User login
Vape lung disease cases exceed 400, 3 dead
Vitamin E acetate is one possible culprit in the mysterious vaping-associated lung disease that has killed three patients, sickened 450, and baffled clinicians and investigators all summer.
Another death may be linked to the disorder, officials said during a joint press briefing held by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration. In all, 450 potential cases have been reported and e-cigarette use confirmed in 215. Cases have occurred in 33 states and one territory. A total of 84% of the patients reported having used tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) products in e-cigarette devices.
A preliminary report on the situation by Jennifer Layden, MD, of the department of public health in Illinois and colleagues – including a preliminary case definition – was simultaneously released in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 Sep 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911614).
No single device or substance was common to all the cases, leading officials to issue a blanket warning against e-cigarettes, especially those containing THC.
“We believe a chemical exposure is likely related, but more information is needed to determine what substances. Some labs have identified vitamin E acetate in some samples,” said Dana Meaney-Delman, MD, MPH, incident manager, CDC 2019 Lung Injury Response. “Continued investigation is needed to identify the risk associated with a specific product or substance.”
Besides vitamin E acetate, federal labs are looking at other cannabinoids, cutting agents, diluting agents, pesticides, opioids, and toxins.
Officials also issued a general warning about the products. Youths, young people, and pregnant women should never use e-cigarettes, they cautioned, and no one should buy them from a noncertified source, a street vendor, or a social contact. Even cartridges originally obtained from a certified source should never have been altered in any way.
Dr. Layden and colleagues reported that bilateral lung infiltrates was characterized in 98% of the 53 patients hospitalized with the recently reported e-cigarette–induced lung injury. Nonspecific constitutional symptoms, including fever, chills, weight loss, and fatigue, were present in all of the patients.
Patients may show some symptoms days or even weeks before acute respiratory failure develops, and many had sought medical help before that. All presented with bilateral lung infiltrates, part of an evolving case definition. Many complained of nonspecific constitutional symptoms, including fever, chills, gastrointestinal symptoms, and weight loss. Of the patients who underwent bronchoscopy, many were diagnosed as having lipoid pneumonia, a rare condition characterized by lipid-laden macrophages.
“We don’t know the significance of the lipid-containing macrophages, and we don’t know if the lipids are endogenous or exogenous,” Dr. Meaney-Delman said.
The incidence of such cases appears to be rising rapidly, Dr. Layden noted. An epidemiologic review of cases in Illinois found that the mean monthly rate of visits related to severe respiratory illness in June-August was twice that observed during the same months last year.
SOURCE: Layden JE et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 6. doi: 1 0.1056/NEJMoa1911614.
Vitamin E acetate is one possible culprit in the mysterious vaping-associated lung disease that has killed three patients, sickened 450, and baffled clinicians and investigators all summer.
Another death may be linked to the disorder, officials said during a joint press briefing held by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration. In all, 450 potential cases have been reported and e-cigarette use confirmed in 215. Cases have occurred in 33 states and one territory. A total of 84% of the patients reported having used tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) products in e-cigarette devices.
A preliminary report on the situation by Jennifer Layden, MD, of the department of public health in Illinois and colleagues – including a preliminary case definition – was simultaneously released in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 Sep 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911614).
No single device or substance was common to all the cases, leading officials to issue a blanket warning against e-cigarettes, especially those containing THC.
“We believe a chemical exposure is likely related, but more information is needed to determine what substances. Some labs have identified vitamin E acetate in some samples,” said Dana Meaney-Delman, MD, MPH, incident manager, CDC 2019 Lung Injury Response. “Continued investigation is needed to identify the risk associated with a specific product or substance.”
Besides vitamin E acetate, federal labs are looking at other cannabinoids, cutting agents, diluting agents, pesticides, opioids, and toxins.
Officials also issued a general warning about the products. Youths, young people, and pregnant women should never use e-cigarettes, they cautioned, and no one should buy them from a noncertified source, a street vendor, or a social contact. Even cartridges originally obtained from a certified source should never have been altered in any way.
Dr. Layden and colleagues reported that bilateral lung infiltrates was characterized in 98% of the 53 patients hospitalized with the recently reported e-cigarette–induced lung injury. Nonspecific constitutional symptoms, including fever, chills, weight loss, and fatigue, were present in all of the patients.
Patients may show some symptoms days or even weeks before acute respiratory failure develops, and many had sought medical help before that. All presented with bilateral lung infiltrates, part of an evolving case definition. Many complained of nonspecific constitutional symptoms, including fever, chills, gastrointestinal symptoms, and weight loss. Of the patients who underwent bronchoscopy, many were diagnosed as having lipoid pneumonia, a rare condition characterized by lipid-laden macrophages.
“We don’t know the significance of the lipid-containing macrophages, and we don’t know if the lipids are endogenous or exogenous,” Dr. Meaney-Delman said.
The incidence of such cases appears to be rising rapidly, Dr. Layden noted. An epidemiologic review of cases in Illinois found that the mean monthly rate of visits related to severe respiratory illness in June-August was twice that observed during the same months last year.
SOURCE: Layden JE et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 6. doi: 1 0.1056/NEJMoa1911614.
Vitamin E acetate is one possible culprit in the mysterious vaping-associated lung disease that has killed three patients, sickened 450, and baffled clinicians and investigators all summer.
Another death may be linked to the disorder, officials said during a joint press briefing held by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration. In all, 450 potential cases have been reported and e-cigarette use confirmed in 215. Cases have occurred in 33 states and one territory. A total of 84% of the patients reported having used tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) products in e-cigarette devices.
A preliminary report on the situation by Jennifer Layden, MD, of the department of public health in Illinois and colleagues – including a preliminary case definition – was simultaneously released in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 Sep 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911614).
