User login
Some women use prescription opioids during pregnancy
and almost a third of those women did not receive counseling from a provider on the effects of opioids on their unborn children, according to analysis from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
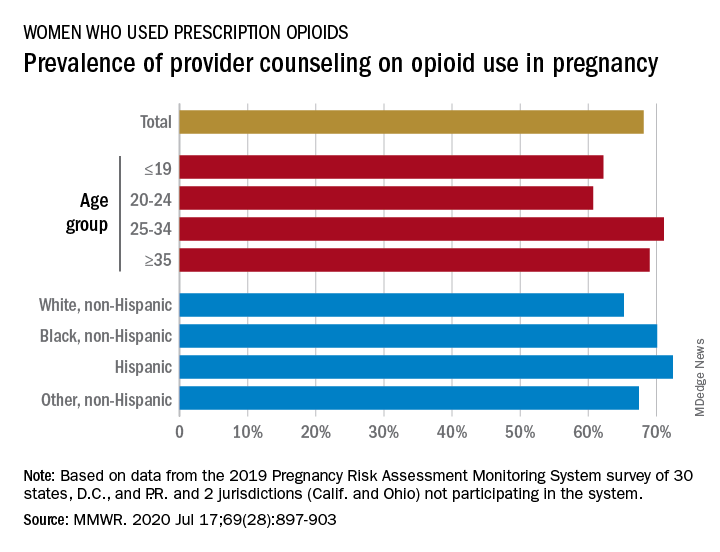
Data from the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System 2019 survey show that 7% of the nearly 21,000 respondents reported using an opioid pain reliever during pregnancy, considerably lower than the fill rates of 14%-22% seen in studies of pharmacy dispensing, Jean Y. Ko, PhD, and associates at the CDC said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In the current analysis, opioid use during pregnancy varied by age – the rate was highest, 10%, in those aged 19 years and under and dropped as age increased to 6% among those aged 35 and older – and by race/ethnicity – 9% of black women reported use, compared with 7% of Hispanics, 6% of whites, and 7% of all others, the investigators reported.
Use of prescription opioids was significantly higher for two specific groups. Women who smoked cigarettes during the last 3 months of their pregnancy had a 16% rate of opioid use, and those with depression during pregnancy had a rate of 13%, they said.
Physicians caring for pregnant women should seek to identify and address substance use and misuse, and mental health conditions such as depression, history of trauma, posttraumatic stress disorder, and anxiety, the CDC researchers pointed out.
The CDC and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists both recommend that caregivers and patients also need to “discuss and carefully weigh risks and benefits when considering initiation of opioid therapy for chronic pain during pregnancy,” Dr. Ko and associates wrote.
That sort of counseling, however, was not always offered: 32% of the women with self-reported prescription opioid use during their pregnancy said that they had not been counseled about the drugs’ effect on an infant. Some variation was seen by age or race/ethnicity, but the differences were not significant, the researchers reported.
“Opioid prescribing consistent with clinical practice guidelines can ensure that patients, particularly those who are pregnant, have access to safer, more effective chronic pain treatment and reduce the number of persons at risk for opioid misuse, opioid use disorder, and overdose,” the investigators concluded.
Survey data from 32 jurisdictions (30 states, along with the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico) that participate in the monitoring system were included in the analysis, as were data from California and Ohio, which do not participate. All of the respondents had a live birth in the preceding 2-6 months, the researchers explained.
SOURCE: Ko JY et al. MMWR. 2020 Jul 17;69(28):897-903.
and almost a third of those women did not receive counseling from a provider on the effects of opioids on their unborn children, according to analysis from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data from the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System 2019 survey show that 7% of the nearly 21,000 respondents reported using an opioid pain reliever during pregnancy, considerably lower than the fill rates of 14%-22% seen in studies of pharmacy dispensing, Jean Y. Ko, PhD, and associates at the CDC said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In the current analysis, opioid use during pregnancy varied by age – the rate was highest, 10%, in those aged 19 years and under and dropped as age increased to 6% among those aged 35 and older – and by race/ethnicity – 9% of black women reported use, compared with 7% of Hispanics, 6% of whites, and 7% of all others, the investigators reported.
Use of prescription opioids was significantly higher for two specific groups. Women who smoked cigarettes during the last 3 months of their pregnancy had a 16% rate of opioid use, and those with depression during pregnancy had a rate of 13%, they said.
Physicians caring for pregnant women should seek to identify and address substance use and misuse, and mental health conditions such as depression, history of trauma, posttraumatic stress disorder, and anxiety, the CDC researchers pointed out.
The CDC and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists both recommend that caregivers and patients also need to “discuss and carefully weigh risks and benefits when considering initiation of opioid therapy for chronic pain during pregnancy,” Dr. Ko and associates wrote.
That sort of counseling, however, was not always offered: 32% of the women with self-reported prescription opioid use during their pregnancy said that they had not been counseled about the drugs’ effect on an infant. Some variation was seen by age or race/ethnicity, but the differences were not significant, the researchers reported.
“Opioid prescribing consistent with clinical practice guidelines can ensure that patients, particularly those who are pregnant, have access to safer, more effective chronic pain treatment and reduce the number of persons at risk for opioid misuse, opioid use disorder, and overdose,” the investigators concluded.
Survey data from 32 jurisdictions (30 states, along with the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico) that participate in the monitoring system were included in the analysis, as were data from California and Ohio, which do not participate. All of the respondents had a live birth in the preceding 2-6 months, the researchers explained.
SOURCE: Ko JY et al. MMWR. 2020 Jul 17;69(28):897-903.
and almost a third of those women did not receive counseling from a provider on the effects of opioids on their unborn children, according to analysis from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data from the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System 2019 survey show that 7% of the nearly 21,000 respondents reported using an opioid pain reliever during pregnancy, considerably lower than the fill rates of 14%-22% seen in studies of pharmacy dispensing, Jean Y. Ko, PhD, and associates at the CDC said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In the current analysis, opioid use during pregnancy varied by age – the rate was highest, 10%, in those aged 19 years and under and dropped as age increased to 6% among those aged 35 and older – and by race/ethnicity – 9% of black women reported use, compared with 7% of Hispanics, 6% of whites, and 7% of all others, the investigators reported.
Use of prescription opioids was significantly higher for two specific groups. Women who smoked cigarettes during the last 3 months of their pregnancy had a 16% rate of opioid use, and those with depression during pregnancy had a rate of 13%, they said.
Physicians caring for pregnant women should seek to identify and address substance use and misuse, and mental health conditions such as depression, history of trauma, posttraumatic stress disorder, and anxiety, the CDC researchers pointed out.
The CDC and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists both recommend that caregivers and patients also need to “discuss and carefully weigh risks and benefits when considering initiation of opioid therapy for chronic pain during pregnancy,” Dr. Ko and associates wrote.
That sort of counseling, however, was not always offered: 32% of the women with self-reported prescription opioid use during their pregnancy said that they had not been counseled about the drugs’ effect on an infant. Some variation was seen by age or race/ethnicity, but the differences were not significant, the researchers reported.
“Opioid prescribing consistent with clinical practice guidelines can ensure that patients, particularly those who are pregnant, have access to safer, more effective chronic pain treatment and reduce the number of persons at risk for opioid misuse, opioid use disorder, and overdose,” the investigators concluded.
Survey data from 32 jurisdictions (30 states, along with the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico) that participate in the monitoring system were included in the analysis, as were data from California and Ohio, which do not participate. All of the respondents had a live birth in the preceding 2-6 months, the researchers explained.
SOURCE: Ko JY et al. MMWR. 2020 Jul 17;69(28):897-903.
FROM MMWR
FDA approves Tremfya (guselkumab) for psoriatic arthritis
, according to a July 14 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The FDA’s approval marks the second indication for guselkumab, which was first approved for adults with plaque psoriasis in 2017.
The agency based its approval on two pivotal phase 3 clinical trials, DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2, which tested the biologic in 1,120 adults with active PsA who were naive to biologics (both trials) or had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or two tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (in about 30% of patients in DISCOVER-1). Part of this pretrial standard treatment could include at least 4 months of Otezla (apremilast), at least 3 months of nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), or at least 4 weeks of NSAIDs. In both trials, about 58% of patients took methotrexate.
