphasized.
Nevertheless, the FDA announcement highlights the potential of the test to identify these other biomarkers.
“Approval of a companion diagnostic that uses a liquid biopsy and leverages next-generation sequencing marks a new era for mutation testing,” Tim Stenzel, MD, PhD, director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostics and Radiological Health in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, commented in a statement.
“In addition to benefiting from less invasive testing, patients are provided with a simultaneous mapping of multiple biomarkers of genomic alterations, rather than one biomarker at a time, which can translate to decreased wait times for starting treatment and provide insight into possible resistance mechanisms,” he noted.
The manufacturer also highlighted this potential. “We are confident that our FDA approval will help accelerate wider adoption of guideline-recommended genomic profiling, increase the number of advanced cancer patients who receive potentially life-changing treatments, and pave the way for new companion diagnostic developments for the Guardant360 CDx,” Helmy Eltoukhy, PhD, CEO of Guardant Health, said in a statement.
NILE Study
The FDA did not cite any specific trial of the assay in its announcement of the approval, but Medscape Medical News has previously reported results from the NILE study presented at the 2019 Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
The NILE trial was conducted in 282 patients with untreated nonsquamous NSCLC who underwent standard-of-care tissue genotyping and had a pretreatment blood sample for cell-free DNA (cfDNA) analysis.
Results showed that a G7 biomarker was identified in a significantly higher proportion of liquid biopsies compared with tissue genotyping (27.3% vs 21.3%; P < .0001).
The lower frequency of G7 biomarkers in tissue genotyping was due to insufficient tissue for sequential sequencing, the authors reported at that time.
Liquid biopsy improved G7 detection frequency by 48%, from 60 to 89 patients, which included samples that were negative by tissue testing (7), not tested (16), or lacked sufficient sample for a tissue-based test (6).
Of 193 patients without a G7 biomarker by tissue or cfDNA, 24 patients (12.4%) had an activating KRAS mutation identified in the tissue alone, and with cfDNA, KRAS-positivity increased from 24 to 92 patients.
The Guardant360 CDx assay has been granted a breakthrough device designation, whereby the FDA provides intensive interaction and guidance on efficient device development to the company.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new test, the first to combine liquid biopsy and next-generation sequencing (NGS), has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) to identify tumors with specific mutation types of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene.
The Guardant360 CDx assay (Guardant Health) is the first to combine the two technologies into a diagnostic test to guide treatment decisions.
Liquid biopsy offers the advantage of obtaining genetic information on a tumor from a simple blood draw instead of a tissue biopsy, which requires fine-needle aspiration of the lung. “ It is less invasive and more easily repeatable in comparison to standard tissue biopsies ... and can be used in cases in which standard tissue biopsies are not feasible, for instance, due to the location of the tumor,” the FDA commented.
NGS offers the advantage of simultaneously detecting mutations in 55 tumor genes, as opposed to conducting a separate test for each gene.
However, although the assay can provide information on multiple solid tumor biomarkers, the approval is specific only to identifying EGFR mutations in patients who will benefit from treatment with osimertinib (Tagrisso, AstraZeneca).
The approval does not validate the test for use in detecting other biomarkers, the FDA noted.
As previously reported, the assay has a comprehensive NGS panel that identifies seven guideline-recommended predictive biomarkers (EGFR, ALK, ROS1, BRAF, RET, MET, ERBB2) — known as the G7 biomarkers — and one prognostic marker (KRAS).
But the FDA noted that “genomic findings for other biomarkers evaluated are not validated for choosing a particular corresponding treatment with this approval.
“If the specific NSCLC mutations associated with today’s approval are not detected in the blood, then a tumor biopsy should be performed to determine if the NSCLC mutations are present,” the agency emphasized.
Nevertheless, the FDA announcement highlights the potential of the test to identify these other biomarkers.
“Approval of a companion diagnostic that uses a liquid biopsy and leverages next-generation sequencing marks a new era for mutation testing,” Tim Stenzel, MD, PhD, director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostics and Radiological Health in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, commented in a statement.
“In addition to benefiting from less invasive testing, patients are provided with a simultaneous mapping of multiple biomarkers of genomic alterations, rather than one biomarker at a time, which can translate to decreased wait times for starting treatment and provide insight into possible resistance mechanisms,” he noted.
The manufacturer also highlighted this potential. “We are confident that our FDA approval will help accelerate wider adoption of guideline-recommended genomic profiling, increase the number of advanced cancer patients who receive potentially life-changing treatments, and pave the way for new companion diagnostic developments for the Guardant360 CDx,” Helmy Eltoukhy, PhD, CEO of Guardant Health, said in a statement.
NILE Study
The FDA did not cite any specific trial of the assay in its announcement of the approval, but Medscape Medical News has previously reported results from the NILE study presented at the 2019 Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
The NILE trial was conducted in 282 patients with untreated nonsquamous NSCLC who underwent standard-of-care tissue genotyping and had a pretreatment blood sample for cell-free DNA (cfDNA) analysis.
Results showed that a G7 biomarker was identified in a significantly higher proportion of liquid biopsies compared with tissue genotyping (27.3% vs 21.3%; P < .0001).
