User login
European committee recommends approval of baricitinib for severe alopecia areata
The European Medicines Agency’s ( (AA).
The development, which was announced in a May 20, 2022, press release from the manufacturer, Eli Lilly and Incyte, marks the first step toward European regulatory approval of baricitinib (Olumiant) for patients with severe AA, and it is now referred to the European Commission for final action. A decision is expected within the next 2 months.
The committee based its positive opinion on the results of the phase 3 BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials, recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of baricitinib in 1,200 patients with severe AA, according to the press release. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score of ≤20 at week 36. In both studies, 1 out of 3 patients treated with baricitinib 4-mg achieved 80% or more scalp hair coverage, compared with 1 out of 20 patients and 1 out of 50 patients taking placebo in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2, respectively (P ≤ .001 for all comparisons to placebo).
According to safety profile information from the phase 3 BRAVE-AA clinical program, few patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events (2.6% or less across both studies), and most treatment-emergent adverse events were mild or moderate in severity.
In February 2022, the Food and Drug Administration granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA. Lilly expects additional regulatory decisions in the United States and Japan in 2022.
Baricitinib is approved in the United States as a treatment for adults with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Prescribing information can be viewed here.
The European Medicines Agency’s ( (AA).
The development, which was announced in a May 20, 2022, press release from the manufacturer, Eli Lilly and Incyte, marks the first step toward European regulatory approval of baricitinib (Olumiant) for patients with severe AA, and it is now referred to the European Commission for final action. A decision is expected within the next 2 months.
The committee based its positive opinion on the results of the phase 3 BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials, recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of baricitinib in 1,200 patients with severe AA, according to the press release. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score of ≤20 at week 36. In both studies, 1 out of 3 patients treated with baricitinib 4-mg achieved 80% or more scalp hair coverage, compared with 1 out of 20 patients and 1 out of 50 patients taking placebo in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2, respectively (P ≤ .001 for all comparisons to placebo).
According to safety profile information from the phase 3 BRAVE-AA clinical program, few patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events (2.6% or less across both studies), and most treatment-emergent adverse events were mild or moderate in severity.
In February 2022, the Food and Drug Administration granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA. Lilly expects additional regulatory decisions in the United States and Japan in 2022.
Baricitinib is approved in the United States as a treatment for adults with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Prescribing information can be viewed here.
The European Medicines Agency’s ( (AA).
The development, which was announced in a May 20, 2022, press release from the manufacturer, Eli Lilly and Incyte, marks the first step toward European regulatory approval of baricitinib (Olumiant) for patients with severe AA, and it is now referred to the European Commission for final action. A decision is expected within the next 2 months.
The committee based its positive opinion on the results of the phase 3 BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials, recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of baricitinib in 1,200 patients with severe AA, according to the press release. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score of ≤20 at week 36. In both studies, 1 out of 3 patients treated with baricitinib 4-mg achieved 80% or more scalp hair coverage, compared with 1 out of 20 patients and 1 out of 50 patients taking placebo in BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2, respectively (P ≤ .001 for all comparisons to placebo).
According to safety profile information from the phase 3 BRAVE-AA clinical program, few patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events (2.6% or less across both studies), and most treatment-emergent adverse events were mild or moderate in severity.
In February 2022, the Food and Drug Administration granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA. Lilly expects additional regulatory decisions in the United States and Japan in 2022.
Baricitinib is approved in the United States as a treatment for adults with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Prescribing information can be viewed here.
Itching at night
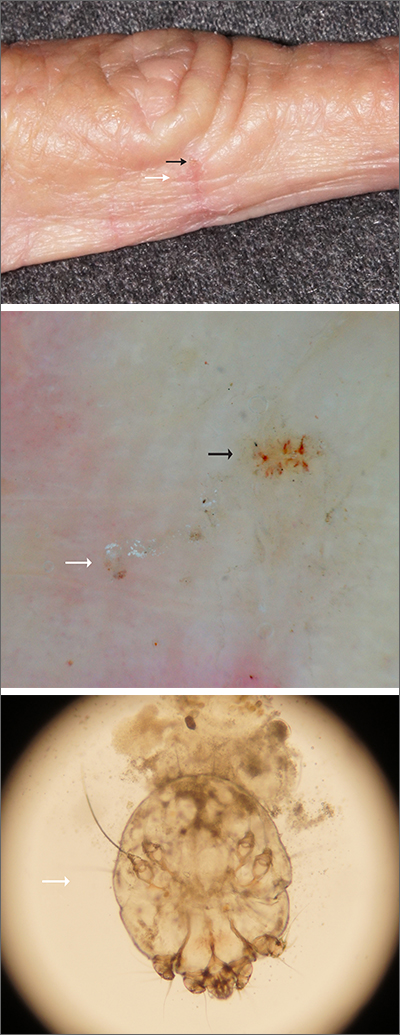
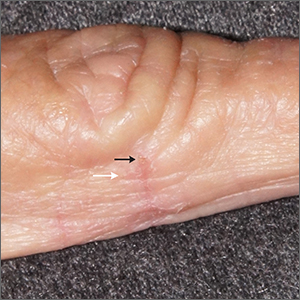
Microscopic evaluation of a dermoscopy-guided skin scraping revealed that this was a case of scabies.
Classically, patients with scabies have many excoriated papules or plaques on their hands, genitals, and trunk with itching so intense that their sleep is interrupted. However, scabies can also be diagnosed in patients who complain of itching but also have very subtle skin findings, such as a small dry patch or fissure (as in this case). Such subtle findings can be easily mistaken for mild hand dermatitis.
In the elderly, itching without a significant rash can arise from many causes. A short list includes dry skin, medications, kidney disease, liver disease, and of course, various dermatologic conditions. Dermoscopy is a sensitive and specific tool for investigating itching and areas of suspected infestation with mites.1 A mite appears as an oval on dermoscopy, but the most recognizable part is the head and front legs, which appear as a single gray triangle. The photo shows that the most erythematous area around a burrow (black arrows) is an excellent place to start when looking through the dermatoscope. In this case, an area of broken skin was connected to a haphazard tunnel that ultimately led to the mite (white arrows).
Scabies may be effectively treated with topical permethrin 5% applied over every inch of the body from the top of the neck to the tips of the toes.
This topical treatment is left on for at least 8 hours and reapplied a week later. Also, remember to take a careful history of close contacts so that others who are affected may receive treatment.
This patient was treated with permethrin, as was her adult son who lived at home with her and had similar itching. Permethrin comes in 60 g tubes, which is enough to treat 1 adult twice. After 6 weeks, all itching symptoms in the patient had cleared.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Dupuy A, Dehen L, Bourrat E, et al. Accuracy of standard dermoscopy for diagnosing scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2006.07.025

Microscopic evaluation of a dermoscopy-guided skin scraping revealed that this was a case of scabies.
Classically, patients with scabies have many excoriated papules or plaques on their hands, genitals, and trunk with itching so intense that their sleep is interrupted. However, scabies can also be diagnosed in patients who complain of itching but also have very subtle skin findings, such as a small dry patch or fissure (as in this case). Such subtle findings can be easily mistaken for mild hand dermatitis.
In the elderly, itching without a significant rash can arise from many causes. A short list includes dry skin, medications, kidney disease, liver disease, and of course, various dermatologic conditions. Dermoscopy is a sensitive and specific tool for investigating itching and areas of suspected infestation with mites.1 A mite appears as an oval on dermoscopy, but the most recognizable part is the head and front legs, which appear as a single gray triangle. The photo shows that the most erythematous area around a burrow (black arrows) is an excellent place to start when looking through the dermatoscope. In this case, an area of broken skin was connected to a haphazard tunnel that ultimately led to the mite (white arrows).
Scabies may be effectively treated with topical permethrin 5% applied over every inch of the body from the top of the neck to the tips of the toes.
This topical treatment is left on for at least 8 hours and reapplied a week later. Also, remember to take a careful history of close contacts so that others who are affected may receive treatment.
This patient was treated with permethrin, as was her adult son who lived at home with her and had similar itching. Permethrin comes in 60 g tubes, which is enough to treat 1 adult twice. After 6 weeks, all itching symptoms in the patient had cleared.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

Microscopic evaluation of a dermoscopy-guided skin scraping revealed that this was a case of scabies.
Classically, patients with scabies have many excoriated papules or plaques on their hands, genitals, and trunk with itching so intense that their sleep is interrupted. However, scabies can also be diagnosed in patients who complain of itching but also have very subtle skin findings, such as a small dry patch or fissure (as in this case). Such subtle findings can be easily mistaken for mild hand dermatitis.
In the elderly, itching without a significant rash can arise from many causes. A short list includes dry skin, medications, kidney disease, liver disease, and of course, various dermatologic conditions. Dermoscopy is a sensitive and specific tool for investigating itching and areas of suspected infestation with mites.1 A mite appears as an oval on dermoscopy, but the most recognizable part is the head and front legs, which appear as a single gray triangle. The photo shows that the most erythematous area around a burrow (black arrows) is an excellent place to start when looking through the dermatoscope. In this case, an area of broken skin was connected to a haphazard tunnel that ultimately led to the mite (white arrows).
Scabies may be effectively treated with topical permethrin 5% applied over every inch of the body from the top of the neck to the tips of the toes.
This topical treatment is left on for at least 8 hours and reapplied a week later. Also, remember to take a careful history of close contacts so that others who are affected may receive treatment.
This patient was treated with permethrin, as was her adult son who lived at home with her and had similar itching. Permethrin comes in 60 g tubes, which is enough to treat 1 adult twice. After 6 weeks, all itching symptoms in the patient had cleared.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Dupuy A, Dehen L, Bourrat E, et al. Accuracy of standard dermoscopy for diagnosing scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2006.07.025
1. Dupuy A, Dehen L, Bourrat E, et al. Accuracy of standard dermoscopy for diagnosing scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2006.07.025
Lenabasum improved skin symptoms in dermatomyositis, but future is uncertain
An – some of it statistically significant – in a phase 2, double-blind, randomized, controlled study.
Patients taking lenabasum experienced greater reductions in the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI) – a validated outcome designed to assess inflammatory skin involvement in the rare autoimmune disease – and improvements in patient-reported and biomarker outcomes, compared with those on placebo, dermatologist Victoria P. Werth, MD, and coinvestigators reported.
And in a recently completed phase 3 trial, reported by the manufacturer, a subpopulation of patients with active skin disease and no active muscle disease again showed greater reductions in CDASI activity scores – a secondary outcome in the trial.
However, the phase 3 DETERMINE trial produced negative findings overall. It enrolled a more heterogeneous group of patients – including those with both muscle weakness and skin involvement – and its primary outcome measure was a broader composite measure, the Total Improvement Score. The trial failed to meet this primary endpoint, Corbus Pharmaceuticals, the developer of lenabasum, announced in a press release in June 2021.
The phase 3 results are “frustrating” for patients with symptomatic and refractory skin manifestations of dermatomyositis (DM), given the promising findings from the phase 2 trial and from an open-label extension study, said Dr. Werth, professor of dermatology and medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and principal investigator and coprincipal investigator of the phase 2 and phase 3 studies, respectively.
Dr. Werth is scheduled to present the results from the phase 3 trial at the annual European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology meeting in June.
“With lenabasum, we have a therapy that doesn’t work for every patient, but does work for quite a number of them,” Dr. Werth said in an interview. “It’s oral, it’s not really that immunosuppressing, and there aren’t many side effects. Right now, patients are often being managed with steroids ... we really need treatments that are not as toxic.”
Robert Spiera, MD, a rheumatologist who led trials of lenabasum for treatment of diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc), agreed. “The CB2 agonist strategy is appealing because it’s nonimmunosuppressing and has both anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties,” he said in an interview. “I wouldn’t want to give up on it ... especially [for patients] with scleroderma and dermatomyositis who are treated with substantial drugs that are associated with morbidity.”
Lenabasum, he said, has proven to be “incredibly safe, and incredibly safe in the long term.”
While the phase 2 trial of the drug for dcSSc showed clear benefit over placebo, the phase 3 trial did not meet its primary endpoint using the American College of Rheumatology Combined Response Index in Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis.
It allowed background immunosuppressant therapy to reflect real-world clinical practice, and “there was such a high response rate to [that therapy, largely mycophenolate] that there was little room to show benefit beyond that,” said Dr. Spiera, director of the vasculitis and scleroderma program, Hospital for Special Surgery, New York.
The drug led to more improvement in the small subset of participants who were not receiving background immunotherapy during the trial, he noted.
Corbus is currently “seeking a partnership to further explore the drug” for treatment in different subpopulations, according to a company spokesperson. Results of a phase 2 trial of lenabasum for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus – with a pain rating as the primary outcome measure – are expected soon.
Phase 2 findings
The single-center phase 2 trial of lenabasum for DM enrolled 22 adults with minimal muscle involvement as evidenced by normal maximal resistance on muscle testing at entry and throughout the study. Most were taking immunosuppressant medication, and all had CDASI scores of at least 20, with mean scores in the severe range (> 26). Symptoms registered on patient-reported outcome measures were moderate to severe.
Patients received a half-dose of lenabasum (20 mg daily) for 1 month and a full dose (20 mg twice daily) for 2 months, or placebo, and were followed for an additional month without dosing.
Starting at day 43 – approximately 2 weeks after the dose was increased – there was “a trend for the change from baseline CDASI to be greater” in the lenabasum group, compared with those on placebo, Dr. Werth and colleagues reported. The differences reached statistical significance on day 113 (P = .038), a month after patients discontinued lenabasum, “suggesting that the modulation of the inflammatory response by lenabasum continued beyond its last dose.”
Five of the 11 patients treated with lenabasum (45%), and none of those on placebo, achieved at least a 40% reduction in the CDASI activity score by the end of the study.
Patients in the lenabasum group also had greater improvement in the Skindex-29 Symptoms scores – an objective measure of itch – and improvements in other secondary efficacy outcomes, including pain, though these did not reach statistical significance.