Participants who took guselkumab achieved 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria at week 24 at rates of 52% in DISCOVER-1 and 64% in DISCOVER-2, whereas placebo-treated patients had rates of 22% and 33%, respectively.
Guselkumab improved patients’ other symptoms, including skin manifestations of psoriasis, physical functioning, enthesitis, dactylitis, and fatigue, according to the Janssen release.
Guselkumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the p19 subunit of IL-23, is administered as a 100-mg subcutaneous injection every 8 weeks, following two starter doses at weeks 0 and 4, and can be used alone or in combination with a conventional DMARD.
In guselkumab clinical trials of patients with PsA, a minority had bronchitis or a decreased neutrophil count, but the safety profile was otherwise generally consistent with what has been seen in patients with plaque psoriasis, according to the company release. Other common side effects described in 1% or more of patients have included upper respiratory infections, headache, injection-site reactions, arthralgia, diarrhea, gastroenteritis, tinea infections, and herpes simplex infections.
, according to a July 14 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The FDA’s approval marks the second indication for guselkumab, which was first approved for adults with plaque psoriasis in 2017.
The agency based its approval on two pivotal phase 3 clinical trials, DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2, which tested the biologic in 1,120 adults with active PsA who were naive to biologics (both trials) or had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or two tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (in about 30% of patients in DISCOVER-1). Part of this pretrial standard treatment could include at least 4 months of Otezla (apremilast), at least 3 months of nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), or at least 4 weeks of NSAIDs. In both trials, about 58% of patients took methotrexate.
Participants who took guselkumab achieved 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria at week 24 at rates of 52% in DISCOVER-1 and 64% in DISCOVER-2, whereas placebo-treated patients had rates of 22% and 33%, respectively.
Guselkumab improved patients’ other symptoms, including skin manifestations of psoriasis, physical functioning, enthesitis, dactylitis, and fatigue, according to the Janssen release.
Guselkumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the p19 subunit of IL-23, is administered as a 100-mg subcutaneous injection every 8 weeks, following two starter doses at weeks 0 and 4, and can be used alone or in combination with a conventional DMARD.
In guselkumab clinical trials of patients with PsA, a minority had bronchitis or a decreased neutrophil count, but the safety profile was otherwise generally consistent with what has been seen in patients with plaque psoriasis, according to the company release. Other common side effects described in 1% or more of patients have included upper respiratory infections, headache, injection-site reactions, arthralgia, diarrhea, gastroenteritis, tinea infections, and herpes simplex infections.
, according to a July 14 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The FDA’s approval marks the second indication for guselkumab, which was first approved for adults with plaque psoriasis in 2017.
The agency based its approval on two pivotal phase 3 clinical trials, DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2, which tested the biologic in 1,120 adults with active PsA who were naive to biologics (both trials) or had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or two tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (in about 30% of patients in DISCOVER-1). Part of this pretrial standard treatment could include at least 4 months of Otezla (apremilast), at least 3 months of nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), or at least 4 weeks of NSAIDs. In both trials, about 58% of patients took methotrexate.
Participants who took guselkumab achieved 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria at week 24 at rates of 52% in DISCOVER-1 and 64% in DISCOVER-2, whereas placebo-treated patients had rates of 22% and 33%, respectively.
Guselkumab improved patients’ other symptoms, including skin manifestations of psoriasis, physical functioning, enthesitis, dactylitis, and fatigue, according to the Janssen release.
Guselkumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the p19 subunit of IL-23, is administered as a 100-mg subcutaneous injection every 8 weeks, following two starter doses at weeks 0 and 4, and can be used alone or in combination with a conventional DMARD.
In guselkumab clinical trials of patients with PsA, a minority had bronchitis or a decreased neutrophil count, but the safety profile was otherwise generally consistent with what has been seen in patients with plaque psoriasis, according to the company release. Other common side effects described in 1% or more of patients have included upper respiratory infections, headache, injection-site reactions, arthralgia, diarrhea, gastroenteritis, tinea infections, and herpes simplex infections.
FDA approves oral therapy for myelodysplastic syndromes, CMML
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Inqovi (decitabine and cedazuridine tablets, Astex Pharmaceuticals) to treat adults with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) or chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML).
Approval of the tablets could obviate the need for some patients to come to healthcare settings for intravenous therapy, a consideration that goes beyond patient convenience. “The FDA remains committed to providing additional treatments to patients during the coronavirus pandemic. In this case, the FDA is making available an oral outpatient treatment option that can reduce the need for frequent visits to health care facilities,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, stated in a news release.
“At this critical time, we continue to focus on providing options to patients with cancer, including regimens that can be taken at home,” added Dr. Pazdur, who is also acting director of the office of oncologic diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
Inqovi received an Orphan Drug designation and a Priority Review from the agency.
The FDA based the new formulation approval on clinical trials that showed patients taking Inqovi had similar drug concentrations, compared with others receiving intravenous decitabine.
The two therapies also had similar safety profiles. Fatigue, constipation, hemorrhage, muscle pain, mucositis, arthralgia, nausea, and fever with low white blood cell count were common side effects reported in people taking Inqovi. The agency noted that Inqovi can cause fetal harm, and that both male and female patients of reproductive age are advised to use effective contraception.
In the clinical trials, approximately half of the patients formerly dependent on transfusions no longer required them during an 8-week period.
Inqovi is taken as one tablet by mouth once daily for 5 consecutive days of each 28-day cycle.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Inqovi (decitabine and cedazuridine tablets, Astex Pharmaceuticals) to treat adults with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) or chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML).
Approval of the tablets could obviate the need for some patients to come to healthcare settings for intravenous therapy, a consideration that goes beyond patient convenience. “The FDA remains committed to providing additional treatments to patients during the coronavirus pandemic. In this case, the FDA is making available an oral outpatient treatment option that can reduce the need for frequent visits to health care facilities,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, stated in a news release.
“At this critical time, we continue to focus on providing options to patients with cancer, including regimens that can be taken at home,” added Dr. Pazdur, who is also acting director of the office of oncologic diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
Inqovi received an Orphan Drug designation and a Priority Review from the agency.
The FDA based the new formulation approval on clinical trials that showed patients taking Inqovi had similar drug concentrations, compared with others receiving intravenous decitabine.
The two therapies also had similar safety profiles. Fatigue, constipation, hemorrhage, muscle pain, mucositis, arthralgia, nausea, and fever with low white blood cell count were common side effects reported in people taking Inqovi. The agency noted that Inqovi can cause fetal harm, and that both male and female patients of reproductive age are advised to use effective contraception.
In the clinical trials, approximately half of the patients formerly dependent on transfusions no longer required them during an 8-week period.
Inqovi is taken as one tablet by mouth once daily for 5 consecutive days of each 28-day cycle.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Inqovi (decitabine and cedazuridine tablets, Astex Pharmaceuticals) to treat adults with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) or chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML).
Approval of the tablets could obviate the need for some patients to come to healthcare settings for intravenous therapy, a consideration that goes beyond patient convenience. “The FDA remains committed to providing additional treatments to patients during the coronavirus pandemic. In this case, the FDA is making available an oral outpatient treatment option that can reduce the need for frequent visits to health care facilities,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, stated in a news release.
“At this critical time, we continue to focus on providing options to patients with cancer, including regimens that can be taken at home,” added Dr. Pazdur, who is also acting director of the office of oncologic diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
Inqovi received an Orphan Drug designation and a Priority Review from the agency.
The FDA based the new formulation approval on clinical trials that showed patients taking Inqovi had similar drug concentrations, compared with others receiving intravenous decitabine.
The two therapies also had similar safety profiles. Fatigue, constipation, hemorrhage, muscle pain, mucositis, arthralgia, nausea, and fever with low white blood cell count were common side effects reported in people taking Inqovi. The agency noted that Inqovi can cause fetal harm, and that both male and female patients of reproductive age are advised to use effective contraception.
In the clinical trials, approximately half of the patients formerly dependent on transfusions no longer required them during an 8-week period.
Inqovi is taken as one tablet by mouth once daily for 5 consecutive days of each 28-day cycle.
FDA OKs first-in-class HIV therapy for patients with few options
Fostemsavir is indicated for use in combination with other antiretroviral (ARV) agents in heavily treatment-experienced adults with multidrug-resistant HIV-1 infection who fail to achieve viral suppression on other regimens due to resistance, intolerance, or safety considerations.
