User login
Use of Biologics for Psoriasis Found to Confer a Survival Benefit
Among patients with psoriasis, the risk of mortality was strongly associated with hepatic injury, cardiovascular disease, and psychiatric affective disorders, but was reduced among those who received systemic therapy with biologics, researchers from Canada report.
Those are key findings from a large retrospective registry study of patients with psoriasis, published in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory condition affecting approximately 3% of the western populations, bears a higher risk of mortality compared to healthy individuals, possibly by inducing systemic inflammation associated with numerous comorbidities, especially cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, and others,” wrote corresponding author Robert Gniadecki, MD, PhD, of the division of dermatology at the University of Alberta, Canada, and colleagues. “It has been argued that the use of systemic immunomodulatory agents quenches systemic inflammation and potentially improves patient survival. However, the evidence to support this hypothesis is limited.”
To investigate the impact of comorbidities and systemic therapies on all-cause mortality in psoriasis, the researchers used the Alberta Health Services Data Repository of Reporting database from January 1, 2012, to June 1, 2019, which represents a population base of 4.47 million individuals. They extracted data on 18,618 psoriasis cases and 55,854 controls, stratified cases according to the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), a surrogate measure for comorbidity burden, and by the type of therapy received, and conducted statistical analyses including Cox proportional hazards regression to determine absolute hazard ratios representing relative effects of specific demographic and comorbidity factors on mortality within groups.
The median age in both cohorts was 48 years, and 51% were male. The researchers observed that mortality in the psoriasis cohort was significantly higher than in the controls (5.7% vs. 3.8%, respectively; P < .05), with a median age at the time of death of 72 vs. 74.4 years.
The CCI and comorbidities strongly predicted mortality, especially drug-induced liver injury (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78), bipolar disorder and suicidal ideation (HR, 1.24-1.58), and major cardiovascular diseases, which included myocardial infarction (MI), congestive heart failure (CHF), and cerebrovascular disease (CVA) (HR, 1.2-1.4).
Among patients in the psoriasis cohort, survival of those treated with biologic agents was higher than in controls, even after matching for CCI (3.2% vs. 4.4%, respectively, P < .05). “These patients also exhibit reduced overall mortality compared to those treated with methotrexate or topical agents,” Dr. Gniadecki and colleagues wrote. “There was no difference in mortality between methotrexate patients and the topical therapy patients, but any of those treatment groups had superior survival compared to the no-treatment cohort.”
They added that despite better survival among patients treated with biologic agents, no significant improvements were detected in their comorbidity profiles. “Notably, the frequency of major cardiovascular disease (MI, CHF, CVA) was the same as in the controls, and overall, the frequency of diseases coded as cardiovascular was slightly increased,” they wrote.
The fact that some factors could not be measured, including the type and severity of psoriasis, response to treatment, smoking history, and alcohol intake, was a study limitation, they noted.
Joel M. Gelfand, MD, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who was asked to comment on the analysis, said the study confirms prior work indicating that having psoriasis is a predictor of mortality. In addition, “there is a strong healthy user affect among patients who take and stay on biologics for psoriasis,” he told this news organization.
“The results are encouraging but are not able to establish a causal relationship between treating psoriasis with biologics and lowering mortality risk. Ultimately, randomized comparative trials will be needed to determine which approach or approaches to treating psoriasis, if any, lower the risk of psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and mortality,” said Dr. Gelfand, who was not involved with the study.
Asked to comment on the results, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the study, said that “data such as these enable us to rationalize the cost of our fleet of biologics, as managing the outpatient/inpatient burden of many of these comorbidities will actually drain the healthcare system, more so than managing psoriasis in the first place. Certainly other interventions to address the well known comorbidities, such as cardiovascular and hepatic, are warranted, but what if you could prevent the problem in the first place? To be continued for that answer.”
The study was funded by Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Alberta Innovates, and by a Health Sciences TD Bank Studentship Award. Dr. Gniadecki reported conducting clinical trials for Bausch Health, AbbVie and Janssen, and he has received honoraria as consultant and/or speaker from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Kyowa Kirin, Sun Pharma and Sanofi. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies. He is on the board of directors for the International Psoriasis Council and the Medical Dermatology Society. Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a speaker for Janssen and Bristol Myers Squibb. He has received grants from Janssen, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Lilly, and has served as an advisor for Arcutis, Dermavant, and Janssen.
Among patients with psoriasis, the risk of mortality was strongly associated with hepatic injury, cardiovascular disease, and psychiatric affective disorders, but was reduced among those who received systemic therapy with biologics, researchers from Canada report.
Those are key findings from a large retrospective registry study of patients with psoriasis, published in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory condition affecting approximately 3% of the western populations, bears a higher risk of mortality compared to healthy individuals, possibly by inducing systemic inflammation associated with numerous comorbidities, especially cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, and others,” wrote corresponding author Robert Gniadecki, MD, PhD, of the division of dermatology at the University of Alberta, Canada, and colleagues. “It has been argued that the use of systemic immunomodulatory agents quenches systemic inflammation and potentially improves patient survival. However, the evidence to support this hypothesis is limited.”
To investigate the impact of comorbidities and systemic therapies on all-cause mortality in psoriasis, the researchers used the Alberta Health Services Data Repository of Reporting database from January 1, 2012, to June 1, 2019, which represents a population base of 4.47 million individuals. They extracted data on 18,618 psoriasis cases and 55,854 controls, stratified cases according to the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), a surrogate measure for comorbidity burden, and by the type of therapy received, and conducted statistical analyses including Cox proportional hazards regression to determine absolute hazard ratios representing relative effects of specific demographic and comorbidity factors on mortality within groups.
The median age in both cohorts was 48 years, and 51% were male. The researchers observed that mortality in the psoriasis cohort was significantly higher than in the controls (5.7% vs. 3.8%, respectively; P < .05), with a median age at the time of death of 72 vs. 74.4 years.
The CCI and comorbidities strongly predicted mortality, especially drug-induced liver injury (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78), bipolar disorder and suicidal ideation (HR, 1.24-1.58), and major cardiovascular diseases, which included myocardial infarction (MI), congestive heart failure (CHF), and cerebrovascular disease (CVA) (HR, 1.2-1.4).
Among patients in the psoriasis cohort, survival of those treated with biologic agents was higher than in controls, even after matching for CCI (3.2% vs. 4.4%, respectively, P < .05). “These patients also exhibit reduced overall mortality compared to those treated with methotrexate or topical agents,” Dr. Gniadecki and colleagues wrote. “There was no difference in mortality between methotrexate patients and the topical therapy patients, but any of those treatment groups had superior survival compared to the no-treatment cohort.”
They added that despite better survival among patients treated with biologic agents, no significant improvements were detected in their comorbidity profiles. “Notably, the frequency of major cardiovascular disease (MI, CHF, CVA) was the same as in the controls, and overall, the frequency of diseases coded as cardiovascular was slightly increased,” they wrote.
The fact that some factors could not be measured, including the type and severity of psoriasis, response to treatment, smoking history, and alcohol intake, was a study limitation, they noted.
Joel M. Gelfand, MD, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who was asked to comment on the analysis, said the study confirms prior work indicating that having psoriasis is a predictor of mortality. In addition, “there is a strong healthy user affect among patients who take and stay on biologics for psoriasis,” he told this news organization.
“The results are encouraging but are not able to establish a causal relationship between treating psoriasis with biologics and lowering mortality risk. Ultimately, randomized comparative trials will be needed to determine which approach or approaches to treating psoriasis, if any, lower the risk of psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and mortality,” said Dr. Gelfand, who was not involved with the study.
Asked to comment on the results, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the study, said that “data such as these enable us to rationalize the cost of our fleet of biologics, as managing the outpatient/inpatient burden of many of these comorbidities will actually drain the healthcare system, more so than managing psoriasis in the first place. Certainly other interventions to address the well known comorbidities, such as cardiovascular and hepatic, are warranted, but what if you could prevent the problem in the first place? To be continued for that answer.”
The study was funded by Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Alberta Innovates, and by a Health Sciences TD Bank Studentship Award. Dr. Gniadecki reported conducting clinical trials for Bausch Health, AbbVie and Janssen, and he has received honoraria as consultant and/or speaker from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Kyowa Kirin, Sun Pharma and Sanofi. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies. He is on the board of directors for the International Psoriasis Council and the Medical Dermatology Society. Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a speaker for Janssen and Bristol Myers Squibb. He has received grants from Janssen, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Lilly, and has served as an advisor for Arcutis, Dermavant, and Janssen.
Among patients with psoriasis, the risk of mortality was strongly associated with hepatic injury, cardiovascular disease, and psychiatric affective disorders, but was reduced among those who received systemic therapy with biologics, researchers from Canada report.
Those are key findings from a large retrospective registry study of patients with psoriasis, published in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory condition affecting approximately 3% of the western populations, bears a higher risk of mortality compared to healthy individuals, possibly by inducing systemic inflammation associated with numerous comorbidities, especially cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, and others,” wrote corresponding author Robert Gniadecki, MD, PhD, of the division of dermatology at the University of Alberta, Canada, and colleagues. “It has been argued that the use of systemic immunomodulatory agents quenches systemic inflammation and potentially improves patient survival. However, the evidence to support this hypothesis is limited.”
To investigate the impact of comorbidities and systemic therapies on all-cause mortality in psoriasis, the researchers used the Alberta Health Services Data Repository of Reporting database from January 1, 2012, to June 1, 2019, which represents a population base of 4.47 million individuals. They extracted data on 18,618 psoriasis cases and 55,854 controls, stratified cases according to the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), a surrogate measure for comorbidity burden, and by the type of therapy received, and conducted statistical analyses including Cox proportional hazards regression to determine absolute hazard ratios representing relative effects of specific demographic and comorbidity factors on mortality within groups.
The median age in both cohorts was 48 years, and 51% were male. The researchers observed that mortality in the psoriasis cohort was significantly higher than in the controls (5.7% vs. 3.8%, respectively; P < .05), with a median age at the time of death of 72 vs. 74.4 years.
The CCI and comorbidities strongly predicted mortality, especially drug-induced liver injury (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78), bipolar disorder and suicidal ideation (HR, 1.24-1.58), and major cardiovascular diseases, which included myocardial infarction (MI), congestive heart failure (CHF), and cerebrovascular disease (CVA) (HR, 1.2-1.4).
Among patients in the psoriasis cohort, survival of those treated with biologic agents was higher than in controls, even after matching for CCI (3.2% vs. 4.4%, respectively, P < .05). “These patients also exhibit reduced overall mortality compared to those treated with methotrexate or topical agents,” Dr. Gniadecki and colleagues wrote. “There was no difference in mortality between methotrexate patients and the topical therapy patients, but any of those treatment groups had superior survival compared to the no-treatment cohort.”
They added that despite better survival among patients treated with biologic agents, no significant improvements were detected in their comorbidity profiles. “Notably, the frequency of major cardiovascular disease (MI, CHF, CVA) was the same as in the controls, and overall, the frequency of diseases coded as cardiovascular was slightly increased,” they wrote.
The fact that some factors could not be measured, including the type and severity of psoriasis, response to treatment, smoking history, and alcohol intake, was a study limitation, they noted.
Joel M. Gelfand, MD, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who was asked to comment on the analysis, said the study confirms prior work indicating that having psoriasis is a predictor of mortality. In addition, “there is a strong healthy user affect among patients who take and stay on biologics for psoriasis,” he told this news organization.
“The results are encouraging but are not able to establish a causal relationship between treating psoriasis with biologics and lowering mortality risk. Ultimately, randomized comparative trials will be needed to determine which approach or approaches to treating psoriasis, if any, lower the risk of psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and mortality,” said Dr. Gelfand, who was not involved with the study.
Asked to comment on the results, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the study, said that “data such as these enable us to rationalize the cost of our fleet of biologics, as managing the outpatient/inpatient burden of many of these comorbidities will actually drain the healthcare system, more so than managing psoriasis in the first place. Certainly other interventions to address the well known comorbidities, such as cardiovascular and hepatic, are warranted, but what if you could prevent the problem in the first place? To be continued for that answer.”
The study was funded by Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Alberta Innovates, and by a Health Sciences TD Bank Studentship Award. Dr. Gniadecki reported conducting clinical trials for Bausch Health, AbbVie and Janssen, and he has received honoraria as consultant and/or speaker from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Kyowa Kirin, Sun Pharma and Sanofi. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies. He is on the board of directors for the International Psoriasis Council and the Medical Dermatology Society. Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a speaker for Janssen and Bristol Myers Squibb. He has received grants from Janssen, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Lilly, and has served as an advisor for Arcutis, Dermavant, and Janssen.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Autoimmune Disease Risk May Rise Following Cushing Disease Remission After Surgery
Patients with Cushing disease have an increased risk for new-onset autoimmune disease in the 3 years after surgical remission, according to a new retrospective study published on February 20 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Outcomes for patients with Cushing disease were compared against those with nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas (NFPAs). New-onset autoimmune disease occurred in 10.4% with Cushing disease and 1.6% among patients with NFPA (hazard ratio, 7.80; 95% CI, 2.88-21.10).
“Understanding and recognizing new and recurrent autoimmune disease in this setting is important to avoid misclassifying such patients with glucocorticoid withdrawal syndrome, which could result in failure to treat underlying autoimmune disease, as well as erroneous diagnosis of steroid withdrawal cases,” wrote Dennis Delasi Nyanyo of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
Given the general population’s annual incidence of major autoimmune diseases, estimated at about 100 cases per 100,000 people, and the 3-year incidence of 10.4% found in this study’s cohort, “our findings suggest that Cushing disease remission may trigger development of autoimmune disease,” the authors wrote.
Monitor Patients With Family History of Autoimmune Disease?
The study results were not necessarily surprising to Anthony P. Heaney, MD, PhD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, because past research has raised similar questions. The authors’ suggestion that the rapid postsurgical drop in cortisol that occurs as a result of treating Cushing disease becomes some sort of autoimmune trigger is interesting but remains speculative, Dr. Heaney pointed out.
