User login
Concurrent Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis Vulgaris: Implications for Targeted Biologic Therapy
Psoriasis vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with notable elevation in helper T cell (TH) production of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammatory cytokines, including IL-17A.1 Upon binding of IL-17A to IL-17 receptors in the skin, an inflammatory cascade is triggered, resulting in the classic clinical appearance of psoriasis. Moderate to severe psoriasis often is managed by suppressing TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation using targeted immune therapy such as secukinumab, an IL-17A inhibitor.2 Atopic dermatitis (AD), another chronic inflammatory dermatosis, is associated with substantial elevation in TH2-mediated inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-4.3 Dupilumab, which interacts with IL-4R, disrupts the IL-4 and IL-13 signaling pathways and demonstrates considerable efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe AD.4
A case series has shown that suppression of the TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation of psoriasis may paradoxically result in the development of TH2-mediated AD.5 Similarly, a recent case report described a patient who developed psoriasis following treatment of AD with dupilumab.6 Herein, we describe a patient with a history of psoriasis that was well controlled with secukinumab who developed severe refractory erythrodermic AD that resolved with dupilumab treatment. Following clearance of AD with dupilumab, he exhibited psoriasis recurrence.
Case Report
A 39-year-old man with a lifelong history of psoriasis was admitted to the hospital for management of severe erythroderma. Four years prior, secukinumab was initiated for treatment of psoriasis, resulting in excellent clinical response. He discontinued secukinumab after 2 years of treatment because of insurance coverage issues and managed his condition with only topical corticosteroids. He restarted secukinumab 10 months before admission because of a psoriasis flare. Shortly after resuming secukinumab, he developed a severe exfoliative erythroderma that was not responsive to corticosteroids, etanercept, methotrexate, or ustekinumab.
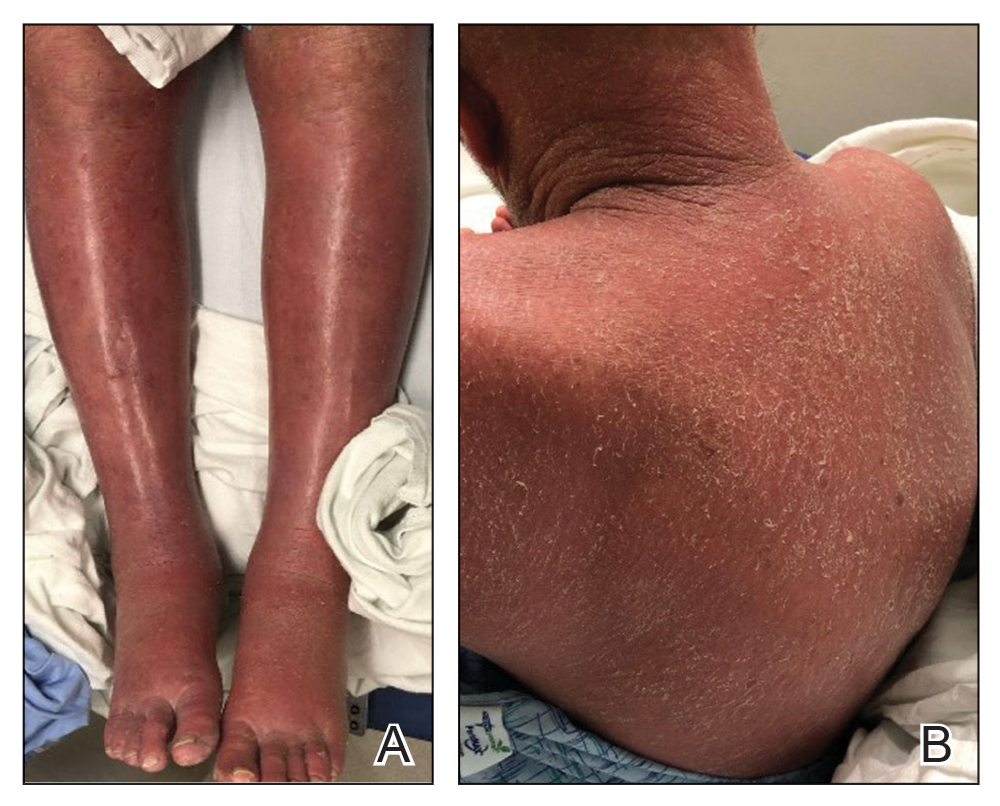
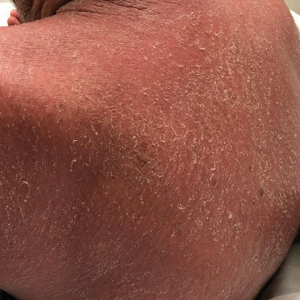
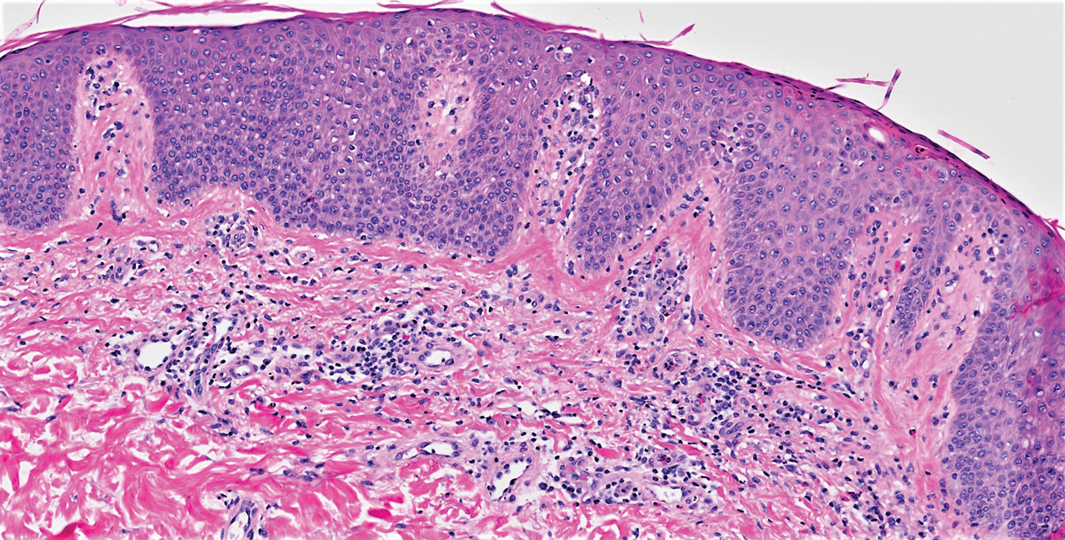
On initial presentation, physical examination revealed diffuse erythema and scaling with associated edema of the face, trunk, and extremities (Figure 1). A biopsy from the patient’s right arm demonstrated a superficial perivascular inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, and scattered eosinophils consistent with spongiotic dermatitis (Figure 2). Cyclosporine 225 mg twice daily and topical corticosteroids were started.
Over the next several months, the patient had several admissions secondary to recurrent skin abscesses in the setting of refractory erythroderma. He underwent trials of infliximab, corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, guselkumab, and acitretin with minimal improvement. He underwent an extensive laboratory and radiologic workup, which was notable for cyclical peripheral eosinophilia and elevated IgE levels correlating with the erythroderma flares. A second biopsy was obtained and continued to demonstrate changes consistent with AD.
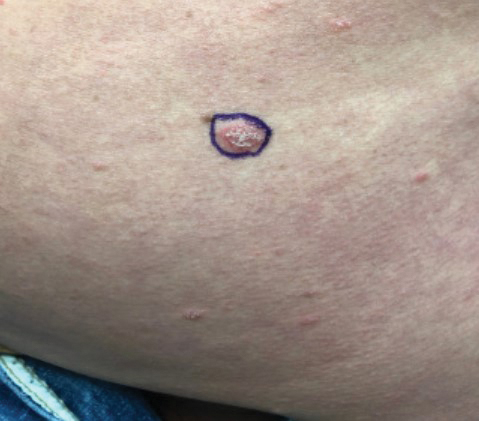
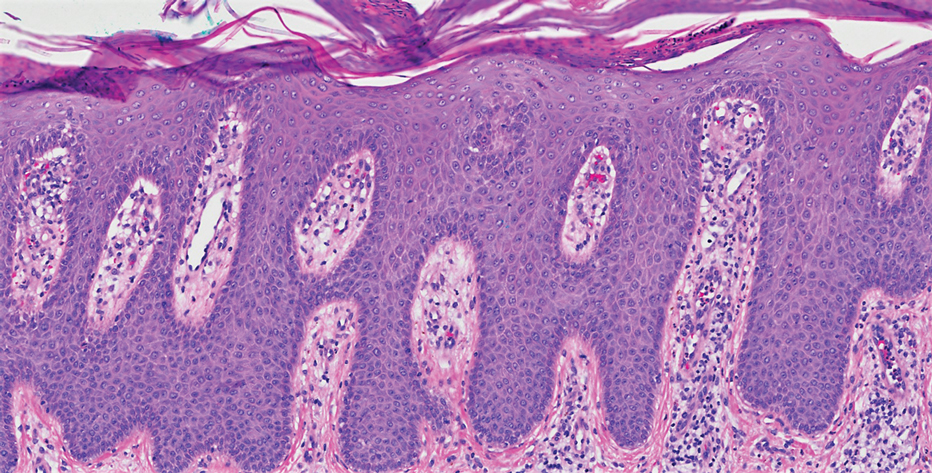
Four months after the initial hospitalization, all psoriasis medications were stopped, and the patient was started on dupilumab 300 mg/2 mL every 2 weeks and an 8-week oral prednisone taper. This combination led to notable clinical improvement and resolution of peripheral eosinophilia. Several months after disease remission, he began to develop worsening erythema and pruritus on the trunk and extremities, followed by the development of new psoriatic lesions (Figure 3) with a biopsy consistent with psoriasis (Figure 4). The patient was continued on dupilumab, but cyclosporine was added. The patient self-discontinued dupilumab owing to injection-site discomfort and has been slowly weaning off oral cyclosporine with 1 to 2 remaining eczematous plaques and 1 to 2 psoriatic plaques managed by topical corticosteroids.
Comment
We present a patient with psoriasis that was well controlled on secukinumab who developed severe AD following treatment with secukinumab. The AD resolved following treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. However, after several months of treatment with dupilumab alone, he began to develop psoriatic lesions again. This case supports findings in a case series describing the development of AD in patients with psoriasis treated with IL-17 inhibitors5 and a recent case report describing a patient with AD who developed psoriasis following treatment with an IL-4/IL-13 inhibitor.6
Recognized adverse effects demonstrate biologic medications’ contributions to both normal as well as aberrant immunologic responses. For example, IL-17 plays an essential role in innate and adaptive immune responses against infections at mucosal and cutaneous interfaces, as demonstrated by chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in patients with genetic defects in IL-17–related pathways.7 Similarly, in patients taking IL-17 antagonists, an increase in the incidence of Candida infections has been observed.8 In patients with concurrent psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), treatment with IL-17 inhibitors is contraindicated due to the risk of exacerbating the IBD. This observation is somewhat paradoxical, as increased IL-17 release by TH17 cells is implicated in the pathogenesis of IBD.9 Interestingly, it is now thought that IL-17 may play a protective role in T-cell–driven intestinal inflammation through induction of protective intestinal epithelial gene expression and increased mucosal defense against gut microbes, explaining the worsening of IBD in patients on IL-17 inhibitors.10 These adverse effects illustrate the complicated and varied roles biologic medications play in immunologic response.
Given that TH1 and TH2 exert opposing immune mechanisms, it is uncommon for psoriasis and AD to coexist in a single patient. However, patients who exhibit concurrent findings may represent a unique population in which psoriasis and AD coexist, perhaps because of an underlying genetic predisposition. Moreover, targeted treatment of pathways unique to these disease processes may result in paradoxical flaring of the nontargeted pathway. It also is possible that inhibition of a specific T-cell pathway in a subset of patients will result in an immunologic imbalance, favoring increased activity of the opposing pathway in the absence of coexisting disease. In the case presented here, the findings may be explained by secukinumab’s inhibition of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation, which resulted in a shift to a TH2-mediated inflammatory response manifesting as AD, as well as dupilumab’s inhibition of TH2-mediated inflammation, which caused a shift back to TH1-mediated inflammatory pathways. Additionally, for patients with changing morphologies exacerbated by biologic medications, alternative diagnoses, such as cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, may be considered.
Conclusion
We report an unusual case of secukinumab-induced AD in a patient with psoriasis that resolved following several months of treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. Subsequently, this same patient developed re-emergence of psoriatic lesions with continued use of dupilumab, which was eventually discontinued by the patient despite appropriate disease control. In addition to illustrating the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms of 2 common inflammatory dermatologic conditions, this case highlights how pharmacologic interventions targeted at specific immunologic pathways may have unintended consequences. Further investigation into the effects of targeted biologics on the TH1/TH2 immune axis is warranted to better understand the mechanism and possible implications of the phenotypic switching presented in this case.
- Diani M, Altomare G, Reali E. T helper cell subsets in clinical manifestations of psoriasis. J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:7692024.
- Langley RG, Elewski BE, Lebwohl M, et al. Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis—results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:326-338.
- van der Heijden FL, Wierenga EA, Bos JD, et al. High frequency of IL-4-producing CD4+ allergen-specific T lymphocytes in atopic dermatitis lesional skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;97:389-394.