“This approval marks a new class of antiretroviral medications that may benefit patients who have run out of HIV treatment options,” Jeff Murray, MD, deputy director of the Division of Antivirals in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
“The availability of new classes of antiretroviral drugs is critical for heavily treatment-experienced patients living with multidrug resistant HIV infection — helping people living with hard-to-treat HIV who are at greater risk for HIV-related complications to potentially live longer, healthier lives,” he said.
Fostemsavir 600 mg extended-release tablets are taken twice daily.
In the phase 3 BRIGHTE study, 60% of adults who added fostemsavir to optimized background ARV therapy achieved and maintained viral suppression through 96 weeks and saw clinically meaningful improvements in CD4+ T cells.
Most of the 371 participants in the study had been on anti-HIV therapy for more than 15 years (71%), had been exposed to five or more different HIV treatment regimens (85%), and/or had a history of AIDS (86%).
The most common adverse reactions with fostemsavir are nausea, fatigue, and diarrhea. Serious drug reactions included liver enzyme elevations in patients co-infected with hepatitis B or C virus and three cases of severe immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome.
“Exciting” Advance
“There is a small group of heavily treatment-experienced adults living with HIV who are not able to maintain viral suppression with currently available medication and, without effective new options, are at great risk of progressing to AIDS,” Deborah Waterhouse, CEO of ViiV Healthcare, said in a news release.
“The approval of Rukobia is a culmination of incredibly complex research, development, and manufacturing efforts to ensure we leave no person living with HIV behind,” she said.
“As a novel HIV attachment inhibitor, fostemsavir targets the first step of the viral lifecycle offering a new mechanism of action to treat people living with HIV,” Jacob P. Lalezari, MD, chief executive officer and director of Quest Clinical Research, commented in the release.
Fostemsavir is an “exciting” advance for the heavily treatment-experienced population and “an advancement the HIV community has long been waiting for. As an activist as well as researcher, I am very grateful to ViiV Healthcare for their commitment to heavily-treatment experienced people living with HIV,” he added.
Fostemsavir was reviewed and approved under the FDA’s fast track and breakthrough therapy designations, which are intended to facilitate and expedite the development and review of new drugs to address unmet medical need in the treatment of a serious or life-threatening condition.
Full prescribing information is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fostemsavir is indicated for use in combination with other antiretroviral (ARV) agents in heavily treatment-experienced adults with multidrug-resistant HIV-1 infection who fail to achieve viral suppression on other regimens due to resistance, intolerance, or safety considerations.
“This approval marks a new class of antiretroviral medications that may benefit patients who have run out of HIV treatment options,” Jeff Murray, MD, deputy director of the Division of Antivirals in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
“The availability of new classes of antiretroviral drugs is critical for heavily treatment-experienced patients living with multidrug resistant HIV infection — helping people living with hard-to-treat HIV who are at greater risk for HIV-related complications to potentially live longer, healthier lives,” he said.
Fostemsavir 600 mg extended-release tablets are taken twice daily.
In the phase 3 BRIGHTE study, 60% of adults who added fostemsavir to optimized background ARV therapy achieved and maintained viral suppression through 96 weeks and saw clinically meaningful improvements in CD4+ T cells.
Most of the 371 participants in the study had been on anti-HIV therapy for more than 15 years (71%), had been exposed to five or more different HIV treatment regimens (85%), and/or had a history of AIDS (86%).
The most common adverse reactions with fostemsavir are nausea, fatigue, and diarrhea. Serious drug reactions included liver enzyme elevations in patients co-infected with hepatitis B or C virus and three cases of severe immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome.
“Exciting” Advance
“There is a small group of heavily treatment-experienced adults living with HIV who are not able to maintain viral suppression with currently available medication and, without effective new options, are at great risk of progressing to AIDS,” Deborah Waterhouse, CEO of ViiV Healthcare, said in a news release.
“The approval of Rukobia is a culmination of incredibly complex research, development, and manufacturing efforts to ensure we leave no person living with HIV behind,” she said.
“As a novel HIV attachment inhibitor, fostemsavir targets the first step of the viral lifecycle offering a new mechanism of action to treat people living with HIV,” Jacob P. Lalezari, MD, chief executive officer and director of Quest Clinical Research, commented in the release.
Fostemsavir is an “exciting” advance for the heavily treatment-experienced population and “an advancement the HIV community has long been waiting for. As an activist as well as researcher, I am very grateful to ViiV Healthcare for their commitment to heavily-treatment experienced people living with HIV,” he added.
Fostemsavir was reviewed and approved under the FDA’s fast track and breakthrough therapy designations, which are intended to facilitate and expedite the development and review of new drugs to address unmet medical need in the treatment of a serious or life-threatening condition.
Full prescribing information is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fostemsavir is indicated for use in combination with other antiretroviral (ARV) agents in heavily treatment-experienced adults with multidrug-resistant HIV-1 infection who fail to achieve viral suppression on other regimens due to resistance, intolerance, or safety considerations.
“This approval marks a new class of antiretroviral medications that may benefit patients who have run out of HIV treatment options,” Jeff Murray, MD, deputy director of the Division of Antivirals in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
“The availability of new classes of antiretroviral drugs is critical for heavily treatment-experienced patients living with multidrug resistant HIV infection — helping people living with hard-to-treat HIV who are at greater risk for HIV-related complications to potentially live longer, healthier lives,” he said.
Fostemsavir 600 mg extended-release tablets are taken twice daily.
In the phase 3 BRIGHTE study, 60% of adults who added fostemsavir to optimized background ARV therapy achieved and maintained viral suppression through 96 weeks and saw clinically meaningful improvements in CD4+ T cells.
Most of the 371 participants in the study had been on anti-HIV therapy for more than 15 years (71%), had been exposed to five or more different HIV treatment regimens (85%), and/or had a history of AIDS (86%).
The most common adverse reactions with fostemsavir are nausea, fatigue, and diarrhea. Serious drug reactions included liver enzyme elevations in patients co-infected with hepatitis B or C virus and three cases of severe immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome.
“Exciting” Advance
“There is a small group of heavily treatment-experienced adults living with HIV who are not able to maintain viral suppression with currently available medication and, without effective new options, are at great risk of progressing to AIDS,” Deborah Waterhouse, CEO of ViiV Healthcare, said in a news release.
“The approval of Rukobia is a culmination of incredibly complex research, development, and manufacturing efforts to ensure we leave no person living with HIV behind,” she said.
“As a novel HIV attachment inhibitor, fostemsavir targets the first step of the viral lifecycle offering a new mechanism of action to treat people living with HIV,” Jacob P. Lalezari, MD, chief executive officer and director of Quest Clinical Research, commented in the release.
Fostemsavir is an “exciting” advance for the heavily treatment-experienced population and “an advancement the HIV community has long been waiting for. As an activist as well as researcher, I am very grateful to ViiV Healthcare for their commitment to heavily-treatment experienced people living with HIV,” he added.
Fostemsavir was reviewed and approved under the FDA’s fast track and breakthrough therapy designations, which are intended to facilitate and expedite the development and review of new drugs to address unmet medical need in the treatment of a serious or life-threatening condition.
Full prescribing information is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of nonopioid pain meds is on the rise
Opioid and nonopioid prescription pain medications have taken different journeys since 2009, but they ended up in the same place in 2018, according to a recent report from the National Center for Health Statistics.
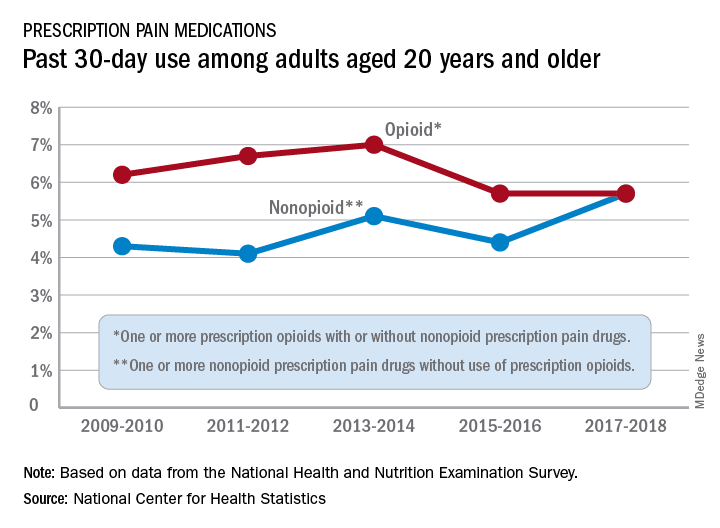
At least by one measure, anyway. Survey data from 2009 to 2010 show that 6.2% of adults aged 20 years and older had taken at least one prescription opioid in the last 30 days and 4.3% had used a prescription nonopioid without an opioid. By 2017-2018, past 30-day use of both drug groups was 5.7%, Craig M. Hales, MD, and associates said in an NCHS data brief.