The lower frequency of G7 biomarkers in tissue genotyping was due to insufficient tissue for sequential sequencing, the authors reported at that time.
Liquid biopsy improved G7 detection frequency by 48%, from 60 to 89 patients, which included samples that were negative by tissue testing (7), not tested (16), or lacked sufficient sample for a tissue-based test (6).
Of 193 patients without a G7 biomarker by tissue or cfDNA, 24 patients (12.4%) had an activating KRAS mutation identified in the tissue alone, and with cfDNA, KRAS-positivity increased from 24 to 92 patients.
The Guardant360 CDx assay has been granted a breakthrough device designation, whereby the FDA provides intensive interaction and guidance on efficient device development to the company.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Health disparity: Race, mortality, and infants of teenage mothers
according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.
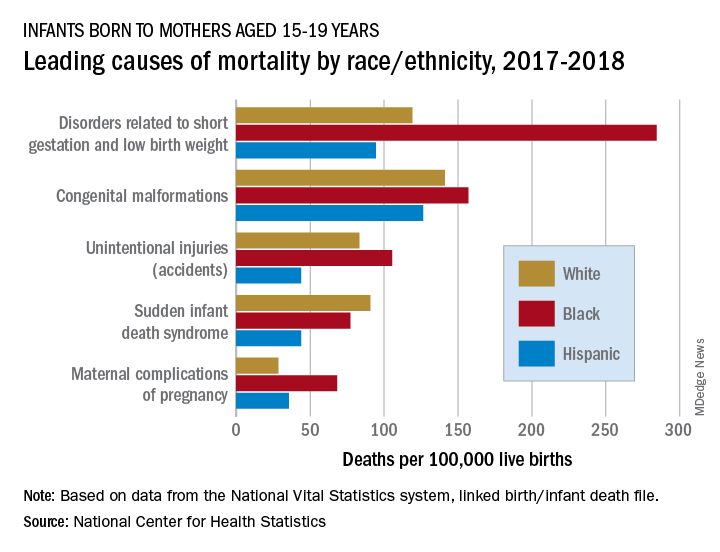
In 2017-2018, overall mortality rates were 12.5 per 100,000 live births for infants born to Black mothers aged 15-19 years, 8.4 per 100,000 for infants born to White teenagers, and 6.5 per 100,000 for those born to Hispanic teens, Ashley M. Woodall, MPH, and Anne K. Driscoll, PhD, of the NCHS said in a data brief.
Looking at the five leading causes of those deaths shows that deaths of Black infants were the highest by significant margins in four, although, when it comes to “disorders related to short gestation and low birth weight,” significant may be an understatement.
The rate of preterm/low-birth-weight deaths for white infants in 2017-2018 was 119 per 100,000 live births; for Hispanic infants it was 94 per 100,000. Among infants born to Black teenagers, however, it was 284 deaths per 100,000, they reported based on data from the National Vital Statistics System’s linked birth/infant death file.
The numbers for congenital malformations and accidents were closer but still significantly different, and with each of the three most common causes, the rates for infants of Hispanic mothers also were significantly lower than those of White infants, the researchers said.
The situation changes for mortality-cause No. 4, sudden infant death syndrome, which was significantly more common among infants born to White teenagers, with a rate of 91 deaths per 100,000 live births, compared with either black (77) or Hispanic (44) infants, Ms. Woodall and Dr. Driscoll said.
Infants born to Black teens had the highest death rate again (68 per 100,000) for maternal complications of pregnancy, the fifth-leading cause of mortality, but for the first time Hispanic infants had a higher rate (36) than did those of White teenagers (29), they reported.
according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.

In 2017-2018, overall mortality rates were 12.5 per 100,000 live births for infants born to Black mothers aged 15-19 years, 8.4 per 100,000 for infants born to White teenagers, and 6.5 per 100,000 for those born to Hispanic teens, Ashley M. Woodall, MPH, and Anne K. Driscoll, PhD, of the NCHS said in a data brief.
Looking at the five leading causes of those deaths shows that deaths of Black infants were the highest by significant margins in four, although, when it comes to “disorders related to short gestation and low birth weight,” significant may be an understatement.
The rate of preterm/low-birth-weight deaths for white infants in 2017-2018 was 119 per 100,000 live births; for Hispanic infants it was 94 per 100,000. Among infants born to Black teenagers, however, it was 284 deaths per 100,000, they reported based on data from the National Vital Statistics System’s linked birth/infant death file.
The numbers for congenital malformations and accidents were closer but still significantly different, and with each of the three most common causes, the rates for infants of Hispanic mothers also were significantly lower than those of White infants, the researchers said.
The situation changes for mortality-cause No. 4, sudden infant death syndrome, which was significantly more common among infants born to White teenagers, with a rate of 91 deaths per 100,000 live births, compared with either black (77) or Hispanic (44) infants, Ms. Woodall and Dr. Driscoll said.
Infants born to Black teens had the highest death rate again (68 per 100,000) for maternal complications of pregnancy, the fifth-leading cause of mortality, but for the first time Hispanic infants had a higher rate (36) than did those of White teenagers (29), they reported.
according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.