Skin biopsies before and after treatment showed significant reductions in inflammatory cytokines relevant to DM pathogenesis. Patients treated with the CB2 agonist had a downward trend in the CD4+ T cell population, which correlated with decreased CDASI activity scores, for instance, and a decrease in IL-31 protein expression, which correlated with decreased Skindex-29 Symptoms scores, the investigators reported.
There were no serious adverse events related to the CB2 agonist, and no treatment discontinuations.
The main part of the phase 2 trial, conducted from 2015 to 2017, was followed by a 3-year, open-label extension, in which 20 of the 22 patients took lenabasum 20 mg twice a day. The drug continued to be safe and well tolerated, and the CDASI activity score and other outcomes improved through year 1 and remained stable thereafter, according to a poster presented by Dr. Werth at the 2021 EULAR meeting.
After 1 year in the open-label extension, 60%-70% of patients had achieved mild skin disease, and 75% had achieved at least a 40% reduction in CDASI activity.
“A lot of patients, even if they weren’t completely cleared, were much happier in terms of their itch,” said Dr. Werth, also chief of dermatology, Corporal Michael J. Crescenz Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Philadelphia. “It’s been difficult for a lot of them now that they’re off the long-term extension ... a lot of them are flaring.”
The future
In the lab, with funding from the National Institutes of Health, Dr. Werth is continuing to investigate how lenabasum may be working in DM. A paper just published in the open access journal Arthritis Research & Therapy describes CB2 receptor distribution and up-regulation on key immune cells in the skin and blood, and how, in DM skin, its highest expression is on dendritic cells.
Through both mechanistic and more clinical research, “it’s important to understand the characteristics of the people [lenabasum] worked in or didn’t work in,” she said.
And in clinical trials, it’s important to capture meaningful improvement from the patient perspective. “It may be,” she noted, “that more global, systemic assessments are not the way to go for autoimmune skin disease.”
For dcSSc, Dr. Spiera said, it’s possible that a CB2 agonist may be helpful for patients who have been on immunosuppressants, particularly mycophenolate, for more than 6 months “and are still struggling.”
The phase 2 trial in DM was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Veterans Affairs, and Corbus Pharmaceuticals. The phase 3 trials in DM and in dcSSc were funded by Corbus. Dr. Werth disclosed grant support from Corbus and several other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Spiera disclosed that he has received grant support or consulting fees from Roche-Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, and several other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An – some of it statistically significant – in a phase 2, double-blind, randomized, controlled study.
Patients taking lenabasum experienced greater reductions in the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI) – a validated outcome designed to assess inflammatory skin involvement in the rare autoimmune disease – and improvements in patient-reported and biomarker outcomes, compared with those on placebo, dermatologist Victoria P. Werth, MD, and coinvestigators reported.
And in a recently completed phase 3 trial, reported by the manufacturer, a subpopulation of patients with active skin disease and no active muscle disease again showed greater reductions in CDASI activity scores – a secondary outcome in the trial.
However, the phase 3 DETERMINE trial produced negative findings overall. It enrolled a more heterogeneous group of patients – including those with both muscle weakness and skin involvement – and its primary outcome measure was a broader composite measure, the Total Improvement Score. The trial failed to meet this primary endpoint, Corbus Pharmaceuticals, the developer of lenabasum, announced in a press release in June 2021.
The phase 3 results are “frustrating” for patients with symptomatic and refractory skin manifestations of dermatomyositis (DM), given the promising findings from the phase 2 trial and from an open-label extension study, said Dr. Werth, professor of dermatology and medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and principal investigator and coprincipal investigator of the phase 2 and phase 3 studies, respectively.
Dr. Werth is scheduled to present the results from the phase 3 trial at the annual European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology meeting in June.
“With lenabasum, we have a therapy that doesn’t work for every patient, but does work for quite a number of them,” Dr. Werth said in an interview. “It’s oral, it’s not really that immunosuppressing, and there aren’t many side effects. Right now, patients are often being managed with steroids ... we really need treatments that are not as toxic.”
Robert Spiera, MD, a rheumatologist who led trials of lenabasum for treatment of diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc), agreed. “The CB2 agonist strategy is appealing because it’s nonimmunosuppressing and has both anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties,” he said in an interview. “I wouldn’t want to give up on it ... especially [for patients] with scleroderma and dermatomyositis who are treated with substantial drugs that are associated with morbidity.”
Lenabasum, he said, has proven to be “incredibly safe, and incredibly safe in the long term.”
While the phase 2 trial of the drug for dcSSc showed clear benefit over placebo, the phase 3 trial did not meet its primary endpoint using the American College of Rheumatology Combined Response Index in Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis.
It allowed background immunosuppressant therapy to reflect real-world clinical practice, and “there was such a high response rate to [that therapy, largely mycophenolate] that there was little room to show benefit beyond that,” said Dr. Spiera, director of the vasculitis and scleroderma program, Hospital for Special Surgery, New York.
The drug led to more improvement in the small subset of participants who were not receiving background immunotherapy during the trial, he noted.
Corbus is currently “seeking a partnership to further explore the drug” for treatment in different subpopulations, according to a company spokesperson. Results of a phase 2 trial of lenabasum for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus – with a pain rating as the primary outcome measure – are expected soon.
Phase 2 findings
The single-center phase 2 trial of lenabasum for DM enrolled 22 adults with minimal muscle involvement as evidenced by normal maximal resistance on muscle testing at entry and throughout the study. Most were taking immunosuppressant medication, and all had CDASI scores of at least 20, with mean scores in the severe range (> 26). Symptoms registered on patient-reported outcome measures were moderate to severe.
Patients received a half-dose of lenabasum (20 mg daily) for 1 month and a full dose (20 mg twice daily) for 2 months, or placebo, and were followed for an additional month without dosing.
Starting at day 43 – approximately 2 weeks after the dose was increased – there was “a trend for the change from baseline CDASI to be greater” in the lenabasum group, compared with those on placebo, Dr. Werth and colleagues reported. The differences reached statistical significance on day 113 (P = .038), a month after patients discontinued lenabasum, “suggesting that the modulation of the inflammatory response by lenabasum continued beyond its last dose.”
Five of the 11 patients treated with lenabasum (45%), and none of those on placebo, achieved at least a 40% reduction in the CDASI activity score by the end of the study.
Patients in the lenabasum group also had greater improvement in the Skindex-29 Symptoms scores – an objective measure of itch – and improvements in other secondary efficacy outcomes, including pain, though these did not reach statistical significance.
Skin biopsies before and after treatment showed significant reductions in inflammatory cytokines relevant to DM pathogenesis. Patients treated with the CB2 agonist had a downward trend in the CD4+ T cell population, which correlated with decreased CDASI activity scores, for instance, and a decrease in IL-31 protein expression, which correlated with decreased Skindex-29 Symptoms scores, the investigators reported.
There were no serious adverse events related to the CB2 agonist, and no treatment discontinuations.
The main part of the phase 2 trial, conducted from 2015 to 2017, was followed by a 3-year, open-label extension, in which 20 of the 22 patients took lenabasum 20 mg twice a day. The drug continued to be safe and well tolerated, and the CDASI activity score and other outcomes improved through year 1 and remained stable thereafter, according to a poster presented by Dr. Werth at the 2021 EULAR meeting.
After 1 year in the open-label extension, 60%-70% of patients had achieved mild skin disease, and 75% had achieved at least a 40% reduction in CDASI activity.
“A lot of patients, even if they weren’t completely cleared, were much happier in terms of their itch,” said Dr. Werth, also chief of dermatology, Corporal Michael J. Crescenz Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Philadelphia. “It’s been difficult for a lot of them now that they’re off the long-term extension ... a lot of them are flaring.”
The future
In the lab, with funding from the National Institutes of Health, Dr. Werth is continuing to investigate how lenabasum may be working in DM. A paper just published in the open access journal Arthritis Research & Therapy describes CB2 receptor distribution and up-regulation on key immune cells in the skin and blood, and how, in DM skin, its highest expression is on dendritic cells.
Through both mechanistic and more clinical research, “it’s important to understand the characteristics of the people [lenabasum] worked in or didn’t work in,” she said.
And in clinical trials, it’s important to capture meaningful improvement from the patient perspective. “It may be,” she noted, “that more global, systemic assessments are not the way to go for autoimmune skin disease.”
For dcSSc, Dr. Spiera said, it’s possible that a CB2 agonist may be helpful for patients who have been on immunosuppressants, particularly mycophenolate, for more than 6 months “and are still struggling.”
The phase 2 trial in DM was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Veterans Affairs, and Corbus Pharmaceuticals. The phase 3 trials in DM and in dcSSc were funded by Corbus. Dr. Werth disclosed grant support from Corbus and several other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Spiera disclosed that he has received grant support or consulting fees from Roche-Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, and several other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An – some of it statistically significant – in a phase 2, double-blind, randomized, controlled study.
Patients taking lenabasum experienced greater reductions in the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI) – a validated outcome designed to assess inflammatory skin involvement in the rare autoimmune disease – and improvements in patient-reported and biomarker outcomes, compared with those on placebo, dermatologist Victoria P. Werth, MD, and coinvestigators reported.
And in a recently completed phase 3 trial, reported by the manufacturer, a subpopulation of patients with active skin disease and no active muscle disease again showed greater reductions in CDASI activity scores – a secondary outcome in the trial.
However, the phase 3 DETERMINE trial produced negative findings overall. It enrolled a more heterogeneous group of patients – including those with both muscle weakness and skin involvement – and its primary outcome measure was a broader composite measure, the Total Improvement Score. The trial failed to meet this primary endpoint, Corbus Pharmaceuticals, the developer of lenabasum, announced in a press release in June 2021.
The phase 3 results are “frustrating” for patients with symptomatic and refractory skin manifestations of dermatomyositis (DM), given the promising findings from the phase 2 trial and from an open-label extension study, said Dr. Werth, professor of dermatology and medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and principal investigator and coprincipal investigator of the phase 2 and phase 3 studies, respectively.
Dr. Werth is scheduled to present the results from the phase 3 trial at the annual European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology meeting in June.
“With lenabasum, we have a therapy that doesn’t work for every patient, but does work for quite a number of them,” Dr. Werth said in an interview. “It’s oral, it’s not really that immunosuppressing, and there aren’t many side effects. Right now, patients are often being managed with steroids ... we really need treatments that are not as toxic.”
Robert Spiera, MD, a rheumatologist who led trials of lenabasum for treatment of diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc), agreed. “The CB2 agonist strategy is appealing because it’s nonimmunosuppressing and has both anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties,” he said in an interview. “I wouldn’t want to give up on it ... especially [for patients] with scleroderma and dermatomyositis who are treated with substantial drugs that are associated with morbidity.”
Lenabasum, he said, has proven to be “incredibly safe, and incredibly safe in the long term.”
While the phase 2 trial of the drug for dcSSc showed clear benefit over placebo, the phase 3 trial did not meet its primary endpoint using the American College of Rheumatology Combined Response Index in Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis.
It allowed background immunosuppressant therapy to reflect real-world clinical practice, and “there was such a high response rate to [that therapy, largely mycophenolate] that there was little room to show benefit beyond that,” said Dr. Spiera, director of the vasculitis and scleroderma program, Hospital for Special Surgery, New York.
The drug led to more improvement in the small subset of participants who were not receiving background immunotherapy during the trial, he noted.
Corbus is currently “seeking a partnership to further explore the drug” for treatment in different subpopulations, according to a company spokesperson. Results of a phase 2 trial of lenabasum for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus – with a pain rating as the primary outcome measure – are expected soon.
Phase 2 findings
The single-center phase 2 trial of lenabasum for DM enrolled 22 adults with minimal muscle involvement as evidenced by normal maximal resistance on muscle testing at entry and throughout the study. Most were taking immunosuppressant medication, and all had CDASI scores of at least 20, with mean scores in the severe range (> 26). Symptoms registered on patient-reported outcome measures were moderate to severe.
Patients received a half-dose of lenabasum (20 mg daily) for 1 month and a full dose (20 mg twice daily) for 2 months, or placebo, and were followed for an additional month without dosing.
Starting at day 43 – approximately 2 weeks after the dose was increased – there was “a trend for the change from baseline CDASI to be greater” in the lenabasum group, compared with those on placebo, Dr. Werth and colleagues reported. The differences reached statistical significance on day 113 (P = .038), a month after patients discontinued lenabasum, “suggesting that the modulation of the inflammatory response by lenabasum continued beyond its last dose.”
Five of the 11 patients treated with lenabasum (45%), and none of those on placebo, achieved at least a 40% reduction in the CDASI activity score by the end of the study.
Patients in the lenabasum group also had greater improvement in the Skindex-29 Symptoms scores – an objective measure of itch – and improvements in other secondary efficacy outcomes, including pain, though these did not reach statistical significance.
Skin biopsies before and after treatment showed significant reductions in inflammatory cytokines relevant to DM pathogenesis. Patients treated with the CB2 agonist had a downward trend in the CD4+ T cell population, which correlated with decreased CDASI activity scores, for instance, and a decrease in IL-31 protein expression, which correlated with decreased Skindex-29 Symptoms scores, the investigators reported.
There were no serious adverse events related to the CB2 agonist, and no treatment discontinuations.
The main part of the phase 2 trial, conducted from 2015 to 2017, was followed by a 3-year, open-label extension, in which 20 of the 22 patients took lenabasum 20 mg twice a day. The drug continued to be safe and well tolerated, and the CDASI activity score and other outcomes improved through year 1 and remained stable thereafter, according to a poster presented by Dr. Werth at the 2021 EULAR meeting.
After 1 year in the open-label extension, 60%-70% of patients had achieved mild skin disease, and 75% had achieved at least a 40% reduction in CDASI activity.
“A lot of patients, even if they weren’t completely cleared, were much happier in terms of their itch,” said Dr. Werth, also chief of dermatology, Corporal Michael J. Crescenz Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Philadelphia. “It’s been difficult for a lot of them now that they’re off the long-term extension ... a lot of them are flaring.”