- Beck LA, Thaçi D, Hamilton JD, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:130-139.
- Lai FYX, Higgins E, Smith CH, et al. Morphologic switch from psoriasiform to eczematous dermatitis after anti-IL-17 therapy: a case series. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1082-1084.
- Varma A, Levitt J. Dupilumab-induced phenotype switching from atopic dermatitis to psoriasis. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:217-218.
- Ling Y, Puel A. IL-17 and infections. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105(suppl 1):34-40.
- Saunte DM, Mrowietz U, Puig L, et al. Candida infections in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with interleukin-17 inhibitors and their practical management. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:47-62.
- Hölttä V, Klemetti P, Sipponen T, et al. IL-23/IL-17 immunity as a hallmark of Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:1175-1184.
- Smith MK, Pai J, Panaccione R, et al. Crohn’s-like disease in a patient exposed to anti-interleukin-17 blockade (ixekizumab) for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019;19:162.
Psoriasis vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with notable elevation in helper T cell (TH) production of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammatory cytokines, including IL-17A.1 Upon binding of IL-17A to IL-17 receptors in the skin, an inflammatory cascade is triggered, resulting in the classic clinical appearance of psoriasis. Moderate to severe psoriasis often is managed by suppressing TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation using targeted immune therapy such as secukinumab, an IL-17A inhibitor.2 Atopic dermatitis (AD), another chronic inflammatory dermatosis, is associated with substantial elevation in TH2-mediated inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-4.3 Dupilumab, which interacts with IL-4R, disrupts the IL-4 and IL-13 signaling pathways and demonstrates considerable efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe AD.4
A case series has shown that suppression of the TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation of psoriasis may paradoxically result in the development of TH2-mediated AD.5 Similarly, a recent case report described a patient who developed psoriasis following treatment of AD with dupilumab.6 Herein, we describe a patient with a history of psoriasis that was well controlled with secukinumab who developed severe refractory erythrodermic AD that resolved with dupilumab treatment. Following clearance of AD with dupilumab, he exhibited psoriasis recurrence.
Case Report
A 39-year-old man with a lifelong history of psoriasis was admitted to the hospital for management of severe erythroderma. Four years prior, secukinumab was initiated for treatment of psoriasis, resulting in excellent clinical response. He discontinued secukinumab after 2 years of treatment because of insurance coverage issues and managed his condition with only topical corticosteroids. He restarted secukinumab 10 months before admission because of a psoriasis flare. Shortly after resuming secukinumab, he developed a severe exfoliative erythroderma that was not responsive to corticosteroids, etanercept, methotrexate, or ustekinumab.

On initial presentation, physical examination revealed diffuse erythema and scaling with associated edema of the face, trunk, and extremities (Figure 1). A biopsy from the patient’s right arm demonstrated a superficial perivascular inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, and scattered eosinophils consistent with spongiotic dermatitis (Figure 2). Cyclosporine 225 mg twice daily and topical corticosteroids were started.

Over the next several months, the patient had several admissions secondary to recurrent skin abscesses in the setting of refractory erythroderma. He underwent trials of infliximab, corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, guselkumab, and acitretin with minimal improvement. He underwent an extensive laboratory and radiologic workup, which was notable for cyclical peripheral eosinophilia and elevated IgE levels correlating with the erythroderma flares. A second biopsy was obtained and continued to demonstrate changes consistent with AD.

Four months after the initial hospitalization, all psoriasis medications were stopped, and the patient was started on dupilumab 300 mg/2 mL every 2 weeks and an 8-week oral prednisone taper. This combination led to notable clinical improvement and resolution of peripheral eosinophilia. Several months after disease remission, he began to develop worsening erythema and pruritus on the trunk and extremities, followed by the development of new psoriatic lesions (Figure 3) with a biopsy consistent with psoriasis (Figure 4). The patient was continued on dupilumab, but cyclosporine was added. The patient self-discontinued dupilumab owing to injection-site discomfort and has been slowly weaning off oral cyclosporine with 1 to 2 remaining eczematous plaques and 1 to 2 psoriatic plaques managed by topical corticosteroids.

Comment
We present a patient with psoriasis that was well controlled on secukinumab who developed severe AD following treatment with secukinumab. The AD resolved following treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. However, after several months of treatment with dupilumab alone, he began to develop psoriatic lesions again. This case supports findings in a case series describing the development of AD in patients with psoriasis treated with IL-17 inhibitors5 and a recent case report describing a patient with AD who developed psoriasis following treatment with an IL-4/IL-13 inhibitor.6
Recognized adverse effects demonstrate biologic medications’ contributions to both normal as well as aberrant immunologic responses. For example, IL-17 plays an essential role in innate and adaptive immune responses against infections at mucosal and cutaneous interfaces, as demonstrated by chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in patients with genetic defects in IL-17–related pathways.7 Similarly, in patients taking IL-17 antagonists, an increase in the incidence of Candida infections has been observed.8 In patients with concurrent psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), treatment with IL-17 inhibitors is contraindicated due to the risk of exacerbating the IBD. This observation is somewhat paradoxical, as increased IL-17 release by TH17 cells is implicated in the pathogenesis of IBD.9 Interestingly, it is now thought that IL-17 may play a protective role in T-cell–driven intestinal inflammation through induction of protective intestinal epithelial gene expression and increased mucosal defense against gut microbes, explaining the worsening of IBD in patients on IL-17 inhibitors.10 These adverse effects illustrate the complicated and varied roles biologic medications play in immunologic response.
Given that TH1 and TH2 exert opposing immune mechanisms, it is uncommon for psoriasis and AD to coexist in a single patient. However, patients who exhibit concurrent findings may represent a unique population in which psoriasis and AD coexist, perhaps because of an underlying genetic predisposition. Moreover, targeted treatment of pathways unique to these disease processes may result in paradoxical flaring of the nontargeted pathway. It also is possible that inhibition of a specific T-cell pathway in a subset of patients will result in an immunologic imbalance, favoring increased activity of the opposing pathway in the absence of coexisting disease. In the case presented here, the findings may be explained by secukinumab’s inhibition of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation, which resulted in a shift to a TH2-mediated inflammatory response manifesting as AD, as well as dupilumab’s inhibition of TH2-mediated inflammation, which caused a shift back to TH1-mediated inflammatory pathways. Additionally, for patients with changing morphologies exacerbated by biologic medications, alternative diagnoses, such as cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, may be considered.
Conclusion
We report an unusual case of secukinumab-induced AD in a patient with psoriasis that resolved following several months of treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. Subsequently, this same patient developed re-emergence of psoriatic lesions with continued use of dupilumab, which was eventually discontinued by the patient despite appropriate disease control. In addition to illustrating the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms of 2 common inflammatory dermatologic conditions, this case highlights how pharmacologic interventions targeted at specific immunologic pathways may have unintended consequences. Further investigation into the effects of targeted biologics on the TH1/TH2 immune axis is warranted to better understand the mechanism and possible implications of the phenotypic switching presented in this case.
Psoriasis vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with notable elevation in helper T cell (TH) production of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammatory cytokines, including IL-17A.1 Upon binding of IL-17A to IL-17 receptors in the skin, an inflammatory cascade is triggered, resulting in the classic clinical appearance of psoriasis. Moderate to severe psoriasis often is managed by suppressing TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation using targeted immune therapy such as secukinumab, an IL-17A inhibitor.2 Atopic dermatitis (AD), another chronic inflammatory dermatosis, is associated with substantial elevation in TH2-mediated inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-4.3 Dupilumab, which interacts with IL-4R, disrupts the IL-4 and IL-13 signaling pathways and demonstrates considerable efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe AD.4
A case series has shown that suppression of the TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation of psoriasis may paradoxically result in the development of TH2-mediated AD.5 Similarly, a recent case report described a patient who developed psoriasis following treatment of AD with dupilumab.6 Herein, we describe a patient with a history of psoriasis that was well controlled with secukinumab who developed severe refractory erythrodermic AD that resolved with dupilumab treatment. Following clearance of AD with dupilumab, he exhibited psoriasis recurrence.
Case Report
A 39-year-old man with a lifelong history of psoriasis was admitted to the hospital for management of severe erythroderma. Four years prior, secukinumab was initiated for treatment of psoriasis, resulting in excellent clinical response. He discontinued secukinumab after 2 years of treatment because of insurance coverage issues and managed his condition with only topical corticosteroids. He restarted secukinumab 10 months before admission because of a psoriasis flare. Shortly after resuming secukinumab, he developed a severe exfoliative erythroderma that was not responsive to corticosteroids, etanercept, methotrexate, or ustekinumab.

On initial presentation, physical examination revealed diffuse erythema and scaling with associated edema of the face, trunk, and extremities (Figure 1). A biopsy from the patient’s right arm demonstrated a superficial perivascular inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, and scattered eosinophils consistent with spongiotic dermatitis (Figure 2). Cyclosporine 225 mg twice daily and topical corticosteroids were started.

Over the next several months, the patient had several admissions secondary to recurrent skin abscesses in the setting of refractory erythroderma. He underwent trials of infliximab, corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, guselkumab, and acitretin with minimal improvement. He underwent an extensive laboratory and radiologic workup, which was notable for cyclical peripheral eosinophilia and elevated IgE levels correlating with the erythroderma flares. A second biopsy was obtained and continued to demonstrate changes consistent with AD.

Four months after the initial hospitalization, all psoriasis medications were stopped, and the patient was started on dupilumab 300 mg/2 mL every 2 weeks and an 8-week oral prednisone taper. This combination led to notable clinical improvement and resolution of peripheral eosinophilia. Several months after disease remission, he began to develop worsening erythema and pruritus on the trunk and extremities, followed by the development of new psoriatic lesions (Figure 3) with a biopsy consistent with psoriasis (Figure 4). The patient was continued on dupilumab, but cyclosporine was added. The patient self-discontinued dupilumab owing to injection-site discomfort and has been slowly weaning off oral cyclosporine with 1 to 2 remaining eczematous plaques and 1 to 2 psoriatic plaques managed by topical corticosteroids.

Comment
We present a patient with psoriasis that was well controlled on secukinumab who developed severe AD following treatment with secukinumab. The AD resolved following treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. However, after several months of treatment with dupilumab alone, he began to develop psoriatic lesions again. This case supports findings in a case series describing the development of AD in patients with psoriasis treated with IL-17 inhibitors5 and a recent case report describing a patient with AD who developed psoriasis following treatment with an IL-4/IL-13 inhibitor.6
Recognized adverse effects demonstrate biologic medications’ contributions to both normal as well as aberrant immunologic responses. For example, IL-17 plays an essential role in innate and adaptive immune responses against infections at mucosal and cutaneous interfaces, as demonstrated by chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in patients with genetic defects in IL-17–related pathways.7 Similarly, in patients taking IL-17 antagonists, an increase in the incidence of Candida infections has been observed.8 In patients with concurrent psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), treatment with IL-17 inhibitors is contraindicated due to the risk of exacerbating the IBD. This observation is somewhat paradoxical, as increased IL-17 release by TH17 cells is implicated in the pathogenesis of IBD.9 Interestingly, it is now thought that IL-17 may play a protective role in T-cell–driven intestinal inflammation through induction of protective intestinal epithelial gene expression and increased mucosal defense against gut microbes, explaining the worsening of IBD in patients on IL-17 inhibitors.10 These adverse effects illustrate the complicated and varied roles biologic medications play in immunologic response.
Given that TH1 and TH2 exert opposing immune mechanisms, it is uncommon for psoriasis and AD to coexist in a single patient. However, patients who exhibit concurrent findings may represent a unique population in which psoriasis and AD coexist, perhaps because of an underlying genetic predisposition. Moreover, targeted treatment of pathways unique to these disease processes may result in paradoxical flaring of the nontargeted pathway. It also is possible that inhibition of a specific T-cell pathway in a subset of patients will result in an immunologic imbalance, favoring increased activity of the opposing pathway in the absence of coexisting disease. In the case presented here, the findings may be explained by secukinumab’s inhibition of TH1/TH17-mediated inflammation, which resulted in a shift to a TH2-mediated inflammatory response manifesting as AD, as well as dupilumab’s inhibition of TH2-mediated inflammation, which caused a shift back to TH1-mediated inflammatory pathways. Additionally, for patients with changing morphologies exacerbated by biologic medications, alternative diagnoses, such as cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, may be considered.
Conclusion
We report an unusual case of secukinumab-induced AD in a patient with psoriasis that resolved following several months of treatment with dupilumab and a tapering dose of prednisone. Subsequently, this same patient developed re-emergence of psoriatic lesions with continued use of dupilumab, which was eventually discontinued by the patient despite appropriate disease control. In addition to illustrating the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms of 2 common inflammatory dermatologic conditions, this case highlights how pharmacologic interventions targeted at specific immunologic pathways may have unintended consequences. Further investigation into the effects of targeted biologics on the TH1/TH2 immune axis is warranted to better understand the mechanism and possible implications of the phenotypic switching presented in this case.
- Diani M, Altomare G, Reali E. T helper cell subsets in clinical manifestations of psoriasis. J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:7692024.
- Langley RG, Elewski BE, Lebwohl M, et al. Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis—results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:326-338.
- van der Heijden FL, Wierenga EA, Bos JD, et al. High frequency of IL-4-producing CD4+ allergen-specific T lymphocytes in atopic dermatitis lesional skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;97:389-394.