“Opioids may be prescribed together with nonopioid pain medications, [but] nonpharmacologic and nonopioid-containing pharmacologic therapies are preferred for management of chronic pain,” the NCHS researchers noted.
as did the short-term increase in nonopioids from 2015-2016 to 2017-2018, but the 10-year trend for opioids was not significant, based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Much of the analysis focused on 2015-2018, when 30-day use of any prescription pain medication was reported by 10.7% of adults aged 20 years and older, with use of opioids at 5.7% and nonopioids at 5.0%. For women, use of any pain drug was 12.6% (6.4% opioid, 6.2% nonopioid) from 2015 to 2018, compared with 8.7% for men (4.9%, 3.8%), Dr. Hales and associates reported.
Past 30-day use of both opioids and nonopioids over those 4 years was highest for non-Hispanic whites and lowest, by a significant margin for both drug groups, among non-Hispanic Asian adults, a pattern that held for both men and women, they said.
Opioid and nonopioid prescription pain medications have taken different journeys since 2009, but they ended up in the same place in 2018, according to a recent report from the National Center for Health Statistics.

At least by one measure, anyway. Survey data from 2009 to 2010 show that 6.2% of adults aged 20 years and older had taken at least one prescription opioid in the last 30 days and 4.3% had used a prescription nonopioid without an opioid. By 2017-2018, past 30-day use of both drug groups was 5.7%, Craig M. Hales, MD, and associates said in an NCHS data brief.
“Opioids may be prescribed together with nonopioid pain medications, [but] nonpharmacologic and nonopioid-containing pharmacologic therapies are preferred for management of chronic pain,” the NCHS researchers noted.
as did the short-term increase in nonopioids from 2015-2016 to 2017-2018, but the 10-year trend for opioids was not significant, based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Much of the analysis focused on 2015-2018, when 30-day use of any prescription pain medication was reported by 10.7% of adults aged 20 years and older, with use of opioids at 5.7% and nonopioids at 5.0%. For women, use of any pain drug was 12.6% (6.4% opioid, 6.2% nonopioid) from 2015 to 2018, compared with 8.7% for men (4.9%, 3.8%), Dr. Hales and associates reported.
Past 30-day use of both opioids and nonopioids over those 4 years was highest for non-Hispanic whites and lowest, by a significant margin for both drug groups, among non-Hispanic Asian adults, a pattern that held for both men and women, they said.
Opioid and nonopioid prescription pain medications have taken different journeys since 2009, but they ended up in the same place in 2018, according to a recent report from the National Center for Health Statistics.

At least by one measure, anyway. Survey data from 2009 to 2010 show that 6.2% of adults aged 20 years and older had taken at least one prescription opioid in the last 30 days and 4.3% had used a prescription nonopioid without an opioid. By 2017-2018, past 30-day use of both drug groups was 5.7%, Craig M. Hales, MD, and associates said in an NCHS data brief.
“Opioids may be prescribed together with nonopioid pain medications, [but] nonpharmacologic and nonopioid-containing pharmacologic therapies are preferred for management of chronic pain,” the NCHS researchers noted.
as did the short-term increase in nonopioids from 2015-2016 to 2017-2018, but the 10-year trend for opioids was not significant, based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Much of the analysis focused on 2015-2018, when 30-day use of any prescription pain medication was reported by 10.7% of adults aged 20 years and older, with use of opioids at 5.7% and nonopioids at 5.0%. For women, use of any pain drug was 12.6% (6.4% opioid, 6.2% nonopioid) from 2015 to 2018, compared with 8.7% for men (4.9%, 3.8%), Dr. Hales and associates reported.
Past 30-day use of both opioids and nonopioids over those 4 years was highest for non-Hispanic whites and lowest, by a significant margin for both drug groups, among non-Hispanic Asian adults, a pattern that held for both men and women, they said.
Declines in infant mortality tempered by disparities
Age-adjusted infant mortality dropped 11% from 2000 to 2017 in the United States, but the even larger decline for infants born to black women still left a death rate more than twice as high as those of white or Hispanic infants, according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.

while the crude mortality rate fell 16% from 6.89 to 5.79, reported Anne K. Driscoll, PhD, and Danielle M. Ely, PhD, of the NCHS.
Over that same time period, age-adjusted infant mortality for births to black women went from 13.59 per 1,000 to 11.19, a drop of 18%. By comparison, age-adjusted mortality declined 7% from 5.59 per 1,000 for infants born to Hispanic women to 5.21 in 2017, they said in a National Vital Statistics Report.
Changes in maternal age distribution had an important effect on infant mortality. Women aged under 25 years, who have higher mortality rates, were less likely to give birth in 2017 than in 2000, and women aged 30-39 years, who have the lowest rates, made up a larger share of births in 2017, they pointed out.
It was, however, changes in age-specific mortality rates (ASMRs) that had the largest influence on the overall drop in the crude mortality rate, accounting for about two-thirds of the overall decline, the NCHS researchers said, noting that the effect varied by race and Hispanic origin.
Births to non-Hispanic white women mirrored the national situation: Approximately two-thirds (68.7%) of the decrease in infant mortality came from changes in ASMRs and one-third (31.3%) from changes in maternal age distribution. Among non-Hispanic black women, the distribution was 95.2% ASMRs and 4.8% age distribution, Dr. Driscoll and Dr. Ely reported based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
The disparity between the two trends went even further for infants born to Hispanic women. Changes in ASMRs were responsible for 133.7% of the overall change in crude mortality versus –33.7% for changes in maternal age distribution. “If no changes occurred in the ASMRs, the changes in the maternal age distribution would have resulted in a higher mortality rate in 2017,” they explained.
The declines in the ASMRs may be related to incremental improved survival of preterm and low-birthweight infants in certain groups. “While little or no progress has been made to lower [these] two key risk factors for poor birth outcomes, progress has been made in lowering the mortality rates of at-risk infants across maternal age and race and Hispanic origin, resulting in lower ASMRs for all age groups,” the investigators suggested.
It also is possible that “changes in other factors, such as maternal education and cigarette smoking during pregnancy, may have indirectly resulted in declining ASMRs for all age groups over time,” they added.
SOURCE: Driscoll AK, Ely DM. National Vital Statistics Reports. 2020;69(5):1-18.
Age-adjusted infant mortality dropped 11% from 2000 to 2017 in the United States, but the even larger decline for infants born to black women still left a death rate more than twice as high as those of white or Hispanic infants, according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.

while the crude mortality rate fell 16% from 6.89 to 5.79, reported Anne K. Driscoll, PhD, and Danielle M. Ely, PhD, of the NCHS.
Over that same time period, age-adjusted infant mortality for births to black women went from 13.59 per 1,000 to 11.19, a drop of 18%. By comparison, age-adjusted mortality declined 7% from 5.59 per 1,000 for infants born to Hispanic women to 5.21 in 2017, they said in a National Vital Statistics Report.
Changes in maternal age distribution had an important effect on infant mortality. Women aged under 25 years, who have higher mortality rates, were less likely to give birth in 2017 than in 2000, and women aged 30-39 years, who have the lowest rates, made up a larger share of births in 2017, they pointed out.
It was, however, changes in age-specific mortality rates (ASMRs) that had the largest influence on the overall drop in the crude mortality rate, accounting for about two-thirds of the overall decline, the NCHS researchers said, noting that the effect varied by race and Hispanic origin.