In 2017-2018, overall mortality rates were 12.5 per 100,000 live births for infants born to Black mothers aged 15-19 years, 8.4 per 100,000 for infants born to White teenagers, and 6.5 per 100,000 for those born to Hispanic teens, Ashley M. Woodall, MPH, and Anne K. Driscoll, PhD, of the NCHS said in a data brief.
Looking at the five leading causes of those deaths shows that deaths of Black infants were the highest by significant margins in four, although, when it comes to “disorders related to short gestation and low birth weight,” significant may be an understatement.
The rate of preterm/low-birth-weight deaths for white infants in 2017-2018 was 119 per 100,000 live births; for Hispanic infants it was 94 per 100,000. Among infants born to Black teenagers, however, it was 284 deaths per 100,000, they reported based on data from the National Vital Statistics System’s linked birth/infant death file.
The numbers for congenital malformations and accidents were closer but still significantly different, and with each of the three most common causes, the rates for infants of Hispanic mothers also were significantly lower than those of White infants, the researchers said.
The situation changes for mortality-cause No. 4, sudden infant death syndrome, which was significantly more common among infants born to White teenagers, with a rate of 91 deaths per 100,000 live births, compared with either black (77) or Hispanic (44) infants, Ms. Woodall and Dr. Driscoll said.
Infants born to Black teens had the highest death rate again (68 per 100,000) for maternal complications of pregnancy, the fifth-leading cause of mortality, but for the first time Hispanic infants had a higher rate (36) than did those of White teenagers (29), they reported.
FDA approves belantamab in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
The first-in-class drug belantamab mafodotin (Blenrep) has been granted an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the treatment of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma in patients who have already tried other therapies.
This follows a recommendation for approval on July 15 by an FDA advisory committee, which voted 12-0 in favor of the drug’s benefits outweighing risks in this patient population.
The product has a novel mechanism of action: it targets B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), a protein that is present on the surface of virtually all multiple myeloma cells but is absent from normal B cells.
The drug had already received an FDA breakthrough therapy designation, which facilitates the development of drugs that have shown clinical promise for conditions in which there is significant unmet need.
Belantamab mafodotin was recommended for conditional marketing approval in the European Union on July 24 and was accepted into the European Medicines Agency PRIME scheme for medicines that have potential to address unmet medical needs.
The new drug is indicated for patients with refractory or relapsed multiple myeloma who have already tried treatment with one of the three major classes of drugs, namely, an immunomolatory agent, a proteasome inhibitor, and a CD38 monoclonal antibody.
For patients who no longer respond to these drugs, the outlook is bleak, the EMA comments. There is an unmet medical need for new treatments that improve survival of these patients beyond the currently observed 3 months or less.
“While treatable, refractory multiple myeloma is a significant clinical challenge with poor outcomes for patients whose disease has become resistant to the current standard of care,” commented Sagar Lonial, MD, chief medical officer of the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta, chair of the department of hematology and medical oncology at Emory, and a principal investigator for the clinical trial that led to the approval.
“Due to the limited options currently available, these patients are often retreated with drugs from the same classes after they relapse, which is why the approval of belantamab mafodotin, the first anti-BCMA therapy, is significant for both patients and physicians alike,” he said.
The product is an antibody-drug conjugate that combines a monoclonal antibody that targets BCMA with the cytotoxic agent maleimidocaproyl monomethyl auristatin F. It homes in on BCMA on myeloma cell surfaces. Once inside the myeloma cell, the cytotoxic agent is released, leading to apoptosis, the programmed death of the cancerous plasma cells.
Approval based on response rates
The accelerated approval from the FDA and the recommendation for conditional approval from the EMA are based on results for overall response rate and duration of response from a phase 2, open-label, randomized, two-arm study known as DREAMM-2. Both agencies said that they are waiting for further data on clinical benefit from ongoing trials.
The DREAMM-2 study investigated the efficacy and safety of two doses of belantamab mafodotin in multiple myeloma patients whose disease was still active after three or more lines of therapy and who no longer responded to treatment with immunomodulatory drugs, proteasome inhibitors, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
Six-month results from this study were published in The Lancet Oncology in December. The overall response rate was 31% in the cohort given a 2.5-mg/kg dose of the drug; 30 of 97 patients had outcomes that met the study’s positive threshold.
Another 99 patients in DREAMM-2 received a dose of 3.4 mg/kg, which was judged to have a less favorable safety profile.
The median duration of response had not been reached at the 6-month analysis, but for 73% of responders, DoR was ≥6 months.
The most commonly reported adverse events (≥20%) were keratopathy (changes in the cornea), decreased visual acuity, nausea, blurred vision, pyrexia, infusion-related reactions, and fatigue, the manufacturer notes.
Ocular toxicity
One of the most common adverse events with this product affects the eyes.
Ocular adverse reactions occurred in 77% of the 218 patients in the pooled safety population and included keratopathy (76%), changes in visual acuity (55%), blurred vision (27%), and dry eye (19%).
Corneal adverse events were monitored with eye exams prior to each dose, allowing dose reductions or interruptions as appropriate, the manufacturer noted. Patients also used preservative-free eyedrops. Keratopathy leading to treatment discontinuation affected 2.1% of patients in the 2.5-mg/kg cohort.