No single device or substance was common to all the cases, leading officials to issue a blanket warning against e-cigarettes, especially those containing THC.
“We believe a chemical exposure is likely related, but more information is needed to determine what substances. Some labs have identified vitamin E acetate in some samples,” said Dana Meaney-Delman, MD, MPH, incident manager, CDC 2019 Lung Injury Response. “Continued investigation is needed to identify the risk associated with a specific product or substance.”
Besides vitamin E acetate, federal labs are looking at other cannabinoids, cutting agents, diluting agents, pesticides, opioids, and toxins.
Officials also issued a general warning about the products. Youths, young people, and pregnant women should never use e-cigarettes, they cautioned, and no one should buy them from a noncertified source, a street vendor, or a social contact. Even cartridges originally obtained from a certified source should never have been altered in any way.
Dr. Layden and colleagues reported that bilateral lung infiltrates was characterized in 98% of the 53 patients hospitalized with the recently reported e-cigarette–induced lung injury. Nonspecific constitutional symptoms, including fever, chills, weight loss, and fatigue, were present in all of the patients.
Patients may show some symptoms days or even weeks before acute respiratory failure develops, and many had sought medical help before that. All presented with bilateral lung infiltrates, part of an evolving case definition. Many complained of nonspecific constitutional symptoms, including fever, chills, gastrointestinal symptoms, and weight loss. Of the patients who underwent bronchoscopy, many were diagnosed as having lipoid pneumonia, a rare condition characterized by lipid-laden macrophages.
“We don’t know the significance of the lipid-containing macrophages, and we don’t know if the lipids are endogenous or exogenous,” Dr. Meaney-Delman said.
The incidence of such cases appears to be rising rapidly, Dr. Layden noted. An epidemiologic review of cases in Illinois found that the mean monthly rate of visits related to severe respiratory illness in June-August was twice that observed during the same months last year.
SOURCE: Layden JE et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 6. doi: 1 0.1056/NEJMoa1911614.
FROM A CDC TELECONFERENCE AND NEJM
Vaping-related lung disease cases rise, case reporting standardized
The number of possible cases of vaping-related pulmonary illness has risen to 215, reported from 25 states, as of Aug. 27, 2019, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta. Additional reports of pulmonary illness are under investigation.
The CDC has released a standardized case definition that states are using to complete their own investigations and verifications of cases. It appears that all cases are linked to e-cigarette product use, but the cause of the respiratory illnesses is still unconfirmed.
In many cases, patients reported a gradual start of symptoms, including breathing difficulty, shortness of breath, and/or chest pain before hospitalization. Some cases reported mild to moderate gastrointestinal illness including vomiting and diarrhea, or other symptoms such as fevers or fatigue. In many cases, patients have also acknowledged recent use of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-containing e-cigarette products while speaking to health care personnel or in follow-up interviews by health department staff, according to a statement from the CDC and the Food and Drug Administration.
The agencies are working with state health departments to standardize information collection at the state level to help build a more comprehensive picture of these incidents, including the brand and types of e-cigarette products, whether any of them would fall within the FDA’s regulatory authority, where they were obtained, and whether there is a link to specific devices, ingredients, or contaminants in the devices or substances associated with e-cigarette product use.
CDC staff have been deployed to Illinois and Wisconsin to assist their state health departments. The agencies have released a Clinician Outreach and Communication Activity (COCA) Clinical Action Alert describing this investigation and asking providers to report possible cases to their state health departments. In addition to a standardized case definition, the agencies have issued a medical chart abstraction form and case interview questionnaire, are reviewing and providing feedback on data collection and health messaging tools for states, and are facilitating information sharing between states with possible cases.
More information on the cases and reporting are available from the CDC.
The number of possible cases of vaping-related pulmonary illness has risen to 215, reported from 25 states, as of Aug. 27, 2019, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta. Additional reports of pulmonary illness are under investigation.
The CDC has released a standardized case definition that states are using to complete their own investigations and verifications of cases. It appears that all cases are linked to e-cigarette product use, but the cause of the respiratory illnesses is still unconfirmed.
In many cases, patients reported a gradual start of symptoms, including breathing difficulty, shortness of breath, and/or chest pain before hospitalization. Some cases reported mild to moderate gastrointestinal illness including vomiting and diarrhea, or other symptoms such as fevers or fatigue. In many cases, patients have also acknowledged recent use of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-containing e-cigarette products while speaking to health care personnel or in follow-up interviews by health department staff, according to a statement from the CDC and the Food and Drug Administration.
The agencies are working with state health departments to standardize information collection at the state level to help build a more comprehensive picture of these incidents, including the brand and types of e-cigarette products, whether any of them would fall within the FDA’s regulatory authority, where they were obtained, and whether there is a link to specific devices, ingredients, or contaminants in the devices or substances associated with e-cigarette product use.
CDC staff have been deployed to Illinois and Wisconsin to assist their state health departments. The agencies have released a Clinician Outreach and Communication Activity (COCA) Clinical Action Alert describing this investigation and asking providers to report possible cases to their state health departments. In addition to a standardized case definition, the agencies have issued a medical chart abstraction form and case interview questionnaire, are reviewing and providing feedback on data collection and health messaging tools for states, and are facilitating information sharing between states with possible cases.
More information on the cases and reporting are available from the CDC.
The number of possible cases of vaping-related pulmonary illness has risen to 215, reported from 25 states, as of Aug. 27, 2019, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta. Additional reports of pulmonary illness are under investigation.
The CDC has released a standardized case definition that states are using to complete their own investigations and verifications of cases. It appears that all cases are linked to e-cigarette product use, but the cause of the respiratory illnesses is still unconfirmed.
