User login
Mohs surgery in the elderly: The dilemma of when to treat
As increasing numbers of patients in their 80s, 90s, and even 100s present for possible Mohs micrographic surgery, surgeons are confronted with deciding when the risks of treatment may outweigh the benefits.
In one of two presentations at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery that addressed this topic, Howard W. Rogers, MD, of Advanced Dermatology in Norwich, Conn., said that the crux of the issue is the concern not to undertreat. He noted that reduced access to dermatologic care during the pandemic has provided a stark lesson in the risks of delaying treatment in all age groups. “Mohs surgeons have all seen the consequences of delayed treatment due to the pandemic with enormous, destructive, and sometimes fatal cancers coming to the office in the last year,” he told this news organization.
“Pandemic-related treatment delay has caused increased suffering and morbidity for countless skin cancer patients across the U.S.,” he said. “In general, not treating skin cancer and hoping it’s not going to grow or having significant delays in treatment are a recipe for disastrous outcomes.”
That said, active monitoring may be appropriate “for select small cancers that tend to grow slowly in the very elderly,” added Dr. Rogers, the incoming ACMS president. Among the key situations where the benefits of active monitoring may outweigh the risks of surgery are small, slowly growing cancers, when frailty is an issue.
Frailty has been equated to compromised functionality, which can increase the risk of an array of complications, including prolonged wound healing and secondary complications stemming from immobility. The toll those issues can take on patients’ quality of life can be considerable, Dr. Rogers said.
When weighing treatment options with elderly patients, he emphasized that careful consideration should be given to whether the “time needed to benefit from a Mohs procedure is longer than the patient’s life expectancy.” Furthermore, a decision not to treat does not have to be the last word. “We need to have an honest dialogue on the consequences of nontreatment, but part of that should be that just because we don’t treat today, doesn’t mean we can’t treat it tomorrow, if necessary.”
Of note, he added, “more than 100,00 patients have surgery for basal cell carcinoma [BCC] in their last year of life.” And that figure will likely rise exponentially if population projections come to fruition, considering that the population of people over the age of 85 is predicted to increase to nearly 18 million in 2050, from 5.8 million in 2012, Dr. Rogers said.
Until more research emerges on how to best treat this age group, Dr. Rogers noted that experts recommend that for elderly patients, “treatment should be individualized with consideration of active monitoring of primary BCC that is not in the H-zone, asymptomatic, smaller than 1 cm, with treatment initiated if there is substantial growth or symptoms.” Ultimately, he urged surgeons to “be sensitive and treat our patients like ourselves or our family members.”
When appropriate – Mohs is safe in the very elderly
Taking on the issue in a separate presentation, Deborah MacFarlane, MD, professor of dermatology and head and neck surgery at MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said that for skin cancer cases that warrant treatment, clinicians should not let age alone stand in the way of Mohs surgery.
The evidence of its safety in the elderly dates back to a paper published in 1997 that Dr. MacFarlane coauthored, describing Mohs surgery of BCCs, squamous cell cancers (SCCs), and melanomas among 115 patients aged 90 and older (average, 92.4 years) who had an average of 1.9 comorbid medical conditions, and were taking an average of 2.3 medications. “Overall, we had just one complication among the patients,” she said.
In a subsequent paper, Dr. MacFarlane and her colleagues found that age at the time of Mohs surgery, even in older patients, was unrelated to survival, stage of cancer, or the type of repair. “We have concluded that this rapidly growing segment of the population can undergo Mohs surgery and should not be relegated to less effective treatment out of fear of its affecting their survival,” Dr. MacFarlane said.
She agreed with the concern about frailty and hence functionality, which may need to be factored in when making a decision to perform Mohs surgery. “I think this is something we do intuitively anyway,” she added. “We’re going to offer Mohs to someone who we think will survive and who is in relatively good health,” Dr. MacFarlane noted.
The point is illustrated in a new multicenter study of 1,181 patients at 22 U.S. sites, aged 85 years and older with nonmelanoma skin cancer referred for Mohs surgery. In the study, published in JAMA Dermatology after the ACMS meeting, patients who had Mohs surgery were almost four times more likely to have high functional status (P < .001) and were more likely to have facial tumors (P < .001), compared with those who had an alternate surgery.
The main reasons provided by the surgeons for opting to treat with Mohs included a patient’s desire for treatment with a high cure rate (66%), good/excellent patient functional status for age (57%), and a high risk associated with the tumor based on histology (40%), noted Dr. MacFarlane, one of the authors.
She reiterated the point raised by Dr. Rogers that “this is something we’re going to increasingly face,” noting that people over 85 represent the fastest growing segment of the population. “I have more patients over the age of 100 than I’ve ever had before,” she said.
Nevertheless, her own experience with elderly patients speaks to the safety of Mohs surgery in this population: Dr. MacFarlane reported a review of her practice’s records of 171 patients aged 85 years and older between May 2016 and May 2022, who received 414 separate procedures, without a single complication.
Sharing many of Dr. Rogers’ concerns about using caution in at-risk patients, Dr. MacFarlane offered recommendations for the optimal treatment of elderly patients receiving Mohs, including handling tissue delicately, and “keep undermining to a minimum.” She noted that intermediate closures and full thickness skin grafts are ideal closures for the elderly, while flaps may be performed in selected robust skin. It is also important to involve caretakers from the onset, talk and listen to patients – and play their choice of music during treatment, she said.
Commenting on the debate, comoderator Nahid Y. Vidal, MD, of the department of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that the expanding older population is accompanied by increases in skin cancer, in addition to more immunosenescence that is related to development of infections, autoimmune disease, and malignant tumors.
“In our academic practice, as with both the reference speakers, we do frequently see elderly, and not uncommonly the super-elderly,” she told this news organization. “The take-home point for me is to treat your whole patient, not just the tumor,” considering social factors, frailty/spry factor, and preferences, “and to do the humanistic thing, while also remaining evidence based,” she said.
“Don’t assume that increased age translates to morbidity, worse outcomes, or futility of treatment,” she added. “Chances are, if [a patient] made it to 90 years old with only a few medications and few medical problems, they may make it to 100, so why put the patient at risk for metastasis and death from a treatable/curable skin cancer,” in the case of SCC, she said.
“By the same token, why not perform more conservative treatments such as ED&C [electrodesiccation and curettage] for very low-risk skin cancers in low-risk locations, such as a superficial basal cell carcinoma on the trunk?” Overall, instead of trying to determine how long a super-elderly individual will live, Dr. Vidal said that “it’s better to educate the patient, engage in a discussion about goals of care, and to make few assumptions.”
Dr. Rogers, Dr. MacFarlane, and Dr. Vidal report no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As increasing numbers of patients in their 80s, 90s, and even 100s present for possible Mohs micrographic surgery, surgeons are confronted with deciding when the risks of treatment may outweigh the benefits.
In one of two presentations at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery that addressed this topic, Howard W. Rogers, MD, of Advanced Dermatology in Norwich, Conn., said that the crux of the issue is the concern not to undertreat. He noted that reduced access to dermatologic care during the pandemic has provided a stark lesson in the risks of delaying treatment in all age groups. “Mohs surgeons have all seen the consequences of delayed treatment due to the pandemic with enormous, destructive, and sometimes fatal cancers coming to the office in the last year,” he told this news organization.
“Pandemic-related treatment delay has caused increased suffering and morbidity for countless skin cancer patients across the U.S.,” he said. “In general, not treating skin cancer and hoping it’s not going to grow or having significant delays in treatment are a recipe for disastrous outcomes.”
That said, active monitoring may be appropriate “for select small cancers that tend to grow slowly in the very elderly,” added Dr. Rogers, the incoming ACMS president. Among the key situations where the benefits of active monitoring may outweigh the risks of surgery are small, slowly growing cancers, when frailty is an issue.
Frailty has been equated to compromised functionality, which can increase the risk of an array of complications, including prolonged wound healing and secondary complications stemming from immobility. The toll those issues can take on patients’ quality of life can be considerable, Dr. Rogers said.
When weighing treatment options with elderly patients, he emphasized that careful consideration should be given to whether the “time needed to benefit from a Mohs procedure is longer than the patient’s life expectancy.” Furthermore, a decision not to treat does not have to be the last word. “We need to have an honest dialogue on the consequences of nontreatment, but part of that should be that just because we don’t treat today, doesn’t mean we can’t treat it tomorrow, if necessary.”
Of note, he added, “more than 100,00 patients have surgery for basal cell carcinoma [BCC] in their last year of life.” And that figure will likely rise exponentially if population projections come to fruition, considering that the population of people over the age of 85 is predicted to increase to nearly 18 million in 2050, from 5.8 million in 2012, Dr. Rogers said.
Until more research emerges on how to best treat this age group, Dr. Rogers noted that experts recommend that for elderly patients, “treatment should be individualized with consideration of active monitoring of primary BCC that is not in the H-zone, asymptomatic, smaller than 1 cm, with treatment initiated if there is substantial growth or symptoms.” Ultimately, he urged surgeons to “be sensitive and treat our patients like ourselves or our family members.”
When appropriate – Mohs is safe in the very elderly
Taking on the issue in a separate presentation, Deborah MacFarlane, MD, professor of dermatology and head and neck surgery at MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said that for skin cancer cases that warrant treatment, clinicians should not let age alone stand in the way of Mohs surgery.
The evidence of its safety in the elderly dates back to a paper published in 1997 that Dr. MacFarlane coauthored, describing Mohs surgery of BCCs, squamous cell cancers (SCCs), and melanomas among 115 patients aged 90 and older (average, 92.4 years) who had an average of 1.9 comorbid medical conditions, and were taking an average of 2.3 medications. “Overall, we had just one complication among the patients,” she said.
In a subsequent paper, Dr. MacFarlane and her colleagues found that age at the time of Mohs surgery, even in older patients, was unrelated to survival, stage of cancer, or the type of repair. “We have concluded that this rapidly growing segment of the population can undergo Mohs surgery and should not be relegated to less effective treatment out of fear of its affecting their survival,” Dr. MacFarlane said.
She agreed with the concern about frailty and hence functionality, which may need to be factored in when making a decision to perform Mohs surgery. “I think this is something we do intuitively anyway,” she added. “We’re going to offer Mohs to someone who we think will survive and who is in relatively good health,” Dr. MacFarlane noted.
The point is illustrated in a new multicenter study of 1,181 patients at 22 U.S. sites, aged 85 years and older with nonmelanoma skin cancer referred for Mohs surgery. In the study, published in JAMA Dermatology after the ACMS meeting, patients who had Mohs surgery were almost four times more likely to have high functional status (P < .001) and were more likely to have facial tumors (P < .001), compared with those who had an alternate surgery.
The main reasons provided by the surgeons for opting to treat with Mohs included a patient’s desire for treatment with a high cure rate (66%), good/excellent patient functional status for age (57%), and a high risk associated with the tumor based on histology (40%), noted Dr. MacFarlane, one of the authors.
She reiterated the point raised by Dr. Rogers that “this is something we’re going to increasingly face,” noting that people over 85 represent the fastest growing segment of the population. “I have more patients over the age of 100 than I’ve ever had before,” she said.
Nevertheless, her own experience with elderly patients speaks to the safety of Mohs surgery in this population: Dr. MacFarlane reported a review of her practice’s records of 171 patients aged 85 years and older between May 2016 and May 2022, who received 414 separate procedures, without a single complication.
Sharing many of Dr. Rogers’ concerns about using caution in at-risk patients, Dr. MacFarlane offered recommendations for the optimal treatment of elderly patients receiving Mohs, including handling tissue delicately, and “keep undermining to a minimum.” She noted that intermediate closures and full thickness skin grafts are ideal closures for the elderly, while flaps may be performed in selected robust skin. It is also important to involve caretakers from the onset, talk and listen to patients – and play their choice of music during treatment, she said.
Commenting on the debate, comoderator Nahid Y. Vidal, MD, of the department of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that the expanding older population is accompanied by increases in skin cancer, in addition to more immunosenescence that is related to development of infections, autoimmune disease, and malignant tumors.
“In our academic practice, as with both the reference speakers, we do frequently see elderly, and not uncommonly the super-elderly,” she told this news organization. “The take-home point for me is to treat your whole patient, not just the tumor,” considering social factors, frailty/spry factor, and preferences, “and to do the humanistic thing, while also remaining evidence based,” she said.
“Don’t assume that increased age translates to morbidity, worse outcomes, or futility of treatment,” she added. “Chances are, if [a patient] made it to 90 years old with only a few medications and few medical problems, they may make it to 100, so why put the patient at risk for metastasis and death from a treatable/curable skin cancer,” in the case of SCC, she said.