The future
In the lab, with funding from the National Institutes of Health, Dr. Werth is continuing to investigate how lenabasum may be working in DM. A paper just published in the open access journal Arthritis Research & Therapy describes CB2 receptor distribution and up-regulation on key immune cells in the skin and blood, and how, in DM skin, its highest expression is on dendritic cells.
Through both mechanistic and more clinical research, “it’s important to understand the characteristics of the people [lenabasum] worked in or didn’t work in,” she said.
And in clinical trials, it’s important to capture meaningful improvement from the patient perspective. “It may be,” she noted, “that more global, systemic assessments are not the way to go for autoimmune skin disease.”
For dcSSc, Dr. Spiera said, it’s possible that a CB2 agonist may be helpful for patients who have been on immunosuppressants, particularly mycophenolate, for more than 6 months “and are still struggling.”
The phase 2 trial in DM was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Veterans Affairs, and Corbus Pharmaceuticals. The phase 3 trials in DM and in dcSSc were funded by Corbus. Dr. Werth disclosed grant support from Corbus and several other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Spiera disclosed that he has received grant support or consulting fees from Roche-Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, and several other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY
Severe infections often accompany severe psoriasis
of nearly 95,000 patients.
Although previous studies have shown a higher risk for comorbid conditions in people with psoriasis, compared with those without psoriasis, data on the occurrence of severe and rare infections in patients with psoriasis are limited, wrote Nikolai Loft, MD, of the department of dermatology and allergy, Copenhagen University Hospital, Gentofte, and colleagues.
Psoriasis patients are often treated with immunosuppressive therapies that may promote or aggravate infections; therefore, a better understanding of psoriasis and risk of infections is needed, they said. In a study published in the British Journal of Dermatology, Dr. Loft and his coinvestigators reviewed data on adults aged 18 years and older from the Danish National Patient Register between Jan. 1, 1997 and Dec. 31, 2018. The study population included 94,450 adults with psoriasis and 566,700 matched controls. Patients with any type of psoriasis and any degree of severity were included.
The primary outcome was the occurrence of severe infections, defined as those requiring assessment at a hospital, and rare infections, defined as HIV, TB, HBV, and HCV. The median age of the participants was 52.3 years, and slightly more than half were women.
Overall, the incidence rate of severe and rare infections among patients with any type of psoriasis was 3,104.9 per 100,000 person-years, compared with 2,381.1 for controls, with a hazard ratio, adjusted for gender, age, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, alcohol-related conditions, and Charlson comorbidity index (aHR) of 1.29.
For any infections resulting in hospitalization, the incidence rate was 2,005.1 vs. 1,531.8 per 100,000 person-years for patients with any type of psoriasis and controls, respectively.
The results were similar when severe infections and rare infections were analyzed separately. The incidence rate of severe infections was 3,080.6 and 2,364.4 per 100,000 person-years for patients with any psoriasis, compared with controls; the incidence rate for rare infections was 42.9 and 31.8 for all psoriasis patients and controls, respectively.
When the data were examined by psoriasis severity, the incidence rate of severe and rare infections among patients with severe psoriasis was 3,847.7 per 100,000 person-years, compared with 2,351.9 per 100,000 person years among controls (aHR, 1.58) and also higher than in patients with mild psoriasis. The incidence rate of severe and rare infections in patients with mild psoriasis (2,979.1 per 100,000 person-years) also was higher than in controls (aHR, 1.26).
Factors that might explain the increased infection risk with severe psoriasis include the altered immune environment in these patients, the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. Also, “patients with severe psoriasis are defined by their eligibility for systemics, either conventional or biologic,” and their increased infection risk may stem from these treatments, rather than disease severity itself, they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on such confounders as weight, body mass index, and smoking status, they added. Other limitations included potential surveillance bias because of greater TB screening, and the use of prescriptions, rather than the Psoriasis Area Severity Index, to define severity. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and suggest that patients with any type of psoriasis have higher rates of any infection, severe or rare, than the general population, the researchers concluded.
Data show need for clinician vigilance
Based on the 2020 Census data, an estimated 7.55 million adults in the United States have psoriasis, David Robles, MD, said in an interview. “Patients with psoriasis have a high risk for multiple comorbid conditions including metabolic syndrome, which is characterized by obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia,” said Dr. Robles, a dermatologist in private practice in Pomona, Calif., who was not involved in the study. “Although these complications were previously attributed to diet and obesity, it has become clear that the proinflammatory cytokines associated with psoriasis may be playing an important role underlying the pathologic basis of these other comorbidities.”
There is an emerging body of literature “indicating that psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of infections,” he added. Research in this area is particularly important because of the increased risk of infections associated with many biologic and immune-modulating treatments for psoriasis, Dr. Robles noted.
The study findings “indicate that, as the severity of psoriasis increases, so does the risk of severe and rare infections,” he said. “This makes it imperative for clinicians to be alert to the possibility of severe or rare infections in patients with psoriasis, especially those with severe psoriasis, so that early intervention can be initiated.”
As for additional research, “as an immunologist and dermatologist, I cannot help but think about the possible role the genetic and cytokine pathways involved in psoriasis may be playing in modulating the immune system and/or microbiome, and whether this contributes to a higher risk of infections,” Dr. Robles said. “Just as it was discovered that patients with atopic dermatitis have decreased levels of antimicrobial peptides in their skin, making them susceptible to recurrent bacterial skin infections, we may find that the genetic and immunological changes associated with psoriasis may independently contribute to infection susceptibility,” he noted. “More basic immunology and virology research may one day shed light on this observation.”
The study was supported by Novartis. Lead author Dr. Loft disclosed serving as a speaker for Eli Lilly and Janssen Cilag, other authors disclosed relationships with multiple companies including Novartis, and two authors are Novartis employees. Dr. Robles had no relevant financial disclosures.
of nearly 95,000 patients.
Although previous studies have shown a higher risk for comorbid conditions in people with psoriasis, compared with those without psoriasis, data on the occurrence of severe and rare infections in patients with psoriasis are limited, wrote Nikolai Loft, MD, of the department of dermatology and allergy, Copenhagen University Hospital, Gentofte, and colleagues.
Psoriasis patients are often treated with immunosuppressive therapies that may promote or aggravate infections; therefore, a better understanding of psoriasis and risk of infections is needed, they said. In a study published in the British Journal of Dermatology, Dr. Loft and his coinvestigators reviewed data on adults aged 18 years and older from the Danish National Patient Register between Jan. 1, 1997 and Dec. 31, 2018. The study population included 94,450 adults with psoriasis and 566,700 matched controls. Patients with any type of psoriasis and any degree of severity were included.
The primary outcome was the occurrence of severe infections, defined as those requiring assessment at a hospital, and rare infections, defined as HIV, TB, HBV, and HCV. The median age of the participants was 52.3 years, and slightly more than half were women.
Overall, the incidence rate of severe and rare infections among patients with any type of psoriasis was 3,104.9 per 100,000 person-years, compared with 2,381.1 for controls, with a hazard ratio, adjusted for gender, age, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, alcohol-related conditions, and Charlson comorbidity index (aHR) of 1.29.
For any infections resulting in hospitalization, the incidence rate was 2,005.1 vs. 1,531.8 per 100,000 person-years for patients with any type of psoriasis and controls, respectively.
The results were similar when severe infections and rare infections were analyzed separately. The incidence rate of severe infections was 3,080.6 and 2,364.4 per 100,000 person-years for patients with any psoriasis, compared with controls; the incidence rate for rare infections was 42.9 and 31.8 for all psoriasis patients and controls, respectively.
When the data were examined by psoriasis severity, the incidence rate of severe and rare infections among patients with severe psoriasis was 3,847.7 per 100,000 person-years, compared with 2,351.9 per 100,000 person years among controls (aHR, 1.58) and also higher than in patients with mild psoriasis. The incidence rate of severe and rare infections in patients with mild psoriasis (2,979.1 per 100,000 person-years) also was higher than in controls (aHR, 1.26).
Factors that might explain the increased infection risk with severe psoriasis include the altered immune environment in these patients, the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. Also, “patients with severe psoriasis are defined by their eligibility for systemics, either conventional or biologic,” and their increased infection risk may stem from these treatments, rather than disease severity itself, they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on such confounders as weight, body mass index, and smoking status, they added. Other limitations included potential surveillance bias because of greater TB screening, and the use of prescriptions, rather than the Psoriasis Area Severity Index, to define severity. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and suggest that patients with any type of psoriasis have higher rates of any infection, severe or rare, than the general population, the researchers concluded.
Data show need for clinician vigilance
Based on the 2020 Census data, an estimated 7.55 million adults in the United States have psoriasis, David Robles, MD, said in an interview. “Patients with psoriasis have a high risk for multiple comorbid conditions including metabolic syndrome, which is characterized by obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia,” said Dr. Robles, a dermatologist in private practice in Pomona, Calif., who was not involved in the study. “Although these complications were previously attributed to diet and obesity, it has become clear that the proinflammatory cytokines associated with psoriasis may be playing an important role underlying the pathologic basis of these other comorbidities.”
There is an emerging body of literature “indicating that psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of infections,” he added. Research in this area is particularly important because of the increased risk of infections associated with many biologic and immune-modulating treatments for psoriasis, Dr. Robles noted.
The study findings “indicate that, as the severity of psoriasis increases, so does the risk of severe and rare infections,” he said. “This makes it imperative for clinicians to be alert to the possibility of severe or rare infections in patients with psoriasis, especially those with severe psoriasis, so that early intervention can be initiated.”
As for additional research, “as an immunologist and dermatologist, I cannot help but think about the possible role the genetic and cytokine pathways involved in psoriasis may be playing in modulating the immune system and/or microbiome, and whether this contributes to a higher risk of infections,” Dr. Robles said. “Just as it was discovered that patients with atopic dermatitis have decreased levels of antimicrobial peptides in their skin, making them susceptible to recurrent bacterial skin infections, we may find that the genetic and immunological changes associated with psoriasis may independently contribute to infection susceptibility,” he noted. “More basic immunology and virology research may one day shed light on this observation.”
The study was supported by Novartis. Lead author Dr. Loft disclosed serving as a speaker for Eli Lilly and Janssen Cilag, other authors disclosed relationships with multiple companies including Novartis, and two authors are Novartis employees. Dr. Robles had no relevant financial disclosures.
of nearly 95,000 patients.
Although previous studies have shown a higher risk for comorbid conditions in people with psoriasis, compared with those without psoriasis, data on the occurrence of severe and rare infections in patients with psoriasis are limited, wrote Nikolai Loft, MD, of the department of dermatology and allergy, Copenhagen University Hospital, Gentofte, and colleagues.
Psoriasis patients are often treated with immunosuppressive therapies that may promote or aggravate infections; therefore, a better understanding of psoriasis and risk of infections is needed, they said. In a study published in the British Journal of Dermatology, Dr. Loft and his coinvestigators reviewed data on adults aged 18 years and older from the Danish National Patient Register between Jan. 1, 1997 and Dec. 31, 2018. The study population included 94,450 adults with psoriasis and 566,700 matched controls. Patients with any type of psoriasis and any degree of severity were included.
The primary outcome was the occurrence of severe infections, defined as those requiring assessment at a hospital, and rare infections, defined as HIV, TB, HBV, and HCV. The median age of the participants was 52.3 years, and slightly more than half were women.
Overall, the incidence rate of severe and rare infections among patients with any type of psoriasis was 3,104.9 per 100,000 person-years, compared with 2,381.1 for controls, with a hazard ratio, adjusted for gender, age, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, alcohol-related conditions, and Charlson comorbidity index (aHR) of 1.29.
For any infections resulting in hospitalization, the incidence rate was 2,005.1 vs. 1,531.8 per 100,000 person-years for patients with any type of psoriasis and controls, respectively.
The results were similar when severe infections and rare infections were analyzed separately. The incidence rate of severe infections was 3,080.6 and 2,364.4 per 100,000 person-years for patients with any psoriasis, compared with controls; the incidence rate for rare infections was 42.9 and 31.8 for all psoriasis patients and controls, respectively.
When the data were examined by psoriasis severity, the incidence rate of severe and rare infections among patients with severe psoriasis was 3,847.7 per 100,000 person-years, compared with 2,351.9 per 100,000 person years among controls (aHR, 1.58) and also higher than in patients with mild psoriasis. The incidence rate of severe and rare infections in patients with mild psoriasis (2,979.1 per 100,000 person-years) also was higher than in controls (aHR, 1.26).
Factors that might explain the increased infection risk with severe psoriasis include the altered immune environment in these patients, the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. Also, “patients with severe psoriasis are defined by their eligibility for systemics, either conventional or biologic,” and their increased infection risk may stem from these treatments, rather than disease severity itself, they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on such confounders as weight, body mass index, and smoking status, they added. Other limitations included potential surveillance bias because of greater TB screening, and the use of prescriptions, rather than the Psoriasis Area Severity Index, to define severity. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and suggest that patients with any type of psoriasis have higher rates of any infection, severe or rare, than the general population, the researchers concluded.
Data show need for clinician vigilance
Based on the 2020 Census data, an estimated 7.55 million adults in the United States have psoriasis, David Robles, MD, said in an interview. “Patients with psoriasis have a high risk for multiple comorbid conditions including metabolic syndrome, which is characterized by obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia,” said Dr. Robles, a dermatologist in private practice in Pomona, Calif., who was not involved in the study. “Although these complications were previously attributed to diet and obesity, it has become clear that the proinflammatory cytokines associated with psoriasis may be playing an important role underlying the pathologic basis of these other comorbidities.”
There is an emerging body of literature “indicating that psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of infections,” he added. Research in this area is particularly important because of the increased risk of infections associated with many biologic and immune-modulating treatments for psoriasis, Dr. Robles noted.