In many cases, patients reported a gradual start of symptoms, including breathing difficulty, shortness of breath, and/or chest pain before hospitalization. Some cases reported mild to moderate gastrointestinal illness including vomiting and diarrhea, or other symptoms such as fevers or fatigue. In many cases, patients have also acknowledged recent use of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-containing e-cigarette products while speaking to health care personnel or in follow-up interviews by health department staff, according to a statement from the CDC and the Food and Drug Administration.
The agencies are working with state health departments to standardize information collection at the state level to help build a more comprehensive picture of these incidents, including the brand and types of e-cigarette products, whether any of them would fall within the FDA’s regulatory authority, where they were obtained, and whether there is a link to specific devices, ingredients, or contaminants in the devices or substances associated with e-cigarette product use.
CDC staff have been deployed to Illinois and Wisconsin to assist their state health departments. The agencies have released a Clinician Outreach and Communication Activity (COCA) Clinical Action Alert describing this investigation and asking providers to report possible cases to their state health departments. In addition to a standardized case definition, the agencies have issued a medical chart abstraction form and case interview questionnaire, are reviewing and providing feedback on data collection and health messaging tools for states, and are facilitating information sharing between states with possible cases.
More information on the cases and reporting are available from the CDC.
FDA approves istradefylline for Parkinson’s disease
The Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 27 approved Nourianz (istradefylline) tablets as an add-on treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in adult patients with Parkinson’s disease experiencing off episodes. During off episodes, patients’ medications do not work well, and symptoms such as tremor and difficulty walking increase.
The effectiveness of Nourianz for this indication was shown in four 12-week placebo-controlled clinical studies that included 1,143 participants. In all four studies, patients treated with Nourianz experienced a statistically significant decrease from baseline in daily off time, compared with patients who received placebo.
The most common adverse reactions to istradefylline with an incidence of 5% or greater and occurring more frequently than with placebo were dyskinesia (15%, 17%, and 8%, for Nourianz 20 mg, 40 mg, and placebo, respectively), dizziness (3%, 6%, and 4%), constipation (5%, 6%, and 3%), nausea (4%, 6%, and 5%), hallucination (2%, 6%, and 3%), and insomnia (1%, 6%, and 4%). In clinical trials, 1% of patients treated with Nourianz 20 mg or 40 mg discontinued treatment because of dyskinesia, compared with no patients who received placebo.
In addition,one patient treated with Nourianz 40 mg experienced impulse control disorder, compared with no patients who received Nourianz 20 mg or placebo.
If hallucinations, psychotic behavior, or impulsive or compulsive behavior occurs, a dosage reduction or stoppage should be considered, according to the FDA. Use of Nourianz during pregnancy is not recommended, and women of childbearing potential should be advised to use contraception during treatment.
The maximum recommended dosage in patients taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is 20 mg once daily, and clinicians should avoid use of Nourianz with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Istradefylline is the first adenosine A2A receptor antagonist for use in Parkinson’s disease in the United States, and the drug provides patients with a novel nondopaminergic daily oral treatment option, according to a news release from Kyowa Kirin, the company that markets the drug.
Since 2013, istradefylline has been marketed at Nouriast in Japan, where it is indicated for the wearing-off phenomenon in patients with Parkinson’s disease who take preparations containing levodopa.
The Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 27 approved Nourianz (istradefylline) tablets as an add-on treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in adult patients with Parkinson’s disease experiencing off episodes. During off episodes, patients’ medications do not work well, and symptoms such as tremor and difficulty walking increase.
The effectiveness of Nourianz for this indication was shown in four 12-week placebo-controlled clinical studies that included 1,143 participants. In all four studies, patients treated with Nourianz experienced a statistically significant decrease from baseline in daily off time, compared with patients who received placebo.
The most common adverse reactions to istradefylline with an incidence of 5% or greater and occurring more frequently than with placebo were dyskinesia (15%, 17%, and 8%, for Nourianz 20 mg, 40 mg, and placebo, respectively), dizziness (3%, 6%, and 4%), constipation (5%, 6%, and 3%), nausea (4%, 6%, and 5%), hallucination (2%, 6%, and 3%), and insomnia (1%, 6%, and 4%). In clinical trials, 1% of patients treated with Nourianz 20 mg or 40 mg discontinued treatment because of dyskinesia, compared with no patients who received placebo.
In addition,one patient treated with Nourianz 40 mg experienced impulse control disorder, compared with no patients who received Nourianz 20 mg or placebo.
If hallucinations, psychotic behavior, or impulsive or compulsive behavior occurs, a dosage reduction or stoppage should be considered, according to the FDA. Use of Nourianz during pregnancy is not recommended, and women of childbearing potential should be advised to use contraception during treatment.
The maximum recommended dosage in patients taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is 20 mg once daily, and clinicians should avoid use of Nourianz with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Istradefylline is the first adenosine A2A receptor antagonist for use in Parkinson’s disease in the United States, and the drug provides patients with a novel nondopaminergic daily oral treatment option, according to a news release from Kyowa Kirin, the company that markets the drug.
Since 2013, istradefylline has been marketed at Nouriast in Japan, where it is indicated for the wearing-off phenomenon in patients with Parkinson’s disease who take preparations containing levodopa.
The Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 27 approved Nourianz (istradefylline) tablets as an add-on treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in adult patients with Parkinson’s disease experiencing off episodes. During off episodes, patients’ medications do not work well, and symptoms such as tremor and difficulty walking increase.
The effectiveness of Nourianz for this indication was shown in four 12-week placebo-controlled clinical studies that included 1,143 participants. In all four studies, patients treated with Nourianz experienced a statistically significant decrease from baseline in daily off time, compared with patients who received placebo.