“By the same token, why not perform more conservative treatments such as ED&C [electrodesiccation and curettage] for very low-risk skin cancers in low-risk locations, such as a superficial basal cell carcinoma on the trunk?” Overall, instead of trying to determine how long a super-elderly individual will live, Dr. Vidal said that “it’s better to educate the patient, engage in a discussion about goals of care, and to make few assumptions.”
Dr. Rogers, Dr. MacFarlane, and Dr. Vidal report no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As increasing numbers of patients in their 80s, 90s, and even 100s present for possible Mohs micrographic surgery, surgeons are confronted with deciding when the risks of treatment may outweigh the benefits.
In one of two presentations at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery that addressed this topic, Howard W. Rogers, MD, of Advanced Dermatology in Norwich, Conn., said that the crux of the issue is the concern not to undertreat. He noted that reduced access to dermatologic care during the pandemic has provided a stark lesson in the risks of delaying treatment in all age groups. “Mohs surgeons have all seen the consequences of delayed treatment due to the pandemic with enormous, destructive, and sometimes fatal cancers coming to the office in the last year,” he told this news organization.
“Pandemic-related treatment delay has caused increased suffering and morbidity for countless skin cancer patients across the U.S.,” he said. “In general, not treating skin cancer and hoping it’s not going to grow or having significant delays in treatment are a recipe for disastrous outcomes.”
That said, active monitoring may be appropriate “for select small cancers that tend to grow slowly in the very elderly,” added Dr. Rogers, the incoming ACMS president. Among the key situations where the benefits of active monitoring may outweigh the risks of surgery are small, slowly growing cancers, when frailty is an issue.
Frailty has been equated to compromised functionality, which can increase the risk of an array of complications, including prolonged wound healing and secondary complications stemming from immobility. The toll those issues can take on patients’ quality of life can be considerable, Dr. Rogers said.
When weighing treatment options with elderly patients, he emphasized that careful consideration should be given to whether the “time needed to benefit from a Mohs procedure is longer than the patient’s life expectancy.” Furthermore, a decision not to treat does not have to be the last word. “We need to have an honest dialogue on the consequences of nontreatment, but part of that should be that just because we don’t treat today, doesn’t mean we can’t treat it tomorrow, if necessary.”
Of note, he added, “more than 100,00 patients have surgery for basal cell carcinoma [BCC] in their last year of life.” And that figure will likely rise exponentially if population projections come to fruition, considering that the population of people over the age of 85 is predicted to increase to nearly 18 million in 2050, from 5.8 million in 2012, Dr. Rogers said.
Until more research emerges on how to best treat this age group, Dr. Rogers noted that experts recommend that for elderly patients, “treatment should be individualized with consideration of active monitoring of primary BCC that is not in the H-zone, asymptomatic, smaller than 1 cm, with treatment initiated if there is substantial growth or symptoms.” Ultimately, he urged surgeons to “be sensitive and treat our patients like ourselves or our family members.”
When appropriate – Mohs is safe in the very elderly
Taking on the issue in a separate presentation, Deborah MacFarlane, MD, professor of dermatology and head and neck surgery at MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said that for skin cancer cases that warrant treatment, clinicians should not let age alone stand in the way of Mohs surgery.
The evidence of its safety in the elderly dates back to a paper published in 1997 that Dr. MacFarlane coauthored, describing Mohs surgery of BCCs, squamous cell cancers (SCCs), and melanomas among 115 patients aged 90 and older (average, 92.4 years) who had an average of 1.9 comorbid medical conditions, and were taking an average of 2.3 medications. “Overall, we had just one complication among the patients,” she said.
In a subsequent paper, Dr. MacFarlane and her colleagues found that age at the time of Mohs surgery, even in older patients, was unrelated to survival, stage of cancer, or the type of repair. “We have concluded that this rapidly growing segment of the population can undergo Mohs surgery and should not be relegated to less effective treatment out of fear of its affecting their survival,” Dr. MacFarlane said.
She agreed with the concern about frailty and hence functionality, which may need to be factored in when making a decision to perform Mohs surgery. “I think this is something we do intuitively anyway,” she added. “We’re going to offer Mohs to someone who we think will survive and who is in relatively good health,” Dr. MacFarlane noted.
The point is illustrated in a new multicenter study of 1,181 patients at 22 U.S. sites, aged 85 years and older with nonmelanoma skin cancer referred for Mohs surgery. In the study, published in JAMA Dermatology after the ACMS meeting, patients who had Mohs surgery were almost four times more likely to have high functional status (P < .001) and were more likely to have facial tumors (P < .001), compared with those who had an alternate surgery.
The main reasons provided by the surgeons for opting to treat with Mohs included a patient’s desire for treatment with a high cure rate (66%), good/excellent patient functional status for age (57%), and a high risk associated with the tumor based on histology (40%), noted Dr. MacFarlane, one of the authors.
She reiterated the point raised by Dr. Rogers that “this is something we’re going to increasingly face,” noting that people over 85 represent the fastest growing segment of the population. “I have more patients over the age of 100 than I’ve ever had before,” she said.
Nevertheless, her own experience with elderly patients speaks to the safety of Mohs surgery in this population: Dr. MacFarlane reported a review of her practice’s records of 171 patients aged 85 years and older between May 2016 and May 2022, who received 414 separate procedures, without a single complication.
Sharing many of Dr. Rogers’ concerns about using caution in at-risk patients, Dr. MacFarlane offered recommendations for the optimal treatment of elderly patients receiving Mohs, including handling tissue delicately, and “keep undermining to a minimum.” She noted that intermediate closures and full thickness skin grafts are ideal closures for the elderly, while flaps may be performed in selected robust skin. It is also important to involve caretakers from the onset, talk and listen to patients – and play their choice of music during treatment, she said.
Commenting on the debate, comoderator Nahid Y. Vidal, MD, of the department of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that the expanding older population is accompanied by increases in skin cancer, in addition to more immunosenescence that is related to development of infections, autoimmune disease, and malignant tumors.
“In our academic practice, as with both the reference speakers, we do frequently see elderly, and not uncommonly the super-elderly,” she told this news organization. “The take-home point for me is to treat your whole patient, not just the tumor,” considering social factors, frailty/spry factor, and preferences, “and to do the humanistic thing, while also remaining evidence based,” she said.
“Don’t assume that increased age translates to morbidity, worse outcomes, or futility of treatment,” she added. “Chances are, if [a patient] made it to 90 years old with only a few medications and few medical problems, they may make it to 100, so why put the patient at risk for metastasis and death from a treatable/curable skin cancer,” in the case of SCC, she said.
“By the same token, why not perform more conservative treatments such as ED&C [electrodesiccation and curettage] for very low-risk skin cancers in low-risk locations, such as a superficial basal cell carcinoma on the trunk?” Overall, instead of trying to determine how long a super-elderly individual will live, Dr. Vidal said that “it’s better to educate the patient, engage in a discussion about goals of care, and to make few assumptions.”
Dr. Rogers, Dr. MacFarlane, and Dr. Vidal report no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACMS 2022
Serum brodalumab levels linked with treatment outcomes in patients with psoriasis
In a study of patients with psoriasis who had previously failed treatment with interleukin-17 receptor A inhibitor therapy, “all patients with quantifiable levels of brodalumab after 12 weeks of therapy experienced PASI reductions” and subquantifiable brodalumab levels were associated with a lack of response after 12 weeks, they wrote in JAMA Dermatology.
Lead study author Christian Enevold, PhD, a researcher at the Institute for Inflammation Research at Copenhagen University Hospital, and colleagues monitored patients with plaque psoriasis who had not improved with previous IL-17A inhibitor therapy, to evaluate whether trough levels and antidrug antibodies were associated with clinical response in this group of patients.
The 20 consecutive adult patients were treated at two academic hospital dermatology clinics between 2018 and 2020 and ranged in age from 19 to 66 years; 13 were male. At baseline, their weight ranged from 59 to 182 kg (median, 103 kg), their body mass index (BMI) ranged from 20 to 50 (median, 32), and their Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores ranged from 7 to 26 (median, 13). All had failed treatment with at least one IL-17A inhibitor, and 90% had failed treatment with at least one tumor necrosis factor–alpha or IL-12/-23 inhibitor.
Patients stopped taking systemic psoriasis therapies for 4 weeks before entering the study, then received subcutaneous injections of 210 mg of the IL-17A inhibitor brodalumab (Siliq) at weeks 0, 1, 2, and every 2 weeks thereafter. Patients whose PASI scores did not improve at least 75% from baseline (PASI 75) after 12 weeks of brodalumab discontinued treatment and left the study, while those who maintained PASI 75 were monitored for up to 52 weeks.
The researchers used assays to compare decreases in PASI score with brodalumab levels as well as with antibrodalumab antibodies at 12 weeks, and determined the following:
- Participants with quantifiable brodalumab levels (≥ 0.05 mcg/mL) showed a greater drop in PASI scores (median, 93%; range, 61%-100%) than those without quantifiable brodalumab levels (median, −3; range, −49% to 94%) (P = .006).
- Four of 5 patients (80%) who did not achieve a PASI 75, compared with 3 of 14 PASI 75 responders (21%), had drug levels too low to be measured (< 0.05 mcg/mL).
- The eight patients who did not have obesity (BMI < 30) had PASI reductions of at least 77%, and seven of the eight patients (88%) had quantifiable brodalumab levels.
- Six of the 12 patients with obesity (BMI ≥ 30) had brodalumab levels too low to be measured. Of those, four had increased PASI after 12 weeks of treatment. For all patients with obesity with quantifiable brodalumab levels, PASI scores dropped by at least 61% after 12 weeks.
- Five of the 12 (42%) patients with obesity versus 7 of the 8 (88%) patients without obesity had quantifiable brodalumab levels.
- None of the seven patients (35%) with subquantifiable drug levels after 12 weeks remained PASI responders.
- No antibrodalumab antibodies were detected in any serum samples.
The authors acknowledged that there were limitations of the study, including its retrospective design and restriction to the few available participants with a history of treatment failure.
George Han, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., said in an interview that he found the study interesting. “The authors did an admirable job looking at many factors to try to understand response to treatment in a challenging population of patients who had failed at least one, and in many cases, numerous, biologics from different classes.”
“The most interesting finding is that patients with higher BMIs had much higher rates of low-to-undetectable drug concentration,” said Dr. Han, who was not involved in the study. “This very practical finding could help patient care immediately. While it’s impractical to start performing assays of drug concentration in clinical practice, this finding certainly would guide my conversations with my heavier-set patients who have had multiple failures on previous biologics.
“I’m looking forward to further studies that explore this issue and provide better evidence-based guidance for treating patients who have experienced multi-biologic failure,” he added.
Robert A. Dorschner, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at the UC San Diego Health System, also welcomed the study’s results.
“Current psoriasis treatment is based on trial-and-error application of various biologics targeting different pathways, with initial selection frequently based on insurance preference, not patient characteristics,” he said in an interview.
“Studies like this help clinicians make more informed decisions about whether a patient may benefit from a different dose or may require a different drug, and make those decisions earlier in therapy,” he said. “This can improve patient care and decrease costs associated with prolonged treatments with ineffective drugs.”
But Dr. Dorschner, who also was not involved in the study, cautions clinicians to not draw conclusions about dose adjustments from these results. “These findings need to be verified in a larger cohort,” he advised, “and they should drive future studies with larger cohorts and prospective designs.”
“The last couple of decades have seen an explosion in the availability of biologics targeting different cytokines, with significant benefits to patients,” Dr. Dorschner explained. “However, there is a dearth of information on how to choose the right biologic for a particular patient and how to assess the benefit of dose alteration versus changing the drug target. Medicine needs more studies like this one.”
Several authors of the study report financial relationships with LEO Pharma and other pharmaceutical companies. Most authors, including Dr. Enevold, reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Dorschner reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Han reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies not involved in the study. The study was funded by LEO Pharma and the Danish Biotechnology Program.
In a study of patients with psoriasis who had previously failed treatment with interleukin-17 receptor A inhibitor therapy, “all patients with quantifiable levels of brodalumab after 12 weeks of therapy experienced PASI reductions” and subquantifiable brodalumab levels were associated with a lack of response after 12 weeks, they wrote in JAMA Dermatology.
Lead study author Christian Enevold, PhD, a researcher at the Institute for Inflammation Research at Copenhagen University Hospital, and colleagues monitored patients with plaque psoriasis who had not improved with previous IL-17A inhibitor therapy, to evaluate whether trough levels and antidrug antibodies were associated with clinical response in this group of patients.
The 20 consecutive adult patients were treated at two academic hospital dermatology clinics between 2018 and 2020 and ranged in age from 19 to 66 years; 13 were male. At baseline, their weight ranged from 59 to 182 kg (median, 103 kg), their body mass index (BMI) ranged from 20 to 50 (median, 32), and their Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores ranged from 7 to 26 (median, 13). All had failed treatment with at least one IL-17A inhibitor, and 90% had failed treatment with at least one tumor necrosis factor–alpha or IL-12/-23 inhibitor.