The study findings “indicate that, as the severity of psoriasis increases, so does the risk of severe and rare infections,” he said. “This makes it imperative for clinicians to be alert to the possibility of severe or rare infections in patients with psoriasis, especially those with severe psoriasis, so that early intervention can be initiated.”
As for additional research, “as an immunologist and dermatologist, I cannot help but think about the possible role the genetic and cytokine pathways involved in psoriasis may be playing in modulating the immune system and/or microbiome, and whether this contributes to a higher risk of infections,” Dr. Robles said. “Just as it was discovered that patients with atopic dermatitis have decreased levels of antimicrobial peptides in their skin, making them susceptible to recurrent bacterial skin infections, we may find that the genetic and immunological changes associated with psoriasis may independently contribute to infection susceptibility,” he noted. “More basic immunology and virology research may one day shed light on this observation.”
The study was supported by Novartis. Lead author Dr. Loft disclosed serving as a speaker for Eli Lilly and Janssen Cilag, other authors disclosed relationships with multiple companies including Novartis, and two authors are Novartis employees. Dr. Robles had no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
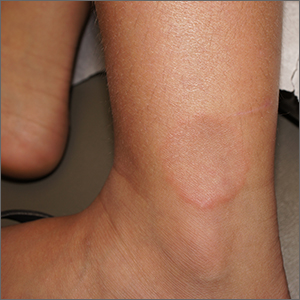
A 64-year-old woman presents with a history of asymptomatic erythematous grouped papules on the right breast
. Recurrences may occur. Rarely, lymph nodes, the gastrointestinal system, lung, bone and bone marrow may be involved as extracutaneous sites.
Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas account for approximately 25% of all cutaneous lymphomas. Clinically, patients present with either solitary or multiple papules or plaques, typically on the upper extremities or trunk.
Histopathology is vital for the correct diagnosis. In this patient, the histologic report was written as follows: “The findings are those of a well-differentiated but atypical diffuse mixed small lymphocytic infiltrate representing a mixture of T-cells and B-cells. The minor component of the infiltrate is of T-cell lineage, whereby the cells do not show any phenotypic abnormalities. The background cell population is interpreted as reactive. However, the dominant cell population is in fact of B-cell lineage. It is extensively highlighted by CD20. Only a minor component of the B cell infiltrate appeared to be in the context of representing germinal centers as characterized by small foci of centrocytic and centroblastic infiltration highlighted by BCL6 and CD10. The overwhelming B-cell component is a non–germinal center small B cell that does demonstrate BCL2 positivity and significant immunoreactivity for CD23. This small lymphocytic infiltrate obscures the germinal centers. There are only a few plasma cells; they do not show light chain restriction.”
The pathologist remarked that “this type of morphology of a diffuse small B-cell lymphocytic infiltrate that is without any evidence of light chain restriction amidst plasma cells, whereby the B cell component is dominant over the T-cell component would in fact be consistent with a unique variant of marginal zone lymphoma derived from a naive mantle zone.”
PCMZL has an excellent prognosis. When limited to the skin, local radiation or excision are effective treatments. Intravenous rituximab has been used to treat multifocal PCMZL. This patient was found to have no extracutaneous involvement and was treated with radiation.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Virmani P et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2017 Jun 14;3(4):269-72.
Magro CM and Olson LC. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2018 Jun;34:116-21.
. Recurrences may occur. Rarely, lymph nodes, the gastrointestinal system, lung, bone and bone marrow may be involved as extracutaneous sites.
Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas account for approximately 25% of all cutaneous lymphomas. Clinically, patients present with either solitary or multiple papules or plaques, typically on the upper extremities or trunk.
Histopathology is vital for the correct diagnosis. In this patient, the histologic report was written as follows: “The findings are those of a well-differentiated but atypical diffuse mixed small lymphocytic infiltrate representing a mixture of T-cells and B-cells. The minor component of the infiltrate is of T-cell lineage, whereby the cells do not show any phenotypic abnormalities. The background cell population is interpreted as reactive. However, the dominant cell population is in fact of B-cell lineage. It is extensively highlighted by CD20. Only a minor component of the B cell infiltrate appeared to be in the context of representing germinal centers as characterized by small foci of centrocytic and centroblastic infiltration highlighted by BCL6 and CD10. The overwhelming B-cell component is a non–germinal center small B cell that does demonstrate BCL2 positivity and significant immunoreactivity for CD23. This small lymphocytic infiltrate obscures the germinal centers. There are only a few plasma cells; they do not show light chain restriction.”
The pathologist remarked that “this type of morphology of a diffuse small B-cell lymphocytic infiltrate that is without any evidence of light chain restriction amidst plasma cells, whereby the B cell component is dominant over the T-cell component would in fact be consistent with a unique variant of marginal zone lymphoma derived from a naive mantle zone.”
PCMZL has an excellent prognosis. When limited to the skin, local radiation or excision are effective treatments. Intravenous rituximab has been used to treat multifocal PCMZL. This patient was found to have no extracutaneous involvement and was treated with radiation.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Virmani P et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2017 Jun 14;3(4):269-72.
Magro CM and Olson LC. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2018 Jun;34:116-21.
. Recurrences may occur. Rarely, lymph nodes, the gastrointestinal system, lung, bone and bone marrow may be involved as extracutaneous sites.
Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas account for approximately 25% of all cutaneous lymphomas. Clinically, patients present with either solitary or multiple papules or plaques, typically on the upper extremities or trunk.
Histopathology is vital for the correct diagnosis. In this patient, the histologic report was written as follows: “The findings are those of a well-differentiated but atypical diffuse mixed small lymphocytic infiltrate representing a mixture of T-cells and B-cells. The minor component of the infiltrate is of T-cell lineage, whereby the cells do not show any phenotypic abnormalities. The background cell population is interpreted as reactive. However, the dominant cell population is in fact of B-cell lineage. It is extensively highlighted by CD20. Only a minor component of the B cell infiltrate appeared to be in the context of representing germinal centers as characterized by small foci of centrocytic and centroblastic infiltration highlighted by BCL6 and CD10. The overwhelming B-cell component is a non–germinal center small B cell that does demonstrate BCL2 positivity and significant immunoreactivity for CD23. This small lymphocytic infiltrate obscures the germinal centers. There are only a few plasma cells; they do not show light chain restriction.”
The pathologist remarked that “this type of morphology of a diffuse small B-cell lymphocytic infiltrate that is without any evidence of light chain restriction amidst plasma cells, whereby the B cell component is dominant over the T-cell component would in fact be consistent with a unique variant of marginal zone lymphoma derived from a naive mantle zone.”
PCMZL has an excellent prognosis. When limited to the skin, local radiation or excision are effective treatments. Intravenous rituximab has been used to treat multifocal PCMZL. This patient was found to have no extracutaneous involvement and was treated with radiation.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Virmani P et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2017 Jun 14;3(4):269-72.
Magro CM and Olson LC. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2018 Jun;34:116-21.
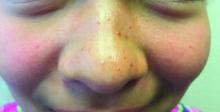
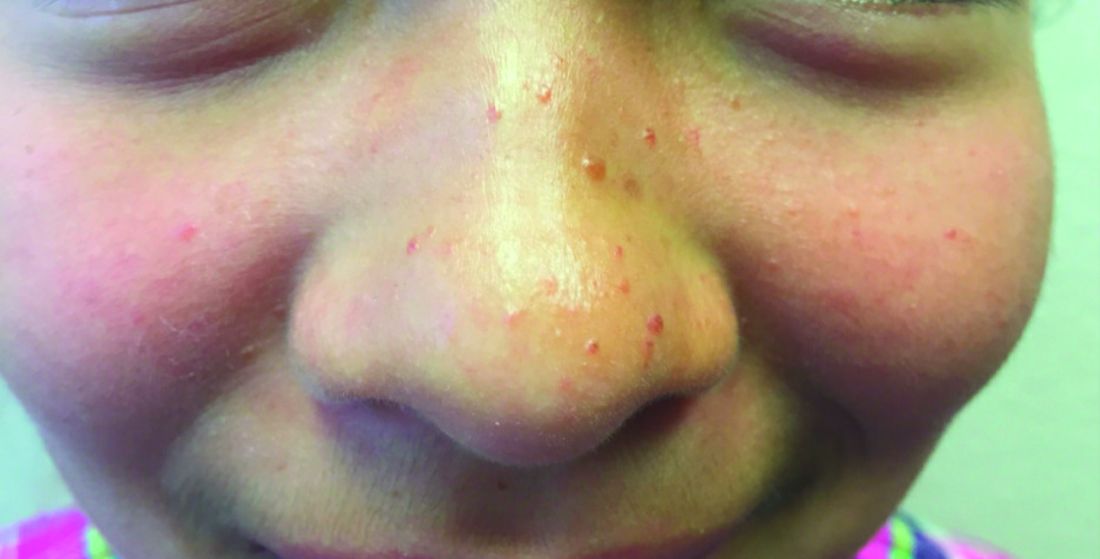
A 7-year-old with red bumps on her nose
The finding of individual, 1- to 4-mm firm, red papules depicted in the image are consistent with facial angiofibromas, which are most commonly seen in pediatric patients as a manifestation of tuberous sclerosis (TSC). Angiofibromas, previously called adenoma sebaceum, a misnomer, are seen in TSC as smooth papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques that typically involve the malar region of the face. These lesions usually develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne. The number of lesions tend to increase with age, though there is no significant risk of malignant transformation. Ultraviolet-induced DNA damage is thought to play a role in the development of facial angiofibromas, so sun protection is called for.1 Patients may seek treatment to minimize deformity and the stigma of angiofibromas. Recently, the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor sirolimus (rapamycin) topical gel received Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of facial angiofibromas associated with TSC in patients age at least 6 years.2
The presence of angiofibromas should prompt consideration of TSC and as such, a thorough family history, medical history, and full-body skin examination. TSC is a rare autosomal-dominant genetic disorder, caused by a pathogenic variant in either the TSC1 or TSC2 gene. This neurocutaneous disorder is characterized by the development of multiple benign hamartomas across many organ systems including the brain, eyes, heart, lung, liver, kidney, and skin. The phenotypic expression of TSC is highly variable. Besides angiofibromas, some other characteristic dermatological findings in TSC include periungual fibromas, hypopigmented macules usually elliptical in shape (known as ash-leaf spots), and irregularly shaped elevated flesh-colored fibrous tissue most often found over the lower back (known as shagreen patches).3
What is on the differential?
Agminated spitz nevi refers to multiple spitz nevi in a localized area. Spitz nevi present as a well-circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papules, most commonly located on the face or lower extremities.4 The finding of agminated spitz nevi is very rare and less likely for this patient given the concomitant skin findings of dental pitting, renal cysts, and cortical tubers.
Juvenile xanthogranulomas are benign,proliferations of histiocytic cells that present as reddish or yellowish-to-brown papules, plaques, or nodules that typically develop in young children around the age of 1. With time, juvenile xanthogranulomas may flatten and become more yellow.
Basal cell carcinomas present as dome-shaped lesions with centralized erosions on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are remarkably uncommon in children but are occasionally seen in basal cell nevus syndrome (also known as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or Gorlin syndrome). Affected patients may have other findings such as developmental anomalies, bifid ribs, palmar and plantar pitting, odontogenic keratocysts, and/or medulloblastomas.5
Flat warts commonly occur in children and occur by direct skin contact with human papillomavirus. Of the various types of warts, flat warts are smaller and tend to be smooth on top. The diagnosis of cutaneous warts is based on clinical appearance, showing thrombosed capillaries underneath the overlying hyperkeratotic debris. Our patient’s history of having a common wart on her hands raises suspicion for inoculation onto her face, but the morphology, distribution, and lack of response to tretinoin makes this diagnosis much less likely.
Disease workup and course
Our patient’s physical exam revealed dental pits but no evidence of hypopigmented macules, shagreen patches, or periungual lesions. Ultrasound of the kidney displayed renal cortical cysts and brain MRI showed cortical tubers, confirming extracutaneous TSC involvement. Over time, our patient developed angiofibromas on the forehead and was ultimately started on topical sirolimus, which led to marked improvement within months.
Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. They have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Tyburczy ME et al. Hum Molec Genet. 2014;23(8):2023-9.
2. Food & Drug Administration. New drug application (NDA) approval for Hyftor (sirolimus topical gel). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/213478Orig1s000ltr.pdf.
3. Webb DW et al. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135(1):1-5.
4. Ricci F et al. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27(1):59-62.
5. Evans DG and Farndon PA. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, in “GeneReviews®.” Seattle: University of Washington, 2002.
The finding of individual, 1- to 4-mm firm, red papules depicted in the image are consistent with facial angiofibromas, which are most commonly seen in pediatric patients as a manifestation of tuberous sclerosis (TSC). Angiofibromas, previously called adenoma sebaceum, a misnomer, are seen in TSC as smooth papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques that typically involve the malar region of the face. These lesions usually develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne. The number of lesions tend to increase with age, though there is no significant risk of malignant transformation. Ultraviolet-induced DNA damage is thought to play a role in the development of facial angiofibromas, so sun protection is called for.1 Patients may seek treatment to minimize deformity and the stigma of angiofibromas. Recently, the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor sirolimus (rapamycin) topical gel received Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of facial angiofibromas associated with TSC in patients age at least 6 years.2
The presence of angiofibromas should prompt consideration of TSC and as such, a thorough family history, medical history, and full-body skin examination. TSC is a rare autosomal-dominant genetic disorder, caused by a pathogenic variant in either the TSC1 or TSC2 gene. This neurocutaneous disorder is characterized by the development of multiple benign hamartomas across many organ systems including the brain, eyes, heart, lung, liver, kidney, and skin. The phenotypic expression of TSC is highly variable. Besides angiofibromas, some other characteristic dermatological findings in TSC include periungual fibromas, hypopigmented macules usually elliptical in shape (known as ash-leaf spots), and irregularly shaped elevated flesh-colored fibrous tissue most often found over the lower back (known as shagreen patches).3
What is on the differential?