The most common adverse reactions to istradefylline with an incidence of 5% or greater and occurring more frequently than with placebo were dyskinesia (15%, 17%, and 8%, for Nourianz 20 mg, 40 mg, and placebo, respectively), dizziness (3%, 6%, and 4%), constipation (5%, 6%, and 3%), nausea (4%, 6%, and 5%), hallucination (2%, 6%, and 3%), and insomnia (1%, 6%, and 4%). In clinical trials, 1% of patients treated with Nourianz 20 mg or 40 mg discontinued treatment because of dyskinesia, compared with no patients who received placebo.
In addition,one patient treated with Nourianz 40 mg experienced impulse control disorder, compared with no patients who received Nourianz 20 mg or placebo.
If hallucinations, psychotic behavior, or impulsive or compulsive behavior occurs, a dosage reduction or stoppage should be considered, according to the FDA. Use of Nourianz during pregnancy is not recommended, and women of childbearing potential should be advised to use contraception during treatment.
The maximum recommended dosage in patients taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is 20 mg once daily, and clinicians should avoid use of Nourianz with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Istradefylline is the first adenosine A2A receptor antagonist for use in Parkinson’s disease in the United States, and the drug provides patients with a novel nondopaminergic daily oral treatment option, according to a news release from Kyowa Kirin, the company that markets the drug.
Since 2013, istradefylline has been marketed at Nouriast in Japan, where it is indicated for the wearing-off phenomenon in patients with Parkinson’s disease who take preparations containing levodopa.
Calquence earns breakthrough designation for CLL monotherapy
The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor is already approved for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy, and multiple trials are underway to evaluate the drug’s use in a variety of B-cell malignancies, according to the drug’s sponsor, AstraZeneca.
The current designation was based on preliminary results from two phase 3 trials – ELEVATE-TN and ASCEND. In the three-arm ELEVATE-TN trial, researchers evaluated acalabrutinib alone or in combination with obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated patients with CLL. In the two-arm ASCEND trial, previously treated patients with CLL were randomized to receive acalabrutinib monotherapy or the physician’s choice of either rituximab plus idelalisib or rituximab plus bendamustine.
Interim analyses of the two trials showed that acalabrutinib alone, or in combination, significantly improved progression-free survival without raising safety concerns.
Breakthrough therapy designation allows for an expedited review by the FDA for treatments aimed at treating serious conditions where there is preliminary clinical evidence showing a substantial improvement over an available therapy or a clinically significant endpoint.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor is already approved for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy, and multiple trials are underway to evaluate the drug’s use in a variety of B-cell malignancies, according to the drug’s sponsor, AstraZeneca.
The current designation was based on preliminary results from two phase 3 trials – ELEVATE-TN and ASCEND. In the three-arm ELEVATE-TN trial, researchers evaluated acalabrutinib alone or in combination with obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated patients with CLL. In the two-arm ASCEND trial, previously treated patients with CLL were randomized to receive acalabrutinib monotherapy or the physician’s choice of either rituximab plus idelalisib or rituximab plus bendamustine.
Interim analyses of the two trials showed that acalabrutinib alone, or in combination, significantly improved progression-free survival without raising safety concerns.
Breakthrough therapy designation allows for an expedited review by the FDA for treatments aimed at treating serious conditions where there is preliminary clinical evidence showing a substantial improvement over an available therapy or a clinically significant endpoint.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor is already approved for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy, and multiple trials are underway to evaluate the drug’s use in a variety of B-cell malignancies, according to the drug’s sponsor, AstraZeneca.
The current designation was based on preliminary results from two phase 3 trials – ELEVATE-TN and ASCEND. In the three-arm ELEVATE-TN trial, researchers evaluated acalabrutinib alone or in combination with obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated patients with CLL. In the two-arm ASCEND trial, previously treated patients with CLL were randomized to receive acalabrutinib monotherapy or the physician’s choice of either rituximab plus idelalisib or rituximab plus bendamustine.
Interim analyses of the two trials showed that acalabrutinib alone, or in combination, significantly improved progression-free survival without raising safety concerns.
Breakthrough therapy designation allows for an expedited review by the FDA for treatments aimed at treating serious conditions where there is preliminary clinical evidence showing a substantial improvement over an available therapy or a clinically significant endpoint.
FDA approves Taltz for treatment of ankylosing spondylitis
(AS), according to a press release from Eli Lilly.
AS is the third indication for ixekizumab, along with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adult patients who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy and active psoriatic arthritis in adults.
Approval of the humanized interleukin-17A antagonist was based on results from a pair of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies involving 657 adult patients with active AS: the COAST-V trial in those naive to biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) and the COAST-W trial in those who were intolerant or had inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors. The primary endpoint in both trials was achievement of 40% improvement in Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society criteria (ASAS40) at 16 weeks, compared with placebo.
In COAST-V, 48% of patients who received ixekizumab achieved ASAS40, compared with 18% of controls (P less than .0001). In COAST-W, 25% of patients who received ixekizumab achieved ASAS40 versus 13% of controls (P less than .05). The adverse events reported during both trials were consistent with the safety profile in patients who receive ixekizumab for the treatment of plaque psoriasis, including injection-site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, nausea, and tinea infections.
“Results from the phase 3 clinical trial program in ankylosing spondylitis show that Taltz helped reduce pain and inflammation and improve function in patients who had never been treated with a bDMARD as well as those who previously failed TNF inhibitors. This approval is an important milestone for patients and physicians who are looking for a much-needed alternative to address symptoms of AS,” said Philip Mease, MD, of Providence St. Joseph Health and the University of Washington, both in Seattle.