- Beck LA, Thaçi D, Hamilton JD, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:130-139.
- Lai FYX, Higgins E, Smith CH, et al. Morphologic switch from psoriasiform to eczematous dermatitis after anti-IL-17 therapy: a case series. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1082-1084.
- Varma A, Levitt J. Dupilumab-induced phenotype switching from atopic dermatitis to psoriasis. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:217-218.
- Ling Y, Puel A. IL-17 and infections. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105(suppl 1):34-40.
- Saunte DM, Mrowietz U, Puig L, et al. Candida infections in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with interleukin-17 inhibitors and their practical management. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:47-62.
- Hölttä V, Klemetti P, Sipponen T, et al. IL-23/IL-17 immunity as a hallmark of Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:1175-1184.
- Smith MK, Pai J, Panaccione R, et al. Crohn’s-like disease in a patient exposed to anti-interleukin-17 blockade (ixekizumab) for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019;19:162.
- Diani M, Altomare G, Reali E. T helper cell subsets in clinical manifestations of psoriasis. J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:7692024.
- Langley RG, Elewski BE, Lebwohl M, et al. Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis—results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:326-338.
- van der Heijden FL, Wierenga EA, Bos JD, et al. High frequency of IL-4-producing CD4+ allergen-specific T lymphocytes in atopic dermatitis lesional skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;97:389-394.
- Beck LA, Thaçi D, Hamilton JD, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:130-139.
- Lai FYX, Higgins E, Smith CH, et al. Morphologic switch from psoriasiform to eczematous dermatitis after anti-IL-17 therapy: a case series. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1082-1084.
- Varma A, Levitt J. Dupilumab-induced phenotype switching from atopic dermatitis to psoriasis. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:217-218.
- Ling Y, Puel A. IL-17 and infections. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105(suppl 1):34-40.
- Saunte DM, Mrowietz U, Puig L, et al. Candida infections in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with interleukin-17 inhibitors and their practical management. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:47-62.
- Hölttä V, Klemetti P, Sipponen T, et al. IL-23/IL-17 immunity as a hallmark of Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:1175-1184.
- Smith MK, Pai J, Panaccione R, et al. Crohn’s-like disease in a patient exposed to anti-interleukin-17 blockade (ixekizumab) for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019;19:162.
Practice Points
- Treatment of psoriasis vulgaris, a helper T cell TH1/TH17-mediated skin condition, with secukinumab may result in phenotypic switching to TH2-mediated atopic dermatitis.
- Atopic dermatitis responds well to dupilumab but may result in phenotypic switching to psoriasis.
- Biologic therapies targeted at specific immunologic pathways may have unintended consequences on the TH1/TH2 immune axis.
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Atopic Dermatitis February 2022
George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences
Washington, DC
Atopic dermatitis can really mess with patients’ lives
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a multi-faceted disease that can cause major burden to the lives of patients. Chronic itch is the most common and burdensome symptom of AD and can be very distressing and debilitating for patients.1 Visible skin lesions of AD can be embarrassing and contribute to decreased self-esteem and psychosocial distress (ref). Recent studies uncovered many additional impacts and sequelae of AD.
- While itch has been long recognized as a burdensome symptom in AD, skin pain was recently shown to be an important symptom of AD. Cheng et al2 performed a cross-sectional national survey of 240 children with AD and their parents, of which 200 had moderate-to-very severe disease. They found that skin pain intensity was associated with increased skin bleeding (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.47 [0.61-2.33]), weeping/oozing (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.18 [0.47-1.90]), and cracking (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.00 [0.27-1.73]). These relationships may be indirectly related to scratching of the skin leading to open sores that hurt but also bleed, weep/ooze, and crack. On the other hand, patients may experience cracking of skin on hands and feet secondary to dryness and inflammation that can cause skin pain. The authors also found that parent-reported pain intensity was associated with impaired quality of life in infants aged 1-4 years (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.16 [0.18-2.14]) and children aged 5-17 years (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.68 [1.00-2.36]). These results show that skin pain is a burdensome symptom in children and adolescents with AD.
- Sleep disturbance is a major problem in patients with AD, especially in those with moderate-to-severe AD. Zhou et al3 conducted a cross-sectional study of 60 children aged 1-4 years with mild-to-severe AD. They found that eczema caused sleep disturbance on 5 or more nights in the past week in 76% of children with severe AD, 24% children with moderate AD, but none with mild AD. Children with more severe AD had greater attention dysregulation (correlation coefficient 0.65). AD severity was a significant predictor of both poor sleep health (β = 0.79) and attention dysregulation (β = 1.22). These results have important ramifications for pediatric health. Previous studies found associations of AD with attention-deficit disorder and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. The results of Zhou et al. suggest that AD is associated with symptoms of attention dysregulation, likely secondary to distraction from itch, chronic sleep deprivation, skin pain, etc.
- AD can affect individuals of all age groups, though there may be distinct ramifications when this debilitating disease occurs in childhood during the formative years of life. Manjunath et al4 examined data from the Fragile Families and Child Wellbeing Study, which is a prospective, longitudinal birth cohort including 4,898 children aged 1, 3, 5, 9, or 15 years. They found that AD in children aged 5 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] [95% CI]: 1.31 [1.04-1.64]) or 9 years (aOR [95% CI]: 1.38 [1.14-1.67]) was associated with ≥75th percentile of mean delinquent behavior scores at age 9 or 15 years. At 9 years of age, a 1-year history of AD was associated with smoking at age 15 years (aOR [95% CI]: 1.46 [1.00-2.13]), damaging property (aOR [95% CI]: 1.38 [1.08-1.77]), cheating on a test (aOR [95% CI]: 1.62 [1.17-2.26]), and school suspension (aOR [95% CI]: 1.36 [1.08-1.71]). These results are provocative and suggest that AD negatively impacts children’s behavior. This study was not able to examine specific clinical aspects of AD that led to delinquent behaviors. However, it is likely that multiple factors contribute to this association, including chronic itch, skin pain, sleep deprivation, attention dysregulation, psychosocial distress, teasing, and bullying.
- A major question on everyone’s mind these days is which individuals have a higher risk of developing COVID-19 infections. There have been many studies since the pandemic began on whether specific immune-mediated disorders are associated with higher risk of COVID-19 or worse outcomes from COVID-19 infections. Previous studies found mixed results about whether individuals with AD have higher risk of COVID-19. Fan et al5 performed a case-control study from a large healthcare system database, including 11,752 patients with AD and 47,008 age, sex and race matched healthy controls. They found that patients with AD were more likely to have a diagnosis of COVID-19 compared to those without AD (4.2% vs. 2.8%; P < .001). This association remained significant even after adjusting for demographic factors and comorbidities (odds ratio 1.29; P < .001). Of note, the effect-size was relatively modest in multivariable models. Residual confounding always remains a possibility, ie, that there are other unexplained factors in common with COVID-19 and AD that explain the association. Nevertheless, the results raise important questions about whether immune dysregulation or different treatments used in AD increase risk of COVID-19. Future studies are certainly warranted. Better yet, I look forward to the end of the pandemic when we will no longer have to worry about the potential harms of COVID-19 on AD patients.
References
- Kim BS. Atopic Dermatitis Clinical Presentation. Medscape (Jan 10, 2022). https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049085-clinical (accessed Jan 28, 2022).
- Cheng BT et al. Burden and characteristics of skin pain among children with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 (Dec 23).
- Zhou et al. Parent report of sleep health and attention regulation in a cross-sectional study of infants and preschool-aged children with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021 (Dec 21).
- Manjunath et al. Association of atopic dermatitis with delinquent behaviors in US children and adolescents. Arch Dermatol Res. 2022 (Jan 10).
- Fan et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and COVID-19 infection: A case-control study in the All of Us research program. JAAD Int. 2021;6:P77-81 (Dec 27).
George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences
Washington, DC
Atopic dermatitis can really mess with patients’ lives
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a multi-faceted disease that can cause major burden to the lives of patients. Chronic itch is the most common and burdensome symptom of AD and can be very distressing and debilitating for patients.1 Visible skin lesions of AD can be embarrassing and contribute to decreased self-esteem and psychosocial distress (ref). Recent studies uncovered many additional impacts and sequelae of AD.
- While itch has been long recognized as a burdensome symptom in AD, skin pain was recently shown to be an important symptom of AD. Cheng et al2 performed a cross-sectional national survey of 240 children with AD and their parents, of which 200 had moderate-to-very severe disease. They found that skin pain intensity was associated with increased skin bleeding (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.47 [0.61-2.33]), weeping/oozing (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.18 [0.47-1.90]), and cracking (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.00 [0.27-1.73]). These relationships may be indirectly related to scratching of the skin leading to open sores that hurt but also bleed, weep/ooze, and crack. On the other hand, patients may experience cracking of skin on hands and feet secondary to dryness and inflammation that can cause skin pain. The authors also found that parent-reported pain intensity was associated with impaired quality of life in infants aged 1-4 years (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.16 [0.18-2.14]) and children aged 5-17 years (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.68 [1.00-2.36]). These results show that skin pain is a burdensome symptom in children and adolescents with AD.
- Sleep disturbance is a major problem in patients with AD, especially in those with moderate-to-severe AD. Zhou et al3 conducted a cross-sectional study of 60 children aged 1-4 years with mild-to-severe AD. They found that eczema caused sleep disturbance on 5 or more nights in the past week in 76% of children with severe AD, 24% children with moderate AD, but none with mild AD. Children with more severe AD had greater attention dysregulation (correlation coefficient 0.65). AD severity was a significant predictor of both poor sleep health (β = 0.79) and attention dysregulation (β = 1.22). These results have important ramifications for pediatric health. Previous studies found associations of AD with attention-deficit disorder and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. The results of Zhou et al. suggest that AD is associated with symptoms of attention dysregulation, likely secondary to distraction from itch, chronic sleep deprivation, skin pain, etc.
- AD can affect individuals of all age groups, though there may be distinct ramifications when this debilitating disease occurs in childhood during the formative years of life. Manjunath et al4 examined data from the Fragile Families and Child Wellbeing Study, which is a prospective, longitudinal birth cohort including 4,898 children aged 1, 3, 5, 9, or 15 years. They found that AD in children aged 5 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] [95% CI]: 1.31 [1.04-1.64]) or 9 years (aOR [95% CI]: 1.38 [1.14-1.67]) was associated with ≥75th percentile of mean delinquent behavior scores at age 9 or 15 years. At 9 years of age, a 1-year history of AD was associated with smoking at age 15 years (aOR [95% CI]: 1.46 [1.00-2.13]), damaging property (aOR [95% CI]: 1.38 [1.08-1.77]), cheating on a test (aOR [95% CI]: 1.62 [1.17-2.26]), and school suspension (aOR [95% CI]: 1.36 [1.08-1.71]). These results are provocative and suggest that AD negatively impacts children’s behavior. This study was not able to examine specific clinical aspects of AD that led to delinquent behaviors. However, it is likely that multiple factors contribute to this association, including chronic itch, skin pain, sleep deprivation, attention dysregulation, psychosocial distress, teasing, and bullying.
- A major question on everyone’s mind these days is which individuals have a higher risk of developing COVID-19 infections. There have been many studies since the pandemic began on whether specific immune-mediated disorders are associated with higher risk of COVID-19 or worse outcomes from COVID-19 infections. Previous studies found mixed results about whether individuals with AD have higher risk of COVID-19. Fan et al5 performed a case-control study from a large healthcare system database, including 11,752 patients with AD and 47,008 age, sex and race matched healthy controls. They found that patients with AD were more likely to have a diagnosis of COVID-19 compared to those without AD (4.2% vs. 2.8%; P < .001). This association remained significant even after adjusting for demographic factors and comorbidities (odds ratio 1.29; P < .001). Of note, the effect-size was relatively modest in multivariable models. Residual confounding always remains a possibility, ie, that there are other unexplained factors in common with COVID-19 and AD that explain the association. Nevertheless, the results raise important questions about whether immune dysregulation or different treatments used in AD increase risk of COVID-19. Future studies are certainly warranted. Better yet, I look forward to the end of the pandemic when we will no longer have to worry about the potential harms of COVID-19 on AD patients.
References
- Kim BS. Atopic Dermatitis Clinical Presentation. Medscape (Jan 10, 2022). https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049085-clinical (accessed Jan 28, 2022).
- Cheng BT et al. Burden and characteristics of skin pain among children with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 (Dec 23).
- Zhou et al. Parent report of sleep health and attention regulation in a cross-sectional study of infants and preschool-aged children with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021 (Dec 21).
- Manjunath et al. Association of atopic dermatitis with delinquent behaviors in US children and adolescents. Arch Dermatol Res. 2022 (Jan 10).
- Fan et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and COVID-19 infection: A case-control study in the All of Us research program. JAAD Int. 2021;6:P77-81 (Dec 27).
George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences
Washington, DC
Atopic dermatitis can really mess with patients’ lives
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a multi-faceted disease that can cause major burden to the lives of patients. Chronic itch is the most common and burdensome symptom of AD and can be very distressing and debilitating for patients.1 Visible skin lesions of AD can be embarrassing and contribute to decreased self-esteem and psychosocial distress (ref). Recent studies uncovered many additional impacts and sequelae of AD.