Because of this ocular toxicity, the company has set up a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) for the product. This requires education for all physicians who prescribe the product as well as their patients regarding the ocular risks associated with treatment. It also requires monitoring that includes regular ophthalmic examinations. Information about the scheme can be found at www.blenreprems.com.
At the FDA advisory committee meeting last month, one of the panelists, Gita Thanarajasingam, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic, in Rochester, Minn., said belantamab appeared to be well tolerated but for ocular toxicity. Physicians need to acknowledge how severe this risk may be for patients while keeping in mind that belantamab still may be more tolerable for some people than current treatments.
“It’s reasonable to leave open the option for decision making. Patients can express their values and preferences,” Dr. Thanarajasingam said. “There’s adequate, albeit not complete, information to guide this risk-benefit discussion in a REMS program.”
Another panelist, Heidi D. Klepin, MD, a professor at Wake Forest University Health Sciences, Winston Salem, N.C., agreed that the informed consent process should allow patients “to choose whether the trade-off is worth it to them” with belantamab.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first-in-class drug belantamab mafodotin (Blenrep) has been granted an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the treatment of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma in patients who have already tried other therapies.
This follows a recommendation for approval on July 15 by an FDA advisory committee, which voted 12-0 in favor of the drug’s benefits outweighing risks in this patient population.
The product has a novel mechanism of action: it targets B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), a protein that is present on the surface of virtually all multiple myeloma cells but is absent from normal B cells.
The drug had already received an FDA breakthrough therapy designation, which facilitates the development of drugs that have shown clinical promise for conditions in which there is significant unmet need.
Belantamab mafodotin was recommended for conditional marketing approval in the European Union on July 24 and was accepted into the European Medicines Agency PRIME scheme for medicines that have potential to address unmet medical needs.
The new drug is indicated for patients with refractory or relapsed multiple myeloma who have already tried treatment with one of the three major classes of drugs, namely, an immunomolatory agent, a proteasome inhibitor, and a CD38 monoclonal antibody.
For patients who no longer respond to these drugs, the outlook is bleak, the EMA comments. There is an unmet medical need for new treatments that improve survival of these patients beyond the currently observed 3 months or less.
“While treatable, refractory multiple myeloma is a significant clinical challenge with poor outcomes for patients whose disease has become resistant to the current standard of care,” commented Sagar Lonial, MD, chief medical officer of the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta, chair of the department of hematology and medical oncology at Emory, and a principal investigator for the clinical trial that led to the approval.
“Due to the limited options currently available, these patients are often retreated with drugs from the same classes after they relapse, which is why the approval of belantamab mafodotin, the first anti-BCMA therapy, is significant for both patients and physicians alike,” he said.
The product is an antibody-drug conjugate that combines a monoclonal antibody that targets BCMA with the cytotoxic agent maleimidocaproyl monomethyl auristatin F. It homes in on BCMA on myeloma cell surfaces. Once inside the myeloma cell, the cytotoxic agent is released, leading to apoptosis, the programmed death of the cancerous plasma cells.
Approval based on response rates
The accelerated approval from the FDA and the recommendation for conditional approval from the EMA are based on results for overall response rate and duration of response from a phase 2, open-label, randomized, two-arm study known as DREAMM-2. Both agencies said that they are waiting for further data on clinical benefit from ongoing trials.
The DREAMM-2 study investigated the efficacy and safety of two doses of belantamab mafodotin in multiple myeloma patients whose disease was still active after three or more lines of therapy and who no longer responded to treatment with immunomodulatory drugs, proteasome inhibitors, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
Six-month results from this study were published in The Lancet Oncology in December. The overall response rate was 31% in the cohort given a 2.5-mg/kg dose of the drug; 30 of 97 patients had outcomes that met the study’s positive threshold.
Another 99 patients in DREAMM-2 received a dose of 3.4 mg/kg, which was judged to have a less favorable safety profile.
The median duration of response had not been reached at the 6-month analysis, but for 73% of responders, DoR was ≥6 months.
The most commonly reported adverse events (≥20%) were keratopathy (changes in the cornea), decreased visual acuity, nausea, blurred vision, pyrexia, infusion-related reactions, and fatigue, the manufacturer notes.
Ocular toxicity
One of the most common adverse events with this product affects the eyes.
Ocular adverse reactions occurred in 77% of the 218 patients in the pooled safety population and included keratopathy (76%), changes in visual acuity (55%), blurred vision (27%), and dry eye (19%).
Corneal adverse events were monitored with eye exams prior to each dose, allowing dose reductions or interruptions as appropriate, the manufacturer noted. Patients also used preservative-free eyedrops. Keratopathy leading to treatment discontinuation affected 2.1% of patients in the 2.5-mg/kg cohort.
Because of this ocular toxicity, the company has set up a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) for the product. This requires education for all physicians who prescribe the product as well as their patients regarding the ocular risks associated with treatment. It also requires monitoring that includes regular ophthalmic examinations. Information about the scheme can be found at www.blenreprems.com.