Agminated spitz nevi refers to multiple spitz nevi in a localized area. Spitz nevi present as a well-circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papules, most commonly located on the face or lower extremities.4 The finding of agminated spitz nevi is very rare and less likely for this patient given the concomitant skin findings of dental pitting, renal cysts, and cortical tubers.
Juvenile xanthogranulomas are benign,proliferations of histiocytic cells that present as reddish or yellowish-to-brown papules, plaques, or nodules that typically develop in young children around the age of 1. With time, juvenile xanthogranulomas may flatten and become more yellow.
Basal cell carcinomas present as dome-shaped lesions with centralized erosions on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are remarkably uncommon in children but are occasionally seen in basal cell nevus syndrome (also known as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or Gorlin syndrome). Affected patients may have other findings such as developmental anomalies, bifid ribs, palmar and plantar pitting, odontogenic keratocysts, and/or medulloblastomas.5
Flat warts commonly occur in children and occur by direct skin contact with human papillomavirus. Of the various types of warts, flat warts are smaller and tend to be smooth on top. The diagnosis of cutaneous warts is based on clinical appearance, showing thrombosed capillaries underneath the overlying hyperkeratotic debris. Our patient’s history of having a common wart on her hands raises suspicion for inoculation onto her face, but the morphology, distribution, and lack of response to tretinoin makes this diagnosis much less likely.
Disease workup and course
Our patient’s physical exam revealed dental pits but no evidence of hypopigmented macules, shagreen patches, or periungual lesions. Ultrasound of the kidney displayed renal cortical cysts and brain MRI showed cortical tubers, confirming extracutaneous TSC involvement. Over time, our patient developed angiofibromas on the forehead and was ultimately started on topical sirolimus, which led to marked improvement within months.
Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. They have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Tyburczy ME et al. Hum Molec Genet. 2014;23(8):2023-9.
2. Food & Drug Administration. New drug application (NDA) approval for Hyftor (sirolimus topical gel). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/213478Orig1s000ltr.pdf.
3. Webb DW et al. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135(1):1-5.
4. Ricci F et al. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27(1):59-62.
5. Evans DG and Farndon PA. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, in “GeneReviews®.” Seattle: University of Washington, 2002.
The finding of individual, 1- to 4-mm firm, red papules depicted in the image are consistent with facial angiofibromas, which are most commonly seen in pediatric patients as a manifestation of tuberous sclerosis (TSC). Angiofibromas, previously called adenoma sebaceum, a misnomer, are seen in TSC as smooth papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques that typically involve the malar region of the face. These lesions usually develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne. The number of lesions tend to increase with age, though there is no significant risk of malignant transformation. Ultraviolet-induced DNA damage is thought to play a role in the development of facial angiofibromas, so sun protection is called for.1 Patients may seek treatment to minimize deformity and the stigma of angiofibromas. Recently, the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor sirolimus (rapamycin) topical gel received Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of facial angiofibromas associated with TSC in patients age at least 6 years.2
The presence of angiofibromas should prompt consideration of TSC and as such, a thorough family history, medical history, and full-body skin examination. TSC is a rare autosomal-dominant genetic disorder, caused by a pathogenic variant in either the TSC1 or TSC2 gene. This neurocutaneous disorder is characterized by the development of multiple benign hamartomas across many organ systems including the brain, eyes, heart, lung, liver, kidney, and skin. The phenotypic expression of TSC is highly variable. Besides angiofibromas, some other characteristic dermatological findings in TSC include periungual fibromas, hypopigmented macules usually elliptical in shape (known as ash-leaf spots), and irregularly shaped elevated flesh-colored fibrous tissue most often found over the lower back (known as shagreen patches).3
What is on the differential?
Agminated spitz nevi refers to multiple spitz nevi in a localized area. Spitz nevi present as a well-circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papules, most commonly located on the face or lower extremities.4 The finding of agminated spitz nevi is very rare and less likely for this patient given the concomitant skin findings of dental pitting, renal cysts, and cortical tubers.
Juvenile xanthogranulomas are benign,proliferations of histiocytic cells that present as reddish or yellowish-to-brown papules, plaques, or nodules that typically develop in young children around the age of 1. With time, juvenile xanthogranulomas may flatten and become more yellow.
Basal cell carcinomas present as dome-shaped lesions with centralized erosions on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are remarkably uncommon in children but are occasionally seen in basal cell nevus syndrome (also known as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or Gorlin syndrome). Affected patients may have other findings such as developmental anomalies, bifid ribs, palmar and plantar pitting, odontogenic keratocysts, and/or medulloblastomas.5
Flat warts commonly occur in children and occur by direct skin contact with human papillomavirus. Of the various types of warts, flat warts are smaller and tend to be smooth on top. The diagnosis of cutaneous warts is based on clinical appearance, showing thrombosed capillaries underneath the overlying hyperkeratotic debris. Our patient’s history of having a common wart on her hands raises suspicion for inoculation onto her face, but the morphology, distribution, and lack of response to tretinoin makes this diagnosis much less likely.
Disease workup and course
Our patient’s physical exam revealed dental pits but no evidence of hypopigmented macules, shagreen patches, or periungual lesions. Ultrasound of the kidney displayed renal cortical cysts and brain MRI showed cortical tubers, confirming extracutaneous TSC involvement. Over time, our patient developed angiofibromas on the forehead and was ultimately started on topical sirolimus, which led to marked improvement within months.
Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. They have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Tyburczy ME et al. Hum Molec Genet. 2014;23(8):2023-9.
2. Food & Drug Administration. New drug application (NDA) approval for Hyftor (sirolimus topical gel). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/213478Orig1s000ltr.pdf.
3. Webb DW et al. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135(1):1-5.
4. Ricci F et al. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27(1):59-62.
5. Evans DG and Farndon PA. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, in “GeneReviews®.” Seattle: University of Washington, 2002.
A 7-year-old female presented with a bump on the bridge of her nose that was present for 10 months, with subsequent development of multiple papules on the nose and cheeks.
A 7-year-old, previously healthy female presented with a bump on the bridge of her nose that was present for 10 months, with subsequent development of multiple papules on the nose and cheeks. She has no significant medical history aside from a wart on her hand that was recently frozen with liquid nitrogen and resolved. She denied pruritus, bumps, or skin changes elsewhere on the body. The patient was prescribed tretinoin 0.1% cream applied nightly for several months without response.
Myositis guidelines aim to standardize adult and pediatric care
All patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) should be screened for swallowing difficulties, according to the first evidence-based guideline to be produced.
The guideline, which has been developed by a working group of the British Society for Rheumatology (BSR), also advises that all diagnosed patients should have their myositis antibody levels checked and have their overall well-being assessed. Other recommendations for all patients include the use of glucocorticoids to reduce muscle inflammation and conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) for long-term treatment.
“Finally, now, we’re able to standardize the way we treat adults and children with IIM,” senior guideline author Hector Chinoy, PhD, said at the society’s annual meeting.
It has been a long labor of love, however, taking 4 years to get the guideline published, said Dr. Chinoy, professor of rheumatology and neuromuscular disease at the University of Manchester (England), and a consultant at Salford (England) Royal Hospital.
“We’re not covering diagnosis, classification, or the investigation of suspected IIM,” said Dr. Chinoy. Inclusion body myositis also is not included.
Altogether, there are 13 recommendations that have been developed using a PICO (patient or population, intervention, comparison, outcome) format, graded based on the quality of the available evidence, and then voted on by the working group members to give a score of the strength of agreement. Dr. Chinoy noted that there was a checklist included in the Supplementary Data section of the guideline to help follow the recommendations.
“The target audience for the guideline reflects the variety of clinicians caring for patients with IIM,” Dr. Chinoy said. So that is not just pediatric and adult rheumatologists, but also neurologists, dermatologists, respiratory physicians, oncologists, gastroenterologists, cardiologists, and of course other health care professionals. This includes rheumatology and neurology nurses, psychologists, speech and language therapists, and podiatrists, as well as rheumatology specialist pharmacists, physiotherapists, and occupational therapists.
With reference to the latter, Liza McCann, MBBS, who co-led the development of the guideline, said in a statement released by the BSR that the guideline “highlights the importance of exercise, led and monitored by specialist physiotherapists and occupational therapists.”
Dr. McCann, a consultant pediatric rheumatologist at Alder Hey Hospital, Liverpool, England, and Honorary Clinical Lecturer at the University of Liverpool, added that the guidelines also cover “the need to address psychological wellbeing as an integral part of treatment, in parallel with pharmacological therapies.”
Recommendation highlights
Some of the highlights of the recommendations include the use of high-dose glucocorticoids to manage skeletal muscle inflammation at the time of treatment induction, with specific guidance on the different doses to use in adults and in children. There also is guidance on the use of csDMARDs in both populations and what to use if there is refractory disease – with the strongest evidence supporting the use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) or cyclophosphamide, and possibly rituximab and abatacept.
“There is insufficient evidence to recommend JAK inhibition,” Dr. Chinoy said. The data search used to develop the guideline had a cutoff of October 2020, but even now there is only anecdotal evidence from case studies, he added.
Importantly, the guidelines recognize that childhood IIM differs from adult disease and call for children to be managed by pediatric specialists.
“Routine assessment of dysphagia should be considered in all patients,” Dr. Chinoy said, “so ask the question.” The recommendation is that a swallowing assessment should involve a speech and language therapist or gastroenterologist, and that IVIG be considered for active disease and dysphagia that is resistant to other treatments.
There also are recommendations to screen adult patients for interstitial lung disease, consider fracture risk, and screen adult patients for cancer if they have specific risk factors that include older age at onset, male gender, dysphagia, and rapid disease onset, among others.
Separate cancer screening guidelines on cards
“Around one in four patients with myositis will develop cancer within the 3 years either before or after myositis onset,” Alexander Oldroyd, MBChB, PhD, said in a separate presentation at the BSR annual meeting.
“It’s a hugely increased risk compared to the general population, and a great worry for patients,” he added. Exactly why there is an increased risk is not known, but “there’s a big link between the biological onset of cancer and myositis.”
Dr. Oldroyd, who is an NIHR Academic Clinical Lecturer at the University of Manchester in England and a coauthor of the BSR myositis guideline, is part of a special interest group set up by the International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group (IMACS) that is in the process of developing separate guidelines for cancer screening in people newly diagnosed with IIM.
The aim was to produce evidence-based recommendations that were both “pragmatic and practical,” that could help clinicians answer patient’s questions on their risk and how best and how often to screen them, Dr. Oldroyd explained. Importantly, IMACS has endeavored to create recommendations that should be applicable across different countries and health care systems.
“We had to acknowledge that there’s not a lot of evidence base there,” Dr. Oldroyd said, noting that he and colleagues conducted a systematic literature review and meta-analysis and used a Delphi process to draft 20 recommendations. These cover identifying risk factors for cancer in people with myositis and categorizing people into low, medium, and high-risk categories. The recommendations also cover what should constitute basic and enhanced screening, and how often someone should be screened.
Moreover, the authors make recommendations on the use of imaging modalities such as PET and CT scans, as well as upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy and naso-endoscopy.
“As rheumatologists, we don’t talk about cancer a lot,” Dr. Oldroyd said. “We pick up a lot of incidental cancers, but we don’t usually talk about cancer screening with patients.” That’s something that needs to change, he said.
“It’s important – just get it out in the open, talk to people about it,” Dr. Oldroyd said.
“Tell them what you’re wanting to do, how you’re wanting to investigate for it, clearly communicate their risk,” he said. “But also acknowledge the limited evidence as well, and clearly communicate the results.”
Dr. Chinoy acknowledged he had received fees for presentations (UCB, Biogen), consultancy (Alexion, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Orphazyme, AstraZeneca), or grant support (Eli Lilly, UCB) that had been paid via his institution for the purpose of furthering myositis research. Dr. Oldroyd had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
All patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) should be screened for swallowing difficulties, according to the first evidence-based guideline to be produced.
The guideline, which has been developed by a working group of the British Society for Rheumatology (BSR), also advises that all diagnosed patients should have their myositis antibody levels checked and have their overall well-being assessed. Other recommendations for all patients include the use of glucocorticoids to reduce muscle inflammation and conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) for long-term treatment.
“Finally, now, we’re able to standardize the way we treat adults and children with IIM,” senior guideline author Hector Chinoy, PhD, said at the society’s annual meeting.
It has been a long labor of love, however, taking 4 years to get the guideline published, said Dr. Chinoy, professor of rheumatology and neuromuscular disease at the University of Manchester (England), and a consultant at Salford (England) Royal Hospital.
“We’re not covering diagnosis, classification, or the investigation of suspected IIM,” said Dr. Chinoy. Inclusion body myositis also is not included.
Altogether, there are 13 recommendations that have been developed using a PICO (patient or population, intervention, comparison, outcome) format, graded based on the quality of the available evidence, and then voted on by the working group members to give a score of the strength of agreement. Dr. Chinoy noted that there was a checklist included in the Supplementary Data section of the guideline to help follow the recommendations.
“The target audience for the guideline reflects the variety of clinicians caring for patients with IIM,” Dr. Chinoy said. So that is not just pediatric and adult rheumatologists, but also neurologists, dermatologists, respiratory physicians, oncologists, gastroenterologists, cardiologists, and of course other health care professionals. This includes rheumatology and neurology nurses, psychologists, speech and language therapists, and podiatrists, as well as rheumatology specialist pharmacists, physiotherapists, and occupational therapists.
With reference to the latter, Liza McCann, MBBS, who co-led the development of the guideline, said in a statement released by the BSR that the guideline “highlights the importance of exercise, led and monitored by specialist physiotherapists and occupational therapists.”
Dr. McCann, a consultant pediatric rheumatologist at Alder Hey Hospital, Liverpool, England, and Honorary Clinical Lecturer at the University of Liverpool, added that the guidelines also cover “the need to address psychological wellbeing as an integral part of treatment, in parallel with pharmacological therapies.”