If future evidence supports that possibility, “it would suggest, in terms of managing those patients in the postoperative setting, that there may be some merit to giving them higher concentrations of glucocorticoids for a short period of time,” Dr. Heaney said, thereby bringing their levels down more gradually rather than taking them off a cliff, in a sense. Or, if more evidence bears out the authors’ hypothesis, another approach might be treating patients with medicine to bring down the cortisol before surgery, though there are challenges to that approach, Dr. Heaney said.
At the same time, those who developed new autoimmune disease remain a small subset of patients with Cushing disease, so such approaches may become only potentially appropriate to consider in patients with risk factors, such as a family history of autoimmune disease.
The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of adult patients who underwent transsphenoidal surgery for either Cushing disease or NFPA at Massachusetts General Hospital between 2005 and 2019.
The study involved 194 patients with Cushing disease who had postsurgical remission and at least one follow-up visit with a pituitary expert and 92 patients with NFPA who were matched to patients with Cushing disease based on age and sex. The authors regarded autoimmune disease diagnosed within 36 months of the surgery to be temporally associated with Cushing disease remission. Among the autoimmune diseases considered were “rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, autoimmune thyroiditis, celiac disease, psoriasis, vitiligo, autoimmune neuropathy, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, and ulcerative colitis.”
Patients differed in average body mass index and tumor size, but family history of autoimmune disease was similar in both groups. Average BMI was 34.5 in the Cushing group and 29.5 in the NFPA group. Average tumor size was 5.7 mm in the Cushing group and 21.3 mm in the NFPA group.
Before surgery, 2.9% of patients with Cushing disease and 15.4% of patients with NFPA had central hypothyroidism, and 8% in the Cushing group and 56.8% in the NFPA group had hyperprolactinemia. Central adrenal insufficiency occurred in 11% with NFPA and in all with Cushing disease, by definition.
After surgery, 93.8% in the Cushing group and 16.5% in the NFPA group had adrenal insufficiency. In addition, patients with Cushing disease had lower postsurgical nadir serum cortisol levels (63.8 nmol/L) than those with NFPA (282.3 nmol/L).
Of the 17 patients with Cushing disease — all women — who developed autoimmune disease within 3 years, 6 had a personal history of autoimmune disease and 7 had a family history of it. In addition, 41.2% of them had adrenal insufficiency when they developed the new autoimmune disease. Among the diseases were six autoimmune thyroiditis cases, three Sjögren syndrome cases, and two autoimmune seronegative spondyloarthropathy.
Dr. Heaney said he found it interesting that more than half of the new autoimmune diseases in patients with Cushing disease were related to the thyroid. “In this kind of setting, where you have a patient who has been producing too much steroid over a period of time and then you take that away, it’s almost like you release a brake on the TSH [thyroid-stimulating hormone],” Dr. Heaney said. “So, there’s probably some rebound in TSH that occurs, and that could be driving the thyroiditis, to some extent, that we see in these patients.”
Only one patient with NFPA developed new-onset autoimmune disease, a woman who developed Graves disease 22 months after surgery. When the researchers excluded patients in both groups with central hypothyroidism, new-onset autoimmune disease was still significantly higher (11.4%) in the Cushing group than in the NFPA group (1.9%; HR, 7.02; 95% CI, 2.54-19.39).
Could Postoperative Adrenal Insufficiency Contribute to Risk?
Within the Cushing cohort, those who developed autoimmune disease had a lower BMI (31.8 vs 34.8) and larger tumor size (7.2 vs 5.6 mm) than those who didn’t develop new autoimmune disease. Patients who developed autoimmune disease also had a lower baseline urine free cortisol ratio (2.7 vs 6.3) before surgery and more family history of autoimmune disease (41.2% vs 20.9%) than those who didn’t develop one.
“The higher prevalence of adrenal insufficiency and the lower nadir serum cortisol levels in the Cushing disease group suggest that the postoperative adrenal insufficiency in the Cushing disease group might have contributed to autoimmune disease pathogenesis,” the authors wrote. “This finding is clinically significant because cortisol plays a pivotal role in modulating the immune system.”
Most postoperative management among patients with Cushing disease was similar, with all but one patient receiving 0.5 or 1 mg daily dexamethasone within the first week after surgery. (The one outlier received 5 mg daily prednisone.) However, fewer patients who developed autoimmune disease (17.6%) received supraphysiologic doses of glucocorticoid — equivalent to at least 25 mg hydrocortisone — compared with patients who didn’t develop autoimmune disease (41.8%).
“Although the daily average hydrocortisone equivalent replacement doses within the first month and during long-term follow-up were within the physiologic range in both subgroups, patients with Cushing disease who had autoimmune disease received slightly lower doses of glucocorticoid replacement within the first month after surgery,” the authors reported. “The immediate postoperative period might be a critical window where supraphysiologic glucocorticoids seem to be protective with regard to development of autoimmune disease,” they wrote, though they acknowledged the study’s retrospective design as a limitation in drawing that conclusion.
At the least, they suggested that new symptoms in patients with Cushing disease, particularly those with a family history of autoimmune disease, should prompt investigation of potential autoimmune disease.
Recordati Rare Diseases funded the study. The research was also conducted with support from Harvard Catalyst (the Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center) as well as financial contributions from Harvard University and its affiliated academic healthcare centers. One author reported holding stocks in Pfizer and Amgen, and another reported receiving consulting fees from Corcept. Dr. Heaney reported receiving institutional grants for trials from Corcept, Ascendis, Crinetics, and Sparrow Pharm; serving on the advisory board for Xeris, Recordati, Corcept, Novo Nordisk, Lundbeck, and Crinetics; and serving as a speaker for Chiesi, Novo Nordisk, and Corcept.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with Cushing disease have an increased risk for new-onset autoimmune disease in the 3 years after surgical remission, according to a new retrospective study published on February 20 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Outcomes for patients with Cushing disease were compared against those with nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas (NFPAs). New-onset autoimmune disease occurred in 10.4% with Cushing disease and 1.6% among patients with NFPA (hazard ratio, 7.80; 95% CI, 2.88-21.10).
“Understanding and recognizing new and recurrent autoimmune disease in this setting is important to avoid misclassifying such patients with glucocorticoid withdrawal syndrome, which could result in failure to treat underlying autoimmune disease, as well as erroneous diagnosis of steroid withdrawal cases,” wrote Dennis Delasi Nyanyo of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
Given the general population’s annual incidence of major autoimmune diseases, estimated at about 100 cases per 100,000 people, and the 3-year incidence of 10.4% found in this study’s cohort, “our findings suggest that Cushing disease remission may trigger development of autoimmune disease,” the authors wrote.
Monitor Patients With Family History of Autoimmune Disease?
The study results were not necessarily surprising to Anthony P. Heaney, MD, PhD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, because past research has raised similar questions. The authors’ suggestion that the rapid postsurgical drop in cortisol that occurs as a result of treating Cushing disease becomes some sort of autoimmune trigger is interesting but remains speculative, Dr. Heaney pointed out.
If future evidence supports that possibility, “it would suggest, in terms of managing those patients in the postoperative setting, that there may be some merit to giving them higher concentrations of glucocorticoids for a short period of time,” Dr. Heaney said, thereby bringing their levels down more gradually rather than taking them off a cliff, in a sense. Or, if more evidence bears out the authors’ hypothesis, another approach might be treating patients with medicine to bring down the cortisol before surgery, though there are challenges to that approach, Dr. Heaney said.
At the same time, those who developed new autoimmune disease remain a small subset of patients with Cushing disease, so such approaches may become only potentially appropriate to consider in patients with risk factors, such as a family history of autoimmune disease.
The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of adult patients who underwent transsphenoidal surgery for either Cushing disease or NFPA at Massachusetts General Hospital between 2005 and 2019.
The study involved 194 patients with Cushing disease who had postsurgical remission and at least one follow-up visit with a pituitary expert and 92 patients with NFPA who were matched to patients with Cushing disease based on age and sex. The authors regarded autoimmune disease diagnosed within 36 months of the surgery to be temporally associated with Cushing disease remission. Among the autoimmune diseases considered were “rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, autoimmune thyroiditis, celiac disease, psoriasis, vitiligo, autoimmune neuropathy, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, and ulcerative colitis.”
Patients differed in average body mass index and tumor size, but family history of autoimmune disease was similar in both groups. Average BMI was 34.5 in the Cushing group and 29.5 in the NFPA group. Average tumor size was 5.7 mm in the Cushing group and 21.3 mm in the NFPA group.
Before surgery, 2.9% of patients with Cushing disease and 15.4% of patients with NFPA had central hypothyroidism, and 8% in the Cushing group and 56.8% in the NFPA group had hyperprolactinemia. Central adrenal insufficiency occurred in 11% with NFPA and in all with Cushing disease, by definition.
After surgery, 93.8% in the Cushing group and 16.5% in the NFPA group had adrenal insufficiency. In addition, patients with Cushing disease had lower postsurgical nadir serum cortisol levels (63.8 nmol/L) than those with NFPA (282.3 nmol/L).
Of the 17 patients with Cushing disease — all women — who developed autoimmune disease within 3 years, 6 had a personal history of autoimmune disease and 7 had a family history of it. In addition, 41.2% of them had adrenal insufficiency when they developed the new autoimmune disease. Among the diseases were six autoimmune thyroiditis cases, three Sjögren syndrome cases, and two autoimmune seronegative spondyloarthropathy.
Dr. Heaney said he found it interesting that more than half of the new autoimmune diseases in patients with Cushing disease were related to the thyroid. “In this kind of setting, where you have a patient who has been producing too much steroid over a period of time and then you take that away, it’s almost like you release a brake on the TSH [thyroid-stimulating hormone],” Dr. Heaney said. “So, there’s probably some rebound in TSH that occurs, and that could be driving the thyroiditis, to some extent, that we see in these patients.”
Only one patient with NFPA developed new-onset autoimmune disease, a woman who developed Graves disease 22 months after surgery. When the researchers excluded patients in both groups with central hypothyroidism, new-onset autoimmune disease was still significantly higher (11.4%) in the Cushing group than in the NFPA group (1.9%; HR, 7.02; 95% CI, 2.54-19.39).
Could Postoperative Adrenal Insufficiency Contribute to Risk?
Within the Cushing cohort, those who developed autoimmune disease had a lower BMI (31.8 vs 34.8) and larger tumor size (7.2 vs 5.6 mm) than those who didn’t develop new autoimmune disease. Patients who developed autoimmune disease also had a lower baseline urine free cortisol ratio (2.7 vs 6.3) before surgery and more family history of autoimmune disease (41.2% vs 20.9%) than those who didn’t develop one.
“The higher prevalence of adrenal insufficiency and the lower nadir serum cortisol levels in the Cushing disease group suggest that the postoperative adrenal insufficiency in the Cushing disease group might have contributed to autoimmune disease pathogenesis,” the authors wrote. “This finding is clinically significant because cortisol plays a pivotal role in modulating the immune system.”
Most postoperative management among patients with Cushing disease was similar, with all but one patient receiving 0.5 or 1 mg daily dexamethasone within the first week after surgery. (The one outlier received 5 mg daily prednisone.) However, fewer patients who developed autoimmune disease (17.6%) received supraphysiologic doses of glucocorticoid — equivalent to at least 25 mg hydrocortisone — compared with patients who didn’t develop autoimmune disease (41.8%).
“Although the daily average hydrocortisone equivalent replacement doses within the first month and during long-term follow-up were within the physiologic range in both subgroups, patients with Cushing disease who had autoimmune disease received slightly lower doses of glucocorticoid replacement within the first month after surgery,” the authors reported. “The immediate postoperative period might be a critical window where supraphysiologic glucocorticoids seem to be protective with regard to development of autoimmune disease,” they wrote, though they acknowledged the study’s retrospective design as a limitation in drawing that conclusion.
At the least, they suggested that new symptoms in patients with Cushing disease, particularly those with a family history of autoimmune disease, should prompt investigation of potential autoimmune disease.
Recordati Rare Diseases funded the study. The research was also conducted with support from Harvard Catalyst (the Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center) as well as financial contributions from Harvard University and its affiliated academic healthcare centers. One author reported holding stocks in Pfizer and Amgen, and another reported receiving consulting fees from Corcept. Dr. Heaney reported receiving institutional grants for trials from Corcept, Ascendis, Crinetics, and Sparrow Pharm; serving on the advisory board for Xeris, Recordati, Corcept, Novo Nordisk, Lundbeck, and Crinetics; and serving as a speaker for Chiesi, Novo Nordisk, and Corcept.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with Cushing disease have an increased risk for new-onset autoimmune disease in the 3 years after surgical remission, according to a new retrospective study published on February 20 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Outcomes for patients with Cushing disease were compared against those with nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas (NFPAs). New-onset autoimmune disease occurred in 10.4% with Cushing disease and 1.6% among patients with NFPA (hazard ratio, 7.80; 95% CI, 2.88-21.10).
“Understanding and recognizing new and recurrent autoimmune disease in this setting is important to avoid misclassifying such patients with glucocorticoid withdrawal syndrome, which could result in failure to treat underlying autoimmune disease, as well as erroneous diagnosis of steroid withdrawal cases,” wrote Dennis Delasi Nyanyo of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
Given the general population’s annual incidence of major autoimmune diseases, estimated at about 100 cases per 100,000 people, and the 3-year incidence of 10.4% found in this study’s cohort, “our findings suggest that Cushing disease remission may trigger development of autoimmune disease,” the authors wrote.
Monitor Patients With Family History of Autoimmune Disease?
The study results were not necessarily surprising to Anthony P. Heaney, MD, PhD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, because past research has raised similar questions. The authors’ suggestion that the rapid postsurgical drop in cortisol that occurs as a result of treating Cushing disease becomes some sort of autoimmune trigger is interesting but remains speculative, Dr. Heaney pointed out.
If future evidence supports that possibility, “it would suggest, in terms of managing those patients in the postoperative setting, that there may be some merit to giving them higher concentrations of glucocorticoids for a short period of time,” Dr. Heaney said, thereby bringing their levels down more gradually rather than taking them off a cliff, in a sense. Or, if more evidence bears out the authors’ hypothesis, another approach might be treating patients with medicine to bring down the cortisol before surgery, though there are challenges to that approach, Dr. Heaney said.
At the same time, those who developed new autoimmune disease remain a small subset of patients with Cushing disease, so such approaches may become only potentially appropriate to consider in patients with risk factors, such as a family history of autoimmune disease.