At the FDA advisory committee meeting last month, one of the panelists, Gita Thanarajasingam, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic, in Rochester, Minn., said belantamab appeared to be well tolerated but for ocular toxicity. Physicians need to acknowledge how severe this risk may be for patients while keeping in mind that belantamab still may be more tolerable for some people than current treatments.
“It’s reasonable to leave open the option for decision making. Patients can express their values and preferences,” Dr. Thanarajasingam said. “There’s adequate, albeit not complete, information to guide this risk-benefit discussion in a REMS program.”
Another panelist, Heidi D. Klepin, MD, a professor at Wake Forest University Health Sciences, Winston Salem, N.C., agreed that the informed consent process should allow patients “to choose whether the trade-off is worth it to them” with belantamab.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first-in-class drug belantamab mafodotin (Blenrep) has been granted an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the treatment of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma in patients who have already tried other therapies.
This follows a recommendation for approval on July 15 by an FDA advisory committee, which voted 12-0 in favor of the drug’s benefits outweighing risks in this patient population.
The product has a novel mechanism of action: it targets B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), a protein that is present on the surface of virtually all multiple myeloma cells but is absent from normal B cells.
The drug had already received an FDA breakthrough therapy designation, which facilitates the development of drugs that have shown clinical promise for conditions in which there is significant unmet need.
Belantamab mafodotin was recommended for conditional marketing approval in the European Union on July 24 and was accepted into the European Medicines Agency PRIME scheme for medicines that have potential to address unmet medical needs.
The new drug is indicated for patients with refractory or relapsed multiple myeloma who have already tried treatment with one of the three major classes of drugs, namely, an immunomolatory agent, a proteasome inhibitor, and a CD38 monoclonal antibody.
For patients who no longer respond to these drugs, the outlook is bleak, the EMA comments. There is an unmet medical need for new treatments that improve survival of these patients beyond the currently observed 3 months or less.
“While treatable, refractory multiple myeloma is a significant clinical challenge with poor outcomes for patients whose disease has become resistant to the current standard of care,” commented Sagar Lonial, MD, chief medical officer of the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta, chair of the department of hematology and medical oncology at Emory, and a principal investigator for the clinical trial that led to the approval.
“Due to the limited options currently available, these patients are often retreated with drugs from the same classes after they relapse, which is why the approval of belantamab mafodotin, the first anti-BCMA therapy, is significant for both patients and physicians alike,” he said.
The product is an antibody-drug conjugate that combines a monoclonal antibody that targets BCMA with the cytotoxic agent maleimidocaproyl monomethyl auristatin F. It homes in on BCMA on myeloma cell surfaces. Once inside the myeloma cell, the cytotoxic agent is released, leading to apoptosis, the programmed death of the cancerous plasma cells.
Approval based on response rates
The accelerated approval from the FDA and the recommendation for conditional approval from the EMA are based on results for overall response rate and duration of response from a phase 2, open-label, randomized, two-arm study known as DREAMM-2. Both agencies said that they are waiting for further data on clinical benefit from ongoing trials.
The DREAMM-2 study investigated the efficacy and safety of two doses of belantamab mafodotin in multiple myeloma patients whose disease was still active after three or more lines of therapy and who no longer responded to treatment with immunomodulatory drugs, proteasome inhibitors, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
Six-month results from this study were published in The Lancet Oncology in December. The overall response rate was 31% in the cohort given a 2.5-mg/kg dose of the drug; 30 of 97 patients had outcomes that met the study’s positive threshold.
Another 99 patients in DREAMM-2 received a dose of 3.4 mg/kg, which was judged to have a less favorable safety profile.
The median duration of response had not been reached at the 6-month analysis, but for 73% of responders, DoR was ≥6 months.
The most commonly reported adverse events (≥20%) were keratopathy (changes in the cornea), decreased visual acuity, nausea, blurred vision, pyrexia, infusion-related reactions, and fatigue, the manufacturer notes.
Ocular toxicity
One of the most common adverse events with this product affects the eyes.
Ocular adverse reactions occurred in 77% of the 218 patients in the pooled safety population and included keratopathy (76%), changes in visual acuity (55%), blurred vision (27%), and dry eye (19%).
Corneal adverse events were monitored with eye exams prior to each dose, allowing dose reductions or interruptions as appropriate, the manufacturer noted. Patients also used preservative-free eyedrops. Keratopathy leading to treatment discontinuation affected 2.1% of patients in the 2.5-mg/kg cohort.
Because of this ocular toxicity, the company has set up a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) for the product. This requires education for all physicians who prescribe the product as well as their patients regarding the ocular risks associated with treatment. It also requires monitoring that includes regular ophthalmic examinations. Information about the scheme can be found at www.blenreprems.com.
At the FDA advisory committee meeting last month, one of the panelists, Gita Thanarajasingam, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic, in Rochester, Minn., said belantamab appeared to be well tolerated but for ocular toxicity. Physicians need to acknowledge how severe this risk may be for patients while keeping in mind that belantamab still may be more tolerable for some people than current treatments.
“It’s reasonable to leave open the option for decision making. Patients can express their values and preferences,” Dr. Thanarajasingam said. “There’s adequate, albeit not complete, information to guide this risk-benefit discussion in a REMS program.”