Recommendation highlights
Some of the highlights of the recommendations include the use of high-dose glucocorticoids to manage skeletal muscle inflammation at the time of treatment induction, with specific guidance on the different doses to use in adults and in children. There also is guidance on the use of csDMARDs in both populations and what to use if there is refractory disease – with the strongest evidence supporting the use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) or cyclophosphamide, and possibly rituximab and abatacept.
“There is insufficient evidence to recommend JAK inhibition,” Dr. Chinoy said. The data search used to develop the guideline had a cutoff of October 2020, but even now there is only anecdotal evidence from case studies, he added.
Importantly, the guidelines recognize that childhood IIM differs from adult disease and call for children to be managed by pediatric specialists.
“Routine assessment of dysphagia should be considered in all patients,” Dr. Chinoy said, “so ask the question.” The recommendation is that a swallowing assessment should involve a speech and language therapist or gastroenterologist, and that IVIG be considered for active disease and dysphagia that is resistant to other treatments.
There also are recommendations to screen adult patients for interstitial lung disease, consider fracture risk, and screen adult patients for cancer if they have specific risk factors that include older age at onset, male gender, dysphagia, and rapid disease onset, among others.
Separate cancer screening guidelines on cards
“Around one in four patients with myositis will develop cancer within the 3 years either before or after myositis onset,” Alexander Oldroyd, MBChB, PhD, said in a separate presentation at the BSR annual meeting.
“It’s a hugely increased risk compared to the general population, and a great worry for patients,” he added. Exactly why there is an increased risk is not known, but “there’s a big link between the biological onset of cancer and myositis.”
Dr. Oldroyd, who is an NIHR Academic Clinical Lecturer at the University of Manchester in England and a coauthor of the BSR myositis guideline, is part of a special interest group set up by the International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group (IMACS) that is in the process of developing separate guidelines for cancer screening in people newly diagnosed with IIM.
The aim was to produce evidence-based recommendations that were both “pragmatic and practical,” that could help clinicians answer patient’s questions on their risk and how best and how often to screen them, Dr. Oldroyd explained. Importantly, IMACS has endeavored to create recommendations that should be applicable across different countries and health care systems.
“We had to acknowledge that there’s not a lot of evidence base there,” Dr. Oldroyd said, noting that he and colleagues conducted a systematic literature review and meta-analysis and used a Delphi process to draft 20 recommendations. These cover identifying risk factors for cancer in people with myositis and categorizing people into low, medium, and high-risk categories. The recommendations also cover what should constitute basic and enhanced screening, and how often someone should be screened.
Moreover, the authors make recommendations on the use of imaging modalities such as PET and CT scans, as well as upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy and naso-endoscopy.
“As rheumatologists, we don’t talk about cancer a lot,” Dr. Oldroyd said. “We pick up a lot of incidental cancers, but we don’t usually talk about cancer screening with patients.” That’s something that needs to change, he said.
“It’s important – just get it out in the open, talk to people about it,” Dr. Oldroyd said.
“Tell them what you’re wanting to do, how you’re wanting to investigate for it, clearly communicate their risk,” he said. “But also acknowledge the limited evidence as well, and clearly communicate the results.”
Dr. Chinoy acknowledged he had received fees for presentations (UCB, Biogen), consultancy (Alexion, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Orphazyme, AstraZeneca), or grant support (Eli Lilly, UCB) that had been paid via his institution for the purpose of furthering myositis research. Dr. Oldroyd had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
All patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) should be screened for swallowing difficulties, according to the first evidence-based guideline to be produced.
The guideline, which has been developed by a working group of the British Society for Rheumatology (BSR), also advises that all diagnosed patients should have their myositis antibody levels checked and have their overall well-being assessed. Other recommendations for all patients include the use of glucocorticoids to reduce muscle inflammation and conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) for long-term treatment.
“Finally, now, we’re able to standardize the way we treat adults and children with IIM,” senior guideline author Hector Chinoy, PhD, said at the society’s annual meeting.
It has been a long labor of love, however, taking 4 years to get the guideline published, said Dr. Chinoy, professor of rheumatology and neuromuscular disease at the University of Manchester (England), and a consultant at Salford (England) Royal Hospital.
“We’re not covering diagnosis, classification, or the investigation of suspected IIM,” said Dr. Chinoy. Inclusion body myositis also is not included.
Altogether, there are 13 recommendations that have been developed using a PICO (patient or population, intervention, comparison, outcome) format, graded based on the quality of the available evidence, and then voted on by the working group members to give a score of the strength of agreement. Dr. Chinoy noted that there was a checklist included in the Supplementary Data section of the guideline to help follow the recommendations.
“The target audience for the guideline reflects the variety of clinicians caring for patients with IIM,” Dr. Chinoy said. So that is not just pediatric and adult rheumatologists, but also neurologists, dermatologists, respiratory physicians, oncologists, gastroenterologists, cardiologists, and of course other health care professionals. This includes rheumatology and neurology nurses, psychologists, speech and language therapists, and podiatrists, as well as rheumatology specialist pharmacists, physiotherapists, and occupational therapists.
With reference to the latter, Liza McCann, MBBS, who co-led the development of the guideline, said in a statement released by the BSR that the guideline “highlights the importance of exercise, led and monitored by specialist physiotherapists and occupational therapists.”
Dr. McCann, a consultant pediatric rheumatologist at Alder Hey Hospital, Liverpool, England, and Honorary Clinical Lecturer at the University of Liverpool, added that the guidelines also cover “the need to address psychological wellbeing as an integral part of treatment, in parallel with pharmacological therapies.”
Recommendation highlights
Some of the highlights of the recommendations include the use of high-dose glucocorticoids to manage skeletal muscle inflammation at the time of treatment induction, with specific guidance on the different doses to use in adults and in children. There also is guidance on the use of csDMARDs in both populations and what to use if there is refractory disease – with the strongest evidence supporting the use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) or cyclophosphamide, and possibly rituximab and abatacept.
“There is insufficient evidence to recommend JAK inhibition,” Dr. Chinoy said. The data search used to develop the guideline had a cutoff of October 2020, but even now there is only anecdotal evidence from case studies, he added.
Importantly, the guidelines recognize that childhood IIM differs from adult disease and call for children to be managed by pediatric specialists.
“Routine assessment of dysphagia should be considered in all patients,” Dr. Chinoy said, “so ask the question.” The recommendation is that a swallowing assessment should involve a speech and language therapist or gastroenterologist, and that IVIG be considered for active disease and dysphagia that is resistant to other treatments.
There also are recommendations to screen adult patients for interstitial lung disease, consider fracture risk, and screen adult patients for cancer if they have specific risk factors that include older age at onset, male gender, dysphagia, and rapid disease onset, among others.
Separate cancer screening guidelines on cards
“Around one in four patients with myositis will develop cancer within the 3 years either before or after myositis onset,” Alexander Oldroyd, MBChB, PhD, said in a separate presentation at the BSR annual meeting.
“It’s a hugely increased risk compared to the general population, and a great worry for patients,” he added. Exactly why there is an increased risk is not known, but “there’s a big link between the biological onset of cancer and myositis.”
Dr. Oldroyd, who is an NIHR Academic Clinical Lecturer at the University of Manchester in England and a coauthor of the BSR myositis guideline, is part of a special interest group set up by the International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group (IMACS) that is in the process of developing separate guidelines for cancer screening in people newly diagnosed with IIM.
The aim was to produce evidence-based recommendations that were both “pragmatic and practical,” that could help clinicians answer patient’s questions on their risk and how best and how often to screen them, Dr. Oldroyd explained. Importantly, IMACS has endeavored to create recommendations that should be applicable across different countries and health care systems.
“We had to acknowledge that there’s not a lot of evidence base there,” Dr. Oldroyd said, noting that he and colleagues conducted a systematic literature review and meta-analysis and used a Delphi process to draft 20 recommendations. These cover identifying risk factors for cancer in people with myositis and categorizing people into low, medium, and high-risk categories. The recommendations also cover what should constitute basic and enhanced screening, and how often someone should be screened.
Moreover, the authors make recommendations on the use of imaging modalities such as PET and CT scans, as well as upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy and naso-endoscopy.
“As rheumatologists, we don’t talk about cancer a lot,” Dr. Oldroyd said. “We pick up a lot of incidental cancers, but we don’t usually talk about cancer screening with patients.” That’s something that needs to change, he said.
“It’s important – just get it out in the open, talk to people about it,” Dr. Oldroyd said.
“Tell them what you’re wanting to do, how you’re wanting to investigate for it, clearly communicate their risk,” he said. “But also acknowledge the limited evidence as well, and clearly communicate the results.”
Dr. Chinoy acknowledged he had received fees for presentations (UCB, Biogen), consultancy (Alexion, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Orphazyme, AstraZeneca), or grant support (Eli Lilly, UCB) that had been paid via his institution for the purpose of furthering myositis research. Dr. Oldroyd had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM BSR 2022
Smooth plaque on ankle
A 4-mm punch biopsy of the annular border confirmed a diagnosis of localized granuloma annulare (GA).
There is a long list of differential diagnoses for annular patches and plaques; it includes tinea corporis and important systemic diseases such as sarcoidosis and Lyme disease. Clinical features of GA include annular, minimally scaly patches to plaques with central clearing on extensor surfaces in children and adults. Sometimes GA is much more widespread. Often, the diagnosis can be made clinically, but a punch biopsy of the deep dermis will confirm the diagnosis by showing palisading or interstitial granulomatous inflammation, necrobiotic collagen, and often mucin.
GA is a common inflammatory disorder with an uncertain etiology. Localized GA affects children and adults and is often self limiting. It may, however, last for months or years before resolving. Disseminated disease is much more recalcitrant with few good treatment options if topical steroids or phototherapy fails. Treatment for localized disease is much more successful with topical or intralesional steroids.
Trauma can cause a localized plaque to resolve; a lesion may resolve soon after a biopsy is performed. Possible related conditions include diabetes, thyroid disease, hepatitis C, and hyperlipidemia; but there is no consensus on focused screening. Similarly, associations or nonassociations with malignancy in adults have been cited, but evidence is lacking.1
In this case, the patient and his family were reassured that the diagnosis wasn’t serious. In a single visit, he received a series of 6 to 7 injections of 10 mg/mL triamcinolone which led to resolution of the lesion in 4 weeks.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: pathogenesis, disease associations and triggers, and therapeutic options. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:467-479. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.055

A 4-mm punch biopsy of the annular border confirmed a diagnosis of localized granuloma annulare (GA).
There is a long list of differential diagnoses for annular patches and plaques; it includes tinea corporis and important systemic diseases such as sarcoidosis and Lyme disease. Clinical features of GA include annular, minimally scaly patches to plaques with central clearing on extensor surfaces in children and adults. Sometimes GA is much more widespread. Often, the diagnosis can be made clinically, but a punch biopsy of the deep dermis will confirm the diagnosis by showing palisading or interstitial granulomatous inflammation, necrobiotic collagen, and often mucin.
GA is a common inflammatory disorder with an uncertain etiology. Localized GA affects children and adults and is often self limiting. It may, however, last for months or years before resolving. Disseminated disease is much more recalcitrant with few good treatment options if topical steroids or phototherapy fails. Treatment for localized disease is much more successful with topical or intralesional steroids.
Trauma can cause a localized plaque to resolve; a lesion may resolve soon after a biopsy is performed. Possible related conditions include diabetes, thyroid disease, hepatitis C, and hyperlipidemia; but there is no consensus on focused screening. Similarly, associations or nonassociations with malignancy in adults have been cited, but evidence is lacking.1
In this case, the patient and his family were reassured that the diagnosis wasn’t serious. In a single visit, he received a series of 6 to 7 injections of 10 mg/mL triamcinolone which led to resolution of the lesion in 4 weeks.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

A 4-mm punch biopsy of the annular border confirmed a diagnosis of localized granuloma annulare (GA).
There is a long list of differential diagnoses for annular patches and plaques; it includes tinea corporis and important systemic diseases such as sarcoidosis and Lyme disease. Clinical features of GA include annular, minimally scaly patches to plaques with central clearing on extensor surfaces in children and adults. Sometimes GA is much more widespread. Often, the diagnosis can be made clinically, but a punch biopsy of the deep dermis will confirm the diagnosis by showing palisading or interstitial granulomatous inflammation, necrobiotic collagen, and often mucin.
GA is a common inflammatory disorder with an uncertain etiology. Localized GA affects children and adults and is often self limiting. It may, however, last for months or years before resolving. Disseminated disease is much more recalcitrant with few good treatment options if topical steroids or phototherapy fails. Treatment for localized disease is much more successful with topical or intralesional steroids.
Trauma can cause a localized plaque to resolve; a lesion may resolve soon after a biopsy is performed. Possible related conditions include diabetes, thyroid disease, hepatitis C, and hyperlipidemia; but there is no consensus on focused screening. Similarly, associations or nonassociations with malignancy in adults have been cited, but evidence is lacking.1
In this case, the patient and his family were reassured that the diagnosis wasn’t serious. In a single visit, he received a series of 6 to 7 injections of 10 mg/mL triamcinolone which led to resolution of the lesion in 4 weeks.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: pathogenesis, disease associations and triggers, and therapeutic options. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:467-479. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.055
1. Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: pathogenesis, disease associations and triggers, and therapeutic options. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:467-479. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.055
Melanoma
THE COMPARISON
A Acral lentiginous melanoma on the sole of the foot of a 30-year-old Black woman. The depth of the lesion was 2 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
B Nodular melanoma on the shoulder of a 63-year-old Hispanic woman. The depth of the lesion was 5.5 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Melanoma occurs less frequently in individuals with darker skin types than in those with lighter skin types but is associated with higher rates of morbidity and mortality in this patient population.1-7 In the cases shown here (A and B), both patients had advanced melanomas with large primary lesions and lymph node metastases.