Patients stopped taking systemic psoriasis therapies for 4 weeks before entering the study, then received subcutaneous injections of 210 mg of the IL-17A inhibitor brodalumab (Siliq) at weeks 0, 1, 2, and every 2 weeks thereafter. Patients whose PASI scores did not improve at least 75% from baseline (PASI 75) after 12 weeks of brodalumab discontinued treatment and left the study, while those who maintained PASI 75 were monitored for up to 52 weeks.
The researchers used assays to compare decreases in PASI score with brodalumab levels as well as with antibrodalumab antibodies at 12 weeks, and determined the following:
- Participants with quantifiable brodalumab levels (≥ 0.05 mcg/mL) showed a greater drop in PASI scores (median, 93%; range, 61%-100%) than those without quantifiable brodalumab levels (median, −3; range, −49% to 94%) (P = .006).
- Four of 5 patients (80%) who did not achieve a PASI 75, compared with 3 of 14 PASI 75 responders (21%), had drug levels too low to be measured (< 0.05 mcg/mL).
- The eight patients who did not have obesity (BMI < 30) had PASI reductions of at least 77%, and seven of the eight patients (88%) had quantifiable brodalumab levels.
- Six of the 12 patients with obesity (BMI ≥ 30) had brodalumab levels too low to be measured. Of those, four had increased PASI after 12 weeks of treatment. For all patients with obesity with quantifiable brodalumab levels, PASI scores dropped by at least 61% after 12 weeks.
- Five of the 12 (42%) patients with obesity versus 7 of the 8 (88%) patients without obesity had quantifiable brodalumab levels.
- None of the seven patients (35%) with subquantifiable drug levels after 12 weeks remained PASI responders.
- No antibrodalumab antibodies were detected in any serum samples.
The authors acknowledged that there were limitations of the study, including its retrospective design and restriction to the few available participants with a history of treatment failure.
George Han, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., said in an interview that he found the study interesting. “The authors did an admirable job looking at many factors to try to understand response to treatment in a challenging population of patients who had failed at least one, and in many cases, numerous, biologics from different classes.”
“The most interesting finding is that patients with higher BMIs had much higher rates of low-to-undetectable drug concentration,” said Dr. Han, who was not involved in the study. “This very practical finding could help patient care immediately. While it’s impractical to start performing assays of drug concentration in clinical practice, this finding certainly would guide my conversations with my heavier-set patients who have had multiple failures on previous biologics.
“I’m looking forward to further studies that explore this issue and provide better evidence-based guidance for treating patients who have experienced multi-biologic failure,” he added.
Robert A. Dorschner, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at the UC San Diego Health System, also welcomed the study’s results.
“Current psoriasis treatment is based on trial-and-error application of various biologics targeting different pathways, with initial selection frequently based on insurance preference, not patient characteristics,” he said in an interview.
“Studies like this help clinicians make more informed decisions about whether a patient may benefit from a different dose or may require a different drug, and make those decisions earlier in therapy,” he said. “This can improve patient care and decrease costs associated with prolonged treatments with ineffective drugs.”
But Dr. Dorschner, who also was not involved in the study, cautions clinicians to not draw conclusions about dose adjustments from these results. “These findings need to be verified in a larger cohort,” he advised, “and they should drive future studies with larger cohorts and prospective designs.”
“The last couple of decades have seen an explosion in the availability of biologics targeting different cytokines, with significant benefits to patients,” Dr. Dorschner explained. “However, there is a dearth of information on how to choose the right biologic for a particular patient and how to assess the benefit of dose alteration versus changing the drug target. Medicine needs more studies like this one.”
Several authors of the study report financial relationships with LEO Pharma and other pharmaceutical companies. Most authors, including Dr. Enevold, reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Dorschner reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Han reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies not involved in the study. The study was funded by LEO Pharma and the Danish Biotechnology Program.
In a study of patients with psoriasis who had previously failed treatment with interleukin-17 receptor A inhibitor therapy, “all patients with quantifiable levels of brodalumab after 12 weeks of therapy experienced PASI reductions” and subquantifiable brodalumab levels were associated with a lack of response after 12 weeks, they wrote in JAMA Dermatology.
Lead study author Christian Enevold, PhD, a researcher at the Institute for Inflammation Research at Copenhagen University Hospital, and colleagues monitored patients with plaque psoriasis who had not improved with previous IL-17A inhibitor therapy, to evaluate whether trough levels and antidrug antibodies were associated with clinical response in this group of patients.
The 20 consecutive adult patients were treated at two academic hospital dermatology clinics between 2018 and 2020 and ranged in age from 19 to 66 years; 13 were male. At baseline, their weight ranged from 59 to 182 kg (median, 103 kg), their body mass index (BMI) ranged from 20 to 50 (median, 32), and their Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores ranged from 7 to 26 (median, 13). All had failed treatment with at least one IL-17A inhibitor, and 90% had failed treatment with at least one tumor necrosis factor–alpha or IL-12/-23 inhibitor.
Patients stopped taking systemic psoriasis therapies for 4 weeks before entering the study, then received subcutaneous injections of 210 mg of the IL-17A inhibitor brodalumab (Siliq) at weeks 0, 1, 2, and every 2 weeks thereafter. Patients whose PASI scores did not improve at least 75% from baseline (PASI 75) after 12 weeks of brodalumab discontinued treatment and left the study, while those who maintained PASI 75 were monitored for up to 52 weeks.
The researchers used assays to compare decreases in PASI score with brodalumab levels as well as with antibrodalumab antibodies at 12 weeks, and determined the following:
- Participants with quantifiable brodalumab levels (≥ 0.05 mcg/mL) showed a greater drop in PASI scores (median, 93%; range, 61%-100%) than those without quantifiable brodalumab levels (median, −3; range, −49% to 94%) (P = .006).
- Four of 5 patients (80%) who did not achieve a PASI 75, compared with 3 of 14 PASI 75 responders (21%), had drug levels too low to be measured (< 0.05 mcg/mL).
- The eight patients who did not have obesity (BMI < 30) had PASI reductions of at least 77%, and seven of the eight patients (88%) had quantifiable brodalumab levels.
- Six of the 12 patients with obesity (BMI ≥ 30) had brodalumab levels too low to be measured. Of those, four had increased PASI after 12 weeks of treatment. For all patients with obesity with quantifiable brodalumab levels, PASI scores dropped by at least 61% after 12 weeks.
- Five of the 12 (42%) patients with obesity versus 7 of the 8 (88%) patients without obesity had quantifiable brodalumab levels.
- None of the seven patients (35%) with subquantifiable drug levels after 12 weeks remained PASI responders.
- No antibrodalumab antibodies were detected in any serum samples.
The authors acknowledged that there were limitations of the study, including its retrospective design and restriction to the few available participants with a history of treatment failure.
George Han, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., said in an interview that he found the study interesting. “The authors did an admirable job looking at many factors to try to understand response to treatment in a challenging population of patients who had failed at least one, and in many cases, numerous, biologics from different classes.”
“The most interesting finding is that patients with higher BMIs had much higher rates of low-to-undetectable drug concentration,” said Dr. Han, who was not involved in the study. “This very practical finding could help patient care immediately. While it’s impractical to start performing assays of drug concentration in clinical practice, this finding certainly would guide my conversations with my heavier-set patients who have had multiple failures on previous biologics.
“I’m looking forward to further studies that explore this issue and provide better evidence-based guidance for treating patients who have experienced multi-biologic failure,” he added.
Robert A. Dorschner, MD, assistant professor of dermatology at the UC San Diego Health System, also welcomed the study’s results.
“Current psoriasis treatment is based on trial-and-error application of various biologics targeting different pathways, with initial selection frequently based on insurance preference, not patient characteristics,” he said in an interview.
“Studies like this help clinicians make more informed decisions about whether a patient may benefit from a different dose or may require a different drug, and make those decisions earlier in therapy,” he said. “This can improve patient care and decrease costs associated with prolonged treatments with ineffective drugs.”
But Dr. Dorschner, who also was not involved in the study, cautions clinicians to not draw conclusions about dose adjustments from these results. “These findings need to be verified in a larger cohort,” he advised, “and they should drive future studies with larger cohorts and prospective designs.”
“The last couple of decades have seen an explosion in the availability of biologics targeting different cytokines, with significant benefits to patients,” Dr. Dorschner explained. “However, there is a dearth of information on how to choose the right biologic for a particular patient and how to assess the benefit of dose alteration versus changing the drug target. Medicine needs more studies like this one.”
Several authors of the study report financial relationships with LEO Pharma and other pharmaceutical companies. Most authors, including Dr. Enevold, reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Dorschner reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Han reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies not involved in the study. The study was funded by LEO Pharma and the Danish Biotechnology Program.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
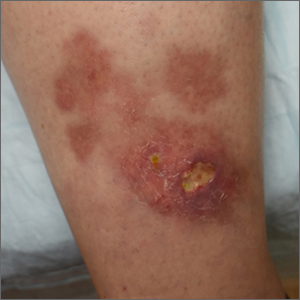
Ulcerated lower leg lesion
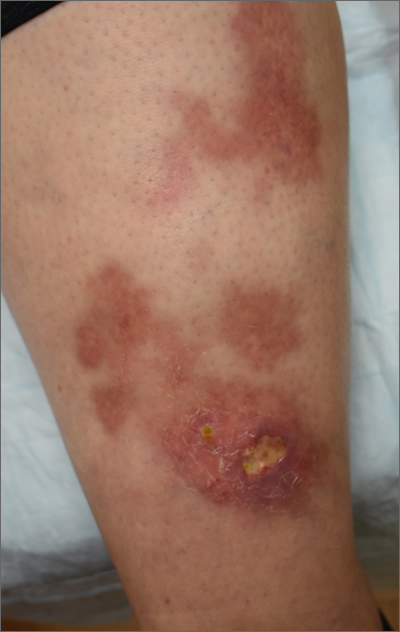
The patient’s atrophic plaques with a violaceous rim, indurated borders, and ulceration on the anterior pretibial surface were consistent with ulcerated necrobiosis lipoidica (NL).
NL typically manifests on the bilateral pretibial region as small papules or nodules that expand into yellow-brown atrophic, telangiectatic plaques with an elevated violaceous rim.1,2 Most lesions are asymptomatic due to nerve damage, but up to 35% of patients may experience pruritus and tenderness.2 Close monitoring of lesions is recommended due to risk of ulceration and potential for malignancy.2 Rare reports show development of squamous cell carcinoma within NL lesions.1
Women are 3 times more likely than men to have NL, with an average age of onset between 30 and 40 years.1 The exact pathogenesis of NL is unknown.2 Theories include vascular abnormalities (immunoglobulin deposition or microangiopathic changes leading to collagen degradation), abnormalities of collagen synthesis, neutrophil migration, and elevated tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels.1,3
While NL can be diagnosed clinically, a skin biopsy may be necessary in atypical lesions. The biopsy will reveal palisading granulomatous inflammation in the dermis, with multinucleated histiocytes palisading around degenerated collagen bundles.2
No treatment has proven to be effective for NL. Glucose control in patients with diabetes does not have a significant effect on the NL lesions.1-3 Corticosteroids (topical, intralesional, and systemic—depending on the severity) are considered first-line therapy.1-3 Lifestyle modifications, such as smoking cessation and trauma avoidance, are recommended to promote healing; proper wound care is important when there is ulceration.1,3 Other treatment options include oral pentoxifylline, topical retinoids or calcineurin inhibitors, and systemic immune system modulators (eg, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and cyclosporine).
Since this patient did not respond to the topical betamethasone, she was started on oral pentoxifylline 400 mg tid. Unfortunately, she had to discontinue the medication because of gastrointestinal upset and was then started on doxycycline 100 mg orally bid. She was lost to follow-up.
Photo courtesy of Cyrelle F. Finan, MD. Text courtesy of Harika Echuri, MD, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, Cyrelle F. Finan, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Lepe K, Riley CA, Salazar FJ. Necrobiosis lipoidica. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated August 26, 2021. Accessed May 31, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459318/
2. Tong LX, Penn L, Meehan SA, Kim RH. Necrobiosis lipoidica. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13030/qt0qg3b3zw. doi: 10.5070/D32412042442
3. Sibbald C, Reid S, Alavi A. Necrobiosis lipoidica. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:343-360. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2015.03.003

The patient’s atrophic plaques with a violaceous rim, indurated borders, and ulceration on the anterior pretibial surface were consistent with ulcerated necrobiosis lipoidica (NL).