- While itch has been long recognized as a burdensome symptom in AD, skin pain was recently shown to be an important symptom of AD. Cheng et al2 performed a cross-sectional national survey of 240 children with AD and their parents, of which 200 had moderate-to-very severe disease. They found that skin pain intensity was associated with increased skin bleeding (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.47 [0.61-2.33]), weeping/oozing (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.18 [0.47-1.90]), and cracking (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.00 [0.27-1.73]). These relationships may be indirectly related to scratching of the skin leading to open sores that hurt but also bleed, weep/ooze, and crack. On the other hand, patients may experience cracking of skin on hands and feet secondary to dryness and inflammation that can cause skin pain. The authors also found that parent-reported pain intensity was associated with impaired quality of life in infants aged 1-4 years (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.16 [0.18-2.14]) and children aged 5-17 years (adjusted β [95% CI]: 1.68 [1.00-2.36]). These results show that skin pain is a burdensome symptom in children and adolescents with AD.
- Sleep disturbance is a major problem in patients with AD, especially in those with moderate-to-severe AD. Zhou et al3 conducted a cross-sectional study of 60 children aged 1-4 years with mild-to-severe AD. They found that eczema caused sleep disturbance on 5 or more nights in the past week in 76% of children with severe AD, 24% children with moderate AD, but none with mild AD. Children with more severe AD had greater attention dysregulation (correlation coefficient 0.65). AD severity was a significant predictor of both poor sleep health (β = 0.79) and attention dysregulation (β = 1.22). These results have important ramifications for pediatric health. Previous studies found associations of AD with attention-deficit disorder and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. The results of Zhou et al. suggest that AD is associated with symptoms of attention dysregulation, likely secondary to distraction from itch, chronic sleep deprivation, skin pain, etc.
- AD can affect individuals of all age groups, though there may be distinct ramifications when this debilitating disease occurs in childhood during the formative years of life. Manjunath et al4 examined data from the Fragile Families and Child Wellbeing Study, which is a prospective, longitudinal birth cohort including 4,898 children aged 1, 3, 5, 9, or 15 years. They found that AD in children aged 5 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] [95% CI]: 1.31 [1.04-1.64]) or 9 years (aOR [95% CI]: 1.38 [1.14-1.67]) was associated with ≥75th percentile of mean delinquent behavior scores at age 9 or 15 years. At 9 years of age, a 1-year history of AD was associated with smoking at age 15 years (aOR [95% CI]: 1.46 [1.00-2.13]), damaging property (aOR [95% CI]: 1.38 [1.08-1.77]), cheating on a test (aOR [95% CI]: 1.62 [1.17-2.26]), and school suspension (aOR [95% CI]: 1.36 [1.08-1.71]). These results are provocative and suggest that AD negatively impacts children’s behavior. This study was not able to examine specific clinical aspects of AD that led to delinquent behaviors. However, it is likely that multiple factors contribute to this association, including chronic itch, skin pain, sleep deprivation, attention dysregulation, psychosocial distress, teasing, and bullying.
- A major question on everyone’s mind these days is which individuals have a higher risk of developing COVID-19 infections. There have been many studies since the pandemic began on whether specific immune-mediated disorders are associated with higher risk of COVID-19 or worse outcomes from COVID-19 infections. Previous studies found mixed results about whether individuals with AD have higher risk of COVID-19. Fan et al5 performed a case-control study from a large healthcare system database, including 11,752 patients with AD and 47,008 age, sex and race matched healthy controls. They found that patients with AD were more likely to have a diagnosis of COVID-19 compared to those without AD (4.2% vs. 2.8%; P < .001). This association remained significant even after adjusting for demographic factors and comorbidities (odds ratio 1.29; P < .001). Of note, the effect-size was relatively modest in multivariable models. Residual confounding always remains a possibility, ie, that there are other unexplained factors in common with COVID-19 and AD that explain the association. Nevertheless, the results raise important questions about whether immune dysregulation or different treatments used in AD increase risk of COVID-19. Future studies are certainly warranted. Better yet, I look forward to the end of the pandemic when we will no longer have to worry about the potential harms of COVID-19 on AD patients.
References
- Kim BS. Atopic Dermatitis Clinical Presentation. Medscape (Jan 10, 2022). https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049085-clinical (accessed Jan 28, 2022).
- Cheng BT et al. Burden and characteristics of skin pain among children with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 (Dec 23).
- Zhou et al. Parent report of sleep health and attention regulation in a cross-sectional study of infants and preschool-aged children with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021 (Dec 21).
- Manjunath et al. Association of atopic dermatitis with delinquent behaviors in US children and adolescents. Arch Dermatol Res. 2022 (Jan 10).
- Fan et al. Association between atopic dermatitis and COVID-19 infection: A case-control study in the All of Us research program. JAAD Int. 2021;6:P77-81 (Dec 27).
Gowning up: Is it necessary when examining patients with atopic dermatitis?
When evaluating patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), it is essential to do a full body exam, rather than simply asking patients to roll up their sleeves to examine the antecubital fossa, advised Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH.
Dr. Silverberg, director of clinical research in the department of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, recommends that patients with AD should be asked to gown up for clinical encounters so that their body surface area (BSA) can be assessed. “Whether you use the palmar method or use the rule of nines (a chart that divides the body into sections representing 9% BSA) ... you need to look at BSA because lesion severity in a localized area doesn’t tell you the whole story,” he said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium.
He described his anecdotal experiences with patients objecting to being asked by office staff to wear a gown for exams, who often say they have never been asked by a doctor to do so, and often tell him that with previous exams, they were asked to roll up their sleeves only. But there are many patients with AD who do not have flexural disease “and if they just roll up their sleeve for an exam, you would miss the fact that they might be covered over their trunk or legs or other parts of the body,” Dr. Silverberg said. “Make a concerted effort to look not just at lesion severity but to assess body surface area. We need to assess both.”
Capturing the patient perspective
From a patient-reported standpoint, Dr. Silverberg favors asking patients to verbally rate the severity of their disease. Clear or almost clear? Mild, moderate, or severe? “This approach correlates beautifully with validated outcome measures for AD,” he said.
“You could use a numeric rating scale (NRS) for itch, pain, or sleep disturbance. I would argue that it’s best to use a 7-day recall period; 24 hours is too short. They may be clear yesterday but may have been bad 3 days earlier.” The NRS will soon be a reportable item on the AAD DataDerm Clinical Registry, he said, but noted that “the NRS by itself does not accurately predict the full severity of AD.”
A tool he finds useful is the Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD), which was developed in 2017 by an international panel of experts. “It’s free, feasible to use, and a great option for clinical practice.” Dr. Silverberg said. “It’s highly clinically relevant, but it doesn’t take into account BSA. So, BSA is a separate tool that you want to use as well.”
Another tool he mentioned is the Atopic Dermatitis Control Tool (ADCT), developed by industry in 2018. It uses six questions about AD control intended to be used during a 1-week recall period.
“To maximize efficiency, consider having patients complete patient-reported outcomes through patient portals prior to the office visit,” he advised. “Collecting this information prior to the encounter can speed up the clinical encounter and improve quality of care.”
Dr. Silverberg disclosed that he is a consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies, and receives fees for non-CME/CE services from Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, as well as contracted research fees from Galderma.
When evaluating patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), it is essential to do a full body exam, rather than simply asking patients to roll up their sleeves to examine the antecubital fossa, advised Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH.
Dr. Silverberg, director of clinical research in the department of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, recommends that patients with AD should be asked to gown up for clinical encounters so that their body surface area (BSA) can be assessed. “Whether you use the palmar method or use the rule of nines (a chart that divides the body into sections representing 9% BSA) ... you need to look at BSA because lesion severity in a localized area doesn’t tell you the whole story,” he said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium.
He described his anecdotal experiences with patients objecting to being asked by office staff to wear a gown for exams, who often say they have never been asked by a doctor to do so, and often tell him that with previous exams, they were asked to roll up their sleeves only. But there are many patients with AD who do not have flexural disease “and if they just roll up their sleeve for an exam, you would miss the fact that they might be covered over their trunk or legs or other parts of the body,” Dr. Silverberg said. “Make a concerted effort to look not just at lesion severity but to assess body surface area. We need to assess both.”
Capturing the patient perspective
From a patient-reported standpoint, Dr. Silverberg favors asking patients to verbally rate the severity of their disease. Clear or almost clear? Mild, moderate, or severe? “This approach correlates beautifully with validated outcome measures for AD,” he said.
“You could use a numeric rating scale (NRS) for itch, pain, or sleep disturbance. I would argue that it’s best to use a 7-day recall period; 24 hours is too short. They may be clear yesterday but may have been bad 3 days earlier.” The NRS will soon be a reportable item on the AAD DataDerm Clinical Registry, he said, but noted that “the NRS by itself does not accurately predict the full severity of AD.”
A tool he finds useful is the Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD), which was developed in 2017 by an international panel of experts. “It’s free, feasible to use, and a great option for clinical practice.” Dr. Silverberg said. “It’s highly clinically relevant, but it doesn’t take into account BSA. So, BSA is a separate tool that you want to use as well.”
Another tool he mentioned is the Atopic Dermatitis Control Tool (ADCT), developed by industry in 2018. It uses six questions about AD control intended to be used during a 1-week recall period.
“To maximize efficiency, consider having patients complete patient-reported outcomes through patient portals prior to the office visit,” he advised. “Collecting this information prior to the encounter can speed up the clinical encounter and improve quality of care.”
Dr. Silverberg disclosed that he is a consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies, and receives fees for non-CME/CE services from Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, as well as contracted research fees from Galderma.
When evaluating patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), it is essential to do a full body exam, rather than simply asking patients to roll up their sleeves to examine the antecubital fossa, advised Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH.
Dr. Silverberg, director of clinical research in the department of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, recommends that patients with AD should be asked to gown up for clinical encounters so that their body surface area (BSA) can be assessed. “Whether you use the palmar method or use the rule of nines (a chart that divides the body into sections representing 9% BSA) ... you need to look at BSA because lesion severity in a localized area doesn’t tell you the whole story,” he said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium.
He described his anecdotal experiences with patients objecting to being asked by office staff to wear a gown for exams, who often say they have never been asked by a doctor to do so, and often tell him that with previous exams, they were asked to roll up their sleeves only. But there are many patients with AD who do not have flexural disease “and if they just roll up their sleeve for an exam, you would miss the fact that they might be covered over their trunk or legs or other parts of the body,” Dr. Silverberg said. “Make a concerted effort to look not just at lesion severity but to assess body surface area. We need to assess both.”
Capturing the patient perspective
From a patient-reported standpoint, Dr. Silverberg favors asking patients to verbally rate the severity of their disease. Clear or almost clear? Mild, moderate, or severe? “This approach correlates beautifully with validated outcome measures for AD,” he said.
“You could use a numeric rating scale (NRS) for itch, pain, or sleep disturbance. I would argue that it’s best to use a 7-day recall period; 24 hours is too short. They may be clear yesterday but may have been bad 3 days earlier.” The NRS will soon be a reportable item on the AAD DataDerm Clinical Registry, he said, but noted that “the NRS by itself does not accurately predict the full severity of AD.”
A tool he finds useful is the Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD), which was developed in 2017 by an international panel of experts. “It’s free, feasible to use, and a great option for clinical practice.” Dr. Silverberg said. “It’s highly clinically relevant, but it doesn’t take into account BSA. So, BSA is a separate tool that you want to use as well.”
Another tool he mentioned is the Atopic Dermatitis Control Tool (ADCT), developed by industry in 2018. It uses six questions about AD control intended to be used during a 1-week recall period.
“To maximize efficiency, consider having patients complete patient-reported outcomes through patient portals prior to the office visit,” he advised. “Collecting this information prior to the encounter can speed up the clinical encounter and improve quality of care.”
Dr. Silverberg disclosed that he is a consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies, and receives fees for non-CME/CE services from Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme, as well as contracted research fees from Galderma.
FROM REVOLUTIONIZING AD 2021
New AAD guidelines eye comorbidities in adults with atopic dermatitis
While it’s well established that atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults is associated with asthma, allergic rhinitis, and other atopic conditions, the links between AD and other comorbidities are coming into clearer focus.
, published evidence supports an association between AD and comorbidities that may not be on the radar of clinicians and patients, including substance use, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), elements of metabolic syndrome, and various cardiovascular conditions.
“There are more comorbidities with AD than we anticipated, that are supported by data in the literature,” Dawn M.R. Davis, MD, cochair and an author of the guidelines, told this news organization. “We are learning more about the interconnectivity of various medical conditions,” she continued. “Many skin diseases over time have been noted to be impactful to the whole person and not only the skin. A classic example of that is psoriasis. We now understand that psoriasis is a multisystem inflammatory disorder.”
As for AD, “we’ve always appreciated that AD patients tend to be at higher risk for other atopic diseases such as asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and food allergies,” said Dr. Davis, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “With further research, we are now able to delineate those associations more intimately and have data to support our suspicions. Additionally, we’re now understanding that these inflammatory conditions can impact more than the end organ involved, such as the skin and AD. We wanted to look at how AD can affect the whole patient.”
For the guidelines, which are the first of their kind and were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Davis and project cochair Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, chief of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital, led a multidisciplinary group of 12 experts to review the association between AD and selected comorbidities. They applied the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) for prognosis approach for assessing the certainty of the evidence and provided statements of association based on the available evidence.
With respect to highlights for atopic and allergic conditions, the guideline authors found high-quality evidence that AD in adults is associated with food allergies, moderate-quality evidence that AD is associated with asthma, and low-quality evidence that AD in adults may be associated with eosinophilic esophagitis.