Epidemiology
A systematic review by Higgins et al6 reported the following on the epidemiology of melanomas in patients with skin of color:
- African Americans have deeper tumors at the time of diagnosis, in addition to increased rates of regionally advanced and distant disease. Lesions generally are located on the lower extremities and have an increased propensity for ulceration. Acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype found in African American patients.6
- In Hispanic individuals, superficial spreading melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype. Lower extremity lesions are more common relative to White individuals. Hispanic individuals have the highest rate of oral cavity melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
- In Asian individuals, acral and subungual sites are most common. Specifically, Pacific Islanders have the highest proportion of mucosal melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Melanomas are found more often on the palms, soles, nail units, oral cavity, and mucosae.6 The melanomas have the same clinical and dermoscopic features found in individuals with lighter skin tones.
Worth noting
Factors that may contribute to the diagnosis of more advanced melanomas in racial/ethnic minorities in the United States include:
- decreased access to health care based on lack of health insurance and low socioeconomic status,
- less awareness of the risk of melanoma among patients and health care providers because melanoma is less common in persons of color, and
- lesions found in areas less likely to be seen in screening examinations, such as the soles of the feet and the oral and genital mucosae.
Health disparity highlight
- In a large US study of 96,953 patients with a diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma from 1992 to 2009, the proportion of later-stage melanoma—stages II to IV—was greater in Black patients compared to White patients.7
- Based on this same data set, White patients had the longest survival time (P <. 05), followed by Hispanic (P < .05), Asian American/Native American/Pacific Islander (P < .05), and Black (P < .05) patients, respectively.7
- In Miami-Dade County, one study of 1690 melanoma cases found that 48% of Black patients had regional or distant disease at presentation compared to 22% of White patients (P = .015).5 Analysis of multiple factors found that only race was a significant predictor for late-stage melanoma (P < .001). Black patients in this study were 3 times more likely than others to be diagnosed with melanoma at a late stage (P = .07).5
- Black patients in the United States are more likely to have a delayed time from diagnosis to definitive surgery even when researchers controlled for type of health insurance and stage of diagnosis.8
Final thoughts
Efforts are needed to overcome these disparities by:
- educating patients with skin of color and their health care providers about the risks of advanced melanoma with the goal of prevention and earlier diagnosis;
- breaking down barriers to care caused by poverty, lack of health insurance, and systemic racism; and
- eliminating factors that lead to delays from diagnosis to definitive surgery.
1. Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2001.05.034
2. Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.17.1907
3. Cress RD, Holly EA. Incidence of cutaneous melanoma among non-Hispanic whites, Hispanics, Asians, and blacks: an analysis of California cancer registry data, 1988-93. Cancer Causes Control. 1997;8:246-252. doi: 10.1023/a:1018432632528
4. Hu S, Parker DF, Thomas AG, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans: the Miami-Dade County experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:1031-1032. doi: 10.1016/ j.jaad.2004.05.005
5. Hu S, Soza-Vento RM, Parker DF, et al. Comparison of stage at diagnosis of melanoma among Hispanic, black, and white patients in Miami-Dade County, Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142: 704-708. doi: 10.1001/archderm.142.6.704
6. Higgins S, Nazemi A, Feinstein S, et al. Clinical presentations of melanoma in African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:791-801. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001759
7. Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival [published online July 28, 2016]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.06.006
8. Qian Y, Johannet P, Sawyers A, et al. The ongoing racial disparities in melanoma: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (1975-2016) [published online August 27, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1585-1593. doi: 10.1016/ j.jaad.2020.08.097
THE COMPARISON
A Acral lentiginous melanoma on the sole of the foot of a 30-year-old Black woman. The depth of the lesion was 2 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
B Nodular melanoma on the shoulder of a 63-year-old Hispanic woman. The depth of the lesion was 5.5 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Melanoma occurs less frequently in individuals with darker skin types than in those with lighter skin types but is associated with higher rates of morbidity and mortality in this patient population.1-7 In the cases shown here (A and B), both patients had advanced melanomas with large primary lesions and lymph node metastases.

Epidemiology
A systematic review by Higgins et al6 reported the following on the epidemiology of melanomas in patients with skin of color:
- African Americans have deeper tumors at the time of diagnosis, in addition to increased rates of regionally advanced and distant disease. Lesions generally are located on the lower extremities and have an increased propensity for ulceration. Acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype found in African American patients.6
- In Hispanic individuals, superficial spreading melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype. Lower extremity lesions are more common relative to White individuals. Hispanic individuals have the highest rate of oral cavity melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
- In Asian individuals, acral and subungual sites are most common. Specifically, Pacific Islanders have the highest proportion of mucosal melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Melanomas are found more often on the palms, soles, nail units, oral cavity, and mucosae.6 The melanomas have the same clinical and dermoscopic features found in individuals with lighter skin tones.
Worth noting
Factors that may contribute to the diagnosis of more advanced melanomas in racial/ethnic minorities in the United States include:
- decreased access to health care based on lack of health insurance and low socioeconomic status,
- less awareness of the risk of melanoma among patients and health care providers because melanoma is less common in persons of color, and
- lesions found in areas less likely to be seen in screening examinations, such as the soles of the feet and the oral and genital mucosae.
Health disparity highlight
- In a large US study of 96,953 patients with a diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma from 1992 to 2009, the proportion of later-stage melanoma—stages II to IV—was greater in Black patients compared to White patients.7
- Based on this same data set, White patients had the longest survival time (P <. 05), followed by Hispanic (P < .05), Asian American/Native American/Pacific Islander (P < .05), and Black (P < .05) patients, respectively.7
- In Miami-Dade County, one study of 1690 melanoma cases found that 48% of Black patients had regional or distant disease at presentation compared to 22% of White patients (P = .015).5 Analysis of multiple factors found that only race was a significant predictor for late-stage melanoma (P < .001). Black patients in this study were 3 times more likely than others to be diagnosed with melanoma at a late stage (P = .07).5
- Black patients in the United States are more likely to have a delayed time from diagnosis to definitive surgery even when researchers controlled for type of health insurance and stage of diagnosis.8
Final thoughts
Efforts are needed to overcome these disparities by:
- educating patients with skin of color and their health care providers about the risks of advanced melanoma with the goal of prevention and earlier diagnosis;
- breaking down barriers to care caused by poverty, lack of health insurance, and systemic racism; and
- eliminating factors that lead to delays from diagnosis to definitive surgery.
THE COMPARISON
A Acral lentiginous melanoma on the sole of the foot of a 30-year-old Black woman. The depth of the lesion was 2 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
B Nodular melanoma on the shoulder of a 63-year-old Hispanic woman. The depth of the lesion was 5.5 mm with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Melanoma occurs less frequently in individuals with darker skin types than in those with lighter skin types but is associated with higher rates of morbidity and mortality in this patient population.1-7 In the cases shown here (A and B), both patients had advanced melanomas with large primary lesions and lymph node metastases.

Epidemiology
A systematic review by Higgins et al6 reported the following on the epidemiology of melanomas in patients with skin of color:
- African Americans have deeper tumors at the time of diagnosis, in addition to increased rates of regionally advanced and distant disease. Lesions generally are located on the lower extremities and have an increased propensity for ulceration. Acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype found in African American patients.6
- In Hispanic individuals, superficial spreading melanoma is the most common melanoma subtype. Lower extremity lesions are more common relative to White individuals. Hispanic individuals have the highest rate of oral cavity melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
- In Asian individuals, acral and subungual sites are most common. Specifically, Pacific Islanders have the highest proportion of mucosal melanomas across all ethnic groups.6
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Melanomas are found more often on the palms, soles, nail units, oral cavity, and mucosae.6 The melanomas have the same clinical and dermoscopic features found in individuals with lighter skin tones.
Worth noting
Factors that may contribute to the diagnosis of more advanced melanomas in racial/ethnic minorities in the United States include:
- decreased access to health care based on lack of health insurance and low socioeconomic status,
- less awareness of the risk of melanoma among patients and health care providers because melanoma is less common in persons of color, and
- lesions found in areas less likely to be seen in screening examinations, such as the soles of the feet and the oral and genital mucosae.
Health disparity highlight
- In a large US study of 96,953 patients with a diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma from 1992 to 2009, the proportion of later-stage melanoma—stages II to IV—was greater in Black patients compared to White patients.7
- Based on this same data set, White patients had the longest survival time (P <. 05), followed by Hispanic (P < .05), Asian American/Native American/Pacific Islander (P < .05), and Black (P < .05) patients, respectively.7
- In Miami-Dade County, one study of 1690 melanoma cases found that 48% of Black patients had regional or distant disease at presentation compared to 22% of White patients (P = .015).5 Analysis of multiple factors found that only race was a significant predictor for late-stage melanoma (P < .001). Black patients in this study were 3 times more likely than others to be diagnosed with melanoma at a late stage (P = .07).5
- Black patients in the United States are more likely to have a delayed time from diagnosis to definitive surgery even when researchers controlled for type of health insurance and stage of diagnosis.8
Final thoughts
Efforts are needed to overcome these disparities by:
- educating patients with skin of color and their health care providers about the risks of advanced melanoma with the goal of prevention and earlier diagnosis;
- breaking down barriers to care caused by poverty, lack of health insurance, and systemic racism; and
- eliminating factors that lead to delays from diagnosis to definitive surgery.
1. Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2001.05.034
2. Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.17.1907
3. Cress RD, Holly EA. Incidence of cutaneous melanoma among non-Hispanic whites, Hispanics, Asians, and blacks: an analysis of California cancer registry data, 1988-93. Cancer Causes Control. 1997;8:246-252. doi: 10.1023/a:1018432632528
4. Hu S, Parker DF, Thomas AG, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans: the Miami-Dade County experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:1031-1032. doi: 10.1016/ j.jaad.2004.05.005
5. Hu S, Soza-Vento RM, Parker DF, et al. Comparison of stage at diagnosis of melanoma among Hispanic, black, and white patients in Miami-Dade County, Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142: 704-708. doi: 10.1001/archderm.142.6.704
6. Higgins S, Nazemi A, Feinstein S, et al. Clinical presentations of melanoma in African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:791-801. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001759
7. Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival [published online July 28, 2016]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.06.006
8. Qian Y, Johannet P, Sawyers A, et al. The ongoing racial disparities in melanoma: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (1975-2016) [published online August 27, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1585-1593. doi: 10.1016/ j.jaad.2020.08.097
1. Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2001.05.034
2. Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.17.1907
3. Cress RD, Holly EA. Incidence of cutaneous melanoma among non-Hispanic whites, Hispanics, Asians, and blacks: an analysis of California cancer registry data, 1988-93. Cancer Causes Control. 1997;8:246-252. doi: 10.1023/a:1018432632528
4. Hu S, Parker DF, Thomas AG, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans: the Miami-Dade County experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:1031-1032. doi: 10.1016/ j.jaad.2004.05.005
5. Hu S, Soza-Vento RM, Parker DF, et al. Comparison of stage at diagnosis of melanoma among Hispanic, black, and white patients in Miami-Dade County, Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142: 704-708. doi: 10.1001/archderm.142.6.704
6. Higgins S, Nazemi A, Feinstein S, et al. Clinical presentations of melanoma in African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:791-801. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001759
7. Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival [published online July 28, 2016]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.06.006
8. Qian Y, Johannet P, Sawyers A, et al. The ongoing racial disparities in melanoma: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (1975-2016) [published online August 27, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1585-1593. doi: 10.1016/ j.jaad.2020.08.097
Steroid phobia drives weaker prescribing, nonadherence for AD
, Nanette B. Silverberg, MD, said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis meeting.
Up to 40% of parents of children with chronic AD cite anxiety surrounding corticosteroids, according to Dr. Silverberg, chief of pediatric dermatology at the Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
When the potential for adverse events are explained to parents who are anxious about a drug, “they take it in a different way than other individuals,” noted Dr. Silverberg, clinical professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
In a systematic review of 16 studies examining topical corticosteroid phobia in AD, published between 1946 and 2016, the prevalence of corticosteroid phobia among patients with AD or their caregivers ranged from 21% to 83.7%, with definitions of phobia that ranged from “concern” to “irrational fear.” In two studies where adherence was evaluated, patients with corticosteroid phobia had a higher rate of partial adherence (49.4%) or nonadherence (14.1%) when compared with patients who didn’t have a phobia of corticosteroids (29.3 % and 9.8%, respectively)..
The source of these fears can be information from friends, relatives, media, the Internet, as well as doctors, Dr. Silverberg noted. “We have to be responsible for providing proper data to these individuals,” she said.
Primary care providers also treat young children with AD differently from older children, when compared with other specialties, according to the results of one study that involved a survey and a retrospective chart review, published in 2020. In the survey, 88% of primary care providers in Chicago said they managed AD differently in children under aged 2 years than in older children, with 65% reporting they were more likely to refer a child under 2 years to a specialist, and 64% said they were less likely to prescribe high-potency topical corticosteroids to children in this age group. The retrospective review found that at PCP visits, significantly more children with AD between aged 2 and 5 years were more likely to be prescribed medium-potency topical corticosteroids (0.66% vs. 0.37%, P < .01) and high-potency topical corticosteroids (0.15% vs. 0.05%; P < .01) than children under 2 years old, respectively.
Of the children who had seen a specialist, more dermatologists (57%) prescribed medium-potency and high-potency topical corticosteroids for children under aged 2 years than did allergists (30%) and pediatricians (15%) (P < .01), according to the study.
“These are our colleagues who are often very strong prescribers using systemic agents, and only 15% of pediatricians will do this,” Dr. Silverberg said. “We’re really looking at a big divide between us and other subspecialties and primary care, and [topical corticosteroids] are frequently underutilized because of these fears.”
In another study looking at the use of topical corticosteroids for AD in the pediatric emergency department (mean age of patients, 6.3 years), from 2012 to 2017, patients at 46 of 167 visits were prescribed over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone, while at 63 of 167 visits, patients were not prescribed or recommended any corticosteroid.