(AS), according to a press release from Eli Lilly.
AS is the third indication for ixekizumab, along with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adult patients who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy and active psoriatic arthritis in adults.
Approval of the humanized interleukin-17A antagonist was based on results from a pair of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies involving 657 adult patients with active AS: the COAST-V trial in those naive to biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) and the COAST-W trial in those who were intolerant or had inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors. The primary endpoint in both trials was achievement of 40% improvement in Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society criteria (ASAS40) at 16 weeks, compared with placebo.
In COAST-V, 48% of patients who received ixekizumab achieved ASAS40, compared with 18% of controls (P less than .0001). In COAST-W, 25% of patients who received ixekizumab achieved ASAS40 versus 13% of controls (P less than .05). The adverse events reported during both trials were consistent with the safety profile in patients who receive ixekizumab for the treatment of plaque psoriasis, including injection-site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, nausea, and tinea infections.
“Results from the phase 3 clinical trial program in ankylosing spondylitis show that Taltz helped reduce pain and inflammation and improve function in patients who had never been treated with a bDMARD as well as those who previously failed TNF inhibitors. This approval is an important milestone for patients and physicians who are looking for a much-needed alternative to address symptoms of AS,” said Philip Mease, MD, of Providence St. Joseph Health and the University of Washington, both in Seattle.
(AS), according to a press release from Eli Lilly.
AS is the third indication for ixekizumab, along with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adult patients who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy and active psoriatic arthritis in adults.
Approval of the humanized interleukin-17A antagonist was based on results from a pair of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies involving 657 adult patients with active AS: the COAST-V trial in those naive to biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) and the COAST-W trial in those who were intolerant or had inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors. The primary endpoint in both trials was achievement of 40% improvement in Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society criteria (ASAS40) at 16 weeks, compared with placebo.
In COAST-V, 48% of patients who received ixekizumab achieved ASAS40, compared with 18% of controls (P less than .0001). In COAST-W, 25% of patients who received ixekizumab achieved ASAS40 versus 13% of controls (P less than .05). The adverse events reported during both trials were consistent with the safety profile in patients who receive ixekizumab for the treatment of plaque psoriasis, including injection-site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, nausea, and tinea infections.
“Results from the phase 3 clinical trial program in ankylosing spondylitis show that Taltz helped reduce pain and inflammation and improve function in patients who had never been treated with a bDMARD as well as those who previously failed TNF inhibitors. This approval is an important milestone for patients and physicians who are looking for a much-needed alternative to address symptoms of AS,” said Philip Mease, MD, of Providence St. Joseph Health and the University of Washington, both in Seattle.
First death from severe lung illness associated with vaping reported in Illinois
The first death to occur in a patient with severe lung illness associated with e-cigarette product use has been reported in Illinois, officials announced at a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention telebriefing.
The cause for the mysterious lung illnesses has not been determined, but an infectious disease does not appear to be implicated. As of yesterday, 193 potential cases have been identified in 22 states since June 28.
No specific product has been implicated in all cases, and it is unclear if there is a common cause or if these are several diseases with a similar presentation.
Wisconsin and Illinois have asked the CDC to directly assist them in their investigations of cases. Other states are handling their own investigations. Further information is available from the CDC at cdc.gov/e-cigarettes.
There have been 22 cases of the illness in Illinois and an additional 12 individuals are being evaluated as possible cases, according to Jennifer Layden, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and state epidemiologist, Illinois Department of Public Health.
Illinois is working with the CDC and the Food and Drug Administration to investigate devices that affected patients have used. No specific product has been implicated across all cases; all patients have reported vaping in recent months Several patients in Illinois have reported using tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) product oils, but Dr. Layden reiterated the investigations are reliant on information reported by affected patients only.
Mitch Zeller, JD, director, Center for Tobacco Products at the FDA, said product samples from a number of states are being evaluated to determine their contents. The FDA is examining samples sent and trying to identify product contents.
The cases reported to date have been in adults aged 17-38 years and have occurred primarily men. The investigation is in a relatively early stage and is working with incomplete case reports. These will become standardized to include more specific information, such as the name of the product, where it was purchased, and whether it was used as intended or whether other products were added, he said.
As e-cigarettes are not a new product, it’s possible that cases of this illness has been occurring but that the link was not recognized, and the cases were neither captured nor reported, said Brian King, PhD, MPH, deputy director, Research Translation, Office on Smoking and Health, CDC. He noted that e-cigarettes may contain “a variety of constituents that could be problematic in terms of pulmonary illness,” such as ingredients in certain flavorings and ultrafine particulates.
The agencies are now trying to harmonize reporting across all states so cases can be evaluated in a more standardized way. Information on standardized reporting on a national level will be issued in the next few days, according to the CDC.
The CDC notified U.S. health care systems and clinicians about the illnesses and what to watch for via a Clinician Outreach and Communication Activity Clinical Action Message.
In general, patients have reported a gradual onset of symptoms including shortness of breath or chest pain that increased over days or weeks before hospital admission. Gastrointestinal symptoms including vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue have been reported by some.
The first death to occur in a patient with severe lung illness associated with e-cigarette product use has been reported in Illinois, officials announced at a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention telebriefing.
The cause for the mysterious lung illnesses has not been determined, but an infectious disease does not appear to be implicated. As of yesterday, 193 potential cases have been identified in 22 states since June 28.
No specific product has been implicated in all cases, and it is unclear if there is a common cause or if these are several diseases with a similar presentation.
Wisconsin and Illinois have asked the CDC to directly assist them in their investigations of cases. Other states are handling their own investigations. Further information is available from the CDC at cdc.gov/e-cigarettes.