NL typically manifests on the bilateral pretibial region as small papules or nodules that expand into yellow-brown atrophic, telangiectatic plaques with an elevated violaceous rim.1,2 Most lesions are asymptomatic due to nerve damage, but up to 35% of patients may experience pruritus and tenderness.2 Close monitoring of lesions is recommended due to risk of ulceration and potential for malignancy.2 Rare reports show development of squamous cell carcinoma within NL lesions.1
Women are 3 times more likely than men to have NL, with an average age of onset between 30 and 40 years.1 The exact pathogenesis of NL is unknown.2 Theories include vascular abnormalities (immunoglobulin deposition or microangiopathic changes leading to collagen degradation), abnormalities of collagen synthesis, neutrophil migration, and elevated tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels.1,3
While NL can be diagnosed clinically, a skin biopsy may be necessary in atypical lesions. The biopsy will reveal palisading granulomatous inflammation in the dermis, with multinucleated histiocytes palisading around degenerated collagen bundles.2
No treatment has proven to be effective for NL. Glucose control in patients with diabetes does not have a significant effect on the NL lesions.1-3 Corticosteroids (topical, intralesional, and systemic—depending on the severity) are considered first-line therapy.1-3 Lifestyle modifications, such as smoking cessation and trauma avoidance, are recommended to promote healing; proper wound care is important when there is ulceration.1,3 Other treatment options include oral pentoxifylline, topical retinoids or calcineurin inhibitors, and systemic immune system modulators (eg, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and cyclosporine).
Since this patient did not respond to the topical betamethasone, she was started on oral pentoxifylline 400 mg tid. Unfortunately, she had to discontinue the medication because of gastrointestinal upset and was then started on doxycycline 100 mg orally bid. She was lost to follow-up.
Photo courtesy of Cyrelle F. Finan, MD. Text courtesy of Harika Echuri, MD, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, Cyrelle F. Finan, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

The patient’s atrophic plaques with a violaceous rim, indurated borders, and ulceration on the anterior pretibial surface were consistent with ulcerated necrobiosis lipoidica (NL).
NL typically manifests on the bilateral pretibial region as small papules or nodules that expand into yellow-brown atrophic, telangiectatic plaques with an elevated violaceous rim.1,2 Most lesions are asymptomatic due to nerve damage, but up to 35% of patients may experience pruritus and tenderness.2 Close monitoring of lesions is recommended due to risk of ulceration and potential for malignancy.2 Rare reports show development of squamous cell carcinoma within NL lesions.1
Women are 3 times more likely than men to have NL, with an average age of onset between 30 and 40 years.1 The exact pathogenesis of NL is unknown.2 Theories include vascular abnormalities (immunoglobulin deposition or microangiopathic changes leading to collagen degradation), abnormalities of collagen synthesis, neutrophil migration, and elevated tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels.1,3
While NL can be diagnosed clinically, a skin biopsy may be necessary in atypical lesions. The biopsy will reveal palisading granulomatous inflammation in the dermis, with multinucleated histiocytes palisading around degenerated collagen bundles.2
No treatment has proven to be effective for NL. Glucose control in patients with diabetes does not have a significant effect on the NL lesions.1-3 Corticosteroids (topical, intralesional, and systemic—depending on the severity) are considered first-line therapy.1-3 Lifestyle modifications, such as smoking cessation and trauma avoidance, are recommended to promote healing; proper wound care is important when there is ulceration.1,3 Other treatment options include oral pentoxifylline, topical retinoids or calcineurin inhibitors, and systemic immune system modulators (eg, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and cyclosporine).
Since this patient did not respond to the topical betamethasone, she was started on oral pentoxifylline 400 mg tid. Unfortunately, she had to discontinue the medication because of gastrointestinal upset and was then started on doxycycline 100 mg orally bid. She was lost to follow-up.
Photo courtesy of Cyrelle F. Finan, MD. Text courtesy of Harika Echuri, MD, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, Cyrelle F. Finan, MD, Department of Dermatology, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Lepe K, Riley CA, Salazar FJ. Necrobiosis lipoidica. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated August 26, 2021. Accessed May 31, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459318/
2. Tong LX, Penn L, Meehan SA, Kim RH. Necrobiosis lipoidica. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13030/qt0qg3b3zw. doi: 10.5070/D32412042442
3. Sibbald C, Reid S, Alavi A. Necrobiosis lipoidica. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:343-360. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2015.03.003
1. Lepe K, Riley CA, Salazar FJ. Necrobiosis lipoidica. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated August 26, 2021. Accessed May 31, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459318/
2. Tong LX, Penn L, Meehan SA, Kim RH. Necrobiosis lipoidica. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13030/qt0qg3b3zw. doi: 10.5070/D32412042442
3. Sibbald C, Reid S, Alavi A. Necrobiosis lipoidica. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:343-360. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2015.03.003
Adjunctive confocal microscopy found to reduce unnecessary skin excisions
results from a large randomized clinical trial showed.
“Skin cancer management exerts a sizable burden on health systems,” researchers led by Giovanni Pellacani, MD, wrote in an article published in JAMA Dermatology. “The systematic application of RCM in the triage of high-risk patients should improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce unnecessary excisions for histopathological diagnostic confirmation, thereby reducing costs, surgical waiting lists, and delayed diagnoses.”
However, they added, “the clinical application of RCM has mainly been limited to retrospective and prospective observational studies producing hypothetical estimates of clinical applicability without intention to affect clinical and therapeutic patient pathways.”
For the current study, Dr. Pellacani, who chairs the department of dermatology at Sapienza University, Rome, and colleagues hypothesized that RCM would reduce unnecessary excisions by more than 30% and would identify all melanoma lesions 0.5 mm or thinner at baseline. They enrolled 3,165 patients with suspect lesions from three dermatology referral centers between January 2017 and December 2019, with a mean follow-up of 9.6 months in the study. Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to standard therapeutic care, which consisted of clinical and dermoscopy evaluation with or without adjunctive RCM, a novel noninvasive technology that provides in vivo imaging of the skin, with a high diagnostic accuracy.
Histopathologic examination of all excised lesions was performed at the pathology department of the referral center. Resulting information guided prospective clinical decision-making (excision or follow-up). The mean age of patients was 49 years, 49% were women, 21% had a personal history of melanoma, and 51% had Fitzpatrick phototype 2 skin.
When compared with standard therapeutic care only, adjunctive RCM was associated with a higher positive predictive value (18.9 vs. 33.3, respectively), lower benign to malignant ratio (3.7:1.0 vs. 1.8:1.0), and a reduction in the number needed to excise of 43.4% (5.3 vs. 3.0). In addition, all 15 lesions with delayed melanoma diagnoses were thinner than 0.5 mm. Of these, eight were diagnosed as melanoma in situ.
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study, said that a strength of the analysis was its follow-up and histopathologic evaluation, “which are both essentially forms of feedback. Good, relevant feedback is necessary for all of us to improve.”
She pointed out that, while RCM does appear to reduce the number of benign lesions unnecessarily removed and increase the number of skin cancers appropriately excised, the authors acknowledged that they had at least 4 years of experience with RCM. “The study also does not address the time factor (the procedure takes about 7 minutes per lesion) and the financial cost of reflectance confocal microscopy, as compared to the cost of standard follow-up alone with an increased number of excisions.”
She added that the findings “are not yet applicable to general dermatology across the world, as the authors comment, given that reflectance confocal microscopy is not yet widely available.”
The Italian Ministry of Health supported the study. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Ko reported having relevant financial conflicts.
results from a large randomized clinical trial showed.
“Skin cancer management exerts a sizable burden on health systems,” researchers led by Giovanni Pellacani, MD, wrote in an article published in JAMA Dermatology. “The systematic application of RCM in the triage of high-risk patients should improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce unnecessary excisions for histopathological diagnostic confirmation, thereby reducing costs, surgical waiting lists, and delayed diagnoses.”
However, they added, “the clinical application of RCM has mainly been limited to retrospective and prospective observational studies producing hypothetical estimates of clinical applicability without intention to affect clinical and therapeutic patient pathways.”
For the current study, Dr. Pellacani, who chairs the department of dermatology at Sapienza University, Rome, and colleagues hypothesized that RCM would reduce unnecessary excisions by more than 30% and would identify all melanoma lesions 0.5 mm or thinner at baseline. They enrolled 3,165 patients with suspect lesions from three dermatology referral centers between January 2017 and December 2019, with a mean follow-up of 9.6 months in the study. Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to standard therapeutic care, which consisted of clinical and dermoscopy evaluation with or without adjunctive RCM, a novel noninvasive technology that provides in vivo imaging of the skin, with a high diagnostic accuracy.
Histopathologic examination of all excised lesions was performed at the pathology department of the referral center. Resulting information guided prospective clinical decision-making (excision or follow-up). The mean age of patients was 49 years, 49% were women, 21% had a personal history of melanoma, and 51% had Fitzpatrick phototype 2 skin.
When compared with standard therapeutic care only, adjunctive RCM was associated with a higher positive predictive value (18.9 vs. 33.3, respectively), lower benign to malignant ratio (3.7:1.0 vs. 1.8:1.0), and a reduction in the number needed to excise of 43.4% (5.3 vs. 3.0). In addition, all 15 lesions with delayed melanoma diagnoses were thinner than 0.5 mm. Of these, eight were diagnosed as melanoma in situ.
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study, said that a strength of the analysis was its follow-up and histopathologic evaluation, “which are both essentially forms of feedback. Good, relevant feedback is necessary for all of us to improve.”
She pointed out that, while RCM does appear to reduce the number of benign lesions unnecessarily removed and increase the number of skin cancers appropriately excised, the authors acknowledged that they had at least 4 years of experience with RCM. “The study also does not address the time factor (the procedure takes about 7 minutes per lesion) and the financial cost of reflectance confocal microscopy, as compared to the cost of standard follow-up alone with an increased number of excisions.”
She added that the findings “are not yet applicable to general dermatology across the world, as the authors comment, given that reflectance confocal microscopy is not yet widely available.”
The Italian Ministry of Health supported the study. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Ko reported having relevant financial conflicts.
results from a large randomized clinical trial showed.
“Skin cancer management exerts a sizable burden on health systems,” researchers led by Giovanni Pellacani, MD, wrote in an article published in JAMA Dermatology. “The systematic application of RCM in the triage of high-risk patients should improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce unnecessary excisions for histopathological diagnostic confirmation, thereby reducing costs, surgical waiting lists, and delayed diagnoses.”
However, they added, “the clinical application of RCM has mainly been limited to retrospective and prospective observational studies producing hypothetical estimates of clinical applicability without intention to affect clinical and therapeutic patient pathways.”
For the current study, Dr. Pellacani, who chairs the department of dermatology at Sapienza University, Rome, and colleagues hypothesized that RCM would reduce unnecessary excisions by more than 30% and would identify all melanoma lesions 0.5 mm or thinner at baseline. They enrolled 3,165 patients with suspect lesions from three dermatology referral centers between January 2017 and December 2019, with a mean follow-up of 9.6 months in the study. Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to standard therapeutic care, which consisted of clinical and dermoscopy evaluation with or without adjunctive RCM, a novel noninvasive technology that provides in vivo imaging of the skin, with a high diagnostic accuracy.
Histopathologic examination of all excised lesions was performed at the pathology department of the referral center. Resulting information guided prospective clinical decision-making (excision or follow-up). The mean age of patients was 49 years, 49% were women, 21% had a personal history of melanoma, and 51% had Fitzpatrick phototype 2 skin.
When compared with standard therapeutic care only, adjunctive RCM was associated with a higher positive predictive value (18.9 vs. 33.3, respectively), lower benign to malignant ratio (3.7:1.0 vs. 1.8:1.0), and a reduction in the number needed to excise of 43.4% (5.3 vs. 3.0). In addition, all 15 lesions with delayed melanoma diagnoses were thinner than 0.5 mm. Of these, eight were diagnosed as melanoma in situ.
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study, said that a strength of the analysis was its follow-up and histopathologic evaluation, “which are both essentially forms of feedback. Good, relevant feedback is necessary for all of us to improve.”
She pointed out that, while RCM does appear to reduce the number of benign lesions unnecessarily removed and increase the number of skin cancers appropriately excised, the authors acknowledged that they had at least 4 years of experience with RCM. “The study also does not address the time factor (the procedure takes about 7 minutes per lesion) and the financial cost of reflectance confocal microscopy, as compared to the cost of standard follow-up alone with an increased number of excisions.”
She added that the findings “are not yet applicable to general dermatology across the world, as the authors comment, given that reflectance confocal microscopy is not yet widely available.”
The Italian Ministry of Health supported the study. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Ko reported having relevant financial conflicts.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Pilonidal disease, other conditions may benefit from laser treatment
SAN DIEGO – Pilonidal disease – a chronic inflammatory condition that can trigger the formation of cysts and sinuses in the superior portion of the intragluteal cleft or the sacrococcygeal area – remains challenging to manage, but mounting evidence supports the use of lasers to enhance treatment success.
“Draining sinuses or acute abscesses are usually associated with an underlying cyst and associated granulation tissue, fibrosis, and tufts of hair,” Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “This is why laser hair removal can help with the treatment of these patients.”
The suspected etiology is a foreign body reaction to the entrapped hairs, which are found in the sinuses in about 75% of cases. “The treatment for that is surgery,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, a laser and cosmetic dermatologist in Boston. Laser hair reduction decreases the recurrence of cyst formation and drainage, and is usually covered by insurance, she noted.
Supportive evidence
In a comparative study, French researchers retrospectively reviewed the efficacy of laser hair removal after surgery in reducing recurrence rate of pilonidal cysts, versus surgery alone. Of the 41 study participants, 12 had laser hair removal plus surgery and 29 had surgery alone. The rate of cyst recurrence was significantly lower in the laser hair removal plus surgery group, compared with the surgery only group (8.3% vs. 51.7%, respectively; P < .001).
In another study, researchers from the United Kingdom and The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, evaluated the use of the long-pulsed Alexandrite laser in 19 patients with recurrent pilonidal disease who had undergone multiple surgeries.They were treated with the laser for hair removal in the sinus area, requiring 4-12 sessions. The researchers found that 84.2% of patients had a reduction of hair density to less than 5 hairs/cm2, while 15.8% had a reduction of hair density to 5-10 hairs/cm2. They also noted a statistically significant increase in disease-free time in the laser-treated group compared with those treated with surgical management only (P < .01).
Lasers for pseudofolliculitis barbae, HS
Lasers also play a significant role in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae, a chronic, inflammatory disease that primarily affects the bearded area of men with thick hairs, usually those with a darker Fitzpatrick skin type. This can also occur in women, particularly those with polycystic ovary syndrome, Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In people with pseudofolliculitis barbae, the hair follicle is positioned at an acute angle to the skin surface and the sharp end of shaved hair reenters the skin, which results in the formation of pustules, papules, secondary infection, and keloids. Treatment involves a variety of medical therapies including retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics, and keratolytics, “but laser hair removal is the best way to get rid of this issue, and results in permanent reduction,” she said. “When treating male patients with laser hair removal in the bearded area, you have to tell them that they won’t be able to grow a beard going forward. Most of them are okay with that.”
A 2002 study, led by E. Victor Ross, MD, of the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, evaluated treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in patients with skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser. For the first phase of the study, the investigators tested epidermal tolerance on the thighs of 37 patients and determined that the laser was safe and effective. For the second phase 2 weeks later, they treated a 15x15-mm submental area with the highest fluence tolerated in phase 1 of the trial and used an adjacent site as the control.
After 90 days, the mean papule count was 6.95 for the control site compared with 1 for the laser-treated site. The researchers observed that miniaturization and elimination of hair shafts resulted in decreased inflamed papules. “We know that this works,” Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In another study from investigators at the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, 22 patients with skin types IV, V, and VI who had pseudofolliculitis barbae underwent 5 weekly treatments with a 1,064 nm Nd:YAG laser. Topical anesthesia was not used, and 10 evaluators used a Global Assessment Scale (GAS) to assess treatment success from photos taken at baseline and at 4 weeks. At 4 weeks, 11 patients demonstrated 83% improvement on the GAS (P < .01), the investigators reported.
Laser and energy-based treatments can also be used to treat hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a chronic condition that affects apocrine gland–bearing skin. “The hypothesized pathogenesis is that it’s an inflammatory disorder of the hair follicle, where the follicle rupture introduces its contents into the surrounding dermis,” Dr. DiGiorgio said. “The skin reacts with a chemotactic response and abscess formation. This results in inflammatory nodules and sterile abscesses, which can lead to sinus tracts and hypertrophic scars and chronic drainage, which can be foul-smelling. This frequently leads to depression and psychological distress for the patients.”
Possible laser and energy-based treatments for HS include follicular destruction with the Nd:YAG laser, the diode laser, the Alexandrite laser, microwave technology, or intense pulsed light, she said. Microwave technology or radiofrequency can be used for sweat gland destruction, while CO2 lasers can be used to debulk tissue, and the ablative fractional CO2 laser can be used to reduce scarring and improve range of motion.
In a prospective, randomized, intraindividual comparative trial conducted at eight centers in France, researchers evaluated the use of a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser to treat 36 patients with mild to moderate HS; 27 had inguinal disease and 9 had axillary disease. They received four laser treatments at 6-week intervals; laser settings varied depending on the patient skin type.
At 1 month, there was a significant reduction in the number of inflammatory lesions on the areas treated with lasers, compared to the untreated areas, but the difference was not significant at 3 months. There was no significant difference in the number of flares between the treated and untreated sites at 1 or 3 months.
In a separate study, researchers found that the Nd:YAG laser in combination with topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin was significantly more effective than topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin alone for the treatment of HS in 22 patients with Hurley stage II disease. The patients received monthly treatments for 4 months and were followed up 2 months after the last treatment; the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Area and Severity Index was used to measure treatment response.
Statistically significant improvements were observed in the inguinal and axillary areas but not in the inframammary areas. Most patients (90%) reported less frequent breakouts while 10% reported no change. “In addition, 92% of subjects felt that the use of laser was more effective than other treatments they had tried but 8% stated it was equal to the other treatments they had tried,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, who was not affiliated with the study. “The researchers noted continued improvement with subsequent laser sessions,” she added.
According to 2019 guidelines from the United States and Canadian HS Foundations on the management of HS – in the section on light, laser, and energy sources – an Nd:YAG laser is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease on the basis of randomized, controlled trials and case series data, and in patients with Hurley stage I disease based on expert consensus. “Other wavelengths that are used for follicular destruction are recommended on the basis of lower-quality evidence,” the recommendations state.
The guidelines also state that CO2 laser excision “is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease with fibrotic sinus tracts” while “external beam radiation and PDT have a limited role in the management of patients with HS.”
Dr. DiGiorgio reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – Pilonidal disease – a chronic inflammatory condition that can trigger the formation of cysts and sinuses in the superior portion of the intragluteal cleft or the sacrococcygeal area – remains challenging to manage, but mounting evidence supports the use of lasers to enhance treatment success.
“Draining sinuses or acute abscesses are usually associated with an underlying cyst and associated granulation tissue, fibrosis, and tufts of hair,” Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “This is why laser hair removal can help with the treatment of these patients.”
The suspected etiology is a foreign body reaction to the entrapped hairs, which are found in the sinuses in about 75% of cases. “The treatment for that is surgery,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, a laser and cosmetic dermatologist in Boston. Laser hair reduction decreases the recurrence of cyst formation and drainage, and is usually covered by insurance, she noted.
Supportive evidence
In a comparative study, French researchers retrospectively reviewed the efficacy of laser hair removal after surgery in reducing recurrence rate of pilonidal cysts, versus surgery alone. Of the 41 study participants, 12 had laser hair removal plus surgery and 29 had surgery alone. The rate of cyst recurrence was significantly lower in the laser hair removal plus surgery group, compared with the surgery only group (8.3% vs. 51.7%, respectively; P < .001).
In another study, researchers from the United Kingdom and The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, evaluated the use of the long-pulsed Alexandrite laser in 19 patients with recurrent pilonidal disease who had undergone multiple surgeries.They were treated with the laser for hair removal in the sinus area, requiring 4-12 sessions. The researchers found that 84.2% of patients had a reduction of hair density to less than 5 hairs/cm2, while 15.8% had a reduction of hair density to 5-10 hairs/cm2. They also noted a statistically significant increase in disease-free time in the laser-treated group compared with those treated with surgical management only (P < .01).
Lasers for pseudofolliculitis barbae, HS
Lasers also play a significant role in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae, a chronic, inflammatory disease that primarily affects the bearded area of men with thick hairs, usually those with a darker Fitzpatrick skin type. This can also occur in women, particularly those with polycystic ovary syndrome, Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In people with pseudofolliculitis barbae, the hair follicle is positioned at an acute angle to the skin surface and the sharp end of shaved hair reenters the skin, which results in the formation of pustules, papules, secondary infection, and keloids. Treatment involves a variety of medical therapies including retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics, and keratolytics, “but laser hair removal is the best way to get rid of this issue, and results in permanent reduction,” she said. “When treating male patients with laser hair removal in the bearded area, you have to tell them that they won’t be able to grow a beard going forward. Most of them are okay with that.”
A 2002 study, led by E. Victor Ross, MD, of the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, evaluated treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in patients with skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser. For the first phase of the study, the investigators tested epidermal tolerance on the thighs of 37 patients and determined that the laser was safe and effective. For the second phase 2 weeks later, they treated a 15x15-mm submental area with the highest fluence tolerated in phase 1 of the trial and used an adjacent site as the control.
After 90 days, the mean papule count was 6.95 for the control site compared with 1 for the laser-treated site. The researchers observed that miniaturization and elimination of hair shafts resulted in decreased inflamed papules. “We know that this works,” Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In another study from investigators at the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, 22 patients with skin types IV, V, and VI who had pseudofolliculitis barbae underwent 5 weekly treatments with a 1,064 nm Nd:YAG laser. Topical anesthesia was not used, and 10 evaluators used a Global Assessment Scale (GAS) to assess treatment success from photos taken at baseline and at 4 weeks. At 4 weeks, 11 patients demonstrated 83% improvement on the GAS (P < .01), the investigators reported.
Laser and energy-based treatments can also be used to treat hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a chronic condition that affects apocrine gland–bearing skin. “The hypothesized pathogenesis is that it’s an inflammatory disorder of the hair follicle, where the follicle rupture introduces its contents into the surrounding dermis,” Dr. DiGiorgio said. “The skin reacts with a chemotactic response and abscess formation. This results in inflammatory nodules and sterile abscesses, which can lead to sinus tracts and hypertrophic scars and chronic drainage, which can be foul-smelling. This frequently leads to depression and psychological distress for the patients.”
Possible laser and energy-based treatments for HS include follicular destruction with the Nd:YAG laser, the diode laser, the Alexandrite laser, microwave technology, or intense pulsed light, she said. Microwave technology or radiofrequency can be used for sweat gland destruction, while CO2 lasers can be used to debulk tissue, and the ablative fractional CO2 laser can be used to reduce scarring and improve range of motion.
In a prospective, randomized, intraindividual comparative trial conducted at eight centers in France, researchers evaluated the use of a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser to treat 36 patients with mild to moderate HS; 27 had inguinal disease and 9 had axillary disease. They received four laser treatments at 6-week intervals; laser settings varied depending on the patient skin type.
At 1 month, there was a significant reduction in the number of inflammatory lesions on the areas treated with lasers, compared to the untreated areas, but the difference was not significant at 3 months. There was no significant difference in the number of flares between the treated and untreated sites at 1 or 3 months.
In a separate study, researchers found that the Nd:YAG laser in combination with topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin was significantly more effective than topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin alone for the treatment of HS in 22 patients with Hurley stage II disease. The patients received monthly treatments for 4 months and were followed up 2 months after the last treatment; the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Area and Severity Index was used to measure treatment response.
Statistically significant improvements were observed in the inguinal and axillary areas but not in the inframammary areas. Most patients (90%) reported less frequent breakouts while 10% reported no change. “In addition, 92% of subjects felt that the use of laser was more effective than other treatments they had tried but 8% stated it was equal to the other treatments they had tried,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, who was not affiliated with the study. “The researchers noted continued improvement with subsequent laser sessions,” she added.
According to 2019 guidelines from the United States and Canadian HS Foundations on the management of HS – in the section on light, laser, and energy sources – an Nd:YAG laser is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease on the basis of randomized, controlled trials and case series data, and in patients with Hurley stage I disease based on expert consensus. “Other wavelengths that are used for follicular destruction are recommended on the basis of lower-quality evidence,” the recommendations state.
The guidelines also state that CO2 laser excision “is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease with fibrotic sinus tracts” while “external beam radiation and PDT have a limited role in the management of patients with HS.”
Dr. DiGiorgio reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – Pilonidal disease – a chronic inflammatory condition that can trigger the formation of cysts and sinuses in the superior portion of the intragluteal cleft or the sacrococcygeal area – remains challenging to manage, but mounting evidence supports the use of lasers to enhance treatment success.
“Draining sinuses or acute abscesses are usually associated with an underlying cyst and associated granulation tissue, fibrosis, and tufts of hair,” Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “This is why laser hair removal can help with the treatment of these patients.”
The suspected etiology is a foreign body reaction to the entrapped hairs, which are found in the sinuses in about 75% of cases. “The treatment for that is surgery,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, a laser and cosmetic dermatologist in Boston. Laser hair reduction decreases the recurrence of cyst formation and drainage, and is usually covered by insurance, she noted.
Supportive evidence
In a comparative study, French researchers retrospectively reviewed the efficacy of laser hair removal after surgery in reducing recurrence rate of pilonidal cysts, versus surgery alone. Of the 41 study participants, 12 had laser hair removal plus surgery and 29 had surgery alone. The rate of cyst recurrence was significantly lower in the laser hair removal plus surgery group, compared with the surgery only group (8.3% vs. 51.7%, respectively; P < .001).
In another study, researchers from the United Kingdom and The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, evaluated the use of the long-pulsed Alexandrite laser in 19 patients with recurrent pilonidal disease who had undergone multiple surgeries.They were treated with the laser for hair removal in the sinus area, requiring 4-12 sessions. The researchers found that 84.2% of patients had a reduction of hair density to less than 5 hairs/cm2, while 15.8% had a reduction of hair density to 5-10 hairs/cm2. They also noted a statistically significant increase in disease-free time in the laser-treated group compared with those treated with surgical management only (P < .01).
Lasers for pseudofolliculitis barbae, HS
Lasers also play a significant role in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae, a chronic, inflammatory disease that primarily affects the bearded area of men with thick hairs, usually those with a darker Fitzpatrick skin type. This can also occur in women, particularly those with polycystic ovary syndrome, Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In people with pseudofolliculitis barbae, the hair follicle is positioned at an acute angle to the skin surface and the sharp end of shaved hair reenters the skin, which results in the formation of pustules, papules, secondary infection, and keloids. Treatment involves a variety of medical therapies including retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics, and keratolytics, “but laser hair removal is the best way to get rid of this issue, and results in permanent reduction,” she said. “When treating male patients with laser hair removal in the bearded area, you have to tell them that they won’t be able to grow a beard going forward. Most of them are okay with that.”
A 2002 study, led by E. Victor Ross, MD, of the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, evaluated treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in patients with skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser. For the first phase of the study, the investigators tested epidermal tolerance on the thighs of 37 patients and determined that the laser was safe and effective. For the second phase 2 weeks later, they treated a 15x15-mm submental area with the highest fluence tolerated in phase 1 of the trial and used an adjacent site as the control.
After 90 days, the mean papule count was 6.95 for the control site compared with 1 for the laser-treated site. The researchers observed that miniaturization and elimination of hair shafts resulted in decreased inflamed papules. “We know that this works,” Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In another study from investigators at the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, 22 patients with skin types IV, V, and VI who had pseudofolliculitis barbae underwent 5 weekly treatments with a 1,064 nm Nd:YAG laser. Topical anesthesia was not used, and 10 evaluators used a Global Assessment Scale (GAS) to assess treatment success from photos taken at baseline and at 4 weeks. At 4 weeks, 11 patients demonstrated 83% improvement on the GAS (P < .01), the investigators reported.
Laser and energy-based treatments can also be used to treat hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a chronic condition that affects apocrine gland–bearing skin. “The hypothesized pathogenesis is that it’s an inflammatory disorder of the hair follicle, where the follicle rupture introduces its contents into the surrounding dermis,” Dr. DiGiorgio said. “The skin reacts with a chemotactic response and abscess formation. This results in inflammatory nodules and sterile abscesses, which can lead to sinus tracts and hypertrophic scars and chronic drainage, which can be foul-smelling. This frequently leads to depression and psychological distress for the patients.”
Possible laser and energy-based treatments for HS include follicular destruction with the Nd:YAG laser, the diode laser, the Alexandrite laser, microwave technology, or intense pulsed light, she said. Microwave technology or radiofrequency can be used for sweat gland destruction, while CO2 lasers can be used to debulk tissue, and the ablative fractional CO2 laser can be used to reduce scarring and improve range of motion.
In a prospective, randomized, intraindividual comparative trial conducted at eight centers in France, researchers evaluated the use of a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser to treat 36 patients with mild to moderate HS; 27 had inguinal disease and 9 had axillary disease. They received four laser treatments at 6-week intervals; laser settings varied depending on the patient skin type.
At 1 month, there was a significant reduction in the number of inflammatory lesions on the areas treated with lasers, compared to the untreated areas, but the difference was not significant at 3 months. There was no significant difference in the number of flares between the treated and untreated sites at 1 or 3 months.
In a separate study, researchers found that the Nd:YAG laser in combination with topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin was significantly more effective than topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin alone for the treatment of HS in 22 patients with Hurley stage II disease. The patients received monthly treatments for 4 months and were followed up 2 months after the last treatment; the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Area and Severity Index was used to measure treatment response.
Statistically significant improvements were observed in the inguinal and axillary areas but not in the inframammary areas. Most patients (90%) reported less frequent breakouts while 10% reported no change. “In addition, 92% of subjects felt that the use of laser was more effective than other treatments they had tried but 8% stated it was equal to the other treatments they had tried,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, who was not affiliated with the study. “The researchers noted continued improvement with subsequent laser sessions,” she added.
According to 2019 guidelines from the United States and Canadian HS Foundations on the management of HS – in the section on light, laser, and energy sources – an Nd:YAG laser is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease on the basis of randomized, controlled trials and case series data, and in patients with Hurley stage I disease based on expert consensus. “Other wavelengths that are used for follicular destruction are recommended on the basis of lower-quality evidence,” the recommendations state.
The guidelines also state that CO2 laser excision “is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease with fibrotic sinus tracts” while “external beam radiation and PDT have a limited role in the management of patients with HS.”
Dr. DiGiorgio reported having no relevant disclosures.
AT ASLMS 2022
Fractional lasers appear to treat more than a fraction of skin, expert says
SAN DIEGO – Using the according to Molly Wanner, MD, MBA.
As a case in point, Dr. Wanner discussed the results of a trial of 48 people over aged 60 years with actinic damage, who received ablative fractional laser treatment on one arm and no treatment on the other arm, which served as the control. At 24 months, only two nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) developed on the treated arms, compared with 26 on the treated arms.
“What I find interesting is that the treated arm did not develop basal cell carcinoma, only squamous cell carcinoma,” she said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “It appears that this is working through more than just treatment of the AK precursor lesions, for which fractional lasers are cleared for use. It appears to impact both types of NMSCs.”
The ablative fractional laser and other wounding therapies can modulate a response to UV light – a process that naturally diminishes with age, according to Dr. Wanner, a dermatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital’s Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center in Boston. “This ability to repair DNA is actually modulated by insulin-like growth factor 1,” she said. “IGF-1 is produced by papillary dermal fibroblasts and communicates with keratinocytes. If keratinocytes are exposed to UV light and there is no IGF-1 around, you get a mutated cell, and that keeps spreading, and you could potentially get a skin cancer.”
On the other hand, she continued, if IGF-1 is injected around the keratinocytes, they are able to respond. “Keratinocytes, which are the most superficial layer of the skin, are really active,” noted Dr. Wanner, who is also an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “They’re dividing and replicating, whereas fibroblasts are more non-proliferative and more long-lived. They stick around for a long time. I think of them as the adults in the room, giving these new keratinocytes direction.”
In a review of wounding therapies for the prevention of photocarcinogenesis, she and her coauthors noted that IGF-1 increases nucleotide excision repair of damaged DNA, promotes checkpoint signaling and suppression of DNA synthesis, favors specialized polymerases that are better able to repair DNA damage, and enhances p53-dependent transcriptional responses to DNA damage.
“Older fibroblasts produce less IGF-1 and lead to a situation where keratinocytes can grow unchecked,” she said. “We can use fractional laser to help with this. Fractional laser increases fibroblast production and decreases senescent fibroblasts.”
In a 2017 review on the impact of age and IGF-1 on DNA damage responses in UV-irradiated skin, the authors noted the high levels of IGF-1 in the skin of younger individuals and lower levels in the skin of their older counterparts.
“But once older skin has been treated with either dermabrasion or fractional laser, the levels of IGF-1 are restored to that of a young adult,” Dr. Wanner said. “The restoration of IGF-1 then restores that level of appropriate response to UV light. So, what’s interesting is that fractional lasers treat more than a fraction [of skin]. Fractional lasers were developed to have an easier way to improve wound healing by leaving the skin intact around these columns [of treated skin]. It turns out that treatment of these columns of skin does not just impact the cells in that area. There is a true global effect that’s allowing us to almost normalize skin.”
Dr. Wanner now thinks of fractional lasers as stimulating a laser-cell biology interaction, not just a laser-tissue interaction. “It’s incredible that we can use these photons to not only impact the tissue itself but how the cells actually respond,” she said. “What’s going to be interesting for us in the next few years is to look at how lasers impact our cellular biology. How can we harness it to help our patients?”
She and her colleagues are conducting a trial of different wounding modalities to assess their impact on IGF-1. “Does depth matter? Does density matter? Does the wavelength matter?” she asked. “The bottom line is, it turns out that when the skin looks healthier, it is healthier. Cosmetic treatments can impact medical outcomes.”
Dr. Wanner disclosed that she is a consultant and advisor to Nu Skin. She has also received research funding and equipment from Solta.
SAN DIEGO – Using the according to Molly Wanner, MD, MBA.
As a case in point, Dr. Wanner discussed the results of a trial of 48 people over aged 60 years with actinic damage, who received ablative fractional laser treatment on one arm and no treatment on the other arm, which served as the control. At 24 months, only two nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) developed on the treated arms, compared with 26 on the treated arms.
“What I find interesting is that the treated arm did not develop basal cell carcinoma, only squamous cell carcinoma,” she said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “It appears that this is working through more than just treatment of the AK precursor lesions, for which fractional lasers are cleared for use. It appears to impact both types of NMSCs.”
The ablative fractional laser and other wounding therapies can modulate a response to UV light – a process that naturally diminishes with age, according to Dr. Wanner, a dermatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital’s Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center in Boston. “This ability to repair DNA is actually modulated by insulin-like growth factor 1,” she said. “IGF-1 is produced by papillary dermal fibroblasts and communicates with keratinocytes. If keratinocytes are exposed to UV light and there is no IGF-1 around, you get a mutated cell, and that keeps spreading, and you could potentially get a skin cancer.”
On the other hand, she continued, if IGF-1 is injected around the keratinocytes, they are able to respond. “Keratinocytes, which are the most superficial layer of the skin, are really active,” noted Dr. Wanner, who is also an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “They’re dividing and replicating, whereas fibroblasts are more non-proliferative and more long-lived. They stick around for a long time. I think of them as the adults in the room, giving these new keratinocytes direction.”
In a review of wounding therapies for the prevention of photocarcinogenesis, she and her coauthors noted that IGF-1 increases nucleotide excision repair of damaged DNA, promotes checkpoint signaling and suppression of DNA synthesis, favors specialized polymerases that are better able to repair DNA damage, and enhances p53-dependent transcriptional responses to DNA damage.
“Older fibroblasts produce less IGF-1 and lead to a situation where keratinocytes can grow unchecked,” she said. “We can use fractional laser to help with this. Fractional laser increases fibroblast production and decreases senescent fibroblasts.”
In a 2017 review on the impact of age and IGF-1 on DNA damage responses in UV-irradiated skin, the authors noted the high levels of IGF-1 in the skin of younger individuals and lower levels in the skin of their older counterparts.
“But once older skin has been treated with either dermabrasion or fractional laser, the levels of IGF-1 are restored to that of a young adult,” Dr. Wanner said. “The restoration of IGF-1 then restores that level of appropriate response to UV light. So, what’s interesting is that fractional lasers treat more than a fraction [of skin]. Fractional lasers were developed to have an easier way to improve wound healing by leaving the skin intact around these columns [of treated skin]. It turns out that treatment of these columns of skin does not just impact the cells in that area. There is a true global effect that’s allowing us to almost normalize skin.”
Dr. Wanner now thinks of fractional lasers as stimulating a laser-cell biology interaction, not just a laser-tissue interaction. “It’s incredible that we can use these photons to not only impact the tissue itself but how the cells actually respond,” she said. “What’s going to be interesting for us in the next few years is to look at how lasers impact our cellular biology. How can we harness it to help our patients?”
She and her colleagues are conducting a trial of different wounding modalities to assess their impact on IGF-1. “Does depth matter? Does density matter? Does the wavelength matter?” she asked. “The bottom line is, it turns out that when the skin looks healthier, it is healthier. Cosmetic treatments can impact medical outcomes.”
Dr. Wanner disclosed that she is a consultant and advisor to Nu Skin. She has also received research funding and equipment from Solta.
SAN DIEGO – Using the according to Molly Wanner, MD, MBA.
As a case in point, Dr. Wanner discussed the results of a trial of 48 people over aged 60 years with actinic damage, who received ablative fractional laser treatment on one arm and no treatment on the other arm, which served as the control. At 24 months, only two nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) developed on the treated arms, compared with 26 on the treated arms.
“What I find interesting is that the treated arm did not develop basal cell carcinoma, only squamous cell carcinoma,” she said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “It appears that this is working through more than just treatment of the AK precursor lesions, for which fractional lasers are cleared for use. It appears to impact both types of NMSCs.”
The ablative fractional laser and other wounding therapies can modulate a response to UV light – a process that naturally diminishes with age, according to Dr. Wanner, a dermatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital’s Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center in Boston. “This ability to repair DNA is actually modulated by insulin-like growth factor 1,” she said. “IGF-1 is produced by papillary dermal fibroblasts and communicates with keratinocytes. If keratinocytes are exposed to UV light and there is no IGF-1 around, you get a mutated cell, and that keeps spreading, and you could potentially get a skin cancer.”
On the other hand, she continued, if IGF-1 is injected around the keratinocytes, they are able to respond. “Keratinocytes, which are the most superficial layer of the skin, are really active,” noted Dr. Wanner, who is also an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “They’re dividing and replicating, whereas fibroblasts are more non-proliferative and more long-lived. They stick around for a long time. I think of them as the adults in the room, giving these new keratinocytes direction.”
In a review of wounding therapies for the prevention of photocarcinogenesis, she and her coauthors noted that IGF-1 increases nucleotide excision repair of damaged DNA, promotes checkpoint signaling and suppression of DNA synthesis, favors specialized polymerases that are better able to repair DNA damage, and enhances p53-dependent transcriptional responses to DNA damage.
“Older fibroblasts produce less IGF-1 and lead to a situation where keratinocytes can grow unchecked,” she said. “We can use fractional laser to help with this. Fractional laser increases fibroblast production and decreases senescent fibroblasts.”
In a 2017 review on the impact of age and IGF-1 on DNA damage responses in UV-irradiated skin, the authors noted the high levels of IGF-1 in the skin of younger individuals and lower levels in the skin of their older counterparts.
“But once older skin has been treated with either dermabrasion or fractional laser, the levels of IGF-1 are restored to that of a young adult,” Dr. Wanner said. “The restoration of IGF-1 then restores that level of appropriate response to UV light. So, what’s interesting is that fractional lasers treat more than a fraction [of skin]. Fractional lasers were developed to have an easier way to improve wound healing by leaving the skin intact around these columns [of treated skin]. It turns out that treatment of these columns of skin does not just impact the cells in that area. There is a true global effect that’s allowing us to almost normalize skin.”
Dr. Wanner now thinks of fractional lasers as stimulating a laser-cell biology interaction, not just a laser-tissue interaction. “It’s incredible that we can use these photons to not only impact the tissue itself but how the cells actually respond,” she said. “What’s going to be interesting for us in the next few years is to look at how lasers impact our cellular biology. How can we harness it to help our patients?”
She and her colleagues are conducting a trial of different wounding modalities to assess their impact on IGF-1. “Does depth matter? Does density matter? Does the wavelength matter?” she asked. “The bottom line is, it turns out that when the skin looks healthier, it is healthier. Cosmetic treatments can impact medical outcomes.”
Dr. Wanner disclosed that she is a consultant and advisor to Nu Skin. She has also received research funding and equipment from Solta.
AT ASLMS 2022
Does taking isotretinoin worsen a patient’s baseline IBD symptoms?
A , results from a small retrospective study suggests.
“Early studies of isotretinoin for use in severe acne suggested the drug may serve as a trigger for new-onset inflammatory bowel disease (IBD),” researchers led by Christina G. Lopez, MD, of the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, wrote in an article published online , in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “While more recent studies have suggested no such causal relationship, little is known about the medication’s effect on patients with a preexisting IBD diagnosis.”
To investigate this topic further, the researchers identified 19 patients who were diagnosed with IBD and treated with isotretinoin between Jan. 1, 2006, and Jan. 1, 2020, at Mass General Brigham Hospitals, Boston. They determined severity of disease and degree of antecedent management of IBD by evaluating flaring two years prior to starting isotretinoin. The patients were considered to have a flare caused by isotretinoin if the IBD flare occurred during or up to 3 months following course completion.
The mean age of the 19 patients was 35 years, 26% were female, and 95% were White. Nearly half of the patients (42%) had ulcerative colitis, 37% had Crohn’s disease, and 21% had both. The researchers found that nine patients had flared two years before starting isotretinoin. Of these, five (56%) flared and four (44%) did not flare during treatment or within three months of completing the course of isotretinoin.
Of the 10 patients who did not flare two years before starting isotretinoin, seven (70%) did not flare during treatment and three (30%) flared during or within three months following completion of isotretinoin use. The researchers found no statistically significant association between isotretinoin use and flaring among patients with IBD (P = .76).
Dr. Lopez and her colleagues also assessed IBD maintenance therapy with respect to IBD flares in the study population. They observed no statistically significant association between the use of maintenance IBD therapy and the likelihood of having flares during isotretinoin treatment (P = .15).
“The results suggest limited association between isotretinoin and the worsening of a patient’s baseline IBD,” the authors concluded. They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and retrospective design, and they called for larger and prospective studies to assess the relationship of IBD flaring in this population of patients.
Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the results, characterized the trial as “an important study highlighting how we continue to understand the safe use of isotretinoin in the IBD cohort.”
Isotretinoin, she added, “continues to be a highly important treatment for acne and in patients such as these where oral antibiotics are relatively contraindicated due to risk of exacerbating their bowel disease.” Such data are reassuring, “albeit future studies with larger patient pools are desirable,” she added. “Future studies could also help to elucidate if diet, smoking, sleep, exercise, and medication adherence are potential confounding factors along with whether the cumulative isotretinoin dose has any effect on IBD flares in those who are susceptible.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Sodha had financial conflicts. The other authors were from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard University, Boston, and the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
A , results from a small retrospective study suggests.
“Early studies of isotretinoin for use in severe acne suggested the drug may serve as a trigger for new-onset inflammatory bowel disease (IBD),” researchers led by Christina G. Lopez, MD, of the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, wrote in an article published online , in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “While more recent studies have suggested no such causal relationship, little is known about the medication’s effect on patients with a preexisting IBD diagnosis.”
To investigate this topic further, the researchers identified 19 patients who were diagnosed with IBD and treated with isotretinoin between Jan. 1, 2006, and Jan. 1, 2020, at Mass General Brigham Hospitals, Boston. They determined severity of disease and degree of antecedent management of IBD by evaluating flaring two years prior to starting isotretinoin. The patients were considered to have a flare caused by isotretinoin if the IBD flare occurred during or up to 3 months following course completion.
The mean age of the 19 patients was 35 years, 26% were female, and 95% were White. Nearly half of the patients (42%) had ulcerative colitis, 37% had Crohn’s disease, and 21% had both. The researchers found that nine patients had flared two years before starting isotretinoin. Of these, five (56%) flared and four (44%) did not flare during treatment or within three months of completing the course of isotretinoin.
Of the 10 patients who did not flare two years before starting isotretinoin, seven (70%) did not flare during treatment and three (30%) flared during or within three months following completion of isotretinoin use. The researchers found no statistically significant association between isotretinoin use and flaring among patients with IBD (P = .76).
Dr. Lopez and her colleagues also assessed IBD maintenance therapy with respect to IBD flares in the study population. They observed no statistically significant association between the use of maintenance IBD therapy and the likelihood of having flares during isotretinoin treatment (P = .15).
“The results suggest limited association between isotretinoin and the worsening of a patient’s baseline IBD,” the authors concluded. They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and retrospective design, and they called for larger and prospective studies to assess the relationship of IBD flaring in this population of patients.
Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the results, characterized the trial as “an important study highlighting how we continue to understand the safe use of isotretinoin in the IBD cohort.”
Isotretinoin, she added, “continues to be a highly important treatment for acne and in patients such as these where oral antibiotics are relatively contraindicated due to risk of exacerbating their bowel disease.” Such data are reassuring, “albeit future studies with larger patient pools are desirable,” she added. “Future studies could also help to elucidate if diet, smoking, sleep, exercise, and medication adherence are potential confounding factors along with whether the cumulative isotretinoin dose has any effect on IBD flares in those who are susceptible.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Sodha had financial conflicts. The other authors were from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard University, Boston, and the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
A , results from a small retrospective study suggests.
“Early studies of isotretinoin for use in severe acne suggested the drug may serve as a trigger for new-onset inflammatory bowel disease (IBD),” researchers led by Christina G. Lopez, MD, of the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, wrote in an article published online , in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “While more recent studies have suggested no such causal relationship, little is known about the medication’s effect on patients with a preexisting IBD diagnosis.”
To investigate this topic further, the researchers identified 19 patients who were diagnosed with IBD and treated with isotretinoin between Jan. 1, 2006, and Jan. 1, 2020, at Mass General Brigham Hospitals, Boston. They determined severity of disease and degree of antecedent management of IBD by evaluating flaring two years prior to starting isotretinoin. The patients were considered to have a flare caused by isotretinoin if the IBD flare occurred during or up to 3 months following course completion.
The mean age of the 19 patients was 35 years, 26% were female, and 95% were White. Nearly half of the patients (42%) had ulcerative colitis, 37% had Crohn’s disease, and 21% had both. The researchers found that nine patients had flared two years before starting isotretinoin. Of these, five (56%) flared and four (44%) did not flare during treatment or within three months of completing the course of isotretinoin.
Of the 10 patients who did not flare two years before starting isotretinoin, seven (70%) did not flare during treatment and three (30%) flared during or within three months following completion of isotretinoin use. The researchers found no statistically significant association between isotretinoin use and flaring among patients with IBD (P = .76).
Dr. Lopez and her colleagues also assessed IBD maintenance therapy with respect to IBD flares in the study population. They observed no statistically significant association between the use of maintenance IBD therapy and the likelihood of having flares during isotretinoin treatment (P = .15).
“The results suggest limited association between isotretinoin and the worsening of a patient’s baseline IBD,” the authors concluded. They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and retrospective design, and they called for larger and prospective studies to assess the relationship of IBD flaring in this population of patients.
Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the results, characterized the trial as “an important study highlighting how we continue to understand the safe use of isotretinoin in the IBD cohort.”
Isotretinoin, she added, “continues to be a highly important treatment for acne and in patients such as these where oral antibiotics are relatively contraindicated due to risk of exacerbating their bowel disease.” Such data are reassuring, “albeit future studies with larger patient pools are desirable,” she added. “Future studies could also help to elucidate if diet, smoking, sleep, exercise, and medication adherence are potential confounding factors along with whether the cumulative isotretinoin dose has any effect on IBD flares in those who are susceptible.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Sodha had financial conflicts. The other authors were from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard University, Boston, and the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Ulcer on knuckle
Since the papules were worrisome for vasculitis, 2 punch biopsies were performed on smaller, younger lesions on the hand and 1 was submitted for direct immunofluorescence. Findings revealed a leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV) with prominent immunoglobulin A (IgA) deposits around the vessel wall. The clinical and pathologic findings were consistent with a rare fibrosing LCV called erythema elevatum diutinum (EED). The practice of sampling nonblanching purpura or papules for both standard pathology (hematoxylin and eosin) and direct immunofluorescence can facilitate the diagnosis of unusual conditions that may occur only a few times in one’s career.
EED is rare, chronic, and may be associated with IgA gammopathy, IgA antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, recent streptococcal or HIV infections, or myelodysplastic syndrome. A robust work-up to identify whether any of these factors are at work is critical.1 Distinct from other vasculitides, EED forms granulation tissue that becomes reinjured.
This patient was found to have an IgA monoclonal gammopathy that was monitored by Hematology. After checking her glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity, she was treated with oral dapsone 25 mg/d. Dapsone was titrated up to 100 mg/d, which improved her symptoms considerably and the ulcerated papule was surgically revised and closed. EED can last for years and ultimately clear or can persist indefinitely.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Sandhu JK, Albrecht J, Agnihotri G, et al. Erythema elevatum et diutinum as a systemic disease. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:679-683. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.07.028

Since the papules were worrisome for vasculitis, 2 punch biopsies were performed on smaller, younger lesions on the hand and 1 was submitted for direct immunofluorescence. Findings revealed a leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV) with prominent immunoglobulin A (IgA) deposits around the vessel wall. The clinical and pathologic findings were consistent with a rare fibrosing LCV called erythema elevatum diutinum (EED). The practice of sampling nonblanching purpura or papules for both standard pathology (hematoxylin and eosin) and direct immunofluorescence can facilitate the diagnosis of unusual conditions that may occur only a few times in one’s career.
EED is rare, chronic, and may be associated with IgA gammopathy, IgA antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, recent streptococcal or HIV infections, or myelodysplastic syndrome. A robust work-up to identify whether any of these factors are at work is critical.1 Distinct from other vasculitides, EED forms granulation tissue that becomes reinjured.
This patient was found to have an IgA monoclonal gammopathy that was monitored by Hematology. After checking her glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity, she was treated with oral dapsone 25 mg/d. Dapsone was titrated up to 100 mg/d, which improved her symptoms considerably and the ulcerated papule was surgically revised and closed. EED can last for years and ultimately clear or can persist indefinitely.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

Since the papules were worrisome for vasculitis, 2 punch biopsies were performed on smaller, younger lesions on the hand and 1 was submitted for direct immunofluorescence. Findings revealed a leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV) with prominent immunoglobulin A (IgA) deposits around the vessel wall. The clinical and pathologic findings were consistent with a rare fibrosing LCV called erythema elevatum diutinum (EED). The practice of sampling nonblanching purpura or papules for both standard pathology (hematoxylin and eosin) and direct immunofluorescence can facilitate the diagnosis of unusual conditions that may occur only a few times in one’s career.
EED is rare, chronic, and may be associated with IgA gammopathy, IgA antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, recent streptococcal or HIV infections, or myelodysplastic syndrome. A robust work-up to identify whether any of these factors are at work is critical.1 Distinct from other vasculitides, EED forms granulation tissue that becomes reinjured.
This patient was found to have an IgA monoclonal gammopathy that was monitored by Hematology. After checking her glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity, she was treated with oral dapsone 25 mg/d. Dapsone was titrated up to 100 mg/d, which improved her symptoms considerably and the ulcerated papule was surgically revised and closed. EED can last for years and ultimately clear or can persist indefinitely.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Sandhu JK, Albrecht J, Agnihotri G, et al. Erythema elevatum et diutinum as a systemic disease. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:679-683. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.07.028
1. Sandhu JK, Albrecht J, Agnihotri G, et al. Erythema elevatum et diutinum as a systemic disease. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:679-683. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.07.028
Manufacturer announces FDA approval for molluscum treatment delayed
Pharmaceuticals, which is developing the product.
VP-102 is a proprietary drug-device combination of cantharidin 0.7% administered through a single-use precision applicator, which has been evaluated in phase 3 studies of patients with molluscum aged 2 years and older. It features a visualization agent so the person applying the drug can see which lesions have been treated. It also contains a bittering agent to mitigate oral ingestion by children.
According to a press release from Verrica, the only deficiency listed in the FDA’s complete response letter stemmed from a general reinspection of Sterling Pharmaceuticals Services, which manufactures Verrica’s bulk solution drug product. Although none of the issues identified by the FDA during the reinspection were specific to the manufacturing of VP-102, FDA policy prevents approval of a new drug application when a contract manufacturing organization has an unresolved classification status or is placed on “official action indicated” status.
According to the press release, Verrica will “continue to work collaboratively” with the FDA to bring VP-102 to the market as soon as possible. The company has completed phase 2 studies of VP-102 for the treatment of common warts and for the treatment of external genital warts, the release said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pharmaceuticals, which is developing the product.
VP-102 is a proprietary drug-device combination of cantharidin 0.7% administered through a single-use precision applicator, which has been evaluated in phase 3 studies of patients with molluscum aged 2 years and older. It features a visualization agent so the person applying the drug can see which lesions have been treated. It also contains a bittering agent to mitigate oral ingestion by children.
According to a press release from Verrica, the only deficiency listed in the FDA’s complete response letter stemmed from a general reinspection of Sterling Pharmaceuticals Services, which manufactures Verrica’s bulk solution drug product. Although none of the issues identified by the FDA during the reinspection were specific to the manufacturing of VP-102, FDA policy prevents approval of a new drug application when a contract manufacturing organization has an unresolved classification status or is placed on “official action indicated” status.
According to the press release, Verrica will “continue to work collaboratively” with the FDA to bring VP-102 to the market as soon as possible. The company has completed phase 2 studies of VP-102 for the treatment of common warts and for the treatment of external genital warts, the release said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pharmaceuticals, which is developing the product.
VP-102 is a proprietary drug-device combination of cantharidin 0.7% administered through a single-use precision applicator, which has been evaluated in phase 3 studies of patients with molluscum aged 2 years and older. It features a visualization agent so the person applying the drug can see which lesions have been treated. It also contains a bittering agent to mitigate oral ingestion by children.
According to a press release from Verrica, the only deficiency listed in the FDA’s complete response letter stemmed from a general reinspection of Sterling Pharmaceuticals Services, which manufactures Verrica’s bulk solution drug product. Although none of the issues identified by the FDA during the reinspection were specific to the manufacturing of VP-102, FDA policy prevents approval of a new drug application when a contract manufacturing organization has an unresolved classification status or is placed on “official action indicated” status.
According to the press release, Verrica will “continue to work collaboratively” with the FDA to bring VP-102 to the market as soon as possible. The company has completed phase 2 studies of VP-102 for the treatment of common warts and for the treatment of external genital warts, the release said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves topical tapinarof for plaque psoriasis
The the manufacturer announced.
Tapinarof is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist and is the first FDA-approved steroid-free topical medication in this class, according to a press release from the manufacturer, Dermavant.
Approval was based on results of three studies in a phase 3 clinical trial program (PSOARING 1, PSOARING 2), and an open-label extension study, (PSOARING 3), the company release said. In PSOARING 1 and 2, approximately 1,000 adults aged 18-75 years (median age, 51 years) with plaque psoriasis were randomized to once-daily topical tapinarof or placebo for up to 12 weeks; 85% were White and 57% were men. The study findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in December 2021.
The primary endpoint for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved Physician Global Assessment (PGA) scores score of “clear” (0) or “almost clear” (1) and improvement of at least two grades from baseline.
After 12 weeks, 36% of the patients in PSOARING 1 and 40% in PSOARING 2 who received tapinarof met the primary outcome, compared with 6% of patients on placebo (P < .001 for both studies). Of these, a total of 73 patients from both studies who achieved PGA scores of 0 were entered in PSOARING 3, a 40-week open-label extension study, in which they stopped tapinarof treatment and retained PGA scores of 0 or 1 for approximately 4 months off treatment. An additional 312 patients who were enrolled in the PSOARING 3 extension study achieved PGA scores of 0 at least once during the study period, with “remittive” effects lasting a mean of 130 days off of treatment.
In addition, patients who received tapinarof in the PSOARING 1 and 2 studies showed significant improvement from baseline, compared with patients on placebo, across a range of secondary endpoints including a 75% or greater improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75).
In PSOARING 1, and 2, respectively, 36.1% and 47.6% of those on tapinarof achieved a PASI 75 response at week 12, compared with 10.2% and 6.9% of those on the vehicle (P < .001 for both).
Across all three studies, the majority adverse events were mild to moderate, and limited to the application site.
The most common adverse events reported by patients in the tapinarof groups were folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, and contact dermatitis. Headaches were more common among those treated with tapinarof than those on vehicle in the studies (3.8% vs. 2.4% in PSOARING 1, and 3.8% vs. 0.6% in PSOARING 2), leading to only three treatment discontinuations.
At the end of the PSOARING 3 study (at either week 40 or early termination), 599 participants responded to satisfaction questionnaires. Of these, 83.6% said they were satisfied with the results of tapinarof treatment, and 81.7% said it was more effective than previous topical treatments they had used, according to the company’s release.
Tapinarof cream can be used on all areas of the body, including the face, skin folds, neck, genitalia, anal crux, inflammatory areas, and axillae, according to the company release.
Full prescribing information is available here.
The the manufacturer announced.
Tapinarof is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist and is the first FDA-approved steroid-free topical medication in this class, according to a press release from the manufacturer, Dermavant.
Approval was based on results of three studies in a phase 3 clinical trial program (PSOARING 1, PSOARING 2), and an open-label extension study, (PSOARING 3), the company release said. In PSOARING 1 and 2, approximately 1,000 adults aged 18-75 years (median age, 51 years) with plaque psoriasis were randomized to once-daily topical tapinarof or placebo for up to 12 weeks; 85% were White and 57% were men. The study findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in December 2021.
The primary endpoint for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved Physician Global Assessment (PGA) scores score of “clear” (0) or “almost clear” (1) and improvement of at least two grades from baseline.
After 12 weeks, 36% of the patients in PSOARING 1 and 40% in PSOARING 2 who received tapinarof met the primary outcome, compared with 6% of patients on placebo (P < .001 for both studies). Of these, a total of 73 patients from both studies who achieved PGA scores of 0 were entered in PSOARING 3, a 40-week open-label extension study, in which they stopped tapinarof treatment and retained PGA scores of 0 or 1 for approximately 4 months off treatment. An additional 312 patients who were enrolled in the PSOARING 3 extension study achieved PGA scores of 0 at least once during the study period, with “remittive” effects lasting a mean of 130 days off of treatment.
In addition, patients who received tapinarof in the PSOARING 1 and 2 studies showed significant improvement from baseline, compared with patients on placebo, across a range of secondary endpoints including a 75% or greater improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75).
In PSOARING 1, and 2, respectively, 36.1% and 47.6% of those on tapinarof achieved a PASI 75 response at week 12, compared with 10.2% and 6.9% of those on the vehicle (P < .001 for both).
Across all three studies, the majority adverse events were mild to moderate, and limited to the application site.
The most common adverse events reported by patients in the tapinarof groups were folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, and contact dermatitis. Headaches were more common among those treated with tapinarof than those on vehicle in the studies (3.8% vs. 2.4% in PSOARING 1, and 3.8% vs. 0.6% in PSOARING 2), leading to only three treatment discontinuations.
At the end of the PSOARING 3 study (at either week 40 or early termination), 599 participants responded to satisfaction questionnaires. Of these, 83.6% said they were satisfied with the results of tapinarof treatment, and 81.7% said it was more effective than previous topical treatments they had used, according to the company’s release.
Tapinarof cream can be used on all areas of the body, including the face, skin folds, neck, genitalia, anal crux, inflammatory areas, and axillae, according to the company release.
Full prescribing information is available here.
The the manufacturer announced.
Tapinarof is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist and is the first FDA-approved steroid-free topical medication in this class, according to a press release from the manufacturer, Dermavant.
Approval was based on results of three studies in a phase 3 clinical trial program (PSOARING 1, PSOARING 2), and an open-label extension study, (PSOARING 3), the company release said. In PSOARING 1 and 2, approximately 1,000 adults aged 18-75 years (median age, 51 years) with plaque psoriasis were randomized to once-daily topical tapinarof or placebo for up to 12 weeks; 85% were White and 57% were men. The study findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in December 2021.
The primary endpoint for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved Physician Global Assessment (PGA) scores score of “clear” (0) or “almost clear” (1) and improvement of at least two grades from baseline.
After 12 weeks, 36% of the patients in PSOARING 1 and 40% in PSOARING 2 who received tapinarof met the primary outcome, compared with 6% of patients on placebo (P < .001 for both studies). Of these, a total of 73 patients from both studies who achieved PGA scores of 0 were entered in PSOARING 3, a 40-week open-label extension study, in which they stopped tapinarof treatment and retained PGA scores of 0 or 1 for approximately 4 months off treatment. An additional 312 patients who were enrolled in the PSOARING 3 extension study achieved PGA scores of 0 at least once during the study period, with “remittive” effects lasting a mean of 130 days off of treatment.
In addition, patients who received tapinarof in the PSOARING 1 and 2 studies showed significant improvement from baseline, compared with patients on placebo, across a range of secondary endpoints including a 75% or greater improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75).
In PSOARING 1, and 2, respectively, 36.1% and 47.6% of those on tapinarof achieved a PASI 75 response at week 12, compared with 10.2% and 6.9% of those on the vehicle (P < .001 for both).
Across all three studies, the majority adverse events were mild to moderate, and limited to the application site.
The most common adverse events reported by patients in the tapinarof groups were folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, and contact dermatitis. Headaches were more common among those treated with tapinarof than those on vehicle in the studies (3.8% vs. 2.4% in PSOARING 1, and 3.8% vs. 0.6% in PSOARING 2), leading to only three treatment discontinuations.
At the end of the PSOARING 3 study (at either week 40 or early termination), 599 participants responded to satisfaction questionnaires. Of these, 83.6% said they were satisfied with the results of tapinarof treatment, and 81.7% said it was more effective than previous topical treatments they had used, according to the company’s release.
Tapinarof cream can be used on all areas of the body, including the face, skin folds, neck, genitalia, anal crux, inflammatory areas, and axillae, according to the company release.
Full prescribing information is available here.