In the realm of mental health and substance use, ample evidence exists to support an association between AD and mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety, the guidelines state. “For many patients, low mood may be driven by the symptoms of AD, including chronic itch and poor sleep,” Dr. Davis and her coauthors wrote. “Successfully treating AD may alleviate depressive symptoms for some patients; for others, assessment and treatment specific to their mental health may be needed.”
The guidelines also state that low-quality evidence exists to suggest that AD in adults may be associated with alcohol abuse disorders and cigarette smoking.
The authors noted “limited but consistent evidence” supporting a link between AD and adverse bone health, including osteoporosis and fractures, while associations between AD and cardiovascular risk factors and comorbidities, including hypertension, myocardial infarction, and stroke, are more controversial.
“I have published on bone health and AD so that was not as surprising to me,” Dr. Davis said in the interview. “I found a lot of the evidence in the guidelines to be validating of patterns that we see in our patients. The most significant learning point for me was [the link to] cardiovascular disease and the link to specific mental health and substance use disorders. It validates how impactful AD is to the individual.”
According to the guidelines, moderate-quality evidence exists linking AD in adults to both alopecia areata and urticaria. “Because we are dermatologists and take care of both of those diseases, be mindful of that in your daily practice,” Dr. Davis advised. “I would also encourage our colleagues to remember to educate patients on the comorbidities of AD so that they are empowered, and to screen for those comorbidities in your office based on the patient and their history and physical exam, to the level that you think is appropriate for that person’s individual’s care.”
Christine Ko, MD, who was asked to comment on the guidelines, characterized some of the reported comorbidity associations as predictable, such as asthma, food allergy, allergic rhinitis, and skin infections. “As the authors comment, ‘associations between AD and other atopic and allergic conditions have been recognized for decades and even contribute to diagnostic criteria for AD,’ ” said Dr. Ko, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn, who was not involved with the guidelines. “I was a bit surprised to see that atopic dermatitis in adults is associated with osteoporosis and fractures. As the authors suggest, this could be secondary to treatment with oral prednisone, and it is possible that use of dupilumab and JAK inhibitors may lessen this association.”
Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, of the department of dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who was not involved with the guidelines, and was also asked to comment, said that the guidelines underscore the importance of informing adults with AD “of the risks of unchecked inflammation and the potential for multiple disease comorbidities.” Dr. Kwatra, who has AD, added that “these results make me want to be more proactive in treating my eczema to reduce the potential for development of these comorbidities.”
He pointed out that the guidelines did not address racial and ethnic differences in the observed comorbidities. “Unfortunately, minority populations have a greater comorbidity burden in many inflammatory skin diseases so this will be another area needing further investigation,” he said. “As an example, our group found from multicenter data that black patients with atopic dermatitis have higher levels of C-reactive protein, blood eosinophils, and other inflammatory biomarkers.”
The AAD guidelines are the first in a four-part series on AD expected to be published over the next 1-2 years, Dr. Davis said. The subsequent guidelines will address topicals, phototherapy/systemics, and pediatrics.
The study was funded by internal funds from the AAD. Dr. Davis reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Sidbury disclosed that he serves as an advisory board member for Pfizer, a principal investigator for Regeneron, and an investigator for Brickell Biotech and Galderma. He is also a consultant for Galderma Global and Microes. Dr. Ko reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Kwatra is a member of the board of directors of the Skin of Color Society. He is also an advisory board member/consultant for AbbVie, Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi, and has served as an investigator for Galderma, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
While it’s well established that atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults is associated with asthma, allergic rhinitis, and other atopic conditions, the links between AD and other comorbidities are coming into clearer focus.
, published evidence supports an association between AD and comorbidities that may not be on the radar of clinicians and patients, including substance use, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), elements of metabolic syndrome, and various cardiovascular conditions.
“There are more comorbidities with AD than we anticipated, that are supported by data in the literature,” Dawn M.R. Davis, MD, cochair and an author of the guidelines, told this news organization. “We are learning more about the interconnectivity of various medical conditions,” she continued. “Many skin diseases over time have been noted to be impactful to the whole person and not only the skin. A classic example of that is psoriasis. We now understand that psoriasis is a multisystem inflammatory disorder.”
As for AD, “we’ve always appreciated that AD patients tend to be at higher risk for other atopic diseases such as asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and food allergies,” said Dr. Davis, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “With further research, we are now able to delineate those associations more intimately and have data to support our suspicions. Additionally, we’re now understanding that these inflammatory conditions can impact more than the end organ involved, such as the skin and AD. We wanted to look at how AD can affect the whole patient.”
For the guidelines, which are the first of their kind and were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Davis and project cochair Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, chief of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital, led a multidisciplinary group of 12 experts to review the association between AD and selected comorbidities. They applied the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) for prognosis approach for assessing the certainty of the evidence and provided statements of association based on the available evidence.
With respect to highlights for atopic and allergic conditions, the guideline authors found high-quality evidence that AD in adults is associated with food allergies, moderate-quality evidence that AD is associated with asthma, and low-quality evidence that AD in adults may be associated with eosinophilic esophagitis.
In the realm of mental health and substance use, ample evidence exists to support an association between AD and mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety, the guidelines state. “For many patients, low mood may be driven by the symptoms of AD, including chronic itch and poor sleep,” Dr. Davis and her coauthors wrote. “Successfully treating AD may alleviate depressive symptoms for some patients; for others, assessment and treatment specific to their mental health may be needed.”
The guidelines also state that low-quality evidence exists to suggest that AD in adults may be associated with alcohol abuse disorders and cigarette smoking.
The authors noted “limited but consistent evidence” supporting a link between AD and adverse bone health, including osteoporosis and fractures, while associations between AD and cardiovascular risk factors and comorbidities, including hypertension, myocardial infarction, and stroke, are more controversial.
“I have published on bone health and AD so that was not as surprising to me,” Dr. Davis said in the interview. “I found a lot of the evidence in the guidelines to be validating of patterns that we see in our patients. The most significant learning point for me was [the link to] cardiovascular disease and the link to specific mental health and substance use disorders. It validates how impactful AD is to the individual.”
According to the guidelines, moderate-quality evidence exists linking AD in adults to both alopecia areata and urticaria. “Because we are dermatologists and take care of both of those diseases, be mindful of that in your daily practice,” Dr. Davis advised. “I would also encourage our colleagues to remember to educate patients on the comorbidities of AD so that they are empowered, and to screen for those comorbidities in your office based on the patient and their history and physical exam, to the level that you think is appropriate for that person’s individual’s care.”
Christine Ko, MD, who was asked to comment on the guidelines, characterized some of the reported comorbidity associations as predictable, such as asthma, food allergy, allergic rhinitis, and skin infections. “As the authors comment, ‘associations between AD and other atopic and allergic conditions have been recognized for decades and even contribute to diagnostic criteria for AD,’ ” said Dr. Ko, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn, who was not involved with the guidelines. “I was a bit surprised to see that atopic dermatitis in adults is associated with osteoporosis and fractures. As the authors suggest, this could be secondary to treatment with oral prednisone, and it is possible that use of dupilumab and JAK inhibitors may lessen this association.”
Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, of the department of dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who was not involved with the guidelines, and was also asked to comment, said that the guidelines underscore the importance of informing adults with AD “of the risks of unchecked inflammation and the potential for multiple disease comorbidities.” Dr. Kwatra, who has AD, added that “these results make me want to be more proactive in treating my eczema to reduce the potential for development of these comorbidities.”
He pointed out that the guidelines did not address racial and ethnic differences in the observed comorbidities. “Unfortunately, minority populations have a greater comorbidity burden in many inflammatory skin diseases so this will be another area needing further investigation,” he said. “As an example, our group found from multicenter data that black patients with atopic dermatitis have higher levels of C-reactive protein, blood eosinophils, and other inflammatory biomarkers.”
The AAD guidelines are the first in a four-part series on AD expected to be published over the next 1-2 years, Dr. Davis said. The subsequent guidelines will address topicals, phototherapy/systemics, and pediatrics.
The study was funded by internal funds from the AAD. Dr. Davis reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Sidbury disclosed that he serves as an advisory board member for Pfizer, a principal investigator for Regeneron, and an investigator for Brickell Biotech and Galderma. He is also a consultant for Galderma Global and Microes. Dr. Ko reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Kwatra is a member of the board of directors of the Skin of Color Society. He is also an advisory board member/consultant for AbbVie, Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi, and has served as an investigator for Galderma, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
While it’s well established that atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults is associated with asthma, allergic rhinitis, and other atopic conditions, the links between AD and other comorbidities are coming into clearer focus.
, published evidence supports an association between AD and comorbidities that may not be on the radar of clinicians and patients, including substance use, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), elements of metabolic syndrome, and various cardiovascular conditions.
“There are more comorbidities with AD than we anticipated, that are supported by data in the literature,” Dawn M.R. Davis, MD, cochair and an author of the guidelines, told this news organization. “We are learning more about the interconnectivity of various medical conditions,” she continued. “Many skin diseases over time have been noted to be impactful to the whole person and not only the skin. A classic example of that is psoriasis. We now understand that psoriasis is a multisystem inflammatory disorder.”
As for AD, “we’ve always appreciated that AD patients tend to be at higher risk for other atopic diseases such as asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and food allergies,” said Dr. Davis, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “With further research, we are now able to delineate those associations more intimately and have data to support our suspicions. Additionally, we’re now understanding that these inflammatory conditions can impact more than the end organ involved, such as the skin and AD. We wanted to look at how AD can affect the whole patient.”
For the guidelines, which are the first of their kind and were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Davis and project cochair Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, chief of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital, led a multidisciplinary group of 12 experts to review the association between AD and selected comorbidities. They applied the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) for prognosis approach for assessing the certainty of the evidence and provided statements of association based on the available evidence.
With respect to highlights for atopic and allergic conditions, the guideline authors found high-quality evidence that AD in adults is associated with food allergies, moderate-quality evidence that AD is associated with asthma, and low-quality evidence that AD in adults may be associated with eosinophilic esophagitis.
In the realm of mental health and substance use, ample evidence exists to support an association between AD and mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety, the guidelines state. “For many patients, low mood may be driven by the symptoms of AD, including chronic itch and poor sleep,” Dr. Davis and her coauthors wrote. “Successfully treating AD may alleviate depressive symptoms for some patients; for others, assessment and treatment specific to their mental health may be needed.”
The guidelines also state that low-quality evidence exists to suggest that AD in adults may be associated with alcohol abuse disorders and cigarette smoking.
The authors noted “limited but consistent evidence” supporting a link between AD and adverse bone health, including osteoporosis and fractures, while associations between AD and cardiovascular risk factors and comorbidities, including hypertension, myocardial infarction, and stroke, are more controversial.
“I have published on bone health and AD so that was not as surprising to me,” Dr. Davis said in the interview. “I found a lot of the evidence in the guidelines to be validating of patterns that we see in our patients. The most significant learning point for me was [the link to] cardiovascular disease and the link to specific mental health and substance use disorders. It validates how impactful AD is to the individual.”
According to the guidelines, moderate-quality evidence exists linking AD in adults to both alopecia areata and urticaria. “Because we are dermatologists and take care of both of those diseases, be mindful of that in your daily practice,” Dr. Davis advised. “I would also encourage our colleagues to remember to educate patients on the comorbidities of AD so that they are empowered, and to screen for those comorbidities in your office based on the patient and their history and physical exam, to the level that you think is appropriate for that person’s individual’s care.”
Christine Ko, MD, who was asked to comment on the guidelines, characterized some of the reported comorbidity associations as predictable, such as asthma, food allergy, allergic rhinitis, and skin infections. “As the authors comment, ‘associations between AD and other atopic and allergic conditions have been recognized for decades and even contribute to diagnostic criteria for AD,’ ” said Dr. Ko, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn, who was not involved with the guidelines. “I was a bit surprised to see that atopic dermatitis in adults is associated with osteoporosis and fractures. As the authors suggest, this could be secondary to treatment with oral prednisone, and it is possible that use of dupilumab and JAK inhibitors may lessen this association.”
Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, of the department of dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who was not involved with the guidelines, and was also asked to comment, said that the guidelines underscore the importance of informing adults with AD “of the risks of unchecked inflammation and the potential for multiple disease comorbidities.” Dr. Kwatra, who has AD, added that “these results make me want to be more proactive in treating my eczema to reduce the potential for development of these comorbidities.”
He pointed out that the guidelines did not address racial and ethnic differences in the observed comorbidities. “Unfortunately, minority populations have a greater comorbidity burden in many inflammatory skin diseases so this will be another area needing further investigation,” he said. “As an example, our group found from multicenter data that black patients with atopic dermatitis have higher levels of C-reactive protein, blood eosinophils, and other inflammatory biomarkers.”
The AAD guidelines are the first in a four-part series on AD expected to be published over the next 1-2 years, Dr. Davis said. The subsequent guidelines will address topicals, phototherapy/systemics, and pediatrics.
The study was funded by internal funds from the AAD. Dr. Davis reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Sidbury disclosed that he serves as an advisory board member for Pfizer, a principal investigator for Regeneron, and an investigator for Brickell Biotech and Galderma. He is also a consultant for Galderma Global and Microes. Dr. Ko reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Kwatra is a member of the board of directors of the Skin of Color Society. He is also an advisory board member/consultant for AbbVie, Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi, and has served as an investigator for Galderma, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Lilly calls it quits on baricitinib’s development for lupus
The company is also in talks with the FDA about how to move forward with the drug’s development for atopic dermatitis.
from two pivotal phase 3 trials, SLE-BRAVE-I and II, the company announced Jan. 28.