The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of adult patients who underwent transsphenoidal surgery for either Cushing disease or NFPA at Massachusetts General Hospital between 2005 and 2019.
The study involved 194 patients with Cushing disease who had postsurgical remission and at least one follow-up visit with a pituitary expert and 92 patients with NFPA who were matched to patients with Cushing disease based on age and sex. The authors regarded autoimmune disease diagnosed within 36 months of the surgery to be temporally associated with Cushing disease remission. Among the autoimmune diseases considered were “rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, autoimmune thyroiditis, celiac disease, psoriasis, vitiligo, autoimmune neuropathy, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, and ulcerative colitis.”
Patients differed in average body mass index and tumor size, but family history of autoimmune disease was similar in both groups. Average BMI was 34.5 in the Cushing group and 29.5 in the NFPA group. Average tumor size was 5.7 mm in the Cushing group and 21.3 mm in the NFPA group.
Before surgery, 2.9% of patients with Cushing disease and 15.4% of patients with NFPA had central hypothyroidism, and 8% in the Cushing group and 56.8% in the NFPA group had hyperprolactinemia. Central adrenal insufficiency occurred in 11% with NFPA and in all with Cushing disease, by definition.
After surgery, 93.8% in the Cushing group and 16.5% in the NFPA group had adrenal insufficiency. In addition, patients with Cushing disease had lower postsurgical nadir serum cortisol levels (63.8 nmol/L) than those with NFPA (282.3 nmol/L).
Of the 17 patients with Cushing disease — all women — who developed autoimmune disease within 3 years, 6 had a personal history of autoimmune disease and 7 had a family history of it. In addition, 41.2% of them had adrenal insufficiency when they developed the new autoimmune disease. Among the diseases were six autoimmune thyroiditis cases, three Sjögren syndrome cases, and two autoimmune seronegative spondyloarthropathy.
Dr. Heaney said he found it interesting that more than half of the new autoimmune diseases in patients with Cushing disease were related to the thyroid. “In this kind of setting, where you have a patient who has been producing too much steroid over a period of time and then you take that away, it’s almost like you release a brake on the TSH [thyroid-stimulating hormone],” Dr. Heaney said. “So, there’s probably some rebound in TSH that occurs, and that could be driving the thyroiditis, to some extent, that we see in these patients.”
Only one patient with NFPA developed new-onset autoimmune disease, a woman who developed Graves disease 22 months after surgery. When the researchers excluded patients in both groups with central hypothyroidism, new-onset autoimmune disease was still significantly higher (11.4%) in the Cushing group than in the NFPA group (1.9%; HR, 7.02; 95% CI, 2.54-19.39).
Could Postoperative Adrenal Insufficiency Contribute to Risk?
Within the Cushing cohort, those who developed autoimmune disease had a lower BMI (31.8 vs 34.8) and larger tumor size (7.2 vs 5.6 mm) than those who didn’t develop new autoimmune disease. Patients who developed autoimmune disease also had a lower baseline urine free cortisol ratio (2.7 vs 6.3) before surgery and more family history of autoimmune disease (41.2% vs 20.9%) than those who didn’t develop one.
“The higher prevalence of adrenal insufficiency and the lower nadir serum cortisol levels in the Cushing disease group suggest that the postoperative adrenal insufficiency in the Cushing disease group might have contributed to autoimmune disease pathogenesis,” the authors wrote. “This finding is clinically significant because cortisol plays a pivotal role in modulating the immune system.”
Most postoperative management among patients with Cushing disease was similar, with all but one patient receiving 0.5 or 1 mg daily dexamethasone within the first week after surgery. (The one outlier received 5 mg daily prednisone.) However, fewer patients who developed autoimmune disease (17.6%) received supraphysiologic doses of glucocorticoid — equivalent to at least 25 mg hydrocortisone — compared with patients who didn’t develop autoimmune disease (41.8%).
“Although the daily average hydrocortisone equivalent replacement doses within the first month and during long-term follow-up were within the physiologic range in both subgroups, patients with Cushing disease who had autoimmune disease received slightly lower doses of glucocorticoid replacement within the first month after surgery,” the authors reported. “The immediate postoperative period might be a critical window where supraphysiologic glucocorticoids seem to be protective with regard to development of autoimmune disease,” they wrote, though they acknowledged the study’s retrospective design as a limitation in drawing that conclusion.
At the least, they suggested that new symptoms in patients with Cushing disease, particularly those with a family history of autoimmune disease, should prompt investigation of potential autoimmune disease.
Recordati Rare Diseases funded the study. The research was also conducted with support from Harvard Catalyst (the Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center) as well as financial contributions from Harvard University and its affiliated academic healthcare centers. One author reported holding stocks in Pfizer and Amgen, and another reported receiving consulting fees from Corcept. Dr. Heaney reported receiving institutional grants for trials from Corcept, Ascendis, Crinetics, and Sparrow Pharm; serving on the advisory board for Xeris, Recordati, Corcept, Novo Nordisk, Lundbeck, and Crinetics; and serving as a speaker for Chiesi, Novo Nordisk, and Corcept.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
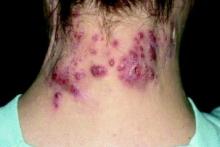
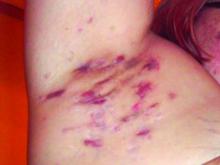
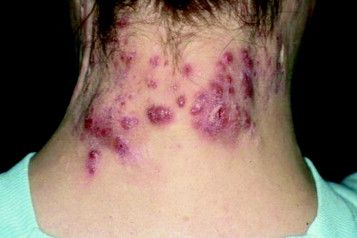
Study Eyes Longer IV Ertapenem for Recalcitrant Hidradenitis Suppurativa
at the completion of treatment, a retrospective study showed.
“These findings suggest a course of 12 to 16 weeks of ertapenem may be appropriate as a new standard length of therapy in HS patients, which is at least twice the current recommendation of the North American treatment guidelines,” wrote corresponding author Steven R. Cohen, MD, MPH, of the departments of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine and Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and his coauthors. The results were published online February 14, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
In an earlier study , some of the same researchers evaluated the efficacy of daily IV ertapenem for 6 weeks in seven patients with HS. The patients experienced “notable remediation of disease that was rapidly lost within 1 month of withdrawal.”
Treatment guidelines published in 2019 recommend ertapenem as a highly effective third-line therapy limited to one 6-week course “as rescue therapy or during surgical planning, given the practical barriers to home infusions and concerns about antibiotic resistance” .
For the current analysis, Dr. Cohen and colleagues explored the effects of a longer duration of treatment with ertapenem in this patient population. They retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 98 patients with HS who received care at Albert Einstein College of Medicine’s Montefiore HS Center between 2018 and 2022. Each patient used an elastomeric pump to self-administer 1 g IV ertapenem daily for 12-16 weeks.
Key outcome measures of interest were the HS Physician Global Assessment (PGA) score (a 6-point scale ranging from clear to very severe) and a numerical rating scale (NRS) for pain (an 11-point scale in which a score of 0 indicates no pain and a score of 10 indicates the worst possible pain) and markers of inflammation such as leukocytes, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein (CRP), and interleukin (IL)-6. The researchers measured these outcomes at baseline, the midcourse of IV ertapenem treatment, at the end of the course, and post therapy.
The mean age of the patients was 35.8 years, 62.2% were female, and 60.2% were Black. The mean treatment duration was 13.1 weeks and the mean posttherapy follow-up occurred after a mean of 7.8 weeks.
Between baseline and posttherapy follow-up, the HS PGA scores dropped from a mean of 3.9 to 2.7 and the NRS for pain dropped from 4.2 to 1.8 (P < .001 for both associations). Markers of inflammation also dropped between baseline and post therapy.
Specifically, values for CRP dropped from 5.4 to 2.4 mg/dL; IL-6 dropped from 25.2 to 13.7, and leukocytes dropped from 11.3 to 10.0 (P < .001 for all associations). Among the 76 patients who participated in a follow-up telephone survey, 63 (80.3%) reported medium to high satisfaction with their course of ertapenem, and 69 (90.8%) said they would recommend the treatment to other patients with HS.
The authors noted certain limitations of their study, including its retrospective, single-center design, the lack of a control group, and the fact that the HS-PGA scores at each visit did not meet the threshold of a 2-point decrease that is considered a clinically meaningful in the medical literature.
The definitive mechanism of ertapenem efficacy remains elusive, the authors pointed out. “Although oral antibiotics are generally accepted as a core therapeutic approach to HS, much less is known about the efficacy of IV antibiotics, especially ertapenem, a parenteral carbapenem possessing activity against many gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria, and anaerobic organisms,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Haley B. Naik, MD, MHSc, a dermatologist at the University of California, San Francisco, said that adopting prolonged courses of ertapenem treatment “comes with substantial individual and public health considerations”.
“Even though HS is a noninfectious disease, microbes might play a role in inciting HS immune dysregulation, prompting the inclusion of antimicrobial therapy in treatment regimens. However, broad-spectrum antibiotics for HS are associated with high levels of antibiotic resistance,” she wrote. Prolonged use of ertapenem and other carbapenems in HS treatment “will likely increase antimicrobial resistance, thereby limiting management of both HS and comorbid infections.”
Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, who was asked to comment on the study, said that, despite significant advances in the management of HS over the past decade, there are still patients who do not respond adequately to standard treatments.
For these patients, IV ertapenem can serve as a valuable bridge to a longer-term therapeutic option, “be it surgery or escalated immunomodulation,” such as dual biologic therapy, she said. “In my personal experience, IV ertapenem, which like the authors I also typically use for a 12-week course, delivers impressive and fast results even in the worst disease cases.
“It can be difficult to maintain the therapeutic benefit of ertapenem after it is discontinued, which is why patients should be on concomitant medications as they were in this study and have a post-ertapenem treatment plan in place,” said Dr. Hsiao, who was not involved with the study. “Hopefully, we will be able to one day understand why ertapenem is so effective for HS and be able to harness that benefit for patients without concern for antimicrobial resistance.”
Dr. Cohen reported receiving personal fees from Verrica Pharmaceuticals and belonging to the Board of Trustees of the American Skin Association outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Naik reported having received grants from AbbVie and the National Institutes of Health; personal fees from Novartis, UCB, Boehringer Ingelheim, 23andMe, Aristea Therapeutics, Medscape, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, DAVA Oncology, and Pfizer; and shares from Radera during the conduct of the study. She is a board member of the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, UCB, as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, and UCB, and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
at the completion of treatment, a retrospective study showed.
“These findings suggest a course of 12 to 16 weeks of ertapenem may be appropriate as a new standard length of therapy in HS patients, which is at least twice the current recommendation of the North American treatment guidelines,” wrote corresponding author Steven R. Cohen, MD, MPH, of the departments of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine and Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and his coauthors. The results were published online February 14, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
In an earlier study , some of the same researchers evaluated the efficacy of daily IV ertapenem for 6 weeks in seven patients with HS. The patients experienced “notable remediation of disease that was rapidly lost within 1 month of withdrawal.”
Treatment guidelines published in 2019 recommend ertapenem as a highly effective third-line therapy limited to one 6-week course “as rescue therapy or during surgical planning, given the practical barriers to home infusions and concerns about antibiotic resistance” .
For the current analysis, Dr. Cohen and colleagues explored the effects of a longer duration of treatment with ertapenem in this patient population. They retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 98 patients with HS who received care at Albert Einstein College of Medicine’s Montefiore HS Center between 2018 and 2022. Each patient used an elastomeric pump to self-administer 1 g IV ertapenem daily for 12-16 weeks.
Key outcome measures of interest were the HS Physician Global Assessment (PGA) score (a 6-point scale ranging from clear to very severe) and a numerical rating scale (NRS) for pain (an 11-point scale in which a score of 0 indicates no pain and a score of 10 indicates the worst possible pain) and markers of inflammation such as leukocytes, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein (CRP), and interleukin (IL)-6. The researchers measured these outcomes at baseline, the midcourse of IV ertapenem treatment, at the end of the course, and post therapy.
The mean age of the patients was 35.8 years, 62.2% were female, and 60.2% were Black. The mean treatment duration was 13.1 weeks and the mean posttherapy follow-up occurred after a mean of 7.8 weeks.
Between baseline and posttherapy follow-up, the HS PGA scores dropped from a mean of 3.9 to 2.7 and the NRS for pain dropped from 4.2 to 1.8 (P < .001 for both associations). Markers of inflammation also dropped between baseline and post therapy.
Specifically, values for CRP dropped from 5.4 to 2.4 mg/dL; IL-6 dropped from 25.2 to 13.7, and leukocytes dropped from 11.3 to 10.0 (P < .001 for all associations). Among the 76 patients who participated in a follow-up telephone survey, 63 (80.3%) reported medium to high satisfaction with their course of ertapenem, and 69 (90.8%) said they would recommend the treatment to other patients with HS.
The authors noted certain limitations of their study, including its retrospective, single-center design, the lack of a control group, and the fact that the HS-PGA scores at each visit did not meet the threshold of a 2-point decrease that is considered a clinically meaningful in the medical literature.
The definitive mechanism of ertapenem efficacy remains elusive, the authors pointed out. “Although oral antibiotics are generally accepted as a core therapeutic approach to HS, much less is known about the efficacy of IV antibiotics, especially ertapenem, a parenteral carbapenem possessing activity against many gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria, and anaerobic organisms,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Haley B. Naik, MD, MHSc, a dermatologist at the University of California, San Francisco, said that adopting prolonged courses of ertapenem treatment “comes with substantial individual and public health considerations”.
“Even though HS is a noninfectious disease, microbes might play a role in inciting HS immune dysregulation, prompting the inclusion of antimicrobial therapy in treatment regimens. However, broad-spectrum antibiotics for HS are associated with high levels of antibiotic resistance,” she wrote. Prolonged use of ertapenem and other carbapenems in HS treatment “will likely increase antimicrobial resistance, thereby limiting management of both HS and comorbid infections.”
Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, who was asked to comment on the study, said that, despite significant advances in the management of HS over the past decade, there are still patients who do not respond adequately to standard treatments.