There have been 22 cases of the illness in Illinois and an additional 12 individuals are being evaluated as possible cases, according to Jennifer Layden, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and state epidemiologist, Illinois Department of Public Health.
Illinois is working with the CDC and the Food and Drug Administration to investigate devices that affected patients have used. No specific product has been implicated across all cases; all patients have reported vaping in recent months Several patients in Illinois have reported using tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) product oils, but Dr. Layden reiterated the investigations are reliant on information reported by affected patients only.
Mitch Zeller, JD, director, Center for Tobacco Products at the FDA, said product samples from a number of states are being evaluated to determine their contents. The FDA is examining samples sent and trying to identify product contents.
The cases reported to date have been in adults aged 17-38 years and have occurred primarily men. The investigation is in a relatively early stage and is working with incomplete case reports. These will become standardized to include more specific information, such as the name of the product, where it was purchased, and whether it was used as intended or whether other products were added, he said.
As e-cigarettes are not a new product, it’s possible that cases of this illness has been occurring but that the link was not recognized, and the cases were neither captured nor reported, said Brian King, PhD, MPH, deputy director, Research Translation, Office on Smoking and Health, CDC. He noted that e-cigarettes may contain “a variety of constituents that could be problematic in terms of pulmonary illness,” such as ingredients in certain flavorings and ultrafine particulates.
The agencies are now trying to harmonize reporting across all states so cases can be evaluated in a more standardized way. Information on standardized reporting on a national level will be issued in the next few days, according to the CDC.
The CDC notified U.S. health care systems and clinicians about the illnesses and what to watch for via a Clinician Outreach and Communication Activity Clinical Action Message.
In general, patients have reported a gradual onset of symptoms including shortness of breath or chest pain that increased over days or weeks before hospital admission. Gastrointestinal symptoms including vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue have been reported by some.
The first death to occur in a patient with severe lung illness associated with e-cigarette product use has been reported in Illinois, officials announced at a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention telebriefing.
The cause for the mysterious lung illnesses has not been determined, but an infectious disease does not appear to be implicated. As of yesterday, 193 potential cases have been identified in 22 states since June 28.
No specific product has been implicated in all cases, and it is unclear if there is a common cause or if these are several diseases with a similar presentation.
Wisconsin and Illinois have asked the CDC to directly assist them in their investigations of cases. Other states are handling their own investigations. Further information is available from the CDC at cdc.gov/e-cigarettes.
There have been 22 cases of the illness in Illinois and an additional 12 individuals are being evaluated as possible cases, according to Jennifer Layden, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and state epidemiologist, Illinois Department of Public Health.
Illinois is working with the CDC and the Food and Drug Administration to investigate devices that affected patients have used. No specific product has been implicated across all cases; all patients have reported vaping in recent months Several patients in Illinois have reported using tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) product oils, but Dr. Layden reiterated the investigations are reliant on information reported by affected patients only.
Mitch Zeller, JD, director, Center for Tobacco Products at the FDA, said product samples from a number of states are being evaluated to determine their contents. The FDA is examining samples sent and trying to identify product contents.
The cases reported to date have been in adults aged 17-38 years and have occurred primarily men. The investigation is in a relatively early stage and is working with incomplete case reports. These will become standardized to include more specific information, such as the name of the product, where it was purchased, and whether it was used as intended or whether other products were added, he said.
As e-cigarettes are not a new product, it’s possible that cases of this illness has been occurring but that the link was not recognized, and the cases were neither captured nor reported, said Brian King, PhD, MPH, deputy director, Research Translation, Office on Smoking and Health, CDC. He noted that e-cigarettes may contain “a variety of constituents that could be problematic in terms of pulmonary illness,” such as ingredients in certain flavorings and ultrafine particulates.
The agencies are now trying to harmonize reporting across all states so cases can be evaluated in a more standardized way. Information on standardized reporting on a national level will be issued in the next few days, according to the CDC.
The CDC notified U.S. health care systems and clinicians about the illnesses and what to watch for via a Clinician Outreach and Communication Activity Clinical Action Message.
In general, patients have reported a gradual onset of symptoms including shortness of breath or chest pain that increased over days or weeks before hospital admission. Gastrointestinal symptoms including vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue have been reported by some.
FDA approves Wakix for excessive daytime sleepiness
The Food and Drug Administration has approved pitolisant (Wakix) for excessive daytime sleepiness among patients with narcolepsy, according to a release from the drug’s developer.
Approval of this once-daily, selective histamine 3–receptor antagonist/inverse agonist was based on a pair of multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies that included a total of 261 patients. Patients in both studies experienced statistically significant improvements in excessive daytime sleepiness according to Epworth Sleepiness Scale scores.
Rates of adverse advents at or greater than 5% and more than double that of placebo included insomnia (6%), nausea (6%), and anxiety (5%). Patients with severe liver disease should not use pitolisant. Pitolisant has not been evaluated in patients under 18 years of age, and patients who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant are encouraged to enroll in a pregnancy exposure registry.
Full prescribing information, including contraindications and warnings, can be found on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved pitolisant (Wakix) for excessive daytime sleepiness among patients with narcolepsy, according to a release from the drug’s developer.
Approval of this once-daily, selective histamine 3–receptor antagonist/inverse agonist was based on a pair of multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies that included a total of 261 patients. Patients in both studies experienced statistically significant improvements in excessive daytime sleepiness according to Epworth Sleepiness Scale scores.
Rates of adverse advents at or greater than 5% and more than double that of placebo included insomnia (6%), nausea (6%), and anxiety (5%). Patients with severe liver disease should not use pitolisant. Pitolisant has not been evaluated in patients under 18 years of age, and patients who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant are encouraged to enroll in a pregnancy exposure registry.