Lilly said that the primary endpoint of the SLE-BRAVE-I trial, the proportion of adults with active SLE who met criteria for response on the SLE Responder Index-4 at week 52, was significantly greater among patients treated with 4 mg baricitinib daily than with placebo. However, this endpoint was not met in SLE-BRAVE-II, and no key secondary endpoints were met in either trial. In the announcement, Lilly noted that safety was not a reason for discontinuation because data from these trials were consistent with those previously seen with baricitinib.
The company statement said that it will work with investigators on concluding the combined long-term extension study of the trials.
Baricitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, had previously shown promising results in a phase 2 trial in patients with SLE. It is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more tumor necrosis factor blockers at a dose of 2 mg once daily and has an emergency use authorization for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
The decision to stop baricitinib’s development for SLE will not affect other research efforts with the drug, the company said.
Development for atopic dermatitis
Lilly also noted that it is in discussion with the FDA about the status of a supplemental new drug application of baricitinib for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD). In its press release, Lilly said, “At this point, the company does not have alignment with the FDA on the indicated population. Given the agency’s position, there is a possibility that this could lead to a Complete Response Letter (CRL). The efficacy and safety profile of Olumiant was evaluated in eight atopic dermatitis clinical trials (six double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled studies and two long-term extension studies) inclusive of patients whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. The safety profile in these trials was consistent with previously published Olumiant data.”
Baricitinib was the first JAK inhibitor approved to treat patients with moderate to severe AD who have an inadequate response to topical treatments in the European Union and Japan.
The Lilly announcement was made with Incyte, the company that discovered baricitinib.
The company is also in talks with the FDA about how to move forward with the drug’s development for atopic dermatitis.
The company is also in talks with the FDA about how to move forward with the drug’s development for atopic dermatitis.
from two pivotal phase 3 trials, SLE-BRAVE-I and II, the company announced Jan. 28.
Lilly said that the primary endpoint of the SLE-BRAVE-I trial, the proportion of adults with active SLE who met criteria for response on the SLE Responder Index-4 at week 52, was significantly greater among patients treated with 4 mg baricitinib daily than with placebo. However, this endpoint was not met in SLE-BRAVE-II, and no key secondary endpoints were met in either trial. In the announcement, Lilly noted that safety was not a reason for discontinuation because data from these trials were consistent with those previously seen with baricitinib.
The company statement said that it will work with investigators on concluding the combined long-term extension study of the trials.
Baricitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, had previously shown promising results in a phase 2 trial in patients with SLE. It is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more tumor necrosis factor blockers at a dose of 2 mg once daily and has an emergency use authorization for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
The decision to stop baricitinib’s development for SLE will not affect other research efforts with the drug, the company said.
Development for atopic dermatitis
Lilly also noted that it is in discussion with the FDA about the status of a supplemental new drug application of baricitinib for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD). In its press release, Lilly said, “At this point, the company does not have alignment with the FDA on the indicated population. Given the agency’s position, there is a possibility that this could lead to a Complete Response Letter (CRL). The efficacy and safety profile of Olumiant was evaluated in eight atopic dermatitis clinical trials (six double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled studies and two long-term extension studies) inclusive of patients whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. The safety profile in these trials was consistent with previously published Olumiant data.”
Baricitinib was the first JAK inhibitor approved to treat patients with moderate to severe AD who have an inadequate response to topical treatments in the European Union and Japan.
The Lilly announcement was made with Incyte, the company that discovered baricitinib.
from two pivotal phase 3 trials, SLE-BRAVE-I and II, the company announced Jan. 28.
Lilly said that the primary endpoint of the SLE-BRAVE-I trial, the proportion of adults with active SLE who met criteria for response on the SLE Responder Index-4 at week 52, was significantly greater among patients treated with 4 mg baricitinib daily than with placebo. However, this endpoint was not met in SLE-BRAVE-II, and no key secondary endpoints were met in either trial. In the announcement, Lilly noted that safety was not a reason for discontinuation because data from these trials were consistent with those previously seen with baricitinib.
The company statement said that it will work with investigators on concluding the combined long-term extension study of the trials.
Baricitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, had previously shown promising results in a phase 2 trial in patients with SLE. It is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more tumor necrosis factor blockers at a dose of 2 mg once daily and has an emergency use authorization for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
The decision to stop baricitinib’s development for SLE will not affect other research efforts with the drug, the company said.
Development for atopic dermatitis
Lilly also noted that it is in discussion with the FDA about the status of a supplemental new drug application of baricitinib for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD). In its press release, Lilly said, “At this point, the company does not have alignment with the FDA on the indicated population. Given the agency’s position, there is a possibility that this could lead to a Complete Response Letter (CRL). The efficacy and safety profile of Olumiant was evaluated in eight atopic dermatitis clinical trials (six double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled studies and two long-term extension studies) inclusive of patients whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. The safety profile in these trials was consistent with previously published Olumiant data.”
Baricitinib was the first JAK inhibitor approved to treat patients with moderate to severe AD who have an inadequate response to topical treatments in the European Union and Japan.
The Lilly announcement was made with Incyte, the company that discovered baricitinib.
Perception of atopic dermatitis severity often differs between patients, physicians
It’s no secret that atopic dermatitis (AD) is associated with a high burden of disease, with an impact on sleep disturbance, increased anxiety, depression, reduced function and productivity at work and school, and overall decreased quality of life.
But to complicate matters, , according to Zelma Chiesa Fuxench, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. For example, a cross-sectional study of 678 patients with AD, which assessed disease severity based on self-reports and physician-reported disease severity using components of the Eczema Area and Severity Index score, found that the level of agreement matched in about 68% of the cases. However, in about 32% of cases, there was a mismatch between how patients and physicians rated disease severity. In about 11% of the cases, patients reported a higher degree of disease severity, compared with physicians, while in about 20% of cases, patients reported lower disease severity, compared with the physician assessment.
“This has potential implications for overestimating or underestimating disease burden and could impact our treatment of AD patients,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium.
The study also found that, while the pattern of agreement was not affected by the extent of AD in terms of the body surface area, the use of immunomodulatory drugs, or the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score, increased sleep disturbance did have an influence. Also, quality of life was lower and a higher impact on work productivity was observed when patients rated their disease severity higher than the rating of physicians.
Measures to assess disease severity
“If we understand that there is mismatch between how a patient experiences their disease and how physicians rate it, what can we do to be better at assessing disease severity in AD to truly capture the full disease burden in patients with AD?” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench asked. She noted that different validated measures have been described in the literature, and objective assessment tools often used in clinical trials include the EASI and the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD). “These are measures that are done by the physician that take into account the extent of the body surface area involvement and also the intensity of the lesions such as how red or thick they are,” she said. “In addition, the SCORAD will also take into account the patient-reported intensity level of itch and sleep loss.”
The Patient-Oriented SCORAD (PO-SCORAD) is similar to the SCORAD except that it is completed by the patient or the patient’s caregiver. In all three outcome measures, a higher score indicates a higher level of disease severity. Other measures that have been frequently described in the literature include the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM), which takes into account seven symptoms scored over the last week (itch, sleep, weeping/oozing, cracking, flaking, and dryness/roughness), with higher scores indicating increased disease severity, and the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), which is a generic measure to assess the burden of skin diseases including AD. The DLQI “asks 10 questions as they relate to the impact of health-related quality of life over the last week, with higher scores indicating more severe disease,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said.
There are also symptom-specific scales such as the Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (Pruritus-NRS) that measures the impact of itch on a scale of 0 to 10, and the Three-Item Severity Scale (TIS) and the Validated Investigator Global Assessment (v-IGA) that are used to assess different measures in terms of intensity of the lesions.”
However, the study that looked at the discordance between AD severity reported by physicians and patients also found that awareness and use of clinical and patient-reported measures for assessing AD disease severity among physicians was low. The authors further divided their findings among primary care physicians, dermatologists, and allergists/immunologists. “While dermatologists and allergists/immunologists reported being more aware of these outcome measures, a high proportion of physicians within this group were not using these outcomes measures in daily clinical practice,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said.
“Is there a need for us to use more than one outcome measure instrument when trying to assess the impact of AD, understanding that many of us practice in a very busy clinical setting? The answer is probably yes. The use of multiple assessment tools that measure different domains could potentially help better capture the broad manifestations of AD, because of the complex nature of disease burden in this population. In addition, there are studies showing poor correlation between patient-reported and physician-assessed disease severity for various instruments, emphasizing the point that these measures may be capturing very different things.”
With so many measures to choose from and limited time in the office, which ones should clinicians use? Harmonizing Outcome Measures for Eczema (HOME), based at the Center of Evidence-based Dermatology, at the University of Nottingham (England), is a consortium of patients and other key stakeholders in AD aiming to develop a consensus-based core outcome set for clinical trials and clinical practice. At a consensus meeting in 2018, the consortium reported that the PO-SCORAD and the POEM could be used in the clinical setting to better capture the true level of disease severity and burden in patients with AD.
The PO-SCORAD is also available as an App. A PO-SCORAD of less than 25 is associated with mild disease; a PO-SCORAD between 25 and 50 is associated with moderate disease, and a PO-SCORAD of greater than 50 is associated with severe disease.
“It’s recommended that patients capture the PO-SCORAD once or twice a week,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said, noting that the newer version of the App includes photos of different skin types to make it more relevant for a larger number of patients.
Another advantage of using the App is that a patient can track their disease severity through time. They can upload photographs, or they can send you a graphical input of their disease severity either through e-mail or print it out and bring it to their office visit to share the results with you.”
A prospective observational European study of 471 adult and pediatric patients with AD found a statistically significant correlation between SCORAD and PO-SCORAD results at day 0 and day 28. A separate large study conducted in 12 countries found that PO-SCORAD was the only self-assessment score to be highly correlated with the SCORAD index and POEM (A Spearman’s correlation coefficient of greater than or equal to 0.70). In that study, PO-SCORAD also correlated most closely with the results of the DLQI (r = 0.67) and the Dermatitis Family Questionnaire Impact DFQI (r = 0.56).
A more recent study of almost 300 adults with AD that examined the correlations between PO-SCORAD, POEM, and DLQI yielded similar findings.
Other researchers are aiming to assess the full burden of AD at the patient level. Drawing from a cross-sectional study called AWARE (Adults With Atopic Dermatitis Reporting on their Experience), an international observational study, investigators sought to identify what terms AD patients were using to describe their disease. The most commonly used terms were itch (37%), embarrassed (37%), annoyed (35%), pain (25%), and frustration (22%). “Although our study did not identify all patient-reported consequences of AD, such as the known impact of AD on sexual health, our qualitative approach has provided an understanding of patient perceptions and the underlying range of physical and emotional consequences of AD, which can inform shared decision-making,” the authors wrote. “These findings suggest the need for broader assessment of the impact of AD on patients’ lives,” they added.
Dr. Chiesa Fuxench reported having no disclosures relevant to her presentation.
The study on AD severity reported by physicians and patients was funded by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and several authors were employees of those companies.
It’s no secret that atopic dermatitis (AD) is associated with a high burden of disease, with an impact on sleep disturbance, increased anxiety, depression, reduced function and productivity at work and school, and overall decreased quality of life.
But to complicate matters, , according to Zelma Chiesa Fuxench, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. For example, a cross-sectional study of 678 patients with AD, which assessed disease severity based on self-reports and physician-reported disease severity using components of the Eczema Area and Severity Index score, found that the level of agreement matched in about 68% of the cases. However, in about 32% of cases, there was a mismatch between how patients and physicians rated disease severity. In about 11% of the cases, patients reported a higher degree of disease severity, compared with physicians, while in about 20% of cases, patients reported lower disease severity, compared with the physician assessment.
“This has potential implications for overestimating or underestimating disease burden and could impact our treatment of AD patients,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium.
The study also found that, while the pattern of agreement was not affected by the extent of AD in terms of the body surface area, the use of immunomodulatory drugs, or the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score, increased sleep disturbance did have an influence. Also, quality of life was lower and a higher impact on work productivity was observed when patients rated their disease severity higher than the rating of physicians.
Measures to assess disease severity
“If we understand that there is mismatch between how a patient experiences their disease and how physicians rate it, what can we do to be better at assessing disease severity in AD to truly capture the full disease burden in patients with AD?” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench asked. She noted that different validated measures have been described in the literature, and objective assessment tools often used in clinical trials include the EASI and the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD). “These are measures that are done by the physician that take into account the extent of the body surface area involvement and also the intensity of the lesions such as how red or thick they are,” she said. “In addition, the SCORAD will also take into account the patient-reported intensity level of itch and sleep loss.”
The Patient-Oriented SCORAD (PO-SCORAD) is similar to the SCORAD except that it is completed by the patient or the patient’s caregiver. In all three outcome measures, a higher score indicates a higher level of disease severity. Other measures that have been frequently described in the literature include the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM), which takes into account seven symptoms scored over the last week (itch, sleep, weeping/oozing, cracking, flaking, and dryness/roughness), with higher scores indicating increased disease severity, and the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), which is a generic measure to assess the burden of skin diseases including AD. The DLQI “asks 10 questions as they relate to the impact of health-related quality of life over the last week, with higher scores indicating more severe disease,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said.