For these patients, IV ertapenem can serve as a valuable bridge to a longer-term therapeutic option, “be it surgery or escalated immunomodulation,” such as dual biologic therapy, she said. “In my personal experience, IV ertapenem, which like the authors I also typically use for a 12-week course, delivers impressive and fast results even in the worst disease cases.
“It can be difficult to maintain the therapeutic benefit of ertapenem after it is discontinued, which is why patients should be on concomitant medications as they were in this study and have a post-ertapenem treatment plan in place,” said Dr. Hsiao, who was not involved with the study. “Hopefully, we will be able to one day understand why ertapenem is so effective for HS and be able to harness that benefit for patients without concern for antimicrobial resistance.”
Dr. Cohen reported receiving personal fees from Verrica Pharmaceuticals and belonging to the Board of Trustees of the American Skin Association outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Naik reported having received grants from AbbVie and the National Institutes of Health; personal fees from Novartis, UCB, Boehringer Ingelheim, 23andMe, Aristea Therapeutics, Medscape, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, DAVA Oncology, and Pfizer; and shares from Radera during the conduct of the study. She is a board member of the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, UCB, as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, and UCB, and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
at the completion of treatment, a retrospective study showed.
“These findings suggest a course of 12 to 16 weeks of ertapenem may be appropriate as a new standard length of therapy in HS patients, which is at least twice the current recommendation of the North American treatment guidelines,” wrote corresponding author Steven R. Cohen, MD, MPH, of the departments of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine and Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and his coauthors. The results were published online February 14, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
In an earlier study , some of the same researchers evaluated the efficacy of daily IV ertapenem for 6 weeks in seven patients with HS. The patients experienced “notable remediation of disease that was rapidly lost within 1 month of withdrawal.”
Treatment guidelines published in 2019 recommend ertapenem as a highly effective third-line therapy limited to one 6-week course “as rescue therapy or during surgical planning, given the practical barriers to home infusions and concerns about antibiotic resistance” .
For the current analysis, Dr. Cohen and colleagues explored the effects of a longer duration of treatment with ertapenem in this patient population. They retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 98 patients with HS who received care at Albert Einstein College of Medicine’s Montefiore HS Center between 2018 and 2022. Each patient used an elastomeric pump to self-administer 1 g IV ertapenem daily for 12-16 weeks.
Key outcome measures of interest were the HS Physician Global Assessment (PGA) score (a 6-point scale ranging from clear to very severe) and a numerical rating scale (NRS) for pain (an 11-point scale in which a score of 0 indicates no pain and a score of 10 indicates the worst possible pain) and markers of inflammation such as leukocytes, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein (CRP), and interleukin (IL)-6. The researchers measured these outcomes at baseline, the midcourse of IV ertapenem treatment, at the end of the course, and post therapy.
The mean age of the patients was 35.8 years, 62.2% were female, and 60.2% were Black. The mean treatment duration was 13.1 weeks and the mean posttherapy follow-up occurred after a mean of 7.8 weeks.
Between baseline and posttherapy follow-up, the HS PGA scores dropped from a mean of 3.9 to 2.7 and the NRS for pain dropped from 4.2 to 1.8 (P < .001 for both associations). Markers of inflammation also dropped between baseline and post therapy.
Specifically, values for CRP dropped from 5.4 to 2.4 mg/dL; IL-6 dropped from 25.2 to 13.7, and leukocytes dropped from 11.3 to 10.0 (P < .001 for all associations). Among the 76 patients who participated in a follow-up telephone survey, 63 (80.3%) reported medium to high satisfaction with their course of ertapenem, and 69 (90.8%) said they would recommend the treatment to other patients with HS.
The authors noted certain limitations of their study, including its retrospective, single-center design, the lack of a control group, and the fact that the HS-PGA scores at each visit did not meet the threshold of a 2-point decrease that is considered a clinically meaningful in the medical literature.
The definitive mechanism of ertapenem efficacy remains elusive, the authors pointed out. “Although oral antibiotics are generally accepted as a core therapeutic approach to HS, much less is known about the efficacy of IV antibiotics, especially ertapenem, a parenteral carbapenem possessing activity against many gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria, and anaerobic organisms,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Haley B. Naik, MD, MHSc, a dermatologist at the University of California, San Francisco, said that adopting prolonged courses of ertapenem treatment “comes with substantial individual and public health considerations”.
“Even though HS is a noninfectious disease, microbes might play a role in inciting HS immune dysregulation, prompting the inclusion of antimicrobial therapy in treatment regimens. However, broad-spectrum antibiotics for HS are associated with high levels of antibiotic resistance,” she wrote. Prolonged use of ertapenem and other carbapenems in HS treatment “will likely increase antimicrobial resistance, thereby limiting management of both HS and comorbid infections.”
Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, who was asked to comment on the study, said that, despite significant advances in the management of HS over the past decade, there are still patients who do not respond adequately to standard treatments.
For these patients, IV ertapenem can serve as a valuable bridge to a longer-term therapeutic option, “be it surgery or escalated immunomodulation,” such as dual biologic therapy, she said. “In my personal experience, IV ertapenem, which like the authors I also typically use for a 12-week course, delivers impressive and fast results even in the worst disease cases.
“It can be difficult to maintain the therapeutic benefit of ertapenem after it is discontinued, which is why patients should be on concomitant medications as they were in this study and have a post-ertapenem treatment plan in place,” said Dr. Hsiao, who was not involved with the study. “Hopefully, we will be able to one day understand why ertapenem is so effective for HS and be able to harness that benefit for patients without concern for antimicrobial resistance.”
Dr. Cohen reported receiving personal fees from Verrica Pharmaceuticals and belonging to the Board of Trustees of the American Skin Association outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Naik reported having received grants from AbbVie and the National Institutes of Health; personal fees from Novartis, UCB, Boehringer Ingelheim, 23andMe, Aristea Therapeutics, Medscape, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, DAVA Oncology, and Pfizer; and shares from Radera during the conduct of the study. She is a board member of the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, UCB, as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, and UCB, and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Updated Clinical Guidelines for the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris
In January 2024, the American Academy of Dermatology released updated clinical guidelines for the treatment of acne. These guidelines include 18 evidence-based recommendations.
As primary care physicians, we commonly encounter acne vulgaris in our practices. While it may not be a life-threatening condition, it deeply affects the quality of life for many who suffer from it. It can be accompanied by stigmatization and bullying and can affect a person’s self-esteem; it can lead to suicidal ideation. It is important to treat it and know when to refer to a dermatologist.
According to the AAD, acne is the most common skin condition, affecting 50 million Americans annually. It can occur at any stage in life, often starting during puberty. It is so common that at least 85% of people between the ages of 12 and 24 experience at least mild acne.
The guidelines stress using multimodal therapies combining multiple mechanisms of action. For example, they show strong evidence for using topical retinoids with topical benzoyl peroxide or topical retinoids with topical antibiotics. They recommend against using oral antibiotics, except in severe cases, to prevent antibiotic resistance. The strongest evidence regarding antibiotics shows doxycycline or minocycline to be the most effective for treating acne and these can be combined with topical medications.
These guidelines also include isotretinoin to be used for severe acne patients, who are defined as “patients with psychosocial burden or scarring.” They recommend monitoring liver function and lipids as good practice and mandatory pregnancy prevention. These guidelines find no conclusive evidence for physical modalities such as lesion extraction, chemical peels, use of laser and light-based devices, microneedling, use of radiofrequency devices, and photodynamic therapy.
A conditional recommendation is given for the use of combined oral contraception pills and spironolactone. The AAD advises considering the risks of these agents along with other conditions present that they may be useful for.
In primary care, we see many complicated patients and often acne is not considered a serious condition. However, it can be as life-altering to the patient as other chronic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. We need to know the appropriate management of acne and start following the evidence-based guidelines. Acne needs follow-up as close as for other chronic diseases. We need to be able to assess the severity of disease and the effectiveness of treatments we have prescribed.
Some patients may be embarrassed to start the discussion about acne. If the patient doesn’t initiate the discussion, we should in an empathetic way. Acne is one of those diseases that doesn’t need any diagnostic tests to discover as it is readily apparent right in front of us.
Some patients may not be bothered by it, but for others, it may be ruining their lives, and they just don’t feel comfortable starting the conversation. Offering them a treatment will alleviate their disease but may also change their lives for the better.
Acne is also one of those conditions that has a host of misinformation and myths surrounding it. These myths range from dietary recommendations to hygiene and many others. As physicians, we need to educate ourselves about these myths and misconceptions. Patients will have questions regarding them and we need to be able to give them answers to their questions. We also shouldn’t give out misinformation ourselves. The evidence around acne treatment is readily available.
Given the availability of multiple acne therapies, shared-decision making is important. We need to discuss options with the patients and devise the best treatment regimen for them. If our therapies are not getting the results we would like, we need to consider referring the patient to a dermatologist.
We need to remember that acne is not just a cosmetic disease. It affects the lives of those suffering from it and we need to address it like any other chronic disease.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J.
In January 2024, the American Academy of Dermatology released updated clinical guidelines for the treatment of acne. These guidelines include 18 evidence-based recommendations.
As primary care physicians, we commonly encounter acne vulgaris in our practices. While it may not be a life-threatening condition, it deeply affects the quality of life for many who suffer from it. It can be accompanied by stigmatization and bullying and can affect a person’s self-esteem; it can lead to suicidal ideation. It is important to treat it and know when to refer to a dermatologist.
According to the AAD, acne is the most common skin condition, affecting 50 million Americans annually. It can occur at any stage in life, often starting during puberty. It is so common that at least 85% of people between the ages of 12 and 24 experience at least mild acne.
The guidelines stress using multimodal therapies combining multiple mechanisms of action. For example, they show strong evidence for using topical retinoids with topical benzoyl peroxide or topical retinoids with topical antibiotics. They recommend against using oral antibiotics, except in severe cases, to prevent antibiotic resistance. The strongest evidence regarding antibiotics shows doxycycline or minocycline to be the most effective for treating acne and these can be combined with topical medications.
These guidelines also include isotretinoin to be used for severe acne patients, who are defined as “patients with psychosocial burden or scarring.” They recommend monitoring liver function and lipids as good practice and mandatory pregnancy prevention. These guidelines find no conclusive evidence for physical modalities such as lesion extraction, chemical peels, use of laser and light-based devices, microneedling, use of radiofrequency devices, and photodynamic therapy.
A conditional recommendation is given for the use of combined oral contraception pills and spironolactone. The AAD advises considering the risks of these agents along with other conditions present that they may be useful for.
In primary care, we see many complicated patients and often acne is not considered a serious condition. However, it can be as life-altering to the patient as other chronic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. We need to know the appropriate management of acne and start following the evidence-based guidelines. Acne needs follow-up as close as for other chronic diseases. We need to be able to assess the severity of disease and the effectiveness of treatments we have prescribed.
Some patients may be embarrassed to start the discussion about acne. If the patient doesn’t initiate the discussion, we should in an empathetic way. Acne is one of those diseases that doesn’t need any diagnostic tests to discover as it is readily apparent right in front of us.
Some patients may not be bothered by it, but for others, it may be ruining their lives, and they just don’t feel comfortable starting the conversation. Offering them a treatment will alleviate their disease but may also change their lives for the better.
Acne is also one of those conditions that has a host of misinformation and myths surrounding it. These myths range from dietary recommendations to hygiene and many others. As physicians, we need to educate ourselves about these myths and misconceptions. Patients will have questions regarding them and we need to be able to give them answers to their questions. We also shouldn’t give out misinformation ourselves. The evidence around acne treatment is readily available.
Given the availability of multiple acne therapies, shared-decision making is important. We need to discuss options with the patients and devise the best treatment regimen for them. If our therapies are not getting the results we would like, we need to consider referring the patient to a dermatologist.
We need to remember that acne is not just a cosmetic disease. It affects the lives of those suffering from it and we need to address it like any other chronic disease.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J.
In January 2024, the American Academy of Dermatology released updated clinical guidelines for the treatment of acne. These guidelines include 18 evidence-based recommendations.
As primary care physicians, we commonly encounter acne vulgaris in our practices. While it may not be a life-threatening condition, it deeply affects the quality of life for many who suffer from it. It can be accompanied by stigmatization and bullying and can affect a person’s self-esteem; it can lead to suicidal ideation. It is important to treat it and know when to refer to a dermatologist.
According to the AAD, acne is the most common skin condition, affecting 50 million Americans annually. It can occur at any stage in life, often starting during puberty. It is so common that at least 85% of people between the ages of 12 and 24 experience at least mild acne.
The guidelines stress using multimodal therapies combining multiple mechanisms of action. For example, they show strong evidence for using topical retinoids with topical benzoyl peroxide or topical retinoids with topical antibiotics. They recommend against using oral antibiotics, except in severe cases, to prevent antibiotic resistance. The strongest evidence regarding antibiotics shows doxycycline or minocycline to be the most effective for treating acne and these can be combined with topical medications.
These guidelines also include isotretinoin to be used for severe acne patients, who are defined as “patients with psychosocial burden or scarring.” They recommend monitoring liver function and lipids as good practice and mandatory pregnancy prevention. These guidelines find no conclusive evidence for physical modalities such as lesion extraction, chemical peels, use of laser and light-based devices, microneedling, use of radiofrequency devices, and photodynamic therapy.
A conditional recommendation is given for the use of combined oral contraception pills and spironolactone. The AAD advises considering the risks of these agents along with other conditions present that they may be useful for.
In primary care, we see many complicated patients and often acne is not considered a serious condition. However, it can be as life-altering to the patient as other chronic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. We need to know the appropriate management of acne and start following the evidence-based guidelines. Acne needs follow-up as close as for other chronic diseases. We need to be able to assess the severity of disease and the effectiveness of treatments we have prescribed.
Some patients may be embarrassed to start the discussion about acne. If the patient doesn’t initiate the discussion, we should in an empathetic way. Acne is one of those diseases that doesn’t need any diagnostic tests to discover as it is readily apparent right in front of us.
Some patients may not be bothered by it, but for others, it may be ruining their lives, and they just don’t feel comfortable starting the conversation. Offering them a treatment will alleviate their disease but may also change their lives for the better.