Another panelist, Heidi D. Klepin, MD, a professor at Wake Forest University Health Sciences, Winston Salem, N.C., agreed that the informed consent process should allow patients “to choose whether the trade-off is worth it to them” with belantamab.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves triple drug combo for melanoma
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the triple-therapy combination of atezolizumab (Tecentriq) plus cobimetinib (Cotellic) and vemurafenib (Zelboraf) for the treatment of BRAF V600 mutation-positive advanced melanoma, according to a press statement from Genentech, which owns all three drugs.
This is the first melanoma indication for the PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab; the other two drugs, cobimetinib and vemurafenib, are a MEK- plus BRAF-inhibitor combination previously approved for BRAF-mutated melanoma.
The new approval is based on safety and efficacy results from the randomized, phase 3 IMspire150 study from patients with previously untreated BRAF V600 mutation-positive metastatic or unresectable locally advanced melanoma.
Progression-free survival (PFS), the primary endpoint, was improved by 4.5 months with the triple therapy compared to the doublet.
The addition of atezolizumab to cobimetinib and vemurafenib led to a longer median PFS of 15.1 months, compared to 10.6 months with placebo plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib (hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.63 – 0.97; P = .025).
The most common adverse reactions (rate ≥ 20%) in patients who received the triple combination were rash (75%), musculoskeletal pain (62%), fatigue (51%), hepatotoxicity (50%), pyrexia (49%), nausea (30%), pruritus (26%), edema (26%), stomatitis (23%), hypothyroidism (22%), and photosensitivity reaction (21%).
The review was conducted under Project Orbis, an initiative of the FDA Oncology Center of Excellence that facilitates concurrent submission and review of oncology products among international partners.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the triple-therapy combination of atezolizumab (Tecentriq) plus cobimetinib (Cotellic) and vemurafenib (Zelboraf) for the treatment of BRAF V600 mutation-positive advanced melanoma, according to a press statement from Genentech, which owns all three drugs.
This is the first melanoma indication for the PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab; the other two drugs, cobimetinib and vemurafenib, are a MEK- plus BRAF-inhibitor combination previously approved for BRAF-mutated melanoma.
The new approval is based on safety and efficacy results from the randomized, phase 3 IMspire150 study from patients with previously untreated BRAF V600 mutation-positive metastatic or unresectable locally advanced melanoma.
Progression-free survival (PFS), the primary endpoint, was improved by 4.5 months with the triple therapy compared to the doublet.
The addition of atezolizumab to cobimetinib and vemurafenib led to a longer median PFS of 15.1 months, compared to 10.6 months with placebo plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib (hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.63 – 0.97; P = .025).
The most common adverse reactions (rate ≥ 20%) in patients who received the triple combination were rash (75%), musculoskeletal pain (62%), fatigue (51%), hepatotoxicity (50%), pyrexia (49%), nausea (30%), pruritus (26%), edema (26%), stomatitis (23%), hypothyroidism (22%), and photosensitivity reaction (21%).
The review was conducted under Project Orbis, an initiative of the FDA Oncology Center of Excellence that facilitates concurrent submission and review of oncology products among international partners.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the triple-therapy combination of atezolizumab (Tecentriq) plus cobimetinib (Cotellic) and vemurafenib (Zelboraf) for the treatment of BRAF V600 mutation-positive advanced melanoma, according to a press statement from Genentech, which owns all three drugs.
This is the first melanoma indication for the PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab; the other two drugs, cobimetinib and vemurafenib, are a MEK- plus BRAF-inhibitor combination previously approved for BRAF-mutated melanoma.
The new approval is based on safety and efficacy results from the randomized, phase 3 IMspire150 study from patients with previously untreated BRAF V600 mutation-positive metastatic or unresectable locally advanced melanoma.
Progression-free survival (PFS), the primary endpoint, was improved by 4.5 months with the triple therapy compared to the doublet.
The addition of atezolizumab to cobimetinib and vemurafenib led to a longer median PFS of 15.1 months, compared to 10.6 months with placebo plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib (hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.63 – 0.97; P = .025).
The most common adverse reactions (rate ≥ 20%) in patients who received the triple combination were rash (75%), musculoskeletal pain (62%), fatigue (51%), hepatotoxicity (50%), pyrexia (49%), nausea (30%), pruritus (26%), edema (26%), stomatitis (23%), hypothyroidism (22%), and photosensitivity reaction (21%).
The review was conducted under Project Orbis, an initiative of the FDA Oncology Center of Excellence that facilitates concurrent submission and review of oncology products among international partners.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
EMA gives green light to avapritinib for GIST, acalabrutinib for CLL
The CHMP recommended granting conditional marketing authorization for avapritinib (Ayvakit, Blueprint Medicines) for use in adults with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) harboring a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) exon 18 mutation, including PDGFRA D842V mutations. About 6%-10% of GIST tumors harbor this mutation, and avapritinib is a selective and potent inhibitor of KIT and PDGFRA mutant kinases.
The CHMP also adopted a positive opinion for acalabrutinib (Calquence, AstraZeneca) for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) as monotherapy in patients who are treatment-naive or have received at least one prior therapy.
The CHMP opinion on both drugs will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to grant marketing authorization for medicinal products in the EU.
Detailed recommendations for the use of both drugs will be provided in the summary of product characteristics, which will be published in the European public assessment report and made available in all official EU languages after the products receive marketing authorization by the European Commission.
First targeted therapy for mutation
If approved by the European Commission, avapritinib would be the first treatment in the EU indicated for patients with PDGFRA D842V-mutant GIST.
Avapritinib was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) earlier this year for the aforementioned indication. The FDA approval was based on findings from the phase 1 NAVIGATOR trial, which included 43 patients with GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, including 38 patients with the most common mutation, PDGFRA D842V.
For patients harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, the overall response rate (ORR) was 84%, with 7% having a complete response and 77% having a partial response. Patients with the PDGFRA D842V mutation achieved an ORR of 89%, with 8% having a complete response and 82% having a partial response.
“GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation do not respond to standard therapies ... Today’s approval provides patients with the first drug specifically approved for GIST harboring this mutation,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, in a statement at the time of approval.
The most common side effects (≥ 20% of patients) observed in patients taking avapritinib include nausea, fatigue, anemia, periorbital edema, face edema, hyperbilirubinemia, diarrhea, vomiting, peripheral edema, increased lacrimation, decreased appetite, and memory impairment. There may also be a risk of intracranial hemorrhage, in which case the dose should be reduced or the drug should be discontinued.
In the EU, conditional marketing authorization is granted to a medicinal product that fulfills an unmet medical need when the benefit to public health of immediate availability outweighs the risk inherent in the fact that additional data are still required, the CHMP notes on its website.
Avapritinib had received an orphan medicine designation during development, which the EMA will review to determine if the designation can be maintained.
New treatment for CLL
Acalabrutinib is already approved in the United States, Canada, and Australia for the treatment of CLL and small lymphocytic lymphoma. The product was approved at the same time by all three regulatory authorities last year. In the United States, acalabrutinib had previously been approved for use in mantle cell lymphoma.
The CHMP’s positive opinion of acalabrutinib is based on results from two phase 3 trials, ELEVATE TN and ASCEND.
In the ASCEND trial, acalabrutinib was compared with investigator’s choice of idelalisib or bendamustine with rituximab. The trial, which involved 310 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL, showed that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival (PFS).
At a median follow-up of 16.1 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib and was 16.5 months with investigator’s choice of therapy (P < .0001).
The most commonly reported adverse events seen with acalabrutinib were respiratory tract infections, headache, bruising, contusion, diarrhea, nausea, rash, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, decreased hemoglobin, and decreased platelets.
In the ELEVATE TN trial, acalabrutinib was given alone or combined with obinutuzumab and compared to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in patients with previously untreated CLL. There were 535 patients randomized to receive acalabrutinib alone (n = 179), acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab (n = 179), and chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab (n = 177).
At a median follow-up of 28 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib alone or with acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab, but the median PFS was 22.6 months in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab arm (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
The most common adverse events in the acalabrutinib arms were headache, diarrhea, neutropenia, and nausea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The CHMP recommended granting conditional marketing authorization for avapritinib (Ayvakit, Blueprint Medicines) for use in adults with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) harboring a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) exon 18 mutation, including PDGFRA D842V mutations. About 6%-10% of GIST tumors harbor this mutation, and avapritinib is a selective and potent inhibitor of KIT and PDGFRA mutant kinases.
The CHMP also adopted a positive opinion for acalabrutinib (Calquence, AstraZeneca) for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) as monotherapy in patients who are treatment-naive or have received at least one prior therapy.
The CHMP opinion on both drugs will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to grant marketing authorization for medicinal products in the EU.
Detailed recommendations for the use of both drugs will be provided in the summary of product characteristics, which will be published in the European public assessment report and made available in all official EU languages after the products receive marketing authorization by the European Commission.
First targeted therapy for mutation
If approved by the European Commission, avapritinib would be the first treatment in the EU indicated for patients with PDGFRA D842V-mutant GIST.
Avapritinib was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) earlier this year for the aforementioned indication. The FDA approval was based on findings from the phase 1 NAVIGATOR trial, which included 43 patients with GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, including 38 patients with the most common mutation, PDGFRA D842V.
For patients harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, the overall response rate (ORR) was 84%, with 7% having a complete response and 77% having a partial response. Patients with the PDGFRA D842V mutation achieved an ORR of 89%, with 8% having a complete response and 82% having a partial response.
“GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation do not respond to standard therapies ... Today’s approval provides patients with the first drug specifically approved for GIST harboring this mutation,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, in a statement at the time of approval.
The most common side effects (≥ 20% of patients) observed in patients taking avapritinib include nausea, fatigue, anemia, periorbital edema, face edema, hyperbilirubinemia, diarrhea, vomiting, peripheral edema, increased lacrimation, decreased appetite, and memory impairment. There may also be a risk of intracranial hemorrhage, in which case the dose should be reduced or the drug should be discontinued.
In the EU, conditional marketing authorization is granted to a medicinal product that fulfills an unmet medical need when the benefit to public health of immediate availability outweighs the risk inherent in the fact that additional data are still required, the CHMP notes on its website.
Avapritinib had received an orphan medicine designation during development, which the EMA will review to determine if the designation can be maintained.
New treatment for CLL
Acalabrutinib is already approved in the United States, Canada, and Australia for the treatment of CLL and small lymphocytic lymphoma. The product was approved at the same time by all three regulatory authorities last year. In the United States, acalabrutinib had previously been approved for use in mantle cell lymphoma.
The CHMP’s positive opinion of acalabrutinib is based on results from two phase 3 trials, ELEVATE TN and ASCEND.
In the ASCEND trial, acalabrutinib was compared with investigator’s choice of idelalisib or bendamustine with rituximab. The trial, which involved 310 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL, showed that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival (PFS).
At a median follow-up of 16.1 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib and was 16.5 months with investigator’s choice of therapy (P < .0001).
The most commonly reported adverse events seen with acalabrutinib were respiratory tract infections, headache, bruising, contusion, diarrhea, nausea, rash, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, decreased hemoglobin, and decreased platelets.
In the ELEVATE TN trial, acalabrutinib was given alone or combined with obinutuzumab and compared to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in patients with previously untreated CLL. There were 535 patients randomized to receive acalabrutinib alone (n = 179), acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab (n = 179), and chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab (n = 177).
At a median follow-up of 28 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib alone or with acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab, but the median PFS was 22.6 months in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab arm (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
The most common adverse events in the acalabrutinib arms were headache, diarrhea, neutropenia, and nausea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The CHMP recommended granting conditional marketing authorization for avapritinib (Ayvakit, Blueprint Medicines) for use in adults with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) harboring a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) exon 18 mutation, including PDGFRA D842V mutations. About 6%-10% of GIST tumors harbor this mutation, and avapritinib is a selective and potent inhibitor of KIT and PDGFRA mutant kinases.
The CHMP also adopted a positive opinion for acalabrutinib (Calquence, AstraZeneca) for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) as monotherapy in patients who are treatment-naive or have received at least one prior therapy.
The CHMP opinion on both drugs will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to grant marketing authorization for medicinal products in the EU.
Detailed recommendations for the use of both drugs will be provided in the summary of product characteristics, which will be published in the European public assessment report and made available in all official EU languages after the products receive marketing authorization by the European Commission.
First targeted therapy for mutation
If approved by the European Commission, avapritinib would be the first treatment in the EU indicated for patients with PDGFRA D842V-mutant GIST.
Avapritinib was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) earlier this year for the aforementioned indication. The FDA approval was based on findings from the phase 1 NAVIGATOR trial, which included 43 patients with GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, including 38 patients with the most common mutation, PDGFRA D842V.
For patients harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, the overall response rate (ORR) was 84%, with 7% having a complete response and 77% having a partial response. Patients with the PDGFRA D842V mutation achieved an ORR of 89%, with 8% having a complete response and 82% having a partial response.
“GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation do not respond to standard therapies ... Today’s approval provides patients with the first drug specifically approved for GIST harboring this mutation,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, in a statement at the time of approval.
The most common side effects (≥ 20% of patients) observed in patients taking avapritinib include nausea, fatigue, anemia, periorbital edema, face edema, hyperbilirubinemia, diarrhea, vomiting, peripheral edema, increased lacrimation, decreased appetite, and memory impairment. There may also be a risk of intracranial hemorrhage, in which case the dose should be reduced or the drug should be discontinued.
In the EU, conditional marketing authorization is granted to a medicinal product that fulfills an unmet medical need when the benefit to public health of immediate availability outweighs the risk inherent in the fact that additional data are still required, the CHMP notes on its website.
Avapritinib had received an orphan medicine designation during development, which the EMA will review to determine if the designation can be maintained.
New treatment for CLL
Acalabrutinib is already approved in the United States, Canada, and Australia for the treatment of CLL and small lymphocytic lymphoma. The product was approved at the same time by all three regulatory authorities last year. In the United States, acalabrutinib had previously been approved for use in mantle cell lymphoma.
The CHMP’s positive opinion of acalabrutinib is based on results from two phase 3 trials, ELEVATE TN and ASCEND.
In the ASCEND trial, acalabrutinib was compared with investigator’s choice of idelalisib or bendamustine with rituximab. The trial, which involved 310 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL, showed that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival (PFS).
At a median follow-up of 16.1 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib and was 16.5 months with investigator’s choice of therapy (P < .0001).
The most commonly reported adverse events seen with acalabrutinib were respiratory tract infections, headache, bruising, contusion, diarrhea, nausea, rash, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, decreased hemoglobin, and decreased platelets.
In the ELEVATE TN trial, acalabrutinib was given alone or combined with obinutuzumab and compared to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in patients with previously untreated CLL. There were 535 patients randomized to receive acalabrutinib alone (n = 179), acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab (n = 179), and chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab (n = 177).
At a median follow-up of 28 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib alone or with acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab, but the median PFS was 22.6 months in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab arm (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
The most common adverse events in the acalabrutinib arms were headache, diarrhea, neutropenia, and nausea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.