There are also symptom-specific scales such as the Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (Pruritus-NRS) that measures the impact of itch on a scale of 0 to 10, and the Three-Item Severity Scale (TIS) and the Validated Investigator Global Assessment (v-IGA) that are used to assess different measures in terms of intensity of the lesions.”
However, the study that looked at the discordance between AD severity reported by physicians and patients also found that awareness and use of clinical and patient-reported measures for assessing AD disease severity among physicians was low. The authors further divided their findings among primary care physicians, dermatologists, and allergists/immunologists. “While dermatologists and allergists/immunologists reported being more aware of these outcome measures, a high proportion of physicians within this group were not using these outcomes measures in daily clinical practice,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said.
“Is there a need for us to use more than one outcome measure instrument when trying to assess the impact of AD, understanding that many of us practice in a very busy clinical setting? The answer is probably yes. The use of multiple assessment tools that measure different domains could potentially help better capture the broad manifestations of AD, because of the complex nature of disease burden in this population. In addition, there are studies showing poor correlation between patient-reported and physician-assessed disease severity for various instruments, emphasizing the point that these measures may be capturing very different things.”
With so many measures to choose from and limited time in the office, which ones should clinicians use? Harmonizing Outcome Measures for Eczema (HOME), based at the Center of Evidence-based Dermatology, at the University of Nottingham (England), is a consortium of patients and other key stakeholders in AD aiming to develop a consensus-based core outcome set for clinical trials and clinical practice. At a consensus meeting in 2018, the consortium reported that the PO-SCORAD and the POEM could be used in the clinical setting to better capture the true level of disease severity and burden in patients with AD.
The PO-SCORAD is also available as an App. A PO-SCORAD of less than 25 is associated with mild disease; a PO-SCORAD between 25 and 50 is associated with moderate disease, and a PO-SCORAD of greater than 50 is associated with severe disease.
“It’s recommended that patients capture the PO-SCORAD once or twice a week,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said, noting that the newer version of the App includes photos of different skin types to make it more relevant for a larger number of patients.
Another advantage of using the App is that a patient can track their disease severity through time. They can upload photographs, or they can send you a graphical input of their disease severity either through e-mail or print it out and bring it to their office visit to share the results with you.”
A prospective observational European study of 471 adult and pediatric patients with AD found a statistically significant correlation between SCORAD and PO-SCORAD results at day 0 and day 28. A separate large study conducted in 12 countries found that PO-SCORAD was the only self-assessment score to be highly correlated with the SCORAD index and POEM (A Spearman’s correlation coefficient of greater than or equal to 0.70). In that study, PO-SCORAD also correlated most closely with the results of the DLQI (r = 0.67) and the Dermatitis Family Questionnaire Impact DFQI (r = 0.56).
A more recent study of almost 300 adults with AD that examined the correlations between PO-SCORAD, POEM, and DLQI yielded similar findings.
Other researchers are aiming to assess the full burden of AD at the patient level. Drawing from a cross-sectional study called AWARE (Adults With Atopic Dermatitis Reporting on their Experience), an international observational study, investigators sought to identify what terms AD patients were using to describe their disease. The most commonly used terms were itch (37%), embarrassed (37%), annoyed (35%), pain (25%), and frustration (22%). “Although our study did not identify all patient-reported consequences of AD, such as the known impact of AD on sexual health, our qualitative approach has provided an understanding of patient perceptions and the underlying range of physical and emotional consequences of AD, which can inform shared decision-making,” the authors wrote. “These findings suggest the need for broader assessment of the impact of AD on patients’ lives,” they added.
Dr. Chiesa Fuxench reported having no disclosures relevant to her presentation.
The study on AD severity reported by physicians and patients was funded by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and several authors were employees of those companies.
It’s no secret that atopic dermatitis (AD) is associated with a high burden of disease, with an impact on sleep disturbance, increased anxiety, depression, reduced function and productivity at work and school, and overall decreased quality of life.
But to complicate matters, , according to Zelma Chiesa Fuxench, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. For example, a cross-sectional study of 678 patients with AD, which assessed disease severity based on self-reports and physician-reported disease severity using components of the Eczema Area and Severity Index score, found that the level of agreement matched in about 68% of the cases. However, in about 32% of cases, there was a mismatch between how patients and physicians rated disease severity. In about 11% of the cases, patients reported a higher degree of disease severity, compared with physicians, while in about 20% of cases, patients reported lower disease severity, compared with the physician assessment.
“This has potential implications for overestimating or underestimating disease burden and could impact our treatment of AD patients,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium.
The study also found that, while the pattern of agreement was not affected by the extent of AD in terms of the body surface area, the use of immunomodulatory drugs, or the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score, increased sleep disturbance did have an influence. Also, quality of life was lower and a higher impact on work productivity was observed when patients rated their disease severity higher than the rating of physicians.
Measures to assess disease severity
“If we understand that there is mismatch between how a patient experiences their disease and how physicians rate it, what can we do to be better at assessing disease severity in AD to truly capture the full disease burden in patients with AD?” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench asked. She noted that different validated measures have been described in the literature, and objective assessment tools often used in clinical trials include the EASI and the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD). “These are measures that are done by the physician that take into account the extent of the body surface area involvement and also the intensity of the lesions such as how red or thick they are,” she said. “In addition, the SCORAD will also take into account the patient-reported intensity level of itch and sleep loss.”
The Patient-Oriented SCORAD (PO-SCORAD) is similar to the SCORAD except that it is completed by the patient or the patient’s caregiver. In all three outcome measures, a higher score indicates a higher level of disease severity. Other measures that have been frequently described in the literature include the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM), which takes into account seven symptoms scored over the last week (itch, sleep, weeping/oozing, cracking, flaking, and dryness/roughness), with higher scores indicating increased disease severity, and the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), which is a generic measure to assess the burden of skin diseases including AD. The DLQI “asks 10 questions as they relate to the impact of health-related quality of life over the last week, with higher scores indicating more severe disease,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said.
There are also symptom-specific scales such as the Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (Pruritus-NRS) that measures the impact of itch on a scale of 0 to 10, and the Three-Item Severity Scale (TIS) and the Validated Investigator Global Assessment (v-IGA) that are used to assess different measures in terms of intensity of the lesions.”
However, the study that looked at the discordance between AD severity reported by physicians and patients also found that awareness and use of clinical and patient-reported measures for assessing AD disease severity among physicians was low. The authors further divided their findings among primary care physicians, dermatologists, and allergists/immunologists. “While dermatologists and allergists/immunologists reported being more aware of these outcome measures, a high proportion of physicians within this group were not using these outcomes measures in daily clinical practice,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said.
“Is there a need for us to use more than one outcome measure instrument when trying to assess the impact of AD, understanding that many of us practice in a very busy clinical setting? The answer is probably yes. The use of multiple assessment tools that measure different domains could potentially help better capture the broad manifestations of AD, because of the complex nature of disease burden in this population. In addition, there are studies showing poor correlation between patient-reported and physician-assessed disease severity for various instruments, emphasizing the point that these measures may be capturing very different things.”
With so many measures to choose from and limited time in the office, which ones should clinicians use? Harmonizing Outcome Measures for Eczema (HOME), based at the Center of Evidence-based Dermatology, at the University of Nottingham (England), is a consortium of patients and other key stakeholders in AD aiming to develop a consensus-based core outcome set for clinical trials and clinical practice. At a consensus meeting in 2018, the consortium reported that the PO-SCORAD and the POEM could be used in the clinical setting to better capture the true level of disease severity and burden in patients with AD.
The PO-SCORAD is also available as an App. A PO-SCORAD of less than 25 is associated with mild disease; a PO-SCORAD between 25 and 50 is associated with moderate disease, and a PO-SCORAD of greater than 50 is associated with severe disease.
“It’s recommended that patients capture the PO-SCORAD once or twice a week,” Dr. Chiesa Fuxench said, noting that the newer version of the App includes photos of different skin types to make it more relevant for a larger number of patients.
Another advantage of using the App is that a patient can track their disease severity through time. They can upload photographs, or they can send you a graphical input of their disease severity either through e-mail or print it out and bring it to their office visit to share the results with you.”
A prospective observational European study of 471 adult and pediatric patients with AD found a statistically significant correlation between SCORAD and PO-SCORAD results at day 0 and day 28. A separate large study conducted in 12 countries found that PO-SCORAD was the only self-assessment score to be highly correlated with the SCORAD index and POEM (A Spearman’s correlation coefficient of greater than or equal to 0.70). In that study, PO-SCORAD also correlated most closely with the results of the DLQI (r = 0.67) and the Dermatitis Family Questionnaire Impact DFQI (r = 0.56).
A more recent study of almost 300 adults with AD that examined the correlations between PO-SCORAD, POEM, and DLQI yielded similar findings.
Other researchers are aiming to assess the full burden of AD at the patient level. Drawing from a cross-sectional study called AWARE (Adults With Atopic Dermatitis Reporting on their Experience), an international observational study, investigators sought to identify what terms AD patients were using to describe their disease. The most commonly used terms were itch (37%), embarrassed (37%), annoyed (35%), pain (25%), and frustration (22%). “Although our study did not identify all patient-reported consequences of AD, such as the known impact of AD on sexual health, our qualitative approach has provided an understanding of patient perceptions and the underlying range of physical and emotional consequences of AD, which can inform shared decision-making,” the authors wrote. “These findings suggest the need for broader assessment of the impact of AD on patients’ lives,” they added.
Dr. Chiesa Fuxench reported having no disclosures relevant to her presentation.
The study on AD severity reported by physicians and patients was funded by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and several authors were employees of those companies.
FROM REVOLUTIONIZING AD 2021
Pruritus in elderly patients: Not a diagnosis
that has appeared seemingly out of the blue.
“They ask: ‘What happened? Why did I get this? Everything was going so well and all of a sudden, I get this itchy rash that keeps me up every night,’ ” Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium. “Is this elderly atopic dermatitis? Is that a real thing?”
But such patients often lack flexural involvement, which is a telltale sign of atopic dermatitis, “so I really struggle with making the diagnosis of new onset AD in the elderly,” he said, adding that existing medical literature on the topic is variable, with the use of terms that include chronic eczematous eruption of the elderly, chronic “eczematiform” eruption in the elderly, chronic eczematous eruption of the aged, eczematous dermatitis not otherwise specified, dermal hypersensitivity reaction, urticarial dermatitis, and eczematous drug eruptions.
“Pruritus of the elderly is not a diagnosis,” Dr. Simpson said. “That’s just a symptom with a million etiologies. Never put that as your assessment. You could put pruritic eruption or pruritus, but try to look for the cause.”
More than 50% of older patients have xerosis, according to a 2013 clinical review on pruritus in the elderly, by Timothy G. Berger, MD, and colleagues at the University of California, San Francisco, which includes advice on the evaluation and management of pruritus in this group of patients based on whether they have a rash or not. For a patient with no rash, Dr. Simpson said, the workup “includes ruling out xerosis, scabies, and effects of medications that could cause rash such as narcotics and Adderall; as well as a generalized pruritus workup including renal and hepatic function, blood count, and thyroid levels.”
In a separate analysis of pruritic elderly patients by the same authors, five rash-related diagnoses accounted for 75% of cases: eczematous dermatitis, lichen simplex/prurigo nodularis, subacute prurigo, transient acantholytic dermatosis, and neuropathic disorder. “Morphology of pruritus with rash is also important,” Dr. Simpson added. “Is it eczematous? Papular? Prurigo nodularis? This helps lead you in the right direction.”
Some case-control studies have shown that calcium channel blockers could be related to eczema in older patients.
“But there aren’t a lot of studies out there that show that when you stop your calcium channel blocker, your eczema gets better,” Dr. Simpson said. “I’m reluctant to stop medications to try to help their eczema. I haven’t had many good results doing that.”
In an abstract presented during the 2021 annual meeting of the Society of Investigative Dermatology, he and his colleagues prospectively reviewed 89 patients over age 65 who had been referred with new-onset eczema. Of these, 34 underwent drug cessation trials for 1-3 months. “Not one patient improved when they stopped medications,” Dr. Simpson said, but “multiple patients were hospitalized for discontinuing their cardiac and antihypertensive medications.” While this was a biased sample of patients coming to him with chronic eczema, “in my experience, if you have chronic eczema in an older patient, stopping medications is likely not going to help.”
Other diagnostic tips he offered included asking patients what skin products they’re using, considering patch testing, and considering biopsy to rule out cutaneous T-cell lymphoma or bullous pemphigoid. “If you’re not sure there’s a rash, you might need to do a pruritus workup,” he said. If an eczematous rash is present and no other cause is found, try treating it like AD, he added.
Dr. Simpson reported serving as an investigator for and consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies.
that has appeared seemingly out of the blue.
“They ask: ‘What happened? Why did I get this? Everything was going so well and all of a sudden, I get this itchy rash that keeps me up every night,’ ” Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium. “Is this elderly atopic dermatitis? Is that a real thing?”
But such patients often lack flexural involvement, which is a telltale sign of atopic dermatitis, “so I really struggle with making the diagnosis of new onset AD in the elderly,” he said, adding that existing medical literature on the topic is variable, with the use of terms that include chronic eczematous eruption of the elderly, chronic “eczematiform” eruption in the elderly, chronic eczematous eruption of the aged, eczematous dermatitis not otherwise specified, dermal hypersensitivity reaction, urticarial dermatitis, and eczematous drug eruptions.