Acne is also one of those conditions that has a host of misinformation and myths surrounding it. These myths range from dietary recommendations to hygiene and many others. As physicians, we need to educate ourselves about these myths and misconceptions. Patients will have questions regarding them and we need to be able to give them answers to their questions. We also shouldn’t give out misinformation ourselves. The evidence around acne treatment is readily available.
Given the availability of multiple acne therapies, shared-decision making is important. We need to discuss options with the patients and devise the best treatment regimen for them. If our therapies are not getting the results we would like, we need to consider referring the patient to a dermatologist.
We need to remember that acne is not just a cosmetic disease. It affects the lives of those suffering from it and we need to address it like any other chronic disease.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J.
What Skin Manifestations Are Associated With Pediatric IBD?
TOPLINE:
Skin conditions burden many children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to the authors of a single-center study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with (CD) or ulcerative (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most common noninfectious dermatologic condition among the 425 children and adolescents was (30.8%), followed by eczema (15.8%) and perianal skin tags (14.6%).
- Angular cheilitis was more common among those with CD than those with UC (7.2% vs 2%, respectively; P = .024) as was keratosis pilaris (6.9% vs 0.7%; P = .003), and perianal skin complications such as skin tags (20.3% vs 4%), fistulas (13.4% vs 2.7%), and abscesses (13.4% vs 2%; P < .001 for all associations).
- Fungal skin infections were more frequently diagnosed in children with UC than those with CD (15.4% vs 8%; P = .017).
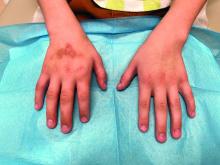
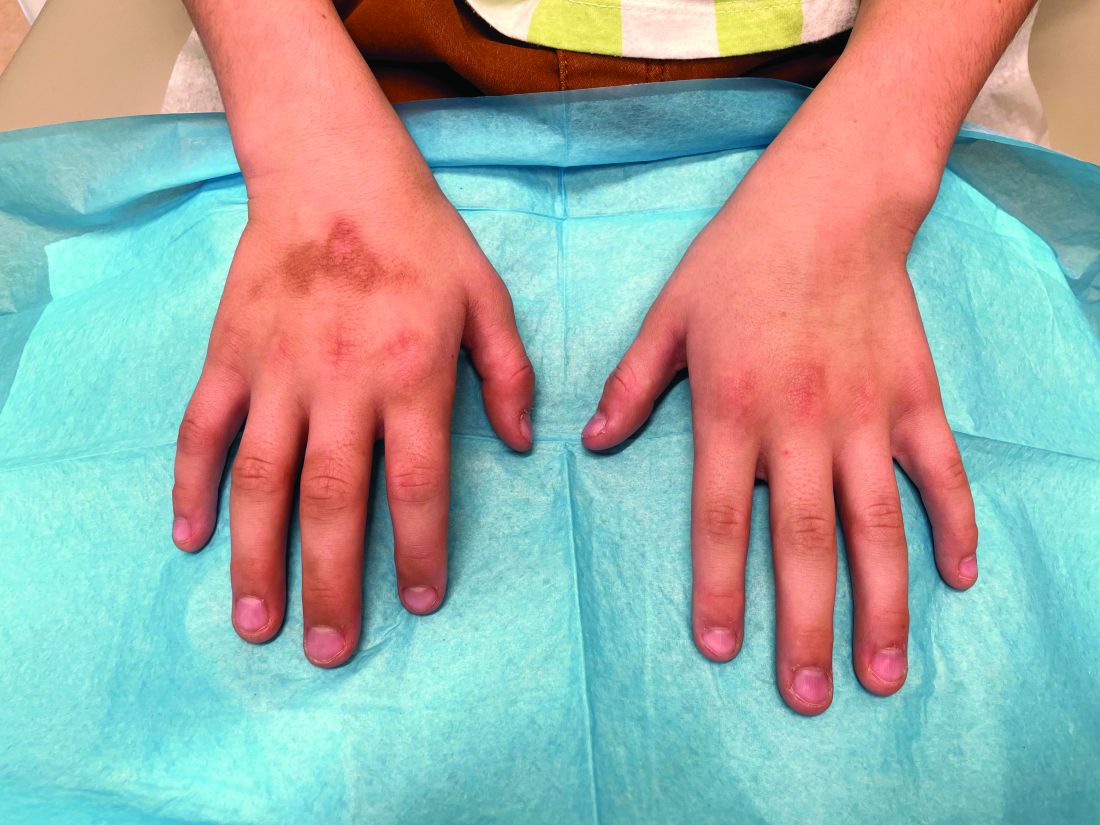
- The researchers observed that the severity of IBD correlated with a higher prevalence of perianal fistula (P = .003), perianal region abscess (P = .041), psoriasis (P < .001), and pyoderma gangrenosum (P = .003).
IN PRACTICE:
“Early identification of common dermatologic conditions in children and adolescents with IBD and recognizing their characteristic associations may alter management and improve skin-related outcomes in this patient population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Megha M. Tollefson, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, and colleagues conducted the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The single-center design and the fact that database studies are subject to extraction error. There was no age- and sex-matched cohort to determine whether the prevalence of cutaneous infections, acne, eczema, and other inflammatory disorders was truly increased in IBD.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Skin conditions burden many children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to the authors of a single-center study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with (CD) or ulcerative (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most common noninfectious dermatologic condition among the 425 children and adolescents was (30.8%), followed by eczema (15.8%) and perianal skin tags (14.6%).
- Angular cheilitis was more common among those with CD than those with UC (7.2% vs 2%, respectively; P = .024) as was keratosis pilaris (6.9% vs 0.7%; P = .003), and perianal skin complications such as skin tags (20.3% vs 4%), fistulas (13.4% vs 2.7%), and abscesses (13.4% vs 2%; P < .001 for all associations).
- Fungal skin infections were more frequently diagnosed in children with UC than those with CD (15.4% vs 8%; P = .017).
- The researchers observed that the severity of IBD correlated with a higher prevalence of perianal fistula (P = .003), perianal region abscess (P = .041), psoriasis (P < .001), and pyoderma gangrenosum (P = .003).
IN PRACTICE:
“Early identification of common dermatologic conditions in children and adolescents with IBD and recognizing their characteristic associations may alter management and improve skin-related outcomes in this patient population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Megha M. Tollefson, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, and colleagues conducted the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The single-center design and the fact that database studies are subject to extraction error. There was no age- and sex-matched cohort to determine whether the prevalence of cutaneous infections, acne, eczema, and other inflammatory disorders was truly increased in IBD.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Skin conditions burden many children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to the authors of a single-center study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with (CD) or ulcerative (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most common noninfectious dermatologic condition among the 425 children and adolescents was (30.8%), followed by eczema (15.8%) and perianal skin tags (14.6%).
- Angular cheilitis was more common among those with CD than those with UC (7.2% vs 2%, respectively; P = .024) as was keratosis pilaris (6.9% vs 0.7%; P = .003), and perianal skin complications such as skin tags (20.3% vs 4%), fistulas (13.4% vs 2.7%), and abscesses (13.4% vs 2%; P < .001 for all associations).
- Fungal skin infections were more frequently diagnosed in children with UC than those with CD (15.4% vs 8%; P = .017).
- The researchers observed that the severity of IBD correlated with a higher prevalence of perianal fistula (P = .003), perianal region abscess (P = .041), psoriasis (P < .001), and pyoderma gangrenosum (P = .003).
IN PRACTICE:
“Early identification of common dermatologic conditions in children and adolescents with IBD and recognizing their characteristic associations may alter management and improve skin-related outcomes in this patient population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Megha M. Tollefson, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, and colleagues conducted the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The single-center design and the fact that database studies are subject to extraction error. There was no age- and sex-matched cohort to determine whether the prevalence of cutaneous infections, acne, eczema, and other inflammatory disorders was truly increased in IBD.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Company Announces Regulatory Filing for Nemolizumab for Two Indications
On February 14, 2024, Galderma announced that .
A first-in-class investigational monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL) IL-31 signaling, nemolizumab has also been granted FDA Priority Review for prurigo nodularis, according to a press release from the company. The European Medicines Agency has also accepted Galderma’s Marketing Authorization Applications for nemolizumab for both prurigo nodularis and atopic dermatitis.
The regulatory developments follow data from the phase III OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in patients with prurigo nodularis (NCT04501679 and NCT04501666). According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a least four-point reduction in itch intensity as measured by the peak-pruritus numerical rating scale (PP-NRS), compared with 17% and 21% in the placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
On February 14, 2024, Galderma announced that .
A first-in-class investigational monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL) IL-31 signaling, nemolizumab has also been granted FDA Priority Review for prurigo nodularis, according to a press release from the company. The European Medicines Agency has also accepted Galderma’s Marketing Authorization Applications for nemolizumab for both prurigo nodularis and atopic dermatitis.
The regulatory developments follow data from the phase III OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in patients with prurigo nodularis (NCT04501679 and NCT04501666). According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a least four-point reduction in itch intensity as measured by the peak-pruritus numerical rating scale (PP-NRS), compared with 17% and 21% in the placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
On February 14, 2024, Galderma announced that .
A first-in-class investigational monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL) IL-31 signaling, nemolizumab has also been granted FDA Priority Review for prurigo nodularis, according to a press release from the company. The European Medicines Agency has also accepted Galderma’s Marketing Authorization Applications for nemolizumab for both prurigo nodularis and atopic dermatitis.
The regulatory developments follow data from the phase III OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in patients with prurigo nodularis (NCT04501679 and NCT04501666). According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a least four-point reduction in itch intensity as measured by the peak-pruritus numerical rating scale (PP-NRS), compared with 17% and 21% in the placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
FDA Approves First Cellular Therapy for Metastatic Melanoma
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved lifileucel (Amtagvi, Iovance Biotherapeutics) for the treatment of certain adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma, marking the first approval of a cellular therapy in the solid tumor setting.
Specifically, the tumor-derived autologous T-cell immunotherapy is indicated for adult patients previously treated with a programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)–blocking antibody, and if BRAF V600–positive, a BRAF inhibitor with or without an MEK inhibitor.
,” Samantha R. Guild, JD, president, AIM at Melanoma Foundation, stated in a press release. “This one-time cell therapy represents a promising innovation for the melanoma community, and we are excited by its potential to transform care for patients who are in dire need of additional therapeutic options.”
The approval was based on findings from the open-label single-arm global C-144-01 clinical trial, which showed an objective response rate of 31.5% in 73 patients treated within the recommended dosing rage of 7.5 x 109 to 72 x 109 viable cells. Complete responses occurred in three patients (4.1%) and partial responses occurred in 20 patients (27.4%)
Median duration of response was not reached at 18.6 months of follow-up. The median time to initial response to the therapy was 1.5 months, according to an FDA press release.
“Unresectable or metastatic melanoma is an aggressive form of cancer that can be fatal,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research stated in the FDA release. “The approval of Amtagvi represents the culmination of scientific and clinical research efforts leading to a novel T cell immunotherapy for patients with limited treatment options.”
“The melanoma community is so grateful to the patients, caregivers, and clinicians who have made the clinical trials of this therapy possible and got lifileucel to approval,” Allison Betof Warner, MD, PhD, director of Melanoma Medical Oncology at Stanford Medicine, wrote on X. “We are very excited to bring this life-saving therapy to patients ASAP! Available immediately at @StanfordCancer!!!”
For the C-144-01 trial, lifileucel was administered after a lymphodepletion regimen of 60 mg/kg/d of cyclophosphamide for 2 days followed by 25 mg/m2/d of fludarabine for 5 days. Between 3 and 34 hours after infusion, patients received 600,000 IU/Kg of the interleukin 2 aldesleukin every 8-12 hours for up to six doses to support cell expansion in vivo.
The full prescribing information for lifileucel contains a boxed warning for treatment-related mortality, prolonged severe cytopenia, severe infection, cardiopulmonary, and renal impairment. The most common adverse reactions, which occurred in at least 20% of patients, were chills, pyrexia, fatigue, tachycardia, diarrhea, febrile neutropenia, edema, rash hypotension, alopecia, infection, hypoxia, and dyspnea.
“Patients receiving this product should be closely monitored before and after infusion for signs and symptoms of adverse reactions. Treatment should be withheld or discontinued in the presence of these symptoms, as indicated,” according to the FDA statement.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved lifileucel (Amtagvi, Iovance Biotherapeutics) for the treatment of certain adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma, marking the first approval of a cellular therapy in the solid tumor setting.
Specifically, the tumor-derived autologous T-cell immunotherapy is indicated for adult patients previously treated with a programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)–blocking antibody, and if BRAF V600–positive, a BRAF inhibitor with or without an MEK inhibitor.
,” Samantha R. Guild, JD, president, AIM at Melanoma Foundation, stated in a press release. “This one-time cell therapy represents a promising innovation for the melanoma community, and we are excited by its potential to transform care for patients who are in dire need of additional therapeutic options.”
The approval was based on findings from the open-label single-arm global C-144-01 clinical trial, which showed an objective response rate of 31.5% in 73 patients treated within the recommended dosing rage of 7.5 x 109 to 72 x 109 viable cells. Complete responses occurred in three patients (4.1%) and partial responses occurred in 20 patients (27.4%)
Median duration of response was not reached at 18.6 months of follow-up. The median time to initial response to the therapy was 1.5 months, according to an FDA press release.
“Unresectable or metastatic melanoma is an aggressive form of cancer that can be fatal,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research stated in the FDA release. “The approval of Amtagvi represents the culmination of scientific and clinical research efforts leading to a novel T cell immunotherapy for patients with limited treatment options.”
“The melanoma community is so grateful to the patients, caregivers, and clinicians who have made the clinical trials of this therapy possible and got lifileucel to approval,” Allison Betof Warner, MD, PhD, director of Melanoma Medical Oncology at Stanford Medicine, wrote on X. “We are very excited to bring this life-saving therapy to patients ASAP! Available immediately at @StanfordCancer!!!”
For the C-144-01 trial, lifileucel was administered after a lymphodepletion regimen of 60 mg/kg/d of cyclophosphamide for 2 days followed by 25 mg/m2/d of fludarabine for 5 days. Between 3 and 34 hours after infusion, patients received 600,000 IU/Kg of the interleukin 2 aldesleukin every 8-12 hours for up to six doses to support cell expansion in vivo.