Births to non-Hispanic white women mirrored the national situation: Approximately two-thirds (68.7%) of the decrease in infant mortality came from changes in ASMRs and one-third (31.3%) from changes in maternal age distribution. Among non-Hispanic black women, the distribution was 95.2% ASMRs and 4.8% age distribution, Dr. Driscoll and Dr. Ely reported based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
The disparity between the two trends went even further for infants born to Hispanic women. Changes in ASMRs were responsible for 133.7% of the overall change in crude mortality versus –33.7% for changes in maternal age distribution. “If no changes occurred in the ASMRs, the changes in the maternal age distribution would have resulted in a higher mortality rate in 2017,” they explained.
The declines in the ASMRs may be related to incremental improved survival of preterm and low-birthweight infants in certain groups. “While little or no progress has been made to lower [these] two key risk factors for poor birth outcomes, progress has been made in lowering the mortality rates of at-risk infants across maternal age and race and Hispanic origin, resulting in lower ASMRs for all age groups,” the investigators suggested.
It also is possible that “changes in other factors, such as maternal education and cigarette smoking during pregnancy, may have indirectly resulted in declining ASMRs for all age groups over time,” they added.
SOURCE: Driscoll AK, Ely DM. National Vital Statistics Reports. 2020;69(5):1-18.
Age-adjusted infant mortality dropped 11% from 2000 to 2017 in the United States, but the even larger decline for infants born to black women still left a death rate more than twice as high as those of white or Hispanic infants, according to a new analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.

while the crude mortality rate fell 16% from 6.89 to 5.79, reported Anne K. Driscoll, PhD, and Danielle M. Ely, PhD, of the NCHS.
Over that same time period, age-adjusted infant mortality for births to black women went from 13.59 per 1,000 to 11.19, a drop of 18%. By comparison, age-adjusted mortality declined 7% from 5.59 per 1,000 for infants born to Hispanic women to 5.21 in 2017, they said in a National Vital Statistics Report.
Changes in maternal age distribution had an important effect on infant mortality. Women aged under 25 years, who have higher mortality rates, were less likely to give birth in 2017 than in 2000, and women aged 30-39 years, who have the lowest rates, made up a larger share of births in 2017, they pointed out.
It was, however, changes in age-specific mortality rates (ASMRs) that had the largest influence on the overall drop in the crude mortality rate, accounting for about two-thirds of the overall decline, the NCHS researchers said, noting that the effect varied by race and Hispanic origin.
Births to non-Hispanic white women mirrored the national situation: Approximately two-thirds (68.7%) of the decrease in infant mortality came from changes in ASMRs and one-third (31.3%) from changes in maternal age distribution. Among non-Hispanic black women, the distribution was 95.2% ASMRs and 4.8% age distribution, Dr. Driscoll and Dr. Ely reported based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
The disparity between the two trends went even further for infants born to Hispanic women. Changes in ASMRs were responsible for 133.7% of the overall change in crude mortality versus –33.7% for changes in maternal age distribution. “If no changes occurred in the ASMRs, the changes in the maternal age distribution would have resulted in a higher mortality rate in 2017,” they explained.
The declines in the ASMRs may be related to incremental improved survival of preterm and low-birthweight infants in certain groups. “While little or no progress has been made to lower [these] two key risk factors for poor birth outcomes, progress has been made in lowering the mortality rates of at-risk infants across maternal age and race and Hispanic origin, resulting in lower ASMRs for all age groups,” the investigators suggested.
It also is possible that “changes in other factors, such as maternal education and cigarette smoking during pregnancy, may have indirectly resulted in declining ASMRs for all age groups over time,” they added.
SOURCE: Driscoll AK, Ely DM. National Vital Statistics Reports. 2020;69(5):1-18.
FDA approves avelumab as maintenance for urothelial carcinoma
The Food and Administration has approved a new indication for the PD-L1 inhibitor avelumab.
Physicians can now prescribe avelumab (Bavencio) as maintenance treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (UC) that has not progressed after first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The new indication adds to avelumab use in other patient populations, including people with locally advanced or metastatic UC who experience disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy. The FDA also previously approved avelumab for patients who experienced UC progression within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The FDA first approved marketing of avelumab in 2017. Other uses include treatment of metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma in combination with axitinib.
The new maintenance therapy indication for avelumab is based on efficacy demonstrated in the JAVELIN Bladder 100 trial. Results from this trial were presented as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Investigators randomly assigned 700 patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic UC to intravenous avelumab and best supportive care or best supportive care alone. All participants had UC that had not progressed after first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The median overall survival was 21.4 months in the avelumab arm and 14.3 months in the best supportive care–alone arm (hazard ratio, 0.69; 95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.86). This difference was statistically significant (P = .001).
Avelumab also was associated with significantly longer overall survival in the 51% of participants with PD-L1–positive tumors (hazard ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.40-0.79; P < .001).
Results from the JAVELIN Bladder 100 trial allowed the FDA to convert an initial accelerated approval of avelumab to a regular approval.
Fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, urinary tract infection, and rash were the most common adverse events reported in 20% or more of trial participants. In all, 28% of patients experienced serious adverse events, and one patient died from sepsis during the trial.
Recommended avelumab dosing is 800 mg administered as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes every 2 weeks until disease progresses or toxicity becomes unacceptable.
See the full prescribing information for more details.
The Food and Administration has approved a new indication for the PD-L1 inhibitor avelumab.
Physicians can now prescribe avelumab (Bavencio) as maintenance treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (UC) that has not progressed after first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The new indication adds to avelumab use in other patient populations, including people with locally advanced or metastatic UC who experience disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy. The FDA also previously approved avelumab for patients who experienced UC progression within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The FDA first approved marketing of avelumab in 2017. Other uses include treatment of metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma in combination with axitinib.
The new maintenance therapy indication for avelumab is based on efficacy demonstrated in the JAVELIN Bladder 100 trial. Results from this trial were presented as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Investigators randomly assigned 700 patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic UC to intravenous avelumab and best supportive care or best supportive care alone. All participants had UC that had not progressed after first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The median overall survival was 21.4 months in the avelumab arm and 14.3 months in the best supportive care–alone arm (hazard ratio, 0.69; 95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.86). This difference was statistically significant (P = .001).
Avelumab also was associated with significantly longer overall survival in the 51% of participants with PD-L1–positive tumors (hazard ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.40-0.79; P < .001).
Results from the JAVELIN Bladder 100 trial allowed the FDA to convert an initial accelerated approval of avelumab to a regular approval.
Fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, urinary tract infection, and rash were the most common adverse events reported in 20% or more of trial participants. In all, 28% of patients experienced serious adverse events, and one patient died from sepsis during the trial.
Recommended avelumab dosing is 800 mg administered as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes every 2 weeks until disease progresses or toxicity becomes unacceptable.
See the full prescribing information for more details.
The Food and Administration has approved a new indication for the PD-L1 inhibitor avelumab.
Physicians can now prescribe avelumab (Bavencio) as maintenance treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (UC) that has not progressed after first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The new indication adds to avelumab use in other patient populations, including people with locally advanced or metastatic UC who experience disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy. The FDA also previously approved avelumab for patients who experienced UC progression within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The FDA first approved marketing of avelumab in 2017. Other uses include treatment of metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma in combination with axitinib.
The new maintenance therapy indication for avelumab is based on efficacy demonstrated in the JAVELIN Bladder 100 trial. Results from this trial were presented as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Investigators randomly assigned 700 patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic UC to intravenous avelumab and best supportive care or best supportive care alone. All participants had UC that had not progressed after first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The median overall survival was 21.4 months in the avelumab arm and 14.3 months in the best supportive care–alone arm (hazard ratio, 0.69; 95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.86). This difference was statistically significant (P = .001).
Avelumab also was associated with significantly longer overall survival in the 51% of participants with PD-L1–positive tumors (hazard ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.40-0.79; P < .001).
Results from the JAVELIN Bladder 100 trial allowed the FDA to convert an initial accelerated approval of avelumab to a regular approval.
Fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, urinary tract infection, and rash were the most common adverse events reported in 20% or more of trial participants. In all, 28% of patients experienced serious adverse events, and one patient died from sepsis during the trial.
Recommended avelumab dosing is 800 mg administered as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes every 2 weeks until disease progresses or toxicity becomes unacceptable.
See the full prescribing information for more details.
FDA approves new indications for pembrolizumab
The Food and Drug Administration recently announced two new types of cancer that can be treated by the anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab.