Full prescribing information, including contraindications and warnings, can be found on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved pitolisant (Wakix) for excessive daytime sleepiness among patients with narcolepsy, according to a release from the drug’s developer.
Approval of this once-daily, selective histamine 3–receptor antagonist/inverse agonist was based on a pair of multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies that included a total of 261 patients. Patients in both studies experienced statistically significant improvements in excessive daytime sleepiness according to Epworth Sleepiness Scale scores.
Rates of adverse advents at or greater than 5% and more than double that of placebo included insomnia (6%), nausea (6%), and anxiety (5%). Patients with severe liver disease should not use pitolisant. Pitolisant has not been evaluated in patients under 18 years of age, and patients who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant are encouraged to enroll in a pregnancy exposure registry.
Full prescribing information, including contraindications and warnings, can be found on the FDA website.
FDA approves lefamulin for community-acquired bacterial pneumonia treatment
The Food and Drug Administration has announced its approval of lefamulin (Xenleta) for the treatment of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in adults.
Approval was based on results of two clinical trials assessing a total of 1,289 people with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. In these trials, lefamulin was compared with moxifloxacin with and without linezolid. Patients who received lefamulin had similar rates of treatment success as those taking moxifloxacin alone or moxifloxacin plus linezolid.
The most common adverse reactions associated with lefamulin include diarrhea, nausea, reactions at the injection site, elevated liver enzymes, and vomiting. Patients with prolonged QT interval, patients with arrhythmias, patients receiving treatment with antiarrhythmic agents, and patients receiving other drugs that prolong the QT interval are contraindicated. In addition, because of evidence of fetal harm in animal studies, pregnant women should be advised of potential risks before receiving lefamulin.
“This new drug provides another option for the treatment of patients with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia, a serious disease. For managing this serious disease, it is important for physicians and patients to have treatment options,” Ed Cox, MD, MPH, director of the FDA’s Office of Antimicrobial Products, said in the press release.
The Food and Drug Administration has announced its approval of lefamulin (Xenleta) for the treatment of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in adults.
Approval was based on results of two clinical trials assessing a total of 1,289 people with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. In these trials, lefamulin was compared with moxifloxacin with and without linezolid. Patients who received lefamulin had similar rates of treatment success as those taking moxifloxacin alone or moxifloxacin plus linezolid.
The most common adverse reactions associated with lefamulin include diarrhea, nausea, reactions at the injection site, elevated liver enzymes, and vomiting. Patients with prolonged QT interval, patients with arrhythmias, patients receiving treatment with antiarrhythmic agents, and patients receiving other drugs that prolong the QT interval are contraindicated. In addition, because of evidence of fetal harm in animal studies, pregnant women should be advised of potential risks before receiving lefamulin.
“This new drug provides another option for the treatment of patients with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia, a serious disease. For managing this serious disease, it is important for physicians and patients to have treatment options,” Ed Cox, MD, MPH, director of the FDA’s Office of Antimicrobial Products, said in the press release.
The Food and Drug Administration has announced its approval of lefamulin (Xenleta) for the treatment of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in adults.
Approval was based on results of two clinical trials assessing a total of 1,289 people with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. In these trials, lefamulin was compared with moxifloxacin with and without linezolid. Patients who received lefamulin had similar rates of treatment success as those taking moxifloxacin alone or moxifloxacin plus linezolid.
The most common adverse reactions associated with lefamulin include diarrhea, nausea, reactions at the injection site, elevated liver enzymes, and vomiting. Patients with prolonged QT interval, patients with arrhythmias, patients receiving treatment with antiarrhythmic agents, and patients receiving other drugs that prolong the QT interval are contraindicated. In addition, because of evidence of fetal harm in animal studies, pregnant women should be advised of potential risks before receiving lefamulin.
“This new drug provides another option for the treatment of patients with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia, a serious disease. For managing this serious disease, it is important for physicians and patients to have treatment options,” Ed Cox, MD, MPH, director of the FDA’s Office of Antimicrobial Products, said in the press release.
FDA approves Xenleta for community-acquired bacterial pneumonia treatment
The Food and Drug Administration has announced its approval of lefamulin (Xenleta) for the treatment of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in adults.
Approval was based on results of two clinical trials assessing a total of 1,289 people with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. In these trials, lefamulin was compared with moxifloxacin with and without linezolid. Patients who received lefamulin had similar rates of treatment success as those taking moxifloxacin alone or moxifloxacin plus linezolid.
The most common adverse reactions associated with lefamulin include diarrhea, nausea, reactions at the injection site, elevated liver enzymes, and vomiting. Patients with prolonged QT interval, patients with arrhythmias, patients receiving treatment with antiarrhythmic agents, and patients receiving other drugs that prolong the QT interval are contraindicated. In addition, because of evidence of fetal harm in animal studies, pregnant women should be advised of potential risks before receiving lefamulin.
“This new drug provides another option for the treatment of patients with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia, a serious disease. For managing this serious disease, it is important for physicians and patients to have treatment options,” Ed Cox, MD, MPH, director of the FDA’s Office of Antimicrobial Products, said in the press release.
The Food and Drug Administration has announced its approval of lefamulin (Xenleta) for the treatment of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in adults.
Approval was based on results of two clinical trials assessing a total of 1,289 people with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. In these trials, lefamulin was compared with moxifloxacin with and without linezolid. Patients who received lefamulin had similar rates of treatment success as those taking moxifloxacin alone or moxifloxacin plus linezolid.
The most common adverse reactions associated with lefamulin include diarrhea, nausea, reactions at the injection site, elevated liver enzymes, and vomiting. Patients with prolonged QT interval, patients with arrhythmias, patients receiving treatment with antiarrhythmic agents, and patients receiving other drugs that prolong the QT interval are contraindicated. In addition, because of evidence of fetal harm in animal studies, pregnant women should be advised of potential risks before receiving lefamulin.
“This new drug provides another option for the treatment of patients with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia, a serious disease. For managing this serious disease, it is important for physicians and patients to have treatment options,” Ed Cox, MD, MPH, director of the FDA’s Office of Antimicrobial Products, said in the press release.
The Food and Drug Administration has announced its approval of lefamulin (Xenleta) for the treatment of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in adults.
Approval was based on results of two clinical trials assessing a total of 1,289 people with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. In these trials, lefamulin was compared with moxifloxacin with and without linezolid. Patients who received lefamulin had similar rates of treatment success as those taking moxifloxacin alone or moxifloxacin plus linezolid.
The most common adverse reactions associated with lefamulin include diarrhea, nausea, reactions at the injection site, elevated liver enzymes, and vomiting. Patients with prolonged QT interval, patients with arrhythmias, patients receiving treatment with antiarrhythmic agents, and patients receiving other drugs that prolong the QT interval are contraindicated. In addition, because of evidence of fetal harm in animal studies, pregnant women should be advised of potential risks before receiving lefamulin.
“This new drug provides another option for the treatment of patients with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia, a serious disease. For managing this serious disease, it is important for physicians and patients to have treatment options,” Ed Cox, MD, MPH, director of the FDA’s Office of Antimicrobial Products, said in the press release.
New measles outbreak reported in western N.Y.
A new measles outbreak in western New York has affected five people within a Mennonite community, according to the New York State Department of Health.
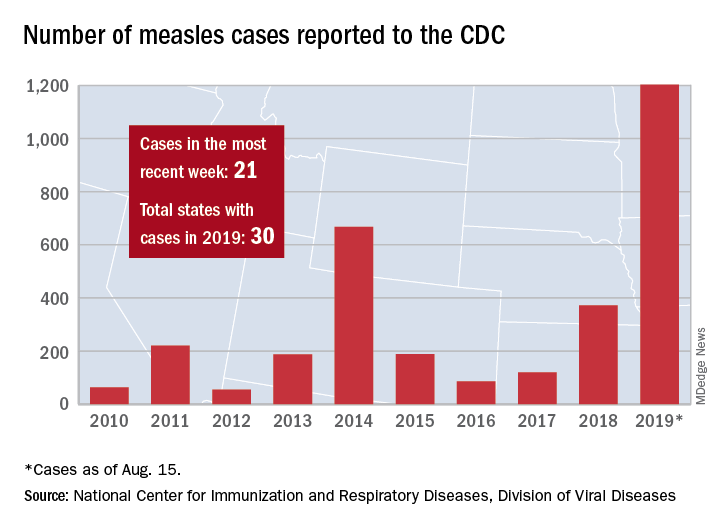
The five cases in Wyoming County, located east of Buffalo, were reported Aug. 8 and no further cases have been confirmed as of Aug. 16, the county health department said on its website.
Those five cases, along with six new cases in Rockland County, N.Y., and 10 more around the country, brought the total for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s latest reporting week to 21 and the total for the year to 1,203, the CDC said Aug. 19.
Along with Wyoming County and Rockland County (296 cases since Sept. 2018), the CDC currently is tracking outbreaks in New York City (653 cases since Sept. 2018), Washington state (85 cases in 2019; 13 in the current outbreak), California (65 cases in 2019; 5 in the current outbreak), and Texas (21 cases in 2019; 6 in the current outbreak).
“More than 75% of the cases this year are linked to outbreaks in New York and New York City,” the CDC said on its website, while also noting that “124 of the people who got measles this year were hospitalized, and 64 reported having complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis.”
A new measles outbreak in western New York has affected five people within a Mennonite community, according to the New York State Department of Health.

The five cases in Wyoming County, located east of Buffalo, were reported Aug. 8 and no further cases have been confirmed as of Aug. 16, the county health department said on its website.
Those five cases, along with six new cases in Rockland County, N.Y., and 10 more around the country, brought the total for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s latest reporting week to 21 and the total for the year to 1,203, the CDC said Aug. 19.
Along with Wyoming County and Rockland County (296 cases since Sept. 2018), the CDC currently is tracking outbreaks in New York City (653 cases since Sept. 2018), Washington state (85 cases in 2019; 13 in the current outbreak), California (65 cases in 2019; 5 in the current outbreak), and Texas (21 cases in 2019; 6 in the current outbreak).
“More than 75% of the cases this year are linked to outbreaks in New York and New York City,” the CDC said on its website, while also noting that “124 of the people who got measles this year were hospitalized, and 64 reported having complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis.”
A new measles outbreak in western New York has affected five people within a Mennonite community, according to the New York State Department of Health.

The five cases in Wyoming County, located east of Buffalo, were reported Aug. 8 and no further cases have been confirmed as of Aug. 16, the county health department said on its website.
Those five cases, along with six new cases in Rockland County, N.Y., and 10 more around the country, brought the total for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s latest reporting week to 21 and the total for the year to 1,203, the CDC said Aug. 19.
Along with Wyoming County and Rockland County (296 cases since Sept. 2018), the CDC currently is tracking outbreaks in New York City (653 cases since Sept. 2018), Washington state (85 cases in 2019; 13 in the current outbreak), California (65 cases in 2019; 5 in the current outbreak), and Texas (21 cases in 2019; 6 in the current outbreak).
“More than 75% of the cases this year are linked to outbreaks in New York and New York City,” the CDC said on its website, while also noting that “124 of the people who got measles this year were hospitalized, and 64 reported having complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis.”