The full prescribing information for lifileucel contains a boxed warning for treatment-related mortality, prolonged severe cytopenia, severe infection, cardiopulmonary, and renal impairment. The most common adverse reactions, which occurred in at least 20% of patients, were chills, pyrexia, fatigue, tachycardia, diarrhea, febrile neutropenia, edema, rash hypotension, alopecia, infection, hypoxia, and dyspnea.
“Patients receiving this product should be closely monitored before and after infusion for signs and symptoms of adverse reactions. Treatment should be withheld or discontinued in the presence of these symptoms, as indicated,” according to the FDA statement.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved lifileucel (Amtagvi, Iovance Biotherapeutics) for the treatment of certain adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma, marking the first approval of a cellular therapy in the solid tumor setting.
Specifically, the tumor-derived autologous T-cell immunotherapy is indicated for adult patients previously treated with a programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)–blocking antibody, and if BRAF V600–positive, a BRAF inhibitor with or without an MEK inhibitor.
,” Samantha R. Guild, JD, president, AIM at Melanoma Foundation, stated in a press release. “This one-time cell therapy represents a promising innovation for the melanoma community, and we are excited by its potential to transform care for patients who are in dire need of additional therapeutic options.”
The approval was based on findings from the open-label single-arm global C-144-01 clinical trial, which showed an objective response rate of 31.5% in 73 patients treated within the recommended dosing rage of 7.5 x 109 to 72 x 109 viable cells. Complete responses occurred in three patients (4.1%) and partial responses occurred in 20 patients (27.4%)
Median duration of response was not reached at 18.6 months of follow-up. The median time to initial response to the therapy was 1.5 months, according to an FDA press release.
“Unresectable or metastatic melanoma is an aggressive form of cancer that can be fatal,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research stated in the FDA release. “The approval of Amtagvi represents the culmination of scientific and clinical research efforts leading to a novel T cell immunotherapy for patients with limited treatment options.”
“The melanoma community is so grateful to the patients, caregivers, and clinicians who have made the clinical trials of this therapy possible and got lifileucel to approval,” Allison Betof Warner, MD, PhD, director of Melanoma Medical Oncology at Stanford Medicine, wrote on X. “We are very excited to bring this life-saving therapy to patients ASAP! Available immediately at @StanfordCancer!!!”
For the C-144-01 trial, lifileucel was administered after a lymphodepletion regimen of 60 mg/kg/d of cyclophosphamide for 2 days followed by 25 mg/m2/d of fludarabine for 5 days. Between 3 and 34 hours after infusion, patients received 600,000 IU/Kg of the interleukin 2 aldesleukin every 8-12 hours for up to six doses to support cell expansion in vivo.
The full prescribing information for lifileucel contains a boxed warning for treatment-related mortality, prolonged severe cytopenia, severe infection, cardiopulmonary, and renal impairment. The most common adverse reactions, which occurred in at least 20% of patients, were chills, pyrexia, fatigue, tachycardia, diarrhea, febrile neutropenia, edema, rash hypotension, alopecia, infection, hypoxia, and dyspnea.
“Patients receiving this product should be closely monitored before and after infusion for signs and symptoms of adverse reactions. Treatment should be withheld or discontinued in the presence of these symptoms, as indicated,” according to the FDA statement.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An 8-Year-Old Male With Asymptomatic Brown Rough Plaques on the Dorsum of the Right Hand and Fingers, Accompanied by Widening of the Knuckles
During examination, the patient was observed repetitively cracking his knuckles, making a fist with the right hand, placing the left hand on top, and rubbing the hand, a behavior he routinely did multiple times daily. The observed pattern of finger involvement on the dorsum of the right hand corresponded to areas subjected to significant pressure during the described activity. Consequently, a diagnosis of lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) secondary to mechanical rubbing, along with associated pachydermodactyly on the fingers of the right hand, was established.
Lichen simplex chronicus and pachydermodactyly are both attributed to microtrauma inflicted upon the skin. Lichen simplex chronicus often constitutes a diagnosis of exclusion and is characterized by repetitive trauma-induced keratinocyte proliferation and melanocyte activation, resulting in hyperpigmentation and skin thickening. Although typically observed in women between the fourth and fifth decades of life, LSC is rarely reported in children. In adults, LSC-related rubbing or scratching frequently arises from chronic pruritic dermatitis such as eczema or psoriasis, neurodermatitis from dysesthesia, or habitual movements, as exhibited by this young patient. While generally benign, LSC may become infected. In rare instances, malignant transformation may occur.
The association with pachydermodactyly implicates microtrauma, necessitating careful observation and questioning to elucidate the cause, as demonstrated in this case. Lesions are typically hyperpigmented, though cases of associated hypopigmentation or depigmentation have been documented. Affected areas typically fall within the patient’s hand and finger reach, with lesion improvement over several months achievable through trigger avoidance.
Pachydermodactyly, a rare but benign fibromatosis around the proximal interphalangeal joints, is often misdiagnosed as juvenile idiopathic arthritis, potentially leading to unnecessary treatments and patient anxiety. Microtrauma history due to digit manipulation is prevalent among affected individuals, with most also exhibiting neuropsychiatric disorders. Histological examination of pachydermodactyly reveals hypergranulosis and dermal thickening, accompanied by increased fibroblasts and collagen types I, III, and V, differing from the epidermal changes seen in LSC.
The differential diagnosis also included phytophotodermatitis, a phototoxic dermatologic reaction following exposure to ultraviolet light subsequent to contact with furocoumarin-containing plant chemicals. However, the persistence of the patient’s lesions for over a year precluded this diagnosis. Secondary hyperpigmentation was also contemplated but excluded due to the absence of preceding inflammatory dermatitis.
Treatment of LSC primarily involves identifying and addressing any underlying conditions, repairing the skin barrier, reducing inflammation, and modifying behaviors contributing to chronic microtrauma, as observed in this patient. Topical corticosteroids may aid in decreasing epidermal thickening and discoloration, though lesion resolution necessitates behavior cessation.
It’s important to identify these types of skin changes in children to avoid unnecessary medical treatments for these benign conditions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Seier JA, Dissemond J. Lichen Simplex Chronicus Due to Mechanical Irritation. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2022 Nov 18;119(46):802. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2022.0213.
Small S et al. A 12-Year-Old Boy Presenting With Unilateral Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Swelling. BMJ Case Rep. 2011 Apr 13:2011:bcr0120113719. doi: 10.1136/bcr.01.2011.3719.
Voicu C et al Lichen Simplex Chronicus as an Essential Part of the Dermatologic Masquerade. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017 Jul 24;5(4):556-557. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.133.
During examination, the patient was observed repetitively cracking his knuckles, making a fist with the right hand, placing the left hand on top, and rubbing the hand, a behavior he routinely did multiple times daily. The observed pattern of finger involvement on the dorsum of the right hand corresponded to areas subjected to significant pressure during the described activity. Consequently, a diagnosis of lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) secondary to mechanical rubbing, along with associated pachydermodactyly on the fingers of the right hand, was established.
Lichen simplex chronicus and pachydermodactyly are both attributed to microtrauma inflicted upon the skin. Lichen simplex chronicus often constitutes a diagnosis of exclusion and is characterized by repetitive trauma-induced keratinocyte proliferation and melanocyte activation, resulting in hyperpigmentation and skin thickening. Although typically observed in women between the fourth and fifth decades of life, LSC is rarely reported in children. In adults, LSC-related rubbing or scratching frequently arises from chronic pruritic dermatitis such as eczema or psoriasis, neurodermatitis from dysesthesia, or habitual movements, as exhibited by this young patient. While generally benign, LSC may become infected. In rare instances, malignant transformation may occur.
The association with pachydermodactyly implicates microtrauma, necessitating careful observation and questioning to elucidate the cause, as demonstrated in this case. Lesions are typically hyperpigmented, though cases of associated hypopigmentation or depigmentation have been documented. Affected areas typically fall within the patient’s hand and finger reach, with lesion improvement over several months achievable through trigger avoidance.
Pachydermodactyly, a rare but benign fibromatosis around the proximal interphalangeal joints, is often misdiagnosed as juvenile idiopathic arthritis, potentially leading to unnecessary treatments and patient anxiety. Microtrauma history due to digit manipulation is prevalent among affected individuals, with most also exhibiting neuropsychiatric disorders. Histological examination of pachydermodactyly reveals hypergranulosis and dermal thickening, accompanied by increased fibroblasts and collagen types I, III, and V, differing from the epidermal changes seen in LSC.
The differential diagnosis also included phytophotodermatitis, a phototoxic dermatologic reaction following exposure to ultraviolet light subsequent to contact with furocoumarin-containing plant chemicals. However, the persistence of the patient’s lesions for over a year precluded this diagnosis. Secondary hyperpigmentation was also contemplated but excluded due to the absence of preceding inflammatory dermatitis.
Treatment of LSC primarily involves identifying and addressing any underlying conditions, repairing the skin barrier, reducing inflammation, and modifying behaviors contributing to chronic microtrauma, as observed in this patient. Topical corticosteroids may aid in decreasing epidermal thickening and discoloration, though lesion resolution necessitates behavior cessation.
It’s important to identify these types of skin changes in children to avoid unnecessary medical treatments for these benign conditions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Seier JA, Dissemond J. Lichen Simplex Chronicus Due to Mechanical Irritation. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2022 Nov 18;119(46):802. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2022.0213.
Small S et al. A 12-Year-Old Boy Presenting With Unilateral Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Swelling. BMJ Case Rep. 2011 Apr 13:2011:bcr0120113719. doi: 10.1136/bcr.01.2011.3719.
Voicu C et al Lichen Simplex Chronicus as an Essential Part of the Dermatologic Masquerade. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017 Jul 24;5(4):556-557. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.133.
During examination, the patient was observed repetitively cracking his knuckles, making a fist with the right hand, placing the left hand on top, and rubbing the hand, a behavior he routinely did multiple times daily. The observed pattern of finger involvement on the dorsum of the right hand corresponded to areas subjected to significant pressure during the described activity. Consequently, a diagnosis of lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) secondary to mechanical rubbing, along with associated pachydermodactyly on the fingers of the right hand, was established.
Lichen simplex chronicus and pachydermodactyly are both attributed to microtrauma inflicted upon the skin. Lichen simplex chronicus often constitutes a diagnosis of exclusion and is characterized by repetitive trauma-induced keratinocyte proliferation and melanocyte activation, resulting in hyperpigmentation and skin thickening. Although typically observed in women between the fourth and fifth decades of life, LSC is rarely reported in children. In adults, LSC-related rubbing or scratching frequently arises from chronic pruritic dermatitis such as eczema or psoriasis, neurodermatitis from dysesthesia, or habitual movements, as exhibited by this young patient. While generally benign, LSC may become infected. In rare instances, malignant transformation may occur.
The association with pachydermodactyly implicates microtrauma, necessitating careful observation and questioning to elucidate the cause, as demonstrated in this case. Lesions are typically hyperpigmented, though cases of associated hypopigmentation or depigmentation have been documented. Affected areas typically fall within the patient’s hand and finger reach, with lesion improvement over several months achievable through trigger avoidance.
Pachydermodactyly, a rare but benign fibromatosis around the proximal interphalangeal joints, is often misdiagnosed as juvenile idiopathic arthritis, potentially leading to unnecessary treatments and patient anxiety. Microtrauma history due to digit manipulation is prevalent among affected individuals, with most also exhibiting neuropsychiatric disorders. Histological examination of pachydermodactyly reveals hypergranulosis and dermal thickening, accompanied by increased fibroblasts and collagen types I, III, and V, differing from the epidermal changes seen in LSC.
The differential diagnosis also included phytophotodermatitis, a phototoxic dermatologic reaction following exposure to ultraviolet light subsequent to contact with furocoumarin-containing plant chemicals. However, the persistence of the patient’s lesions for over a year precluded this diagnosis. Secondary hyperpigmentation was also contemplated but excluded due to the absence of preceding inflammatory dermatitis.
Treatment of LSC primarily involves identifying and addressing any underlying conditions, repairing the skin barrier, reducing inflammation, and modifying behaviors contributing to chronic microtrauma, as observed in this patient. Topical corticosteroids may aid in decreasing epidermal thickening and discoloration, though lesion resolution necessitates behavior cessation.
It’s important to identify these types of skin changes in children to avoid unnecessary medical treatments for these benign conditions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Seier JA, Dissemond J. Lichen Simplex Chronicus Due to Mechanical Irritation. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2022 Nov 18;119(46):802. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2022.0213.
Small S et al. A 12-Year-Old Boy Presenting With Unilateral Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Swelling. BMJ Case Rep. 2011 Apr 13:2011:bcr0120113719. doi: 10.1136/bcr.01.2011.3719.
Voicu C et al Lichen Simplex Chronicus as an Essential Part of the Dermatologic Masquerade. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017 Jul 24;5(4):556-557. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.133.
The patient was otherwise healthy, with no current medication intake, and he engaged in baseball and soccer activities. Upon physical examination, a hyperpigmented lichenified irregular plaque was observed on the dorsum of the right hand, along with irregular hyperpigmented macules and plaques on the fingers. Fusiform widening of the interphalangeal joints on the second, third, and fourth fingers of the right hand was noted, without associated pain, edema, or erythema.
Lichen Sclerosus: The Silent Genital Health Concern Often Missed
Ashley Winter, MD, remembers the first time she Googled the skin condition lichen sclerosus. Most of the websites listed the autoimmune condition as a rare disease.
In the realm of genital health, some conditions remain shrouded in silence and consequently are more likely to go undercounted and underdiagnosed, said Dr. Winter, a urologist based in Los Angeles.
“I truly believe that we just miss the diagnosis a vast majority of the time because there isn’t enough training on [detecting] it,” said Dr. Winter.
, according to the US National Institutes of Health. The condition also more commonly occurs among women, and symptoms include hypopigmentation, itching, pain, changes in skin appearance, and skin atrophy.
“Most cases [affect the] genital [area] only, so often patients don’t bring it up because they don’t want to be examined,” said Sarah Lonowski, MD, assistant professor of dermatology and codirector of the Multidisciplinary Autoimmune Skin Disease/Derm-Rheum Program at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln. “It’s a sensitive area, it’s an uncomfortable area to have examined, so it comes with a lot of emotional burden,” for patients, Dr. Lonowski said.