“Pruritus of the elderly is not a diagnosis,” Dr. Simpson said. “That’s just a symptom with a million etiologies. Never put that as your assessment. You could put pruritic eruption or pruritus, but try to look for the cause.”
More than 50% of older patients have xerosis, according to a 2013 clinical review on pruritus in the elderly, by Timothy G. Berger, MD, and colleagues at the University of California, San Francisco, which includes advice on the evaluation and management of pruritus in this group of patients based on whether they have a rash or not. For a patient with no rash, Dr. Simpson said, the workup “includes ruling out xerosis, scabies, and effects of medications that could cause rash such as narcotics and Adderall; as well as a generalized pruritus workup including renal and hepatic function, blood count, and thyroid levels.”
In a separate analysis of pruritic elderly patients by the same authors, five rash-related diagnoses accounted for 75% of cases: eczematous dermatitis, lichen simplex/prurigo nodularis, subacute prurigo, transient acantholytic dermatosis, and neuropathic disorder. “Morphology of pruritus with rash is also important,” Dr. Simpson added. “Is it eczematous? Papular? Prurigo nodularis? This helps lead you in the right direction.”
Some case-control studies have shown that calcium channel blockers could be related to eczema in older patients.
“But there aren’t a lot of studies out there that show that when you stop your calcium channel blocker, your eczema gets better,” Dr. Simpson said. “I’m reluctant to stop medications to try to help their eczema. I haven’t had many good results doing that.”
In an abstract presented during the 2021 annual meeting of the Society of Investigative Dermatology, he and his colleagues prospectively reviewed 89 patients over age 65 who had been referred with new-onset eczema. Of these, 34 underwent drug cessation trials for 1-3 months. “Not one patient improved when they stopped medications,” Dr. Simpson said, but “multiple patients were hospitalized for discontinuing their cardiac and antihypertensive medications.” While this was a biased sample of patients coming to him with chronic eczema, “in my experience, if you have chronic eczema in an older patient, stopping medications is likely not going to help.”
Other diagnostic tips he offered included asking patients what skin products they’re using, considering patch testing, and considering biopsy to rule out cutaneous T-cell lymphoma or bullous pemphigoid. “If you’re not sure there’s a rash, you might need to do a pruritus workup,” he said. If an eczematous rash is present and no other cause is found, try treating it like AD, he added.
Dr. Simpson reported serving as an investigator for and consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies.
that has appeared seemingly out of the blue.
“They ask: ‘What happened? Why did I get this? Everything was going so well and all of a sudden, I get this itchy rash that keeps me up every night,’ ” Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium. “Is this elderly atopic dermatitis? Is that a real thing?”
But such patients often lack flexural involvement, which is a telltale sign of atopic dermatitis, “so I really struggle with making the diagnosis of new onset AD in the elderly,” he said, adding that existing medical literature on the topic is variable, with the use of terms that include chronic eczematous eruption of the elderly, chronic “eczematiform” eruption in the elderly, chronic eczematous eruption of the aged, eczematous dermatitis not otherwise specified, dermal hypersensitivity reaction, urticarial dermatitis, and eczematous drug eruptions.
“Pruritus of the elderly is not a diagnosis,” Dr. Simpson said. “That’s just a symptom with a million etiologies. Never put that as your assessment. You could put pruritic eruption or pruritus, but try to look for the cause.”
More than 50% of older patients have xerosis, according to a 2013 clinical review on pruritus in the elderly, by Timothy G. Berger, MD, and colleagues at the University of California, San Francisco, which includes advice on the evaluation and management of pruritus in this group of patients based on whether they have a rash or not. For a patient with no rash, Dr. Simpson said, the workup “includes ruling out xerosis, scabies, and effects of medications that could cause rash such as narcotics and Adderall; as well as a generalized pruritus workup including renal and hepatic function, blood count, and thyroid levels.”
In a separate analysis of pruritic elderly patients by the same authors, five rash-related diagnoses accounted for 75% of cases: eczematous dermatitis, lichen simplex/prurigo nodularis, subacute prurigo, transient acantholytic dermatosis, and neuropathic disorder. “Morphology of pruritus with rash is also important,” Dr. Simpson added. “Is it eczematous? Papular? Prurigo nodularis? This helps lead you in the right direction.”
Some case-control studies have shown that calcium channel blockers could be related to eczema in older patients.
“But there aren’t a lot of studies out there that show that when you stop your calcium channel blocker, your eczema gets better,” Dr. Simpson said. “I’m reluctant to stop medications to try to help their eczema. I haven’t had many good results doing that.”
In an abstract presented during the 2021 annual meeting of the Society of Investigative Dermatology, he and his colleagues prospectively reviewed 89 patients over age 65 who had been referred with new-onset eczema. Of these, 34 underwent drug cessation trials for 1-3 months. “Not one patient improved when they stopped medications,” Dr. Simpson said, but “multiple patients were hospitalized for discontinuing their cardiac and antihypertensive medications.” While this was a biased sample of patients coming to him with chronic eczema, “in my experience, if you have chronic eczema in an older patient, stopping medications is likely not going to help.”
Other diagnostic tips he offered included asking patients what skin products they’re using, considering patch testing, and considering biopsy to rule out cutaneous T-cell lymphoma or bullous pemphigoid. “If you’re not sure there’s a rash, you might need to do a pruritus workup,” he said. If an eczematous rash is present and no other cause is found, try treating it like AD, he added.
Dr. Simpson reported serving as an investigator for and consultant to numerous pharmaceutical companies.
FROM REVOLUTIONIZING AD 2021
Skin pain increases disease burden and decreases QoL in children with atopic dermatitis
Key clinical point: In children with atopic dermatitis (AD), skin pain is a burdensome symptom with heterogeneous presentation and is associated with decreased quality of life (QoL).
Major finding: Skin pain intensity was associated with conditions such as bleeding (adjusted β 1.47; 95% CI 0.61-2.33), weeping/oozing (adjusted β 1.18; 95% CI 0.47-1.90), and cracking of skin (adjusted β 1.00; 95% CI 0.27-1.73). Parent-reported pain intensity was associated with impaired QoL in infants aged 1-4 years (adjusted β 1.16; 95% CI 0.18-2.14) and children aged 5-17 years (adjusted β 1.68; 95% CI 1.00-2.36).
Study details: Findings are from a cross-sectional national survey of 240 children with AD and their parents, of which 60 and 180 were aged 1-4 years and 5-17 years, respectively, and 200 had moderate-to-very severe disease.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Cheng BT et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 (Dec 23). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2021.12.012.
Key clinical point: In children with atopic dermatitis (AD), skin pain is a burdensome symptom with heterogeneous presentation and is associated with decreased quality of life (QoL).
Major finding: Skin pain intensity was associated with conditions such as bleeding (adjusted β 1.47; 95% CI 0.61-2.33), weeping/oozing (adjusted β 1.18; 95% CI 0.47-1.90), and cracking of skin (adjusted β 1.00; 95% CI 0.27-1.73). Parent-reported pain intensity was associated with impaired QoL in infants aged 1-4 years (adjusted β 1.16; 95% CI 0.18-2.14) and children aged 5-17 years (adjusted β 1.68; 95% CI 1.00-2.36).
Study details: Findings are from a cross-sectional national survey of 240 children with AD and their parents, of which 60 and 180 were aged 1-4 years and 5-17 years, respectively, and 200 had moderate-to-very severe disease.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Cheng BT et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 (Dec 23). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2021.12.012.
Key clinical point: In children with atopic dermatitis (AD), skin pain is a burdensome symptom with heterogeneous presentation and is associated with decreased quality of life (QoL).
Major finding: Skin pain intensity was associated with conditions such as bleeding (adjusted β 1.47; 95% CI 0.61-2.33), weeping/oozing (adjusted β 1.18; 95% CI 0.47-1.90), and cracking of skin (adjusted β 1.00; 95% CI 0.27-1.73). Parent-reported pain intensity was associated with impaired QoL in infants aged 1-4 years (adjusted β 1.16; 95% CI 0.18-2.14) and children aged 5-17 years (adjusted β 1.68; 95% CI 1.00-2.36).
Study details: Findings are from a cross-sectional national survey of 240 children with AD and their parents, of which 60 and 180 were aged 1-4 years and 5-17 years, respectively, and 200 had moderate-to-very severe disease.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Cheng BT et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 (Dec 23). Doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2021.12.012.
Antibiotic use in infancy may increase the risk of developing atopic dermatitis
Key clinical point: Antibiotic use in infants younger than 12 months is associated with an increased risk of developing atopic dermatitis (AD) if shared familial and environmental factors are disregarded.
Major finding: A higher proportion of infants exposed (13.7%) vs. not exposed (13.4%) to antibiotics developed AD after 12 months of age. The risk of developing AD was higher in infants exposed to antibiotics in the first 12 months after birth (adjusted hazard ratio 1.12; 95% CI 1.04-1.21); however, this association disappeared when the data were matched with those obtained from their siblings.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective, large-scale study including 85,954 infants, of which 10.1% were exposed to antibiotics at <12 months of age.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research and the Project Promoting Clinical Trials for Development of New Drugs in Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. Dr. Kawakami declared holding stock options and receiving research funds, consulting fees, and executive compensation from several sources.
Source: Tsuchida T et al. Acta Paediatr. 2021 (Dec 17). Doi: 10.1111/apa.16221.
Key clinical point: Antibiotic use in infants younger than 12 months is associated with an increased risk of developing atopic dermatitis (AD) if shared familial and environmental factors are disregarded.
Major finding: A higher proportion of infants exposed (13.7%) vs. not exposed (13.4%) to antibiotics developed AD after 12 months of age. The risk of developing AD was higher in infants exposed to antibiotics in the first 12 months after birth (adjusted hazard ratio 1.12; 95% CI 1.04-1.21); however, this association disappeared when the data were matched with those obtained from their siblings.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective, large-scale study including 85,954 infants, of which 10.1% were exposed to antibiotics at <12 months of age.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research and the Project Promoting Clinical Trials for Development of New Drugs in Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. Dr. Kawakami declared holding stock options and receiving research funds, consulting fees, and executive compensation from several sources.
Source: Tsuchida T et al. Acta Paediatr. 2021 (Dec 17). Doi: 10.1111/apa.16221.
Key clinical point: Antibiotic use in infants younger than 12 months is associated with an increased risk of developing atopic dermatitis (AD) if shared familial and environmental factors are disregarded.
Major finding: A higher proportion of infants exposed (13.7%) vs. not exposed (13.4%) to antibiotics developed AD after 12 months of age. The risk of developing AD was higher in infants exposed to antibiotics in the first 12 months after birth (adjusted hazard ratio 1.12; 95% CI 1.04-1.21); however, this association disappeared when the data were matched with those obtained from their siblings.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective, large-scale study including 85,954 infants, of which 10.1% were exposed to antibiotics at <12 months of age.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research and the Project Promoting Clinical Trials for Development of New Drugs in Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. Dr. Kawakami declared holding stock options and receiving research funds, consulting fees, and executive compensation from several sources.
Source: Tsuchida T et al. Acta Paediatr. 2021 (Dec 17). Doi: 10.1111/apa.16221.
More severe atopic dermatitis tied with poor sleep health and attention dysregulation
Key clinical point: Children aged <5 years with atopic dermatitis (AD) show a disease severity-dependent increased risk for poor sleep health and attention dysregulation (AdR).
Major finding: AD-induced sleep disturbance on ≥5 nights/week was reported in 76% children with severe AD, 24% children with moderate AD, and none with mild AD (P = .01), and children with more severe AD had greater AdR (correlation coefficient 0.65; P < .01). Severity of AD was a significant predictor of poor sleep health (β 0.79; P < .01) and AdR (β 1.22; P < .01).
Study details: Findings are from a cross-sectional study including 60 children aged 1-4 years with mild-to-severe AD.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhou NY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021 (Dec 21). Doi: 10.1111/pde.14889.
Key clinical point: Children aged <5 years with atopic dermatitis (AD) show a disease severity-dependent increased risk for poor sleep health and attention dysregulation (AdR).
Major finding: AD-induced sleep disturbance on ≥5 nights/week was reported in 76% children with severe AD, 24% children with moderate AD, and none with mild AD (P = .01), and children with more severe AD had greater AdR (correlation coefficient 0.65; P < .01). Severity of AD was a significant predictor of poor sleep health (β 0.79; P < .01) and AdR (β 1.22; P < .01).
Study details: Findings are from a cross-sectional study including 60 children aged 1-4 years with mild-to-severe AD.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhou NY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021 (Dec 21). Doi: 10.1111/pde.14889.
Key clinical point: Children aged <5 years with atopic dermatitis (AD) show a disease severity-dependent increased risk for poor sleep health and attention dysregulation (AdR).
Major finding: AD-induced sleep disturbance on ≥5 nights/week was reported in 76% children with severe AD, 24% children with moderate AD, and none with mild AD (P = .01), and children with more severe AD had greater AdR (correlation coefficient 0.65; P < .01). Severity of AD was a significant predictor of poor sleep health (β 0.79; P < .01) and AdR (β 1.22; P < .01).
Study details: Findings are from a cross-sectional study including 60 children aged 1-4 years with mild-to-severe AD.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhou NY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021 (Dec 21). Doi: 10.1111/pde.14889.