The new indications expand the use of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to include treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic tumor mutational burden–high (TMB-H) solid tumors as well as patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC). The FDA announced the new indications just 8 days apart, on June 16 and June 24.
In addition, on June 29, the FDA approved a third new indication for pembrolizumab, this time as first-line treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic microsatellite instability–high or mismatch repair–deficient colorectal cancer.
The new approvals add to a wide range of oncology indications for which pembrolizumab can be used.
Accelerated approval to treat solid tumors
The FDA granted accelerated approval for pembrolizumab to treat children and adults with unresectable or metastatic TMB-H solid tumors that progressed after previous treatment or in instances where there are no satisfactory alternative treatment options.
The tumor mutational burden must be confirmed by an FDA-approved test. To that end, the FDA approved the FoundationOneCDx assay, which is designed to help physicians determine which patients meet the threshold for TMB-H malignancies (10 or more mutations per megabase).
The efficacy of pembrolizumab in TMB-H solid tumors was investigated in 10 cohorts from the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-158 trial. Participants received 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until their disease progressed or they experienced unacceptable toxicity.
Within this population, 102 patients had tumors that met the TMB-H definition. In this group, the overall response rate was 29%, including a 25% partial response rate and a 4% complete response rate.
The median duration of response was not reached, but 57% of participants experienced a response lasting 12 months or longer, and 50% had a response lasting 24 months or longer.
The most common adverse events associated with pembrolizumab in this trial were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, decreased appetite, pruritus, diarrhea, nausea, rash, pyrexia, cough, dyspnea, constipation, pain, and abdominal pain. Pembrolizumab is associated with immune-mediated side effects, including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, and skin adverse reactions, the FDA noted.
Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab in pediatric patients with TMB-H central nervous system cancers have not been established.
New option for recurrent or metastatic cSCC
Physicians treating patients with cSCC that is not curable by surgery or radiation now have pembrolizumab to consider as another treatment option.
The cSCC approval is based on results of the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-629 trial. The dosage regimen was 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until cancer progressed, unacceptable toxicity arose, or 24 months of treatment were completed.
The objective response rate was 34%, and the median duration of response was not reached.
Adverse events were similar to those occurring in patients who received pembrolizumab as a single agent in other clinical trials, the FDA noted.
The Food and Drug Administration recently announced two new types of cancer that can be treated by the anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab.
The new indications expand the use of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to include treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic tumor mutational burden–high (TMB-H) solid tumors as well as patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC). The FDA announced the new indications just 8 days apart, on June 16 and June 24.
In addition, on June 29, the FDA approved a third new indication for pembrolizumab, this time as first-line treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic microsatellite instability–high or mismatch repair–deficient colorectal cancer.
The new approvals add to a wide range of oncology indications for which pembrolizumab can be used.
Accelerated approval to treat solid tumors
The FDA granted accelerated approval for pembrolizumab to treat children and adults with unresectable or metastatic TMB-H solid tumors that progressed after previous treatment or in instances where there are no satisfactory alternative treatment options.
The tumor mutational burden must be confirmed by an FDA-approved test. To that end, the FDA approved the FoundationOneCDx assay, which is designed to help physicians determine which patients meet the threshold for TMB-H malignancies (10 or more mutations per megabase).
The efficacy of pembrolizumab in TMB-H solid tumors was investigated in 10 cohorts from the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-158 trial. Participants received 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until their disease progressed or they experienced unacceptable toxicity.
Within this population, 102 patients had tumors that met the TMB-H definition. In this group, the overall response rate was 29%, including a 25% partial response rate and a 4% complete response rate.
The median duration of response was not reached, but 57% of participants experienced a response lasting 12 months or longer, and 50% had a response lasting 24 months or longer.
The most common adverse events associated with pembrolizumab in this trial were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, decreased appetite, pruritus, diarrhea, nausea, rash, pyrexia, cough, dyspnea, constipation, pain, and abdominal pain. Pembrolizumab is associated with immune-mediated side effects, including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, and skin adverse reactions, the FDA noted.
Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab in pediatric patients with TMB-H central nervous system cancers have not been established.
New option for recurrent or metastatic cSCC
Physicians treating patients with cSCC that is not curable by surgery or radiation now have pembrolizumab to consider as another treatment option.
The cSCC approval is based on results of the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-629 trial. The dosage regimen was 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until cancer progressed, unacceptable toxicity arose, or 24 months of treatment were completed.
The objective response rate was 34%, and the median duration of response was not reached.
Adverse events were similar to those occurring in patients who received pembrolizumab as a single agent in other clinical trials, the FDA noted.
The Food and Drug Administration recently announced two new types of cancer that can be treated by the anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab.
The new indications expand the use of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to include treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic tumor mutational burden–high (TMB-H) solid tumors as well as patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC). The FDA announced the new indications just 8 days apart, on June 16 and June 24.
In addition, on June 29, the FDA approved a third new indication for pembrolizumab, this time as first-line treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic microsatellite instability–high or mismatch repair–deficient colorectal cancer.
The new approvals add to a wide range of oncology indications for which pembrolizumab can be used.
Accelerated approval to treat solid tumors
The FDA granted accelerated approval for pembrolizumab to treat children and adults with unresectable or metastatic TMB-H solid tumors that progressed after previous treatment or in instances where there are no satisfactory alternative treatment options.
The tumor mutational burden must be confirmed by an FDA-approved test. To that end, the FDA approved the FoundationOneCDx assay, which is designed to help physicians determine which patients meet the threshold for TMB-H malignancies (10 or more mutations per megabase).
The efficacy of pembrolizumab in TMB-H solid tumors was investigated in 10 cohorts from the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-158 trial. Participants received 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until their disease progressed or they experienced unacceptable toxicity.
Within this population, 102 patients had tumors that met the TMB-H definition. In this group, the overall response rate was 29%, including a 25% partial response rate and a 4% complete response rate.
The median duration of response was not reached, but 57% of participants experienced a response lasting 12 months or longer, and 50% had a response lasting 24 months or longer.
The most common adverse events associated with pembrolizumab in this trial were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, decreased appetite, pruritus, diarrhea, nausea, rash, pyrexia, cough, dyspnea, constipation, pain, and abdominal pain. Pembrolizumab is associated with immune-mediated side effects, including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, and skin adverse reactions, the FDA noted.
Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab in pediatric patients with TMB-H central nervous system cancers have not been established.
New option for recurrent or metastatic cSCC
Physicians treating patients with cSCC that is not curable by surgery or radiation now have pembrolizumab to consider as another treatment option.
The cSCC approval is based on results of the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-629 trial. The dosage regimen was 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until cancer progressed, unacceptable toxicity arose, or 24 months of treatment were completed.
The objective response rate was 34%, and the median duration of response was not reached.
Adverse events were similar to those occurring in patients who received pembrolizumab as a single agent in other clinical trials, the FDA noted.
Pembro approved for first-line use in MSI-H/dMMR colorectal cancer
This is the first time that an immunotherapy agent has been approved in this setting and as monotherapy, without added chemotherapy.
“Metastatic colorectal cancer is a serious and life-threatening disease with a poor prognosis,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases at the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in a statement. “Available current therapy with chemotherapy combinations and other biologics are associated with substantial toxicity.”
“Having a nonchemotherapy option available for selected patients is a noteworthy paradigm shift in treatment,” he commented.
Pembrolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction between PD-1 and its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, and has demonstrated robust antitumor activity and a favorable safety profile in multiple tumor types.
The current approval is based on data from the multicenter, randomized KEYNOTE-177 trial, which found that pembrolizumab more than doubled median progression-free survival (PFS) compared with chemotherapy, the current standard of care. The study results were presented earlier this year at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) virtual scientific program, as reported by Medscape Medical News. In a commentary about that study, David Kerr, MD, professor of cancer medicine at the Oxford Cancer Centre, UK, said: “We know that MSI-H/dMMR tumors occur in only 4% or 5% of all patients in the advanced setting. Nevertheless, for that small but important subgroup, we now have a well-tolerated new treatment.”
New standard of care
The KEYNOTE-177 trial involved 307 patients with previously untreated unresectable or metastatic MSI-H or dMMR colorectal cancer. They were randomized to receive either pembrolizumab at 200 mg every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles (n = 153) or to the investigators’ choice of chemotherapy (n = 154).
Chemotherapy regimens were modified FOLFOX (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin) used alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab, or FOLFIRI (leucovorin, fluorouracil, irinotecan) alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab.
Crossover from the chemotherapy arm to immunotherapy was permitted for up to 35 cycles if the patient experienced disease progression confirmed by central review.
The primary endpoints were PFS and overall survival, and the trial would be considered successful if either primary endpoint was met.
Treatment with pembrolizumab monotherapy significantly reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 40% (HR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.45 - 0.80; P = .0004), with a median PFS of 16.5 months versus 8.2 months for chemotherapy. At the time of the PFS analysis, overall survival data were not yet mature (66% of the required number of events for final analysis).
The overall response rate with pembrolizumab was 44%, with a complete response achieved in 11% of patients and a partial response rate of 33%. For the chemotherapy arm, the overall response rate was 33%, with a complete response rate of 4% and a partial response rate of 29%.
The median duration of response was not reached in the pembrolizumab arm versus 10.6 months with chemotherapy.
“In the past, no medical treatment has shown such difference in terms of improvement of PFS in metastatic colorectal cancer,” said study investigator Thierry André, MD, of Hôpital Saint Antoine in Paris, France, at a press briefing held prior to the presentation at the ASCO meeting.
At that time, Michael J. Overman, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, told Medscape Medical News that “I think this is setting a new standard of care.”
Grade 3 or greater treatment-related adverse events occurred in 22% of patients on pembrolizumab and 66% on chemotherapy.
Immune-mediated adverse events and infusion reactions were more common with pembrolizumab than chemotherapy (31% and 13%, respectively). Adverse events that were common with chemotherapy included gastrointestinal events, fatigue, neutropenia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This is the first time that an immunotherapy agent has been approved in this setting and as monotherapy, without added chemotherapy.
“Metastatic colorectal cancer is a serious and life-threatening disease with a poor prognosis,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases at the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in a statement. “Available current therapy with chemotherapy combinations and other biologics are associated with substantial toxicity.”
“Having a nonchemotherapy option available for selected patients is a noteworthy paradigm shift in treatment,” he commented.
Pembrolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction between PD-1 and its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, and has demonstrated robust antitumor activity and a favorable safety profile in multiple tumor types.
The current approval is based on data from the multicenter, randomized KEYNOTE-177 trial, which found that pembrolizumab more than doubled median progression-free survival (PFS) compared with chemotherapy, the current standard of care. The study results were presented earlier this year at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) virtual scientific program, as reported by Medscape Medical News. In a commentary about that study, David Kerr, MD, professor of cancer medicine at the Oxford Cancer Centre, UK, said: “We know that MSI-H/dMMR tumors occur in only 4% or 5% of all patients in the advanced setting. Nevertheless, for that small but important subgroup, we now have a well-tolerated new treatment.”
New standard of care
The KEYNOTE-177 trial involved 307 patients with previously untreated unresectable or metastatic MSI-H or dMMR colorectal cancer. They were randomized to receive either pembrolizumab at 200 mg every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles (n = 153) or to the investigators’ choice of chemotherapy (n = 154).
Chemotherapy regimens were modified FOLFOX (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin) used alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab, or FOLFIRI (leucovorin, fluorouracil, irinotecan) alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab.
Crossover from the chemotherapy arm to immunotherapy was permitted for up to 35 cycles if the patient experienced disease progression confirmed by central review.
The primary endpoints were PFS and overall survival, and the trial would be considered successful if either primary endpoint was met.
Treatment with pembrolizumab monotherapy significantly reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 40% (HR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.45 - 0.80; P = .0004), with a median PFS of 16.5 months versus 8.2 months for chemotherapy. At the time of the PFS analysis, overall survival data were not yet mature (66% of the required number of events for final analysis).
The overall response rate with pembrolizumab was 44%, with a complete response achieved in 11% of patients and a partial response rate of 33%. For the chemotherapy arm, the overall response rate was 33%, with a complete response rate of 4% and a partial response rate of 29%.
The median duration of response was not reached in the pembrolizumab arm versus 10.6 months with chemotherapy.
“In the past, no medical treatment has shown such difference in terms of improvement of PFS in metastatic colorectal cancer,” said study investigator Thierry André, MD, of Hôpital Saint Antoine in Paris, France, at a press briefing held prior to the presentation at the ASCO meeting.
At that time, Michael J. Overman, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, told Medscape Medical News that “I think this is setting a new standard of care.”
Grade 3 or greater treatment-related adverse events occurred in 22% of patients on pembrolizumab and 66% on chemotherapy.
Immune-mediated adverse events and infusion reactions were more common with pembrolizumab than chemotherapy (31% and 13%, respectively). Adverse events that were common with chemotherapy included gastrointestinal events, fatigue, neutropenia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This is the first time that an immunotherapy agent has been approved in this setting and as monotherapy, without added chemotherapy.
“Metastatic colorectal cancer is a serious and life-threatening disease with a poor prognosis,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases at the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in a statement. “Available current therapy with chemotherapy combinations and other biologics are associated with substantial toxicity.”
“Having a nonchemotherapy option available for selected patients is a noteworthy paradigm shift in treatment,” he commented.
Pembrolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction between PD-1 and its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, and has demonstrated robust antitumor activity and a favorable safety profile in multiple tumor types.
The current approval is based on data from the multicenter, randomized KEYNOTE-177 trial, which found that pembrolizumab more than doubled median progression-free survival (PFS) compared with chemotherapy, the current standard of care. The study results were presented earlier this year at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) virtual scientific program, as reported by Medscape Medical News. In a commentary about that study, David Kerr, MD, professor of cancer medicine at the Oxford Cancer Centre, UK, said: “We know that MSI-H/dMMR tumors occur in only 4% or 5% of all patients in the advanced setting. Nevertheless, for that small but important subgroup, we now have a well-tolerated new treatment.”
New standard of care
The KEYNOTE-177 trial involved 307 patients with previously untreated unresectable or metastatic MSI-H or dMMR colorectal cancer. They were randomized to receive either pembrolizumab at 200 mg every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles (n = 153) or to the investigators’ choice of chemotherapy (n = 154).
Chemotherapy regimens were modified FOLFOX (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin) used alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab, or FOLFIRI (leucovorin, fluorouracil, irinotecan) alone or in combination with either bevacizumab or cetuximab.
Crossover from the chemotherapy arm to immunotherapy was permitted for up to 35 cycles if the patient experienced disease progression confirmed by central review.
The primary endpoints were PFS and overall survival, and the trial would be considered successful if either primary endpoint was met.
Treatment with pembrolizumab monotherapy significantly reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 40% (HR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.45 - 0.80; P = .0004), with a median PFS of 16.5 months versus 8.2 months for chemotherapy. At the time of the PFS analysis, overall survival data were not yet mature (66% of the required number of events for final analysis).
The overall response rate with pembrolizumab was 44%, with a complete response achieved in 11% of patients and a partial response rate of 33%. For the chemotherapy arm, the overall response rate was 33%, with a complete response rate of 4% and a partial response rate of 29%.
The median duration of response was not reached in the pembrolizumab arm versus 10.6 months with chemotherapy.
“In the past, no medical treatment has shown such difference in terms of improvement of PFS in metastatic colorectal cancer,” said study investigator Thierry André, MD, of Hôpital Saint Antoine in Paris, France, at a press briefing held prior to the presentation at the ASCO meeting.
At that time, Michael J. Overman, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, told Medscape Medical News that “I think this is setting a new standard of care.”
Grade 3 or greater treatment-related adverse events occurred in 22% of patients on pembrolizumab and 66% on chemotherapy.
Immune-mediated adverse events and infusion reactions were more common with pembrolizumab than chemotherapy (31% and 13%, respectively). Adverse events that were common with chemotherapy included gastrointestinal events, fatigue, neutropenia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves in-home breast cancer treatment
Advantageous for infusion centers?
The Food and Drug Administration approved a combination of pertuzumab (Perjeta, Genentech/Roche), trastuzumab (Herceptin, Genentech/Roche) and hyaluronidase (Phesgo, Genentech/Roche) that is administered subcutaneously – rather than intravenously – for the treatment of early and metastatic HER2-positive breast cancers.