Receiving a lichen sclerosis diagnosis can take 5 years or longer, in part because the condition’s symptoms can lead clinicians to first make a diagnosis of a yeast infection or bacterial vaginosis, according to Christina Kraus, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at UCI Health in Irvine, California.
“There is still limited information on this condition in medical education, and it is not uncommon for clinicians who are not in dermatology or gynecology to be unfamiliar with this diagnosis,” Dr. Kraus said.
Because no medical tests are available to confirm lichen sclerosus, clinicians diagnose the condition based on the skin’s appearance and symptoms. In some cases, a skin biopsy may help differentiate it from similar rashes that occur in the genital area.
Prepubescent children and postmenopausal women are most likely to develop genital lichen sclerosis, so pediatricians and primary care physicians may be the first to see possible cases, Dr. Lonowski said.
Patients “may not mention it unless they’re asked,” Dr. Lonowski said, adding clinicians can inquire with patients about genital health, examine bothersome areas, “and refer if you’re not sure.”
Clinicians may also miss the condition during physical exams if they do not examine the vulvar skin, she said. The exact cause also remains elusive, but researchers believe genetic and hormonal factors, as well as an overactive immune response, may contribute to development of the condition.
Watch Out for Presentation
While lichen sclerosus more frequently occurs in women, men are also affected by the condition. Benjamin N. Breyer, MD, professor and chair of urology at the University of California San Francisco, said lichen sclerosus is one of the most common skin conditions he treats in his male patients.
“Advanced cases can cause urethral narrowing, which is a condition I treat commonly,” said Dr. Breyer. “Lichen sclerosus is often an underrecognized cause of pain or tearing with erections and sex in men.”
Similar to women, lichen sclerosus presents as white color changes on the skin. For men, the condition can also result in fusion of the shaft skin to the head of the penis and burying or concealment of the penis, Dr. Breyer said.
“This leads to challenges with intimacy and urination and can have extensive impacts on quality of life,” said Dr. Breyer.
For women, the skin changes often extend to the perianal area and can cause scarring, said Dr. Kraus.
“Early scarring may present as adherence of the labia minora to the labia majora or inability to fully retract the clitoral hood from the clitoris,” said Dr. Kraus.
In both men and women, lichen sclerosus and another autoimmune condition known as morphea, characterized by skin hardening and discoloration, often present together, said Dr. Lonowski.
“If you have a patient with known morphea, it’s important to ask about genital symptoms,” said Dr. Lonowski. “The association between the two is fairly strong.”
Circumcision is often the first step to help prevent chronic inflammation among male patients, said Dr. Breyer. Because lichen sclerosus is associated with an increased risk for penile cancer, “it is important to biopsy suspicious lesions,” Dr. Breyer added.
Increasing awareness of lichen sclerosus is crucial for early detection and timely intervention, said Dr. Lonowski. The first-line treatment of genital lichen sclerosus is strong topical steroid ointments to reduce inflammation. Clinicians might prescribe this treatment for use twice daily for 2-3 months and then assesses the patient on their response.
“It is fairly responsive to treatment in most cases,” said Dr. Lonowski.
Once symptoms have improved, Dr. Lonowski transitions patients to a maintenance regimen, which might include using the same steroid but only three times a week, switching to a topical with a less potent steroid dosage, or using a combination of a topical steroid and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory cream. Despite the prolonged use of the drug, she said patients with lichen sclerosus usually do not present with side effects like discoloration or thinning of skin.
“You may achieve control or remission, but we don’t stop treatment completely because we know the natural history of the disease is to have flares and recurrence.”
If left untreated, the condition can lead to atrophy, scarring, and distortion of the genital anatomy and, in some cases, develop into squamous cell carcinoma.
“The fact that you can do a topical cream intervention and prevent cancer is huge,” said Dr. Winter.
She said open discussions surrounding genital health led by primary care providers can destigmatize conditions like lichen sclerosus and promote early detection and management.
“We need to foster an environment where individuals feel comfortable discussing their symptoms openly,” Dr. Winter said. “Increased awareness can pave the way for early detection, which is crucial for managing the condition effectively.”
The experts included in the story reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Ashley Winter, MD, remembers the first time she Googled the skin condition lichen sclerosus. Most of the websites listed the autoimmune condition as a rare disease.
In the realm of genital health, some conditions remain shrouded in silence and consequently are more likely to go undercounted and underdiagnosed, said Dr. Winter, a urologist based in Los Angeles.
“I truly believe that we just miss the diagnosis a vast majority of the time because there isn’t enough training on [detecting] it,” said Dr. Winter.
, according to the US National Institutes of Health. The condition also more commonly occurs among women, and symptoms include hypopigmentation, itching, pain, changes in skin appearance, and skin atrophy.
“Most cases [affect the] genital [area] only, so often patients don’t bring it up because they don’t want to be examined,” said Sarah Lonowski, MD, assistant professor of dermatology and codirector of the Multidisciplinary Autoimmune Skin Disease/Derm-Rheum Program at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln. “It’s a sensitive area, it’s an uncomfortable area to have examined, so it comes with a lot of emotional burden,” for patients, Dr. Lonowski said.
Receiving a lichen sclerosis diagnosis can take 5 years or longer, in part because the condition’s symptoms can lead clinicians to first make a diagnosis of a yeast infection or bacterial vaginosis, according to Christina Kraus, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at UCI Health in Irvine, California.
“There is still limited information on this condition in medical education, and it is not uncommon for clinicians who are not in dermatology or gynecology to be unfamiliar with this diagnosis,” Dr. Kraus said.
Because no medical tests are available to confirm lichen sclerosus, clinicians diagnose the condition based on the skin’s appearance and symptoms. In some cases, a skin biopsy may help differentiate it from similar rashes that occur in the genital area.
Prepubescent children and postmenopausal women are most likely to develop genital lichen sclerosis, so pediatricians and primary care physicians may be the first to see possible cases, Dr. Lonowski said.
Patients “may not mention it unless they’re asked,” Dr. Lonowski said, adding clinicians can inquire with patients about genital health, examine bothersome areas, “and refer if you’re not sure.”
Clinicians may also miss the condition during physical exams if they do not examine the vulvar skin, she said. The exact cause also remains elusive, but researchers believe genetic and hormonal factors, as well as an overactive immune response, may contribute to development of the condition.
Watch Out for Presentation
While lichen sclerosus more frequently occurs in women, men are also affected by the condition. Benjamin N. Breyer, MD, professor and chair of urology at the University of California San Francisco, said lichen sclerosus is one of the most common skin conditions he treats in his male patients.
“Advanced cases can cause urethral narrowing, which is a condition I treat commonly,” said Dr. Breyer. “Lichen sclerosus is often an underrecognized cause of pain or tearing with erections and sex in men.”
Similar to women, lichen sclerosus presents as white color changes on the skin. For men, the condition can also result in fusion of the shaft skin to the head of the penis and burying or concealment of the penis, Dr. Breyer said.
“This leads to challenges with intimacy and urination and can have extensive impacts on quality of life,” said Dr. Breyer.
For women, the skin changes often extend to the perianal area and can cause scarring, said Dr. Kraus.
“Early scarring may present as adherence of the labia minora to the labia majora or inability to fully retract the clitoral hood from the clitoris,” said Dr. Kraus.
In both men and women, lichen sclerosus and another autoimmune condition known as morphea, characterized by skin hardening and discoloration, often present together, said Dr. Lonowski.
“If you have a patient with known morphea, it’s important to ask about genital symptoms,” said Dr. Lonowski. “The association between the two is fairly strong.”
Circumcision is often the first step to help prevent chronic inflammation among male patients, said Dr. Breyer. Because lichen sclerosus is associated with an increased risk for penile cancer, “it is important to biopsy suspicious lesions,” Dr. Breyer added.
Increasing awareness of lichen sclerosus is crucial for early detection and timely intervention, said Dr. Lonowski. The first-line treatment of genital lichen sclerosus is strong topical steroid ointments to reduce inflammation. Clinicians might prescribe this treatment for use twice daily for 2-3 months and then assesses the patient on their response.
“It is fairly responsive to treatment in most cases,” said Dr. Lonowski.
Once symptoms have improved, Dr. Lonowski transitions patients to a maintenance regimen, which might include using the same steroid but only three times a week, switching to a topical with a less potent steroid dosage, or using a combination of a topical steroid and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory cream. Despite the prolonged use of the drug, she said patients with lichen sclerosus usually do not present with side effects like discoloration or thinning of skin.
“You may achieve control or remission, but we don’t stop treatment completely because we know the natural history of the disease is to have flares and recurrence.”
If left untreated, the condition can lead to atrophy, scarring, and distortion of the genital anatomy and, in some cases, develop into squamous cell carcinoma.
“The fact that you can do a topical cream intervention and prevent cancer is huge,” said Dr. Winter.
She said open discussions surrounding genital health led by primary care providers can destigmatize conditions like lichen sclerosus and promote early detection and management.
“We need to foster an environment where individuals feel comfortable discussing their symptoms openly,” Dr. Winter said. “Increased awareness can pave the way for early detection, which is crucial for managing the condition effectively.”
The experts included in the story reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Ashley Winter, MD, remembers the first time she Googled the skin condition lichen sclerosus. Most of the websites listed the autoimmune condition as a rare disease.
In the realm of genital health, some conditions remain shrouded in silence and consequently are more likely to go undercounted and underdiagnosed, said Dr. Winter, a urologist based in Los Angeles.
“I truly believe that we just miss the diagnosis a vast majority of the time because there isn’t enough training on [detecting] it,” said Dr. Winter.
, according to the US National Institutes of Health. The condition also more commonly occurs among women, and symptoms include hypopigmentation, itching, pain, changes in skin appearance, and skin atrophy.
“Most cases [affect the] genital [area] only, so often patients don’t bring it up because they don’t want to be examined,” said Sarah Lonowski, MD, assistant professor of dermatology and codirector of the Multidisciplinary Autoimmune Skin Disease/Derm-Rheum Program at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln. “It’s a sensitive area, it’s an uncomfortable area to have examined, so it comes with a lot of emotional burden,” for patients, Dr. Lonowski said.
Receiving a lichen sclerosis diagnosis can take 5 years or longer, in part because the condition’s symptoms can lead clinicians to first make a diagnosis of a yeast infection or bacterial vaginosis, according to Christina Kraus, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at UCI Health in Irvine, California.
“There is still limited information on this condition in medical education, and it is not uncommon for clinicians who are not in dermatology or gynecology to be unfamiliar with this diagnosis,” Dr. Kraus said.
Because no medical tests are available to confirm lichen sclerosus, clinicians diagnose the condition based on the skin’s appearance and symptoms. In some cases, a skin biopsy may help differentiate it from similar rashes that occur in the genital area.
Prepubescent children and postmenopausal women are most likely to develop genital lichen sclerosis, so pediatricians and primary care physicians may be the first to see possible cases, Dr. Lonowski said.
Patients “may not mention it unless they’re asked,” Dr. Lonowski said, adding clinicians can inquire with patients about genital health, examine bothersome areas, “and refer if you’re not sure.”
Clinicians may also miss the condition during physical exams if they do not examine the vulvar skin, she said. The exact cause also remains elusive, but researchers believe genetic and hormonal factors, as well as an overactive immune response, may contribute to development of the condition.
Watch Out for Presentation
While lichen sclerosus more frequently occurs in women, men are also affected by the condition. Benjamin N. Breyer, MD, professor and chair of urology at the University of California San Francisco, said lichen sclerosus is one of the most common skin conditions he treats in his male patients.
“Advanced cases can cause urethral narrowing, which is a condition I treat commonly,” said Dr. Breyer. “Lichen sclerosus is often an underrecognized cause of pain or tearing with erections and sex in men.”
Similar to women, lichen sclerosus presents as white color changes on the skin. For men, the condition can also result in fusion of the shaft skin to the head of the penis and burying or concealment of the penis, Dr. Breyer said.
“This leads to challenges with intimacy and urination and can have extensive impacts on quality of life,” said Dr. Breyer.
For women, the skin changes often extend to the perianal area and can cause scarring, said Dr. Kraus.
“Early scarring may present as adherence of the labia minora to the labia majora or inability to fully retract the clitoral hood from the clitoris,” said Dr. Kraus.
In both men and women, lichen sclerosus and another autoimmune condition known as morphea, characterized by skin hardening and discoloration, often present together, said Dr. Lonowski.
“If you have a patient with known morphea, it’s important to ask about genital symptoms,” said Dr. Lonowski. “The association between the two is fairly strong.”
Circumcision is often the first step to help prevent chronic inflammation among male patients, said Dr. Breyer. Because lichen sclerosus is associated with an increased risk for penile cancer, “it is important to biopsy suspicious lesions,” Dr. Breyer added.
Increasing awareness of lichen sclerosus is crucial for early detection and timely intervention, said Dr. Lonowski. The first-line treatment of genital lichen sclerosus is strong topical steroid ointments to reduce inflammation. Clinicians might prescribe this treatment for use twice daily for 2-3 months and then assesses the patient on their response.
“It is fairly responsive to treatment in most cases,” said Dr. Lonowski.
Once symptoms have improved, Dr. Lonowski transitions patients to a maintenance regimen, which might include using the same steroid but only three times a week, switching to a topical with a less potent steroid dosage, or using a combination of a topical steroid and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory cream. Despite the prolonged use of the drug, she said patients with lichen sclerosus usually do not present with side effects like discoloration or thinning of skin.
“You may achieve control or remission, but we don’t stop treatment completely because we know the natural history of the disease is to have flares and recurrence.”
If left untreated, the condition can lead to atrophy, scarring, and distortion of the genital anatomy and, in some cases, develop into squamous cell carcinoma.
“The fact that you can do a topical cream intervention and prevent cancer is huge,” said Dr. Winter.
She said open discussions surrounding genital health led by primary care providers can destigmatize conditions like lichen sclerosus and promote early detection and management.
“We need to foster an environment where individuals feel comfortable discussing their symptoms openly,” Dr. Winter said. “Increased awareness can pave the way for early detection, which is crucial for managing the condition effectively.”