The mean class of the topical corticosteroid prescribed was 5.5, and the most commonly recommended corticosteroid was class 7 (the least potent available) in 61 of 104 patients (P < .001). A dermatologist was consulted in 14 of 167 visits (8.6%), and in those cases, topical corticosteroids were often prescribed (P = .018), as was a higher class of corticosteroids (a mean of 3.1 vs. 5.9; P < .001).
Topical corticosteroids also tend to be prescribed less by internal medicine physicians than by family medicine physicians or dermatologists. A 2020 study of ambulatory care data in the United States from 2006 to 2016 found that internists were 22 times less likely to prescribe topical corticosteroids for AD compared with dermatologists (5.1% vs. 52.2%; P = .001). But there was no significant difference in prescribing between family medicine physicians and dermatologists (39.1% vs. 52.2%, P = .27).
“We know they [corticosteroids] work, but so many people are fearful of them ... even with a low, low side effect profile,” Dr. Silverberg said.
For children with AD, corticosteroid use is “suboptimal” across the United States, with evidence that Medicaid-insured pediatric patients with AD are less likely to see a specialist and less likely to be prescribed high-potency topical corticosteroids compared with commercially-insured patients.
Discussing efficacy and safety
Dr. Silverberg said providers who care for children with AD should talk about the fear surrounding these medications and educate parents with anxiety surrounding corticosteroids. “Side effects are usually short term and limited, so we really can assure parents that there is a long safety profile,” she said.
Asked to comment on this topic, Adelaide Hebert, MD, professor of dermatology and director of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston, said that she often sees concerns surrounding the use of topical corticosteroids, both in her practice with parents and when teaching residents in other disciplines, such as pediatrics, family medicine, and emergency medicine.
“We don’t do a good job in medical school educating the students about the safety, applicability, and proper use of topical steroids, and I think that leads to some of the confusion when it comes to properly using this class of medications in treating atopic dermatitis,” she said in an interview.
The use of a high-potency topical steroid is important, she noted, as lower doses may not adequately control AD. “If the patient has very mild disease, this may be just fine,” she noted. Those patients often do not see a pediatric dermatologist, “but the ones with moderate or severe atopic dermatitis often do, and I would say [the problem of] undertreatment is all too common.”
Like Dr. Silverberg, Dr. Hebert said that in her clinical experience, side effects from topical corticosteroids have been rare. “I could count on one hand the number of patients in a 38-year pediatric dermatology practice where they had an adverse effect from a topical steroid,” she said.
Dr. Silverberg reports receiving consulting fees from Amryt Pharma, Galderma, Incyte, and Vyne; non-CME related fees from Pfizer and Regeneron; and contracted research fees from Incyte and the Vitiligo Research Foundation. Dr. Hebert reports receiving research funds from GSK, Leo, Ortho Dermatologics, Galderma, Dermavant, Pfizer, and Arcutis Biotherapeutics paid to her institution; honoraria from Pfizer, Arcutis, Incyte; and having served on the data safety monitoring board for Regeneron-Sanofi, GSK, and Ortho Dermatologics.
, Nanette B. Silverberg, MD, said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis meeting.
Up to 40% of parents of children with chronic AD cite anxiety surrounding corticosteroids, according to Dr. Silverberg, chief of pediatric dermatology at the Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
When the potential for adverse events are explained to parents who are anxious about a drug, “they take it in a different way than other individuals,” noted Dr. Silverberg, clinical professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
In a systematic review of 16 studies examining topical corticosteroid phobia in AD, published between 1946 and 2016, the prevalence of corticosteroid phobia among patients with AD or their caregivers ranged from 21% to 83.7%, with definitions of phobia that ranged from “concern” to “irrational fear.” In two studies where adherence was evaluated, patients with corticosteroid phobia had a higher rate of partial adherence (49.4%) or nonadherence (14.1%) when compared with patients who didn’t have a phobia of corticosteroids (29.3 % and 9.8%, respectively)..
The source of these fears can be information from friends, relatives, media, the Internet, as well as doctors, Dr. Silverberg noted. “We have to be responsible for providing proper data to these individuals,” she said.
Primary care providers also treat young children with AD differently from older children, when compared with other specialties, according to the results of one study that involved a survey and a retrospective chart review, published in 2020. In the survey, 88% of primary care providers in Chicago said they managed AD differently in children under aged 2 years than in older children, with 65% reporting they were more likely to refer a child under 2 years to a specialist, and 64% said they were less likely to prescribe high-potency topical corticosteroids to children in this age group. The retrospective review found that at PCP visits, significantly more children with AD between aged 2 and 5 years were more likely to be prescribed medium-potency topical corticosteroids (0.66% vs. 0.37%, P < .01) and high-potency topical corticosteroids (0.15% vs. 0.05%; P < .01) than children under 2 years old, respectively.
Of the children who had seen a specialist, more dermatologists (57%) prescribed medium-potency and high-potency topical corticosteroids for children under aged 2 years than did allergists (30%) and pediatricians (15%) (P < .01), according to the study.
“These are our colleagues who are often very strong prescribers using systemic agents, and only 15% of pediatricians will do this,” Dr. Silverberg said. “We’re really looking at a big divide between us and other subspecialties and primary care, and [topical corticosteroids] are frequently underutilized because of these fears.”
In another study looking at the use of topical corticosteroids for AD in the pediatric emergency department (mean age of patients, 6.3 years), from 2012 to 2017, patients at 46 of 167 visits were prescribed over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone, while at 63 of 167 visits, patients were not prescribed or recommended any corticosteroid.
The mean class of the topical corticosteroid prescribed was 5.5, and the most commonly recommended corticosteroid was class 7 (the least potent available) in 61 of 104 patients (P < .001). A dermatologist was consulted in 14 of 167 visits (8.6%), and in those cases, topical corticosteroids were often prescribed (P = .018), as was a higher class of corticosteroids (a mean of 3.1 vs. 5.9; P < .001).
Topical corticosteroids also tend to be prescribed less by internal medicine physicians than by family medicine physicians or dermatologists. A 2020 study of ambulatory care data in the United States from 2006 to 2016 found that internists were 22 times less likely to prescribe topical corticosteroids for AD compared with dermatologists (5.1% vs. 52.2%; P = .001). But there was no significant difference in prescribing between family medicine physicians and dermatologists (39.1% vs. 52.2%, P = .27).
“We know they [corticosteroids] work, but so many people are fearful of them ... even with a low, low side effect profile,” Dr. Silverberg said.
For children with AD, corticosteroid use is “suboptimal” across the United States, with evidence that Medicaid-insured pediatric patients with AD are less likely to see a specialist and less likely to be prescribed high-potency topical corticosteroids compared with commercially-insured patients.
Discussing efficacy and safety
Dr. Silverberg said providers who care for children with AD should talk about the fear surrounding these medications and educate parents with anxiety surrounding corticosteroids. “Side effects are usually short term and limited, so we really can assure parents that there is a long safety profile,” she said.
Asked to comment on this topic, Adelaide Hebert, MD, professor of dermatology and director of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston, said that she often sees concerns surrounding the use of topical corticosteroids, both in her practice with parents and when teaching residents in other disciplines, such as pediatrics, family medicine, and emergency medicine.
“We don’t do a good job in medical school educating the students about the safety, applicability, and proper use of topical steroids, and I think that leads to some of the confusion when it comes to properly using this class of medications in treating atopic dermatitis,” she said in an interview.
The use of a high-potency topical steroid is important, she noted, as lower doses may not adequately control AD. “If the patient has very mild disease, this may be just fine,” she noted. Those patients often do not see a pediatric dermatologist, “but the ones with moderate or severe atopic dermatitis often do, and I would say [the problem of] undertreatment is all too common.”
Like Dr. Silverberg, Dr. Hebert said that in her clinical experience, side effects from topical corticosteroids have been rare. “I could count on one hand the number of patients in a 38-year pediatric dermatology practice where they had an adverse effect from a topical steroid,” she said.
Dr. Silverberg reports receiving consulting fees from Amryt Pharma, Galderma, Incyte, and Vyne; non-CME related fees from Pfizer and Regeneron; and contracted research fees from Incyte and the Vitiligo Research Foundation. Dr. Hebert reports receiving research funds from GSK, Leo, Ortho Dermatologics, Galderma, Dermavant, Pfizer, and Arcutis Biotherapeutics paid to her institution; honoraria from Pfizer, Arcutis, Incyte; and having served on the data safety monitoring board for Regeneron-Sanofi, GSK, and Ortho Dermatologics.
, Nanette B. Silverberg, MD, said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis meeting.
Up to 40% of parents of children with chronic AD cite anxiety surrounding corticosteroids, according to Dr. Silverberg, chief of pediatric dermatology at the Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
When the potential for adverse events are explained to parents who are anxious about a drug, “they take it in a different way than other individuals,” noted Dr. Silverberg, clinical professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
In a systematic review of 16 studies examining topical corticosteroid phobia in AD, published between 1946 and 2016, the prevalence of corticosteroid phobia among patients with AD or their caregivers ranged from 21% to 83.7%, with definitions of phobia that ranged from “concern” to “irrational fear.” In two studies where adherence was evaluated, patients with corticosteroid phobia had a higher rate of partial adherence (49.4%) or nonadherence (14.1%) when compared with patients who didn’t have a phobia of corticosteroids (29.3 % and 9.8%, respectively)..
The source of these fears can be information from friends, relatives, media, the Internet, as well as doctors, Dr. Silverberg noted. “We have to be responsible for providing proper data to these individuals,” she said.
Primary care providers also treat young children with AD differently from older children, when compared with other specialties, according to the results of one study that involved a survey and a retrospective chart review, published in 2020. In the survey, 88% of primary care providers in Chicago said they managed AD differently in children under aged 2 years than in older children, with 65% reporting they were more likely to refer a child under 2 years to a specialist, and 64% said they were less likely to prescribe high-potency topical corticosteroids to children in this age group. The retrospective review found that at PCP visits, significantly more children with AD between aged 2 and 5 years were more likely to be prescribed medium-potency topical corticosteroids (0.66% vs. 0.37%, P < .01) and high-potency topical corticosteroids (0.15% vs. 0.05%; P < .01) than children under 2 years old, respectively.
Of the children who had seen a specialist, more dermatologists (57%) prescribed medium-potency and high-potency topical corticosteroids for children under aged 2 years than did allergists (30%) and pediatricians (15%) (P < .01), according to the study.
“These are our colleagues who are often very strong prescribers using systemic agents, and only 15% of pediatricians will do this,” Dr. Silverberg said. “We’re really looking at a big divide between us and other subspecialties and primary care, and [topical corticosteroids] are frequently underutilized because of these fears.”
In another study looking at the use of topical corticosteroids for AD in the pediatric emergency department (mean age of patients, 6.3 years), from 2012 to 2017, patients at 46 of 167 visits were prescribed over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone, while at 63 of 167 visits, patients were not prescribed or recommended any corticosteroid.
The mean class of the topical corticosteroid prescribed was 5.5, and the most commonly recommended corticosteroid was class 7 (the least potent available) in 61 of 104 patients (P < .001). A dermatologist was consulted in 14 of 167 visits (8.6%), and in those cases, topical corticosteroids were often prescribed (P = .018), as was a higher class of corticosteroids (a mean of 3.1 vs. 5.9; P < .001).
Topical corticosteroids also tend to be prescribed less by internal medicine physicians than by family medicine physicians or dermatologists. A 2020 study of ambulatory care data in the United States from 2006 to 2016 found that internists were 22 times less likely to prescribe topical corticosteroids for AD compared with dermatologists (5.1% vs. 52.2%; P = .001). But there was no significant difference in prescribing between family medicine physicians and dermatologists (39.1% vs. 52.2%, P = .27).
“We know they [corticosteroids] work, but so many people are fearful of them ... even with a low, low side effect profile,” Dr. Silverberg said.
For children with AD, corticosteroid use is “suboptimal” across the United States, with evidence that Medicaid-insured pediatric patients with AD are less likely to see a specialist and less likely to be prescribed high-potency topical corticosteroids compared with commercially-insured patients.
Discussing efficacy and safety
Dr. Silverberg said providers who care for children with AD should talk about the fear surrounding these medications and educate parents with anxiety surrounding corticosteroids. “Side effects are usually short term and limited, so we really can assure parents that there is a long safety profile,” she said.
Asked to comment on this topic, Adelaide Hebert, MD, professor of dermatology and director of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston, said that she often sees concerns surrounding the use of topical corticosteroids, both in her practice with parents and when teaching residents in other disciplines, such as pediatrics, family medicine, and emergency medicine.
“We don’t do a good job in medical school educating the students about the safety, applicability, and proper use of topical steroids, and I think that leads to some of the confusion when it comes to properly using this class of medications in treating atopic dermatitis,” she said in an interview.
The use of a high-potency topical steroid is important, she noted, as lower doses may not adequately control AD. “If the patient has very mild disease, this may be just fine,” she noted. Those patients often do not see a pediatric dermatologist, “but the ones with moderate or severe atopic dermatitis often do, and I would say [the problem of] undertreatment is all too common.”
Like Dr. Silverberg, Dr. Hebert said that in her clinical experience, side effects from topical corticosteroids have been rare. “I could count on one hand the number of patients in a 38-year pediatric dermatology practice where they had an adverse effect from a topical steroid,” she said.
Dr. Silverberg reports receiving consulting fees from Amryt Pharma, Galderma, Incyte, and Vyne; non-CME related fees from Pfizer and Regeneron; and contracted research fees from Incyte and the Vitiligo Research Foundation. Dr. Hebert reports receiving research funds from GSK, Leo, Ortho Dermatologics, Galderma, Dermavant, Pfizer, and Arcutis Biotherapeutics paid to her institution; honoraria from Pfizer, Arcutis, Incyte; and having served on the data safety monitoring board for Regeneron-Sanofi, GSK, and Ortho Dermatologics.
FROM RAD 2022