Phesgo is initially used in combination with chemotherapy at an infusion center but could continue to be administered in a patient’s home by a qualified health care professional once chemotherapy is complete, according to the FDA.
Administration takes approximately 8 minutes for the initial loading dose and approximately 5 minutes for maintenance doses, according to a Genentech press statement. This compares favorably with the 150 minutes needed for the combined loading dose of intravenous pertuzumab and trastuzumab, and the 60-150 minutes for intravenous maintenance infusions, the company said.
“Currently, most patients with HER2-positive breast cancer receive trastuzumab and pertuzumab at infusion centers. With a new administration route, Phesgo offers an outpatient option for patients to receive trastuzumab and pertuzumab,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in an agency press release.
“The fixed-dose combination of trastuzumab and pertuzumab offers a simpler, faster, and easier treatment experience for patients with HER2-positive breast cancer,” said Antoinette Tan, MD, MHSc, chief of breast medical oncology at Levine Cancer Institute, Charlotte, N.C., in the company statement.
Dr. Tan also said that home administration “can be advantageous for patients and infusion centers.”
However, in April, the Community Oncology Alliance strenuously objected to this type of treatment in a patient’s home, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The group, which represents U.S. community-based practices, said it “fundamentally opposes home infusion of chemotherapy, cancer immunotherapy, and cancer treatment supportive drugs because of serious patient safety concerns.”
The FDA’s approval was based on the results of the pivotal phase 3 FeDeriCa trial, a noninferiority study in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer, which demonstrated that the new product had comparable efficacy and safety as intravenous pertuzumab and intravenous trastuzumab.
In terms of efficacy, the subcutaneous product demonstrated noninferior plasma levels of pertuzumab, which was the primary endpoint, when compared with IV administration of pertuzumab.
Safety was comparable between the two approaches, with no new safety signals using the subcutaneous delivery method, including no “meaningful difference” in cardiac toxicity, according to Genentech. However, there were more administration-related reactions with the new product. The most common adverse events in both groups were alopecia, nausea, diarrhea, and anemia.
The new product uses a drug delivery technology (Enhanze, Halozyme Therapeutics) that employs a proprietary enzyme that temporarily degrades hyaluronan, a glycosaminoglycan or chain of natural sugars in the body, to facilitate the dispersion and absorption of injected therapeutic drugs, according to Genentech.
In May, at the European Society for Medical Oncology Breast Cancer Virtual Meeting 2020, investigators of the phase 2 PHranceSCa study reported that “more than 80%” of patients preferred subcutaneous to intravenous administration of pertuzumab and trastuzumab.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Advantageous for infusion centers?
Advantageous for infusion centers?
The Food and Drug Administration approved a combination of pertuzumab (Perjeta, Genentech/Roche), trastuzumab (Herceptin, Genentech/Roche) and hyaluronidase (Phesgo, Genentech/Roche) that is administered subcutaneously – rather than intravenously – for the treatment of early and metastatic HER2-positive breast cancers.
Phesgo is initially used in combination with chemotherapy at an infusion center but could continue to be administered in a patient’s home by a qualified health care professional once chemotherapy is complete, according to the FDA.
Administration takes approximately 8 minutes for the initial loading dose and approximately 5 minutes for maintenance doses, according to a Genentech press statement. This compares favorably with the 150 minutes needed for the combined loading dose of intravenous pertuzumab and trastuzumab, and the 60-150 minutes for intravenous maintenance infusions, the company said.
“Currently, most patients with HER2-positive breast cancer receive trastuzumab and pertuzumab at infusion centers. With a new administration route, Phesgo offers an outpatient option for patients to receive trastuzumab and pertuzumab,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in an agency press release.
“The fixed-dose combination of trastuzumab and pertuzumab offers a simpler, faster, and easier treatment experience for patients with HER2-positive breast cancer,” said Antoinette Tan, MD, MHSc, chief of breast medical oncology at Levine Cancer Institute, Charlotte, N.C., in the company statement.
Dr. Tan also said that home administration “can be advantageous for patients and infusion centers.”
However, in April, the Community Oncology Alliance strenuously objected to this type of treatment in a patient’s home, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The group, which represents U.S. community-based practices, said it “fundamentally opposes home infusion of chemotherapy, cancer immunotherapy, and cancer treatment supportive drugs because of serious patient safety concerns.”
The FDA’s approval was based on the results of the pivotal phase 3 FeDeriCa trial, a noninferiority study in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer, which demonstrated that the new product had comparable efficacy and safety as intravenous pertuzumab and intravenous trastuzumab.
In terms of efficacy, the subcutaneous product demonstrated noninferior plasma levels of pertuzumab, which was the primary endpoint, when compared with IV administration of pertuzumab.
Safety was comparable between the two approaches, with no new safety signals using the subcutaneous delivery method, including no “meaningful difference” in cardiac toxicity, according to Genentech. However, there were more administration-related reactions with the new product. The most common adverse events in both groups were alopecia, nausea, diarrhea, and anemia.
The new product uses a drug delivery technology (Enhanze, Halozyme Therapeutics) that employs a proprietary enzyme that temporarily degrades hyaluronan, a glycosaminoglycan or chain of natural sugars in the body, to facilitate the dispersion and absorption of injected therapeutic drugs, according to Genentech.
In May, at the European Society for Medical Oncology Breast Cancer Virtual Meeting 2020, investigators of the phase 2 PHranceSCa study reported that “more than 80%” of patients preferred subcutaneous to intravenous administration of pertuzumab and trastuzumab.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration approved a combination of pertuzumab (Perjeta, Genentech/Roche), trastuzumab (Herceptin, Genentech/Roche) and hyaluronidase (Phesgo, Genentech/Roche) that is administered subcutaneously – rather than intravenously – for the treatment of early and metastatic HER2-positive breast cancers.
Phesgo is initially used in combination with chemotherapy at an infusion center but could continue to be administered in a patient’s home by a qualified health care professional once chemotherapy is complete, according to the FDA.
Administration takes approximately 8 minutes for the initial loading dose and approximately 5 minutes for maintenance doses, according to a Genentech press statement. This compares favorably with the 150 minutes needed for the combined loading dose of intravenous pertuzumab and trastuzumab, and the 60-150 minutes for intravenous maintenance infusions, the company said.
“Currently, most patients with HER2-positive breast cancer receive trastuzumab and pertuzumab at infusion centers. With a new administration route, Phesgo offers an outpatient option for patients to receive trastuzumab and pertuzumab,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in an agency press release.
“The fixed-dose combination of trastuzumab and pertuzumab offers a simpler, faster, and easier treatment experience for patients with HER2-positive breast cancer,” said Antoinette Tan, MD, MHSc, chief of breast medical oncology at Levine Cancer Institute, Charlotte, N.C., in the company statement.
Dr. Tan also said that home administration “can be advantageous for patients and infusion centers.”
However, in April, the Community Oncology Alliance strenuously objected to this type of treatment in a patient’s home, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The group, which represents U.S. community-based practices, said it “fundamentally opposes home infusion of chemotherapy, cancer immunotherapy, and cancer treatment supportive drugs because of serious patient safety concerns.”
The FDA’s approval was based on the results of the pivotal phase 3 FeDeriCa trial, a noninferiority study in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer, which demonstrated that the new product had comparable efficacy and safety as intravenous pertuzumab and intravenous trastuzumab.
In terms of efficacy, the subcutaneous product demonstrated noninferior plasma levels of pertuzumab, which was the primary endpoint, when compared with IV administration of pertuzumab.
Safety was comparable between the two approaches, with no new safety signals using the subcutaneous delivery method, including no “meaningful difference” in cardiac toxicity, according to Genentech. However, there were more administration-related reactions with the new product. The most common adverse events in both groups were alopecia, nausea, diarrhea, and anemia.
The new product uses a drug delivery technology (Enhanze, Halozyme Therapeutics) that employs a proprietary enzyme that temporarily degrades hyaluronan, a glycosaminoglycan or chain of natural sugars in the body, to facilitate the dispersion and absorption of injected therapeutic drugs, according to Genentech.
In May, at the European Society for Medical Oncology Breast Cancer Virtual Meeting 2020, investigators of the phase 2 PHranceSCa study reported that “more than 80%” of patients preferred subcutaneous to intravenous administration of pertuzumab and trastuzumab.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.