The experts included in the story reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite Good Prognosis, Early Melanoma Sparks Fear of Recurrence
Localized melanoma of the skin is highly curable with surgery, especially when the malignancy is in its early stages. Yet .
These findings come from a study of 51 patients who were treated for stage 0 (melanoma in situ) to stage IIA (Breslow thickness 1.01-2.0 mm without lymph node invasion or metastasis) disease, and who were interviewed about their experiences as survivors and their fear of recurrence.
“Consistent themes and subthemes brought up by participants included anxiety associated with follow-up skin examinations, frequent biopsy procedures attributable to screening intensity, fear of the sun, changes in sun exposure behavior, and increasing thoughts about death. Many of these experiences profoundly affected participants’ lives, despite the favorable prognosis for this group,” wrote Ayisha N. Mahama, MD, MPH, from the Dell Medical School at the University of Texas at Austin, and colleagues, in an article published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Interviews and Inventory
The investigators sought to characterize the psychological well-being of localized melanoma survivors who were treated in their practice. Participants took part in a semistructured interview and the Fear of Cancer Recurrence Inventory short form, with a score of 13 or greater indicating potential cases of clinically significant fear of recurrence.
The mean patient age was 48.5 years, and there were twice as many women as men (34 and 17, respectively). In all, 17 of the patients were treated for stage 0 melanoma, and the remainder were treated for stage I-IIA disease.
The interviews and survey revealed four main “themes” among the patients: anxiety surrounding follow-up appointments and relief after a normal examination; concerns about intensity of melanoma surveillance, including anxiety or reassurance about frequent biopsies and worries regarding familial melanoma risk; lifestyle changes related to sun exposure, such as limiting time outdoors, using sunscreen, and wearing protective clothing; and thoughts about life and death.
On the Fear of Cancer Recurrence Inventory short form, 38 of the 51 participants (75%) had a score of 13 or more points, indicating clinically significant fear of cancer recurrence, and when a higher threshold of 16 or more points were was applied, 34 participants (67%) still met the definition for clinically significant fear of recurrence.
Inform, Reassure, Counsel
“Given the crucial role that dermatologists play in diagnosing melanomas, there may be an opportunity to provide reassurance and support for patients to mitigate the psychological consequences of the diagnosis, by emphasizing the excellent life expectancy at a localized stage, particularly at stage 0. In addition, a referral to a mental health practitioner could be placed for patients with higher levels of anxiety and fear of recurrence,” Dr. Mahama and her coauthors wrote.
They also noted that their findings suggest that some individuals who undergo screening for melanoma might experience “psychological harms” from receiving a melanoma diagnosis “particularly given that many or most screening-detected early-stage melanomas will not progress.”
In an interview seeking objective commentary, a surgical oncologist who was not involved in the study said that anxiety about recurrence is common among patients with melanoma, many of whom may be unfamiliar with significant recent advances such as immunotherapy in the care of patients with more advanced disease.
“Often what we will do in addition to just sharing statistics, which are historical and don’t even necessarily reflect how much better we can do for patients now if the melanoma does recur or metastasize, is recommend close surveillance by their dermatologist,” said Sonia Cohen, MD, PhD, from the Mass General Cancer Center in Boston.
“The earlier we capture a recurrence the better we can help the patients. So that’s something we’ll recommend for patients to help give them a sense of control, and that they’re doing everything they can to capture current or new skin cancers,” she said.
Dr. Cohen and colleagues also instruct patients how to look for potential signs of recurrence, such as swollen lymph nodes or suspicious lesions. Patients who express extreme anxiety may also be referred to an oncology social worker or other support services, she said.
Also asked to comment on the results, Allison Dibiaso MSW, LICSW, a social worker at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts, who specializes in melanoma, said that she often sees patients who have been successfully treated for early localized malignant melanoma who experience a fear of recurrence. “These patients frequently express feelings of uncertainty and worry, with the fear of another occurrence always on their mind. Managing this fear on a day-to-day basis can be challenging,” she told this news organization.
Moreover, patients with previous treatment for melanoma often experience significant anxiety before skin exams. “Some may feel anxious and worried a few days or weeks before their appointment wondering if something will reoccur and be discovered during the examination,” she said. “While some individuals develop coping skills to manage their anxiety beforehand, many still feel anxious about the possibility of recurrence until after the exam is over and results are confirmed.”
At Dana-Farber, patients with completely resected lesions are provided with individual counseling and have access to support groups specifically designed for patients with melanoma. In addition, a caregiver group is also available for those supporting patients with melanoma, and, “if needed, we provide referrals to therapists in their local community,” Ms. Dibiaso said.
The study was supported by awards/grants to senior author Adewole S. Adamson, MD, MPP from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Dermatology Foundation, National Institutes of Health, and the American Cancer Society. All authors reported having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Cohen had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. Ms. Dibiaso had no relevant conflicts to disclose.
Localized melanoma of the skin is highly curable with surgery, especially when the malignancy is in its early stages. Yet .
These findings come from a study of 51 patients who were treated for stage 0 (melanoma in situ) to stage IIA (Breslow thickness 1.01-2.0 mm without lymph node invasion or metastasis) disease, and who were interviewed about their experiences as survivors and their fear of recurrence.
“Consistent themes and subthemes brought up by participants included anxiety associated with follow-up skin examinations, frequent biopsy procedures attributable to screening intensity, fear of the sun, changes in sun exposure behavior, and increasing thoughts about death. Many of these experiences profoundly affected participants’ lives, despite the favorable prognosis for this group,” wrote Ayisha N. Mahama, MD, MPH, from the Dell Medical School at the University of Texas at Austin, and colleagues, in an article published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Interviews and Inventory
The investigators sought to characterize the psychological well-being of localized melanoma survivors who were treated in their practice. Participants took part in a semistructured interview and the Fear of Cancer Recurrence Inventory short form, with a score of 13 or greater indicating potential cases of clinically significant fear of recurrence.
The mean patient age was 48.5 years, and there were twice as many women as men (34 and 17, respectively). In all, 17 of the patients were treated for stage 0 melanoma, and the remainder were treated for stage I-IIA disease.
The interviews and survey revealed four main “themes” among the patients: anxiety surrounding follow-up appointments and relief after a normal examination; concerns about intensity of melanoma surveillance, including anxiety or reassurance about frequent biopsies and worries regarding familial melanoma risk; lifestyle changes related to sun exposure, such as limiting time outdoors, using sunscreen, and wearing protective clothing; and thoughts about life and death.
On the Fear of Cancer Recurrence Inventory short form, 38 of the 51 participants (75%) had a score of 13 or more points, indicating clinically significant fear of cancer recurrence, and when a higher threshold of 16 or more points were was applied, 34 participants (67%) still met the definition for clinically significant fear of recurrence.
Inform, Reassure, Counsel
“Given the crucial role that dermatologists play in diagnosing melanomas, there may be an opportunity to provide reassurance and support for patients to mitigate the psychological consequences of the diagnosis, by emphasizing the excellent life expectancy at a localized stage, particularly at stage 0. In addition, a referral to a mental health practitioner could be placed for patients with higher levels of anxiety and fear of recurrence,” Dr. Mahama and her coauthors wrote.
They also noted that their findings suggest that some individuals who undergo screening for melanoma might experience “psychological harms” from receiving a melanoma diagnosis “particularly given that many or most screening-detected early-stage melanomas will not progress.”
In an interview seeking objective commentary, a surgical oncologist who was not involved in the study said that anxiety about recurrence is common among patients with melanoma, many of whom may be unfamiliar with significant recent advances such as immunotherapy in the care of patients with more advanced disease.
“Often what we will do in addition to just sharing statistics, which are historical and don’t even necessarily reflect how much better we can do for patients now if the melanoma does recur or metastasize, is recommend close surveillance by their dermatologist,” said Sonia Cohen, MD, PhD, from the Mass General Cancer Center in Boston.
“The earlier we capture a recurrence the better we can help the patients. So that’s something we’ll recommend for patients to help give them a sense of control, and that they’re doing everything they can to capture current or new skin cancers,” she said.
Dr. Cohen and colleagues also instruct patients how to look for potential signs of recurrence, such as swollen lymph nodes or suspicious lesions. Patients who express extreme anxiety may also be referred to an oncology social worker or other support services, she said.
Also asked to comment on the results, Allison Dibiaso MSW, LICSW, a social worker at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts, who specializes in melanoma, said that she often sees patients who have been successfully treated for early localized malignant melanoma who experience a fear of recurrence. “These patients frequently express feelings of uncertainty and worry, with the fear of another occurrence always on their mind. Managing this fear on a day-to-day basis can be challenging,” she told this news organization.
Moreover, patients with previous treatment for melanoma often experience significant anxiety before skin exams. “Some may feel anxious and worried a few days or weeks before their appointment wondering if something will reoccur and be discovered during the examination,” she said. “While some individuals develop coping skills to manage their anxiety beforehand, many still feel anxious about the possibility of recurrence until after the exam is over and results are confirmed.”
At Dana-Farber, patients with completely resected lesions are provided with individual counseling and have access to support groups specifically designed for patients with melanoma. In addition, a caregiver group is also available for those supporting patients with melanoma, and, “if needed, we provide referrals to therapists in their local community,” Ms. Dibiaso said.
The study was supported by awards/grants to senior author Adewole S. Adamson, MD, MPP from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Dermatology Foundation, National Institutes of Health, and the American Cancer Society. All authors reported having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Cohen had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. Ms. Dibiaso had no relevant conflicts to disclose.
Localized melanoma of the skin is highly curable with surgery, especially when the malignancy is in its early stages. Yet .
These findings come from a study of 51 patients who were treated for stage 0 (melanoma in situ) to stage IIA (Breslow thickness 1.01-2.0 mm without lymph node invasion or metastasis) disease, and who were interviewed about their experiences as survivors and their fear of recurrence.
“Consistent themes and subthemes brought up by participants included anxiety associated with follow-up skin examinations, frequent biopsy procedures attributable to screening intensity, fear of the sun, changes in sun exposure behavior, and increasing thoughts about death. Many of these experiences profoundly affected participants’ lives, despite the favorable prognosis for this group,” wrote Ayisha N. Mahama, MD, MPH, from the Dell Medical School at the University of Texas at Austin, and colleagues, in an article published online in JAMA Dermatology.
Interviews and Inventory
The investigators sought to characterize the psychological well-being of localized melanoma survivors who were treated in their practice. Participants took part in a semistructured interview and the Fear of Cancer Recurrence Inventory short form, with a score of 13 or greater indicating potential cases of clinically significant fear of recurrence.
The mean patient age was 48.5 years, and there were twice as many women as men (34 and 17, respectively). In all, 17 of the patients were treated for stage 0 melanoma, and the remainder were treated for stage I-IIA disease.
The interviews and survey revealed four main “themes” among the patients: anxiety surrounding follow-up appointments and relief after a normal examination; concerns about intensity of melanoma surveillance, including anxiety or reassurance about frequent biopsies and worries regarding familial melanoma risk; lifestyle changes related to sun exposure, such as limiting time outdoors, using sunscreen, and wearing protective clothing; and thoughts about life and death.
On the Fear of Cancer Recurrence Inventory short form, 38 of the 51 participants (75%) had a score of 13 or more points, indicating clinically significant fear of cancer recurrence, and when a higher threshold of 16 or more points were was applied, 34 participants (67%) still met the definition for clinically significant fear of recurrence.
Inform, Reassure, Counsel
“Given the crucial role that dermatologists play in diagnosing melanomas, there may be an opportunity to provide reassurance and support for patients to mitigate the psychological consequences of the diagnosis, by emphasizing the excellent life expectancy at a localized stage, particularly at stage 0. In addition, a referral to a mental health practitioner could be placed for patients with higher levels of anxiety and fear of recurrence,” Dr. Mahama and her coauthors wrote.
They also noted that their findings suggest that some individuals who undergo screening for melanoma might experience “psychological harms” from receiving a melanoma diagnosis “particularly given that many or most screening-detected early-stage melanomas will not progress.”
In an interview seeking objective commentary, a surgical oncologist who was not involved in the study said that anxiety about recurrence is common among patients with melanoma, many of whom may be unfamiliar with significant recent advances such as immunotherapy in the care of patients with more advanced disease.
“Often what we will do in addition to just sharing statistics, which are historical and don’t even necessarily reflect how much better we can do for patients now if the melanoma does recur or metastasize, is recommend close surveillance by their dermatologist,” said Sonia Cohen, MD, PhD, from the Mass General Cancer Center in Boston.
“The earlier we capture a recurrence the better we can help the patients. So that’s something we’ll recommend for patients to help give them a sense of control, and that they’re doing everything they can to capture current or new skin cancers,” she said.
Dr. Cohen and colleagues also instruct patients how to look for potential signs of recurrence, such as swollen lymph nodes or suspicious lesions. Patients who express extreme anxiety may also be referred to an oncology social worker or other support services, she said.
Also asked to comment on the results, Allison Dibiaso MSW, LICSW, a social worker at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts, who specializes in melanoma, said that she often sees patients who have been successfully treated for early localized malignant melanoma who experience a fear of recurrence. “These patients frequently express feelings of uncertainty and worry, with the fear of another occurrence always on their mind. Managing this fear on a day-to-day basis can be challenging,” she told this news organization.
Moreover, patients with previous treatment for melanoma often experience significant anxiety before skin exams. “Some may feel anxious and worried a few days or weeks before their appointment wondering if something will reoccur and be discovered during the examination,” she said. “While some individuals develop coping skills to manage their anxiety beforehand, many still feel anxious about the possibility of recurrence until after the exam is over and results are confirmed.”
At Dana-Farber, patients with completely resected lesions are provided with individual counseling and have access to support groups specifically designed for patients with melanoma. In addition, a caregiver group is also available for those supporting patients with melanoma, and, “if needed, we provide referrals to therapists in their local community,” Ms. Dibiaso said.
The study was supported by awards/grants to senior author Adewole S. Adamson, MD, MPP from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Dermatology Foundation, National Institutes of Health, and the American Cancer Society. All authors reported having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Cohen had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. Ms. Dibiaso had no relevant conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY